JP5259059B2 - 半導体装置 - Google Patents
半導体装置 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP5259059B2 JP5259059B2 JP2006183993A JP2006183993A JP5259059B2 JP 5259059 B2 JP5259059 B2 JP 5259059B2 JP 2006183993 A JP2006183993 A JP 2006183993A JP 2006183993 A JP2006183993 A JP 2006183993A JP 5259059 B2 JP5259059 B2 JP 5259059B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- wiring board
- wiring
- chip
- semiconductor device
- memory chip
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G11—INFORMATION STORAGE
- G11C—STATIC STORES
- G11C29/00—Checking stores for correct operation ; Subsequent repair; Testing stores during standby or offline operation
- G11C29/04—Detection or location of defective memory elements, e.g. cell constructio details, timing of test signals
- G11C29/08—Functional testing, e.g. testing during refresh, power-on self testing [POST] or distributed testing
- G11C29/48—Arrangements in static stores specially adapted for testing by means external to the store, e.g. using direct memory access [DMA] or using auxiliary access paths
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G11—INFORMATION STORAGE
- G11C—STATIC STORES
- G11C29/00—Checking stores for correct operation ; Subsequent repair; Testing stores during standby or offline operation
- G11C29/04—Detection or location of defective memory elements, e.g. cell constructio details, timing of test signals
- G11C29/08—Functional testing, e.g. testing during refresh, power-on self testing [POST] or distributed testing
- G11C29/12—Built-in arrangements for testing, e.g. built-in self testing [BIST] or interconnection details
- G11C29/1201—Built-in arrangements for testing, e.g. built-in self testing [BIST] or interconnection details comprising I/O circuitry
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G11—INFORMATION STORAGE
- G11C—STATIC STORES
- G11C5/00—Details of stores covered by group G11C11/00
- G11C5/02—Disposition of storage elements, e.g. in the form of a matrix array
-
- H10W70/09—
-
- H10W70/60—
-
- H10W90/00—
-
- H10W70/63—
-
- H10W70/655—
-
- H10W72/552—
-
- H10W72/884—
-
- H10W72/922—
-
- H10W72/9223—
-
- H10W72/923—
-
- H10W72/9415—
-
- H10W72/942—
-
- H10W72/952—
-
- H10W74/15—
-
- H10W90/271—
-
- H10W90/724—
-
- H10W90/732—
-
- H10W90/734—
-
- H10W90/754—
Landscapes
- Semiconductor Integrated Circuits (AREA)
- Structures For Mounting Electric Components On Printed Circuit Boards (AREA)
Description
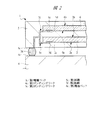
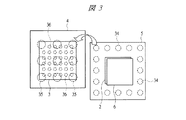
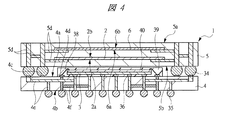
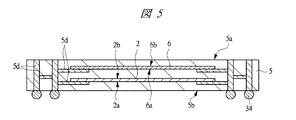
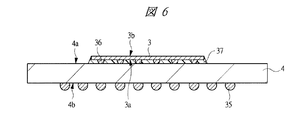
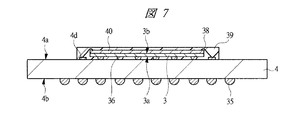
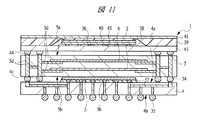
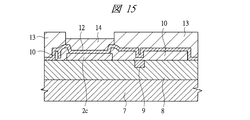
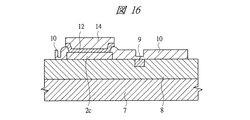
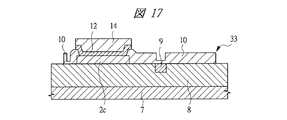
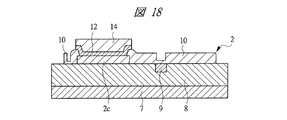
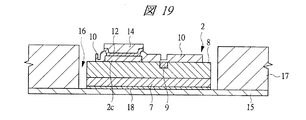
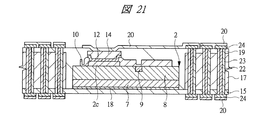
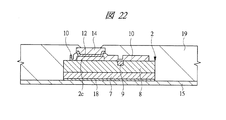
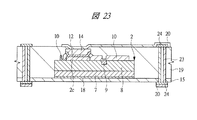
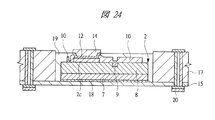
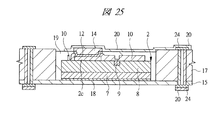
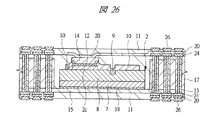
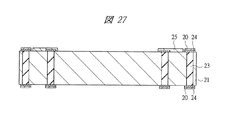
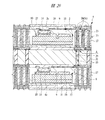
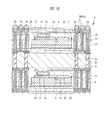
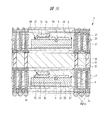
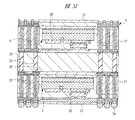
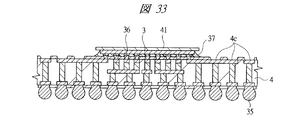
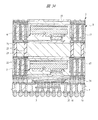
図1は本発明の実施の形態1の半導体装置の構造の一例を模式的に示す断面図、図2は図1に示す半導体装置の等長配線構造を模式的に示す部分構造図、図3は図1に示す半導体装置を基板ごとに展開して構造を示す平面図、図4は本発明の実施の形態1の変形例の半導体装置の構造を模式的に示す断面図である。また、図5は図1に示す半導体装置の上段側パッケージの構造を示す断面図、図6は図1に示す半導体装置の下段側パッケージの構造を示す断面図、図7は図4に示す半導体装置の下段側パッケージの構造を示す断面図、図8は本発明の実施の形態1の変形例の半導体装置の構造を模式的に示す断面図、図9は本発明の実施の形態1の変形例の半導体装置の構造を模式的に示す断面図である。さらに、図10は図8に示す半導体装置を基板ごとに展開して構造を示す平面図、図11は本発明の実施の形態1の変形例の半導体装置の構造を模式的に示す断面図、図12は本発明の実施の形態1の変形例の半導体装置の構造を模式的に示す断面図である。
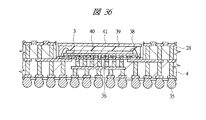
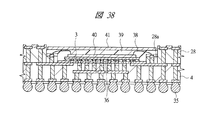
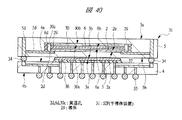
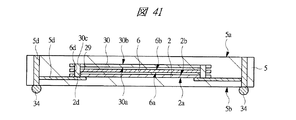
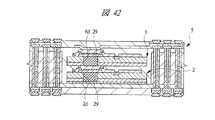
図40は本発明の実施の形態2の半導体装置の構造の一例を模式的に示す断面図、図41は図40に示す半導体装置の上段側パッケージの構造を示す断面図、図42は図41に示す上段側パッケージの基板の内部構造の一例を示す部分断面図である。
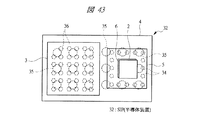
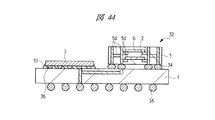
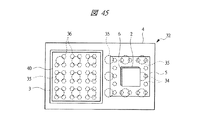
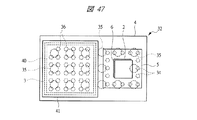
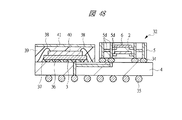
図43は本発明の実施の形態3の半導体装置の構造の一例を模式的に透過して示す平面図、図44は図43に示す半導体装置の断面図、図45乃至図48はそれぞれ本発明の実施の形態3の変形例の半導体装置の構造を模式的に透過して示す平面図と断面図である。
2 第1メモリチップ
2a 主面
2b 裏面
2c 第1電極パッド
2d 貫通孔
3 マイコンチップ
3a 主面
3b 裏面
4 第1配線基板
4a 主面
4b 裏面
4c 第1ボンディングリード
4d 端子
4e 第1内部配線
4f 第2内部配線
5 第2配線基板
5a 主面
5b 裏面
5c 第2ボンディングリード
5d 内部配線
5e 第1距離
5f 第2距離
5g 端子
5h 他の内部配線
6 第2メモリチップ
6a 主面
6b 裏面
6c 第2電極パッド
6d 貫通孔
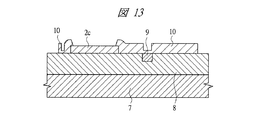
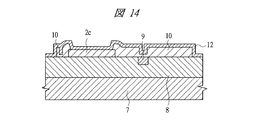
7 Siベース
8 デバイス層
9 ヒューズ
10 パッシベーション膜
11 絶縁層
12 シード層
13 レジスト膜
14 Cu電極
15 第1ベース基板
16 キャビティ
17 樹脂層
18 ダイボンド材
19 絶縁材
20 導体パターン
21 第2ベース基板
22 充填材
23 スルーホール配線
24 ビアパッド
25 中継パターン
26 パッド
27 レジスト膜
28 スペーサ基板
28a 段差部
29 導体
30 第3メモリチップ
30a 主面
30b 裏面
30c 貫通孔
31,32 SIP(半導体装置)
33 薄膜化デバイス
34 第1はんだバンプ(第1バンプ電極)
35 第2はんだバンプ(第2バンプ電極)
36 金バンプ
37 アンダーフィル
38 ワイヤ
39 封止体
40 メモリチップ
41 放熱板
42 接着剤
43 第3配線基板
44 第3はんだバンプ
45 マイコンチップ
46 はんだペースト
Claims (6)
- 第1主面、前記第1主面に形成された第1ボンディングリード、及び前記第1主面とは反対側の第1裏面を有する第1配線基板と、
演算処理機能を有し、前記第1配線基板の前記第1主面に搭載されたマイコンチップと、
第2主面、前記第2主面に形成された端子、前記第2主面とは反対側の第2裏面、及び前記第2裏面に形成された第2ボンディングリードを有し、前記マイコンチップが搭載された前記第1配線基板上に配置された第2配線基板と、
前記第1配線基板の前記第1ボンディングリードと前記第2配線基板の前記第2ボンディングリードとを電気的に接続する第1バンプ電極と、
前記第1配線基板の前記第1裏面に配置された第2バンプ電極と、
前記第2配線基板の前記第2主面と前記第2配線基板の前記第2裏面との間に配置された第1メモリチップと、
前記第2配線基板の前記第2主面と前記第2配線基板の前記第2裏面との間において、前記第1メモリチップ上に配置された第2メモリチップと、を含み、
前記マイコンチップは、前記第1配線基板の内部に形成された第1内部配線を介して前記第1ボンディングリードと電気的に接続され、
前記マイコンチップは、前記第1配線基板の内部に形成された第2内部配線を介して前記第2バンプ電極と電気的に接続され、
前記第1メモリチップは、前記第2配線基板の内部に形成された第3内部配線を介して前記第2ボンディングリードと電気的に接続され、
前記第2メモリチップは、前記第2配線基板の内部に形成された第4内部配線を介して前記第2ボンディングリードと電気的に接続されており、
前記マイコンチップは、前記第1及び第2メモリチップと外部機器とのインタフェースであり、
前記第1及び第2メモリチップのそれぞれは、外部クロック信号の立ち上がりと立ち下がりの両方に同期してデータを転送するダブル・データ・レート・シンクロナスDRAMであることを特徴とする半導体装置。 - 請求項1記載の半導体装置において、前記マイコンチップと前記第1及び第2メモリチップのそれぞれは、前記第1ボンディングリード、前記第1バンプ電極、及び前記第2ボンディングリードを介して電気的に接続されていることを特徴とする半導体装置。
- 請求項2記載の半導体装置において、前記第1メモリチップの第1電極パッドから前記第2ボンディングリードまでの第1距離と、前記第2メモリチップの第2電極パッドから前記第2ボンディングリードまでの第2距離は等しいことを特徴とする半導体装置。
- 請求項3記載の半導体装置において、前記第1距離と前記第2距離の差の許容範囲は、±1mm以内であることを特徴とする半導体装置。
- 請求項1記載の半導体装置において、前記端子は、前記第2配線基板の内部に形成された第5内部配線を介して、前記第1配線基板と前記第2配線基板との間に設けられた第3バンプ電極と電気的に接続されていることを特徴とする半導体装置。
- 請求項5記載の半導体装置において、前記端子は、前記第5内部配線、前記第3バンプ電極、及び前記第1配線基板の内部に形成された第6内部配線を介して、前記第1配線基板の前記第1裏面に形成された第4バンプ電極と電気的に接続されていることを特徴とする半導体装置。
Priority Applications (5)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2006183993A JP5259059B2 (ja) | 2006-07-04 | 2006-07-04 | 半導体装置 |
| US11/798,737 US7847413B2 (en) | 2006-07-04 | 2007-05-16 | Semiconductor device and method of manufacturing the same |
| TW096118100A TW200816435A (en) | 2006-07-04 | 2007-05-22 | Semiconductor device and method of manufacturing the same |
| CNA2007101101300A CN101101909A (zh) | 2006-07-04 | 2007-06-18 | 半导体器件及其制造方法 |
| KR1020070065074A KR20080004356A (ko) | 2006-07-04 | 2007-06-29 | 반도체 장치 및 그 제조 방법 |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2006183993A JP5259059B2 (ja) | 2006-07-04 | 2006-07-04 | 半導体装置 |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2008016519A JP2008016519A (ja) | 2008-01-24 |
| JP2008016519A5 JP2008016519A5 (ja) | 2009-08-20 |
| JP5259059B2 true JP5259059B2 (ja) | 2013-08-07 |
Family
ID=38918408
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2006183993A Expired - Fee Related JP5259059B2 (ja) | 2006-07-04 | 2006-07-04 | 半導体装置 |
Country Status (5)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US7847413B2 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JP5259059B2 (ja) |
| KR (1) | KR20080004356A (ja) |
| CN (1) | CN101101909A (ja) |
| TW (1) | TW200816435A (ja) |
Families Citing this family (33)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP4185499B2 (ja) * | 2005-02-18 | 2008-11-26 | 富士通マイクロエレクトロニクス株式会社 | 半導体装置 |
| SG166773A1 (en) * | 2007-04-24 | 2010-12-29 | United Test & Assembly Ct Lt | Bump on via-packaging and methodologies |
| US7759212B2 (en) * | 2007-12-26 | 2010-07-20 | Stats Chippac, Ltd. | System-in-package having integrated passive devices and method therefor |
| US8258015B2 (en) * | 2008-02-22 | 2012-09-04 | Stats Chippac Ltd. | Integrated circuit package system with penetrable film adhesive |
| US8304869B2 (en) * | 2008-08-01 | 2012-11-06 | Stats Chippac Ltd. | Fan-in interposer on lead frame for an integrated circuit package on package system |
| JP5140565B2 (ja) * | 2008-11-28 | 2013-02-06 | 三洋電機株式会社 | 素子搭載用基板、半導体モジュール、および携帯機器 |
| US8097956B2 (en) * | 2009-03-12 | 2012-01-17 | Apple Inc. | Flexible packaging for chip-on-chip and package-on-package technologies |
| JP2010238995A (ja) * | 2009-03-31 | 2010-10-21 | Sanyo Electric Co Ltd | 半導体モジュールおよびこれを搭載したカメラモジュール |
| JP5521424B2 (ja) * | 2009-07-28 | 2014-06-11 | セイコーエプソン株式会社 | 集積回路装置、電子機器及び電子機器の製造方法 |
| US8064202B2 (en) * | 2010-02-24 | 2011-11-22 | Monolithic Power Systems, Inc. | Sandwich structure with double-sided cooling and EMI shielding |
| KR101686199B1 (ko) | 2010-03-26 | 2016-12-14 | 삼성전자주식회사 | 반도체 패키지 구조물 |
| KR101817159B1 (ko) | 2011-02-17 | 2018-02-22 | 삼성전자 주식회사 | Tsv를 가지는 인터포저를 포함하는 반도체 패키지 및 그 제조 방법 |
| CN102157394A (zh) * | 2011-03-22 | 2011-08-17 | 南通富士通微电子股份有限公司 | 高密度系统级封装方法 |
| US8674516B2 (en) * | 2011-06-22 | 2014-03-18 | Stats Chippac Ltd. | Integrated circuit packaging system with vertical interconnects and method of manufacture thereof |
| KR20130007049A (ko) * | 2011-06-28 | 2013-01-18 | 삼성전자주식회사 | 쓰루 실리콘 비아를 이용한 패키지 온 패키지 |
| US8816404B2 (en) * | 2011-09-16 | 2014-08-26 | Stats Chippac, Ltd. | Semiconductor device and method of forming stacked semiconductor die and conductive interconnect structure through an encapsulant |
| KR101797079B1 (ko) * | 2011-12-30 | 2017-11-14 | 삼성전자 주식회사 | Pop 구조의 반도체 패키지 |
| US8742597B2 (en) * | 2012-06-29 | 2014-06-03 | Intel Corporation | Package substrates with multiple dice |
| CN103579128B (zh) * | 2012-07-26 | 2016-12-21 | 碁鼎科技秦皇岛有限公司 | 芯片封装基板、芯片封装结构及其制作方法 |
| US9368477B2 (en) * | 2012-08-27 | 2016-06-14 | Invensas Corporation | Co-support circuit panel and microelectronic packages |
| US8860202B2 (en) * | 2012-08-29 | 2014-10-14 | Macronix International Co., Ltd. | Chip stack structure and manufacturing method thereof |
| JP5996500B2 (ja) * | 2013-09-11 | 2016-09-21 | 株式会社東芝 | 半導体装置および記憶装置 |
| US9281284B2 (en) * | 2014-06-20 | 2016-03-08 | Freescale Semiconductor Inc. | System-in-packages having vertically-interconnected leaded components and methods for the fabrication thereof |
| JP6543129B2 (ja) | 2015-07-29 | 2019-07-10 | ルネサスエレクトロニクス株式会社 | 電子装置 |
| KR102438753B1 (ko) * | 2015-10-01 | 2022-09-01 | 에스케이하이닉스 주식회사 | 반도체 장치 |
| JP6939568B2 (ja) * | 2016-01-15 | 2021-09-22 | ソニーグループ株式会社 | 半導体装置および撮像装置 |
| US11487445B2 (en) * | 2016-11-22 | 2022-11-01 | Intel Corporation | Programmable integrated circuit with stacked memory die for storing configuration data |
| CN108400117A (zh) * | 2017-02-06 | 2018-08-14 | 钰桥半导体股份有限公司 | 三维整合的散热增益型半导体组件及其制作方法 |
| US10475770B2 (en) * | 2017-02-28 | 2019-11-12 | Amkor Technology, Inc. | Semiconductor device having stacked dies and stacked pillars and method of manufacturing thereof |
| JP6679528B2 (ja) * | 2017-03-22 | 2020-04-15 | キオクシア株式会社 | 半導体装置 |
| TWI678747B (zh) * | 2018-10-01 | 2019-12-01 | 點序科技股份有限公司 | 測試裝置及其晶片承載板 |
| JP2020150145A (ja) * | 2019-03-14 | 2020-09-17 | キオクシア株式会社 | 半導体装置 |
| US11443776B2 (en) * | 2019-06-14 | 2022-09-13 | Qualcomm Incorporated | Memory system design for signal integrity crosstalk reduction with asymmetry |
Family Cites Families (13)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2001068617A (ja) * | 1999-08-27 | 2001-03-16 | Toshiba Corp | 半導体装置 |
| JP3853219B2 (ja) * | 2002-01-18 | 2006-12-06 | イビデン株式会社 | 半導体素子内蔵基板および多層回路基板 |
| JP4069771B2 (ja) * | 2003-03-17 | 2008-04-02 | セイコーエプソン株式会社 | 半導体装置、電子機器および半導体装置の製造方法 |
| JP2004281920A (ja) * | 2003-03-18 | 2004-10-07 | Seiko Epson Corp | 半導体装置、電子デバイス、電子機器、半導体装置の製造方法および電子デバイスの製造方法 |
| JP4419049B2 (ja) * | 2003-04-21 | 2010-02-24 | エルピーダメモリ株式会社 | メモリモジュール及びメモリシステム |
| JP4174013B2 (ja) * | 2003-07-18 | 2008-10-29 | 株式会社ルネサステクノロジ | 半導体装置 |
| JP3858854B2 (ja) | 2003-06-24 | 2006-12-20 | 富士通株式会社 | 積層型半導体装置 |
| JP2006032379A (ja) * | 2004-07-12 | 2006-02-02 | Akita Denshi Systems:Kk | 積層半導体装置及びその製造方法 |
| JP4199724B2 (ja) * | 2004-12-03 | 2008-12-17 | エルピーダメモリ株式会社 | 積層型半導体パッケージ |
| JP4408090B2 (ja) * | 2005-03-01 | 2010-02-03 | パナソニック株式会社 | 部品内蔵モジュールの製造方法 |
| TWI267967B (en) * | 2005-07-14 | 2006-12-01 | Chipmos Technologies Inc | Chip package without a core and stacked chip package structure using the same |
| US7550680B2 (en) * | 2006-06-14 | 2009-06-23 | Stats Chippac Ltd. | Package-on-package system |
| US7667338B2 (en) * | 2006-08-08 | 2010-02-23 | Lin Paul T | Package with solder-filled via holes in molding layers |
-
2006
- 2006-07-04 JP JP2006183993A patent/JP5259059B2/ja not_active Expired - Fee Related
-
2007
- 2007-05-16 US US11/798,737 patent/US7847413B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2007-05-22 TW TW096118100A patent/TW200816435A/zh unknown
- 2007-06-18 CN CNA2007101101300A patent/CN101101909A/zh active Pending
- 2007-06-29 KR KR1020070065074A patent/KR20080004356A/ko not_active Withdrawn
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| US7847413B2 (en) | 2010-12-07 |
| KR20080004356A (ko) | 2008-01-09 |
| US20080006947A1 (en) | 2008-01-10 |
| CN101101909A (zh) | 2008-01-09 |
| JP2008016519A (ja) | 2008-01-24 |
| TW200816435A (en) | 2008-04-01 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5259059B2 (ja) | 半導体装置 | |
| JP3685947B2 (ja) | 半導体装置及びその製造方法 | |
| CN102456677B (zh) | 球栅阵列封装结构及其制造方法 | |
| CN100407422C (zh) | 半导体装置及其制造方法 | |
| KR20090039411A (ko) | 솔더 볼과 칩 패드가 접합된 구조를 갖는 반도체 패키지,모듈, 시스템 및 그 제조방법 | |
| JP2007158331A (ja) | 半導体デバイスのパッケージング方法 | |
| JP2013162128A (ja) | パッケージ−オン−パッケージタイプの半導体パッケージ及びその製造方法 | |
| JP2006049569A (ja) | スタック型半導体装置パッケージおよびその製造方法 | |
| KR20090025593A (ko) | 반도체 패키지가 삽입된 인쇄회로기판 | |
| JP2008218979A (ja) | 電子パッケージ及びその製造方法 | |
| JP2008258522A (ja) | 半導体装置の製造方法 | |
| JP4033968B2 (ja) | 複数チップ混載型半導体装置 | |
| CN101425510A (zh) | 半导体元件的叠层封装结构及其方法 | |
| WO2004112129A1 (ja) | 電子装置 | |
| JP5016811B2 (ja) | 半導体装置 | |
| JPWO2003012863A1 (ja) | 半導体装置及びその製造方法 | |
| JP2009065066A (ja) | 半導体装置 | |
| CN100424863C (zh) | 芯片埋入基板的封装结构 | |
| JP2008270597A (ja) | 半導体装置 | |
| JP2008270303A (ja) | 積層型半導体装置 | |
| JP2008010705A (ja) | チップ埋め込み基板のパッケージ構造 | |
| CN113707651A (zh) | 半导体封装结构和半导体封装结构的制备方法 | |
| JP2010098225A (ja) | 半導体装置 | |
| TWI435667B (zh) | 印刷電路板組件 | |
| JP2009246313A (ja) | 半導体装置及びその製造方法 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20090701 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20090701 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20091127 |
|
| A711 | Notification of change in applicant |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A712 Effective date: 20100528 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20120306 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20120426 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20130115 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20130313 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20130402 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20130424 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20160502 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 5259059 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| S531 | Written request for registration of change of domicile |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R313531 |
|
| R350 | Written notification of registration of transfer |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R350 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |