JP6089535B2 - R−t−b系焼結磁石 - Google Patents
R−t−b系焼結磁石 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP6089535B2 JP6089535B2 JP2012212333A JP2012212333A JP6089535B2 JP 6089535 B2 JP6089535 B2 JP 6089535B2 JP 2012212333 A JP2012212333 A JP 2012212333A JP 2012212333 A JP2012212333 A JP 2012212333A JP 6089535 B2 JP6089535 B2 JP 6089535B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- main phase
- mass
- sintered magnet
- alloy
- hcj
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 239000002245 particle Substances 0.000 claims description 77
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 claims description 52
- 229910052761 rare earth metal Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 39
- 229910052802 copper Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 18
- 229910052742 iron Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 18
- 229910052779 Neodymium Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 11
- 229910052796 boron Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 10
- 229910052727 yttrium Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 10
- VWQVUPCCIRVNHF-UHFFFAOYSA-N yttrium atom Chemical compound [Y] VWQVUPCCIRVNHF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 8
- 229910052799 carbon Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 7
- 229910052723 transition metal Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 7
- OKTJSMMVPCPJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N Carbon Chemical compound [C] OKTJSMMVPCPJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 6
- 229910052777 Praseodymium Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 5
- 150000003624 transition metals Chemical class 0.000 claims description 5
- 229910052689 Holmium Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 4
- 229910052771 Terbium Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 4
- 229910052684 Cerium Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 3
- 229910052691 Erbium Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 3
- 229910052688 Gadolinium Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 3
- 229910052775 Thulium Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 3
- 229910052769 Ytterbium Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 3
- 229910052746 lanthanum Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000012071 phase Substances 0.000 description 105
- 239000000956 alloy Substances 0.000 description 91
- 229910045601 alloy Inorganic materials 0.000 description 91
- 239000000843 powder Substances 0.000 description 52
- 239000002994 raw material Substances 0.000 description 52
- 230000000052 comparative effect Effects 0.000 description 50
- 150000001875 compounds Chemical class 0.000 description 41
- 238000010298 pulverizing process Methods 0.000 description 36
- 239000000523 sample Substances 0.000 description 33
- XKRFYHLGVUSROY-UHFFFAOYSA-N Argon Chemical compound [Ar] XKRFYHLGVUSROY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 32
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 30
- XEEYBQQBJWHFJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N iron Substances [Fe] XEEYBQQBJWHFJM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 26
- 238000005245 sintering Methods 0.000 description 21
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 description 20
- 239000000654 additive Substances 0.000 description 18
- 230000000996 additive effect Effects 0.000 description 17
- 238000011156 evaluation Methods 0.000 description 17
- 239000007789 gas Substances 0.000 description 17
- IJGRMHOSHXDMSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N Atomic nitrogen Chemical compound N#N IJGRMHOSHXDMSA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 16
- 229910052786 argon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 16
- 229910052782 aluminium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 15
- 238000006467 substitution reaction Methods 0.000 description 12
- 229910052692 Dysprosium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 11
- 238000004458 analytical method Methods 0.000 description 11
- 230000006872 improvement Effects 0.000 description 11
- 230000032683 aging Effects 0.000 description 10
- 239000011247 coating layer Substances 0.000 description 9
- 238000001816 cooling Methods 0.000 description 8
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 8
- 238000000576 coating method Methods 0.000 description 7
- 239000013078 crystal Substances 0.000 description 7
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 description 7
- 230000008018 melting Effects 0.000 description 7
- 238000002844 melting Methods 0.000 description 7
- 238000002156 mixing Methods 0.000 description 7
- 229910052757 nitrogen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 7
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 description 6
- 230000007423 decrease Effects 0.000 description 6
- 239000011261 inert gas Substances 0.000 description 6
- 239000011248 coating agent Substances 0.000 description 5
- 238000009826 distribution Methods 0.000 description 5
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 5
- 239000000047 product Substances 0.000 description 5
- ZOXJGFHDIHLPTG-UHFFFAOYSA-N Boron Chemical compound [B] ZOXJGFHDIHLPTG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 4
- 229910001873 dinitrogen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 4
- 239000010931 gold Substances 0.000 description 4
- 239000007791 liquid phase Substances 0.000 description 4
- 239000011812 mixed powder Substances 0.000 description 4
- PXHVJJICTQNCMI-UHFFFAOYSA-N nickel Substances [Ni] PXHVJJICTQNCMI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 239000010955 niobium Substances 0.000 description 4
- FATBGEAMYMYZAF-KTKRTIGZSA-N oleamide Chemical compound CCCCCCCC\C=C/CCCCCCCC(N)=O FATBGEAMYMYZAF-KTKRTIGZSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 150000002910 rare earth metals Chemical class 0.000 description 4
- QCWXUUIWCKQGHC-UHFFFAOYSA-N Zirconium Chemical compound [Zr] QCWXUUIWCKQGHC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 239000000470 constituent Substances 0.000 description 3
- 229910052739 hydrogen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 239000012535 impurity Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000011572 manganese Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 3
- 238000000465 moulding Methods 0.000 description 3
- 229910052710 silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 229910052726 zirconium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 229910052582 BN Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- PZNSFCLAULLKQX-UHFFFAOYSA-N Boron nitride Chemical compound N#B PZNSFCLAULLKQX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- GYHNNYVSQQEPJS-UHFFFAOYSA-N Gallium Chemical compound [Ga] GYHNNYVSQQEPJS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- UFHFLCQGNIYNRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N Hydrogen Chemical compound [H][H] UFHFLCQGNIYNRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- ATJFFYVFTNAWJD-UHFFFAOYSA-N Tin Chemical compound [Sn] ATJFFYVFTNAWJD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 230000002159 abnormal effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N atomic oxygen Chemical compound [O] QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 2
- 229910052797 bismuth Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- JCXGWMGPZLAOME-UHFFFAOYSA-N bismuth atom Chemical compound [Bi] JCXGWMGPZLAOME-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000011575 calcium Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000005266 casting Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000011258 core-shell material Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000004907 flux Effects 0.000 description 2
- 229910052733 gallium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- PCHJSUWPFVWCPO-UHFFFAOYSA-N gold Chemical compound [Au] PCHJSUWPFVWCPO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229910052737 gold Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 229910052735 hafnium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- VBJZVLUMGGDVMO-UHFFFAOYSA-N hafnium atom Chemical compound [Hf] VBJZVLUMGGDVMO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000001307 helium Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910052734 helium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- SWQJXJOGLNCZEY-UHFFFAOYSA-N helium atom Chemical compound [He] SWQJXJOGLNCZEY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000001257 hydrogen Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000010410 layer Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000005415 magnetization Effects 0.000 description 2
- 229910052748 manganese Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 229910052759 nickel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 229910052758 niobium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- GUCVJGMIXFAOAE-UHFFFAOYSA-N niobium atom Chemical compound [Nb] GUCVJGMIXFAOAE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000001301 oxygen Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910052760 oxygen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 238000004445 quantitative analysis Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000000700 radioactive tracer Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000010703 silicon Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910052709 silver Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000004332 silver Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000002791 soaking Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000003860 storage Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229910052715 tantalum Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- GUVRBAGPIYLISA-UHFFFAOYSA-N tantalum atom Chemical compound [Ta] GUVRBAGPIYLISA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- WFKWXMTUELFFGS-UHFFFAOYSA-N tungsten Chemical compound [W] WFKWXMTUELFFGS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229910052721 tungsten Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000010937 tungsten Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910000521 B alloy Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910052580 B4C Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- OYPRJOBELJOOCE-UHFFFAOYSA-N Calcium Chemical compound [Ca] OYPRJOBELJOOCE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- PWHULOQIROXLJO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Manganese Chemical compound [Mn] PWHULOQIROXLJO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- KJTLSVCANCCWHF-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ruthenium Chemical compound [Ru] KJTLSVCANCCWHF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052772 Samarium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910052581 Si3N4 Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- NRTOMJZYCJJWKI-UHFFFAOYSA-N Titanium nitride Chemical compound [Ti]#N NRTOMJZYCJJWKI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- LRTTZMZPZHBOPO-UHFFFAOYSA-N [B].[B].[Hf] Chemical compound [B].[B].[Hf] LRTTZMZPZHBOPO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052788 barium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- DSAJWYNOEDNPEQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N barium atom Chemical compound [Ba] DSAJWYNOEDNPEQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000008901 benefit Effects 0.000 description 1
- INAHAJYZKVIDIZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N boron carbide Chemical compound B12B3B4C32B41 INAHAJYZKVIDIZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052791 calcium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 238000009750 centrifugal casting Methods 0.000 description 1
- ZMIGMASIKSOYAM-UHFFFAOYSA-N cerium Chemical compound [Ce][Ce][Ce][Ce][Ce][Ce][Ce][Ce][Ce][Ce][Ce][Ce][Ce][Ce][Ce][Ce][Ce][Ce][Ce][Ce][Ce][Ce][Ce][Ce][Ce][Ce][Ce][Ce][Ce][Ce][Ce][Ce][Ce][Ce][Ce][Ce][Ce][Ce] ZMIGMASIKSOYAM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910017052 cobalt Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000010941 cobalt Substances 0.000 description 1
- GUTLYIVDDKVIGB-UHFFFAOYSA-N cobalt atom Chemical compound [Co] GUTLYIVDDKVIGB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- PMHQVHHXPFUNSP-UHFFFAOYSA-M copper(1+);methylsulfanylmethane;bromide Chemical compound Br[Cu].CSC PMHQVHHXPFUNSP-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- 238000006356 dehydrogenation reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000000280 densification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000006866 deterioration Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000002542 deteriorative effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000009792 diffusion process Methods 0.000 description 1
- KBQHZAAAGSGFKK-UHFFFAOYSA-N dysprosium atom Chemical compound [Dy] KBQHZAAAGSGFKK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- UYAHIZSMUZPPFV-UHFFFAOYSA-N erbium Chemical compound [Er] UYAHIZSMUZPPFV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000005496 eutectics Effects 0.000 description 1
- UIWYJDYFSGRHKR-UHFFFAOYSA-N gadolinium atom Chemical compound [Gd] UIWYJDYFSGRHKR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000005324 grain boundary diffusion Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000000227 grinding Methods 0.000 description 1
- 150000004820 halides Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- KJZYNXUDTRRSPN-UHFFFAOYSA-N holmium atom Chemical compound [Ho] KJZYNXUDTRRSPN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 150000004678 hydrides Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- FZLIPJUXYLNCLC-UHFFFAOYSA-N lanthanum atom Chemical compound [La] FZLIPJUXYLNCLC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000005381 magnetic domain Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000012423 maintenance Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000001247 metal acetylides Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 230000006911 nucleation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010899 nucleation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000003647 oxidation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000007254 oxidation reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000002093 peripheral effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000005240 physical vapour deposition Methods 0.000 description 1
- PUDIUYLPXJFUGB-UHFFFAOYSA-N praseodymium atom Chemical compound [Pr] PUDIUYLPXJFUGB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000002244 precipitate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000011802 pulverized particle Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000010791 quenching Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000171 quenching effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000009467 reduction Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000001226 reprecipitation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000630 rising effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229910052707 ruthenium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- KZUNJOHGWZRPMI-UHFFFAOYSA-N samarium atom Chemical compound [Sm] KZUNJOHGWZRPMI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- HBMJWWWQQXIZIP-UHFFFAOYSA-N silicon carbide Chemical compound [Si+]#[C-] HBMJWWWQQXIZIP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910010271 silicon carbide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- HQVNEWCFYHHQES-UHFFFAOYSA-N silicon nitride Chemical compound N12[Si]34N5[Si]62N3[Si]51N64 HQVNEWCFYHHQES-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000004544 sputter deposition Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000003756 stirring Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910052712 strontium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- CIOAGBVUUVVLOB-UHFFFAOYSA-N strontium atom Chemical compound [Sr] CIOAGBVUUVVLOB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- GZCRRIHWUXGPOV-UHFFFAOYSA-N terbium atom Chemical compound [Tb] GZCRRIHWUXGPOV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- UONOETXJSWQNOL-UHFFFAOYSA-N tungsten carbide Chemical compound [W+]#[C-] UONOETXJSWQNOL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- -1 two or more of them Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 238000007740 vapor deposition Methods 0.000 description 1
- NAWDYIZEMPQZHO-UHFFFAOYSA-N ytterbium Chemical compound [Yb] NAWDYIZEMPQZHO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- XOOUIPVCVHRTMJ-UHFFFAOYSA-L zinc stearate Chemical compound [Zn+2].CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC([O-])=O.CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC([O-])=O XOOUIPVCVHRTMJ-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01F—MAGNETS; INDUCTANCES; TRANSFORMERS; SELECTION OF MATERIALS FOR THEIR MAGNETIC PROPERTIES
- H01F1/00—Magnets or magnetic bodies characterised by the magnetic materials therefor; Selection of materials for their magnetic properties
- H01F1/01—Magnets or magnetic bodies characterised by the magnetic materials therefor; Selection of materials for their magnetic properties of inorganic materials
- H01F1/03—Magnets or magnetic bodies characterised by the magnetic materials therefor; Selection of materials for their magnetic properties of inorganic materials characterised by their coercivity
- H01F1/032—Magnets or magnetic bodies characterised by the magnetic materials therefor; Selection of materials for their magnetic properties of inorganic materials characterised by their coercivity of hard-magnetic materials
- H01F1/04—Magnets or magnetic bodies characterised by the magnetic materials therefor; Selection of materials for their magnetic properties of inorganic materials characterised by their coercivity of hard-magnetic materials metals or alloys
- H01F1/047—Alloys characterised by their composition
- H01F1/053—Alloys characterised by their composition containing rare earth metals
- H01F1/0536—Alloys characterised by their composition containing rare earth metals sintered
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C22—METALLURGY; FERROUS OR NON-FERROUS ALLOYS; TREATMENT OF ALLOYS OR NON-FERROUS METALS
- C22C—ALLOYS
- C22C19/00—Alloys based on nickel or cobalt
- C22C19/07—Alloys based on nickel or cobalt based on cobalt
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C22—METALLURGY; FERROUS OR NON-FERROUS ALLOYS; TREATMENT OF ALLOYS OR NON-FERROUS METALS
- C22C—ALLOYS
- C22C38/00—Ferrous alloys, e.g. steel alloys
- C22C38/001—Ferrous alloys, e.g. steel alloys containing N
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C22—METALLURGY; FERROUS OR NON-FERROUS ALLOYS; TREATMENT OF ALLOYS OR NON-FERROUS METALS
- C22C—ALLOYS
- C22C38/00—Ferrous alloys, e.g. steel alloys
- C22C38/005—Ferrous alloys, e.g. steel alloys containing rare earths, i.e. Sc, Y, Lanthanides
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C22—METALLURGY; FERROUS OR NON-FERROUS ALLOYS; TREATMENT OF ALLOYS OR NON-FERROUS METALS
- C22C—ALLOYS
- C22C38/00—Ferrous alloys, e.g. steel alloys
- C22C38/06—Ferrous alloys, e.g. steel alloys containing aluminium
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C22—METALLURGY; FERROUS OR NON-FERROUS ALLOYS; TREATMENT OF ALLOYS OR NON-FERROUS METALS
- C22C—ALLOYS
- C22C38/00—Ferrous alloys, e.g. steel alloys
- C22C38/10—Ferrous alloys, e.g. steel alloys containing cobalt
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C22—METALLURGY; FERROUS OR NON-FERROUS ALLOYS; TREATMENT OF ALLOYS OR NON-FERROUS METALS
- C22C—ALLOYS
- C22C38/00—Ferrous alloys, e.g. steel alloys
- C22C38/16—Ferrous alloys, e.g. steel alloys containing copper
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01F—MAGNETS; INDUCTANCES; TRANSFORMERS; SELECTION OF MATERIALS FOR THEIR MAGNETIC PROPERTIES
- H01F1/00—Magnets or magnetic bodies characterised by the magnetic materials therefor; Selection of materials for their magnetic properties
- H01F1/01—Magnets or magnetic bodies characterised by the magnetic materials therefor; Selection of materials for their magnetic properties of inorganic materials
- H01F1/03—Magnets or magnetic bodies characterised by the magnetic materials therefor; Selection of materials for their magnetic properties of inorganic materials characterised by their coercivity
- H01F1/032—Magnets or magnetic bodies characterised by the magnetic materials therefor; Selection of materials for their magnetic properties of inorganic materials characterised by their coercivity of hard-magnetic materials
- H01F1/04—Magnets or magnetic bodies characterised by the magnetic materials therefor; Selection of materials for their magnetic properties of inorganic materials characterised by their coercivity of hard-magnetic materials metals or alloys
- H01F1/047—Alloys characterised by their composition
- H01F1/053—Alloys characterised by their composition containing rare earth metals
- H01F1/055—Alloys characterised by their composition containing rare earth metals and magnetic transition metals, e.g. SmCo5
- H01F1/057—Alloys characterised by their composition containing rare earth metals and magnetic transition metals, e.g. SmCo5 and IIIa elements, e.g. Nd2Fe14B
- H01F1/0571—Alloys characterised by their composition containing rare earth metals and magnetic transition metals, e.g. SmCo5 and IIIa elements, e.g. Nd2Fe14B in the form of particles, e.g. rapid quenched powders or ribbon flakes
- H01F1/0575—Alloys characterised by their composition containing rare earth metals and magnetic transition metals, e.g. SmCo5 and IIIa elements, e.g. Nd2Fe14B in the form of particles, e.g. rapid quenched powders or ribbon flakes pressed, sintered or bonded together
- H01F1/0577—Alloys characterised by their composition containing rare earth metals and magnetic transition metals, e.g. SmCo5 and IIIa elements, e.g. Nd2Fe14B in the form of particles, e.g. rapid quenched powders or ribbon flakes pressed, sintered or bonded together sintered
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C22—METALLURGY; FERROUS OR NON-FERROUS ALLOYS; TREATMENT OF ALLOYS OR NON-FERROUS METALS
- C22C—ALLOYS
- C22C2202/00—Physical properties
- C22C2202/02—Magnetic
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C22—METALLURGY; FERROUS OR NON-FERROUS ALLOYS; TREATMENT OF ALLOYS OR NON-FERROUS METALS
- C22C—ALLOYS
- C22C33/00—Making ferrous alloys
- C22C33/02—Making ferrous alloys by powder metallurgy
Landscapes
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Materials Engineering (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Metallurgy (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Power Engineering (AREA)
- Crystallography & Structural Chemistry (AREA)
- Inorganic Chemistry (AREA)
- Hard Magnetic Materials (AREA)
- Powder Metallurgy (AREA)
Description
好ましくは、前記主相粒子の2粒子粒界の粒界相において、R(RはY(イットリウム)および希土類元素の1種又は2種以上)が10〜30at%であり、T(Fe又はFe及びCoを必須とする1種又は2種以上の遷移金属)が65〜85at%であって、Cuが0.70〜4.0at%、Alが0.07〜2.0at%、である。
また、より好ましくは、前記LRはNdまたは/およびPrであり、HRはDyまたは/およびTbである。
また、より好ましくは、前記主相粒子全体に占めるコア部の体積比率が90.0%以上である。
また、より好ましくは前記R−T−B系焼結磁石の組成は、LRが29.4〜31.5mass%、HRが0.15〜0.65mass%、Alが0.03〜0.40mass%、Coが0.03〜1.10mass%、Cuが0.03〜0.18mass%、Bが0.75〜1.25mass%、残部がFeである。
本発明のR−T−B系焼結磁石は、主相LR(2−x)HRxT14B(LR:Ndを必須とし、Y、La、Ce、Pr、Smの1種または2種以上を含む軽希土類元素、HR:Dyまたは/およびTbを必須とし、Gd、Ho、Er、Tm、Yb,Luの1種または2種以上を含む重希土類元素、T:Feまたは/およびCoを必須とし、Mn、Niの1種または2種を含む、B:(ホウ素、一部C(炭素)で置換されているものを含む))を主相とする主相粒子と、R(RはY(イットリウム)および希土類元素の1種又は2種以上)、およびT(TはFe又はFe及びCoを必須とする1種又は2種以上)を主組成とする粒界相とから構成される。さらに、主相粒子は、主相LR(2−x)HRxT14Bがx=0.00〜0.07の範囲であるコア部と、主相LR(2−x)HRxT14Bがx=0.02〜0.40の範囲であるシェル部から形成された構造をもつ。
図1はコア部2とシェル部3をもつ本発明の主相粒子1の模式図を示している。このコア部2はシェル部3に比べHR濃度が低い。シェル部の最大厚み4は、観察した主相粒子1のシェル部において最大の厚みをとる。
本発明のR−T−B系焼結磁石において、主相粒子のコア部の主相LR(2−x)HRxT14Bのxは、好ましくは、0.00〜0.02であり、主相粒子のシェル部の主相LR(2−x)HRxT14Bのxは、好ましくは0.20〜0.40の範囲である。本発明のR−T−B系焼結磁石において、主相粒子のコア部のHR量を少なくすることでBrを高く維持でき、シェル部のHR量を多くすることでHcJを大きく向上することができるが、主相粒子のコア部の主相LR(2−x)HRxT14Bのxが0.00〜0.02であると、解析の誤差を含めて、コア部にHRが含まれておらず、Brを十分に高くすることができ、主相粒子のシェル部の主相LR(2−x)HRxT14Bのxが0.20〜0.40であると、シェル部にHRを多く含ませた状態にでき、HcJの向上が大きくできる。
前記2粒子粒界の粒界相は、粒界相のうち、隣り合う2つの主相粒子の間に存在し、RならびにTを主組成とする相、および組成によっては針状や板状の析出物を有する、幅数nm程度の領域で、粒界3重点とは区別される。
本発明のR−T−B系焼結磁石は、好適には原料合金が1種類の1合金法、および原料合金が2種類の2合金法において、前記原料合金とは別に準備された、HRを含有し、表面を高融点成分によりコーティングされた化合物粉を、原料合金の微粉砕粉にごく少量添加して成形体を作製し、前記成形体の焼結工程において、原料合金の微粉砕粉のみでの焼結に対し、高温でごく短時間の焼結過程を、冷却を挟まずに行うことで得られる。
添加する添加化合物粉は、HRを25.0mass%以上で含有することが必須とする。HRの含有量が25.0mass%よりも少な過ぎると、十分なHcJ向上の効果が得られなかったり、R−T−B系焼結磁石の焼結において緻密化を阻害する成分や、磁気特性、特にHcJを低下させる成分の影響が顕著になる。HRを含有する化合物として、HR単体、ハロゲン化物、水素化物、合金などが利用できる。
コーティング層に使用する高融点成分としては、焼結において容易に溶解しない程度の融点が必要となる。また、焼結中に発生するRリッチな液相成分との濡れ性が低い層であれば、添加化合物の反応開始を焼結温度により制御し易くなるので好ましい。コーティング層の例としては、炭化ホウ素、窒化ホウ素、炭化ケイ素、窒化ケイ素、窒化アルミニウム、窒化チタン、ホウ化ジルコニウム、ホウ化ハフニウム、炭化タングステンなどがある。コーティングの方法としてはPVD、CVD、蒸着法、HR化合物表面に化学反応を利用して形成するなど、使用するコーティング層の成分に適したコーティング方法を選択すればよい。
また、コーティング層の厚みに特に制限はないが、焼結において容易に反応して溶解したり、あるいは反応し切らないまま残ることがない程度の厚みがよい。コーティング層の成分に含まれる元素について、炭素、窒素などはR−T−B系焼結磁石の組織においては不純物として磁気特性の低下につながりやすく、ホウ素も過剰に存在すると粒界にFe2Bなど軟磁性相あるいは非磁性相を形成して磁気特性の低下につながる。そのため、過剰に厚いコーティング層を形成することは避けることが好ましい。使用する成分により変わるが、コーティング層の厚みとしては100nm〜1μm未満の層が形成できれば十分である。
この高温過程により、前記適正な焼結温度では反応が抑制されていた高融点成分にコーティングされた添加化合物粉と、Rリッチな液相成分との反応を促進させ、主相粒子の粒界近傍で主相のLRをHRで置換させる。この高温過程の温度は、多数の成形体を焼結する場合の均熱と添加化合物粉からのHR放出のバランスを考慮し、前記適正な焼結温度に対し40℃〜80℃高い温度範囲とすることが好ましい。
昇温速度は8〜20℃/分が好ましく、これより遅い場合は添加化合物粉のHRの主相内への拡散が進行し過ぎてBr低下が顕著になる恐れがある。また、昇温速度がこれより速い場合は、均熱がとりにくくなって、磁石表面での異常粒成長が急速に促進され、1つの焼結体内および焼結炉内の位置が異なる焼結体でHcJのばらつきが無視できなくなり、磁気特性および生産安定性を悪化させる恐れがある。また、維持時間は60分以下が好ましく、これより長時間となると異常粒成長が促進してHcJ低下が顕著となる。焼結過程でサブナノサイズのきわめて微細な主相粒子が溶解−再析出によって大きな主相粒子に取り込まれて無くなるが、ジェットミルで粉砕した微粉砕粉の粒度分布では少ない存在量なので、過剰な粒成長が起きない適切な焼結条件で作製した焼結体では主相粒子の平均粒径は使用した微粉砕粉の平均粒径とほぼ同じ大きさと考えてよい。
表1のAとDの組成の原料合金を、ストリップキャストにて作製した。
作製した原料合金Aと原料合金Dを混合比0.95/0.05で混合し、室温にて90分間の水素吸蔵をさせた後、アルゴンガス雰囲気中で650℃×60分の脱水素処理を施して粗粉砕を行った。
原料合金の粗粉砕粉に粉砕助剤としてオレイン酸アミドを0.10mass%添加した。その後、高圧窒素ガスを用いたジェットミルによる微粉砕を行い、平均粒径4.0μmの微粉砕粉を得た。
前記コーティングした化合物粉を、前記原料合金の微粉砕粉へ0.25mass%で添加し、小型のナウタミキサーにて混合を行った。
次に、化合物粉と混合した微粉砕粉を、窒素ガス雰囲気中にて、15kOe(1200kA/m)の磁場中で1.5tonf/cm2(150MPa)の圧力で成形して成形体を得た。
続いて、得られた焼結体を、大気圧アルゴンガス雰囲気中にて780℃/90分の熱処理(1段目時効処理)を行い、冷却後、大気圧アルゴンガス雰囲気中にて540℃/90分の熱処理(2段目時効処理)を行い、評価試料を作製した。
表1のAとDの組成の原料合金を、実施例1と同様に微粉砕まで行い、表1のGの組成のDyを含む合金の化合物を、実施例1と同様に準備し、原料合金の微粉砕粉へ0.80mass%で添加し、実施例1と同様に評価試料を作製した。
表1のBとDの組成の原料合金を用いることを除き、実施例1と同様に評価試料を作製した。
表1のBとDの組成の原料合金を、実施例1と同様に微粉砕まで行い、表1のGの組成を含む合金の化合物を、実施例1と同様に準備し、原料合金の微粉砕粉へ0.40mass%で添加し、実施例1と同様に評価試料を作製した。
表1のAとDの組成の原料合金を、実施例1と同様に粗粉砕まで行い、粉砕助剤としてオレイン酸アミドを0.10mass%添加して、高圧アルゴンガスを用いたジェットミルによる微粉砕を行い、平均粒径2.0μmの微粉砕粉を得た。
続いて、得られた焼結体を、大気圧アルゴンガス雰囲気中にて780℃/90分の熱処理(1段目時効処理)を行い、冷却後、大気圧アルゴンガス雰囲気中にて540℃/90分の熱処理(2段目時効処理)を行い、評価試料を作製した。
表1のAとDの組成の原料合金を、実施例1と同様に粗粉砕まで行い、砕助剤としてオレイン酸アミドを0.10mass%添加して、高圧アルゴンガスを用いたジェットミルによる微粉砕を行い、平均粒径3.0μmの微粉砕粉を得た。その後、表1のGの組成のDyを含む合金の化合物を、実施例1と同様に準備し、原料合金の微粉砕粉へ0.25mass%で添加し、小型のナウタミキサーにて混合を行った。その後、窒素ガス雰囲気中にて、15kOe(1200kA/m)の磁場中で1.5tonf/cm2(150MPa)の圧力で成形して成形体を得た。
続いて、得られた焼結体を、大気圧アルゴンガス雰囲気中にて780℃/90分の熱処理(1段目時効処理)を行い、冷却後、大気圧アルゴンガス雰囲気中にて540℃/90分の熱処理(2段目時効処理)を行い、評価試料を作製した。
表1のJとDの組成の原料合金を用いることを除き、実施例1と同様に評価試料を作製した。
表1のHとDの組成の原料合金を用いることを除き、実施例1と同様に評価試料を作製した。
表1のIとDの組成の原料合金を用いることを除き、実施例1と同様に評価試料を作製した。
表1のAとDの組成の原料合金を、実施例1と同様に微粉砕まで行い、表1のLの組成を含む合金の化合物を、実施例1と同様に準備し、原料合金の微粉砕粉へ0.25mass%で添加し、実施例1と同様に評価試料を作製した。
表1のAとDの組成の原料合金を、実施例1と同様に微粉砕まで行い、表1のMの組成を含む合金の化合物を、実施例1と同様に準備し、原料合金の微粉砕粉へ0.25mass%で添加し、実施例1と同様に評価試料を作製した。
表1のAとDの組成の原料合金を、実施例1と同様に微粉砕まで行い、表1のNの組成を含む合金の化合物を、実施例1と同様に準備し、原料合金の微粉砕粉へ0.30mass%で添加し、実施例1と同様に評価試料を作製した。
表1のAとFの組成の原料合金を、実施例1と同様に微粉砕まで行い、表1のGの組成を含む合金の化合物を、実施例1と同様に準備し、原料合金の微粉砕粉へ0.25mass%で添加し、実施例1と同様に評価試料を作製した。
<比較例1>
表1のBとDの組成の原料合金を、実施例1と同様に微粉砕まで行い、表1のGの組成のDyを含む合金の化合物を添加せずに、実施例1と同様に評価試料を作製した。
表1のAとDの組成の原料合金を、実施例1と同様に微粉砕まで行い、表1のGの組成のDyを含む合金の化合物を実施例1と同様に粉砕した後、c−BNのコーティングは形成せずに、前記原料合金の微粉砕粉へ0.25mass%で添加し、小型のナウタミキサーにて混合を行った。得られた混合粉は、実施例1と同様に評価試料を作製した。
表1のBとEの組成の原料合金を、実施例1と同様に微粉砕まで行い、表1のGの組成のDyを含む合金の化合物を添加せずに、実施例1と同様に評価試料を作製した。
表1のCとEの組成の原料合金を、実施例1と同様に微粉砕まで行い、表1のGの組成のDyを含む合金の化合物を添加せずに、実施例1と同様に評価試料を作製した。
表1のAとDの組成の原料合金を、実施例5と同様に微粉砕まで行い、表1のGの組成のDyを含む合金の化合物を実施例5と同様に粉砕した後、c−BNのコーティングは形成せずに、前記原料合金の微粉砕粉へ0.25mass%で添加し、小型のナウタミキサーにて混合を行った。得られた混合粉は、実施例5と同様に評価試料を作製した。
表1のAとDの組成の原料合金を、実施例6と同様に微粉砕まで行い、表1のGの組成のDyを含む合金の化合物を実施例6と同様に粉砕した後、c−BNのコーティングは形成せずに、前記原料合金の微粉砕粉へ0.25mass%で添加し、小型のナウタミキサーにて混合を行った。得られた混合粉は、実施例6と同様に評価試料を作製した。
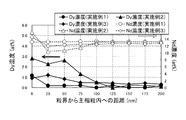
また、実施例1〜3および比較例1〜4のHcJをDy含有量に対する変化として図2に、実施例1〜3および比較例1〜4のBrをDy含有量に対する変化として図3に示した。
実施例3のDy置換範囲は、およそ75nmであるが、Dy濃度は実施例2より小さい。これは、主相粒子内にあらかじめDyが存在することで、主相のDy置換が抑制されていることを示すと思われる。
また、Ndの濃度分布が、シェル部に比べほぼ一定となっている範囲をコア部ととり、そのコア部の中でxの最小値〜最大値を見積もると、実施例2では0.00〜0.03、実施例3では0.05〜0.07であった。
シェル部のxの最小値〜最大値は、比較例1が0.01〜0.02、比較例2が0.03〜0.05、比較例3が0.01〜0.02、比較例4が0.06〜0.11となった。またコア部のxの最小値〜最大値は、比較例1が0.01〜0.02、比較例2が0.01〜0.03、比較例3が0.00〜0.02、比較例4が0.04〜0.0.07となった。
Dy置換によりHcJが向上されるのは、Dyの高い異方性磁界によって逆磁区の核形成が抑制されるためであるとされるが、実施例1における7nmのDy置換範囲でも、その効果が大きく作用して高いHcJが得られている。
一方、比較例5および比較例6は、実施例5および実施例6で添加したDyを含有する合金の微粉砕粉にc−BNコーティングを施していないため、焼結過程において主相粒子中にDyが多量に取り込まれて厚いシェル部が形成されており、原料合金のみより作製した場合よりBrが大きく低下しているが、HcJが実施例5および実施例6ほど大きくは向上していない。
しかしながら、実施例5において、磁気特性としては大きな問題ではないが、原料合金のみの場合に対しBrの低下がやや大きくなっており、Brも十分に高く維持しながらHcJを向上させる上では主相粒子のコア部体積割合を90%以上とすることが好ましい。
しかしながら、製品として適するHcJを得る上では原料合金のみによるもともとのHcJもある程度必要であるといえ、実施例7のようにB含有量を少なくし過ぎることはFeを含む軟磁性相を形成してHcJが低くなることにつながるため、B含有量は0.75mass%以上とすることが好ましい。
また、実施例7について2粒子粒界のアトムプローブ解析を行ったところ、NdとDyを合わせたR量が7.39at%、FeとCoを合わせたT量が91.01at%、Cuが0.80at%、Alが0.02at%で、R量が少なくなり、T量が多く存在している。このことから、実施例7ではB含有量を過剰に少なくしているため主相を組まないFeやCoの余剰ができて粒界相においてRと軟磁性相を形成してしまい、もともとのHcJが小さい結果となっていると考えられる。ただ、実施例7においても本発明によるHcJ向上の効果は現れている。
したがって、製品として適するHcJを得る上で、焼結体の2粒子粒界においてR(RはY(イットリウム)および希土類元素の1種又は2種以上)が10〜30at%であり、T(Fe又はFe及びCoを必須とする1種又は2種以上の遷移金属)が65〜85at%であって、Cuが0.70〜4.0at%、Alが0.07〜2.0at%、であることが好ましい。
いずれにせよ、多量のCo、Cu、AlによるHcJの向上を完全に残しながらDyによるHcJのさらなる向上を実現するのは難しい。しかし、DyによるHcJの向上は原料合金からDyを単純に含有させるよりもずっと大きな効果が得られており、十分に実用可能な手法である。このことから、Co、Cu、Alの含有量の上限については、Coが1.10mass%、Cuが0.18mass%、Alが0.40mass%である。
2 コア部
3 シェル部
4 シェル部の最大厚み
Claims (4)
- R−T−B系焼結磁石であって、主相粒子と粒界相を有し、前記主相粒子は、コア部とシェル部を含み、前記コア部の主相LR(2−x)HRxT14B(LR:Ndを必須とし、Y、La、Ce、Pr、Smの1種または2種以上を含んでもよい軽希土類元素、HR:Dyまたは/およびTbを必須とし、Gd、Ho、Er、Tm、Yb,Luの1種または2種以上を含んでもよい重希土類元素、T:Feまたは/およびCoを必須とし、Mn、Niの1種または2種を含んでもよい、B:ホウ素、一部C(炭素)で置換されているものを含む)においてx=0.00〜0.07であり、前記シェル部の主相LR(2−x)HRxT14Bにおいてx=0.02〜0.40であり、前記コア部は前記シェル部に比べHR濃度が低く、前記シェル部の最大厚みが、7nm〜100nmであり、かつ、前記主相粒子の2粒子粒界の粒界相において、R(RはY(イットリウム)および希土類元素の1種又は2種以上)が10〜30at%であり、T(Fe又はFe及びCoを必須とする1種又は2種以上の遷移金属)が65〜85at%であって、Cuが0.70〜4.0at%、Alが0.07〜2.0at%、であることを特徴とするR−T−B系焼結磁石。
- 請求項1記載のR−T−B系焼結磁石であって、前記LRはNdまたは/およびPrであり、HRはDyまたは/およびTbであることを特徴とするR−T−B系焼結磁石。
- 請求項1乃至請求項2記載のR−T−B系焼結磁石であって、前記主相粒子全体に占めるコア部の体積比率が、90.0%以上であることを特徴とするR−T−B系焼結磁石。
- 請求項1乃至請求項3のR−T−B系焼結磁石であって、組成がLRが29.4〜31.5mass%、HRが0.15〜0.65mass%、Alが0.03〜0.40mass%、Coが0.03〜1.10mass%、Cuが0.03〜0.18mass%、Bが0.75〜1.25mass%、残部がFeであることを特徴とするR−T−B系焼結磁石。
Priority Applications (5)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012212333A JP6089535B2 (ja) | 2011-10-28 | 2012-09-26 | R−t−b系焼結磁石 |
| DE112012004502.5T DE112012004502T5 (de) | 2011-10-28 | 2012-10-04 | R-T-B basierter gesinterter Magnet |
| PCT/JP2012/075740 WO2013061744A1 (ja) | 2011-10-28 | 2012-10-04 | R-t-b系焼結磁石 |
| US14/354,865 US9548148B2 (en) | 2011-10-28 | 2012-10-04 | R-T-B based sintered magnet |
| CN201280053073.6A CN103890868B (zh) | 2011-10-28 | 2012-10-04 | R‑t‑b系烧结磁铁 |
Applications Claiming Priority (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2011236617 | 2011-10-28 | ||
| JP2011236617 | 2011-10-28 | ||
| JP2012212333A JP6089535B2 (ja) | 2011-10-28 | 2012-09-26 | R−t−b系焼結磁石 |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2013110387A JP2013110387A (ja) | 2013-06-06 |
| JP6089535B2 true JP6089535B2 (ja) | 2017-03-08 |
Family
ID=48167579
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012212333A Active JP6089535B2 (ja) | 2011-10-28 | 2012-09-26 | R−t−b系焼結磁石 |
Country Status (5)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US9548148B2 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JP6089535B2 (ja) |
| CN (1) | CN103890868B (ja) |
| DE (1) | DE112012004502T5 (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2013061744A1 (ja) |
Families Citing this family (34)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP5790617B2 (ja) | 2012-10-18 | 2015-10-07 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | 希土類磁石の製造方法 |
| JP5464289B1 (ja) * | 2013-04-22 | 2014-04-09 | Tdk株式会社 | R−t−b系焼結磁石 |
| JP6183457B2 (ja) | 2013-06-05 | 2017-08-23 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | 希土類磁石とその製造方法 |
| WO2014205002A2 (en) * | 2013-06-17 | 2014-12-24 | Miha Zakotnik | Magnet recycling to create nd-fe-b magnets with improved or restored magnetic performance |
| KR102215818B1 (ko) * | 2013-09-24 | 2021-02-17 | 엘지전자 주식회사 | 비자성 합금을 포함하는 열간가압변형 자석 및 이의 제조방법 |
| CN104674115A (zh) | 2013-11-27 | 2015-06-03 | 厦门钨业股份有限公司 | 一种低b的稀土磁铁 |
| JP6142793B2 (ja) * | 2013-12-20 | 2017-06-07 | Tdk株式会社 | 希土類磁石 |
| JP6142794B2 (ja) * | 2013-12-20 | 2017-06-07 | Tdk株式会社 | 希土類磁石 |
| JP6142792B2 (ja) * | 2013-12-20 | 2017-06-07 | Tdk株式会社 | 希土類磁石 |
| CN105900216B (zh) * | 2014-02-07 | 2019-05-10 | 株式会社神户制钢所 | 平板显示器用配线膜 |
| JP6003920B2 (ja) | 2014-02-12 | 2016-10-05 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | 希土類磁石の製造方法 |
| CN104952574A (zh) | 2014-03-31 | 2015-09-30 | 厦门钨业股份有限公司 | 一种含W的Nd-Fe-B-Cu系烧结磁铁 |
| JP6269279B2 (ja) * | 2014-04-15 | 2018-01-31 | Tdk株式会社 | 永久磁石およびモータ |
| CN105321699B (zh) * | 2014-07-07 | 2017-11-24 | 厦门钨业股份有限公司 | 一种钕铁硼系烧结磁体的制造方法及其磁体 |
| JP6511779B2 (ja) * | 2014-11-12 | 2019-05-15 | Tdk株式会社 | R−t−b系焼結磁石 |
| CN107077935A (zh) | 2014-12-08 | 2017-08-18 | Lg电子株式会社 | 包含非磁性合金的热压变形的磁体及其制造方法 |
| JP6504044B2 (ja) * | 2015-02-16 | 2019-04-24 | Tdk株式会社 | 希土類系永久磁石 |
| JP6424664B2 (ja) * | 2015-02-16 | 2018-11-21 | Tdk株式会社 | 希土類系永久磁石 |
| JP6468435B2 (ja) * | 2015-04-15 | 2019-02-13 | Tdk株式会社 | R−t−b系焼結磁石 |
| JP2017098537A (ja) * | 2015-11-13 | 2017-06-01 | Tdk株式会社 | R−t−b系焼結磁石 |
| JP6645219B2 (ja) * | 2016-02-01 | 2020-02-14 | Tdk株式会社 | R−t−b系焼結磁石用合金、及びr−t−b系焼結磁石 |
| JP6848736B2 (ja) | 2016-07-15 | 2021-03-24 | Tdk株式会社 | R−t−b系希土類永久磁石 |
| JP6848735B2 (ja) | 2016-07-15 | 2021-03-24 | Tdk株式会社 | R−t−b系希土類永久磁石 |
| US10748685B2 (en) * | 2017-03-30 | 2020-08-18 | Tdk Corporation | R-T-B based sintered magnet |
| CN108735413A (zh) * | 2018-05-18 | 2018-11-02 | 宁波科田磁业有限公司 | 一种含Tb高性能高矫顽力磁体及其制备方法 |
| CN110619984B (zh) | 2018-06-19 | 2021-12-07 | 厦门钨业股份有限公司 | 一种低B含量的R-Fe-B系烧结磁铁及其制备方法 |
| CN110047636B (zh) * | 2019-04-17 | 2021-09-10 | 南京理工大学 | 一种高矫顽力富La/Ce烧结磁体的制备方法 |
| CN111243807B (zh) * | 2020-02-26 | 2021-08-27 | 厦门钨业股份有限公司 | 一种钕铁硼磁体材料、原料组合物及制备方法和应用 |
| CN111223625B (zh) * | 2020-02-26 | 2022-08-16 | 福建省长汀金龙稀土有限公司 | 钕铁硼磁体材料、原料组合物及制备方法和应用 |
| CN111223628B (zh) * | 2020-02-26 | 2022-02-01 | 厦门钨业股份有限公司 | 钕铁硼磁体材料、原料组合物、制备方法、应用 |
| CN111223627B (zh) * | 2020-02-26 | 2021-12-17 | 厦门钨业股份有限公司 | 钕铁硼磁体材料、原料组合物、制备方法、应用 |
| JP7303157B2 (ja) * | 2020-06-01 | 2023-07-04 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | 希土類磁石及びその製造方法 |
| CN113838620B (zh) * | 2020-06-23 | 2023-03-14 | 比亚迪股份有限公司 | 一种稀土永磁材料及其制备方法 |
| CN114203380A (zh) * | 2021-12-17 | 2022-03-18 | 沈阳中北通磁科技股份有限公司 | 一种高性能稀土永磁体 |
Family Cites Families (14)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2510806B2 (ja) | 1992-03-10 | 1996-06-26 | ミサワホーム株式会社 | サイザ―装置におけるワ―クストッパの位置決め構造 |
| JPH07122413A (ja) | 1993-10-28 | 1995-05-12 | Hitachi Metals Ltd | 希土類永久磁石およびその製造方法 |
| US7618497B2 (en) | 2003-06-30 | 2009-11-17 | Tdk Corporation | R-T-B based rare earth permanent magnet and method for production thereof |
| EP1860668B1 (en) | 2005-03-14 | 2015-01-14 | TDK Corporation | R-t-b based sintered magnet |
| JP4900085B2 (ja) * | 2007-06-29 | 2012-03-21 | Tdk株式会社 | 希土類磁石の製造方法 |
| CN101652822B (zh) * | 2007-07-27 | 2012-06-13 | 日立金属株式会社 | R-Fe-B系稀土类烧结磁铁 |
| CN102282279B (zh) * | 2009-01-16 | 2013-10-02 | 日立金属株式会社 | R-t-b系烧结磁铁的制造方法 |
| JP5510457B2 (ja) | 2009-07-15 | 2014-06-04 | 日立金属株式会社 | R−t−b系焼結磁石の製造方法 |
| US9154004B2 (en) * | 2010-03-04 | 2015-10-06 | Tdk Corporation | Rare earth sintered magnet and motor |
| JP5429002B2 (ja) * | 2010-03-30 | 2014-02-26 | Tdk株式会社 | 焼結磁石、モーター及び自動車 |
| JP2011211056A (ja) * | 2010-03-30 | 2011-10-20 | Tdk Corp | 希土類焼結磁石、モーター及び自動車 |
| JP2011211071A (ja) * | 2010-03-30 | 2011-10-20 | Tdk Corp | 焼結磁石、モーター、自動車、及び焼結磁石の製造方法 |
| WO2011122667A1 (ja) * | 2010-03-30 | 2011-10-06 | Tdk株式会社 | 希土類焼結磁石、その製造方法、モーター、及び自動車 |
| WO2011122638A1 (ja) * | 2010-03-30 | 2011-10-06 | Tdk株式会社 | 焼結磁石、モーター、自動車、及び焼結磁石の製造方法 |
-
2012
- 2012-09-26 JP JP2012212333A patent/JP6089535B2/ja active Active
- 2012-10-04 CN CN201280053073.6A patent/CN103890868B/zh active Active
- 2012-10-04 DE DE112012004502.5T patent/DE112012004502T5/de active Pending
- 2012-10-04 US US14/354,865 patent/US9548148B2/en active Active
- 2012-10-04 WO PCT/JP2012/075740 patent/WO2013061744A1/ja not_active Ceased
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| US9548148B2 (en) | 2017-01-17 |
| DE112012004502T5 (de) | 2014-12-18 |
| US20140283649A1 (en) | 2014-09-25 |
| CN103890868A (zh) | 2014-06-25 |
| WO2013061744A1 (ja) | 2013-05-02 |
| CN103890868B (zh) | 2017-05-03 |
| JP2013110387A (ja) | 2013-06-06 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP6089535B2 (ja) | R−t−b系焼結磁石 | |
| CN107871582B (zh) | R-Fe-B烧结磁体 | |
| CN106024253B (zh) | R-Fe-B烧结磁体及制备方法 | |
| CN107871581B (zh) | 制备R-Fe-B烧结磁体的方法 | |
| TWI413136B (zh) | 稀土族永久磁體 | |
| US10573438B2 (en) | R-(Fe, Co)-B sintered magnet and making method | |
| JP5477282B2 (ja) | R−t−b系焼結磁石およびその製造方法 | |
| US10410775B2 (en) | R—Fe—B sintered magnet and making method | |
| JP5856953B2 (ja) | 希土類永久磁石の製造方法および希土類永久磁石 | |
| JP7418598B2 (ja) | 重希土類合金、ネオジム鉄ホウ素永久磁石材料、原料及び製造方法 | |
| JP3891307B2 (ja) | Nd−Fe−B系希土類永久焼結磁石材料 | |
| CN107527699A (zh) | R‑Fe‑B烧结磁体及制备方法 | |
| CN114255949B (zh) | 磁性材料及其制造方法 | |
| JP2014216338A (ja) | R−t−b系焼結磁石 | |
| WO2005015580A1 (ja) | R-t-b系焼結磁石および希土類合金 | |
| JP4900085B2 (ja) | 希土類磁石の製造方法 | |
| JP4895027B2 (ja) | R−t−b系焼結磁石及びr−t−b系焼結磁石の製造方法 | |
| JP4543940B2 (ja) | R−t−b系焼結磁石の製造方法 | |
| JP4821128B2 (ja) | R−Fe−B系希土類永久磁石 | |
| JP2018174311A (ja) | R−t−b系焼結磁石の製造方法 | |
| JP4076080B2 (ja) | 希土類永久磁石の製造方法 | |
| JP4955217B2 (ja) | R−t−b系焼結磁石用原料合金及びr−t−b系焼結磁石の製造方法 | |
| JP4702522B2 (ja) | R−t−b系焼結磁石及びその製造方法 | |
| JP4556727B2 (ja) | 希土類焼結磁石の製造方法 | |
| JP2005286174A (ja) | R−t−b系焼結磁石 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20150508 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20160405 |
|
| A601 | Written request for extension of time |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A601 Effective date: 20160530 |
|
| RD02 | Notification of acceptance of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7422 Effective date: 20160701 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20160725 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20170110 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20170123 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 6089535 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |