JP2014514766A - フリップチップ、フェイスアップワイヤボンド、およびフェイスダウンワイヤボンドの組み合わせパッケージ - Google Patents
フリップチップ、フェイスアップワイヤボンド、およびフェイスダウンワイヤボンドの組み合わせパッケージ Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2014514766A JP2014514766A JP2014506416A JP2014506416A JP2014514766A JP 2014514766 A JP2014514766 A JP 2014514766A JP 2014506416 A JP2014506416 A JP 2014506416A JP 2014506416 A JP2014506416 A JP 2014506416A JP 2014514766 A JP2014514766 A JP 2014514766A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- microelectronic
- microelectronic element
- assembly
- substrate
- front surface
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
- 238000004377 microelectronic Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 404
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 76
- 230000006870 function Effects 0.000 claims description 23
- 125000006850 spacer group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 17
- 230000005055 memory storage Effects 0.000 claims description 11
- 230000003750 conditioning effect Effects 0.000 claims description 9
- 238000012546 transfer Methods 0.000 claims description 7
- 230000000712 assembly Effects 0.000 claims description 6
- 238000000429 assembly Methods 0.000 claims description 6
- 230000003139 buffering effect Effects 0.000 claims description 4
- 239000010410 layer Substances 0.000 description 40
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 36
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 36
- 229910000679 solder Inorganic materials 0.000 description 25
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 24
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 description 18
- 239000000853 adhesive Substances 0.000 description 16
- 230000001070 adhesive effect Effects 0.000 description 16
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 15
- RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Copper Chemical compound [Cu] RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 13
- 229910052802 copper Inorganic materials 0.000 description 13
- 239000010949 copper Substances 0.000 description 13
- 239000007787 solid Substances 0.000 description 10
- PXHVJJICTQNCMI-UHFFFAOYSA-N Nickel Chemical compound [Ni] PXHVJJICTQNCMI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 8
- 239000003989 dielectric material Substances 0.000 description 8
- 238000005530 etching Methods 0.000 description 8
- 239000004020 conductor Substances 0.000 description 7
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 description 7
- PCHJSUWPFVWCPO-UHFFFAOYSA-N gold Chemical compound [Au] PCHJSUWPFVWCPO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- 229910052737 gold Inorganic materials 0.000 description 5
- 239000010931 gold Substances 0.000 description 5
- 238000005304 joining Methods 0.000 description 5
- 238000001465 metallisation Methods 0.000 description 4
- 229910052759 nickel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 4
- 229920002120 photoresistant polymer Polymers 0.000 description 4
- 238000013461 design Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000002844 melting Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000008018 melting Effects 0.000 description 3
- 150000002739 metals Chemical class 0.000 description 3
- 238000007747 plating Methods 0.000 description 3
- 229910052710 silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 239000010703 silicon Substances 0.000 description 3
- 229910000881 Cu alloy Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000004593 Epoxy Substances 0.000 description 2
- VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicium dioxide Chemical compound O=[Si]=O VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000010953 base metal Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000003990 capacitor Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000009713 electroplating Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000002955 isolation Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000000926 separation method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000002356 single layer Substances 0.000 description 2
- JBRZTFJDHDCESZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N AsGa Chemical compound [As]#[Ga] JBRZTFJDHDCESZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- VYZAMTAEIAYCRO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Chromium Chemical compound [Cr] VYZAMTAEIAYCRO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910001218 Gallium arsenide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000004642 Polyimide Substances 0.000 description 1
- ATJFFYVFTNAWJD-UHFFFAOYSA-N Tin Chemical compound [Sn] ATJFFYVFTNAWJD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- RTAQQCXQSZGOHL-UHFFFAOYSA-N Titanium Chemical compound [Ti] RTAQQCXQSZGOHL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000001133 acceleration Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000012790 adhesive layer Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052782 aluminium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N aluminium Chemical compound [Al] XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000000919 ceramic Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052804 chromium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000011651 chromium Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000011248 coating agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000000576 coating method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000004132 cross linking Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000001419 dependent effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000009977 dual effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000003822 epoxy resin Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000835 fiber Substances 0.000 description 1
- -1 for example Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000011521 glass Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000003384 imaging method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910052738 indium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- APFVFJFRJDLVQX-UHFFFAOYSA-N indium atom Chemical compound [In] APFVFJFRJDLVQX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910010272 inorganic material Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000011147 inorganic material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000009434 installation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000003287 optical effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000002161 passivation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229920000647 polyepoxide Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920001721 polyimide Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920000642 polymer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000002861 polymer material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000009467 reduction Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000001105 regulatory effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229920005989 resin Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000011347 resin Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000027756 respiratory electron transport chain Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000006903 response to temperature Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000003566 sealing material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000012239 silicon dioxide Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000000377 silicon dioxide Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920002379 silicone rubber Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 230000003068 static effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000010936 titanium Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052719 titanium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- MAKDTFFYCIMFQP-UHFFFAOYSA-N titanium tungsten Chemical compound [Ti].[W] MAKDTFFYCIMFQP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L25/00—Assemblies consisting of a plurality of individual semiconductor or other solid state devices ; Multistep manufacturing processes thereof
- H01L25/03—Assemblies consisting of a plurality of individual semiconductor or other solid state devices ; Multistep manufacturing processes thereof all the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/00, or in a single subclass of H10K, H10N, e.g. assemblies of rectifier diodes
- H01L25/04—Assemblies consisting of a plurality of individual semiconductor or other solid state devices ; Multistep manufacturing processes thereof all the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/00, or in a single subclass of H10K, H10N, e.g. assemblies of rectifier diodes the devices not having separate containers
- H01L25/065—Assemblies consisting of a plurality of individual semiconductor or other solid state devices ; Multistep manufacturing processes thereof all the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/00, or in a single subclass of H10K, H10N, e.g. assemblies of rectifier diodes the devices not having separate containers the devices being of a type provided for in group H01L27/00
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L25/00—Assemblies consisting of a plurality of individual semiconductor or other solid state devices ; Multistep manufacturing processes thereof
- H01L25/03—Assemblies consisting of a plurality of individual semiconductor or other solid state devices ; Multistep manufacturing processes thereof all the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/00, or in a single subclass of H10K, H10N, e.g. assemblies of rectifier diodes
- H01L25/04—Assemblies consisting of a plurality of individual semiconductor or other solid state devices ; Multistep manufacturing processes thereof all the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/00, or in a single subclass of H10K, H10N, e.g. assemblies of rectifier diodes the devices not having separate containers
- H01L25/07—Assemblies consisting of a plurality of individual semiconductor or other solid state devices ; Multistep manufacturing processes thereof all the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/00, or in a single subclass of H10K, H10N, e.g. assemblies of rectifier diodes the devices not having separate containers the devices being of a type provided for in group H01L29/00
- H01L25/071—Assemblies consisting of a plurality of individual semiconductor or other solid state devices ; Multistep manufacturing processes thereof all the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/00, or in a single subclass of H10K, H10N, e.g. assemblies of rectifier diodes the devices not having separate containers the devices being of a type provided for in group H01L29/00 the devices being arranged next and on each other, i.e. mixed assemblies
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L23/00—Details of semiconductor or other solid state devices
- H01L23/28—Encapsulations, e.g. encapsulating layers, coatings, e.g. for protection
- H01L23/31—Encapsulations, e.g. encapsulating layers, coatings, e.g. for protection characterised by the arrangement or shape
- H01L23/3107—Encapsulations, e.g. encapsulating layers, coatings, e.g. for protection characterised by the arrangement or shape the device being completely enclosed
- H01L23/3121—Encapsulations, e.g. encapsulating layers, coatings, e.g. for protection characterised by the arrangement or shape the device being completely enclosed a substrate forming part of the encapsulation
- H01L23/3128—Encapsulations, e.g. encapsulating layers, coatings, e.g. for protection characterised by the arrangement or shape the device being completely enclosed a substrate forming part of the encapsulation the substrate having spherical bumps for external connection
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/04—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof the devices having potential barriers, e.g. a PN junction, depletion layer or carrier concentration layer
- H01L21/34—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof the devices having potential barriers, e.g. a PN junction, depletion layer or carrier concentration layer the devices having semiconductor bodies not provided for in groups H01L21/0405, H01L21/0445, H01L21/06, H01L21/16 and H01L21/18 with or without impurities, e.g. doping materials
- H01L21/38—Diffusion of impurity materials, e.g. doping materials, electrode materials, into or out of a semiconductor body, or between semiconductor regions
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L23/00—Details of semiconductor or other solid state devices
- H01L23/28—Encapsulations, e.g. encapsulating layers, coatings, e.g. for protection
- H01L23/31—Encapsulations, e.g. encapsulating layers, coatings, e.g. for protection characterised by the arrangement or shape
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L25/00—Assemblies consisting of a plurality of individual semiconductor or other solid state devices ; Multistep manufacturing processes thereof
- H01L25/03—Assemblies consisting of a plurality of individual semiconductor or other solid state devices ; Multistep manufacturing processes thereof all the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/00, or in a single subclass of H10K, H10N, e.g. assemblies of rectifier diodes
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L25/00—Assemblies consisting of a plurality of individual semiconductor or other solid state devices ; Multistep manufacturing processes thereof
- H01L25/03—Assemblies consisting of a plurality of individual semiconductor or other solid state devices ; Multistep manufacturing processes thereof all the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/00, or in a single subclass of H10K, H10N, e.g. assemblies of rectifier diodes
- H01L25/04—Assemblies consisting of a plurality of individual semiconductor or other solid state devices ; Multistep manufacturing processes thereof all the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/00, or in a single subclass of H10K, H10N, e.g. assemblies of rectifier diodes the devices not having separate containers
- H01L25/065—Assemblies consisting of a plurality of individual semiconductor or other solid state devices ; Multistep manufacturing processes thereof all the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/00, or in a single subclass of H10K, H10N, e.g. assemblies of rectifier diodes the devices not having separate containers the devices being of a type provided for in group H01L27/00
- H01L25/0652—Assemblies consisting of a plurality of individual semiconductor or other solid state devices ; Multistep manufacturing processes thereof all the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/00, or in a single subclass of H10K, H10N, e.g. assemblies of rectifier diodes the devices not having separate containers the devices being of a type provided for in group H01L27/00 the devices being arranged next and on each other, i.e. mixed assemblies
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L25/00—Assemblies consisting of a plurality of individual semiconductor or other solid state devices ; Multistep manufacturing processes thereof
- H01L25/03—Assemblies consisting of a plurality of individual semiconductor or other solid state devices ; Multistep manufacturing processes thereof all the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/00, or in a single subclass of H10K, H10N, e.g. assemblies of rectifier diodes
- H01L25/04—Assemblies consisting of a plurality of individual semiconductor or other solid state devices ; Multistep manufacturing processes thereof all the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/00, or in a single subclass of H10K, H10N, e.g. assemblies of rectifier diodes the devices not having separate containers
- H01L25/065—Assemblies consisting of a plurality of individual semiconductor or other solid state devices ; Multistep manufacturing processes thereof all the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/00, or in a single subclass of H10K, H10N, e.g. assemblies of rectifier diodes the devices not having separate containers the devices being of a type provided for in group H01L27/00
- H01L25/0657—Stacked arrangements of devices
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L25/00—Assemblies consisting of a plurality of individual semiconductor or other solid state devices ; Multistep manufacturing processes thereof
- H01L25/03—Assemblies consisting of a plurality of individual semiconductor or other solid state devices ; Multistep manufacturing processes thereof all the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/00, or in a single subclass of H10K, H10N, e.g. assemblies of rectifier diodes
- H01L25/10—Assemblies consisting of a plurality of individual semiconductor or other solid state devices ; Multistep manufacturing processes thereof all the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/00, or in a single subclass of H10K, H10N, e.g. assemblies of rectifier diodes the devices having separate containers
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L25/00—Assemblies consisting of a plurality of individual semiconductor or other solid state devices ; Multistep manufacturing processes thereof
- H01L25/03—Assemblies consisting of a plurality of individual semiconductor or other solid state devices ; Multistep manufacturing processes thereof all the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/00, or in a single subclass of H10K, H10N, e.g. assemblies of rectifier diodes
- H01L25/10—Assemblies consisting of a plurality of individual semiconductor or other solid state devices ; Multistep manufacturing processes thereof all the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/00, or in a single subclass of H10K, H10N, e.g. assemblies of rectifier diodes the devices having separate containers
- H01L25/105—Assemblies consisting of a plurality of individual semiconductor or other solid state devices ; Multistep manufacturing processes thereof all the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/00, or in a single subclass of H10K, H10N, e.g. assemblies of rectifier diodes the devices having separate containers the devices being of a type provided for in group H01L27/00
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L25/00—Assemblies consisting of a plurality of individual semiconductor or other solid state devices ; Multistep manufacturing processes thereof
- H01L25/50—Multistep manufacturing processes of assemblies consisting of devices, each device being of a type provided for in group H01L27/00 or H01L29/00
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/02—Bonding areas; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/04—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bonding areas prior to the connecting process
- H01L2224/0401—Bonding areas specifically adapted for bump connectors, e.g. under bump metallisation [UBM]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/02—Bonding areas; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/04—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bonding areas prior to the connecting process
- H01L2224/06—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bonding areas prior to the connecting process of a plurality of bonding areas
- H01L2224/061—Disposition
- H01L2224/0612—Layout
- H01L2224/0613—Square or rectangular array
- H01L2224/06134—Square or rectangular array covering only portions of the surface to be connected
- H01L2224/06135—Covering only the peripheral area of the surface to be connected, i.e. peripheral arrangements
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/02—Bonding areas; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/04—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bonding areas prior to the connecting process
- H01L2224/06—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bonding areas prior to the connecting process of a plurality of bonding areas
- H01L2224/061—Disposition
- H01L2224/0612—Layout
- H01L2224/0613—Square or rectangular array
- H01L2224/06134—Square or rectangular array covering only portions of the surface to be connected
- H01L2224/06136—Covering only the central area of the surface to be connected, i.e. central arrangements
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/10—Bump connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/15—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors after the connecting process
- H01L2224/16—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors after the connecting process of an individual bump connector
- H01L2224/161—Disposition
- H01L2224/16151—Disposition the bump connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive
- H01L2224/16221—Disposition the bump connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked
- H01L2224/16225—Disposition the bump connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked the item being non-metallic, e.g. insulating substrate with or without metallisation
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/10—Bump connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/15—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors after the connecting process
- H01L2224/16—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors after the connecting process of an individual bump connector
- H01L2224/161—Disposition
- H01L2224/16151—Disposition the bump connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive
- H01L2224/16221—Disposition the bump connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked
- H01L2224/16225—Disposition the bump connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked the item being non-metallic, e.g. insulating substrate with or without metallisation
- H01L2224/16227—Disposition the bump connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked the item being non-metallic, e.g. insulating substrate with or without metallisation the bump connector connecting to a bond pad of the item
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/10—Bump connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/15—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors after the connecting process
- H01L2224/16—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors after the connecting process of an individual bump connector
- H01L2224/161—Disposition
- H01L2224/16151—Disposition the bump connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive
- H01L2224/16221—Disposition the bump connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked
- H01L2224/16245—Disposition the bump connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked the item being metallic
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/26—Layer connectors, e.g. plate connectors, solder or adhesive layers; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/31—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the layer connectors after the connecting process
- H01L2224/32—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the layer connectors after the connecting process of an individual layer connector
- H01L2224/321—Disposition
- H01L2224/32135—Disposition the layer connector connecting between different semiconductor or solid-state bodies, i.e. chip-to-chip
- H01L2224/32145—Disposition the layer connector connecting between different semiconductor or solid-state bodies, i.e. chip-to-chip the bodies being stacked
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/26—Layer connectors, e.g. plate connectors, solder or adhesive layers; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/31—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the layer connectors after the connecting process
- H01L2224/32—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the layer connectors after the connecting process of an individual layer connector
- H01L2224/321—Disposition
- H01L2224/32151—Disposition the layer connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive
- H01L2224/32221—Disposition the layer connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked
- H01L2224/32225—Disposition the layer connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked the item being non-metallic, e.g. insulating substrate with or without metallisation
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/42—Wire connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/47—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors after the connecting process
- H01L2224/48—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors after the connecting process of an individual wire connector
- H01L2224/4805—Shape
- H01L2224/4809—Loop shape
- H01L2224/48095—Kinked
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/42—Wire connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/47—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors after the connecting process
- H01L2224/48—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors after the connecting process of an individual wire connector
- H01L2224/481—Disposition
- H01L2224/48151—Connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive
- H01L2224/48221—Connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked
- H01L2224/48225—Connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked the item being non-metallic, e.g. insulating substrate with or without metallisation
- H01L2224/48227—Connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked the item being non-metallic, e.g. insulating substrate with or without metallisation connecting the wire to a bond pad of the item
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/42—Wire connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/47—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors after the connecting process
- H01L2224/48—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors after the connecting process of an individual wire connector
- H01L2224/481—Disposition
- H01L2224/48151—Connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive
- H01L2224/48221—Connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked
- H01L2224/48225—Connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked the item being non-metallic, e.g. insulating substrate with or without metallisation
- H01L2224/4824—Connecting between the body and an opposite side of the item with respect to the body
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/42—Wire connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/47—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors after the connecting process
- H01L2224/48—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors after the connecting process of an individual wire connector
- H01L2224/481—Disposition
- H01L2224/48151—Connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive
- H01L2224/48221—Connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked
- H01L2224/48245—Connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked the item being metallic
- H01L2224/48247—Connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked the item being metallic connecting the wire to a bond pad of the item
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/42—Wire connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/47—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors after the connecting process
- H01L2224/48—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors after the connecting process of an individual wire connector
- H01L2224/481—Disposition
- H01L2224/48151—Connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive
- H01L2224/48221—Connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked
- H01L2224/48245—Connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked the item being metallic
- H01L2224/4826—Connecting between the body and an opposite side of the item with respect to the body
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/73—Means for bonding being of different types provided for in two or more of groups H01L2224/10, H01L2224/18, H01L2224/26, H01L2224/34, H01L2224/42, H01L2224/50, H01L2224/63, H01L2224/71
- H01L2224/732—Location after the connecting process
- H01L2224/73201—Location after the connecting process on the same surface
- H01L2224/73203—Bump and layer connectors
- H01L2224/73204—Bump and layer connectors the bump connector being embedded into the layer connector
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/73—Means for bonding being of different types provided for in two or more of groups H01L2224/10, H01L2224/18, H01L2224/26, H01L2224/34, H01L2224/42, H01L2224/50, H01L2224/63, H01L2224/71
- H01L2224/732—Location after the connecting process
- H01L2224/73201—Location after the connecting process on the same surface
- H01L2224/73215—Layer and wire connectors
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/73—Means for bonding being of different types provided for in two or more of groups H01L2224/10, H01L2224/18, H01L2224/26, H01L2224/34, H01L2224/42, H01L2224/50, H01L2224/63, H01L2224/71
- H01L2224/732—Location after the connecting process
- H01L2224/73251—Location after the connecting process on different surfaces
- H01L2224/73253—Bump and layer connectors
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/73—Means for bonding being of different types provided for in two or more of groups H01L2224/10, H01L2224/18, H01L2224/26, H01L2224/34, H01L2224/42, H01L2224/50, H01L2224/63, H01L2224/71
- H01L2224/732—Location after the connecting process
- H01L2224/73251—Location after the connecting process on different surfaces
- H01L2224/73265—Layer and wire connectors
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2225/00—Details relating to assemblies covered by the group H01L25/00 but not provided for in its subgroups
- H01L2225/03—All the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/648 and H10K99/00
- H01L2225/04—All the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/648 and H10K99/00 the devices not having separate containers
- H01L2225/065—All the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/648 and H10K99/00 the devices not having separate containers the devices being of a type provided for in group H01L27/00
- H01L2225/06503—Stacked arrangements of devices
- H01L2225/06555—Geometry of the stack, e.g. form of the devices, geometry to facilitate stacking
- H01L2225/06558—Geometry of the stack, e.g. form of the devices, geometry to facilitate stacking the devices having passive surfaces facing each other, i.e. in a back-to-back arrangement
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2225/00—Details relating to assemblies covered by the group H01L25/00 but not provided for in its subgroups
- H01L2225/03—All the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/648 and H10K99/00
- H01L2225/04—All the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/648 and H10K99/00 the devices not having separate containers
- H01L2225/065—All the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/648 and H10K99/00 the devices not having separate containers the devices being of a type provided for in group H01L27/00
- H01L2225/06503—Stacked arrangements of devices
- H01L2225/06555—Geometry of the stack, e.g. form of the devices, geometry to facilitate stacking
- H01L2225/06562—Geometry of the stack, e.g. form of the devices, geometry to facilitate stacking at least one device in the stack being rotated or offset
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L24/00—Arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies; Methods or apparatus related thereto
- H01L24/73—Means for bonding being of different types provided for in two or more of groups H01L24/10, H01L24/18, H01L24/26, H01L24/34, H01L24/42, H01L24/50, H01L24/63, H01L24/71
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01087—Francium [Fr]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/095—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00 with a principal constituent of the material being a combination of two or more materials provided in the groups H01L2924/013 - H01L2924/0715
- H01L2924/097—Glass-ceramics, e.g. devitrified glass
- H01L2924/09701—Low temperature co-fired ceramic [LTCC]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/10—Details of semiconductor or other solid state devices to be connected
- H01L2924/146—Mixed devices
- H01L2924/1461—MEMS
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/15—Details of package parts other than the semiconductor or other solid state devices to be connected
- H01L2924/151—Die mounting substrate
- H01L2924/153—Connection portion
- H01L2924/1531—Connection portion the connection portion being formed only on the surface of the substrate opposite to the die mounting surface
- H01L2924/15311—Connection portion the connection portion being formed only on the surface of the substrate opposite to the die mounting surface being a ball array, e.g. BGA
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/15—Details of package parts other than the semiconductor or other solid state devices to be connected
- H01L2924/181—Encapsulation
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/30—Technical effects
- H01L2924/301—Electrical effects
- H01L2924/3011—Impedance
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Microelectronics & Electronic Packaging (AREA)
- Power Engineering (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Condensed Matter Physics & Semiconductors (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Computer Hardware Design (AREA)
- Manufacturing & Machinery (AREA)
- Wire Bonding (AREA)
- Semiconductor Integrated Circuits (AREA)
Abstract
Description
本願は、2011年4月21日に出願された米国仮特許出願第61/477,833号および2011年11月29日に出願された米国特許出願第13/306,182号の出願日の利得を主張するものであり、これらの開示内容は、参照することによって、ここに含まれるものとする。以下の本願の譲渡人に譲渡された出願:いずれも2011年4月21日に出願された米国仮特許出願第61/477,820号、第61/477,877号、および第61/477,967号も、参照することによって、ここに含まれるものとする。
本発明は、積層超小型電子アセンブリ、このようなアセンブリを製造する方法、およびこのようなアセンブリに有用な構成要素に関する。
Claims (27)
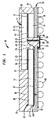
- 互いに反対側を向く第1および第2の表面および前記第1および第2の表面間に延在する少なくとも1つの開口を有する基板であって、前記第1の表面における基板接点および前記第2の表面における端子を有している基板と、
前記第1の表面と向き合う前面、そこから遠く離れた裏面、および前記前面と前記裏面との間に延在する縁を有する第1の超小型電子素子であって、前記第1の超小型電子素子は、前記前面に複数の接点を有しており、該複数の接点は、前記基板接点の対応するものと向き合い、かつ接合されている第1の超小型電子素子と、
前記第1の超小型電子素子と向き合う前面を有する第2の超小型電子素子であって、前記第1の超小型電子素子の前記縁を超えて前記第2の超小型電子素子の前記前面に露出した複数の接点を有しており、任意の他の機能よりもメモリ記憶アレイ機能をもたらす極めて多数の能動素子から構成されている第2の超小型電子素子と、
前記第2の超小型電子素子の前記接点を前記端子に電気的に接続するリードであって、前記少なくとも1つの開口と真っ直ぐに並んだ部分を有しているリードと、
を備えており、
前記第1の超小型電子素子は、前記端子において前記超小型電子アセンブリによって受信された少なくともいくつかの信号を再生し、前記信号を前記第2の超小型電子素子に転送するように、構成されている超小型電子アセンブリ。 - 前記第1の超小型電子素子は、前記超小型電子アセンブリの外部のコンポーネントと前記第2の超小型電子素子との間でデータの転送を制御するように構成されている請求項1に記載の超小型電子アセンブリ。
- 前記第1の超小型電子素子は、前記外部コンポーネントと前記第2の超小型電子素子との間に信号のバッファリングをもたらすように構成されている請求項2に記載の超小型電子アセンブリ。
- 前記第1の超小型電子素子は、論理機能を主に果たすように構成されている請求項1に記載の超小型電子アセンブリ。
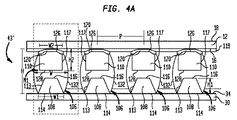
- 前記第2の超小型電子素子に少なくとも部分的に重なる第3の超小型電子素子であって、前記第3の超小型電子素子は、その前面に露出した複数の接点を有しており、該複数の接点は、前記第2の超小型電子素子の縁を超えており、前記基板接点の少なくともいくつかに電気的に接続されている第3の超小型電子素子と、
前記第3の超小型電子素子の前記接点を前記端子に電気的に接続する第2のリードであって、前記少なくとも1つの開口と真っ直ぐに並んだ部分を有している第2のリードと、
をさらに備えている請求項1に記載の超小型電子アセンブリ。 - 前記第2および第3の超小型電子素子は、各々、不揮発性フラッシュメモリを含んでいる請求項5に記載の超小型電子アセンブリ。
- 前記第1の超小型電子素子は、メモリ記憶アレイをもたらす以外の優先的機能を有している請求項5に記載の超小型電子アセンブリ。
- 前記第2の超小型電子素子の前記接点は、前記第2の超小型電子素子の前記縁に隣接して配置されており、前記第3の超小型電子素子の前記接点は、前記第3の超小型電子素子の前記縁に隣接して配置されている請求項5に記載の超小型電子アセンブリ。
- 前記第2の超小型電子素子の前記接点は、その前記前面の中央領域内に配置されており、前記中央領域は、前記第2の超小型電子素子の互いに向き合った第1および第2の縁から離間している請求項1に記載の超小型電子アセンブリ。
- 前記基板は、前記第1および第2の基板表面を画定する第1および第2の表面を有する誘電体要素を含んでおり、前記誘電体要素の前記第1または第2の表面の少なくとも1つに沿って前記少なくとも1つの開口の縁を超えて延在する前記リードは、前記第2の超小型電子素子の前記接点に接合されている請求項1に記載の超小型電子アセンブリ。
- 前記基板は、7ppm/℃未満の熱膨張係数を有している請求項1に記載の超小型電子アセンブリ。
- 前記リードは、前記少なくとも1つの開口内を通って、前記基板の前記第2の表面のボンディング接点に延在するワイヤボンドを含んでいる請求項1に記載の超小型電子アセンブリ。
- 前記基板または前記第1の超小型電子素子の少なくとも1つから延在する実質的に剛性の導電ポストをさらに備えている請求項1に記載の超小型電子アセンブリ。
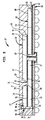
- 前記第2の超小型電子素子の前記前面と前記基板の前記第1の表面との間にスペーサ要素をさらに備えている請求項1に記載の超小型電子アセンブリ。
- 前面およびそこから遠く離れた裏面を有する第3の超小型電子素子であって、前記裏面は、前記第1の超小型電子素子の前記裏面と向き合っており、前記第3の超小型電子素子は、その前記前面に露出した複数の接点を有している、前記第3の超小型電子素子と、前記第3の超小型電子素子の前記接点を前記基板接点の少なくともいくつかに電気的に接続する複数のリードと、をさらに備えている請求項1に記載の超小型電子アセンブリ。
- 前記第3の超小型電子素子の前記接点を前記基板接点の少なくともいくつかに接続する前記リードは、ワイヤボンドを含んでいる請求項15に記載の超小型電子アセンブリ。
- 前記第3の超小型電子素子の前記接点を前記基板接点の少なくともいくつかに接続する前記リードは、前記第3の超小型電子素子の縁を超えて延在するリードボンドを含んでおり、前記第3の超小型電子素子の前記縁は、前記第3の超小型電子素子の前記前面と前記裏面との間に延在している請求項15に記載の超小型電子アセンブリ。
- 前記誘電体要素と向き合う前面およびそこから遠く離れた裏面を有する第4の超小型電子素子をさらに備えており、前記第4の超小型電子素子は、その前記前面に露出した複数の接点を有しており、該複数の接点は、前記第1の導電要素の少なくともいくつかに電気的に接続されており、前記第2の超小型電子素子は、前記第4の超小型電子素子に少なくとも部分的に重なっている請求項15に記載の超小型電子アセンブリ。
- 前記基板と向き合う前面およびそこから遠く離れた裏面を有する第3の超小型電子素子をさらに備えており、前記第3の超小型電子素子は、その前記前面に露出した複数の接点を有しており、該複数の接点は、前記基板接点の少なくともいくつかに電気的に接続されており、前記第2の超小型電子素子は、前記第3の超小型電子素子に少なくとも部分的に重なっている請求項1に記載の超小型電子アセンブリ。
- 前記第3の超小型電子素子は、論理機能を主に果たすように構成されたチップを含んでいる請求項19に記載の超小型電子アセンブリ。
- 請求項1に記載のアセンブリと、前記アセンブリに電気的に接続された1つまたは複数の他の電子コンポーネントとを備えるシステム。
- ハウジングをさらに備えており、前記アセンブリおよび前記他の電子コンポーネントは、前記ハウジングに実装されている請求項21に記載のシステム。
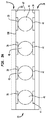
- 互いに反対側を向く第1および第2の表面および前記第1および第2の表面間に延在する第1の開口を有する基板であって、その上に複数の導電要素をさらに有している基板と、
前記基板の前記第1の表面と向き合う表面、そこから遠く離れた他の表面、およびその前記表面間に延在する縁を有する第1の超小型電子素子と、
前記第1の超小型電子素子と向き合う前面を有する第2の超小型電子素子であって、前記第2の超小型電子素子は、その前記前面に露出した複数の接点を有しており、前記第2の超小型電子素子は、前記第1の超小型電子素子の前記縁を超えて突出している第2の超小型電子素子と、
前記第2の超小型電子素子に接続され、前記第1の開口を通って、前記基板上の前記導電要素の少なくともいくつかに延在する信号リードと、
前記基板の前記第1の表面と前記第2の超小型電子素子の前記前面との間に配置された能動回路要素を有する少なくとも1つの電力調整コンポーネントと、
を備えている超小型電子アセンブリ。 - 前記基板は、前記第1および第2の表面間に延在する第2の開口を備えており、前記超小型電子アセンブリは、前記第1の超小型電子素子を前記基板上の前記導電要素に電気的に接続する付加的な信号リードをさらに備えており、前記付加的な信号リードは、前記第2の開口と真っ直ぐに並んだ部分を有している請求項23に記載の超小型電子アセンブリ。
- 前記少なくとも動力調整コンポーネントは、オン/オフスイッチを含んでいる請求項23に記載の超小型電子アセンブリ。
- 請求項23に記載のアセンブリと、前記アセンブリに電気的に接続された1つまたは複数の他の電子コンポーネントとを備えるシステム。
- ハウジングをさらに備えており、前記アセンブリおよび前記他の電子コンポーネントは、前記ハウジングに実装されている請求項26に記載のシステム。
Applications Claiming Priority (5)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US201161477883P | 2011-04-21 | 2011-04-21 | |
| US61/477,883 | 2011-04-21 | ||
| US13/306,182 US8304881B1 (en) | 2011-04-21 | 2011-11-29 | Flip-chip, face-up and face-down wirebond combination package |
| US13/306,182 | 2011-11-29 | ||
| PCT/US2012/029873 WO2012145114A1 (en) | 2011-04-21 | 2012-03-21 | Flip-chip, face-up and face-down wirebond combination package |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2014514766A true JP2014514766A (ja) | 2014-06-19 |
| JP2014514766A5 JP2014514766A5 (ja) | 2015-05-07 |
Family
ID=47020673
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2014506416A Pending JP2014514766A (ja) | 2011-04-21 | 2012-03-21 | フリップチップ、フェイスアップワイヤボンド、およびフェイスダウンワイヤボンドの組み合わせパッケージ |
Country Status (7)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (3) | US8304881B1 (ja) |
| EP (1) | EP2700097A1 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JP2014514766A (ja) |
| KR (1) | KR20140028015A (ja) |
| CN (1) | CN103620774B (ja) |
| TW (1) | TWI523174B (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2012145114A1 (ja) |
Families Citing this family (42)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP5667381B2 (ja) * | 2010-06-01 | 2015-02-12 | ピーエスフォー ルクスコ エスエイアールエルPS4 Luxco S.a.r.l. | 半導体装置及びその製造方法 |
| US8836101B2 (en) * | 2010-09-24 | 2014-09-16 | Infineon Technologies Ag | Multi-chip semiconductor packages and assembly thereof |
| US8553420B2 (en) | 2010-10-19 | 2013-10-08 | Tessera, Inc. | Enhanced stacked microelectronic assemblies with central contacts and improved thermal characteristics |
| US9013033B2 (en) | 2011-04-21 | 2015-04-21 | Tessera, Inc. | Multiple die face-down stacking for two or more die |
| US8304881B1 (en) * | 2011-04-21 | 2012-11-06 | Tessera, Inc. | Flip-chip, face-up and face-down wirebond combination package |
| US8928153B2 (en) | 2011-04-21 | 2015-01-06 | Tessera, Inc. | Flip-chip, face-up and face-down centerbond memory wirebond assemblies |
| US8952516B2 (en) | 2011-04-21 | 2015-02-10 | Tessera, Inc. | Multiple die stacking for two or more die |
| US8970028B2 (en) | 2011-12-29 | 2015-03-03 | Invensas Corporation | Embedded heat spreader for package with multiple microelectronic elements and face-down connection |
| US8633576B2 (en) | 2011-04-21 | 2014-01-21 | Tessera, Inc. | Stacked chip-on-board module with edge connector |
| US8823165B2 (en) | 2011-07-12 | 2014-09-02 | Invensas Corporation | Memory module in a package |
| US8569884B2 (en) | 2011-08-15 | 2013-10-29 | Tessera, Inc. | Multiple die in a face down package |
| US8659140B2 (en) | 2011-10-03 | 2014-02-25 | Invensas Corporation | Stub minimization using duplicate sets of signal terminals in assemblies without wirebonds to package substrate |
| US8525327B2 (en) | 2011-10-03 | 2013-09-03 | Invensas Corporation | Stub minimization for assemblies without wirebonds to package substrate |
| US8653646B2 (en) | 2011-10-03 | 2014-02-18 | Invensas Corporation | Stub minimization using duplicate sets of terminals for wirebond assemblies without windows |
| TWI515864B (zh) * | 2011-10-03 | 2016-01-01 | 英帆薩斯公司 | 具有自封裝中心偏移之端子格柵之短線最小化 |
| US8659143B2 (en) | 2011-10-03 | 2014-02-25 | Invensas Corporation | Stub minimization for wirebond assemblies without windows |
| EP2769409A1 (en) | 2011-10-03 | 2014-08-27 | Invensas Corporation | Stub minimization for multi-die wirebond assemblies with orthogonal windows |
| KR101894823B1 (ko) | 2011-10-03 | 2018-09-04 | 인벤사스 코포레이션 | 평행한 윈도우를 갖는 다중-다이 와이어 본드 어셈블리를 위한 스터브 최소화 |
| US8848392B2 (en) | 2012-08-27 | 2014-09-30 | Invensas Corporation | Co-support module and microelectronic assembly |
| US9368477B2 (en) | 2012-08-27 | 2016-06-14 | Invensas Corporation | Co-support circuit panel and microelectronic packages |
| US8848391B2 (en) | 2012-08-27 | 2014-09-30 | Invensas Corporation | Co-support component and microelectronic assembly |
| TWI508238B (zh) | 2012-12-17 | 2015-11-11 | Princo Corp | 晶片散熱系統 |
| US8907500B2 (en) | 2013-02-04 | 2014-12-09 | Invensas Corporation | Multi-die wirebond packages with elongated windows |
| US9070423B2 (en) | 2013-06-11 | 2015-06-30 | Invensas Corporation | Single package dual channel memory with co-support |
| JP2015216263A (ja) * | 2014-05-12 | 2015-12-03 | マイクロン テクノロジー, インク. | 半導体装置 |
| US9281296B2 (en) | 2014-07-31 | 2016-03-08 | Invensas Corporation | Die stacking techniques in BGA memory package for small footprint CPU and memory motherboard design |
| US9691437B2 (en) | 2014-09-25 | 2017-06-27 | Invensas Corporation | Compact microelectronic assembly having reduced spacing between controller and memory packages |
| CN107113485B (zh) * | 2014-11-06 | 2019-10-15 | 罗伯特·博世有限公司 | 在mems换能器封装件的制造中使用的基于引线框架的芯片载体 |
| US9799628B2 (en) | 2015-03-31 | 2017-10-24 | Qualcomm Incorporated | Stacked package configurations and methods of making the same |
| US10367284B2 (en) | 2015-07-27 | 2019-07-30 | Hewlett Packard Enterprise Development Lp | Socket to support boards in a spaced relation |
| WO2017023257A1 (en) * | 2015-07-31 | 2017-02-09 | Hewlett Packard Enterprise Development Lp | Multi-chip module |
| US9484080B1 (en) | 2015-11-09 | 2016-11-01 | Invensas Corporation | High-bandwidth memory application with controlled impedance loading |
| US9679613B1 (en) | 2016-05-06 | 2017-06-13 | Invensas Corporation | TFD I/O partition for high-speed, high-density applications |
| US10121766B2 (en) * | 2016-06-30 | 2018-11-06 | Micron Technology, Inc. | Package-on-package semiconductor device assemblies including one or more windows and related methods and packages |
| US10068879B2 (en) * | 2016-09-19 | 2018-09-04 | General Electric Company | Three-dimensional stacked integrated circuit devices and methods of assembling the same |
| US9953904B1 (en) | 2016-10-25 | 2018-04-24 | Nxp Usa, Inc. | Electronic component package with heatsink and multiple electronic components |
| KR102592640B1 (ko) | 2016-11-04 | 2023-10-23 | 삼성전자주식회사 | 반도체 패키지 및 반도체 패키지의 제조 방법 |
| US10741525B2 (en) * | 2017-06-02 | 2020-08-11 | Ultramemory Inc. | Semiconductor module |
| TWI642158B (zh) * | 2017-07-21 | 2018-11-21 | 致伸科技股份有限公司 | 指紋感測晶片封裝結構 |
| TWI710075B (zh) * | 2019-08-14 | 2020-11-11 | 力成科技股份有限公司 | 半導體封裝結構及其製造方法 |
| US11527480B2 (en) * | 2020-04-30 | 2022-12-13 | Advanced Semiconductor Engineering, Inc. | Semiconductor device package and method of manufacturing the same |
| JP2022010482A (ja) * | 2020-06-29 | 2022-01-17 | キオクシア株式会社 | メモリシステム |
Citations (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002076252A (ja) * | 2000-08-31 | 2002-03-15 | Nec Kyushu Ltd | 半導体装置 |
| JP2004063767A (ja) * | 2002-07-29 | 2004-02-26 | Renesas Technology Corp | 半導体装置 |
| JP2006093189A (ja) * | 2004-09-21 | 2006-04-06 | Renesas Technology Corp | 半導体装置 |
| JP2008135597A (ja) * | 2006-11-29 | 2008-06-12 | Elpida Memory Inc | メモリモジュール |
| JP2008187146A (ja) * | 2007-01-31 | 2008-08-14 | Sanyo Electric Co Ltd | 回路装置 |
| JP2010501118A (ja) * | 2006-08-16 | 2010-01-14 | テッセラ,インコーポレイテッド | マイクロエレクトロニクスパッケージ |
| JP2010514080A (ja) * | 2006-12-14 | 2010-04-30 | ラムバス・インコーポレーテッド | マルチダイメモリ素子 |
| JP2010098098A (ja) * | 2008-10-16 | 2010-04-30 | Denso Corp | 電子装置の製造方法 |
| JP2010232653A (ja) * | 2009-03-25 | 2010-10-14 | Samsung Electronics Co Ltd | 積層メモリ素子 |
Family Cites Families (161)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS62107391A (ja) | 1985-11-06 | 1987-05-18 | Nippon Texas Instr Kk | 情報記憶媒体 |
| JPH02174255A (ja) | 1988-12-27 | 1990-07-05 | Mitsubishi Electric Corp | 半導体集積回路装置 |
| US5679977A (en) | 1990-09-24 | 1997-10-21 | Tessera, Inc. | Semiconductor chip assemblies, methods of making same and components for same |
| US5148266A (en) | 1990-09-24 | 1992-09-15 | Ist Associates, Inc. | Semiconductor chip assemblies having interposer and flexible lead |
| US5148265A (en) | 1990-09-24 | 1992-09-15 | Ist Associates, Inc. | Semiconductor chip assemblies with fan-in leads |
| US5369552A (en) | 1992-07-14 | 1994-11-29 | Ncr Corporation | Multi-chip module with multiple compartments |
| US5998864A (en) | 1995-05-26 | 1999-12-07 | Formfactor, Inc. | Stacking semiconductor devices, particularly memory chips |
| US5861666A (en) | 1995-08-30 | 1999-01-19 | Tessera, Inc. | Stacked chip assembly |
| US5892660A (en) | 1996-08-29 | 1999-04-06 | Micron Technology, Inc. | Single in line memory module adapter |
| JP2978861B2 (ja) | 1997-10-28 | 1999-11-15 | 九州日本電気株式会社 | モールドbga型半導体装置及びその製造方法 |
| US6742098B1 (en) | 2000-10-03 | 2004-05-25 | Intel Corporation | Dual-port buffer-to-memory interface |
| US6021048A (en) | 1998-02-17 | 2000-02-01 | Smith; Gary W. | High speed memory module |
| US6150724A (en) | 1998-03-02 | 2000-11-21 | Motorola, Inc. | Multi-chip semiconductor device and method for making the device by using multiple flip chip interfaces |
| US5977640A (en) | 1998-06-26 | 1999-11-02 | International Business Machines Corporation | Highly integrated chip-on-chip packaging |
| US7525813B2 (en) | 1998-07-06 | 2009-04-28 | Renesas Technology Corp. | Semiconductor device |
| US6353539B1 (en) | 1998-07-21 | 2002-03-05 | Intel Corporation | Method and apparatus for matched length routing of back-to-back package placement |
| US6121576A (en) | 1998-09-02 | 2000-09-19 | Micron Technology, Inc. | Method and process of contact to a heat softened solder ball array |
| US6201695B1 (en) | 1998-10-26 | 2001-03-13 | Micron Technology, Inc. | Heat sink for chip stacking applications |
| US6815251B1 (en) | 1999-02-01 | 2004-11-09 | Micron Technology, Inc. | High density modularity for IC's |
| SE519108C2 (sv) | 1999-05-06 | 2003-01-14 | Sandvik Ab | Belagt skärverktyg för bearbetning av grått gjutjärn |
| TW409377B (en) | 1999-05-21 | 2000-10-21 | Siliconware Precision Industries Co Ltd | Small scale ball grid array package |
| KR100393095B1 (ko) | 1999-06-12 | 2003-07-31 | 앰코 테크놀로지 코리아 주식회사 | 반도체패키지와 그 제조방법 |
| JP3360655B2 (ja) | 1999-07-08 | 2002-12-24 | 日本電気株式会社 | 半導体装置 |
| US6199743B1 (en) * | 1999-08-19 | 2001-03-13 | Micron Technology, Inc. | Apparatuses for forming wire bonds from circuitry on a substrate to a semiconductor chip, and methods of forming semiconductor chip assemblies |
| JP2001196407A (ja) | 2000-01-14 | 2001-07-19 | Seiko Instruments Inc | 半導体装置および半導体装置の形成方法 |
| US6369448B1 (en) | 2000-01-21 | 2002-04-09 | Lsi Logic Corporation | Vertically integrated flip chip semiconductor package |
| US6414396B1 (en) | 2000-01-24 | 2002-07-02 | Amkor Technology, Inc. | Package for stacked integrated circuits |
| JP3768761B2 (ja) | 2000-01-31 | 2006-04-19 | 株式会社日立製作所 | 半導体装置およびその製造方法 |
| JP2001223324A (ja) | 2000-02-10 | 2001-08-17 | Mitsubishi Electric Corp | 半導体装置 |
| US6731009B1 (en) | 2000-03-20 | 2004-05-04 | Cypress Semiconductor Corporation | Multi-die assembly |
| KR100583491B1 (ko) | 2000-04-07 | 2006-05-24 | 앰코 테크놀로지 코리아 주식회사 | 반도체패키지 및 그 제조방법 |
| US6578754B1 (en) | 2000-04-27 | 2003-06-17 | Advanpack Solutions Pte. Ltd. | Pillar connections for semiconductor chips and method of manufacture |
| US6592109B2 (en) | 2000-07-31 | 2003-07-15 | Toyo Tire & Rubber Co., Ltd. | Liquid sealing type body mount |
| JP3874062B2 (ja) | 2000-09-05 | 2007-01-31 | セイコーエプソン株式会社 | 半導体装置 |
| JP3462166B2 (ja) | 2000-09-08 | 2003-11-05 | 富士通カンタムデバイス株式会社 | 化合物半導体装置 |
| US6492726B1 (en) | 2000-09-22 | 2002-12-10 | Chartered Semiconductor Manufacturing Ltd. | Chip scale packaging with multi-layer flip chip arrangement and ball grid array interconnection |
| TW511405B (en) | 2000-12-27 | 2002-11-21 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | Device built-in module and manufacturing method thereof |
| SG95637A1 (en) | 2001-03-15 | 2003-04-23 | Micron Technology Inc | Semiconductor/printed circuit board assembly, and computer system |
| SG106054A1 (en) | 2001-04-17 | 2004-09-30 | Micron Technology Inc | Method and apparatus for package reduction in stacked chip and board assemblies |
| JP2002353398A (ja) | 2001-05-25 | 2002-12-06 | Nec Kyushu Ltd | 半導体装置 |
| US6472741B1 (en) | 2001-07-14 | 2002-10-29 | Siliconware Precision Industries Co., Ltd. | Thermally-enhanced stacked-die ball grid array semiconductor package and method of fabricating the same |
| US6385049B1 (en) | 2001-07-05 | 2002-05-07 | Walsin Advanced Electronics Ltd | Multi-board BGA package |
| JP2003101207A (ja) | 2001-09-27 | 2003-04-04 | Nec Kyushu Ltd | 半田ボールおよびそれを用いた部品接続構造 |
| US6977440B2 (en) | 2001-10-09 | 2005-12-20 | Tessera, Inc. | Stacked packages |
| SG118103A1 (en) | 2001-12-12 | 2006-01-27 | Micron Technology Inc | BOC BGA package for die with I-shaped bond pad layout |
| KR100480909B1 (ko) | 2001-12-29 | 2005-04-07 | 주식회사 하이닉스반도체 | 적층 칩 패키지의 제조 방법 |
| TW523890B (en) | 2002-02-07 | 2003-03-11 | Macronix Int Co Ltd | Stacked semiconductor packaging device |
| US7196415B2 (en) | 2002-03-22 | 2007-03-27 | Broadcom Corporation | Low voltage drop and high thermal performance ball grid array package |
| DE10215654A1 (de) | 2002-04-09 | 2003-11-06 | Infineon Technologies Ag | Elektronisches Bauteil mit mindestens einem Halbleiterchip und Flip-Chip-Kontakten sowie Verfahren zu seiner Herstellung |
| KR100958400B1 (ko) | 2002-06-05 | 2010-05-18 | 가부시끼가이샤 르네사스 테크놀로지 | 반도체장치 |
| US6762942B1 (en) | 2002-09-05 | 2004-07-13 | Gary W. Smith | Break away, high speed, folded, jumperless electronic assembly |
| TW557556B (en) | 2002-09-10 | 2003-10-11 | Siliconware Precision Industries Co Ltd | Window-type multi-chip semiconductor package |
| AU2003301632A1 (en) | 2002-10-22 | 2004-05-13 | Unitive International Limited | Stacked electronic structures including offset substrates |
| US7268425B2 (en) | 2003-03-05 | 2007-09-11 | Intel Corporation | Thermally enhanced electronic flip-chip packaging with external-connector-side die and method |
| TW200419752A (en) | 2003-03-18 | 2004-10-01 | United Test Ct Inc | Semiconductor package with heat sink |
| US7528421B2 (en) | 2003-05-05 | 2009-05-05 | Lamina Lighting, Inc. | Surface mountable light emitting diode assemblies packaged for high temperature operation |
| KR20050001159A (ko) | 2003-06-27 | 2005-01-06 | 삼성전자주식회사 | 복수개의 플립 칩들을 갖는 멀티칩 패키지 및 그 제조방법 |
| SG148877A1 (en) | 2003-07-22 | 2009-01-29 | Micron Technology Inc | Semiconductor substrates including input/output redistribution using wire bonds and anisotropically conductive film, methods of fabrication and assemblies including same |
| US7462936B2 (en) | 2003-10-06 | 2008-12-09 | Tessera, Inc. | Formation of circuitry with modification of feature height |
| US7061121B2 (en) | 2003-11-12 | 2006-06-13 | Tessera, Inc. | Stacked microelectronic assemblies with central contacts |
| US7095104B2 (en) | 2003-11-21 | 2006-08-22 | International Business Machines Corporation | Overlap stacking of center bus bonded memory chips for double density and method of manufacturing the same |
| DE10360708B4 (de) | 2003-12-19 | 2008-04-10 | Infineon Technologies Ag | Halbleitermodul mit einem Halbleiterstapel, Umverdrahtungsplatte, und Verfahren zur Herstellung derselben |
| WO2005065207A2 (en) | 2003-12-30 | 2005-07-21 | Tessera, Inc. | Microelectronic packages and methods therefor |
| US20050173807A1 (en) | 2004-02-05 | 2005-08-11 | Jianbai Zhu | High density vertically stacked semiconductor device |
| JP2005251957A (ja) | 2004-03-04 | 2005-09-15 | Renesas Technology Corp | 半導体装置 |
| US7489517B2 (en) | 2004-04-05 | 2009-02-10 | Thomas Joel Massingill | Die down semiconductor package |
| US7078808B2 (en) | 2004-05-20 | 2006-07-18 | Texas Instruments Incorporated | Double density method for wirebond interconnect |
| WO2005114728A1 (ja) | 2004-05-21 | 2005-12-01 | Nec Corporation | 半導体装置並びに配線基板及びその製造方法 |
| KR20050119414A (ko) | 2004-06-16 | 2005-12-21 | 삼성전자주식회사 | 에지 패드형 반도체 칩의 스택 패키지 및 그 제조방법 |
| KR20060004298A (ko) | 2004-07-09 | 2006-01-12 | 삼성테크윈 주식회사 | 무선 전자 라벨 |
| US7381593B2 (en) | 2004-08-05 | 2008-06-03 | St Assembly Test Services Ltd. | Method and apparatus for stacked die packaging |
| JP4445351B2 (ja) | 2004-08-31 | 2010-04-07 | 株式会社東芝 | 半導体モジュール |
| US20060097400A1 (en) | 2004-11-03 | 2006-05-11 | Texas Instruments Incorporated | Substrate via pad structure providing reliable connectivity in array package devices |
| US7786567B2 (en) | 2004-11-10 | 2010-08-31 | Chung-Cheng Wang | Substrate for electrical device and methods for making the same |
| US7217994B2 (en) | 2004-12-01 | 2007-05-15 | Kyocera Wireless Corp. | Stack package for high density integrated circuits |
| TWI256092B (en) | 2004-12-02 | 2006-06-01 | Siliconware Precision Industries Co Ltd | Semiconductor package and fabrication method thereof |
| JP2006172122A (ja) | 2004-12-15 | 2006-06-29 | Toshiba Corp | カード状記憶装置 |
| WO2006068643A1 (en) | 2004-12-20 | 2006-06-29 | Semiconductor Components Industries, L.L.C. | Semiconductor package structure having enhanced thermal dissipation characteristics |
| JP4086068B2 (ja) | 2004-12-27 | 2008-05-14 | 日本電気株式会社 | 半導体装置 |
| KR20060080424A (ko) | 2005-01-05 | 2006-07-10 | 삼성전자주식회사 | 멀티 칩 패키지를 장착하는 메모리 카드 |
| US7205656B2 (en) * | 2005-02-22 | 2007-04-17 | Micron Technology, Inc. | Stacked device package for peripheral and center device pad layout device |
| US7196427B2 (en) | 2005-04-18 | 2007-03-27 | Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. | Structure having an integrated circuit on another integrated circuit with an intervening bent adhesive element |
| US7250675B2 (en) | 2005-05-05 | 2007-07-31 | International Business Machines Corporation | Method and apparatus for forming stacked die and substrate structures for increased packing density |
| KR101070913B1 (ko) | 2005-05-19 | 2011-10-06 | 삼성테크윈 주식회사 | 반도체 칩 적층 패키지 |
| US7402911B2 (en) | 2005-06-28 | 2008-07-22 | Infineon Technologies Ag | Multi-chip device and method for producing a multi-chip device |
| SG130066A1 (en) * | 2005-08-26 | 2007-03-20 | Micron Technology Inc | Microelectronic device packages, stacked microelectronic device packages, and methods for manufacturing microelectronic devices |
| JP4108701B2 (ja) | 2005-09-12 | 2008-06-25 | 株式会社ルネサステクノロジ | Icカードの製造方法 |
| US7602054B2 (en) | 2005-10-05 | 2009-10-13 | Semiconductor Components Industries, L.L.C. | Method of forming a molded array package device having an exposed tab and structure |
| US20070152310A1 (en) | 2005-12-29 | 2007-07-05 | Tessera, Inc. | Electrical ground method for ball stack package |
| KR100673965B1 (ko) | 2006-01-11 | 2007-01-24 | 삼성테크윈 주식회사 | 인쇄회로기판 및 반도체 패키지 제조방법 |
| JP2007188916A (ja) | 2006-01-11 | 2007-07-26 | Renesas Technology Corp | 半導体装置 |
| KR100690247B1 (ko) | 2006-01-16 | 2007-03-12 | 삼성전자주식회사 | 이중 봉합된 반도체 패키지 및 그의 제조 방법 |
| US20070176297A1 (en) | 2006-01-31 | 2007-08-02 | Tessera, Inc. | Reworkable stacked chip assembly |
| JP4946872B2 (ja) | 2006-02-02 | 2012-06-06 | パナソニック株式会社 | メモリカードの製造方法 |
| SG135074A1 (en) | 2006-02-28 | 2007-09-28 | Micron Technology Inc | Microelectronic devices, stacked microelectronic devices, and methods for manufacturing such devices |
| KR20070088177A (ko) | 2006-02-24 | 2007-08-29 | 삼성테크윈 주식회사 | 반도체 패키지 및 그 제조 방법 |
| US20080029879A1 (en) | 2006-03-01 | 2008-02-07 | Tessera, Inc. | Structure and method of making lidded chips |
| US7514780B2 (en) | 2006-03-15 | 2009-04-07 | Hitachi, Ltd. | Power semiconductor device |
| US7368319B2 (en) | 2006-03-17 | 2008-05-06 | Stats Chippac Ltd. | Stacked integrated circuit package-in-package system |
| US7768075B2 (en) | 2006-04-06 | 2010-08-03 | Fairchild Semiconductor Corporation | Semiconductor die packages using thin dies and metal substrates |
| CN100511588C (zh) | 2006-04-14 | 2009-07-08 | 泰特科技股份有限公司 | 导线架型芯片级封装方法 |
| SG136822A1 (en) * | 2006-04-19 | 2007-11-29 | Micron Technology Inc | Integrated circuit devices with stacked package interposers |
| TW200743190A (en) | 2006-05-10 | 2007-11-16 | Chung-Cheng Wang | A heat spreader for electrical device |
| JP5026736B2 (ja) | 2006-05-15 | 2012-09-19 | パナソニックヘルスケア株式会社 | 冷凍装置 |
| WO2008007257A2 (en) | 2006-06-20 | 2008-01-17 | Nxp B.V. | Integrated circuit and assembly therewith |
| US20080023805A1 (en) | 2006-07-26 | 2008-01-31 | Texas Instruments Incorporated | Array-Processed Stacked Semiconductor Packages |
| TWI306658B (en) | 2006-08-07 | 2009-02-21 | Chipmos Technologies Inc | Leadframe on offset stacked chips package |
| US7906844B2 (en) | 2006-09-26 | 2011-03-15 | Compass Technology Co. Ltd. | Multiple integrated circuit die package with thermal performance |
| TWI370515B (en) * | 2006-09-29 | 2012-08-11 | Megica Corp | Circuit component |
| KR100825784B1 (ko) | 2006-10-18 | 2008-04-28 | 삼성전자주식회사 | 휨 및 와이어 단선을 억제하는 반도체 패키지 및 그제조방법 |
| US7772683B2 (en) | 2006-12-09 | 2010-08-10 | Stats Chippac Ltd. | Stacked integrated circuit package-in-package system |
| JP2010514217A (ja) | 2006-12-19 | 2010-04-30 | テセラ・インターコネクト・マテリアルズ,インコーポレイテッド | チップ・コンデンサ組み込み型pwb |
| JP2008177241A (ja) | 2007-01-16 | 2008-07-31 | Toshiba Corp | 半導体パッケージ |
| KR101057368B1 (ko) | 2007-01-31 | 2011-08-18 | 후지쯔 세미컨덕터 가부시키가이샤 | 반도체 장치 및 그 제조 방법 |
| JP2008198841A (ja) | 2007-02-14 | 2008-08-28 | Elpida Memory Inc | 半導体装置 |
| JP2008235576A (ja) | 2007-03-20 | 2008-10-02 | Fujitsu Ltd | 電子部品の放熱構造及び半導体装置 |
| US7872356B2 (en) | 2007-05-16 | 2011-01-18 | Qualcomm Incorporated | Die stacking system and method |
| US20080296717A1 (en) | 2007-06-01 | 2008-12-04 | Tessera, Inc. | Packages and assemblies including lidded chips |
| JP2008306128A (ja) | 2007-06-11 | 2008-12-18 | Shinko Electric Ind Co Ltd | 半導体装置およびその製造方法 |
| US7868445B2 (en) | 2007-06-25 | 2011-01-11 | Epic Technologies, Inc. | Integrated structures and methods of fabrication thereof with fan-out metallization on a chips-first chip layer |
| SG148901A1 (en) | 2007-07-09 | 2009-01-29 | Micron Technology Inc | Packaged semiconductor assemblies and methods for manufacturing such assemblies |
| KR101341566B1 (ko) | 2007-07-10 | 2013-12-16 | 삼성전자주식회사 | 소켓, 검사 장치, 그리고 적층형 반도체 소자 제조 방법 |
| US20090071707A1 (en) | 2007-08-15 | 2009-03-19 | Tessera, Inc. | Multilayer substrate with interconnection vias and method of manufacturing the same |
| US8505199B2 (en) | 2007-08-15 | 2013-08-13 | Tessera, Inc. | Method of fabricating an interconnection element having conductive posts |
| US8299626B2 (en) | 2007-08-16 | 2012-10-30 | Tessera, Inc. | Microelectronic package |
| US7442045B1 (en) | 2007-08-17 | 2008-10-28 | Centipede Systems, Inc. | Miniature electrical ball and tube socket with self-capturing multiple-contact-point coupling |
| US20090051043A1 (en) | 2007-08-21 | 2009-02-26 | Spansion Llc | Die stacking in multi-die stacks using die support mechanisms |
| US7872340B2 (en) | 2007-08-31 | 2011-01-18 | Stats Chippac Ltd. | Integrated circuit package system employing an offset stacked configuration |
| CN101874296B (zh) | 2007-09-28 | 2015-08-26 | 泰塞拉公司 | 利用成对凸柱进行倒装芯片互连 |
| US7880310B2 (en) * | 2007-09-28 | 2011-02-01 | Intel Corporation | Direct device attachment on dual-mode wirebond die |
| US7851267B2 (en) | 2007-10-18 | 2010-12-14 | Infineon Technologies Ag | Power semiconductor module method |
| US20090166065A1 (en) | 2008-01-02 | 2009-07-02 | Clayton James E | Thin multi-chip flex module |
| US8138610B2 (en) | 2008-02-08 | 2012-03-20 | Qimonda Ag | Multi-chip package with interconnected stacked chips |
| JP5207868B2 (ja) | 2008-02-08 | 2013-06-12 | ルネサスエレクトロニクス株式会社 | 半導体装置 |
| US8354742B2 (en) | 2008-03-31 | 2013-01-15 | Stats Chippac, Ltd. | Method and apparatus for a package having multiple stacked die |
| US8159052B2 (en) | 2008-04-10 | 2012-04-17 | Semtech Corporation | Apparatus and method for a chip assembly including a frequency extending device |
| US7928562B2 (en) | 2008-07-22 | 2011-04-19 | International Business Machines Corporation | Segmentation of a die stack for 3D packaging thermal management |
| US8253231B2 (en) * | 2008-09-23 | 2012-08-28 | Marvell International Ltd. | Stacked integrated circuit package using a window substrate |
| KR101479461B1 (ko) | 2008-10-14 | 2015-01-06 | 삼성전자주식회사 | 적층 패키지 및 이의 제조 방법 |
| US8049339B2 (en) | 2008-11-24 | 2011-11-01 | Powertech Technology Inc. | Semiconductor package having isolated inner lead |
| US7951643B2 (en) | 2008-11-29 | 2011-05-31 | Stats Chippac Ltd. | Integrated circuit packaging system with lead frame and method of manufacture thereof |
| KR101011863B1 (ko) | 2008-12-02 | 2011-01-31 | 앰코 테크놀로지 코리아 주식회사 | 반도체 패키지 및 그 제조 방법 |
| US20100193930A1 (en) | 2009-02-02 | 2010-08-05 | Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. | Multi-chip semiconductor devices having conductive vias and methods of forming the same |
| US8026589B1 (en) | 2009-02-23 | 2011-09-27 | Amkor Technology, Inc. | Reduced profile stackable semiconductor package |
| TWI401785B (zh) | 2009-03-27 | 2013-07-11 | Chipmos Technologies Inc | 多晶片堆疊封裝 |
| US8039316B2 (en) | 2009-04-14 | 2011-10-18 | Stats Chippac Ltd. | Integrated circuit packaging system with stacked integrated circuit and heat spreader with openings and method of manufacture thereof |
| KR101601847B1 (ko) | 2009-05-21 | 2016-03-09 | 삼성전자주식회사 | 반도체 패키지 |
| KR20100134354A (ko) | 2009-06-15 | 2010-12-23 | 삼성전자주식회사 | 반도체 패키지, 스택 모듈, 카드 및 전자 시스템 |
| TWM370767U (en) | 2009-06-19 | 2009-12-11 | fu-zhi Huang | Modulized computer |
| US20100327419A1 (en) | 2009-06-26 | 2010-12-30 | Sriram Muthukumar | Stacked-chip packages in package-on-package apparatus, methods of assembling same, and systems containing same |
| US20110085304A1 (en) | 2009-10-14 | 2011-04-14 | Irvine Sensors Corporation | Thermal management device comprising thermally conductive heat spreader with electrically isolated through-hole vias |
| US10128206B2 (en) | 2010-10-14 | 2018-11-13 | Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company, Ltd. | Conductive pillar structure |
| US8553420B2 (en) | 2010-10-19 | 2013-10-08 | Tessera, Inc. | Enhanced stacked microelectronic assemblies with central contacts and improved thermal characteristics |
| US8378478B2 (en) | 2010-11-24 | 2013-02-19 | Tessera, Inc. | Enhanced stacked microelectronic assemblies with central contacts and vias connected to the central contacts |
| KR101061531B1 (ko) | 2010-12-17 | 2011-09-01 | 테세라 리써치 엘엘씨 | 중앙 콘택을 구비하며 접지 또는 배전을 개선한 적층형 마이크로전자 조립체 |
| US8338963B2 (en) | 2011-04-21 | 2012-12-25 | Tessera, Inc. | Multiple die face-down stacking for two or more die |
| US8304881B1 (en) * | 2011-04-21 | 2012-11-06 | Tessera, Inc. | Flip-chip, face-up and face-down wirebond combination package |
| US8970028B2 (en) | 2011-12-29 | 2015-03-03 | Invensas Corporation | Embedded heat spreader for package with multiple microelectronic elements and face-down connection |
| US8928153B2 (en) | 2011-04-21 | 2015-01-06 | Tessera, Inc. | Flip-chip, face-up and face-down centerbond memory wirebond assemblies |
| US8436457B2 (en) | 2011-10-03 | 2013-05-07 | Invensas Corporation | Stub minimization for multi-die wirebond assemblies with parallel windows |
| US8723327B2 (en) | 2011-10-20 | 2014-05-13 | Invensas Corporation | Microelectronic package with stacked microelectronic units and method for manufacture thereof |
-
2011
- 2011-11-29 US US13/306,182 patent/US8304881B1/en active Active
-
2012
- 2012-03-21 JP JP2014506416A patent/JP2014514766A/ja active Pending
- 2012-03-21 EP EP12715768.3A patent/EP2700097A1/en not_active Withdrawn
- 2012-03-21 WO PCT/US2012/029873 patent/WO2012145114A1/en active Application Filing
- 2012-03-21 CN CN201280030799.8A patent/CN103620774B/zh not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2012-03-21 KR KR1020137030856A patent/KR20140028015A/ko not_active Application Discontinuation
- 2012-04-09 TW TW101112514A patent/TWI523174B/zh not_active IP Right Cessation
- 2012-11-05 US US13/668,974 patent/US8436458B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
-
2013
- 2013-10-21 US US14/058,908 patent/US9093291B2/en active Active
Patent Citations (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002076252A (ja) * | 2000-08-31 | 2002-03-15 | Nec Kyushu Ltd | 半導体装置 |
| JP2004063767A (ja) * | 2002-07-29 | 2004-02-26 | Renesas Technology Corp | 半導体装置 |
| JP2006093189A (ja) * | 2004-09-21 | 2006-04-06 | Renesas Technology Corp | 半導体装置 |
| JP2010501118A (ja) * | 2006-08-16 | 2010-01-14 | テッセラ,インコーポレイテッド | マイクロエレクトロニクスパッケージ |
| JP2008135597A (ja) * | 2006-11-29 | 2008-06-12 | Elpida Memory Inc | メモリモジュール |
| JP2010514080A (ja) * | 2006-12-14 | 2010-04-30 | ラムバス・インコーポレーテッド | マルチダイメモリ素子 |
| JP2008187146A (ja) * | 2007-01-31 | 2008-08-14 | Sanyo Electric Co Ltd | 回路装置 |
| JP2010098098A (ja) * | 2008-10-16 | 2010-04-30 | Denso Corp | 電子装置の製造方法 |
| JP2010232653A (ja) * | 2009-03-25 | 2010-10-14 | Samsung Electronics Co Ltd | 積層メモリ素子 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN103620774A (zh) | 2014-03-05 |
| US20120267797A1 (en) | 2012-10-25 |
| US20130056870A1 (en) | 2013-03-07 |
| EP2700097A1 (en) | 2014-02-26 |
| TW201248809A (en) | 2012-12-01 |
| US8304881B1 (en) | 2012-11-06 |
| US20140042644A1 (en) | 2014-02-13 |
| KR20140028015A (ko) | 2014-03-07 |
| TWI523174B (zh) | 2016-02-21 |
| WO2012145114A1 (en) | 2012-10-26 |
| US9093291B2 (en) | 2015-07-28 |
| US8436458B2 (en) | 2013-05-07 |
| CN103620774B (zh) | 2016-10-05 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP2014514766A (ja) | フリップチップ、フェイスアップワイヤボンド、およびフェイスダウンワイヤボンドの組み合わせパッケージ | |
| US9508629B2 (en) | Memory module in a package | |
| TWI505420B (zh) | 覆晶、面向上型及面向下型中心接合記憶體導線接合總成 | |
| US8513817B2 (en) | Memory module in a package | |
| US8952516B2 (en) | Multiple die stacking for two or more die | |
| TWI524440B (zh) | 具有貫穿之半導體通孔之積體電路封裝系統及其製造方法 | |
| US9312239B2 (en) | Enhanced stacked microelectronic assemblies with central contacts and improved thermal characteristics | |
| US8786069B1 (en) | Reconfigurable pop | |
| US9165906B2 (en) | High performance package on package | |
| JP2001223326A (ja) | 半導体装置 | |
| US9543277B1 (en) | Wafer level packages with mechanically decoupled fan-in and fan-out areas | |
| US9659848B1 (en) | Stiffened wires for offset BVA | |
| JP2008117937A (ja) | マルチチップモジュールおよびインターポーザ |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20150319 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20150319 |
|
| A871 | Explanation of circumstances concerning accelerated examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A871 Effective date: 20150319 |
|
| A975 | Report on accelerated examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971005 Effective date: 20150615 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20150619 |
|
| A601 | Written request for extension of time |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A601 Effective date: 20150924 |
|
| A601 | Written request for extension of time |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A601 Effective date: 20151016 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20151119 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20160216 |
|
| A601 | Written request for extension of time |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A601 Effective date: 20160513 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20160714 |
|
| A02 | Decision of refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 Effective date: 20160916 |