WO2016052243A1 - 転写シート - Google Patents
転写シート Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2016052243A1 WO2016052243A1 PCT/JP2015/076572 JP2015076572W WO2016052243A1 WO 2016052243 A1 WO2016052243 A1 WO 2016052243A1 JP 2015076572 W JP2015076572 W JP 2015076572W WO 2016052243 A1 WO2016052243 A1 WO 2016052243A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- mass
- parts
- release layer
- transfer sheet
- resin
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B41—PRINTING; LINING MACHINES; TYPEWRITERS; STAMPS
- B41J—TYPEWRITERS; SELECTIVE PRINTING MECHANISMS, i.e. MECHANISMS PRINTING OTHERWISE THAN FROM A FORME; CORRECTION OF TYPOGRAPHICAL ERRORS
- B41J31/00—Ink ribbons; Renovating or testing ink ribbons
- B41J31/05—Ink ribbons having coatings other than impression-material coatings
- B41J31/06—Ink ribbons having coatings other than impression-material coatings the coatings being directly on the base material, i.e. below impression transfer material; Ink ribbons having base material impregnated with material other than impression material
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B32—LAYERED PRODUCTS
- B32B—LAYERED PRODUCTS, i.e. PRODUCTS BUILT-UP OF STRATA OF FLAT OR NON-FLAT, e.g. CELLULAR OR HONEYCOMB, FORM
- B32B27/00—Layered products comprising a layer of synthetic resin
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B32—LAYERED PRODUCTS
- B32B—LAYERED PRODUCTS, i.e. PRODUCTS BUILT-UP OF STRATA OF FLAT OR NON-FLAT, e.g. CELLULAR OR HONEYCOMB, FORM
- B32B27/00—Layered products comprising a layer of synthetic resin
- B32B27/06—Layered products comprising a layer of synthetic resin as the main or only constituent of a layer, which is next to another layer of the same or of a different material
- B32B27/08—Layered products comprising a layer of synthetic resin as the main or only constituent of a layer, which is next to another layer of the same or of a different material of synthetic resin
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B32—LAYERED PRODUCTS
- B32B—LAYERED PRODUCTS, i.e. PRODUCTS BUILT-UP OF STRATA OF FLAT OR NON-FLAT, e.g. CELLULAR OR HONEYCOMB, FORM
- B32B27/00—Layered products comprising a layer of synthetic resin
- B32B27/28—Layered products comprising a layer of synthetic resin comprising synthetic resins not wholly covered by any one of the sub-groups B32B27/30 - B32B27/42
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B41—PRINTING; LINING MACHINES; TYPEWRITERS; STAMPS
- B41J—TYPEWRITERS; SELECTIVE PRINTING MECHANISMS, i.e. MECHANISMS PRINTING OTHERWISE THAN FROM A FORME; CORRECTION OF TYPOGRAPHICAL ERRORS
- B41J31/00—Ink ribbons; Renovating or testing ink ribbons
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B41—PRINTING; LINING MACHINES; TYPEWRITERS; STAMPS
- B41M—PRINTING, DUPLICATING, MARKING, OR COPYING PROCESSES; COLOUR PRINTING
- B41M5/00—Duplicating or marking methods; Sheet materials for use therein
- B41M5/26—Thermography ; Marking by high energetic means, e.g. laser otherwise than by burning, and characterised by the material used
- B41M5/382—Contact thermal transfer or sublimation processes
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B41—PRINTING; LINING MACHINES; TYPEWRITERS; STAMPS
- B41M—PRINTING, DUPLICATING, MARKING, OR COPYING PROCESSES; COLOUR PRINTING
- B41M5/00—Duplicating or marking methods; Sheet materials for use therein
- B41M5/26—Thermography ; Marking by high energetic means, e.g. laser otherwise than by burning, and characterised by the material used
- B41M5/40—Thermography ; Marking by high energetic means, e.g. laser otherwise than by burning, and characterised by the material used characterised by the base backcoat, intermediate, or covering layers, e.g. for thermal transfer dye-donor or dye-receiver sheets; Heat, radiation filtering or absorbing means or layers; combined with other image registration layers or compositions; Special originals for reproduction by thermography
- B41M5/42—Intermediate, backcoat, or covering layers
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B41—PRINTING; LINING MACHINES; TYPEWRITERS; STAMPS
- B41M—PRINTING, DUPLICATING, MARKING, OR COPYING PROCESSES; COLOUR PRINTING
- B41M5/00—Duplicating or marking methods; Sheet materials for use therein
- B41M5/26—Thermography ; Marking by high energetic means, e.g. laser otherwise than by burning, and characterised by the material used
- B41M5/40—Thermography ; Marking by high energetic means, e.g. laser otherwise than by burning, and characterised by the material used characterised by the base backcoat, intermediate, or covering layers, e.g. for thermal transfer dye-donor or dye-receiver sheets; Heat, radiation filtering or absorbing means or layers; combined with other image registration layers or compositions; Special originals for reproduction by thermography
- B41M5/42—Intermediate, backcoat, or covering layers
- B41M5/423—Intermediate, backcoat, or covering layers characterised by non-macromolecular compounds, e.g. waxes
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B41—PRINTING; LINING MACHINES; TYPEWRITERS; STAMPS
- B41M—PRINTING, DUPLICATING, MARKING, OR COPYING PROCESSES; COLOUR PRINTING
- B41M5/00—Duplicating or marking methods; Sheet materials for use therein
- B41M5/26—Thermography ; Marking by high energetic means, e.g. laser otherwise than by burning, and characterised by the material used
- B41M5/40—Thermography ; Marking by high energetic means, e.g. laser otherwise than by burning, and characterised by the material used characterised by the base backcoat, intermediate, or covering layers, e.g. for thermal transfer dye-donor or dye-receiver sheets; Heat, radiation filtering or absorbing means or layers; combined with other image registration layers or compositions; Special originals for reproduction by thermography
- B41M5/42—Intermediate, backcoat, or covering layers
- B41M5/44—Intermediate, backcoat, or covering layers characterised by the macromolecular compounds
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B41—PRINTING; LINING MACHINES; TYPEWRITERS; STAMPS
- B41M—PRINTING, DUPLICATING, MARKING, OR COPYING PROCESSES; COLOUR PRINTING
- B41M5/00—Duplicating or marking methods; Sheet materials for use therein
- B41M5/26—Thermography ; Marking by high energetic means, e.g. laser otherwise than by burning, and characterised by the material used
- B41M5/40—Thermography ; Marking by high energetic means, e.g. laser otherwise than by burning, and characterised by the material used characterised by the base backcoat, intermediate, or covering layers, e.g. for thermal transfer dye-donor or dye-receiver sheets; Heat, radiation filtering or absorbing means or layers; combined with other image registration layers or compositions; Special originals for reproduction by thermography
- B41M5/42—Intermediate, backcoat, or covering layers
- B41M5/44—Intermediate, backcoat, or covering layers characterised by the macromolecular compounds
- B41M5/443—Silicon-containing polymers, e.g. silicones, siloxanes
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B41—PRINTING; LINING MACHINES; TYPEWRITERS; STAMPS
- B41M—PRINTING, DUPLICATING, MARKING, OR COPYING PROCESSES; COLOUR PRINTING
- B41M7/00—After-treatment of prints, e.g. heating, irradiating, setting of the ink, protection of the printed stock
- B41M7/0027—After-treatment of prints, e.g. heating, irradiating, setting of the ink, protection of the printed stock using protective coatings or layers by lamination or by fusion of the coatings or layers
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B41—PRINTING; LINING MACHINES; TYPEWRITERS; STAMPS
- B41J—TYPEWRITERS; SELECTIVE PRINTING MECHANISMS, i.e. MECHANISMS PRINTING OTHERWISE THAN FROM A FORME; CORRECTION OF TYPOGRAPHICAL ERRORS
- B41J31/00—Ink ribbons; Renovating or testing ink ribbons
- B41J31/09—Ink ribbons characterised by areas carrying media for obliteration or removal of typing errors
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B41—PRINTING; LINING MACHINES; TYPEWRITERS; STAMPS
- B41M—PRINTING, DUPLICATING, MARKING, OR COPYING PROCESSES; COLOUR PRINTING
- B41M2205/00—Printing methods or features related to printing methods; Location or type of the layers
- B41M2205/06—Printing methods or features related to printing methods; Location or type of the layers relating to melt (thermal) mass transfer
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B41—PRINTING; LINING MACHINES; TYPEWRITERS; STAMPS
- B41M—PRINTING, DUPLICATING, MARKING, OR COPYING PROCESSES; COLOUR PRINTING
- B41M2205/00—Printing methods or features related to printing methods; Location or type of the layers
- B41M2205/30—Thermal donors, e.g. thermal ribbons
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B41—PRINTING; LINING MACHINES; TYPEWRITERS; STAMPS
- B41M—PRINTING, DUPLICATING, MARKING, OR COPYING PROCESSES; COLOUR PRINTING
- B41M2205/00—Printing methods or features related to printing methods; Location or type of the layers
- B41M2205/38—Intermediate layers; Layers between substrate and imaging layer
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B41—PRINTING; LINING MACHINES; TYPEWRITERS; STAMPS
- B41M—PRINTING, DUPLICATING, MARKING, OR COPYING PROCESSES; COLOUR PRINTING
- B41M5/00—Duplicating or marking methods; Sheet materials for use therein
- B41M5/26—Thermography ; Marking by high energetic means, e.g. laser otherwise than by burning, and characterised by the material used
- B41M5/382—Contact thermal transfer or sublimation processes
- B41M5/38207—Contact thermal transfer or sublimation processes characterised by aspects not provided for in groups B41M5/385 - B41M5/395
- B41M5/38214—Structural details, e.g. multilayer systems
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a thermal transfer sheet, and more particularly, to a transfer sheet comprising a base material and a release layer and a transfer layer on the base material in this order.
- the thermal transfer recording method is widely used as a simple printing method. Since the thermal transfer recording method can easily form various images, printed materials that require a relatively small number of copies, such as creation of ID cards such as identification cards, business photographs, personal computer printers, video printers, etc. Is used.
- the thermal transfer sheet used in the thermal transfer recording system can be roughly classified into a so-called melt transfer type thermal transfer sheet in which the heat-fusible colored layer is melted and softened by heating, and the heat-fusible colored layer is transferred to a transfer target, that is, an image receiving sheet. And a so-called sublimation type thermal transfer sheet in which the dye in the color material layer sublimes due to heat and the dye moves to the image receiving sheet.
- a heat melting type thermal transfer sheet is used.
- a heat melting type heat transfer sheet for example, a heat transfer sheet in which a base material, a release layer made of an acrylic-styrene resin, and a heat melting colored layer are laminated in this order is known.
- the release layer is softened by the heat applied from the thermal head, and the peeling force between the release layer and the transfer layer is increased. Problems such as transfer failure where the layer is not transferred, whitening of the image due to roughening of the peeling interface, and abnormal noise during peeling may occur.
- an ID such as an identification card
- a release layer composed of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) and water-dispersed urethane and a protective layer thermal transfer sheet in which a protective layer is laminated in this order are superposed, and the protective layer is transferred using a thermal head, a heating roll, etc.
- a method for forming a protective layer thereon is known.
- a method of forming a laminate material using a heating roll after forming a protective layer on the image is also known.
- the water-based release layer (release layer made of polyvinyl alcohol and water-dispersed urethane) is unstable with respect to humidity, and in a high humidity environment, the whitening of the image due to the roughened peeling interface of the transfer layer, Problems such as abnormal noise during peeling may occur.
- a thermal transfer sheet provided with a release layer containing a polyamide-based resin is provided to reduce the effects of heat applied to the thermal head and the humidity environment and to improve releasability. It has been proposed (see Patent Document 1).
- the present invention has been made in view of the above-described background art.
- the purpose of the present invention is to prevent the transfer layer from slipping and the transfer layer when the printed material is produced even after the transfer sheet is stored in a high temperature environment.
- An object of the present invention is to provide a transfer sheet having improved blurring (excellent storage stability).
- a transfer sheet comprising a base material, and a release layer and a transfer layer in order on the base material,
- the release layer comprises a binder resin and a silicone oil and / or wax component, and the total content of the silicone oil and the wax component in the release layer is 0 with respect to the solid mass of the binder resin.
- a transfer sheet that is 1% by mass or more and 15% by mass or less is provided.
- the release layer preferably contains an epoxy-modified silicone oil.
- the release layer preferably contains polyethylene wax.
- the binder resin is at least selected from the group consisting of acrylic resins, vinyl resins, polyester resins, urethane resins, acetal resins, cellulose resins, and polyvinyl alcohol resins.
- acrylic resins vinyl resins
- polyester resins polyester resins
- urethane resins urethane resins
- acetal resins acetal resins
- cellulose resins and polyvinyl alcohol resins.
- polyvinyl alcohol resins One type is preferable.
- the content of the binder resin in the release layer is preferably 60% by mass or more and 99% by mass or less with respect to the solid content mass of the release layer.
- a release layer is further provided between the base material and the release layer.
- the transfer layer preferably contains a colorant.
- a transfer sheet that has improved transfer layer slippage and transfer layer blurring (excellent storage stability) when a printed material is produced even after the transfer sheet is stored in a high temperature environment. Can be provided.
- the transfer sheet according to the present invention comprises a release layer and a transfer layer in this order, and may further comprise a release layer between the substrate and the release layer, and the surface opposite to the release layer of the substrate is heat resistant. A layer may further be provided.
- the layer structure of the transfer sheet according to the present invention will be described with reference to the drawings.
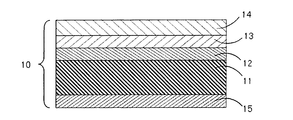
- FIG. 1 shows a schematic cross-sectional view of an embodiment of a transfer sheet according to the present invention.
- a transfer sheet 10 shown in FIG. 1 includes a base material 11, a release layer 12, a release layer 13, and a transfer layer 14 in this order on the base material 11.
- a heat-resistant layer 15 is further provided on the surface opposite to the layer 12.
- the base material in the present invention has a role of holding the transfer layer and heat is applied during thermal transfer. Therefore, the base material is preferably a material having a mechanical strength that does not hinder handling even in a heated state.
- Such base materials include polyethylene terephthalate film, 1,4-polycyclohexylenedimethylene terephthalate film, polyethylene naphthalate film, polyphenylene sulfide film, polystyrene film, polypropylene film, polysulfone film, aramid film, polycarbonate film , Polyvinyl alcohol film, cellophane, cellulose derivatives such as cellulose acetate, polyethylene film, polyvinyl chloride film, nylon film, polyimide film, ionomer film and the like.
- the thickness of the substrate is preferably 0.5 ⁇ m or more and 50 ⁇ m or less, more preferably 1 ⁇ m or more and 10 ⁇ m or less.
- the base material a material whose surface is subjected to an easy adhesion treatment may be used.
- the easy adhesion treatment is a treatment for forming an easy adhesion layer between the base material and a later-described release layer.
- an easy-adhesion layer for example, those composed of aqueous acrylic, aqueous polyester and aqueous epoxy compound are preferable.
- the water-based acrylic is a water-soluble or water-dispersible acrylic resin, preferably having an alkyl acrylate or alkyl methacrylate as a main component, and the component is 30 mol% or more and 90 mol% or less and is copolymerized. The ones made are preferred.
- the water-based polyester is a water-soluble or water-dispersible polyester resin, and examples of components constituting the polyester resin include polyvalent carboxylic acids and polyvalent hydroxy compounds.
- An aqueous epoxy compound is a compound containing an epoxy group that is water-soluble or water-dispersible, preferably water-soluble, and contains at least one, preferably two or more epoxy groups in the molecule. is there. Examples of such aqueous epoxy compounds include glycols, polyethers, glycidyl ethers of polyols, glycidyl esters of carboxylic acids, glycidyl-substituted amines, and the like, but glycidyl ethers are preferred.
- For the easy adhesion treatment a method of forming an easily adhesive coating film on the surface of the substrate is preferably used.
- the release layer in the present invention is a layer provided so that the transfer layer can be easily peeled off from the substrate during thermal transfer.
- the release layer is preferably formed of a material having releasability, and for example, preferably contains a binder resin and an additive such as a release agent.
- the binder resin include a urethane resin, an acetal resin, a polyamide resin, a melamine resin, a polyol resin, a cellulose resin, and polyvinyl alcohol. It is preferable to use a urethane resin and an acetal resin.
- the release agent include silicone oil, phosphate plasticizer, fluorine compound, wax, metal soap, filler, and the like, and it is preferable to use silicone oil.
- the formation method of the release layer is not particularly limited, but can be formed by a conventionally known coating method. For example, after adding the binder resin and an additive such as a mold release agent in an appropriate solvent and dissolving or dispersing each component to prepare a coating solution, the coating solution is applied to the base material. Furthermore, it can be formed by applying and drying using a known means such as a gravure coating method, a roll coating method, a comma coating method, a gravure printing method, a screen printing method, and a gravure reverse roll coating method.
- the thickness of the release layer is not particularly limited, but is preferably 0.05 ⁇ m or more and 5.0 ⁇ m or less, more preferably 0.1 ⁇ m or more and 3 ⁇ m or less.
- the release layer in the present invention is a layer provided so that the transfer layer can be easily peeled from the substrate during thermal transfer.
- the release layer contains a binder resin and a release agent.
- the content of the release agent in the release layer (total content of silicone oil and wax component) is 0.1% by mass or more and 15% by mass or less, preferably 0.5%, based on the solid content mass of the binder resin. It is at least 12% by mass and more preferably at least 1% by mass and at most 10% by mass. If the content of the release agent is within the above range, even after the transfer sheet is stored in a high temperature environment, the transfer layer slippage and transfer layer blurring when the printed matter is produced are improved (storage stability). Transfer sheet can be obtained.
- silicone oil and / or a wax component is used as the release agent.
- silicone oil include amino-modified silicone, epoxy-modified silicone, aralkyl-modified silicone, epoxy-aralkyl-modified silicone, alcohol-modified silicone, vinyl-modified silicone, urethane-modified silicone, and it is preferable to use epoxy-modified silicone oil.
- wax component examples include microcrystalline wax, carnauba wax, paraffin wax, Fischer-Tropsch wax, various low molecular weight polyethylene, wood wax, beeswax, whale wax, ibota wax, wool wax, shellac wax, candelilla wax, petrolactam, one Various waxes such as partially modified waxes, fatty acid esters, and fatty acid amides can be used, and polyethylene wax is preferably used.
- the content of the binder resin in the release layer is preferably 60% by mass or more and 99% by mass or less, more preferably 70% by mass or more and 95% by mass or less, with respect to the total solid content mass of the release layer. Preferably they are 80 mass% or more and 90 mass% or less. If the content of the binder resin is within the above range, even after the transfer sheet is stored in a high temperature environment, the transfer layer slippage and the transfer layer blurring when the printed material is produced are improved (storage stability). Transfer sheet can be obtained.
- Binder resins used in the release layer include acrylic resins such as poly (meth) acrylate and poly (meth) acrylamide, polyvinyl alcohol resins, polyvinyl acetate resins, and vinyl chloride-vinyl acetate copolymers (vinyl acetate resin).
- vinyl resins such as polyvinyl pyrrolidone
- polyethylene terephthalate resin polyester resins such as polyethylene naphthalate tree
- urethane resins such as polyurethane acrylate,
- the acrylic resin means a polymer of a (meth) acrylic acid monomer or a derivative thereof, a polymer of a monomer of a (meth) acrylic acid ester or a derivative thereof, a (meth) acrylic monomer and other derivatives. Copolymers with monomers or derivatives thereof, and copolymers of (meth) acrylic acid ester monomers with other monomers or derivatives thereof. Other “system resins” may also contain copolymers with other monomers other than the main component or derivatives thereof.
- the formation method of the release layer is not particularly limited, but can be formed by a conventionally known coating method.
- the coating solution is applied to the substrate or the release layer.
- it can be formed by applying and drying using a known means such as a gravure coating method, a roll coating method, a comma coating method, a gravure printing method, a screen printing method, and a gravure reverse roll coating method.
- the thickness of the release layer is not particularly limited, but is preferably 0.05 ⁇ m or more and 5.0 ⁇ m or less, more preferably 0.1 ⁇ m or more and 3 ⁇ m or less.
- the transfer layer in the present invention is conventionally known, such as a printer having a transfer sheet and an object to be transferred, and a back side of the base material (side on which the transfer layer of the base material is not provided) provided with a thermal head for thermal transfer. It is a layer which is peeled off from the release layer and / or release layer by being heated by the heating means and transferred onto the transfer target.
- the transfer layer preferably contains a binder resin and a colorant in order to form an image such as letters and numbers by being transferred onto the transfer target.
- Binder resins used for the transfer layer include acrylic resins such as poly (meth) acrylate and poly (meth) acrylamide, polyvinyl alcohol resins, polyvinyl acetate resins, vinyl acetate resins, polyvinyl butyral resins, polyvinyl acetal resins, polyvinyl resins.
- Vinyl resins such as pyrrolidone, polyester resins such as polyethylene terephthalate resin, polyethylene naphthalate tree, urethane resins such as polyurethane acrylate, cellulose such as ethyl cellulose resin, hydroxyethyl cellulose resin, ethyl hydroxy cellulose resin, methyl cellulose resin, cellulose acetate resin Resins, polyamide resins, aromatic polyamide resins, polyamideimide resins and other polyamide resins, acetal resins, polycarbonate resins, etc. Gerare, it is preferable to use a vinyl resin.
- the colorant conventionally known colorants can be used, but those having good characteristics as a printing material, for example, those having a sufficient color density and not discolored by light, heat, temperature, etc. preferable. Further, it may be a substance that develops color when heated or a substance that develops color when it comes into contact with a component applied to the surface of the transfer target.
- the colorant preferably exhibits at least one color selected from the group consisting of black, white, silver, cyan, magenta, yellow, red, green, and blue.
- carbon black for black, titanium oxide for white, and inorganic materials such as aluminum for silver, and C.I. for cyan, magenta, yellow, red, green, and blue. I. It is preferable to use each pigment described in Pigment.
- the method for forming the transfer layer is not particularly limited, but can be formed by a conventionally known coating method. For example, after adding the above binder resin and a colorant in an appropriate solvent and dissolving or dispersing each component to prepare a coating solution, the coating solution is applied to the release layer on the gravure coating method, roll coating. It can be formed by applying and drying using known means such as a method, a comma coating method, a gravure printing method, a screen printing method, and a gravure reverse roll coating method.
- the thickness of the transfer layer is not particularly limited, but is preferably 0.5 ⁇ m or more and 30 ⁇ m or less, more preferably 1 ⁇ m or more and 20 ⁇ m or less.
- the heat-resistant layer in the present invention is a layer provided to prevent adverse effects such as sticking and wrinkles due to heating from the back side of the base material (the side where the base material transfer layer is not provided) during thermal transfer. .
- thermal printing can be performed without causing sticking even in a thermal transfer sheet based on a plastic film that is inferior in heat resistance. Benefit from the benefits.
- the heat-resistant layer preferably contains a binder resin and additives such as a slip agent.
- the binder resin used for the heat-resistant layer includes acrylic resins such as poly (meth) acrylate and poly (meth) acrylamide, polyvinyl alcohol resin, polyvinyl acetate resin, vinyl acetate resin, polyvinyl butyral resin, polyvinyl acetal resin, polyvinyl Vinyl resins such as pyrrolidone, polyester resins such as polyethylene terephthalate resin, polyethylene naphthalate tree, urethane resins such as polyurethane acrylate, cellulose such as ethyl cellulose resin, hydroxyethyl cellulose resin, ethyl hydroxy cellulose resin, methyl cellulose resin, cellulose acetate resin Resins, polyamide resins, aromatic polyamide resins, polyamideimide resins and other polyamide resins, acetal resins, polycarbonate resins, etc. It is below.
- the slip agent include metal
- the formation method of the heat-resistant layer is not particularly limited, but can be formed by a conventionally known coating method. For example, after adding the above-mentioned binder resin and an additive such as a slipping agent in an appropriate solvent and dissolving or dispersing each component to prepare a coating solution, the coating solution is applied to the substrate. Furthermore, it can be formed by applying and drying using a known means such as a gravure coating method, a roll coating method, a comma coating method, a gravure printing method, a screen printing method, and a gravure reverse roll coating method. Further, the thickness of the heat-resistant layer is not particularly limited, but is preferably 0.05 ⁇ m or more and 5.0 ⁇ m or less, and more preferably 0.1 ⁇ m or more and 3 ⁇ m or less.
- the transfer medium that can be used for transfer of the thermal transfer sheet according to the present invention is not particularly limited, and examples thereof include a conventionally known base material provided with a receiving layer having dye receptivity.
- Examples of the substrate in the transfer target include plain paper, high-quality paper, tracing paper, plastic film, and the like, and the substrate is not particularly limited.
- the receiving layer in the transfer target can be formed by a coating method, a forming method using a thermal head, a hot roll, or the like.
- the base material itself has dye receptivity, it is not necessary to provide a receiving layer for the transfer target.
- Transfer of the transfer layer onto the transfer medium by the thermal transfer method using the transfer sheet according to the present invention can be performed directly on the transfer medium using a conventionally known thermal transfer printer, or can be received by the intermediate transfer recording medium. It can also be carried out by transferring the receptive layer of the intermediate transfer recording medium to a transfer target (retransfer) after transfer onto the layer (primary transfer).
- transfer conditions may be set separately such as for sublimation transfer, thermal melt transfer, and protective layer transfer. May be.
- the heating means is not particularly limited, and transfer may be performed using a thermal head, a hot plate, a hot stamper, a heat roll, a line heater, an iron, or the like.
- Example 1 A polyester film with an easy adhesion treatment having a thickness of 6 ⁇ m was prepared as a substrate.
- a heat-resistant layer is formed by applying the heat-resistant layer coating solution 1 having the following composition to the surface of the polyester film that has not been subjected to the easy-adhesion treatment so that the heat-resistant layer is 1.0 g / m 2 when dried.
- a release layer was formed by applying a release layer coating solution 1 having the following composition to the surface on which the coating layer was dried at 0.3 g / m 2 .
- a release layer was formed by applying a release layer coating solution 1 having the following composition on the release layer so as to be 1.0 g / m 2 when dried.
- a transfer layer coating liquid having the following composition was applied onto the release layer so as to be 1.0 g / m 2 upon drying to form a transfer layer, whereby a transfer sheet 1 was produced.
- ⁇ Coating solution 1 for heat-resistant layer> ⁇ Polyvinyl butyral resin (manufactured by Sekisui Chemical Co., Ltd., trade name: ESREC BX-1) 2.0 parts by mass ⁇ Isocyanate (manufactured by DIC Corporation, trade name: Bernock D750) 4.4 parts by mass-Phosphate ester surfactant (Daiichi Kogyo Seiyaku Co., Ltd., trade name: Prisurf A208N) 1.3 parts by mass-Talc (Nihon Talc Co., Ltd., trade name: Microace P-3) 0.3 part by mass / viscosity adjusting solvent (toluene / methyl ethyl ketone 1/1) 92 parts by mass ⁇ Coating liquid 1 for release layer> ⁇ 25 parts by mass of urethane-based resin ⁇ Acetal-based resin (manufactured by Sekisui Chemical Co., Ltd., trade name: ESREC
- Example 2 A transfer sheet 2 was produced in the same manner as in Example 1 except that the composition of the release layer coating solution was as follows.
- Example 3 A transfer sheet 3 was produced in the same manner as in Example 1 except that the composition of the release layer coating solution was as follows.
- Example 4 A transfer sheet 4 was produced in the same manner as in Example 1 except that the composition of the release layer coating solution was as follows.
- Example 5 A transfer sheet 5 was produced in the same manner as in Example 1 except that the composition of the release layer coating solution was as follows.
- Example 6 A transfer sheet 6 was produced in the same manner as in Example 1 except that the composition of the release layer coating solution was as follows.
- Example 7 A transfer sheet 7 was produced in the same manner as in Example 1 except that the composition of the release layer coating solution was as follows.
- Example 8 A transfer sheet 8 was produced in the same manner as in Example 1 except that the composition of the release layer coating solution was as follows.
- Example 9 A transfer sheet 9 was produced in the same manner as in Example 1 except that the composition of the release layer coating solution was as follows.
- Example 10 A transfer sheet 10 was produced in the same manner as in Example 1 except that the composition of the release layer coating solution was as follows.
- Example 11 A transfer sheet 11 was produced in the same manner as in Example 1 except that the composition of the release layer coating solution was as follows.
- Example 12 A transfer sheet 12 was produced in the same manner as in Example 1 except that the composition of the release layer coating solution was as follows.
- Example 13 A transfer sheet 13 was produced in the same manner as in Example 1 except that the composition of the release layer coating solution was as follows.
- Example 14 A transfer sheet 14 was produced in the same manner as in Example 1 except that the composition of the release layer coating solution was as follows.
- Example 15 A transfer sheet 15 was produced in the same manner as in Example 1 except that the composition of the release layer coating solution was as follows.
- Example 16 A transfer sheet 16 was produced in the same manner as in Example 1 except that the composition of the release layer coating solution was as follows.
- Example 17 A transfer sheet 17 was produced in the same manner as in Example 1 except that the composition of the release layer coating solution was as follows.
- Example 18 A transfer sheet 18 was produced in the same manner as in Example 1 except that the composition of the release layer coating solution was as follows.
- ⁇ Peeling layer coating solution 18> Cellulose resin (Eastman Chemical Co., Ltd., trade name: CAB-381-0.5) 100 parts by mass Epoxy-modified silicone oil (Shin-Etsu Chemical Co., Ltd., trade name: KP-1800U) 5 parts by mass Polyethylene wax 5 parts by mass Viscosity adjusting solvent (toluene / methyl ethyl ketone 1/1) 300 parts by mass
- Example 19 A transfer sheet 19 was produced in the same manner as in Example 1 except that the composition of the release layer coating solution was as follows.
- ⁇ Peeling layer coating solution 19> Polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) resin (manufactured by Nippon Synthetic Chemical Co., Ltd., trade name: Gohsenol C-500) 100 parts by mass Polyethylene wax 10 parts by mass Viscosity adjusting solvent (water / isopropyl alcohol 1/1) 300 parts by mass
- PVA Polyvinyl alcohol
- a transfer sheet 20 was produced in the same manner as in Example 1 except that the composition of the release layer coating solution was as follows.
- ⁇ Peeling layer coating solution 20> ⁇ Acrylic resin (Mitsubishi Rayon Co., Ltd., trade name: BR-85) 100 parts by mass / viscosity adjusting solvent (toluene / methyl ethyl ketone 1/1) 300 parts by mass
- a transfer sheet 21 was produced in the same manner as in Example 1 except that the composition of the release layer coating solution was as follows.
- a transfer sheet 22 was produced in the same manner as in Example 1 except that the composition of the release layer coating solution was as follows.
- ⁇ Peeling layer coating solution 22> ⁇ Polyester resin (product name: Byron 220, manufactured by Toyobo Co., Ltd.) 100 parts by mass / viscosity adjusting solvent (toluene / methyl ethyl ketone 1/1) 300 parts by mass
- a transfer sheet 23 was produced in the same manner as in Example 1 except that the composition of the release layer coating solution was as follows.
- a transfer sheet 24 was produced in the same manner as in Example 1 except that the composition of the release layer coating solution was as follows.
- a transfer sheet 25 was produced in the same manner as in Example 1 except that the composition of the release layer coating solution was as follows.
- a transfer sheet 26 was produced in the same manner as in Example 1 except that the composition of the release layer coating solution was as follows.
- a transfer sheet 27 was produced in the same manner as in Example 1 except that the composition of the release layer coating solution was as follows.
- a transfer sheet 28 was produced in the same manner as in Example 1 except that the composition of the release layer coating solution was as follows.
- a transfer sheet 29 was produced in the same manner as in Example 1 except that the composition of the release layer coating solution was as follows.
- a transfer sheet 30 was produced in the same manner as in Example 1 except that the composition of the release layer coating solution was as follows.
- Table 1 shows the compositions of the release layers formed in the above examples and comparative examples.
Landscapes
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Optics & Photonics (AREA)
- Thermal Transfer Or Thermal Recording In General (AREA)
- Laminated Bodies (AREA)
- Impression-Transfer Materials And Handling Thereof (AREA)
Abstract
【課題】転写シートが高温保存後であっても、印画物を作製した際の転写層のツブレおよび転写層のカスレを改善した(保存安定性に優れる)転写シートの提供。 【解決手段】本発明による転写シートは、基材と、基材上に剥離層と転写層とを順に備えてなるものであって、剥離層が、バインダー樹脂と、シリコーンオイルおよび/またはワックス成分とを含んでなり、剥離層中のシリコーンオイルおよびワックス成分の総含有量が、バインダー樹脂の固形分質量に対して、0.1質量%以上15質量%以下である。
Description
本発明は、熱転写シートに関し、より詳細には、基材と、基材上に剥離層と転写層とを順に備えてなる転写シートに関する。
現在、簡便な印刷方法として熱転写記録方法が広く使用されている。熱転写記録方法は、各種画像を簡便に形成できるため、印刷枚数が比較的少なくてもよい印刷物、例えば、身分証明書などのIDカードの作成や営業写真、あるいはパーソナルコンピュータのプリンタや、ビデオプリンタなどにおいて利用されている。
熱転写記録方式に用いられる熱転写シートは大別すると、加熱によって熱溶融性着色層が溶融軟化して熱溶融性着色層が被転写体、すなわち受像シートに転写移行する、いわゆる溶融転写タイプの熱転写シートと、感熱により色材層中の染料が昇華して染料が受像シートに移行する、いわゆる昇華タイプの熱転写シートとに分類される。ここで、身分証明書などのIDを作製する場合、特に、文字や数字等の単調な画像を形成する場合は、熱溶融型の熱転写シートが使用される。このような熱溶融型の熱転写シートとして、例えば、基材と、アクリル-スチレン系樹脂からなる離型層と熱溶融性着色層とがこの順で積層された熱転写シートが知られている。しかし、熱転写シートの離型層としてアクリル-スチレン系樹脂を用いた場合には、サーマルヘッドからかかる熱により離型層が軟化してしまい、離型層と転写層間の剥離力が高くなり、転写層が転写されない転写不良、剥離界面が荒れることによる画像の白化、剥離時の異音等の問題が生じることがある。
また、上記のような熱転写シートを使用して、身分証明書等のIDを作製した場合、画像を保護する目的で、熱溶融性着色層の熱転写によって得られた画像上に、基材と、ポリビニルアルコール(PVA)と水分散ウレタンからなる離型層と、保護層とがこの順で積層された保護層熱転写シートを重ね合わせ、サーマルヘッドや加熱ロール等を用いて保護層を転写させ、画像上に保護層を形成する方法が知られている。また更に、画像の耐久性を向上させるために、画像上に保護層を形成した後に、加熱ロール等を用いて、ラミネート材を形成する方法も知られている。しかし、水系の離型層(ポリビニルアルコールと水分散ウレタンからなる離型層)は湿度に対して不安定であり、特に高い湿度環境下では、転写層の剥離界面が荒れることによる画像の白化、剥離時の異音等の問題が生じることがある。
上記のような問題を解決するために、サーマルヘッドにかかる熱や、湿度環境による影響を低減し、剥離性を向上させるために、ポリアミド系樹脂を含有する離型層を設けた熱転写シートを提供することが提案されている(特許文献1参照)。
しかしながら、特許文献1に記載の熱転写シートでは、特に転写シートを高温環境下で保存した後では、微細な文字や数字等の画像を形成するには転写層のツブレおよび転写層のカスレが発生するという新たな技術的課題を知見した。
本発明は上記の背景技術に鑑みてなされたものであり、その目的は、転写シートを高温環境下で保存した後であっても、印画物を作製した際の転写層のツブレおよび転写層のカスレを改善した(保存安定性に優れる)転写シートを提供することにある。
本発明者らは、上記課題を解決するため、鋭意検討した結果、バインダー樹脂と、シリコーンオイルおよび/またはワックス成分とを含む特定の組成の剥離層を備えた転写シートを用いることで、上記課題を解決できることを知見した。本発明は、かかる知見に基づいて完成されたものである。
すなわち、本発明の一態様によれば、
基材と、前記基材上に剥離層と転写層とを順に備えてなる転写シートであって、
前記剥離層が、バインダー樹脂と、シリコーンオイルおよび/またはワックス成分とを含んでなり、前記剥離層中のシリコーンオイルおよびワックス成分の総含有量が、前記バインダー樹脂の固形分質量に対して、0.1質量%以上15質量%以下である、転写シートが提供される。
基材と、前記基材上に剥離層と転写層とを順に備えてなる転写シートであって、
前記剥離層が、バインダー樹脂と、シリコーンオイルおよび/またはワックス成分とを含んでなり、前記剥離層中のシリコーンオイルおよびワックス成分の総含有量が、前記バインダー樹脂の固形分質量に対して、0.1質量%以上15質量%以下である、転写シートが提供される。
本発明の上記態様においては、前記剥離層が、エポキシ変性シリコーンオイルを含むことが好ましい。
本発明の上記態様においては、前記剥離層が、ポリエチレンワックスを含むことが好ましい。
本発明の上記態様においては、前記バインダー樹脂が、アクリル系樹脂、ビニル系樹脂、ポリエステル系樹脂、ウレタン系樹脂、アセタール系樹脂、セルロース系樹脂、およびポリビニルアルコール系樹脂からなる群より選択される少なくとも1種であることが好ましい。
本発明の上記態様においては、前記剥離層中のバインダー樹脂の含有量が、前記剥離層の固形分質量に対して、60質量%以上99質量%以下であることが好ましい。
本発明の上記態様においては、前記基材と前記剥離層との間に、離型層をさらに備えてなることが好ましい。
本発明の上記態様においては、前記転写層が、着色剤を含むことが好ましい。
本発明によれば、転写シートを高温環境下で保存した後であっても、印画物を作製した際の転写層のツブレおよび転写層のカスレを改善した(保存安定性に優れる)転写シートを提供することができる。
<転写シート>
本発明による転写シートは、剥離層と転写層とを順に備えてなり、基材と剥離層との間に離型層をさらに備えてもよく、基材の剥離層と反対側の面に耐熱層をさらに備えてもよい。以下、本発明による転写シートの層構成を、図面を参照しながら説明する。
本発明による転写シートは、剥離層と転写層とを順に備えてなり、基材と剥離層との間に離型層をさらに備えてもよく、基材の剥離層と反対側の面に耐熱層をさらに備えてもよい。以下、本発明による転写シートの層構成を、図面を参照しながら説明する。
本発明による転写シートの一実施形態の模式断面図を図1に示す。図1に示される転写シート10は、基材11と、該基材11上に、離型層12と、剥離層13と、転写層14とをこの順に備えてなり、基材11の離型層12と反対側の面に、耐熱層15をさらに備えてなるものである。以下、本発明による転写シートを構成する各層について詳述する。
<基材>
本発明における基材は、転写層を保持するという役割を有するとともに、熱転写時には熱が加えられるため、加熱された状態でも取り扱い上支障のない程度の機械的強度を有する材料であることが好ましい。このような基材の材料としては、ポリエチレンテレフタレートフィルム、1,4-ポリシクロヘキシレンジメチレンテレフタレートフィルム、ポリエチレンナフタレートフィルム、ポリフェニレンサルフィドフィルム、ポリスチレンフィルム、ポリプロピレンフィルム、ポリサルホンフィルム、アラミドフィルム、ポリカーボネートフィルム、ポリビニルアルコールフィルム、セロハン、酢酸セルロース等のセルロース誘導体、ポリエチレンフィルム、ポリ塩化ビニルフィルム、ナイロンフィルム、ポリイミドフィルム、アイオノマーフィルム等が挙げられる。また、基材の厚さは、好ましくは0.5μm以上50μm以下、より好ましくは1μm以上10μm以下である。
本発明における基材は、転写層を保持するという役割を有するとともに、熱転写時には熱が加えられるため、加熱された状態でも取り扱い上支障のない程度の機械的強度を有する材料であることが好ましい。このような基材の材料としては、ポリエチレンテレフタレートフィルム、1,4-ポリシクロヘキシレンジメチレンテレフタレートフィルム、ポリエチレンナフタレートフィルム、ポリフェニレンサルフィドフィルム、ポリスチレンフィルム、ポリプロピレンフィルム、ポリサルホンフィルム、アラミドフィルム、ポリカーボネートフィルム、ポリビニルアルコールフィルム、セロハン、酢酸セルロース等のセルロース誘導体、ポリエチレンフィルム、ポリ塩化ビニルフィルム、ナイロンフィルム、ポリイミドフィルム、アイオノマーフィルム等が挙げられる。また、基材の厚さは、好ましくは0.5μm以上50μm以下、より好ましくは1μm以上10μm以下である。
基材は、表面に易接着処理を行ったものを用いてもよい。易接着処理は、基材と後述する離型層との間に易接着層を形成する処理である。このような易接着層としては、例えば、水性アクリル、水性ポリエステルおよび水性エポキシ化合物からなるものが好ましい。水性アクリルとは、水溶性あるいは水分散性アクリル系樹脂のことであり、アルキルアクリレートあるいはアルキルメタクリレートを主要な成分とするものが好ましく、当該成分が30モル%以上90モル%以下であって共重合されたものが好ましい。水性ポリエステルとは、水溶性あるいは水分散性ポリエステル系樹脂のことであり、かかるポリエステル系樹脂を構成する成分として、多価カルボン酸および多価ヒドロキシ化合物を例示できる。水性エポキシ化合物とは、水溶性あるいは水分散性、好ましくは水溶性のエポキシ基を含有する化合物のことであり、分子内にエポキシ基を少なくとも一つ以上、好ましくは二つ以上含有するもののことである。かかる水性エポキシ化合物としては、グリコール、ポリエーテル、ポリオール類のグリシジルエーテル、カルボン酸類のグリシジルエステル、グリシジル置換されたアミン類等が挙げられるが、好ましくはグリシジルエーテル類である。易接着処理は、基材の表面に易接着性の塗膜を形成させる方法が好ましく用いられる。
<離型層>
本発明における離型層は、熱転写時に転写層が基材から容易に剥離することが可能となるように設けられる層である。離型層は、離型性を有する材料により形成することが好ましく、例えば、バインダー樹脂と、離型剤等の添加剤とを含むことが好ましい。バインダー樹脂としては、ウレタン系樹脂、アセタール系樹脂、ポリアミド系樹脂、メラミン系樹脂、ポリオール樹脂、セルロース樹脂およびポリビニルアルコール等が挙げられ、ウレタン系樹脂およびアセタール系樹脂を用いることが好ましい。離型剤としては、シリコーンオイル、リン酸エステル系可塑剤、フッ素系化合物、ワックス、金属石鹸、およびフィラー等を挙げることができ、シリコーンオイルを用いることが好ましい。
本発明における離型層は、熱転写時に転写層が基材から容易に剥離することが可能となるように設けられる層である。離型層は、離型性を有する材料により形成することが好ましく、例えば、バインダー樹脂と、離型剤等の添加剤とを含むことが好ましい。バインダー樹脂としては、ウレタン系樹脂、アセタール系樹脂、ポリアミド系樹脂、メラミン系樹脂、ポリオール樹脂、セルロース樹脂およびポリビニルアルコール等が挙げられ、ウレタン系樹脂およびアセタール系樹脂を用いることが好ましい。離型剤としては、シリコーンオイル、リン酸エステル系可塑剤、フッ素系化合物、ワックス、金属石鹸、およびフィラー等を挙げることができ、シリコーンオイルを用いることが好ましい。
離型層の形成方法は特に限定されないが、従来公知の塗布方法により形成することができる。例えば、適当な溶剤中に上記のバインダー樹脂と、必要に応じて離型剤等の添加剤を加えて、各成分を溶解または分散させて塗布液を調製した後、この塗布液を基材の上に、グラビアコート法、ロールコート法、コンマコート法、グラビア印刷法、スクリーン印刷法、およびグラビアリバースロールコーティング法等の公知の手段を用い塗布、乾燥させて形成することができる。また、離型層の厚さは、特に限定されないが、好ましく0.05μm以上5.0μm以下であり、より好ましくは0.1μm以上3μm以下である。
<剥離層>
本発明における剥離層は、熱転写時に転写層が基材から容易に剥離することが可能となるように設けられる層である。剥離層はバインダー樹脂と、剥離剤とを含むものである。剥離層中の剥離剤の含有量(シリコーンオイルおよびワックス成分の総含有量)は、バインダー樹脂の固形分質量に対して、0.1質量%以上15質量%以下であり、好ましくは0.5質量%以上12質量%以下であり、より好ましくは1質量%以上10質量%以下である。剥離剤の含有量が上記範囲内であれば、転写シートを高温環境下で保存した後であっても、印画物を作製した際の転写層のツブレおよび転写層のカスレを改善した(保存安定性に優れる)転写シートを得ることができる。
本発明における剥離層は、熱転写時に転写層が基材から容易に剥離することが可能となるように設けられる層である。剥離層はバインダー樹脂と、剥離剤とを含むものである。剥離層中の剥離剤の含有量(シリコーンオイルおよびワックス成分の総含有量)は、バインダー樹脂の固形分質量に対して、0.1質量%以上15質量%以下であり、好ましくは0.5質量%以上12質量%以下であり、より好ましくは1質量%以上10質量%以下である。剥離剤の含有量が上記範囲内であれば、転写シートを高温環境下で保存した後であっても、印画物を作製した際の転写層のツブレおよび転写層のカスレを改善した(保存安定性に優れる)転写シートを得ることができる。
剥離剤としては、シリコーンオイルおよび/またはワックス成分が用いられる。シリコーンオイルとしては、アミノ変性シリコーン、エポキシ変性シリコーン、アラルキル変性シリコーン、エポキシ-アラルキル変性シリコーン、アルコール変性シリコーン、ビニル変性シリコーン、ウレタン変性シリコーン等が挙げられ、エポキシ変性シリコーンオイルを用いることが好ましい。ワックス成分としては、例えば、マイクロクリスタリンワックス、カルナバワックス、パラフィンワックス、フィッシャートロプシュワックス、各種低分子量ポリエチレン、木ロウ、ミツロウ、鯨ロウ、イボタロウ、羊毛ロウ、セラックワックス、キャンデリラワックス、ペトロラクタム、一部変性ワックス、脂肪酸エステル、脂肪酸アミド等、種々のワックス等が挙げられ、ポリエチレンワックスを用いることが好ましい。
剥離層中のバインダー樹脂の含有量は、剥離層の総固形分質量に対して、好ましくは60質量%以上99質量%以下であり、より好ましくは70質量%以上95質量%以下であり、さらに好ましくは80質量%以上90質量%以下である。バインダー樹脂の含有量が上記範囲内であれば、転写シートを高温環境下で保存した後であっても、印画物を作製した際の転写層のツブレおよび転写層のカスレを改善した(保存安定性に優れる)転写シートを得ることができる。
剥離層に用いられるバインダー樹脂としては、ポリ(メタ)アクリレート、ポリ(メタ)アクリルアミド等のアクリル系樹脂、ポリビニルアルコール樹脂、ポリ酢酸ビニル樹脂、塩化ビニル―酢酸ビニル共重合体(塩酢ビ樹脂)、ポリビニルブチラール樹脂、ポリビニルアセタール樹脂、ポリビニルピロリドン等のビニル系樹脂、ポリエチレンテレフタレート樹脂、ポリエチレンナフタレート樹等のポリエステル系樹脂、ポリウレタンアクリレート等のウレタン系樹脂、エチルセルロース樹脂、ヒドロキシエチルセルロース樹脂、エチルヒドロキシセルロース樹脂、メチルセルロース樹脂、酢酸セルロース樹脂等のセルロース系樹脂、ポリアミド樹脂、芳香族ポリアミド樹脂、ポリアミドイミド樹脂等のポリアミド系樹脂、アセタール系樹脂、およびポリカーボネート系樹脂等が挙げられ、アクリル系樹脂、ビニル系樹脂、ポリエステル系樹脂、ウレタン系樹脂、アセタール系樹脂、およびセルロース系樹脂を用いることが好ましい。
なお、本発明において、アクリル系樹脂とは、(メタ)アクリル酸のモノマーの重合体もしくはその誘導体、(メタ)アクリル酸エステルのモノマーの重合体もしくはその誘導体、(メタ)アクリルのモノマーと他のモノマーとの共重合体もしくはその誘導体、および(メタ)アクリル酸エステルのモノマーと他のモノマーとの共重合体もしくはその誘導体を含むものである。他の「系樹脂」も同様に、主成分以外の他のモノマーとの共重合体もしくはその誘導体を含んでもよい。
剥離層の形成方法は特に限定されないが、従来公知の塗布方法により形成することができる。例えば、適当な溶剤中に上記のバインダー樹脂と、剥離剤等の添加剤を加えて、各成分を溶解または分散させて塗布液を調製した後、この塗布液を基材または離型層の上に、グラビアコート法、ロールコート法、コンマコート法、グラビア印刷法、スクリーン印刷法、およびグラビアリバースロールコーティング法等の公知の手段を用い塗布、乾燥させて形成することができる。また、剥離層の厚さは、特に限定されないが、好ましく0.05μm以上5.0μm以下であり、より好ましくは0.1μm以上3μm以下である。
<転写層>
本発明における転写層は、転写シートと被転写体とを重ね合わせ、基材の裏面側(基材の転写層が設けられていない側)を熱転写用のサーマルヘッドを備えたプリンタ等、従来公知の加熱手段により加熱することで離型層および/または剥離層から剥離され被転写体上に転写される層である。
本発明における転写層は、転写シートと被転写体とを重ね合わせ、基材の裏面側(基材の転写層が設けられていない側)を熱転写用のサーマルヘッドを備えたプリンタ等、従来公知の加熱手段により加熱することで離型層および/または剥離層から剥離され被転写体上に転写される層である。
転写層は、被転写体上に転写されて文字や数字等の画像を形成するために、バインダー樹脂と、着色剤とを含むことが好ましい。転写層に用いられるバインダー樹脂としては、ポリ(メタ)アクリレート、ポリ(メタ)アクリルアミド等のアクリル系樹脂、ポリビニルアルコール樹脂、ポリ酢酸ビニル樹脂、塩酢ビ樹脂、ポリビニルブチラール樹脂、ポリビニルアセタール樹脂、ポリビニルピロリドン等のビニル系樹脂、ポリエチレンテレフタレート樹脂、ポリエチレンナフタレート樹等のポリエステル系樹脂、ポリウレタンアクリレート等のウレタン系樹脂、エチルセルロース樹脂、ヒドロキシエチルセルロース樹脂、エチルヒドロキシセルロース樹脂、メチルセルロース樹脂、酢酸セルロース樹脂等のセルロース系樹脂、ポリアミド樹脂、芳香族ポリアミド樹脂、ポリアミドイミド樹脂等のポリアミド系樹脂、アセタール系樹脂、およびポリカーボネート系樹脂等が挙げられ、ビニル系樹脂を用いることが好ましい。
着色剤としては、従来公知の着色剤を使用することができるが、印画材料として良好な特性を有するもの、例えば、十分な着色濃度を有し、光、熱、温度等により変褪色しないものが好ましい。また、加熱により発色する物質や、被転写体の表面に塗布されている成分と接触することにより発色するような物質であってもよい。着色剤は、墨、白、シルバー、シアン、マゼンダ、イエロー、レッド、グリーン、およびブルーからなる群から選択される少なくとも一つの色を呈するものがよい。例えば、着色剤としては、墨にはカーボンブラック、白には酸化チタン、およびシルバーにはアルミ等の無機材料、シアン、マゼンタ、イエロー、レッド、グリーン、およびブルーには C.I.Pigmentに記載される各顔料を使用することが好ましい。
転写層の形成方法は特に限定されないが、従来公知の塗布方法により形成することができる。例えば、適当な溶剤中に上記のバインダー樹脂と、着色剤を加えて、各成分を溶解または分散させて塗布液を調製した後、この塗布液を剥離層の上に、グラビアコート法、ロールコート法、コンマコート法、グラビア印刷法、スクリーン印刷法、およびグラビアリバースロールコーティング法等の公知の手段を用い塗布、乾燥させて形成することができる。また、転写層の厚さは、特に限定されないが、好ましく0.5μm以上30μm以下であり、より好ましくは1μm以上20μm以下である。
<耐熱層>
本発明における耐熱層は、熱転写する際の基材の裏面側(基材の転写層が設けられていない側)からの加熱によるスティキングやシワ等の悪影響を防止するために設けられる層である。耐熱層を設けることによって、耐熱性に劣るプラスチックフィルムを基材とした熱転写シートにおいてもスティッキングが起こることなく熱印字が可能であって、プラスチックフィルムの持つ切れにくさ、加工のし易さ等のメリットが生かせる。
本発明における耐熱層は、熱転写する際の基材の裏面側(基材の転写層が設けられていない側)からの加熱によるスティキングやシワ等の悪影響を防止するために設けられる層である。耐熱層を設けることによって、耐熱性に劣るプラスチックフィルムを基材とした熱転写シートにおいてもスティッキングが起こることなく熱印字が可能であって、プラスチックフィルムの持つ切れにくさ、加工のし易さ等のメリットが生かせる。
耐熱層は、バインダー樹脂と、滑り剤等の添加剤とを含むことが好ましい。耐熱層に用いられるバインダー樹脂としては、ポリ(メタ)アクリレート、ポリ(メタ)アクリルアミド等のアクリル系樹脂、ポリビニルアルコール樹脂、ポリ酢酸ビニル樹脂、塩酢ビ樹脂、ポリビニルブチラール樹脂、ポリビニルアセタール樹脂、ポリビニルピロリドン等のビニル系樹脂、ポリエチレンテレフタレート樹脂、ポリエチレンナフタレート樹等のポリエステル系樹脂、ポリウレタンアクリレート等のウレタン系樹脂、エチルセルロース樹脂、ヒドロキシエチルセルロース樹脂、エチルヒドロキシセルロース樹脂、メチルセルロース樹脂、酢酸セルロース樹脂等のセルロース系樹脂、ポリアミド樹脂、芳香族ポリアミド樹脂、ポリアミドイミド樹脂等のポリアミド系樹脂、アセタール系樹脂、およびポリカーボネート系樹脂等が挙げられる。滑り剤としては、金属石鹸、ワックス、シリコーンオイル、脂肪酸エステル、フィラー、タルク等が挙げられる。
耐熱層の形成方法は特に限定されないが、従来公知の塗布方法により形成することができる。例えば、適当な溶剤中に上記のバインダー樹脂と、必要に応じて滑り剤等の添加剤を加えて、各成分を溶解または分散させて塗布液を調製した後、この塗布液を基材の上に、グラビアコート法、ロールコート法、コンマコート法、グラビア印刷法、スクリーン印刷法、およびグラビアリバースロールコーティング法等の公知の手段を用い塗布、乾燥させて形成することができる。また、耐熱層の厚さは、特に限定されないが、好ましく0.05μm以上5.0μm以下であり、より好ましくは0.1μm以上3μm以下である。
<被転写体>
本発明による熱転写シートの転写に使用可能な被転写体としては、特に限定されず、例えば、従来公知の基材上に色素受容性を有する受容層を設けたもの等を挙げることができる。被転写体における基材としては、例えば、普通紙、上質紙、トレーシングペーパー、プラスチックフィルム等を挙げることができ、その基材について特に限定されない。上記被転写体における受容層は、コーティング法、サーマルヘッドや熱ロール等による形成法等にて形成することができる。なお、被転写体は、基材自体が色素受容性を有していれば、受容層を設ける必要がない。
本発明による熱転写シートの転写に使用可能な被転写体としては、特に限定されず、例えば、従来公知の基材上に色素受容性を有する受容層を設けたもの等を挙げることができる。被転写体における基材としては、例えば、普通紙、上質紙、トレーシングペーパー、プラスチックフィルム等を挙げることができ、その基材について特に限定されない。上記被転写体における受容層は、コーティング法、サーマルヘッドや熱ロール等による形成法等にて形成することができる。なお、被転写体は、基材自体が色素受容性を有していれば、受容層を設ける必要がない。
<転写方法>
本発明による転写シートを用いる熱転写法により転写層を被転写体上への転写は、従来公知の熱転写プリンタを用いて、被転写体に直接行う(ダイレクト)ことや、中間転写記録媒体が備える受容層上へ転写後(一次転写)、この中間転写記録媒体の受容層を被転写体へ転写する(再転写)ことによっても行うことができる。熱転写プリンタは、例えば、昇華転写用、熱溶融転写用、保護層転写用というように別々に転写条件を設定してもよいし、また、共通のプリンタでそれぞれ印字エネルギーを適切に調整して行ってもよい。また、加熱手段として特に限定されず、サーマルヘッド、熱板、ホットスタンパー、ヒートロール、ラインヒーター、アイロンなどを用いて転写を行うこととしてもよい。
本発明による転写シートを用いる熱転写法により転写層を被転写体上への転写は、従来公知の熱転写プリンタを用いて、被転写体に直接行う(ダイレクト)ことや、中間転写記録媒体が備える受容層上へ転写後(一次転写)、この中間転写記録媒体の受容層を被転写体へ転写する(再転写)ことによっても行うことができる。熱転写プリンタは、例えば、昇華転写用、熱溶融転写用、保護層転写用というように別々に転写条件を設定してもよいし、また、共通のプリンタでそれぞれ印字エネルギーを適切に調整して行ってもよい。また、加熱手段として特に限定されず、サーマルヘッド、熱板、ホットスタンパー、ヒートロール、ラインヒーター、アイロンなどを用いて転写を行うこととしてもよい。
以下に、実施例と比較例を挙げて本発明をさらに具体的に説明するが、本発明は以下の実施例に限定解釈されるものではない。なお、バインダー樹脂、シリコーンオイル、およびワックス成分の質量部は固形分で記載した。
[実施例1]
基材として、厚さ6μmの易接着処理つきポリエステルフィルムを用意した。該ポリエステルフィルムの易接着処理がされていない面に下記組成の耐熱層用塗布液1を乾燥時1.0g/m2になるように塗布して耐熱層を形成し、易接着処理がされている面に下記組成の離型層用塗布液1を乾燥時0.3g/m2になるように塗布して離型層を形成した。次いで、離型層上に下記組成の剥離層用塗布液1を乾燥時1.0g/m2になるように塗布して剥離層を形成した。次いで、剥離層上に下記組成の転写層用塗布液を乾燥時1.0g/m2になるように塗布して転写層を形成して、転写シート1を製造した。
基材として、厚さ6μmの易接着処理つきポリエステルフィルムを用意した。該ポリエステルフィルムの易接着処理がされていない面に下記組成の耐熱層用塗布液1を乾燥時1.0g/m2になるように塗布して耐熱層を形成し、易接着処理がされている面に下記組成の離型層用塗布液1を乾燥時0.3g/m2になるように塗布して離型層を形成した。次いで、離型層上に下記組成の剥離層用塗布液1を乾燥時1.0g/m2になるように塗布して剥離層を形成した。次いで、剥離層上に下記組成の転写層用塗布液を乾燥時1.0g/m2になるように塗布して転写層を形成して、転写シート1を製造した。
<耐熱層用塗布液1>
・ポリビニルブチラール樹脂(積水化学工業(株)製、商品名:エスレックBX-1) 2.0質量部
・イソシアネート(DIC(株)製、商品名:バーノックD750)
4.4質量部
・リン酸エステル系界面活性剤
(第一工業製薬(株)製、商品名:プライサーフA208N) 1.3質量部
・タルク(日本タルク(株)製、商品名:ミクロエースP-3)
0.3質量部
・粘度調整溶剤(トルエン/メチルエチルケトン=1/1) 92質量部
<離型層用塗布液1>
・ウレタン系樹脂 25質量部
・アセタール系樹脂(積水化学(株)製、商品名:エスレックK KS-5) 75質量部
・粘度調整溶剤(トルエン/イソプロピルアルコール=1/1)
1900質量部
<剥離層用塗布液1>
・アクリル系樹脂(三菱レイヨン(株)製、商品名:BR―85 )
100質量部
・ポリエチレンワックス 1質量部
・粘度調整溶剤(トルエン/メチルエチルケトン=1/1) 300質量部
<転写層用塗布液1>
・塩化ビニル―酢酸ビニル共重合体 60質量部
・カーボンブラック 40質量部
・粘度調整溶剤(トルエン/メチルエチルケトン=1/1) 200質量部
・ポリビニルブチラール樹脂(積水化学工業(株)製、商品名:エスレックBX-1) 2.0質量部
・イソシアネート(DIC(株)製、商品名:バーノックD750)
4.4質量部
・リン酸エステル系界面活性剤
(第一工業製薬(株)製、商品名:プライサーフA208N) 1.3質量部
・タルク(日本タルク(株)製、商品名:ミクロエースP-3)
0.3質量部
・粘度調整溶剤(トルエン/メチルエチルケトン=1/1) 92質量部
<離型層用塗布液1>
・ウレタン系樹脂 25質量部
・アセタール系樹脂(積水化学(株)製、商品名:エスレックK KS-5) 75質量部
・粘度調整溶剤(トルエン/イソプロピルアルコール=1/1)
1900質量部
<剥離層用塗布液1>
・アクリル系樹脂(三菱レイヨン(株)製、商品名:BR―85 )
100質量部
・ポリエチレンワックス 1質量部
・粘度調整溶剤(トルエン/メチルエチルケトン=1/1) 300質量部
<転写層用塗布液1>
・塩化ビニル―酢酸ビニル共重合体 60質量部
・カーボンブラック 40質量部
・粘度調整溶剤(トルエン/メチルエチルケトン=1/1) 200質量部
[実施例2]
剥離層用塗布液の組成を下記のとおりにした以外は、実施例1と同様にして転写シート2を製造した。
<剥離層用塗布液2>
・アクリル系樹脂(三菱レイヨン(株)製、商品名:BR―85 )
100質量部
・エポキシ変性シリコーンオイル(信越化学工業(株)製、商品名:KP-1800U) 1質量部
・粘度調整溶剤(トルエン/メチルエチルケトン=1/1) 300質量部
剥離層用塗布液の組成を下記のとおりにした以外は、実施例1と同様にして転写シート2を製造した。
<剥離層用塗布液2>
・アクリル系樹脂(三菱レイヨン(株)製、商品名:BR―85 )
100質量部
・エポキシ変性シリコーンオイル(信越化学工業(株)製、商品名:KP-1800U) 1質量部
・粘度調整溶剤(トルエン/メチルエチルケトン=1/1) 300質量部
[実施例3]
剥離層用塗布液の組成を下記のとおりにした以外は、実施例1と同様にして転写シート3を製造した。
<剥離層用塗布液3>
・アクリル系樹脂(三菱レイヨン(株)製、商品名:BR―85 )
100質量部
・エポキシ変性シリコーンオイル(信越化学工業(株)製、商品名:KP-1800U) 2質量部
・ポリエチレンワックス 2質量部
・粘度調整溶剤(トルエン/メチルエチルケトン=1/1) 300質量部
剥離層用塗布液の組成を下記のとおりにした以外は、実施例1と同様にして転写シート3を製造した。
<剥離層用塗布液3>
・アクリル系樹脂(三菱レイヨン(株)製、商品名:BR―85 )
100質量部
・エポキシ変性シリコーンオイル(信越化学工業(株)製、商品名:KP-1800U) 2質量部
・ポリエチレンワックス 2質量部
・粘度調整溶剤(トルエン/メチルエチルケトン=1/1) 300質量部
[実施例4]
剥離層用塗布液の組成を下記のとおりにした以外は、実施例1と同様にして転写シート4を製造した。
<剥離層用塗布液4>
・アクリル系樹脂(三菱レイヨン(株)製、商品名:BR―85 )
100質量部
・エポキシ変性シリコーンオイル(信越化学工業(株)製、商品名:KP-1800U) 3質量部
・ポリエチレンワックス 4質量部
・粘度調整溶剤(トルエン/メチルエチルケトン=1/1) 300質量部
剥離層用塗布液の組成を下記のとおりにした以外は、実施例1と同様にして転写シート4を製造した。
<剥離層用塗布液4>
・アクリル系樹脂(三菱レイヨン(株)製、商品名:BR―85 )
100質量部
・エポキシ変性シリコーンオイル(信越化学工業(株)製、商品名:KP-1800U) 3質量部
・ポリエチレンワックス 4質量部
・粘度調整溶剤(トルエン/メチルエチルケトン=1/1) 300質量部
[実施例5]
剥離層用塗布液の組成を下記のとおりにした以外は、実施例1と同様にして転写シート5を製造した。
<剥離層用塗布液5>
・アクリル系樹脂(三菱レイヨン(株)製、商品名:BR―85)
100質量部
・エポキシ変性シリコーンオイル(信越化学工業(株)製、商品名:KP-1800U) 10質量部
・ポリエチレンワックス 5質量部
・粘度調整溶剤(トルエン/メチルエチルケトン=1/1) 300質量部
剥離層用塗布液の組成を下記のとおりにした以外は、実施例1と同様にして転写シート5を製造した。
<剥離層用塗布液5>
・アクリル系樹脂(三菱レイヨン(株)製、商品名:BR―85)
100質量部
・エポキシ変性シリコーンオイル(信越化学工業(株)製、商品名:KP-1800U) 10質量部
・ポリエチレンワックス 5質量部
・粘度調整溶剤(トルエン/メチルエチルケトン=1/1) 300質量部
[実施例6]
剥離層用塗布液の組成を下記のとおりにした以外は、実施例1と同様にして転写シート6を製造した。
<剥離層用塗布液6>
・塩酢ビ樹脂(日信化学工業(株)製、商品名:ソルバインCNL)
100質量部
・ポリエチレンワックス 2質量部
・粘度調整溶剤(トルエン/メチルエチルケトン=1/1) 300質量部
剥離層用塗布液の組成を下記のとおりにした以外は、実施例1と同様にして転写シート6を製造した。
<剥離層用塗布液6>
・塩酢ビ樹脂(日信化学工業(株)製、商品名:ソルバインCNL)
100質量部
・ポリエチレンワックス 2質量部
・粘度調整溶剤(トルエン/メチルエチルケトン=1/1) 300質量部
[実施例7]
剥離層用塗布液の組成を下記のとおりにした以外は、実施例1と同様にして転写シート7を製造した。
<剥離層用塗布液7>
・塩酢ビ樹脂(日信化学工業(株)製、商品名:ソルバインCNL)
100質量部
・エポキシ変性シリコーンオイル(信越化学工業(株)製、商品名:KP-1800U) 2質量部
・粘度調整溶剤(トルエン/メチルエチルケトン=1/1) 300質量部
剥離層用塗布液の組成を下記のとおりにした以外は、実施例1と同様にして転写シート7を製造した。
<剥離層用塗布液7>
・塩酢ビ樹脂(日信化学工業(株)製、商品名:ソルバインCNL)
100質量部
・エポキシ変性シリコーンオイル(信越化学工業(株)製、商品名:KP-1800U) 2質量部
・粘度調整溶剤(トルエン/メチルエチルケトン=1/1) 300質量部
[実施例8]
剥離層用塗布液の組成を下記のとおりにした以外は、実施例1と同様にして転写シート8を製造した。
<剥離層用塗布液8>
・塩酢ビ樹脂(日信化学工業(株)製、商品名:ソルバインCNL)
100質量部
・エポキシ変性シリコーンオイル(信越化学工業(株)製、商品名:KP-1800U) 2質量部
・ポリエチレンワックス 5質量部
・粘度調整溶剤(トルエン/メチルエチルケトン=1/1) 300質量部
剥離層用塗布液の組成を下記のとおりにした以外は、実施例1と同様にして転写シート8を製造した。
<剥離層用塗布液8>
・塩酢ビ樹脂(日信化学工業(株)製、商品名:ソルバインCNL)
100質量部
・エポキシ変性シリコーンオイル(信越化学工業(株)製、商品名:KP-1800U) 2質量部
・ポリエチレンワックス 5質量部
・粘度調整溶剤(トルエン/メチルエチルケトン=1/1) 300質量部
[実施例9]
剥離層用塗布液の組成を下記のとおりにした以外は、実施例1と同様にして転写シート9を製造した。
<剥離層用塗布液9>
・塩酢ビ樹脂(日信化学工業(株)製、商品名:ソルバインCNL)
100質量部
・エポキシ変性シリコーンオイル(信越化学工業(株)製、商品名:KP-1800U) 3質量部
・ポリエチレンワックス 5質量部
・粘度調整溶剤(トルエン/メチルエチルケトン=1/1) 300質量部
剥離層用塗布液の組成を下記のとおりにした以外は、実施例1と同様にして転写シート9を製造した。
<剥離層用塗布液9>
・塩酢ビ樹脂(日信化学工業(株)製、商品名:ソルバインCNL)
100質量部
・エポキシ変性シリコーンオイル(信越化学工業(株)製、商品名:KP-1800U) 3質量部
・ポリエチレンワックス 5質量部
・粘度調整溶剤(トルエン/メチルエチルケトン=1/1) 300質量部
[実施例10]
剥離層用塗布液の組成を下記のとおりにした以外は、実施例1と同様にして転写シート10を製造した。
<剥離層用塗布液10>
・塩酢ビ樹脂(日信化学工業(株)製、商品名:ソルバインCNL)
100質量部
・エポキシ変性シリコーンオイル(信越化学工業(株)製、商品名:KP-1800U) 5質量部
・ポリエチレンワックス 10質量部
・粘度調整溶剤(トルエン/メチルエチルケトン=1/1) 300質量部
剥離層用塗布液の組成を下記のとおりにした以外は、実施例1と同様にして転写シート10を製造した。
<剥離層用塗布液10>
・塩酢ビ樹脂(日信化学工業(株)製、商品名:ソルバインCNL)
100質量部
・エポキシ変性シリコーンオイル(信越化学工業(株)製、商品名:KP-1800U) 5質量部
・ポリエチレンワックス 10質量部
・粘度調整溶剤(トルエン/メチルエチルケトン=1/1) 300質量部
[実施例11]
剥離層用塗布液の組成を下記のとおりにした以外は、実施例1と同様にして転写シート11を製造した。
<剥離層用塗布液11>
・ポリエステル系樹脂(東洋紡(株)製、商品名:バイロン220)
100質量部
・ポリエチレンワックス 3質量部
・粘度調整溶剤(トルエン/メチルエチルケトン=1/1) 300質量部
剥離層用塗布液の組成を下記のとおりにした以外は、実施例1と同様にして転写シート11を製造した。
<剥離層用塗布液11>
・ポリエステル系樹脂(東洋紡(株)製、商品名:バイロン220)
100質量部
・ポリエチレンワックス 3質量部
・粘度調整溶剤(トルエン/メチルエチルケトン=1/1) 300質量部
[実施例12]
剥離層用塗布液の組成を下記のとおりにした以外は、実施例1と同様にして転写シート12を製造した。
<剥離層用塗布液12>
・ポリエステル系樹脂(東洋紡(株)製、商品名:バイロン220)
100質量部
・エポキシ変性シリコーンオイル(信越化学工業(株)製、商品名:KP-1800U) 1質量部
・ポリエチレンワックス 5質量部
・粘度調整溶剤(トルエン/メチルエチルケトン=1/1) 300質量部
剥離層用塗布液の組成を下記のとおりにした以外は、実施例1と同様にして転写シート12を製造した。
<剥離層用塗布液12>
・ポリエステル系樹脂(東洋紡(株)製、商品名:バイロン220)
100質量部
・エポキシ変性シリコーンオイル(信越化学工業(株)製、商品名:KP-1800U) 1質量部
・ポリエチレンワックス 5質量部
・粘度調整溶剤(トルエン/メチルエチルケトン=1/1) 300質量部
[実施例13]
剥離層用塗布液の組成を下記のとおりにした以外は、実施例1と同様にして転写シート13を製造した。
<剥離層用塗布液13>
・ポリエステル系樹脂(東洋紡(株)製、商品名:バイロン220)
100質量部
・エポキシ変性シリコーンオイル(信越化学工業(株)製、商品名:KP-1800U) 1質量部
・ポリエチレンワックス 4質量部
・粘度調整溶剤(トルエン/メチルエチルケトン=1/1) 300質量部
剥離層用塗布液の組成を下記のとおりにした以外は、実施例1と同様にして転写シート13を製造した。
<剥離層用塗布液13>
・ポリエステル系樹脂(東洋紡(株)製、商品名:バイロン220)
100質量部
・エポキシ変性シリコーンオイル(信越化学工業(株)製、商品名:KP-1800U) 1質量部
・ポリエチレンワックス 4質量部
・粘度調整溶剤(トルエン/メチルエチルケトン=1/1) 300質量部
[実施例14]
剥離層用塗布液の組成を下記のとおりにした以外は、実施例1と同様にして転写シート14を製造した。
<剥離層用塗布液14>
・ポリエステル系樹脂(東洋紡(株)製、商品名:バイロン220)
100質量部
・エポキシ変性シリコーンオイル(信越化学工業(株)製、商品名:KP-1800U) 2質量部
・ポリエチレンワックス 4質量部
・粘度調整溶剤(トルエン/メチルエチルケトン=1/1) 300質量部
剥離層用塗布液の組成を下記のとおりにした以外は、実施例1と同様にして転写シート14を製造した。
<剥離層用塗布液14>
・ポリエステル系樹脂(東洋紡(株)製、商品名:バイロン220)
100質量部
・エポキシ変性シリコーンオイル(信越化学工業(株)製、商品名:KP-1800U) 2質量部
・ポリエチレンワックス 4質量部
・粘度調整溶剤(トルエン/メチルエチルケトン=1/1) 300質量部
[実施例15]
剥離層用塗布液の組成を下記のとおりにした以外は、実施例1と同様にして転写シート15を製造した。
<剥離層用塗布液15>
・ポリエステル系樹脂(東洋紡(株)製、商品名:バイロン220)
100質量部
・エポキシ変性シリコーンオイル(信越化学工業(株)製、商品名:KP-1800U) 7質量部
・ポリエチレンワックス 8質量部
・粘度調整溶剤(トルエン/メチルエチルケトン=1/1) 300質量部
剥離層用塗布液の組成を下記のとおりにした以外は、実施例1と同様にして転写シート15を製造した。
<剥離層用塗布液15>
・ポリエステル系樹脂(東洋紡(株)製、商品名:バイロン220)
100質量部
・エポキシ変性シリコーンオイル(信越化学工業(株)製、商品名:KP-1800U) 7質量部
・ポリエチレンワックス 8質量部
・粘度調整溶剤(トルエン/メチルエチルケトン=1/1) 300質量部
[実施例16]
剥離層用塗布液の組成を下記のとおりにした以外は、実施例1と同様にして転写シート16を製造した。
<剥離層用塗布液16>
・ウレタン系樹脂(DIC(株)製、商品名:NY―373)
100質量部
・エポキシ変性シリコーンオイル(信越化学工業(株)製、商品名:KP-1800U) 3質量部
・ポリエチレンワックス 4質量部
・粘度調整溶剤(トルエン/メチルエチルケトン=1/1) 300質量部
剥離層用塗布液の組成を下記のとおりにした以外は、実施例1と同様にして転写シート16を製造した。
<剥離層用塗布液16>
・ウレタン系樹脂(DIC(株)製、商品名:NY―373)
100質量部
・エポキシ変性シリコーンオイル(信越化学工業(株)製、商品名:KP-1800U) 3質量部
・ポリエチレンワックス 4質量部
・粘度調整溶剤(トルエン/メチルエチルケトン=1/1) 300質量部
[実施例17]
剥離層用塗布液の組成を下記のとおりにした以外は、実施例1と同様にして転写シート17を製造した。
<剥離層用塗布液17>
・アセタール系樹脂(積水化学(株)製、商品名:エスレックK KS-5)
100質量部
・エポキシ変性シリコーンオイル(信越化学工業(株)製、商品名:KP-1800U) 4質量部
・ポリエチレンワックス 5質量部
・粘度調整溶剤(トルエン/メチルエチルケトン=1/1) 300質量部
剥離層用塗布液の組成を下記のとおりにした以外は、実施例1と同様にして転写シート17を製造した。
<剥離層用塗布液17>
・アセタール系樹脂(積水化学(株)製、商品名:エスレックK KS-5)
100質量部
・エポキシ変性シリコーンオイル(信越化学工業(株)製、商品名:KP-1800U) 4質量部
・ポリエチレンワックス 5質量部
・粘度調整溶剤(トルエン/メチルエチルケトン=1/1) 300質量部
[実施例18]
剥離層用塗布液の組成を下記のとおりにした以外は、実施例1と同様にして転写シート18を製造した。
<剥離層用塗布液18>
・セルロース系樹脂(イーストマンケミカル社製、商品名:CAB-381-0.5) 100質量部
・エポキシ変性シリコーンオイル(信越化学工業(株)製、商品名:KP-1800U) 5質量部
・ポリエチレンワックス 5質量部
・粘度調整溶剤(トルエン/メチルエチルケトン=1/1) 300質量部
剥離層用塗布液の組成を下記のとおりにした以外は、実施例1と同様にして転写シート18を製造した。
<剥離層用塗布液18>
・セルロース系樹脂(イーストマンケミカル社製、商品名:CAB-381-0.5) 100質量部
・エポキシ変性シリコーンオイル(信越化学工業(株)製、商品名:KP-1800U) 5質量部
・ポリエチレンワックス 5質量部
・粘度調整溶剤(トルエン/メチルエチルケトン=1/1) 300質量部
[実施例19]
剥離層用塗布液の組成を下記のとおりにした以外は、実施例1と同様にして転写シート19を製造した。
<剥離層用塗布液19>
・ポリビニルアルコール(PVA)樹脂
(日本合成化学(株)製、商品名:ゴーセノールC-500) 100質量部
・ポリエチレンワックス 10質量部
・粘度調整溶剤(水/イソプロピルアルコール=1/1) 300質量部
剥離層用塗布液の組成を下記のとおりにした以外は、実施例1と同様にして転写シート19を製造した。
<剥離層用塗布液19>
・ポリビニルアルコール(PVA)樹脂
(日本合成化学(株)製、商品名:ゴーセノールC-500) 100質量部
・ポリエチレンワックス 10質量部
・粘度調整溶剤(水/イソプロピルアルコール=1/1) 300質量部
[比較例1]
剥離層用塗布液の組成を下記のとおりにした以外は、実施例1と同様にして転写シート20を製造した。
<剥離層用塗布液20>
・アクリル系樹脂(三菱レイヨン(株)製、商品名:BR―85)
100質量部
・粘度調整溶剤(トルエン/メチルエチルケトン=1/1) 300質量部
剥離層用塗布液の組成を下記のとおりにした以外は、実施例1と同様にして転写シート20を製造した。
<剥離層用塗布液20>
・アクリル系樹脂(三菱レイヨン(株)製、商品名:BR―85)
100質量部
・粘度調整溶剤(トルエン/メチルエチルケトン=1/1) 300質量部
[比較例2]
剥離層用塗布液の組成を下記のとおりにした以外は、実施例1と同様にして転写シート21を製造した。
<剥離層用塗布液21>
・塩酢ビ樹脂(日信化学工業(株)製、商品名:ソルバインCNL)
100質量部
・粘度調整溶剤(トルエン/メチルエチルケトン=1/1) 300質量部
剥離層用塗布液の組成を下記のとおりにした以外は、実施例1と同様にして転写シート21を製造した。
<剥離層用塗布液21>
・塩酢ビ樹脂(日信化学工業(株)製、商品名:ソルバインCNL)
100質量部
・粘度調整溶剤(トルエン/メチルエチルケトン=1/1) 300質量部
[比較例3]
剥離層用塗布液の組成を下記のとおりにした以外は、実施例1と同様にして転写シート22を製造した。
<剥離層用塗布液22>
・ポリエステル系樹脂(東洋紡(株)製、商品名:バイロン220)
100質量部
・粘度調整溶剤(トルエン/メチルエチルケトン=1/1) 300質量部
剥離層用塗布液の組成を下記のとおりにした以外は、実施例1と同様にして転写シート22を製造した。
<剥離層用塗布液22>
・ポリエステル系樹脂(東洋紡(株)製、商品名:バイロン220)
100質量部
・粘度調整溶剤(トルエン/メチルエチルケトン=1/1) 300質量部
[比較例4]
剥離層用塗布液の組成を下記のとおりにした以外は、実施例1と同様にして転写シート23を製造した。
<剥離層用塗布液23>
・ポリエステル系樹脂(東洋紡(株)製、商品名:バイロン220)
100質量部
・ポリエチレンワックス 20質量部
・粘度調整溶剤(トルエン/メチルエチルケトン=1/1) 300質量部
剥離層用塗布液の組成を下記のとおりにした以外は、実施例1と同様にして転写シート23を製造した。
<剥離層用塗布液23>
・ポリエステル系樹脂(東洋紡(株)製、商品名:バイロン220)
100質量部
・ポリエチレンワックス 20質量部
・粘度調整溶剤(トルエン/メチルエチルケトン=1/1) 300質量部
[比較例5]
剥離層用塗布液の組成を下記のとおりにした以外は、実施例1と同様にして転写シート24を製造した。
<剥離層用塗布液24>
・塩酢ビ樹脂(日信化学工業(株)製、商品名:ソルバインCNL)
100質量部
・エポキシ変性シリコーンオイル(信越化学工業(株)製、商品名:KP-1800U) 7質量部
・ポリエチレンワックス 10質量部
・粘度調整溶剤(トルエン/メチルエチルケトン=1/1) 300質量部
剥離層用塗布液の組成を下記のとおりにした以外は、実施例1と同様にして転写シート24を製造した。
<剥離層用塗布液24>
・塩酢ビ樹脂(日信化学工業(株)製、商品名:ソルバインCNL)
100質量部
・エポキシ変性シリコーンオイル(信越化学工業(株)製、商品名:KP-1800U) 7質量部
・ポリエチレンワックス 10質量部
・粘度調整溶剤(トルエン/メチルエチルケトン=1/1) 300質量部
[比較例6]
剥離層用塗布液の組成を下記のとおりにした以外は、実施例1と同様にして転写シート25を製造した。
<剥離層用塗布液25>
・ポリエステル系樹脂(東洋紡(株)製、商品名:バイロン220)
100質量部
・エポキシ変性シリコーンオイル(信越化学工業(株)製、商品名:KP-1800U) 5質量部
・ポリエチレンワックス 15質量部
・粘度調整溶剤(トルエン/メチルエチルケトン=1/1) 300質量部
剥離層用塗布液の組成を下記のとおりにした以外は、実施例1と同様にして転写シート25を製造した。
<剥離層用塗布液25>
・ポリエステル系樹脂(東洋紡(株)製、商品名:バイロン220)
100質量部
・エポキシ変性シリコーンオイル(信越化学工業(株)製、商品名:KP-1800U) 5質量部
・ポリエチレンワックス 15質量部
・粘度調整溶剤(トルエン/メチルエチルケトン=1/1) 300質量部
[比較例7]
剥離層用塗布液の組成を下記のとおりにした以外は、実施例1と同様にして転写シート26を製造した。
<剥離層用塗布液26>
・セルロース系樹脂(イーストマンケミカル社製、商品名:CAB-381-0.5) 100質量部
・エポキシ変性シリコーンオイル(信越化学工業(株)製、商品名:KP-1800U) 8質量部
・ポリエチレンワックス 8質量部
・粘度調整溶剤(トルエン/メチルエチルケトン=1/1) 300質量部
剥離層用塗布液の組成を下記のとおりにした以外は、実施例1と同様にして転写シート26を製造した。
<剥離層用塗布液26>
・セルロース系樹脂(イーストマンケミカル社製、商品名:CAB-381-0.5) 100質量部
・エポキシ変性シリコーンオイル(信越化学工業(株)製、商品名:KP-1800U) 8質量部
・ポリエチレンワックス 8質量部
・粘度調整溶剤(トルエン/メチルエチルケトン=1/1) 300質量部
[比較例8]
剥離層用塗布液の組成を下記のとおりにした以外は、実施例1と同様にして転写シート27を製造した。
<剥離層用塗布液27>
・アクリル系樹脂(三菱レイヨン(株)製、商品名:BR―85)
100質量部
・エポキシ変性シリコーンオイル(信越化学工業(株)製、商品名:KP-1800U) 10質量部
・ポリエチレンワックス 8質量部
・粘度調整溶剤(トルエン/メチルエチルケトン=1/1) 300質量部
剥離層用塗布液の組成を下記のとおりにした以外は、実施例1と同様にして転写シート27を製造した。
<剥離層用塗布液27>
・アクリル系樹脂(三菱レイヨン(株)製、商品名:BR―85)
100質量部
・エポキシ変性シリコーンオイル(信越化学工業(株)製、商品名:KP-1800U) 10質量部
・ポリエチレンワックス 8質量部
・粘度調整溶剤(トルエン/メチルエチルケトン=1/1) 300質量部
[比較例9]
剥離層用塗布液の組成を下記のとおりにした以外は、実施例1と同様にして転写シート28を製造した。
<剥離層用塗布液28>
・アクリル系樹脂(三菱レイヨン(株)製、商品名:BR―85)
100質量部
・エポキシ変性シリコーンオイル(信越化学工業(株)製、商品名:KP-1800U) 10質量部
・ポリエチレンワックス 10質量部
・粘度調整溶剤(トルエン/メチルエチルケトン=1/1) 300質量部
剥離層用塗布液の組成を下記のとおりにした以外は、実施例1と同様にして転写シート28を製造した。
<剥離層用塗布液28>
・アクリル系樹脂(三菱レイヨン(株)製、商品名:BR―85)
100質量部
・エポキシ変性シリコーンオイル(信越化学工業(株)製、商品名:KP-1800U) 10質量部
・ポリエチレンワックス 10質量部
・粘度調整溶剤(トルエン/メチルエチルケトン=1/1) 300質量部
[比較例10]
剥離層用塗布液の組成を下記のとおりにした以外は、実施例1と同様にして転写シート29を製造した。
<剥離層用塗布液29>
・アセタール系樹脂(積水化学(株)製、商品名:エスレックK KS-5) 100質量部
・エポキシ変性シリコーンオイル(信越化学工業(株)製、商品名:KP-1800U) 13質量部
・ポリエチレンワックス 6質量部
・粘度調整溶剤(トルエン/メチルエチルケトン=1/1) 300質量部
剥離層用塗布液の組成を下記のとおりにした以外は、実施例1と同様にして転写シート29を製造した。
<剥離層用塗布液29>
・アセタール系樹脂(積水化学(株)製、商品名:エスレックK KS-5) 100質量部
・エポキシ変性シリコーンオイル(信越化学工業(株)製、商品名:KP-1800U) 13質量部
・ポリエチレンワックス 6質量部
・粘度調整溶剤(トルエン/メチルエチルケトン=1/1) 300質量部
[比較例11]
剥離層用塗布液の組成を下記のとおりにした以外は、実施例1と同様にして転写シート30を製造した。
<剥離層用塗布液30>
・塩酢ビ樹脂(日信化学工業(株)製、商品名:ソルバインCNL)
100質量部
・シリコーンオイル(信越化学工業(株)製、商品名:KP-1800U)
20質量部
・粘度調整溶剤(トルエン/メチルエチルケトン=1/1) 300質量部
剥離層用塗布液の組成を下記のとおりにした以外は、実施例1と同様にして転写シート30を製造した。
<剥離層用塗布液30>
・塩酢ビ樹脂(日信化学工業(株)製、商品名:ソルバインCNL)
100質量部
・シリコーンオイル(信越化学工業(株)製、商品名:KP-1800U)
20質量部
・粘度調整溶剤(トルエン/メチルエチルケトン=1/1) 300質量部
[転写シートの性能評価]
上記の実施例および比較例で製造した転写シートについて、保存安定性の評価を行った。
上記の実施例および比較例で製造した転写シートについて、保存安定性の評価を行った。
[保存安定性の評価]
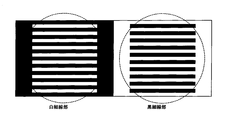
上記の実施例および比較例で製造した転写シートを50℃dry環境で96時間保存した。保存前の転写シートおよび保存後の転写シートのそれぞれと、テストプリンタ(サーマルヘッド:京セラ(株)製、商品名:KEE-5712GAN2-STA)とを用いて、ポリ塩化ビニル製カード上に、下記の転写条件で転写して、印画物を作製した。保存前の転写シートを用いて作製した印画物の白色および黒色の細線部の面積に対する、保存後の転写シートを用いて作製した印画物の白色および黒色の細線部の面積の割合を算出して、細線再現性を評価した。
<転写条件>
・印画条件:3.0msec/line、18.5V
・印画パターン:図2に示す印画パターン(白線および黒線)
・被転写体:ポリ塩化ビニル製カード
上記の実施例および比較例で製造した転写シートを50℃dry環境で96時間保存した。保存前の転写シートおよび保存後の転写シートのそれぞれと、テストプリンタ(サーマルヘッド:京セラ(株)製、商品名:KEE-5712GAN2-STA)とを用いて、ポリ塩化ビニル製カード上に、下記の転写条件で転写して、印画物を作製した。保存前の転写シートを用いて作製した印画物の白色および黒色の細線部の面積に対する、保存後の転写シートを用いて作製した印画物の白色および黒色の細線部の面積の割合を算出して、細線再現性を評価した。
<転写条件>
・印画条件:3.0msec/line、18.5V
・印画パターン:図2に示す印画パターン(白線および黒線)
・被転写体:ポリ塩化ビニル製カード
10 転写シート
11 基材
12 離型層
13 剥離層
14 転写層
15 耐熱層
11 基材
12 離型層
13 剥離層
14 転写層
15 耐熱層
Claims (7)
- 基材と、前記基材上に剥離層と転写層とを順に備えてなる転写シートであって、
前記剥離層が、バインダー樹脂と、シリコーンオイルおよび/またはワックス成分とを含んでなり、前記剥離層中のシリコーンオイルおよびワックス成分の総含有量が、前記バインダー樹脂の固形分質量に対して、0.1質量%以上15質量%以下である、転写シート。 - 前記剥離層が、エポキシ変性シリコーンオイルを含む、請求項1に記載の転写シート。
- 前記剥離層が、ポリエチレンワックスを含む、請求項1または2に記載に転写シート。
- 前記バインダー樹脂が、アクリル系樹脂、ビニル系樹脂、ポリエステル系樹脂、ウレタン系樹脂、アセタール系樹脂、およびセルロース系樹脂からなる群より選択される少なくとも1種である、請求項1~3のいずれか一項に記載の転写シート。
- 前記剥離層中のバインダー樹脂の含有量が、前記剥離層の固形分質量に対して、60質量%以上99質量%以下である、請求項1~4のいずれか一項に記載の転写シート。
- 前記基材と前記剥離層との間に、離型層をさらに備えてなる、請求項1~5のいずれか一項に記載の転写シート。
- 前記転写層が、着色剤を含む、請求項1~6のいずれか一項に記載の転写シート。
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US15/504,077 US10000081B2 (en) | 2014-09-30 | 2015-09-17 | Transfer sheet |
| EP15846060.0A EP3202585B1 (en) | 2014-09-30 | 2015-09-17 | Transfer sheet |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2014202100 | 2014-09-30 | ||
| JP2014-202100 | 2014-09-30 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2016052243A1 true WO2016052243A1 (ja) | 2016-04-07 |
Family
ID=55630283
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2015/076572 WO2016052243A1 (ja) | 2014-09-30 | 2015-09-17 | 転写シート |
Country Status (5)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US10000081B2 (ja) |
| EP (1) | EP3202585B1 (ja) |
| JP (3) | JP6481572B2 (ja) |
| MY (1) | MY187869A (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2016052243A1 (ja) |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2020067272A1 (ja) * | 2018-09-28 | 2020-04-02 | 大日本印刷株式会社 | 熱転写シート、及び印画物 |
| CN111791614A (zh) * | 2020-07-17 | 2020-10-20 | 焦作卓立膜材料有限责任公司 | 一种珠光转色热转印碳带及其制备方法 |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP6680448B1 (ja) * | 2018-12-11 | 2020-04-15 | 関西ペイント株式会社 | 複層塗膜形成方法 |
Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH07276831A (ja) * | 1994-02-21 | 1995-10-24 | Dainippon Printing Co Ltd | 保護層転写フィルム及び印画物 |
| WO1996031355A1 (fr) * | 1995-04-06 | 1996-10-10 | Dai Nippon Printing Co., Ltd. | Feuille de transfert a couche autocollante et son utilisation |
| JP2002230738A (ja) * | 2001-02-01 | 2002-08-16 | Dainippon Ink & Chem Inc | 転写型磁気記録シート |
| JP2009286040A (ja) * | 2008-05-30 | 2009-12-10 | Toppan Printing Co Ltd | 熱転写シートおよび印画物 |
| JP2011073383A (ja) * | 2009-09-30 | 2011-04-14 | Dainippon Printing Co Ltd | 熱転写シート及び印画物 |
| JP2013059884A (ja) * | 2011-09-12 | 2013-04-04 | Dainippon Printing Co Ltd | 熱転写記録媒体 |
| WO2014041779A1 (ja) * | 2012-09-11 | 2014-03-20 | 凸版印刷株式会社 | 感熱転写記録媒体 |
Family Cites Families (14)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS5655283A (en) * | 1979-10-11 | 1981-05-15 | Toyo Ink Mfg Co Ltd | Thermal transfer sheet |
| JPH0367694A (ja) * | 1989-05-10 | 1991-03-22 | Ricoh Co Ltd | 熱転写記録媒体 |
| JP3009062B2 (ja) * | 1991-01-17 | 2000-02-14 | 大日本印刷株式会社 | 受容層転写シート |
| JP3123001B2 (ja) * | 1991-08-22 | 2001-01-09 | 大日本印刷株式会社 | 複合熱転写シートの製造方法及び画像形成方法 |
| JPH05278351A (ja) * | 1992-04-06 | 1993-10-26 | Dainippon Printing Co Ltd | 受容層転写シート、熱転写受像シート及びその製造方法 |
| JP3210065B2 (ja) * | 1992-03-13 | 2001-09-17 | 大日本印刷株式会社 | 受容層転写シート、熱転写受像シート及びその製造方法。 |
| JPH05229273A (ja) * | 1992-02-20 | 1993-09-07 | Dainippon Printing Co Ltd | 受容層転写シート、熱転写受像シート及びその製造方法 |
| JP3256278B2 (ja) * | 1992-06-02 | 2002-02-12 | 大日本印刷株式会社 | 熱転写受像シート及びその製造方法 |
| JPH06312565A (ja) * | 1993-04-30 | 1994-11-08 | Fujicopian Co Ltd | 耐熱性熱転写記録媒体 |
| JP2804709B2 (ja) * | 1993-12-16 | 1998-09-30 | フジコピアン株式会社 | 熱転写記録媒体 |
| EP0677397B1 (en) | 1994-02-21 | 1997-11-12 | Dai Nippon Printing Co., Ltd. | Protective layer transfer film and image-printed matter |
| JPH1142864A (ja) * | 1997-07-25 | 1999-02-16 | Dainippon Printing Co Ltd | 受容層転写シート用熱転写シート |
| JP2002187370A (ja) * | 2000-12-19 | 2002-07-02 | Dainippon Printing Co Ltd | 中間転写記録媒体 |
| DE602005013992D1 (de) * | 2004-09-30 | 2009-05-28 | Dainippon Printing Co Ltd | Wärmeübertragungsschutzsschichtfilm |
-
2015
- 2015-09-15 JP JP2015181667A patent/JP6481572B2/ja active Active
- 2015-09-17 US US15/504,077 patent/US10000081B2/en active Active
- 2015-09-17 EP EP15846060.0A patent/EP3202585B1/en active Active
- 2015-09-17 MY MYPI2017700642A patent/MY187869A/en unknown
- 2015-09-17 WO PCT/JP2015/076572 patent/WO2016052243A1/ja active Application Filing
-
2019
- 2019-02-14 JP JP2019024589A patent/JP2019142219A/ja active Pending
-
2020
- 2020-07-16 JP JP2020122358A patent/JP2020175671A/ja active Pending
Patent Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH07276831A (ja) * | 1994-02-21 | 1995-10-24 | Dainippon Printing Co Ltd | 保護層転写フィルム及び印画物 |
| WO1996031355A1 (fr) * | 1995-04-06 | 1996-10-10 | Dai Nippon Printing Co., Ltd. | Feuille de transfert a couche autocollante et son utilisation |
| JP2002230738A (ja) * | 2001-02-01 | 2002-08-16 | Dainippon Ink & Chem Inc | 転写型磁気記録シート |
| JP2009286040A (ja) * | 2008-05-30 | 2009-12-10 | Toppan Printing Co Ltd | 熱転写シートおよび印画物 |
| JP2011073383A (ja) * | 2009-09-30 | 2011-04-14 | Dainippon Printing Co Ltd | 熱転写シート及び印画物 |
| JP2013059884A (ja) * | 2011-09-12 | 2013-04-04 | Dainippon Printing Co Ltd | 熱転写記録媒体 |
| WO2014041779A1 (ja) * | 2012-09-11 | 2014-03-20 | 凸版印刷株式会社 | 感熱転写記録媒体 |
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2020067272A1 (ja) * | 2018-09-28 | 2020-04-02 | 大日本印刷株式会社 | 熱転写シート、及び印画物 |
| JP6680429B1 (ja) * | 2018-09-28 | 2020-04-15 | 大日本印刷株式会社 | 熱転写シート、及び印画物 |
| CN111791614A (zh) * | 2020-07-17 | 2020-10-20 | 焦作卓立膜材料有限责任公司 | 一种珠光转色热转印碳带及其制备方法 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2020175671A (ja) | 2020-10-29 |
| EP3202585A4 (en) | 2018-07-04 |
| US10000081B2 (en) | 2018-06-19 |
| EP3202585B1 (en) | 2019-05-15 |
| JP6481572B2 (ja) | 2019-03-13 |
| JP2019142219A (ja) | 2019-08-29 |
| US20170282621A1 (en) | 2017-10-05 |
| JP2016068562A (ja) | 2016-05-09 |
| EP3202585A1 (en) | 2017-08-09 |
| MY187869A (en) | 2021-10-26 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| TWI691562B (zh) | 轉印薄片 | |
| JP5534151B2 (ja) | 熱転写シート及び印画物 | |
| JP2006306017A (ja) | 熱転写シート | |
| JP2020175671A (ja) | 転写シート | |
| JP6690159B2 (ja) | 転写シート | |
| WO2016043236A1 (ja) | 転写シート | |
| JP2016068373A (ja) | 熱転写箔及び印画物形成方法 | |
| JP6677919B2 (ja) | 転写シート | |
| JP5789956B2 (ja) | 熱転写シート | |
| JP6709521B2 (ja) | 転写シート | |
| JP6795110B2 (ja) | 転写シート | |
| JP2017217844A (ja) | 昇華転写用受像シート | |
| JP5674242B2 (ja) | 感熱転写記録媒体 | |
| JP6677918B2 (ja) | 転写シート | |
| JP6645082B2 (ja) | 転写シート | |
| JP5994872B2 (ja) | 熱転写シート | |
| JP5751436B2 (ja) | 感熱転写記録媒体 | |
| JP2014237289A (ja) | 感熱転写記録媒体 | |
| JP5924032B2 (ja) | 感熱転写記録媒体 | |
| JP6273938B2 (ja) | 感熱転写記録媒体 | |
| JP2017077630A (ja) | 熱転写受像シート | |
| JP2017177381A (ja) | 中間転写媒体上に透明な凸形状を形成する方法およびそれを用いた印画物の形成方法 | |
| JP2016068374A (ja) | 熱転写箔及び画像形成方法 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 15846060 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 15504077 Country of ref document: US |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| REEP | Request for entry into the european phase |
Ref document number: 2015846060 Country of ref document: EP |