KR20130040779A - 양면에 칩이 장착되는 웨이퍼를 제작하기 위한 방법 - Google Patents
양면에 칩이 장착되는 웨이퍼를 제작하기 위한 방법 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- KR20130040779A KR20130040779A KR1020127023406A KR20127023406A KR20130040779A KR 20130040779 A KR20130040779 A KR 20130040779A KR 1020127023406 A KR1020127023406 A KR 1020127023406A KR 20127023406 A KR20127023406 A KR 20127023406A KR 20130040779 A KR20130040779 A KR 20130040779A
- Authority
- KR
- South Korea
- Prior art keywords
- wafer
- adhesive layer
- intermediate layer
- layer
- carrier
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/67—Apparatus specially adapted for handling semiconductor or electric solid state devices during manufacture or treatment thereof; Apparatus specially adapted for handling wafers during manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or electric solid state devices or components ; Apparatus not specifically provided for elsewhere
- H01L21/683—Apparatus specially adapted for handling semiconductor or electric solid state devices during manufacture or treatment thereof; Apparatus specially adapted for handling wafers during manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or electric solid state devices or components ; Apparatus not specifically provided for elsewhere for supporting or gripping
- H01L21/6835—Apparatus specially adapted for handling semiconductor or electric solid state devices during manufacture or treatment thereof; Apparatus specially adapted for handling wafers during manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or electric solid state devices or components ; Apparatus not specifically provided for elsewhere for supporting or gripping using temporarily an auxiliary support
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/67—Apparatus specially adapted for handling semiconductor or electric solid state devices during manufacture or treatment thereof; Apparatus specially adapted for handling wafers during manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or electric solid state devices or components ; Apparatus not specifically provided for elsewhere
- H01L21/68—Apparatus specially adapted for handling semiconductor or electric solid state devices during manufacture or treatment thereof; Apparatus specially adapted for handling wafers during manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or electric solid state devices or components ; Apparatus not specifically provided for elsewhere for positioning, orientation or alignment
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/04—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof the devices having at least one potential-jump barrier or surface barrier, e.g. PN junction, depletion layer or carrier concentration layer
- H01L21/18—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof the devices having at least one potential-jump barrier or surface barrier, e.g. PN junction, depletion layer or carrier concentration layer the devices having semiconductor bodies comprising elements of Group IV of the Periodic System or AIIIBV compounds with or without impurities, e.g. doping materials
- H01L21/185—Joining of semiconductor bodies for junction formation
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L23/00—Details of semiconductor or other solid state devices
- H01L23/28—Encapsulations, e.g. encapsulating layers, coatings, e.g. for protection
- H01L23/31—Encapsulations, e.g. encapsulating layers, coatings, e.g. for protection characterised by the arrangement or shape
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L24/00—Arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies; Methods or apparatus related thereto
- H01L24/93—Batch processes
- H01L24/95—Batch processes at chip-level, i.e. with connecting carried out on a plurality of singulated devices, i.e. on diced chips
- H01L24/97—Batch processes at chip-level, i.e. with connecting carried out on a plurality of singulated devices, i.e. on diced chips the devices being connected to a common substrate, e.g. interposer, said common substrate being separable into individual assemblies after connecting
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L25/00—Assemblies consisting of a plurality of individual semiconductor or other solid state devices ; Multistep manufacturing processes thereof
- H01L25/03—Assemblies consisting of a plurality of individual semiconductor or other solid state devices ; Multistep manufacturing processes thereof all the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/00, or in a single subclass of H10K, H10N, e.g. assemblies of rectifier diodes
- H01L25/04—Assemblies consisting of a plurality of individual semiconductor or other solid state devices ; Multistep manufacturing processes thereof all the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/00, or in a single subclass of H10K, H10N, e.g. assemblies of rectifier diodes the devices not having separate containers
- H01L25/065—Assemblies consisting of a plurality of individual semiconductor or other solid state devices ; Multistep manufacturing processes thereof all the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/00, or in a single subclass of H10K, H10N, e.g. assemblies of rectifier diodes the devices not having separate containers the devices being of a type provided for in group H01L27/00
- H01L25/0657—Stacked arrangements of devices
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L25/00—Assemblies consisting of a plurality of individual semiconductor or other solid state devices ; Multistep manufacturing processes thereof
- H01L25/50—Multistep manufacturing processes of assemblies consisting of devices, each device being of a type provided for in group H01L27/00 or H01L29/00
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/04—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof the devices having at least one potential-jump barrier or surface barrier, e.g. PN junction, depletion layer or carrier concentration layer
- H01L21/48—Manufacture or treatment of parts, e.g. containers, prior to assembly of the devices, using processes not provided for in a single one of the subgroups H01L21/06 - H01L21/326
- H01L21/4814—Conductive parts
- H01L21/4846—Leads on or in insulating or insulated substrates, e.g. metallisation
- H01L21/486—Via connections through the substrate with or without pins
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/04—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof the devices having at least one potential-jump barrier or surface barrier, e.g. PN junction, depletion layer or carrier concentration layer
- H01L21/50—Assembly of semiconductor devices using processes or apparatus not provided for in a single one of the subgroups H01L21/06 - H01L21/326, e.g. sealing of a cap to a base of a container
- H01L21/56—Encapsulations, e.g. encapsulation layers, coatings
- H01L21/561—Batch processing
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2221/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof covered by H01L21/00
- H01L2221/67—Apparatus for handling semiconductor or electric solid state devices during manufacture or treatment thereof; Apparatus for handling wafers during manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or electric solid state devices or components; Apparatus not specifically provided for elsewhere
- H01L2221/683—Apparatus for handling semiconductor or electric solid state devices during manufacture or treatment thereof; Apparatus for handling wafers during manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or electric solid state devices or components; Apparatus not specifically provided for elsewhere for supporting or gripping
- H01L2221/68304—Apparatus for handling semiconductor or electric solid state devices during manufacture or treatment thereof; Apparatus for handling wafers during manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or electric solid state devices or components; Apparatus not specifically provided for elsewhere for supporting or gripping using temporarily an auxiliary support
- H01L2221/68318—Auxiliary support including means facilitating the separation of a device or wafer from the auxiliary support
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2221/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof covered by H01L21/00
- H01L2221/67—Apparatus for handling semiconductor or electric solid state devices during manufacture or treatment thereof; Apparatus for handling wafers during manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or electric solid state devices or components; Apparatus not specifically provided for elsewhere
- H01L2221/683—Apparatus for handling semiconductor or electric solid state devices during manufacture or treatment thereof; Apparatus for handling wafers during manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or electric solid state devices or components; Apparatus not specifically provided for elsewhere for supporting or gripping
- H01L2221/68304—Apparatus for handling semiconductor or electric solid state devices during manufacture or treatment thereof; Apparatus for handling wafers during manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or electric solid state devices or components; Apparatus not specifically provided for elsewhere for supporting or gripping using temporarily an auxiliary support
- H01L2221/68327—Apparatus for handling semiconductor or electric solid state devices during manufacture or treatment thereof; Apparatus for handling wafers during manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or electric solid state devices or components; Apparatus not specifically provided for elsewhere for supporting or gripping using temporarily an auxiliary support used during dicing or grinding
- H01L2221/68331—Apparatus for handling semiconductor or electric solid state devices during manufacture or treatment thereof; Apparatus for handling wafers during manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or electric solid state devices or components; Apparatus not specifically provided for elsewhere for supporting or gripping using temporarily an auxiliary support used during dicing or grinding of passive members, e.g. die mounting substrate
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2221/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof covered by H01L21/00
- H01L2221/67—Apparatus for handling semiconductor or electric solid state devices during manufacture or treatment thereof; Apparatus for handling wafers during manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or electric solid state devices or components; Apparatus not specifically provided for elsewhere
- H01L2221/683—Apparatus for handling semiconductor or electric solid state devices during manufacture or treatment thereof; Apparatus for handling wafers during manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or electric solid state devices or components; Apparatus not specifically provided for elsewhere for supporting or gripping
- H01L2221/68304—Apparatus for handling semiconductor or electric solid state devices during manufacture or treatment thereof; Apparatus for handling wafers during manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or electric solid state devices or components; Apparatus not specifically provided for elsewhere for supporting or gripping using temporarily an auxiliary support
- H01L2221/68372—Apparatus for handling semiconductor or electric solid state devices during manufacture or treatment thereof; Apparatus for handling wafers during manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or electric solid state devices or components; Apparatus not specifically provided for elsewhere for supporting or gripping using temporarily an auxiliary support used to support a device or wafer when forming electrical connections thereto
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2221/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof covered by H01L21/00
- H01L2221/67—Apparatus for handling semiconductor or electric solid state devices during manufacture or treatment thereof; Apparatus for handling wafers during manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or electric solid state devices or components; Apparatus not specifically provided for elsewhere
- H01L2221/683—Apparatus for handling semiconductor or electric solid state devices during manufacture or treatment thereof; Apparatus for handling wafers during manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or electric solid state devices or components; Apparatus not specifically provided for elsewhere for supporting or gripping
- H01L2221/68304—Apparatus for handling semiconductor or electric solid state devices during manufacture or treatment thereof; Apparatus for handling wafers during manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or electric solid state devices or components; Apparatus not specifically provided for elsewhere for supporting or gripping using temporarily an auxiliary support
- H01L2221/68381—Details of chemical or physical process used for separating the auxiliary support from a device or wafer
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2221/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof covered by H01L21/00
- H01L2221/67—Apparatus for handling semiconductor or electric solid state devices during manufacture or treatment thereof; Apparatus for handling wafers during manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or electric solid state devices or components; Apparatus not specifically provided for elsewhere
- H01L2221/683—Apparatus for handling semiconductor or electric solid state devices during manufacture or treatment thereof; Apparatus for handling wafers during manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or electric solid state devices or components; Apparatus not specifically provided for elsewhere for supporting or gripping
- H01L2221/68304—Apparatus for handling semiconductor or electric solid state devices during manufacture or treatment thereof; Apparatus for handling wafers during manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or electric solid state devices or components; Apparatus not specifically provided for elsewhere for supporting or gripping using temporarily an auxiliary support
- H01L2221/68381—Details of chemical or physical process used for separating the auxiliary support from a device or wafer
- H01L2221/68386—Separation by peeling
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2221/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof covered by H01L21/00
- H01L2221/67—Apparatus for handling semiconductor or electric solid state devices during manufacture or treatment thereof; Apparatus for handling wafers during manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or electric solid state devices or components; Apparatus not specifically provided for elsewhere
- H01L2221/683—Apparatus for handling semiconductor or electric solid state devices during manufacture or treatment thereof; Apparatus for handling wafers during manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or electric solid state devices or components; Apparatus not specifically provided for elsewhere for supporting or gripping
- H01L2221/68304—Apparatus for handling semiconductor or electric solid state devices during manufacture or treatment thereof; Apparatus for handling wafers during manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or electric solid state devices or components; Apparatus not specifically provided for elsewhere for supporting or gripping using temporarily an auxiliary support
- H01L2221/68381—Details of chemical or physical process used for separating the auxiliary support from a device or wafer
- H01L2221/68386—Separation by peeling
- H01L2221/6839—Separation by peeling using peeling wedge or knife or bar
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/10—Bump connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/15—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors after the connecting process
- H01L2224/16—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors after the connecting process of an individual bump connector
- H01L2224/161—Disposition
- H01L2224/16151—Disposition the bump connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive
- H01L2224/16221—Disposition the bump connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked
- H01L2224/16225—Disposition the bump connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked the item being non-metallic, e.g. insulating substrate with or without metallisation
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/10—Bump connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/15—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors after the connecting process
- H01L2224/16—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors after the connecting process of an individual bump connector
- H01L2224/161—Disposition
- H01L2224/16151—Disposition the bump connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive
- H01L2224/16221—Disposition the bump connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked
- H01L2224/16225—Disposition the bump connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked the item being non-metallic, e.g. insulating substrate with or without metallisation
- H01L2224/16235—Disposition the bump connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked the item being non-metallic, e.g. insulating substrate with or without metallisation the bump connector connecting to a via metallisation of the item
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/80—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected
- H01L2224/81—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected using a bump connector
- H01L2224/81001—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected using a bump connector involving a temporary auxiliary member not forming part of the bonding apparatus
- H01L2224/81005—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected using a bump connector involving a temporary auxiliary member not forming part of the bonding apparatus being a temporary or sacrificial substrate
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/80—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected
- H01L2224/81—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected using a bump connector
- H01L2224/8119—Arrangement of the bump connectors prior to mounting
- H01L2224/81192—Arrangement of the bump connectors prior to mounting wherein the bump connectors are disposed only on another item or body to be connected to the semiconductor or solid-state body
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/93—Batch processes
- H01L2224/95—Batch processes at chip-level, i.e. with connecting carried out on a plurality of singulated devices, i.e. on diced chips
- H01L2224/95001—Batch processes at chip-level, i.e. with connecting carried out on a plurality of singulated devices, i.e. on diced chips involving a temporary auxiliary member not forming part of the bonding apparatus, e.g. removable or sacrificial coating, film or substrate
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/93—Batch processes
- H01L2224/95—Batch processes at chip-level, i.e. with connecting carried out on a plurality of singulated devices, i.e. on diced chips
- H01L2224/97—Batch processes at chip-level, i.e. with connecting carried out on a plurality of singulated devices, i.e. on diced chips the devices being connected to a common substrate, e.g. interposer, said common substrate being separable into individual assemblies after connecting
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2225/00—Details relating to assemblies covered by the group H01L25/00 but not provided for in its subgroups
- H01L2225/03—All the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/648 and H10K99/00
- H01L2225/04—All the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/648 and H10K99/00 the devices not having separate containers
- H01L2225/065—All the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/648 and H10K99/00 the devices not having separate containers the devices being of a type provided for in group H01L27/00
- H01L2225/06503—Stacked arrangements of devices
- H01L2225/06517—Bump or bump-like direct electrical connections from device to substrate
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2225/00—Details relating to assemblies covered by the group H01L25/00 but not provided for in its subgroups
- H01L2225/03—All the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/648 and H10K99/00
- H01L2225/04—All the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/648 and H10K99/00 the devices not having separate containers
- H01L2225/065—All the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/648 and H10K99/00 the devices not having separate containers the devices being of a type provided for in group H01L27/00
- H01L2225/06503—Stacked arrangements of devices
- H01L2225/06541—Conductive via connections through the device, e.g. vertical interconnects, through silicon via [TSV]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2225/00—Details relating to assemblies covered by the group H01L25/00 but not provided for in its subgroups
- H01L2225/03—All the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/648 and H10K99/00
- H01L2225/04—All the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/648 and H10K99/00 the devices not having separate containers
- H01L2225/065—All the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/648 and H10K99/00 the devices not having separate containers the devices being of a type provided for in group H01L27/00
- H01L2225/06503—Stacked arrangements of devices
- H01L2225/06572—Auxiliary carrier between devices, the carrier having an electrical connection structure
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L23/00—Details of semiconductor or other solid state devices
- H01L23/52—Arrangements for conducting electric current within the device in operation from one component to another, i.e. interconnections, e.g. wires, lead frames
- H01L23/538—Arrangements for conducting electric current within the device in operation from one component to another, i.e. interconnections, e.g. wires, lead frames the interconnection structure between a plurality of semiconductor chips being formed on, or in, insulating substrates
- H01L23/5384—Conductive vias through the substrate with or without pins, e.g. buried coaxial conductors
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L24/00—Arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies; Methods or apparatus related thereto
- H01L24/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L24/10—Bump connectors ; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L24/15—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors after the connecting process
- H01L24/16—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors after the connecting process of an individual bump connector
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L24/00—Arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies; Methods or apparatus related thereto
- H01L24/80—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected
- H01L24/81—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected using a bump connector
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L25/00—Assemblies consisting of a plurality of individual semiconductor or other solid state devices ; Multistep manufacturing processes thereof
- H01L25/03—Assemblies consisting of a plurality of individual semiconductor or other solid state devices ; Multistep manufacturing processes thereof all the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/00, or in a single subclass of H10K, H10N, e.g. assemblies of rectifier diodes
- H01L25/04—Assemblies consisting of a plurality of individual semiconductor or other solid state devices ; Multistep manufacturing processes thereof all the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/00, or in a single subclass of H10K, H10N, e.g. assemblies of rectifier diodes the devices not having separate containers
- H01L25/065—Assemblies consisting of a plurality of individual semiconductor or other solid state devices ; Multistep manufacturing processes thereof all the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/00, or in a single subclass of H10K, H10N, e.g. assemblies of rectifier diodes the devices not having separate containers the devices being of a type provided for in group H01L27/00
- H01L25/0652—Assemblies consisting of a plurality of individual semiconductor or other solid state devices ; Multistep manufacturing processes thereof all the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/00, or in a single subclass of H10K, H10N, e.g. assemblies of rectifier diodes the devices not having separate containers the devices being of a type provided for in group H01L27/00 the devices being arranged next and on each other, i.e. mixed assemblies
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L25/00—Assemblies consisting of a plurality of individual semiconductor or other solid state devices ; Multistep manufacturing processes thereof
- H01L25/03—Assemblies consisting of a plurality of individual semiconductor or other solid state devices ; Multistep manufacturing processes thereof all the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/00, or in a single subclass of H10K, H10N, e.g. assemblies of rectifier diodes
- H01L25/10—Assemblies consisting of a plurality of individual semiconductor or other solid state devices ; Multistep manufacturing processes thereof all the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/00, or in a single subclass of H10K, H10N, e.g. assemblies of rectifier diodes the devices having separate containers
- H01L25/105—Assemblies consisting of a plurality of individual semiconductor or other solid state devices ; Multistep manufacturing processes thereof all the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/00, or in a single subclass of H10K, H10N, e.g. assemblies of rectifier diodes the devices having separate containers the devices being of a type provided for in group H01L27/00
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01005—Boron [B]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01013—Aluminum [Al]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01033—Arsenic [As]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01052—Tellurium [Te]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01082—Lead [Pb]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/095—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00 with a principal constituent of the material being a combination of two or more materials provided in the groups H01L2924/013 - H01L2924/0715
- H01L2924/097—Glass-ceramics, e.g. devitrified glass
- H01L2924/09701—Low temperature co-fired ceramic [LTCC]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/10—Details of semiconductor or other solid state devices to be connected
- H01L2924/11—Device type
- H01L2924/12—Passive devices, e.g. 2 terminal devices
- H01L2924/1204—Optical Diode
- H01L2924/12042—LASER
Abstract
본 발명은 칩(12, 15)이 양면에 장착되는 제품 웨이퍼(1)를 제작하기 위한 방법에 관한 것이며, 상기 방법은, 특히, 제품 웨이퍼의 제 1 면(3)을 가공하는 단계와, 제품 웨이퍼(1)의 제 1 면(3)을, 적어도 변부 측에 제공되는 하나의 제 1 접착 층(6)으로 구성된 제 1 중간 층(18)을 갖는 제 1 강성 캐리어 웨이퍼(8)로 접합하는 단계와, 상기 제 1 면(3)의 반대편의 제품 웨이퍼(1)의 제 2 면(2)을 가공하는 단계, 제품 웨이퍼(1)의 제 2 면(2)을, 적어도 변부 측에 제공되는 하나의 제 2 접착 층(14)으로 구성된 제 2 중간 층(17)을 갖는 제 2 강성 캐리어 웨이퍼(13)로 접합하는 단계를 포함하며, 제 2 캐리어 웨이퍼(13)보다 먼저 제 1 캐리어 웨이퍼(8)가 선택적으로 분리될 수 있도록 제 1 중간 층(18)과 제 2 중간 층(17)은 상이하게 만들어진다.
Description
본 발명은 청구항 1에서 청구되는 바와 같이, 특히, 양면에 칩(chip)이 제공되는 제품 웨이퍼(product wafer)를 제작하기 위한 방법에 관한 것이다.
오늘날 생산되는 웨이퍼의 대부분은 하나의 면에만, 칩(chip), 즉 이른바 다이스(dice)가 제공되어 있다. 웨이퍼는 대량 생산되게 되었으며, 동시에, 점점 더 작아지는 구조를 구현하기 위한 산업상 요건이 존재한다. 이는 또한, 특히, 반복적으로 적층되는 다층 웨이퍼의 경우, 웨이퍼의 두께에 적용된다.
이용 가능한 공간을 더 최적으로 사용하기 위해, 최근 들어 점차 웨이퍼의 양면에 칩 또는 다이스가 위치하고, TSV(Through Silicon Via)가 제품 웨이퍼의 앞면과 뒷면 사이의 전기적 접촉을 가능하게 할 수 있는 것이 필요하다.
이들 양면 웨이퍼를 생산함에 있어 가장 큰 문제점은, 여러 다른 생산 단계, 가령, 접합(bonding), 분리(debonding), 정렬(alignment), 연마(grinding), 에칭(etching), 및 그 밖의 다른 많은 단계를 포함할 수 있는 대량 생산 동안의 핸들링을 포함한다. 특히, 생산 공정 중에 제공되는 제품 웨이퍼의 씨닝/백 씨닝(thinning/back thinning) 공정 때문에, 캐리어 웨이퍼(carrier wafer)가, 일반적으로 300㎜의 지름을 갖는 대면적 제품 웨이퍼(product wafer)를 안정화할 필요가 있다.
따라서 캐리어 웨이퍼가 칩이 제공되는 면의 반대편 면에 임시로 접합될 수 있기 때문에, 1면 장착 웨이퍼들에서, 캐리어 웨이퍼에 의한 안정화 또는 지지(support)는 비교적 단순하다. 그러나 여기서 공정 단계가 앞면과 뒷면에서도 필요할 수 있다.
일반적으로, 임시 접합의 경우, 여러 다른 공정 단계를 거치는 제품 웨이퍼를, 이들 공정 단계가 완료된 후, 캐리어 웨이퍼로부터 조심스럽고, 비파괴적으로 분리해야 하는 문제가 있다. 따라서 서로 다른 생산 단계들을 이용하는 동안 캐리어 웨이퍼와 제품 웨이퍼 간의 연결이 제품 웨이퍼를 고정하고 안정화할 만큼 충분히 강력해야 한다. 그러나 동시에 연결은 쉽고 빠르게 분리될 수 있어야 한다.
WO 2009/0945558 A2는 1면 장착 제품 웨이퍼를 위한 임시 접합 방법을 기재하고 있다.
따라서 일반적인 방법은 생산 공정에서 각각의 제품 웨이퍼가 각각의 면을 적어도 하나의 공정 단계에서 노출시켜야 한다는 공통점을 가진다. 오늘날 제품 웨이퍼는, 먼저, 그들의 초기 두께에서의 손쉬운 핸들링, 즉, 제 1 면에서의 백-씨닝 공정(예를 들어, 범프 또는 범프 그룹의 생산 공정) 전의 초기 두께에서의 더 손쉬운 핸들링을 위해, 처리된다. 그 후, 제품 웨이퍼가 캐리어로 접합되어, 제품 웨이퍼가 상기 캐리어 상에서 백-씨닝의 공정 단계를 겪도록 할 수 있다. 백-씨닝 후, 일반적으로 나머지 공정 단계들(예를 들어, 범프 및/또는 범프 그룹 및/또는 그 밖의 다른 인터커넥션 층의 제작 및/또는 칩의 제공)이 제 2 면에서 수행된다. 제 2 면의 가공 후, 제품 웨이퍼의 제 1 면에 하나의 공정 단계가 다시 필요한 경우, 종래 기술에서, 비싼 칩이 부분적으로 이미 제공되어 있고, 제 1 면이 추가적인 공정 단계들에 의해 접근되도록 하기 위해, 얇아진 매우 민감한 제품 웨이퍼가 캐리어로부터 분리되어야 한다는 큰 문제점이 있다.
본 발명의 목적은, 생산 공정 동안 제품 웨이퍼가 신뢰할만하고 주의 깊게 다뤄질 수 있도록 하는 제품 웨이퍼 제작 방법, 특히 양면에 칩이 제공되는 제품 웨이퍼 제작 방법을 제공하는 것이다.
이러한 목적은 청구항 1의 특징에 의해 이뤄진다. 본 발명의 바람직한 형태는 종속 청구항에서 제공된다. 상세한 설명, 청구항, 및/또는 도면에서 제공되는 적어도 2개의 특징의 모든 조합이 본 발명의 범위 내에 있다. 특정 수치 범위에서, 명시된 한계 내의 값들이 경곗값으로서도 개시된 것이며, 임의의 조합으로 청구될 것이다.
본 발명의 기본 아이디어는 각각의 제품 웨이퍼로 접합 또는 연결되는 2개의 강성 캐리어 웨이퍼(rigid carrier wafer)가 선택적으로 분리될 수 있어서, 제 1 캐리어 웨이퍼에서 제 2 캐리어 웨이퍼로의 제품 웨이퍼의 이송이 가능해지며, 그동안 제품 웨이퍼가 연속으로 안정화되도록 하는 방법을 제공하는 것이다. 이는, 접착력 및/또는 인터커넥션 층에 가해지는 작용(특히, 기계적, 열적, 광학적, 및/또는 화학적 방법)에 의한 접착력의 변화와 관련하여, 서로 다른 속성을 갖는 2개의 캐리어 웨이퍼의 인터커넥션 층에 의해 이뤄진다. 여기서, 2개의 중간 층(intermediate layer)의 서로 다른 속성 때문에, 2개의 중간 층 중 하나가, 나머지 중간 층에 대해 상대적으로, 선택적 형성되거나 변경될 수 있어서, 하나의 중간 층이 다른 중간 층의 접합력보다 더 강하게 유지하는 동안 상기 다른 중간 층이 분리될 수 있도록 한다. 접착력은 인터커넥션 층의 유효 표면을 기준으로 한다.
기본적으로, 본 발명에서 청구되는 선택적 분리는 항상, 캐리어 웨이퍼와 제품 웨이퍼 간의 상이한 접착력에 의해 이뤄지며, 접착력은 각각의 캐리어 웨이퍼와 제품 웨이퍼 사이의 중간 층 전체와 관련된다. 본 발명에서 청구되는 방법은, 캐리어 웨이퍼와 제품 웨이퍼 사이에 작용하는 접착력이 본질적으로 상이함(즉, 처음부터 상이함)을 특징으로 한다. 따라서 이러한 경우, 중간 층들이 처음부터 상이한 접착력을 가지며, 한 편, 이는 중간 층들이 상이한 물질들로 구성됨으로써, 또는 각각의 캐리어 웨이퍼 및/또는 제품 웨이퍼에 대한 중간 층의 접촉 표면을, 각각의 접촉 표면에 작용하는 힘에 영향을 미치도록 전처리(pretreat)함으로써, 이뤄진다. 본 발명의 한 가지 가능한 실시예에서, 캐리어 웨이퍼의 표면을 전체적으로 또는 부분적으로 처리하기 위해, 및/또는 제품 웨이퍼의 표면을 전체적으로 또는 부분적으로 처리하기 위해, 접착력을 감소시키는 재료, 또는 접착력을 증가시키는 재료가 사용될 수 있다. 개별적으로, 또는 조합되어, 적용될 수 있는 버전이 하기에서 나열된다:
- 중간 층의 상이한 접착성 물질
- 적어도 하나의 표면/접촉 표면의 상이한 (전체적 또는 부분적인) 전처리
- 접착력 감소 재료
- 접착력 증가 재료
- 접촉 표면의 서로 다른 크기 또는 중간 층의 서로 다른 두께.
본 발명에 따르는 또 다른 방법에 의해, 특정 수단에 의해 중간 층의 접착력의 지시된 변경이 수행된다. 이와 관련하여, 접착력의 지시된 변경 후 2개의 중간 층의 접착력이 서로 상이해지도록, 선택가능한 지정 시점에서, 2개의 중간 층 중 하나 또는 2개의 중간 층 모두의 접착력을 변경한다. 본 발명에 따르는 다음의 실시예가 있다:
- 하나의 중간 층을 조사(irradiation)하면서, 다른 중간 층은 조사하지 않거나, 부분적으로만 조사함으로써, 제어되는 국부적인 동작. 본 발명의 또 다른 구성에서, 하나의 중간 층에만 용매를 작용시키고, 다른 중간 층은 용매에 노출하지 않거나 부분적으로만 노출함으로써, 제어되는 국부적인 동작이 가능하다.
- 물질의 선택, 및 적용되는 방법 단계(특히, 온도의 상승)에 대해 하나의 중간 층이 적어도 부분적으로 비활성화되는 것에 의한 선택성. 여기서 2개의 중간 층 중 하나의 중간 층이 덜 확연한 점성 강하를 갖고 반응하며, 이 결과로, 이 중간 층은 전단력에 대해 더 강한 접합력을 갖게 된다. 2개의 중간 층 중 하나의 중간 층이 하나의 용매에 대해 비활성이 되고, 상기 용매가 다른 하나의 중간 층을 용해하는 것이 특히 바람직하다.
- 제 2 중간 층이 도포되기 전에, 제 1 중간 층에 작용함으로써, 제 1 중간 층의 접착력을 변경하기.
- 앞서 기재된 수단에 의한 제 1 층의 접착력의 변화가 제 2 층의 접착력의 변화보다 더 급격하도록, 처음부터 상이한 크기를 갖는 변부 접착성 구역의 링 폭(ring width)에 의한 선택성.
강성 캐리어 웨이퍼는, 높은 상호연결 강성도를 특징으로 한다. 특히, 적합한 물질로는, 실리콘, 석영, 유리, 세라믹, 금속, 또는 이들의 조합이다.
따라서 2개의 캐리어 웨이퍼 중 하나의 캐리어 웨이퍼의 선택적 분리 전에, 또는 분리 동안에, 이 캐리어 웨이퍼에 할당되는 중간 층 또는 중간 층에 제공되는 접착 층이, 접착 층의 화학적, 열적, 광학적, 및/또는 기계적 속성에 의해, 또는 제품 웨이퍼의 다른 한 면에 캐리어 웨이퍼를 유지하면서 캐리어 웨이퍼가 손상되지 않도록 주의 깊게 제거될 수 있을 정도로 영향을 받음으로써, 변경될 수 있다. 동시에 또 다른 캐리어 웨이퍼가 제품 웨이퍼를 안정화한다.
본 발명의 목적을 위한 칩은, 종래 방식으로 웨이퍼에 제공되는 구조물 또는 집적 전자 부품이다. 칩을 제품 웨이퍼에 고정하기 위해, 또는 칩의 개별 회로를 제품 웨이퍼의 반대편 면에 위치하는 대응하는 칩 또는 회로로 전기적으로 인터커넥트하기 위해, 및/또는 전체 시스템을 회로 기판에 추후 장착하기 위해, 범프 또는 범프 그룹이 사용된다.
본 발명에 따르는 방법의 결과로서, 제품 웨이퍼의 양면에 칩이 제공될 수 있을 뿐만 아니라, 본 발명에 따르는 방법은 칩이 양면에 제공되는 제품 웨이퍼의 스택(stack)의 경우에도 바람직하다. 왜냐하면, 캐리어 웨이퍼의 선택적 제거가, 적층된 제품 웨이퍼를 제작하기 위한 주의 깊고 효과적일 뿐 아니라 유연한 방법을 제공하기 때문이다.
제품 웨이퍼를 가공하는 것은 하나 이상의 알려진 공정, 특히, 범프 및/또는 범프 그룹 및/또는 칩을 제 2 면에 제공하는 공정 및/또는 제품 웨이퍼의 백-씨닝(back-thinning)/연마(grinding)뿐 아니라, 이른바 재배선 층(RDL: redistribution layer)의 제작까지 포함할 수 있다. 본 발명의 목적을 위한 제품 웨이퍼는 능동 구조물(active structure)을 칩에 추후 수용하기 위한 배선 층(RDL 층)만 갖는 이른바 실리콘 임포저(silicon imposer)를 포함한다.
본 발명의 또 다른 실시예에서, 제 1 접착 층의 접합력은 제 2 접착 층의 접합력보다 작다. 접합력(bonding force)은, 제품 웨이퍼와 캐리어 웨이퍼 사이의 각각의 중간 층을 통해 작용하며, 각각의 제품 웨이퍼로부터의 캐리어 웨이퍼의 분리를 억제하는 연결력 또는 접착력을 의미하고, 각각은 활성 접합 영역/접착 영역을 기초로 한다. 본 발명에 따라, 제 1 접착 층의 접합력과 제 2 접착 층의 접합력 간의 차이는, 제 1 캐리어 웨이퍼가 제품 웨이퍼로부터 분리될 때, 제 2 캐리어 웨이퍼가 제품 웨이퍼와 상호연결된 상태를 유지할 만큼 큰 것이 바람직하다.
제 2 접착 층보다 작은 크기를 갖는 제 1 접착 층에 의해, 특히, 제 1 캐리어 웨이퍼 및 제품 웨이퍼와 제 1 접착 층의 접촉 영역이 더 작고, 및/또는 층 두께가 더 얇음으로써, 화학적 속성이 동일한 중간 층 또는 동일한 물질의 중간 층이 사용될 수 있도록, 기하학적 구성만 선택함으로써, 본 발명이 구현될 수 있다.
본 발명의 또 다른 바람직한 실시예에 따르면, 제 1 접착 층이 제 1 용매에 의해 적어도 부분적으로 용해되는 동안, 제 2 접착 층은 제 1 용매에 대해 적어도 대부분 비활성이도록, 제 1 접착 층이 화학적 속성을 가진다. 이러한 방식으로, 접착 층 또는 중간 층의 화학적 속성에 의해 본 발명이 구현된다.
다시 말하면, 용매를 선택할 수 있음으로써, 각각의 접착 층 또는 중간 층의 지정된 영역, 특히, 변부 영역의 용해가 제어될 수 있으며, 따라서 유효 접착 영역/접합 영역의 크기의 선택적 감소가 가능하다.
본원에서, 제 2 접착 층과 관련된 제 2 용매의 용해율(dissolution rate) A2에 대한 제 1 접착 층과 관련된 제 1 용매의 용해율 A1의 비는, 1:3 미만, 특히, 1:10 미만, 바람직하게는 1:20 미만, 더 바람직하게는 1:100 미만이다.
제 1 중간 층과 제 2 중간 층의 상이한 열물성(thermal property) 때문에, 온도 상승을 이용하여 제품 웨이퍼로부터 제 1 캐리어 웨이퍼를 분리하는 것이, 제 2 캐리어 웨이퍼의 분리보다 먼저 발생하는 경우, 온도 제어에 의해 본 발명이 바람직하게 구현될 수 있다. 이 실시예에서 접착 층들의 열물성, 특히, 온도에 따른 점성(viscosity)이 서로 다르다. 먼저 분리될 캐리어 웨이퍼가, 특정 온도에서 나머지 캐리어 웨이퍼보다 더 낮은 점성을 갖는 시멘트를 이용해 중간 층에 접합된다. 그 후, 분리될 캐리어 웨이퍼를 전단 가공(shearing off)함으로써, 상기 분리될 캐리어 웨이퍼가 비파괴적으로 분리될 수 있다.
본 발명의 또 다른 실시예에 따르면, 특히, 지정된 광 파장 및/또는 지정된 광 강도의 작용에 대한, 제 1 및 제 2 인터커넥션 층의 서로 다른 광학적 속성의 결과로 선택적으로, 제품 웨이퍼로부터 제 1 캐리어 웨이퍼가 분리되는 것이 바람직하다. 여기서, 입사광의 복사선에 의해 선택적 분리가 제어된다. 입사광은 2개의 특징적인 물리 파라미터를 가지며, 이들은 구체적으로, 에너지와 상관되고 화학적 가교 프로세스를 주로 제어할 수 있는 광자(photon)의 파장과, 열 출력과 직접 관련이 있는 강도, 즉, 시간 및 단위면적당 광자의 수이다. 각각의 접착 층의 물질은 물질의 유전 속성(dielectric property)의 특성 주파수-종속적인, 따라서, 파장-종속적인 스펙트럼을 갖고, 이는 또한 공명 스펙트럼(resonance spectrum)이라고 일컬어질 수 있다. 이와 관련하여 입사광의 대응하는 파장을 선택함으로써, 화학적 및 물리적 프로세스가 제어될 수 있다.
예를 들어, UV 복사, 또는 반대로 적외선 복사 하에서의 일부 중합체 가교결합이 사용되어, 물질을 직접 가열하고, 따라서 물리적 속성, 가령, 점도가 제어될 수 있다. 예를 들어, 레이저 광에 의해, 접착 층의 국소 가열이 발생할 수 있고, 이는 특히, 중간 층의 둘레 영역 또는 웨이퍼 둘레 영역에 제공되는 접착 층(즉, 환형 접착 층)의 경우 바람직하다. UV 조명에 의해 없어질 수 있는 가교 결합을 제공하는 것이 특히 바람직하다.
본 발명의 또 다른 이점에 따르면, 특히, 전단 강도(shear strength)에 대한 제 1 중간 층과 제 2 중간 층의 서로 다른 기계적 속성의 결과로, 선택적으로 제품 웨이퍼로부터 제 1 캐리어 웨이퍼가 분리된다. 더 낮은 전단 강도를 갖는 중간 층이 외부로부터 적용되는 전단력에 대한 더 작은 저항에 부딪혀서, 이 중간 층에 의해 제품 웨이퍼에 부착된 캐리어 웨이퍼가 반대편 캐리어 웨이퍼로부터 분리될 수 있다. 접착력은 주로 반데르발스 힘(Van der Waals force)에 의해 야기된다.
전단 가공에 의한 캐리어 웨이퍼의 분리가, 온도 처리와의 조합에 의해(특히, 온도에 따라 상이한 점성 거동(viscosity behavior)을 갖는 연결 수단으로서 열가소성 시멘트를 이용하는 경우), 더 최적화된다.
제 1 중간 층 또는 제 1 접착 층의 두께 B1가, 제 2 중간 층 또는 제 2 접착 층의 두께 B2보다 큰 경우, 이러한 수단에 의해, 특히, 3/2, 바람직하게는 2/1, 더 바람직하게는 3/1, 이상적으로는 4/1인 비 B1/B2에서 제 1 캐리어 웨이퍼를 분리하기 위해 필요한 전단력이 감소한다. 분리되지 않거나, 추후 분리될 제 2 중간 층은, 15 내지 50㎛, 바람직하게는 20 내지 40㎛, 더 바람직하게는 25 내지 30㎛의 두께 B2를 가진다.
본 발명의 또 다른 바람직한 실시예에서, 제 1 및/또는 제 2 접착 층은, 특히, 제품 웨이퍼의 둘레 영역에서, 환형으로 만들어진다. 이러한 방식으로, 접착 층이 둘레와 관련해 가공될 수 있고, 이는 특히, 용매를 사용할 때 바람직하다. 왜냐하면 이 경우 용매는 매우 짧은 거리로만 확산할 필요가 있기 때문이다.
본 발명의 또 다른 실시예에 따르면, 제 1 중간 층, 특히, 환형 접착 층 내의 제 1 중간 층은 낮은 접착 효과를 갖는 필름을 포함하고, 및/또는 제 2 중간 층, 특히, 환형 접착 층 내의 제 2 중간 층은 낮은 접착 효과를 갖는 필름을 포함한다. 접착 층의 접착 효과에 비해 낮은 접착 거동을 의미하고, 구체적으로 적어도 2배, 바람직하게는 적어도 3배, 더 바람직하게는 적어도 5배, 이상적으로는 적어도 10배 더 강하다. 관계는 동적 상태(dynamic state)에서의 접착 효과, 즉, 분리 프로세스 동안의 접착 효과를 참조하지만, 이에 추가로, 정적 상태(static state)에서의 접착 효과, 즉, 분리 프로세스 전의 접착 효과도 참조할 수 있다. 본 발명의 하나의 실시예에 따르는 필름은 제 1 및/또는 제 2 중간 층 또는 제 1 및/또는 제 2 접착 층의 부분 코팅으로서 제공될 수 있고, 부분 코팅은, 특히 접착방지 코팅(antiadhesion coating)으로서, 접착 효과의 감소를 야기한다. 본원에서, 필름이, 대응하는 캐리어 웨이퍼와 각각의 중간 층의 유효 접촉 표면 중 일부분의 접착 효과를 감소시킨다는 것이 중요하다.
본 발명에 따라 제공되는 장치는 앞서 기재된 방법을 적용하기에 적합한 수단을 가지는데, 구체적으로, 제 1 중간 층과 제 2 중간 층의 서로 다른 속성의 결과로서, 제품 웨이퍼로부터 제 1 캐리어 웨이퍼를 선택적으로 분리하기 위한 선택적 분리 에이전트를 가진다. 예를 들어, 제 1 캐리어 웨이퍼와 제 2 캐리어 웨이퍼에, 제품 웨이퍼와 반대방향 장력을 적용하거나, 제품 웨이퍼를 따르는 반대 방향으로 제 1 캐리어 웨이퍼와 제 2 캐리어 웨이퍼에 전단력(shearing force)을 적용함으로써, 기계적 분리를 수행하기 위한 공지된 장치가 사용될 수 있다. 그러나 본 발명에서, 선택적 분리 에이전트는 선택적 분리에 적합한 장치가 존재하도록 청구된다.
본 발명의 또 다른 이점, 특징, 및 세부사항이, 바람직한 실시예에 대한 다음의 기재로부터 자명해질 것이다.
도 1은 본 발명에 따르는 첫 번째 방법 단계에서의 제품 웨이퍼를 도시한다.
도 2는 본 발명에 따르는 두 번째 방법 단계에서의 제품 웨이퍼를 도시한다.
도 3은 본 발명에 따르는 세 번째 방법 단계에서의 제품 웨이퍼를 도시한다.
도 4는 본 발명에 따르는 네 번째 방법 단계에서의 제품 웨이퍼를 도시한다.
도 5는 본 발명에 따르는 다섯 번째 방법 단계에서의 제품 웨이퍼를 도시한다.
도 6은 본 발명에 따르는 여섯 번째 방법 단계에서의 제품 웨이퍼를 도시한다.
도 7은 본 발명에 따르는 일곱 번째 방법 단계에서의 제품 웨이퍼를 도시한다.
도 8은 본 발명에 따르는 여덟 번째 방법 단계에서의 제품 웨이퍼를 도시한다.
도 9는 본 발명에 따르는 아홉 번째 방법 단계에서의 제품 웨이퍼를 도시한다.
도 10은 본 발명에 따르는 열 번째 방법 단계에서의 제품 웨이퍼를 도시한다.
도 11은 본 발명에 따르는 대안적인 일곱 번째 방법 단계에서의 제품 웨이퍼를 도시한다.
도 12는 본 발명에 따르는 대안적인 일곱 번째 방법 단계에서의 제품 웨이퍼를 도시한다.
도 2는 본 발명에 따르는 두 번째 방법 단계에서의 제품 웨이퍼를 도시한다.
도 3은 본 발명에 따르는 세 번째 방법 단계에서의 제품 웨이퍼를 도시한다.
도 4는 본 발명에 따르는 네 번째 방법 단계에서의 제품 웨이퍼를 도시한다.
도 5는 본 발명에 따르는 다섯 번째 방법 단계에서의 제품 웨이퍼를 도시한다.
도 6은 본 발명에 따르는 여섯 번째 방법 단계에서의 제품 웨이퍼를 도시한다.
도 7은 본 발명에 따르는 일곱 번째 방법 단계에서의 제품 웨이퍼를 도시한다.
도 8은 본 발명에 따르는 여덟 번째 방법 단계에서의 제품 웨이퍼를 도시한다.
도 9는 본 발명에 따르는 아홉 번째 방법 단계에서의 제품 웨이퍼를 도시한다.
도 10은 본 발명에 따르는 열 번째 방법 단계에서의 제품 웨이퍼를 도시한다.
도 11은 본 발명에 따르는 대안적인 일곱 번째 방법 단계에서의 제품 웨이퍼를 도시한다.
도 12는 본 발명에 따르는 대안적인 일곱 번째 방법 단계에서의 제품 웨이퍼를 도시한다.
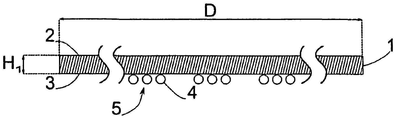
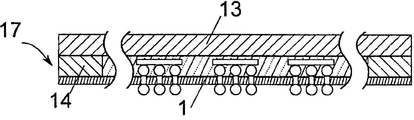
도 1은 방법의 이 시점에서는 비교적 두껍고, 범프(4), 또는 범프(4)들로 구성된 범프 그룹(5)이 제공된 제품 웨이퍼(1)를 도시한다. 이 시점에서의 제품 웨이퍼(1)는, 그 두께(H1) 때문에, 비교적 안정적이며, 이와 관련해, 보조 없이도, 자체적으로 비교적 안정적이다. 범프 그룹(5) 내 범프(4)의 개수 및 그들의 위치는, 후속 방법 단계(4 및 9 참조)에서 범프(4)로 제공되는 각각의 칩(15)(이른바, 다이스)에 따라 달라진다.
제품 웨이퍼(1)는 제 1 면(3) 및 제 2 면(2)을 가지며, 도 1에서 도시된 바와 같은 제 1 공정 단계에서 범프(4) 또는 범프 그룹(5)이 상기 제 1 면(3) 상으로 도포된다. 도포는 종래 기술에서 알려진 바와 같이 이뤄진다.
도 2에 도시된 제 2 공정 단계에서, 안정화를 위해 제 1 면(3)을 갖는 제품 웨이퍼(1)가 제 1 캐리어 웨이퍼(8)로 임시로 접합되고, 제 1 중간 층(18)이 접합을 위해 사용된다. 본원에 도시된 실시예에서, 제 1 중간 층(18)은 제 1 접착 층(6)과 제 1 필름(7)을 포함하고, 제 1 접착 층(6)이 접합을 위해 사용되고, 필름(7)이 범프(4)의 매립(embedding)을 위해 사용된다. 도 1 내지 12는, 예시적 실시예에서의 하나의 단면을 도시하며, 여기서, 제품 웨이퍼(1)는 300밀리미터의 지름(D)을 갖는 둥근 디스크(disk)로 만들어진다. 그러나 제품 웨이퍼(1)는 그 밖의 다른 임의의 디스크 형태 및 상이한 지름(D)을 가질 수 있다.
도 2에 도시된 실시예에서, 제 1 접착 층(6)은, 외측 웨이퍼 둘레(19) 영역에 위치하고, 웨이퍼 둘레(19)로부터 지름(D)의 분할 값(fraction) 만큼, 구체적으로, 10분의 1 미만의 링 폭(R1) 만큼 뻗어 있어서, 도시된 실시예에서, 제 1 접착 층(6)에 대한 환형체(annular body)가 나타난다. 비 R1/D는 구체적으로 1/20 미만이고, 바람직하게는 1/30 미만이며, 더 바람직하게는 1/60 미만이고, 더 더욱 바람직하게는 1/120 미만이다. 링의 폭(R1)은 구체적으로 15㎜ 미만이고, 바람직하게는 10㎜ 미만이며, 더 바람직하게는 5㎜ 미만이고, 더 더욱 바람직하게는 2㎜ 미만이다. 필름(7)이 환형체 내에 있고, 필름이, 제품 웨이퍼(1), 제 1 접착 층(6) 및 제 1 캐리어 웨이퍼(8)에 의해 완전히 둘러싸인다.
하나의 바람직한 실시예에 따르는 필름(7)이, 제 1 접착 층(6)의 부분 코팅으로서 제공되며, 이 대안적 실시예에서, 접착 층(6)은 제 1 캐리어 웨이퍼(8) 전체에 걸쳐 뻗어 있다. 도 2에 도시된 필름(7)과 유사한 크기로 부분 코팅이 제공된다.
도 11에 도시된 대안적 실시예의 경우, 제 1 중간 층(18')이 단일 물질로부터 형성되고, 제품 웨이퍼(1)의 전체 영역에 걸쳐 뻗어 있다. 이 경우, 제 1 중간 층(18')의 접착력(adhesion capacity)은 온도에 따라 달라져서, 온도가 높아질수록, 특히 점성의 감소 때문에, 접착력, 따라서, 접합력(bonding force)이 감소하고, 시멘트(cement)가 전단력에 대한 저항을 감소시켰다.
도 3에 도시된 본 발명에 따르는 제 1 공정 단계에서, 공지된 방법에 의해, 제품 웨이퍼(1)는, 도 1에 도시된 본래의 두께(H1)에서부터, 도 10에 도시된 최종 제품에 대응하는 150㎛ 미만, 구체적으로 100㎛ 미만, 바람직하게는 70㎛ 미만, 더 바람직하게는 50㎛ 미만, 더 더욱 바람직하게는 30㎛ 미만, 더 더욱 바람직하게는 20㎛ 미만의 두께(H2)까지로, 백-씨닝 가공된다.
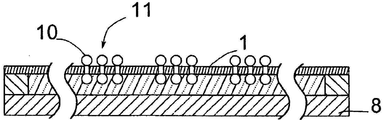
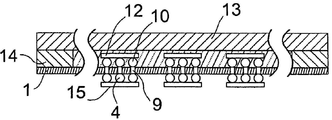
도 4에 도시된 네 번째 방법 단계에서, 제품 웨이퍼(1)를 관통하는 비아(VIA)(9)가 제품 웨이퍼(1) 내부로 에칭-형성되어, 범프(4)들 사이에서 제 1 면(3)에서 제 2 면(2)으로의 전기 연결이 형성될 수 있고, 도 5에 도시된 다섯 번째 방법 단계에서, 제 2 면(2)으로 도포될 범프(10) 또는 범프 그룹(11)이 형성될 수 있다.
도 6에 도시된 여섯 번째 단계에서, 칩(12)이 적절한 범프(10) 또는 범프 그룹(11)으로 제공된다.
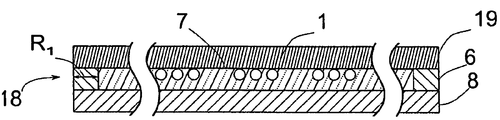
본 발명에 따르는 방법 단계들 중 하나가 도 7에 도시된 일곱 번째 방법 단계이며, 여기서, 도 2에 도시된 방법 단계와 유사한 방식으로, 제 2 면(2)이, 제 1 중간 층(18)과 상이한 하나 이상의 관련 속성을 갖는 제 2 중간 층(17)을 통해, 제 2 캐리어 웨이퍼(13)로 접합된다.
이 실시예에서, 제 2 중간 층(17)은, 마찬가지로, 제품 웨이퍼(1)의 외측 웨이퍼 둘레(19)로부터 지름(D)의 분할 값만큼, 구체적으로 링 폭(R2)(최대, 지름(D)의 10분의 1)만큼 뻗어 있는 제 2 접착 층(14)으로 구성된다. 이 실시예에서, 제 2 접착 층(14)은 링 폭(R2)을 갖는 환형 링으로 만들어지며, 여기서 링 폭(R2)은 제 1 접착 층(6)의 링 폭(R1)보다 크다. 비 R1/R2는 1/10 내지 9/10이며, 특히, 1/5 내지 4/5이고, 바람직하게는 1/4 내지 3/4이며, 더 바람직하게는 1/3 내지 2/3이다. 비 R2/D는 구체적으로 1/20 미만이며, 바람직하게는 1/30 미만이고, 더 바람직하게는 1/60 미만이며, 더 더욱 바람직하게는 1/120이다. 링 폭(R2)은 구체적으로 15㎜ 미만이며, 바람직하게는 10㎜ 미만이고, 더 바람직하게는 5㎜이며, 더 더욱 바람직하게는 2㎜ 미만이다.
이러한 방식으로, 제품 웨이퍼(1)와 제 2 캐리어 웨이퍼(13) 사이의 제 2 접착 층(14)에 대한 유효 접착 영역/접합 영역이 더 넓어진다.
이 실시예와 조합될 수 있는 본 발명의 하나의 대안적 실시예에서, 제 1 중간 층(18)의 두께(B1)가 제 2 중간 층(17)의 두께(B2)보다 크며, 특히, 비 B1/B2는 적어도 3/2이고, 바람직하게는 2/1이며, 더 바람직하게는 3/1이며, 이상적으로는 적어도 4/1이다.
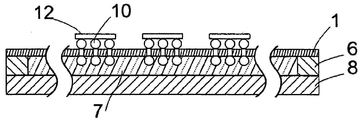
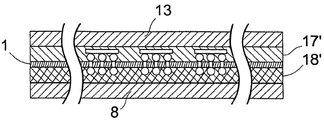
도 8에 도시된 방법 단계에서, 제 1 접착 층(6)의 접합력을 감소시키고, 제품 웨이퍼(2)로부터 멀어지는 방향의 장력을 적용함으로써, 제 1 캐리어 웨이퍼(8)가 분리된다. 접합력의 감소는 이전 방법 단계에서 이미 구현되거나, 수행됐을 수 있다. 또는, 제품 웨이퍼(1)에 평행하게 제 1 및 제 2 캐리어 웨이퍼(8, 13)에 전단력을 반대 방향으로 작용시킴으로써, 제 2 캐리어 웨이퍼(8)가 잘라내질 수 있다. 또 다른 대안예가, 캐리어 웨이퍼를, 캐리어 웨이퍼의 변부에서부터 박리(peel off)하는 것을 포함한다. 박리 중에, 캐리어 웨이퍼는 자신의 변부에서, 탄성적으로 휘어지고, 그 결과로, 제 2 캐리어 웨이퍼와 제품 웨이퍼의 휘어짐을 상쇄하기 위해, 제 2 캐리어 웨이퍼와 제품 웨이퍼가 지지대에 고정되어 있는 동안, 캐리어 웨이퍼의 변부에서부터 시작하여, 중심 쪽으로, 그리고 반대편 변부까지로, 분리 전선(separating front)이 전파된다. 한 가지 바람직한 실시예에서, 기계적 분리에 의해, 특히, 중간 층의 둘레 변부 상의 하나의 지점(site)에 기계적 요소를 도입함으로써, 분리가 이뤄질 수 있다. 예를 들어, 기계적 요소는 평판형 쐐기일 수 있다.
제 1 접착 층(6)에 비해 제 2 접착 층(14)의 접착 영역이 더 넓고, 접합력이 더 강함으로써, 제 1 캐리어 웨이퍼(8)가 자동으로 분리된다. 분리 동안, 필름(7)과 접착 층(6)의 잔여물이 제품 웨이퍼(2) 상에 남아 있는 경우, 상기 잔여물은 세정 단계에 의해 제거될 수 있다. 도 7 및 8에 도시된 실시예에서, 제 1 캐리어 웨이퍼(8)가 기하학적 구성을 기초로, 즉, 제 2 접착 층(14)의 더 커진 접착 영역 때문에 분리된다. 도 11에 도시된 대안적 실시예에서, 제 1 중간 층(18')이 자신의 접착력 또는 접합력을, 제 2 중간 층(17')보다 더 빨리 감소시키도록, 제 1 중간 층(18')은 제 2 중간 층(17')과 다른 열물성을 가진다.
본 발명의 하나의 바람직한 실시예에 따르면, 방법은 다음과 같이 진행된다:
- 제품 웨이퍼(1)의 제 1 면(3)을, 적어도 변부 측에 도포되는 하나의 제 1 접착 층으로 구성되는 제 1 중간 층(18)을 갖는 제 1 강성 캐리어 웨이퍼(8) 상에 접합하기,
- 제 1 접착 층(6)을 적어도 부분적으로 용해하기,
- 제품 웨이퍼(1)의 제 2 면(2)을, 적어도 변부 측에 도포되는 제 2 접착 층(14)으로 구성되는 제 2 중간 층(17)을 갖는 제 2 강성 캐리어 웨이퍼(13) 상에 접합하기,
- 특히, 제품 웨이퍼(1)에 평행하게 제 1 캐리어 웨이퍼(8)와 제 2 캐리어 웨이퍼(13)로 반대방향으로 전단력을 적용하거나, 제 1 캐리어 웨이퍼(8)를 박리함으로써, 제 1 캐리어 웨이퍼를 분리하기.
제 1 및 제 2 접착 층(6, 14)은 동일한 물질이며, 각각의 캐리어 웨이퍼의 전체 영역에 걸쳐 분포되어 있으며, 캐리어 웨이퍼의 제 1 및 제 2 접착 층(6, 14)의 제 1 및 제 2 부분 코팅으로의 접착 층의 각각의 접합 영역/접착 영역에 제공되어, 도포의 영역에서의 접착력의 개별적인 감소가 이뤄질 수 있다.
도 12에 도시된 대안적 실시예에서, 제 1 접착 층(18")이 도 7에 도시된 실시예와 유사하게 만들어지며, 이때, 링 폭(R1')은 제 2 접착 층(17")의 링 폭(R2')보다 더 작아서, 두 접착 층(17", 18")이 서로 동일한 물질인 경우, 광원(29)이 제 1 접착 층(18")과 제 2 접착 층(17")에 작용하도록 할 수 있다. 제 2 접착 층(17")의 더 넓은 링 폭(R2')으로 인해, 특히, 광원(29)이 비교적 집중된 방식으로 작용하도록 만들어지기 때문에, 제 2 캐리어 웨이퍼(13)보다 먼저, 제 1 캐리어 웨이퍼(8)가 분리될 수 있다. 예를 들어 광원은 UV 광원일 수 있다.
또는 제 1 접착 층(18")과 제 2 접착 층(17")이 서로 다른 광 강도/광 주파수에 대해 반응하도록 만들어질 수 있다.
앞서 기재된 실시예들의 공통점은, 대응하는 동작에 대해, 제품 웨이퍼(1)와 제 1 캐리어 웨이퍼(8) 간의 접착력 또는 접합력이, 제품 웨이퍼(1)와 제 2 캐리어 웨이퍼(13) 간의 접착력 또는 접합력에 비해 더 작도록, 제 1 접착 층(18, 18', 18")이 제 2 접착 층(17, 17', 17")과 상이하다는 것이다.
도 9에 도시된 아홉 번째 방법 단계에서, 칩(15)이 범프(4)에 제공되고, 따라서, 도 6에서 도시된 여섯 번째 방법 단계와 유사하게 전도성 방식으로 칩(12)으로 전기 연결된다.
도 10에서 도시된 열 번째 단계에서의 제 2 캐리어 웨이퍼(13)의 분리 후, 두 면에 장착되는 제품 웨이퍼(16)가 유지된다. 제품 웨이퍼(16)의 스택(stack)이 생산될 경우, 도 9에 도시된 아홉 번째 방법 단계에 따라, 칩(12, 15)이 장착된 거의 임의의 개수의 제품 웨이퍼(1)가 적층될 수 있고, N번째 접착 층은, 분리 동안, N+1번째 접착 층보다 더 작은 접합력을 가져야 한다. 이는, 앞서 기재된 절차와 유사하게, N번째 접착 층/중간 층의 수정이, N번째 캐리어 웨이퍼가 분리될 때 바로 발생하거나, N번째 캐리어 웨이퍼의 분리 전에, 특히, N+1번째 캐리어 웨이퍼의 접합 전에 발생한다.
필름(7)을 대신하여, 필름(7)이 차지하는 영역이 기체로 채워지거나, 배기될 수 있다.
도 1 내지 9에서 도시된 실시예에서, 제 1 및 제 2 접착 층(6, 14)의 용해 가 화학적 용매에 의해 보조되는 것이 바람직하다. 따라서 접착 층을 용해하기 위한 화학적, 열적, 광학적, 및 기계적 방법 단계들의 조합이 가능하다.
블랭킷(blanket) 중간 층을 이용하는 방법(예를 들어, 도 11에 도시된 방법)에서, 광학적 및/또는 열적 용해 방법이 추천되며, 용매의 사용은 확산 시간 때문에 웨이퍼 둘레(19)에서는 덜 적합하다.
1 제품 웨이퍼
2 제 2 면
3 제 1 면
4 범프
5 범프 그룹
6 제 1 접착 층
7 필름
8 제 1 캐리어 웨이퍼
9 비아
10 범프
11 범프 그룹
12 칩
13 제 2 캐리어 웨이퍼
14 제 2 접착 층
15 칩
16 양면 장착 제품 웨이퍼
17, 17', 17" 제 2 중간 층
18, 18', 18" 제 1 중간 층
19 웨이퍼 둘레
29 광원
D 지름
H1 웨이퍼 두께
H2 웨이퍼 두께
R1, R1' 링 폭
R2, R2' 링 폭
B1 중간 층의 두께
B2 중간 층의 두께
2 제 2 면
3 제 1 면
4 범프
5 범프 그룹
6 제 1 접착 층
7 필름
8 제 1 캐리어 웨이퍼
9 비아
10 범프
11 범프 그룹
12 칩
13 제 2 캐리어 웨이퍼
14 제 2 접착 층
15 칩
16 양면 장착 제품 웨이퍼
17, 17', 17" 제 2 중간 층
18, 18', 18" 제 1 중간 층
19 웨이퍼 둘레
29 광원
D 지름
H1 웨이퍼 두께
H2 웨이퍼 두께
R1, R1' 링 폭
R2, R2' 링 폭
B1 중간 층의 두께
B2 중간 층의 두께
Claims (11)
- 칩(12, 15)이 특히 양면에 제공되는 제품 웨이퍼(1)를 제작하기 위한 방법에 있어서, 상기 방법은
제품 웨이퍼(1)의 제 1 면(3)을 가공하는 단계,
제품 웨이퍼(1)의 제 1 면(3)을, 적어도 변부 측에 제공되는 하나의 제 1 접착 층(6)으로 구성된 제 1 중간 층(18, 18', 18")을 갖는 제 1 강성 캐리어 웨이퍼(8)로 접합하는 단계,
상기 제 1 면(3)의 반대편의 제품 웨이퍼(1)의 제 2 면(2)을 가공하는 단계,
제품 웨이퍼(1)의 제 2 면(2)을, 적어도 변부 측에 제공되는 하나의 제 2 접착 층(14)으로 구성된 제 2 중간 층(17, 17', 17")을 갖는 제 2 강성 캐리어 웨이퍼(13)로 접합하는 단계
를 포함하며, 제 2 캐리어 웨이퍼(13)보다 먼저 제 1 캐리어 웨이퍼(8)가 선택적으로 분리될 수 있도록 제 1 중간 층(18, 18', 18")과 제 2 중간 층(17, 17', 17")은 상이하게 만들어지는 것을 특징으로 하는 제품 웨이퍼를 제작하기 위한 방법. - 제 1 항에 있어서, 제 1 접착 층(6)의 접합력(bonding force)이 제 2 접착 층(14)의 접합력보다 작은 것을 특징으로 하는 제품 웨이퍼를 제작하기 위한 방법.
- 제 1 항 또는 제 2 항에 있어서, 제 1 접착 층(6)은 제 2 접착 층(14)보다 작은 치수를 가지는데, 특히, 제 1 캐리어 웨이퍼(8) 및 제품 웨이퍼(1)와 제 1 접착 층(6)의 접촉 영역이 더 작거나, 층 두께가 더 얇거나, 접촉 영역이 작고 층 두께가 얇은 것을 특징으로 하는 제품 웨이퍼를 제작하기 위한 방법.
- 제 1 항 내지 제 3 항 중 어느 한 항에 있어서, 제 2 접착 층(14)이 제 1 용매에 대해 적어도 대부분 비활성인 동안, 제 1 접착 층(6)이 상기 제 1 용매에 의해 적어도 부분적으로 용해되도록, 제 1 접착 층(6)은 제 2 접착 층(14)과 상이한 화학적 속성을 갖는 것을 특징으로 하는 제품 웨이퍼를 제작하기 위한 방법.
- 제 1 항 내지 제 4 항 중 어느 한 항에 있어서, 온도가 상승할 때 제 1 중간 층(18, 18', 18")이 적어도 부분적으로 용해되어, 제 2 캐리어 웨이퍼(13)의 분리 전에, 제 1 캐리어 웨이퍼(8)의 분리가 시작될 수 있도록, 제 1 중간 층(18, 18', 18")은 제 2 중간 층(17, 17', 17")과 상이한 열물성(thermal property)을 갖는 것을 특징으로 하는 제품 웨이퍼를 제작하기 위한 방법.
- 제 4 항 또는 제 5 항에 있어서, 제 1 중간 층(18, 18', 18")의 용해, 특히, 제 1 접착 층(14)의 용해가, 제 2 면(2)의 가공 후에, 또는 제품 웨이퍼(1)를 제 2 캐리어 웨이퍼(13)에 접합하기 전 또는 후에, 발생하는 것을 특징으로 하는 제품 웨이퍼를 제작하기 위한 방법.
- 제 1 항 내지 제 6 항 중 어느 한 항에 있어서, 제품 웨이퍼(1)로부터의 제 1 캐리어 웨이퍼(8)의 분리는, 특히, 제 1 접착 층(6) 및 제 2 접착 층(14) 중 적어도 하나에 선택적으로 작용하는 것이 바람직한 광원(29)의 지정 광 파장 및/또는 지정 광 강도와 관련된 제 1 중간 층(18, 18', 18")과 제 2 중간 층(17, 17', 17")의 상이한 광학적 속성의 결과로서, 선택적으로 발생하는 것을 특징으로 하는 제품 웨이퍼를 제작하기 위한 방법.
- 제 1 항 내지 제 7 항 중 어느 한 항에 있어서, 제품 웨이퍼(1)로부터의 제 1 캐리어 웨이퍼(8)의 분리는, 특히, 전단 강도, 바람직하게는 온도에 따르는 전단 강도와 관련된 제 1 중간 층(18, 18', 18")과 제 2 중간 층(17, 17', 17")의 상이한 기계적 속성의 결과로서, 선택적으로 발생하는 것을 특징으로 하는 제품 웨이퍼를 제작하기 위한 방법.
- 제 1 항 내지 제 8 항 중 어느 한 항에 있어서, 제 1 접착 층(6) 및 제 2 접착 층(14) 중 적어도 하나가 환형으로, 특히, 제품 웨이퍼(1)의 둘레(19)의 영역에서 만들어지는 것을 특징으로 하는 제품 웨이퍼를 제작하기 위한 방법.
- 제 1 항 내지 제 9 항 중 어느 한 항에 있어서, 제 1 접착 층(6) 내에 있는 제 1 중간 층(18, 18") 및 제 2 접착 층(14) 내에 있는 제 2 중간 층(17, 17") 중 적어도 하나가 필름(7)을 포함하는 것을 특징으로 하는 제품 웨이퍼를 제작하기 위한 방법.
- 제 1 항 내지 제 10 항 중 어느 한 항에 있어서, 제 1 캐리어 웨이퍼(8)와 제 1 중간 층(18, 18', 18") 사이에서, 특히 제 1 캐리어 웨이퍼(8)에 도포되는 제 1 부분 코팅이, 제 1 부분 코팅의 영역에서의 접합력/접착력을 감소시키도록 제공되며, 및/또는 제 2 캐리어 웨이퍼(13)와 제 2 중간 층(17, 17', 17") 사이에서, 특히 제 2 캐리어 웨이퍼(13) 상에 도포되는 제 2 부분 코팅이, 상기 제 2 부분 코팅의 영역에서의 접합력/접착력을 감소시키도록 제공되는 것을 특징으로 하는 제품 웨이퍼를 제작하기 위한 방법.
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/EP2010/002055 WO2011120537A1 (de) | 2010-03-31 | 2010-03-31 | Verfahren zur herstellung eines doppelseitig mit chips bestückten wafers |
Related Child Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020167016168A Division KR20160075845A (ko) | 2010-03-31 | 2010-03-31 | 양면에 칩이 장착되는 웨이퍼를 제작하기 위한 방법 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| KR20130040779A true KR20130040779A (ko) | 2013-04-24 |
Family
ID=42286741
Family Applications (3)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020177009655A KR101856429B1 (ko) | 2010-03-31 | 2010-03-31 | 양면에 칩이 장착되는 웨이퍼를 제작하기 위한 방법 |
| KR1020167016168A KR20160075845A (ko) | 2010-03-31 | 2010-03-31 | 양면에 칩이 장착되는 웨이퍼를 제작하기 위한 방법 |
| KR1020127023406A KR20130040779A (ko) | 2010-03-31 | 2010-03-31 | 양면에 칩이 장착되는 웨이퍼를 제작하기 위한 방법 |
Family Applications Before (2)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020177009655A KR101856429B1 (ko) | 2010-03-31 | 2010-03-31 | 양면에 칩이 장착되는 웨이퍼를 제작하기 위한 방법 |
| KR1020167016168A KR20160075845A (ko) | 2010-03-31 | 2010-03-31 | 양면에 칩이 장착되는 웨이퍼를 제작하기 위한 방법 |
Country Status (8)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US9224630B2 (ko) |
| EP (1) | EP2553719B1 (ko) |
| JP (1) | JP5763169B2 (ko) |
| KR (3) | KR101856429B1 (ko) |
| CN (1) | CN102812546B (ko) |
| SG (1) | SG183820A1 (ko) |
| TW (1) | TWI518758B (ko) |
| WO (1) | WO2011120537A1 (ko) |
Families Citing this family (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US9827757B2 (en) | 2011-07-07 | 2017-11-28 | Brewer Science Inc. | Methods of transferring device wafers or layers between carrier substrates and other surfaces |
| WO2015156854A1 (en) * | 2014-04-09 | 2015-10-15 | Electranix Corporation | Multi-module dc-to-dc power transformation system |
| WO2020178080A1 (en) * | 2019-03-05 | 2020-09-10 | Evatec Ag | Method for processing fragile substrates employing temporary bonding of the substrates to carriers |
| WO2021164855A1 (de) | 2020-02-18 | 2021-08-26 | Ev Group E. Thallner Gmbh | Verfahren und vorrichtung zur übertragung von bauteilen |
| WO2023179868A1 (de) | 2022-03-25 | 2023-09-28 | Ev Group E. Thallner Gmbh | Verfahren und substratsystem zum trennen von trägersubstraten |
Family Cites Families (39)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS6198784A (ja) * | 1984-10-20 | 1986-05-17 | Kimurashin Kk | ロール状又は積層状の両面接着テープ |
| JPH04283283A (ja) * | 1991-03-08 | 1992-10-08 | Nippon Synthetic Chem Ind Co Ltd:The | 開封自在テープ |
| JP3686454B2 (ja) * | 1995-05-10 | 2005-08-24 | 日東電工株式会社 | 接着型使捨てカイロ用粘着シート及びそのカイロ |
| WO1997039481A1 (en) | 1996-04-12 | 1997-10-23 | Northeastern University | An integrated complex-transition metal oxide device and a method of fabricating such a device |
| JPH11105924A (ja) * | 1997-10-06 | 1999-04-20 | Nitto Denko Corp | 電子部品搬送用テ−プ |
| JPH11238375A (ja) * | 1998-02-20 | 1999-08-31 | Sony Corp | 電子機器の放熱装置とディスクドライブ装置 |
| JP2000326995A (ja) * | 1999-05-17 | 2000-11-28 | Ogawa Sangyo Kk | 滅菌袋 |
| JP2002097041A (ja) * | 2000-07-17 | 2002-04-02 | Sekisui Chem Co Ltd | 合わせガラス用中間膜及び合わせガラス |
| FR2823596B1 (fr) * | 2001-04-13 | 2004-08-20 | Commissariat Energie Atomique | Substrat ou structure demontable et procede de realisation |
| JP3861669B2 (ja) | 2001-11-22 | 2006-12-20 | ソニー株式会社 | マルチチップ回路モジュールの製造方法 |
| JP2003218063A (ja) * | 2002-01-24 | 2003-07-31 | Canon Inc | ウエハ貼着用粘着シート及び該シートを利用する加工方法 |
| US6794273B2 (en) | 2002-05-24 | 2004-09-21 | Fujitsu Limited | Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof |
| JP4565804B2 (ja) * | 2002-06-03 | 2010-10-20 | スリーエム イノベイティブ プロパティズ カンパニー | 被研削基材を含む積層体、その製造方法並びに積層体を用いた極薄基材の製造方法及びそのための装置 |
| JP4364535B2 (ja) * | 2003-03-27 | 2009-11-18 | シャープ株式会社 | 半導体装置の製造方法 |
| JP4405246B2 (ja) | 2003-11-27 | 2010-01-27 | スリーエム イノベイティブ プロパティズ カンパニー | 半導体チップの製造方法 |
| US7232740B1 (en) | 2005-05-16 | 2007-06-19 | The United States Of America As Represented By The National Security Agency | Method for bumping a thin wafer |
| US8592286B2 (en) | 2005-10-05 | 2013-11-26 | Stats Chippac Ltd. | Ultra-thin wafer system and method of manufacture thereof |
| DE102006000687B4 (de) | 2006-01-03 | 2010-09-09 | Thallner, Erich, Dipl.-Ing. | Kombination aus einem Träger und einem Wafer, Vorrichtung zum Trennen der Kombination und Verfahren zur Handhabung eines Trägers und eines Wafers |
| US20080003780A1 (en) | 2006-06-30 | 2008-01-03 | Haixiao Sun | Detachable stiffener for ultra-thin die |
| US20080044984A1 (en) * | 2006-08-16 | 2008-02-21 | Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Co., Ltd. | Methods of avoiding wafer breakage during manufacture of backside illuminated image sensors |
| US7838391B2 (en) | 2007-05-07 | 2010-11-23 | Stats Chippac, Ltd. | Ultra thin bumped wafer with under-film |
| JP2009043962A (ja) | 2007-08-09 | 2009-02-26 | Sony Corp | 半導体装置の製造方法 |
| CN101925996B (zh) * | 2008-01-24 | 2013-03-20 | 布鲁尔科技公司 | 将器件晶片可逆地安装在载体基片上的方法 |
| EP2104138A1 (de) * | 2008-03-18 | 2009-09-23 | EV Group E. Thallner GmbH | Verfahren zum Bonden von Chips auf Wafer |
| JP4572243B2 (ja) * | 2008-03-27 | 2010-11-04 | 信越化学工業株式会社 | 熱伝導性積層体およびその製造方法 |
| JP2010010644A (ja) * | 2008-05-27 | 2010-01-14 | Toshiba Corp | 半導体装置の製造方法 |
| JP2010092931A (ja) * | 2008-10-03 | 2010-04-22 | Toshiba Corp | 半導体装置の製造方法及び半導体装置の製造装置 |
| WO2010121068A2 (en) | 2009-04-16 | 2010-10-21 | Suss Microtec, Inc. | Improved apparatus for temporary wafer bonding and debonding |
| US8689437B2 (en) * | 2009-06-24 | 2014-04-08 | International Business Machines Corporation | Method for forming integrated circuit assembly |
| EP2299486B1 (de) * | 2009-09-18 | 2015-02-18 | EV Group E. Thallner GmbH | Verfahren zum Bonden von Chips auf Wafer |
| US8008121B2 (en) * | 2009-11-04 | 2011-08-30 | Stats Chippac, Ltd. | Semiconductor package and method of mounting semiconductor die to opposite sides of TSV substrate |
| US9136144B2 (en) * | 2009-11-13 | 2015-09-15 | Stats Chippac, Ltd. | Method of forming protective material between semiconductor die stacked on semiconductor wafer to reduce defects during singulation |
| US8017439B2 (en) * | 2010-01-26 | 2011-09-13 | Texas Instruments Incorporated | Dual carrier for joining IC die or wafers to TSV wafers |
| TWI419302B (zh) * | 2010-02-11 | 2013-12-11 | Advanced Semiconductor Eng | 封裝製程 |
| US8252682B2 (en) * | 2010-02-12 | 2012-08-28 | Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company, Ltd. | Method for thinning a wafer |
| JP4976522B2 (ja) * | 2010-04-16 | 2012-07-18 | 日東電工株式会社 | 熱硬化型ダイボンドフィルム、ダイシング・ダイボンドフィルム、及び、半導体装置の製造方法 |
| US8852391B2 (en) * | 2010-06-21 | 2014-10-07 | Brewer Science Inc. | Method and apparatus for removing a reversibly mounted device wafer from a carrier substrate |
| US8492197B2 (en) * | 2010-08-17 | 2013-07-23 | Stats Chippac, Ltd. | Semiconductor device and method of forming vertically offset conductive pillars over first substrate aligned to vertically offset BOT interconnect sites formed over second substrate |
| JP2012069919A (ja) * | 2010-08-25 | 2012-04-05 | Toshiba Corp | 半導体装置の製造方法 |
-
2010
- 2010-03-31 CN CN201080065914.6A patent/CN102812546B/zh active Active
- 2010-03-31 JP JP2013501635A patent/JP5763169B2/ja active Active
- 2010-03-31 KR KR1020177009655A patent/KR101856429B1/ko active IP Right Grant
- 2010-03-31 SG SG2012063681A patent/SG183820A1/en unknown
- 2010-03-31 EP EP10715497.3A patent/EP2553719B1/de active Active
- 2010-03-31 WO PCT/EP2010/002055 patent/WO2011120537A1/de active Application Filing
- 2010-03-31 KR KR1020167016168A patent/KR20160075845A/ko active Application Filing
- 2010-03-31 KR KR1020127023406A patent/KR20130040779A/ko not_active Application Discontinuation
- 2010-03-31 US US13/635,457 patent/US9224630B2/en active Active
-
2011
- 2011-02-25 TW TW100106549A patent/TWI518758B/zh active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2013524493A (ja) | 2013-06-17 |
| JP5763169B2 (ja) | 2015-08-12 |
| SG183820A1 (en) | 2012-10-30 |
| EP2553719B1 (de) | 2019-12-04 |
| TW201145370A (en) | 2011-12-16 |
| WO2011120537A1 (de) | 2011-10-06 |
| CN102812546A (zh) | 2012-12-05 |
| US20130011997A1 (en) | 2013-01-10 |
| KR20160075845A (ko) | 2016-06-29 |
| US9224630B2 (en) | 2015-12-29 |
| CN102812546B (zh) | 2015-08-26 |
| EP2553719A1 (de) | 2013-02-06 |
| TWI518758B (zh) | 2016-01-21 |
| KR101856429B1 (ko) | 2018-05-09 |
| KR20170042817A (ko) | 2017-04-19 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN104022016B (zh) | 薄晶片处理的多粘合层 | |
| TWI446420B (zh) | 用於半導體製程之載體分離方法 | |
| US20070077728A1 (en) | Adhesive system for supporting thin silicon wafer | |
| KR101454985B1 (ko) | 제작 기판을 캐리어 기판으로부터 분리하기 위한 장치 및 방법 | |
| KR101143797B1 (ko) | 반도체 기판을 얇게 하는 방법 | |
| EP1815509A2 (fr) | Amincissement d'une plaquette semiconductrice | |
| KR101856429B1 (ko) | 양면에 칩이 장착되는 웨이퍼를 제작하기 위한 방법 | |
| JP2007188967A (ja) | 基板支持体、基板処理方法及び半導体装置の製造方法 | |
| JP2008028325A (ja) | 半導体装置の製造方法 | |
| TW200426907A (en) | Fabrication method of semiconductor device | |
| US7863104B2 (en) | Method of producing a thin semiconductor chip | |
| JP2008130704A (ja) | 半導体装置の製造方法 | |
| US20160163590A1 (en) | Methods of manufacturing semiconductor devices | |
| JP2019514199A (ja) | 2枚の基板を接合する方法および装置 | |
| JP5409084B2 (ja) | 半導体装置の製造方法 | |
| JP6341554B2 (ja) | 半導体装置の製造方法 | |
| JP2005277103A (ja) | 半導体ウェハ、支持体および半導体ウェハ製造方法ならびにスペーサ製造方法および半導体素子製造方法 | |
| JP2007005366A (ja) | 半導体装置の製造方法 | |
| JP2005294472A (ja) | 半導体装置、半導体ウェーハ、およびこれらの製造方法 | |
| JP2018206936A (ja) | 基板処理システム、基板処理方法 | |
| JP2015201548A (ja) | 半導体装置の製造方法 | |
| JP7233225B2 (ja) | ウェーハの割段方法 | |
| TW201140749A (en) | Method for manufacturing semiconductor device | |
| KR100834381B1 (ko) | 반도체 디바이스 제조방법 | |
| JP2010219267A (ja) | 半導体装置の製造方法 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| N231 | Notification of change of applicant | ||
| A201 | Request for examination | ||
| E902 | Notification of reason for refusal | ||
| E601 | Decision to refuse application | ||
| E601 | Decision to refuse application | ||
| E801 | Decision on dismissal of amendment | ||
| A107 | Divisional application of patent | ||
| WITB | Written withdrawal of application |