EP3436638B1 - Übergangskonstruktion zur überbrückung einer bauwerksfuge - Google Patents
Übergangskonstruktion zur überbrückung einer bauwerksfuge Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP3436638B1 EP3436638B1 EP17714432.6A EP17714432A EP3436638B1 EP 3436638 B1 EP3436638 B1 EP 3436638B1 EP 17714432 A EP17714432 A EP 17714432A EP 3436638 B1 EP3436638 B1 EP 3436638B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- cover element
- transition construction
- anchoring structure
- transition
- building
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 230000007704 transition Effects 0.000 title claims description 60
- 238000010276 construction Methods 0.000 claims description 39
- 238000004873 anchoring Methods 0.000 claims description 34
- 125000006850 spacer group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 18
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 8
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 claims description 8
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 claims description 5
- 230000001154 acute effect Effects 0.000 claims description 4
- 230000002787 reinforcement Effects 0.000 claims description 2
- 238000007789 sealing Methods 0.000 claims description 2
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Substances O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 13
- 230000008901 benefit Effects 0.000 description 8
- 238000012423 maintenance Methods 0.000 description 5
- 230000000149 penetrating effect Effects 0.000 description 5
- 230000007797 corrosion Effects 0.000 description 4
- 238000005260 corrosion Methods 0.000 description 4
- 238000013461 design Methods 0.000 description 4
- 238000011161 development Methods 0.000 description 4
- 230000018109 developmental process Effects 0.000 description 4
- 229920001971 elastomer Polymers 0.000 description 4
- 238000012546 transfer Methods 0.000 description 4
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 3
- 229910000831 Steel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000009415 formwork Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229920001296 polysiloxane Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 230000036316 preload Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000010959 steel Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000003860 storage Methods 0.000 description 2
- 241001465754 Metazoa Species 0.000 description 1
- 229910052782 aluminium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N aluminium Chemical compound [Al] XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000004888 barrier function Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000001413 cellular effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000000806 elastomer Substances 0.000 description 1
- 210000001145 finger joint Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 238000009434 installation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000011835 investigation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000003825 pressing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000009467 reduction Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000001105 regulatory effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000000284 resting effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000003466 welding Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- E—FIXED CONSTRUCTIONS
- E01—CONSTRUCTION OF ROADS, RAILWAYS, OR BRIDGES
- E01D—CONSTRUCTION OF BRIDGES, ELEVATED ROADWAYS OR VIADUCTS; ASSEMBLY OF BRIDGES
- E01D19/00—Structural or constructional details of bridges
- E01D19/06—Arrangement, construction or bridging of expansion joints
-
- E—FIXED CONSTRUCTIONS
- E01—CONSTRUCTION OF ROADS, RAILWAYS, OR BRIDGES
- E01D—CONSTRUCTION OF BRIDGES, ELEVATED ROADWAYS OR VIADUCTS; ASSEMBLY OF BRIDGES
- E01D19/00—Structural or constructional details of bridges
- E01D19/06—Arrangement, construction or bridging of expansion joints
- E01D19/065—Joints having sliding plates
-
- E—FIXED CONSTRUCTIONS
- E01—CONSTRUCTION OF ROADS, RAILWAYS, OR BRIDGES
- E01C—CONSTRUCTION OF, OR SURFACES FOR, ROADS, SPORTS GROUNDS, OR THE LIKE; MACHINES OR AUXILIARY TOOLS FOR CONSTRUCTION OR REPAIR
- E01C11/00—Details of pavings
- E01C11/02—Arrangement or construction of joints; Methods of making joints; Packing for joints
-
- E—FIXED CONSTRUCTIONS
- E01—CONSTRUCTION OF ROADS, RAILWAYS, OR BRIDGES
- E01C—CONSTRUCTION OF, OR SURFACES FOR, ROADS, SPORTS GROUNDS, OR THE LIKE; MACHINES OR AUXILIARY TOOLS FOR CONSTRUCTION OR REPAIR
- E01C11/00—Details of pavings
- E01C11/02—Arrangement or construction of joints; Methods of making joints; Packing for joints
- E01C11/04—Arrangement or construction of joints; Methods of making joints; Packing for joints for cement concrete paving
- E01C11/08—Packing of metal
-
- E—FIXED CONSTRUCTIONS
- E01—CONSTRUCTION OF ROADS, RAILWAYS, OR BRIDGES
- E01D—CONSTRUCTION OF BRIDGES, ELEVATED ROADWAYS OR VIADUCTS; ASSEMBLY OF BRIDGES
- E01D19/00—Structural or constructional details of bridges
- E01D19/06—Arrangement, construction or bridging of expansion joints
- E01D19/067—Flat continuous joints cast in situ
-
- E—FIXED CONSTRUCTIONS
- E04—BUILDING
- E04B—GENERAL BUILDING CONSTRUCTIONS; WALLS, e.g. PARTITIONS; ROOFS; FLOORS; CEILINGS; INSULATION OR OTHER PROTECTION OF BUILDINGS
- E04B1/00—Constructions in general; Structures which are not restricted either to walls, e.g. partitions, or floors or ceilings or roofs
- E04B1/62—Insulation or other protection; Elements or use of specified material therefor
- E04B1/66—Sealings
- E04B1/68—Sealings of joints, e.g. expansion joints
-
- E—FIXED CONSTRUCTIONS
- E04—BUILDING
- E04B—GENERAL BUILDING CONSTRUCTIONS; WALLS, e.g. PARTITIONS; ROOFS; FLOORS; CEILINGS; INSULATION OR OTHER PROTECTION OF BUILDINGS
- E04B1/00—Constructions in general; Structures which are not restricted either to walls, e.g. partitions, or floors or ceilings or roofs
- E04B1/62—Insulation or other protection; Elements or use of specified material therefor
- E04B1/66—Sealings
- E04B1/68—Sealings of joints, e.g. expansion joints
- E04B1/6803—Joint covers
- E04B1/6804—Joint covers specially adapted for floor parts
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a transition structure for bridging a structural joint between two components of a building with at least one cover element which at least partially covers the structural joint and which can be fastened to a structural component via an anchor structure.
- transition constructions are known in various embodiments. What they all have in common is that they are used to safely cross a building joint by traffic, for example by people, animals, vehicles, loads and the like. Bridge building is a particularly common area of application. However, all other structures that have structural joints are also relevant for the subject matter of the invention.
- the WO 2011/079487 A1 discloses a transition structure for bridging a building joint between two components of a building with at least one cover element which at least partially covers the building joint and which can be fastened to a component of the building via an anchor structure, the anchor structure being designed so that the at least one cover element is supported selectively on it is.
- the DE 12 31 740 B also discloses a transition structure, the anchor structure having consoles on which the cover element is supported at points via support beam sections.
- a known form of such a generic transition structure is the so-called finger joint.
- This has at least two cover elements arranged opposite one another, which in turn have a number of fingers lying next to one another. This results in two comb-like finger plates. These are designed or arranged in such a way that the opposing finger plates mesh with one another. Depending on how the structural joint changes, the fingers can be pushed together or apart.
- the cover elements are each attached to the structural components that adjoin the structural joint with the aid of anchor structures.
- the anchor construction thus serves to fasten at least one cover element to the respective component and can accordingly be configured in a wide variety of ways.
- the anchor structure can be made in one piece or in several parts. It can be fastening flanges that are welded to a component made of steel and to which the cover element can be fastened. It can also only be a screw connection with which a cover element is attached to the relevant component of the structure.
- such an anchor structure is an independent structure made up of several components, such as anchor brackets, system plates, multi-wall sheets and the like, which are in any case partially concreted into the component.
- a known solution for anchoring the cover elements is to screw the respective cover element either directly through the structure or to an anchor structure below.
- the cover element or the cover elements in these known solutions lie flat on the component of the building or the intermediate anchor structure.
- the invention is therefore based on the object of improving the generic transition structure in such a way that it can be serviced with less effort than before.
- the transition structure according to the invention is thus characterized in that the anchor structure is designed in such a way that the at least one cover element is stored selectively on it.
- the planar support that has always been used up to now is specifically avoided and, ideally, completely replaced by a point support.
- the selective mounting of the cover element results in a much more controlled introduction of forces into the structure than before. It is thus possible to dimension the fastening of the cover elements much more precisely than before and to avoid losses of prestressing force due to unevenness, relaxation and creep. This reduces the risk of the anchoring of the cover element being oversized or undersized.
- Another advantage is that the selective mounting of the cover element means that significantly less moisture can accumulate between the anchor structure or between the component and the cover element. This reduces the risk of corrosion. In addition, corrosion protection can be applied more easily and the drainage of the structure is improved overall.
- the point-to-point support is generated by a corresponding design of the anchor structure. This then ensures that the cover element only rests selectively on the structure. This creates a clearly defined or, in other words, planned storage. This leads to a much more permanent solution than in the prior art.
- Pointed mounting is to be understood here as a mounting in which only part of the base area of the cover element comes into contact with the component or the anchor structure. This part should be smaller than half of the base area of the cover element.
- the anchor structure has several support points, at least one of which can be adjusted and / or aligned in its position independently of the others. Because at least one support point is independent of the others, tolerances and unevenness can be compensated practically perfectly.
- the individual support points are all adaptable with regard to their position, so that there is no influence on neighboring support points.
- the at least one cover element is releasably attached to the anchor structure with the aid of at least one screw connection and the anchor structure is designed so that at least one screw connection has a clamping length that is at least three times the thickness of the cover element in the area of the respective screw connection.
- the screw connection is preferably tightened from below.
- the cover element is not screwed directly into the component, but is fastened by means of a correspondingly designed anchor structure, a loss of the prestressing force of the screw connection due to changes in the material of the component, such as creeping and / or shrinking of a concrete component within the Structure to be avoided.
- the screw connection can be designed in any form in which a thread is used. Investigations by the applicant have shown that, with the aid of the appropriately dimensioned clamping length, a permanent preload can be applied more securely than before with the loads in question here. Because compared to the known anchor constructions, the clamping lengths are significantly larger than before. The targeted, significantly increased clamping length generally increases the screw elongation and thus a reduction in the proportionate loss of pre-tensioning force.
- the clamp length is generally understood to mean the thickness of the elements to be connected. This is partly calculated with or without a washer that may be used. Here, however, the definition of grip length should be used as it is regulated in the version of the standard DIN EN 14399-4 valid on the filing date. This defines the clamping length taking into account the thickness of any washer.
- the thickness of the cover element should be the distance between the contact surface of the screw connection on the top of the cover element and the contact surface of the cover element on the anchor structure in the area of the screw be understood. Depressions in the cover element in the area of the screw connection are therefore not taken into account.
- a seal is preferably arranged on the screw connection in the area of the cover element, which prevents the water from penetrating into the structure in this area. Loosening of the screw connection can also be additionally prevented by the seal.
- At least one screw connection expediently has a threaded bolt and at least one tensioning means.
- the threaded bolt can be designed in such a way that it has a bolt head at at least one of its ends.
- the thread can also be designed continuously or in sections. Solutions should also be included here in which a threaded bolt fixes the cover element to the anchor structure at both ends by means of at least one nut.
- the threaded bolt is part of a screw that complies with the regulations.
- the screw connection can be reliably dimensioned using existing regulations. In this way, a corresponding oversizing or undersizing of the fastening can be prevented at the planning stage.
- At least one tensioning means is advantageously designed as a nut, bolt head and / or thread on the anchor structure or the cover element.
- the position and type of a tensioning means is therefore not restricted to one variant, but can instead rest and / or be designed accordingly both on the cover element and on the anchor structure.
- the anchor structure on a side facing away from the cover element, has a clamping means system for a clamping means designed as a nut or bolt head.
- a clamping means system for a clamping means designed as a nut or bolt head.
- the corresponding nut or bolt head needs a system as an abutment. As a result, the forces that occur can be absorbed and a certain preload force can be achieved.
- the anchor structure has a spacer which ensures a defined distance between the cover element and the clamping device system.
- the spacer is preferably made of a material, for example a metal, which ensures the distance between the cover plate and the clamping means system even when a great deal of force is applied.
- the spacer is expediently tubular, preferably designed as a square tube.
- tubular is understood to mean not only a circular cross-section, but also a polygonal tube which, for example, has a square or hexagonal cross-section.
- the tubular structure makes it possible for part of the screw connection to run inside the spacer. The screw connection is thus protected from external influences such as moisture.
- the anchor structure can be designed in such a way that it is attached directly to a reinforcement of a component of the structure.
- the anchor structure is then directly connected to the parts of the structure that can absorb large tensile forces and / or compressive forces.
- the corresponding fastening can take place, for example, by screwing or welding.
- the anchor structure expediently has at least one anchoring element for anchoring in a component.
- the anchoring element is preferably designed as a headed bolt. The latter in particular causes good interlocking of the anchor structure with the adjacent concrete. In this way, the cover element can be attached to the structure even more securely.
- the anchoring element can connect directly to the spacer or be part of it. By arranging several anchoring elements, which preferably extend radially in different directions on several levels, the anchor structure can be fixed to the structure even better.
- head bolts other configurations are also possible, such as, for example, washers that surround the spacer.
- anchoring aids that conform to the regulations, such as the headed bolts just described, are preferably used.
- the transition structure has at least one access shaft for a screw connection, the access shaft extending from the anchor structure to one end of the structure.
- the access shaft preferably extends from the lower end of the structure to the clamping device system. In this way, the screw connection can be serviced and adjusted from below even when it is installed. This has the advantage that it is not necessary to block the corresponding traffic areas on the upper side of the cover element during maintenance work.
- the access shaft is preferably formed by means of a formwork pipe concreted into the component of the building. In addition to a circular tubular design of the shaft, it is also possible to design this appropriately polygonal.
- a support anchor can also have the anchoring elements already mentioned for better interlocking in the concrete of the component.
- Such support anchors can easily be prefabricated in large numbers and installed as an assembly in the corresponding structures.
- the anchor structure has several spaced apart support anchors and the selective mounting of the cover element is implemented such that the cover element rests on the anchor structure in the area of the upper end faces of the support anchors.
- This has the advantage that the point-based storage can be ensured in a simple manner by means of the support anchors.
- the support anchors can simply be concreted into the component in such a way that they protrude slightly over the top of the concrete of the respective component.
- the end faces of the support anchors form the surfaces which face the covering element lying on it and are in contact with it. By resting only on the end faces of the support anchors, it can also be guaranteed that the cover elements do not transfer loads into the structure other than via the support anchors.
- the anchor construction expediently has at least one row of support anchors running parallel to the building joint, and preferably a further row of supporting anchors also running parallel to the building joint, behind it.
- the arrangement in rows simplifies production.
- the cover element is additionally fixed and moments that occur due to off-center loading are thus carried away as a force couple.
- the transition structure has a drainage element which is below and at a distance from the cover element, preferably at an acute angle running downwards towards the cover element and towards the building joint, is arranged on the anchor structure.
- a drainage element which is below and at a distance from the cover element, preferably at an acute angle running downwards towards the cover element and towards the building joint.
- water reaching under the cover element can be diverted in the direction of the structural joint.
- the acute angle ensures that the water runs off well and that no large amounts of water accumulate in this area of the structure, which would promote corrosion.
- the arrangement of the drainage element on the anchor structure has the advantage that the element can provide the necessary support against the water that is pressing downwards.
- the drainage element is preferably designed to be flat in order to protect the largest possible area of the structure below the cover element from penetrating water.
- the drainage element is designed as a sheet metal which is folded down on its side facing the structural joint in such a way that this side forms a drip edge.
- the sheet metal can be made of aluminum, steel or similar materials, for example. It is also possible for the sheet metal to be covered with a further layer which additionally protects against moisture or also enables the moisture to be better conducted away in the direction of the structural joint.
- the sheet metal drainage element is folded up on its side facing away from the structural joint and preferably rests against an end face of the cover element.
- This has the advantage that water that penetrates between the upper edge of the drainage element and the structural joint is only diverted in one direction, specifically in the direction of the structural joint.
- the fold can be designed in any shape upwards. It is thus possible for this to be guided vertically upwards or also to be designed at an angle or with any desired profile.
- the end face of the cover element is understood to mean the horizontal end of the cover element on the side remote from the building joint.
- the drainage element is advantageously attached resiliently to the anchor structure. This has the advantage that the drainage element can easily be attached to the anchor structure in such a way that it does not contribute to load transfer. An unwanted, two-dimensional load introduction of forces from the at least one cover element via the drainage into the structure cannot therefore occur.
- the drainage element is resiliently supported on the structure. This means that there is no need to attach the drainage element to the anchor structure. This also ensures that there is no unwanted load transfer to the underlying component of the structure.
- At least one support anchor of the anchor structure penetrates the drainage element and a flexible, watertight seal is arranged in this area.
- the flat drainage element can surround the at least one support anchor in order to achieve comprehensive protection against penetrating water.
- the flexible, watertight seal can be designed, for example, as a silicone seal or a rubber ring. The sealing prevents the drained water from penetrating further down into the structure in the area of the support anchors.
- the transition structure expediently has a seal, in particular an elastomer strip, below the cover element.
- a seal in particular an elastomer strip
- the seal is preferably designed to cover the entire area. For example, waterproof mats, strips or sheets can be used for this.
- the at least one cover element is preferably designed as a finger plate. This has proven to be particularly suitable.
- the transition structure has two anchor structures with opposing cover elements, based on the structural joint to be bridged by it, the cover elements preferably being designed as intermeshing finger plates. This arrangement makes it possible to distribute the load transfer between the two opposing components of the structure. Furthermore, small to medium-sized structural joints can be bridged safely.
- the transition construction is modular and has several cover elements and / or drainage elements lying next to one another, each narrower than a car lane, with a seal preferably being arranged at least between adjacent drainage elements.
- the elements can also be close together be welded.
- the transition structure is preferably designed as a subassembly preassembled in the manufacturing plant, in which the at least one cover element is releasably fastened to the anchor structure with the aid of at least one screw connection. Furthermore, the assembly as a whole, preferably with the aid of a transport and / or assembly device, can be fastened to the component via the anchor structure, in particular it can be set in concrete. This has the advantage that the named transition structure can be produced inexpensively and efficiently in the manufacturing plant and, in particular, the screw connection can also be produced under defined conditions. On site, the transition structure then only needs to be attached to the component using the anchor structure. This enables the transition structure to be installed quickly.
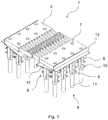
- the transition structure 1 has two cover elements 3 which are designed as finger plates and which mesh with the projecting sections opposite one another. As a result, a building joint between two components of the building 2 is bridged.
- the cover elements 3 are each fastened to a specific component of the building 2 via an anchor structure 4 embedded in concrete and adjoin a roadway 5 with the end face remote from the building joint.
- the anchor structure 4 of a cover element 3 consists of two rows of several support anchors 6 arranged parallel to the building joint.
- the cover element 3 is releasably fastened to the support anchors 6 of the anchor structure 4 with a screw connection 7.
- the cover element 3 is supported at points by the anchor structure 4 and does not lie flat on the structure 2.
- a bracket 14 is arranged between each support anchor 6 of the row near the roadway and the roadway 5.
- the roadway 5 does not lie directly on the consoles 14, but rather on an insulating flange 13 which is arranged between the consoles 14 and the roadway 5 along the cover element 3.
- the screw connection 7 consists of a threaded bolt 7a with a bolt head in the form of a screw which conforms to the regulations and which rests in a recess on the upper side of the cover element 3.
- a nut is attached to the threaded bolt 7a on the remote side of the cover element 3 as an associated tensioning means 7b.
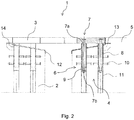
- the support anchor 6 has a spacer 8 as an elongated square tube and a clamping device system 9 on which the clamping device 7b rests.
- the spacer 8 is arranged between the cover element 3 and the clamping device 9 and thereby determines the clamping length of the associated screw connection 7.
- the threaded bolt 7a passes through the spacer 8 and the clamping device 9 to come into contact with the clamping device 7b.
- the clamping length of the screw connection 7 is at least three times the thickness of the cover element 3 in the area of the screw connection 7.
- the thickness of the cover element in this case corresponds to the distance between the contact surface of the bolt head of the threaded bolt 7a in the recess of the cover element 3 and the contact surface of the Cover element 3 on the support anchor 6.
- the clamping length is the distance between the contact surface of the bolt head of the threaded bolt 7a on the cover element 3 and the contact surface of the clamping device 7b on the clamping device system 9.
- the anchor structure 4 has several anchoring elements 10 which are arranged as head bolts on the spacers 8 of the several support anchors 6. As in Fig. 1 shown, two anchoring elements 10 are perpendicular to the building joint in the direction of the building joint and in the opposite direction at each a spacer 8 attached at the same height. In the installed state, the anchoring elements 10 act like shear dowels.
- the transition structure 1 also has an access shaft 11 which runs between the clamping device system 9 and the lower end of the structure 2.
- the access shaft 11 is designed as an elongated formwork tube which surrounds the clamping means 7b. In the installed or concreted-in state of the transition structure 1, access to the clamping means 7b is thus possible from below and the screw connection 7 can thereby be adjusted during maintenance work.
- the transition structure 1 has a drainage element 12, which extends below and at a distance from the cover element 3 and at an acute angle to the building joint downwards.
- the drainage element 12 is arranged on the anchor structure 4 and is penetrated by all support anchors 6.
- the drainage element 12 encloses all support anchors 6 over the whole area in order to divert water penetrating from above to the structural joint.
- the drainage element 12 is designed as a sheet metal which forms a drip edge downwards towards the building joint and is bent upwards on its side facing away from the building joint.
- a small gap is to be provided between the upwardly angled end piece of the drainage element 12 and the end face of the cover element 3 remote from the building joints in order to avoid constraints.
- a water-impermeable seal is attached between the drainage element 12 and the support anchor 6.
- This seal is designed as a rubber ring or silicone joint.
- the cover plate as a whole can be lined with a flexible layer (for example cellular rubber), and the connection to the spacers 8 can then be made by watertight weld seams.
- the transition structure 1 is constructed in a modular manner by means of finger plates opposite one another, which can also be expanded along the structural joint. After the transition structure 1 is designed as a subassembly preassembled in the manufacturing plant, it only needs to be installed at the installation site, as in FIG Fig. 2 shown, be concreted in by means of the anchor structure 4 on the structure 2. In this exemplary embodiment, the section of the anchor construction 4 that is set in concrete extends to the drainage element 12.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Architecture (AREA)
- Civil Engineering (AREA)
- Structural Engineering (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Electromagnetism (AREA)
- Building Environments (AREA)
- Bridges Or Land Bridges (AREA)
- Road Paving Structures (AREA)
- Joining Of Building Structures In Genera (AREA)
- Application Of Or Painting With Fluid Materials (AREA)
- Foundations (AREA)
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE102016205081.8A DE102016205081A1 (de) | 2016-03-29 | 2016-03-29 | Übergangskonstruktion zur Überbrückung einer Bauwerksfuge |
| PCT/EP2017/057461 WO2017167830A1 (de) | 2016-03-29 | 2017-03-29 | Übergangskonstruktion zur überbrückung einer bauwerksfuge |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP3436638A1 EP3436638A1 (de) | 2019-02-06 |
| EP3436638B1 true EP3436638B1 (de) | 2021-04-28 |
Family
ID=58455042
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP17714432.6A Active EP3436638B1 (de) | 2016-03-29 | 2017-03-29 | Übergangskonstruktion zur überbrückung einer bauwerksfuge |
Country Status (10)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US11236473B2 (zh) |
| EP (1) | EP3436638B1 (zh) |
| JP (1) | JP6970119B2 (zh) |
| CN (1) | CN109072572B (zh) |
| CA (1) | CA3017425C (zh) |
| DE (1) | DE102016205081A1 (zh) |
| ES (1) | ES2870966T3 (zh) |
| RU (1) | RU2725438C2 (zh) |
| UA (1) | UA123404C2 (zh) |
| WO (1) | WO2017167830A1 (zh) |
Families Citing this family (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR101795337B1 (ko) * | 2017-01-25 | 2017-11-08 | 주식회사 케이이테크 | 걸침판부를 가지는 핑거 조인트 |
| IT201800007848A1 (it) * | 2018-08-03 | 2020-02-03 | Univergom Srl | Giunto di dilatazione a grande escursione |
| KR102248040B1 (ko) * | 2020-10-16 | 2021-05-04 | 매이크앤 주식회사 | 볼트 풀림에 의한 강판 이탈 방지 교량이음장치 |
Family Cites Families (38)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US2013195A (en) * | 1935-04-18 | 1935-09-03 | Howard E Ward | Expansion joint structure |
| US2286019A (en) * | 1940-03-18 | 1942-06-09 | Floyd R Smith | Expansion joint |
| CH360411A (de) * | 1958-02-14 | 1962-02-28 | Moesch Schneider & Cie | Fugenabdeckungseinrichtung, insbesondere an Betonbrücken |
| DE1231740B (de) | 1963-07-06 | 1967-01-05 | Gutehoffnungshuette Sterkrade | Abdeckvorrichtung fuer Dehnungsfugen von Bruecken |
| US3273473A (en) * | 1963-12-05 | 1966-09-20 | David R Black Jr | Road expansion joint |
| DE2344225A1 (de) * | 1973-09-01 | 1975-03-13 | Hammerschmidt & Co Migua | Abdeckprofil fuer dehnungsfugen |
| US4063840A (en) * | 1977-03-09 | 1977-12-20 | The General Tire & Rubber Company | Expansion joint seal assembly |
| US4111583A (en) * | 1977-05-23 | 1978-09-05 | Felt Products Mfg. Co. | Roadway joint seal and sealing assembly |
| JPS53145330A (en) | 1977-05-25 | 1978-12-18 | Motonosuke Arai | Road joint structure |
| US4307974A (en) * | 1980-03-06 | 1981-12-29 | George Joseph D | Expansion joint seal |
| JPS6032164Y2 (ja) | 1981-05-21 | 1985-09-26 | 阪神高速道路公団 | 橋梁の伸縮継目部における水密装置 |
| US4397579A (en) * | 1981-06-08 | 1983-08-09 | Columbia Chase Corporation | Expansion joint structures |
| JPS63156103A (ja) | 1986-12-17 | 1988-06-29 | ニッタ株式会社 | 橋梁用伸縮継手 |
| SU1507894A1 (ru) * | 1987-08-18 | 1989-09-15 | Государственный Институт По Проектированию Коммунальных Дорожно-Транспортных Сооружений | Деформационный шов моста |
| US4876759A (en) * | 1988-06-14 | 1989-10-31 | Yang Jesse S | Bridge expansion joint |
| RU2012705C1 (ru) * | 1990-04-04 | 1994-05-15 | Белорусская государственная политехническая академия | Конструкция деформационного шва между плитами проезжей части моста |
| CA2091948C (en) * | 1993-03-18 | 1996-04-09 | Konrad Baerveldt | Joint seal retaining element |
| CN1097827A (zh) * | 1993-07-19 | 1995-01-25 | 杨更新 | 交互承插式桥梁伸缩缝 |
| JP2572934B2 (ja) | 1993-08-09 | 1997-01-16 | 株式会社横河メンテック | 橋梁の伸縮装置用フェイスプレート |
| US5966876A (en) * | 1997-10-17 | 1999-10-19 | Southwestern Packing & Seals Inc. | Manhole insert and tether apparatus and method |
| JP3086202B2 (ja) | 1997-10-22 | 2000-09-11 | 帝都高速度交通営団 | 砂利保持部材を有する鉄道用弾性軌道 |
| KR200224501Y1 (ko) * | 2000-12-04 | 2001-05-15 | 주식회사경동기술공사 | 교량의 요철형 앵커 볼트를 이용한 조인트 구조 |
| US6460214B1 (en) * | 2001-03-27 | 2002-10-08 | Ming-Huang Chang | Vibration resistive instant responding roadway or bridge expansion joint and construction method of the same |
| JP3495997B2 (ja) | 2001-04-11 | 2004-02-09 | 元之助 新井 | 道路橋用伸縮装置 |
| AT413989B (de) * | 2002-04-30 | 2006-08-15 | Reisner & Wolff Eng | Vorrichtung zum überbrücken von dehnungsfugen an bauwerken |
| JP2004143845A (ja) | 2002-10-25 | 2004-05-20 | Kyoryo Maintenance:Kk | 橋梁の伸縮装置 |
| CH696402A5 (de) * | 2003-04-16 | 2007-05-31 | Hebag Ag | Wasserdichte Dehnfugenkonstruktion. |
| CN1333137C (zh) * | 2004-01-08 | 2007-08-22 | 徐斌 | 一种特大抗挠变梳型桥梁伸缩缝装置 |
| CN100406650C (zh) * | 2005-06-05 | 2008-07-30 | 徐斌 | 一种抗特大变位的模块式梳型桥梁伸缩缝装置 |
| WO2009078829A2 (en) * | 2007-12-14 | 2009-06-25 | Construction Research & Technology Gmbh | Expansion joint system |
| JP5317359B2 (ja) | 2009-06-09 | 2013-10-16 | 東京ファブリック工業株式会社 | 跨座式モノレール用軌道桁の落下防止装置 |
| JP2011074742A (ja) | 2009-10-02 | 2011-04-14 | Juichi Yamauchi | 道路橋継ぎ目部からの漏水誘導装置 |
| CN101956366B (zh) | 2009-12-29 | 2016-09-28 | 吴树超 | 互支式桥梁伸缩装置 |
| CN101725108A (zh) * | 2009-12-31 | 2010-06-09 | 徐斌 | 一种具有竖向变位能力的桥梁伸缩缝装置 |
| JP2011163079A (ja) | 2010-02-15 | 2011-08-25 | Juichi Yamauchi | 道路橋用伸縮継手の漏水誘導装置 |
| CN102296531B (zh) * | 2011-05-19 | 2013-10-30 | 成都市新筑路桥机械股份有限公司 | 一种多向变位大位移梳齿形桥梁伸缩装置 |
| JP3174898U (ja) | 2012-02-01 | 2012-04-12 | 株式会社橋梁メンテナンス | 伸縮装置遊間部の排水装置 |
| US8967904B1 (en) * | 2012-10-05 | 2015-03-03 | Pioneer Detectable, LLC | Tactile plate assembly |
-
2016
- 2016-03-29 DE DE102016205081.8A patent/DE102016205081A1/de active Pending
-
2017
- 2017-03-29 UA UAA201809136A patent/UA123404C2/uk unknown
- 2017-03-29 EP EP17714432.6A patent/EP3436638B1/de active Active
- 2017-03-29 US US16/083,963 patent/US11236473B2/en active Active
- 2017-03-29 CA CA3017425A patent/CA3017425C/en active Active
- 2017-03-29 WO PCT/EP2017/057461 patent/WO2017167830A1/de active Application Filing
- 2017-03-29 JP JP2018551854A patent/JP6970119B2/ja active Active
- 2017-03-29 RU RU2018132202A patent/RU2725438C2/ru active
- 2017-03-29 ES ES17714432T patent/ES2870966T3/es active Active
- 2017-03-29 CN CN201780020562.4A patent/CN109072572B/zh active Active
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| None * |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| RU2018132202A (ru) | 2020-04-29 |
| CN109072572A (zh) | 2018-12-21 |
| US11236473B2 (en) | 2022-02-01 |
| DE102016205081A1 (de) | 2017-10-05 |
| RU2018132202A3 (zh) | 2020-04-29 |
| UA123404C2 (uk) | 2021-03-31 |
| JP6970119B2 (ja) | 2021-11-24 |
| CA3017425A1 (en) | 2017-10-05 |
| CN109072572B (zh) | 2020-11-17 |
| WO2017167830A1 (de) | 2017-10-05 |
| RU2725438C2 (ru) | 2020-07-02 |
| ES2870966T3 (es) | 2021-10-28 |
| CA3017425C (en) | 2022-06-21 |
| EP3436638A1 (de) | 2019-02-06 |
| JP2019510904A (ja) | 2019-04-18 |
| US20200157752A1 (en) | 2020-05-21 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CH633648A5 (de) | Vorrichtung zum befestigen von zur aufnahme von brennelement-buendeln dienenden lagerkaesten am boden eines wasserbeckens. | |
| EP3436638B1 (de) | Übergangskonstruktion zur überbrückung einer bauwerksfuge | |
| EP1630315A1 (de) | Bauelement zur Schub- und Durchstanzbewehrung | |
| DE202014106083U1 (de) | Schnell-Montage-Wetterschutzdach | |
| DE202011002283U1 (de) | Trapezschuhförmige Halterung für Dachaufbauten an einem Sandwichdachelement | |
| EP1703036B1 (de) | Bauelement zur Schub- bzw. Durchstanzbewehrung | |
| DE102007063511B4 (de) | Schutzeinrichtung an Verkehrswegen | |
| DE19910824A1 (de) | Entwässerungsrinne aus Stahlblech | |
| DE69631838T2 (de) | Verkleidung, miteinander verbundene naturstein-halterungseinheiten und naturstein-halterungseinheit | |
| DE102017206316B3 (de) | Schalungselement | |
| DE10356220B4 (de) | Sicherungseinrichtung für befahrbare oder begehbare Flächen | |
| DE202006007948U1 (de) | Stützsytem zur Einleitung von Lasten in eine Dachunterkonstruktion | |
| EP2336446A2 (de) | Gelenkiges Fugenschalungselement | |
| DE3541282A1 (de) | Balkon zum nachtraeglichen anbringen an ein gebaeude | |
| EP3569783B1 (de) | Bauelement zur thermischen isolierung | |
| AT508798A2 (de) | Schalung | |
| DE2559459C3 (de) | In Betonkonstruktionen bündig einbettbarer Schwerlastanker | |
| AT400465B (de) | Schalung und verfahren zum giessen eines behälters aus beton | |
| DE19964360B4 (de) | Fugenabdichtungsvorrichtung | |
| DE102004015935B4 (de) | Abdeckung für befahrbare Beckenkronen | |
| DE202022101904U1 (de) | Entwässerungsvorrichtung für eine bauseitige Montage und Entwässerungssystem | |
| EP4163452A1 (de) | Schrägdachaufbau | |
| DE202024101335U1 (de) | Vorrichtung zum Verspannen von Bauplatten | |
| AT502646B1 (de) | Befestigungseinrichtung für eine absturzsicherung an dachflächen | |
| DE2504162C3 (de) | In Betonkonstruktionen bündig einbettbarer Schwerlastanker |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: UNKNOWN |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: THE INTERNATIONAL PUBLICATION HAS BEEN MADE |
|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: REQUEST FOR EXAMINATION WAS MADE |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20180913 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Extension state: BA ME |
|
| DAV | Request for validation of the european patent (deleted) | ||
| DAX | Request for extension of the european patent (deleted) | ||
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: EXAMINATION IS IN PROGRESS |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 20191127 |
|
| GRAP | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR1 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: GRANT OF PATENT IS INTENDED |
|
| INTG | Intention to grant announced |
Effective date: 20201123 |
|
| GRAS | Grant fee paid |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR3 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: THE PATENT HAS BEEN GRANTED |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: NOT ENGLISH |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: EP |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R096 Ref document number: 502017010205 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: AT Ref legal event code: REF Ref document number: 1387161 Country of ref document: AT Kind code of ref document: T Effective date: 20210515 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: LANGUAGE OF EP DOCUMENT: GERMAN |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: LT Ref legal event code: MG9D |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: ES Ref legal event code: FG2A Ref document number: 2870966 Country of ref document: ES Kind code of ref document: T3 Effective date: 20211028 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: HR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20210428 Ref country code: BG Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20210728 Ref country code: NL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20210428 Ref country code: FI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20210428 Ref country code: LT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20210428 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: PT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20210830 Ref country code: PL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20210428 Ref country code: NO Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20210728 Ref country code: SE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20210428 Ref country code: RS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20210428 Ref country code: GR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20210729 Ref country code: IS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20210828 Ref country code: LV Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20210428 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: NL Ref legal event code: MP Effective date: 20210428 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: RO Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20210428 Ref country code: CZ Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20210428 Ref country code: DK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20210428 Ref country code: EE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20210428 Ref country code: SK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20210428 Ref country code: SM Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20210428 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R097 Ref document number: 502017010205 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed |
Effective date: 20220131 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20210828 Ref country code: AL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20210428 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MC Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20210428 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: BE Ref legal event code: MM Effective date: 20220331 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20220329 Ref country code: IE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20220329 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20220331 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: HU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT; INVALID AB INITIO Effective date: 20170329 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AT Payment date: 20240318 Year of fee payment: 8 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20210428 Ref country code: CY Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20210428 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20240321 Year of fee payment: 8 Ref country code: GB Payment date: 20240322 Year of fee payment: 8 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Payment date: 20240329 Year of fee payment: 8 Ref country code: FR Payment date: 20240319 Year of fee payment: 8 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: TR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20210428 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CH Payment date: 20240401 Year of fee payment: 8 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: ES Payment date: 20240417 Year of fee payment: 8 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20210428 |