EP3467125B1 - Utilisation de nucléases foki à guidage arn (rfn) pour augmenter la spécificité pour la modification d'un génome à guidage arn - Google Patents
Utilisation de nucléases foki à guidage arn (rfn) pour augmenter la spécificité pour la modification d'un génome à guidage arn Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP3467125B1 EP3467125B1 EP18208105.9A EP18208105A EP3467125B1 EP 3467125 B1 EP3467125 B1 EP 3467125B1 EP 18208105 A EP18208105 A EP 18208105A EP 3467125 B1 EP3467125 B1 EP 3467125B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- target
- site
- egfp
- grna
- cas9
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 101710163270 Nuclease Proteins 0.000 title claims description 78
- 238000010362 genome editing Methods 0.000 title description 20
- 108020005004 Guide RNA Proteins 0.000 claims description 262
- 108091033409 CRISPR Proteins 0.000 claims description 125
- 108020004414 DNA Proteins 0.000 claims description 67
- 230000035772 mutation Effects 0.000 claims description 66
- 108090000623 proteins and genes Proteins 0.000 claims description 46
- 239000002773 nucleotide Substances 0.000 claims description 35
- 125000003729 nucleotide group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 35
- 108020001507 fusion proteins Proteins 0.000 claims description 33
- 102000037865 fusion proteins Human genes 0.000 claims description 33
- 108091028113 Trans-activating crRNA Proteins 0.000 claims description 26
- 230000000295 complement effect Effects 0.000 claims description 24
- 102000004169 proteins and genes Human genes 0.000 claims description 20
- 150000001413 amino acids Chemical class 0.000 claims description 18
- 241000193996 Streptococcus pyogenes Species 0.000 claims description 12
- 102100035102 E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase MYCBP2 Human genes 0.000 claims description 9
- 230000003197 catalytic effect Effects 0.000 claims description 5
- 102220605874 Cytosolic arginine sensor for mTORC1 subunit 2_D10A_mutation Human genes 0.000 claims description 4
- 125000002924 primary amino group Chemical group [H]N([H])* 0.000 claims description 2
- 238000010354 CRISPR gene editing Methods 0.000 claims 2
- 125000000539 amino acid group Chemical group 0.000 claims 1
- 108010048367 enhanced green fluorescent protein Proteins 0.000 description 189
- 210000004027 cell Anatomy 0.000 description 108
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 75
- 108010008532 Deoxyribonuclease I Proteins 0.000 description 62
- 102000007260 Deoxyribonuclease I Human genes 0.000 description 62
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 52
- 239000013612 plasmid Substances 0.000 description 43
- 230000014509 gene expression Effects 0.000 description 39
- 238000003556 assay Methods 0.000 description 36
- 210000005260 human cell Anatomy 0.000 description 36
- 238000002474 experimental method Methods 0.000 description 30
- 102100039037 Vascular endothelial growth factor A Human genes 0.000 description 25
- 230000008685 targeting Effects 0.000 description 21
- 102100030262 Regucalcin Human genes 0.000 description 20
- 239000013613 expression plasmid Substances 0.000 description 20
- 125000006850 spacer group Chemical group 0.000 description 20
- 239000013598 vector Substances 0.000 description 20
- 108091032973 (ribonucleotides)n+m Proteins 0.000 description 19
- 238000001890 transfection Methods 0.000 description 19
- 230000001404 mediated effect Effects 0.000 description 18
- 231100000350 mutagenesis Toxicity 0.000 description 18
- 238000003776 cleavage reaction Methods 0.000 description 17
- 150000007523 nucleic acids Chemical class 0.000 description 17
- 230000007017 scission Effects 0.000 description 17
- 230000004927 fusion Effects 0.000 description 16
- 235000018102 proteins Nutrition 0.000 description 16
- 108010022012 Fanconi Anemia Complementation Group F protein Proteins 0.000 description 14
- 238000002703 mutagenesis Methods 0.000 description 14
- 102000039446 nucleic acids Human genes 0.000 description 14
- 108020004707 nucleic acids Proteins 0.000 description 14
- 102000012216 Fanconi Anemia Complementation Group F protein Human genes 0.000 description 13
- 238000012350 deep sequencing Methods 0.000 description 13
- 235000001014 amino acid Nutrition 0.000 description 12
- 238000006471 dimerization reaction Methods 0.000 description 12
- 108091028043 Nucleic acid sequence Proteins 0.000 description 11
- 241000894006 Bacteria Species 0.000 description 10
- 230000004075 alteration Effects 0.000 description 10
- 230000036438 mutation frequency Effects 0.000 description 10
- 230000009437 off-target effect Effects 0.000 description 10
- 108091034117 Oligonucleotide Proteins 0.000 description 9
- 108700008625 Reporter Genes Proteins 0.000 description 9
- 238000004458 analytical method Methods 0.000 description 9
- 239000013604 expression vector Substances 0.000 description 9
- 230000006870 function Effects 0.000 description 9
- 230000006780 non-homologous end joining Effects 0.000 description 9
- 238000012360 testing method Methods 0.000 description 9
- 101001048956 Homo sapiens Homeobox protein EMX1 Proteins 0.000 description 8
- 102000013609 MutL Protein Homolog 1 Human genes 0.000 description 8
- 108010026664 MutL Protein Homolog 1 Proteins 0.000 description 8
- 238000012217 deletion Methods 0.000 description 8
- 230000037430 deletion Effects 0.000 description 8
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 description 8
- 125000005647 linker group Chemical group 0.000 description 8
- 238000011160 research Methods 0.000 description 8
- 230000008901 benefit Effects 0.000 description 7
- 238000003780 insertion Methods 0.000 description 7
- 230000037431 insertion Effects 0.000 description 7
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 7
- 229920002401 polyacrylamide Polymers 0.000 description 7
- 230000001225 therapeutic effect Effects 0.000 description 7
- 102100021122 DNA damage-binding protein 2 Human genes 0.000 description 6
- 102100023823 Homeobox protein EMX1 Human genes 0.000 description 6
- 238000010459 TALEN Methods 0.000 description 6
- 108010043645 Transcription Activator-Like Effector Nucleases Proteins 0.000 description 6
- JLCPHMBAVCMARE-UHFFFAOYSA-N [3-[[3-[[3-[[3-[[3-[[3-[[3-[[3-[[3-[[3-[[3-[[5-(2-amino-6-oxo-1H-purin-9-yl)-3-[[3-[[3-[[3-[[3-[[3-[[5-(2-amino-6-oxo-1H-purin-9-yl)-3-[[5-(2-amino-6-oxo-1H-purin-9-yl)-3-hydroxyoxolan-2-yl]methoxy-hydroxyphosphoryl]oxyoxolan-2-yl]methoxy-hydroxyphosphoryl]oxy-5-(5-methyl-2,4-dioxopyrimidin-1-yl)oxolan-2-yl]methoxy-hydroxyphosphoryl]oxy-5-(6-aminopurin-9-yl)oxolan-2-yl]methoxy-hydroxyphosphoryl]oxy-5-(6-aminopurin-9-yl)oxolan-2-yl]methoxy-hydroxyphosphoryl]oxy-5-(6-aminopurin-9-yl)oxolan-2-yl]methoxy-hydroxyphosphoryl]oxy-5-(6-aminopurin-9-yl)oxolan-2-yl]methoxy-hydroxyphosphoryl]oxyoxolan-2-yl]methoxy-hydroxyphosphoryl]oxy-5-(5-methyl-2,4-dioxopyrimidin-1-yl)oxolan-2-yl]methoxy-hydroxyphosphoryl]oxy-5-(4-amino-2-oxopyrimidin-1-yl)oxolan-2-yl]methoxy-hydroxyphosphoryl]oxy-5-(5-methyl-2,4-dioxopyrimidin-1-yl)oxolan-2-yl]methoxy-hydroxyphosphoryl]oxy-5-(5-methyl-2,4-dioxopyrimidin-1-yl)oxolan-2-yl]methoxy-hydroxyphosphoryl]oxy-5-(6-aminopurin-9-yl)oxolan-2-yl]methoxy-hydroxyphosphoryl]oxy-5-(6-aminopurin-9-yl)oxolan-2-yl]methoxy-hydroxyphosphoryl]oxy-5-(4-amino-2-oxopyrimidin-1-yl)oxolan-2-yl]methoxy-hydroxyphosphoryl]oxy-5-(4-amino-2-oxopyrimidin-1-yl)oxolan-2-yl]methoxy-hydroxyphosphoryl]oxy-5-(4-amino-2-oxopyrimidin-1-yl)oxolan-2-yl]methoxy-hydroxyphosphoryl]oxy-5-(6-aminopurin-9-yl)oxolan-2-yl]methoxy-hydroxyphosphoryl]oxy-5-(4-amino-2-oxopyrimidin-1-yl)oxolan-2-yl]methyl [5-(6-aminopurin-9-yl)-2-(hydroxymethyl)oxolan-3-yl] hydrogen phosphate Polymers Cc1cn(C2CC(OP(O)(=O)OCC3OC(CC3OP(O)(=O)OCC3OC(CC3O)n3cnc4c3nc(N)[nH]c4=O)n3cnc4c3nc(N)[nH]c4=O)C(COP(O)(=O)OC3CC(OC3COP(O)(=O)OC3CC(OC3COP(O)(=O)OC3CC(OC3COP(O)(=O)OC3CC(OC3COP(O)(=O)OC3CC(OC3COP(O)(=O)OC3CC(OC3COP(O)(=O)OC3CC(OC3COP(O)(=O)OC3CC(OC3COP(O)(=O)OC3CC(OC3COP(O)(=O)OC3CC(OC3COP(O)(=O)OC3CC(OC3COP(O)(=O)OC3CC(OC3COP(O)(=O)OC3CC(OC3COP(O)(=O)OC3CC(OC3COP(O)(=O)OC3CC(OC3COP(O)(=O)OC3CC(OC3COP(O)(=O)OC3CC(OC3CO)n3cnc4c(N)ncnc34)n3ccc(N)nc3=O)n3cnc4c(N)ncnc34)n3ccc(N)nc3=O)n3ccc(N)nc3=O)n3ccc(N)nc3=O)n3cnc4c(N)ncnc34)n3cnc4c(N)ncnc34)n3cc(C)c(=O)[nH]c3=O)n3cc(C)c(=O)[nH]c3=O)n3ccc(N)nc3=O)n3cc(C)c(=O)[nH]c3=O)n3cnc4c3nc(N)[nH]c4=O)n3cnc4c(N)ncnc34)n3cnc4c(N)ncnc34)n3cnc4c(N)ncnc34)n3cnc4c(N)ncnc34)O2)c(=O)[nH]c1=O JLCPHMBAVCMARE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- 230000001580 bacterial effect Effects 0.000 description 6
- 239000000539 dimer Substances 0.000 description 6
- 238000000338 in vitro Methods 0.000 description 6
- 230000003505 mutagenic effect Effects 0.000 description 6
- 108020004705 Codon Proteins 0.000 description 5
- 108010043471 Core Binding Factor Alpha 2 Subunit Proteins 0.000 description 5
- 238000001712 DNA sequencing Methods 0.000 description 5
- 101001041466 Homo sapiens DNA damage-binding protein 2 Proteins 0.000 description 5
- 101001026790 Homo sapiens Tyrosine-protein kinase Fes/Fps Proteins 0.000 description 5
- 102100037333 Tyrosine-protein kinase Fes/Fps Human genes 0.000 description 5
- 102000005789 Vascular Endothelial Growth Factors Human genes 0.000 description 5
- 108010019530 Vascular Endothelial Growth Factors Proteins 0.000 description 5
- 230000003247 decreasing effect Effects 0.000 description 5
- 230000001965 increasing effect Effects 0.000 description 5
- -1 4-12 amino acids Chemical class 0.000 description 4
- 108700020463 BRCA1 Proteins 0.000 description 4
- 102000036365 BRCA1 Human genes 0.000 description 4
- 101150072950 BRCA1 gene Proteins 0.000 description 4
- 241000238631 Hexapoda Species 0.000 description 4
- 101000642815 Homo sapiens Protein SSXT Proteins 0.000 description 4
- 102100035586 Protein SSXT Human genes 0.000 description 4
- 102100025373 Runt-related transcription factor 1 Human genes 0.000 description 4
- 108700009124 Transcription Initiation Site Proteins 0.000 description 4
- ISAKRJDGNUQOIC-UHFFFAOYSA-N Uracil Chemical compound O=C1C=CNC(=O)N1 ISAKRJDGNUQOIC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 102000009524 Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor A Human genes 0.000 description 4
- 108010073929 Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor A Proteins 0.000 description 4
- 108010016200 Zinc Finger Protein GLI1 Proteins 0.000 description 4
- 102100035535 Zinc finger protein GLI1 Human genes 0.000 description 4
- 230000027455 binding Effects 0.000 description 4
- 230000001419 dependent effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- 210000003527 eukaryotic cell Anatomy 0.000 description 4
- 230000037433 frameshift Effects 0.000 description 4
- 210000004962 mammalian cell Anatomy 0.000 description 4
- 230000007246 mechanism Effects 0.000 description 4
- 231100000243 mutagenic effect Toxicity 0.000 description 4
- 241000894007 species Species 0.000 description 4
- 238000006467 substitution reaction Methods 0.000 description 4
- 238000013518 transcription Methods 0.000 description 4
- 230000035897 transcription Effects 0.000 description 4
- 102000052567 Anaphase-Promoting Complex-Cyclosome Apc1 Subunit Human genes 0.000 description 3
- 238000010453 CRISPR/Cas method Methods 0.000 description 3
- 102000053602 DNA Human genes 0.000 description 3
- 230000007018 DNA scission Effects 0.000 description 3
- 102000016928 DNA-directed DNA polymerase Human genes 0.000 description 3
- 108010014303 DNA-directed DNA polymerase Proteins 0.000 description 3
- IAZDPXIOMUYVGZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Dimethylsulphoxide Chemical compound CS(C)=O IAZDPXIOMUYVGZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 102100037964 E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase RING2 Human genes 0.000 description 3
- 102000004533 Endonucleases Human genes 0.000 description 3
- 108010042407 Endonucleases Proteins 0.000 description 3
- 101001095815 Homo sapiens E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase RING2 Proteins 0.000 description 3
- 206010028400 Mutagenic effect Diseases 0.000 description 3
- 230000004570 RNA-binding Effects 0.000 description 3
- 108091027981 Response element Proteins 0.000 description 3
- 108091006463 SLC25A24 Proteins 0.000 description 3
- 240000004808 Saccharomyces cerevisiae Species 0.000 description 3
- 235000014680 Saccharomyces cerevisiae Nutrition 0.000 description 3
- 241000194020 Streptococcus thermophilus Species 0.000 description 3
- 241001633172 Streptococcus thermophilus LMD-9 Species 0.000 description 3
- 101150063416 add gene Proteins 0.000 description 3
- 238000013459 approach Methods 0.000 description 3
- 210000004899 c-terminal region Anatomy 0.000 description 3
- 238000005251 capillar electrophoresis Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000008045 co-localization Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000009977 dual effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000000684 flow cytometry Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000001939 inductive effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 239000013642 negative control Substances 0.000 description 3
- 108010054624 red fluorescent protein Proteins 0.000 description 3
- 230000009467 reduction Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000008439 repair process Effects 0.000 description 3
- 229920002477 rna polymer Polymers 0.000 description 3
- 238000007480 sanger sequencing Methods 0.000 description 3
- 241000701447 unidentified baculovirus Species 0.000 description 3
- 238000011144 upstream manufacturing Methods 0.000 description 3
- WGNUTGFETAXDTJ-OOJXKGFFSA-N 2'-O-methylpseudouridine Chemical compound CO[C@@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O[C@H]1C1=CNC(=O)NC1=O WGNUTGFETAXDTJ-OOJXKGFFSA-N 0.000 description 2
- KPPPLADORXGUFI-KCRXGDJASA-N 4-amino-1-[(2r,3r,4s,5r)-3,4-dihydroxy-5-(1-hydroxyethyl)oxolan-2-yl]pyrimidin-2-one Chemical compound O[C@@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](C(O)C)O[C@H]1N1C(=O)N=C(N)C=C1 KPPPLADORXGUFI-KCRXGDJASA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229930024421 Adenine Natural products 0.000 description 2
- GFFGJBXGBJISGV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Adenine Chemical compound NC1=NC=NC2=C1N=CN2 GFFGJBXGBJISGV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 206010053138 Congenital aplastic anaemia Diseases 0.000 description 2
- 241000196324 Embryophyta Species 0.000 description 2
- 241000588724 Escherichia coli Species 0.000 description 2
- 201000004939 Fanconi anemia Diseases 0.000 description 2
- DHMQDGOQFOQNFH-UHFFFAOYSA-N Glycine Chemical compound NCC(O)=O DHMQDGOQFOQNFH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 235000007688 Lycopersicon esculentum Nutrition 0.000 description 2
- 108091093037 Peptide nucleic acid Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 239000004952 Polyamide Substances 0.000 description 2
- 101710182846 Polyhedrin Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 240000003768 Solanum lycopersicum Species 0.000 description 2
- 241000700605 Viruses Species 0.000 description 2
- 241000435411 Wolinella succinogenes DSM 1740 Species 0.000 description 2
- 229960000643 adenine Drugs 0.000 description 2
- PPQRONHOSHZGFQ-LMVFSUKVSA-N aldehydo-D-ribose 5-phosphate Chemical group OP(=O)(O)OC[C@@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H](O)C=O PPQRONHOSHZGFQ-LMVFSUKVSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000011324 bead Substances 0.000 description 2
- 210000004369 blood Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- 239000008280 blood Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000010276 construction Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000005547 deoxyribonucleotide Substances 0.000 description 2
- 125000002637 deoxyribonucleotide group Chemical group 0.000 description 2
- 238000011161 development Methods 0.000 description 2
- UYTPUPDQBNUYGX-UHFFFAOYSA-N guanine Chemical compound O=C1NC(N)=NC2=C1N=CN2 UYTPUPDQBNUYGX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 238000009396 hybridization Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000001727 in vivo Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000013383 initial experiment Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000000178 monomer Substances 0.000 description 2
- 231100000219 mutagenic Toxicity 0.000 description 2
- 230000009438 off-target cleavage Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000005457 optimization Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229920002647 polyamide Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 238000002360 preparation method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 210000001236 prokaryotic cell Anatomy 0.000 description 2
- 238000011002 quantification Methods 0.000 description 2
- 102000005912 ran GTP Binding Protein Human genes 0.000 description 2
- 230000001105 regulatory effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 108091008146 restriction endonucleases Proteins 0.000 description 2
- 238000012216 screening Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000035945 sensitivity Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000010561 standard procedure Methods 0.000 description 2
- UCSJYZPVAKXKNQ-HZYVHMACSA-N streptomycin Chemical compound CN[C@H]1[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H](CO)O[C@H]1O[C@@H]1[C@](C=O)(O)[C@H](C)O[C@H]1O[C@@H]1[C@@H](NC(N)=N)[C@H](O)[C@@H](NC(N)=N)[C@H](O)[C@H]1O UCSJYZPVAKXKNQ-HZYVHMACSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 238000004448 titration Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000007862 touchdown PCR Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000009466 transformation Effects 0.000 description 2
- 229940035893 uracil Drugs 0.000 description 2
- DIGQNXIGRZPYDK-WKSCXVIASA-N (2R)-6-amino-2-[[2-[[(2S)-2-[[2-[[(2R)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2R,3S)-2-[[2-[[(2S)-2-[[2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2R)-2-[[(2S,3S)-2-[[(2R)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2R)-2-[[2-[[2-[[2-[(2-amino-1-hydroxyethylidene)amino]-3-carboxy-1-hydroxypropylidene]amino]-1-hydroxy-3-sulfanylpropylidene]amino]-1-hydroxyethylidene]amino]-1-hydroxy-3-sulfanylpropylidene]amino]-1,3-dihydroxypropylidene]amino]-1-hydroxyethylidene]amino]-1-hydroxypropylidene]amino]-1,3-dihydroxypropylidene]amino]-1,3-dihydroxypropylidene]amino]-1-hydroxy-3-sulfanylpropylidene]amino]-1,3-dihydroxybutylidene]amino]-1-hydroxy-3-sulfanylpropylidene]amino]-1-hydroxypropylidene]amino]-1,3-dihydroxypropylidene]amino]-1-hydroxyethylidene]amino]-1,5-dihydroxy-5-iminopentylidene]amino]-1-hydroxy-3-sulfanylpropylidene]amino]-1,3-dihydroxybutylidene]amino]-1-hydroxy-3-sulfanylpropylidene]amino]-1,3-dihydroxypropylidene]amino]-1-hydroxyethylidene]amino]-1-hydroxy-3-sulfanylpropylidene]amino]-1-hydroxyethylidene]amino]hexanoic acid Chemical compound C[C@@H]([C@@H](C(=N[C@@H](CS)C(=N[C@@H](C)C(=N[C@@H](CO)C(=NCC(=N[C@@H](CCC(=N)O)C(=NC(CS)C(=N[C@H]([C@H](C)O)C(=N[C@H](CS)C(=N[C@H](CO)C(=NCC(=N[C@H](CS)C(=NCC(=N[C@H](CCCCN)C(=O)O)O)O)O)O)O)O)O)O)O)O)O)O)O)N=C([C@H](CS)N=C([C@H](CO)N=C([C@H](CO)N=C([C@H](C)N=C(CN=C([C@H](CO)N=C([C@H](CS)N=C(CN=C(C(CS)N=C(C(CC(=O)O)N=C(CN)O)O)O)O)O)O)O)O)O)O)O)O DIGQNXIGRZPYDK-WKSCXVIASA-N 0.000 description 1
- MTCFGRXMJLQNBG-REOHCLBHSA-N (2S)-2-Amino-3-hydroxypropansäure Chemical compound OC[C@H](N)C(O)=O MTCFGRXMJLQNBG-REOHCLBHSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 102000040650 (ribonucleotides)n+m Human genes 0.000 description 1
- AZUYLZMQTIKGSC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 1-[6-[4-(5-chloro-6-methyl-1H-indazol-4-yl)-5-methyl-3-(1-methylindazol-5-yl)pyrazol-1-yl]-2-azaspiro[3.3]heptan-2-yl]prop-2-en-1-one Chemical compound ClC=1C(=C2C=NNC2=CC=1C)C=1C(=NN(C=1C)C1CC2(CN(C2)C(C=C)=O)C1)C=1C=C2C=NN(C2=CC=1)C AZUYLZMQTIKGSC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 101150090724 3 gene Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 241001430193 Absiella dolichum Species 0.000 description 1
- 241000916337 Acidaminococcus intestini RyC-MR95 Species 0.000 description 1
- 241001041760 Acidothermus cellulolyticus 11B Species 0.000 description 1
- 241001437069 Acidovorax ebreus TPSY Species 0.000 description 1
- 241000778935 Akkermansia muciniphila ATCC BAA-835 Species 0.000 description 1
- HJCMDXDYPOUFDY-WHFBIAKZSA-N Ala-Gln Chemical compound C[C@H](N)C(=O)N[C@H](C(O)=O)CCC(N)=O HJCMDXDYPOUFDY-WHFBIAKZSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 108700028369 Alleles Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 241001614497 Aminomonas paucivorans DSM 12260 Species 0.000 description 1
- 108091093088 Amplicon Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 241000589941 Azospirillum Species 0.000 description 1
- 241001079703 Bacillus cereus Rock1-15 Species 0.000 description 1
- 241000194110 Bacillus sp. (in: Bacteria) Species 0.000 description 1
- 108091032955 Bacterial small RNA Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 241000423333 Bacteroides fragilis NCTC 9343 Species 0.000 description 1
- KWIUHFFTVRNATP-UHFFFAOYSA-N Betaine Natural products C[N+](C)(C)CC([O-])=O KWIUHFFTVRNATP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 241000722293 Bifidobacterium bifidum S17 Species 0.000 description 1
- 241000586987 Bifidobacterium dentium Bd1 Species 0.000 description 1
- 241001209261 Bifidobacterium longum DJO10A Species 0.000 description 1
- 241000589173 Bradyrhizobium Species 0.000 description 1
- 206010006187 Breast cancer Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 108091079001 CRISPR RNA Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 238000010356 CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 101100491335 Caenorhabditis elegans mat-2 gene Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 101100084595 Caenorhabditis elegans pam-1 gene Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 241000589875 Campylobacter jejuni Species 0.000 description 1
- 241001453245 Campylobacter jejuni subsp. jejuni Species 0.000 description 1
- 241000283765 Candidatus Puniceispirillum marinum IMCC1322 Species 0.000 description 1
- 241001034636 Capnocytophaga ochracea DSM 7271 Species 0.000 description 1
- OKTJSMMVPCPJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N Carbon Chemical compound [C] OKTJSMMVPCPJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 241000761552 Catenibacterium mitsuokai DSM 15897 Species 0.000 description 1
- 108010077544 Chromatin Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 241001544469 Clostridium perfringens D Species 0.000 description 1
- 108091026890 Coding region Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 241000220677 Coprococcus catus Species 0.000 description 1
- 241001405991 Corynebacterium diphtheriae NCTC 13129 Species 0.000 description 1
- 101710137105 DNA damage-binding protein 2 Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 238000007399 DNA isolation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000007067 DNA methylation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 101710135281 DNA polymerase III PolC-type Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 241000252212 Danio rerio Species 0.000 description 1
- 241000933091 Dinoroseobacter shibae DFL 12 = DSM 16493 Species 0.000 description 1
- 241000448576 Elusimicrobium minutum Pei191 Species 0.000 description 1
- 241001274896 Enterococcus faecalis TX0012 Species 0.000 description 1
- 102000004190 Enzymes Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108090000790 Enzymes Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 101001091269 Escherichia coli Hygromycin-B 4-O-kinase Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 101150058673 FANCF gene Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 101150041213 FES1 gene Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 241000605895 Fibrobacter succinogenes subsp. succinogenes Species 0.000 description 1
- 241000162065 Filifactor alocis ATCC 35896 Species 0.000 description 1
- 241000359186 Finegoldia magna ATCC 29328 Species 0.000 description 1
- 241001277182 Flavobacterium columnare ATCC 49512 Species 0.000 description 1
- 241000588088 Francisella tularensis subsp. novicida U112 Species 0.000 description 1
- 241000233866 Fungi Species 0.000 description 1
- 241000009790 Fusobacterium nucleatum subsp. vincentii Species 0.000 description 1
- 108010001515 Galectin 4 Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 102100039556 Galectin-4 Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 229940123611 Genome editing Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 239000004471 Glycine Substances 0.000 description 1
- 241001013689 Helicobacter mustelae 12198 Species 0.000 description 1
- 108091027305 Heteroduplex Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 229920000209 Hexadimethrine bromide Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 101000924577 Homo sapiens Adenomatous polyposis coli protein Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 101100263585 Homo sapiens VEGFA gene Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 241000701044 Human gammaherpesvirus 4 Species 0.000 description 1
- 206010021143 Hypoxia Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 241000411974 Ilyobacter polytropus Species 0.000 description 1
- 241000256602 Isoptera Species 0.000 description 1
- QNAYBMKLOCPYGJ-REOHCLBHSA-N L-alanine Chemical compound C[C@H](N)C(O)=O QNAYBMKLOCPYGJ-REOHCLBHSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 108010054278 Lac Repressors Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 241000202367 Lactobacillus coryniformis subsp. torquens Species 0.000 description 1
- 241001070016 Lactobacillus gasseri JV-V03 Species 0.000 description 1
- 241000917009 Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG Species 0.000 description 1
- 241000589242 Legionella pneumophila Species 0.000 description 1
- 241000186805 Listeria innocua Species 0.000 description 1
- 241000432054 Listeria innocua Clip11262 Species 0.000 description 1
- 201000009906 Meningitis Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 102000003792 Metallothionein Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108090000157 Metallothionein Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 241001465754 Metazoa Species 0.000 description 1
- 241001529936 Murinae Species 0.000 description 1
- 241000699670 Mus sp. Species 0.000 description 1
- 241001678529 Mycoplasma canis PG 14 Species 0.000 description 1
- 241001465821 Mycoplasma gallisepticum str. F Species 0.000 description 1
- 241000107400 Mycoplasma mobile 163K Species 0.000 description 1
- 241000839520 Mycoplasma ovipneumoniae SC01 Species 0.000 description 1
- 241000051161 Mycoplasma synoviae 53 Species 0.000 description 1
- KWIUHFFTVRNATP-UHFFFAOYSA-O N,N,N-trimethylglycinium Chemical compound C[N+](C)(C)CC(O)=O KWIUHFFTVRNATP-UHFFFAOYSA-O 0.000 description 1
- 108091061960 Naked DNA Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 241000588650 Neisseria meningitidis Species 0.000 description 1
- 241000529650 Neisseria meningitidis Z2491 Species 0.000 description 1
- 208000009869 Neu-Laxova syndrome Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 241001276274 Nitratifractor salsuginis DSM 16511 Species 0.000 description 1
- 241001648684 Nitrobacter hamburgensis X14 Species 0.000 description 1
- 108010077850 Nuclear Localization Signals Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 241001333977 Oenococcus kitaharae DSM 17330 Species 0.000 description 1
- 241001119040 Olsenella uli DSM 7084 Species 0.000 description 1
- 238000012408 PCR amplification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 241001631646 Papillomaviridae Species 0.000 description 1
- 241000267607 Parasutterella excrementihominis YIT 11859 Species 0.000 description 1
- 241000601272 Parvibaculum lavamentivorans DS-1 Species 0.000 description 1
- 241000178955 Pasteurella multocida subsp. multocida Species 0.000 description 1
- 229930182555 Penicillin Natural products 0.000 description 1
- JGSARLDLIJGVTE-MBNYWOFBSA-N Penicillin G Chemical compound N([C@H]1[C@H]2SC([C@@H](N2C1=O)C(O)=O)(C)C)C(=O)CC1=CC=CC=C1 JGSARLDLIJGVTE-MBNYWOFBSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 241001643580 Peptoniphilus duerdenii ATCC BAA-1640 Species 0.000 description 1
- 241000721659 Prevotella micans F0438 Species 0.000 description 1
- 241000078168 Prevotella ruminicola 23 Species 0.000 description 1
- 241000863326 Ralstonia syzygii R24 Species 0.000 description 1
- 241001303434 Rhodopseudomonas palustris BisB18 Species 0.000 description 1
- 241000134686 Rhodospirillum rubrum ATCC 11170 Species 0.000 description 1
- 102000006382 Ribonucleases Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108010083644 Ribonucleases Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 101150062997 Rnf2 gene Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 241001451515 Roseburia intestinalis L1-82 Species 0.000 description 1
- 241000714474 Rous sarcoma virus Species 0.000 description 1
- 241001025897 Ruminococcus albus 8 Species 0.000 description 1
- 241000607142 Salmonella Species 0.000 description 1
- MTCFGRXMJLQNBG-UHFFFAOYSA-N Serine Natural products OCC(N)C(O)=O MTCFGRXMJLQNBG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 108091027967 Small hairpin RNA Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 108020004459 Small interfering RNA Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 241001438274 Solobacterium moorei F0204 Species 0.000 description 1
- 241000044624 Sphaerochaeta globosa str. Buddy Species 0.000 description 1
- 241001069987 Staphylococcus lugdunensis M23590 Species 0.000 description 1
- 241000446756 Staphylococcus pseudintermedius ED99 Species 0.000 description 1
- 241001521783 Streptococcus mutans UA159 Species 0.000 description 1
- 241000320123 Streptococcus pyogenes M1 GAS Species 0.000 description 1
- 101001091268 Streptomyces hygroscopicus Hygromycin-B 7''-O-kinase Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 108091027544 Subgenomic mRNA Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 241000123713 Sutterella wadsworthensis Species 0.000 description 1
- 241000255588 Tephritidae Species 0.000 description 1
- 239000004098 Tetracycline Substances 0.000 description 1
- 108010022394 Threonine synthase Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 102000006601 Thymidine Kinase Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 108020004440 Thymidine kinase Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 108010073062 Transcription Activator-Like Effectors Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 241000999858 Treponema denticola ATCC 35405 Species 0.000 description 1
- 241001533207 Veillonella atypica Species 0.000 description 1
- 241000847071 Verminephrobacter eiseniae EF01-2 Species 0.000 description 1
- HCHKCACWOHOZIP-UHFFFAOYSA-N Zinc Chemical compound [Zn] HCHKCACWOHOZIP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 241000883281 [Clostridium] cellulolyticum H10 Species 0.000 description 1
- 241000714896 [Eubacterium] rectale ATCC 33656 Species 0.000 description 1
- 239000002253 acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000007513 acids Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000012574 advanced DMEM Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000004279 alanine Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 210000004102 animal cell Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 238000000137 annealing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000003491 array Methods 0.000 description 1
- QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N atomic oxygen Chemical compound [O] QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000037429 base substitution Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229960003237 betaine Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 230000003115 biocidal effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000033228 biological regulation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229910000389 calcium phosphate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000001506 calcium phosphate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000011010 calcium phosphates Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 229910052799 carbon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 238000000423 cell based assay Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000004113 cell culture Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000001413 cellular effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000012512 characterization method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000003153 chemical reaction reagent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 210000003483 chromatin Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 208000029664 classic familial adenomatous polyposis Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 238000010367 cloning Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004186 co-expression Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000000052 comparative effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000002299 complementary DNA Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000000205 computational method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000012790 confirmation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 210000004748 cultured cell Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 230000009089 cytolysis Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000013461 design Methods 0.000 description 1
- 102000004419 dihydrofolate reductase Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 201000010099 disease Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 208000037265 diseases, disorders, signs and symptoms Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 238000009826 distribution Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000004520 electroporation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 108010026638 endodeoxyribonuclease FokI Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 239000003623 enhancer Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000002255 enzymatic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000002349 favourable effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000001943 fluorescence-activated cell sorting Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000012634 fragment Substances 0.000 description 1
- 231100000221 frame shift mutation induction Toxicity 0.000 description 1
- 230000002538 fungal effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 241000846566 gamma proteobacterium HTCC5015 Species 0.000 description 1
- 230000002068 genetic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010353 genetic engineering Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000037442 genomic alteration Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000036541 health Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000012165 high-throughput sequencing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 102000055691 human APC Human genes 0.000 description 1
- 230000007954 hypoxia Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000000415 inactivating effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000006698 induction Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000013101 initial test Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000011835 investigation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229940059406 lactobacillus rhamnosus gg Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 229940115932 legionella pneumophila Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 239000002502 liposome Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000011159 matrix material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000000520 microinjection Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000010369 molecular cloning Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000030648 nucleus localization Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000009401 outcrossing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000002018 overexpression Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229910052760 oxygen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000001301 oxygen Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229940049954 penicillin Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 239000013600 plasmid vector Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000008488 polyadenylation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000023603 positive regulation of transcription initiation, DNA-dependent Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 description 1
- 108090000765 processed proteins & peptides Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 230000000750 progressive effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000001742 protein purification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 210000001938 protoplast Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 238000000746 purification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000007115 recruitment Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000010076 replication Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010845 search algorithm Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000002864 sequence alignment Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000012163 sequencing technique Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000004904 shortening Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000013605 shuttle vector Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000003384 small molecules Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 238000003860 storage Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229960005322 streptomycin Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 230000009897 systematic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229930101283 tetracycline Natural products 0.000 description 1
- 229960002180 tetracycline Drugs 0.000 description 1
- 235000019364 tetracycline Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 150000003522 tetracyclines Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 210000001519 tissue Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 230000002103 transcriptional effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000003151 transfection method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000012546 transfer Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000007704 transition Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000013519 translation Methods 0.000 description 1
- QORWJWZARLRLPR-UHFFFAOYSA-H tricalcium bis(phosphate) Chemical compound [Ca+2].[Ca+2].[Ca+2].[O-]P([O-])([O-])=O.[O-]P([O-])([O-])=O QORWJWZARLRLPR-UHFFFAOYSA-H 0.000 description 1
- 230000009452 underexpressoin Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010200 validation analysis Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000012795 verification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000013603 viral vector Substances 0.000 description 1
- 210000005253 yeast cell Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 239000011701 zinc Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052725 zinc Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C12—BIOCHEMISTRY; BEER; SPIRITS; WINE; VINEGAR; MICROBIOLOGY; ENZYMOLOGY; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING
- C12N—MICROORGANISMS OR ENZYMES; COMPOSITIONS THEREOF; PROPAGATING, PRESERVING, OR MAINTAINING MICROORGANISMS; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING; CULTURE MEDIA
- C12N15/00—Mutation or genetic engineering; DNA or RNA concerning genetic engineering, vectors, e.g. plasmids, or their isolation, preparation or purification; Use of hosts therefor
- C12N15/09—Recombinant DNA-technology
- C12N15/11—DNA or RNA fragments; Modified forms thereof; Non-coding nucleic acids having a biological activity
- C12N15/113—Non-coding nucleic acids modulating the expression of genes, e.g. antisense oligonucleotides; Antisense DNA or RNA; Triplex- forming oligonucleotides; Catalytic nucleic acids, e.g. ribozymes; Nucleic acids used in co-suppression or gene silencing
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C12—BIOCHEMISTRY; BEER; SPIRITS; WINE; VINEGAR; MICROBIOLOGY; ENZYMOLOGY; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING
- C12N—MICROORGANISMS OR ENZYMES; COMPOSITIONS THEREOF; PROPAGATING, PRESERVING, OR MAINTAINING MICROORGANISMS; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING; CULTURE MEDIA
- C12N15/00—Mutation or genetic engineering; DNA or RNA concerning genetic engineering, vectors, e.g. plasmids, or their isolation, preparation or purification; Use of hosts therefor
- C12N15/09—Recombinant DNA-technology
- C12N15/87—Introduction of foreign genetic material using processes not otherwise provided for, e.g. co-transformation
- C12N15/90—Stable introduction of foreign DNA into chromosome
- C12N15/902—Stable introduction of foreign DNA into chromosome using homologous recombination
- C12N15/907—Stable introduction of foreign DNA into chromosome using homologous recombination in mammalian cells
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07K—PEPTIDES
- C07K14/00—Peptides having more than 20 amino acids; Gastrins; Somatostatins; Melanotropins; Derivatives thereof
- C07K14/005—Peptides having more than 20 amino acids; Gastrins; Somatostatins; Melanotropins; Derivatives thereof from viruses
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07K—PEPTIDES
- C07K14/00—Peptides having more than 20 amino acids; Gastrins; Somatostatins; Melanotropins; Derivatives thereof
- C07K14/195—Peptides having more than 20 amino acids; Gastrins; Somatostatins; Melanotropins; Derivatives thereof from bacteria
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C12—BIOCHEMISTRY; BEER; SPIRITS; WINE; VINEGAR; MICROBIOLOGY; ENZYMOLOGY; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING
- C12N—MICROORGANISMS OR ENZYMES; COMPOSITIONS THEREOF; PROPAGATING, PRESERVING, OR MAINTAINING MICROORGANISMS; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING; CULTURE MEDIA
- C12N15/00—Mutation or genetic engineering; DNA or RNA concerning genetic engineering, vectors, e.g. plasmids, or their isolation, preparation or purification; Use of hosts therefor
- C12N15/01—Preparation of mutants without inserting foreign genetic material therein; Screening processes therefor
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C12—BIOCHEMISTRY; BEER; SPIRITS; WINE; VINEGAR; MICROBIOLOGY; ENZYMOLOGY; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING
- C12N—MICROORGANISMS OR ENZYMES; COMPOSITIONS THEREOF; PROPAGATING, PRESERVING, OR MAINTAINING MICROORGANISMS; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING; CULTURE MEDIA
- C12N15/00—Mutation or genetic engineering; DNA or RNA concerning genetic engineering, vectors, e.g. plasmids, or their isolation, preparation or purification; Use of hosts therefor
- C12N15/09—Recombinant DNA-technology
- C12N15/10—Processes for the isolation, preparation or purification of DNA or RNA
- C12N15/102—Mutagenizing nucleic acids
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C12—BIOCHEMISTRY; BEER; SPIRITS; WINE; VINEGAR; MICROBIOLOGY; ENZYMOLOGY; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING
- C12N—MICROORGANISMS OR ENZYMES; COMPOSITIONS THEREOF; PROPAGATING, PRESERVING, OR MAINTAINING MICROORGANISMS; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING; CULTURE MEDIA
- C12N15/00—Mutation or genetic engineering; DNA or RNA concerning genetic engineering, vectors, e.g. plasmids, or their isolation, preparation or purification; Use of hosts therefor
- C12N15/09—Recombinant DNA-technology
- C12N15/10—Processes for the isolation, preparation or purification of DNA or RNA
- C12N15/102—Mutagenizing nucleic acids
- C12N15/1031—Mutagenizing nucleic acids mutagenesis by gene assembly, e.g. assembly by oligonucleotide extension PCR
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C12—BIOCHEMISTRY; BEER; SPIRITS; WINE; VINEGAR; MICROBIOLOGY; ENZYMOLOGY; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING
- C12N—MICROORGANISMS OR ENZYMES; COMPOSITIONS THEREOF; PROPAGATING, PRESERVING, OR MAINTAINING MICROORGANISMS; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING; CULTURE MEDIA
- C12N15/00—Mutation or genetic engineering; DNA or RNA concerning genetic engineering, vectors, e.g. plasmids, or their isolation, preparation or purification; Use of hosts therefor
- C12N15/09—Recombinant DNA-technology
- C12N15/11—DNA or RNA fragments; Modified forms thereof; Non-coding nucleic acids having a biological activity
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C12—BIOCHEMISTRY; BEER; SPIRITS; WINE; VINEGAR; MICROBIOLOGY; ENZYMOLOGY; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING
- C12N—MICROORGANISMS OR ENZYMES; COMPOSITIONS THEREOF; PROPAGATING, PRESERVING, OR MAINTAINING MICROORGANISMS; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING; CULTURE MEDIA
- C12N15/00—Mutation or genetic engineering; DNA or RNA concerning genetic engineering, vectors, e.g. plasmids, or their isolation, preparation or purification; Use of hosts therefor
- C12N15/09—Recombinant DNA-technology
- C12N15/63—Introduction of foreign genetic material using vectors; Vectors; Use of hosts therefor; Regulation of expression
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C12—BIOCHEMISTRY; BEER; SPIRITS; WINE; VINEGAR; MICROBIOLOGY; ENZYMOLOGY; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING
- C12N—MICROORGANISMS OR ENZYMES; COMPOSITIONS THEREOF; PROPAGATING, PRESERVING, OR MAINTAINING MICROORGANISMS; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING; CULTURE MEDIA
- C12N15/00—Mutation or genetic engineering; DNA or RNA concerning genetic engineering, vectors, e.g. plasmids, or their isolation, preparation or purification; Use of hosts therefor
- C12N15/09—Recombinant DNA-technology
- C12N15/63—Introduction of foreign genetic material using vectors; Vectors; Use of hosts therefor; Regulation of expression
- C12N15/79—Vectors or expression systems specially adapted for eukaryotic hosts
- C12N15/85—Vectors or expression systems specially adapted for eukaryotic hosts for animal cells
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C12—BIOCHEMISTRY; BEER; SPIRITS; WINE; VINEGAR; MICROBIOLOGY; ENZYMOLOGY; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING
- C12N—MICROORGANISMS OR ENZYMES; COMPOSITIONS THEREOF; PROPAGATING, PRESERVING, OR MAINTAINING MICROORGANISMS; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING; CULTURE MEDIA
- C12N9/00—Enzymes; Proenzymes; Compositions thereof; Processes for preparing, activating, inhibiting, separating or purifying enzymes
- C12N9/0004—Oxidoreductases (1.)
- C12N9/0071—Oxidoreductases (1.) acting on paired donors with incorporation of molecular oxygen (1.14)
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C12—BIOCHEMISTRY; BEER; SPIRITS; WINE; VINEGAR; MICROBIOLOGY; ENZYMOLOGY; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING
- C12N—MICROORGANISMS OR ENZYMES; COMPOSITIONS THEREOF; PROPAGATING, PRESERVING, OR MAINTAINING MICROORGANISMS; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING; CULTURE MEDIA
- C12N9/00—Enzymes; Proenzymes; Compositions thereof; Processes for preparing, activating, inhibiting, separating or purifying enzymes
- C12N9/10—Transferases (2.)
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C12—BIOCHEMISTRY; BEER; SPIRITS; WINE; VINEGAR; MICROBIOLOGY; ENZYMOLOGY; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING
- C12N—MICROORGANISMS OR ENZYMES; COMPOSITIONS THEREOF; PROPAGATING, PRESERVING, OR MAINTAINING MICROORGANISMS; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING; CULTURE MEDIA
- C12N9/00—Enzymes; Proenzymes; Compositions thereof; Processes for preparing, activating, inhibiting, separating or purifying enzymes
- C12N9/10—Transferases (2.)
- C12N9/1003—Transferases (2.) transferring one-carbon groups (2.1)
- C12N9/1007—Methyltransferases (general) (2.1.1.)
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C12—BIOCHEMISTRY; BEER; SPIRITS; WINE; VINEGAR; MICROBIOLOGY; ENZYMOLOGY; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING
- C12N—MICROORGANISMS OR ENZYMES; COMPOSITIONS THEREOF; PROPAGATING, PRESERVING, OR MAINTAINING MICROORGANISMS; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING; CULTURE MEDIA
- C12N9/00—Enzymes; Proenzymes; Compositions thereof; Processes for preparing, activating, inhibiting, separating or purifying enzymes
- C12N9/14—Hydrolases (3)
- C12N9/16—Hydrolases (3) acting on ester bonds (3.1)
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C12—BIOCHEMISTRY; BEER; SPIRITS; WINE; VINEGAR; MICROBIOLOGY; ENZYMOLOGY; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING
- C12N—MICROORGANISMS OR ENZYMES; COMPOSITIONS THEREOF; PROPAGATING, PRESERVING, OR MAINTAINING MICROORGANISMS; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING; CULTURE MEDIA
- C12N9/00—Enzymes; Proenzymes; Compositions thereof; Processes for preparing, activating, inhibiting, separating or purifying enzymes
- C12N9/14—Hydrolases (3)
- C12N9/16—Hydrolases (3) acting on ester bonds (3.1)
- C12N9/22—Ribonucleases RNAses, DNAses
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C12—BIOCHEMISTRY; BEER; SPIRITS; WINE; VINEGAR; MICROBIOLOGY; ENZYMOLOGY; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING
- C12N—MICROORGANISMS OR ENZYMES; COMPOSITIONS THEREOF; PROPAGATING, PRESERVING, OR MAINTAINING MICROORGANISMS; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING; CULTURE MEDIA
- C12N9/00—Enzymes; Proenzymes; Compositions thereof; Processes for preparing, activating, inhibiting, separating or purifying enzymes
- C12N9/96—Stabilising an enzyme by forming an adduct or a composition; Forming enzyme conjugates
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C12—BIOCHEMISTRY; BEER; SPIRITS; WINE; VINEGAR; MICROBIOLOGY; ENZYMOLOGY; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING
- C12Y—ENZYMES
- C12Y114/00—Oxidoreductases acting on paired donors, with incorporation or reduction of molecular oxygen (1.14)
- C12Y114/11—Oxidoreductases acting on paired donors, with incorporation or reduction of molecular oxygen (1.14) with 2-oxoglutarate as one donor, and incorporation of one atom each of oxygen into both donors (1.14.11)
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C12—BIOCHEMISTRY; BEER; SPIRITS; WINE; VINEGAR; MICROBIOLOGY; ENZYMOLOGY; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING
- C12Y—ENZYMES
- C12Y201/00—Transferases transferring one-carbon groups (2.1)
- C12Y201/01—Methyltransferases (2.1.1)
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C12—BIOCHEMISTRY; BEER; SPIRITS; WINE; VINEGAR; MICROBIOLOGY; ENZYMOLOGY; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING
- C12Y—ENZYMES
- C12Y301/00—Hydrolases acting on ester bonds (3.1)
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C12—BIOCHEMISTRY; BEER; SPIRITS; WINE; VINEGAR; MICROBIOLOGY; ENZYMOLOGY; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING
- C12Y—ENZYMES
- C12Y301/00—Hydrolases acting on ester bonds (3.1)
- C12Y301/21—Endodeoxyribonucleases producing 5'-phosphomonoesters (3.1.21)
- C12Y301/21004—Type II site-specific deoxyribonuclease (3.1.21.4)
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07K—PEPTIDES
- C07K2319/00—Fusion polypeptide
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07K—PEPTIDES
- C07K2319/00—Fusion polypeptide
- C07K2319/01—Fusion polypeptide containing a localisation/targetting motif
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C07—ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C07K—PEPTIDES
- C07K2319/00—Fusion polypeptide
- C07K2319/80—Fusion polypeptide containing a DNA binding domain, e.g. Lacl or Tet-repressor
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C12—BIOCHEMISTRY; BEER; SPIRITS; WINE; VINEGAR; MICROBIOLOGY; ENZYMOLOGY; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING
- C12N—MICROORGANISMS OR ENZYMES; COMPOSITIONS THEREOF; PROPAGATING, PRESERVING, OR MAINTAINING MICROORGANISMS; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING; CULTURE MEDIA
- C12N2310/00—Structure or type of the nucleic acid
- C12N2310/10—Type of nucleic acid
- C12N2310/20—Type of nucleic acid involving clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats [CRISPRs]
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C12—BIOCHEMISTRY; BEER; SPIRITS; WINE; VINEGAR; MICROBIOLOGY; ENZYMOLOGY; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING
- C12N—MICROORGANISMS OR ENZYMES; COMPOSITIONS THEREOF; PROPAGATING, PRESERVING, OR MAINTAINING MICROORGANISMS; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING; CULTURE MEDIA
- C12N2710/00—MICROORGANISMS OR ENZYMES; COMPOSITIONS THEREOF; PROPAGATING, PRESERVING, OR MAINTAINING MICROORGANISMS; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING; CULTURE MEDIA dsDNA viruses
- C12N2710/00011—Details
- C12N2710/00033—Use of viral protein as therapeutic agent other than vaccine, e.g. apoptosis inducing or anti-inflammatory
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C12—BIOCHEMISTRY; BEER; SPIRITS; WINE; VINEGAR; MICROBIOLOGY; ENZYMOLOGY; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING
- C12N—MICROORGANISMS OR ENZYMES; COMPOSITIONS THEREOF; PROPAGATING, PRESERVING, OR MAINTAINING MICROORGANISMS; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING; CULTURE MEDIA
- C12N2770/00—MICROORGANISMS OR ENZYMES; COMPOSITIONS THEREOF; PROPAGATING, PRESERVING, OR MAINTAINING MICROORGANISMS; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING; CULTURE MEDIA ssRNA viruses positive-sense
- C12N2770/00011—Details
- C12N2770/00033—Use of viral protein as therapeutic agent other than vaccine, e.g. apoptosis inducing or anti-inflammatory
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C12—BIOCHEMISTRY; BEER; SPIRITS; WINE; VINEGAR; MICROBIOLOGY; ENZYMOLOGY; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING
- C12N—MICROORGANISMS OR ENZYMES; COMPOSITIONS THEREOF; PROPAGATING, PRESERVING, OR MAINTAINING MICROORGANISMS; MUTATION OR GENETIC ENGINEERING; CULTURE MEDIA
- C12N2800/00—Nucleic acids vectors
- C12N2800/80—Vectors containing sites for inducing double-stranded breaks, e.g. meganuclease restriction sites
Definitions
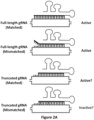
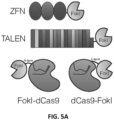
- RNA-guided FokI Nucleases e.g., FokI-dCas9 fusion proteins and guide RNAs.
- CRISPR clustered, regularly interspaced, short palindromic repeats
- Cas CRISPR-associated systems
- CRISPR can serve as the basis genome editing in bacteria, yeast and human cells, as well as in vivo in whole organisms such as fruit flies, zebrafish and mice
- the Cas9 nuclease from S. pyogenes can be guided via base pair complementarity between the first 20 nucleotides of an engineered gRNA and the complementary strand of a target genomic DNA sequence of interest that lies next to a protospacer adjacent motif (PAM), e.g., a PAM matching the sequence NGG or NAG ( Shen et al., Cell Res (2013 ); Dicarlo et al., Nucleic Acids Res (2013 ); Jiang et al., Nat Biotechnol 31, 233-239 (2013 ); Jinek et al., Elife 2, e00471 (2013 ); Hwang et al., Nat Biotechnol 31, 227-229 (2013 ); Cong et al., Science 339, 819-823 (2013 ); Mali et al., Science 339, 823-826 (2013 c); Cho et al., Nat Biotechnol 31,
- PAM protospacer adjacent
- CRISPR-Cas nucleases can tolerate up to five mismatches and still cleave; it is hard to predict the effects of any given single or combination of mismatches on activity. Taken together, these nucleases can show significant off-target effects but it can be challenging to predict these sites.
- RNA-guided FokI Nucleases RNNs
- FokI-Cas9 or FokI-dCas9-based fusion proteins e.g., FokI-Cas9 or FokI-dCas9-based fusion proteins.
- the invention provides FokI-dCas9 fusion proteins, comprising a FokI catalytic domain sequence fused to the amino terminus, of dCas9, with an intervening linker of from 2-30 amino acids, e.g., 4-12 amino acids, e.g., Gly 4 Ser and guide RNAs (gRNAs) that direct the RFN fusion proteins to two target genomic sequences wherein the guide RNAs that direct the RFN fusion proteins to a first target genomic sequence and a second target genomic sequence are spaced 14 to 17 or 26 nucleotides apart, and wherein the first target genomic sequence is on a first strand of DNA and the second target genomic sequence is on a complementary second strand of DNA wherein the two target genomic sequences each have a PAM sequence at the 3' end and a PAM outward orientation to create a double-stranded break.
- the FokI catalytic domain comprises amino acids 388-583 or 408-583 of SEQ ID NO:
- the disclosure provides nucleic acids encoding these fusion proteins, vector comprising the nucleic acids, and host cells harboring or expressing the nucleic acids, vectors, or fusion proteins.
- the disclosure provides methods for inducing a sequence-specific break in a double-stranded DNA molecule, e.g., in a genomic sequence in a cell, the method comprising expressing in the cell, or contacting the cell with, the FokI-dCas9 fusion protein described herein, and:
- the disclosure provides methods for increasing specificity of RNA-guided genome editing in a cell, the method comprising contacting the cell with an RNA-guided FokI Nuclease (RFN) fusion protein described herein.
- RFN RNA-guided FokI Nuclease
- the method may further comprise expressing in the cell, or contacting the cell with, (a) two single guide RNAs, wherein each of the two single guide RNAs include sequences that are each complementary to one strand of the target sequence such that using both guide RNAs results in targeting both strands (i.e., one single guide RNA targets a first strand, and the other guide RNA targets the complementary strand), and FokI cuts each strand resulting in a pair of nicks on opposite DNA strands, thereby creating a double-stranded break, or (b) a tracrRNA and two crRNAs wherein each of the two crRNAs include sequences that are complementary to one strand of the target sequence such that using both crRNAs results in targeting both strands (i.e., one crRNA targets a first strand, and the other crRNA targets the complementary strand), and FokI cuts each strand resulting in a pair of nicks on opposite DNA strands, thereby creating a double-stranded break, or (
- the two target genomic sequences are spaced 14-17 or 26 base pairs apart.
- an indel mutation is induced between the two target sequences.
- the specificity of RNA-guided genome editing in a cell is increased.
- RGNs CRISPR RNA-guided nucleases
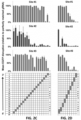
- off-target sites were seen for a number of RGNs, identification of these sites was neither comprehensive nor genome-wide in scale. For the six RGNs studied, only a very small subset of the much larger total number of potential off-target sequences in the human genome was examined. Although examining such large numbers of loci for off-target mutations by T7EI assay is neither a practical nor a cost-effective strategy, the use of high-throughput sequencing in future studies might enable the interrogation of larger numbers of candidate off-target sites and provide a more sensitive method for detecting bona fide off-target mutations. For example, such an approach might enable the unveiling of additional off-target sites for the two RGNs for which we failed to uncover any off-target mutations.
- a number of strategies can be used to minimize the frequencies of genomic off-target mutations.
- the specific choice of RGN target site can be optimized; given that off-target sites that differ at up to five positions from the intended target site can be efficiently mutated by RGNs, choosing target sites with minimal numbers of off-target sites as judged by mismatch counting seems unlikely to be effective; thousands of potential off-target sites that differ by four or five positions within the 20 bp RNA:DNA complementarity region will typically exist for any given RGN targeted to a sequence in the human genome. It is also possible that the nucleotide content of the gRNA complementarity region might influence the range of potential off-target effects.
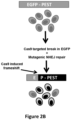
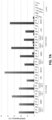
- RGN-induced off-target effects might be to reduce the concentrations of gRNA and Cas9 nuclease expressed in the cell. This idea was tested using the RGNs for VEGFA target sites 2 and 3 in U2OS.EGFP cells; transfecting less gRNA- and Cas9-expressing plasmid decreased the mutation rate at the on-target site but did not appreciably change the relative rates of off-target mutations. Consistent with this, high-level off-target mutagenesis rates were also observed in two other human cell types (HEK293 and K562 cells) even though the absolute rates of on-target mutagenesis are lower than in U2OS.EGFP cells.
- CRISPR-Cas RNA-guided nucleases based on the S. pyogenes Cas9 protein can have significant off-target mutagenic effects that are comparable to or higher than the intended on-target activity (Example 1). Such off-target effects can be problematic for research and in particular for potential therapeutic applications. Therefore, methods for improving the specificity of CRISPR-Cas RNA guided nucleases (RGNs) are needed.
- RGNs CRISPR-Cas RNA guided nucleases
- Cas9 RGNs can induce high-frequency indel mutations at off-target sites in human cells (see also Cradick et al., 2013; Fu et al., 2013; Hsu et al., 2013; Pattanayak et al., 2013). These undesired alterations can occur at genomic sequences that differ by as many as five mismatches from the intended on-target site (see Example 1).
- Dimerization is an attractive potential strategy for improving the specificity of Cas9 nucleases. This is distinct from a paired Cas9 nickase approach, which is not a true dimeric system. Paired nickases work by co-localizing two Cas9 nickases on a segment of DNA, thereby inducing high efficiency genome editing via an undefined mechanism. Because dimerization is not required for enzymatic activity, single Cas9 nickases can also induce indels with high efficiencies at certain sites (via an unknown mechanism) and can therefore potentially cause unwanted off-target mutations in the genome.
- one strategy to improve the specificity of RGNs is fusing a FokI endonuclease domain to a catalytically inactive form of Cas9 bearing the D10A and H840A mutations (also known as dCas9).
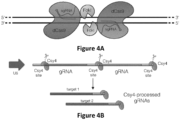
- FokI nuclease domain functions as a dimer and therefore two subunits must be recruited to the same local piece of DNA in order to induce a double-stranded break.
- two FokI-dCas9 fusions are recruited in an appropriate configuration using two different gRNAs to yield a double-stranded break.
- the FokI-dCas9 fusions would bind to a site that is twice as long as that of a single RGN and therefore this system would be expected to be more specific.
- FokI-dCas9 fusion proteins wherein the FokI sequence is fused to dCas9 (preferably to the amino-terminal end of dCas9, but also optionally to the carboxy terminus), with an intervening linker of from 2-30 amino acids, e.g., 4-12 amino acids, e.g., Gly 4 Ser (SEQ ID NO:23) or (Gly 4 Ser) 3 .
- the fusion proteins include a linker between the dCas9 and the FokI domains. Linkers that can be used in these fusion proteins (or between fusion proteins in a concatenated structure) can include any sequence that does not interfere with the function of the fusion proteins.
- the linkers are short, e.g., 2-20 amino acids, and are typically flexible (i.e., comprising amino acids with a high degree of freedom such as glycine, alanine, and serine).
- the linker comprises one or more units consisting of GGGS (SEQ ID NO:22) or GGGGS (SEQ ID NO:23), e.g., two, three, four, or more repeats of the GGGS (SEQ ID NO:22) or GGGGS (SEQ ID NO:23) unit.
- Other linker sequences can also be used.
- RNA-guided FokI nuclease platform in which dimerization, rather than just co-localization, is required for efficient genome editing activity.
- These nucleases can robustly mediate highly efficient genome editing in human cells and can reduce off-target mutations to undetectable levels as judged by sensitive deep sequencing methods.
- an efficient system for expressing pairs of gRNAs with any 5' end nucleotide a method that confers a wider targeting range on the RFN platform.
- monomeric Cas9 nickases generally introduce more undesirable indels and point mutations than the nucleases described herein in the presence of a single gRNA.
- RNA-guided FokI Nuclease (RFN) platform for performing robust and highly specific genome editing in human cells.
- RFNs require two gRNAs for activity and function as dimers.
- the engineering of an active RFN required fusion of the FokI nuclease domain to the amino-terminal end of the dCas9 protein, an architecture different from ZFNs and TALENs in which the FokI domain is fused to the carboxy-terminal end of engineered zinc finger or transcription activator-like effector repeat arrays.
- RFNs also require that the half-sites bound by each Fok-dCas9/gRNA complex have a particular relative orientation (PAMs out) with a relatively restricted intervening spacer length of 14 to 17 bps (although activity may be possible at additional spacings but with less consistent success).
- PAMs out relative orientation
- RFNs The dimeric nature of RFNs provides important specificity advantages relative to standard monomeric Cas9 nucleases. In an ideal dimeric system, little to no activity will be observed with monomers on half-sites.
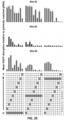
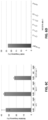
- the present data demonstrate that FokI-dCas9 directed by a single gRNA induces very little or no mutagenesis at RFN half-sites. 12 single gRNAs (for six RFN target sites) were tested with co-expressed FokI-dCas9 and indels were observed at very low frequencies (range of 0.0045% to 0.47%), in some cases at levels as low as background rates observed in control cells in which there was no expression of gRNA or nuclease.
- FokI nuclease domain functions as a dimer
- any indels observed with a single gRNA are likely due to recruitment of a FokI-dCas9 dimer to the DNA.
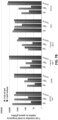
- FokI-dCas9 dimer Regardless of mechanism, given that only very low level mutagenesis was observed when FokI-dCas9 was tested with single gRNAs at 12 on-target half-sites, it is very unlikely that any mutagenesis will be induced at partially mismatched, off-target half-sites. Indeed, an RFN targeted to VEGF A did not induce detectable mutations at known off-target sites of one of the gRNAs as judged by deep sequencing.
- RFNs are a true dimeric system, they possess a number of important advantages over paired nickase technology, which depends on co-localization but does not require dimerization.
- paired Cas9 nickases show greater promiscuity in the orientation and spacing of target half-sites than dimeric RFNs and therefore have a greater potential range of sites at which off-target mutations might be induced.
- Paired nickase half-sites can be oriented with their PAMs in or PAMs out and with spacer sequences ranging in length from 0 to 1000 bps ( Ran et al., Cell 154, 1380-1389 (2013 ); Mali et al., Nat Biotechnol 31, 833-838 (2013 ); Cho et al., Genome Res (2013 )).
- This promiscuity exists because the genome editing activities of Cas9 nickases do not depend on dimerization of the enzyme but rather just co-localization of the two nicks.
- RFNs are much more stringent in their specificities -- half-sites must have their PAMs out and must be spaced apart by 14 to 17 bps, due to the requirement for two appropriately positioned FokI cleavage domains for efficient cleavage.
- FokI is a type IIs restriction endonuclease that includes a DNA recognition domain and a catalytic (endonuclease) domain.
- the fusion proteins described herein can include all of FokI or just the catalytic endonuclease domain, e.g., amino acids 388-583 or 408-583 of GenBank Acc. No. AAA24927.1, e.g., as described in Li et al., Nucleic Acids Res. 39(1): 359-372 (2011 ); Cathomen and Joung, Mol. Ther. 16: 1200-1207 (2008 ), or a mutated form of FokI as described in Miller et al.
- An exemplary nucleic acid sequence encoding FokI is as follows:
- the FokI nuclease used herein is at least about 50% identical SEQ ID NO:4, e.g., to amino acids 388-583 or 408-583 of SEQ ID NO:4. These variant nucleases must retain the ability to cleave DNA.
- the nucleotide sequences are about 50%, 55%, 60%, 65%, 70%, 75%, 80%, 85%, 90%, 95%, 99% or 100% identical to amino acids 388-583 or 408-583 of SEQ ID NO:4. In some embodiments, any differences from amino acids 388-583 or 408-583 of SEQ ID NO:4 are in non-conserved regions.
- the sequences are aligned for optimal comparison purposes (gaps are introduced in one or both of a first and a second amino acid or nucleic acid sequence as required for optimal alignment, and non-homologous sequences can be disregarded for comparison purposes).
- the length of a reference sequence aligned for comparison purposes is at least 50% (in some embodiments, about 50%, 55%, 60%, 65%, 70%, 75%, 85%, 90%, 95%, or 100% of the length of the reference sequence is aligned).
- the nucleotides or residues at corresponding positions are then compared. When a position in the first sequence is occupied by the same nucleotide or residue as the corresponding position in the second sequence, then the molecules are identical at that position.
- the percent identity between the two sequences is a function of the number of identical positions shared by the sequences, taking into account the number of gaps, and the length of each gap, which need to be introduced for optimal alignment of the two sequences.
- the comparison of sequences and determination of percent identity between two sequences can be accomplished using a mathematical algorithm.
- the percent identity between two amino acid sequences is determined using the Needleman and Wunsch ((1970) J. Mol. Biol. 48:444-453 ) algorithm which has been incorporated into the GAP program in the GCG software package, using a Blossum 62 scoring matrix with a gap penalty of 12, a gap extend penalty of 4, and a frameshift gap penalty of 5.
- Cas9 protein variants A number of bacteria express Cas9 protein variants.
- the Cas9 from Streptococcus pyogenes is presently the most commonly used; some of the other Cas9 proteins have high levels of sequence identity with the S. pyogenes Cas9 and use the same guide RNAs. Others are more diverse, use different gRNAs, and recognize different PAM sequences as well (the 2-5 nucleotide sequence specified by the protein which is adjacent to the sequence specified by the RNA).
- Chylinski et al. classified Cas9 proteins from a large group of bacteria (RNA Biology 10:5, 1-12; 2013 ), and a large number of Cas9 proteins are listed in supplementary figure 1 and supplementary table 1 thereof.
- Cas9 molecules of a variety of species can be used in the methods and compositions described herein. While the S. pyogenes and S. thermophilus Cas9 molecules are the subject of much of the disclosure herein, Cas9 molecules of, derived from, or based on the Cas9 proteins of other species listed herein can be used as well. In other words, while the much of the description herein uses S. pyogenes and S. thermophilus Cas9 molecules, Cas9 molecules from the other species can replace them. Such species include those set forth in the following table, which was created based on supplementary figure 1 of Chylinski et al., 2013. Alternative Cas9 proteins GenBank Acc No.
- Cas9 orthologs from N. meningitides are described in Hou et al., Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2013 Sep 24;110(39):15644-9 and Esvelt et al., Nat Methods. 2013 Nov;10(11):1116-21 . Additionally, Jinek et al. showed in vitro that Cas9 orthologs from S. thermophilus and L. innocua, (but not from N. meningitidis or C . jejuni, which likely use a different guide RNA), can be guided by a dual S. pyogenes gRNA to cleave target plasmid DNA, albeit with slightly decreased efficiency.
- the present system utilizes the Cas9 protein from S. pyogenes, either as encoded in bacteria or codon-optimized for expression in mammalian cells, containing mutations D10Aand H840A, to render the nuclease portion of the protein catalytically inactive
- S. pyogenes Cas9 that can be used in the methods and compositions described herein is as follows; the mutations of D10A and H840A are in bold and underlined.
- the Cas9 nuclease used herein is at least about 50% identical to the sequence of S. pyogenes Cas9, i.e., at least 50% identical to SEQ ID NO:5.
- the nucleotide sequences are about 50%, 55%, 60%, 65%, 70%, 75%, 80%, 85%, 90%, 95%, 99% or 100% identical to SEQ ID NO:5.
- any differences from SEQ ID NO:5 are in non-conserved regions, as identified by sequence alignment of sequences set forth in Chylinski et al., RNA Biology 10:5, 1-12; 2013 (e.g., in supplementary figure 1 and supplementary table 1 thereof); Esvelt et al., Nat Methods. 2013 Nov;10(11):1116-21 and Fonfara et al., Nucl. Acids Res. (2014) 42 (4): 2577-2590. [Epub ahead of print 2013 Nov 22] doi:10.1093/nar/gkt1074 . Identity is determined as set forth above.
- gRNAs Guide RNAs
- RNAs generally speaking come in two different systems: System 1, which uses separate crRNA and tracrRNAs that function together to guide cleavage by Cas9, and System 2, which uses a chimeric crRNA-tracrRNA hybrid that combines the two separate guide RNAs in a single system (referred to as a single guide RNA or sgRNA, see also Jinek et al., Science 2012; 337:816-821 ).
- the tracrRNAcan be variably truncated and a range of lengths has been shown to function in both the separate system (system 1) and the chimeric gRNA system (system 2).
- tracrRNA may be truncated from its 3' end by at least 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35 or 40 nts.
- the tracrRNA molecule may be truncated from its 5' end by at least 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35 or 40 nts.
- the tracrRNA molecule may be truncated from both the 5' and 3' end, e.g., by at least 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 15 or 20 nts on the 5' end and at least 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35 or 40 nts on the 3' end.
- the gRNAs are complementary to a region that is within about 100-800 bp upstream of the transcription start site, e.g., is within about 500 bp upstream of the transcription start site, includes the transcription start site, or within about 100-800 bp, e.g., within about 500 bp, downstream of the transcription start site.
- vectors e.g., plasmids
- plasmids encoding more than one gRNA are used, e.g., plasmids encoding, 2, 3, 4, 5, or more gRNAs directed to different sites in the same region of the target gene.
- Cas9 nuclease can be guided to specific 17-20 nt genomic targets bearing an additional proximal protospacer adjacent motif (PAM), e.g., of sequence NGG, using a guide RNA, e.g., a single gRNA or a tracrRNA/crRNA, bearing 17-20 nts at its 5' end that are complementary to the complementary strand of the genomic DNA target site.
- PAM proximal protospacer adjacent motif
- the present methods can include the use of a single guide RNA comprising a crRNA fused to a normally trans-encoded tracrRNA, e.g., a single Cas9 guide RNA as described in Mali et al., Science 2013 Feb 15; 339(6121):823-6 , with a sequence at the 5' end that is complementary to the target sequence, e.g., of 25-17, optionally 20 or fewer nucleotides (nts), e.g., 20, 19, 18, or 17 nts, preferably 17 or 18 nts, of the complementary strand to a target sequence immediately 5' of a protospacer adjacent motif (PAM), e.g., NGG, NAG, or NNGG.
- PAM protospacer adjacent motif
- the single Cas9 guide RNA consists of the sequence: or wherein X 17-20 is the nucleotide sequence complementary to 17-20 consecutive nucleotides of the target sequence.
- DNAs encoding the single guide RNAs have been described previously in the literature ( Jinek et al., Science. 337(6096):816-21 (2012 ) and Jinek et al., Elife. 2:e00471 (2013 )).
- the guide RNAs can include X N which can be any sequence, wherein N (in the RNA) can be 0-200, e.g., 0-100, 0-50, or 0-20, that does not interfere with the binding of the ribonucleic acid to Cas9.
- the guide RNA includes one or more Adenine (A) or Uracil (U) nucleotides on the 3' end.
- the RNA includes one or more U, e.g., 1 to 8 or more Us (e.g., U, UU, UUU, UUUU, UUUUU, UUUUU, UUUUUU, UUUUUU, UUUUUU, UUUUUUUUUU, UUUUUUUUUUUUU) at the 3' end of the molecule, as a result of the optional presence of one or more Ts used as a termination signal to terminate RNA PolIII transcription.
- a single tracrRNA would be used in conjunction with multiple different crRNAs expressed using the present system, e.g., the following: (X 17-20 )GUUUUAGAGCUA (SEQ ID NO: 13); (X 17-20 )GUUUUAGAGCUAUGCUGUUUUG (SEQ ID NO: 14); or (X 17-20 )GUUUUAGAGCUAUGCU (SEQ ID NO: 15); and a tracrRNA sequence.
- the crRNA is used as the guide RNA in the methods and molecules described herein, and the tracrRNA can be expressed from the same or a different DNA molecule.
- the methods include contacting the cell with a tracrRNA comprising or consisting of the sequence GGAACCAUUCAAAACAGCAUAGCAAGUUAAAAUAAGGCUAGUCCGUUA UCAACUUGAAAAAGUGGCACCGAGUCGGUGC (SEQ ID NO: 16) or an active portion thereof (an active portion is one that retains the ability to form complexes with Cas9 or dCas9).
- the tracrRNA molecule may be truncated from its 3' end by at least 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35 or 40 nts. In another embodiment, the tracrRNA molecule may be truncated from its 5' end by at least 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35 or 40 nts. Alternatively, the tracrRNA molecule may be truncated from both the 5' and 3' end, e.g., by at least 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 15 or 20 nts on the 5' end and at least 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35 or 40 nts on the 3' end.
- Exemplary tracrRNA sequences in addition to SEQ ID NO:8 include the following: UAGCAAGUUAAAAUAAGGCUAGUCCGUUAUCAACUUGAAAAAGUGGCA CCGAGUCGGUGC (SEQ ID NO: 17) or an active portion thereof; or AGCAUAGCAAGUUAAAAUAAGGCUAGUCCGUUAUCAACUUGAAAAAGU GGCACCGAGUCGGUGC (SEQ ID NO: 18) or an active portion thereof.
- (X 17-20 )GUUUUAGAGCUAUGCUGUUUUG (SEQ ID NO: 14) is used as a crRNA
- the following tracrRNA is used: GGAACCAUUCAAAACAGCAUAGCAAGUUAAAAUAAGGCUAGUCCGUUA UCAACUUGAAAAAGUGGCACCGAGUCGGUGC (SEQ ID NO: 16) or an active portion thereof.
- (X 17-20 )GUUUUAGAGCUA (SEQ ID NO: 13) is used as a crRNA
- the following tracrRNA is used: UAGCAAGUUAAAAUAAGGCUAGUCCGUUAUCAACUUGAAAAAGUGGCA CCGAGUCGGUGC (SEQ ID NO: 17) or an active portion thereof.
- the following tracrRNA is used: AGCAUAGCAAGUUAAAAUAAGGCUAGUCCGUUAUCAACUUGAAAAAGU GGCACCGAGUCGGUGC (SEQ ID NO: 18) or an active portion thereof.
- the gRNA is targeted to a site that is at least three or more mismatches different from any sequence in the rest of the genome in order to minimize off-target effects.
- RNA oligonucleotides such as locked nucleic acids (LNAs) have been demonstrated to increase the specificity of RNA-DNA hybridization by locking the modified oligonucleotides in a more favorable (stable) conformation.
- LNAs locked nucleic acids
- 2'-O-methyl RNA is a modified base where there is an additional covalent linkage between the 2' oxygen and 4' carbon which when incorporated into oligonucleotides can improve overall thermal stability and selectivity ( Formula I ).
- the tru-gRNAs disclosed herein may comprise one or more modified RNA oligonucleotides.
- the truncated guide RNAs molecules described herein can have one, some or all of the 17-18 or 17-19 nts 5' region of the guideRNA complementary to the target sequence are modified, e.g., locked (2'-O-4'-C methylene bridge), 5'-methylcytidine, 2'-O-methyl-pseudouridine, or in which the ribose phosphate backbone has been replaced by a polyamide chain (peptide nucleic acid), e.g., a synthetic ribonucleic acid.
- a polyamide chain peptide nucleic acid
- one, some or all of the nucleotides of the tru-gRNA sequence may be modified, e.g., locked (2'-O-4'-C methylene bridge), 5'-methylcytidine, 2'-O-methyl-pseudouridine, or in which the ribose phosphate backbone has been replaced by a polyamide chain (peptide nucleic acid), e.g., a synthetic ribonucleic acid.
- a polyamide chain peptide nucleic acid
- the single guide RNAs and/or crRNAs and/or tracrRNAs can include one or more Adenine (A) or Uracil (U) nucleotides on the 3' end.
- A Adenine
- U Uracil
- RNA-DNA heteroduplexes can form a more promiscuous range of structures than their DNA-DNA counterparts.
- DNA-DNA duplexes are more sensitive to mismatches, suggesting that a DNA-guided nuclease may not bind as readily to off-target sequences, making them comparatively more specific than RNA-guided nucleases.
- the guide RNAs usable in the methods described herein can be hybrids, i.e., wherein one or more deoxyribonucleotides, e.g., a short DNA oligonucleotide, replaces all or part of the gRNA, e.g., all or part of the complementarity region of a gRNA.
- This DNA-based molecule could replace either all or part of the gRNA in a single gRNA system or alternatively might replace all of part of the crRNA and/or tracrRNA in a dual crRNA/tracrRNA system.
- Such a system that incorporates DNA into the complementarity region should more reliably target the intended genomic DNA sequences due to the general intolerance of DNA-DNA duplexes to mismatching compared to RNA-DNA duplexes.
- Methods for making such duplexes are known in the art, See, e.g., Barker et al., BMC Genomics. 2005 Apr 22;6:57 ; and Sugimoto et al., Biochemistry. 2000 Sep 19;39(37): 11270-81 .
- one or both can be synthetic and include one or more modified (e.g., locked) nucleotides or deoxyribonucleotides.
- complexes of Cas9 with these synthetic gRNAs could be used to improve the genome-wide specificity of the CRISPR/Cas9 nuclease system.
- the methods described can include expressing in a cell, or contacting the cell with, a Cas9 gRNA plus a fusion protein as described herein.
- the nucleic acid encoding the guide RNA can be cloned into an intermediate vector for transformation into prokaryotic or eukaryotic cells for replication and/or expression.
- Intermediate vectors are typically prokaryote vectors, e.g., plasmids, or shuttle vectors, or insect vectors, for storage or manipulation of the nucleic acid encoding the fusion proteins for production of the fusion proteins.
- the nucleic acid encoding the fusion proteins can also be cloned into an expression vector, for administration to a plant cell, animal cell, preferably a mammalian cell or a human cell, fungal cell, bacterial cell, or protozoan cell.
- a sequence encoding a fusion protein is typically subcloned into an expression vector that contains a promoter to direct transcription.
- Suitable bacterial and eukaryotic promoters are well known in the art and described, e.g., in Sambrook et al., Molecular Cloning, A Laboratory Manual (3d ed. 2001 ); Kriegler, Gene Transfer and Expression: A Laboratory Manual (1990 ); and Current Protocols in Molecular Biology (Ausubel et al., eds., 2010 ).
- Bacterial expression systems for expressing the engineered protein are available in, e.g., E. coli, Bacillus sp., and Salmonella ( Palva et al., 1983, Gene 22:229-235 ). Kits for such expression systems are commercially available.
- Eukaryotic expression systems for mammalian cells, yeast, and insect cells are well known in the art and are also commercially available.
- the promoter used to direct expression of a nucleic acid depends on the particular application. For example, a strong constitutive promoter is typically used for expression and purification of fusion proteins. In contrast, when the guide RNA is to be administered in vivo for gene regulation, either a constitutive or an inducible promoter can be used, depending on the particular use of the guide RNA. In addition, a preferred promoter for administration of the guide RNA can be a weak promoter, such as HSV TK or a promoter having similar activity.
- the promoter can also include elements that are responsive to transactivation, e.g., hypoxia response elements, Gal4 response elements, lac repressor response element, and small molecule control systems such as tetracycline-regulated systems and the RU-486 system (see, e.g., Gossen & Bujard, 1992, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 89:5547 ; Oligino et al., 1998, Gene Ther., 5:491-496 ; Wang et al., 1997, Gene Ther., 4:432-441 ; Neering et al., 1996, Blood, 88:1147-55 ; and Rendahl et al., 1998, Nat. Biotechnol., 16:757-761 ).
- elements that are responsive to transactivation e.g., hypoxia response elements, Gal4 response elements, lac repressor response element, and small molecule control systems such as tetracycline-regulated systems and the
- the expression vector typically contains a transcription unit or expression cassette that contains all the additional elements required for the expression of the nucleic acid in host cells, either prokaryotic or eukaryotic.
- a typical expression cassette thus contains a promoter operably linked, e.g., to the nucleic acid sequence encoding the gRNA, and any signals required, e.g., for efficient polyadenylation of the transcript, transcriptional termination, ribosome binding sites, or translation termination. Additional elements of the cassette may include, e.g., enhancers, and heterologous spliced intronic signals.
- the particular expression vector used to transport the genetic information into the cell is selected with regard to the intended use of the gRNA, e.g., expression in plants, animals, bacteria, fungus, protozoa, etc.
- Standard bacterial expression vectors include plasmids such as pBR322 based plasmids, pSKF, pET23D, and commercially available tag-fusion expression systems such as GST and LacZ.
- Expression vectors containing regulatory elements from eukaryotic viruses are often used in eukaryotic expression vectors, e.g., SV40 vectors, papilloma virus vectors, and vectors derived from Epstein-Barr virus.
- eukaryotic vectors include pMSG, pAV009/A+, pMTO10/A+, pMAMneo-5, baculovirus pDSVE, and any other vector allowing expression of proteins under the direction of the SV40 early promoter, SV40 late promoter, metallothionein promoter, murine mammary tumor virus promoter, Rous sarcoma virus promoter, polyhedrin promoter, or other promoters shown effective for expression in eukaryotic cells.
- the vectors for expressing the guide RNAs can include RNAPol III promoters to drive expression of the guide RNAs, e.g., the H1, U6 or 7SK promoters. These human promoters allow for expression of gRNAs in mammalian cells following plasmid transfection. Alternatively, a T7 promoter may be used, e.g., for in vitro transcription, and the RNA can be transcribed in vitro and purified. Vectors suitable for the expression of short RNAs, e.g., siRNAs, shRNAs, or other small RNAs, can be used. With the Cys4-based multiplex system described in Figure 4B , multiple gRNAs can be expressed in a single transcript (driven by a RNAPol II or Pol III promoter) and then cleaved out from that larger transcript.
- RNAPol III promoters to drive expression of the guide RNAs.
- Some expression systems have markers for selection of stably transfected cell lines such as thymidine kinase, hygromycin B phosphotransferase, and dihydrofolate reductase.
- High yield expression systems are also suitable, such as using a baculovirus vector in insect cells, with the gRNA encoding sequence under the direction of the polyhedrin promoter or other strong baculovirus promoters.
- the elements that are typically included in expression vectors also include a replicon that functions in E. coli, a gene encoding antibiotic resistance to permit selection of bacteria that harbor recombinant plasmids, and unique restriction sites in nonessential regions of the plasmid to allow insertion of recombinant sequences.
- Standard transfection methods are used to produce bacterial, mammalian, yeast or insect cell lines that express large quantities of protein, which are then purified using standard techniques (see, e.g., Colley et al., 1989, J. Biol. Chem., 264:17619-22 ; Guide to Protein Purification, in Methods in Enzymology, vol. 182 (Deutscher, ed., 1990 )). Transformation of eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells are performed according to standard techniques (see, e.g., Morrison, 1977, J. Bacteriol. 132:349-351 ; Clark-Curtiss & Curtiss, Methods in Enzymology 101:347-362 (Wu et al., eds, 1983 ).
- Any of the known procedures for introducing foreign nucleotide sequences into host cells may be used. These include the use of calcium phosphate transfection, polybrene, protoplast fusion, electroporation, nucleofection, liposomes, microinjection, naked DNA, plasmid vectors, viral vectors, both episomal and integrative, and any of the other well-known methods for introducing cloned genomic DNA, cDNA, synthetic DNA or other foreign genetic material into a host cell (see, e.g., Sambrook et al., supra). It is only necessary that the particular genetic engineering procedure used be capable of successfully introducing at least one gene into the host cell capable of expressing the gRNA.
- the present disclosure which does not form part of the claimed invention, includes the vectors and cells comprising the vectors.
- RGNs CRISPR RNA-guided nucleases
- Example 1 The following materials and methods were used in Example 1.
- DNA oligonucleotides harboring variable 20 nt sequences for Cas9 targeting were annealed to generate short double-strand DNA fragments with 4 bp overhangs compatible with ligation into BsmBI-digested plasmid pMLM3636. Cloning of these annealed oligonucleotides generates plasmids encoding a chimeric +103 single-chain guide RNA with 20 variable 5' nucleotides under expression of a U6 promoter ( Hwang et al., Nat Biotechnol 31, 227-229 (2013 ); Mali et al., Science 339, 823-826 (2013 )).
- pMLM3636 and the expression plasmid pJDS246 (encoding a codon optimized version of Cas9) used in this study are both available through the non-profit plasmid distribution service Addgene (addgene.org/crispr-cas).
- U2OS.EGFP cells harboring a single integrated copy of an EGFP-PEST fusion gene were cultured as previously described ( Reyon et al., Nat Biotech 30, 460-465 (2012 )).
- 200,000 cells were Nucleofected with the indicated amounts of gRNA expression plasmid and pJDS246 together with 30 ng of a Td-tomato-encoding plasmid using the SE Cell Line 4D-Nucleofector TM X Kit (Lonza) according to the manufacturer's protocol. Cells were analyzed 2 days posttransfection using a BD LSRII flow cytometer. Transfections for optimizing gRNA/Cas9 plasmid concentration were performed in triplicate and all other transfections were performed in duplicate.
- PCR reactions were performed using Phusion Hot Start II high-fidelity DNA polymerase (NEB). Most loci amplified successfully using touchdown PCR (98 °C, 10 s; 72-62 °C, -1 °C/cycle, 15 s; 72 °C, 30 s]10 cycles, [98 °C, 10 s; 62 °C, 15 s; 72 °C, 30 s]25 cycles). PCR for the remaining targets were performed with 35 cycles at a constant annealing temperature of 68 °C or 72 °C and 3% DMSO or 1M betaine, if necessary. PCR products were analyzed on a QIAXCEL capillary electrophoresis system to verify both size and purity. Validated products were treated with ExoSap-IT (Affymetrix) and sequenced by the Sanger method (MGH DNA Sequencing Core) to verify each target site.
- NEB Phusion Hot Start II high-fidelity DNA polymerase
- HEK293 cells 1.65 ⁇ 10 5 cells were transfected with 125 ng of gRNA expression plasmid or an empty U6 promoter plasmid (for the negative control), 375 ng of Cas9 expression plasmid, and 30 ng of a td-Tomato expression plasmid using Lipofectamine LTX reagent according to the manufacturer's instructions (Life Technologies). Genomic DNA was harvested from transfected U2OS.EGFP, HEK293, or K562 cells using the QIAamp DNA Blood Mini Kit (QIAGEN), according to the manufacturer's instructions.
- QIAamp DNA Blood Mini Kit QIAamp DNA Blood Mini Kit
- PCR products used for the T7EI assay were cloned into Zero Blunt TOPO vector (Life Technologies) and plasmid DNAs were isolated using an alkaline lysis miniprep method by the MGH DNA Automation Core. Plasmids were sequenced using an M13 forward primer (5' - GTAAAACGACGGCCAG - 3' (SEQ ID NO: 19)) by the Sanger method (MGH DNA Sequencing Core).
- EGFP enhanced green fluorescent protein
- the activities of nucleases targeted to a single integrated EGFP reporter gene can be quantified by assessing loss of fluorescence signal in human U2OS.EGFP cells caused by inactivating frameshift insertion/deletion (indel) mutations introduced by error prone non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ) repair of nuclease-induced double-stranded breaks (DSBs) ( Fig. 2B ).
- sgRNAs three -100 nt single gRNAs targeted to different sequences within EGFP were used, as follows:
- variant sgRNAs were generated for each of the three target sites harboring Watson-Crick transversion mismatches at positions 1 through 19 (numbered 1 to 20 in the 3' to 5' direction; see Fig. 1 ) and the abilities of these various sgRNAs to direct Cas9-mediated EGFP disruption in human cells tested (variant sgRNAs bearing a substitution at position 20 were not generated because this nucleotide is part of the U6 promoter sequence and therefore must remain a guanine to avoid affecting expression.)
- target site #1 was particularly sensitive to a mismatch at position 2 whereas target site #3 was most sensitive to mismatches at positions 1 and 8.
- variant sgRNAs were constructed bearing increasing numbers of mismatched positions ranging from positions 19 to 15 in the 5' end of the gRNA targeting region (where single and double mismatches appeared to be better tolerated).
- sgRNAs that target three different sites in the VEGF A gene, one in the EMX1 gene, one in the RNF2 gene, and one in the FANCF gene were used. These six sgRNAs efficiently directed Cas9-mediated indels at their respective endogenous loci in human U2OS.EGFP cells as detected by T7 Endonuclease I ( T7EI ) assay (Methods above).
- U2OS.EGFP cells had been chosen for initial experiments because these cells were previously used to evaluate the activities of TALENs 15 but human HEK293 and K562 cells have been more widely used to test the activities of targeted nucleases. Therefore, the activities of the four RGNs targeted to VEGFA sites 1, 2, and 3 and the EMX1 site were also assessed in HEK293 and K562 cells.
- Example 1e Titration of gRNA- and Cas9-expressing plasmid amounts used for the EGFP disruption assay
- Single guide RNAs were generated for three different sequences (EGFP SITES 1-3, shown above) located upstream of EGFP nucleotide 502, a position at which the introduction of frameshift mutations via non-homologous end-joining can robustly disrupt expression of EGFP ( Maeder, M.L. et al., Mol Cell 31, 294-301 (2008 ); Reyon, D. et al., Nat Biotech 30, 460-465 (2012 )).
- gRNA-expressing plasmid amounts (12.5 to 250 ng) was initially transfected together with 750 ng of a plasmid expressing a codon-optimized version of the Cas9 nuclease into our U2OS.EGFP reporter cells bearing a single copy, constitutively expressed EGFP-PEST reporter gene. All three RGNs efficiently disrupted EGFP expression at the highest concentration of gRNA plasmid (250 ng) ( Fig. 3E (top)) .
- RGNs for target sites #1 and #3 exhibited equivalent levels of disruption when lower amounts of gRNA-expressing plasmid were transfected whereas RGN activity at target site #2 dropped immediately when the amount of gRNA-expressing plasmid transfected was decreased ( Fig. 3E (top)) .
- the amount of Cas9-encoding plasmid (range from 50 ng to 750 ng) transfected into our U2OS.EGFP reporter cells was titrated EGFP disruption assayed. As shown in Fig. 3F (top), target site #1 tolerated a three-fold decrease in the amount of Cas9-encoding plasmid transfected without substantial loss of EGFP disruption activity. However, the activities of RGNs targeting target sites #2 and #3 decreased immediately with a three-fold reduction in the amount of Cas9 plasmid transfected ( Fig. 3F (top)) .
- Target 1 ( VEGFA Site 1) 1 1 4 32 280 2175 13873 Target 2 ( VEGFA Site 2) 1 0 2 35 443 3889 17398 Target 3 ( VEGFA Site 3) 1 1 17 377 6028 13398 35517 Target 4 ( EMX ) 1 0 1 18 276 2309 15731 Target 5 ( RNF2 ) 1 0 0 6 116 976 7443 Target 6 ( FANCF ) 1 0 1 18 271 1467 9551 EGFP Target Site #1 0 0 3 10 156 1365 9755 EGFP Target Site #2 0 0 0 11 96 974 7353 EGFP Target Site #3 0 0 1 14 165 1439 10361
- Off-target sites for each of the six RGNs targeted to the VEGFA, RNF2, FANCF, and EMX1 genes and the three RGNs targeted to EGFP Target Sites #1, #2 and #3 were identified in human genome sequence build GRCh37. Mismatches were only allowed for the 20 nt region to which the gRNA anneals and not to the PAM sequence.
- Example 2 Using pairs of guideRNAs with FokI-dCas9 fusion proteins
- Monomeric CRISPR-Cas9 nucleases are widely used for targeted genome editing but can induce unwanted off-target mutations with high frequencies.
- This example describes new dimeric RNA-guided FokI Nucleases ( RFN s) that recognize an extended, double-length sequence and that strictly depend on two single guide RNAs ( gRNA s) for cleavage activity. RFNs can robustly edit DNA sequences in endogenous human genes with high efficiencies. Additionally, a method for expressing gRNAs bearing any 5' end nucleotide is described, a critical advance that gives dimeric RFNs a useful targeting range.
- monomeric Cas9 nickases In direct comparisons, monomeric Cas9 nickases generally induce unwanted indels and unexpected focal point mutations with higher frequencies than RFNs directed by a matched single gRNA.
- RFNs combine the ease of CRISPR RNA-based targeting with the specificity enhancements of dimerization and provide an important new platform for research and therapeutic applications that require highly precise genome editing.
- Plasmids encoding single or multiplex gRNAs were assembled in a single-step ligation of annealed target site oligosduplexes (Integrated DNA Technologies) and a constant region oligoduplex (for multiplex gRNAs) with BsmBI-digested Csy4-flanked gRNA backbone (pSQT1313; Addgene).
- Multiplex gRNA encoding plasmids were constructed by ligating: 1) annealed oligos encoding the first target site, 2) phosphorylated annealed oligos encoding crRNA, tracrRNA, and Csy4-binding site, and 3) annealed oligos encoding the second target site, into a U6-Csy4site-gRNA plasmid backbone digested with BsmBI Type IIs restriction enzyme. Csy4 RNA binding sites were attached to the 3' and 5' ends of a gRNA sequence and expressed with Cas9 in cells.
- the Csy4 RNA binding site sequence 'GUUCACUGCCGUAUAGGCAGCUAAGAAA' was fused to the 5' and 3' end of the standard gRNA sequence.
- This sequence is a multiplex gRNA sequence flanked by Csy4 sites (underlined). Functionally, encoding these in multiplex on one transcript should have the same result as encoding them separately.
- the sgRNAs can be encoded in multiplex sgRNAs separated by Csy4 sites encoded on one transcript as well as individual sgRNAs that have an additional Csy4 sequence.
- the first N20 sequence represents the sequence complementary to one strand of the target genomic sequence
- the second N20 sequence represents the sequence complementary to the other strand of the target genomic sequence.
- a plasmid encoding the Csy4 recognition site containing gRNA was cotransfected with plasmid encoding Cas9 and Csy4 proteins separated by a '2A' peptide linkage.
- the results showed that gRNAs with Csy4 sites fused to the 5' and 3' ends remained capable of directing Cas9-mediated cleavage in human cells using the U2OS-EGFP disruption assay previously described.
- Csy4 RNA binding sites can be attached to 3' end of a gRNA sequence and complexes of these Csy4 sitecontaining gRNAs with Cas9 remain functional in the cell.
- Csy4-T2A-FokI-dCas9 was used.
- the sequences of the FokI-dCas9 fusions are shown below, and include a GGGGS (SEQ ID NO:23) linker (underlined) between the FokI and dCas9 and a nuclear localization sequence.
- U2OS.EGFP cells All cell culture experiments were carried out in HEK 293 cells, U2OS cells, or in U2OS cells harboring a stably integrated, single-copy, destabilized EGFP gene (U2OS.EGFP cells).
- Cell lines were cultured in Advanced DMEM (Life Technologies) supplemented with 10% FBS, 2 mM GlutaMax (Life Technologies) and penicillin/streptomycin at 37C with 5% CO2. Additionally, U2OS.EGFP cells were cultured in the presence of 400 ⁇ g/ml of G418.
- U2OS cells and U2OS.EGFP cells were transfected using the DN-100 program of a Lonza 4D-Nucleofector according to the manufacturer's instructions.
- 750 ng of pCAG-Csy4-FokI-dCas9-nls nuclease plasmid and 250 ng of gRNA encoding plasmids were transfected together with 50 ng tdTomato expression plasmid (Clontech) as a transfection control.
- HEK293 cells were transfected with 750 ng of nuclease plasmid, 250 ng of gRNA expression plasmid and 10 ng of Td tomato, using Lipofectamine (Life Technologies) according to the manufacturer's instructions and analyzed for NHEJ-mediated mutagenesis 3 days after transfection.
- the EGFP disruption assay was performed as previously described (see Example 1 and Reyon et al., Nat Biotech 30, 460-465 (2012 )) using U2OS.EGFP reporter cells. Cells were assayed for EGFP and tdTomato expression using an BD Biosciences LSR II or Fortessa FACS analyzer.
- T7E1 assays were performed as previously described ( Reyon et al., Nat Biotech 30, 460-465 (2012 )). Briefly, genomic DNA was isolated 72 hours post transfection using the Agencourt DNAdvance Genomic DNA Isolation kit (Beckman Coulter Genomics) according to the manufacturer's instructions with a Sciclone G3 liquid-handling workstation (Caliper). PCR reactions to amplify genomic loci were performed using Phusion Hot-start Flex DNA polymerase (New England Biolabs).
- Samples were amplified using a two-step protocol (98 °C, 30 sec; (98 °C, 7 sec; 72 °C, 30 sec) ⁇ 35; 72 °C, 5 min) or a touchdown PCR protocol ((98 °C, 10 s; 72-62 °C, -1 °C/cycle, 15 s; 72 °C, 30 s) ⁇ 10 cycles, (98 °C, 10 s; 62 °C, 15 s; 72 °C, 30 s) ⁇ 25 cycles).
- 200 ng of purified PCR amplicons were denatured, hybridized, and treated with T7 Endonuclease I (New England Biolabs). Mutation frequency was quantified using a Qiaxcel capillary electrophoresis instrument (Qiagen) as previously described ( Reyon et al., Nat Biotech 30, 460-465 (2012 )).
- Short 200-350 bp PCR products were amplified using Phusion Hot-start FLEX DNA polymerase. PCR products were purified using Ampure XP beads (Beckman Coulter Genomics) according to manufacturer's instructions. Dual-indexed TruSeq Illumina deep sequencing libraries were prepared using a high-throughput library preparation system (Kapa Biosystems) on a Sciclone G3 liquid-handling workstation. Final adapter-ligated libraries were quantified using a Qiaxcel capillary electrophoresis instrument (Qiagen). 150 bp paired end sequencing was performed on an Illumina MiSeq Sequencer by the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute Molecular Biology Core.
- MiSeq paired-end reads were mapped to human genome reference GChr37 using bwa. Reads with an average quality score >30 were analyzed for insertion or deletion mutations that overlapped the intended target or candidate off-target nuclease binding site. Mutation analyses were conducted using the Genome Analysis Toolkit (GATK) and Python.
- GATK Genome Analysis Toolkit
- a target-site matching algorithm was implemented that looks for matches with less than a specified number of mismatches in a sliding window across the human genome.
- Example 2a Rationale for designing dimeric RNA-guided nucleases
- Example 2b Multiplex expression of gRNAs without 5 '-end nucleotide limitations
- the targeting range for a dimeric RNA-guided nuclease would be low using existing gRNA expression methods.
- Two sequence requirements typically restrict the targeting range of a dCas9 monomer: the requirement for a PAM sequence of 5'-NGG that is specified by the dCas9 and a requirement for a G nucleotide at the 5' end of the gRNA imposed by the use of a U6 promoter in most expression vectors. If, however, the requirement for the 5' G in the gRNA could be relieved, then the targeting range would improve by 16-fold.
- a plasmid was constructed from which two gRNAs, each flanked by cleavage sites for the Csy4 ribonuclease ( Haurwitz et al., Science 329, 1355-1358 (2010 )), can be expressed within a single RNA transcribed from a U6 promoter ( Fig. 4B ). Csy4 would be expected to process this transcript thereby releasing the two gRNAs.
- each processed gRNA should retain a Csy4 recognition site on its 3' end with a Csy4 protein bound to that site ( Fig. 4B ).
- gRNAs with any 5' nucleotide. This system was tested by using it to express two gRNAs targeted to sites within the EGFP reporter gene.
- Example 2c Construction and optimization of dimeric RNA-guided nucleases
- dCas9-FokI carboxy-terminus of dCas9
- FokI-dCas9 amino-terminus
- the dCas9-FokI protein is analogous in architecture to ZFNs and TALENs ( Fig. 5A ).
- the dCas9-FokI protein did not show detectable EGFP disruption activity when co-expressed with any of the 60 gRNA pairs in human U2OS.EGFP cells ( Fig. 5E ).
- screening of the FokI-dCas9 protein with the same 60 gRNA pairs did reveal EGFP disruption activity on target sites composed of half-sites in the PAM out orientation and with spacer lengths of 13 to 17 bps and of 26 bps (approximately one turn of the DNA helix more than the 13-17 bp spacer lengths) ( Fig. 5B ).
- FokI-dCas9 can be directed by two appropriately positioned gRNAs to efficiently cleave a full-length target site of interest.
- the complex of two FokI-dCas9 fusions and two gRNAs are referred to herein as RNA-guided FokI Nucleases ( RFN s).
- gRNA pairs were designed for 12 different target sites in nine different human genes (Table 2 ). Eleven of the 12 RFNs tested introduced indels with high efficiencies (range of 3 to 40%) at their intended target sites in human U2OS.EGFP cells as judged by T7EI assay ( Table 2 ). Similar results were obtained with these same 12 RFN pairs in HEK293 cells ( Table 2 ). Sanger sequencing of successfully targeted alleles from U2OS.EGFP cells revealed the introduction of a range of indels (primarily deletions) at the expected cleavage site ( Fig. 5F ). The high success rate and high efficiencies of modifications observed in two different human cell lines demonstrate the robustness of RFNs for modifying endogenous human genes.
- GLI1 MLH1 RARA1 RUNX TAGGGCTAGAGGGGTGAGGC 281. CCGAGGTGAAACAAGCTGCC 282. SS18 VEGFA - site 1 ATGAGGGCTCCAGATGGCAC 283. TTCACCCAGCTTCCCTGTGG 284. VEGFA - site 2 VEGFA - site 3
- Example 2e Monomeric Cas9 nickases induce higher rates of mutagenesis than single gRNA / FokI-dCas9 complexes
- FokI-dCas9 and Cas9 nickase were compared in the presence of a single gRNA at six dimeric human gene target sites (a total of 12 half-sites; Table 4 ). These particular sites were chosen because monomeric Cas9 nickases directed by just one and/or the other gRNA in a pair could induce indel mutations at these targets.
- Table 4 the activities of FokI-dCas9 or Cas9 nickase were assessed in the presence of both or only one or the other gRNAs.
- FokI-dCas9 induced indels with lower frequencies than Cas9 nickase for 10 of the 12 single gRNAs ( Fig. 7A and Table 5 ).
- FokI-dCas9 showed greater fold-reductions in indel frequencies than Cas9 nickase at 11 of the 12 half-sites when comparing paired gRNA rates to single gRNA rates ( Fig. 7B ).
- Example 2f Dimeric RFNs possess a high degree of specificity
- Dimeric RFNs directed by two gRNAs are not expected to induce appreciable off-target mutations in human cells.
- RFNs directed by a pair of gRNAs to cleave a full-length sequence composed of two half-sites, would be expected to specify up to 44 bps of DNA in the target site. A sequence of this length will, by chance, almost always be unique (except in certain circumstances where the target might lie in duplicated genome sequence).
- the most closely matched sites in the genome to this full-length site should, in most cases, possess a large number of mismatches, which in turn would be expected to minimize or abolish cleavage activity by an RFN dimer.
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Genetics & Genomics (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Wood Science & Technology (AREA)
- Bioinformatics & Cheminformatics (AREA)
- Zoology (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Biotechnology (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Biochemistry (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Microbiology (AREA)
- Biophysics (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Plant Pathology (AREA)
- Crystallography & Structural Chemistry (AREA)
- Proteomics, Peptides & Aminoacids (AREA)
- Gastroenterology & Hepatology (AREA)
- Virology (AREA)
- Cell Biology (AREA)
- Mycology (AREA)
- Micro-Organisms Or Cultivation Processes Thereof (AREA)
- Peptides Or Proteins (AREA)
- Enzymes And Modification Thereof (AREA)
- Pharmaceuticals Containing Other Organic And Inorganic Compounds (AREA)
- Measuring Or Testing Involving Enzymes Or Micro-Organisms (AREA)
- Preparation Of Compounds By Using Micro-Organisms (AREA)
- Developing Agents For Electrophotography (AREA)
- Prostheses (AREA)
- Lubricants (AREA)
Claims (5)
- Protéines de fusion de nucléases Fokl à guidage ARN (RFN) comprenant un domaine catalytique Fokl fusionné à la terminaison amino d'une protéine 9 associée à CRISPR catalytiquement inactive (dCas9), ladite Cas9 catalytiquement inactive de S. pyogenes présentant des mutations au niveau de résidus d'acides aminés correspondant aux positions D10A et H840A, ainsi qu'un lieur intermédiaire de 2 à 30 acides aminés ; et ARN guides (ARNg) dirigeant les protéines de fusion RFN vers deux séquences génomiques cibles, les ARN guides dirigeant les protéines de fusion RFN vers une première séquence génomique cible et une seconde séquence génomique cible étant espacés de 14 à 17 ou 26 nucléotides, la première séquence génomique cible se trouvant sur un premier brin d'ADN et la seconde séquence génomique cible se trouvant sur un second brin d'ADN complémentaire, les deux séquences génomiques cibles ayant chacune une séquence PAM à l'extrémité 3' et une orientation PAM vers l'extérieur pour créer une cassure double-brin.
- Protéines de fusion RFN et ARN guides selon la revendication 1, les ARNg comprenant :(a) deux ARN guides simples, un ARN guide simple ciblant un premier brin et l'autre ARN guide ciblant le brin complémentaire, et Fokl coupant chaque brin pour donner lieu à une paire d'entailles sur des brins d'ADN opposés, créant ainsi une cassure double-brin, ou(b) un ARNtracr et deux ARNcr, un ARNcr ciblant un premier brin et l'autre ARN guide ciblant le brin complémentaire, et Fokl coupant chaque brin pour donner lieu à une paire d'entailles sur des brins d'ADN opposés, créant ainsi une cassure double-brin.
- Protéines de fusion RFN et ARN guides selon la revendication 1 ou 2, le lieur intermédiaire étant un lieur de 4 à 12 acides aminés.
- Protéines de fusion RFN et ARN guides selon l'une quelconque des revendications 1 à 3, la dCas9 étant une protéine 9 associée à CRISPR catalytiquement inactive (dCas9) de Streptococcus pyogenes.
- Protéines de fusion RFN et ARN guides selon l'une quelconque des revendications 1 à 4, le lieur intermédiaire étant Gly4Ser ou (Gly4Ser)3.
Applications Claiming Priority (6)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US201361799647P | 2013-03-15 | 2013-03-15 | |
| US201361838178P | 2013-06-21 | 2013-06-21 | |
| US201361838148P | 2013-06-21 | 2013-06-21 | |
| US201361921007P | 2013-12-26 | 2013-12-26 | |
| PCT/US2014/028630 WO2014144288A1 (fr) | 2013-03-15 | 2014-03-14 | Utilisation de nucléases foki à guidage arn (rfn) pour augmenter la spécificité pour la modification d'un génome à guidage arn |
| EP14764159.1A EP2971041B1 (fr) | 2013-03-15 | 2014-03-14 | Utilisation de nucléases foki à guidage arn (rfn) pour augmenter la spécificité pour la modification d'un génome à guidage arn |
Related Parent Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP14764159.1A Division EP2971041B1 (fr) | 2013-03-15 | 2014-03-14 | Utilisation de nucléases foki à guidage arn (rfn) pour augmenter la spécificité pour la modification d'un génome à guidage arn |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP3467125A1 EP3467125A1 (fr) | 2019-04-10 |
| EP3467125B1 true EP3467125B1 (fr) | 2023-08-30 |
Family
ID=51537665
Family Applications (10)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP21151899.8A Pending EP3865586A1 (fr) | 2013-03-15 | 2014-03-14 | Augmentation de la spécificité pour la modification du génome à guidage arn |
| EP20172393.9A Withdrawn EP3744842A1 (fr) | 2013-03-15 | 2014-03-14 | Utilisation d'arn de guidage tronqués (arng tron) pour une augmentation de la spécificité d'édition génomique guidée par arn |
| EP20171165.2A Active EP3741868B1 (fr) | 2013-03-15 | 2014-03-14 | Direction, par guidage arn, de protéines régulatrices génétiques et épigénomiques vers des loci génomiques spécifiques |
| EP14768877.4A Active EP2970986B1 (fr) | 2013-03-15 | 2014-03-14 | Direction, par guidage arn, de protéines régulatrices génétiques et épigénomiques vers des loci génomiques spécifiques |
| EP14764159.1A Active EP2971041B1 (fr) | 2013-03-15 | 2014-03-14 | Utilisation de nucléases foki à guidage arn (rfn) pour augmenter la spécificité pour la modification d'un génome à guidage arn |
| EP14764117.9A Withdrawn EP2970208A4 (fr) | 2013-03-15 | 2014-03-14 | Augmentation de la spécificité pour la modification du génome à guidage arn |
| EP14763916.5A Active EP2971125B2 (fr) | 2013-03-15 | 2014-03-14 | Utilisation d'arn de guidage tronqués (arng tron) pour une augmentation de la spécificité d'édition génomique guidée par arn |
| EP24176701.1A Pending EP4428141A2 (fr) | 2013-03-15 | 2014-03-14 | Direction, par guidage arn, de protéines régulatrices génétiques et épigénomiques vers des loci génomiques spécifiques |
| EP18208105.9A Active EP3467125B1 (fr) | 2013-03-15 | 2014-03-14 | Utilisation de nucléases foki à guidage arn (rfn) pour augmenter la spécificité pour la modification d'un génome à guidage arn |
| EP21197664.2A Pending EP3988667A1 (fr) | 2013-03-15 | 2014-03-14 | Utilisation d'arn de guidage tronqués (arng tron) pour une augmentation de la spécificité d'édition génomique guidée par arn |
Family Applications Before (8)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP21151899.8A Pending EP3865586A1 (fr) | 2013-03-15 | 2014-03-14 | Augmentation de la spécificité pour la modification du génome à guidage arn |
| EP20172393.9A Withdrawn EP3744842A1 (fr) | 2013-03-15 | 2014-03-14 | Utilisation d'arn de guidage tronqués (arng tron) pour une augmentation de la spécificité d'édition génomique guidée par arn |
| EP20171165.2A Active EP3741868B1 (fr) | 2013-03-15 | 2014-03-14 | Direction, par guidage arn, de protéines régulatrices génétiques et épigénomiques vers des loci génomiques spécifiques |
| EP14768877.4A Active EP2970986B1 (fr) | 2013-03-15 | 2014-03-14 | Direction, par guidage arn, de protéines régulatrices génétiques et épigénomiques vers des loci génomiques spécifiques |
| EP14764159.1A Active EP2971041B1 (fr) | 2013-03-15 | 2014-03-14 | Utilisation de nucléases foki à guidage arn (rfn) pour augmenter la spécificité pour la modification d'un génome à guidage arn |
| EP14764117.9A Withdrawn EP2970208A4 (fr) | 2013-03-15 | 2014-03-14 | Augmentation de la spécificité pour la modification du génome à guidage arn |
| EP14763916.5A Active EP2971125B2 (fr) | 2013-03-15 | 2014-03-14 | Utilisation d'arn de guidage tronqués (arng tron) pour une augmentation de la spécificité d'édition génomique guidée par arn |
| EP24176701.1A Pending EP4428141A2 (fr) | 2013-03-15 | 2014-03-14 | Direction, par guidage arn, de protéines régulatrices génétiques et épigénomiques vers des loci génomiques spécifiques |
Family Applications After (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP21197664.2A Pending EP3988667A1 (fr) | 2013-03-15 | 2014-03-14 | Utilisation d'arn de guidage tronqués (arng tron) pour une augmentation de la spécificité d'édition génomique guidée par arn |
Country Status (12)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (16) | US9567603B2 (fr) |
| EP (10) | EP3865586A1 (fr) |
| JP (11) | JP6980380B2 (fr) |
| KR (8) | KR102602047B1 (fr) |
| CN (6) | CN113563476A (fr) |
| AU (10) | AU2014228981B2 (fr) |
| BR (1) | BR112015023489B1 (fr) |
| CA (4) | CA2907198C (fr) |
| ES (1) | ES2713503T3 (fr) |
| IL (2) | IL289396B2 (fr) |
| WO (4) | WO2014144761A2 (fr) |
| ZA (1) | ZA201506814B (fr) |
Families Citing this family (366)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2008027558A2 (fr) | 2006-08-31 | 2008-03-06 | Codon Devices, Inc. | Assemblage itératif d'acides nucléiques utilisant l'activation de caractères codés par vecteurs |
| US20140031250A1 (en) | 2010-10-07 | 2014-01-30 | David Tsai Ting | Biomarkers of Cancer |
| EP2638157B1 (fr) | 2010-11-12 | 2015-07-22 | Gen9, Inc. | Procédés et dispositifs pour la synthèse d'acides nucléiques |
| EP4039363A1 (fr) | 2010-11-12 | 2022-08-10 | Gen9, Inc. | Puces à protéines et leurs procédés d'utilisation et de fabrication |
| EP3461896B1 (fr) | 2011-07-15 | 2023-11-29 | The General Hospital Corporation | Procédés d'assemblage d'effecteurs de type activateur de la transcription |
| CA2853829C (fr) | 2011-07-22 | 2023-09-26 | President And Fellows Of Harvard College | Evaluation et amelioration de la specificite de clivage des nucleases |
| LT2944693T (lt) | 2011-08-26 | 2019-08-26 | Gen9, Inc. | Kompozicijos ir būdai, skirti nukleorūgščių didelio tikslumo sąrankai |
| US11021737B2 (en) | 2011-12-22 | 2021-06-01 | President And Fellows Of Harvard College | Compositions and methods for analyte detection |
| GB201122458D0 (en) | 2011-12-30 | 2012-02-08 | Univ Wageningen | Modified cascade ribonucleoproteins and uses thereof |
| US10039777B2 (en) | 2012-03-20 | 2018-08-07 | Neuro-Lm Sas | Methods and pharmaceutical compositions of the treatment of autistic syndrome disorders |
| US9150853B2 (en) | 2012-03-21 | 2015-10-06 | Gen9, Inc. | Methods for screening proteins using DNA encoded chemical libraries as templates for enzyme catalysis |
| EP4001427A1 (fr) | 2012-04-24 | 2022-05-25 | Gen9, Inc. | Procédés de tri d'acides nucléiques et de clonage in vitro multiplex préparatoire |
| WO2013163628A2 (fr) | 2012-04-27 | 2013-10-31 | Duke University | Correction génétique de gènes ayant subi une mutation |
| DK2800811T3 (en) | 2012-05-25 | 2017-07-17 | Univ Vienna | METHODS AND COMPOSITIONS FOR RNA DIRECTIVE TARGET DNA MODIFICATION AND FOR RNA DIRECTIVE MODULATION OF TRANSCRIPTION |
| US9890364B2 (en) | 2012-05-29 | 2018-02-13 | The General Hospital Corporation | TAL-Tet1 fusion proteins and methods of use thereof |
| CN104685116A (zh) | 2012-06-25 | 2015-06-03 | Gen9股份有限公司 | 用于核酸组装和高通量测序的方法 |
| US20150267176A1 (en) * | 2012-10-12 | 2015-09-24 | The General Hospital Corporation | Transcription activator-like effector (tale) - lysine-specific demethylase 1 (lsd1) fusion proteins |
| KR102243092B1 (ko) | 2012-12-06 | 2021-04-22 | 시그마-알드리치 컴퍼니., 엘엘씨 | Crispr-기초된 유전체 변형과 조절 |
| WO2014093709A1 (fr) | 2012-12-12 | 2014-06-19 | The Broad Institute, Inc. | Procédés, modèles, systèmes et appareil pour identifier des séquences cibles pour les enzymes cas ou des systèmes crispr-cas pour des séquences cibles et transmettre les résultats associés |
| SG11201504523UA (en) | 2012-12-12 | 2015-07-30 | Broad Inst Inc | Delivery, engineering and optimization of systems, methods and compositions for sequence manipulation and therapeutic applications |
| CA2898184A1 (fr) | 2013-01-16 | 2014-07-24 | Emory University | Complexes d'acide nucleique cas9 et leurs utilisations |
| EP3623463B1 (fr) | 2013-02-07 | 2021-10-20 | The General Hospital Corporation | Activateurs transcriptionnels tale |
| EP2971184B1 (fr) | 2013-03-12 | 2019-04-17 | President and Fellows of Harvard College | Procédé de génération d'une matrice tridimensionnelle contenant des acides nucléiques |
| EP2971167B1 (fr) | 2013-03-14 | 2019-07-31 | Caribou Biosciences, Inc. | Compositions et procédés pour des acides nucléiques à ciblage d'acide nucléique |
| IL289396B2 (en) | 2013-03-15 | 2023-12-01 | The General Hospital Coporation | Using tru-grnas to increase the specificity of RNA-guided genome editing |
| US10760064B2 (en) | 2013-03-15 | 2020-09-01 | The General Hospital Corporation | RNA-guided targeting of genetic and epigenomic regulatory proteins to specific genomic loci |
| WO2014165825A2 (fr) | 2013-04-04 | 2014-10-09 | President And Fellows Of Harvard College | Utilisations thérapeutiques de l'édition de génome au moyen de systèmes crispr/cas |
| US20140356956A1 (en) * | 2013-06-04 | 2014-12-04 | President And Fellows Of Harvard College | RNA-Guided Transcriptional Regulation |
| EP3603679B1 (fr) | 2013-06-04 | 2022-08-10 | President and Fellows of Harvard College | Régulation transcriptionnelle guidée par arn |
| EP3004370B1 (fr) * | 2013-06-05 | 2024-08-21 | Duke University | Édition et régulation géniques à guidage arn |
| WO2014204727A1 (fr) | 2013-06-17 | 2014-12-24 | The Broad Institute Inc. | Génomique fonctionnelle utilisant des systèmes crispr-cas, procédés de composition, cribles et applications de ces derniers |
| CN106062197A (zh) | 2013-06-17 | 2016-10-26 | 布罗德研究所有限公司 | 用于序列操纵的串联指导系统、方法和组合物的递送、工程化和优化 |
| EP4245853A3 (fr) | 2013-06-17 | 2023-10-18 | The Broad Institute, Inc. | Systèmes, procédés et compositions à double nickase crispr-cas optimisés, pour la manipulation de séquences |
| KR20160056869A (ko) | 2013-06-17 | 2016-05-20 | 더 브로드 인스티튜트, 인코퍼레이티드 | 바이러스 구성성분을 사용하여 장애 및 질환을 표적화하기 위한 crispr-cas 시스템 및 조성물의 전달, 용도 및 치료 적용 |
| CA2915842C (fr) | 2013-06-17 | 2022-11-29 | The Broad Institute, Inc. | Administration et utilisation de systemes crispr-cas, vecteurs et compositions pour le ciblage et le traitement du foie |
| US10011850B2 (en) | 2013-06-21 | 2018-07-03 | The General Hospital Corporation | Using RNA-guided FokI Nucleases (RFNs) to increase specificity for RNA-Guided Genome Editing |
| EP3019595A4 (fr) | 2013-07-09 | 2016-11-30 | Utilisations thérapeutiques d'édition du génome avec des systèmes crispr/cas | |
| WO2015021426A1 (fr) * | 2013-08-09 | 2015-02-12 | Sage Labs, Inc. | Nouvelle protéine de fusion à base de système crispr/cas et son application en édition de génome |
| US20150044192A1 (en) | 2013-08-09 | 2015-02-12 | President And Fellows Of Harvard College | Methods for identifying a target site of a cas9 nuclease |
| MX2016002306A (es) | 2013-08-22 | 2016-07-08 | Du Pont | Promotor u6 de polimerasa iii de soja y metodos de uso. |
| US9359599B2 (en) | 2013-08-22 | 2016-06-07 | President And Fellows Of Harvard College | Engineered transcription activator-like effector (TALE) domains and uses thereof |
| US9737604B2 (en) | 2013-09-06 | 2017-08-22 | President And Fellows Of Harvard College | Use of cationic lipids to deliver CAS9 |
| US9228207B2 (en) | 2013-09-06 | 2016-01-05 | President And Fellows Of Harvard College | Switchable gRNAs comprising aptamers |
| US9388430B2 (en) * | 2013-09-06 | 2016-07-12 | President And Fellows Of Harvard College | Cas9-recombinase fusion proteins and uses thereof |
| DE202014010413U1 (de) | 2013-09-18 | 2015-12-08 | Kymab Limited | Zellen und Organismen |
| US10584358B2 (en) | 2013-10-30 | 2020-03-10 | North Carolina State University | Compositions and methods related to a type-II CRISPR-Cas system in Lactobacillus buchneri |
| CA2930015A1 (fr) | 2013-11-07 | 2015-05-14 | Editas Medicine, Inc. | Methodes et compositions associees a crispr avec arng de regulation |
| JP6793547B2 (ja) * | 2013-12-12 | 2020-12-02 | ザ・ブロード・インスティテュート・インコーポレイテッド | 最適化機能CRISPR−Cas系による配列操作のための系、方法および組成物 |
| CA2932472A1 (fr) | 2013-12-12 | 2015-06-18 | Massachusetts Institute Of Technology | Compositions et procedes d'utilisation de systemes crispr-cas dans les maladies dues a une repetition de nucleotides |
| WO2015089364A1 (fr) | 2013-12-12 | 2015-06-18 | The Broad Institute Inc. | Structure cristalline d'un système crispr-cas, et ses utilisations |
| WO2015089462A1 (fr) | 2013-12-12 | 2015-06-18 | The Broad Institute Inc. | Distribution, utilisation et applications thérapeutiques des systèmes crispr-cas et compositions pour l'édition du génome |
| US11053481B2 (en) | 2013-12-12 | 2021-07-06 | President And Fellows Of Harvard College | Fusions of Cas9 domains and nucleic acid-editing domains |
| WO2015089277A1 (fr) | 2013-12-12 | 2015-06-18 | The Regents Of The University Of California | Procédés et compositions pour modifier un acide nucléique cible monobrin |
| JP6721508B2 (ja) * | 2013-12-26 | 2020-07-15 | ザ ジェネラル ホスピタル コーポレイション | 多重ガイドrna |
| US10787654B2 (en) | 2014-01-24 | 2020-09-29 | North Carolina State University | Methods and compositions for sequence guiding Cas9 targeting |
| EP4063503A1 (fr) | 2014-02-11 | 2022-09-28 | The Regents of the University of Colorado, a body corporate | Ingénierie génomique multiplexe validée ayant recours au système crispr |
| EP3114227B1 (fr) | 2014-03-05 | 2021-07-21 | Editas Medicine, Inc. | Méthodes et compositions liées à crispr/cas et destinées à traiter le syndrome de usher et la rétinite pigmentaire |
| US11141493B2 (en) | 2014-03-10 | 2021-10-12 | Editas Medicine, Inc. | Compositions and methods for treating CEP290-associated disease |
| WO2015138510A1 (fr) | 2014-03-10 | 2015-09-17 | Editas Medicine., Inc. | Méthodes et compositions associées aux crispr/cas, utilisées dans le traitement de l'amaurose congénitale de leber 10 (lca10) |
| US11339437B2 (en) | 2014-03-10 | 2022-05-24 | Editas Medicine, Inc. | Compositions and methods for treating CEP290-associated disease |
| EP3981876A1 (fr) | 2014-03-26 | 2022-04-13 | Editas Medicine, Inc. | Méthodes liées à crispr/cas et compositions pour le traitement de la drépanocytose |
| CA2944978C (fr) | 2014-04-08 | 2024-02-13 | North Carolina State University | Procedes et compositions pour la repression dirigee par l'arn de la transcription au moyen de genes associes a crispr |
| JP2017518372A (ja) | 2014-05-30 | 2017-07-06 | ザ ボード オブ トラスティーズ オブ ザ レランド スタンフォード ジュニア ユニバーシティー | 潜伏性ウイルス感染用の処置剤を送達するための組成物および方法 |
| CA2953362A1 (fr) | 2014-06-23 | 2015-12-30 | The General Hospital Corporation | Identification non biaisee, pangenomique, de dsb evaluee par sequencage (guide-seq) |
| US20150376586A1 (en) * | 2014-06-25 | 2015-12-31 | Caribou Biosciences, Inc. | RNA Modification to Engineer Cas9 Activity |
| US20170198268A1 (en) * | 2014-07-09 | 2017-07-13 | Gen9, Inc. | Compositions and Methods for Site-Directed DNA Nicking and Cleaving |
| AU2015288157A1 (en) | 2014-07-11 | 2017-01-19 | E. I. Du Pont De Nemours And Company | Compositions and methods for producing plants resistant to glyphosate herbicide |
| US10077453B2 (en) | 2014-07-30 | 2018-09-18 | President And Fellows Of Harvard College | CAS9 proteins including ligand-dependent inteins |
| WO2016022866A1 (fr) | 2014-08-07 | 2016-02-11 | Agilent Technologies, Inc. | Arn guide bloqué en cis |
| US10450584B2 (en) | 2014-08-28 | 2019-10-22 | North Carolina State University | Cas9 proteins and guiding features for DNA targeting and genome editing |
| MX2017002930A (es) | 2014-09-12 | 2017-06-06 | Du Pont | Generacion de sitios de integracion especifica de sitio para loci de rasgos complejos en maiz y soja, y metodos de uso. |
| WO2016049258A2 (fr) * | 2014-09-25 | 2016-03-31 | The Broad Institute Inc. | Criblage fonctionnel avec systèmes crisp-cas fonctionnels optimisés |
| WO2016054106A1 (fr) * | 2014-09-29 | 2016-04-07 | The Regents Of The University Of California | Arn d'échafaudage |
| EP3204496A1 (fr) * | 2014-10-10 | 2017-08-16 | Editas Medicine, Inc. | Compositions et procédés pour activer une réparation dirigée par homologie |
| US9816080B2 (en) | 2014-10-31 | 2017-11-14 | President And Fellows Of Harvard College | Delivery of CAS9 via ARRDC1-mediated microvesicles (ARMMs) |
| CA2963820A1 (fr) | 2014-11-07 | 2016-05-12 | Editas Medicine, Inc. | Procedes pour ameliorer l'edition genomique mediee par crispr/cas |
| US11352666B2 (en) | 2014-11-14 | 2022-06-07 | Institute For Basic Science | Method for detecting off-target sites of programmable nucleases in a genome |
| CN107109486B (zh) * | 2014-11-14 | 2021-08-13 | 基础科学研究院 | 用于检测基因组中遗传剪刀的脱靶位点的方法 |
| CN104531633A (zh) * | 2014-11-18 | 2015-04-22 | 李云英 | Cas9-scForkI融合蛋白及其应用 |
| KR20160059994A (ko) | 2014-11-19 | 2016-05-27 | 기초과학연구원 | 두 개의 벡터로부터 발현된 Cas9 단백질을 이용한 유전자 발현 조절 방법 |
| AU2015355546B2 (en) * | 2014-12-03 | 2021-10-14 | Agilent Technologies, Inc. | Guide RNA with chemical modifications |
| CN107208079B (zh) * | 2014-12-05 | 2021-06-29 | 应用干细胞有限公司 | 整合转基因的位点定向crispr/重组酶组合物和方法 |
| EP3229586A4 (fr) | 2014-12-10 | 2018-10-24 | Regents of the University of Minnesota | Cellules, tissus et organes génétiquement modifiés pour le traitement d'une maladie |
| EP3230452A1 (fr) * | 2014-12-12 | 2017-10-18 | The Broad Institute Inc. | Guides désactivés pour facteurs de transcription crispr |
| WO2016094867A1 (fr) * | 2014-12-12 | 2016-06-16 | The Broad Institute Inc. | Arn guides protégés (pgrnas) |
| US20180179523A1 (en) * | 2014-12-18 | 2018-06-28 | Integrated Dna Technologies, Inc. | Crispr-based compositions and methods of use |
| DK3234133T3 (da) * | 2014-12-18 | 2021-02-08 | Integrated Dna Tech Inc | Crispr-baserede sammensætninger og fremgangsmåder til anvendelse |
| US10190106B2 (en) * | 2014-12-22 | 2019-01-29 | Univesity Of Massachusetts | Cas9-DNA targeting unit chimeras |
| US11208638B2 (en) | 2015-01-12 | 2021-12-28 | The Regents Of The University Of California | Heterodimeric Cas9 and methods of use thereof |
| EP3250689B1 (fr) | 2015-01-28 | 2020-11-04 | The Regents of The University of California | Procédés et compositions pour le marquage d'un acide nucléique cible monocaténaire |
| CN111518811A (zh) * | 2015-01-28 | 2020-08-11 | 先锋国际良种公司 | Crispr杂合dna/rna多核苷酸及使用方法 |
| JP6929791B2 (ja) | 2015-02-09 | 2021-09-01 | デューク ユニバーシティ | エピゲノム編集のための組成物および方法 |
| KR20240014627A (ko) * | 2015-02-18 | 2024-02-01 | 아이오와 스테이트 유니버시티 리서치 파운데이션, 인코퍼레이티드 | 증가된 단백질 함량 및 스트레스에 대한 저항성을 위한 nf-yc4 프로모터 내 전사 리프레서 결합 부위의 변형 |
| WO2016141224A1 (fr) | 2015-03-03 | 2016-09-09 | The General Hospital Corporation | Nucléases crispr-cas9 génétiquement modifiées présentant une spécificité pam modifiée |
| BR112017017260A2 (pt) | 2015-03-27 | 2018-04-17 | Du Pont | construções de dna, vetor, célula, plantas, semente, método de expressão de rna e método de modificação de local alvo |
| EP3280803B1 (fr) | 2015-04-06 | 2021-05-26 | The Board of Trustees of the Leland Stanford Junior University | Arn guides chimiquement modifiés pour la régulation génétique médiée par crispr/cas |
| JP2018522249A (ja) | 2015-04-24 | 2018-08-09 | エディタス・メディシン、インコーポレイテッド | Cas9分子/ガイドrna分子複合体の評価 |
| AU2016261600B2 (en) | 2015-05-08 | 2021-09-23 | President And Fellows Of Harvard College | Universal donor stem cells and related methods |
| EP3294896A1 (fr) | 2015-05-11 | 2018-03-21 | Editas Medicine, Inc. | Systèmes crispr/cas9 optimisés et procédés d'édition de gènes dans des cellules souches |
| US10117911B2 (en) | 2015-05-29 | 2018-11-06 | Agenovir Corporation | Compositions and methods to treat herpes simplex virus infections |
| JP2018516984A (ja) | 2015-05-29 | 2018-06-28 | アジェノビア コーポレーション | 細胞を標的にしたhpv処置のための組成物および方法 |
| EP4039816A1 (fr) | 2015-05-29 | 2022-08-10 | North Carolina State University | Procédés pour le criblage de bactéries, d'archées, d'algues et de levure à l'aide d'acides nucléiques crispr |
| WO2016196655A1 (fr) | 2015-06-03 | 2016-12-08 | The Regents Of The University Of California | Variants de cas9 et procédés d'utilisation associés |
| EP3302525A2 (fr) | 2015-06-05 | 2018-04-11 | Novartis AG | Méthodes et compositions permettant de diagnostiquer, traiter et surveiller le traitement de troubles associés à une déficience en shank3 |
| JP7396783B2 (ja) | 2015-06-09 | 2023-12-12 | エディタス・メディシン、インコーポレイテッド | 移植を改善するためのcrispr/cas関連方法および組成物 |
| CA2987078A1 (fr) * | 2015-06-10 | 2016-12-15 | Firmenich Sa | Lignees cellulaires pour le depistage de recepteurs d'odeurs et d'aromes |
| IL298524B2 (en) | 2015-06-12 | 2024-03-01 | Lonza Walkersville Inc | Methods for nuclear reprogramming using synthetic transcription factors |
| JP7051438B2 (ja) | 2015-06-15 | 2022-04-11 | ノース カロライナ ステート ユニバーシティ | 核酸およびrnaに基づく抗菌剤の効率的な送達のための方法および組成物 |
| WO2016205759A1 (fr) | 2015-06-18 | 2016-12-22 | The Broad Institute Inc. | Modification et optimisation de systèmes, de méthodes, d'enzymes et d'échafaudages guides d'orthologues de cas9 et variant pour la manipulation de séquences |
| CN109536474A (zh) | 2015-06-18 | 2019-03-29 | 布罗德研究所有限公司 | 降低脱靶效应的crispr酶突变 |
| CA2990699A1 (fr) | 2015-06-29 | 2017-01-05 | Ionis Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Arn crispr modifie et arn crispr simple modifie et utilisations correspondantes |
| WO2017004279A2 (fr) * | 2015-06-29 | 2017-01-05 | Massachusetts Institute Of Technology | Compositions comprenant des acides nucléiques et leurs méthodes d'utilisation |
| CN108291218B (zh) * | 2015-07-15 | 2022-08-19 | 新泽西鲁特格斯州立大学 | 核酸酶非依赖性靶向基因编辑平台及其用途 |
| EP3325018A4 (fr) * | 2015-07-22 | 2019-04-24 | Duke University | Criblage à haut rendement d'une fonction d'élément de régulation à l'aide de technologies d'édition de l'épigénome |
| EP3328399B1 (fr) | 2015-07-31 | 2023-12-27 | Regents of the University of Minnesota | Cellules modifiées et méthodes de thérapie |
| US20180230450A1 (en) * | 2015-08-03 | 2018-08-16 | President And Fellows Of Harvard College | Cas9 Genome Editing and Transcriptional Regulation |
| WO2017024047A1 (fr) * | 2015-08-03 | 2017-02-09 | Emendobio Inc. | Compositions et procédés d'augmentation des taux de recombinaison induits par la nucléase dans les cellules |
| EP3341727B1 (fr) * | 2015-08-25 | 2022-08-10 | Duke University | Compositions et procédés d'amélioration de la spécificité dans l'ingénierie génomique à l'aide d'endonucléases guidées par arn |
| US9512446B1 (en) | 2015-08-28 | 2016-12-06 | The General Hospital Corporation | Engineered CRISPR-Cas9 nucleases |
| CA2996888A1 (fr) * | 2015-08-28 | 2017-03-09 | The General Hospital Corporation | Nucleases crispr-cas9 modifiees |
| US9926546B2 (en) | 2015-08-28 | 2018-03-27 | The General Hospital Corporation | Engineered CRISPR-Cas9 nucleases |
| CN107922949A (zh) | 2015-08-31 | 2018-04-17 | 安捷伦科技有限公司 | 用于通过同源重组的基于crispr/cas的基因组编辑的化合物和方法 |
| WO2017044776A1 (fr) * | 2015-09-10 | 2017-03-16 | Texas Tech University System | Arn de guidage unique (sgrna) présentant une efficacité d'inactivation améliorée |
| WO2017044843A1 (fr) * | 2015-09-11 | 2017-03-16 | The General Hospital Corporation | Interrogation complète de dsb nucléasiques et séquençage (find-seq) |
| US11667911B2 (en) | 2015-09-24 | 2023-06-06 | Editas Medicine, Inc. | Use of exonucleases to improve CRISPR/CAS-mediated genome editing |
| EP3356533A1 (fr) | 2015-09-28 | 2018-08-08 | North Carolina State University | Méthodes et compositions pour agents antimicrobiens spécifiques d'une séquence |
| CA3000762A1 (fr) | 2015-09-30 | 2017-04-06 | The General Hospital Corporation | Rapport in vitro complet d'evenements de clivage par sequencage (circle-seq) |
| MX2018004265A (es) | 2015-10-06 | 2018-11-09 | Inst Basic Science | Metodo para producir plantas de genoma modificado a partir de protoplastos de planta a alta eficiencia. |
| WO2017066497A2 (fr) | 2015-10-13 | 2017-04-20 | Duke University | Ingénierie génomique avec systèmes crispr de type i dans des cellules eucaryotes |
| EP3350327B1 (fr) | 2015-10-23 | 2018-09-26 | Caribou Biosciences, Inc. | Acides nucléiques ciblant les acides nucléiques crispr de classe 2 réticulés modifiés |
| IL294014B2 (en) | 2015-10-23 | 2024-07-01 | Harvard College | Nucleobase editors and their uses |
| WO2017079406A1 (fr) | 2015-11-03 | 2017-05-11 | President And Fellows Of Harvard College | Procédé et appareil pour imagerie volumétrique d'une matrice tridimensionnelle contenant des acides nucléiques |
| US11566052B2 (en) | 2015-11-11 | 2023-01-31 | Lonza Ltd. | CRISPR-associated (Cas) proteins with reduced immunogenicity |
| WO2017087979A1 (fr) | 2015-11-20 | 2017-05-26 | Washington University | Procédé électrophorétique préparatif pour la purification ciblée de fragments d'adn génomique |
| US10612044B2 (en) | 2015-11-25 | 2020-04-07 | National University Corporation Gunma University | DNA methylation editing kit and DNA methylation editing method |
| WO2017106251A1 (fr) * | 2015-12-14 | 2017-06-22 | President And Fellows Of Harvard College | Discrimination de cas au moyen d'arn guide "réglé" |
| WO2017112620A1 (fr) | 2015-12-22 | 2017-06-29 | North Carolina State University | Méthodes et compositions pour l'administration d'agents antimicrobiens à base de crispr |
| CA3009727A1 (fr) * | 2015-12-28 | 2017-07-06 | Novartis Ag | Compositions et methodes de traitement d'hemoglobinopathies |
| IL260532B2 (en) | 2016-01-11 | 2023-12-01 | Univ Leland Stanford Junior | Systems containing chaperone proteins and their uses for controlling gene expression |
| KR20180095719A (ko) | 2016-01-11 | 2018-08-27 | 더 보드 어브 트러스티스 어브 더 리랜드 스탠포드 주니어 유니버시티 | 키메라 단백질 및 면역요법 방법 |
| WO2017136794A1 (fr) | 2016-02-03 | 2017-08-10 | Massachusetts Institute Of Technology | Modification chimique guidée par la structure d'un arn guide et ses applications |
| US20190048415A1 (en) | 2016-02-10 | 2019-02-14 | The Regents Of The University Of Michigan | Detection of nucleic acids |
| US20190249172A1 (en) | 2016-02-18 | 2019-08-15 | The Regents Of The University Of California | Methods and compositions for gene editing in stem cells |
| WO2017151444A1 (fr) * | 2016-02-29 | 2017-09-08 | Agilent Technologies, Inc. | Procédés et compositions pour le blocage d'acides nucléiques hors cible d'un clivage par des protéines à crispr |
| CN115927299A (zh) | 2016-03-15 | 2023-04-07 | 核糖核酸复兴股份有限责任公司 | 增加双链rna产生的方法和组合物 |
| EP3429567B1 (fr) | 2016-03-16 | 2024-01-10 | The J. David Gladstone Institutes | Procédés et compositions pour traiter l'obésité et/ou le diabète et pour identifier des agents de traitement candidats |
| EP3219799A1 (fr) | 2016-03-17 | 2017-09-20 | IMBA-Institut für Molekulare Biotechnologie GmbH | Expression sgrna crispr conditionnelle |
| EP3433364A1 (fr) | 2016-03-25 | 2019-01-30 | Editas Medicine, Inc. | Systèmes et procédés pour traiter une déficience en alpha 1-antitrypsine (a1at) |
| US11597924B2 (en) | 2016-03-25 | 2023-03-07 | Editas Medicine, Inc. | Genome editing systems comprising repair-modulating enzyme molecules and methods of their use |
| CN106701765A (zh) * | 2016-04-11 | 2017-05-24 | 广东赤萌医疗科技有限公司 | 用于hiv感染治疗的多核苷酸及其制备药物应用 |
| US20190127713A1 (en) * | 2016-04-13 | 2019-05-02 | Duke University | Crispr/cas9-based repressors for silencing gene targets in vivo and methods of use |
| EP4047092A1 (fr) | 2016-04-13 | 2022-08-24 | Editas Medicine, Inc. | Molécules de fusion cas9, systèmes d'édition génique et leurs procédés d'utilisation |
| CN116200465A (zh) | 2016-04-25 | 2023-06-02 | 哈佛学院董事及会员团体 | 用于原位分子检测的杂交链反应方法 |
| CN107326046A (zh) * | 2016-04-28 | 2017-11-07 | 上海邦耀生物科技有限公司 | 一种提高外源基因同源重组效率的方法 |
| AU2017268458B2 (en) | 2016-05-20 | 2022-07-21 | Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Methods for breaking immunological tolerance using multiple guide RNAS |
| WO2017208247A1 (fr) | 2016-06-02 | 2017-12-07 | Yissum Research Development Company Of The Hebrew University Of Jerusalem Ltd. | Essai pour l'élimination de résidus de méthyle-cytosine de l'adn |
| EP3907286A1 (fr) * | 2016-06-02 | 2021-11-10 | Sigma-Aldrich Co., LLC | Utilisation de protéines de liaison à l'adn programmables pour améliorer la modification ciblée du génome |
| US10767175B2 (en) | 2016-06-08 | 2020-09-08 | Agilent Technologies, Inc. | High specificity genome editing using chemically modified guide RNAs |
| WO2017217768A1 (fr) * | 2016-06-15 | 2017-12-21 | 주식회사 툴젠 | Procédé de criblage de ciseaux génétiques ciblés à l'aide d'un système à cibles multiples d'activité sur cible et hors cible et son utilisation |
| JP2019518478A (ja) | 2016-06-24 | 2019-07-04 | ザ リージェンツ オブ ザ ユニバーシティ オブ コロラド,ア ボディー コーポレイトTHE REGENTS OF THE UNIVERSITY OF COLORADO,a body corporate | バーコードを付けたコンビナトリアルライブラリーを生成する方法 |
| US11471462B2 (en) | 2016-06-27 | 2022-10-18 | The Broad Institute, Inc. | Compositions and methods for detecting and treating diabetes |
| WO2018005117A1 (fr) * | 2016-07-01 | 2018-01-04 | Microsoft Technology Licensing, Llc | Stockage par édition itérative d'adn |
| US11359234B2 (en) | 2016-07-01 | 2022-06-14 | Microsoft Technology Licensing, Llc | Barcoding sequences for identification of gene expression |
| US20180004537A1 (en) | 2016-07-01 | 2018-01-04 | Microsoft Technology Licensing, Llc | Molecular State Machines |
| WO2018010516A1 (fr) * | 2016-07-13 | 2018-01-18 | 陈奇涵 | Procédé pour l'édition spécifique d'adn génomique et son application |
| US11124805B2 (en) * | 2016-07-13 | 2021-09-21 | Vertex Pharmaceuticals Incorporated | Methods, compositions and kits for increasing genome editing efficiency |
| US11168313B2 (en) * | 2016-07-26 | 2021-11-09 | The General Hospital Corporation | Variants of CRISPR from Prevotella and Francisella 1 (Cpf1) |
| JP6875500B2 (ja) * | 2016-07-28 | 2021-05-26 | インスティテュート フォー ベーシック サイエンスInstitute For Basic Science | Cas9タンパク質およびガイドRNAを含む眼疾患治療用薬学組成物 |
| AU2017302657A1 (en) | 2016-07-29 | 2019-02-14 | Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Mice comprising mutations resulting in expression of c-truncated fibrillin-1 |
| BR112019001887A2 (pt) | 2016-08-02 | 2019-07-09 | Editas Medicine Inc | composições e métodos para o tratamento de doença associada a cep290 |
| IL308426A (en) | 2016-08-03 | 2024-01-01 | Harvard College | Adenosine nuclear base editors and their uses |
| US11661590B2 (en) | 2016-08-09 | 2023-05-30 | President And Fellows Of Harvard College | Programmable CAS9-recombinase fusion proteins and uses thereof |
| TW202319540A (zh) | 2016-08-10 | 2023-05-16 | 日商領先基因生技股份有限公司 | 檢測標的部位中的檢測對象核酸序列之存在或不存在之方法 |
| SG11201901306XA (en) * | 2016-08-19 | 2019-03-28 | Toolgen Inc | Artificially engineered angiogenesis regulatory system |
| EP3500675A4 (fr) * | 2016-08-19 | 2020-01-29 | Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research | Méthodes d'édition de la méthylation de l'adn |
| US11542509B2 (en) | 2016-08-24 | 2023-01-03 | President And Fellows Of Harvard College | Incorporation of unnatural amino acids into proteins using base editing |
| PE20190568A1 (es) | 2016-08-24 | 2019-04-22 | Sangamo Therapeutics Inc | Regulacion de la expresion genica usando nucleasas modificadas |
| KR20220145913A (ko) | 2016-08-24 | 2022-10-31 | 상가모 테라퓨틱스, 인코포레이티드 | 가공된 표적 특이적 뉴클레아제 |
| EP3510152A4 (fr) | 2016-09-07 | 2020-04-29 | Flagship Pioneering, Inc. | Méthodes et compositions pour moduler l'expression génique |
| WO2018048194A1 (fr) * | 2016-09-07 | 2018-03-15 | 울산대학교 산학협력단 | Composition et procédé pour améliorer la sensibilité et la spécificité de la détection d'acides nucléiques à l'aide d'une protéine dcas9 et de la liaison d'arng à une séquence d'acide nucléique cible |
| CN107880132B (zh) * | 2016-09-30 | 2022-06-17 | 北京大学 | 一种融合蛋白及使用其进行同源重组的方法 |
| JP2019532644A (ja) | 2016-09-30 | 2019-11-14 | ザ リージェンツ オブ ザ ユニバーシティ オブ カリフォルニア | Rna誘導型核酸修飾酵素及びその使用方法 |
| US10669539B2 (en) | 2016-10-06 | 2020-06-02 | Pioneer Biolabs, Llc | Methods and compositions for generating CRISPR guide RNA libraries |
| CN118726313A (zh) | 2016-10-07 | 2024-10-01 | 综合Dna技术公司 | 化脓链球菌cas9突变基因和由其编码的多肽 |
| US11242542B2 (en) | 2016-10-07 | 2022-02-08 | Integrated Dna Technologies, Inc. | S. pyogenes Cas9 mutant genes and polypeptides encoded by same |
| SG11201903089RA (en) | 2016-10-14 | 2019-05-30 | Harvard College | Aav delivery of nucleobase editors |
| KR20190067209A (ko) | 2016-10-14 | 2019-06-14 | 더 제너럴 하스피탈 코포레이션 | 후성적으로 조절되는 부위-특이적 뉴클레아제 |
| GB2604416B (en) | 2016-10-18 | 2023-03-15 | Univ Minnesota | Tumor infiltating lymphocytes and methods of therapy |
| WO2018083606A1 (fr) | 2016-11-01 | 2018-05-11 | Novartis Ag | Procédés et compositions pour améliorer l'édition de gènes |
| US20180282722A1 (en) * | 2016-11-21 | 2018-10-04 | Massachusetts Institute Of Technology | Chimeric DNA:RNA Guide for High Accuracy Cas9 Genome Editing |
| US11136567B2 (en) | 2016-11-22 | 2021-10-05 | Integrated Dna Technologies, Inc. | CRISPR/CPF1 systems and methods |
| JP2019536464A (ja) | 2016-12-08 | 2019-12-19 | インテリア セラピューティクス,インコーポレイテッド | 修飾されたガイドrna |
| WO2018111947A1 (fr) | 2016-12-12 | 2018-06-21 | Integrated Dna Technologies, Inc. | Amélioration de l'édition du génome |
| WO2018112282A1 (fr) | 2016-12-14 | 2018-06-21 | Ligandal, Inc. | Compositions et procédés d'administration de charge d'acide nucléique et/ou de protéine |
| WO2018119359A1 (fr) | 2016-12-23 | 2018-06-28 | President And Fellows Of Harvard College | Édition du gène récepteur ccr5 pour protéger contre l'infection par le vih |
| JP2020503017A (ja) * | 2016-12-28 | 2020-01-30 | アイオーニス ファーマシューティカルズ, インコーポレーテッドIonis Pharmaceuticals,Inc. | 修飾crispr rna及びその使用 |
| US12065666B2 (en) | 2017-01-05 | 2024-08-20 | Rutgers, The State University Of New Jersey | Targeted gene editing platform independent of DNA double strand break and uses thereof |
| EP4095263A1 (fr) | 2017-01-06 | 2022-11-30 | Editas Medicine, Inc. | Procédés d'évaluation de la coupure par les nucléases |
| EP4249501A3 (fr) | 2017-01-09 | 2024-01-03 | Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research | Procédés de modification de l'expression génique par perturbation de multimères du facteur de transcription qui structurent les boucles régulatrices |
| CN110234770A (zh) * | 2017-01-17 | 2019-09-13 | 基础科学研究院 | 通过dna单链断裂识别碱基编辑脱靶位点的方法 |
| KR102619197B1 (ko) | 2017-01-23 | 2024-01-03 | 리제너론 파마슈티칼스 인코포레이티드 | Hsd17b13 변종 및 이것의 용도 |
| TW201839136A (zh) | 2017-02-06 | 2018-11-01 | 瑞士商諾華公司 | 治療血色素異常症之組合物及方法 |
| KR20190116282A (ko) | 2017-02-10 | 2019-10-14 | 지머젠 인코포레이티드 | 복수의 숙주를 위한 다중 dna 구조체의 조립 및 편집을 위한 모듈식 범용 플라스미드 디자인 전략 |
| WO2018154096A1 (fr) | 2017-02-24 | 2018-08-30 | Georg-August-Universität Göttingen Stiftung Öffentlichen Rechts, Universitätsmedizin | Méthode de réexpression de différents gènes hyperméthylés impliqués dans la fibrose, comme rasal1 hyperméthylé et son utilisation dans le traitement de la fibrose ainsi que kit de pièces pour réexpression de gènes hyperméthylés comprenant rasal1 chez un sujet |
| US11898179B2 (en) | 2017-03-09 | 2024-02-13 | President And Fellows Of Harvard College | Suppression of pain by gene editing |
| EP3592777A1 (fr) | 2017-03-10 | 2020-01-15 | President and Fellows of Harvard College | Éditeur de base cytosine à guanine |
| EP3596217A1 (fr) | 2017-03-14 | 2020-01-22 | Editas Medicine, Inc. | Systèmes et méthodes pour le traitement d'hémoglobinopathies |
| JP7191388B2 (ja) | 2017-03-23 | 2022-12-19 | プレジデント アンド フェローズ オブ ハーバード カレッジ | 核酸によってプログラム可能なdna結合蛋白質を含む核酸塩基編集因子 |
| CN108660161B (zh) * | 2017-03-31 | 2023-05-09 | 中国科学院脑科学与智能技术卓越创新中心 | 基于CRISPR/Cas9技术的制备无嵌合基因敲除动物的方法 |
| WO2018187779A1 (fr) | 2017-04-07 | 2018-10-11 | Sage Science, Inc. | Systèmes et procédés de détection d'une variation structurale génétique à l'aide d'une purification d'adn électrophorétique intégrée |
| EP3612204A4 (fr) | 2017-04-21 | 2021-01-27 | The General Hospital Corporation | Régulation de gène humain inductible, accordable et multiplex à l'aide de crispr-cpf1 |
| WO2018195545A2 (fr) | 2017-04-21 | 2018-10-25 | The General Hospital Corporation | Variantes de cpf1 (cas12a) à spécificité pam modifiée |
| WO2018201086A1 (fr) | 2017-04-28 | 2018-11-01 | Editas Medicine, Inc. | Procédés et systèmes d'analyse de molécules d'arn |
| EP3622070A2 (fr) | 2017-05-10 | 2020-03-18 | Editas Medicine, Inc. | Crispr/arn-guidé systèmes et procédés nucléases transgéniques |
| US11560566B2 (en) | 2017-05-12 | 2023-01-24 | President And Fellows Of Harvard College | Aptazyme-embedded guide RNAs for use with CRISPR-Cas9 in genome editing and transcriptional activation |
| AU2018273968A1 (en) | 2017-05-25 | 2019-11-28 | The General Hospital Corporation | Using split deaminases to limit unwanted off-target base editor deamination |
| CN108977442B (zh) * | 2017-06-05 | 2023-01-06 | 广州市锐博生物科技有限公司 | 用于dna编辑的系统及其应用 |
| CA3065938A1 (fr) | 2017-06-05 | 2018-12-13 | Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Variants de b4galt1 et utilisations associees |
| WO2018227114A1 (fr) | 2017-06-09 | 2018-12-13 | Editas Medicine, Inc. | Nucléases cas9 modifiées |
| KR102634727B1 (ko) | 2017-06-14 | 2024-02-07 | 위스콘신 얼럼나이 리서어치 화운데이션 | 변형된 가이드 rna, crispr-리보뉴클레오프로테인 복합체 및 사용 방법 |
| MX2019015188A (es) | 2017-06-15 | 2020-08-03 | Univ California | Inserciones de adn no virales orientadas. |
| US9982279B1 (en) | 2017-06-23 | 2018-05-29 | Inscripta, Inc. | Nucleic acid-guided nucleases |
| US10011849B1 (en) | 2017-06-23 | 2018-07-03 | Inscripta, Inc. | Nucleic acid-guided nucleases |
| WO2019003193A1 (fr) | 2017-06-30 | 2019-01-03 | Novartis Ag | Méthodes pour le traitement d'une maladie à l'aide de systèmes d'édition de gènes |
| EP3645021A4 (fr) | 2017-06-30 | 2021-04-21 | Intima Bioscience, Inc. | Vecteurs viraux adéno-associés destinés à la thérapie génique |
| IL309801B1 (en) | 2017-07-11 | 2024-08-01 | Sigma Aldrich Co Llc | Use of protein domains interacting with the nucleosome to enhance targeted genome modification |
| US11866726B2 (en) | 2017-07-14 | 2024-01-09 | Editas Medicine, Inc. | Systems and methods for targeted integration and genome editing and detection thereof using integrated priming sites |
| CN111801345A (zh) | 2017-07-28 | 2020-10-20 | 哈佛大学的校长及成员们 | 使用噬菌体辅助连续进化(pace)的进化碱基编辑器的方法和组合物 |
| CA3067872A1 (fr) | 2017-07-31 | 2019-02-07 | Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Cellules souches embryonnaires de souris transgeniques cas et souris et leurs utilisations |
| US11021719B2 (en) | 2017-07-31 | 2021-06-01 | Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Methods and compositions for assessing CRISPER/Cas-mediated disruption or excision and CRISPR/Cas-induced recombination with an exogenous donor nucleic acid in vivo |
| BR112019027673A2 (pt) | 2017-07-31 | 2020-09-15 | Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | animal não humano, e, métodos para testar a recombinação induzida por crispr/cas e para otimizar a capacidade de crispr/cas |
| EP3663310A4 (fr) | 2017-08-04 | 2021-08-11 | Peking University | Rvd de tale reconnaissant spécifiquement une base d'adn modifiée par méthylation et application correspondante |
| CN111278983A (zh) | 2017-08-08 | 2020-06-12 | 北京大学 | 基因敲除方法 |
| BR112020003596A2 (pt) | 2017-08-23 | 2020-09-01 | The General Hospital Corporation | nucleases de crispr-cas9 engenheiradas com especificidade de pam alterada |
| US11319532B2 (en) | 2017-08-30 | 2022-05-03 | President And Fellows Of Harvard College | High efficiency base editors comprising Gam |
| BR112020003609A2 (pt) | 2017-09-29 | 2020-09-01 | Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | sistema e método para formar uma emulsão |
| EP3694993A4 (fr) | 2017-10-11 | 2021-10-13 | The General Hospital Corporation | Procédés de détection de désamination génomique parasite et spécifique de site induite par des technologies d'édition de base |
| CN111757937A (zh) | 2017-10-16 | 2020-10-09 | 布罗德研究所股份有限公司 | 腺苷碱基编辑器的用途 |
| CN107602707B (zh) * | 2017-10-17 | 2021-04-23 | 湖北大学 | 一种特异性调节枯草芽孢杆菌外源基因表达的dcas9-ω融合蛋白及其应用 |
| IL274179B2 (en) | 2017-10-27 | 2024-02-01 | Univ California | Targeted replacement of endogenous T cell receptors |
| EP3704245A1 (fr) | 2017-11-01 | 2020-09-09 | Novartis AG | Arn synthétiques et procédés d'utilisation |
| EP3710583A1 (fr) | 2017-11-16 | 2020-09-23 | Astrazeneca AB | Compositions et méthodes pour améliorer l'efficacité de stratégies knock-in basées sur cas9 |
| US11293019B2 (en) | 2017-12-22 | 2022-04-05 | Gflas Life Sciences, Inc. | Chimeric genome engineering molecules and methods |
| CN109504711A (zh) * | 2018-02-14 | 2019-03-22 | 复旦大学 | 基于CRISPR/cas9和过氧化物酶APEX2系统识别分析特异性基因组位点相互作用DNA的方法 |
| US11718849B2 (en) | 2018-02-19 | 2023-08-08 | Agilent Technologies, Inc. | Phosphopeptide-encoding oligonucleotide libraries and methods for detecting phosphorylation-dependent molecular interactions |
| WO2019165168A1 (fr) | 2018-02-23 | 2019-08-29 | Pioneer Hi-Bred International, Inc. | Nouveaux orthologues de cas9 |
| SG11202008956XA (en) | 2018-03-14 | 2020-10-29 | Editas Medicine Inc | Systems and methods for the treatment of hemoglobinopathies |
| JP7334178B2 (ja) | 2018-03-19 | 2023-08-28 | リジェネロン・ファーマシューティカルズ・インコーポレイテッド | CRISPR/Cas系を使用した動物での転写モジュレーション |
| KR20200141470A (ko) | 2018-04-06 | 2020-12-18 | 칠드런'즈 메디컬 센터 코포레이션 | 체세포 재프로그래밍 및 각인의 조정을 위한 조성물 및 방법 |
| WO2019204378A1 (fr) | 2018-04-17 | 2019-10-24 | The General Hospital Corporation | Dosages in vitro sensibles pour des préférences de substrat et de sites d'agents de liaison, de modification et de clivage d'acide nucléique |
| JP7555822B2 (ja) | 2018-04-19 | 2024-09-25 | ザ・リージエンツ・オブ・ザ・ユニバーシテイー・オブ・カリフオルニア | ゲノム編集のための組成物および方法 |
| WO2019213430A1 (fr) * | 2018-05-03 | 2019-11-07 | The Board Of Trustees Of The Leland Stanford Junior University | Compositions et procédés pour casser des séquences d'adn cibles |
| CN108588123A (zh) * | 2018-05-07 | 2018-09-28 | 南京医科大学 | CRISPR/Cas9载体组合在制备基因敲除猪的血液制品中的应用 |
| KR20210045360A (ko) | 2018-05-16 | 2021-04-26 | 신테고 코포레이션 | 가이드 rna 설계 및 사용을 위한 방법 및 시스템 |
| US10227576B1 (en) | 2018-06-13 | 2019-03-12 | Caribou Biosciences, Inc. | Engineered cascade components and cascade complexes |
| CN110592141B (zh) * | 2018-06-13 | 2023-07-07 | 中国科学院上海有机化学研究所 | 用于调控基因编辑效率的化合物及其应用 |
| EP3821012A4 (fr) | 2018-07-13 | 2022-04-20 | The Regents of The University of California | Véhicule d'administration à base de rétrotransposon et ses procédés d'utilisation |
| EP3821020A4 (fr) | 2018-08-15 | 2022-05-04 | Zymergen Inc. | Applications de crispri dans l'ingénierie métabolique à haut rendement |
| AU2019326408A1 (en) | 2018-08-23 | 2021-03-11 | Sangamo Therapeutics, Inc. | Engineered target specific base editors |
| WO2020049158A1 (fr) | 2018-09-07 | 2020-03-12 | Astrazeneca Ab | Compositions et procédés pour des nucléases améliorées |
| EP3861120A4 (fr) | 2018-10-01 | 2023-08-16 | North Carolina State University | Système crispr-cas de type i recombinant |
| WO2020076976A1 (fr) | 2018-10-10 | 2020-04-16 | Readcoor, Inc. | Indexation moléculaire spatiale tridimensionnelle |
| US11407995B1 (en) | 2018-10-26 | 2022-08-09 | Inari Agriculture Technology, Inc. | RNA-guided nucleases and DNA binding proteins |
| US11434477B1 (en) | 2018-11-02 | 2022-09-06 | Inari Agriculture Technology, Inc. | RNA-guided nucleases and DNA binding proteins |
| US11739320B2 (en) | 2018-11-05 | 2023-08-29 | Wisconsin Alumni Research Foundation | Gene correction of Pompe disease and other autosomal recessive disorders via RNA-guided nucleases |
| CN113166744A (zh) | 2018-12-14 | 2021-07-23 | 先锋国际良种公司 | 用于基因组编辑的新颖crispr-cas系统 |
| CA3120799A1 (fr) | 2018-12-20 | 2020-06-25 | Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Expansion de repetition a mediation par nuclease |
| EP3911746A1 (fr) | 2019-01-14 | 2021-11-24 | Institut National de la Santé et de la Recherche Médicale (INSERM) | Procédés et kits de génération et de sélection de variante de protéine de liaison avec une affinité et/ou une spécificité de liaison accrues |
| EP3921417A4 (fr) | 2019-02-04 | 2022-11-09 | The General Hospital Corporation | Variants d'éditeur de base d'adn adénine avec édition d'arn hors cible réduite |
| US20220145330A1 (en) | 2019-02-10 | 2022-05-12 | The J. David Gladstone Institutes, a testamentary trust established under the Will of J. David Glads | Modified mitochondrion and methods of use thereof |
| CA3130789A1 (fr) | 2019-03-07 | 2020-09-10 | The Regents Of The University Of California | Polypeptides effecteurs crispr-cas et procedes d'utilisation associes |
| WO2020190927A1 (fr) | 2019-03-18 | 2020-09-24 | Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Plate-forme de criblage crispr/cas pour révéler des vulnérabilités génétiques associées à une agrégation de tau |
| IL286357B2 (en) | 2019-03-18 | 2024-10-01 | Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc | A CRISPR/CAS screening platform to identify genetic modifiers of tau seeding or aggregation |
| WO2020191243A1 (fr) | 2019-03-19 | 2020-09-24 | The Broad Institute, Inc. | Procédés et compositions pour l'édition de séquences de nucléotides |
| WO2020206162A1 (fr) | 2019-04-03 | 2020-10-08 | Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Procédés et compositions pour l'insertion de séquences de codage d'anticorps dans un locus d'hébergement sûr |
| SG11202108454RA (en) | 2019-04-04 | 2021-09-29 | Regeneron Pharma | Non-human animals comprising a humanized coagulation factor 12 locus |
| CA3133359C (fr) | 2019-04-04 | 2023-04-11 | Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Procedes pour l'introduction sans cicatrice de modifications ciblees dans des vecteurs de ciblage |
| MA55598A (fr) | 2019-04-12 | 2022-02-16 | Astrazeneca Ab | Compositions et méthodes pour l'édition génétique améliorée |
| JP2022534867A (ja) | 2019-06-04 | 2022-08-04 | リジェネロン・ファーマシューティカルズ・インコーポレイテッド | ベータスリップ変異を有するヒト化ttr遺伝子座を含む非ヒト動物と使用方法 |
| CN113939595A (zh) | 2019-06-07 | 2022-01-14 | 瑞泽恩制药公司 | 包括人源化白蛋白基因座的非人动物 |
| WO2020252340A1 (fr) | 2019-06-14 | 2020-12-17 | Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Modèles de tauopathie |
| EP3783104A1 (fr) * | 2019-08-20 | 2021-02-24 | Kemijski Institut | Connexion à médiation de superhélice de crispr-cas et d'exonucléases pour améliorer l'édition de génomes |
| EP4028063A1 (fr) | 2019-09-13 | 2022-07-20 | Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Modulation de la transcription chez des animaux à l'aide de systèmes crispr/cas administrés par des nanoparticules lipidiques |
| US11987791B2 (en) | 2019-09-23 | 2024-05-21 | Omega Therapeutics, Inc. | Compositions and methods for modulating hepatocyte nuclear factor 4-alpha (HNF4α) gene expression |
| EP3812472B1 (fr) | 2019-10-21 | 2022-11-23 | Albert-Ludwigs-Universität Freiburg | Dosage in vitro vraiment non biaisé pour profiler une activité hors cible d'une ou de plusieurs nucléases programmables spécifiques à une cible dans des cellules (abnoba-seq) |
| US11331333B2 (en) | 2019-11-08 | 2022-05-17 | Georg-August-Universität Göttingen Stiftung Öffentichen Rechts, Universitätsmadizin | Treatment of aberrant fibroblast proliferation |
| CN114746125A (zh) | 2019-11-08 | 2022-07-12 | 瑞泽恩制药公司 | 用于x连锁青少年型视网膜劈裂症疗法的crispr和aav策略 |
| US20230042198A1 (en) * | 2019-11-25 | 2023-02-09 | La Jolla Institute For Immunology | Methods and Compositions for Modulationg Heterochromatin Dysfunction, Genomic Instability, and Associate Conditions |
| WO2021108363A1 (fr) | 2019-11-25 | 2021-06-03 | Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Régulation à la hausse médiée par crispr/cas d'un allèle ttr humanisé |
| CN115176001A (zh) | 2019-12-11 | 2022-10-11 | 因特利亚治疗公司 | 用于基因编辑的修饰的引导rna |
| CN111088357B (zh) * | 2019-12-31 | 2022-09-20 | 深圳大学 | 针对escc的肿瘤标志物及其应用 |
| US20210261932A1 (en) * | 2020-01-24 | 2021-08-26 | The General Hospital Corporation | Crispr-cas enzymes with enhanced on-target activity |
| EP4093864A4 (fr) * | 2020-01-24 | 2024-04-10 | The General Hospital Corporation | Ciblage de génome non contraint avec des variants de crispr-cas9 génétiquement modifiés presque sans pam |
| KR20230004456A (ko) | 2020-03-04 | 2023-01-06 | 리제너론 파아마슈티컬스, 인크. | 면역 요법에 대한 종양 세포의 감작화를 위한 방법 및 조성물 |
| US20230102342A1 (en) | 2020-03-23 | 2023-03-30 | Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Non-human animals comprising a humanized ttr locus comprising a v30m mutation and methods of use |
| AU2021253959A1 (en) * | 2020-04-09 | 2022-11-17 | Verve Therapeutics, Inc. | Base editing of PCSK9 and methods of using same for treatment of disease |
| BR112022022384A2 (pt) * | 2020-05-04 | 2022-12-13 | Editas Medicine Inc | Seleção por knock-in de gene essencial |
| US20230193212A1 (en) | 2020-05-06 | 2023-06-22 | Orchard Therapeutics (Europe) Limited | Treatment for neurodegenerative diseases |
| DE112021002672T5 (de) | 2020-05-08 | 2023-04-13 | President And Fellows Of Harvard College | Vefahren und zusammensetzungen zum gleichzeitigen editieren beider stränge einer doppelsträngigen nukleotid-zielsequenz |
| JP2023526007A (ja) | 2020-05-13 | 2023-06-20 | アンスティチュ ナショナル ドゥ ラ サンテ エ ドゥ ラ ルシェルシュ メディカル | β-ヘモグロビン異常症の処置のための塩基編集アプローチ |
| WO2021246165A1 (fr) * | 2020-06-03 | 2021-12-09 | 国立大学法人広島大学 | Acide nucléique pour la déméthylation d'un gène oasis et procédé de déméthylation l'utilisant |
| US20230235315A1 (en) | 2020-07-10 | 2023-07-27 | Horizon Discovery Limited | Method for producing genetically modified cells |
| CA3188895A1 (fr) | 2020-08-11 | 2022-02-17 | Rami Aqeilan | Procede de traitement de maladies associees a wwox |
| KR102674574B1 (ko) * | 2020-09-02 | 2024-06-13 | 한국과학기술연구원 | Cas9을 위한 신규 tracrRNA 시스템 |
| KR20230082676A (ko) | 2020-10-13 | 2023-06-08 | 쌍트르 나시오날 드 라 르쉐르쉐 싸이엉띠피끄(쎄.엔.에르.에스.) | 표적-항균-플라스미드 조합 접합 및 crispr/cas 시스템 및 그의 용도 |
| RU2762831C1 (ru) * | 2020-10-26 | 2021-12-23 | Федеральное государственное бюджетное научное учреждение "Всероссийский научно-исследовательский институт сельскохозяйственной биотехнологии" (ФГБНУ ВНИИСБ) | Молекула рнк-проводника для геномного редактирования протомоторной области гена vrn-a1 однодольных зерновых с применением системы crispr/cas9 |
| CN112430622A (zh) * | 2020-10-26 | 2021-03-02 | 扬州大学 | 一种FokI和dCpf1融合蛋白表达载体及其介导的定点基因编辑方法 |
| EP4256052A1 (fr) | 2020-12-02 | 2023-10-11 | Decibel Therapeutics, Inc. | Lignées cellulaires de biocapteurs crispr sam et procédés d'utilisation associés |
| KR20220082186A (ko) | 2020-12-10 | 2022-06-17 | 한세준 | 유,무선 충전이 가능한 보조배터리형 uv-led살균기 |
| JP2024501757A (ja) | 2021-01-05 | 2024-01-15 | ホライズン・ディスカバリー・リミテッド | 遺伝子組換え細胞の製造方法 |
| EP4297799A1 (fr) | 2021-02-25 | 2024-01-03 | Institut National de la Santé et de la Recherche Médicale (INSERM) | Édition du génome spécifique d'un allèle de la mutation g56r de nr2e3 |
| KR20220124652A (ko) | 2021-03-03 | 2022-09-14 | 중앙대학교 산학협력단 | CRISPR/Cas9 시스템을 이용한 유전체 단일염기 편집 방법 및 이의 용도 |
| CN113846019B (zh) * | 2021-03-05 | 2023-08-01 | 海南师范大学 | 一种海洋微拟球藻靶向表观基因组遗传调控方法 |
| EP4095243A1 (fr) | 2021-05-25 | 2022-11-30 | European Molecular Biology Laboratory | Système de clivage et d'édition de précision du génome basé sur l'hybridation et utilisations associées |
| CN117396602A (zh) | 2021-05-27 | 2024-01-12 | 阿斯利康(瑞典)有限公司 | 具有增强的稳定性的cas9效应蛋白 |
| BR112023025724A2 (pt) | 2021-06-10 | 2024-02-27 | Intellia Therapeutics Inc | Rnas-guia modificados que compreendem um ligante interno para edição de gene |
| WO2023010133A2 (fr) | 2021-07-30 | 2023-02-02 | Tune Therapeutics, Inc. | Compositions et procédés de modulation de l'expression de la frataxine |
| WO2023010135A1 (fr) | 2021-07-30 | 2023-02-02 | Tune Therapeutics, Inc. | Compositions et procédés pour moduler l'expression de la protéine 2 de liaison méthyle-cpg (mecp2) |
| CA3229450A1 (fr) | 2021-08-20 | 2023-02-23 | Wisconsin Alumni Research Foundation | Generation non virale de lymphocytes t porteurs de recepteurs antigeniques chimeriques obtenus par edition genique |
| JP2024534945A (ja) | 2021-09-10 | 2024-09-26 | アジレント・テクノロジーズ・インク | 化学修飾を有するプライム編集のためのガイドrna |
| WO2023052366A1 (fr) | 2021-09-28 | 2023-04-06 | INSERM (Institut National de la Santé et de la Recherche Médicale) | Approches d'édition de bases pour le traitement de bétahémoglobinopathies |
| EP4408996A2 (fr) | 2021-09-30 | 2024-08-07 | Astrazeneca AB | Utilisation d'inhibiteurs pour augmenter l'efficacité d'insertions de crispr/cas |
| AU2022366987A1 (en) | 2021-10-14 | 2024-05-16 | Arsenal Biosciences, Inc. | Immune cells having co-expressed shrnas and logic gate systems |
| EP4419119A1 (fr) | 2021-10-20 | 2024-08-28 | University of Rochester | Cellules progénitrices gliales isolées destinées à être utilisées dans le traitement par compétition de la perte de matière blanche liée à l'âge |
| CN118251491A (zh) | 2021-10-28 | 2024-06-25 | 瑞泽恩制药公司 | 用于敲除C5的CRISPR/Cas相关方法及组合物 |
| MX2024005242A (es) | 2021-11-03 | 2024-07-02 | Intellia Therapeutics Inc | Polinucleotidos, composiciones y metodos para la edicion del genoma. |
| CA3237482A1 (fr) | 2021-11-03 | 2023-05-11 | The J. David Gladstone Institutes, A Testamentary Trust Established Under The Will Of J. David Gladstone | Edition precise du genome a l'aide de retrons |
| EP4441089A1 (fr) | 2021-12-01 | 2024-10-09 | INSERM (Institut National de la Santé et de la Recherche Médicale) | Procédés d'augmentation de la teneur en hémoglobine f?tale par édition de la région +55-kb de l'amplificateur bcl11a spécifique de l'érythroïde |
| KR20240117571A (ko) | 2021-12-08 | 2024-08-01 | 리제너론 파마슈티칼스 인코포레이티드 | 돌연변이 마이오실린 질환 모델 및 이의 용도 |
| US20230279442A1 (en) | 2021-12-15 | 2023-09-07 | Versitech Limited | Engineered cas9-nucleases and method of use thereof |
| WO2023137471A1 (fr) | 2022-01-14 | 2023-07-20 | Tune Therapeutics, Inc. | Compositions, systèmes et procédés de programmation de phénotypes de lymphocytes t par activation génique ciblée |
| WO2023137472A2 (fr) | 2022-01-14 | 2023-07-20 | Tune Therapeutics, Inc. | Compositions, systèmes et procédés de programmation de phénotypes de lymphocytes t par répression génique ciblée |
| WO2023141487A1 (fr) * | 2022-01-20 | 2023-07-27 | Inari Agriculture Technology, Inc. | Préparation et transformation d'explants de soja améliorés |
| WO2023141602A2 (fr) | 2022-01-21 | 2023-07-27 | Renagade Therapeutics Management Inc. | Rétrons modifiés et méthodes d'utilisation |
| WO2023144104A1 (fr) | 2022-01-25 | 2023-08-03 | INSERM (Institut National de la Santé et de la Recherche Médicale) | Approches d'édition de bases pour le traitement de la βeta-thalassémie |
| WO2023150620A1 (fr) | 2022-02-02 | 2023-08-10 | Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Insertion de transgène médiée par crispr dans des cellules néonatales |
| WO2023152351A1 (fr) | 2022-02-14 | 2023-08-17 | INSERM (Institut National de la Santé et de la Recherche Médicale) | Traitement des cancers hépatiques par la perturbation du site de liaison bêta-caténine/tcf-4 situé en amont de meg3 dans le locus dlk1/dio3 |
| WO2023212677A2 (fr) | 2022-04-29 | 2023-11-02 | Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Identification de zones de sécurité extragéniques spécifiques de tissu pour des approches de thérapie génique |
| WO2023220603A1 (fr) | 2022-05-09 | 2023-11-16 | Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Vecteurs et procédés de production d'anticorps in vivo |
| WO2023217888A1 (fr) | 2022-05-10 | 2023-11-16 | Institut National de la Santé et de la Recherche Médicale | Approches d'édition de base pour corriger la mutation cd39 (cag>tag) chez des patients souffrant de βêta-thalassémie |
| WO2023235726A2 (fr) | 2022-05-31 | 2023-12-07 | Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Agents thérapeutiques d'interférence crispr pour une maladie d'expansion de répétition c9orf72 |
| WO2023235725A2 (fr) | 2022-05-31 | 2023-12-07 | Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Agents thérapeutiques à base de crispr pour une maladie d'expansion de répétition c9orf72 |
| WO2023250511A2 (fr) | 2022-06-24 | 2023-12-28 | Tune Therapeutics, Inc. | Compositions, systèmes et procédés de réduction de lipoprotéine de faible densité par répression génique ciblée |
| WO2024015881A2 (fr) | 2022-07-12 | 2024-01-18 | Tune Therapeutics, Inc. | Compositions, systèmes et procédés d'activation transcriptionnelle ciblée |
| WO2024020346A2 (fr) | 2022-07-18 | 2024-01-25 | Renagade Therapeutics Management Inc. | Composants d'édition génique, systèmes et procédés d'utilisation |
| WO2024018056A1 (fr) | 2022-07-22 | 2024-01-25 | Institut National de la Santé et de la Recherche Médicale | Approches d'édition de base pour corriger la mutation ivs2-1 (g>a) chez les patients souffrant de βeta-thalassémie |
| WO2024026474A1 (fr) | 2022-07-29 | 2024-02-01 | Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Compositions et méthodes d'administration médiée par le récepteur de la transferrine (tfr) au cerveau et au muscle |
| US20240067969A1 (en) | 2022-08-19 | 2024-02-29 | Tune Therapeutics, Inc. | Compositions, systems, and methods for regulation of hepatitis b virus through targeted gene repression |
| WO2024044723A1 (fr) | 2022-08-25 | 2024-02-29 | Renagade Therapeutics Management Inc. | Rétrons modifiés et méthodes d'utilisation |
| WO2024047247A1 (fr) | 2022-09-02 | 2024-03-07 | Institut National de la Santé et de la Recherche Médicale | Approches d'édition de bases pour le traitement de la sclérose latérale amyotrophique |
| WO2024064642A2 (fr) | 2022-09-19 | 2024-03-28 | Tune Therapeutics, Inc. | Compositions, systèmes et méthodes de modulation de fonction de lymphocyte t |
| WO2024073606A1 (fr) | 2022-09-28 | 2024-04-04 | Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Récepteurs modifiés résistants aux anticorps pour améliorer des thérapies à base de cellules |
| WO2024084025A1 (fr) | 2022-10-21 | 2024-04-25 | Keygene N.V. | Transfection d'arn dans des cellules végétales avec arn modifié |
| WO2024098002A1 (fr) | 2022-11-04 | 2024-05-10 | Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Protéines de liaison de sous-unité auxiliaire gamma 1 du canal calcique dépendant de la tension (cacng1) et administration médiée par cacng1 au muscle squelettique |
| WO2024107765A2 (fr) | 2022-11-14 | 2024-05-23 | Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | Compositions et procédés d'administration médiée par le récepteur 3 du facteur de croissance des fibroblastes à des astrocytes |
| CN115820603B (zh) * | 2022-11-15 | 2024-07-05 | 吉林大学 | 一种基于dCasRx-NSUN6单基因特异性M5C修饰编辑方法 |
| WO2024121354A1 (fr) | 2022-12-08 | 2024-06-13 | Keygene N.V. | Séquençage duplex avec extrémités d'adn fermées de manière covalente |
| WO2024131940A1 (fr) * | 2022-12-23 | 2024-06-27 | 益杰立科(上海)生物科技有限公司 | Fusion et son utilisation |
| WO2024163683A2 (fr) | 2023-02-01 | 2024-08-08 | Tune Therapeutics, Inc. | Systèmes, compositions et procédés de modulation de l'expression de la protéine-2 de liaison au cpg méthylé (mecp2) et du transcrit spécifique du x inactif (xist) |
| WO2024163678A2 (fr) | 2023-02-01 | 2024-08-08 | Tune Therapeutics, Inc. | Protéines de fusion et systèmes d'activation ciblée de frataxine (fxn) et procédés associés |
| WO2024165484A1 (fr) | 2023-02-06 | 2024-08-15 | Institut National de la Santé et de la Recherche Médicale | Enrichissement de cellules souches hématopoïétiques génétiquement modifiées par édition de bases multiplex |
| CN116376975B (zh) * | 2023-02-27 | 2024-05-14 | 中国科学院脑科学与智能技术卓越创新中心 | 激活异染色质基因的方法及应用 |
| WO2024186890A1 (fr) | 2023-03-06 | 2024-09-12 | Intellia Therapeutics, Inc. | Compositions et méthodes d'édition du génome du virus de l'hépatite b (vhb) |
| CN118684781A (zh) * | 2023-03-21 | 2024-09-24 | 深圳赫兹生命科学技术有限公司 | GnRH-VLP重组去势疫苗及其制备方法 |
| WO2024201368A1 (fr) | 2023-03-29 | 2024-10-03 | Astrazeneca Ab | Utilisation d'inhibiteurs pour augmenter l'efficacité d'insertions crispr/cas |
| WO2024209000A1 (fr) | 2023-04-04 | 2024-10-10 | Keygene N.V. | Lieurs pour séquençage duplex |
Family Cites Families (166)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US4603044A (en) | 1983-01-06 | 1986-07-29 | Technology Unlimited, Inc. | Hepatocyte Directed Vesicle delivery system |
| US4957773A (en) | 1989-02-13 | 1990-09-18 | Syracuse University | Deposition of boron-containing films from decaborane |
| US5436150A (en) * | 1992-04-03 | 1995-07-25 | The Johns Hopkins University | Functional domains in flavobacterium okeanokoities (foki) restriction endonuclease |
| USRE39229E1 (en) | 1994-08-20 | 2006-08-08 | Gendaq Limited | Binding proteins for recognition of DNA |
| US20030017149A1 (en) | 1996-10-10 | 2003-01-23 | Hoeffler James P. | Single chain monoclonal antibody fusion reagents that regulate transcription in vivo |
| US6534261B1 (en) | 1999-01-12 | 2003-03-18 | Sangamo Biosciences, Inc. | Regulation of endogenous gene expression in cells using zinc finger proteins |
| US6503717B2 (en) | 1999-12-06 | 2003-01-07 | Sangamo Biosciences, Inc. | Methods of using randomized libraries of zinc finger proteins for the identification of gene function |
| US20020164575A1 (en) | 1999-09-14 | 2002-11-07 | Sangamo Biosciences, Inc., A Delaware Corporation | Gene identification |
| WO2001083819A2 (fr) | 2000-04-28 | 2001-11-08 | Sangamo Biosciences, Inc. | Procédés d'élaboration de molécules régulatrices exogènes |
| AU2001253914B2 (en) | 2000-04-28 | 2006-06-08 | Sangamo Therapeutics, Inc. | Targeted modification of chromatin structure |
| US20030198627A1 (en) | 2001-09-01 | 2003-10-23 | Gert-Jan Arts | siRNA knockout assay method and constructs |
| WO2003072788A1 (fr) | 2002-02-21 | 2003-09-04 | The Wistar Institute Of Anatomy And Biology | Procedes et compositions pour reguler de maniere reversible l'expression de genes cibles dans des cellules |
| US20070020627A1 (en) | 2002-06-11 | 2007-01-25 | The Scripps Research Institute | Artificial transcription factors |
| WO2004099366A2 (fr) | 2002-10-23 | 2004-11-18 | The General Hospital Corporation | Optimisation parallele sensible au contexte de domaines de liaison a l'adn en doigt de zinc |
| US20070134796A1 (en) | 2005-07-26 | 2007-06-14 | Sangamo Biosciences, Inc. | Targeted integration and expression of exogenous nucleic acid sequences |
| US7021555B2 (en) | 2004-01-06 | 2006-04-04 | Zoo Med Laboratories, Inc. | Spraying/misting for plants and animals |
| US7919277B2 (en) | 2004-04-28 | 2011-04-05 | Danisco A/S | Detection and typing of bacterial strains |
| US20080131962A1 (en) | 2006-05-25 | 2008-06-05 | Sangamo Biosciences, Inc. | Engineered cleavage half-domains |
| HUE027400T2 (en) | 2005-02-18 | 2016-10-28 | Glaxosmithkline Biologicals Sa | Proteins and nucleic acids from meningitis / sepsis with Escherichia coli |
| WO2007014181A2 (fr) | 2005-07-25 | 2007-02-01 | Johns Hopkins University | Modification specifique au site du genome humain utilisant des nucleases en doigt a zinc personnalisees |
| US10066233B2 (en) | 2005-08-26 | 2018-09-04 | Dupont Nutrition Biosciences Aps | Method of modulating cell resistance |
| WO2007062422A2 (fr) | 2005-11-28 | 2007-05-31 | The Scripps Research Institute | Domaines liant des doigts de zinc pour le triplet tnn |
| ES2590925T3 (es) | 2006-05-19 | 2016-11-24 | Dupont Nutrition Biosciences Aps | Microorganismos marcados y métodos de marcado |
| AU2007258872A1 (en) | 2006-06-16 | 2007-12-21 | Danisco A/S | Bacterium |
| US9201063B2 (en) | 2006-11-16 | 2015-12-01 | General Electric Company | Sequential analysis of biological samples |
| WO2008093152A1 (fr) * | 2007-02-01 | 2008-08-07 | Cellectis | Meganucleases heterodimeres obligatoires et leurs utilisations |
| TR201905633T4 (tr) | 2007-03-02 | 2019-05-21 | Dupont Nutrition Biosci Aps | İyileştirilmiş faj direnci olan kültürler. |
| CA2681661C (fr) | 2007-03-23 | 2015-11-24 | New York University | Methodes visant l'augmentation de la capacite d'assimilation d'azote chez les plantes transgeniques exprimant la cca1 et la glk1 |
| US8252535B2 (en) | 2007-04-10 | 2012-08-28 | Qiagen Gmbh | RNA interference tags |
| WO2008151032A2 (fr) | 2007-05-31 | 2008-12-11 | Washington University In St. Louis | Ensembles et procédés comprenant des produits géniques de m. smithii |
| WO2009041832A2 (fr) | 2007-09-25 | 2009-04-02 | Pastoral Greenhouse Gas Research Ltd | Vaccins et composants vaccinaux permettant d'inhiber des cellules microbiennes |
| FR2925918A1 (fr) | 2007-12-28 | 2009-07-03 | Pasteur Institut | Typage et sous-typage moleculaire de salmonella par identification des sequences nucleotidiques variables des loci crispr |
| FR2930264B1 (fr) | 2008-04-18 | 2013-02-22 | Gervais Danone Sa | Nouvelle souche de lactobacillus paracasei subsp. paracasei dotee de proprietes antimicrobiennes et immunomodulatrices. |
| JP2010017178A (ja) | 2008-06-11 | 2010-01-28 | Sumitomo Chemical Co Ltd | Dnaを定量又は検出する方法 |
| JP2010017179A (ja) | 2008-06-11 | 2010-01-28 | Sumitomo Chemical Co Ltd | Dnaを定量又は検出する方法 |
| US8546553B2 (en) | 2008-07-25 | 2013-10-01 | University Of Georgia Research Foundation, Inc. | Prokaryotic RNAi-like system and methods of use |
| JP2010048566A (ja) | 2008-08-19 | 2010-03-04 | Sumitomo Chemical Co Ltd | Dnaを定量又は検出する方法 |
| JP2010068800A (ja) | 2008-08-19 | 2010-04-02 | Sumitomo Chemical Co Ltd | Dnaを定量又は検出する方法 |
| US20100076057A1 (en) | 2008-09-23 | 2010-03-25 | Northwestern University | TARGET DNA INTERFERENCE WITH crRNA |
| WO2010037001A2 (fr) * | 2008-09-26 | 2010-04-01 | Immune Disease Institute, Inc. | Oxydation sélective de 5-méthylcytosine par des protéines de la famille tet |
| EP2344673B1 (fr) | 2008-10-21 | 2014-05-07 | Animal Health Trust | Essai diagnostique pour streptococcus equi |
| EP2344641A2 (fr) | 2008-10-23 | 2011-07-20 | Université de Lausanne | Vecteurs de transfert de gène comprenant au moins une molécule d'adn isolés ayant isolant et ou les limites et methodes pour identifier le même |
| WO2010054108A2 (fr) | 2008-11-06 | 2010-05-14 | University Of Georgia Research Foundation, Inc. | Polypeptides cas6 et procédés d'utilisation |
| RU2570562C2 (ru) | 2008-11-07 | 2015-12-10 | ДюПон НЬЮТРИШН БАЙОСАЙЕНСИЗ АпС | Последовательности crispr бифидобактерий |
| MX349706B (es) | 2008-11-11 | 2017-08-09 | Alimentary Health Ltd | Bifidobacterium longum. |
| GB2466177A (en) | 2008-12-03 | 2010-06-16 | Arab Science & Technology Found | Bacteriophage selection and breeding |
| EP2367938B1 (fr) | 2008-12-12 | 2014-06-11 | DuPont Nutrition Biosciences ApS | Groupe génétique de souches de Streptococcus thermophilus dotés de propriétés rhéologiques uniques pour la fermentation lactique |
| KR20100093626A (ko) | 2009-02-17 | 2010-08-26 | 서강대학교산학협력단 | 슈도모나스 애루지노사에 대한 파아지 치료 |
| EP2414524B1 (fr) | 2009-04-03 | 2017-08-23 | Centre National De La Recherche Scientifique | Vecteurs de transfert de gènes comprenant des isolants génétiques et procédés d'identification d'isolants génétiques |
| WO2010129019A2 (fr) | 2009-04-27 | 2010-11-11 | Pacific Biosciences Of California, Inc. | Procédés et systèmes de séquençage en temps réel |
| WO2010144151A2 (fr) | 2009-06-12 | 2010-12-16 | Pacific Biosciences Of California, Inc. | Analyse monomoléculaire en temps réel de la protéinogenèse |
| WO2011017293A2 (fr) | 2009-08-03 | 2011-02-10 | The General Hospital Corporation | Transformation de matrices à doigts de zinc par un assemblage dépendant du contexte |
| CN102648282A (zh) | 2009-09-25 | 2012-08-22 | 巴斯夫植物科学有限公司 | 具有增强的产量相关性状的植物和用于产生该植物的方法 |
| US9677125B2 (en) | 2009-10-21 | 2017-06-13 | General Electric Company | Detection of plurality of targets in biological samples |
| US20110269119A1 (en) | 2009-10-30 | 2011-11-03 | Synthetic Genomics, Inc. | Encoding text into nucleic acid sequences |
| JP6137596B2 (ja) | 2010-02-08 | 2017-05-31 | サンガモ セラピューティクス, インコーポレイテッド | 遺伝子操作された切断ハーフドメイン |
| WO2011101696A1 (fr) * | 2010-02-18 | 2011-08-25 | Cellectis | Système de recombinaison de méganucléase amélioré |
| US20120027786A1 (en) | 2010-02-23 | 2012-02-02 | Massachusetts Institute Of Technology | Genetically programmable pathogen sense and destroy |
| US10087431B2 (en) | 2010-03-10 | 2018-10-02 | The Regents Of The University Of California | Methods of generating nucleic acid fragments |
| CN105707123A (zh) | 2010-03-12 | 2016-06-29 | 布鲁克哈文科学协会有限责任公司 | 肠杆菌638及其应用方法 |
| BR112012028805A2 (pt) | 2010-05-10 | 2019-09-24 | The Regents Of The Univ Of California E Nereus Pharmaceuticals Inc | composições de endorribonuclease e métodos de uso das mesmas. |
| US20110201118A1 (en) | 2010-06-14 | 2011-08-18 | Iowa State University Research Foundation, Inc. | Nuclease activity of tal effector and foki fusion protein |
| WO2012047726A1 (fr) | 2010-09-29 | 2012-04-12 | The Broad Institute, Inc. | Procédés d'immunoprécipitation de la chromatine |
| DK2630156T3 (en) | 2010-10-20 | 2018-12-17 | Dupont Nutrition Biosci Aps | CRISPR-CAS SEQUENCES OF LACTOCOCCUS |
| US20130337454A1 (en) | 2010-10-27 | 2013-12-19 | Philippe Duchateau | Method for increasing the efficiency of double-strand break-induced mutagenesis |
| WO2012093833A2 (fr) * | 2011-01-03 | 2012-07-12 | Toolgen Incorporation | Ingéniérie des génomes faisant appel à des nucléases effectrices tal remodelées |
| US20120214160A1 (en) | 2011-01-14 | 2012-08-23 | Life Technologies Corporation | Methods, compositions, and kits for detecting rare cells |
| US20140113376A1 (en) | 2011-06-01 | 2014-04-24 | Rotem Sorek | Compositions and methods for downregulating prokaryotic genes |
| DK2543255T4 (da) | 2011-07-04 | 2023-03-20 | Dsm Ip Assets Bv | Antilisteriel blandet kultur og fremgangsmåde til fremstilling af ost |
| EP3461896B1 (fr) | 2011-07-15 | 2023-11-29 | The General Hospital Corporation | Procédés d'assemblage d'effecteurs de type activateur de la transcription |
| GB201122458D0 (en) | 2011-12-30 | 2012-02-08 | Univ Wageningen | Modified cascade ribonucleoproteins and uses thereof |
| ES2641840T3 (es) | 2012-02-24 | 2017-11-14 | Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center | Composiciones y métodos para el tratamiento de hemoglobinopatías |
| AU2013225950B2 (en) | 2012-02-29 | 2018-02-15 | Sangamo Therapeutics, Inc. | Methods and compositions for treating huntington's disease |
| WO2013141680A1 (fr) | 2012-03-20 | 2013-09-26 | Vilnius University | Clivage d'adn dirigé par arn par le complexe cas9-arncr |
| US9637739B2 (en) | 2012-03-20 | 2017-05-02 | Vilnius University | RNA-directed DNA cleavage by the Cas9-crRNA complex |
| AU2013256240B2 (en) | 2012-05-02 | 2018-09-20 | Corteva Agriscience Llc | Targeted modification of malate dehydrogenase |
| CN104471067B (zh) | 2012-05-07 | 2020-08-14 | 桑格摩生物治疗股份有限公司 | 用于核酸酶介导的转基因靶向整合的方法和组合物 |
| US11120889B2 (en) | 2012-05-09 | 2021-09-14 | Georgia Tech Research Corporation | Method for synthesizing a nuclease with reduced off-site cleavage |
| DK2800811T3 (en) | 2012-05-25 | 2017-07-17 | Univ Vienna | METHODS AND COMPOSITIONS FOR RNA DIRECTIVE TARGET DNA MODIFICATION AND FOR RNA DIRECTIVE MODULATION OF TRANSCRIPTION |
| WO2013188037A2 (fr) | 2012-06-11 | 2013-12-19 | Agilent Technologies, Inc | Procédé de soustraction adaptateur-dimère à l'aide d'une protéine crispr cas6 |
| EP2674501A1 (fr) | 2012-06-14 | 2013-12-18 | Agence nationale de sécurité sanitaire de l'alimentation,de l'environnement et du travail | Composition de catalyseur pour la polymérisation des oléfines |
| US10025647B2 (en) * | 2012-06-30 | 2018-07-17 | Intel Corporation | Memory poisoning with hints |
| JP6329537B2 (ja) | 2012-07-11 | 2018-05-23 | サンガモ セラピューティクス, インコーポレイテッド | 生物学的薬剤の送達のための方法および組成物 |
| JP2015527889A (ja) | 2012-07-25 | 2015-09-24 | ザ ブロード インスティテュート, インコーポレイテッド | 誘導可能なdna結合タンパク質およびゲノム撹乱ツール、ならびにそれらの適用 |
| JP6775953B2 (ja) | 2012-09-07 | 2020-10-28 | ダウ アグロサイエンシィズ エルエルシー | Fad3性能座および標的化切断を誘導可能である対応する標的部位特異的結合タンパク質 |
| AU2013329308B2 (en) | 2012-10-09 | 2018-11-01 | Liposcience, Inc. | NMR quantification of branched chain amino acids |
| US20150267176A1 (en) | 2012-10-12 | 2015-09-24 | The General Hospital Corporation | Transcription activator-like effector (tale) - lysine-specific demethylase 1 (lsd1) fusion proteins |
| US20150315576A1 (en) | 2012-11-01 | 2015-11-05 | Massachusetts Institute Of Technology | Genetic device for the controlled destruction of dna |
| KR102243092B1 (ko) | 2012-12-06 | 2021-04-22 | 시그마-알드리치 컴퍼니., 엘엘씨 | Crispr-기초된 유전체 변형과 조절 |
| SG11201504523UA (en) | 2012-12-12 | 2015-07-30 | Broad Inst Inc | Delivery, engineering and optimization of systems, methods and compositions for sequence manipulation and therapeutic applications |
| US20140310830A1 (en) | 2012-12-12 | 2014-10-16 | Feng Zhang | CRISPR-Cas Nickase Systems, Methods And Compositions For Sequence Manipulation in Eukaryotes |
| WO2014093655A2 (fr) | 2012-12-12 | 2014-06-19 | The Broad Institute, Inc. | Fabrication et optimisation de systèmes, de procédés et de compositions pour la manipulation de séquence avec des domaines fonctionnels |
| US8697359B1 (en) | 2012-12-12 | 2014-04-15 | The Broad Institute, Inc. | CRISPR-Cas systems and methods for altering expression of gene products |
| WO2014093709A1 (fr) | 2012-12-12 | 2014-06-19 | The Broad Institute, Inc. | Procédés, modèles, systèmes et appareil pour identifier des séquences cibles pour les enzymes cas ou des systèmes crispr-cas pour des séquences cibles et transmettre les résultats associés |
| EP4286402A3 (fr) | 2012-12-12 | 2024-02-14 | The Broad Institute, Inc. | Systèmes de composants crispr-cas, procédés et compositions pour la manipulation de séquence |
| EP2931899A1 (fr) | 2012-12-12 | 2015-10-21 | The Broad Institute, Inc. | Génomique fonctionnelle employant des systèmes crispr-cas, des compositions, des procédés, des banques d'inactivation et leurs applications |
| KR20150105633A (ko) | 2012-12-12 | 2015-09-17 | 더 브로드 인스티튜트, 인코퍼레이티드 | 서열 조작을 위한 시스템, 방법 및 최적화된 가이드 조성물의 조작 |
| EP3031921A1 (fr) | 2012-12-12 | 2016-06-15 | The Broad Institute, Inc. | Administration, ingénierie et optimisation de systèmes, procédés et compositions pour manipulation de séquence et applications thérapeutiques |
| DK3064585T3 (da) | 2012-12-12 | 2020-04-27 | Broad Inst Inc | Konstruering og optimering af forbedrede systemer, fremgangsmåder og enzymsammensætninger til sekvensmanipulation |
| JP6473419B2 (ja) | 2012-12-13 | 2019-02-20 | ダウ アグロサイエンシィズ エルエルシー | 部位特異的ヌクレアーゼ活性のdna検出方法 |
| CN105121641A (zh) | 2012-12-17 | 2015-12-02 | 哈佛大学校长及研究员协会 | Rna-引导的人类基因组工程化 |
| JP2016502853A (ja) * | 2012-12-19 | 2016-02-01 | ダウ アグロサイエンシィズ エルエルシー | 効率的なハイスループットトランスジェニック事象生成のための改善されたダイズ形質転換 |
| CA2897932A1 (fr) | 2013-01-14 | 2014-07-17 | Recombinetics, Inc. | Betail sans corne |
| CN103233028B (zh) | 2013-01-25 | 2015-05-13 | 南京徇齐生物技术有限公司 | 一种无物种限制无生物安全性问题的真核生物基因打靶方法及螺旋结构dna序列 |
| US20140212869A1 (en) | 2013-01-25 | 2014-07-31 | Agilent Technologies, Inc. | Nucleic Acid Proximity Assay Involving the Formation of a Three-way junction |
| EP3623463B1 (fr) | 2013-02-07 | 2021-10-20 | The General Hospital Corporation | Activateurs transcriptionnels tale |
| US10660943B2 (en) | 2013-02-07 | 2020-05-26 | The Rockefeller University | Sequence specific antimicrobials |
| WO2014127287A1 (fr) | 2013-02-14 | 2014-08-21 | Massachusetts Institute Of Technology | Procédé pour la mutagenèse ciblée in vivo |
| US10227610B2 (en) | 2013-02-25 | 2019-03-12 | Sangamo Therapeutics, Inc. | Methods and compositions for enhancing nuclease-mediated gene disruption |
| EP2922393B2 (fr) | 2013-02-27 | 2022-12-28 | Helmholtz Zentrum München - Deutsches Forschungszentrum für Gesundheit und Umwelt (GmbH) | Édition de gène dans l'ovocyte au moyen de cas9 nucléases |
| CN105209634B (zh) * | 2013-03-08 | 2020-05-12 | 牛津纳米孔技术公司 | 酶停滞方法 |
| US10612043B2 (en) | 2013-03-09 | 2020-04-07 | Agilent Technologies, Inc. | Methods of in vivo engineering of large sequences using multiple CRISPR/cas selections of recombineering events |
| EP2971167B1 (fr) | 2013-03-14 | 2019-07-31 | Caribou Biosciences, Inc. | Compositions et procédés pour des acides nucléiques à ciblage d'acide nucléique |
| US20140273230A1 (en) | 2013-03-15 | 2014-09-18 | Sigma-Aldrich Co., Llc | Crispr-based genome modification and regulation |
| US9234213B2 (en) | 2013-03-15 | 2016-01-12 | System Biosciences, Llc | Compositions and methods directed to CRISPR/Cas genomic engineering systems |
| JP2016512048A (ja) | 2013-03-15 | 2016-04-25 | リージェンツ オブ ザ ユニバーシティ オブ ミネソタ | CRISPR/Casシステムを使用した植物ゲノム操作 |
| US10760064B2 (en) | 2013-03-15 | 2020-09-01 | The General Hospital Corporation | RNA-guided targeting of genetic and epigenomic regulatory proteins to specific genomic loci |
| US11332719B2 (en) | 2013-03-15 | 2022-05-17 | The Broad Institute, Inc. | Recombinant virus and preparations thereof |
| IL289396B2 (en) | 2013-03-15 | 2023-12-01 | The General Hospital Coporation | Using tru-grnas to increase the specificity of RNA-guided genome editing |
| US20140349400A1 (en) | 2013-03-15 | 2014-11-27 | Massachusetts Institute Of Technology | Programmable Modification of DNA |
| KR102192599B1 (ko) | 2013-04-05 | 2020-12-18 | 다우 아그로사이언시즈 엘엘씨 | 식물의 게놈 내의 외인성 서열의 통합을 위한 방법 및 조성물 |
| US20150056629A1 (en) | 2013-04-14 | 2015-02-26 | Katriona Guthrie-Honea | Compositions, systems, and methods for detecting a DNA sequence |
| RS62263B1 (sr) | 2013-04-16 | 2021-09-30 | Regeneron Pharma | Ciljana modifikacija genoma pacova |
| CN103224947B (zh) | 2013-04-28 | 2015-06-10 | 陕西师范大学 | 一种基因打靶系统 |
| AU2014262867B2 (en) | 2013-05-10 | 2019-12-05 | Sangamo Therapeutics, Inc. | Delivery methods and compositions for nuclease-mediated genome engineering |
| US9873907B2 (en) | 2013-05-29 | 2018-01-23 | Agilent Technologies, Inc. | Method for fragmenting genomic DNA using CAS9 |
| WO2014194190A1 (fr) | 2013-05-30 | 2014-12-04 | The Penn State Research Foundation | Ciblage génique et modification génétique de végétaux par le biais de l'édition du génome guidée par l'arn |
| US20150315252A1 (en) | 2013-06-11 | 2015-11-05 | Clontech Laboratories, Inc. | Protein enriched microvesicles and methods of making and using the same |
| CN106062197A (zh) | 2013-06-17 | 2016-10-26 | 布罗德研究所有限公司 | 用于序列操纵的串联指导系统、方法和组合物的递送、工程化和优化 |
| US10011850B2 (en) | 2013-06-21 | 2018-07-03 | The General Hospital Corporation | Using RNA-guided FokI Nucleases (RFNs) to increase specificity for RNA-Guided Genome Editing |
| CN103343120B (zh) | 2013-07-04 | 2015-03-04 | 中国科学院遗传与发育生物学研究所 | 一种小麦基因组定点改造方法 |
| CN105392885B (zh) | 2013-07-19 | 2020-11-03 | 赖瑞克斯生物科技公司 | 用于产生双等位基因敲除的方法和组合物 |
| WO2015021426A1 (fr) | 2013-08-09 | 2015-02-12 | Sage Labs, Inc. | Nouvelle protéine de fusion à base de système crispr/cas et son application en édition de génome |
| WO2015031775A1 (fr) | 2013-08-29 | 2015-03-05 | Temple University Of The Commonwealth System Of Higher Education | Procédés et compositions pour le traitement guidé par arn de l'infection par le vih |
| SG10201801782PA (en) | 2013-09-04 | 2018-04-27 | Csir | Site-specific nuclease single-cell assay targeting gene regulatory elements to silence gene expression |
| US9388430B2 (en) | 2013-09-06 | 2016-07-12 | President And Fellows Of Harvard College | Cas9-recombinase fusion proteins and uses thereof |
| US9074199B1 (en) | 2013-11-19 | 2015-07-07 | President And Fellows Of Harvard College | Mutant Cas9 proteins |
| RU2725520C2 (ru) | 2013-12-11 | 2020-07-02 | Регенерон Фармасьютикалс, Инк. | Способы и композиции для направленной модификации генома |
| CN106536729A (zh) | 2013-12-12 | 2017-03-22 | 布罗德研究所有限公司 | 使用粒子递送组分靶向障碍和疾病的crispr‑cas系统和组合物的递送、用途和治疗应用 |
| WO2015089364A1 (fr) | 2013-12-12 | 2015-06-18 | The Broad Institute Inc. | Structure cristalline d'un système crispr-cas, et ses utilisations |
| US20150191744A1 (en) | 2013-12-17 | 2015-07-09 | University Of Massachusetts | Cas9 effector-mediated regulation of transcription, differentiation and gene editing/labeling |
| JP6721508B2 (ja) | 2013-12-26 | 2020-07-15 | ザ ジェネラル ホスピタル コーポレイション | 多重ガイドrna |
| US20160362688A1 (en) | 2014-02-12 | 2016-12-15 | Thomas Jefferson University | Compositions and methods of using microrna inhibitors |
| WO2015138510A1 (fr) | 2014-03-10 | 2015-09-17 | Editas Medicine., Inc. | Méthodes et compositions associées aux crispr/cas, utilisées dans le traitement de l'amaurose congénitale de leber 10 (lca10) |
| EP3117004A4 (fr) | 2014-03-14 | 2017-12-06 | University of Washington | Éléments isolateurs génomiques et leurs utilisations |
| AU2015234204A1 (en) | 2014-03-20 | 2016-10-06 | Universite Laval | CRISPR-based methods and products for increasing frataxin levels and uses thereof |
| WO2015153940A1 (fr) | 2014-04-03 | 2015-10-08 | Massachusetts Institute Of Technology | Procédés et compositions pour la production d'arn de guidage |
| CA2963820A1 (fr) | 2014-11-07 | 2016-05-12 | Editas Medicine, Inc. | Procedes pour ameliorer l'edition genomique mediee par crispr/cas |
| MA41349A (fr) | 2015-01-14 | 2017-11-21 | Univ Temple | Éradication de l'herpès simplex de type i et d'autres virus de l'herpès associés guidée par arn |
| CN111518811A (zh) | 2015-01-28 | 2020-08-11 | 先锋国际良种公司 | Crispr杂合dna/rna多核苷酸及使用方法 |
| EP3250693B2 (fr) | 2015-01-30 | 2023-12-20 | The Regents of The University of California | Livraison de protéines dans des cellules hématopoïétiques primaires |
| JP6929791B2 (ja) | 2015-02-09 | 2021-09-01 | デューク ユニバーシティ | エピゲノム編集のための組成物および方法 |
| WO2016141224A1 (fr) | 2015-03-03 | 2016-09-09 | The General Hospital Corporation | Nucléases crispr-cas9 génétiquement modifiées présentant une spécificité pam modifiée |
| US20180148711A1 (en) | 2015-05-28 | 2018-05-31 | Coda Biotherapeutics, Inc. | Genome editing vectors |
| WO2016205759A1 (fr) | 2015-06-18 | 2016-12-22 | The Broad Institute Inc. | Modification et optimisation de systèmes, de méthodes, d'enzymes et d'échafaudages guides d'orthologues de cas9 et variant pour la manipulation de séquences |
| US9790490B2 (en) | 2015-06-18 | 2017-10-17 | The Broad Institute Inc. | CRISPR enzymes and systems |
| WO2017031370A1 (fr) | 2015-08-18 | 2017-02-23 | The Broad Institute, Inc. | Procédés et compositions permettant de changer la fonction et la structure de boucles et/ou de domaines de chromatine |
| US9926546B2 (en) | 2015-08-28 | 2018-03-27 | The General Hospital Corporation | Engineered CRISPR-Cas9 nucleases |
| CA2996888A1 (fr) | 2015-08-28 | 2017-03-09 | The General Hospital Corporation | Nucleases crispr-cas9 modifiees |
| US9512446B1 (en) | 2015-08-28 | 2016-12-06 | The General Hospital Corporation | Engineered CRISPR-Cas9 nucleases |
| KR20190067209A (ko) | 2016-10-14 | 2019-06-14 | 더 제너럴 하스피탈 코포레이션 | 후성적으로 조절되는 부위-특이적 뉴클레아제 |
| WO2018148256A1 (fr) | 2017-02-07 | 2018-08-16 | The Regents Of The University Of California | Thérapie génique contre l'haplo-insuffisance |
| EP3612204A4 (fr) | 2017-04-21 | 2021-01-27 | The General Hospital Corporation | Régulation de gène humain inductible, accordable et multiplex à l'aide de crispr-cpf1 |
| EP3793584A4 (fr) | 2018-05-17 | 2022-10-26 | The General Hospital Corporation | Variants du facteur de liaison à la séquence ccctc |
| US20230036273A1 (en) | 2019-11-27 | 2023-02-02 | The General Hospital Corporation | System and method for activating gene expression |
| EP4176434A4 (fr) | 2020-05-29 | 2024-09-11 | Massachusetts Gen Hospital | Systèmes et procédés de modification stable et héréditaire par édition de précision (shape) |
-
2014
- 2014-03-14 IL IL289396A patent/IL289396B2/en unknown
- 2014-03-14 CN CN202110709688.0A patent/CN113563476A/zh active Pending
- 2014-03-14 CA CA2907198A patent/CA2907198C/fr active Active
- 2014-03-14 CA CA2906553A patent/CA2906553C/fr active Active
- 2014-03-14 CN CN201910766412.9A patent/CN110540991B/zh active Active
- 2014-03-14 US US14/213,479 patent/US9567603B2/en active Active
- 2014-03-14 KR KR1020227018265A patent/KR102602047B1/ko active Application Filing
- 2014-03-14 CA CA2906724A patent/CA2906724A1/fr active Pending
- 2014-03-14 KR KR1020157029170A patent/KR102210319B1/ko active IP Right Grant
- 2014-03-14 CN CN202010996829.7A patent/CN112301024A/zh active Pending
- 2014-03-14 EP EP21151899.8A patent/EP3865586A1/fr active Pending
- 2014-03-14 EP EP20172393.9A patent/EP3744842A1/fr not_active Withdrawn
- 2014-03-14 US US14/775,930 patent/US10119133B2/en active Active
- 2014-03-14 WO PCT/US2014/029304 patent/WO2014144761A2/fr active Application Filing
- 2014-03-14 CA CA3161835A patent/CA3161835A1/fr active Pending
- 2014-03-14 BR BR112015023489-5A patent/BR112015023489B1/pt active IP Right Grant
- 2014-03-14 AU AU2014228981A patent/AU2014228981B2/en active Active
- 2014-03-14 WO PCT/US2014/028630 patent/WO2014144288A1/fr active Application Filing
- 2014-03-14 CN CN201480026276.5A patent/CN105408483A/zh active Pending
- 2014-03-14 US US14/213,723 patent/US9567604B2/en active Active
- 2014-03-14 JP JP2016502976A patent/JP6980380B2/ja active Active
- 2014-03-14 EP EP20171165.2A patent/EP3741868B1/fr active Active
- 2014-03-14 KR KR1020237038728A patent/KR20230157540A/ko active Application Filing
- 2014-03-14 KR KR1020217002427A patent/KR102271291B1/ko active IP Right Grant
- 2014-03-14 AU AU2014239665A patent/AU2014239665B2/en active Active
- 2014-03-14 EP EP14768877.4A patent/EP2970986B1/fr active Active
- 2014-03-14 JP JP2016502853A patent/JP6622183B2/ja active Active
- 2014-03-14 AU AU2014227653A patent/AU2014227653B2/en active Active
- 2014-03-14 WO PCT/US2014/029068 patent/WO2014144592A2/fr active Application Filing
- 2014-03-14 KR KR1020157029177A patent/KR102210322B1/ko active IP Right Grant
- 2014-03-14 JP JP2016502406A patent/JP6657069B2/ja active Active
- 2014-03-14 US US14/775,869 patent/US10378027B2/en active Active
- 2014-03-14 EP EP14764159.1A patent/EP2971041B1/fr active Active
- 2014-03-14 ES ES14764159T patent/ES2713503T3/es active Active
- 2014-03-14 EP EP14764117.9A patent/EP2970208A4/fr not_active Withdrawn
- 2014-03-14 EP EP14763916.5A patent/EP2971125B2/fr active Active
- 2014-03-14 KR KR1020217002428A patent/KR102405549B1/ko active IP Right Grant
- 2014-03-14 WO PCT/US2014/027335 patent/WO2014152432A2/fr active Application Filing
- 2014-03-14 KR KR1020157029171A patent/KR102210323B1/ko active IP Right Grant
- 2014-03-14 EP EP24176701.1A patent/EP4428141A2/fr active Pending
- 2014-03-14 KR KR1020217002429A patent/KR102271292B1/ko active IP Right Grant
- 2014-03-14 US US14/776,620 patent/US9885033B2/en active Active
- 2014-03-14 EP EP18208105.9A patent/EP3467125B1/fr active Active
- 2014-03-14 CN CN201480027950.1A patent/CN105247066B/zh active Active
- 2014-03-14 CN CN201480026133.4A patent/CN105408497B/zh active Active
- 2014-03-14 EP EP21197664.2A patent/EP3988667A1/fr active Pending
-
2015
- 2015-09-15 ZA ZA2015/06814A patent/ZA201506814B/en unknown
- 2015-09-16 IL IL241671A patent/IL241671B/en unknown
-
2017
- 2017-01-25 US US15/415,431 patent/US10138476B2/en active Active
- 2017-02-10 US US15/430,218 patent/US10415059B2/en active Active
- 2017-07-17 AU AU2017204909A patent/AU2017204909B2/en active Active
-
2018
- 2018-01-12 US US15/870,659 patent/US10844403B2/en active Active
- 2018-06-08 US US16/003,973 patent/US10544433B2/en active Active
-
2019
- 2019-07-01 AU AU2019204675A patent/AU2019204675B2/en active Active
- 2019-08-08 US US16/535,199 patent/US11168338B2/en active Active
- 2019-09-16 US US16/572,248 patent/US11634731B2/en active Active
- 2019-09-27 JP JP2019176599A patent/JP6960438B2/ja active Active
- 2019-11-21 JP JP2019210428A patent/JP6878554B2/ja active Active
-
2020
- 2020-01-24 US US16/751,578 patent/US11098326B2/en active Active
- 2020-02-28 AU AU2020201465A patent/AU2020201465B2/en active Active
- 2020-03-26 JP JP2020055863A patent/JP7053706B2/ja active Active
- 2020-07-23 AU AU2020207840A patent/AU2020207840B2/en active Active
- 2020-11-16 US US17/099,503 patent/US11920152B2/en active Active
-
2021
- 2021-04-28 JP JP2021075869A patent/JP7126588B2/ja active Active
- 2021-05-25 AU AU2021203370A patent/AU2021203370B2/en active Active
- 2021-08-27 JP JP2021138479A patent/JP2021192624A/ja active Pending
- 2021-10-06 US US17/450,135 patent/US12065668B2/en active Active
-
2022
- 2022-03-30 JP JP2022056499A patent/JP7379572B2/ja active Active
- 2022-07-27 AU AU2022209254A patent/AU2022209254A1/en active Pending
- 2022-10-13 AU AU2022252788A patent/AU2022252788A1/en active Pending
-
2023
- 2023-01-30 JP JP2023011473A patent/JP2023061983A/ja active Pending
- 2023-03-06 US US18/178,675 patent/US20230407341A1/en active Pending
- 2023-10-31 JP JP2023186663A patent/JP2024012446A/ja active Pending
-
2024
- 2024-01-18 US US18/415,999 patent/US20240240207A1/en active Pending
Also Published As
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US11098326B2 (en) | Using RNA-guided FokI nucleases (RFNs) to increase specificity for RNA-guided genome editing | |
| US10011850B2 (en) | Using RNA-guided FokI Nucleases (RFNs) to increase specificity for RNA-Guided Genome Editing |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: THE APPLICATION HAS BEEN PUBLISHED |
|
| AC | Divisional application: reference to earlier application |
Ref document number: 2971041 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: P |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: REQUEST FOR EXAMINATION WAS MADE |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: EXAMINATION IS IN PROGRESS |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20191009 |
|
| RBV | Designated contracting states (corrected) |
Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 20191114 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: EXAMINATION IS IN PROGRESS |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: EXAMINATION IS IN PROGRESS |
|
| GRAP | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR1 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: GRANT OF PATENT IS INTENDED |
|
| INTG | Intention to grant announced |
Effective date: 20230330 |
|
| GRAS | Grant fee paid |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR3 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: THE PATENT HAS BEEN GRANTED |
|
| P01 | Opt-out of the competence of the unified patent court (upc) registered |
Effective date: 20230715 |
|
| AC | Divisional application: reference to earlier application |
Ref document number: 2971041 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: P |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: FG4D |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: EP |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R096 Ref document number: 602014088164 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: FG4D |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: LT Ref legal event code: MG9D |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: NL Ref legal event code: MP Effective date: 20230830 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: AT Ref legal event code: MK05 Ref document number: 1605507 Country of ref document: AT Kind code of ref document: T Effective date: 20230830 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20231201 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20231230 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20230830 Ref country code: RS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20230830 Ref country code: NO Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20231130 Ref country code: LV Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20230830 Ref country code: LT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20230830 Ref country code: IS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20231230 Ref country code: HR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20230830 Ref country code: GR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20231201 Ref country code: FI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20230830 Ref country code: AT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20230830 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: PL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20230830 Ref country code: NL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20230830 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: ES Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20230830 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SM Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20230830 Ref country code: RO Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20230830 Ref country code: ES Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20230830 Ref country code: EE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20230830 Ref country code: DK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20230830 Ref country code: CZ Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20230830 Ref country code: SK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20230830 Ref country code: PT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20240102 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20230830 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R097 Ref document number: 602014088164 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 20240527 Year of fee payment: 11 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20230830 |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed |
Effective date: 20240603 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Payment date: 20240725 Year of fee payment: 11 |