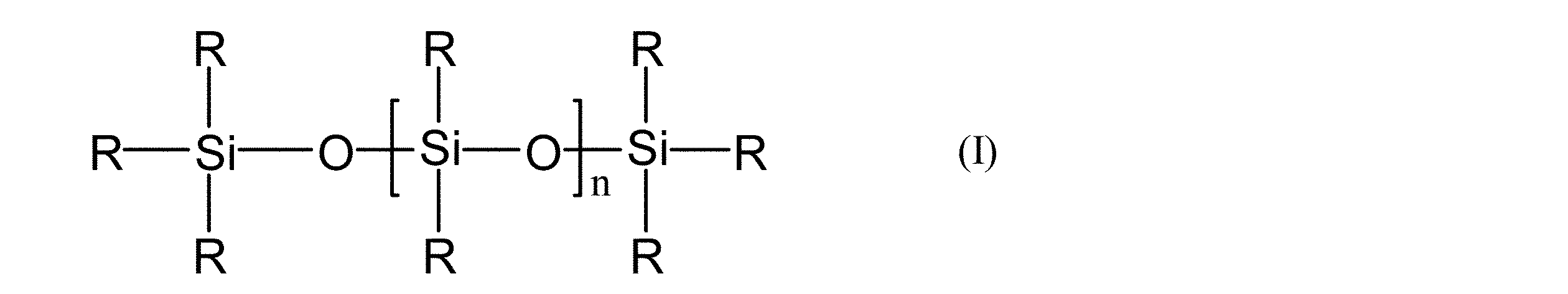WO2012050105A1 - 硬化性ポリオルガノシロキサン組成物 - Google Patents
硬化性ポリオルガノシロキサン組成物 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2012050105A1 WO2012050105A1 PCT/JP2011/073375 JP2011073375W WO2012050105A1 WO 2012050105 A1 WO2012050105 A1 WO 2012050105A1 JP 2011073375 W JP2011073375 W JP 2011073375W WO 2012050105 A1 WO2012050105 A1 WO 2012050105A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- group
- sio
- units
- polyorganosiloxane composition
- independently
- Prior art date
Links
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B05—SPRAYING OR ATOMISING IN GENERAL; APPLYING FLUENT MATERIALS TO SURFACES, IN GENERAL
- B05D—PROCESSES FOR APPLYING FLUENT MATERIALS TO SURFACES, IN GENERAL
- B05D3/00—Pretreatment of surfaces to which liquids or other fluent materials are to be applied; After-treatment of applied coatings, e.g. intermediate treating of an applied coating preparatory to subsequent applications of liquids or other fluent materials
- B05D3/02—Pretreatment of surfaces to which liquids or other fluent materials are to be applied; After-treatment of applied coatings, e.g. intermediate treating of an applied coating preparatory to subsequent applications of liquids or other fluent materials by baking
- B05D3/0254—After-treatment
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08G—MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS OBTAINED OTHERWISE THAN BY REACTIONS ONLY INVOLVING UNSATURATED CARBON-TO-CARBON BONDS
- C08G77/00—Macromolecular compounds obtained by reactions forming a linkage containing silicon with or without sulfur, nitrogen, oxygen or carbon in the main chain of the macromolecule
- C08G77/04—Polysiloxanes
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08K—Use of inorganic or non-macromolecular organic substances as compounding ingredients
- C08K5/00—Use of organic ingredients
- C08K5/56—Organo-metallic compounds, i.e. organic compounds containing a metal-to-carbon bond
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08L—COMPOSITIONS OF MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS
- C08L83/00—Compositions of macromolecular compounds obtained by reactions forming in the main chain of the macromolecule a linkage containing silicon with or without sulfur, nitrogen, oxygen or carbon only; Compositions of derivatives of such polymers
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08L—COMPOSITIONS OF MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS
- C08L83/00—Compositions of macromolecular compounds obtained by reactions forming in the main chain of the macromolecule a linkage containing silicon with or without sulfur, nitrogen, oxygen or carbon only; Compositions of derivatives of such polymers
- C08L83/04—Polysiloxanes
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09D—COATING COMPOSITIONS, e.g. PAINTS, VARNISHES OR LACQUERS; FILLING PASTES; CHEMICAL PAINT OR INK REMOVERS; INKS; CORRECTING FLUIDS; WOODSTAINS; PASTES OR SOLIDS FOR COLOURING OR PRINTING; USE OF MATERIALS THEREFOR
- C09D183/00—Coating compositions based on macromolecular compounds obtained by reactions forming in the main chain of the macromolecule a linkage containing silicon, with or without sulfur, nitrogen, oxygen, or carbon only; Coating compositions based on derivatives of such polymers
- C09D183/04—Polysiloxanes
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C09—DYES; PAINTS; POLISHES; NATURAL RESINS; ADHESIVES; COMPOSITIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; APPLICATIONS OF MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- C09J—ADHESIVES; NON-MECHANICAL ASPECTS OF ADHESIVE PROCESSES IN GENERAL; ADHESIVE PROCESSES NOT PROVIDED FOR ELSEWHERE; USE OF MATERIALS AS ADHESIVES
- C09J183/00—Adhesives based on macromolecular compounds obtained by reactions forming in the main chain of the macromolecule a linkage containing silicon, with or without sulfur, nitrogen, oxygen, or carbon only; Adhesives based on derivatives of such polymers
- C09J183/04—Polysiloxanes
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L23/00—Details of semiconductor or other solid state devices
- H01L23/28—Encapsulations, e.g. encapsulating layers, coatings, e.g. for protection
- H01L23/29—Encapsulations, e.g. encapsulating layers, coatings, e.g. for protection characterised by the material, e.g. carbon
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L23/00—Details of semiconductor or other solid state devices
- H01L23/28—Encapsulations, e.g. encapsulating layers, coatings, e.g. for protection
- H01L23/29—Encapsulations, e.g. encapsulating layers, coatings, e.g. for protection characterised by the material, e.g. carbon
- H01L23/293—Organic, e.g. plastic
- H01L23/295—Organic, e.g. plastic containing a filler
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L23/00—Details of semiconductor or other solid state devices
- H01L23/28—Encapsulations, e.g. encapsulating layers, coatings, e.g. for protection
- H01L23/29—Encapsulations, e.g. encapsulating layers, coatings, e.g. for protection characterised by the material, e.g. carbon
- H01L23/293—Organic, e.g. plastic
- H01L23/296—Organo-silicon compounds
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08G—MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS OBTAINED OTHERWISE THAN BY REACTIONS ONLY INVOLVING UNSATURATED CARBON-TO-CARBON BONDS
- C08G77/00—Macromolecular compounds obtained by reactions forming a linkage containing silicon with or without sulfur, nitrogen, oxygen or carbon in the main chain of the macromolecule
- C08G77/04—Polysiloxanes
- C08G77/12—Polysiloxanes containing silicon bound to hydrogen
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08G—MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS OBTAINED OTHERWISE THAN BY REACTIONS ONLY INVOLVING UNSATURATED CARBON-TO-CARBON BONDS
- C08G77/00—Macromolecular compounds obtained by reactions forming a linkage containing silicon with or without sulfur, nitrogen, oxygen or carbon in the main chain of the macromolecule
- C08G77/04—Polysiloxanes
- C08G77/20—Polysiloxanes containing silicon bound to unsaturated aliphatic groups
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08G—MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS OBTAINED OTHERWISE THAN BY REACTIONS ONLY INVOLVING UNSATURATED CARBON-TO-CARBON BONDS
- C08G77/00—Macromolecular compounds obtained by reactions forming a linkage containing silicon with or without sulfur, nitrogen, oxygen or carbon in the main chain of the macromolecule
- C08G77/70—Siloxanes defined by use of the MDTQ nomenclature
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08L—COMPOSITIONS OF MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS
- C08L2203/00—Applications
- C08L2203/20—Applications use in electrical or conductive gadgets
- C08L2203/206—Applications use in electrical or conductive gadgets use in coating or encapsulating of electronic parts
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08L—COMPOSITIONS OF MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS
- C08L2205/00—Polymer mixtures characterised by other features
- C08L2205/02—Polymer mixtures characterised by other features containing two or more polymers of the same C08L -group
- C08L2205/025—Polymer mixtures characterised by other features containing two or more polymers of the same C08L -group containing two or more polymers of the same hierarchy C08L, and differing only in parameters such as density, comonomer content, molecular weight, structure
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C08—ORGANIC MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS; THEIR PREPARATION OR CHEMICAL WORKING-UP; COMPOSITIONS BASED THEREON
- C08L—COMPOSITIONS OF MACROMOLECULAR COMPOUNDS
- C08L2314/00—Polymer mixtures characterised by way of preparation
- C08L2314/08—Polymer mixtures characterised by way of preparation prepared by late transition metal, i.e. Ni, Pd, Pt, Co, Rh, Ir, Fe, Ru or Os, single site catalyst
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/0001—Technical content checked by a classifier
- H01L2924/0002—Not covered by any one of groups H01L24/00, H01L24/00 and H01L2224/00
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a curable polyorganosiloxane composition that is cured by an addition reaction.
- a curable polyorganosiloxane composition that is cured by an addition reaction is known to give a rubber-like cured product having excellent heat resistance, weather resistance, and electrical insulation, and is widely used in various fields.
- it is attracting attention in the fields of automobiles and semiconductors, but in these fields, extremely strict reliability is required for its purpose of use, and one of them is cold resistance that can withstand use even in cold regions and low temperature environments.
- Patent Document 1 In order to improve cold resistance, it is known to introduce a phenyl group into a base polymer (Patent Document 1). It is also known to blend an organopolysiloxane having a resin structure (Patent Document 2).
- base polymers in which phenyl groups are introduced into the base polymer and organopolysiloxanes having a resin structure have a high relative viscosity with respect to the degree of polymerization and are inferior in workability.
- a base polymer containing a large amount of phenyl groups The cured product had a problem that the temperature dependence of the elastic modulus was large.
- An object of the present invention is to provide a curable polyorganosiloxane composition that gives a cured product excellent in cold resistance.
- the cold resistance can be evaluated by comparing the shear modulus of the cured product at a low temperature ( ⁇ 100 to ⁇ 50 ° C.) and room temperature (0 to 40 ° C.).
- a cured product of a polyorganosiloxane composition has a melting point in the vicinity of ⁇ 40 ° C., and the shear elastic modulus often changes significantly across the melting point.
- the present inventor has made extensive studies to solve the above-mentioned problems, and uses a large amount of branched polyorganosiloxane as a base polymer by utilizing the compatibility of a specific linear polyorganosiloxane and a branched polyorganosiloxane. It has been found that by using it, it is possible to suppress a rapid change in the elastic modulus of the cured product at low temperature and room temperature and to improve cold resistance, and the present invention has been completed.
- the present invention (A) (A1) Formula (I): (Where R is independently R 1 or R 2 , of which at least two are R 1 , R 1 is independently a C 2 -C 6 alkenyl group, R 2 is independently a C 1 -C 6 alkyl group, n is a linear polyorganosiloxane having a viscosity of 10 to 10,000 cP at 23 ° C.), and (A2) SiO 4/2 units and R ′ 3 SiO 1/2 units, and In some cases, R ′ 2 SiO units and / or R′SiO 3/2 units (wherein R ′ are each independently an unsubstituted or substituted monovalent aliphatic group or alicyclic group).
- the weight ratio of (A2) to (A1) is 1 to 5
- the present invention also relates to an adhesive comprising the above curable polyorganosiloxane composition, and relates to a semiconductor device sealed using the above curable polyorganosiloxane composition.
- a curable polyorganosiloxane composition that provides a cured product having excellent cold resistance can be obtained.
- the polyorganosiloxane composition of the present invention comprises: (A) (A1) Formula (I):
- R is independently R 1 or R 2 , of which at least two are R 1 , R 1 is independently a C 2 -C 6 alkenyl group, R 2 is independently a C 1 -C 6 alkyl group, n is a linear polyorganosiloxane having a viscosity of 10 to 10,000 cP at 23 ° C.), and (A2) SiO 4/2 units and R ′ 3 SiO 1/2 units, and Optionally further comprising R ′ 2 SiO units and / or R′SiO 3/2 units, wherein each R ′ is independently a monovalent unsubstituted or substituted hydrocarbon group, A branched polyorganosiloxane in which at least three R ′ are alkenyl groups per molecule; The weight ratio of (A2) to (A1) ((A2) / (A1)) is 1 to 5, An alkenyl group-containing polyorganosiloxane in which the weight ratio of SiO 4/2 units and R′SiO 3/2 units in the
- (A1) is a linear polyorganosiloxane represented by the formula (I), and is a component that becomes a base polymer together with (A2).
- R 1 is a C 2 -C 6 alkenyl group, which may be branched or linear, such as vinyl, allyl, 3-butenyl, 5-hexenyl, etc. Is exemplified.
- a vinyl group is most preferred because it is easy to synthesize and does not impair the fluidity of the composition or the heat resistance of the cured product.
- R 1 may be present in any siloxane unit in the molecule, but in order to obtain good reactivity, at least a part of R 1 is preferably present at the molecular end, and at each end, More preferably, there are two R 1 , one by one.
- R 2 is a C 1 -C 6 alkyl group.
- the C 1 -C 6 alkyl group may be branched or linear, and examples thereof include methyl, ethyl, propyl and the like.
- a methyl group is particularly preferred because it is easy to synthesize and handle and gives a cured product having excellent thermal and mechanical properties.
- n is a number that makes the viscosity at 23 ° C. 10 to 10,000 cP.
- the viscosity is preferably 20 to 5,000 cP, more preferably 50 to 2,500 cP, still more preferably 150 to 2,500 cP, and particularly preferably 1,100 to 2,500 cP.
- the viscosity is a value measured according to a method based on JIS K6249, section 7.1 rotational viscosity.
- (A2) is a branched polyorganosiloxane, and together with the above (A1), is a component that becomes a base polymer, and can give particularly excellent mechanical strength to the cured product.
- (A2) is SiO 4/2 units and R ′ 3 SiO 1/2 units, and optionally further R ′ 2 SiO and / or R′SiO 3/2 units (wherein R ′ is independently And at least three R ′ are alkenyl groups per molecule so that they become crosslinking points in the curing reaction.
- (A2) is preferably a solid or viscous semi-solid resinous or liquid at room temperature.
- 'Molar ratio of between 3 SiO 1/2 units (R' R for SiO 4/2 units 3 number of moles / SiO 4/2 units of SiO 1/2 units), 0.25-1.5 Is preferred.
- the molar ratio is preferably 0.4 to 1.2, more preferably 0.5 to 1.0.
- R ′ is an alkenyl group
- a C 2 -C 6 alkenyl group can be mentioned. These may be branched or linear, and examples thereof include vinyl, allyl, 3-butenyl, and 5-hexenyl.
- the vinyl group is most preferable because it is easy to synthesize and does not impair the fluidity of the composition before curing and the heat resistance of the composition after curing.
- Alkenyl groups can exist as R ′ in R ′ 3 SiO 1/2 units. Alkenyl groups may optionally be present as R ′ 2 SiO units or R′SiO 3/2 units R ′, but in order to obtain fast cure at room temperature, at least some of the alkenyl groups are It is preferably present in R ′ 3 SiO 1/2 units.
- R ′ other than an alkenyl group examples include an unsubstituted or substituted monovalent aliphatic group or alicyclic group that does not contain an aliphatic unsaturated carbon-carbon bond, and includes methyl, ethyl, propyl, butyl, Alkyl groups such as pentyl, hexyl, octyl, decyl, dodecyl; cycloalkyl groups such as cyclohexyl; halogens such as chloromethyl, 2-cyanoethyl, 3,3,3-trifluoropropyl (eg, chloro or fluoro) Or the monovalent
- the weight ratio of (A2) to (A1) is 1 to 5.
- the weight ratio is preferably 1 to 4, more preferably 1.5 to 2.5.
- the total weight ratio of SiO 4/2 units and optionally present R′SiO 3/2 units in the total amount of (A1) and (A2) is 20 to 60% by weight.
- the weight ratio is within this range, the cured product has excellent mechanical strength and low temperature characteristics.
- the weight ratio is preferably 25 to 50% by weight.
- the polyorganosiloxane composition of the present invention comprises (B) a polyorganohydrogensiloxane having more than two hydrogen atoms bonded to silicon atoms in the molecule.
- (B) functions as a crosslinking agent of (A) by the addition reaction of the hydrosilyl group in the molecule with the alkenyl group in (A).
- Such (B) has more than two hydrosilyl groups in the molecule, preferably 3 or more, in the molecule in order to reticulate the cured product.
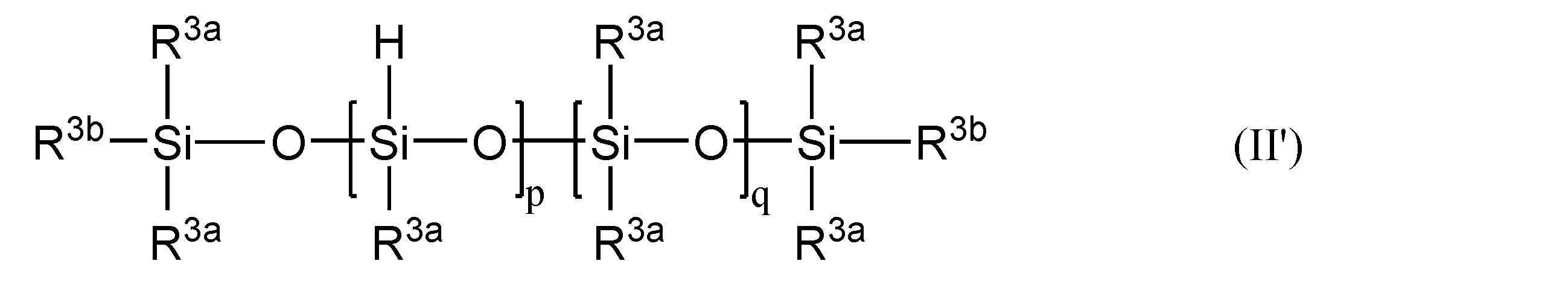
- the component (B) is typically represented by the general formula (II): (R 3 ) c H d SiO (4-cd) / 2 (II) (Where R 3 represents an unsubstituted or substituted monovalent aliphatic group or alicyclic group that does not contain an aliphatic unsaturated carbon-carbon bond; c is an integer from 0 to 2; d is 1 or 2, provided that c + d is an integer of 1 to 3) In the molecule, the number of units is more than 2, preferably 3 or more.
- Examples of the organic group bonded to the silicon atom of the other siloxane unit in R 3 and (B) are the same as those of R ′ other than the alkenyl group in the above (A2), and among these, synthesis is easy. From the viewpoint, a methyl group is most preferable. Further, d is preferably 1 from the viewpoint of easy synthesis.
- the siloxane skeleton in (B) may be linear, branched or cyclic. Moreover, you may use these mixtures.
- the degree of polymerization of (B) is not particularly limited, but since polyorganohydrogensiloxane in which two or more hydrogen atoms are bonded to the same silicon atom is difficult to synthesize, it is preferably composed of three or more siloxane units.
- the number of siloxane units is more preferably from 6 to 200, and particularly preferably from 10 to 150, since they do not volatilize even when heated to temperature and are excellent in fluidity and easily mixed with (A).
- R 3a is independently an unsubstituted or substituted monovalent aliphatic group or alicyclic group that does not contain an aliphatic unsaturated carbon-carbon bond
- R 3b independently A hydrogen atom, or an unsubstituted or substituted monovalent aliphatic group or alicyclic group
- p is a number of 2 to 100, preferably a number of 3 to 50
- q is a number from 0 to 100, preferably a number from 3 to 50).
- an unsubstituted or substituted monovalent aliphatic group or alicyclic group that does not contain an aliphatic unsaturated carbon-carbon bond includes methyl, ethyl, propyl, butyl, pentyl, Alkyl groups such as hexyl, octyl, decyl, dodecyl; cycloalkyl groups such as cyclohexyl; halogens such as chloromethyl, 2-cyanoethyl, 3,3,3-trifluoropropyl (eg chloro or fluoro) or cyano And a monovalent aliphatic group or alicyclic group substituted by.
- a methyl group is preferable.
- the blending amount of (B) is the ratio of hydrogen atoms bonded to silicon atoms in (B) with respect to alkenyl groups in (A) (H / Vi), because a cured product having excellent mechanical properties can be obtained.
- the amount is preferably 0.3 to 5.0.
- H / Vi is more preferably 0.5 to 5.0, and still more preferably 0.7 to 2.0.
- the polyorganosiloxane composition of the present invention comprises (C) a platinum group metal compound.
- (C) functions as a catalyst for promoting the addition reaction between the alkenyl group in (A) and the hydrosilyl group in (B).
- (C) is a compound of a platinum group metal atom such as platinum, rhodium, and palladium.
- Chloroplatinic acid reaction product of chloroplatinic acid and alcohol, platinum-olefin complex, platinum-vinylsiloxane complex, platinum Examples thereof include platinum compounds such as ketone complexes and platinum-phosphine complexes; rhodium compounds such as rhodium-phosphine complexes and rhodium-sulfide complexes; palladium compounds such as palladium-phosphine complexes.
- a reaction product of chloroplatinic acid and alcohol and a platinum-vinylsiloxane complex are preferable because of their good catalytic activity.
- platinum- 1,3-divinyl-1,1,3,3-tetramethyldisiloxane complex and platinum-1,3,5,7-tetravinyl-1,3,5,7-tetramethylcyclotetrasiloxane are preferred.
- the necessary curing speed varies depending on the shape of the portion where the cured product is provided and the required working time, and therefore can be arbitrarily selected depending on the combination of (C) and the curing retarder.
- the blending amount of (C) is an amount that is 0.1 to 1,000 ppm by weight in terms of platinum group metal atoms with respect to the total amount of (A) and (B), because an excellent curing rate is obtained. Is preferred. More preferably, it is 0.5 to 200 ppm by weight.
- an adhesiveness-imparting agent can be blended within a range not inhibiting the catalytic ability of (C).
- Adhesive agents include 3-glycidoxypropyl group-containing alkoxy such as 3-glycidoxypropyltrimethoxysilane, 3-glycidoxypropyltriethoxysilane, and 3-glycidoxypropyl (methyl) dimethoxysilane.
- Q 1 represents a linear or branched alkylene group forming a carbon chain having two or more carbon atoms between a silicon atom and an ester bond
- Q 2 represents an oxygen atom and a side.
- R 4 represents an unsubstituted or substituted alkyl group having 1 to 6 carbon atoms
- An aluminum silicon alkoxide such as aluminum triethoxide, aluminum tripropoxide, aluminum tributoxide; titanium tetraethoxide, titanium tetrapropoxide, titanium tetraisopropoxide, Titanium alkoxides such as titanium tetrabutoxide, titanium tetraisobutoxide, titanium tetraisopropenyl oxide; Tetra isopropoxide, zirconium alkoxides such as zirconium tetrabutoxide; dially
- examples of Q 1 include an alkylene group such as ethylene, trimethylene, 2-methylethylene, and tetramethylene. From the viewpoint of easy synthesis and handling, an ethylene group and 2 -A methylethylene group is preferred. Examples of Q 2 include alkylene groups such as trimethylene, 2-methyltrimethylene and tetramethylene, and a trimethylene group is preferable from the viewpoint of easy synthesis and handling.
- R 4 examples include alkyl groups such as methyl, ethyl, propyl, isopropyl and butyl; and alkyl groups substituted with alkoxy such as 2-methoxyethyl, which give good adhesion and are alcohols generated by hydrolysis From the viewpoint of easily volatilizing, a methyl group and an ethyl group are preferable, and a methyl group is particularly preferable.
- the compounding amount of the adhesion-imparting agent can be 0.01 to 20 parts by weight with respect to 100 parts by weight of (A), preferably 0.1 to 10 parts by weight from the viewpoint of adhesion, More preferred is ⁇ 5 parts by weight.
- a curing inhibitor can be blended.
- the diallyl maleate is effective not only as an adhesion-imparting agent but also as a curing inhibitor.
- Other curing inhibitors include 3-methyl-1-butyn-3-ol, 3-methyl-1-pentyn-3-ol, 3,5-dimethyl-1-hexyn-3-ol, 1-ethynyl- Acetylene alcohols such as 1-cyclohexane-1-ol are exemplified.
- the blending amount of the curing inhibitor can be selected in any amount depending on the desired curability.
- the polyorganosiloxane composition of the present invention is provided with an inorganic filler for the purpose of providing appropriate fluidity at the stage before curing, and imparting the cured product with high mechanical strength required according to its use.
- an inorganic filler for the purpose of providing appropriate fluidity at the stage before curing, and imparting the cured product with high mechanical strength required according to its use.
- the inorganic filler include silica such as fumed silica, dry process silica such as arc silica; and wet process silica such as precipitated silica. These may be used as they are, or may be used after surface treatment with a hydrophobizing agent such as hexamethyldisilazane.
- diatomaceous earth ground quartz, fused quartz, titanium oxide, aluminum oxide, zinc oxide, aluminosilicate, calcium carbonate, organic acid surface treatment calcium carbonate, magnesium carbonate, zinc carbonate, calcium silicate, talc, ferric oxide are selected according to the extrusion workability and the physical properties required for the cured product.
- a conductive filler such as carbon black may be blended depending on the purpose.
- the blending amount of the inorganic filler can be 0 to 500 parts by weight with respect to 100 parts by weight of (A), and particularly 0 to 200 from the viewpoint of durability, mechanical strength and workability (viscosity) of the cured product. Part by weight is preferred.
- the polyorganosiloxane composition of the present invention includes a pigment, a thixotropy imparting agent, a viscosity modifier for improving extrusion workability, an ultraviolet ray inhibitor, a fungicide, a heat resistance improver, a difficulty
- a flame retardant may be added. In some cases, it may be dissolved or dispersed in an organic solvent such as toluene or xylene.
- the polyorganosiloxane composition of the present invention is prepared by uniformly kneading (A) to (C) and other components to be blended as necessary by a mixing means such as a universal kneader or a kneader. Can do.
- a mixing means such as a universal kneader or a kneader. Can do.
- two pre-blends are appropriately prepared and stored so that (B) and (C) are included in separate pre-blends.
- the silicone rubber composition may be prepared by mixing uniformly by a mixing means such as a mixing head of a quantitative mixer, and defoaming under reduced pressure for use.
- the polyorganosiloxane composition of the present invention can be cured by heating to obtain a cured product that is a rubber-like elastic body.
- cured material is not specifically limited, For example, after inject
- the conditions for heat curing can be appropriately selected, and the heating temperature can be arbitrarily set, for example, between 50 and 250 ° C.
- the heating time can be, for example, 1 minute to 24 hours.
- the cured product of the polyorganosiloxane composition of the present invention has excellent cold resistance, and the ratio of the elastic modulus at ⁇ 60 ° C. to the elastic modulus at 23 ° C. (shear elastic modulus ⁇ 60 ° C./shear elastic modulus 23 ° C. ) Can be set to 0.5 to 9.0.
- the ratio of the shear modulus is preferably 4.0 or less.
- the shear elastic modulus is a value measured with a viscoelasticity measuring device ARES (manufactured by TA Instruments).
- the silicone rubber product comprising the cured product of the polyorganosiloxane composition of the present invention is highly useful because it has excellent cold resistance and can also be expected to have the inherent heat resistance, cold resistance, weather resistance, and electrical insulation properties of silicone rubber. .
- it can be suitably used for adhesives, sealants and the like for parts of automobiles, vehicles, ships, airplanes, etc., and members of semiconductor devices.
- siloxane units are indicated by the following symbols.
- A1-1 both terminals blocked with M v basis, will intermediate units from D units, linear polymethylvinylsiloxane having a viscosity at 23 ° C.
- A2-1 branched polymethylvinylsiloxane consisting of M units, M v units and Q units and having a molar unit ratio of M 5 M v Q 8 ;
- A2-2 M units consist D v and Q units, branched polymethylvinylsiloxane molar units ratio represented by M 6 D v Q 8;
- B A linear polymethylhydrogensiloxane having both ends blocked with M units, an intermediate unit consisting of 50 mol% DH units and the remaining D units and represented by MD H 20 D 20 M.
- E-1 Formula: An isomer mixture of cyclic siloxanes represented by E-2:
- F-1 pulverized quartz having an average particle diameter of 4 ⁇ m (CRYSTALITE VX-S, manufactured by Tatsumori Co., Ltd., average particle diameter is 50% weight average when measuring particle size distribution by laser method)
- F-2 Surface-treated fumed silica obtained by surface treatment of fumed silica having a BET specific surface area of 300 m 2 / g with hexamethyldisilazane
- Examples 1-6, Comparative Examples 1-3 A polyorganosiloxane composition was prepared by the following method using the raw materials shown in Table 1.
- shear modulus Using the viscoelasticity measuring device ARES (manufactured by TA Instruments), the compositions of Examples and Comparative Examples were cured in a parallel plate at 150 ° C. for 1 hour so as to have a thickness of 1 mm. Thereafter, the shear elastic modulus was continuously measured at a measurement frequency of 1 Hz, a measurement strain of 0.5%, at a temperature of ⁇ 100 ° C. to 100 ° C., and at a rate of temperature increase of 10 ° C./min. Specifically, the stress on the opposite side was measured by twisting one plate.
- ARES viscoelasticity measuring device
- the ratio of the shear elastic modulus at ⁇ 60 ° C. to the shear elastic modulus at 23 ° C. of the cured product of the composition of each example was as small as 4.0 or less, and the Type D and Type A hardness were also in a favorable range.
- the silicone rubber product comprising the cured product of the polyorganosiloxane composition of the present invention has excellent cold resistance and can also be expected to have the inherent heat resistance, cold resistance, weather resistance, and electrical insulation properties of silicone rubber. Useful.
Landscapes
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- Polymers & Plastics (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Condensed Matter Physics & Semiconductors (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Computer Hardware Design (AREA)
- Microelectronics & Electronic Packaging (AREA)
- Power Engineering (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Materials Engineering (AREA)
- Wood Science & Technology (AREA)
- Compositions Of Macromolecular Compounds (AREA)
- Adhesives Or Adhesive Processes (AREA)
- Structures Or Materials For Encapsulating Or Coating Semiconductor Devices Or Solid State Devices (AREA)
Abstract
Description
(A)(A1)式(I):
Rは、独立して、R1又はR2であり、Rのうち、少なくとも2個はR1であり、
R1は、独立して、C2-C6アルケニル基であり、
R2は、独立して、C1-C6アルキル基であり、
nは、23℃での粘度を10~10,000cPとする数である)で示される直鎖状ポリオルガノシロキサン、及び
(A2)SiO4/2単位及びR'3SiO1/2単位、並びに場合によってはさらにR'2SiO単位及び/又はR'SiO3/2単位(式中、R'は、それぞれ独立して、非置換又は置換の、1価の脂肪族基又は脂環式基である)からなり、1分子当たり、少なくとも3個のR'がアルケニル基である分岐状ポリオルガノシロキサン
であり、
(A1)に対する(A2)の重量比が、1~5であり、
(A1)及び(A2)の合計量に占める、SiO4/2単位及び場合により存在するR'SiO3/2単位の重量割合が、20~60重量%である、アルケニル基含有ポリオルガノシロキサン;
(B)ケイ素原子に結合した水素原子を分子中に2個を越える数で有するポリオルガノハイドロジェンシロキサン;並びに
(C)白金族金属化合物
を含む硬化性ポリオルガノシロキサン組成物に関する。
本発明のポリオルガノシロキサン組成物は、(A)(A1)式(I):
Rは、独立して、R1又はR2であり、Rのうち、少なくとも2個はR1であり、
R1は、独立して、C2-C6アルケニル基であり、
R2は、独立して、C1-C6アルキル基であり、
nは、23℃での粘度を10~10,000cPとする数である)で示される直鎖状ポリオルガノシロキサン、及び
(A2)SiO4/2単位及びR'3SiO1/2単位、並びに場合によってはさらにR'2SiO単位及び/又はR'SiO3/2単位(式中、R'は、それぞれ独立して、1価の非置換又は置換の炭化水素基である)からなり、1分子当たり、少なくとも3個のR'がアルケニル基である分岐状ポリオルガノシロキサン
であり、
(A1)に対する(A2)の重量比((A2)/(A1))が、1~5であり、
(A1)及び(A2)の合計量に占める、SiO4/2単位及びR'SiO3/2単位の重量割合が、20~60重量%である、アルケニル基含有ポリオルガノシロキサンを含む。
本発明のポリオルガノシロキサン組成物は、(B)ケイ素原子に結合した水素原子を分子中に2個を越える数で有するポリオルガノハイドロジェンシロキサンを含む。(B)は、その分子中のヒドロシリル基が、(A)中のアルケニル基と付加反応することにより、(A)の架橋剤として機能する。そのような、(B)は、硬化物を網状化するために、付加反応に関与するヒドロシリル基を、分子中に2個を越える数、好ましくは3個以上有する。
(R3)cHdSiO(4-c-d)/2 (II)
(式中、
R3は、脂肪族不飽和炭素-炭素結合を含まない、非置換又は置換の、1価の脂肪族基又は脂環式基を表し;
cは、0~2の整数であり;
dは、1又は2であり、ただし、c+dは1~3の整数である)
で示される単位を、分子中に2個を越える数、好ましくは3個以上有する。
本発明のポリオルガノシロキサン組成物は、(C)白金族金属化合物を含む。(C)は、(A)中のアルケニル基と(B)中のヒドロシリル基との間の付加反応を促進させるための触媒として機能する。(C)としては、白金、ロジウム、パラジウムのような白金族金属原子の化合物が用いられ、塩化白金酸、塩化白金酸とアルコールの反応生成物、白金-オレフィン錯体、白金-ビニルシロキサン錯体、白金-ケトン錯体、白金-ホスフィン錯体のような白金化合物;ロジウム-ホスフィン錯体、ロジウム-スルフィド錯体のようなロジウム化合物;パラジウム-ホスフィン錯体のようなパラジウム化合物などが例示される。
M 単位: (CH3)3SiO1/2-
Mv単位: (CH3)2(CH2=CH)SiO1/2-
D 単位: -(CH3)2SiO-
DH単位: -(CH3)HSiO-
Dv単位: -(CH3)(CH2=CH)SiO-
Q 単位: SiO4/2(4官能性)
A1-1:両末端がMv単位で封鎖され、中間単位がD単位からなり、23℃における粘度が1500cPである直鎖状ポリメチルビニルシロキサン;
A1-2:両末端がMv単位で封鎖され、中間単位がD単位からなり、23℃における粘度が250cPである直鎖状ポリメチルビニルシロキサン;
A1-3:両末端がMv単位で封鎖され、中間単位がD単位からなり、23℃における粘度が60cPである直鎖状ポリメチルビニルシロキサン;
A1-4:両末端がMv単位で封鎖され、中間単位がD単位からなり、23℃における粘度が10,000cPである直鎖状ポリメチルビニルシロキサン;
A2-1:M単位、Mv単位及びQ単位からなり、モル単位比がM5MvQ8で示される分岐状ポリメチルビニルシロキサン;
A2-2:M単位、Dv単位及びQ単位からなり、モル単位比がM6DvQ8で示される分岐状ポリメチルビニルシロキサン;
B:両末端がM単位で封鎖され、中間単位が50モル%のDH単位と残余のD単位からなり、MDH 20D20Mで示される直鎖状ポリメチルハイドロジェンシロキサン。
C:塩化白金酸をDv 4で示される環状シロキサンと加熱することによって得られ、白金含有量が2重量%である錯体。
D:サーフィノール61(3,5-ジメチル-1-ヘキシン-3-オール(エアープロダクツジャパン株式会社製))
F-1:平均粒径4μmの粉砕石英(CRYSTALITE VX-S、龍森社製。平均粒径はレーザー法で粒度分布を測定した際の50%重量平均)
F-2:BET比表面積300m2/gの煙霧質シリカをヘキサメチルジシラザンで表面処理した表面処理煙霧質シリカ
下記の方法により、表1に示す原料を用いて、ポリオルガノシロキサン組成物を調製した。
実施例及び比較例の組成物について、弾性率及び硬さを以下のようにして測定した。評価結果を表1に示す。
粘弾性測定装置ARES(TAインストルメンツ社製)を用い、実施例及び比較例の組成物をパラレルプレート内に厚さ1mmになるように150℃、1時間で硬化させた。その後、測定周波数1Hz・測定歪0.5%で-100℃~100℃、昇温速度10℃/分で、せん断弾性率を連続的に測定した。具体的には、片方のプレートを捻って、反対側への応力を測定した。
縦60mm×横30mm×深さ6mmのテフロン(登録商標)コートしたアルミ製金型に、実施例及び比較例の組成物を流し込み、150℃、1時間で硬化させ、23℃まで冷却後、TypeAについては、JIS K6249に記載のようにして、TypeDについては、JIS K6253に記載のようにして、測定を行った。
Claims (7)
- (A)(A1)式(I):
Rは、独立して、R1又はR2であり、Rのうち、少なくとも2個はR1であり、
R1は、独立して、C2-C6アルケニル基であり、
R2は、独立して、C1-C6アルキル基であり、
nは、23℃での粘度を10~10,000cPとする数である)で示される直鎖状ポリオルガノシロキサン、及び
(A2)SiO4/2単位及びR'3SiO1/2単位、並びに場合によってはさらにR'2SiO単位及び/又はR'SiO3/2単位(式中、R'は、それぞれ独立して、非置換又は置換の、1価の脂肪族基又は脂環式基である)からなり、1分子当たり、少なくとも3個のR'がアルケニル基である分岐状ポリオルガノシロキサン
であり、
(A1)に対する(A2)の重量比が、1~5であり、
(A1)及び(A2)の合計量に占める、SiO4/2単位及び場合により存在するR'SiO3/2単位の重量割合が、20~60重量%である、アルケニル基含有ポリオルガノシロキサン;
(B)ケイ素原子に結合した水素原子を分子中に2個を越える数で有するポリオルガノハイドロジェンシロキサン;並びに
(C)白金族金属化合物
を含む硬化性ポリオルガノシロキサン組成物。 - (A)のR1がビニル基であり、かつ(A2)のアルケニル基であるR'がビニル基である、請求項1記載の硬化性ポリオルガノシロキサン組成物。
- (C)が、白金-ビニルシロキサン錯体である、請求項1~3のいずれか1項記載の硬化性ポリオルガノシロキサン組成物。
- さらに、無機充填剤を含有する、請求項1~4のいずれか1項記載の硬化性ポリオルガノシロキサン組成物。
- 請求項1~5のいずれか1項記載の硬化性ポリオルガノシロキサン組成物を含む接着剤。
- 請求項1~5のいずれか1項記載の硬化性ポリオルガノシロキサン組成物を用いて封止された半導体装置。
Priority Applications (6)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US13/699,433 US20130065999A1 (en) | 2010-10-14 | 2011-10-12 | Curable polyorganosiloxane composition |
| CN2011800493836A CN103154144A (zh) | 2010-10-14 | 2011-10-12 | 固化性聚有机硅氧烷组合物 |
| EP11832540.6A EP2628770B1 (en) | 2010-10-14 | 2011-10-12 | Curable polyorganosiloxane composition |
| KR1020137004748A KR101795109B1 (ko) | 2010-10-14 | 2011-10-12 | 경화성 폴리오르가노실록산 조성물 |
| JP2011544519A JP5002075B2 (ja) | 2010-10-14 | 2011-10-12 | 硬化性ポリオルガノシロキサン組成物 |
| US14/524,036 US9303164B2 (en) | 2010-10-14 | 2014-10-27 | Method of preparing a curable polyorganosiloxane composition |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010231383 | 2010-10-14 | ||
| JP2010-231383 | 2010-10-14 |
Related Child Applications (2)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| US13/699,433 A-371-Of-International US20130065999A1 (en) | 2010-10-14 | 2011-10-12 | Curable polyorganosiloxane composition |
| US14/524,036 Division US9303164B2 (en) | 2010-10-14 | 2014-10-27 | Method of preparing a curable polyorganosiloxane composition |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2012050105A1 true WO2012050105A1 (ja) | 2012-04-19 |
Family
ID=45938334
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2011/073375 WO2012050105A1 (ja) | 2010-10-14 | 2011-10-12 | 硬化性ポリオルガノシロキサン組成物 |
Country Status (7)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (2) | US20130065999A1 (ja) |
| EP (1) | EP2628770B1 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JP5002075B2 (ja) |
| KR (1) | KR101795109B1 (ja) |
| CN (1) | CN103154144A (ja) |
| TW (1) | TWI526499B (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2012050105A1 (ja) |
Cited By (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2014040522A (ja) * | 2012-08-22 | 2014-03-06 | Shin Etsu Chem Co Ltd | シリコーンゴム硬化物の難燃性向上方法 |
| JP2015172146A (ja) * | 2014-03-12 | 2015-10-01 | Jnc株式会社 | 熱硬化性樹脂組成物及びそれを用いた物品 |
| JP2019214640A (ja) * | 2018-06-11 | 2019-12-19 | 信越化学工業株式会社 | 付加硬化型液状導電性シリコーンゴム組成物及び電子写真式画像形成部材 |
| WO2019240123A1 (ja) * | 2018-06-12 | 2019-12-19 | モメンティブ・パフォーマンス・マテリアルズ・ジャパン合同会社 | 難燃性ポリオルガノシロキサン組成物、難燃性硬化物、および光学用部材 |
| JP2020023088A (ja) * | 2018-08-07 | 2020-02-13 | 日本特殊陶業株式会社 | 複合部材および接着剤組成物 |
| WO2020080326A1 (ja) | 2018-10-18 | 2020-04-23 | ダウ・東レ株式会社 | 耐寒性に優れる硬化性オルガノポリシロキサン組成物、パターン形成方法および電子部品等 |
| JP2020523422A (ja) * | 2018-06-29 | 2020-08-06 | ダウ シリコーンズ コーポレーション | 無溶剤シリコーン感圧接着剤並びにその製造方法及び使用方法 |
| JP2020132739A (ja) * | 2019-02-18 | 2020-08-31 | 信越化学工業株式会社 | ダイボンディング用シリコーン樹脂組成物、硬化物及び発光ダイオード素子 |
Families Citing this family (14)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP5854041B2 (ja) * | 2011-03-31 | 2016-02-09 | 住友ベークライト株式会社 | シリコーンゴム系硬化性組成物、シリコーンゴム系硬化性組成物の製造方法、シリコーンゴムの製造方法、シリコーンゴム、成形体および医療用チューブ |
| US20150307759A1 (en) | 2014-04-28 | 2015-10-29 | Ames Rubber Corporation | Solventless curable coating systems and uses thereof |
| CN105368064B (zh) * | 2014-08-27 | 2018-01-23 | 广州慧谷化学有限公司 | 有机聚硅氧烷组合物及其制备方法及半导体器件 |
| CN105713391B (zh) * | 2014-12-03 | 2018-11-09 | 广州慧谷化学有限公司 | 触变型有机聚硅氧烷组合物及半导体器件 |
| JP6657037B2 (ja) * | 2015-12-22 | 2020-03-04 | 信越化学工業株式会社 | 付加硬化性シリコーン樹脂組成物および半導体装置 |
| CN105670298A (zh) * | 2016-03-07 | 2016-06-15 | 惠州赛力珑新材料有限公司 | 一种加成型硅橡胶配方及粘接方法 |
| US10190031B2 (en) * | 2016-06-06 | 2019-01-29 | Jiali Wu | Thermally conductive interface composition and use thereof |
| EP3473677B1 (en) * | 2016-06-15 | 2021-08-04 | Momentive Performance Materials Japan LLC | Curable polyorganosiloxane composition and use thereof |
| CN106167621B (zh) * | 2016-08-03 | 2019-10-29 | 深圳市安品有机硅材料有限公司 | 阻燃型室温硫化液体硅橡胶 |
| CN110719939B (zh) * | 2017-05-31 | 2022-02-18 | 迈图高新材料日本合同公司 | 导热性聚硅氧烷组合物 |
| US20210395582A1 (en) * | 2018-11-13 | 2021-12-23 | Momentive Performance Materials Japan Llc | Adhesive polyorganosiloxane composition |
| JP6763105B1 (ja) * | 2018-12-25 | 2020-09-30 | モメンティブ・パフォーマンス・マテリアルズ・ジャパン合同会社 | 接着性ポリオルガノシロキサン組成物 |
| JP7003075B2 (ja) * | 2019-02-15 | 2022-01-20 | 信越化学工業株式会社 | ウェハーレベル光半導体デバイス用樹脂組成物及び該組成物を用いたウェハーレベル光半導体デバイス |
| CN115975200B (zh) * | 2022-12-27 | 2023-07-18 | 杭州崇耀科技发展有限公司 | 一种硅油离型剂用锚固剂及其使用方法 |
Citations (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH0753872A (ja) * | 1993-08-17 | 1995-02-28 | Shin Etsu Chem Co Ltd | 硬化性シリコーンゴム組成物 |
| JP2000169714A (ja) | 1998-12-07 | 2000-06-20 | Dow Corning Toray Silicone Co Ltd | 硬化性シリコーン組成物 |
| JP2001002922A (ja) | 1999-06-21 | 2001-01-09 | Shin Etsu Chem Co Ltd | 半導体装置封止用付加硬化型シリコーン組成物及び半導体装置 |
| JP2005042099A (ja) * | 2003-07-09 | 2005-02-17 | Shin Etsu Chem Co Ltd | シリコーンゴム組成物並びに発光半導体被覆保護材及び発光半導体装置 |
| JP2007002234A (ja) * | 2005-05-27 | 2007-01-11 | Shin Etsu Chem Co Ltd | 硬化性シリコーンゴム組成物及び半導体装置 |
| JP2007191504A (ja) * | 2006-01-17 | 2007-08-02 | Shin Etsu Chem Co Ltd | 硬化性シリコーンゴム組成物及びその硬化物 |
| JP2009215434A (ja) * | 2008-03-11 | 2009-09-24 | Shin Etsu Chem Co Ltd | シリコーン樹脂組成物及び発光半導体装置 |
| JP2009235265A (ja) * | 2008-03-27 | 2009-10-15 | Shin Etsu Chem Co Ltd | 硬化性シリコーンゴム組成物、およびそれを封止材料として用いた光半導体装置 |
| JP2009256603A (ja) * | 2008-03-24 | 2009-11-05 | Shin Etsu Chem Co Ltd | 硬化性シリコーンゴム組成物及び半導体装置 |
Family Cites Families (13)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US4988779A (en) * | 1989-04-17 | 1991-01-29 | General Electric Company | Addition cured silicone pressure sensitive adhesive |
| JP2001115025A (ja) * | 1999-10-20 | 2001-04-24 | Dow Corning Toray Silicone Co Ltd | 液状シリコーンゴム組成物、その製造方法およびシリコーンゴム発泡体の製造方法 |
| JP3912525B2 (ja) * | 2002-12-12 | 2007-05-09 | 信越化学工業株式会社 | 付加硬化型シリコーンゴム組成物及び粘着ゴムシート |
| TWI373150B (en) | 2003-07-09 | 2012-09-21 | Shinetsu Chemical Co | Silicone rubber composition, light-emitting semiconductor embedding/protecting material and light-emitting semiconductor device |
| US7588967B2 (en) * | 2005-05-27 | 2009-09-15 | Shin-Etsu Chemical Co., Ltd. | Curable silicone rubber composition and semiconductor device |
| JP5247979B2 (ja) * | 2005-06-01 | 2013-07-24 | モメンティブ・パフォーマンス・マテリアルズ・ジャパン合同会社 | 透明な硬化物を与えるポリオルガノシロキサン組成物 |
| JP2007161862A (ja) * | 2005-12-13 | 2007-06-28 | Momentive Performance Materials Japan Kk | 低温保存キット |
| EP2463343B1 (en) * | 2006-10-19 | 2014-04-02 | Momentive Performance Materials Japan LLC | Curable polyorganosiloxane composition |
| EP2727925B1 (en) * | 2007-04-17 | 2016-04-06 | Kaneka Corporation | Polyhedral polysiloxane modified product and composition using the modified product |
| JP2009021534A (ja) | 2007-06-15 | 2009-01-29 | Nuflare Technology Inc | 気相成長装置及び気相成長方法 |
| JP2009236265A (ja) | 2008-03-28 | 2009-10-15 | Mitsuba Corp | エンジン始動装置 |
| JP5342830B2 (ja) * | 2008-08-19 | 2013-11-13 | モメンティブ・パフォーマンス・マテリアルズ・ジャパン合同会社 | 光硬化性オルガノポリシロキサン組成物 |
| JP5499774B2 (ja) * | 2009-03-04 | 2014-05-21 | 信越化学工業株式会社 | 光半導体封止用組成物及びそれを用いた光半導体装置 |
-
2011
- 2011-10-12 KR KR1020137004748A patent/KR101795109B1/ko active IP Right Grant
- 2011-10-12 CN CN2011800493836A patent/CN103154144A/zh active Pending
- 2011-10-12 EP EP11832540.6A patent/EP2628770B1/en active Active
- 2011-10-12 JP JP2011544519A patent/JP5002075B2/ja active Active
- 2011-10-12 US US13/699,433 patent/US20130065999A1/en not_active Abandoned
- 2011-10-12 WO PCT/JP2011/073375 patent/WO2012050105A1/ja active Application Filing
- 2011-10-13 TW TW100137121A patent/TWI526499B/zh active
-
2014
- 2014-10-27 US US14/524,036 patent/US9303164B2/en active Active
Patent Citations (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH0753872A (ja) * | 1993-08-17 | 1995-02-28 | Shin Etsu Chem Co Ltd | 硬化性シリコーンゴム組成物 |
| JP2000169714A (ja) | 1998-12-07 | 2000-06-20 | Dow Corning Toray Silicone Co Ltd | 硬化性シリコーン組成物 |
| JP2001002922A (ja) | 1999-06-21 | 2001-01-09 | Shin Etsu Chem Co Ltd | 半導体装置封止用付加硬化型シリコーン組成物及び半導体装置 |
| JP2005042099A (ja) * | 2003-07-09 | 2005-02-17 | Shin Etsu Chem Co Ltd | シリコーンゴム組成物並びに発光半導体被覆保護材及び発光半導体装置 |
| JP2007002234A (ja) * | 2005-05-27 | 2007-01-11 | Shin Etsu Chem Co Ltd | 硬化性シリコーンゴム組成物及び半導体装置 |
| JP2007191504A (ja) * | 2006-01-17 | 2007-08-02 | Shin Etsu Chem Co Ltd | 硬化性シリコーンゴム組成物及びその硬化物 |
| JP2009215434A (ja) * | 2008-03-11 | 2009-09-24 | Shin Etsu Chem Co Ltd | シリコーン樹脂組成物及び発光半導体装置 |
| JP2009256603A (ja) * | 2008-03-24 | 2009-11-05 | Shin Etsu Chem Co Ltd | 硬化性シリコーンゴム組成物及び半導体装置 |
| JP2009235265A (ja) * | 2008-03-27 | 2009-10-15 | Shin Etsu Chem Co Ltd | 硬化性シリコーンゴム組成物、およびそれを封止材料として用いた光半導体装置 |
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| See also references of EP2628770A4 * |
Cited By (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2014040522A (ja) * | 2012-08-22 | 2014-03-06 | Shin Etsu Chem Co Ltd | シリコーンゴム硬化物の難燃性向上方法 |
| JP2015172146A (ja) * | 2014-03-12 | 2015-10-01 | Jnc株式会社 | 熱硬化性樹脂組成物及びそれを用いた物品 |
| JP2019214640A (ja) * | 2018-06-11 | 2019-12-19 | 信越化学工業株式会社 | 付加硬化型液状導電性シリコーンゴム組成物及び電子写真式画像形成部材 |
| WO2019240123A1 (ja) * | 2018-06-12 | 2019-12-19 | モメンティブ・パフォーマンス・マテリアルズ・ジャパン合同会社 | 難燃性ポリオルガノシロキサン組成物、難燃性硬化物、および光学用部材 |
| JPWO2019240123A1 (ja) * | 2018-06-12 | 2020-06-25 | モメンティブ・パフォーマンス・マテリアルズ・ジャパン合同会社 | 難燃性ポリオルガノシロキサン組成物、難燃性硬化物、および光学用部材 |
| JP2020523422A (ja) * | 2018-06-29 | 2020-08-06 | ダウ シリコーンズ コーポレーション | 無溶剤シリコーン感圧接着剤並びにその製造方法及び使用方法 |
| JP2020023088A (ja) * | 2018-08-07 | 2020-02-13 | 日本特殊陶業株式会社 | 複合部材および接着剤組成物 |
| WO2020080326A1 (ja) | 2018-10-18 | 2020-04-23 | ダウ・東レ株式会社 | 耐寒性に優れる硬化性オルガノポリシロキサン組成物、パターン形成方法および電子部品等 |
| KR20210080433A (ko) | 2018-10-18 | 2021-06-30 | 다우 도레이 캄파니 리미티드 | 내한성이 우수한 경화성 오가노폴리실록산 조성물, 패턴 형성 방법 및 전자 부품 등 |
| JP2020132739A (ja) * | 2019-02-18 | 2020-08-31 | 信越化学工業株式会社 | ダイボンディング用シリコーン樹脂組成物、硬化物及び発光ダイオード素子 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP2628770A1 (en) | 2013-08-21 |
| US20130065999A1 (en) | 2013-03-14 |
| CN103154144A (zh) | 2013-06-12 |
| US20150045487A1 (en) | 2015-02-12 |
| JPWO2012050105A1 (ja) | 2014-02-24 |
| TW201221582A (en) | 2012-06-01 |
| KR20130099921A (ko) | 2013-09-06 |
| EP2628770B1 (en) | 2014-12-31 |
| US9303164B2 (en) | 2016-04-05 |
| KR101795109B1 (ko) | 2017-11-07 |
| TWI526499B (zh) | 2016-03-21 |
| EP2628770A4 (en) | 2013-11-20 |
| JP5002075B2 (ja) | 2012-08-15 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5002075B2 (ja) | 硬化性ポリオルガノシロキサン組成物 | |
| JP6383885B2 (ja) | 熱伝導性ポリオルガノシロキサン組成物 | |
| JP4804775B2 (ja) | シール用硬化性ポリオルガノシロキサン組成物、およびガスケット | |
| JPWO2009044763A1 (ja) | 表示素子用シール剤 | |
| KR101802736B1 (ko) | 가교결합성 실리콘 조성물 및 그의 가교결합 생성물 | |
| JP5068988B2 (ja) | 接着性ポリオルガノシロキサン組成物 | |
| JP2013124297A (ja) | 硬化性ポリオルガノシロキサン組成物 | |
| JP6945934B2 (ja) | 接着性ポリオルガノシロキサン組成物 | |
| JP2004323764A (ja) | 接着性ポリオルガノシロキサン組成物 | |
| JP5031436B2 (ja) | 低透湿性ポリオルガノシロキサン組成物 | |
| JP4522816B2 (ja) | 難燃性を有する接着性ポリオルガノシロキサン組成物 | |
| JP5080224B2 (ja) | 耐溶剤性シリコーンゴム組成物 | |
| JP5060165B2 (ja) | 低透湿性ポリオルガノシロキサン組成物 | |
| JP4553562B2 (ja) | 接着性ポリオルガノシロキサン組成物 | |
| WO2018139506A1 (ja) | 熱伝導性ポリオルガノシロキサン組成物 | |
| JP5117320B2 (ja) | ポリオルガノシロキサン組成物 | |
| JP6763105B1 (ja) | 接着性ポリオルガノシロキサン組成物 | |
| JP2021167283A (ja) | 無水コハク酸基含有環状オルガノシロキサン、前記無水コハク酸基含有環状オルガノシロキサンを含む付加硬化型シリコーン組成物、及びそれらの使用 | |
| TWI838442B (zh) | 接著性聚有機矽氧烷組成物 | |
| JP2012237007A (ja) | 耐溶剤性シリコーンゴム組成物 | |
| EP4370606A1 (en) | Thermal conductive silicone composition | |
| JP2017036416A (ja) | 硬化性シリコーン樹脂組成物及びその硬化物 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 201180049383.6 Country of ref document: CN |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 2011544519 Country of ref document: JP |
|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 11832540 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 13699433 Country of ref document: US |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 2011832540 Country of ref document: EP |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 20137004748 Country of ref document: KR Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |