JP5547076B2 - 半導体光素子アレイおよびその製造方法 - Google Patents
半導体光素子アレイおよびその製造方法 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP5547076B2 JP5547076B2 JP2010526554A JP2010526554A JP5547076B2 JP 5547076 B2 JP5547076 B2 JP 5547076B2 JP 2010526554 A JP2010526554 A JP 2010526554A JP 2010526554 A JP2010526554 A JP 2010526554A JP 5547076 B2 JP5547076 B2 JP 5547076B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- fine columnar
- semiconductor
- active layer
- semiconductor optical
- columnar crystal
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 title claims description 166
- 230000003287 optical effect Effects 0.000 title claims description 52
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 title claims description 28
- 239000013078 crystal Substances 0.000 claims description 213
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 claims description 89
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 claims description 57
- JMASRVWKEDWRBT-UHFFFAOYSA-N Gallium nitride Chemical compound [Ga]#N JMASRVWKEDWRBT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 56
- 229910002601 GaN Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 53
- 150000004767 nitrides Chemical class 0.000 claims description 40
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 23
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 claims description 23
- 239000010936 titanium Substances 0.000 claims description 21
- 229910052719 titanium Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 18
- RTAQQCXQSZGOHL-UHFFFAOYSA-N Titanium Chemical compound [Ti] RTAQQCXQSZGOHL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 15
- PXHVJJICTQNCMI-UHFFFAOYSA-N Nickel Chemical compound [Ni] PXHVJJICTQNCMI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 9
- 238000005530 etching Methods 0.000 claims description 8
- BASFCYQUMIYNBI-UHFFFAOYSA-N platinum Chemical compound [Pt] BASFCYQUMIYNBI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 8
- 239000010931 gold Substances 0.000 claims description 7
- XEEYBQQBJWHFJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N Iron Chemical compound [Fe] XEEYBQQBJWHFJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 5
- 230000004888 barrier function Effects 0.000 claims description 5
- 229910052984 zinc sulfide Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 5
- 150000002739 metals Chemical class 0.000 claims description 4
- 229910052697 platinum Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 4
- 239000003086 colorant Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- 229910052750 molybdenum Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 3
- 229910052759 nickel Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 3
- ZOKXTWBITQBERF-UHFFFAOYSA-N Molybdenum Chemical compound [Mo] ZOKXTWBITQBERF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000010941 cobalt Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- 229910017052 cobalt Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 2
- GUTLYIVDDKVIGB-UHFFFAOYSA-N cobalt atom Chemical compound [Co] GUTLYIVDDKVIGB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- PCHJSUWPFVWCPO-UHFFFAOYSA-N gold Chemical compound [Au] PCHJSUWPFVWCPO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- 229910052737 gold Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000011733 molybdenum Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- 229910052715 tantalum Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 2
- GUVRBAGPIYLISA-UHFFFAOYSA-N tantalum atom Chemical compound [Ta] GUVRBAGPIYLISA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- WFKWXMTUELFFGS-UHFFFAOYSA-N tungsten Chemical compound [W] WFKWXMTUELFFGS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 2
- 229910052721 tungsten Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000010937 tungsten Substances 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000010410 layer Substances 0.000 description 158
- 239000011247 coating layer Substances 0.000 description 21
- 239000010408 film Substances 0.000 description 17
- 238000009826 distribution Methods 0.000 description 16
- 238000001451 molecular beam epitaxy Methods 0.000 description 15
- 238000001878 scanning electron micrograph Methods 0.000 description 15
- IJGRMHOSHXDMSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N Atomic nitrogen Chemical compound N#N IJGRMHOSHXDMSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 12
- 229910002704 AlGaN Inorganic materials 0.000 description 11
- 239000010409 thin film Substances 0.000 description 11
- 206010053759 Growth retardation Diseases 0.000 description 9
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 9
- 238000005259 measurement Methods 0.000 description 9
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 8
- 229910052594 sapphire Inorganic materials 0.000 description 8
- 239000010980 sapphire Substances 0.000 description 8
- 238000001228 spectrum Methods 0.000 description 7
- 238000005253 cladding Methods 0.000 description 6
- 230000031700 light absorption Effects 0.000 description 6
- 229910052757 nitrogen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 6
- 230000006798 recombination Effects 0.000 description 6
- 238000005215 recombination Methods 0.000 description 6
- 230000007423 decrease Effects 0.000 description 4
- 238000004020 luminiscence type Methods 0.000 description 4
- 238000010521 absorption reaction Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 description 3
- PMHQVHHXPFUNSP-UHFFFAOYSA-M copper(1+);methylsulfanylmethane;bromide Chemical compound Br[Cu].CSC PMHQVHHXPFUNSP-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 3
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000005284 excitation Effects 0.000 description 3
- 239000012535 impurity Substances 0.000 description 3
- AMGQUBHHOARCQH-UHFFFAOYSA-N indium;oxotin Chemical compound [In].[Sn]=O AMGQUBHHOARCQH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 238000001000 micrograph Methods 0.000 description 3
- 239000002096 quantum dot Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000000969 carrier Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000005229 chemical vapour deposition Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000003247 decreasing effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000010884 ion-beam technique Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000000059 patterning Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000005424 photoluminescence Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229910052582 BN Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- PZNSFCLAULLKQX-UHFFFAOYSA-N Boron nitride Chemical compound N#B PZNSFCLAULLKQX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- OAICVXFJPJFONN-UHFFFAOYSA-N Phosphorus Chemical compound [P] OAICVXFJPJFONN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicium dioxide Chemical compound O=[Si]=O VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicon Chemical compound [Si] XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ATJFFYVFTNAWJD-UHFFFAOYSA-N Tin Chemical compound [Sn] ATJFFYVFTNAWJD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- GWEVSGVZZGPLCZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Titan oxide Chemical compound O=[Ti]=O GWEVSGVZZGPLCZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000003491 array Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000009835 boiling Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000470 constituent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000007789 gas Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000005484 gravity Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000003384 imaging method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 150000002500 ions Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 230000001678 irradiating effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010030 laminating Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000001459 lithography Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000002844 melting Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000008018 melting Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000002061 nanopillar Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000002073 nanorod Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000000704 physical effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000001737 promoting effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229910052710 silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000010703 silicon Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052814 silicon oxide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 238000009751 slip forming Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910052596 spinel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000011029 spinel Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000002195 synergetic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 150000003608 titanium Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- OGIDPMRJRNCKJF-UHFFFAOYSA-N titanium oxide Inorganic materials [Ti]=O OGIDPMRJRNCKJF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B82—NANOTECHNOLOGY
- B82Y—SPECIFIC USES OR APPLICATIONS OF NANOSTRUCTURES; MEASUREMENT OR ANALYSIS OF NANOSTRUCTURES; MANUFACTURE OR TREATMENT OF NANOSTRUCTURES
- B82Y20/00—Nanooptics, e.g. quantum optics or photonic crystals
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02104—Forming layers
- H01L21/02365—Forming inorganic semiconducting materials on a substrate
- H01L21/02367—Substrates
- H01L21/0237—Materials
- H01L21/0242—Crystalline insulating materials
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02104—Forming layers
- H01L21/02365—Forming inorganic semiconducting materials on a substrate
- H01L21/02436—Intermediate layers between substrates and deposited layers
- H01L21/02439—Materials
- H01L21/02455—Group 13/15 materials
- H01L21/02458—Nitrides
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02104—Forming layers
- H01L21/02365—Forming inorganic semiconducting materials on a substrate
- H01L21/02518—Deposited layers
- H01L21/02521—Materials
- H01L21/02538—Group 13/15 materials
- H01L21/0254—Nitrides
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02104—Forming layers
- H01L21/02365—Forming inorganic semiconducting materials on a substrate
- H01L21/02518—Deposited layers
- H01L21/02587—Structure
- H01L21/0259—Microstructure
- H01L21/02603—Nanowires
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02104—Forming layers
- H01L21/02365—Forming inorganic semiconducting materials on a substrate
- H01L21/02612—Formation types
- H01L21/02617—Deposition types
- H01L21/02636—Selective deposition, e.g. simultaneous growth of mono- and non-monocrystalline semiconductor materials
- H01L21/02639—Preparation of substrate for selective deposition
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L27/00—Devices consisting of a plurality of semiconductor or other solid-state components formed in or on a common substrate
- H01L27/15—Devices consisting of a plurality of semiconductor or other solid-state components formed in or on a common substrate including semiconductor components having potential barriers, specially adapted for light emission
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L27/00—Devices consisting of a plurality of semiconductor or other solid-state components formed in or on a common substrate
- H01L27/15—Devices consisting of a plurality of semiconductor or other solid-state components formed in or on a common substrate including semiconductor components having potential barriers, specially adapted for light emission
- H01L27/153—Devices consisting of a plurality of semiconductor or other solid-state components formed in or on a common substrate including semiconductor components having potential barriers, specially adapted for light emission in a repetitive configuration, e.g. LED bars
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/02—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/06—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions
- H01L29/0657—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions characterised by the shape of the body
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/02—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/06—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions
- H01L29/0657—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions characterised by the shape of the body
- H01L29/0665—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions characterised by the shape of the body the shape of the body defining a nanostructure
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/02—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/06—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions
- H01L29/0657—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions characterised by the shape of the body
- H01L29/0665—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions characterised by the shape of the body the shape of the body defining a nanostructure
- H01L29/0669—Nanowires or nanotubes
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/02—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/06—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions
- H01L29/0657—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions characterised by the shape of the body
- H01L29/0665—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions characterised by the shape of the body the shape of the body defining a nanostructure
- H01L29/0669—Nanowires or nanotubes
- H01L29/0676—Nanowires or nanotubes oriented perpendicular or at an angle to a substrate
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L31/00—Semiconductor devices sensitive to infrared radiation, light, electromagnetic radiation of shorter wavelength or corpuscular radiation and specially adapted either for the conversion of the energy of such radiation into electrical energy or for the control of electrical energy by such radiation; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof
- H01L31/0248—Semiconductor devices sensitive to infrared radiation, light, electromagnetic radiation of shorter wavelength or corpuscular radiation and specially adapted either for the conversion of the energy of such radiation into electrical energy or for the control of electrical energy by such radiation; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof characterised by their semiconductor bodies
- H01L31/0352—Semiconductor devices sensitive to infrared radiation, light, electromagnetic radiation of shorter wavelength or corpuscular radiation and specially adapted either for the conversion of the energy of such radiation into electrical energy or for the control of electrical energy by such radiation; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof characterised by their semiconductor bodies characterised by their shape or by the shapes, relative sizes or disposition of the semiconductor regions
- H01L31/035209—Semiconductor devices sensitive to infrared radiation, light, electromagnetic radiation of shorter wavelength or corpuscular radiation and specially adapted either for the conversion of the energy of such radiation into electrical energy or for the control of electrical energy by such radiation; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof characterised by their semiconductor bodies characterised by their shape or by the shapes, relative sizes or disposition of the semiconductor regions comprising a quantum structures
- H01L31/035227—Semiconductor devices sensitive to infrared radiation, light, electromagnetic radiation of shorter wavelength or corpuscular radiation and specially adapted either for the conversion of the energy of such radiation into electrical energy or for the control of electrical energy by such radiation; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof characterised by their semiconductor bodies characterised by their shape or by the shapes, relative sizes or disposition of the semiconductor regions comprising a quantum structures the quantum structure being quantum wires, or nanorods
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L31/00—Semiconductor devices sensitive to infrared radiation, light, electromagnetic radiation of shorter wavelength or corpuscular radiation and specially adapted either for the conversion of the energy of such radiation into electrical energy or for the control of electrical energy by such radiation; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof
- H01L31/0248—Semiconductor devices sensitive to infrared radiation, light, electromagnetic radiation of shorter wavelength or corpuscular radiation and specially adapted either for the conversion of the energy of such radiation into electrical energy or for the control of electrical energy by such radiation; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof characterised by their semiconductor bodies
- H01L31/0352—Semiconductor devices sensitive to infrared radiation, light, electromagnetic radiation of shorter wavelength or corpuscular radiation and specially adapted either for the conversion of the energy of such radiation into electrical energy or for the control of electrical energy by such radiation; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof characterised by their semiconductor bodies characterised by their shape or by the shapes, relative sizes or disposition of the semiconductor regions
- H01L31/035272—Semiconductor devices sensitive to infrared radiation, light, electromagnetic radiation of shorter wavelength or corpuscular radiation and specially adapted either for the conversion of the energy of such radiation into electrical energy or for the control of electrical energy by such radiation; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof characterised by their semiconductor bodies characterised by their shape or by the shapes, relative sizes or disposition of the semiconductor regions characterised by at least one potential jump barrier or surface barrier
- H01L31/035281—Shape of the body
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L31/00—Semiconductor devices sensitive to infrared radiation, light, electromagnetic radiation of shorter wavelength or corpuscular radiation and specially adapted either for the conversion of the energy of such radiation into electrical energy or for the control of electrical energy by such radiation; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof
- H01L31/04—Semiconductor devices sensitive to infrared radiation, light, electromagnetic radiation of shorter wavelength or corpuscular radiation and specially adapted either for the conversion of the energy of such radiation into electrical energy or for the control of electrical energy by such radiation; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof adapted as photovoltaic [PV] conversion devices
- H01L31/06—Semiconductor devices sensitive to infrared radiation, light, electromagnetic radiation of shorter wavelength or corpuscular radiation and specially adapted either for the conversion of the energy of such radiation into electrical energy or for the control of electrical energy by such radiation; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof adapted as photovoltaic [PV] conversion devices characterised by potential barriers
- H01L31/075—Semiconductor devices sensitive to infrared radiation, light, electromagnetic radiation of shorter wavelength or corpuscular radiation and specially adapted either for the conversion of the energy of such radiation into electrical energy or for the control of electrical energy by such radiation; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof adapted as photovoltaic [PV] conversion devices characterised by potential barriers the potential barriers being only of the PIN type, e.g. amorphous silicon PIN solar cells
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L33/00—Semiconductor devices having potential barriers specially adapted for light emission; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof
- H01L33/02—Semiconductor devices having potential barriers specially adapted for light emission; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof characterised by the semiconductor bodies
- H01L33/16—Semiconductor devices having potential barriers specially adapted for light emission; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof characterised by the semiconductor bodies with a particular crystal structure or orientation, e.g. polycrystalline, amorphous or porous
- H01L33/18—Semiconductor devices having potential barriers specially adapted for light emission; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof characterised by the semiconductor bodies with a particular crystal structure or orientation, e.g. polycrystalline, amorphous or porous within the light emitting region
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L33/00—Semiconductor devices having potential barriers specially adapted for light emission; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof
- H01L33/02—Semiconductor devices having potential barriers specially adapted for light emission; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof characterised by the semiconductor bodies
- H01L33/20—Semiconductor devices having potential barriers specially adapted for light emission; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof characterised by the semiconductor bodies with a particular shape, e.g. curved or truncated substrate
- H01L33/24—Semiconductor devices having potential barriers specially adapted for light emission; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof characterised by the semiconductor bodies with a particular shape, e.g. curved or truncated substrate of the light emitting region, e.g. non-planar junction
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01S—DEVICES USING THE PROCESS OF LIGHT AMPLIFICATION BY STIMULATED EMISSION OF RADIATION [LASER] TO AMPLIFY OR GENERATE LIGHT; DEVICES USING STIMULATED EMISSION OF ELECTROMAGNETIC RADIATION IN WAVE RANGES OTHER THAN OPTICAL
- H01S5/00—Semiconductor lasers
- H01S5/02—Structural details or components not essential to laser action
- H01S5/0206—Substrates, e.g. growth, shape, material, removal or bonding
- H01S5/0213—Sapphire, quartz or diamond based substrates
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01S—DEVICES USING THE PROCESS OF LIGHT AMPLIFICATION BY STIMULATED EMISSION OF RADIATION [LASER] TO AMPLIFY OR GENERATE LIGHT; DEVICES USING STIMULATED EMISSION OF ELECTROMAGNETIC RADIATION IN WAVE RANGES OTHER THAN OPTICAL
- H01S5/00—Semiconductor lasers
- H01S5/10—Construction or shape of the optical resonator, e.g. extended or external cavity, coupled cavities, bent-guide, varying width, thickness or composition of the active region
- H01S5/1042—Optical microcavities, e.g. cavity dimensions comparable to the wavelength
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01S—DEVICES USING THE PROCESS OF LIGHT AMPLIFICATION BY STIMULATED EMISSION OF RADIATION [LASER] TO AMPLIFY OR GENERATE LIGHT; DEVICES USING STIMULATED EMISSION OF ELECTROMAGNETIC RADIATION IN WAVE RANGES OTHER THAN OPTICAL
- H01S5/00—Semiconductor lasers
- H01S5/10—Construction or shape of the optical resonator, e.g. extended or external cavity, coupled cavities, bent-guide, varying width, thickness or composition of the active region
- H01S5/18—Surface-emitting [SE] lasers, e.g. having both horizontal and vertical cavities
- H01S5/183—Surface-emitting [SE] lasers, e.g. having both horizontal and vertical cavities having only vertical cavities, e.g. vertical cavity surface-emitting lasers [VCSEL]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01S—DEVICES USING THE PROCESS OF LIGHT AMPLIFICATION BY STIMULATED EMISSION OF RADIATION [LASER] TO AMPLIFY OR GENERATE LIGHT; DEVICES USING STIMULATED EMISSION OF ELECTROMAGNETIC RADIATION IN WAVE RANGES OTHER THAN OPTICAL
- H01S5/00—Semiconductor lasers
- H01S5/30—Structure or shape of the active region; Materials used for the active region
- H01S5/32—Structure or shape of the active region; Materials used for the active region comprising PN junctions, e.g. hetero- or double- heterostructures
- H01S5/3202—Structure or shape of the active region; Materials used for the active region comprising PN junctions, e.g. hetero- or double- heterostructures grown on specifically orientated substrates, or using orientation dependent growth
- H01S5/3203—Structure or shape of the active region; Materials used for the active region comprising PN junctions, e.g. hetero- or double- heterostructures grown on specifically orientated substrates, or using orientation dependent growth on non-planar substrates to create thickness or compositional variations
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01S—DEVICES USING THE PROCESS OF LIGHT AMPLIFICATION BY STIMULATED EMISSION OF RADIATION [LASER] TO AMPLIFY OR GENERATE LIGHT; DEVICES USING STIMULATED EMISSION OF ELECTROMAGNETIC RADIATION IN WAVE RANGES OTHER THAN OPTICAL
- H01S5/00—Semiconductor lasers
- H01S5/30—Structure or shape of the active region; Materials used for the active region
- H01S5/32—Structure or shape of the active region; Materials used for the active region comprising PN junctions, e.g. hetero- or double- heterostructures
- H01S5/323—Structure or shape of the active region; Materials used for the active region comprising PN junctions, e.g. hetero- or double- heterostructures in AIIIBV compounds, e.g. AlGaAs-laser, InP-based laser
- H01S5/32308—Structure or shape of the active region; Materials used for the active region comprising PN junctions, e.g. hetero- or double- heterostructures in AIIIBV compounds, e.g. AlGaAs-laser, InP-based laser emitting light at a wavelength less than 900 nm
- H01S5/32341—Structure or shape of the active region; Materials used for the active region comprising PN junctions, e.g. hetero- or double- heterostructures in AIIIBV compounds, e.g. AlGaAs-laser, InP-based laser emitting light at a wavelength less than 900 nm blue laser based on GaN or GaP
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01S—DEVICES USING THE PROCESS OF LIGHT AMPLIFICATION BY STIMULATED EMISSION OF RADIATION [LASER] TO AMPLIFY OR GENERATE LIGHT; DEVICES USING STIMULATED EMISSION OF ELECTROMAGNETIC RADIATION IN WAVE RANGES OTHER THAN OPTICAL
- H01S5/00—Semiconductor lasers
- H01S5/40—Arrangement of two or more semiconductor lasers, not provided for in groups H01S5/02 - H01S5/30
- H01S5/4025—Array arrangements, e.g. constituted by discrete laser diodes or laser bar
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01S—DEVICES USING THE PROCESS OF LIGHT AMPLIFICATION BY STIMULATED EMISSION OF RADIATION [LASER] TO AMPLIFY OR GENERATE LIGHT; DEVICES USING STIMULATED EMISSION OF ELECTROMAGNETIC RADIATION IN WAVE RANGES OTHER THAN OPTICAL
- H01S5/00—Semiconductor lasers
- H01S5/40—Arrangement of two or more semiconductor lasers, not provided for in groups H01S5/02 - H01S5/30
- H01S5/42—Arrays of surface emitting lasers
- H01S5/423—Arrays of surface emitting lasers having a vertical cavity
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02E—REDUCTION OF GREENHOUSE GAS [GHG] EMISSIONS, RELATED TO ENERGY GENERATION, TRANSMISSION OR DISTRIBUTION
- Y02E10/00—Energy generation through renewable energy sources
- Y02E10/50—Photovoltaic [PV] energy
- Y02E10/548—Amorphous silicon PV cells
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Power Engineering (AREA)
- Microelectronics & Electronic Packaging (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Computer Hardware Design (AREA)
- Condensed Matter Physics & Semiconductors (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Nanotechnology (AREA)
- Manufacturing & Machinery (AREA)
- Crystallography & Structural Chemistry (AREA)
- Electromagnetism (AREA)
- Materials Engineering (AREA)
- Ceramic Engineering (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Biophysics (AREA)
- Optics & Photonics (AREA)
- Led Devices (AREA)
- Physical Deposition Of Substances That Are Components Of Semiconductor Devices (AREA)
- Crystals, And After-Treatments Of Crystals (AREA)
- Photovoltaic Devices (AREA)
Description
特に、発光波長のピーク波長は、前記各微細柱状結晶の径が大きいほど長波長側にシフトし、前記各微細柱状結晶の径が小さいほど短波長側にシフトするように定めることができる。
ここで、微細柱状結晶は、径が10nm以上、1000nm以下であることが好ましい。
(第1の実施形態)
図1(A)〜(D)は、本発明に係る一実施形態の半導体光素子アレイ10の製造工程を概略的に示す断面図である。図1(D)には、本実施形態の半導体光素子アレイ10の構造が概略的に示されている。
マスクパターン13Pは、このIII族窒化物半導体層12Pの主面上に形成されており、複数の凹部14,…,14の直上にそれぞれ開口部(以下、マスク開口部と呼ぶ。)を有している。すなわち、開口部が凹部14にかさなりあい、開口部から凹部14が露出するように凹部14が形成される。
複数の細柱状結晶20,…,20は、III族窒化物半導体層12Pの凹部14,…,14からマスク開口部を介してマスクパターン13Pの上方に向けて成長したIII族窒化物半導体からなる。微細柱状結晶20上には活性層21が形成され、さらに活性層21を被覆する半導体被覆層22が形成されている。微細柱状結晶20、活性層21および半導体被覆層22によってナノコラム23が構成される。
微細柱状結晶20は、径が10nm以上、1000nm以下であることが好ましい。なかでも、700nm以下、さらには、650nm以下、より好ましくは600nm以下であることが好ましい。700nm以下、特に600nm以下とすれば、貫通転位の発生を抑制しやすくなる。
微細柱状結晶20の径とは、マスク開口部から露出した柱状部201の径である。柱状部201の径は、柱状部201が円柱形状の場合には、その径である。円柱形状以外の場合には、柱状部201を半導体基板の基板面側から平面視した際の重心点(平面中心)を通るとともに、柱状部201と2点で交差する直線のうち、交点間の距離が最も長い直線の長さをいう。
微細柱状結晶20は、柱状部201と、この柱状部201の先端に設けられたファセット構造202とを備える。柱状部201の形状は、特に限定されないが、たとえば、円柱形状、四角柱形状、六角柱形状等とすることができる。
また、微細柱状結晶20は、製造安定性の観点から、結晶構造が六方晶の材料で構成されていることが好ましい。
半導体被覆層22は、活性層21上に設けられており、活性層21を完全に被覆している。
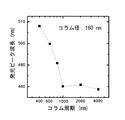
よって、微細柱状結晶20の径Δを制御することで所望の発光波長を得ることができる。後述するようにこの微細柱状結晶20の径Δは、テンプレート基板のIII族窒化物半導体層12Pに形成された各凹部14の径δ(図1(C))を調整することで所望の値にすることができる。凹部14の径δは、マスク開口部の大きさに依存するので、予めマスク開口部の大きさを定めておけば、この大きさに応じた径δを得ることができる。
よって、微細柱状結晶20の先端部におけるファセット構造の表面積を制御することで所望の発光波長を得ることが可能である。
ここで、マスクパターンには、複数の開口部の配置密度が高い領域と、前記複数の開口部の配置密度が低い領域とを形成した場合、開口部の配置密度が高い領域にある複数の微細柱状結晶20上の活性層21から放出される光のピーク波長は、開口部の配置密度が低い領域にある複数の微細柱状結晶20上の活性層21から放出される光のピーク波長よりも長波長となる。
すなわち、活性層21から放出される光のピーク波長は、微細柱状結晶20,…,20の面内密度が高いほど長波長側へシフトし、かつ微細柱状結晶20,…,20の面内密度が低いほど短波長側へシフトするように定めることができる。面内密度は、微細柱状結晶20,…,20の空間的な周期が短いほど高くなり、あるいは、微細柱状結晶20の径が大きいほど高くなる。
また、微細柱状結晶20を横方向成長させることで、以下のような効果がある。
マスク開口部径を小さくすることで、微細柱状結晶20の成長初期での貫通転位の発生が抑制される。その後に横方向成長で径を太くすれば貫通転位のない比較的、径の大きな微細柱状結晶(例えば、直径1000nm)を得ることが可能となる。
なお、微細柱状結晶20を横方向成長させるためには、相対的に窒素供給量を増加する方法や、Alを添加する方法(たとえば、AlGaNとする方法)等がある。
この先端部の形状は六角錐形状である。ここで、半極性面20aとしては、たとえば、(10−1−1)面、(10−1−3)面、(11−22)面、(11−24)面、(10−12)面が挙げられる。一方、図4(B)に示される先端部もファセット構造となっているが、斜め上方を向いたファセット面、および、直上方を向いた面として、ウルツ鉱型結晶構造の半極性面20aからなる傾斜面と平坦な極性面20bとを有している。結晶の成長条件に応じて、図4(A)の先端部形状あるいは図4(B)の先端部形状のいずれかが形成される。
なお、ファセット構造とは、下地基板11水平面に対して斜めに位置するファセット面を側面とする多面体構造のことである。
その後、各微細柱状結晶20上に活性層21を設け、さらに、活性層21上に半導体被覆層22を形成する。活性層21、半導体被覆層22は、MOCVD法や、MBE法により形成することができる。
なお、活性層21や、半導体被覆層22を構成する材料は、マスクパターン13P上にも堆積することとなる。
また、半導体被覆層22を形成する際には、横方向成長させて、活性層21上面のみならず、側面を被覆することが好ましい。
図5は、III族窒化物半導体層12Pに形成された凹部14の径(以下「ホール径」と呼ぶ。)δとナノコラム23の発光波長との間の関係を示すグラフである。
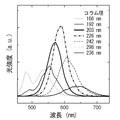
次に、図12は、ナノコラム23から放出されたCL(カソードルミネッセンス)光のスペクトルの測定結果を示すグラフである。このグラフの横軸は発光波長に対応し、グラフの縦軸はCL強度(任意単位)に対応している。図13(A)は、ナノコラム23の上面視からのSEM像を示し、図13(B),(C)は、それぞれ異なる波長405nm,510nmのCL像(カソードルミネッセンス像)の上面視図である。図14(A)は、ナノコラム23を横方向から撮像したSEM像を示し、図14(B),(C),(D)は、それぞれ異なる波長365nm,435nm,500nmの断面CL像(図14(A)のナノコラム23の断面CL像)を示す図である。
なお、ここでは、InGaN結晶21s,21tを有するナノコラム23について言及したが、InGaN結晶21tはなくてもよい。
このようなナノコラムであっても、ナノコラムの径により、発光波長を制御することができることが確認されている。すなわち、径が小さなナノコラムの活性層から放出される光のピーク波長は、径が大きなナノコラム上の活性層から放出される光のピーク波長よりも低波長となることが確認されている。
図19(A)〜(F)は、三角格子状に規則的に配列されたナノコラム群の上面視でのSEM像を示す図である。図19(A),(B),(C),(D),(E),(F)は、それぞれ、空間周期(各微細柱状結晶20の中心間の距離)400nm,600nm,800nm,1μm,2μm,4μmの場合の配列を示している。また、空間周期400nm,600nm,800nm,1μm,2μm,4μmの配列に対応するPL発光のピーク波長は、それぞれ、508nm,500nm,490nm,480nm,480nm,479nmと測定された。
次に、本発明に係る第2の実施形態について説明する。図23(A),(B)は、それぞれ、第2の実施形態の半導体発光素子の構成の一部を概略的に示す図である。図23(A),(B)に示される構造は、上記第1の実施形態の半導体光素子アレイ10の構造を含むものである。
微細柱状結晶20は、n型半導体層で構成されており、たとえば、GaN/AlGaN/GaNの3層構成であってもよい。
p型半導体層25を横方向成長を促進させるためには、Mgをドープする方法、成長温度を下げる方法、Alを添加する方法等がある。そして、p型半導体層25に電気的に接続されるように、Ni/Au多層膜やITO(Indium Tin Oxide)などのp側電極32が成膜されている。p側電極から注入された正孔とn側電極からの電子とが活性層21で再結合することにより活性層21は光を放出する。
また、図23(A)または図23(B)の構造を、太陽電池などの光電変換素子に変形することも可能である。たとえば、各ナノコラム23において、活性層21の代わりにpin構造(光吸収構造)を形成すればよい。このpin構造では、i型半導体層を量子ドット構造とすることができる。複数の量子ドット層を中間層を介して積層してi型半導体層を構成することにより、変換効率を向上させることができる。上述の通り、微細柱状結晶20の径、微細柱状結晶20,…,20の面内密度あるいは微細柱状結晶20の先端形状を制御することにより、pin構造を所望の吸収波長に適合させることが可能である。
次に、本発明の第3の実施形態について説明する。図24および図25は、それぞれ、第3の実施形態の半導体発光素子の構成の一部を示す斜視図である。第3の実施形態の半導体発光素子は、上記第1の実施形態の半導体光素子アレイ10の構造を含むものである。
Claims (17)
- 複数の凹部が形成された主面を有する半導体基板と、
前記半導体基板の当該主面上に形成され、かつ前記複数の凹部の直上にそれぞれ設けられた複数の開口部を有するマスクパターンと、
前記複数の凹部から前記複数の開口部を介して前記マスクパターンの上方に向けて成長したIII族窒化物半導体からなる複数の微細柱状結晶と、
前記複数の微細柱状結晶上にそれぞれ成長した活性層と、
前記各活性層を被覆する半導体層と、
を備え、
前記マスクパターンには、前記複数の開口部の配置密度が高い領域と、前記複数の開口部の配置密度が低い領域とがあり、
前記複数の開口部の配置密度が高い前記領域にある前記複数の微細柱状結晶上の前記活性層から放出される発光のピーク波長は、前記複数の開口部の配置密度が低い前記領域にある前記複数の微細柱状結晶上の前記活性層から放出される発光のピーク波長よりも長波長である半導体光素子アレイ。 - 複数の凹部が形成された主面を有する半導体基板と、
前記半導体基板の当該主面上に形成され、かつ前記複数の凹部の直上にそれぞれ設けられた複数の開口部を有するマスクパターンと、
前記複数の凹部から前記複数の開口部を介して前記マスクパターンの上方に向けて成長したIII族窒化物半導体からなる複数の微細柱状結晶と、
前記複数の微細柱状結晶上にそれぞれ成長した活性層と、
前記各活性層を被覆する半導体層と、
を備え、
径が異なる前記複数の前記微細柱状結晶を含み、
径が小さな前記微細柱状結晶上の前記活性層から放出される発光のピーク波長は、径が大きな前記微細柱状結晶上の前記活性層から放出される発光のピーク波長よりも短波長であり、
前記活性層はInGaN膜を含み、
前記微細柱状結晶は、ウルツ鉱型結晶構造を有し、先端部にファセット構造を有し、
前記ファセット構造は、直上方を向いた第1の面と、斜め上方を向いた第2の面を有し、
前記第1の面上に形成された前記InGaN膜のIn組成比は、前記第2の面上に形成された前記InGaN膜のIn組成比率よりも高い半導体光素子アレイ。 - 請求項1に記載の半導体光素子アレイであって、
異なる径の前記微細柱状結晶を含み、
径が小さな前記微細柱状結晶上の前記活性層から放出される発光のピーク波長は、径が大きな前記微細柱状結晶上の前記活性層から放出される発光のピーク波長よりも短波長である半導体光素子アレイ。 - 請求項1から3のうちのいずれか1項に記載の半導体光素子アレイであって、
前記各微細柱状結晶の径は、10nm以上、1000nm以下である半導体光素子アレイ。 - 請求項4に記載の半導体光素子アレイであって、
前記微細柱状結晶の先端部には、ファセット面が形成されており、
前記活性層は、このファセット面を被覆する半導体光素子アレイ。 - 請求項1から5のうちのいずれか1項に記載の半導体光素子アレイであって、
前記活性層は、前記半導体層により完全に被覆されている、半導体光素子アレイ。 - 請求項1から6のうちのいずれか1項に記載の半導体光素子アレイであって、
前記微細柱状結晶の導電型は、第1導電型であり、
前記半導体層は、前記第1導電型とは逆の第2導電型のIII族窒化物半導体層を含む、
半導体光素子アレイ。 - 請求項1から7のうちのいずれか1項に記載の半導体光素子アレイであって、
前記複数の微細柱状結晶は、発光波長の異なる複数の柱状結晶群からなる、半導体光素子アレイ。 - 請求項8に記載の半導体光素子アレイであって、
前記複数の柱状結晶群は、少なくとも、3原色の波長の光をそれぞれ放出する3つの柱状結晶群を含む、半導体光素子アレイ。 - 請求項1から9のうちのいずれか1項に記載の半導体光素子アレイであって、
前記活性層は、量子井戸層と、前記量子井戸層よりも大きなバンドギャップを有し前記量子井戸層を挟み込む障壁層とを含む量子井戸構造を有する、半導体光素子アレイ。 - 請求項1から10のうちのいずれか1項に記載の半導体光素子アレイであって、
前記マスクパターンの構成材料は、チタン(Ti)、タンタル(Ta)、鉄(Fe)、ニッケル(Ni)、白金(Pt)、金(Au)、コバルト(Co)およびタングステン(W)、モリブデン(Mo)からなる群より選択された1種または2種以上の金属である、半導体光素子アレイ。 - 請求項1から11のうちのいずれか1項に記載の半導体光素子アレイであって、
前記III族窒化物半導体は窒化ガリウムを含む、半導体光素子アレイ。 - 請求項1から12のうちのいずれか1項に記載の半導体光素子アレイであって、
前記III族窒化物半導体はAlxGayIn1−x−yN(0≦x≦1、0≦y≦1、かつ0≦x+y≦1)を含む、半導体光素子アレイ。 - 半導体基板上に複数の開口部を有するマスクパターンを形成する工程と、
前記マスクパターンをエッチングマスクとして前記半導体基板をエッチングすることにより前記半導体基板の主面に複数の凹部を形成する工程と、
前記各凹部から前記各開口部を介して前記マスクパターンの上方に向けて複数の微細柱状結晶を成長させる工程と、
前記微細柱状結晶上に活性層を成長させる工程と、
前記活性層を被覆する半導体層を形成する工程と、
を備え、
前記マスクパターンには、前記複数の開口部の配置密度が高い領域と、前記複数の開口部の配置密度が低い領域とがあり、
前記複数の開口部の配置密度が高い前記領域にある前記複数の微細柱状結晶上の前記活性層から放出される発光のピーク波長は、前記複数の開口部の配置密度が低い前記領域にある前記複数の微細柱状結晶上の前記活性層から放出される発光のピーク波長よりも長波長である半導体光素子アレイの製造方法。 - 半導体基板上に複数の開口部を有するマスクパターンを形成する工程と、
前記マスクパターンをエッチングマスクとして前記半導体基板をエッチングすることにより前記半導体基板の主面に複数の凹部を形成する工程と、
前記各凹部から前記各開口部を介して前記マスクパターンの上方に向けて複数の微細柱状結晶を成長させる工程と、
前記微細柱状結晶上にInGaN膜を含む活性層を成長させる工程と、
前記活性層を被覆する半導体層を形成する工程と、
を備え、
前記マスクパターンを形成する前記工程において、前記マスクパターンは径が異なる前記複数の前記開口部を有し、
前記微細柱状結晶を成長させる前記工程において、
前記微細柱状結晶はウルツ鉱型結晶構造を有し、先端部にファセット構造を有し、
前記ファセット構造は、直上方を向いた第1の面と、斜め上方を向いた第2の面を有するよう前記微細柱状結晶を成長させ、
前記活性層を成長させる前記工程において、
前記第1の面上に形成された前記InGaN膜のIn組成比が、前記第2の面上に形成された前記InGaN膜のIn組成比率よりも高くなるよう前記活性層を成長させ、
径が小さな前記微細柱状結晶上の前記活性層から放出される発光のピーク波長は、径が大きな前記微細柱状結晶上の前記活性層から放出される発光のピーク波長よりも短波長である半導体光素子アレイの製造方法。 - 請求項14または15に記載の半導体光素子アレイの製造方法であって、
前記マスクパターンの上方に向けて複数の微細柱状結晶を成長させる前記工程と同時に、前記微細柱状結晶を前記半導体基板の面内方向に沿った横方向へ成長させる工程をさらに備える半導体光素子アレイの製造方法。 - 請求項14から16のうちいずれか1項に記載の半導体光素子アレイの製造方法であって、
前記微細柱状結晶の導電型は、第1導電型であり、
前記半導体層は、前記第1導電型とは逆の第2導電型のIII族窒化物半導体層を含む半導体光素子アレイの製造方法。
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010526554A JP5547076B2 (ja) | 2008-09-01 | 2009-08-27 | 半導体光素子アレイおよびその製造方法 |
Applications Claiming Priority (6)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008224129 | 2008-09-01 | ||
| JP2008224129 | 2008-09-01 | ||
| JP2008224131 | 2008-09-01 | ||
| JP2008224131 | 2008-09-01 | ||
| JP2010526554A JP5547076B2 (ja) | 2008-09-01 | 2009-08-27 | 半導体光素子アレイおよびその製造方法 |
| PCT/JP2009/004173 WO2010023921A1 (ja) | 2008-09-01 | 2009-08-27 | 半導体光素子アレイおよびその製造方法 |
Related Child Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013132114A Division JP5687731B2 (ja) | 2008-09-01 | 2013-06-24 | 半導体光素子アレイおよびその製造方法 |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JPWO2010023921A1 JPWO2010023921A1 (ja) | 2012-01-26 |
| JP5547076B2 true JP5547076B2 (ja) | 2014-07-09 |
Family
ID=41721104
Family Applications (2)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010526554A Active JP5547076B2 (ja) | 2008-09-01 | 2009-08-27 | 半導体光素子アレイおよびその製造方法 |
| JP2013132114A Active JP5687731B2 (ja) | 2008-09-01 | 2013-06-24 | 半導体光素子アレイおよびその製造方法 |
Family Applications After (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013132114A Active JP5687731B2 (ja) | 2008-09-01 | 2013-06-24 | 半導体光素子アレイおよびその製造方法 |
Country Status (7)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US9224595B2 (ja) |
| EP (1) | EP2333847B1 (ja) |
| JP (2) | JP5547076B2 (ja) |
| KR (1) | KR101567121B1 (ja) |
| CN (1) | CN102187479B (ja) |
| TW (1) | TWI470828B (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2010023921A1 (ja) |
Families Citing this family (73)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE102010012711A1 (de) * | 2010-03-25 | 2011-09-29 | Osram Opto Semiconductors Gmbh | Strahlungsemittierendes Halbleiterbauelement und Verfahren zur Herstellung eines strahlungsemittierenden Halbleiterbauelements |
| KR101710159B1 (ko) * | 2010-09-14 | 2017-03-08 | 삼성전자주식회사 | Ⅲ족 질화물 나노로드 발광소자 및 그 제조 방법 |
| US8969890B2 (en) * | 2010-11-04 | 2015-03-03 | Koninklijke Philips N.V. | Solid state light emitting devices based on crystallographically relaxed structures |
| GB201020843D0 (en) * | 2010-12-09 | 2011-01-19 | Univ Nottingham | Solar cells based on InGaN |
| FR2983639B1 (fr) * | 2011-12-01 | 2014-07-18 | Commissariat Energie Atomique | Dispositif optoelectronique comprenant des nanofils de structure coeur/coquille |
| CN104205294B (zh) * | 2012-02-14 | 2017-05-10 | 六边钻公司 | 基于氮化镓纳米线的电子器件 |
| SE537434C2 (sv) | 2012-06-26 | 2015-04-28 | Polar Light Technologies Ab | Grupp III-nitridstruktur |
| TWI476953B (zh) | 2012-08-10 | 2015-03-11 | Univ Nat Taiwan | 半導體發光元件及其製作方法 |
| JP2014060198A (ja) * | 2012-09-14 | 2014-04-03 | Oki Electric Ind Co Ltd | 窒化物半導体発光ダイオードの製造方法、及び窒化物半導体発光ダイオード |
| JP6060652B2 (ja) * | 2012-11-28 | 2017-01-18 | 富士通株式会社 | 太陽電池及びその製造方法 |
| EP2939276B1 (fr) | 2012-12-28 | 2019-06-12 | Aledia | Dispositif opto-électronique à microfils ou nanofils |
| FR3000612B1 (fr) | 2012-12-28 | 2016-05-06 | Commissariat Energie Atomique | Dispositif optoelectronique a microfils ou nanofils |
| US11502219B2 (en) * | 2013-03-14 | 2022-11-15 | The Royal Institution For The Advancement Of Learning/Mcgill University | Methods and devices for solid state nanowire devices |
| DE102013104273A1 (de) | 2013-04-26 | 2014-10-30 | Osram Opto Semiconductors Gmbh | Anordnung mit säulenartiger Struktur und einer aktiven Zone |
| JP6227128B2 (ja) * | 2013-06-07 | 2017-11-08 | グロ アーベーGlo Ab | マルチカラーled及びその製造方法 |
| KR102190675B1 (ko) * | 2013-10-10 | 2020-12-15 | 삼성전자주식회사 | 반도체 소자의 미세 패턴 형성 방법 |
| FR3023410A1 (fr) * | 2014-07-02 | 2016-01-08 | Aledia | Dispositif optoelectronique a elements semiconducteurs et son procede de fabrication |
| FR3026564B1 (fr) * | 2014-09-30 | 2018-02-16 | Commissariat A L'energie Atomique Et Aux Energies Alternatives | Dispositif optoelectronique a elements semiconducteurs tridimensionnels |
| KR102212557B1 (ko) | 2014-11-03 | 2021-02-08 | 삼성전자주식회사 | 나노구조 반도체 발광소자 |
| DE102014116999A1 (de) * | 2014-11-20 | 2016-05-25 | Osram Opto Semiconductors Gmbh | Verfahren zur Herstellung eines optoelektronischen Halbleiterchips und optoelektronischer Halbleiterchip |
| FR3029015B1 (fr) * | 2014-11-24 | 2018-03-02 | Commissariat A L'energie Atomique Et Aux Energies Alternatives | Dispositif optoelectronique a elements semiconducteurs tridimensionnels et son procede de fabrication |
| DE102016104616B4 (de) * | 2016-03-14 | 2021-09-23 | OSRAM Opto Semiconductors Gesellschaft mit beschränkter Haftung | Halbleiterlichtquelle |
| FR3050322B1 (fr) * | 2016-04-18 | 2019-01-25 | Centre National De La Recherche Scientifique (Cnrs) | Dispositif photorecepteur multicouche, a parametres de maille differents |
| JP6873409B2 (ja) * | 2016-04-21 | 2021-05-19 | 富士通株式会社 | 発光素子及びその製造方法 |
| FR3053434B1 (fr) * | 2016-06-30 | 2019-06-28 | Valeo Vision | Module d'emission de lumiere blanche a spectre enrichi |
| EP3522240B1 (en) | 2016-09-29 | 2021-06-30 | Nichia Corporation | Light emitting element |
| JP7090861B2 (ja) * | 2017-02-28 | 2022-06-27 | 学校法人上智学院 | 光デバイスおよび光デバイスの製造方法 |
| JP7333666B2 (ja) * | 2017-02-28 | 2023-08-25 | 学校法人上智学院 | 光デバイスおよび光デバイスの製造方法 |
| JP6972665B2 (ja) * | 2017-05-31 | 2021-11-24 | セイコーエプソン株式会社 | 発光装置、プロジェクター、および発光装置の製造方法 |
| JP7147132B2 (ja) * | 2017-05-31 | 2022-10-05 | セイコーエプソン株式会社 | 発光装置、プロジェクター、および発光装置の製造方法 |
| JP6947386B2 (ja) * | 2017-06-29 | 2021-10-13 | 学校法人 名城大学 | 半導体発光素子および半導体発光素子の製造方法 |
| FR3068517B1 (fr) * | 2017-06-30 | 2019-08-09 | Aledia | Dispositif optoelectronique comportant des structures semiconductrices tridimensionnelles en configuration axiale |
| US10263151B2 (en) * | 2017-08-18 | 2019-04-16 | Globalfoundries Inc. | Light emitting diodes |
| CN107482094A (zh) * | 2017-09-21 | 2017-12-15 | 山西飞虹微纳米光电科技有限公司 | 基于GaN基轴向纳米棒阵列的LED及其制备方法 |
| JP7053209B2 (ja) * | 2017-10-02 | 2022-04-12 | 株式会社小糸製作所 | 半導体成長用基板、半導体素子、半導体発光素子及び半導体成長用基板の製造方法 |
| JP7329798B2 (ja) * | 2018-02-01 | 2023-08-21 | 株式会社レゾナック | ナノ結晶膜の製造方法 |
| JP7105442B2 (ja) | 2018-08-06 | 2022-07-25 | セイコーエプソン株式会社 | 発光装置およびプロジェクター |
| CN109148651B (zh) * | 2018-08-06 | 2019-10-15 | 复旦大学 | 基于GaN条纹模板的多色发光InGaN量子阱外延片的制备方法 |
| JP7188690B2 (ja) * | 2018-08-22 | 2022-12-13 | セイコーエプソン株式会社 | プロジェクター |
| KR102652501B1 (ko) | 2018-09-13 | 2024-03-29 | 삼성디스플레이 주식회사 | 발광 소자의 제조방법 및 발광 소자를 포함하는 표시 장치 |
| JP7320770B2 (ja) * | 2018-09-28 | 2023-08-04 | セイコーエプソン株式会社 | 発光装置およびプロジェクター |
| JP7312997B2 (ja) * | 2018-11-09 | 2023-07-24 | 学校法人 名城大学 | 半導体発光素子 |
| CN111463659B (zh) * | 2019-01-21 | 2021-08-13 | 华为技术有限公司 | 量子点半导体光放大器及其制备方法 |
| EP3696300A1 (de) | 2019-02-18 | 2020-08-19 | Aixatech GmbH | Verfahren zur herstellung eines verbundmaterialkörpers insbesondere für die verwendung bei der herstellung von elektronischen oder optoelektronischen bauelementen |
| JP7207012B2 (ja) | 2019-02-27 | 2023-01-18 | セイコーエプソン株式会社 | 発光装置の製造方法、発光装置、およびプロジェクター |
| JP7232461B2 (ja) | 2019-02-28 | 2023-03-03 | セイコーエプソン株式会社 | 発光装置およびプロジェクター |
| JP7232465B2 (ja) | 2019-03-26 | 2023-03-03 | セイコーエプソン株式会社 | 発光装置およびプロジェクター |
| JP7232464B2 (ja) | 2019-03-26 | 2023-03-03 | セイコーエプソン株式会社 | 発光装置およびプロジェクター |
| JP6981444B2 (ja) | 2019-04-01 | 2021-12-15 | セイコーエプソン株式会社 | 発光装置、発光装置の製造方法、およびプロジェクター |
| US11637219B2 (en) | 2019-04-12 | 2023-04-25 | Google Llc | Monolithic integration of different light emitting structures on a same substrate |
| FR3098019B1 (fr) * | 2019-06-25 | 2022-05-20 | Aledia | Dispositif optoélectronique comprenant des éléments semi-conducteurs tridimensionnels et procédé pour sa fabrication |
| JP7392426B2 (ja) | 2019-11-28 | 2023-12-06 | セイコーエプソン株式会社 | 発光装置およびプロジェクター |
| RU2758776C2 (ru) * | 2019-12-05 | 2021-11-01 | Федеральное государственное бюджетное учреждение науки Физико-технический институт им. А.Ф. Иоффе Российской академии наук | Способ изготовления наноколончатой гетероструктуры на основе соединений iii-n |
| US11404473B2 (en) | 2019-12-23 | 2022-08-02 | Lumileds Llc | III-nitride multi-wavelength LED arrays |
| US11923398B2 (en) | 2019-12-23 | 2024-03-05 | Lumileds Llc | III-nitride multi-wavelength LED arrays |
| US11581450B2 (en) * | 2020-06-11 | 2023-02-14 | Globalfoundries U.S. Inc. | Photodiode and/or pin diode structures with one or more vertical surfaces |
| US20230335400A1 (en) * | 2020-06-22 | 2023-10-19 | Kyocera Corporation | Method for producing semiconductor device, semiconductor device, electronic device, method for producing semiconductor epitaxial substrate, and semiconductor epitaxial substrate |
| JP7176700B2 (ja) * | 2020-07-31 | 2022-11-22 | セイコーエプソン株式会社 | 発光装置およびプロジェクター |
| JP7520305B2 (ja) | 2020-08-31 | 2024-07-23 | 株式会社小糸製作所 | 半導体発光素子および半導体発光素子の製造方法 |
| US11094846B1 (en) | 2020-08-31 | 2021-08-17 | 4233999 Canada Inc. | Monolithic nanocolumn structures |
| US11322649B2 (en) | 2020-09-15 | 2022-05-03 | Applied Materials, Inc. | Three color light sources integrated on a single wafer |
| JP7556246B2 (ja) | 2020-09-23 | 2024-09-26 | セイコーエプソン株式会社 | 発光装置、発光装置の製造方法およびプロジェクター |
| JP7203390B2 (ja) | 2020-10-13 | 2023-01-13 | セイコーエプソン株式会社 | 発光装置およびプロジェクター |
| US11631786B2 (en) | 2020-11-12 | 2023-04-18 | Lumileds Llc | III-nitride multi-wavelength LED arrays with etch stop layer |
| JPWO2022190353A1 (ja) * | 2021-03-12 | 2022-09-15 | ||
| JP7320794B2 (ja) * | 2021-03-15 | 2023-08-04 | セイコーエプソン株式会社 | 発光装置、プロジェクター、およびディスプレイ |
| JP2022190630A (ja) * | 2021-06-14 | 2022-12-26 | 豊田合成株式会社 | 半導体発光素子の製造方法 |
| US20240332339A1 (en) * | 2021-07-08 | 2024-10-03 | Koito Manufacturing Co., Ltd. | Semiconductor light emitting element and method for producing semiconductor light emitting element |
| JP2023065945A (ja) * | 2021-10-28 | 2023-05-15 | セイコーエプソン株式会社 | 発光装置およびプロジェクター |
| JP7272412B1 (ja) | 2021-12-03 | 2023-05-12 | 信越半導体株式会社 | 接合型半導体ウェーハの製造方法 |
| CN114300580B (zh) * | 2021-12-30 | 2024-06-04 | 长春理工大学 | 一种探测器材料及其制备方法 |
| WO2024164078A1 (en) * | 2023-02-08 | 2024-08-15 | 4233999 Canada Inc. | Light emitters on coalesced selective area growth nanocolumns |
| US11799054B1 (en) | 2023-02-08 | 2023-10-24 | 4233999 Canada Inc. | Monochromatic emitters on coalesced selective area growth nanocolumns |
Citations (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2003282942A (ja) * | 2001-08-22 | 2003-10-03 | Sony Corp | 窒化物半導体素子及び窒化物半導体素子の製造方法 |
| WO2006025407A1 (ja) * | 2004-08-31 | 2006-03-09 | Akihiko Kikuchi | 発光素子及びその製造方法 |
| JP2007027298A (ja) * | 2005-07-14 | 2007-02-01 | Matsushita Electric Works Ltd | 半導体発光素子およびそれを用いる照明装置ならびに半導体発光素子の製造方法 |
| JP2008022014A (ja) * | 2006-07-13 | 2008-01-31 | Sharp Corp | 窒化物半導体を加工してなる発光デバイスの処理方法 |
| JP2008034483A (ja) * | 2006-07-26 | 2008-02-14 | Matsushita Electric Works Ltd | 化合物半導体素子およびそれを用いる照明装置ならびに化合物半導体素子の製造方法 |
| JP2008034482A (ja) * | 2006-07-26 | 2008-02-14 | Matsushita Electric Works Ltd | 化合物半導体発光素子およびそれを用いる照明装置ならびに化合物半導体素子の製造方法 |
| WO2008048704A2 (en) * | 2006-03-10 | 2008-04-24 | Stc.Unm | Pulsed growth of gan nanowires and applications in group iii nitride semiconductor substrate materials and devices |
| JP2008108757A (ja) * | 2006-10-23 | 2008-05-08 | Matsushita Electric Works Ltd | 化合物半導体発光素子およびそれを用いる照明装置ならびに化合物半導体素子の製造方法 |
Family Cites Families (17)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP0504851B1 (en) * | 1991-03-22 | 1997-07-16 | Hitachi, Ltd. | Semiconductor optical device |
| JP4780113B2 (ja) | 2000-09-18 | 2011-09-28 | 三菱化学株式会社 | 半導体発光素子 |
| JP3556916B2 (ja) | 2000-09-18 | 2004-08-25 | 三菱電線工業株式会社 | 半導体基材の製造方法 |
| JP4381397B2 (ja) | 2000-10-04 | 2009-12-09 | 三洋電機株式会社 | 窒化物系半導体素子および窒化物系半導体の形成方法 |
| JP3863720B2 (ja) | 2000-10-04 | 2006-12-27 | 三洋電機株式会社 | 窒化物系半導体素子および窒化物系半導体の形成方法 |
| JP3679720B2 (ja) | 2001-02-27 | 2005-08-03 | 三洋電機株式会社 | 窒化物系半導体素子および窒化物系半導体の形成方法 |
| JP3454791B2 (ja) | 2001-03-01 | 2003-10-06 | 三洋電機株式会社 | 窒化物系半導体素子および窒化物系半導体の形成方法 |
| US6818465B2 (en) * | 2001-08-22 | 2004-11-16 | Sony Corporation | Nitride semiconductor element and production method for nitride semiconductor element |
| DE10213643A1 (de) | 2002-03-27 | 2003-10-09 | Geka Brush Gmbh | Kosmetikeinheit |
| US7485902B2 (en) | 2002-09-18 | 2009-02-03 | Sanyo Electric Co., Ltd. | Nitride-based semiconductor light-emitting device |
| US6936851B2 (en) * | 2003-03-21 | 2005-08-30 | Tien Yang Wang | Semiconductor light-emitting device and method for manufacturing the same |
| JP2004354617A (ja) | 2003-05-28 | 2004-12-16 | Sharp Corp | フォトニック結晶とその製造方法 |
| US7132677B2 (en) * | 2004-02-13 | 2006-11-07 | Dongguk University | Super bright light emitting diode of nanorod array structure having InGaN quantum well and method for manufacturing the same |
| JP2006339534A (ja) | 2005-06-03 | 2006-12-14 | Sony Corp | 発光ダイオード、発光ダイオードの製造方法、発光ダイオードバックライト、発光ダイオード照明装置、発光ダイオードディスプレイおよび電子機器 |
| EP2064745A1 (en) * | 2006-09-18 | 2009-06-03 | QuNano AB | Method of producing precision vertical and horizontal layers in a vertical semiconductor structure |
| JP2008108924A (ja) | 2006-10-26 | 2008-05-08 | Matsushita Electric Works Ltd | 化合物半導体発光素子およびそれを用いる照明装置ならびに化合物半導体発光素子の製造方法 |
| US8030108B1 (en) * | 2008-06-30 | 2011-10-04 | Stc.Unm | Epitaxial growth of in-plane nanowires and nanowire devices |
-
2009
- 2009-08-27 WO PCT/JP2009/004173 patent/WO2010023921A1/ja active Application Filing
- 2009-08-27 CN CN200980141161.XA patent/CN102187479B/zh active Active
- 2009-08-27 EP EP09809577.1A patent/EP2333847B1/en active Active
- 2009-08-27 US US13/061,425 patent/US9224595B2/en active Active
- 2009-08-27 KR KR1020117007423A patent/KR101567121B1/ko active IP Right Grant
- 2009-08-27 JP JP2010526554A patent/JP5547076B2/ja active Active
- 2009-09-01 TW TW98129403A patent/TWI470828B/zh active
-
2013
- 2013-06-24 JP JP2013132114A patent/JP5687731B2/ja active Active
Patent Citations (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2003282942A (ja) * | 2001-08-22 | 2003-10-03 | Sony Corp | 窒化物半導体素子及び窒化物半導体素子の製造方法 |
| WO2006025407A1 (ja) * | 2004-08-31 | 2006-03-09 | Akihiko Kikuchi | 発光素子及びその製造方法 |
| JP2007027298A (ja) * | 2005-07-14 | 2007-02-01 | Matsushita Electric Works Ltd | 半導体発光素子およびそれを用いる照明装置ならびに半導体発光素子の製造方法 |
| WO2008048704A2 (en) * | 2006-03-10 | 2008-04-24 | Stc.Unm | Pulsed growth of gan nanowires and applications in group iii nitride semiconductor substrate materials and devices |
| JP2008022014A (ja) * | 2006-07-13 | 2008-01-31 | Sharp Corp | 窒化物半導体を加工してなる発光デバイスの処理方法 |
| JP2008034483A (ja) * | 2006-07-26 | 2008-02-14 | Matsushita Electric Works Ltd | 化合物半導体素子およびそれを用いる照明装置ならびに化合物半導体素子の製造方法 |
| JP2008034482A (ja) * | 2006-07-26 | 2008-02-14 | Matsushita Electric Works Ltd | 化合物半導体発光素子およびそれを用いる照明装置ならびに化合物半導体素子の製造方法 |
| JP2008108757A (ja) * | 2006-10-23 | 2008-05-08 | Matsushita Electric Works Ltd | 化合物半導体発光素子およびそれを用いる照明装置ならびに化合物半導体素子の製造方法 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| US20110169025A1 (en) | 2011-07-14 |
| CN102187479A (zh) | 2011-09-14 |
| TW201027800A (en) | 2010-07-16 |
| EP2333847A1 (en) | 2011-06-15 |
| TWI470828B (zh) | 2015-01-21 |
| JP2013239718A (ja) | 2013-11-28 |
| US9224595B2 (en) | 2015-12-29 |
| KR101567121B1 (ko) | 2015-11-06 |
| EP2333847A4 (en) | 2015-02-25 |
| EP2333847B1 (en) | 2018-02-14 |
| WO2010023921A1 (ja) | 2010-03-04 |
| JP5687731B2 (ja) | 2015-03-18 |
| CN102187479B (zh) | 2014-06-18 |
| KR20110063799A (ko) | 2011-06-14 |
| JPWO2010023921A1 (ja) | 2012-01-26 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5687731B2 (ja) | 半導体光素子アレイおよびその製造方法 | |
| JP4786691B2 (ja) | 半導体デバイスおよびその製造方法 | |
| JP3852000B2 (ja) | 発光素子 | |
| EP2731151B1 (en) | Method of manufacture for nitride semiconductor light emitting element, wafer, and nitride semiconductor light emitting element | |
| JP5162016B1 (ja) | 半導体素子、ウェーハ、半導体素子の製造方法及びウェーハの製造方法 | |
| US9190559B2 (en) | Semiconductor light emitting device, nitride semiconductor layer, and method for forming nitride semiconductor layer | |
| US8791025B2 (en) | Method of producing microstructure of nitride semiconductor and photonic crystal prepared according to the method | |
| KR20220066948A (ko) | 물질의 조성물 | |
| US10995403B2 (en) | Method of forming aluminum nitride film and method of manufacturing semiconductor light-emitting element | |
| JP2008117902A (ja) | 窒化物半導体素子の製造方法 | |
| TWI828945B (zh) | 氮化物半導體紫外線發光元件 | |
| US20230307578A1 (en) | Nitride Semiconductor Ultraviolet Light Emitting Element | |
| US20230197889A1 (en) | Nitride semiconductor ultraviolet light-emitting element and production method therefor | |
| JP5227870B2 (ja) | エピタキシャル基板、半導体素子構造、およびエピタキシャル基板の作製方法 | |
| TW202107734A (zh) | 發光二極體及其製造方法 | |
| JP2009224704A (ja) | 窒化物系半導体発光素子、エピタキシャルウエハ、及び窒化物系半導体発光素子を作製する方法 | |
| JP2020077832A (ja) | 半導体素子及び半導体レーザダイオード | |
| WO2024029553A1 (ja) | 半導体光素子アレイ | |
| Kishino et al. | Molecular beam epitaxial growth of GaN nanocolumns and related nanocolumn emitters | |
| JP2011187993A (ja) | 半導体発光素子および半導体発光素子の製造方法 | |
| JP4055794B2 (ja) | 窒化ガリウム系化合物半導体発光素子 | |
| JP2009253047A (ja) | Iii族窒化物発光素子及びエピタキシャルウエハ | |
| WO2024042221A1 (en) | Nanostructure/microstructure device | |
| JP2022118051A (ja) | 光デバイスおよび光デバイスの製造方法 | |
| JP2013135016A (ja) | 窒化物半導体発光素子およびその製造方法 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20120823 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20120823 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20130423 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20130624 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20131008 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20131204 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20140507 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20140514 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 5547076 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |