JP6816046B2 - 半導体装置の製造方法 - Google Patents
半導体装置の製造方法 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP6816046B2 JP6816046B2 JP2018019434A JP2018019434A JP6816046B2 JP 6816046 B2 JP6816046 B2 JP 6816046B2 JP 2018019434 A JP2018019434 A JP 2018019434A JP 2018019434 A JP2018019434 A JP 2018019434A JP 6816046 B2 JP6816046 B2 JP 6816046B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- support substrate
- manufacturing
- semiconductor device
- layer
- peripheral portion
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 title claims description 98
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 title claims description 57
- 239000010410 layer Substances 0.000 claims description 165
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 claims description 156
- 238000005520 cutting process Methods 0.000 claims description 73
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 claims description 51
- 230000002093 peripheral effect Effects 0.000 claims description 36
- RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Copper Chemical compound [Cu] RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 35
- 229910052802 copper Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 33
- 239000010949 copper Substances 0.000 claims description 33
- 239000011229 interlayer Substances 0.000 claims description 29
- 238000007789 sealing Methods 0.000 claims description 24
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 claims description 22
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 22
- 238000009713 electroplating Methods 0.000 claims description 6
- 239000011521 glass Substances 0.000 claims description 6
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 24
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 24
- 238000007747 plating Methods 0.000 description 11
- 229910000679 solder Inorganic materials 0.000 description 11
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 description 9
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 7
- 229920002120 photoresistant polymer Polymers 0.000 description 7
- 238000000926 separation method Methods 0.000 description 6
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 5
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 5
- 239000000853 adhesive Substances 0.000 description 4
- 230000001070 adhesive effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- 238000004544 sputter deposition Methods 0.000 description 4
- 239000011347 resin Substances 0.000 description 3
- 229920005989 resin Polymers 0.000 description 3
- OKTJSMMVPCPJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N Carbon Chemical compound [C] OKTJSMMVPCPJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 238000002679 ablation Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000002411 adverse Effects 0.000 description 2
- 229910045601 alloy Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000000956 alloy Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910052799 carbon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 229910052804 chromium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 238000000748 compression moulding Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000011889 copper foil Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000007772 electroless plating Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000005530 etching Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000004907 flux Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000003999 initiator Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000007689 inspection Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000005304 joining Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910052759 nickel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 229910052719 titanium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000004215 Carbon black (E152) Substances 0.000 description 1
- XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicon Chemical compound [Si] XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910003481 amorphous carbon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000003990 capacitor Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000011203 carbon fibre reinforced carbon Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000919 ceramic Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000003795 chemical substances by application Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000007822 coupling agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000003822 epoxy resin Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000945 filler Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000007429 general method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910021385 hard carbon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229930195733 hydrocarbon Natural products 0.000 description 1
- 150000002430 hydrocarbons Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 230000001678 irradiating effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010030 laminating Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000000608 laser ablation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000007246 mechanism Effects 0.000 description 1
- 150000002739 metals Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 229910052750 molybdenum Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 210000003205 muscle Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 229920000647 polyepoxide Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 238000007639 printing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910052710 silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000010703 silicon Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052715 tantalum Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910052721 tungsten Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 238000001771 vacuum deposition Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L24/00—Arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies; Methods or apparatus related thereto
- H01L24/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L24/18—High density interconnect [HDI] connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L24/19—Manufacturing methods of high density interconnect preforms
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L23/00—Details of semiconductor or other solid state devices
- H01L23/12—Mountings, e.g. non-detachable insulating substrates
- H01L23/13—Mountings, e.g. non-detachable insulating substrates characterised by the shape
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/67—Apparatus specially adapted for handling semiconductor or electric solid state devices during manufacture or treatment thereof; Apparatus specially adapted for handling wafers during manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or electric solid state devices or components ; Apparatus not specifically provided for elsewhere
- H01L21/683—Apparatus specially adapted for handling semiconductor or electric solid state devices during manufacture or treatment thereof; Apparatus specially adapted for handling wafers during manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or electric solid state devices or components ; Apparatus not specifically provided for elsewhere for supporting or gripping
- H01L21/6835—Apparatus specially adapted for handling semiconductor or electric solid state devices during manufacture or treatment thereof; Apparatus specially adapted for handling wafers during manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or electric solid state devices or components ; Apparatus not specifically provided for elsewhere for supporting or gripping using temporarily an auxiliary support
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/04—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof the devices having potential barriers, e.g. a PN junction, depletion layer or carrier concentration layer
- H01L21/50—Assembly of semiconductor devices using processes or apparatus not provided for in a single one of the subgroups H01L21/06 - H01L21/326, e.g. sealing of a cap to a base of a container
- H01L21/56—Encapsulations, e.g. encapsulation layers, coatings
- H01L21/561—Batch processing
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/70—Manufacture or treatment of devices consisting of a plurality of solid state components formed in or on a common substrate or of parts thereof; Manufacture of integrated circuit devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/71—Manufacture of specific parts of devices defined in group H01L21/70
- H01L21/76—Making of isolation regions between components
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/70—Manufacture or treatment of devices consisting of a plurality of solid state components formed in or on a common substrate or of parts thereof; Manufacture of integrated circuit devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/77—Manufacture or treatment of devices consisting of a plurality of solid state components or integrated circuits formed in, or on, a common substrate
- H01L21/78—Manufacture or treatment of devices consisting of a plurality of solid state components or integrated circuits formed in, or on, a common substrate with subsequent division of the substrate into plural individual devices
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L23/00—Details of semiconductor or other solid state devices
- H01L23/28—Encapsulations, e.g. encapsulating layers, coatings, e.g. for protection
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L23/00—Details of semiconductor or other solid state devices
- H01L23/32—Holders for supporting the complete device in operation, i.e. detachable fixtures
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L23/00—Details of semiconductor or other solid state devices
- H01L23/48—Arrangements for conducting electric current to or from the solid state body in operation, e.g. leads, terminal arrangements ; Selection of materials therefor
- H01L23/482—Arrangements for conducting electric current to or from the solid state body in operation, e.g. leads, terminal arrangements ; Selection of materials therefor consisting of lead-in layers inseparably applied to the semiconductor body
- H01L23/485—Arrangements for conducting electric current to or from the solid state body in operation, e.g. leads, terminal arrangements ; Selection of materials therefor consisting of lead-in layers inseparably applied to the semiconductor body consisting of layered constructions comprising conductive layers and insulating layers, e.g. planar contacts
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L23/00—Details of semiconductor or other solid state devices
- H01L23/52—Arrangements for conducting electric current within the device in operation from one component to another, i.e. interconnections, e.g. wires, lead frames
- H01L23/522—Arrangements for conducting electric current within the device in operation from one component to another, i.e. interconnections, e.g. wires, lead frames including external interconnections consisting of a multilayer structure of conductive and insulating layers inseparably formed on the semiconductor body
- H01L23/525—Arrangements for conducting electric current within the device in operation from one component to another, i.e. interconnections, e.g. wires, lead frames including external interconnections consisting of a multilayer structure of conductive and insulating layers inseparably formed on the semiconductor body with adaptable interconnections
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H05—ELECTRIC TECHNIQUES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H05K—PRINTED CIRCUITS; CASINGS OR CONSTRUCTIONAL DETAILS OF ELECTRIC APPARATUS; MANUFACTURE OF ASSEMBLAGES OF ELECTRICAL COMPONENTS
- H05K3/00—Apparatus or processes for manufacturing printed circuits
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H05—ELECTRIC TECHNIQUES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H05K—PRINTED CIRCUITS; CASINGS OR CONSTRUCTIONAL DETAILS OF ELECTRIC APPARATUS; MANUFACTURE OF ASSEMBLAGES OF ELECTRICAL COMPONENTS
- H05K3/00—Apparatus or processes for manufacturing printed circuits
- H05K3/46—Manufacturing multilayer circuits
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/04—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof the devices having potential barriers, e.g. a PN junction, depletion layer or carrier concentration layer
- H01L21/50—Assembly of semiconductor devices using processes or apparatus not provided for in a single one of the subgroups H01L21/06 - H01L21/326, e.g. sealing of a cap to a base of a container
- H01L21/56—Encapsulations, e.g. encapsulation layers, coatings
- H01L21/568—Temporary substrate used as encapsulation process aid
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2221/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof covered by H01L21/00
- H01L2221/67—Apparatus for handling semiconductor or electric solid state devices during manufacture or treatment thereof; Apparatus for handling wafers during manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or electric solid state devices or components; Apparatus not specifically provided for elsewhere
- H01L2221/683—Apparatus for handling semiconductor or electric solid state devices during manufacture or treatment thereof; Apparatus for handling wafers during manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or electric solid state devices or components; Apparatus not specifically provided for elsewhere for supporting or gripping
- H01L2221/68304—Apparatus for handling semiconductor or electric solid state devices during manufacture or treatment thereof; Apparatus for handling wafers during manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or electric solid state devices or components; Apparatus not specifically provided for elsewhere for supporting or gripping using temporarily an auxiliary support
- H01L2221/68318—Auxiliary support including means facilitating the separation of a device or wafer from the auxiliary support
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2221/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof covered by H01L21/00
- H01L2221/67—Apparatus for handling semiconductor or electric solid state devices during manufacture or treatment thereof; Apparatus for handling wafers during manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or electric solid state devices or components; Apparatus not specifically provided for elsewhere
- H01L2221/683—Apparatus for handling semiconductor or electric solid state devices during manufacture or treatment thereof; Apparatus for handling wafers during manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or electric solid state devices or components; Apparatus not specifically provided for elsewhere for supporting or gripping
- H01L2221/68304—Apparatus for handling semiconductor or electric solid state devices during manufacture or treatment thereof; Apparatus for handling wafers during manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or electric solid state devices or components; Apparatus not specifically provided for elsewhere for supporting or gripping using temporarily an auxiliary support
- H01L2221/68327—Apparatus for handling semiconductor or electric solid state devices during manufacture or treatment thereof; Apparatus for handling wafers during manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or electric solid state devices or components; Apparatus not specifically provided for elsewhere for supporting or gripping using temporarily an auxiliary support used during dicing or grinding
- H01L2221/68331—Apparatus for handling semiconductor or electric solid state devices during manufacture or treatment thereof; Apparatus for handling wafers during manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or electric solid state devices or components; Apparatus not specifically provided for elsewhere for supporting or gripping using temporarily an auxiliary support used during dicing or grinding of passive members, e.g. die mounting substrate
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2221/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof covered by H01L21/00
- H01L2221/67—Apparatus for handling semiconductor or electric solid state devices during manufacture or treatment thereof; Apparatus for handling wafers during manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or electric solid state devices or components; Apparatus not specifically provided for elsewhere
- H01L2221/683—Apparatus for handling semiconductor or electric solid state devices during manufacture or treatment thereof; Apparatus for handling wafers during manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or electric solid state devices or components; Apparatus not specifically provided for elsewhere for supporting or gripping
- H01L2221/68304—Apparatus for handling semiconductor or electric solid state devices during manufacture or treatment thereof; Apparatus for handling wafers during manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or electric solid state devices or components; Apparatus not specifically provided for elsewhere for supporting or gripping using temporarily an auxiliary support
- H01L2221/68345—Apparatus for handling semiconductor or electric solid state devices during manufacture or treatment thereof; Apparatus for handling wafers during manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or electric solid state devices or components; Apparatus not specifically provided for elsewhere for supporting or gripping using temporarily an auxiliary support used as a support during the manufacture of self supporting substrates
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2221/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof covered by H01L21/00
- H01L2221/67—Apparatus for handling semiconductor or electric solid state devices during manufacture or treatment thereof; Apparatus for handling wafers during manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or electric solid state devices or components; Apparatus not specifically provided for elsewhere
- H01L2221/683—Apparatus for handling semiconductor or electric solid state devices during manufacture or treatment thereof; Apparatus for handling wafers during manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or electric solid state devices or components; Apparatus not specifically provided for elsewhere for supporting or gripping
- H01L2221/68304—Apparatus for handling semiconductor or electric solid state devices during manufacture or treatment thereof; Apparatus for handling wafers during manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or electric solid state devices or components; Apparatus not specifically provided for elsewhere for supporting or gripping using temporarily an auxiliary support
- H01L2221/68381—Details of chemical or physical process used for separating the auxiliary support from a device or wafer
- H01L2221/68386—Separation by peeling
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2223/00—Details relating to semiconductor or other solid state devices covered by the group H01L23/00
- H01L2223/58—Structural electrical arrangements for semiconductor devices not otherwise provided for
- H01L2223/64—Impedance arrangements
- H01L2223/66—High-frequency adaptations
- H01L2223/6661—High-frequency adaptations for passive devices
- H01L2223/6677—High-frequency adaptations for passive devices for antenna, e.g. antenna included within housing of semiconductor device
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/10—Bump connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/12—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors prior to the connecting process
- H01L2224/13—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors prior to the connecting process of an individual bump connector
- H01L2224/13001—Core members of the bump connector
- H01L2224/13099—Material
- H01L2224/131—Material with a principal constituent of the material being a metal or a metalloid, e.g. boron [B], silicon [Si], germanium [Ge], arsenic [As], antimony [Sb], tellurium [Te] and polonium [Po], and alloys thereof
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/10—Bump connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/12—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors prior to the connecting process
- H01L2224/13—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors prior to the connecting process of an individual bump connector
- H01L2224/13001—Core members of the bump connector
- H01L2224/13099—Material
- H01L2224/131—Material with a principal constituent of the material being a metal or a metalloid, e.g. boron [B], silicon [Si], germanium [Ge], arsenic [As], antimony [Sb], tellurium [Te] and polonium [Po], and alloys thereof
- H01L2224/13138—Material with a principal constituent of the material being a metal or a metalloid, e.g. boron [B], silicon [Si], germanium [Ge], arsenic [As], antimony [Sb], tellurium [Te] and polonium [Po], and alloys thereof the principal constituent melting at a temperature of greater than or equal to 950°C and less than 1550°C
- H01L2224/13147—Copper [Cu] as principal constituent
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/10—Bump connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/15—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors after the connecting process
- H01L2224/16—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors after the connecting process of an individual bump connector
- H01L2224/161—Disposition
- H01L2224/16151—Disposition the bump connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive
- H01L2224/16221—Disposition the bump connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked
- H01L2224/16225—Disposition the bump connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked the item being non-metallic, e.g. insulating substrate with or without metallisation
- H01L2224/16238—Disposition the bump connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked the item being non-metallic, e.g. insulating substrate with or without metallisation the bump connector connecting to a bonding area protruding from the surface of the item
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/80—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected
- H01L2224/81—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected using a bump connector
- H01L2224/81001—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected using a bump connector involving a temporary auxiliary member not forming part of the bonding apparatus
- H01L2224/81005—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected using a bump connector involving a temporary auxiliary member not forming part of the bonding apparatus being a temporary or sacrificial substrate
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/80—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected
- H01L2224/81—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected using a bump connector
- H01L2224/81009—Pre-treatment of the bump connector or the bonding area
- H01L2224/81024—Applying flux to the bonding area
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/80—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected
- H01L2224/81—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected using a bump connector
- H01L2224/812—Applying energy for connecting
- H01L2224/81201—Compression bonding
- H01L2224/81205—Ultrasonic bonding
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/93—Batch processes
- H01L2224/95—Batch processes at chip-level, i.e. with connecting carried out on a plurality of singulated devices, i.e. on diced chips
- H01L2224/97—Batch processes at chip-level, i.e. with connecting carried out on a plurality of singulated devices, i.e. on diced chips the devices being connected to a common substrate, e.g. interposer, said common substrate being separable into individual assemblies after connecting
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L23/00—Details of semiconductor or other solid state devices
- H01L23/28—Encapsulations, e.g. encapsulating layers, coatings, e.g. for protection
- H01L23/31—Encapsulations, e.g. encapsulating layers, coatings, e.g. for protection characterised by the arrangement or shape
- H01L23/3107—Encapsulations, e.g. encapsulating layers, coatings, e.g. for protection characterised by the arrangement or shape the device being completely enclosed
- H01L23/3121—Encapsulations, e.g. encapsulating layers, coatings, e.g. for protection characterised by the arrangement or shape the device being completely enclosed a substrate forming part of the encapsulation
- H01L23/3128—Encapsulations, e.g. encapsulating layers, coatings, e.g. for protection characterised by the arrangement or shape the device being completely enclosed a substrate forming part of the encapsulation the substrate having spherical bumps for external connection
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L24/00—Arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies; Methods or apparatus related thereto
- H01L24/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L24/10—Bump connectors ; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L24/12—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors prior to the connecting process
- H01L24/13—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors prior to the connecting process of an individual bump connector
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L24/00—Arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies; Methods or apparatus related thereto
- H01L24/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L24/10—Bump connectors ; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L24/15—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors after the connecting process
- H01L24/16—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors after the connecting process of an individual bump connector
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L24/00—Arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies; Methods or apparatus related thereto
- H01L24/80—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected
- H01L24/81—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected using a bump connector
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/15—Details of package parts other than the semiconductor or other solid state devices to be connected
- H01L2924/151—Die mounting substrate
- H01L2924/153—Connection portion
- H01L2924/1531—Connection portion the connection portion being formed only on the surface of the substrate opposite to the die mounting surface
- H01L2924/15311—Connection portion the connection portion being formed only on the surface of the substrate opposite to the die mounting surface being a ball array, e.g. BGA
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/15—Details of package parts other than the semiconductor or other solid state devices to be connected
- H01L2924/181—Encapsulation
- H01L2924/182—Disposition
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/19—Details of hybrid assemblies other than the semiconductor or other solid state devices to be connected
- H01L2924/1901—Structure
- H01L2924/1904—Component type
- H01L2924/19041—Component type being a capacitor
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/19—Details of hybrid assemblies other than the semiconductor or other solid state devices to be connected
- H01L2924/1901—Structure
- H01L2924/1904—Component type
- H01L2924/19042—Component type being an inductor
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/19—Details of hybrid assemblies other than the semiconductor or other solid state devices to be connected
- H01L2924/191—Disposition
- H01L2924/19101—Disposition of discrete passive components
- H01L2924/19105—Disposition of discrete passive components in a side-by-side arrangement on a common die mounting substrate
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Microelectronics & Electronic Packaging (AREA)
- Computer Hardware Design (AREA)
- Power Engineering (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Condensed Matter Physics & Semiconductors (AREA)
- Manufacturing & Machinery (AREA)
- Internal Circuitry In Semiconductor Integrated Circuit Devices (AREA)
- Production Of Multi-Layered Print Wiring Board (AREA)
- Dicing (AREA)
- Bipolar Transistors (AREA)
- Crystals, And After-Treatments Of Crystals (AREA)
Description
特許文献1には、表面上に密着金属層、剥離層、反射防止層および極薄銅層を備えたガラスで構成されるキャリア(支持基板)を用いるプリント配線板(半導体装置)の製造方法が開示される。
しかし、支持基板の周辺部は、成膜条件が不安定なため配線層や絶縁層を安定した膜厚で成膜することが難しく、また、周辺部には配線層の形成のための電気めっき工程において給電機構(給電用電極)を接触させる必要があり、これによりキズ等が発生し易い。
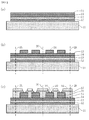
図1から図6は、本発明の第1の実施形態による半導体装置30の製造方法を説明するための図である。図1から図5は、支持基板11上に、配線層16、半導体チップ23、封止層24等からなる中間積層体29を形成していく工程等を説明する断面図であり、図6は、支持基板11上に中間積層体29が複数並列して形成された状態を示す上面図である。ただし、図6では後述する封止層24等の一部の部材は図示を省略している。
図6を参照して、本例の製造工程の概要を説明する。
図6に示すように、本例では、支持基板11は略正方形で、一辺が100〜300mm程度である。そして、本例においては、図6に示すとおり、この支持基板11上に、後述する封止層や半導体チップおよび配線層を含む中間積層体29を複数並列して形成する。
その後、図6中に破線で示した左端切断線2L、右端切断線2R、上端切断線2U、下端切断線2Dの位置にて、支持基板11の周辺部を切断する。左端切断線2L、右端切断線2R、上端切断線2Uおよび下端切断線2Dを、総称して切断線2と呼ぶ。
中間積層体29は、後述するその後の工程を経て、半導体装置30として完成される。 切断線2の位置および分離線3の間隔は、半導体装置30の大きさ(面積)に応じて設定される。
以下、図1から図5を参照して、支持基板11上に、配線層16、半導体チップ23、封止層24等からなる中間積層体29を形成する工程、および半導体装置30を形成する
工程を説明する。
図1(a)は、製造工程の初期おける支持基板11の断面構造を示す図である。支持基板11の構成は、特許第6203988号公報に開示されるキャリア付き銅箔と同様の構成である。支持基板11自体はガラスからなり、その主面(おもて側の面であって、図中の上方の面)に、基板側から順に密着金属層12と、剥離層13と、反射防止層14と、薄銅層15が形成されている。上記の各層を構成する材料や厚さも、特許第6203988号公報に開示されるキャリア付き銅箔と同様の構成でよい。
密着金属層12は支持基板11との密着性を確保する点から、Ti、Cr及びNiからなる群から選択される少なくとも1種の金属で構成される層であるのが好ましく、純金属であってもよいし、合金であってもよい。密着金属層12の厚さは、10〜300nm程度が好ましい。
剥離層13は、主として炭素を含んでなる層であるのが剥離容易性や膜形成性の点等から好ましく、より好ましくは主として炭素又は炭化水素からなる層であり、さらに好ましくは硬質炭素膜であるアモルファスカーボンからなる。剥離層13の厚さは、1〜20nm程度が好ましい。
薄銅層15は、厚さが50〜2000nm程度の銅を主成分とする層である。薄銅層15は、真空蒸着やスパッタリングまたはめっきにより形成することが好ましい。
また、上記の条件に適した、剥離層13等の形成された支持基板11が販売されていれば、それを購入して、すなわち用意して、使用してもよい。
図1(b)は、支持基板11上の最上層である薄銅層15の上に、半導体装置30の一部となる下段パッド16を形成した状態を示している。下段パッド16の形成に際しては、始めに薄銅層15上の全面に不図示のフォトレジスト層を形成し、このフォトレジスト層に下段パッド16の形状に対応する所望のパターンを形成する。
図1(b)は、下段パッド16を形成した後にフォトレジストを除去した状態を示している。
下段パッド16と後述する層間絶縁膜17との密着性を向上するために、下段パッド16の表面および側面に粗面化処理を行うか、あるいはカップリング剤を形成して、両者の密着性を向上させてもよい。
また、上記の工程に基づいて、フォトレジストに形成するパターンの形状により、下段パッド16と同時に支持基板11上の異なる2箇所を電気的に導通させるための配線を形成することもできる。
図1(c)は、支持基板11上に、下段パッド16を覆うように層間絶縁膜17を形成し、その上にドライフィルムレジスト19を形成した状態を示している。層間絶縁膜17の材料としては、シリコンフィラーを80%以上含有するエポキシ樹脂等を使用する。層間絶縁膜17は、印刷法や圧縮成型法、またはシート状の樹脂フィルムを真空ラミネートする方法で形成し、形成後にある程度の硬化処理を行う。
そして、その上にドライフィルムレジスト19を形成し、レーザー照射によるアブレーション等によりドライフィルムレジスト19内の所定の箇所であってスルーホール18と部分的に重なる箇所に、開口20を形成する。
図1(c)は、開口20が形成された状態を示している。
切断線2より外側の支持基板11上の層間絶縁膜17の上に形成された上記の不図示のめっきシード層に給電用電極を取り付ける。そして、支持基板11をめっき液に浸し銅めっき等の電解めっきを行うことで、スルーホール18および開口20の内部に銅等の金属を堆積させることで、ビアおよび上段パッド21(以下、併せて上段パッド21と呼ぶ)を形成する。
図2(a)は、スルーホール18および開口20の内部に上段パッド21が形成された状態を示している。
なお、下段パッド16と上段パッド21はともに導電性の部材であるため、これらを配線層と呼ぶこともできる。
その後、ドライフィルムレジスト19を除去し、層間絶縁膜17の硬化処理を行う。また、層間絶縁膜17上に形成した上記の不図示のめっきシード層の除去(エッチング)を行う。これらの除去は、公知の一般的な方法で行えばよい。
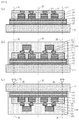
図2(b)は、上記で形成した支持基板11上の積層物(下段パッド16、上段パッド21および層間絶縁膜17)の上に、半導体チップ23を接合し、半導体チップ23を封止層24で封止した状態を表している。
半導体チップ23の接合に際しては、予め半導体チップ23の電極端子としてはんだ付き銅ピラー22を形成しておき、各銅ピラー22が所定の上段パッド21上の重なるように、半導体チップ23を配置する。そして、銅ピラー22と上段パッド21とをフラックス剤を使用して仮固定し、その後C4(Controlled Collapse Chip Connection)接合する。
この後、半導体チップ23および支持基板11の主面(図2(b)中の上側の面)を覆うように、コンプレッションモールド法などにより樹脂による封止層24を形成する。封止層24は、下段パッド16、上段パッド21および層間絶縁膜17の上面や側面も覆い、支持基板11上に形成されている剥離層13または剥離層13より上層にある反射防止層14も覆う。
中間積層体29の形成後、支持基板11の周辺部を切断する。すなわち、支持基板11のうち、図6に示した上述の切断線2よりも外側の部分を切断する。
図2(c)は、周辺部の切断のために中間積層体29が形成された主面を下側に向けて配置された支持基板11を示している。なお、図2(b)と図2(c)では、支持基板11が紙面に垂直な線を回転中心として180度回転しているため、右端切断線2Rと左端切断線2Lの位置関係が入れ替わっている。
同様に、支持基板11の裏面の上端切断線2Uと下端切断線2Dに相当する部分にも、切り筋を形成する。
同様に、上端切断線2Uと下端切断線2Dに相当する部分においても、支持基板11の主面側の封止層24等の積層物を切断する。
この状態の支持基板11に対し周辺部(切断線2よりも外周部)に撃力を加えることにより、支持基板11を切断線2の位置で割断(ブレーク)する。
なお、切り筋4R、4Lは、この割断(ブレーク)を行うために形成するクラックであるので、割断予定線とみることもできる。
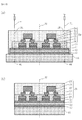
図4(a)は、周辺部を割断した支持基板11および中間積層体29を、剥離装置(80、81)に装着し、支持基板11から中間積層体29を剥離する状態を示している。
剥離装置は、一例として、支持基板11を載置する載置台80と、ニードル等の亀裂イニシエータ82が設けられた剥離アーム81を備える装置である。
続いて、支持基板11から剥離した中間積層体29から、剥離面に残存する剥離層13の残骸、反射防止層14、および薄銅層15を除去する。
図5(a)は、中間積層体29の下段パッド16に、はんだボールを形成するために、
層間絶縁膜17の上にソルダーレジスト25を形成し、下段パッド16上のソルダーレジスト25に開口27を形成した状態を示している。図5(a)では、中間積層体29は図4(b)に示した状態から回転(上下反転)して表されている。
この後、フラックスをソルダーレジスト25の開口27上に塗布し、はんだボール26を下段パッド16上に仮固定し、その後リフローを行ってはんだボール26を固定する。
図5(b)は、はんだボール26が固定された状態の中間積層体29を示している。
その後、複数並列して、すなわち複数個が連続したままの中間積層体29のそれぞれを回路テスター等でテストし、ダイシングソーを使用してダイシング(個片化)する。
図5(c)は、ダイシングされ完成した状態の半導体装置30を示している。
なお、図1から図5の各図では、説明を容易にするために、支持基板11の面内方向の長さに対して厚さ方向の長さを拡大して示している。
なお、製造する半導体装置30の用途によっては、上述のはんだボールの形成工程を省略してもよい。
以下、図7を参照して、変形例1から4について説明する。
以下の変形例は、支持基板11の切断方法に関する変形例である。よって、支持基板11の切断方法以外については、上述の第1の実施形態と同様であるので説明を省略する。
図7(a)は、変形例1で使用する支持基板11aを示す。
支持基板11aには、上述の第1の実施形態で使用する支持基板11と同様に、その主面に基板側から順に密着金属層12と、剥離層13と、反射防止層14と、薄銅層15が形成されている。ただし、その裏面(上記の主面とは反対側の面)には、左端切断線2Lおよび右端切断線2R等の切断線2に相当する位置に、予め切り筋4aLおよび4aRを形成しておく。
切り筋4aLおよび4aRと、密着金属層12、剥離層13、反射防止層14および薄銅層15は、どちらを先に形成してもかまわない。ただし、切り筋4aLおよび4aRは、支持基板11a上に配線層(下段パッド16)を形成する前に行うことが好ましい。
なお、変形例1の切り筋4aLおよび4aRについても、上述の第1の実施形態での切り筋4Lおよび4Rと同様に、割断予定線とみることもできる。
図7(b)は、変形例2で使用する支持基板11bを示す。
変形例2では、支持基板11bの主面の左端切断線2Lおよび右端切断線2R等の切断線2に相当する位置に、予め切り筋4bLおよび4bRを形成しておく。そして、その後に、不図示ではあるがその主面に、基板側から順に密着金属層12、剥離層13と、反射防止層14と、薄銅層15を形成しておく。
なお、変形例2の切り筋4bLおよび4bRについても、上述の第1の実施形態での切り筋4Lおよび4Rと同様に、割断予定線とみることもできる。
図7(c)は、変形例3で使用する支持基板11cを示す。
支持基板11cには、上述の第1の実施形態で使用する支持基板11と同様に、その主面に基板側から順に密着金属層12、剥離層13と、反射防止層14と、薄銅層15が形成されている。そして、支持基板11cの内部の、左端切断線2Lおよび右端切断線2R等の切断線2に相当する位置には、他の部分と比較して強度の弱い劣化部分4cLおよび4cRを形成しておく。
劣化部分4cLおよび4cRが割断(ブレーク)の開始点として機能するため、本変形例3でも、半導体装置の製造工程の中で支持基板11cの裏面に切り筋を形成する工程を削減することができる。
変形例4においては、支持基板11の周辺部の切断に際して、支持基板11に切り筋を設けて割断を行うのではなく、ダイシングソーを用いて支持基板11全体を切断する。
よって、変形例4においては、上述の第1の実施形態や各変形例に比べ、切り筋を形成する工程(例えば、図2(c)参照)や割断の工程が削減できるので、切断工程が簡略化される。
以上の第1の実施形態および変形例1から4によれば、以下の効果を得られる。
(1)本実施形態の半導体装置30の製造方法は、主面側に剥離層13が形成された支持基板11を用意すること、支持基板11上の剥離層13よりも上に、部分的に配線層(下段パッド16、上段パッド21)を形成すること、半導体チップ23を支持基板11上に配置すること、配線層(下段パッド16、上段パッド21)の少なくとも一部および半導体チップ23を包含するとともに、支持基板11上の剥離層13またはそれよりも上の層と接触する封止層24を形成し、支持基板11上に、半導体チップ23および配線層16、21、封止層24を含む中間積層体29を形成すること、中間積層体29を形成した後に、支持基板11の周辺部を切断すること、周辺部を切断した支持基板11から剥離層13を境界として中間積層体29を機械的に剥離すること、とを含んでいる。
このような製造方法としたので、支持基板11の周辺部に、成膜ムラや電解めっき電極の接触によるキズが生じても、それらの悪影響は支持基板11の中央部に及びことがなく、中間積層体29を安定して支持基板11から剥離することができる。その結果、中間積層体29およびその中間積層体を含む半導体装置の歩留まりを向上させることができる。
(2)さらに、支持基板11の周辺部の切断を、支持基板11の周辺部に割断予定線を形成すること、支持基板11上に形成されている剥離層13および封止層24を割断予定線に対応する位置で支持基板11の主面側から切断すること、支持基板11の周辺部を割断予定線に沿って割断すること、を経て行うことにより、さらに安定して支持基板11の周辺部の切断を行うことができ、一層の歩留まりの向上が得られる。
(3)さらに、支持基板11として、その主面に基板側から順に金属層12、剥離層13、薄銅層14が形成されている支持基板を用いることで、剥離層13からの剥離をより安定して実現することができる。
(4)さらに、支持基板11上に、複数並列して中間積層体29を形成し、かつ、複数並列して形成された中間積層体29を一体的に支持基板11から剥離するとともに、剥離後に中間積層体29を個々に切断する構成とすることで、生産効率の高い製造方法を実現できる。
図8を参照して、半導体装置30aの製造方法の第2の実施形態を説明する。
第2の実施形態においては、形成する配線層の層数が3層となる。なお、以下で説明する箇所を除いては、第2の実施形態においても、その製造工程は上述の第1の実施形態と同様である。
本変形例においては、上述の第1の実施形態において上段パッド21を形成しドライフィルムレジスト19を除去した後に(すなわち図2(a)に示した状態からドライフィルムレジスト19を除去した後に)、上段パッド21および層間絶縁膜17の上に第2の層間絶縁膜31を形成し、第2の層間絶縁膜31の所定の部分にスルーホール32を形成する。
そして、その上にドライフィルムレジスト33を形成し、ドライフィルムレジスト33内の所定箇所に開口34を形成する。図7(a)は、開口34が形成された状態を示している。
そして、ドライフィルムレジスト33を除去し、第2の層間絶縁膜31の硬化処理を行う。また、第2の層間絶縁膜31上に形成した上記の不図示のめっきシード層の除去(エッチン)を行う。
図7(b)は最上段パッド35が形成され、ドライフィルムレジスト33が除去された状態を示している。
なお、上述の第1実施形態に対して第2実施形態で加えた工程と同様の工程を、第2実施形態にさらに加えることで、配線層の層数が4層以上の半導体装置を製造可能である。
以上の第2の実施形態の製造方法によれば、上述の第1の実施形態および変形例1から4の効果に加えて、3層の配線層を持つ半導体装置を、高い歩留まりで製造できるという効果がある。
また、下段パッド16、上段パッド21、最上段パッド35は銅には限らず、他の金属で形成しても良い。各種のフォトレジストは、感光性のドライフィルムでもよく、レーザーアブレーションによってパターン形成を行っても良い。
また、各中間積層体29中に配置する電子部品は半導体チップ23には限定されず、コンデンサ、コイル、アンテナ等の受動部品を半導体チップ23とともに配置しても良い。これにより、半導体チップ23だけでは実現できない機能を持った、高機能の中間積層体29および半導体装置30を実現できる。
Claims (15)
- 主面側に剥離層が形成された支持基板を用意すること、
前記支持基板上の前記剥離層よりも上に、部分的に配線層および層間絶縁膜を形成すること、
半導体チップのパッドの少なくとも一部が、前記配線層の少なくとも一部に電気的に接続するように、前記半導体チップを前記支持基板上に配置すること、
前記配線層の少なくとも一部、前記層間絶縁膜の少なくとも一部、および前記半導体チップを包含するとともに、前記支持基板の前記主面上の前記剥離層またはそれよりも上の層と接触し、前記支持基板の前記主面以外の面とは接触しない封止層を形成し、前記支持基板上に、前記半導体チップおよび前記配線層、前記封止層を含む中間積層体を形成すること、
前記中間積層体を形成した後に、前記支持基板の周辺部であって前記封止層が形成されている部分を切断すること、
前記周辺部を切断した前記支持基板から、前記剥離層を境界として、前記中間積層体を機械的に剥離すること、とを含む半導体装置の製造方法。 - 請求項1に記載の半導体装置の製造方法において、
前記配線層の形成は、前記支持基板の前記周辺部に給電用電極を取り付け、前記支持基板に対して電解めっきを行うことにより形成する、半導体装置の製造方法。 - 請求項1または請求項2に記載の半導体装置の製造方法において、
前記切断において、前記支持基板の周辺部であって前記封止層と前記層間絶縁膜とがともに形成されている部分を切断する、半導体装置の製造方法。 - 請求項1から請求項3までのいずれか一項に記載の半導体装置の製造方法において、
前記支持基板の前記周辺部の前記切断は、
前記支持基板の周辺部に、割断予定線を形成すること、
前記支持基板上に形成されている前記剥離層および前記封止層を、前記割断予定線に対応する位置で前記支持基板の主面側から切断すること、
前記支持基板の周辺部を、前記割断予定線に沿って割断すること、とを含む半導体装置の製造方法。 - 請求項4に記載の半導体装置の製造方法において、
前記割断予定線の形成は、前記支持基板の裏面に切り筋を形成することにより行う半導体装置の製造方法。 - 請求項5に記載の半導体装置の製造方法において、
前記切り筋の形成は、前記支持基板上に前記中間積層体を形成した後に行う半導体装置の製造方法。 - 請求項5に記載の半導体装置の製造方法において、
前記切り筋の形成は、前記支持基板上に前記配線層を形成する前に行う半導体装置の製造方法。 - 請求項4に記載の半導体装置の製造方法において、
前記割断予定線の形成は、前記剥離層を形成する前に、前記支持基板の主面に切り筋を形成することにより行う半導体装置の製造方法。 - 請求項4に記載の半導体装置の製造方法において、
前記割断予定線の形成は、前記支持基板の内部に、他の部分と比較して強度の弱い部分を形成することにより行う半導体装置の製造方法。 - 請求項1から請求項9までのいずれか一項に記載の半導体装置の製造方法において、
前記支持基板としてガラス基板を使用する、半導体装置の製造方法。 - 請求項1から請求項10までのいずれか一項に記載の半導体装置の製造方法において、
前記支持基板として、前記主面に基板側から順に金属層、前記剥離層、薄銅層が形成されている支持基板を用いる半導体装置の製造方法。 - 請求項1から請求項11までのいずれか一項に記載の半導体装置の製造方法において、
前記配線層の形成を複数回行い、多層配線型の配線層を形成する半導体装置の製造方法。 - 請求項1から請求項12までのいずれか一項に記載の半導体装置の製造方法において、
前記支持基板上に、複数並列して前記中間積層体を形成し、かつ、前記複数並列して形成された前記中間積層体を一体的に前記支持基板から剥離するとともに、前記剥離後に前記中間積層体を個々に切断する半導体装置の製造方法。 - 請求項1から請求項13までのいずれか一項に記載の半導体装置の製造方法において、
前記中間積層体中に前記半導体チップを複数個配置する半導体装置の製造方法。 - 請求項1から請求項14までのいずれか一項に記載の半導体装置の製造方法において、
前記中間積層体中に前記半導体チップとともに受動部品を配置する半導体装置の製造方法。
Priority Applications (6)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2018019434A JP6816046B2 (ja) | 2018-02-06 | 2018-02-06 | 半導体装置の製造方法 |
| KR1020207019198A KR102407800B1 (ko) | 2018-02-06 | 2019-01-30 | 반도체 장치의 제조 방법 |
| US16/967,480 US11521948B2 (en) | 2018-02-06 | 2019-01-30 | Method of manufacturing semiconductor device |
| PCT/JP2019/003169 WO2019155959A1 (ja) | 2018-02-06 | 2019-01-30 | 半導体装置の製造方法 |
| CN201980011621.0A CN111684585A (zh) | 2018-02-06 | 2019-01-30 | 半导体装置的制造方法 |
| TW108104296A TWI802648B (zh) | 2018-02-06 | 2019-02-01 | 半導體裝置之製造方法 |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2018019434A JP6816046B2 (ja) | 2018-02-06 | 2018-02-06 | 半導体装置の製造方法 |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2019140150A JP2019140150A (ja) | 2019-08-22 |
| JP2019140150A5 JP2019140150A5 (ja) | 2019-11-28 |
| JP6816046B2 true JP6816046B2 (ja) | 2021-01-20 |
Family
ID=67547988
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2018019434A Active JP6816046B2 (ja) | 2018-02-06 | 2018-02-06 | 半導体装置の製造方法 |
Country Status (6)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US11521948B2 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JP6816046B2 (ja) |
| KR (1) | KR102407800B1 (ja) |
| CN (1) | CN111684585A (ja) |
| TW (1) | TWI802648B (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2019155959A1 (ja) |
Families Citing this family (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2020131552A (ja) * | 2019-02-20 | 2020-08-31 | 株式会社東芝 | キャリアおよび半導体装置の製造方法 |
| JP7362378B2 (ja) * | 2019-09-12 | 2023-10-17 | 株式会社東芝 | キャリア及び半導体装置の製造方法 |
| JP7395898B2 (ja) * | 2019-09-18 | 2023-12-12 | 大日本印刷株式会社 | 半導体多面付け基板用部材、半導体多面付け基板、および半導体部材 |
| CN112786513B (zh) * | 2019-11-11 | 2023-06-09 | 上海新微技术研发中心有限公司 | 一种薄膜器件的加工方法及薄膜器件 |
| CN112786515B (zh) * | 2019-11-11 | 2022-12-13 | 上海新微技术研发中心有限公司 | 一种薄膜器件的加工方法 |
| JP7474608B2 (ja) * | 2020-03-09 | 2024-04-25 | アオイ電子株式会社 | 半導体装置の製造方法、および半導体封止体 |
| JP7521258B2 (ja) | 2020-05-26 | 2024-07-24 | Toppanホールディングス株式会社 | 基板ユニット、基板ユニットの製造方法及び半導体装置の製造方法 |
| JP6985477B1 (ja) * | 2020-09-25 | 2021-12-22 | アオイ電子株式会社 | 半導体装置および半導体装置の製造方法 |
| KR102684002B1 (ko) * | 2020-12-14 | 2024-07-11 | 주식회사 네패스 | 반도체 패키지 제조방법 및 이에 이용되는 가이드 프레임 |
| WO2024053565A1 (ja) * | 2022-09-05 | 2024-03-14 | 三井金属鉱業株式会社 | 配線基板の製造方法 |
Family Cites Families (17)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS56158480A (en) | 1980-05-12 | 1981-12-07 | Nippon Telegr & Teleph Corp <Ntt> | Field effect transistor |
| JP3455762B2 (ja) * | 1999-11-11 | 2003-10-14 | カシオ計算機株式会社 | 半導体装置およびその製造方法 |
| JP2004134672A (ja) * | 2002-10-11 | 2004-04-30 | Sony Corp | 超薄型半導体装置の製造方法および製造装置、並びに超薄型の裏面照射型固体撮像装置の製造方法および製造装置 |
| JP2006222164A (ja) * | 2005-02-08 | 2006-08-24 | Shinko Electric Ind Co Ltd | 半導体装置及びその製造方法 |
| JP4103896B2 (ja) * | 2005-03-16 | 2008-06-18 | ヤマハ株式会社 | 半導体装置の製造方法および半導体装置 |
| JP2009147270A (ja) | 2007-12-18 | 2009-07-02 | Nec Electronics Corp | 配線基板の製造方法、配線基板、および半導体装置 |
| JP2010251682A (ja) * | 2009-03-26 | 2010-11-04 | Kyocera Corp | 多数個取り配線基板 |
| JP5042297B2 (ja) * | 2009-12-10 | 2012-10-03 | 日東電工株式会社 | 半導体装置の製造方法 |
| JP2011204765A (ja) * | 2010-03-24 | 2011-10-13 | Toshiba Corp | 半導体装置の製造方法及び半導体装置 |
| US8507322B2 (en) * | 2010-06-24 | 2013-08-13 | Akihiro Chida | Semiconductor substrate and method for manufacturing semiconductor device |
| JP5458029B2 (ja) * | 2011-01-19 | 2014-04-02 | 日本特殊陶業株式会社 | 多数個取り配線基板 |
| JP5225451B2 (ja) * | 2011-11-04 | 2013-07-03 | 新光電気工業株式会社 | 配線基板の製造方法及び半導体パッケージの製造方法 |
| JP2016134497A (ja) * | 2015-01-19 | 2016-07-25 | 凸版印刷株式会社 | 配線基板積層体及びこれを用いた半導体装置の製造方法 |
| JP6511695B2 (ja) * | 2015-01-20 | 2019-05-15 | ローム株式会社 | 半導体装置およびその製造方法 |
| JP2017017238A (ja) * | 2015-07-03 | 2017-01-19 | 株式会社ジェイデバイス | 半導体装置及びその製造方法 |
| WO2017149810A1 (ja) * | 2016-02-29 | 2017-09-08 | 三井金属鉱業株式会社 | キャリア付銅箔及びその製造方法、並びに配線層付コアレス支持体及びプリント配線板の製造方法 |
| JP2017162876A (ja) | 2016-03-07 | 2017-09-14 | 株式会社ジェイデバイス | 半導体パッケージの製造方法 |
-
2018
- 2018-02-06 JP JP2018019434A patent/JP6816046B2/ja active Active
-
2019
- 2019-01-30 WO PCT/JP2019/003169 patent/WO2019155959A1/ja active Application Filing
- 2019-01-30 CN CN201980011621.0A patent/CN111684585A/zh not_active Withdrawn
- 2019-01-30 US US16/967,480 patent/US11521948B2/en active Active
- 2019-01-30 KR KR1020207019198A patent/KR102407800B1/ko active IP Right Grant
- 2019-02-01 TW TW108104296A patent/TWI802648B/zh active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| US11521948B2 (en) | 2022-12-06 |
| KR20200094780A (ko) | 2020-08-07 |
| TWI802648B (zh) | 2023-05-21 |
| KR102407800B1 (ko) | 2022-06-10 |
| TW201935576A (zh) | 2019-09-01 |
| CN111684585A (zh) | 2020-09-18 |
| US20210217719A1 (en) | 2021-07-15 |
| WO2019155959A1 (ja) | 2019-08-15 |
| JP2019140150A (ja) | 2019-08-22 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP6816046B2 (ja) | 半導体装置の製造方法 | |
| US8209856B2 (en) | Printed wiring board and method for manufacturing the same | |
| JP3983146B2 (ja) | 多層配線基板の製造方法 | |
| JP5599276B2 (ja) | 半導体素子、半導体素子実装体及び半導体素子の製造方法 | |
| JP5902931B2 (ja) | 配線基板の製造方法、及び、配線基板製造用の支持体 | |
| JP4219951B2 (ja) | はんだボール搭載方法及びはんだボール搭載基板の製造方法 | |
| JP6029958B2 (ja) | 配線基板の製造方法 | |
| JP2007242888A (ja) | 半導体パッケージ製造方法 | |
| JP2000216330A (ja) | 積層型半導体装置およびその製造方法 | |
| JP2008311592A (ja) | 電子装置の製造方法 | |
| TW201110267A (en) | An electronic device package and method of manufacture | |
| JP5877673B2 (ja) | 配線基板及びその製造方法、半導体パッケージ | |
| JP2008235555A (ja) | 電子装置の製造方法及び基板及び半導体装置 | |
| JP2009117771A (ja) | 半導体パッケージの製造方法 | |
| WO2022124394A1 (ja) | 支持体付き基板ユニット、基板ユニット、および支持体付き基板ユニットの製造方法 | |
| JP7347440B2 (ja) | 半導体パッケージ用配線基板の製造方法 | |
| JP2008108849A (ja) | 半導体装置および半導体装置の製造方法 | |
| JP2006073953A (ja) | 半導体装置および半導体装置の製造方法 | |
| JP6534700B2 (ja) | 半導体装置の製造方法 | |
| JP4483136B2 (ja) | 半導体デバイスの実装方法及び半導体装置の製造方法 | |
| JP2008147367A (ja) | 半導体装置及びその製造方法 | |
| JP2011040610A (ja) | 半導体装置及びその製造方法 | |
| JP2007250834A (ja) | 電子部品装置の製造方法 | |
| CN116711067A (zh) | 带支撑体的基板单元、基板单元以及带支撑体的基板单元的制造方法 | |
| JP2021190473A (ja) | 基板ユニット、基板ユニットの製造方法及び半導体装置の製造方法 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20191016 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20191016 |
|
| A871 | Explanation of circumstances concerning accelerated examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A871 Effective date: 20191016 |
|
| A975 | Report on accelerated examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971005 Effective date: 20191204 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20200121 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20200312 |
|
| A02 | Decision of refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 Effective date: 20200707 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20200925 |
|
| C60 | Trial request (containing other claim documents, opposition documents) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: C60 Effective date: 20200925 |
|
| A911 | Transfer to examiner for re-examination before appeal (zenchi) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A911 Effective date: 20201005 |
|
| C21 | Notice of transfer of a case for reconsideration by examiners before appeal proceedings |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: C21 Effective date: 20201006 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20201222 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20201223 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 6816046 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |