EP0933486B1 - Fassade oder Glasdach in Brandschutzausführung - Google Patents
Fassade oder Glasdach in Brandschutzausführung Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0933486B1 EP0933486B1 EP98101515A EP98101515A EP0933486B1 EP 0933486 B1 EP0933486 B1 EP 0933486B1 EP 98101515 A EP98101515 A EP 98101515A EP 98101515 A EP98101515 A EP 98101515A EP 0933486 B1 EP0933486 B1 EP 0933486B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- profile
- facade
- roof according
- glazed roof
- core
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
- 229910052782 aluminium Inorganic materials 0.000 claims abstract description 15
- XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N aluminium Chemical compound [Al] XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims abstract description 15
- 230000003068 static effect Effects 0.000 claims abstract description 5
- 239000004411 aluminium Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 4
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Substances O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims abstract description 4
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 12
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 claims description 12
- 239000003463 adsorbent Substances 0.000 claims description 9
- 238000013461 design Methods 0.000 claims description 4
- 230000002829 reductive effect Effects 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000004020 conductor Substances 0.000 claims 1
- 238000004079 fireproofing Methods 0.000 claims 1
- 239000007787 solid Substances 0.000 claims 1
- 238000001179 sorption measurement Methods 0.000 claims 1
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 abstract description 8
- 239000011521 glass Substances 0.000 description 21
- 230000002787 reinforcement Effects 0.000 description 10
- 238000010276 construction Methods 0.000 description 7
- 238000004080 punching Methods 0.000 description 4
- 238000005253 cladding Methods 0.000 description 3
- 239000012212 insulator Substances 0.000 description 3
- 238000000465 moulding Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000002844 melting Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000008018 melting Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000012546 transfer Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229910000831 Steel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 238000005452 bending Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000011248 coating agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000000576 coating method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000003111 delayed effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000001125 extrusion Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000009970 fire resistant effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000006260 foam Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000006870 function Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000007789 gas Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000005338 heat storage Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000009413 insulation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 210000002414 leg Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 230000000670 limiting effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000036961 partial effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000009993 protective function Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000005855 radiation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000005096 rolling process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000007789 sealing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000000926 separation method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000010959 steel Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000007704 transition Effects 0.000 description 1
- 210000000689 upper leg Anatomy 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- E—FIXED CONSTRUCTIONS
- E06—DOORS, WINDOWS, SHUTTERS, OR ROLLER BLINDS IN GENERAL; LADDERS
- E06B—FIXED OR MOVABLE CLOSURES FOR OPENINGS IN BUILDINGS, VEHICLES, FENCES OR LIKE ENCLOSURES IN GENERAL, e.g. DOORS, WINDOWS, BLINDS, GATES
- E06B5/00—Doors, windows, or like closures for special purposes; Border constructions therefor
- E06B5/10—Doors, windows, or like closures for special purposes; Border constructions therefor for protection against air-raid or other war-like action; for other protective purposes
- E06B5/16—Fireproof doors or similar closures; Adaptations of fixed constructions therefor
- E06B5/165—Fireproof windows
-
- E—FIXED CONSTRUCTIONS
- E04—BUILDING
- E04B—GENERAL BUILDING CONSTRUCTIONS; WALLS, e.g. PARTITIONS; ROOFS; FLOORS; CEILINGS; INSULATION OR OTHER PROTECTION OF BUILDINGS
- E04B1/00—Constructions in general; Structures which are not restricted either to walls, e.g. partitions, or floors or ceilings or roofs
- E04B1/62—Insulation or other protection; Elements or use of specified material therefor
- E04B1/92—Protection against other undesired influences or dangers
- E04B1/94—Protection against other undesired influences or dangers against fire
- E04B1/941—Building elements specially adapted therefor
- E04B1/943—Building elements specially adapted therefor elongated
-
- E—FIXED CONSTRUCTIONS
- E04—BUILDING
- E04B—GENERAL BUILDING CONSTRUCTIONS; WALLS, e.g. PARTITIONS; ROOFS; FLOORS; CEILINGS; INSULATION OR OTHER PROTECTION OF BUILDINGS
- E04B2/00—Walls, e.g. partitions, for buildings; Wall construction with regard to insulation; Connections specially adapted to walls
- E04B2/88—Curtain walls
- E04B2/96—Curtain walls comprising panels attached to the structure through mullions or transoms
- E04B2/967—Details of the cross-section of the mullions or transoms
-
- E—FIXED CONSTRUCTIONS
- E04—BUILDING
- E04D—ROOF COVERINGS; SKY-LIGHTS; GUTTERS; ROOF-WORKING TOOLS
- E04D3/00—Roof covering by making use of flat or curved slabs or stiff sheets
- E04D3/02—Roof covering by making use of flat or curved slabs or stiff sheets of plane slabs, slates, or sheets, or in which the cross-section is unimportant
- E04D3/06—Roof covering by making use of flat or curved slabs or stiff sheets of plane slabs, slates, or sheets, or in which the cross-section is unimportant of glass or other translucent material; Fixing means therefor
- E04D3/08—Roof covering by making use of flat or curved slabs or stiff sheets of plane slabs, slates, or sheets, or in which the cross-section is unimportant of glass or other translucent material; Fixing means therefor with metal glazing bars
-
- E—FIXED CONSTRUCTIONS
- E04—BUILDING
- E04D—ROOF COVERINGS; SKY-LIGHTS; GUTTERS; ROOF-WORKING TOOLS
- E04D3/00—Roof covering by making use of flat or curved slabs or stiff sheets
- E04D3/02—Roof covering by making use of flat or curved slabs or stiff sheets of plane slabs, slates, or sheets, or in which the cross-section is unimportant
- E04D3/06—Roof covering by making use of flat or curved slabs or stiff sheets of plane slabs, slates, or sheets, or in which the cross-section is unimportant of glass or other translucent material; Fixing means therefor
- E04D3/08—Roof covering by making use of flat or curved slabs or stiff sheets of plane slabs, slates, or sheets, or in which the cross-section is unimportant of glass or other translucent material; Fixing means therefor with metal glazing bars
- E04D2003/0806—Roof covering by making use of flat or curved slabs or stiff sheets of plane slabs, slates, or sheets, or in which the cross-section is unimportant of glass or other translucent material; Fixing means therefor with metal glazing bars the supporting section of the glazing bar consisting of one single extruded or rolled metal part
-
- E—FIXED CONSTRUCTIONS
- E04—BUILDING
- E04D—ROOF COVERINGS; SKY-LIGHTS; GUTTERS; ROOF-WORKING TOOLS
- E04D3/00—Roof covering by making use of flat or curved slabs or stiff sheets
- E04D3/02—Roof covering by making use of flat or curved slabs or stiff sheets of plane slabs, slates, or sheets, or in which the cross-section is unimportant
- E04D3/06—Roof covering by making use of flat or curved slabs or stiff sheets of plane slabs, slates, or sheets, or in which the cross-section is unimportant of glass or other translucent material; Fixing means therefor
- E04D3/08—Roof covering by making use of flat or curved slabs or stiff sheets of plane slabs, slates, or sheets, or in which the cross-section is unimportant of glass or other translucent material; Fixing means therefor with metal glazing bars
- E04D2003/0818—Roof covering by making use of flat or curved slabs or stiff sheets of plane slabs, slates, or sheets, or in which the cross-section is unimportant of glass or other translucent material; Fixing means therefor with metal glazing bars the supporting section of the glazing bar consisting of several parts, e.g. compound sections
- E04D2003/0837—Sections comprising intermediate parts of insulating material
Definitions
- the invention relates to a facade or a glass roof in fire protection design according to the preamble of claim 1.
- the facade profile shown in Figure 3 of EP-A-0 716 194 is for fire protection Shield with an aluminum sheathing behind which there are appropriate fire protection panels for cladding the facade profile.
- the fire protection cladding is therefore not an integral part of the Facade profile itself. This results in a construction, the inside view is enlarged to the facade view width.
- Figure 2 of EP 0 716 194 shows a frame profile for windows and doors, which a wall reveal or a wall is oriented and fixed.
- DE 38 12 223 A1 also shows a facade in which the mullion and transom profiles are designed as hollow profiles made of aluminum.
- the mullion and / transom profiles a steel reinforcement profile is used and fixed with screws.
- the reinforcement profiles have a higher one Melting point on than the aluminum profiles, so that these reinforcement profiles in In the event of fire, the static stability over the respective period of time of the desired Ensure fire protection class.
- the complete coating or covering or cladding is also known reinforcement profiles to be inserted into the inner chambers of the mullion and / or transom profiles with fire protection material to melt or soften it to delay these profiles and achieve a long stability period.
- fire protection constructions provide the protective function of those interested Components secure by using more temperature stable materials than aluminum be, or that the components against direct flame or against Heat radiation shielded over the intended and specified period become.
- a joint processing is forbidden on the one hand from a different Material selection and on the other hand from the presence of the fasteners.
- the invention is based on the generic prior art
- the task is based on the generic facade or the generic glass roof to be designed so that the transom and post profiles made of aluminum and under No reinforcement profiles made of a different material and can be closed, jointly processed units for represent the use of fire protection constructions, the interior view for Facade view width, preferably should not be enlarged.
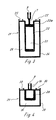
- the post profile 1 has a hollow chamber 2, which is used to hold reinforcement profiles 3 can be used.
- the post profile 1 is also with longitudinal webs 4 provided, the end receiving grooves 5, in the support seals 6 for Glass panes are used.
- the locking profile 11 is a hollow profile with a hollow chamber 12, the top of which has two grooves 13 for receiving the glass support seals 14, which are symmetrical are arranged to the central plane of the transom profile.
- the wall 15 of the hollow chamber 12 facing the glass pane is at the same time a base for the groove bottom of the grooves 13 for receiving the glass support seals 14 and for two parallel webs 16, which form a screw channel 8 between them, in which the base of an insulator 9 is also used.
- connection between the transom profile 11 and the post profile 1 takes place in the Way that the hollow chamber 12 is released so far below the wall 15, that the wall 15 on the grooves 5 or on the groove-forming webs of the grooves 5th rests and extends into the area of the drainage grooves 10.
- the transom profile is fixed to the post profile using an additional connector.
- the glass unit 17 is held on such a facade construction by that a pressure profile 18 through a seal 19 from the glass on the substructure Tighten the transoms and posts, the clamping being carried out by means of screws 20, which are screwed into the screw channels 8 of transoms and posts.
- FIG 3 shows a post profile 21 according to the invention, the core of which preferably consists of a rectangular core profile 22, which in the illustrated embodiment is equipped with a hollow chamber 23.
- the core profile 22 can also be designed as a full profile without an inner chamber.
- This core profile 22 is equipped with a tuning fork-shaped fastening web 7, which forms the screw groove 8.
- the core profile 22 is designed and dimensioned to withstand the static loads the facade or the glass roof not only under normal conditions but can also record in the event of a fire.
- the core structure which is formed by the core profile 22 and the tuning fork-shaped web 7 or the screw groove 8 is formed, includes a substantially U-shaped Box profile 24.
- the legs of the U-shaped box section 24 protrude above Core profile 22 a little towards the glazing side.
- the from the thighs of the Box profile towering wall 22a of the core profile 22 is in one piece with the tuning fork-shaped web 7, which forms the screw groove 8.
- the core profile 22 and the U-shaped box profile 24 are in the embodiment 3 formed as an integral, extruded aluminum profile.
- the thickness of the walls of the core profile 22 is greater, preferably by a multiple greater than the thickness of the walls of the box section 24.
- the groove bottom of the groove 25 is directly U-shaped Hollow chamber 26 limited by the core profile 22 and the box profile 24 is formed.
- FIG. 4 shows the transom profile 27 belonging to the post profile according to FIG. 3, whose core profile 28 is also a rectangular profile, the hollow profile or can be designed as a full profile.
- the core profile 28 is in one piece with the webs 16, which form a screw groove 8.
- the latch profile also has a box profile 29, which encloses the core profile 28 in a U-shape and on the side facing the glazing Wall is equipped with grooves 30 for system seals.
- the box profile 29 is smaller with one wall Provide thickness.
- the walls of the receiving grooves 30 forming the groove bottom are largely aligned with the upper wall of the core profile 28, so that with appropriate latching the aligned walls at the point of intersection between the bars and posts rest on the edge strips of the receiving groove 25 of the post profile 21 can.
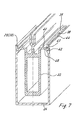
- FIG 5 shows a section through a post profile 21 of a fire protection facade in assembled condition.
- the post profile 21 is with the contact seals 6 for the ' Glass panes equipped, the seals being fixed in the receiving grooves 25 are. On this seal 6 or on the seal 14 of the associated latch comes the fire protection glazing 32 to the system.
- Fig. 5 a fire protection glazing is shown, which with insulating glazing is combined.
- An insulator 9 is inserted in the screw groove 8 of the fastening device on the profile side. which is penetrated by the screw 20, the screw 20 a Determines pressure profile 33 with the interposition of a pressure seal 19.
- the insulator 9 and the tuning fork-shaped web 7 separate the rebate made between the individual panes of fire protection glazing 32. On both sides of this separation, as shown in FIG. 5 Fire protection strips 34 are provided, which in the event of fire under the influence of temperature foam and the glass rebate and thus the fire protection glazing to the outside seal off. The access of hot fire gases to the glass rebate is thus blocked.
- the glass rebate area can be covered by a cover profile 35, which is clipped onto the pressure profile 33.
- the U-shaped chamber between the core profile 22 and the box profile 24 is partially or completely with plates or other shaped bodies made of a heat-binding, hydrophilic adsorbent with a high water content or with plates or Shaped bodies that contain such an adsorbent, filled.
- the plates or Shaped bodies are inserted into the U-shaped hollow chamber and only through Spring elements 37 non-positively fixed. 5 are the hydrophilic plates Assigned reference numerals 36 and 36.1.
- the U-shaped one is also used for the transom profile 37 Chamber 31 with plates or moldings made of a heat-binding, hydrophilic Partially or completely filled adsorbent with a high water content.
- hydrophilic adsorbent components used in the U-shaped hollow chambers 26 and 31, respectively are energy-consuming, i.e. by absorbing energy through these adsorbent components takes place beyond the target and predetermined period of time only a slight increase in temperature Fire protection facade profiles instead.
- This low heat conduction from the outer wall of the hollow chamber 26, 31 to the core profile is by connecting webs between the outer wall of the hollow chambers 26.31 and the core profile. These connecting webs can be used as walls be formed, the U-shaped 26 and 31 on the fire protection glazing limit facing side.
- Fig. 6 shows a post profile 21, in which the core profile 22 and the box profile 24 are made in one piece from aluminum.
- punchings 38 are provided which arranged one behind the other in the longitudinal direction of the profiles and by means of bridge webs 39 are separated.
- the bridge webs 39 limited heat conduction or heat flow from the outer wall of the hollow chamber reduced to core profile 22 or 28.
- These bridges 39 do not serve Thermal insulation of the facade in terms of the glazing level, but are exclusively intended for the heat flow in case of fire from box section 24 or 29 to minimize towards the core profile 22 or 28.
- FIG. 7 shows a modification of the post profile compared to FIG. 6.
- the core profile 22 has fastening webs in the transition to the box profile 24 40 on that with a prismatic border in a corresponding Engage the receiving groove 42 of the box section 24.
- the prismatic borders of the Fastening webs 40 are by rolling a groove web 43 of the box section 24 set.
- the receiving groove 25 for a system seal is through a with the mounting web 40 one-piece edge strip 41 and by one with the outer wall of the Box profile 24 one-piece edge strip limited.
- punchings 38 can be provided through the bridge webs 39 remain between two punchings.
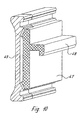
- Fig. 8 shows an embodiment of the post profile 21, in which both the core profile 22 and the box section 24 with their openings directed receiving grooves 42 for a metal strip 45.
- the metal strip 45 has longitudinal edges, which are formed by trapezoidal edge strips become. These trapezoidal edge strips engage positively in the grooves 42 and are formed by molding webs 43 of the box section 24 and 46 of the Core profile 22 set.
- the metal strip 45 is with an edge strip 41 for limiting the receiving groove for the system seal 6 equipped on one long side, while for the limitation the other long side provided with the box profile 24 one-piece edge strip 44 is.
- the metal strip 45 also has, as in the embodiments according to FIGS. 6 and 7 provided, die cuts 38 in dense order.
- the locking profile can also be in accordance with the embodiment according to FIG. 8 with a Metal bar 45 can be equipped.
- Fig. 9 shows a further embodiment of the post profile, in which instead of Metal bar 45 a connecting bar 47 is provided, which from a bad thermally conductive plastic is produced and the core profile 22 with the box profile 24 connects.
- the connecting bar 47 is equipped with an edge bar 48 which together with the edge strip 44 of the box section 24, the receiving groove for one Forms gasket for the glass pane.
- this connecting bar 47 is shown in FIG. 10.
- the trapezoidal edge strips are notched so that a bridge link 49 made of metal can be used. Through these pontics Metal becomes a small heat flow between the core profile 22 and the box profile 24 maintained.
- This constructive design can not only with the post profile, but also be provided for the transom profile.
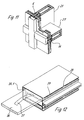
- FIG. 11 shows a node or a crossing point between one Post profile 21 and a transom profile 27. From this illustration it follows that the transom profile 27 the post profile 21 in the joint area on the whole View width overlaps, namely the overlap extends over the Sealing receiving grooves of the post profiles so that leachate from the Receivers of the transom profiles in the leachate of the Post profiles can flow without notches or notches in the post profile Routings are made.
- the core profiles of the post and the transom are the load-bearing components of the frame construction on which the entire Fireproof glazing supports, while the post and box profiles the bar only has the function of the heat-binding, hydrophilic plates and encapsulate other moldings, so that there is a closed and constructively appealing facade profiles result.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Architecture (AREA)
- Civil Engineering (AREA)
- Structural Engineering (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Electromagnetism (AREA)
- Load-Bearing And Curtain Walls (AREA)
- Building Environments (AREA)
- Glass Compositions (AREA)
- Laminated Bodies (AREA)
- Joining Of Glass To Other Materials (AREA)
- Special Wing (AREA)
Description
- Figur 1 und 2
- bekannte, aus Aluminium gefertigte Fassadenprofile,
- Figur 3
- ein erfindungsgemäßes Pfostenprofil und
- Figur 4
- ein erfindungsgemäßes Riegelprofil im Schnitt,
- Figur 5
- ein Pfostenprofil einer erfindungsgemäßen Brandschutzfassade in montiertem Zustand im Schnitt,
- Figuren 6,7,8 und 9
- weitere Ausführungsbeispiele eines erfindungsgemäßen Pfostenprofils,
- Figur 10
- eine konstruktive Einzelheit,
- Figur 11
- einen Kreuzungspunkt zwischen einem Pfostenprofil und einem Riegelprofil einer erfindungsgemäßen Fassade in Brandschutzausführung in perspektivischer Darstellung und
- Figur 12
- eine weitere konstruktive Einzelheit in perspektivischer Darstellung.
- 1
- Pfostenprofil
- 2
- Hohlkammer
- 3
- Verstärkungsprofil
- 4
- Längssteg
- 5
- Aufnahmenut
- 6
- Auflagedichtung
- 7
- Befestigungssteg
- 8
- Schraubnut
- 9
- Isolierleiste
- 10
- Entwässerungsnut
- 11
- Riegelprofil
- 12
- Hohlkammer
- 13
- Nut
- 14
- Glasauflagedichtung
- 15
- Wandung
- 16
- Steg
- 17
- Glaseinheit
- 18
- Druckprofil
- 19
- Dichtung
- 20
- Schraube
- 21
- Pfostenprofil
- 22
- Kernprofil
- 23
- Hohlkammer
- 24
- Kastenprofil
- 25
- Nut
- 26
- Hohlkammer
- 27
- Riegelprofil
- 28
- Kernprofil
- 29
- Kastenprofil
- 30
- Aufnahmenut
- 31
- Kammer
- 22a
- Wandung
- 32
- Brandschutzverglasung
- 33
- Druckprofil
- 34
- Brandschutzstreifen
- 35
- Deckprofil
- 36
- Platte
- 36.1
- Platte
- 37
- Federelement
- 38
- Ausstanzung
- 39
- Brückensteg
- 40
- Befestigungssteg
- 41
- Randleiste
- 42
- Aufnahmenut
- 43
- Nutsteg
- 44
- Randleiste
- 45
- Metalleiste
- 46
- Kastenprofil
- 47
- Verbindungsleiste
- 48
- Randleiste
- 49
- Brückenglied
Claims (20)
- Fassade oder Glasdach in Brandschutzausführung mit einer aus Pfosten- und Riegelprofilen bestehenden Tragkonstruktion, bei der die Pfosten- und Riegelprofile mit einer Brandschutzverglasung versehene Rahmenfelder begrenzen, wobei die Pfosten- und Riegelprofile aus Aluminium gefertigt sind und ein die statischen Belastungen aufnehmendes, tragendes Kernprofil aufweisen, wobei das Kernprofil von Formkörpern aus einem wärmebindenden, hydrophilen Adsorbens mit hohem Wasseranteil oder von Formkörpern, die ein wärmebindendes hydrophiles Adsorbens enthalten, umgeben ist, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß das Kemprofil (22, 28) in seinem Außenwandbereich von einer Hohlkammer (26, 31) zur Aufnahmme der Formkörper (36,36.1) umschlossen ist, wobei Verbindungsstege zwischen der Außenwand der Hohlkammer (26, 31) und dem Kernprofil (22, 28) für eine geringe Wärmeleitung bzw. für einen geringen Wärmefluß von der Außenwand der Hohlkammer (26, 31) zum Kernprofil (22, 28) vorgesehen sind.
- Fassade oder Glasdach nach Anspruch 1, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß die Verbindungsstege die Hohlkammer (26,31) an der Verglasungsseite begrenzen und zumindest ein Teil der Verbindungsstege jeweils den Boden einer Aufnahmenut (25,30) für eine Anlagedichtung (6) der Scheiben bildet.
- Fassade oder Glasdach nach Anspruch 1, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß die Hohlkammern (26,31) durch ein U-förmiges Kastenprofil (24,29) gebildet sind und das Kernprofil (22,28) als rechteckiges Hohlprofil gestaltet ist.
- Fassade oder Glasdach nach Anspruch 3, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß beim Pfostenprofil (21) die Schenkel des U-förmigen Kastenprofils (24) das Kemprofil (22) zur Verglassungsseite hin ein wenig überragen.
- Fassade oder Glasdach nach Anspruch 2, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß beim Riegelprofil (27) die Böden der Aufnahmenuten (30) mit der Wandung des Kernprofils (28) an der der Verglasung zugewandten Seite fluchten.
- Fassade oder Glasdach nach Anspruch 4, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß die von den Schenkeln des Kastenprofils (24) überragte Wandung (22a) des Kemprofils (22) einstückig mit einem mittigen Steg (7) ist, der stimmgabelförmig ausgebildet ist und eine Schraubnut (8) bildet.
- Fassade oder Glasdach nach einem der Ansprüche 3,4 oder 6, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß das Kemprofil (22,28) und das U-förmige Kastenprofil (24,29) als einstückig gefertigtes stranggepreßtes Aluminiumprofil ausgebildet ist.
- Fassade oder Glasdach nach Anspruch 7, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß die Dicke der Wandungen des Kernprofils (22,28) größer ist, vorzugsweise um ein Mehrfaches, als die Dicke der Wandungen des Kastenprofils (24).
- Fassade oder Glasdach nach Anspruch 1, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß das Kernprofil (22,28) als keine Innenkammer aufweisendes Vollprofil ausgebildet ist.
- Fassade oder Glasdach nach einem der vorhergehenden Ansprüche, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß das Kernprofil (22,28) rechteckförmig ausgebildet ist.
- Fassade oder Glasdach nach Anspruch 2, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß die Böden der Aufnahmenuten (26,30) mit einer Reihe von Ausstanzungen (38) versehen sind und die zwischen den Ausstanzungen (38) vorhandenen Brükkenstege (39) einen reduzierten Wärmefluß vom äußeren Kastenprofil (24,29) zum Kernprofil (22,28) sicherstellen.
- Fassade oder Glasdach nach Anspruch 6, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß im Glasfalz zu beiden Seiten der Schraubnut (8) Brandschutzstreifen (34) vorgesehen sind, die im Brandfall unter Temperatureinwirkung aufschäumen.
- Fassade oder Glasdach nach Anspruch 1, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß die hydrophilen Adsorbtionseinlagen (36,36.1) in der U-förmigen Hohlkammer (26,31) durch Federelemente (37) kraftschlüssig fixiert sind.
- Fassade oder Glasdach nach Anspruch 2, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß das Kernprofil (22,28) an der der Verglasung zugewandten Seite beidseitig einen Befestigungssteg (40) aufweist, der mit einer prismatischen Randleiste in eine entsprechende Aufnahmenut (42) des Kastenprofils (24) eingreift.
- Fassade oder Glasdach nach Anspruch 14, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß die prismatischen Randleisten der Befestigungsstege (40) durch Anwalzen eines Nutsteges (43) des Kastenprofils (24) festgelegt werden.
- Fassade oder Glasdach nach Anspruch 15, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß die Aufnahmenut (25) für eine Anlagedichtung durch eine mit dem Befestigungssteg (40) einstückige Randleiste (41) und eine mit der Außenwandung des Kastenprofils (24) einstückige Randleiste (44) begrenzt wird.
- Fassade oder Glasdach nach Anspruch 15, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß in den Befestigungsstegen (40) jeweils eine Reihe von Ausstanzungen (38) vorgesehen ist.
- Fassade oder Glasdach nach Anspruch 3, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß sowohl das Kernprofil (22) als auch das Kastenprofil (24) Aufnahmenuten (42) für eine Metalleiste (45) oder für eine Verbindungsleiste (47) aus einem schlecht wärmeleitenden Kunststoff mit trapezförmigen Randleisten aufweisen, die durch Anformen von Anformstegen (43,46) festgelegt werden.
- Fassade oder Glasdach nach Anspruch 18, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß die Metalleiste (45) eine Randleiste (41) oder die Verbindungsleiste (47) eine Randleiste (48) zur Begrenzung der Aufnahmenut für eine Anlagedichtung (6) an einer Längsseite, während für die Begrenzung der anderen Längsseite eine mit dem Kastenprofil (24) einstückige Randleiste (44) vorgesehen ist.
- Fassade oder Glasdach nach Anspruch 18, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß die Verbindungsleiste (47) in Ausklinkungen eingesetzte Brückenglieder (49) aus Metall für einen geringen Wärmefluß von der Außenwandung des Kastenprofils zum Kernprofil aufweist.
Priority Applications (9)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE19700696A DE19700696B4 (de) | 1997-01-13 | 1997-01-13 | Fassade oder Glasdach in Brandschutzausführung |
| RU98101504/03A RU2186180C2 (ru) | 1997-01-13 | 1998-01-29 | Фасад или стеклянная крыша в противопожарном варианте исполнения |
| EP98101515A EP0933486B2 (de) | 1997-01-13 | 1998-01-29 | Fassade oder Glasdach in Brandschutzausführung |
| AT98101515T ATE217046T1 (de) | 1997-01-13 | 1998-01-29 | Fassade oder glasdach in brandschutzausführung |
| DK98101515T DK0933486T3 (da) | 1997-01-13 | 1998-01-29 | Facade eller glastag i brandbeskyttende udformning |
| NO19980398A NO315334B1 (no) | 1997-01-13 | 1998-01-29 | Brannsikker fasade eller glasstak |
| CA002230408A CA2230408C (en) | 1997-01-13 | 1998-02-24 | Fire-resistant facade or glass roof |
| US09/049,592 US6141923A (en) | 1997-01-13 | 1998-03-27 | Fire-resistant frame structure for a facade or glass roof |
| HK99104449.1A HK1019467B (en) | 1999-10-08 | Curtain wall or glazed roof with a fire protection |
Applications Claiming Priority (6)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE19700696A DE19700696B4 (de) | 1997-01-13 | 1997-01-13 | Fassade oder Glasdach in Brandschutzausführung |
| RU98101504/03A RU2186180C2 (ru) | 1997-01-13 | 1998-01-29 | Фасад или стеклянная крыша в противопожарном варианте исполнения |
| EP98101515A EP0933486B2 (de) | 1997-01-13 | 1998-01-29 | Fassade oder Glasdach in Brandschutzausführung |
| NO19980398A NO315334B1 (no) | 1997-01-13 | 1998-01-29 | Brannsikker fasade eller glasstak |
| CA002230408A CA2230408C (en) | 1997-01-13 | 1998-02-24 | Fire-resistant facade or glass roof |
| US09/049,592 US6141923A (en) | 1997-01-13 | 1998-03-27 | Fire-resistant frame structure for a facade or glass roof |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0933486A1 EP0933486A1 (de) | 1999-08-04 |
| EP0933486B1 true EP0933486B1 (de) | 2002-05-02 |
| EP0933486B2 EP0933486B2 (de) | 2006-01-18 |
Family
ID=31950879
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP98101515A Expired - Lifetime EP0933486B2 (de) | 1997-01-13 | 1998-01-29 | Fassade oder Glasdach in Brandschutzausführung |
Country Status (8)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US6141923A (de) |
| EP (1) | EP0933486B2 (de) |
| AT (1) | ATE217046T1 (de) |
| CA (1) | CA2230408C (de) |
| DE (1) | DE19700696B4 (de) |
| DK (1) | DK0933486T3 (de) |
| NO (1) | NO315334B1 (de) |
| RU (1) | RU2186180C2 (de) |
Families Citing this family (82)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE19700696B4 (de) * | 1997-01-13 | 2008-07-31 | SCHÜCO International KG | Fassade oder Glasdach in Brandschutzausführung |
| DE19848767A1 (de) * | 1998-10-22 | 2000-04-27 | Pitscheider Karl | Einlage für Hohlprofile |
| DE10003953A1 (de) * | 2000-01-29 | 2001-08-09 | Wicona Bausysteme Gmbh | Fassade oder Glasdach in Brandschutzausführung mit einer aus vertikalen und horizontalen Profilen bestehenden Tragkonstruktion |
| FR2805882B1 (fr) * | 2000-03-03 | 2002-11-08 | Concept Alu | Profile composite formant au moins une feuillure susceptible d'accueillir la bordure de panneaux divers, d'epaisseur differente |
| DE10101720A1 (de) * | 2001-01-15 | 2002-07-18 | Schueco Int Kg | Riegel-Pfosten-Konstruktion |
| GB2373002B (en) * | 2001-03-09 | 2004-04-07 | Levolux At Ltd | Apparatus for and a method of attaching items to curtain walling |
| US8484916B2 (en) * | 2001-03-22 | 2013-07-16 | F. Aziz Farag | Panel-sealing and securing system |
| US6857233B2 (en) * | 2001-03-22 | 2005-02-22 | F. Aziz Farag | Fire resistant rated fenestration, including curtain wall systems, for multiple story buildings |
| US7832160B2 (en) * | 2001-03-22 | 2010-11-16 | Media Curtainwall Corp. | Seismic safe and fire resistant rated edge attached stopless glazing |
| EP1283311A3 (de) * | 2001-08-01 | 2004-02-11 | Aspect Management Ltd | Wintergartenstrukturen |
| DE10144551A1 (de) * | 2001-09-10 | 2003-03-27 | Bemofensterbau Gmbh | Brandschutzelement, Verfahren zu dessen Herstellung und brandschutzgesichertes Rahmenwerk für ein Gebäudeteil, wie für eine Gebäudefassade oder dgl. |
| DE10144820A1 (de) * | 2001-09-10 | 2003-03-27 | Bemofensterbau Gmbh | Brandschutzelement, Verfahren zu dessen Herstellung und brandschutzgesichertes Rahmenwerk für ein Gebäudeteil, wie für eine Gebäudefassade oder dgl. |
| RU2217570C2 (ru) * | 2002-02-15 | 2003-11-27 | Галашин Анатолий Евгеньевич | Огнестойкая строительная конструкция и способ ее изготовления |
| FR2836497B1 (fr) * | 2002-02-22 | 2004-11-05 | Virtual Travel | Dispositif de fixation d'un panneau acoustique sur une paroi |
| US7059092B2 (en) * | 2002-02-26 | 2006-06-13 | Washington Hardwoods Co., Llc | Fire-resistant wood assemblies for building |
| US6804920B2 (en) * | 2002-06-05 | 2004-10-19 | X-Clad, Inc. | Tube-lock curtain wall system |
| WO2004042159A1 (en) * | 2002-11-08 | 2004-05-21 | Alprogetti S.R.L. | System for joining mullions to transoms by frontal link |
| RU2321707C2 (ru) * | 2003-09-16 | 2008-04-10 | Реновизион | Опорная рамная конструкция для фасада |
| CN100425778C (zh) * | 2003-09-16 | 2008-10-15 | 莱诺视觉公司 | 用于正面组装结构的支撑框架 |
| DE202004007805U1 (de) * | 2004-05-14 | 2004-07-29 | SCHÜCO International KG | Andruckprofil und Fassaden- oder Lichtdachkonstruktion |
| ITMI20061534A1 (it) * | 2006-08-02 | 2008-02-03 | Norsk Hydro As | Profilato non isolato adatto a realizzare profilati isolati per serramenti a taglio termico e relativo metodo di assemblaggio |
| RU2335614C1 (ru) * | 2007-01-18 | 2008-10-10 | Общество с ограниченной ответственностью "Урало-Сибирская профильная компания" | Способ сборки элементов фасадных конструкций |
| DE202007002304U1 (de) | 2007-02-16 | 2007-04-26 | SCHÜCO International KG | Fassade oder Lichtdach für ein Gebäude |
| CN101270594B (zh) * | 2007-03-20 | 2011-05-25 | 王广武 | 隔热幕墙型材 |
| IL183640A (en) * | 2007-06-04 | 2011-06-30 | Dan Pal | Assemblies for structural panels |
| ITMI20071932A1 (it) * | 2007-10-05 | 2009-04-06 | Norsk Hydro As | Semiguscio per realizzare serramenti a taglio termico o simili, relativo profilato e relativo processo di assemblaggio |
| DE202007015301U1 (de) * | 2007-11-03 | 2009-03-19 | Raico Bautechnik Gmbh | Tragkonstruktion, insbesondere für Fassaden und Wintergärten |
| DE102007053659A1 (de) * | 2007-11-08 | 2009-05-20 | Hermann Gutmann Werke Ag | Gebäudefassade in Brandschutzausführung |
| US8011146B2 (en) * | 2007-12-19 | 2011-09-06 | William Krause | Blast-proof window and mullion system |
| RU2361984C1 (ru) * | 2008-01-21 | 2009-07-20 | Александр Арнольдович Мищенко | Стеклопанель для заполнения проемов фасадных систем |
| DE202008001191U1 (de) * | 2008-01-28 | 2009-06-10 | SCHÜCO International KG | Tragprofilanordnung in sprenghemmender Ausgestaltung für eine Fassadenkonstruktion |
| GB0902627D0 (en) * | 2009-02-17 | 2009-04-01 | Pilkington Group Ltd | Improvements in or relating to structural glass assemblies |
| US8240109B2 (en) * | 2009-03-20 | 2012-08-14 | Northern States Metals Company | Support system for solar panels |
| US8256169B2 (en) * | 2009-03-20 | 2012-09-04 | Northern States Metals Company | Support system for solar panels |
| US8316590B2 (en) | 2009-03-20 | 2012-11-27 | Northern States Metals Company | Support system for solar panels |
| CA2704067C (en) * | 2009-05-19 | 2017-01-24 | Groupe Lessard Inc. | Pressure plate assembly for curtain wall panels |
| EP2322732B1 (de) * | 2009-11-16 | 2012-06-20 | W.M.K.Secur S.r.l. | Fassade oder Glaswand in Brandschutzausführung |
| IT1398045B1 (it) * | 2010-01-29 | 2013-02-07 | Politec Polimeri Tecnici S A Ora Koscon Ind S A | Elementi di giunzione per pannelli e assiemi di copertura a pannelli |
| US20120031039A1 (en) * | 2010-08-06 | 2012-02-09 | Northern States Metals Company | Hinged clip to eliminate rail |
| US8839573B2 (en) * | 2011-02-11 | 2014-09-23 | Northern States Metals Company | Spring clip |
| AT12680U1 (de) * | 2011-06-01 | 2012-09-15 | Josko Fenster Und Tueren Gmbh | Vorrichtung zur statischen bewehrung von wandteilen, insbesondere von glaselementen |
| US10508441B2 (en) | 2012-02-01 | 2019-12-17 | Krueger International, Inc. | Demountable wall system |
| US10053858B2 (en) * | 2012-02-01 | 2018-08-21 | Krueger International, Inc. | Demountable wall system |
| WO2014055617A1 (en) * | 2012-10-02 | 2014-04-10 | Technical Glass Products | Barrier to heat transparent wall system |
| KR101365731B1 (ko) * | 2012-12-03 | 2014-02-25 | 주식회사 포스코건설 | 커튼월 멀리언의 차음유닛 |
| US9303663B2 (en) | 2013-04-11 | 2016-04-05 | Northern States Metals Company | Locking rail alignment system |
| DE202013104191U1 (de) * | 2013-09-13 | 2014-12-16 | SCHÜCO International KG | Pfosten-Riegel-Konstruktion |
| CN103572871A (zh) * | 2013-10-22 | 2014-02-12 | 谢增厚 | 插接式组合幕墙 |
| US10450743B2 (en) * | 2014-02-24 | 2019-10-22 | Fremarq Innovations, Inc. | Window and curtain wall mullions, transoms and systems |
| US9212482B2 (en) * | 2014-02-24 | 2015-12-15 | Steelglaze, Inc. | Curtain wall mullions, transoms and systems |
| US9598892B2 (en) | 2014-09-15 | 2017-03-21 | Gregory Header | Quick release cladding system for door, window, sloped and vertical glazing systems frames, and the like |
| DE102015100524A1 (de) * | 2015-01-14 | 2016-07-14 | SCHÜCO International KG | Pfosten-Riegel-Konstruktion |
| EP3245345B1 (de) * | 2015-01-14 | 2021-02-24 | SCHÜCO International KG | Pfosten-riegel-konstruktion |
| US9234345B1 (en) | 2015-04-21 | 2016-01-12 | William F. O'Keeffe | Snap-together fire resistant fenestration frame apparatus |
| US9909306B2 (en) * | 2015-07-20 | 2018-03-06 | Arconic Inc. | Manufactures, methods and structures to reduce energy transfer in building curtain walls |
| CN105421672B (zh) * | 2015-12-10 | 2017-08-29 | 台州建筑安装工程公司 | 阳光房的玻璃屋面 |
| RU2760389C2 (ru) | 2016-02-29 | 2021-11-24 | Шюко Интернациональ Кг | Брусок коробки и/или брусок створной рамы и дверь, окно или фасадный элемент |
| DE102017100336A1 (de) | 2016-02-29 | 2017-08-31 | SCHÜCO International KG | Tür, Fenster oder Fassadenelement |
| DE102016121068A1 (de) | 2016-02-29 | 2017-08-31 | SCHÜCO International KG | Verbundprofil für eine Tür, ein Fenster oder ein Fassadenelement sowie Verfahren zur Herstellung des Verbundprofils |
| CA2989713A1 (en) | 2016-12-20 | 2018-06-20 | Clarkwestern Dietrich Building Systems Llc | Finishing accessory with backing strip seal for wall construction |
| CN106812247B (zh) * | 2017-03-10 | 2019-02-15 | 中建八局装饰工程有限公司 | 一种金属板圆柱的安装方法 |
| CZ31540U1 (cs) * | 2017-05-24 | 2018-03-06 | Jakub Řehák | Přídavná izolace a krycí profil nosného profilového systému prosklených fasád |
| US10619399B2 (en) * | 2017-09-14 | 2020-04-14 | Arconic Inc. | Combination pressure plate |
| JP6925927B2 (ja) * | 2017-10-03 | 2021-08-25 | Ykk Ap株式会社 | カーテンウォール |
| US10533317B2 (en) * | 2018-04-25 | 2020-01-14 | Arconic Inc. | Curtain wall expansion joint |
| CA3096735A1 (en) * | 2018-06-12 | 2019-12-19 | Arconic Technologies Llc | Thermal separator with integrated fluid seal |
| US10731402B2 (en) * | 2018-07-26 | 2020-08-04 | Matrex Window System Inc. | Jacking screw for adjusting a window frame |
| US10689899B2 (en) | 2018-10-17 | 2020-06-23 | Matrex Window System Inc. | Gasket railing system for a window frame |
| US10711514B2 (en) * | 2018-07-26 | 2020-07-14 | Matrex Window System Inc. | Male and female gasket coupling for a window frame |
| US10590696B2 (en) * | 2018-07-26 | 2020-03-17 | Matrex Window System Inc. | Sill track seal for a window frame |
| US10844651B2 (en) | 2018-07-26 | 2020-11-24 | Matrex Window System Inc. | Compression gasket for sealing a window in a window frame |
| US11199045B2 (en) * | 2018-07-26 | 2021-12-14 | Matrex Window System Inc. | Jacking screw for adjusting a window frame |
| CN111197358A (zh) * | 2018-11-20 | 2020-05-26 | 中建材创新科技研究院有限公司 | 一种用于改造的幕墙与内墙一体化的建筑结构 |
| CN109577531A (zh) * | 2018-12-26 | 2019-04-05 | 北京苏鑫华安幕墙装饰工程有限公司 | 一种外包铝型材幕墙 |
| US11473307B2 (en) * | 2019-09-05 | 2022-10-18 | Greg Smyth | Skylight and smoke vent gutter uplift channel assembly |
| US11808078B2 (en) * | 2020-09-01 | 2023-11-07 | Visionwall International, Inc. | Retrofit adaptor for glazing structures and method therefor |
| USD1026252S1 (en) | 2020-11-12 | 2024-05-07 | Clarkwestern Dietrich Building Systems Llc | Control joint |
| US11885138B2 (en) | 2020-11-12 | 2024-01-30 | Clarkwestern Dietrich Building Systems Llc | Control joint |
| BE1029077B1 (nl) * | 2021-02-02 | 2022-08-29 | Arlu | Bevestigingsinrichting voor het monteren van wandelementen voor het opbouwen van een wand |
| CN114892858A (zh) * | 2022-05-17 | 2022-08-12 | 同济大学建筑设计研究院(集团)有限公司 | 一种用于消防救援窗可调节洞口尺寸的格栅幕墙系统 |
| WO2024187124A1 (en) * | 2023-03-08 | 2024-09-12 | O'keeffe's, Inc. | Snap-together fire resistant fenestration frame apparatus |
| CN116905703A (zh) * | 2023-07-20 | 2023-10-20 | 中建八局发展建设有限公司 | 一种洞口式小单元框架玻璃幕墙结构 |
Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP0086976A1 (de) * | 1982-02-03 | 1983-08-31 | Trube & Kings KG | Brandschutzelement |
| EP0717165B1 (de) * | 1994-12-08 | 1999-05-12 | SCHÜCO International KG | Rahmenwerk aus Metallprofilen in Brandschutzausführung für Fenster, Türen, Fassaden oder Glasdächer |
Family Cites Families (13)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US3932974A (en) * | 1973-12-26 | 1976-01-20 | Helmerich & Payne, Inc. | Glazing system |
| FI76616C (fi) * | 1984-05-25 | 1991-08-07 | Schuermann & Co Heinz | Fasad eller tak som en metall-glas-konstruktion. |
| US4650702A (en) * | 1985-10-15 | 1987-03-17 | Kawneer Company, Inc. | Structural interface and weatherseal for structurally bonded glazing |
| DE3540385A1 (de) * | 1985-11-14 | 1987-05-21 | Eltreva Ag | Fassadenkonstruktion aus metallprofilen |
| DE3812223A1 (de) * | 1988-04-13 | 1989-11-02 | Schueco Int Gmbh & Co | Fassade mit einer aus pfosten- und riegelprofilen bestehenden tragkonstruktion und einer brandschutzverglasung |
| DE8916016U1 (de) * | 1989-12-02 | 1993-02-11 | Schüco International KG, 4800 Bielefeld | Verbundprofil, insbesondere für Fenster, Türen und Fassaden |
| DE4224923C2 (de) * | 1992-07-28 | 1996-08-29 | Sommer Metallbau Stahlbau Gmbh | Bauelement |
| DE9211944U1 (de) * | 1992-09-04 | 1994-01-13 | Hörmann KG Eckelhausen, 66625 Nohfelden | Feuerschutzabschluß im Gebäudebereich |
| ATE182388T1 (de) * | 1994-06-09 | 1999-08-15 | Hartmann & Co W | Bauwerksfassade |
| DE4427682C2 (de) * | 1994-08-04 | 1996-12-12 | Ensinger Gmbh & Co | Verbundprofil für Rahmen von Fenstern, Türen, Fassadenelementen u. dgl. |
| DE4438113A1 (de) * | 1994-10-26 | 1996-05-02 | Eberspaecher J | Brandsichere Halterung mindestens einer Scheibe |
| DE4443761A1 (de) * | 1994-12-08 | 1996-06-13 | Schueco Int Kg | Wärmebindendes Bauteil für den Innen- und Außenausbau in Brandschutzausführung |
| DE19700696B4 (de) * | 1997-01-13 | 2008-07-31 | SCHÜCO International KG | Fassade oder Glasdach in Brandschutzausführung |
-
1997
- 1997-01-13 DE DE19700696A patent/DE19700696B4/de not_active Expired - Lifetime
-
1998
- 1998-01-29 DK DK98101515T patent/DK0933486T3/da active
- 1998-01-29 EP EP98101515A patent/EP0933486B2/de not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1998-01-29 NO NO19980398A patent/NO315334B1/no not_active IP Right Cessation
- 1998-01-29 AT AT98101515T patent/ATE217046T1/de active
- 1998-01-29 RU RU98101504/03A patent/RU2186180C2/ru not_active IP Right Cessation
- 1998-02-24 CA CA002230408A patent/CA2230408C/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1998-03-27 US US09/049,592 patent/US6141923A/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
Patent Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP0086976A1 (de) * | 1982-02-03 | 1983-08-31 | Trube & Kings KG | Brandschutzelement |
| EP0717165B1 (de) * | 1994-12-08 | 1999-05-12 | SCHÜCO International KG | Rahmenwerk aus Metallprofilen in Brandschutzausführung für Fenster, Türen, Fassaden oder Glasdächer |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| HK1019467A1 (en) | 2000-02-11 |
| DE19700696B4 (de) | 2008-07-31 |
| NO980398L (no) | 1999-07-30 |
| EP0933486B2 (de) | 2006-01-18 |
| DE19700696A1 (de) | 1998-07-16 |
| CA2230408A1 (en) | 1999-08-24 |
| NO315334B1 (no) | 2003-08-18 |
| RU2186180C2 (ru) | 2002-07-27 |
| NO980398D0 (no) | 1998-01-29 |
| CA2230408C (en) | 2006-12-19 |
| EP0933486A1 (de) | 1999-08-04 |
| US6141923A (en) | 2000-11-07 |
| DK0933486T3 (da) | 2002-08-19 |
| ATE217046T1 (de) | 2002-05-15 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP0933486B1 (de) | Fassade oder Glasdach in Brandschutzausführung | |
| DE3419538C2 (de) | ||
| DE19528498C1 (de) | Isolierkern für Verbundprofil, insbesondere für Fenster, Türen und Fassadenkonstruktionen | |
| DE3541730A1 (de) | Verkleidung fuer aussenflaechen von gebaeuden | |
| CH651342A5 (de) | Rahmenbauteil. | |
| DE4410075A1 (de) | Fenster | |
| EP1194673A1 (de) | Feuerhemmendes flächenelement mit mindestens zwei lichtdurchlässigen brandschutz-glasplatten | |
| EP0566070A1 (de) | Wärmegedämmtes Verglasungssystem oder dergl. | |
| DE19635409B4 (de) | Glastür für Brandschutzzwecke sowie Verfahren zum Herstellen einer Glastür für Brandschutzzwecke | |
| DE3402226C1 (de) | Verbundprofil fuer einen Fluegel- oder Blendrahmen fuer Fenster oder verglaste Tueren | |
| DE3742723C1 (en) | Frame structure by the post/crossmember construction method, in particular for facades, roofs or the like | |
| EP0971081A2 (de) | Gebäudefassade oder Dachfassade mit einem Rahmenwerk aus Pfosten und Riegeln | |
| DE202014010902U1 (de) | Isolierelement für Fassaden- oder Lichtdachkonstruktionen | |
| EP0298283B1 (de) | Abdichtungsbauwerk aus einer vertikalen Schlitzwand und einer darin angeordneten Dichtwand | |
| EP0619403A1 (de) | Aussenwandkonstruktion für Gebäude oder Schrägdächer | |
| DE2800811A1 (de) | Kastenfoermige bautafel aus extrudiertem lichtdurchlaessigem kunststoff | |
| DE10008370C2 (de) | Rahmenkonstruktion mit verbesserter Wärmedämmung | |
| EP1835084B1 (de) | Isolator für eine aus Profilen bestehende Pfosten/Riegel-Fassadenkonstruktion | |
| CH648380A5 (de) | Fluegel- und blendrahmen fuer fenster oder verglaste tueren. | |
| DE3504989C2 (de) | Verglasung mit einer schußsicheren Scheibe | |
| AT404747B (de) | Rahmen für plattenelemente | |
| DE9318201U1 (de) | Brandschutzverbundprofil | |
| EP1020576B1 (de) | Fassade oder Lichtdach mit einem Rahmenwerk aus Pfosten- und Sprossenprofilen | |
| DE3719803C2 (de) | Feuerhemmende verglaste Trennwand | |
| DE3110874A1 (de) | Mehrfach verglastes fenster |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 19980711 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AT BE CH DK FI FR GB IE IT LI LU NL SE |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Free format text: AL;LT;LV;MK;RO;SI |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 19991215 |
|
| AKX | Designation fees paid |
Free format text: AT BE CH DK FI FR GB IE IT LI LU NL SE |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: 8566 |
|
| GRAG | Despatch of communication of intention to grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS AGRA |
|
| GRAG | Despatch of communication of intention to grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS AGRA |
|
| GRAH | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS IGRA |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: IF02 |
|
| GRAH | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS IGRA |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AT BE CH DK FI FR GB IE IT LI LU NL SE |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 217046 Country of ref document: AT Date of ref document: 20020515 Kind code of ref document: T |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: NOT ENGLISH |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: NV Representative=s name: ISLER & PEDRAZZINI AG Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: EP |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: GERMAN |
|
| GBT | Gb: translation of ep patent filed (gb section 77(6)(a)/1977) |
Effective date: 20020717 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DK Ref legal event code: T3 |
|
| ET | Fr: translation filed | ||
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DK Payment date: 20030124 Year of fee payment: 6 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Payment date: 20030127 Year of fee payment: 6 Ref country code: LU Payment date: 20030127 Year of fee payment: 6 |
|
| PLBQ | Unpublished change to opponent data |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS OPPO |
|
| PLBI | Opposition filed |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009260 |
|
| PLBF | Reply of patent proprietor to notice(s) of opposition |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS OBSO |
|
| 26 | Opposition filed |
Opponent name: BEMOFENSTERBAU GMBH Effective date: 20030131 |
|
| PLAX | Notice of opposition and request to file observation + time limit sent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNOBS2 |
|
| PLBB | Reply of patent proprietor to notice(s) of opposition received |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNOBS3 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20040129 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20040130 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20040202 |
|
| EUG | Se: european patent has lapsed | ||
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DK Ref legal event code: EBP |
|
| PLAB | Opposition data, opponent's data or that of the opponent's representative modified |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009299OPPO |
|
| R26 | Opposition filed (corrected) |
Opponent name: BEMO BRANDSCHUTZSYSTEME GMBH Effective date: 20030131 |
|
| NLR1 | Nl: opposition has been filed with the epo |
Opponent name: BEMO BRANDSCHUTZSYSTEME GMBH |
|
| PUAH | Patent maintained in amended form |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009272 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: PATENT MAINTAINED AS AMENDED |
|
| 27A | Patent maintained in amended form |
Effective date: 20060118 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B2 Designated state(s): AT BE CH DK FI FR GB IE IT LI LU NL SE |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: AEN Free format text: AUFRECHTERHALTUNG DES PATENTES IN GEAENDERTER FORM |
|
| NLR2 | Nl: decision of opposition |
Effective date: 20060118 |
|
| GBTA | Gb: translation of amended ep patent filed (gb section 77(6)(b)/1977) | ||
| NLR3 | Nl: receipt of modified translations in the netherlands language after an opposition procedure | ||
| ET3 | Fr: translation filed ** decision concerning opposition | ||
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PCAR Free format text: ISLER & PEDRAZZINI AG;POSTFACH 1772;8027 ZUERICH (CH) |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IE Payment date: 20090122 Year of fee payment: 12 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: MM4A |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20100129 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FI Payment date: 20110128 Year of fee payment: 14 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20120129 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: PLFP Year of fee payment: 19 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Payment date: 20160121 Year of fee payment: 19 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CH Payment date: 20160121 Year of fee payment: 19 Ref country code: IT Payment date: 20160122 Year of fee payment: 19 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Payment date: 20160121 Year of fee payment: 19 Ref country code: BE Payment date: 20160121 Year of fee payment: 19 Ref country code: AT Payment date: 20160120 Year of fee payment: 19 Ref country code: GB Payment date: 20160122 Year of fee payment: 19 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20170131 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: NL Ref legal event code: MM Effective date: 20170201 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: AT Ref legal event code: MM01 Ref document number: 217046 Country of ref document: AT Kind code of ref document: T Effective date: 20170129 |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 20170129 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: ST Effective date: 20170929 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20170129 Ref country code: FR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20170131 Ref country code: CH Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20170131 Ref country code: LI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20170131 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20170129 Ref country code: NL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20170201 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: BE Ref legal event code: MM Effective date: 20170131 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20170129 |