JP3877401B2 - 半導体装置の製造方法 - Google Patents
半導体装置の製造方法 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP3877401B2 JP3877401B2 JP32796797A JP32796797A JP3877401B2 JP 3877401 B2 JP3877401 B2 JP 3877401B2 JP 32796797 A JP32796797 A JP 32796797A JP 32796797 A JP32796797 A JP 32796797A JP 3877401 B2 JP3877401 B2 JP 3877401B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- island
- semiconductor device
- semiconductor chip
- lead
- frame
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L23/00—Details of semiconductor or other solid state devices
- H01L23/28—Encapsulations, e.g. encapsulating layers, coatings, e.g. for protection
- H01L23/31—Encapsulations, e.g. encapsulating layers, coatings, e.g. for protection characterised by the arrangement or shape
- H01L23/3107—Encapsulations, e.g. encapsulating layers, coatings, e.g. for protection characterised by the arrangement or shape the device being completely enclosed
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L23/00—Details of semiconductor or other solid state devices
- H01L23/48—Arrangements for conducting electric current to or from the solid state body in operation, e.g. leads, terminal arrangements ; Selection of materials therefor
- H01L23/488—Arrangements for conducting electric current to or from the solid state body in operation, e.g. leads, terminal arrangements ; Selection of materials therefor consisting of soldered or bonded constructions
- H01L23/495—Lead-frames or other flat leads
- H01L23/49541—Geometry of the lead-frame
- H01L23/49548—Cross section geometry
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L23/00—Details of semiconductor or other solid state devices
- H01L23/48—Arrangements for conducting electric current to or from the solid state body in operation, e.g. leads, terminal arrangements ; Selection of materials therefor
- H01L23/488—Arrangements for conducting electric current to or from the solid state body in operation, e.g. leads, terminal arrangements ; Selection of materials therefor consisting of soldered or bonded constructions
- H01L23/495—Lead-frames or other flat leads
- H01L23/49541—Geometry of the lead-frame
- H01L23/49562—Geometry of the lead-frame for devices being provided for in H01L29/00
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L24/00—Arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies; Methods or apparatus related thereto
- H01L24/93—Batch processes
- H01L24/95—Batch processes at chip-level, i.e. with connecting carried out on a plurality of singulated devices, i.e. on diced chips
- H01L24/97—Batch processes at chip-level, i.e. with connecting carried out on a plurality of singulated devices, i.e. on diced chips the devices being connected to a common substrate, e.g. interposer, said common substrate being separable into individual assemblies after connecting
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/02—Bonding areas; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/04—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bonding areas prior to the connecting process
- H01L2224/05—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bonding areas prior to the connecting process of an individual bonding area
- H01L2224/0554—External layer
- H01L2224/0555—Shape
- H01L2224/05552—Shape in top view
- H01L2224/05554—Shape in top view being square
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/26—Layer connectors, e.g. plate connectors, solder or adhesive layers; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/31—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the layer connectors after the connecting process
- H01L2224/32—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the layer connectors after the connecting process of an individual layer connector
- H01L2224/321—Disposition
- H01L2224/32151—Disposition the layer connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive
- H01L2224/32221—Disposition the layer connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked
- H01L2224/32245—Disposition the layer connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked the item being metallic
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/42—Wire connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/44—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors prior to the connecting process
- H01L2224/45—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors prior to the connecting process of an individual wire connector
- H01L2224/45001—Core members of the connector
- H01L2224/4501—Shape
- H01L2224/45012—Cross-sectional shape
- H01L2224/45015—Cross-sectional shape being circular
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/42—Wire connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/44—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors prior to the connecting process
- H01L2224/45—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors prior to the connecting process of an individual wire connector
- H01L2224/45001—Core members of the connector
- H01L2224/45099—Material
- H01L2224/451—Material with a principal constituent of the material being a metal or a metalloid, e.g. boron (B), silicon (Si), germanium (Ge), arsenic (As), antimony (Sb), tellurium (Te) and polonium (Po), and alloys thereof
- H01L2224/45138—Material with a principal constituent of the material being a metal or a metalloid, e.g. boron (B), silicon (Si), germanium (Ge), arsenic (As), antimony (Sb), tellurium (Te) and polonium (Po), and alloys thereof the principal constituent melting at a temperature of greater than or equal to 950°C and less than 1550°C
- H01L2224/45144—Gold (Au) as principal constituent
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/42—Wire connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/47—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors after the connecting process
- H01L2224/48—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors after the connecting process of an individual wire connector
- H01L2224/4805—Shape
- H01L2224/4809—Loop shape
- H01L2224/48091—Arched
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/42—Wire connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/47—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors after the connecting process
- H01L2224/48—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors after the connecting process of an individual wire connector
- H01L2224/481—Disposition
- H01L2224/48151—Connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive
- H01L2224/48221—Connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked
- H01L2224/48245—Connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked the item being metallic
- H01L2224/48247—Connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked the item being metallic connecting the wire to a bond pad of the item
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/42—Wire connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/47—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors after the connecting process
- H01L2224/49—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors after the connecting process of a plurality of wire connectors
- H01L2224/491—Disposition
- H01L2224/4912—Layout
- H01L2224/49171—Fan-out arrangements
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/73—Means for bonding being of different types provided for in two or more of groups H01L2224/10, H01L2224/18, H01L2224/26, H01L2224/34, H01L2224/42, H01L2224/50, H01L2224/63, H01L2224/71
- H01L2224/732—Location after the connecting process
- H01L2224/73251—Location after the connecting process on different surfaces
- H01L2224/73265—Layer and wire connectors
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/93—Batch processes
- H01L2224/95—Batch processes at chip-level, i.e. with connecting carried out on a plurality of singulated devices, i.e. on diced chips
- H01L2224/97—Batch processes at chip-level, i.e. with connecting carried out on a plurality of singulated devices, i.e. on diced chips the devices being connected to a common substrate, e.g. interposer, said common substrate being separable into individual assemblies after connecting
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L24/00—Arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies; Methods or apparatus related thereto
- H01L24/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L24/42—Wire connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L24/44—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors prior to the connecting process
- H01L24/45—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors prior to the connecting process of an individual wire connector
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L24/00—Arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies; Methods or apparatus related thereto
- H01L24/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L24/42—Wire connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L24/47—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors after the connecting process
- H01L24/48—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors after the connecting process of an individual wire connector
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L24/00—Arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies; Methods or apparatus related thereto
- H01L24/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L24/42—Wire connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L24/47—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors after the connecting process
- H01L24/49—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors after the connecting process of a plurality of wire connectors
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/0001—Technical content checked by a classifier
- H01L2924/00014—Technical content checked by a classifier the subject-matter covered by the group, the symbol of which is combined with the symbol of this group, being disclosed without further technical details
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01005—Boron [B]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01006—Carbon [C]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01019—Potassium [K]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01021—Scandium [Sc]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01027—Cobalt [Co]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01029—Copper [Cu]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01033—Arsenic [As]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01047—Silver [Ag]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01078—Platinum [Pt]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01079—Gold [Au]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01082—Lead [Pb]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/013—Alloys
- H01L2924/0132—Binary Alloys
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/013—Alloys
- H01L2924/0132—Binary Alloys
- H01L2924/01322—Eutectic Alloys, i.e. obtained by a liquid transforming into two solid phases
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/10—Details of semiconductor or other solid state devices to be connected
- H01L2924/11—Device type
- H01L2924/12—Passive devices, e.g. 2 terminal devices
- H01L2924/1204—Optical Diode
- H01L2924/12041—LED
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/10—Details of semiconductor or other solid state devices to be connected
- H01L2924/11—Device type
- H01L2924/13—Discrete devices, e.g. 3 terminal devices
- H01L2924/1304—Transistor
- H01L2924/1305—Bipolar Junction Transistor [BJT]
- H01L2924/13055—Insulated gate bipolar transistor [IGBT]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/10—Details of semiconductor or other solid state devices to be connected
- H01L2924/11—Device type
- H01L2924/13—Discrete devices, e.g. 3 terminal devices
- H01L2924/1304—Transistor
- H01L2924/1306—Field-effect transistor [FET]
- H01L2924/13091—Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor [MOSFET]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/10—Details of semiconductor or other solid state devices to be connected
- H01L2924/11—Device type
- H01L2924/14—Integrated circuits
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/15—Details of package parts other than the semiconductor or other solid state devices to be connected
- H01L2924/181—Encapsulation
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/19—Details of hybrid assemblies other than the semiconductor or other solid state devices to be connected
- H01L2924/1901—Structure
- H01L2924/1904—Component type
- H01L2924/19041—Component type being a capacitor
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/19—Details of hybrid assemblies other than the semiconductor or other solid state devices to be connected
- H01L2924/1901—Structure
- H01L2924/1904—Component type
- H01L2924/19043—Component type being a resistor
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/30—Technical effects
- H01L2924/35—Mechanical effects
- H01L2924/351—Thermal stress
Landscapes
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Computer Hardware Design (AREA)
- Microelectronics & Electronic Packaging (AREA)
- Power Engineering (AREA)
- Condensed Matter Physics & Semiconductors (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Geometry (AREA)
- Structures Or Materials For Encapsulating Or Coating Semiconductor Devices Or Solid State Devices (AREA)
- Lead Frames For Integrated Circuits (AREA)
- Encapsulation Of And Coatings For Semiconductor Or Solid State Devices (AREA)
Description
【発明の属する技術分野】
本発明は半導体装置に関し、特に、半導体装置のチップ面積と、半導体装置をプリント基板等の実装基板上に実装する実装面積との比率で表す実装有効面積率を向上させた半導体装置に関する。
【0002】
【従来の技術】
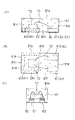
一般的にシリコン基板上にトランジスタ素子が形成された半導体装置は、図10Aに示すような構成が主に用いられる。1はシリコン基板、2はシリコン基板1が実装される放熱板等のアイランド、3はリード端子、及び4は封止用の樹脂モールドである。
トランジスタ素子が形成されたシリコン基板1は、同図に示すように、銅ベースの放熱板等のアイランド2に半田等のろう材5を介して固着実装され、シリコン基板1の周辺に配置されたリード端子3にトランジスタ素子のベース電極、エミッタ電極とがそれぞれワイヤーボンディングによってワイヤー6で電気的に接続されている。コレクタ電極に接続されるリード端子はアイランドと一体に形成されており、シリコン基板をアイランド上に実装することで電気的に接続された後、エポキシ樹脂等の熱硬化型樹脂4によりトランスファーモールドによって、シリコン基板とリード端子の一部を完全に被覆保護し、3端子構造の半導体装置が提供される。
図10Bを参照して、上記のトランスファーモールドでは、上下金型7、8で形成したキャビティ9の内部にダイボンド及びワイヤボンドを施したリードフレーム10を設置し、この状態でキャビティ9内に樹脂を注入することにより行われる。
【0003】
【発明が解決しようとする課題】
第1の課題:
樹脂モールドされた半導体装置は、通常、ガラスエポキシ基板等の実装基板に実装され、実装基板上に実装された他の半導体装置、回路素子と電気的に接続され所定の回路動作を行うための一部品として取り扱われる。
【0004】
図11は、実装基板上に半導体装置を実装したときの断面図を示し、20は半導体装置、21、23はベース又はエミッタ電極用のリード端子、22はコレクタ用のリード端子、30は実装基板である。
実装基板30上に半導体装置20が実装される実装面積は、リード端子21、22、23とそのリード端子と接続される導電パッドで囲まれた領域によって表される。実装面積は半導体装置20内のシリコン基板(半導体チップ)面積に比べ大きく、実際に機能を持つ半導体チップの面積に比べ実装面積の殆どはモールド樹脂、リード端子によって取られている。
【0005】
ここで、実際に機能を持つ半導体チップ面積と実装面積との比率を有効面積率として考慮すると、樹脂モールドされた半導体装置では有効面積率が極めて低いことが確認されている。有効面積率が低いことは、半導体装置20を実装基板30上の他の回路素子と接続使用とする場合に、実装面積の殆どが機能を有する半導体チップとは直接関係のないデッドスペースとなる。有効面積率が小さいと上記したように、実装基板30上でデットスペースが大きくなり、実装基板30の高密度小型化の妨げとなる。
【0006】
特に、この問題はパッケージサイズが小さい半導体装置に顕著に現れる。例えば、EIAJ規格であるSC−75A外形に搭載される半導体チップの最大サイズは、図12に示すように、0.40mm×0.40mmが最大である。この半導体チップを金属リード端子とワイヤーで接続し、樹脂モールドすると半導体装置の全体のサイズは、1.6mm×1.6mmとなる。この半導体装置のチップ面積は0.16mmで、半導体装置を実装する実装面積は半導体装置の面積とほぼ同様として考えて、2.56mmであるため、この半導体装置の有効面積率は約6.25%となり、実装面積の殆どが機能を持つ半導体チップ面積と直接関係のないデットスペースとなっている。
【0007】
この有効面積率に関する問題は、特に、上記したようにパッケージサイズが極めて小さく、チップサイズが大きい半導体装置において顕著に現れるが、半導体チップを金属リード端子でワイヤー接続し、樹脂モールドする、樹脂封止型の半導体装置であれば同様に問題となる。
近年の電子機器、例えば、パーソナルコンピュータ、電子手帳等の携帯情報処理装置、8mmビデオカメラ、携帯電話、カメラ、液晶テレビ等において用いられる実装基板は、電子機器本体の小型化に伴い、その内部に使用される実装基板も高密度小型化の傾向にある。
【0008】
しかし、上記の先行技術の樹脂封止型の半導体装置では、上述したように、半導体装置を実装する実装面積にデットスペースが大きいため、実装基板の小型化に限界があり、実装基板の小型化の妨げの一つの要因となっていた。
第2の課題:
ところで、有効面積率を向上させる先行技術として特開平3−248551号公報がある。この先行技術について、図13にもとづいて簡単に説明する。この先行技術は、樹脂モールド型半導体装置を実装基板等に実装したときの実装面積をできるだけ小さくするために、半導体チップ40のベース、エミッタ、及びコレクタ電極と接続するリード端子41、42、43を樹脂モールド44の側面より外側に導出させず、リード端子41、42、43を樹脂モールド44側面と同一面となるように形成することが記載されている。
【0009】
この構成によれば、リード端子41、42、43の先端部分が導出しない分だけ実装面積を小さくすることができ、有効面積率を若干向上させることはできる。
しかし、上記の半導体装置では、半導体チップと接続されるリード端子の先端部分は樹脂モールド44の底面部のコーナー部で折り曲げ加工されるために、その折り曲げ工程時の応力に十分耐えられる構造することから、樹脂モールド内に埋め込まれた各リード端子の長さを十分にしなければならず、結果的に樹脂モールドサイズが実装する半導体チップサイズに比べて大きくなり有効面積率の低下には至らない。さらに、半導体チップと接続される各リード端子を必要とし、材料コスト面及び製造工程が煩雑となり、製造コストを低減できない課題がある。
【0010】
第3の課題:
有効面積率を最大限大きくするには、上記したように、半導体チップを直接実装基板上に実装することにより、半導体チップ面積と実装面積とがほぼ同一となり有効面積率が最大となる。
半導体チップを実装基板等の基板上に実装する一つの先行技術として、例えば、特開平6−338504号公報に示すように、半導体チップ45上に複数のバンプ電極46を形成したフリップチップを実装基板47にフェイスダウンボンディングする技術が知られている(図14参照)。この先行技術は、通常、MOSFET等、シリコン基板の同一主面にゲート(ベース)電極、ソース(エミッタ)電極、ドレイン(コレクタ)電極が形成され、電流或いは電圧のパスが横方向に形成される比較的発熱量の少ない横型の半導体装置に主に用いられる。
【0011】
しかし、トランジスタデバイス等のようにシリコン基板が電極の一つとなり、各電極が異なる面に形成され電流のパスが縦方向に流れる縦型の半導体装置では、上記のフリップチップ技術を使用することは困難である。
第4の課題:
半導体チップを実装基板等の基板上に実装する他の先行技術として、例えば、特開平7−38334号公報に記載されている示すように、実装基板51上に形成された導電パターン52上に半導体チップ53をダイボンディングし、半導体チップ53周辺に配置された導電パターン52と半導体チップ53との電極をワイヤ54で接続する技術が知られている(図15参照)。この先行技術では、先に述べたシリコン基板が一つの電極を構成した縦型構造のトランジスタ等の半導体チップに用いることはできる。
【0012】
半導体チップ53とその周辺に配置された導電パターン52とを接続するワイヤ54は通常、金細線が用いられることから、金細線とボンディング接続されるボンディング接合部のピール強度(引張力)を大きくするために、約200℃〜300℃の加熱雰囲気中でボンディングを行うことが好ましい。しかし、絶縁樹脂系の実装基板上に半導体チップをダイボンディングする場合には、上記した温度まで加熱すると実装基板に歪みが生じること、及び、実装基板上に実装されたチップコンデンサ、チップ抵抗等の他の回路素子を固着する半田が溶融するために、加熱温度を約100℃〜150℃程度にしてワイヤボンディング接続が行われているため、ボンディング接合部のピール強度が低下する問題がある。
【0013】
この先行技術では、通常、ダイボンディングされた半導体チップはエポキシ樹脂等の封止用樹脂で被覆保護されるために、ピール強度の低下はエポキシ樹脂の熱硬化時の収縮等によって接合部が剥離されるという問題がある。
第5の課題:
金型内に設置したときのリードフレーム10とキャビティ9との位置合わせ精度はプラス・マイナス50μ程度が限界である。このため、アイランド2の大きさは前記合わせ精度を考慮した大きさに設計しなければならない。従って、合わせ精度の問題は、パッケージの外形寸法に対するアイランド2の寸法を小さくし、これがパッケージの外形寸法に対して収納可能な半導体チップ1の最大寸法に制限を与えていた。
【0014】
本発明は、上述した事情に鑑みて成されたものであり、本発明は、半導体装置のベース、エミッタ及びコレクタ用の外部接続電極を同一平面上に配置し、半導体チップ面積と実装基板上に実装される半導体装置の実装面積との比率である有効面積率を最大限向上させ、実装面積のデットスペースを最小限小さくできる半導体装置の製造方法を提供する。
【0015】
【課題を解決するための手段】
本発明は、上記の課題を解決するために、以下の特徴を持つものでる。
第1に、アイランド上に半導体チップを設置し、チップとリード端子とを電気的に接続し、全体を封止して、パッケージ外形の少なくとも一部を前記絶縁材料に切断した面によって構成したものである。
【0016】
第2に、樹脂と共にリード端子を切断し、切断面を用いて外部接続端子を構成するものである。
第3に、半導体チップを固着するアイランドと前記アイランドから延在形成され隣接する前記アイランド上に固着した前記半導体チップの外部接続用電極となる複数のリード端子とからなるフレームが連結バーによって複数の列方向(又は行方向)に配置されたリードフレームを準備する工程と、前記アイランドの一主面上に半導体チップを固着し、前記半導体チップが固着された前記アイランドと前記列方向(又は行方向)に隣接する前記リード端子とを電気的に接続する工程と、少なくとも前記半導体チップ、及び前記リード端子の表面を被覆し前記アイランド及び前記リード端子の反主面を露出するように前記リードフレーム上に樹脂層を形成する工程と、前記半導体チップが固着された前記アイランドと前記半導体チップと電気的に接続された前記リード端子とを囲む領域で個々に分割する工程とを具備することを特徴としている。
【0017】
【発明の実施の形態】
以下に本発明の実施の形態を詳細に説明する。
図1は本発明の半導体装置を示す(A)断面図、(B)上面図、(C)側面図で、図2(A)は裏面図、図2(B)はその概略斜視図である。所望の能動素子を形成したシリコン半導体チップ72が導電性の接着剤やAu−Si共晶によってアイランド61の一主面上に接着されている。アイランド61は外部接続電極の一部100として使用される。リード端子62、63がアイランド61とは離れた位置に複数本設けられている。半導体チップ72の表面部分に形成した電極パッドとリード端子62、63の表面とがボンディングワイヤ73によって電気的に接続される。半導体チップ72とボンディングワイヤ73を含めて、アイランド61とリード端子62、63が樹脂81でモールドされて、大略直方体のパッケージ形状を形成する。樹脂81は熱硬化性エポキシ樹脂である。アイランド61とリード端子62、63は、厚さが約0.2mmの銅系の金属材料から成る。樹脂81の外形寸法は、縦×横×高さが、約0.7mm×1.0mm×0.6mmである。アイランド61の裏面側と、リード端子62、63の裏面側は樹脂81の表面に露出する。アイランド61とリード端子62、63の露出した表面には金属メッキ層82が形成される。そして、アイランド61とリード端子62、63はそれぞれ、外部接続端子100、101、102を構成する。
【0018】
直方体のパッケージ外形を形成する6面のうち、少なくとも上面81aはモールド金型等によって形成された面で構成される。前記6面の内、側面81c、81d、81e、81fは樹脂81を切断した切断面で構成される。該切断面に沿ってリード端子62、63の切断面が露出する。アイランド61は複数の突起部61aを有し、これらの突起部61aの切断面も露出する。そして、プリント基板に対してアイランド61及びリード端子62、63の、裏面81bと側面81c、81eに露出した部分を外部接続電極100、101、102として半田付けし、この装置を実装する。
【0019】
以上に説明した半導体装置は、以下の方法によって得ることができる。
第1工程:(図3)
先ず、図3に示すようなリードフレーム60を準備する。図3Aはリードフレーム60の平面図であり、図3Bは図3AのX−X断面図である。本発明で用いられるリードフレーム60は、多数のフレーム64が行方向(又は列方向)に複数個配置されており、複数のフレーム64は連結バー65によって互いに連結されている。該フレーム64は、半導体チップの搭載部となるアイランド61と、外部接続用電極となる複数のリード端子62、63を有する。そして、互いに連結された複数のフレーム64が同じく連結バー65によって外枠66、66の間に連結される。更に、フレーム64に隣接して他のフレーム64Aが連結バー65Aによって同様に連結される。フレーム64のアイランド61に対して、隣のフレーム64Aのアイランド61Aに保持されたリード端子62A、63Aが対応する。この様にフレーム64を行・列方向に複数配置することで、1本の短冊状のリードフレーム60に例えば100個のフレーム64を配置する。各アイランド61、61Aから延在される各リード端子62、63、62A、63Aは、その中間部分の両側がくさび状に形成され、部分的に細く形成されている。
また、このリードフレーム60内には、アイランド61、61A..及びリード端子62、63、62A、63Aの表面より凹んだ底板67が形成される。この底板67はアイランド61、61A..及びリード端子62、63、62A、63Aの裏面側と連続している。
【0020】
上記の底板67を有するリードフレーム60は、例えば、約0.2mm厚の銅系の金属材料で形成された帯状あるいは矩形状のリードフレーム用金属薄板を用意し、このリードフレーム用金属薄板の一主面上に、上記したアイランド61、61A..及び62、63、62A、63Aからなるフレーム64、64A、連結バー65、65A及び外枠部66、66のパターンに合致したハードマスクまたホトレジストマスクを形成し、該マスクで被覆されない前記金属薄板の露出表面を約0.15mm程度エッチングする事によって得ることができる。この様なハーフエッチング処理によって、アイランド61、61A..等の周囲(図3A内でハッチングした領域)に板厚約0.05mmの底板67を選択的に設けることができる。ここでは、リードフレーム60の板厚及び底板67の板厚は必要に応じて適宜に設定することができる。また、板厚が一様な底板67だけを別に用意し、フレーム64を形成したリードフレーム60と張り合わせることによっても形成することができる。
【0021】
第2工程:(図4)
次に、リードフレーム60に対してダイボンド工程とワイヤボンド工程を行う。図4A及び図4Bに示すように、各アイランド61、61Aの一主面上にAgペースト、半田等の導電ペースト71を塗布し、その導電ペースト71を介して各アイランド61、61A上に半導体チップ72を固着する。ここでは、導電ペースト71で各アイランド上に半導体チップを固着したが、各アイランド表面に金メッキを行い、そのメッキ上に半導体チップを共晶接続することも可能である。
【0022】
更に、半導体チップ72の表面に形成されたボンディングパッドと、これに対応するリード端子62、63とをワイヤ73でワイヤボンディングする。ワイヤ73は例えば直径が20μの金線から成る。ここで、ワイヤ73は各アイランド61上に固着した半導体チップ72の表面電極と、その隣に隣接した他のアイランド61Aから延在するリード端子62A、63Aとを接続する。
半導体チップ72が固着された各アイランド61、61Aの裏面は、係る半導体チップ72の一つの外部接続用電極100となり、ワイヤで電気的に接続されたリード62A、63A、62、63は他の外部接続用電極101、102となる。アイランド61、61Aの裏面を接続用端子の1つとして用いる形態は、半導体チップ72として例えばトランジスタ、パワーMOSFET等の、電流経路が垂直方向になる半導体デバイス素子に適している。
【0023】
半導体チップ72を固着するために塗布された導電性ペースト71は、図4から明らかなように、半導体チップ72が固着されるアイランド61、61A上に選択的に塗布形成する。リード端子62,63...上に導電性ペースト71が付着すると、ワイヤボンディングを行う場合に、ボンディング装置のキャピラリーの先端部分に導電性ペーストがつまりボンディング不良が生じ生産性が低下する恐れがあるためである。この様な問題がない場合には、導電性ペーストをフレーム64、64A全面に塗布しても良い。
【0024】
第3工程:(図5)
次に、全体を樹脂モールドする。図5Aに示すように、リードフレーム60上にエポキシ樹脂等の熱硬化性の封止用樹脂層81を形成し、各フレーム64、64A..、半導体チップ72及びワイヤ72を封止保護する。樹脂層81は、素子A、素子B、素子C……を個別にパッケージングするものではなく、半導体チップ72の全部を被うように形成する。モールド後のリードフレーム60の状態を図5Bに示す。
この樹脂層81は、リードフレーム60の外周に高さ数mmの枠材(図示しない)を配置し、その枠材で囲まれた領域内にエポキシ樹脂等の熱硬化性の樹脂を充填し、約150℃〜約200℃の温度で加熱処理を行い形成する。あるいは別の方法として、リードフレーム60を射出成形用の金型内に配置し、該金型内にエポキシ樹脂を充填、成形するトランスファーモールド技術によっても形成することもできる。
【0025】
第4工程:(図6)
次に、リードフレーム60の裏面側にスリット孔91を形成する。このスリット孔91は、ダイシング装置のブレードによってリードフレーム60の裏面側をハーフカットすることにより形成したものであり、ハーフカットしたスリット孔91の深さは、少なくとも底板67の板厚を超えるものとする。そして、このスリット孔91は、各リード端子62、63...の中間に形成されたくさび状部分の付近に一本あるいは複数本形成する。
【0026】
第5工程:(図7A)
次に、図7Aに示すように、リードフレーム60の裏面側表面を機械的あるいは化学的に削り、底板67を除去する。底板67の厚みは比較的薄いためにバフ等の研磨でリードフレーム60の裏面を削ることで容易に除去することができる。この工程により、各アイランド61、各リード端子62、63のパターンが裏面側に露出し、これらが連結バー65によって連結された状態になる。
【0027】
第6工程:(図7B)
底板67を除去した後、同図に示すように、外部接続電極となる露出したアイランド61、61A..、リード端子62、63、62A、63A..及びスリット孔91の表面に半田メッキ等のメッキ層82を形成する。このメッキ層82は、リードフレーム60を電極の一方とする電解メッキ法により行われる。スリット孔91はリード端子62、63の板厚の全部を切断していないので、アイランド61とリード端子62、63はまだ電気的な導通が保たれている。更に各アイランド61、61A..等を形成するフレーム64、64A..が連結バー65、65Aによって共通接続されている。このように露出した金属表面のすべてが電気的に導通しているので、一回のメッキ工程でメッキ層82を形成することができる。
【0028】
第7工程:(図8)
次に、樹脂層81を切断して各々の素子A、素子B、素子C....を分離する。即ち、半導体チップ72を固着したアイランド61と半導体チップ72と電気的に接続されたリード端子62A、63Aとを囲む領域(同図の矢印83、及び図4Aの一点鎖線83)で切断することにより、図1に示した半導体装置を形成する。切断にはダイシング装置が用いられ、ダイシング装置のブレードによって樹脂層81とリードフレーム60とを同時に切断する。切断する際には裏面側(スリット孔91を設けた側)にブルーシート(例えば、商品名:UVシート、リンテック株式会社製)を貼り付けた状態で、前記ダイシングブレードがブルーシートの表面に到達するような切削深さで行う。スリット孔91が位置する箇所では、少なくともスリット孔91の側壁に付着したメッキ層82を残すように形成する。この様に残存させたメッキ層82は、半導体装置をプリント基板上に実装する際に利用される。また、切断したリード端子の他方はアイランドに連続する突起部61aとして残存し、切断した連結バー65、65Aは突起部61b(図1Bに示した)として残存する。切断されたリード端子62、63及び突起部61a、61bの切断面は、樹脂層81の切断面と同一平面を形成し、該同一平面に露出する。
【0029】
以上の方法によって製造された半導体装置は、以下のメリットを有する。
分割された半導体装置の各外部接続用電極の側面にはメッキ層82が形成されるので、実装基板上に半田固着した際に該半田が切断面の上部まで(スリット孔91の側壁に相当する部分)容易に盛り上がって半田フィレットを形成する。従って半田接合力が向上し熱ストレス等の応力による劣化を防止することができる。
【0030】
また、分割された半導体装置の各外部接続用電極100、101、102の終端は、図2Aに示すように、半導体装置の終端部分でくさび状に形成されるために各接続用電極100、101、102が樹脂層81の側面から抜け落ちることを防止している。
本願発明者は、チップサイズが0.40mm×0.40mmのトランジスタチップをアイランド61上に設置し、上述の製造方法によってパッケージサイズが1.0mm×0.7mmの半導体装置(図1(B)参照)を実現した。この時の、アイランドから形成された外部接続用電極100のサイズは0.6mm×0.6mm,リード端子62、63から形成された外部接続用電極101、102のサイズは0.25mm×0.15mmとすることができた。これら各外部接続用電極100、101、102及び半導体装置自体のサイズは実装される半導体チップサイズに応じて任意に設定することができる。
ここで、上述した本発明の半導体装置の製造方法によって製造された半導体装置の有効面積率を、図12に示した従来の半導体装置と比較してみると、従来例で説明した半導体装置のチップサイズは、0.40mm×0.40mmで、この半導体チップ61を金属リード端子とワイヤーで接続し、樹脂モールドすると半導体装置の全体のサイズが1.6mm×1.6mmとなる。従って、半導体装置の面積は2.56mm2となり、チップ面積が0.16mm2になる。
一方、半導体装置を実装する実装面積は半導体装置の面積とほぼ同様として考えて2.56mm2であるため、従来の半導体装置の有効面積率は約6.25%であった。
【0031】
それに対して、本発明の製造方法によって製造された半導体装置は、チップサイズを同様にしても、金属製リード端子がパッケージから導出しないため、半導体装置サイズを1.0mm×0.7mmとすることができ、その面積が0.7mm2となる。従って、有効面積率は22.85%と従来と比べて約3.6倍向上する事ができ、実装基板上に実装する実装面積のデットスペースを小さくすることができ、実装基板の小型化に寄与することができる。
【0032】
そして、多数個の素子をまとめてパッケージングするので、個々にパッケージングする場合に比べて無駄にする材料を少なくでき。材料費の低減につながる 更に、パッケージの外形をダイシング装置のブレードで切断することにより構成したので、あらかじめリードフレーム60の外枠66、66に位置あわせマークを形成しておき、該マークを使用してダイシングを行うことにより、リードフレーム60のパターンに対する樹脂外形の精度を向上できる。即ち、モールド金型による合わせ精度がプラス・マイナス50μ程度であるのに対して、ダイシング装置によって切断した樹脂外形はプラス・マイナス10μ程度に小さくできる。合わせ精度を小さくできることは、アイランド61の面積を増大して、搭載可能な半導体チップ72のチップ面積を増大できることを意味する。
【0033】
尚、上述した実施形態では、3端子用のリードフレームを用いて説明をしたが、4端子用にする場合には、図9に示すように、アイランド61から3本のリード端子62、63、68を延在させて上述した方法で製造を行えば4端子用の半導体装置を提供することができる。
また、上述した実施形態では、各アイランドに1つの半導体チップを固着したが、1つのアイランドに、例えばトランジスタを複数個固着すること、及び、トタンジスタと縦型パワーMOSFET等の他の素子との複合固着も可能である。この様な場合には、リードフレームは図9に示すような多数のリード端子を有するものが使用される。
【0034】
さらに、本実施形態では、半導体チップ72にトランジスタを形成したが、縦型或いは比較的発熱量の少ない横型のデバイスであればこれに限らず、例えば、パワーMOSFET、IGBT、HBT等のデバイスを形成した半導体チップであっても、本発明に応用ができることは説明するまでもない。加えて、リード端子の本数を増大することでBIP、MOS型等の集積回路等にも応用することができる。
【0035】
【発明の効果】
以上に説明したように、本発明によれば、少なくとも一つの樹脂面をダイシングブレードによる切断面で構成することにより、アイランド61と樹脂面との寸法精度を向上できる。従って、アイランド61の面積を増大して、収納可能な半導体チップ72のチップサイズを増大できる。
【0036】
更に、本発明の半導体装置の製造方法によれば、半導体チップを固着し外部接続用電極となるアイランドとそのアイランドから延在形成され隣接するアイランド上に固着した半導体チップの他の外部接続用電極となる複数のリード端子とからなるフレームが連結バーによって複数の列方向(又は行方向)に配置されたリードフレームの各アイランド上に導電ペーストを付着して半導体チップを固着し、列方向(又は行方向)に隣接するリード端子と電気的に接続して、半導体チップ、及びリード端子の表面を被覆しアイランド及びリード端子の反主面を露出するようにリードフレーム上に樹脂層を形成し、半導体チップが固着されたアイランドと半導体チップと電気的に接続されたリード端子とを囲む領域で個々に分割することにより、外部接続用電極となるアイランド及びリード端子とが封止用の樹脂層の側面から導出せずに同一平面上に形成し外観寸法を著しく小型化にした半導体装置を容易に形成することができる。その結果、半導体装置の外観寸法を著しく小型化にすることができ、実装基板上に実装したときの不必要なデットスペースを無くすことができ、実装基板の小型化に大きく寄与することができる。
【図面の簡単な説明】
【図1】本発明の半導体装置を示す図。
【図2】本発明の半導体装置を示す図。
【図3】本発明の半導体装置の製造方法を説明する図。
【図4】本発明の半導体装置の製造方法を説明する図。
【図5】本発明の半導体装置の製造方法を説明する図。
【図6】本発明の半導体装置の製造方法を説明する図。
【図7】本発明の半導体装置の製造方法を説明する図。
【図8】本発明の半導体装置の製造方法を説明する図。
【図9】他の実施の形態を説明する図。
【図10】従来の半導体装置を説明する断面図。
【図11】従来の半導体装置を説明する断面図。
【図12】従来の半導体装置を説明する平面図。
【図13】従来の半導体装置を説明する平面図。
【図14】従来の半導体装置を実装基板上に実装した断面図。
【図15】従来の半導体装置を実装基板上に実装した断面図。
Claims (5)
- 半導体チップを固着するアイランドと、前記アイランドに近接する複数のリード端子と、前記アイランドおよび前記リード端子表面より凹み、且つ、前記アイランドおよび前記リード端子の裏面側と連続した底板とで形成されたリードフレームを準備する工程と、
前記アイランドの表面に半導体チップを固着し、前記半導体チップと前記リード端子とを電気的に接続する工程と、
少なくとも前記半導体チップ及び前記リード端子を含む前記リードフレームの表面全体を被覆し、前記リードフレームの裏面の前記底板を露出するように樹脂層で封止する工程と、
前記リードフレームの前記底板を除去して前記アイランドと前記リード端子の裏面を前記樹脂層から露出させる工程と、
前記樹脂層を切断して前記半導体チップを含む個々の素子に分離する工程とを具備することを特徴とする半導体装置の製造方法。 - 前記リードフレームは帯状あるいは矩形状の金属薄板をその表面からハーフエッチングして前記アイランドおよび前記リード端子を形成することを特徴とする請求項1に記載の半導体装置の製造方法。
- 前記リードフレームは予め前記アイランドおよびリード端子を形成したフレームに板厚が一様の底板を張り合わせて形成することを特徴とする請求項1に記載の半導体装置の製造方法。
- 前記樹脂層を形成する工程の後、前記リード端子を裏面からハーフカットしスリット孔を形成することを特徴とする請求項1に記載の半導体装置の製造方法。
- 前記スリット孔を形成して前記底板を除去した後、前記アイランド、前記リード端子及び前記スリット孔の表面にメッキ層を形成することを特徴とする請求項4に記載の半導体装置の製造方法。
Priority Applications (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP32796797A JP3877401B2 (ja) | 1997-03-10 | 1997-11-28 | 半導体装置の製造方法 |
| US09/543,861 US6410363B1 (en) | 1997-03-10 | 2000-04-05 | Semiconductor device and method of manufacturing same |
| US10/136,368 US6911353B2 (en) | 1997-03-10 | 2002-05-02 | Semiconductor device and method of manufacturing same |
Applications Claiming Priority (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP9-55166 | 1997-03-10 | ||
| JP5516697 | 1997-03-10 | ||
| JP32796797A JP3877401B2 (ja) | 1997-03-10 | 1997-11-28 | 半導体装置の製造方法 |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JPH10313082A JPH10313082A (ja) | 1998-11-24 |
| JP3877401B2 true JP3877401B2 (ja) | 2007-02-07 |
Family
ID=26396028
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP32796797A Expired - Lifetime JP3877401B2 (ja) | 1997-03-10 | 1997-11-28 | 半導体装置の製造方法 |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (2) | US6410363B1 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JP3877401B2 (ja) |
Families Citing this family (50)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP3877401B2 (ja) * | 1997-03-10 | 2007-02-07 | 三洋電機株式会社 | 半導体装置の製造方法 |
| JP3901427B2 (ja) | 1999-05-27 | 2007-04-04 | 松下電器産業株式会社 | 電子装置とその製造方法およびその製造装置 |
| US6548328B1 (en) * | 2000-01-31 | 2003-04-15 | Sanyo Electric Co., Ltd. | Circuit device and manufacturing method of circuit device |
| US7091606B2 (en) * | 2000-01-31 | 2006-08-15 | Sanyo Electric Co., Ltd. | Circuit device and manufacturing method of circuit device and semiconductor module |
| DE10004410A1 (de) * | 2000-02-02 | 2001-08-16 | Infineon Technologies Ag | Halbleiterbauelement mit an der Unterseite befindlichen Kontakten und Verfahren zur Herstellung |
| JP3510841B2 (ja) * | 2000-05-09 | 2004-03-29 | 三洋電機株式会社 | 板状体、リードフレームおよび半導体装置の製造方法 |
| JP3883784B2 (ja) * | 2000-05-24 | 2007-02-21 | 三洋電機株式会社 | 板状体および半導体装置の製造方法 |
| US6545364B2 (en) * | 2000-09-04 | 2003-04-08 | Sanyo Electric Co., Ltd. | Circuit device and method of manufacturing the same |
| US20020081772A1 (en) * | 2000-12-21 | 2002-06-27 | Madrid Ruben P. | Method and system for manufacturing ball grid array ("BGA") packages |
| US6740603B2 (en) * | 2001-02-01 | 2004-05-25 | Texas Instruments Incorporated | Control of Vmin transient voltage drift by maintaining a temperature less than or equal to 350° C. after the protective overcoat level |
| JP2002252318A (ja) | 2001-02-27 | 2002-09-06 | Nec Kansai Ltd | チップ型半導体装置 |
| JP4611569B2 (ja) * | 2001-05-30 | 2011-01-12 | ルネサスエレクトロニクス株式会社 | リードフレーム及び半導体装置の製造方法 |
| JP2003023134A (ja) * | 2001-07-09 | 2003-01-24 | Hitachi Ltd | 半導体装置およびその製造方法 |
| KR100455698B1 (ko) * | 2002-03-07 | 2004-11-06 | 주식회사 케이이씨 | 칩 싸이즈 패키지 및 그 제조 방법 |
| KR100439407B1 (ko) * | 2002-04-11 | 2004-07-09 | 삼성전기주식회사 | 반도체소자 패키지 제조방법 |
| US7119421B2 (en) | 2002-06-06 | 2006-10-10 | Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. | Quad flat non-leaded package comprising a semiconductor device |
| US6872599B1 (en) * | 2002-12-10 | 2005-03-29 | National Semiconductor Corporation | Enhanced solder joint strength and ease of inspection of leadless leadframe package (LLP) |
| JP4159348B2 (ja) * | 2002-12-20 | 2008-10-01 | 三洋電機株式会社 | 回路装置の製造方法 |
| JP3897704B2 (ja) | 2003-01-16 | 2007-03-28 | 松下電器産業株式会社 | リードフレーム |
| JP4141340B2 (ja) * | 2003-07-16 | 2008-08-27 | 三洋電機株式会社 | 半導体装置の製造方法 |
| WO2005010985A1 (ja) * | 2003-07-25 | 2005-02-03 | Renesas Technology Corp. | 半導体装置、半導体装置の製造方法、半導体モジュール及びパソコンカード |
| JP2005117009A (ja) * | 2003-09-17 | 2005-04-28 | Denso Corp | 半導体装置およびその製造方法 |
| US8039363B2 (en) * | 2003-12-23 | 2011-10-18 | Tessera, Inc. | Small chips with fan-out leads |
| JP2005303107A (ja) * | 2004-04-14 | 2005-10-27 | New Japan Radio Co Ltd | リードフレームおよび半導体装置並びにそれらの製造方法 |
| JP3915992B2 (ja) * | 2004-06-08 | 2007-05-16 | ローム株式会社 | 面実装型電子部品の製造方法 |
| JP2006165411A (ja) * | 2004-12-10 | 2006-06-22 | New Japan Radio Co Ltd | 半導体装置およびその製造方法 |
| US20060159680A1 (en) * | 2005-01-14 | 2006-07-20 | Smith Henry J | Targeted apherisis for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis |
| JP2005277434A (ja) * | 2005-05-09 | 2005-10-06 | Renesas Technology Corp | 半導体装置 |
| DE102005039165B4 (de) * | 2005-08-17 | 2010-12-02 | Infineon Technologies Ag | Draht- und streifengebondetes Halbleiterleistungsbauteil und Verfahren zu dessen Herstellung |
| DE102005049687B4 (de) * | 2005-10-14 | 2008-09-25 | Infineon Technologies Ag | Leistungshalbleiterbauteil in Flachleitertechnik mit vertikalem Strompfad und Verfahren zur Herstellung |
| DE102005052563B4 (de) * | 2005-11-02 | 2016-01-14 | Infineon Technologies Ag | Halbleiterchip, Halbleiterbauteil und Verfahren zu deren Herstellung |
| TWI320594B (en) * | 2006-05-04 | 2010-02-11 | Cyntec Co Ltd | Package structure |
| JP2008034830A (ja) * | 2006-06-27 | 2008-02-14 | Seiko Instruments Inc | 半導体装置およびリードフレームとその製造方法 |
| JP4994148B2 (ja) * | 2007-08-10 | 2012-08-08 | ルネサスエレクトロニクス株式会社 | 半導体装置の製造方法 |
| US8116102B2 (en) * | 2007-12-26 | 2012-02-14 | Infineon Technologies Ag | Integrated circuit device and method of producing |
| WO2009125250A1 (en) * | 2008-04-11 | 2009-10-15 | Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. | Integrated circuit package, method of manufacturing an integrated circuit package and printed circuit board |
| JP5171803B2 (ja) * | 2009-12-28 | 2013-03-27 | ローム株式会社 | 半導体装置 |
| CN102117753A (zh) * | 2010-01-05 | 2011-07-06 | 飞思卡尔半导体公司 | 封装半导体器件的方法 |
| JP5264797B2 (ja) * | 2010-02-09 | 2013-08-14 | ローム株式会社 | 半導体装置 |
| US9418919B2 (en) * | 2010-07-29 | 2016-08-16 | Nxp B.V. | Leadless chip carrier having improved mountability |
| CN102468196A (zh) * | 2010-10-29 | 2012-05-23 | 于振海 | 具有铜块电极的分立电路元件及其制造方法 |
| JP2012114311A (ja) * | 2010-11-26 | 2012-06-14 | Toshiba Corp | Ledモジュール |
| JP5657591B2 (ja) | 2011-03-23 | 2015-01-21 | 株式会社東芝 | 半導体発光装置およびその製造方法 |
| US8890301B2 (en) | 2012-08-01 | 2014-11-18 | Analog Devices, Inc. | Packaging and methods for packaging |
| US8865523B2 (en) * | 2013-03-15 | 2014-10-21 | Alpha & Omega Semiconductor, Inc. | Semiconductor package and fabrication method thereof |
| JP6634117B2 (ja) * | 2013-04-16 | 2020-01-22 | ローム株式会社 | 半導体装置 |
| CN104347431B (zh) * | 2013-07-23 | 2017-04-12 | 万国半导体股份有限公司 | 一种暴露器件顶面和底面的封装结构及其制作方法 |
| JP6486074B2 (ja) * | 2013-12-20 | 2019-03-20 | キヤノン株式会社 | 樹脂成形方法および液体吐出ヘッドの製造方法 |
| US9287236B2 (en) * | 2014-07-17 | 2016-03-15 | Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. | Flexible packaged integrated circuit |
| US10084503B2 (en) * | 2014-10-15 | 2018-09-25 | Skyworks Solutions, Inc. | Surface-mount technology devices and related methods |
Family Cites Families (20)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US4426773A (en) * | 1981-05-15 | 1984-01-24 | General Electric Ceramics, Inc. | Array of electronic packaging substrates |
| JPH0243745A (ja) * | 1988-08-04 | 1990-02-14 | Fuji Electric Co Ltd | 透明樹脂でモールドした光電変換素子の製造方法 |
| US5200362A (en) * | 1989-09-06 | 1993-04-06 | Motorola, Inc. | Method of attaching conductive traces to an encapsulated semiconductor die using a removable transfer film |
| JPH0821670B2 (ja) | 1990-02-27 | 1996-03-04 | ローム株式会社 | 合成樹脂封止型電子部品 |
| US5172214A (en) * | 1991-02-06 | 1992-12-15 | Motorola, Inc. | Leadless semiconductor device and method for making the same |
| KR0128251Y1 (ko) | 1992-08-21 | 1998-10-15 | 문정환 | 리드 노출형 반도체 조립장치 |
| JP2934357B2 (ja) | 1992-10-20 | 1999-08-16 | 富士通株式会社 | 半導体装置 |
| US5302849A (en) | 1993-03-01 | 1994-04-12 | Motorola, Inc. | Plastic and grid array semiconductor device and method for making the same |
| JP3115155B2 (ja) | 1993-05-28 | 2000-12-04 | 株式会社東芝 | 半導体装置およびその製造方法 |
| JPH0738334A (ja) | 1993-07-22 | 1995-02-07 | Seikosha Co Ltd | 水晶発振器 |
| US5656550A (en) * | 1994-08-24 | 1997-08-12 | Fujitsu Limited | Method of producing a semicondutor device having a lead portion with outer connecting terminal |
| US5832600A (en) * | 1995-06-06 | 1998-11-10 | Seiko Epson Corporation | Method of mounting electronic parts |
| US5977613A (en) * | 1996-03-07 | 1999-11-02 | Matsushita Electronics Corporation | Electronic component, method for making the same, and lead frame and mold assembly for use therein |
| US6001671A (en) * | 1996-04-18 | 1999-12-14 | Tessera, Inc. | Methods for manufacturing a semiconductor package having a sacrificial layer |
| KR0179924B1 (ko) | 1996-06-14 | 1999-03-20 | 문정환 | 버텀리드 반도체 패키지 |
| KR0185512B1 (ko) * | 1996-08-19 | 1999-03-20 | 김광호 | 칼럼리드구조를갖는패키지및그의제조방법 |
| JP3012816B2 (ja) | 1996-10-22 | 2000-02-28 | 松下電子工業株式会社 | 樹脂封止型半導体装置およびその製造方法 |
| US6583444B2 (en) * | 1997-02-18 | 2003-06-24 | Tessera, Inc. | Semiconductor packages having light-sensitive chips |
| JP3877401B2 (ja) * | 1997-03-10 | 2007-02-07 | 三洋電機株式会社 | 半導体装置の製造方法 |
| JP3819574B2 (ja) * | 1997-12-25 | 2006-09-13 | 三洋電機株式会社 | 半導体装置の製造方法 |
-
1997
- 1997-11-28 JP JP32796797A patent/JP3877401B2/ja not_active Expired - Lifetime
-
2000
- 2000-04-05 US US09/543,861 patent/US6410363B1/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
-
2002
- 2002-05-02 US US10/136,368 patent/US6911353B2/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| US20020119603A1 (en) | 2002-08-29 |
| JPH10313082A (ja) | 1998-11-24 |
| US6911353B2 (en) | 2005-06-28 |
| US6410363B1 (en) | 2002-06-25 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP3877401B2 (ja) | 半導体装置の製造方法 | |
| US7586180B2 (en) | Semiconductor packaging device comprising a semiconductor chip including a MOSFET | |
| JP3521758B2 (ja) | 半導体装置の製造方法 | |
| US7238549B2 (en) | Surface-mounting semiconductor device and method of making the same | |
| TWI450373B (zh) | 雙側冷卻整合功率裝置封裝及模組,以及製造方法 | |
| US7410834B2 (en) | Method of manufacturing a semiconductor device | |
| JP3420057B2 (ja) | 樹脂封止型半導体装置 | |
| US20120181676A1 (en) | Power semiconductor device packaging | |
| US11574855B2 (en) | Package with dies mounted on opposing surfaces of a leadframe | |
| US20130017652A1 (en) | Method of manufacturing a semiconductor device package with a heatsink | |
| JP2000243887A (ja) | 半導体装置とその製造方法 | |
| JP3877409B2 (ja) | 半導体装置の製造方法 | |
| US20030228720A1 (en) | Semiconductor device and a method of manufacturing the same | |
| JP3877402B2 (ja) | 半導体装置の製造方法 | |
| JP3877410B2 (ja) | 半導体装置の製造方法 | |
| JP3877405B2 (ja) | 半導体装置の製造方法 | |
| US20120181677A1 (en) | Semiconductor device package with two component lead frame | |
| JP2000150543A (ja) | 半導体装置の製造方法 | |
| JP4784945B2 (ja) | 半導体装置の製造方法 | |
| JPH11186481A (ja) | リードフレーム | |
| JPH11186449A (ja) | 半導体装置およびその製造方法 | |
| JPH09213871A (ja) | 半導体装置 | |
| JPH1012651A (ja) | 半導体装置 | |
| JP2001284370A (ja) | 半導体装置の製造方法 | |
| JP2000277563A (ja) | 半導体装置 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20040903 |
|
| RD01 | Notification of change of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7421 Effective date: 20051226 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20060711 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20060907 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20061017 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20061031 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20101110 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20101110 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20111110 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20111110 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20121110 Year of fee payment: 6 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20131110 Year of fee payment: 7 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| EXPY | Cancellation because of completion of term |