JP5919121B2 - ダイオードおよび半導体装置 - Google Patents
ダイオードおよび半導体装置 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP5919121B2 JP5919121B2 JP2012166576A JP2012166576A JP5919121B2 JP 5919121 B2 JP5919121 B2 JP 5919121B2 JP 2012166576 A JP2012166576 A JP 2012166576A JP 2012166576 A JP2012166576 A JP 2012166576A JP 5919121 B2 JP5919121 B2 JP 5919121B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- region
- diode
- electrode
- anode
- barrier
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 title claims description 329
- 230000004888 barrier function Effects 0.000 claims description 169
- 230000005684 electric field Effects 0.000 claims description 109
- 210000000746 body region Anatomy 0.000 claims description 37
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 32
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 claims description 32
- 230000002265 prevention Effects 0.000 claims description 18
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 description 47
- 239000012535 impurity Substances 0.000 description 45
- 238000011084 recovery Methods 0.000 description 36
- 238000002347 injection Methods 0.000 description 32
- 239000007924 injection Substances 0.000 description 32
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 20
- 230000015556 catabolic process Effects 0.000 description 17
- 230000003071 parasitic effect Effects 0.000 description 11
- XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicon Chemical compound [Si] XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 9
- 229910052710 silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 9
- 239000010703 silicon Substances 0.000 description 9
- 230000000052 comparative effect Effects 0.000 description 6
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 6
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 description 3
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000000149 penetrating effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- JBRZTFJDHDCESZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N AsGa Chemical compound [As]#[Ga] JBRZTFJDHDCESZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ZOXJGFHDIHLPTG-UHFFFAOYSA-N Boron Chemical compound [B] ZOXJGFHDIHLPTG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910002601 GaN Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910001218 Gallium arsenide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- JMASRVWKEDWRBT-UHFFFAOYSA-N Gallium nitride Chemical compound [Ga]#N JMASRVWKEDWRBT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- OAICVXFJPJFONN-UHFFFAOYSA-N Phosphorus Chemical compound [P] OAICVXFJPJFONN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052796 boron Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000012141 concentrate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000007796 conventional method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229910052698 phosphorus Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000011574 phosphorus Substances 0.000 description 1
- HBMJWWWQQXIZIP-UHFFFAOYSA-N silicon carbide Chemical compound [Si+]#[C-] HBMJWWWQQXIZIP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910010271 silicon carbide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/02—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/36—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities in the bulk material
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L27/00—Devices consisting of a plurality of semiconductor or other solid-state components formed in or on a common substrate
- H01L27/02—Devices consisting of a plurality of semiconductor or other solid-state components formed in or on a common substrate including semiconductor components specially adapted for rectifying, oscillating, amplifying or switching and having potential barriers; including integrated passive circuit elements having potential barriers
- H01L27/04—Devices consisting of a plurality of semiconductor or other solid-state components formed in or on a common substrate including semiconductor components specially adapted for rectifying, oscillating, amplifying or switching and having potential barriers; including integrated passive circuit elements having potential barriers the substrate being a semiconductor body
- H01L27/06—Devices consisting of a plurality of semiconductor or other solid-state components formed in or on a common substrate including semiconductor components specially adapted for rectifying, oscillating, amplifying or switching and having potential barriers; including integrated passive circuit elements having potential barriers the substrate being a semiconductor body including a plurality of individual components in a non-repetitive configuration
- H01L27/0611—Devices consisting of a plurality of semiconductor or other solid-state components formed in or on a common substrate including semiconductor components specially adapted for rectifying, oscillating, amplifying or switching and having potential barriers; including integrated passive circuit elements having potential barriers the substrate being a semiconductor body including a plurality of individual components in a non-repetitive configuration integrated circuits having a two-dimensional layout of components without a common active region
- H01L27/0617—Devices consisting of a plurality of semiconductor or other solid-state components formed in or on a common substrate including semiconductor components specially adapted for rectifying, oscillating, amplifying or switching and having potential barriers; including integrated passive circuit elements having potential barriers the substrate being a semiconductor body including a plurality of individual components in a non-repetitive configuration integrated circuits having a two-dimensional layout of components without a common active region comprising components of the field-effect type
- H01L27/0629—Devices consisting of a plurality of semiconductor or other solid-state components formed in or on a common substrate including semiconductor components specially adapted for rectifying, oscillating, amplifying or switching and having potential barriers; including integrated passive circuit elements having potential barriers the substrate being a semiconductor body including a plurality of individual components in a non-repetitive configuration integrated circuits having a two-dimensional layout of components without a common active region comprising components of the field-effect type in combination with diodes, or resistors, or capacitors
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/02—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/06—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions
- H01L29/0603—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions characterised by particular constructional design considerations, e.g. for preventing surface leakage, for controlling electric field concentration or for internal isolations regions
- H01L29/0607—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions characterised by particular constructional design considerations, e.g. for preventing surface leakage, for controlling electric field concentration or for internal isolations regions for preventing surface leakage or controlling electric field concentration
- H01L29/0611—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions characterised by particular constructional design considerations, e.g. for preventing surface leakage, for controlling electric field concentration or for internal isolations regions for preventing surface leakage or controlling electric field concentration for increasing or controlling the breakdown voltage of reverse biased devices
- H01L29/0615—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions characterised by particular constructional design considerations, e.g. for preventing surface leakage, for controlling electric field concentration or for internal isolations regions for preventing surface leakage or controlling electric field concentration for increasing or controlling the breakdown voltage of reverse biased devices by the doping profile or the shape or the arrangement of the PN junction, or with supplementary regions, e.g. junction termination extension [JTE]
- H01L29/0619—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions characterised by particular constructional design considerations, e.g. for preventing surface leakage, for controlling electric field concentration or for internal isolations regions for preventing surface leakage or controlling electric field concentration for increasing or controlling the breakdown voltage of reverse biased devices by the doping profile or the shape or the arrangement of the PN junction, or with supplementary regions, e.g. junction termination extension [JTE] with a supplementary region doped oppositely to or in rectifying contact with the semiconductor containing or contacting region, e.g. guard rings with PN or Schottky junction
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/02—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/06—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions
- H01L29/0603—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions characterised by particular constructional design considerations, e.g. for preventing surface leakage, for controlling electric field concentration or for internal isolations regions
- H01L29/0607—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions characterised by particular constructional design considerations, e.g. for preventing surface leakage, for controlling electric field concentration or for internal isolations regions for preventing surface leakage or controlling electric field concentration
- H01L29/0611—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions characterised by particular constructional design considerations, e.g. for preventing surface leakage, for controlling electric field concentration or for internal isolations regions for preventing surface leakage or controlling electric field concentration for increasing or controlling the breakdown voltage of reverse biased devices
- H01L29/0615—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions characterised by particular constructional design considerations, e.g. for preventing surface leakage, for controlling electric field concentration or for internal isolations regions for preventing surface leakage or controlling electric field concentration for increasing or controlling the breakdown voltage of reverse biased devices by the doping profile or the shape or the arrangement of the PN junction, or with supplementary regions, e.g. junction termination extension [JTE]
- H01L29/0619—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions characterised by particular constructional design considerations, e.g. for preventing surface leakage, for controlling electric field concentration or for internal isolations regions for preventing surface leakage or controlling electric field concentration for increasing or controlling the breakdown voltage of reverse biased devices by the doping profile or the shape or the arrangement of the PN junction, or with supplementary regions, e.g. junction termination extension [JTE] with a supplementary region doped oppositely to or in rectifying contact with the semiconductor containing or contacting region, e.g. guard rings with PN or Schottky junction
- H01L29/0623—Buried supplementary region, e.g. buried guard ring
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/02—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/06—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions
- H01L29/0603—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions characterised by particular constructional design considerations, e.g. for preventing surface leakage, for controlling electric field concentration or for internal isolations regions
- H01L29/0642—Isolation within the component, i.e. internal isolation
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/02—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/06—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions
- H01L29/0684—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions characterised by the shape, relative sizes or dispositions of the semiconductor regions or junctions between the regions
- H01L29/0692—Surface layout
- H01L29/0696—Surface layout of cellular field-effect devices, e.g. multicellular DMOS transistors or IGBTs
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/02—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/06—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions
- H01L29/08—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions with semiconductor regions connected to an electrode carrying current to be rectified, amplified or switched and such electrode being part of a semiconductor device which comprises three or more electrodes
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/02—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/06—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions
- H01L29/08—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions with semiconductor regions connected to an electrode carrying current to be rectified, amplified or switched and such electrode being part of a semiconductor device which comprises three or more electrodes
- H01L29/0843—Source or drain regions of field-effect devices
- H01L29/0847—Source or drain regions of field-effect devices of field-effect transistors with insulated gate
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/02—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/06—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions
- H01L29/08—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions with semiconductor regions connected to an electrode carrying current to be rectified, amplified or switched and such electrode being part of a semiconductor device which comprises three or more electrodes
- H01L29/0843—Source or drain regions of field-effect devices
- H01L29/0847—Source or drain regions of field-effect devices of field-effect transistors with insulated gate
- H01L29/0852—Source or drain regions of field-effect devices of field-effect transistors with insulated gate of DMOS transistors
- H01L29/0873—Drain regions
- H01L29/0878—Impurity concentration or distribution
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/02—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/06—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions
- H01L29/10—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions with semiconductor regions connected to an electrode not carrying current to be rectified, amplified or switched and such electrode being part of a semiconductor device which comprises three or more electrodes
- H01L29/1095—Body region, i.e. base region, of DMOS transistors or IGBTs
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/02—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/12—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by the materials of which they are formed
- H01L29/16—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by the materials of which they are formed including, apart from doping materials or other impurities, only elements of Group IV of the Periodic Table
- H01L29/1608—Silicon carbide
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/02—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/12—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by the materials of which they are formed
- H01L29/20—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by the materials of which they are formed including, apart from doping materials or other impurities, only AIIIBV compounds
- H01L29/2003—Nitride compounds
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/40—Electrodes ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/402—Field plates
- H01L29/407—Recessed field plates, e.g. trench field plates, buried field plates
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/66—Types of semiconductor device ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/68—Types of semiconductor device ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor controllable by only the electric current supplied, or only the electric potential applied, to an electrode which does not carry the current to be rectified, amplified or switched
- H01L29/70—Bipolar devices
- H01L29/72—Transistor-type devices, i.e. able to continuously respond to applied control signals
- H01L29/739—Transistor-type devices, i.e. able to continuously respond to applied control signals controlled by field-effect, e.g. bipolar static induction transistors [BSIT]
- H01L29/7393—Insulated gate bipolar mode transistors, i.e. IGBT; IGT; COMFET
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/66—Types of semiconductor device ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/68—Types of semiconductor device ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor controllable by only the electric current supplied, or only the electric potential applied, to an electrode which does not carry the current to be rectified, amplified or switched
- H01L29/70—Bipolar devices
- H01L29/72—Transistor-type devices, i.e. able to continuously respond to applied control signals
- H01L29/739—Transistor-type devices, i.e. able to continuously respond to applied control signals controlled by field-effect, e.g. bipolar static induction transistors [BSIT]
- H01L29/7393—Insulated gate bipolar mode transistors, i.e. IGBT; IGT; COMFET
- H01L29/7395—Vertical transistors, e.g. vertical IGBT
- H01L29/7396—Vertical transistors, e.g. vertical IGBT with a non planar surface, e.g. with a non planar gate or with a trench or recess or pillar in the surface of the emitter, base or collector region for improving current density or short circuiting the emitter and base regions
- H01L29/7397—Vertical transistors, e.g. vertical IGBT with a non planar surface, e.g. with a non planar gate or with a trench or recess or pillar in the surface of the emitter, base or collector region for improving current density or short circuiting the emitter and base regions and a gate structure lying on a slanted or vertical surface or formed in a groove, e.g. trench gate IGBT
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/66—Types of semiconductor device ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/68—Types of semiconductor device ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor controllable by only the electric current supplied, or only the electric potential applied, to an electrode which does not carry the current to be rectified, amplified or switched
- H01L29/76—Unipolar devices, e.g. field effect transistors
- H01L29/772—Field effect transistors
- H01L29/78—Field effect transistors with field effect produced by an insulated gate
- H01L29/7801—DMOS transistors, i.e. MISFETs with a channel accommodating body or base region adjoining a drain drift region
- H01L29/7802—Vertical DMOS transistors, i.e. VDMOS transistors
- H01L29/7803—Vertical DMOS transistors, i.e. VDMOS transistors structurally associated with at least one other device
- H01L29/7806—Vertical DMOS transistors, i.e. VDMOS transistors structurally associated with at least one other device the other device being a Schottky barrier diode
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/66—Types of semiconductor device ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/68—Types of semiconductor device ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor controllable by only the electric current supplied, or only the electric potential applied, to an electrode which does not carry the current to be rectified, amplified or switched
- H01L29/76—Unipolar devices, e.g. field effect transistors
- H01L29/772—Field effect transistors
- H01L29/78—Field effect transistors with field effect produced by an insulated gate
- H01L29/7801—DMOS transistors, i.e. MISFETs with a channel accommodating body or base region adjoining a drain drift region
- H01L29/7802—Vertical DMOS transistors, i.e. VDMOS transistors
- H01L29/7813—Vertical DMOS transistors, i.e. VDMOS transistors with trench gate electrode, e.g. UMOS transistors
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/66—Types of semiconductor device ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/68—Types of semiconductor device ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor controllable by only the electric current supplied, or only the electric potential applied, to an electrode which does not carry the current to be rectified, amplified or switched
- H01L29/76—Unipolar devices, e.g. field effect transistors
- H01L29/772—Field effect transistors
- H01L29/78—Field effect transistors with field effect produced by an insulated gate
- H01L29/7839—Field effect transistors with field effect produced by an insulated gate with Schottky drain or source contact
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/66—Types of semiconductor device ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/86—Types of semiconductor device ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor controllable only by variation of the electric current supplied, or only the electric potential applied, to one or more of the electrodes carrying the current to be rectified, amplified, oscillated or switched
- H01L29/861—Diodes
- H01L29/8611—Planar PN junction diodes
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/66—Types of semiconductor device ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/86—Types of semiconductor device ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor controllable only by variation of the electric current supplied, or only the electric potential applied, to one or more of the electrodes carrying the current to be rectified, amplified, oscillated or switched
- H01L29/861—Diodes
- H01L29/872—Schottky diodes
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/02—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/06—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions
- H01L29/0684—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions characterised by the shape, relative sizes or dispositions of the semiconductor regions or junctions between the regions
- H01L29/0692—Surface layout
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/02—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/06—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions
- H01L29/08—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions with semiconductor regions connected to an electrode carrying current to be rectified, amplified or switched and such electrode being part of a semiconductor device which comprises three or more electrodes
- H01L29/083—Anode or cathode regions of thyristors or gated bipolar-mode devices
- H01L29/0834—Anode regions of thyristors or gated bipolar-mode devices, e.g. supplementary regions surrounding anode regions
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/02—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/12—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by the materials of which they are formed
- H01L29/20—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by the materials of which they are formed including, apart from doping materials or other impurities, only AIIIBV compounds
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/40—Electrodes ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/41—Electrodes ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape, relative sizes or dispositions
- H01L29/417—Electrodes ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape, relative sizes or dispositions carrying the current to be rectified, amplified or switched
- H01L29/41725—Source or drain electrodes for field effect devices
- H01L29/41766—Source or drain electrodes for field effect devices with at least part of the source or drain electrode having contact below the semiconductor surface, e.g. the source or drain electrode formed at least partially in a groove or with inclusions of conductor inside the semiconductor
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Power Engineering (AREA)
- Microelectronics & Electronic Packaging (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Condensed Matter Physics & Semiconductors (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Computer Hardware Design (AREA)
- Ceramic Engineering (AREA)
- Electrodes Of Semiconductors (AREA)
- Metal-Oxide And Bipolar Metal-Oxide Semiconductor Integrated Circuits (AREA)
Description
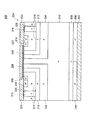
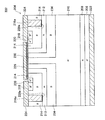
図1に示すように、本実施例のダイオード2は、シリコンの半導体基板4を用いて形成されている。半導体基板4には、高濃度n型半導体領域であるn+カソード領域6と、n型半導体領域であるnバッファ領域8と、低濃度n型半導体領域であるn−ドリフト領域10と、n型半導体領域であるnバリア領域12と、p型半導体領域であるpアノード領域14が順に積層されている。本実施例では、n型半導体領域には不純物として例えばリンが添加されており、p型半導体領域には不純物として例えばボロンが添加されている。本実施例では、n+カソード領域6の不純物濃度は1×1017〜5×1020[cm-3]程度であり、nバッファ領域8の不純物濃度は1×1016〜1×1019[cm-3]程度であり、n−ドリフト領域10の不純物濃度は1×1012〜1×1015[cm-3]程度であり、nバリア領域12の不純物濃度は1×1015〜1×1018[cm-3]程度であり、pアノード領域14の不純物濃度は1×1016〜1×1019[cm-3]程度である。また、nバリア領域12の厚みは0.5〜3.0[μm]程度である。
図4に示すように、本実施例のダイオード32は、シリコンの半導体基板34を用いて形成されている。半導体基板34には、高濃度n型半導体領域であるn+カソード領域6と、n型半導体領域であるnバッファ領域8と、低濃度n型半導体領域であるn−ドリフト領域10と、p型半導体領域であるp電界進展防止領域36と、n型半導体領域であるnバリア領域12と、p型半導体領域であるpアノード領域14が順に積層されている。本実施例では、p電界進展防止領域36の不純物濃度は1×1015〜1×1019[cm-3]程度である。また、p電界進展防止領域36の厚みは0.5〜3.0[μm]程度である。
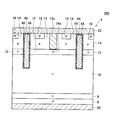
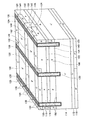
図7に示すように、本実施例のダイオード42は、実施例1のダイオード2と同様に、シリコンの半導体基板4を用いて形成されている。半導体基板4には、高濃度n型半導体領域であるn+カソード領域6と、n型半導体領域であるnバッファ領域8と、低濃度n型半導体領域であるn−ドリフト領域10と、n型半導体領域であるnバリア領域12と、p型半導体領域であるpアノード領域14が順に積層されている。半導体基板4の上側表面には、n型半導体領域であるnピラー領域16が、所定の間隔を隔てて複数形成されている。nピラー領域16は、pアノード領域14を貫通して、nバリア領域12の上側表面まで達するように形成されている。また、半導体基板4の上側には、複数のトレンチ44が所定の間隔で形成されている。それぞれのトレンチ44は、pアノード領域14の上側表面からnバリア領域12を貫通してn−ドリフト領域10の内部まで達している。トレンチ44の内部には、絶縁膜46によって被覆されたトレンチ電極48が充填されている。また、pアノード領域14の上側表面には、高濃度p型半導体領域であるp+コンタクト領域18が所定の間隔を隔てて複数形成されている。
図8に示すように、本実施例のダイオード52は、実施例2のダイオード32と同様に、シリコンの半導体基板34を用いて形成されている。半導体基板34には、高濃度n型半導体領域であるn+カソード領域6と、n型半導体領域であるnバッファ領域8と、低濃度n型半導体領域であるn−ドリフト領域10と、p型半導体領域であるp電界進展防止領域36と、n型半導体領域であるnバリア領域12と、p型半導体領域であるpアノード領域14が順に積層されている。半導体基板34の上側表面には、n型半導体領域であるnピラー領域16が、所定の間隔を隔てて複数形成されている。nピラー領域16は、pアノード領域14を貫通して、nバリア領域12の上側表面まで達するように形成されている。また、半導体基板34の上側には、複数のトレンチ44が所定の間隔で形成されている。それぞれのトレンチ44は、pアノード領域14の上側表面からnバリア領域12とp電界進展防止領域36を貫通してn−ドリフト領域10の内部まで達している。トレンチ44の内部には、絶縁膜46によって被覆されたトレンチ電極48が充填されている。また、pアノード領域14の上側表面には、高濃度p型半導体領域であるp+コンタクト領域18が所定の間隔を隔てて複数形成されている。
図10に示すように、本実施例のダイオード62は、実施例4のダイオード52とほぼ同様の構成を備えている。本実施例のダイオード62では、n+カソード領域6に、高濃度p型半導体領域であるp+カソードショート領域64が、所定の間隔を隔てて複数形成されている点で、実施例4のダイオード52と異なる。本実施例では、p+カソードショート領域64の不純物濃度は1×1017〜5×1020[cm-3]程度である。
図14に示すように、本実施例の半導体装置72は、実施例3のダイオード42とほぼ同様の構成を備えている。半導体装置72では、pアノード領域14の上側表面において、トレンチ44に隣接する箇所に、高濃度n型半導体領域であるn+エミッタ領域74が形成されている。本実施例では、n+エミッタ領域74の不純物濃度は1×1017〜5×1020[cm-3]程度である。n+エミッタ領域74は、アノード電極22とオーミック接合によって接合している。
図15に示すように、本実施例の半導体装置82は、実施例4のダイオード52とほぼ同様の構成を備えている。半導体装置82では、pアノード領域14の上側表面において、トレンチ44に隣接する箇所に、n+エミッタ領域74が形成されている。n+エミッタ領域74は、アノード電極22とオーミック接合によって接合している。
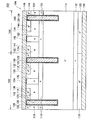
図16に示すように、本実施例の半導体装置102は、シリコンの半導体基板104を用いて形成されている。半導体装置102は、IGBT領域106と、ダイオード領域108を備えている。IGBT領域106において、半導体基板104は、高濃度p型半導体領域であるp+コレクタ領域110と、n型半導体領域であるnバッファ領域112と、低濃度n型半導体領域であるn−ドリフト領域114と、n型半導体領域であるnバリア領域116と、p型半導体領域であるpボディ領域118が順に積層されている。本実施例では、p+コレクタ領域110の不純物濃度は1×1017〜5×1020[cm-3]程度であり、nバッファ領域112の不純物濃度は1×1016〜1×1019[cm-3]程度であり、n−ドリフト領域114の不純物濃度は1×1012〜1×1015[cm-3]程度であり、nバリア領域116の不純物濃度は1×1015〜1×1018[cm-3]程度であり、pボディ領域118の不純物濃度は1×1016〜1×1019[cm-3]程度である。また、nバリア領域116の厚みは0.5〜3.0[μm]程度である。ダイオード領域108において、半導体基板104は、高濃度n型半導体領域であるn+カソード領域120と、nバッファ領域112と、n−ドリフト領域114と、nバリア領域122と、p型半導体領域であるpアノード領域124が順に積層されている。本実施例では、n+カソード領域120の不純物濃度は1×1017〜5×1020[cm-3]程度であり、nバリア領域122の不純物濃度は1×1015〜1×1018[cm-3]程度であり、pアノード領域124の不純物濃度は1×1016〜1×1019[cm-3]程度である。また、nバリア領域122の厚みは0.5〜3.0[μm]程度である。半導体基板4の上側には、複数のトレンチ126が所定の間隔で形成されている。
図17に示すように、本実施例の半導体装置162は、実施例8の半導体装置102とほぼ同様の構成を備えている。半導体装置162は、シリコンの半導体基板164を用いて形成されている。半導体基板164は、実施例8の半導体基板104とほぼ同様の構成を備えている。半導体基板164では、IGBT領域106において、n−ドリフト領域114とnバリア領域116の間に、p型半導体領域であるp電界進展防止領域166が形成されており、ダイオード領域108において、n−ドリフト領域114とnバリア領域122の間に、p型半導体領域であるp電界進展防止領域168が形成されている。p電界進展防止領域166およびp電界進展防止領域168の不純物濃度は1×1015〜1×1019[cm-3]程度である。また、p電界進展防止領域166およびp電界進展防止領域168の厚みは0.5〜3.0[μm]程度である。IGBT領域106において、トレンチ126は、pボディ領域118の上側表面からnバリア領域116およびp電界進展防止領域166を貫通して、n−ドリフト領域114の内部まで達している。ダイオード領域108において、トレンチ126は、pアノード領域124の上側表面からnバリア領域122およびp電界進展防止領域168を貫通して、n−ドリフト領域114の内部まで達している。
図19に示すように、本実施例の半導体装置172は、実施例8の半導体装置102とほぼ同様の構成を備えている。本実施例の半導体装置172では、ダイオード領域108のn+カソード領域120に、高濃度p型半導体領域であるp+カソードショート領域174が、所定の間隔を隔てて複数形成されている点で、実施例8の半導体装置102と異なる。本実施例では、p+カソードショート領域174の不純物濃度は1×1017〜5×1020[cm-3]程度である。本実施例の半導体装置172によれば、順バイアスの印加時において、n+カソード領域120からn−ドリフト領域114への電子の注入が抑制されているので、実施例8の半導体装置102に比べて、逆回復電流をさらに小さくし、逆回復時間をさらに短くすることができる。本実施例の半導体装置172によれば、さらにスイッチング損失を小さくすることが出来る。
図20に示すように、本実施例の半導体装置182は、実施例9の半導体装置162とほぼ同様の構成を備えている。本実施例の半導体装置182では、ダイオード領域108のn+カソード領域120に、p+カソードショート領域174が、所定の間隔を隔てて複数形成されている点で、実施例9の半導体装置162と異なる。本実施例の半導体装置182によれば、順バイアスの印加時において、n+カソード領域120からn−ドリフト領域114への電子の注入が抑制されているので、実施例9の半導体装置162に比べて、逆回復電流をさらに小さくし、逆回復時間をさらに短くすることができる。本実施例の半導体装置182によれば、さらにスイッチング損失を小さくすることが出来る。
図21に示すように、本実施例の半導体装置202は、シリコンの半導体基板204を用いて形成されている。半導体基板204は、高濃度n型半導体領域であるn+カソード領域206と、n型半導体領域であるnバッファ領域208と、低濃度n型半導体領域であるn−ドリフト領域210が順に積層されている。本実施例では、n+カソード領域206の不純物濃度は1×1017〜5×1020[cm-3]程度であり、nバッファ領域208の不純物濃度は1×1016〜1×1019[cm-3]程度であり、n−ドリフト領域210の不純物濃度は1×1012〜1×1015[cm-3]程度である。
図22に示すように、本実施例の半導体装置232は、実施例12の半導体装置202とほぼ同様の構成を備えている。本実施例の半導体装置232も、実施例12の半導体装置202と同様に、縦型のMOSFETの構造を有している。本実施例の半導体装置232では、n−ドリフト領域210とnバリア領域212の間に、p型半導体領域であるp電界進展防止領域234が形成されている。p電界進展防止領域234の不純物濃度は1×1015〜1×1019[cm-3]程度である。また、p電界進展防止領域234厚さは0.5〜3.0[μm]程度である。
図23に示すように、本実施例の半導体装置242は、実施例12の半導体装置202とほぼ同様の構成を備えている。本実施例の半導体装置242では、n+カソード領域206において、高濃度p型半導体領域であるp+コレクタ領域244が部分的に形成されている。本実施例では、p+コレクタ領域244の不純物濃度は1×1017〜5×1020[cm-3]程度である。
図24に示すように、本実施例の半導体装置252は、実施例14の半導体装置242とほぼ同様の構成を備えている。本実施例の半導体装置252では、n−ドリフト領域210とnバリア領域212の間に、p型半導体領域であるp電界進展防止領域234が形成されている。p電界進展防止領域234の不純物濃度は1×1015〜1×1019[cm-3]程度である。また、p電界進展防止領域234厚さは0.5〜3.0[μm]程度である。半導体装置252は、プレーナ型のIGBTとフリーホイーリングダイオードが逆並列に接続された構造を有している。
図25に示すように、本実施例のダイオード302は、実施例1のダイオード2とほぼ同様の構成を備えている。本実施例のダイオード302は、nピラー領域16の代わりに、金属製のピラー電極16aを備えている。ピラー電極16aは、半導体基板4の上側表面にpアノード領域14を貫通してnバリア領域12まで達するトレンチを形成し、そのトレンチに金属を充填することで形成される。ピラー電極16aはアノード電極22と導通しており、nバリア領域12とショットキー界面24aを介してショットキー接合している。
図26に示すように、本実施例のダイオード304は、実施例2のダイオード32とほぼ同様の構成を備えている。本実施例のダイオード304は、nピラー領域16の代わりに、金属製のピラー電極16aを備えている。ピラー電極16aは、半導体基板34の上側表面にpアノード領域14を貫通してnバリア領域12まで達するトレンチを形成し、そのトレンチに金属を充填することで形成される。ピラー電極16aはアノード電極22と導通しており、nバリア領域12とショットキー界面24aを介してショットキー接合している。
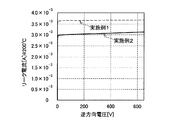
図7に示すダイオード42、図8に示すダイオード52、図10に示すダイオード62、図11に示すダイオード66、図12に示すダイオード68、図13に示すダイオード70のそれぞれにおいて、nピラー領域16を上述のピラー電極16aで置き換えることによって、図27に示すダイオード306、図28に示すダイオード308、図29に示すダイオード310、図30に示すダイオード312、図31に示すダイオード314、図32に示すダイオード316のように構成することもできる。
Claims (6)
- カソード電極と、第1導電型の半導体からなるカソード領域と、前記カソード領域よりも濃度が低い第1導電型の半導体からなるドリフト領域と、第2導電型の半導体からなるアノード領域と、金属からなるアノード電極を備えるダイオードであって、
前記ドリフト領域と前記アノード領域の間に形成された、前記ドリフト領域よりも濃度が高い第1導電型の半導体からなるバリア領域と、
前記バリア領域と前記アノード電極を接続するように形成された、前記バリア領域よりも濃度が高い第1導電型の半導体からなるピラー領域を備えており、
前記ピラー領域が、前記アノード電極側から前記アノード領域を貫通して前記バリア領域まで達するように形成されており、
前記ピラー領域と前記アノード電極がショットキー接合していることを特徴とするダイオード。 - 前記バリア領域と前記ドリフト領域の間に形成された、第2導電型の半導体からなる電界進展防止領域をさらに備えていることを特徴とする請求項1のダイオード。
- 前記アノード領域から前記ドリフト領域まで達するトレンチが形成されており、
前記トレンチの内部に絶縁膜で被覆されたトレンチ電極が形成されていることを特徴とする請求項1または2のダイオード。 - 前記カソード領域に部分的に形成された、第2導電型の半導体からなるカソードショート領域をさらに備えていることを特徴とする請求項1から3の何れか一項のダイオード。
- 請求項1から4の何れか一項のダイオードとIGBTが一体化された半導体装置であって、
前記IGBTが、コレクタ電極と、第2導電型の半導体からなるコレクタ領域と、前記ドリフト領域から連続しており、第1導電型の半導体からなる第2ドリフト領域と、第2導電型の半導体からなるボディ領域と、第1導電型の半導体からなるエミッタ領域と、金属からなるエミッタ電極と、前記エミッタ領域と前記第2ドリフト領域の間の前記ボディ領域に対して絶縁膜を挟んで対向するゲート電極を備えており、
前記IGBTが、前記第2ドリフト領域と前記ボディ領域の間に形成された、前記第2ドリフト領域よりも濃度が高い第1導電型の半導体からなる第2バリア領域と、前記第2バリア領域と前記エミッタ電極を接続するように形成された、前記第2バリア領域よりも濃度が高い第1導電型の半導体からなる第2ピラー領域を備えており、
前記第2ピラー領域が、前記エミッタ電極側から前記ボディ領域を貫通して前記第2バリア領域まで達するように形成されており、
前記第2ピラー領域と前記エミッタ電極がショットキー接合していることを特徴とする半導体装置。 - 前記第2バリア領域と前記第2ドリフト領域の間に形成された、第2導電型の半導体からなる第2電界進展防止領域をさらに備えることを特徴とする請求項5の半導体装置。
Priority Applications (9)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201280035577.5A CN103890955B (zh) | 2011-07-27 | 2012-07-27 | 半导体器件 |
| DE112012003111.3T DE112012003111T5 (de) | 2011-07-27 | 2012-07-27 | Diode, Halbleitervorrichtung und Mosfet |
| US14/113,276 US9520465B2 (en) | 2011-07-27 | 2012-07-27 | Diode, semiconductor device, and MOSFET |
| JP2012166576A JP5919121B2 (ja) | 2011-07-27 | 2012-07-27 | ダイオードおよび半導体装置 |
| PCT/JP2012/004804 WO2013014943A2 (en) | 2011-07-27 | 2012-07-27 | Diode, semiconductor device, and mosfet |
| DE112012007322.3T DE112012007322B3 (de) | 2011-07-27 | 2012-07-27 | Diode, Halbleitervorrichtung und MOSFET |
| CN201611257527.8A CN107068733B (zh) | 2011-07-27 | 2012-07-27 | 半导体器件 |
| US15/342,858 US10147812B2 (en) | 2011-07-27 | 2016-11-03 | Diode, semiconductor device, and MOSFET |
| US16/111,745 US10658503B2 (en) | 2011-07-27 | 2018-08-24 | Diode, semiconductor device, and MOSFET |
Applications Claiming Priority (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011164746 | 2011-07-27 | ||
| JP2011164746 | 2011-07-27 | ||
| JP2012166576A JP5919121B2 (ja) | 2011-07-27 | 2012-07-27 | ダイオードおよび半導体装置 |
Related Child Applications (2)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2015153160A Division JP6011696B2 (ja) | 2011-07-27 | 2015-08-03 | ダイオード、半導体装置およびmosfet |
| JP2015153159A Division JP6001735B2 (ja) | 2011-07-27 | 2015-08-03 | Mosfet |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2013048230A JP2013048230A (ja) | 2013-03-07 |
| JP5919121B2 true JP5919121B2 (ja) | 2016-05-18 |
Family
ID=47143235
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012166576A Active JP5919121B2 (ja) | 2011-07-27 | 2012-07-27 | ダイオードおよび半導体装置 |
Country Status (5)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (3) | US9520465B2 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JP5919121B2 (ja) |
| CN (2) | CN107068733B (ja) |
| DE (2) | DE112012003111T5 (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2013014943A2 (ja) |
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2019149511A (ja) * | 2018-02-28 | 2019-09-05 | 株式会社 日立パワーデバイス | 半導体装置および電力変換装置 |
| JP2021040070A (ja) * | 2019-09-04 | 2021-03-11 | 株式会社デンソー | 半導体装置 |
| JP2021040071A (ja) * | 2019-09-04 | 2021-03-11 | 株式会社デンソー | 半導体装置 |
Families Citing this family (102)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US9214458B2 (en) | 2012-09-06 | 2015-12-15 | Mitsubishi Electric Corporation | Semiconductor device |
| US9219138B2 (en) | 2012-10-05 | 2015-12-22 | Semiconductor Components Industries, Llc | Semiconductor device having localized charge balance structure and method |
| KR101427948B1 (ko) * | 2012-12-18 | 2014-08-08 | 현대자동차 주식회사 | 쇼트키 배리어 다이오드 및 그 제조 방법 |
| JP5981859B2 (ja) | 2013-02-15 | 2016-08-31 | 株式会社豊田中央研究所 | ダイオード及びダイオードを内蔵する半導体装置 |
| JP5992094B2 (ja) * | 2013-04-03 | 2016-09-14 | 三菱電機株式会社 | 半導体装置 |
| CN105378931A (zh) * | 2013-05-23 | 2016-03-02 | 丰田自动车株式会社 | 内置有二极管的igbt |
| US9331197B2 (en) | 2013-08-08 | 2016-05-03 | Cree, Inc. | Vertical power transistor device |
| CN105556668B (zh) * | 2013-08-26 | 2017-09-01 | 丰田自动车株式会社 | 半导体装置 |
| JP6242633B2 (ja) | 2013-09-03 | 2017-12-06 | 株式会社東芝 | 半導体装置 |
| JP2015056486A (ja) | 2013-09-11 | 2015-03-23 | 株式会社東芝 | 半導体装置およびその製造方法 |
| US10600903B2 (en) | 2013-09-20 | 2020-03-24 | Cree, Inc. | Semiconductor device including a power transistor device and bypass diode |
| US10868169B2 (en) * | 2013-09-20 | 2020-12-15 | Cree, Inc. | Monolithically integrated vertical power transistor and bypass diode |
| US9318597B2 (en) | 2013-09-20 | 2016-04-19 | Cree, Inc. | Layout configurations for integrating schottky contacts into a power transistor device |
| CN104465791B (zh) * | 2013-09-22 | 2018-10-26 | 南京励盛半导体科技有限公司 | 一种快恢复二极管的结构和背面的制备方法 |
| DE102013220011A1 (de) * | 2013-10-02 | 2015-04-02 | Robert Bosch Gmbh | Halbleiteranordnung mit temperaturkompensierter Durchbruchsspannung |
| EP2966683B1 (en) | 2013-10-04 | 2020-12-09 | Fuji Electric Co., Ltd. | Semiconductor device |
| JP6154292B2 (ja) | 2013-11-06 | 2017-06-28 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | 半導体装置及び半導体装置の製造方法 |
| WO2015093190A1 (ja) * | 2013-12-16 | 2015-06-25 | 富士電機株式会社 | 半導体装置および半導体装置の製造方法 |
| JP5918288B2 (ja) | 2014-03-03 | 2016-05-18 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | 半導体装置 |
| JP2015170654A (ja) * | 2014-03-05 | 2015-09-28 | 株式会社東芝 | 半導体装置 |
| US9634128B2 (en) | 2014-03-17 | 2017-04-25 | Kabushiki Kaisha Toshiba | Semiconductor device |
| KR20150108291A (ko) * | 2014-03-17 | 2015-09-25 | 가부시끼가이샤 도시바 | 반도체 장치 |
| JP6237408B2 (ja) * | 2014-03-28 | 2017-11-29 | 住友電気工業株式会社 | 炭化珪素半導体装置およびその製造方法 |
| US10608104B2 (en) * | 2014-03-28 | 2020-03-31 | Infineon Technologies Ag | Trench transistor device |
| JP2015216200A (ja) * | 2014-05-09 | 2015-12-03 | 株式会社豊田中央研究所 | 半導体装置 |
| JP2015216270A (ja) * | 2014-05-12 | 2015-12-03 | ローム株式会社 | 半導体装置および半導体装置の製造方法 |
| JP2016009712A (ja) * | 2014-06-23 | 2016-01-18 | 住友電気工業株式会社 | 炭化珪素半導体装置 |
| JP6036765B2 (ja) | 2014-08-22 | 2016-11-30 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | 半導体装置及び半導体装置の製造方法 |
| JP6135636B2 (ja) * | 2014-10-17 | 2017-05-31 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | 半導体装置 |
| JP6003961B2 (ja) * | 2014-11-04 | 2016-10-05 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | 半導体装置 |
| CN104393056B (zh) * | 2014-11-10 | 2017-02-15 | 电子科技大学 | 一种积累型二极管 |
| JP2016096307A (ja) * | 2014-11-17 | 2016-05-26 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | 半導体装置 |
| JP6164201B2 (ja) * | 2014-11-17 | 2017-07-19 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | 半導体装置 |
| JP6063915B2 (ja) * | 2014-12-12 | 2017-01-18 | 株式会社豊田中央研究所 | 逆導通igbt |
| JP6053050B2 (ja) | 2014-12-12 | 2016-12-27 | 株式会社豊田中央研究所 | 逆導通igbt |
| DE102014226161B4 (de) * | 2014-12-17 | 2017-10-26 | Infineon Technologies Ag | Halbleitervorrichtung mit Überlaststrombelastbarkeit |
| JP6288315B2 (ja) * | 2015-02-09 | 2018-03-07 | 三菱電機株式会社 | 半導体装置 |
| JP6152861B2 (ja) * | 2015-02-09 | 2017-06-28 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | ダイオードの製造方法 |
| JP6293688B2 (ja) * | 2015-03-02 | 2018-03-14 | 株式会社豊田中央研究所 | ダイオード及びそのダイオードを内蔵する逆導通igbt |
| CN107068742B (zh) * | 2015-03-02 | 2020-04-21 | 常州中明半导体技术有限公司 | 具有不连续p型基区嵌入原胞结构的半导体器件 |
| JP6222140B2 (ja) * | 2015-03-04 | 2017-11-01 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | 半導体装置 |
| JP6126150B2 (ja) * | 2015-03-06 | 2017-05-10 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | 半導体装置 |
| US10217738B2 (en) * | 2015-05-15 | 2019-02-26 | Smk Corporation | IGBT semiconductor device |
| US9929260B2 (en) | 2015-05-15 | 2018-03-27 | Fuji Electric Co., Ltd. | IGBT semiconductor device |
| JP6185511B2 (ja) | 2015-05-26 | 2017-08-23 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | 半導体装置 |
| JP6274154B2 (ja) | 2015-05-27 | 2018-02-07 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | 逆導通igbt |
| JP6213522B2 (ja) | 2015-06-03 | 2017-10-18 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | 半導体装置 |
| CN106298774A (zh) * | 2015-06-10 | 2017-01-04 | 北大方正集团有限公司 | 一种mps二极管及其制造方法 |
| JP6217700B2 (ja) * | 2015-07-21 | 2017-10-25 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | ダイオード |
| JP6217708B2 (ja) | 2015-07-30 | 2017-10-25 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | 半導体装置とその製造方法 |
| JP6441192B2 (ja) * | 2015-09-11 | 2018-12-19 | 株式会社東芝 | 半導体装置 |
| JP6281548B2 (ja) * | 2015-09-17 | 2018-02-21 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | 半導体装置 |
| DE102015120210B4 (de) * | 2015-11-23 | 2019-02-21 | Infineon Technologies Ag | Leistungshalbleitertransistor mit vergrößerter bipolarer Verstärkung |
| JP6304221B2 (ja) * | 2015-12-08 | 2018-04-04 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | Igbt |
| JP6451869B2 (ja) * | 2015-12-11 | 2019-01-16 | 富士電機株式会社 | 半導体装置 |
| JP6658021B2 (ja) * | 2016-02-03 | 2020-03-04 | 株式会社デンソー | 半導体装置 |
| WO2017149607A1 (ja) * | 2016-02-29 | 2017-09-08 | 三菱電機株式会社 | 半導体装置 |
| JP6846119B2 (ja) * | 2016-05-02 | 2021-03-24 | 株式会社 日立パワーデバイス | ダイオード、およびそれを用いた電力変換装置 |
| US9768247B1 (en) | 2016-05-06 | 2017-09-19 | Semiconductor Components Industries, Llc | Semiconductor device having improved superjunction trench structure and method of manufacture |
| DE102016112721B4 (de) | 2016-07-12 | 2022-02-03 | Infineon Technologies Ag | n-Kanal-Leistungshalbleitervorrichtung mit p-Schicht im Driftvolumen |
| US9935188B2 (en) * | 2016-07-22 | 2018-04-03 | Pakal Technologies Llc | Insulated gate turn-off device with turn-off Schottky-Barrier MOSFET |
| JP6702423B2 (ja) | 2016-08-12 | 2020-06-03 | 富士電機株式会社 | 半導体装置および半導体装置の製造方法 |
| JP6805655B2 (ja) * | 2016-09-07 | 2020-12-23 | 富士電機株式会社 | 半導体装置 |
| JP6624300B2 (ja) * | 2016-10-17 | 2019-12-25 | 富士電機株式会社 | 半導体装置 |
| JP6589817B2 (ja) | 2016-10-26 | 2019-10-16 | 株式会社デンソー | 半導体装置 |
| JP6939300B2 (ja) * | 2016-11-17 | 2021-09-22 | 富士電機株式会社 | 半導体装置 |
| JP6784164B2 (ja) * | 2016-12-15 | 2020-11-11 | 株式会社豊田中央研究所 | 半導体装置 |
| DE102016125879B3 (de) * | 2016-12-29 | 2018-06-21 | Infineon Technologies Ag | Halbleitervorrichtung mit einer IGBT-Region und einer nicht schaltbaren Diodenregion |
| JP6852541B2 (ja) * | 2017-04-20 | 2021-03-31 | 株式会社デンソー | 半導体装置 |
| US10439054B2 (en) * | 2017-06-29 | 2019-10-08 | Kabushiki Kaisha Toshiba | Insulated gate bipolar transistor |
| CN107359125A (zh) * | 2017-07-03 | 2017-11-17 | 苏州达晶微电子有限公司 | 一种优化体二极管反向恢复特性的方法及装置 |
| DE102017118665A1 (de) * | 2017-08-16 | 2019-02-21 | Infineon Technologies Ag | Rc-igbt |
| JP6740986B2 (ja) * | 2017-08-31 | 2020-08-19 | 株式会社デンソー | 炭化珪素半導体装置およびその製造方法 |
| JP6946922B2 (ja) * | 2017-10-18 | 2021-10-13 | 株式会社デンソー | 半導体装置 |
| US11393812B2 (en) * | 2017-12-28 | 2022-07-19 | Fuji Electric Co., Ltd. | Semiconductor device and method of manufacturing semiconductor device |
| JP7334407B2 (ja) * | 2017-12-28 | 2023-08-29 | 富士電機株式会社 | 半導体装置および半導体装置の製造方法 |
| JP7151084B2 (ja) | 2018-01-11 | 2022-10-12 | 株式会社デンソー | 半導体装置 |
| JP7095303B2 (ja) | 2018-02-14 | 2022-07-05 | 富士電機株式会社 | 半導体装置 |
| JP7119422B2 (ja) * | 2018-02-28 | 2022-08-17 | 富士電機株式会社 | 縦型半導体装置及び縦型半導体装置の製造方法 |
| US10608122B2 (en) * | 2018-03-13 | 2020-03-31 | Semicondutor Components Industries, Llc | Schottky device and method of manufacture |
| JP6935351B2 (ja) * | 2018-03-20 | 2021-09-15 | 株式会社東芝 | 半導体装置 |
| DE102018106967B3 (de) * | 2018-03-23 | 2019-05-23 | Infineon Technologies Ag | SILIZIUMCARBID HALBLEITERBAUELEMENT und Halbleiterdiode |
| JP7263740B2 (ja) * | 2018-11-06 | 2023-04-25 | 富士電機株式会社 | 炭化珪素半導体装置および炭化珪素半導体装置の製造方法 |
| JP6972382B2 (ja) | 2018-11-30 | 2021-11-24 | 三菱電機株式会社 | 半導体装置 |
| CN110416319B (zh) * | 2019-08-21 | 2023-05-05 | 江苏中科君芯科技有限公司 | 双面肖特基控制的快恢复二极管器件及制备方法 |
| WO2021038699A1 (ja) * | 2019-08-26 | 2021-03-04 | 株式会社デンソー | 半導体装置とその製造方法 |
| US11469333B1 (en) * | 2020-02-19 | 2022-10-11 | Semiq Incorporated | Counter-doped silicon carbide Schottky barrier diode |
| US10910478B1 (en) * | 2020-03-04 | 2021-02-02 | Shuming Xu | Metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistor having enhanced high-frequency performance |
| JP7296907B2 (ja) * | 2020-03-10 | 2023-06-23 | 株式会社東芝 | 半導体装置 |
| JP7359053B2 (ja) * | 2020-03-26 | 2023-10-11 | 三菱電機株式会社 | 半導体装置 |
| US20230207707A1 (en) | 2020-07-16 | 2023-06-29 | Mitsubishi Electric Corporation | Power semiconductor device |
| JP7486373B2 (ja) * | 2020-07-29 | 2024-05-17 | 三菱電機株式会社 | 半導体装置 |
| JP7528687B2 (ja) * | 2020-09-30 | 2024-08-06 | 三菱電機株式会社 | 半導体装置 |
| US12080790B2 (en) | 2020-10-28 | 2024-09-03 | Wolfspeed, Inc. | Power semiconductor devices including angled gate trenches |
| US11769828B2 (en) | 2020-10-28 | 2023-09-26 | Wolfspeed, Inc. | Gate trench power semiconductor devices having improved deep shield connection patterns |
| US11610991B2 (en) | 2020-10-28 | 2023-03-21 | Wolfspeed, Inc. | Gate trench power semiconductor devices having improved deep shield connection patterns |
| JP7528743B2 (ja) * | 2020-11-27 | 2024-08-06 | 三菱電機株式会社 | 半導体装置 |
| JP7476129B2 (ja) * | 2021-03-12 | 2024-04-30 | 株式会社東芝 | 半導体装置及び半導体回路 |
| JP7517218B2 (ja) | 2021-03-24 | 2024-07-17 | 株式会社デンソー | 半導体装置 |
| JP2023036341A (ja) * | 2021-09-02 | 2023-03-14 | 株式会社 日立パワーデバイス | 半導体装置、半導体装置の製造方法、電力変換装置 |
| CN116632053B (zh) * | 2023-07-25 | 2024-01-30 | 深圳市美浦森半导体有限公司 | 一种rc-igbt器件的控制方法 |
| CN118553763B (zh) * | 2024-07-24 | 2024-10-18 | 江西萨瑞微电子技术有限公司 | 一种sgt器件制备方法及外延片 |
Family Cites Families (19)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GB1558506A (en) | 1976-08-09 | 1980-01-03 | Mullard Ltd | Semiconductor devices having a rectifying metalto-semicondductor junction |
| JPH0286173A (ja) * | 1988-09-22 | 1990-03-27 | Fuji Electric Co Ltd | 半導体ダイオード |
| US5998833A (en) * | 1998-10-26 | 1999-12-07 | North Carolina State University | Power semiconductor devices having improved high frequency switching and breakdown characteristics |
| JP3968912B2 (ja) | 1999-05-10 | 2007-08-29 | 富士電機デバイステクノロジー株式会社 | ダイオード |
| US6252258B1 (en) | 1999-08-10 | 2001-06-26 | Rockwell Science Center Llc | High power rectifier |
| JP2003163357A (ja) | 2001-11-26 | 2003-06-06 | Fuji Electric Co Ltd | 半導体装置およびその製造方法 |
| JP4047153B2 (ja) * | 2002-12-03 | 2008-02-13 | 株式会社東芝 | 半導体装置 |
| EP1935007B1 (en) * | 2005-09-16 | 2023-02-22 | Wolfspeed, Inc. | Methods of processing semiconductor wafers having silicon carbide power devices thereon |
| JP2008066708A (ja) * | 2006-08-09 | 2008-03-21 | Toshiba Corp | 半導体装置 |
| US7595241B2 (en) * | 2006-08-23 | 2009-09-29 | General Electric Company | Method for fabricating silicon carbide vertical MOSFET devices |
| JP4532536B2 (ja) * | 2007-12-19 | 2010-08-25 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | 半導体装置 |
| KR100936808B1 (ko) * | 2007-12-26 | 2010-01-14 | 주식회사 하이닉스반도체 | 저 시트저항 워드라인과 수직채널트랜지스터를 구비한반도체소자 및 그 제조 방법 |
| JP5617175B2 (ja) | 2008-04-17 | 2014-11-05 | 富士電機株式会社 | ワイドバンドギャップ半導体装置とその製造方法 |
| JP5206096B2 (ja) * | 2008-04-25 | 2013-06-12 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | ダイオードとそのダイオードを備えている半導体装置 |
| CN102804359B (zh) * | 2009-06-11 | 2014-06-04 | 丰田自动车株式会社 | 半导体装置 |
| US7910486B2 (en) * | 2009-06-12 | 2011-03-22 | Alpha & Omega Semiconductor, Inc. | Method for forming nanotube semiconductor devices |
| JP5706275B2 (ja) * | 2011-08-31 | 2015-04-22 | 株式会社豊田中央研究所 | ダイオード、半導体装置およびmosfet |
| JP2013051345A (ja) | 2011-08-31 | 2013-03-14 | Toyota Central R&D Labs Inc | ダイオード、半導体装置およびmosfet |
| JP5753814B2 (ja) | 2012-04-16 | 2015-07-22 | 株式会社豊田中央研究所 | ダイオード、半導体装置およびmosfet |
-
2012
- 2012-07-27 CN CN201611257527.8A patent/CN107068733B/zh active Active
- 2012-07-27 JP JP2012166576A patent/JP5919121B2/ja active Active
- 2012-07-27 US US14/113,276 patent/US9520465B2/en active Active
- 2012-07-27 DE DE112012003111.3T patent/DE112012003111T5/de active Granted
- 2012-07-27 CN CN201280035577.5A patent/CN103890955B/zh active Active
- 2012-07-27 WO PCT/JP2012/004804 patent/WO2013014943A2/en active Application Filing
- 2012-07-27 DE DE112012007322.3T patent/DE112012007322B3/de active Active
-
2016
- 2016-11-03 US US15/342,858 patent/US10147812B2/en active Active
-
2018
- 2018-08-24 US US16/111,745 patent/US10658503B2/en active Active
Cited By (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2019149511A (ja) * | 2018-02-28 | 2019-09-05 | 株式会社 日立パワーデバイス | 半導体装置および電力変換装置 |
| WO2019167543A1 (ja) * | 2018-02-28 | 2019-09-06 | 株式会社 日立パワーデバイス | 半導体装置および電力変換装置 |
| US11282937B2 (en) | 2018-02-28 | 2022-03-22 | Hitachi Power Semiconductor Device, Ltd. | Semiconductor device and power conversion device |
| JP2021040070A (ja) * | 2019-09-04 | 2021-03-11 | 株式会社デンソー | 半導体装置 |
| JP2021040071A (ja) * | 2019-09-04 | 2021-03-11 | 株式会社デンソー | 半導体装置 |
| JP7172920B2 (ja) | 2019-09-04 | 2022-11-16 | 株式会社デンソー | 半導体装置 |
| JP7294004B2 (ja) | 2019-09-04 | 2023-06-20 | 株式会社デンソー | 半導体装置 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN107068733B (zh) | 2020-08-11 |
| WO2013014943A3 (en) | 2013-05-02 |
| JP2013048230A (ja) | 2013-03-07 |
| US10147812B2 (en) | 2018-12-04 |
| US9520465B2 (en) | 2016-12-13 |
| US20170098700A1 (en) | 2017-04-06 |
| US10658503B2 (en) | 2020-05-19 |
| WO2013014943A2 (en) | 2013-01-31 |
| CN103890955B (zh) | 2017-06-13 |
| US20140048847A1 (en) | 2014-02-20 |
| DE112012007322B3 (de) | 2022-06-09 |
| CN107068733A (zh) | 2017-08-18 |
| CN103890955A (zh) | 2014-06-25 |
| DE112012003111T5 (de) | 2014-04-10 |
| US20180374947A1 (en) | 2018-12-27 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5919121B2 (ja) | ダイオードおよび半導体装置 | |
| JP5981859B2 (ja) | ダイオード及びダイオードを内蔵する半導体装置 | |
| JP6011696B2 (ja) | ダイオード、半導体装置およびmosfet | |
| JP5753814B2 (ja) | ダイオード、半導体装置およびmosfet | |
| JP5787853B2 (ja) | 電力用半導体装置 | |
| JP5190485B2 (ja) | 半導体装置 | |
| JP6063915B2 (ja) | 逆導通igbt | |
| JP5922886B2 (ja) | ダイオードおよび半導体装置 | |
| JP6053050B2 (ja) | 逆導通igbt | |
| US9082815B2 (en) | Semiconductor device having carrier extraction in electric field alleviating layer | |
| JP2013051345A (ja) | ダイオード、半導体装置およびmosfet | |
| JP5706275B2 (ja) | ダイオード、半導体装置およびmosfet | |
| JP5781383B2 (ja) | パワー半導体デバイス | |
| WO2014112239A1 (ja) | 半導体素子 | |
| JP2013201360A (ja) | 半導体装置 | |
| JP6674395B2 (ja) | 半導体装置 | |
| JP6077309B2 (ja) | ダイオード及びダイオードを内蔵した半導体装置 | |
| WO2015008458A1 (ja) | 半導体装置 | |
| JP2016149429A (ja) | 逆導通igbt | |
| JP2017139415A (ja) | 半導体装置 | |
| US9147757B2 (en) | Power semiconductor device and method for manufacturing the same | |
| JP2009182205A (ja) | 半導体装置 | |
| JP2017199723A (ja) | 半導体装置 | |
| KR20150076815A (ko) | 전력 반도체 소자 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20130917 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20141111 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20150602 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20150803 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20160405 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20160411 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 5919121 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| S111 | Request for change of ownership or part of ownership |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R313117 |
|
| R350 | Written notification of registration of transfer |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R350 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |