EP0674086B2 - Verfahren zum Zusammenbauen von Isolierglasscheiben, deren Innenraum mit einem Schwergas gefüllt ist und Vorrichtung zum Füllen von Isolierglasscheiben mit Schwergas - Google Patents
Verfahren zum Zusammenbauen von Isolierglasscheiben, deren Innenraum mit einem Schwergas gefüllt ist und Vorrichtung zum Füllen von Isolierglasscheiben mit Schwergas Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0674086B2 EP0674086B2 EP95890063A EP95890063A EP0674086B2 EP 0674086 B2 EP0674086 B2 EP 0674086B2 EP 95890063 A EP95890063 A EP 95890063A EP 95890063 A EP95890063 A EP 95890063A EP 0674086 B2 EP0674086 B2 EP 0674086B2
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- channel
- spacer
- glass pane
- glass panes
- plates
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title claims description 16
- 239000011521 glass Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 103
- 238000007789 sealing Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 33
- 125000006850 spacer group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 32
- 230000001360 synchronised effect Effects 0.000 claims 1
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 description 4
- 238000005429 filling process Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000000630 rising effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 229910018503 SF6 Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 230000002411 adverse Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010276 construction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000001419 dependent effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000009413 insulation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000002093 peripheral effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000005086 pumping Methods 0.000 description 1
- SFZCNBIFKDRMGX-UHFFFAOYSA-N sulfur hexafluoride Chemical compound FS(F)(F)(F)(F)F SFZCNBIFKDRMGX-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229960000909 sulfur hexafluoride Drugs 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- E—FIXED CONSTRUCTIONS
- E06—DOORS, WINDOWS, SHUTTERS, OR ROLLER BLINDS IN GENERAL; LADDERS
- E06B—FIXED OR MOVABLE CLOSURES FOR OPENINGS IN BUILDINGS, VEHICLES, FENCES OR LIKE ENCLOSURES IN GENERAL, e.g. DOORS, WINDOWS, BLINDS, GATES
- E06B3/00—Window sashes, door leaves, or like elements for closing wall or like openings; Layout of fixed or moving closures, e.g. windows in wall or like openings; Features of rigidly-mounted outer frames relating to the mounting of wing frames
- E06B3/66—Units comprising two or more parallel glass or like panes permanently secured together
- E06B3/677—Evacuating or filling the gap between the panes ; Equilibration of inside and outside pressure; Preventing condensation in the gap between the panes; Cleaning the gap between the panes
- E06B3/6775—Evacuating or filling the gap during assembly
-
- E—FIXED CONSTRUCTIONS
- E06—DOORS, WINDOWS, SHUTTERS, OR ROLLER BLINDS IN GENERAL; LADDERS
- E06B—FIXED OR MOVABLE CLOSURES FOR OPENINGS IN BUILDINGS, VEHICLES, FENCES OR LIKE ENCLOSURES IN GENERAL, e.g. DOORS, WINDOWS, BLINDS, GATES
- E06B3/00—Window sashes, door leaves, or like elements for closing wall or like openings; Layout of fixed or moving closures, e.g. windows in wall or like openings; Features of rigidly-mounted outer frames relating to the mounting of wing frames
- E06B3/66—Units comprising two or more parallel glass or like panes permanently secured together
- E06B3/673—Assembling the units
- E06B3/67365—Transporting or handling panes, spacer frames or units during assembly
- E06B3/67386—Presses; Clamping means holding the panes during assembly
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y10—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC
- Y10T—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER US CLASSIFICATION
- Y10T156/00—Adhesive bonding and miscellaneous chemical manufacture
- Y10T156/17—Surface bonding means and/or assemblymeans with work feeding or handling means
Definitions
- the invention relates to a method with the features of the introductory part of the independent claim 1.
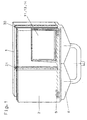
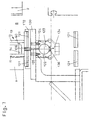
- the well-known, 1 and 2 schematically shown device consists of two plates 1 and 2, of which the plate 2 is adjustable relative to the plate 1.
- a conveyor 9 provided in the form of a roller conveyor, the one in the entire length of the lower one Edge of the plates 1 and 2 extending channel 8, above the heavy gas in the space between the plates 1 and 2 can be introduced is arranged.
- Between plates 1 and 2 is a sliding seal 31 provided.
- the outlet side (right in Fig. 1) provided seal 30 is in the space between the Plates 1 and 2 can be swiveled in.
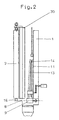
- the bottom of the adjustable plate 1 is opposite a seal 15 sealed the channel 8 (see. Fig. 2).
- the known Device is a package consisting of two Glass panes 11 and 13 and one on the glass sheet 11 attached spacer 14 (only schematic in Fig. 1 indicated) by supplied via the channel 8 Heavy gas filled, the package during the filling process stands on the conveyor 9.
- the effective length of the Channel 8 to the length of the insulating glass pane to be produced be limited by the fact that the movable Seal extends into channel 8.
- the device made known by sselling works with assembling Heavy gas filled insulating glass panes after the procedure of the introductory part of claim 1.
- the inflow of heavy gas from the channel into the package of glass panes and spacers is included the known device hindered by the roller conveyor, so that swirls arise and much Gas is consumed until the desired fill level is reached is.
- the invention has for its object a method for filling insulating glass panes with heavy gas specify that when assembling the insulating glass panes can be applied and where both for the entry of heavy gas and for that Sufficient leakage of air or air-gas mixture large cross sections are available.
- this task is performed by one Process of the type mentioned by the solved in claim 1 features.
- a gap is available which extends over the entire length of the insulating glass pane extends. Also for the escape of air or air-gas mixture there is a sufficiently large cross-section, e.g. one across from the entrance slit Extending peripheral portion of the insulating glass pane Gap available.
- Another advantage of the method according to the invention is that the size of the space between the plates that are filled with heavy gas that for the heavy gas filled insulating glass pane to be manufactured limited extent just required can be.
- the invention further relates to a device the features of the introductory part of claim 6.
- the invention relates to the device Task based on such a device Feeding heavy gas into an insulating glass pane, the is still open at least at the bottom, so there has an edge gap to improve.
- the device is also intended for performing the invention Be suitable procedure.
- that the facility to limit the effective Length of the channel is a piston that can be moved in the channel is.
- the piston By moving the piston, the length of the Range above the heavy gas into the Space enters between the two panels, in size adapted to the insulating glass pane to be produced become.
- the piston can be adjusted, for example combined with the adjustment of the sliding sealing strip become.
- This can be provided according to the invention be that the piston displaceable in the channel an approach through a slot in the channel that is sealed by a seal, protrudes with an adjusting device is coupled.
- the piston is sealed by two seals and that the seal the slot of the channel in the area between the Seals are deflected into the interior of the channel and lies radially within the approach.
- the seal the slot of the channel in the area between the Seals are deflected into the interior of the channel and lies radially within the approach.
- the shoulder protrudes from the two seals of the piston through the slot of the channel to the outside, whereby in this area (the unpressurized space between the Seals) the sealing tape from the slot to the inside is lifted off and carried out under the approach.
- An alternative embodiment is that the seal in the area of the slot of the channel a lip seal with overlapping sealing lips is.
- the way the channel connects to the room connected between the two plates is arbitrary. So several round or slit-shaped openings be provided.
- the channel is attached to the guide bar of the belt conveyor is, it can be provided that the belt conveyor two endless belts, in particular two endless toothed belts, and that the openings of the channel in the area a gap between the endless belts provided are. In this way, the openings, through which the channel with the space between the two Plates communicates between the two endless belts be extended upwards and from below something in the space between the two plates protrude.
- the belt conveyor in the area of the fixed Plate of the two plates is arranged.
- the belt conveyor and the channel connected to it transversely to the fixed plate is adjustable. This embodiment enables the at least one opening through which the channel connects the space between the two panels stands, in relation to the insulating glass pane to be filled align that the spacer frame one insulating glass pane arranged between the plates is arranged opposite.
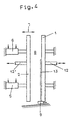
- the device shown in Figs. 3 to 6 has two essentially perpendicular, preferably over the Verticals slightly, e.g. 3 to 5 °, inclined backwards, parallel plates 1 and 2.
- the plates 1 and 2 can be the plates of a device for pressing insulating glass panes 10 his.
- the plate is 1st attached to the frame of the device.
- the plate 2 is via pressure medium cylinders 5 and 6 in the direction of the double arrow 7 slidable.
- a belt conveyor 9 is provided, on the getting up and against the for example designed as an air cushion wall, fixed to the frame Plate 1 leaning a package consisting of two glass panes 11 and 13 and a spacer 14 in the Room 8 can be funded.
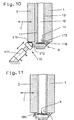
- the sealing strip 170 is used by at least two Pressure medium cylinders 171 worn and carries on their the lower edge of plate 2 and the guide bar 172, on which the upper run 173 of the belt conveyor 9 an elongated seal 175 slides on the opposite side.
- the seal 175 is in the embodiment shown in FIG. 10 formed and exists as a hose seal for example made of elastically deformable plastic. The seal can be used to increase the sealing effect 175, as soon as the sealing strip 170 in its operative position, in the the seal 175 at the bottom of the adjustable Plate 2 and against the guide bar 172, under Pressure.
- the guide bar 172 of the belt conveyor 9 is on its side opposite the sealing strip 170 continuously, for example via a bar 176, with the fixed plate 1 connected, so that there too a gas-tight seal is guaranteed.
- an elastically deformable sealing tab 180 is provided, which is when the movable plate is pushed forward 2 on the arranged below the movable plate 2 Edge of the guide bar 172 of the belt conveyor 9 creates.
- the sealing tab 180 shown in FIG. 11 can also be designed as an inflatable hose seal.
- fixed plate 1 For loading the air cushion wall, fixed plate 1 is this with a connection 12 equipped for supplying compressed air.
- the sealing device 30 arranged on the outlet side is in the embodiment of the device shown in Fig. 12 at their upper and lower ends, respectively attached to an arm 107, which is via a pair of parallelogram links 108, 109, in the machine frame is pivotally mounted, is worn.
- a Pressure cylinder 110 provided on a lever 111 attacks.
- the lever 111 is one of the two connecting link 109 arranged one above the other Shaft 112 non-rotatably connected.
- Fig. 12 it is shown that the sealing device 30 in their operative position not on the vertical outlet side Edges of the insulating glass pane 10, but at the vertical edges 105 and 106 of the plates 1 and 2 abuts.
- the second sealing device 31 is in the device in the direction of the double arrow in Fig. 3.
- the sealing device 30 and / or the sealing device 31 can in a modified embodiment also be arranged on the sliding plate 2.
- a channel 122 is provided, from which Heavy gas as symbolized by arrows 156, 157 the belt conveyor 9 flows from below into the room 8.
- the effective length of channel 122 is determined by a piston 130 to the length of the insulating glass pane 10 limited.
- Channel 122 shown for supplying heavy gas.
- channel 122 is below the Carrier 120 for the guide bar 172 of the longitudinally Belt conveyor 9 (in the example two endless toothed belts 121) attached.
- boreholes 124 go out with holes 125 in Align carrier 120 and finally to pipe sections 126 cause the gap between the two timing belts Push 121 of the belt conveyor 9 through.
- the pipe pieces 126 open in room 8 between plates 1 and 2 and especially between the two panes of glass 11 and 13 of the insulating glass pane which has not yet been completed 10 and are aligned so that they the spacer 14 are opposite.
- bores 124, 125 and the raw pieces 126 via which the interior 123 of the channel 122 the space 8 between the plates 1 and 2 in connection stands, can also be a series of longitudinal slots be provided.
- the interior 123 of the channel 122 is over a Connection line (not shown) with a source for Heavy gas (rare gas, sulfur hexafluoride or the like) in Connection.
- a source for Heavy gas rare gas, sulfur hexafluoride or the like
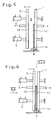
- the piston 130 through which the effective length of the Interior 123 of the channel 122 on the horizontal Direction of measured length of the insulating glass pane 10 can be adjusted is opposite channel 122 sealed by two seals 131. Through a Longitudinal slot 134 in the opposite of the holes 124 A portion of channel 122 protrudes 135, which is connected to the piston 130, to the outside. Via this approach 135, the piston 130 can Channel 122 can be adjusted.
- the slot 134 in the channel 122 is through a seal 136 sealed in the area of the piston 130, i.e. in the area between the two seals 131 (depressurized space) redirected inwards and under approach 135 is performed. That way the piston 130 can be adjusted as desired without the Tightness of the channel 122 to the outside through the Slot 134 is affected.
- the piston be adjusted 130 via its approach 135 with the adjustment of the movable Seal 31 is combined.
- the device works, for example, as follows: For example in the one from AT 370 201 B or the device known from AT 370 706 B or by hand from compiled package of glass panes 11 and 13 and a spacer 14, one of which is a sheet of glass 13 below from the one to the other glass pane 11 attached spacers 14 a distance (gap 60) and on the other glass pane 11 attached spacer 14 only in the upper Area rests so that the bottom and partially on the vertical Edges of the glass panes 11 and 13 an access is present in the interior of the package the belt conveyor 9 rising into space 8 between promoted the plates 1 and 2 until you, referred on the conveying direction (arrow 25) more front, more vertical Edge next to the advanced or swung-in Sealing device 30 is located. Now the second sealing device 31 in room 8 between the two plates 1 and 2 moved until they are next to, based on the Conveying direction (arrow 25) rear, vertical edge of the Insulating glass pane 10 lies.
- the device according to the invention (cf. Fig. 4 to 6) can also be worked so that during the filling process, the one glass pane 13 on the movable Plate 2 entirely at a distance from the another glass pane 11 attached spacer 14 is held.
- the Plate 2 is set up for holding the glass pane 13.
- the plate 2 in its space 8 between the plates 1 and 2 facing surface Have openings through a line 12 'with negative pressure are applied to the glass pane 13 hold.
- an insulating glass pane filled with heavy gas 10 is a first glass sheet 13 on the Plate 1 leaning and supported by the conveyor belt 9 below in space 8 between plates 1 and 2 into one predetermined end position moves (Fig. 4).
- the Plate 1 be designed as an air cushion wall and it will you when transporting the glass sheet 13 via a connecting line 12 compressed air supplied.
- the adjustable plate 2 is advanced, until they turned towards plate 1 Surface rests on the glass pane 13. Once that is achieved is the plate 2, which at its 8th between the plates 1 and 2 facing side openings has, via a line 12 'with negative pressure charged and at most until then via the line 12 applied to the plate 1 vacuum (for Holding the glass sheet 13 in the predetermined End position) canceled.
- the plate 2 is with the her captured glass sheet 13 in that shown in Fig. 5 Position moved back.
- the next step is the second glass plate 11 with a spacer 14 attached to it in the Space 8 between the plates 1 and 2 up to the predetermined End position transported.
- the actual gas exchange can begin be, in which 9 heavy gas through the belt conveyor initiated and withdrawn air or air-gas mixture is, the withdrawal of air or air-gas mixture can be supported by pumping.
- the Heavy gas supply interrupted.
- the insulating glass panel 10 can also be the same be pressed. Possible constructions for such Press and drive to move the moving Press plate 2 are in DE 31 30 645 Al and AT-A 2956/87, published on June 15, 1990 described.
- the drives described there rack and pinion drives or spindle drives) instead of the pressure medium cylinders 5 and 6.
- the movable Plate 2 moved away from plate 1 and the Completely pressed insulating glass pane filled with heavy gas 10, consisting of the two glass panes 11 and 13 and the spacer inserted between them 14, the belt conveyor 9 becomes, for example Sealing station transported.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Civil Engineering (AREA)
- Structural Engineering (AREA)
- Securing Of Glass Panes Or The Like (AREA)
- Joining Of Glass To Other Materials (AREA)
- Laminated Bodies (AREA)
- Filling Or Discharging Of Gas Storage Vessels (AREA)
Description
Claims (14)
- Verfahren zum Zusammenbauen von mit Schwergas gefüllten Isolierglasscheiben (10, bei dem man zwischen Platten (1, 2) ein Paket aus einer ersten Glasscheibe (13), einer zweiten Glasscheibe (11) und einem auf die zweite Glasscheibe (11) angesetzten Abstandhalter (14) im wesentlichen lotrecht stehend anordnet, wobei zwischen dem Abstandhalter (14) und der ersten Glasscheibe (13) wenigstens im Bereich des unteren Randes des Paketes aus den Glasscheiben (11, 13) und dem Abstandhalter (14) ein spaltförmiger Zugang (60) in den Raum zwischen den Glasscheiben (11, 13) des Paketes vorliegt, bei dem man neben dem Paket aus den Glasscheiben (11, 13) und dem Abstandhalter (14) im wesentlichen lotrecht ausgerichtete Dichteinrichtungen (30, 31) vorsieht, bei dem man Schwergas aus einem unter den Glasscheiben (11, 13) angeordneten Kanal (122) in dem Raum zwischen den Glasscheiben (11, 13) einleitet, und bei dem man, nachdem der Raum zwischen den Glasscheiben (11, 13) mit Schwergas (40) gefüllt worden ist, die eine Glasscheibe (13) an den auf der anderen Glasscheibe (11) angesetzten Abstandhalter (14) anlegt, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß man den unteren, horizontalen Rand des Paketes aus den Glasscheiben (11, 13) und dem Abstandhalter (14) durch eine Dichtung (9) abdichtet, und daß man Schwergas an mehreren Stellen, über den abgedichteten, unteren Rand des Paketes aus den Glasscheiben (11, 13) und dem Abstandhalter (14) durch ausschließlich dem Abstandhalter (14) gegenüberliegende Öffnungen (124), über die der Raum zwischen den Glasscheiben (11, 13) mit dem Kanal (122) in Verbindung steht, zuführt.
- Verfahren nach Anspruch 1, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß man das Paket aus den Glasscheiben (11, 13) und dem Abstandhalter (14) an seinem unteren, horizontalen Rand durch eine als Bandförderer (9) ausgebildete Fördereinrichtung abdichtet und das Schwergas durch den Bandförderer (9) hindurch zuführt.
- Verfahren nach Anspruch 1 oder 2, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß man die Glasscheiben (11, 13) bis in unmittelbare Nähe der einen Dichteinrichtung (30) bewegt und daß man dann die andere Dichteinrichtung (31) auf die Glasscheiben (11, 13) zu verfährt.
- Vorfahren nach einem der Ansprüche 1 bis 3, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß man die erste Glasscheibe (13) bis unmittelbar vor die eine Dichtung (30) fördert, daß man diese Glasscheibe (13) senkrecht zu ihrer Flächenerstrekkung aus der Förderebene entfernt, daß man eine zweite Glasscheibe (11) mit an ihr angesetztem Abstandhafter (14) in eine die erste Glasscheibe (13) überdeckende Lage fördert und daß man dann die erste Glasscheibe (13) bis knapp vor den Abstandhalter (14) auf die zweite Glasscheibe (11) zu bewegt.
- Verfahren nach einem der Ansprüche 1 bis 3, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß man ein Paket aus zwei Glasscheiben (11,13) und dem Abstandhalter (14), bei dem die erste Glasscheibe (13) oben am Abstandhalter (14) anliegt und unten vom Abstandhalter (14) einen Abstand (Spalt 60) aufweist, in den Raum (8) zwischen den Platten (1, 2) fördert.
- Vorrichtung zum Zusammenbauen von mit Schwergas gefüllten Isolierglasscheiben (10) mit zwei zu beiden Seiten der Glasscheiben (11, 13) der Isolierglasscheibe (10) angeordneten, im wesentlichen lotrechten Platten (1,2), von welchen wenigstens eine (2) quer zu ihrer Ebene relativ zur anderen Platte (1) verschiebbar ist, mit zwei Dichteinrichtungen (30, 31), die in ihrer Wirkstellung neben zwei einander gegenüberliegenden Rändern der Glasscheiben (11, 13) der Isolierglasscheibe (10) angeordnet sind, mit einer im Bereich des unteren horizontalen Randes der Platten (1, 2) angeordneten Fördereinrichtung (9) und mit einem Kanal (122), der über Öffnungen (124) mit dem Raum (8) zwischen den Platten (1, 2) in Verbindung steht, als Einrichtung zum Zuführen von Schwergas über einen am unteren Rand der lsolierglasscheibe (10) vorliegenden Spalt (60) zwischen der eirien Glasscheibe (13) und einem auf die andere Glasscheibe (11) angesetzte Abstandhalter (14), wobei eine Einrichtung (130) zum Begrenzen der wirksamen Länge des Innenraums (123) des Kanals (122) auf die in der Richtung der Längserstreckung des Kanals (122) gemessene Länge der Isolierglasscheibe (10) vorgesehen ist, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß die Fördereinrichtung ein Bandförderer (9) ist, und daß die Öffnungen (124), über die der Kanal (122) mit dem Raum (8) zwischen den Platten (1, 2) in Verbindung steht, den Bandförderer (9) nach oben hin durchsetzten und ausschließlich dem Abstandhalter (14) gegenüberliegend angeordnet sind.
- Vorrichtung nach Anspruch 6, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß die Einrichtung zum Begrenzen der wirksamen Länge des Kanals (122) ein im Kanal (122) verschiebbarer Kolben (130) ist.
- Vorrichtung nach Anspruch 7, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß der im Kanal (122) verschiebbare Kolben (130) über einen Ansatz (135), der durch einen Schlitz (134) im Kanal (122) ragt, der durch eine Dichtung (136) abgedichtet ist, mit einer Verstellvorrichtung gekuppelt ist.
- Vorrichtung nach Anspruch 8, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß die Dichtung im Bereich des Schlitzes (134) des Kanals (122) eine Lippendichtung mit einander überlappenden Dichtlippen ist.
- Vorrichtung nach Anspruch 8, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß der Kolben (130) durch zwei Dichtungen (131) abgedichtet ist und daß die Dichtung (136) des Schlitzes (134) des Kanals (122) im Bereich zwischen den Dichtungen (131) in den Innenraum (123) des Kanals (122) umgelenkt ist und radial innerhalb des Ansatzes (135) liegt.
- Vorrichtung nach Anspruch 6, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß die Öffnungen schlitzförmige Öffnungen sind.
- Vorrichtung nach einem der Ansprüche 6 bis 11, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß der Bandförderer (9) zwei Endlosriemen (121), insbesondere zwei Endloszahnriemen, aufweist und daß die Öffnungen (124) des Kanals (122) im Bereich eines Spaltes zwischen den Endlosriemen (121) vorgesehen sind.
- Vorrichtung nach einem der Ansprüche 6 bis 12, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß der Bandförderer (9) im Bereich der feststehenden Platte (1) angeordnet ist.
- Vorrichtung nach Anspruch 13, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß der Bandförderer (9) und der mit ihm verbundene Kanal (122) quer zur feststehenden Platte (1) verstellbar ist.
Applications Claiming Priority (12)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| AT62894A AT404132B (de) | 1994-03-24 | 1994-03-24 | Vorrichtung zum füllen von isolierglasscheiben mit füllgas |
| AT63194A AT409128B (de) | 1994-03-24 | 1994-03-24 | Verfahren zum zusammenbauen von isolierglasscheiben, deren innenraum mit einem schwergas gefüllt ist |
| AT62894 | 1994-03-24 | ||
| AT63194 | 1994-03-24 | ||
| AT120494A AT405932B (de) | 1994-06-17 | 1994-06-17 | Vorrichtung zum herstellen von mit füllgas gefüllten isolierglasscheiben |
| AT120494 | 1994-06-17 | ||
| AT631/94 | 1994-09-13 | ||
| AT628/94 | 1994-09-13 | ||
| AT1749/94 | 1994-09-13 | ||
| AT174994 | 1994-09-13 | ||
| AT1204/94 | 1994-09-13 | ||
| AT174994A AT409263B (de) | 1994-09-13 | 1994-09-13 | Vorrichtung zum füllen von isolierglasscheiben mit füllgas |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0674086A1 EP0674086A1 (de) | 1995-09-27 |
| EP0674086B1 EP0674086B1 (de) | 1998-05-20 |
| EP0674086B2 true EP0674086B2 (de) | 2004-08-18 |
Family
ID=27421294
Family Applications (3)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP95890063A Expired - Lifetime EP0674086B2 (de) | 1994-03-24 | 1995-03-22 | Verfahren zum Zusammenbauen von Isolierglasscheiben, deren Innenraum mit einem Schwergas gefüllt ist und Vorrichtung zum Füllen von Isolierglasscheiben mit Schwergas |
| EP95890061A Expired - Lifetime EP0674085B1 (de) | 1994-03-24 | 1995-03-22 | Vorrichtung zum Füllen von Isolierglasscheiben mit Schwergas |
| EP95890064A Expired - Lifetime EP0674087B1 (de) | 1994-03-24 | 1995-03-22 | Vorrichtung zum Herstellen von mit Schwergas gefüllten Isolierglasscheiben |
Family Applications After (2)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP95890061A Expired - Lifetime EP0674085B1 (de) | 1994-03-24 | 1995-03-22 | Vorrichtung zum Füllen von Isolierglasscheiben mit Schwergas |
| EP95890064A Expired - Lifetime EP0674087B1 (de) | 1994-03-24 | 1995-03-22 | Vorrichtung zum Herstellen von mit Schwergas gefüllten Isolierglasscheiben |
Country Status (6)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (3) | US5626712A (de) |
| EP (3) | EP0674086B2 (de) |
| JP (3) | JPH0840754A (de) |
| AT (3) | ATE166420T1 (de) |
| DE (8) | DE59502206D1 (de) |
| ES (3) | ES2118002T3 (de) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP2093370A2 (de) | 2008-02-20 | 2009-08-26 | For El Base- Di Davanzo Nadia & C.S.N.C. | Automatikvorrichtung zum Befüllen isolierender Verglasungselemente und entsprechendes Verfahren |
Families Citing this family (38)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US6216751B1 (en) | 1997-10-24 | 2001-04-17 | Cardinal Ig Company | Method of reliably detecting seal failures |
| US5957169A (en) * | 1997-10-24 | 1999-09-28 | Cardinal Ig Company | Apparatus and method for filling insulated glass units with insulating gas |
| AT407552B (de) | 1999-06-22 | 2001-04-25 | Lisec Peter | Vorrichtung zum zusammenbauen von isolierglasscheiben, deren innenraum mit einem schwergas gefüllt ist |
| US6916392B2 (en) | 2001-06-21 | 2005-07-12 | Cardinal Ig Company | Producing and servicing insulating glass units |
| US6606837B2 (en) * | 2001-08-28 | 2003-08-19 | Cardinal Ig | Methods and devices for simultaneous application of end sealant and sash sealant |
| US6804924B2 (en) | 2001-10-12 | 2004-10-19 | Cardinal Ig Company | Repair of insulating glass units |
| US20030085238A1 (en) * | 2001-11-06 | 2003-05-08 | Segro Bradley A | Apparatus for dosing liquid gas into a multipane gas unit |
| US6793971B2 (en) | 2001-12-03 | 2004-09-21 | Cardinal Ig Company | Methods and devices for manufacturing insulating glass units |
| DE50300158D1 (de) * | 2003-02-22 | 2004-12-23 | Tecnopat Ag St Gallen | Vorrichtung zum Zusammenbauen von Isolierglasscheiben, deren Innenraum mit einem Schwergas gefüllt ist |
| DE102004009860B4 (de) * | 2004-02-25 | 2006-05-04 | Karl Lenhardt | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zum Zusammenbauen von Isolierglasscheiben, die mit einem von Luft verschiedenen Gas gefüllt sind |
| DE102004009858B4 (de) * | 2004-02-25 | 2006-05-04 | Karl Lenhardt | Verfahren zum Positionieren von Glastafeln in einer vertikalen Zusammenbau- und Pressvorrichtung für Isolierglasscheiben |
| DE102004032436A1 (de) * | 2004-07-05 | 2006-02-16 | Lenhardt Maschinenbau Gmbh | Vorrichtung zum Zusammenbauen von Isolierglasscheiben, die mit einem von Luft verschiedenen Gas gefüllt sind. |
| DE102004032435B4 (de) * | 2004-07-05 | 2006-12-21 | Lenhardt Maschinenbau Gmbh | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zum Zusammenbauen von Isolierglasscheiben, die mit einem von Luft verschiedenen Gas gefüllt sind. |
| DE102005033040B3 (de) * | 2005-07-15 | 2007-03-22 | Lenhardt Maschinenbau Gmbh | Vorrichtung zum Zusammenbauen von Isolierglasscheiben, die mit einem von Luft verschiedenen Gas gefüllt sind |
| DE102005044861B3 (de) | 2005-09-13 | 2007-02-15 | Lenhardt Maschinenbau Gmbh | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zum Füllen von Isolierglasscheiben mit einem von Luft verschiedenen Gas |
| DE102006018333A1 (de) * | 2006-04-19 | 2007-10-25 | Karl Lenhardt | Vorrichtung zum Zusammenbauen von Insolierglasscheiben, die mit einem von Luft verschiedenen Gas gefüllt sind |
| TW200930883A (en) * | 2007-11-13 | 2009-07-16 | Infinite Edge Technologies Llc | Box spacer with sidewalls |
| DE202008008117U1 (de) * | 2008-06-19 | 2009-10-29 | Bc Prozesstechnik Gmbh | Vorrichtung zur Aufnahme und zum Transport von Profilen und flächigen Elementen |
| US8181400B2 (en) * | 2009-05-12 | 2012-05-22 | Kindschuh Rodney G | Gas fill device for multiple pane windows |
| EP2454437B1 (de) * | 2009-07-14 | 2017-05-10 | Guardian IG, LLC | Gedehnte streifen für distanzstück und abgedichtete einheit |
| DE102009048641B4 (de) | 2009-09-30 | 2014-02-06 | Bystronic Lenhardt Gmbh | Verfahren zum Zusammenbauen eines Fensterflügels mit integrierter Isolierglasscheibe |
| AT11889U1 (de) | 2009-10-22 | 2011-06-15 | Inova Lisec Technologiezentrum | Vorrichtung zum applizieren von abstandhalterbändern auf glasscheiben |
| US8381382B2 (en) | 2009-12-31 | 2013-02-26 | Cardinal Ig Company | Methods and equipment for assembling triple-pane insulating glass units |
| FR2956149B1 (fr) * | 2010-02-08 | 2012-01-27 | Saint Gobain | Procede de fabrication d'un triple vitrage rempli de gaz |
| GB2483249A (en) * | 2010-09-01 | 2012-03-07 | Inagas | Gas filling apparatus |
| AT510165B1 (de) * | 2010-09-23 | 2012-02-15 | Inova Lisec Technologiezentrum | Verfahren zum herstellen von mit einem von luft verschiedenen gas gefülltem isolierglas |
| US8905085B2 (en) | 2011-09-09 | 2014-12-09 | Erdman Automation Corporation | Apparatus for edge sealing and simultaneous gas filling of insulated glass units |
| FR2984300B1 (fr) | 2011-12-15 | 2014-11-21 | Saint Gobain | Procede de fabrication d'un vitrage multiple rempli de gaz |
| US10113354B2 (en) | 2013-12-31 | 2018-10-30 | Cardinal Ig Company | Multiple-pane insulating glazing unit assembly, gas filling, and pressing machine |
| US9951553B2 (en) | 2014-06-05 | 2018-04-24 | Erdman Automation Corporation | High speed parallel process insulated glass manufacturing line |
| US10538954B2 (en) * | 2015-03-20 | 2020-01-21 | Tenon (Beijing) Equipment Co., Ltd. | External inflator |
| DE102015005612A1 (de) * | 2015-04-30 | 2016-11-03 | Lisec Austria Gmbh | Zusammenbaupresse und Verfahren zur Herstellung von Isolierglaselementen |
| DE102015118960A1 (de) * | 2015-08-21 | 2017-02-23 | Bystronic Lenhardt Gmbh | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zum Zusammenbauen von Glastafeln zu Isolierglasscheiben |
| US10968685B2 (en) | 2016-01-04 | 2021-04-06 | PDS IG Holding LLC | Gas filling of an insulating glass unit |
| US10253552B2 (en) | 2016-04-21 | 2019-04-09 | Erdman Automation Corporation | High speed parallel process insulated glass manufacturing line |
| CN105776898B (zh) * | 2016-04-29 | 2017-02-01 | 济南威力机器有限公司 | 一种幕墙中空玻璃在线多功能板压机 |
| US11187028B2 (en) | 2017-07-01 | 2021-11-30 | PDSD IG Holding LLC | Filling and sealing device and method for an insulated glass unit |
| CN113585926B (zh) * | 2021-09-02 | 2022-12-27 | 山东沃能德数控机械有限公司 | 一种中空玻璃注惰性气体方法 |
Family Cites Families (17)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LU58848A1 (de) * | 1969-06-11 | 1971-03-09 | ||
| AT370201B (de) * | 1977-05-18 | 1983-03-10 | Lisec Peter Glastech Ind | Vorrichtung zum zusammenstellen von mehrscheiben- isolierglas |
| DE3101342C2 (de) * | 1981-01-17 | 1984-08-02 | Vereinigte Glaswerke Gmbh, 5100 Aachen | "Verfahren zur Herstellung von gasgefüllten Isolierglaseinheiten und Vorrichtung zur Durchführung des Verfahrens" |
| AT370706B (de) * | 1981-04-03 | 1983-04-25 | Lisec Peter | Vorrichtung zum zusammenstellen von isolierglasscheiben |
| DE3115566A1 (de) * | 1981-04-16 | 1982-10-28 | Import-Export KG Interpane Isolierglas Handelsgesellschaft mbH & Co, 3471 Lauenförde | Verfahren zur herstellung von gasgefuellten isolierglasscheiben und plattenpresse zur ausfuehrung dieses verfahrens |
| AT385499B (de) * | 1981-05-11 | 1988-04-11 | Lisec Peter | Vorrichtung zum pressen von isolierglas |
| AT368985B (de) * | 1981-05-26 | 1982-11-25 | Lisec Peter | Vorrichtung zum fuellen von isolierglas mit schwergas |
| DE3402323A1 (de) * | 1984-01-24 | 1985-08-01 | Interpane Entwicklungs- und Beratungsgesellschaft mbH & Co. KG, 3471 Lauenförde | Verfahren zum herstellen eines wenigstens aus zwei scheiben bestehenden isolierglases |
| EP0406325B2 (de) * | 1988-05-04 | 1997-07-16 | Lenhardt Maschinenbau GmbH | Verfahren und vorrichtung zum füllen von isolierglasscheiben mit einem schwergas |
| DE3914706A1 (de) * | 1988-05-04 | 1989-12-14 | Lenhardt Maschinenbau | Verfahren und vorrichtung zum zusammenbauen von isolierglasscheiben, die mit einem von luft verschiedenen gas gefuellt sind |
| US4909874A (en) * | 1989-03-30 | 1990-03-20 | Cardinal Ig Company | Method and apparatus for producing gas-containing insulating glass assemblies |
| AT408982B (de) * | 1990-02-28 | 2002-04-25 | Lisec Peter | Verfahren zum füllen des innenraumes von isolierglasscheiben mit gas |
| DE4022185A1 (de) * | 1990-07-13 | 1992-01-16 | Lenhardt Maschinenbau | Verfahren und vorrichtung zum zusammenbauen von isolierglasscheiben, die mit einem von luft verschiedenen gas gefuellt sind |
| DE4029669C1 (de) * | 1990-09-19 | 1991-07-18 | Lenhardt Maschinenbau Gmbh, 7531 Neuhausen, De | |
| EP0498787A3 (en) * | 1991-02-04 | 1992-10-14 | Peter Lisec | Method and device for manufacturing insulating glazing units |
| DE9302744U1 (de) * | 1992-12-18 | 1994-05-19 | Lisec, Peter, Amstetten-Hausmening | Vorrichtung zum Füllen von Isolierglasscheiben mit einem von Luft unterschiedlichen Gas |
| DE4307403A1 (de) * | 1993-03-09 | 1994-09-15 | Cta Composite Tech Autom Gmbh | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zum Einrichten, Gasfüllen und Verpressen von Einzelscheiben und/oder bereits vorgefertigten Scheibenanordnungen als zwei Komponenten bei der Herstellung von Isolierglasscheiben |
-
1995
- 1995-03-22 AT AT95890063T patent/ATE166420T1/de active
- 1995-03-22 EP EP95890063A patent/EP0674086B2/de not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1995-03-22 EP EP95890061A patent/EP0674085B1/de not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1995-03-22 ES ES95890064T patent/ES2118002T3/es not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1995-03-22 AT AT95890061T patent/ATE166419T1/de active
- 1995-03-22 DE DE59502206T patent/DE59502206D1/de not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1995-03-22 AT AT95890064T patent/ATE166421T1/de active
- 1995-03-22 ES ES95890061T patent/ES2118527T3/es not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1995-03-22 ES ES95890063T patent/ES2117379T5/es not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1995-03-22 DE DE59502208T patent/DE59502208D1/de not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1995-03-22 DE DE59502207T patent/DE59502207D1/de not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1995-03-22 EP EP95890064A patent/EP0674087B1/de not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1995-03-23 DE DE19510663A patent/DE19510663C2/de not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 1995-03-23 DE DE19510561A patent/DE19510561C2/de not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 1995-03-23 DE DE29504911U patent/DE29504911U1/de not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1995-03-23 DE DE29504900U patent/DE29504900U1/de not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1995-03-23 DE DE19510516A patent/DE19510516C2/de not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1995-03-24 JP JP7066421A patent/JPH0840754A/ja active Pending
- 1995-03-24 US US08/410,307 patent/US5626712A/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1995-03-24 US US08/410,311 patent/US5676782A/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1995-03-24 JP JP7066393A patent/JPH0840753A/ja active Pending
- 1995-03-24 JP JP7066494A patent/JPH0840755A/ja active Pending
- 1995-03-24 US US08/410,306 patent/US5645678A/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP2093370A2 (de) | 2008-02-20 | 2009-08-26 | For El Base- Di Davanzo Nadia & C.S.N.C. | Automatikvorrichtung zum Befüllen isolierender Verglasungselemente und entsprechendes Verfahren |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| ES2118002T3 (es) | 1998-09-01 |
| DE29504900U1 (de) | 1995-06-14 |
| DE19510561C2 (de) | 2002-02-28 |
| EP0674085A1 (de) | 1995-09-27 |
| EP0674087B1 (de) | 1998-05-20 |
| DE19510663C2 (de) | 2002-06-27 |
| DE59502207D1 (de) | 1998-06-25 |
| US5645678A (en) | 1997-07-08 |
| ES2118527T3 (es) | 1998-09-16 |
| DE19510516C2 (de) | 2002-04-11 |
| DE59502206D1 (de) | 1998-06-25 |
| EP0674086B1 (de) | 1998-05-20 |
| JPH0840755A (ja) | 1996-02-13 |
| ES2117379T3 (es) | 1998-08-01 |
| ATE166421T1 (de) | 1998-06-15 |
| EP0674086A1 (de) | 1995-09-27 |
| DE59502208D1 (de) | 1998-06-25 |
| EP0674087A1 (de) | 1995-09-27 |
| DE19510663A1 (de) | 1995-09-28 |
| DE29504911U1 (de) | 1995-06-14 |
| US5676782A (en) | 1997-10-14 |
| DE19510516A1 (de) | 1995-10-05 |
| ATE166420T1 (de) | 1998-06-15 |
| US5626712A (en) | 1997-05-06 |
| DE19510561A1 (de) | 1995-10-05 |
| EP0674085B1 (de) | 1998-05-20 |
| ATE166419T1 (de) | 1998-06-15 |
| ES2117379T5 (es) | 2005-03-16 |
| JPH0840754A (ja) | 1996-02-13 |
| JPH0840753A (ja) | 1996-02-13 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP0674086B2 (de) | Verfahren zum Zusammenbauen von Isolierglasscheiben, deren Innenraum mit einem Schwergas gefüllt ist und Vorrichtung zum Füllen von Isolierglasscheiben mit Schwergas | |
| EP0603148B1 (de) | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zum Füllen von Isolierglasscheiben mit einem von Luft unterschiedlichen Gas | |
| DE2905841C2 (de) | Verfahren und Anlage zur Herstellung einer Verbundplatte | |
| DE3101342A1 (de) | "verfahren zur herstellung von gasgefuellten isolierglaseinheiten und vorrichtung zur durchfuehrung des verfahrens" | |
| EP1769130B1 (de) | Verfahren und vorrichtung zum zusammenbauen von isolierglasscheiben, die mit einem von luft verschiedenen gas gefüllt sind | |
| DE3539879A1 (de) | Vorrichtung fuer das schlupffreie foerdern von zwei tafeln, insbesondere von glastafeln | |
| AT412719B (de) | Verfahren und vorrichtung zum bereichsweisen entschichten von glasscheiben | |
| EP1730378A2 (de) | Verfahren zum positionieren von glastafeln in einer vertikalen zusammenbau- und pressvorrichtung für isolierglasscheiben | |
| EP0250647A1 (de) | Vorrichtung zum Überziehen und Anschrumpfen einer Schrumpffolienhaube über bzw. an einen Stapel | |
| DE102005044861B3 (de) | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zum Füllen von Isolierglasscheiben mit einem von Luft verschiedenen Gas | |
| DE4238254C2 (de) | Vorrichtung zum Fördern von Isolierglasscheiben | |
| DE102004009860B4 (de) | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zum Zusammenbauen von Isolierglasscheiben, die mit einem von Luft verschiedenen Gas gefüllt sind | |
| DE4437998C2 (de) | Vorrichtung zum Zusammenbauen von Isolierglasscheiben | |
| EP0857849B1 (de) | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zum Zusammenbauen und Versiegeln von Isolierglasscheiben | |
| EP0498787A2 (de) | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zum Herstellen von Isolierglasscheiben | |
| AT407552B (de) | Vorrichtung zum zusammenbauen von isolierglasscheiben, deren innenraum mit einem schwergas gefüllt ist | |
| DE8527256U1 (de) | Vorrichtung zum Reinigen von Glastafeln | |
| AT409128B (de) | Verfahren zum zusammenbauen von isolierglasscheiben, deren innenraum mit einem schwergas gefüllt ist | |
| AT409263B (de) | Vorrichtung zum füllen von isolierglasscheiben mit füllgas | |
| AT399145B (de) | Verfahren und vorrichtung zum herstellen von isolierglasscheiben | |
| AT404132B (de) | Vorrichtung zum füllen von isolierglasscheiben mit füllgas | |
| DE7728259U1 (de) | Maschine zum bearbeiten der bretter von tuerrahmen | |
| DE10049930A1 (de) | Ummantelungsvorrichtung | |
| DE2728828A1 (de) | Maschine zum bearbeiten der bretter von tuerrahmen |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AT BE CH DE DK ES FR GB GR IE IT LI LU MC NL PT SE |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 19951005 |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 19970213 |
|
| GRAG | Despatch of communication of intention to grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS AGRA |
|
| GRAG | Despatch of communication of intention to grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS AGRA |
|
| GRAH | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS IGRA |
|
| GRAH | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS IGRA |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AT BE CH DE DK ES FR GB GR IE IT LI LU MC NL PT SE |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 19980520 |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 166420 Country of ref document: AT Date of ref document: 19980615 Kind code of ref document: T |
|
| ITF | It: translation for a ep patent filed | ||
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: NV Representative=s name: TROESCH SCHEIDEGGER WERNER AG Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: EP |
|
| ET | Fr: translation filed | ||
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 59502207 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 19980625 |
|
| GBT | Gb: translation of ep patent filed (gb section 77(6)(a)/1977) |
Effective date: 19980624 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: ES Ref legal event code: FG2A Ref document number: 2117379 Country of ref document: ES Kind code of ref document: T3 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: PT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 19980820 Ref country code: DK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 19980820 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: GERMAN |
|
| PLBQ | Unpublished change to opponent data |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS OPPO |
|
| PLBI | Opposition filed |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009260 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 19990322 |
|
| PLBF | Reply of patent proprietor to notice(s) of opposition |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS OBSO |
|
| 26 | Opposition filed |
Opponent name: LENHARDT MASCHINENBAU GMBH Effective date: 19990220 |
|
| PLBF | Reply of patent proprietor to notice(s) of opposition |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS OBSO |
|
| NLR1 | Nl: opposition has been filed with the epo |
Opponent name: LENHARDT MASCHINENBAU GMBH |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MC Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 19990930 |
|
| PLAW | Interlocutory decision in opposition |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS IDOP |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: IF02 |
|
| APAC | Appeal dossier modified |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS NOAPO |
|
| APAE | Appeal reference modified |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS REFNO |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IE Payment date: 20020308 Year of fee payment: 8 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BE Payment date: 20020312 Year of fee payment: 8 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Payment date: 20020329 Year of fee payment: 8 |
|
| APAC | Appeal dossier modified |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS NOAPO |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20030324 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20030331 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: 732E |
|
| BERE | Be: lapsed |
Owner name: *LISEC PETER Effective date: 20030331 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20031001 |
|
| NLV4 | Nl: lapsed or anulled due to non-payment of the annual fee |
Effective date: 20031001 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: TP |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: MM4A |
|
| APBU | Appeal procedure closed |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNNOA9O |
|
| APBU | Appeal procedure closed |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNNOA9O |
|
| PUAH | Patent maintained in amended form |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009272 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: PATENT MAINTAINED AS AMENDED |
|
| 27A | Patent maintained in amended form |
Effective date: 20040818 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B2 Designated state(s): AT BE CH DE DK ES FR GB GR IE IT LI LU MC NL PT SE |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: SE Ref legal event code: RPEO |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: AEN Free format text: AUFRECHTERHALTUNG DES PATENTES IN GEAENDERTER FORM |
|
| GBTA | Gb: translation of amended ep patent filed (gb section 77(6)(b)/1977) | ||
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: ES Ref legal event code: DC2A Date of ref document: 20041013 Kind code of ref document: T5 |
|
| ET3 | Fr: translation filed ** decision concerning opposition | ||
| APAH | Appeal reference modified |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSCREFNO |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Payment date: 20080313 Year of fee payment: 14 |
|
| EUG | Se: european patent has lapsed | ||
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20090323 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R082 Ref document number: 59502207 Country of ref document: DE Representative=s name: PATENTANWAELTE HENKEL, BREUER & PARTNER, DE |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CH Payment date: 20140319 Year of fee payment: 20 Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20140328 Year of fee payment: 20 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Payment date: 20140326 Year of fee payment: 20 Ref country code: AT Payment date: 20140327 Year of fee payment: 20 Ref country code: FR Payment date: 20140319 Year of fee payment: 20 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 20140319 Year of fee payment: 20 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R071 Ref document number: 59502207 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: PE20 Expiry date: 20150321 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: AT Ref legal event code: MK07 Ref document number: 166420 Country of ref document: AT Kind code of ref document: T Effective date: 20150322 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF EXPIRATION OF PROTECTION Effective date: 20150321 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: ES Ref legal event code: FD2A Effective date: 20150826 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: ES Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF EXPIRATION OF PROTECTION Effective date: 20150323 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: ES Payment date: 20140331 Year of fee payment: 20 |