WO2020153284A1 - 内容物入り容器の製造装置、製造方法および容器 - Google Patents
内容物入り容器の製造装置、製造方法および容器 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2020153284A1 WO2020153284A1 PCT/JP2020/001647 JP2020001647W WO2020153284A1 WO 2020153284 A1 WO2020153284 A1 WO 2020153284A1 JP 2020001647 W JP2020001647 W JP 2020001647W WO 2020153284 A1 WO2020153284 A1 WO 2020153284A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- surface layer
- laminated sheet
- recess
- layer
- container
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Ceased
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B29—WORKING OF PLASTICS; WORKING OF SUBSTANCES IN A PLASTIC STATE IN GENERAL
- B29C—SHAPING OR JOINING OF PLASTICS; SHAPING OF MATERIAL IN A PLASTIC STATE, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; AFTER-TREATMENT OF THE SHAPED PRODUCTS, e.g. REPAIRING
- B29C51/00—Shaping by thermoforming, i.e. shaping sheets or sheet like preforms after heating, e.g. shaping sheets in matched moulds or by deep-drawing; Apparatus therefor
- B29C51/08—Deep drawing or matched-mould forming, i.e. using mechanical means only
- B29C51/082—Deep drawing or matched-mould forming, i.e. using mechanical means only by shaping between complementary mould parts
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B29—WORKING OF PLASTICS; WORKING OF SUBSTANCES IN A PLASTIC STATE IN GENERAL
- B29B—PREPARATION OR PRETREATMENT OF THE MATERIAL TO BE SHAPED; MAKING GRANULES OR PREFORMS; RECOVERY OF PLASTICS OR OTHER CONSTITUENTS OF WASTE MATERIAL CONTAINING PLASTICS
- B29B13/00—Conditioning or physical treatment of the material to be shaped
- B29B13/02—Conditioning or physical treatment of the material to be shaped by heating
- B29B13/023—Half-products, e.g. films, plates
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B29—WORKING OF PLASTICS; WORKING OF SUBSTANCES IN A PLASTIC STATE IN GENERAL
- B29C—SHAPING OR JOINING OF PLASTICS; SHAPING OF MATERIAL IN A PLASTIC STATE, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; AFTER-TREATMENT OF THE SHAPED PRODUCTS, e.g. REPAIRING
- B29C51/00—Shaping by thermoforming, i.e. shaping sheets or sheet like preforms after heating, e.g. shaping sheets in matched moulds or by deep-drawing; Apparatus therefor
- B29C51/04—Combined thermoforming and prestretching, e.g. biaxial stretching
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B29—WORKING OF PLASTICS; WORKING OF SUBSTANCES IN A PLASTIC STATE IN GENERAL
- B29C—SHAPING OR JOINING OF PLASTICS; SHAPING OF MATERIAL IN A PLASTIC STATE, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; AFTER-TREATMENT OF THE SHAPED PRODUCTS, e.g. REPAIRING
- B29C51/00—Shaping by thermoforming, i.e. shaping sheets or sheet like preforms after heating, e.g. shaping sheets in matched moulds or by deep-drawing; Apparatus therefor
- B29C51/04—Combined thermoforming and prestretching, e.g. biaxial stretching
- B29C51/06—Combined thermoforming and prestretching, e.g. biaxial stretching using pressure difference for prestretching
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B29—WORKING OF PLASTICS; WORKING OF SUBSTANCES IN A PLASTIC STATE IN GENERAL
- B29C—SHAPING OR JOINING OF PLASTICS; SHAPING OF MATERIAL IN A PLASTIC STATE, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; AFTER-TREATMENT OF THE SHAPED PRODUCTS, e.g. REPAIRING
- B29C51/00—Shaping by thermoforming, i.e. shaping sheets or sheet like preforms after heating, e.g. shaping sheets in matched moulds or by deep-drawing; Apparatus therefor
- B29C51/08—Deep drawing or matched-mould forming, i.e. using mechanical means only
- B29C51/082—Deep drawing or matched-mould forming, i.e. using mechanical means only by shaping between complementary mould parts
- B29C51/087—Deep drawing or matched-mould forming, i.e. using mechanical means only by shaping between complementary mould parts with at least one of the mould parts comprising independently movable sections
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B29—WORKING OF PLASTICS; WORKING OF SUBSTANCES IN A PLASTIC STATE IN GENERAL
- B29C—SHAPING OR JOINING OF PLASTICS; SHAPING OF MATERIAL IN A PLASTIC STATE, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; AFTER-TREATMENT OF THE SHAPED PRODUCTS, e.g. REPAIRING
- B29C51/00—Shaping by thermoforming, i.e. shaping sheets or sheet like preforms after heating, e.g. shaping sheets in matched moulds or by deep-drawing; Apparatus therefor
- B29C51/14—Shaping by thermoforming, i.e. shaping sheets or sheet like preforms after heating, e.g. shaping sheets in matched moulds or by deep-drawing; Apparatus therefor using multilayered preforms or sheets
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B29—WORKING OF PLASTICS; WORKING OF SUBSTANCES IN A PLASTIC STATE IN GENERAL
- B29C—SHAPING OR JOINING OF PLASTICS; SHAPING OF MATERIAL IN A PLASTIC STATE, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; AFTER-TREATMENT OF THE SHAPED PRODUCTS, e.g. REPAIRING
- B29C51/00—Shaping by thermoforming, i.e. shaping sheets or sheet like preforms after heating, e.g. shaping sheets in matched moulds or by deep-drawing; Apparatus therefor
- B29C51/26—Component parts, details or accessories; Auxiliary operations
- B29C51/264—Auxiliary operations prior to the thermoforming operation, e.g. cutting
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B29—WORKING OF PLASTICS; WORKING OF SUBSTANCES IN A PLASTIC STATE IN GENERAL
- B29C—SHAPING OR JOINING OF PLASTICS; SHAPING OF MATERIAL IN A PLASTIC STATE, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; AFTER-TREATMENT OF THE SHAPED PRODUCTS, e.g. REPAIRING
- B29C51/00—Shaping by thermoforming, i.e. shaping sheets or sheet like preforms after heating, e.g. shaping sheets in matched moulds or by deep-drawing; Apparatus therefor
- B29C51/26—Component parts, details or accessories; Auxiliary operations
- B29C51/42—Heating or cooling
- B29C51/421—Heating or cooling of preforms, specially adapted for thermoforming
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B29—WORKING OF PLASTICS; WORKING OF SUBSTANCES IN A PLASTIC STATE IN GENERAL
- B29C—SHAPING OR JOINING OF PLASTICS; SHAPING OF MATERIAL IN A PLASTIC STATE, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; AFTER-TREATMENT OF THE SHAPED PRODUCTS, e.g. REPAIRING
- B29C51/00—Shaping by thermoforming, i.e. shaping sheets or sheet like preforms after heating, e.g. shaping sheets in matched moulds or by deep-drawing; Apparatus therefor
- B29C51/26—Component parts, details or accessories; Auxiliary operations
- B29C51/42—Heating or cooling
- B29C51/421—Heating or cooling of preforms, specially adapted for thermoforming
- B29C51/422—Heating or cooling of preforms, specially adapted for thermoforming to produce a temperature differential
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B29—WORKING OF PLASTICS; WORKING OF SUBSTANCES IN A PLASTIC STATE IN GENERAL
- B29C—SHAPING OR JOINING OF PLASTICS; SHAPING OF MATERIAL IN A PLASTIC STATE, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; AFTER-TREATMENT OF THE SHAPED PRODUCTS, e.g. REPAIRING
- B29C65/00—Joining or sealing of preformed parts, e.g. welding of plastics materials; Apparatus therefor
- B29C65/48—Joining or sealing of preformed parts, e.g. welding of plastics materials; Apparatus therefor using adhesives, i.e. using supplementary joining material; solvent bonding
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B29—WORKING OF PLASTICS; WORKING OF SUBSTANCES IN A PLASTIC STATE IN GENERAL
- B29C—SHAPING OR JOINING OF PLASTICS; SHAPING OF MATERIAL IN A PLASTIC STATE, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; AFTER-TREATMENT OF THE SHAPED PRODUCTS, e.g. REPAIRING
- B29C69/00—Combinations of shaping techniques not provided for in a single one of main groups B29C39/00 - B29C67/00, e.g. associations of moulding and joining techniques; Apparatus therefore
- B29C69/001—Combinations of shaping techniques not provided for in a single one of main groups B29C39/00 - B29C67/00, e.g. associations of moulding and joining techniques; Apparatus therefore a shaping technique combined with cutting, e.g. in parts or slices combined with rearranging and joining the cut parts
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B65—CONVEYING; PACKING; STORING; HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL
- B65B—MACHINES, APPARATUS OR DEVICES FOR, OR METHODS OF, PACKAGING ARTICLES OR MATERIALS; UNPACKING
- B65B9/00—Enclosing successive articles, or quantities of material, e.g. liquids or semiliquids, in flat, folded, or tubular webs of flexible sheet material; Subdividing filled flexible tubes to form packages
- B65B9/02—Enclosing successive articles, or quantities of material between opposed webs
- B65B9/04—Enclosing successive articles, or quantities of material between opposed webs one or both webs being formed with pockets for the reception of the articles, or of the quantities of material
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B65—CONVEYING; PACKING; STORING; HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL
- B65D—CONTAINERS FOR STORAGE OR TRANSPORT OF ARTICLES OR MATERIALS, e.g. BAGS, BARRELS, BOTTLES, BOXES, CANS, CARTONS, CRATES, DRUMS, JARS, TANKS, HOPPERS, FORWARDING CONTAINERS; ACCESSORIES, CLOSURES, OR FITTINGS THEREFOR; PACKAGING ELEMENTS; PACKAGES
- B65D81/00—Containers, packaging elements, or packages, for contents presenting particular transport or storage problems, or adapted to be used for non-packaging purposes after removal of contents
- B65D81/24—Adaptations for preventing deterioration or decay of contents; Applications to the container or packaging material of food preservatives, fungicides, pesticides or animal repellants
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B65—CONVEYING; PACKING; STORING; HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL
- B65D—CONTAINERS FOR STORAGE OR TRANSPORT OF ARTICLES OR MATERIALS, e.g. BAGS, BARRELS, BOTTLES, BOXES, CANS, CARTONS, CRATES, DRUMS, JARS, TANKS, HOPPERS, FORWARDING CONTAINERS; ACCESSORIES, CLOSURES, OR FITTINGS THEREFOR; PACKAGING ELEMENTS; PACKAGES
- B65D9/00—Containers having bodies formed by interconnecting or uniting two or more rigid, or substantially rigid, components made wholly or mainly of wood or substitutes therefor
- B65D9/02—Containers of curved cross-section, e.g. cylindrical boxes
- B65D9/04—Containers of curved cross-section, e.g. cylindrical boxes made up of staves, e.g. barrels for liquids
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B29—WORKING OF PLASTICS; WORKING OF SUBSTANCES IN A PLASTIC STATE IN GENERAL
- B29L—INDEXING SCHEME ASSOCIATED WITH SUBCLASS B29C, RELATING TO PARTICULAR ARTICLES
- B29L2031/00—Other particular articles
- B29L2031/56—Stoppers or lids for bottles, jars, or the like, e.g. closures
- B29L2031/565—Stoppers or lids for bottles, jars, or the like, e.g. closures for containers
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B29—WORKING OF PLASTICS; WORKING OF SUBSTANCES IN A PLASTIC STATE IN GENERAL
- B29L—INDEXING SCHEME ASSOCIATED WITH SUBCLASS B29C, RELATING TO PARTICULAR ARTICLES
- B29L2031/00—Other particular articles
- B29L2031/712—Containers; Packaging elements or accessories, Packages
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a manufacturing apparatus, a manufacturing method and a container for a container containing contents.
- a container body in which a cup-shaped recess is formed and a lid for sealing the recess are joined.
- the container body in such a container, is formed of a laminated sheet, and the interlayer adhesive force between the surface layer and the lower layer of the laminated sheet is determined by the adhesive force between the container body and the lid body.
- a technique of forming a notch in the surface layer with a flange portion extending from the opening end of the recess while making the structure weaker is also described.
- Patent Document 3 FFS (Form Fill Seal) type bag-making technology, that is, molding of the bag-shaped container and A technique has been developed in which filling and sealing of a bag-shaped container are performed in a series of steps.
- Patent Document 4 and Patent Document 5 as for a container in which a container body having a cup-shaped recess and a lid are joined, the container is manufactured and the contents are filled by the FFS method, for example, in a sterile state. It is described that the filling of the contents of the above becomes possible.
- JP 62-251363 A JP-A-63-78 JP, 2018-188196, A Japanese Patent Laid-Open No. 9-52311 JP 2004-59062A
- Patent Document 1 and Patent Document 2 described above, and formed a notch along the opening end of the recess.
- the introduction of the FFS system was also considered for the formed container.
- Patent Documents 4 and 5 only mention the FFS method for a container in which a notch is not formed.
- the present invention uses a FFS method in a container in which a container body having a cup-shaped recess formed therein and a lid that seals the recess are joined, and a notch is formed in a flange portion extending from the opening end of the recess.
- An object of the present invention is to provide a manufacturing apparatus, a manufacturing method and a container for a container containing contents, which realizes manufacturing.
- a method for manufacturing a container containing contents which comprises:
- a cup-shaped recess formed of a laminated sheet including a surface layer and a subsurface layer formed of at least one layer adjacent to the surface layer, and forming a storage space facing the surface layer
- a container body comprising a container body having a notch formed in at least a surface layer along the opening end of the recess, and a lid body made of a film which is joined to the surface layer outside the notch and seals the recess
- the subsurface layer includes a barrier layer and at least one layer that is laminated on the surface layer side of the barrier layer and on the side opposite to the surface layer, respectively, and the barrier layer is defined from the center of the total thickness of the laminated sheet to the surface layer.
- Containers are provided that are 10% or more eccentric on the opposite side.
- the container body in which the cup-shaped recess is formed and the lid that seals the recess are joined, and the notch is formed in the flange portion extending from the opening end of the recess. It is possible to realize the FFS manufacturing in the container.
- FIG. 1 It is a figure which shows schematically the manufacturing apparatus of the container with a content which concerns on one Embodiment of this invention. It is sectional drawing of the container with contents manufactured by the manufacturing apparatus shown in FIG. It is a figure which shows the structural example of the laminated sheet in one Embodiment of this invention. It is a figure which shows the structural example of the laminated sheet in one Embodiment of this invention. It is a figure which shows the structural example of the preheating apparatus contained in the manufacturing apparatus shown in FIG. It is a figure which shows the structural example of the shaping
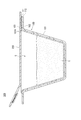
- FIG. 1 is a diagram schematically showing an apparatus for manufacturing a container with contents according to an embodiment of the present invention.
- the manufacturing apparatus 1 includes a preheating device 2, a molding device 3, a notch forming device 4, a filling device 5, a sealing device 6, and a trimming device 7.
- the laminated sheet 10, which is a raw material for the container body, is supplied to the preheating device 2 by a conveyance means such as a roll 11.
- the preheating device 2 includes heating plates 21 and 22 arranged on both surface sides of the laminated sheet 10, respectively, and preheats the laminated sheet 10 by bringing the heating plates 21 and 22 into contact with each other.
- the preheated laminated sheet 10 is supplied to the molding device 3.
- the molding device 3 is, for example, a pneumatic molding device or a plug molding device, and forms a cup-shaped recess 101, which will be described later, in the laminated sheet 10.
- the notch forming device 4 includes a blade portion as described later, and forms a notch in the laminated sheet 10 along the opening end of the formed recess 101.
- the notch is formed at least in the surface layer of the laminated sheet 10, that is, in the layer facing the storage space formed by the recess 101.
- a cooling device 35 may be disposed between the molding device 3 and the notch forming device 4. By disposing the cooling device 35, it is possible to suppress the shrinkage of the surface layer of the laminated sheet 10 after the recess 101 is formed, and improve the processing accuracy of the notch forming device 4 in the depth direction of the notch.
- the filling device 5 fills the storage space formed by the recess 101 with the content C. It should be noted that the filling here is not necessarily limited to the case where the contents C are packed in the storage space without a gap, and includes, for example, the case where the solid contents C are simply arranged in the storage space.
- the sealing device 6 includes, for example, two-stage sealing devices 61 and 62 having different temperatures and shapes of sealing regions, and the film 20 is bonded to the laminated sheet 10. The film 20 seals the recess 101 formed in the laminated sheet 10. The laminated sheet 10 and the film 20 are joined to each other outside the notch formed by the notch forming device 4.
- the trimming device 7 cuts the laminated sheet 10 together with the joined film 20.
- the container body 100 and the lid body 200 are punched from the laminated sheet 10 having the recess 101 formed therein and the film 20 bonded to the laminated sheet 10.
- the portion of the laminated sheet 10 other than the concave portion 101 becomes the flange portion 102 of the container body 100.
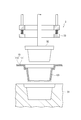
- the container 300 includes a container body 100 and a lid body 200.
- a laminated sheet including at least a surface layer 111 and a lower surface layer 112 adjacent to the surface layer 111 is formed into a shape including a cup-shaped concave portion 101 and a flange portion 102 extending from an open end 101A of the concave portion 101. It was done.
- the lower surface layer 112 of the container body 100 may include a plurality of layers, and such an example will be described later.
- a notch 103 is formed along the opening end 101A.
- the notch 103 is formed in at least the surface layer 111.
- the notch 103 may be formed to a depth halfway through the surface layer 111, may be formed to the same depth as the surface layer 111, or may be formed deeper than the surface layer 111 in the subsurface layer 112. You may have reached.
- the storage space S formed by the recess 101 faces the surface layer 111 of the container body 100.
- the storage space S is filled with the contents C.
- the lid 200 is a single-layer or multi-layer film cut into a predetermined shape.
- the lid body 200 is joined to the surface layer 111 of the container body 100 in a joining region formed on the flange portion 102 outside the notch 103, thereby sealing the concave portion 101.
- the interlayer adhesive force between the surface layer 111 and the lower surface layer 112 of the container body 100 is weaker than the adhesive force between the lid body 200 and the surface layer 111.
- the interlayer adhesive force between the surface layer 111 and the lower surface layer 112 is 0.1 kgf/25 mm or more and 2.5 kgf/25 mm or less.
- the planar shape of the container 300 including the container main body 100 and the lid 200 may be any shape such as a circle or a rectangle.
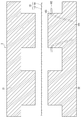
- the laminated sheet 10A includes a surface layer 111 and a lower surface layer 112.
- the surface layer 111 is formed of, for example, a polyolefin resin.
- the polyolefin resin include polypropylene resins such as homopolypropylene (HPP), random polypropylene (RPP), and block polypropylene, polyethylene resins such as high density polyethylene (HDPE) and low density polyethylene (LDPE), and Examples thereof include linear ethylene- ⁇ -olefin copolymers.
- the subsurface layer 112 includes, for example, first base material layers 121 and 127, second base material layers 122 and 126, adhesive layers 123 and 125, and an EVOH layer 124 as described below.
- the first base material layers 121, 127 and the second base material layers 122, 126 are formed of, for example, a resin containing at least one of the group consisting of an olefin resin, a polystyrene resin, and a polyester resin.
- the olefin resin include polypropylene and polyethylene.
- the polyester resin include polyethylene terephthalate (PET).
- An inorganic filler such as talc may be added to these resins in order to improve rigidity.
- the first base material layers 121 and 127 are provided with functions such as peel strength adjustment with the surface layer 111
- the second base material layers 122 and 126 are provided with functions such as cold resistance, impact resistance, and water vapor barrier property.
- the resin composition may be adjusted for these functions, and appropriate additives may be added.
- the EVOH layer 124 is formed of a resin composition containing ethylene vinyl alcohol such as ethylene-vinyl alcohol copolymer (EVOH) and functions as a barrier layer having an oxygen barrier property.
- EVOH ethylene-vinyl alcohol copolymer
- the first base material layers 121 and 127 that are respectively laminated on the surface layer 111 side of the EVOH layer 124 and on the side opposite to the surface layer 111 have substantially the same layer thickness.
- the second base material layers 122 and 126 that are respectively laminated on the surface layer 111 side of the EVOH layer 124 and on the side opposite to the surface layer 111 have substantially the same layer thickness.
- the EVOH layer 124 which is the barrier layer, is located near the total layer thickness center C t of the laminated sheet 10A in which the surface layer 111 and the lower surface layer 112 are combined.
- the layer thickness center of the EVOH layer 124 is in a range from the total layer thickness center C t of the laminated sheet 10A to less than 10% (0.1t) of the total layer thickness t of the laminated sheet 10A. Located in.
- the laminated structure of the laminated sheet 10B is the same as that of the first example, but the first base material layer 121 laminated on the surface layer 111 side of the EVOH layer 124.
- the layer thickness is larger than that of the first base material layer 121 laminated on the side opposite to the surface layer 111.
- the layer thickness of the second base material layer 122 laminated on the surface layer 111 side of the EVOH layer 124 is larger than that of the second base material layer 126 laminated on the side opposite to the surface layer 111.
- the EVOH layer 124 which is the barrier layer, is eccentric by 10% or more from the center C t of the total layer thickness of the laminated sheet 10B on the side opposite to the surface layer 111. That is, in the second example, the layer thickness center of the EVOH layer 124 is positioned away 10% (0.1 t) or more of the total thickness t of the laminated sheet 10B from the total thickness center C t of the laminated sheet 10B.
- the allowable fluctuation range of the depth of the notch 103 (see FIG. 2) formed in the surface layer 111 becomes large. That is, in the second example, even if the notch 103 is formed deeper than the designed depth, the notch 103 hardly reaches the EVOH layer 124. Therefore, in the case of the second example, the notch forming device 4 shown in FIG. 1 can tolerate a larger processing error than in the case of the first example.
- the first base material layers 121 and 127 or the second base material layers 122 and 126 may be used on the opposite side of the surface layer 111 and the surface layer 111.
- the EVOH layer 124 may be eccentric by providing a difference in layer thickness.
- the subsurface layer 112 may include an additional layer laminated only on the surface layer 111 side of the EVOH layer 124, and the EVOH layer 124 may be eccentric depending on the layer thickness of the additional layer.
- FIG. 5 is a diagram showing a configuration example of a preheating device included in the manufacturing apparatus shown in FIG.
- the preheating device 2 includes the heating plates 21 and 22 arranged on both surface sides of the laminated sheet 10, respectively.
- the heating plates 21 and 22 approaching and separating from each other in synchronization with the conveyance of the laminated sheet 10, the region of the laminated sheet 10 in which the concave portion 101 is formed and its vicinity are spotwise heated in the molding device 3 in the subsequent stage.
- the heating plate 21 is brought into contact with the surface layer 111 side of the laminated sheet 10
- the heating plate 22 is brought into contact with the lower surface layer 112 side of the laminated sheet 10, that is, the side opposite to the surface layer 111.
- the heating temperature by the heating plate 21 is lower than the heating temperature by the heating plate 22.
- the heating temperature by the heating plate 21 is lower than the heating temperature by the heating plate 22 by 10° C. or more.
- the heating temperature is higher, it is delayed that some regions of the laminated sheet 10 are attached to and separated from the heating plates 21 and 22 when the heating plates 21 and 22 are separated from the laminated sheet 10, and as a result, the temperature of the regions is increased. Higher temperature unevenness than other parts occurs.
- the heating temperature by the heating plate 21 By lowering the heating temperature by the heating plate 21, the occurrence of such temperature unevenness on the surface layer 111 side of the laminated sheet 10 is suppressed, and the notch 103 formed in the surface layer 111 by the notch forming device 4 in the subsequent stage is suppressed.
- the depth accuracy can be improved.
- FIG. 5 virtually shows a position where the trim device 7 cuts the laminated sheet 10 together with the film 20 after the recess 101 and the notch 103 are formed in the laminated sheet 10.
- This cutting position is outside the notch 103 and outside the region of the preheating device 2 where the heating plate 21 on the surface layer 111 side is in contact.
- the preheating of the laminated sheet 10 in the preheating device 2 is performed to form the recess 101, but in the region outside the opening end of the recess 101, that is, in the region where the flange 102 will be formed later, the layer thickness of the surface layer 111 due to heating is
- the preheated region is preferably as small as possible. Therefore, in the illustrated example, the area to which the heating plate 21 is brought into contact is smaller than the cutting position by the trimming device 7, that is, the outer edge of the flange portion 102, although it includes the notch 103 formed near the opening end.
- FIG. 6 is a diagram showing a configuration example of a molding apparatus included in the manufacturing apparatus shown in FIG.
- the molding device 3 includes a concave member 31 having a shape corresponding to the concave portion 101 formed in the laminated sheet 10, a plug 32, and a pressing member 33.
- the laminated sheet 10 is pressed against the concave member 31 using the plug 32, and the concave portion 101 is formed by performing pressure molding by suction means (not shown).
- the pressing member 33 presses the laminated sheet 10 toward the peripheral edge portion of the concave member 31 in a region adjacent to the outside of the opening end 101A of the concave portion 101.
- the pressing member 33 and the peripheral portion of the concave member 31 constitute a means for sandwiching the laminated sheet 10 in a region adjacent to the outside of the opening end 101A when forming the concave portion 101.
- the depth accuracy of the notch 103 formed in the surface layer 111 by the notch forming device 4 in the subsequent stage can be improved.
- the recess 101 is formed by plug-assisted pressure molding, but the recess 101 may be formed by pressure molding without a plug, plug molding, or the like.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Food Science & Technology (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Thermal Sciences (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Wood Science & Technology (AREA)
- Packages (AREA)
- Containers And Plastic Fillers For Packaging (AREA)
- Blow-Moulding Or Thermoforming Of Plastics Or The Like (AREA)
- Containers Having Bodies Formed In One Piece (AREA)
- Laminated Bodies (AREA)
- Wrappers (AREA)
Priority Applications (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020217023676A KR102690116B1 (ko) | 2019-01-23 | 2020-01-20 | 내용물들이 용기의 제조 장치, 제조 방법 및 용기 |
| CN202080010243.7A CN113329860B (zh) | 2019-01-23 | 2020-01-20 | 内容物放入容器的制造装置、制造方法以及容器 |
| KR1020247025255A KR20240118906A (ko) | 2019-01-23 | 2020-01-20 | 내용물들이 용기의 제조 장치, 제조 방법 및 용기 |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2019009087A JP6882350B2 (ja) | 2019-01-23 | 2019-01-23 | 内容物入り容器の製造装置、製造方法および容器 |
| JP2019-009087 | 2019-01-23 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2020153284A1 true WO2020153284A1 (ja) | 2020-07-30 |
Family
ID=71736665
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2020/001647 Ceased WO2020153284A1 (ja) | 2019-01-23 | 2020-01-20 | 内容物入り容器の製造装置、製造方法および容器 |
Country Status (5)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (2) | JP6882350B2 (enExample) |
| KR (2) | KR102690116B1 (enExample) |
| CN (1) | CN113329860B (enExample) |
| TW (1) | TWI820293B (enExample) |
| WO (1) | WO2020153284A1 (enExample) |
Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS6396062A (ja) * | 1986-09-30 | 1988-04-26 | 出光石油化学株式会社 | 物品の充填包装方法および装置 |
| JPH03111269A (ja) * | 1989-09-22 | 1991-05-13 | Showa Alum Corp | 食品包装用容器 |
| JPH03281218A (ja) * | 1990-03-30 | 1991-12-11 | Sumitomo Bakelite Co Ltd | 多層容器の成形方法 |
| JP2003081206A (ja) * | 2001-09-10 | 2003-03-19 | Omori Mach Co Ltd | Ptp包装機並びに包装方法 |
| JP2007069972A (ja) * | 2005-09-09 | 2007-03-22 | Asahi Kasei Fibers Corp | 通気性の成型容器およびその製造方法 |
| JP2014198408A (ja) * | 2013-03-29 | 2014-10-23 | 出光ユニテック株式会社 | 積層シート、容器本体、包装容器、該積層シートの製造方法および該容器本体の製造方法 |
Family Cites Families (17)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CA1303522C (en) * | 1986-04-08 | 1992-06-16 | Takanori Suzuki | Easily-openable packaging container |
| JPS62251363A (ja) | 1986-04-08 | 1987-11-02 | 出光石油化学株式会社 | 簡易ピ−ル容器 |
| JP2724355B2 (ja) * | 1990-06-15 | 1998-03-09 | 出光石油化学株式会社 | 易開封性容器及びその製造方法 |
| IL110356A (en) * | 1993-07-29 | 1997-04-15 | Int Paper Co | Radio-frequency-sealable, non-foil packaging structures |
| JPH0952311A (ja) | 1995-08-10 | 1997-02-25 | Idemitsu Petrochem Co Ltd | 多層構造物及びそれを用いた容器 |
| DE19840046A1 (de) * | 1998-09-02 | 2000-03-09 | Convenience Food Sys Bv | Verpackungsmaterial mit einer Schicht aus geschäumtenm Polyolefin |
| AU5976100A (en) * | 1999-06-21 | 2001-01-09 | Cryovac, Inc. | Easy-openable pouch and oriented multi-layer thermoplastic film suitably employed in the manufacture thereof |
| JP2004059062A (ja) | 2002-07-29 | 2004-02-26 | Denki Kagaku Kogyo Kk | 蓋材及び、包装体の製造方法 |
| KR101032194B1 (ko) * | 2002-11-19 | 2011-05-02 | 이데미쓰 유니테크 가부시키가이샤 | 다층 시이트, 용기, 용이개봉성 포장체 |
| JP4133436B2 (ja) * | 2003-02-26 | 2008-08-13 | 出光ユニテック株式会社 | 易開封性包装体および易開封性包装体の製造方法 |
| JP4146267B2 (ja) * | 2003-04-08 | 2008-09-10 | 出光ユニテック株式会社 | 容器、包装体及び容器の製造方法 |
| TWI482726B (zh) * | 2009-09-02 | 2015-05-01 | Idemitsu Unitech Co Ltd | 包裝容器、其製造方法及製造裝置 |
| TWI617489B (zh) * | 2013-04-09 | 2018-03-11 | 陶氏全球科技有限責任公司 | 用於製造超音波封口之方法以及具有該封口之薄膜結構及軟容器 |
| JP6263907B2 (ja) * | 2013-08-30 | 2018-01-24 | 凸版印刷株式会社 | 容器封止構造およびインナーシール材 |
| TWI540468B (zh) * | 2014-06-04 | 2016-07-01 | Position and track detection device | |
| CN107428145B (zh) * | 2015-04-08 | 2019-12-20 | 电化株式会社 | 热塑性多层树脂片材及使用该热塑性多层树脂片材的容器 |
| JP6894753B2 (ja) | 2017-05-08 | 2021-06-30 | 出光ユニテック株式会社 | 袋体、フィルム体、及び袋体の製造方法 |
-
2019
- 2019-01-23 JP JP2019009087A patent/JP6882350B2/ja active Active
-
2020
- 2020-01-20 KR KR1020217023676A patent/KR102690116B1/ko active Active
- 2020-01-20 CN CN202080010243.7A patent/CN113329860B/zh active Active
- 2020-01-20 WO PCT/JP2020/001647 patent/WO2020153284A1/ja not_active Ceased
- 2020-01-20 KR KR1020247025255A patent/KR20240118906A/ko active Pending
- 2020-01-22 TW TW109102471A patent/TWI820293B/zh active
-
2021
- 2021-04-27 JP JP2021075014A patent/JP6915185B2/ja active Active
Patent Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS6396062A (ja) * | 1986-09-30 | 1988-04-26 | 出光石油化学株式会社 | 物品の充填包装方法および装置 |
| JPH03111269A (ja) * | 1989-09-22 | 1991-05-13 | Showa Alum Corp | 食品包装用容器 |
| JPH03281218A (ja) * | 1990-03-30 | 1991-12-11 | Sumitomo Bakelite Co Ltd | 多層容器の成形方法 |
| JP2003081206A (ja) * | 2001-09-10 | 2003-03-19 | Omori Mach Co Ltd | Ptp包装機並びに包装方法 |
| JP2007069972A (ja) * | 2005-09-09 | 2007-03-22 | Asahi Kasei Fibers Corp | 通気性の成型容器およびその製造方法 |
| JP2014198408A (ja) * | 2013-03-29 | 2014-10-23 | 出光ユニテック株式会社 | 積層シート、容器本体、包装容器、該積層シートの製造方法および該容器本体の製造方法 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN113329860A (zh) | 2021-08-31 |
| JP6915185B2 (ja) | 2021-08-04 |
| KR20210116499A (ko) | 2021-09-27 |
| CN113329860B (zh) | 2023-12-19 |
| KR20240118906A (ko) | 2024-08-05 |
| JP2021104865A (ja) | 2021-07-26 |
| JP2020117262A (ja) | 2020-08-06 |
| KR102690116B1 (ko) | 2024-07-31 |
| TWI820293B (zh) | 2023-11-01 |
| JP6882350B2 (ja) | 2021-06-02 |
| TW202039313A (zh) | 2020-11-01 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN101426688B (zh) | 一种用于生产具有阻隔特性的可分离地连接的容器 | |
| JP2724355B2 (ja) | 易開封性容器及びその製造方法 | |
| KR20160084435A (ko) | 용기 본체, 용기 및 용기의 제조 방법 | |
| JP4717656B2 (ja) | 易開封性容器、容器本体、易開封性容器の製造方法、及び易開封性容器の製造装置 | |
| JP6915185B2 (ja) | 内容物入り容器の製造装置、製造方法、容器および積層シート | |
| JPH10202801A (ja) | 多層シート及び易開封容器 | |
| JP2009034986A (ja) | 多層シート、容器および包装体 | |
| JP2006021409A (ja) | 積層シート、当該積層シートからなる容器、及び当該容器の製造方法 | |
| JP2018167862A (ja) | 蓋付容器 | |
| JP7119489B2 (ja) | 被覆積層体、複合成形容器および複合成形容器の製造方法 | |
| JP3966947B2 (ja) | 易開封性密封容器とその製造方法 | |
| JP2000343603A (ja) | パウチフィルムへの膨らみ部の形成方法、及びその形成方法による膨らみ部を備えたパウチ | |
| JP2022062924A (ja) | 内容物入り容器の製造装置および製造方法 | |
| JP7075424B2 (ja) | 充填食品用紙容器 | |
| JP2018118485A (ja) | 容器の製造装置、および、容器の製造方法 | |
| JP2575709B2 (ja) | 易開封性密封容器およびその製造方法 | |
| JP7639290B2 (ja) | 多層フイルム、食品包装用シート、および食品容器、ならびに容器製造方法 | |
| KR20190050290A (ko) | 포장체 및 그 제조 방법 | |
| JP6527722B2 (ja) | 容器、包装体、容器の加工方法、包装体の製造方法、および、容器の加工装置 | |
| JP2020117262A5 (enExample) | ||
| JP2545529B2 (ja) | 容器の成形打抜き方法 | |
| JP2014198575A (ja) | 容器本体、容器、成形方法、および成形機 | |
| JP6183587B2 (ja) | 容器のヒートシール方法、ヒートシールヘッド及び容器 | |
| WO2021130872A1 (ja) | 包装容器、並びにその製造方法及びリサイクル方法 | |
| JPH0696263B2 (ja) | 容器の製造方法 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 20745722 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 20745722 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |