WO2015045677A1 - 透明樹脂成形品の射出成形装置および射出成形方法 - Google Patents
透明樹脂成形品の射出成形装置および射出成形方法 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2015045677A1 WO2015045677A1 PCT/JP2014/071698 JP2014071698W WO2015045677A1 WO 2015045677 A1 WO2015045677 A1 WO 2015045677A1 JP 2014071698 W JP2014071698 W JP 2014071698W WO 2015045677 A1 WO2015045677 A1 WO 2015045677A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- mold
- injection molding
- molded product
- transparent resin
- resin molded
- Prior art date
Links
- 239000011347 resin Substances 0.000 title claims abstract description 192
- 229920005989 resin Polymers 0.000 title claims abstract description 192
- 238000001746 injection moulding Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 126
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 124
- 230000002093 peripheral effect Effects 0.000 claims abstract description 25
- 238000000465 moulding Methods 0.000 claims description 59
- 238000002347 injection Methods 0.000 claims description 35
- 239000007924 injection Substances 0.000 claims description 35
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 claims description 21
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 claims description 15
- 230000001939 inductive effect Effects 0.000 claims description 5
- 230000007547 defect Effects 0.000 abstract description 14
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 abstract description 13
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 abstract description 4
- 230000009467 reduction Effects 0.000 abstract description 2
- 230000009471 action Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000003287 optical effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 229920000515 polycarbonate Polymers 0.000 description 3
- 239000004417 polycarbonate Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000004925 Acrylic resin Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229920000178 Acrylic resin Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 238000001816 cooling Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000003111 delayed effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000012778 molding material Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000005498 polishing Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000007493 shaping process Methods 0.000 description 2
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Substances O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- NIXOWILDQLNWCW-UHFFFAOYSA-N acrylic acid group Chemical group C(C=C)(=O)O NIXOWILDQLNWCW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000002950 deficient Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000002474 experimental method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000006872 improvement Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B29—WORKING OF PLASTICS; WORKING OF SUBSTANCES IN A PLASTIC STATE IN GENERAL
- B29C—SHAPING OR JOINING OF PLASTICS; SHAPING OF MATERIAL IN A PLASTIC STATE, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; AFTER-TREATMENT OF THE SHAPED PRODUCTS, e.g. REPAIRING
- B29C45/00—Injection moulding, i.e. forcing the required volume of moulding material through a nozzle into a closed mould; Apparatus therefor
- B29C45/14—Injection moulding, i.e. forcing the required volume of moulding material through a nozzle into a closed mould; Apparatus therefor incorporating preformed parts or layers, e.g. injection moulding around inserts or for coating articles
- B29C45/14778—Injection moulding, i.e. forcing the required volume of moulding material through a nozzle into a closed mould; Apparatus therefor incorporating preformed parts or layers, e.g. injection moulding around inserts or for coating articles the article consisting of a material with particular properties, e.g. porous, brittle
- B29C45/14811—Multilayered articles
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B29—WORKING OF PLASTICS; WORKING OF SUBSTANCES IN A PLASTIC STATE IN GENERAL
- B29C—SHAPING OR JOINING OF PLASTICS; SHAPING OF MATERIAL IN A PLASTIC STATE, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; AFTER-TREATMENT OF THE SHAPED PRODUCTS, e.g. REPAIRING
- B29C45/00—Injection moulding, i.e. forcing the required volume of moulding material through a nozzle into a closed mould; Apparatus therefor
- B29C45/0025—Preventing defects on the moulded article, e.g. weld lines, shrinkage marks
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B29—WORKING OF PLASTICS; WORKING OF SUBSTANCES IN A PLASTIC STATE IN GENERAL
- B29C—SHAPING OR JOINING OF PLASTICS; SHAPING OF MATERIAL IN A PLASTIC STATE, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; AFTER-TREATMENT OF THE SHAPED PRODUCTS, e.g. REPAIRING
- B29C45/00—Injection moulding, i.e. forcing the required volume of moulding material through a nozzle into a closed mould; Apparatus therefor
- B29C45/0046—Details relating to the filling pattern or flow paths or flow characteristics of moulding material in the mould cavity
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B29—WORKING OF PLASTICS; WORKING OF SUBSTANCES IN A PLASTIC STATE IN GENERAL
- B29C—SHAPING OR JOINING OF PLASTICS; SHAPING OF MATERIAL IN A PLASTIC STATE, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; AFTER-TREATMENT OF THE SHAPED PRODUCTS, e.g. REPAIRING
- B29C45/00—Injection moulding, i.e. forcing the required volume of moulding material through a nozzle into a closed mould; Apparatus therefor
- B29C45/16—Making multilayered or multicoloured articles
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B29—WORKING OF PLASTICS; WORKING OF SUBSTANCES IN A PLASTIC STATE IN GENERAL
- B29C—SHAPING OR JOINING OF PLASTICS; SHAPING OF MATERIAL IN A PLASTIC STATE, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; AFTER-TREATMENT OF THE SHAPED PRODUCTS, e.g. REPAIRING
- B29C45/00—Injection moulding, i.e. forcing the required volume of moulding material through a nozzle into a closed mould; Apparatus therefor
- B29C45/17—Component parts, details or accessories; Auxiliary operations
- B29C45/26—Moulds
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B29—WORKING OF PLASTICS; WORKING OF SUBSTANCES IN A PLASTIC STATE IN GENERAL
- B29C—SHAPING OR JOINING OF PLASTICS; SHAPING OF MATERIAL IN A PLASTIC STATE, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; AFTER-TREATMENT OF THE SHAPED PRODUCTS, e.g. REPAIRING
- B29C45/00—Injection moulding, i.e. forcing the required volume of moulding material through a nozzle into a closed mould; Apparatus therefor
- B29C45/0025—Preventing defects on the moulded article, e.g. weld lines, shrinkage marks
- B29C2045/0027—Gate or gate mark locations
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B29—WORKING OF PLASTICS; WORKING OF SUBSTANCES IN A PLASTIC STATE IN GENERAL
- B29K—INDEXING SCHEME ASSOCIATED WITH SUBCLASSES B29B, B29C OR B29D, RELATING TO MOULDING MATERIALS OR TO MATERIALS FOR MOULDS, REINFORCEMENTS, FILLERS OR PREFORMED PARTS, e.g. INSERTS
- B29K2033/00—Use of polymers of unsaturated acids or derivatives thereof as moulding material
- B29K2033/04—Polymers of esters
- B29K2033/08—Polymers of acrylic acid esters, e.g. PMA, i.e. polymethylacrylate
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B29—WORKING OF PLASTICS; WORKING OF SUBSTANCES IN A PLASTIC STATE IN GENERAL
- B29K—INDEXING SCHEME ASSOCIATED WITH SUBCLASSES B29B, B29C OR B29D, RELATING TO MOULDING MATERIALS OR TO MATERIALS FOR MOULDS, REINFORCEMENTS, FILLERS OR PREFORMED PARTS, e.g. INSERTS
- B29K2069/00—Use of PC, i.e. polycarbonates or derivatives thereof, as moulding material
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B29—WORKING OF PLASTICS; WORKING OF SUBSTANCES IN A PLASTIC STATE IN GENERAL
- B29K—INDEXING SCHEME ASSOCIATED WITH SUBCLASSES B29B, B29C OR B29D, RELATING TO MOULDING MATERIALS OR TO MATERIALS FOR MOULDS, REINFORCEMENTS, FILLERS OR PREFORMED PARTS, e.g. INSERTS
- B29K2995/00—Properties of moulding materials, reinforcements, fillers, preformed parts or moulds
- B29K2995/0018—Properties of moulding materials, reinforcements, fillers, preformed parts or moulds having particular optical properties, e.g. fluorescent or phosphorescent
- B29K2995/0026—Transparent
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B29—WORKING OF PLASTICS; WORKING OF SUBSTANCES IN A PLASTIC STATE IN GENERAL
- B29L—INDEXING SCHEME ASSOCIATED WITH SUBCLASS B29C, RELATING TO PARTICULAR ARTICLES
- B29L2009/00—Layered products
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B29—WORKING OF PLASTICS; WORKING OF SUBSTANCES IN A PLASTIC STATE IN GENERAL
- B29L—INDEXING SCHEME ASSOCIATED WITH SUBCLASS B29C, RELATING TO PARTICULAR ARTICLES
- B29L2031/00—Other particular articles
- B29L2031/30—Vehicles, e.g. ships or aircraft, or body parts thereof
- B29L2031/3076—Aircrafts
- B29L2031/3079—Cockpits, canopies
Definitions
- the present invention relates to an injection molding apparatus and an injection molding method for a transparent resin molded product.
- Patent Document 1 As injection molding methods for transparent resin molded products, those disclosed in the following Patent Documents 1 and 2 are known. As shown in FIGS. 2 to 4 of the same document, the method for producing a transparent resin member disclosed in Patent Document 1 is obtained by converting a polycarbonate intermediate molded product 2 having a convex shape into an appearance of the intermediate molded product 2. It is placed inside the molding die 6 composed of the lower die 60 and the upper die 61 having the same cavity surfaces 60a and 61a as the shape, and is clamped, and is placed in the gap between the intermediate molded product 2 and the cavity surfaces 60a and 61a. A transparent acrylic resin is poured, and thereby the canopy 1 in which the acrylic resin is laminated on both surfaces of the intermediate molded product 2 made of polycarbonate is molded.
- the manufacturing method of the contact lens material currently disclosed by patent document 2 is the 1st resin type and 2nd resin for manufacturing a contact lens material, as FIG. 8, FIG. 9 of the literature shows.
- the mold is injection-molded, the contact lens material molding material is supplied to one of the first resin mold and the second resin mold which are molded into the mold, and the first resin mold and the second resin mold are matched.
- a contact lens molding cavity is formed, and a molding material filled in the cavity is molded to obtain a target contact lens material.
- the methods for producing transparent resin molded articles in Patent Documents 1 and 2 are methods for molding a molded article having a comparatively thin and small size with a thickness of the molded article of about 1 mm or less to about 8 mm. Since problems are unlikely to occur, they are unlikely to become major problems. However, in the case of a thick and large transparent resin molded product having a thickness of about 20 mm, such as an aircraft canopy, the above problems A to C become significant.
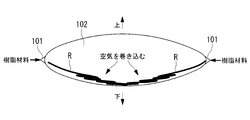
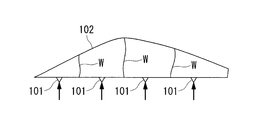
- the mold 102 is kept in a horizontal position and a gate 101 is formed on the uppermost part thereof, or as shown in FIG. Gates 101 are formed at both front and rear ends of the mold 102, and a resin material R is injected.
- the resin material R is injected into the mold 102 from such a position, the resin material R injected from the gate 101 does not adhere to the inner wall of the mold 102 because the internal space of the mold 102 is wide. As shown in FIG. 16, it is pushed out linearly and piles up, and a large amount of bubbles are mixed.
- the resin material R is injected by providing a gate.
- a so-called boundary surface (water bath) where the resin materials R injected from the gates 101 are in contact with each other inside the mold 102 remains visually.
- a weld line W is generated. Since this weld line W is accompanied by optical distortion, it becomes a serious defect in an aircraft canopy.
- An object of the present invention is to provide an injection molding apparatus and injection molding method for a transparent resin molded product.
- the present invention employs the following means.
- an injection molding apparatus for a transparent resin molded product is provided with a molding die for injection molding a transparent resin molded product, and a peripheral portion of the molding die, and the inside of the molding die. And a gate serving as an inlet for injecting a resin material, wherein the mold has a thickness dimension of 15 to 25 mm, and the diameter dimension of the gate and the thickness dimension of the mold are The ratio is set within the range of 1: 6 to 1: 3.
- the transparent resin molded product injection molding method includes a molding die for injection molding a transparent resin molded product, a peripheral portion of the molding die, and an interior of the molding die.
- An injection molding method using a gate serving as an inlet for injecting a resin material wherein a diameter dimension of the gate and a thickness dimension of the molding die when the thickness dimension of the molding die is in the range of 15 to 25 mm. Is set within the range of 1: 6 to 1: 3.
- the ratio of the diameter dimension of the gate and the thickness dimension of the mold is optimized, so that the resin material injected from the gate into the mold is inside the mold.
- the injected resin material flows in a fountain flow through the inside of the mold. For this reason, bubbles are not mixed into the resin material, and defects due to the mixing of bubbles can be prevented to improve the yield of molded products, and the manufacturing cost can be reduced.
- an injection molding apparatus for a transparent resin molded product includes a molding die for injection molding a concave transparent resin molded product, and an inlet for injecting a resin material into the molding die.
- the gate is provided at the periphery of the mold, the mold has an angle of the concave open surface, and the gate is at the lower part of the mold. The resin material is injected upward from the lower part inside the mold by the gate.
- the method for injection molding a transparent resin molded product according to the second aspect of the present invention includes a molding die for injection molding a concave transparent resin molded product, and an inlet for injecting a resin material into the molding die.
- An injection molding method using the gate wherein the molding die is maintained in a posture in which the concave open surface is substantially vertical, and the gate is provided at the lower part of the peripheral edge of the open surface, The resin material is injected upward from the lower part inside the mold by the gate.
- the resin material is injected into the mold from the gate located at the lower part of the mold, and the resin material is filled upward in the mold. For this reason, the resin material injected from the gate into the mold is not pushed out linearly and falls to the bottom of the mold so that it does not pile up. Occurrence can be prevented.
- a resin material pool having an inner width larger than the thickness dimension of the molding die is juxtaposed along at least the lower edge of the open surface of the molding die, and the resin material
- the pool and the lower edge of the mold may be continuously communicated along the longitudinal direction, and the gate may be provided at a plurality of locations along the longitudinal direction of the resin material pool.
- a resin material pool having an inner width larger than the thickness dimension of the molding die is juxtaposed along at least the lower edge of the open surface of the molding die,
- the resin material pool and the lower edge of the mold are continuously communicated along the longitudinal direction, and the gates are provided at a plurality of locations along the longitudinal direction of the resin material pool.
- the resin material injected from the gate to the inside of the resin material pool may be flown and mixed in the resin material pool and then filled in the mold.
- a resin material pool having an inner width larger than the thickness dimension of the mold is formed in the lower part of the mold, and a plurality of gates are provided in the resin material pool. Resin material is injected.
- the resin materials injected into the resin material pool from the plurality of gates are mixed with each other by first flowing through the resin material pool. Then, the mixed resin material is widely injected from the resin material pool along the lower edge of the mold. For this reason, it is possible to prevent the occurrence of defects such that the resin material injected from a plurality of gates (multi-point gates) forms a boundary surface (weld line) inside the mold.
- the passage width of the connection passage connecting the lower edge of the open surface of the mold and the inside of the resin material pool is set to the concave shape of the mold. It is preferable to increase the length of the cross-sectional arch.
- An injection molding apparatus for a transparent resin molded product includes a molding die for injection molding a concave transparent resin molded product, and the molding die includes: An outer part molding die for injection-molding an outer part from the intermediate portion in the thickness direction of the transparent resin molded product to the outer surface between the first outer mold and the first inner mold; a second outer mold; An inner part molding die for injection-molding an inner part from the intermediate portion of the transparent resin molded product to the inner surface between the inner mold and the inner mold, and the first outer mold and the second inner mold.
- the transparent resin molded product injection molding method is a method for injection molding a concave transparent resin molded product, and is an intermediate portion in the plate thickness direction of the transparent resin molded product.
- a secondary curing step for inducing sink marks on the surface, the first outer mold after the primary curing step, and the And combined mold and the second inner die after the next curing step comprising and a tertiary injection step of injecting the resin material into the injection space formed between the outer portion and the inner portion.
- the outer side from the intermediate portion in the plate thickness direction of the concave transparent resin molded product to the outer surface is formed by the first outer mold and the first inner mold of the outer partial molding die.
- the part is injection molded (primary injection process).
- the inner part from the intermediate part in the plate thickness direction to the inner surface of the concave transparent resin molded product is injection-molded by the second outer mold and the second inner mold of the inner part molding die (secondary injection step). ).
- the injection molding apparatus and the injection molding method of the transparent resin molded product according to the present invention it is possible to prevent the occurrence of defects such as bubbles, weld lines, sink marks, etc., and to improve the yield of the transparent resin molded product. Manufacturing cost can be reduced.
- FIG. 4 is a longitudinal sectional view showing a first embodiment of the present invention by enlarging the IV part of FIG. 3. It is a side view of the injection molding apparatus which shows 2nd Embodiment of this invention. It is a longitudinal cross-sectional view of the injection molding apparatus which follows the VI-VI line of FIG. It is a top view of the injection molding apparatus which shows 3rd Embodiment of this invention. It is a side view of the injection molding apparatus by the VIII arrow of FIG.
- FIG. 5 shows a fifth embodiment of the present invention, where (a) is a primary injection process, (b) is a primary curing process, (c) is a secondary injection process, (d) is a secondary curing process, and (e) is a tertiary injection process.
- Step (f) is a view showing a longitudinal section of the finished product. It is a longitudinal cross-sectional view of the injection molding apparatus which shows the problem of the prior art. It is a side view of the injection molding apparatus which shows the problem of the prior art. It is a side view of the injection molding apparatus which shows the problem of the prior art. It is a top view of the injection molded product which shows the problem of the prior art.
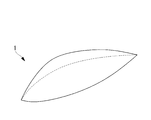
- FIG. 1 is a perspective view of an aircraft canopy showing an example of a transparent resin molded product.
- the canopy 1 is a large resin molded product that extends long along the front-rear direction and has a concave shape (a bowl shape) that protrudes upward, and has an overall length of, for example, 3 m or more.
- the canopy 1 is integrally injection-molded with a transparent resin material on acrylic, polycarbonate or the like, and its thickness is set in the range of 15 to 25 mm.
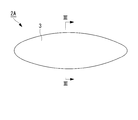
- FIG. 2 is a side view of the injection molding apparatus 2A (molding die 3) for the canopy 1 according to the first embodiment of the present invention
- FIG. 3 is a longitudinal sectional view taken along line III-III in FIG.
- These drawings conceptually show only the internal space of the mold 3.
- the molding die 3 is maintained in a sideways posture in which the concave open surface 4 (see FIG. 3) is substantially vertical.
- the injection molding apparatus 2A includes a molding die 3 and a gate 5 serving as an inlet for injecting a resin material into the molding die 3.
- a gate 5 serving as an inlet for injecting a resin material into the molding die 3.
- one gate 5 is provided at the uppermost portion of the peripheral edge of the mold 3. The resin material injected from the gate 5 is filled in the mold 3 and cured to form the canopy 1.
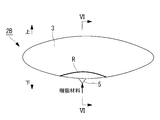
- FIG. 4 is a vertical cross-sectional view showing the connection part of the mold 3 and the gate 5 by enlarging the IV part of FIG.
- the thickness dimension Ta of the mold 3 is set in the range of 15 to 25 mm.
- the diameter D of the gate 5 is preferably set so that the ratio with the thickness dimension Ta is in the range of 1: 6 to 1: 3.
- the diameter dimension D is preferably in the range of 3.3 mm to 6.7 mm.
- the ratio of the diameter dimension D of the gate 5 to the thickness dimension Ta of the mold 3 is 1: 3
- the ratio of D and Ta is optimized and the best injection molding can be performed.
- the resin material injected from the gate 5 into the molding die 3 is not extruded linearly as shown in FIG. 16 and falls to the bottom of the molding die 3 and does not accumulate.
- the inside of the mold 3 flows in the form of a fountain flow, and bubbles are not mixed in the resin material.
- D is larger than 1: 3 with respect to Ta, the fluidity of the resin material is lowered, and there is a possibility that a defective filling of the resin material into the mold 3 may occur.
- the ratio between the diameter dimension D of the gate 5 and the thickness dimension Ta of the molding die 3 is set within a range of 1: 6 to 1: 3.
- FIG. 5 is a side view of an injection molding apparatus 2B (molding die 3) showing a second embodiment of the present invention
- FIG. 6 is a longitudinal sectional view taken along line VI-VI in FIG. Also in this injection molding apparatus 2B, the molding die 3 is maintained in a sideways posture in which the concave open surface 4 (see FIG. 6) is substantially vertical.
- the gate 5 for injecting the resin material into the mold 3 is provided at one place at the lowermost part of the peripheral edge of the mold 3. By this gate 5, the resin material R is injected upward from the lowermost part inside the mold 3.
- the resin material R is injected into the inside of the molding die 3 from the gate 5 located at the lowermost part of the molding die 3, and the resin material R is directed upward from the lowermost part to the upper side of the molding die 3. Will be filled.
- the resin material R injected from the gate 5 into the mold 3 is extruded linearly as shown in FIGS. 17 and 18 and dropped as it is, and is piled up on the bottom of the mold 3. There is no such thing. Therefore, it is possible to prevent defects in which bubbles are mixed into the molded product.
- the open surface 4 of the mold 3 does not necessarily have to be strictly vertical, and the gate 5 is positioned at the lowermost part of the mold 3, and the resin material R injected therefrom hangs down inside the mold 3. Instead, any angle may be used as long as the inside of the mold 3 is sequentially filled from below.
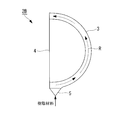
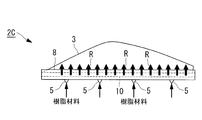
- FIG. 7 is a plan view of an injection molding apparatus 2C (molding die 3) showing a third embodiment of the present invention
- FIG. 8 is a side view taken along arrow VIII in FIG. 7
- FIG. 9 is IX-IX in FIG. It is a longitudinal cross-sectional view which follows a line.
- the molding die 3 is maintained in a sideways posture in which the concave open surface 4 (see FIG. 9) is substantially vertical.
- the gate 5 may be at an angle at which the gate 5 is positioned at the lowermost portion of the mold 3.
- resin material pools 7 and 8 are juxtaposed along the upper and lower edges of the mold 3. These resin material pools 7 and 8 have inner widths Tb and Tc larger than the thickness dimension Ta of the mold 3 as shown in FIG.
- each resin material pool 7 and 8 is curving according to the outer periphery shape of the shaping
- the upper and lower resin material pools 7 and 8 and the upper and lower edges of the mold 3 are connected by connecting passages 9 and 10, respectively.
- the sizes of the passage widths Td and Te of the connection passages 9 and 10 are smaller than the inner widths Tb and Tc of the resin material pools 7 and 8.
- the ratio between the passage widths Td and Te of the connection passages 9 and 10 and the thickness dimension Ta of the molding die 3 is such that the diameter dimension D of the gate 5 and the thickness dimension of the molding die 3 in the injection molding apparatus 2A of the first embodiment.
- it is preferably set within the range of 1: 6 to 1: 3.
- the diameter dimension D of the passage widths Td and Te is set in the range of 3.3 mm to 6.7 mm.
- connection passages 9 and 10 continuously connect the upper and lower edges of the mold 3 and the inside of the resin material pools 7 and 8 along the longitudinal direction.
- connection passages 9 and 10 are narrow slit-like passages connecting the edge of the mold 3 and the resin material pools 7 and 8.
- the lower resin material pool 8 is provided with a plurality of (for example, four points) gates 5 along the longitudinal direction thereof.
- the resin material R injected into the resin material pool 8 from the plurality of gates 5 first merges inside the resin material pool 8, as shown in FIG. They are mixed with each other by distributing them. Then, as shown in FIG. 10, the mixed resin material R is extruded into a planar shape by passing through the narrow slit-shaped connection passage 10, and widely spreads along the lower edge of the mold 3. It is injected all at once. The surplus of the resin material R that has spread to the inside of the mold 3 flows out to the resin material pool 7 through the connection passage 9.
- the resin material R injected from the plurality of gates 5 (multi-point gates) having a wind number once joins inside the resin material pool 8 and then passes through the slit-like connection passage 10 to form a plane. Therefore, the resin material R does not form a boundary surface (weld line) inside the molding die 3 because it is filled from the lower edge of the molding die 3. Therefore, the defect which can make a weld line in a molded article can be prevented effectively.
- FIG. 11 is a plan view of an injection molding apparatus 2D (molding die 3) showing a fourth embodiment of the present invention.
- FIGS. 12 (a) and 12 (b) are the XIIa-XIIa line and XIIb- in FIG. 11, respectively. It is a longitudinal cross-sectional view which follows a XIIb line.
- the injection molding apparatus 2D has substantially the same configuration as the injection molding apparatus 2C of the third embodiment, but the passage width Tf of the connection passages 9 and 10 is a concave cross-sectional arch length L (see FIG. 12) is set to increase as the length increases. That is, the connection passages 9 and 10 are tapered slits having a passage width Tf that is large in the middle portion in the front-rear direction of the mold 3 and that the passage width Tf becomes smaller toward both ends in the front-rear direction.
- the resin material R injected into the resin material pool 8 from the plurality of gates 5 is merged inside the resin material pool 8 as in the injection molding apparatus 2C of the third embodiment. It is injected into the mold 3 through the connection passage 10.
- the injection amount of the resin material R increases at a position where the concave cross-sectional arch length L of the mold 3 is long (near the center in the longitudinal direction), and the cross-sectional arch length At a position where the length L is short (near both ends in the longitudinal direction), the injection amount of the resin material R is small.
- the speed at which the resin material R is filled from one end to the other end of the concave shape of the mold 3 becomes uniform over the entire length in the length direction of the mold 3. For this reason, it is possible to prevent generation of a boundary surface (weld line) due to a difference in arrival speed of the resin material R inside the mold 3.
- FIG. 15 (f) are longitudinal sectional views of an injection molding apparatus 2E showing the fifth embodiment of the present invention.
- This injection molding apparatus 2E includes a molding die 13 for injection molding a concave transparent resin molded product such as the above-described canopy 1 (see FIG. 15 (f)).
- the mold 13 includes an outer partial mold 14 and an inner partial mold 15.
- the outer partial mold 14 is a mold for injection-molding the outer portion 1a from the intermediate portion in the plate thickness direction of the canopy 1 to the outer surface
- the inner partial mold 15 is from the intermediate portion in the plate thickness direction of the canopy 1 to the inner surface. This is a mold for injection-molding the inner portion 1b.
- the outer partial mold 14 includes a first outer mold 14a and a first inner mold 14b
- the inner partial mold 15 includes a second outer mold 15a and a second inner mold 15b. Yes.
- the first outer mold 14a and the second inner mold 15b can be matched with each other (see FIG. 15E).
- the resin material R is injected between the first outer mold 14a and the first inner mold 14b of the outer partial mold 14 to inject the outer portion 1a of the canopy 1. Molding (primary injection process P1).
- Step P2 the first inner mold 14b is removed leaving the first outer mold 14a, and sink marks Z (dents) are induced on the inner peripheral surface of the outer portion 1a (primary curing).
- Step P2 the outer peripheral surface of the outer part 1a that has been injection-molded is rapidly cooled because it is in contact with the first outer mold 14a, so that there is no sink.
- the inner peripheral surface of the outer part 1a is not the first inner part.
- a resin material is provided between the second outer mold 15a and the second inner mold 15b of the inner part molding die 15. R is injected and the inner part 1b of the canopy 1 is injection-molded (secondary injection step P3).
- Step P4 the inner peripheral surface of the injection molded inner portion 1b is in contact with the second inner mold 15b so that it is rapidly cooled and no sink marks occur, but the outer peripheral surface of the inner portion 1b is not
- the mold 15a is removed, the air is kept warm, and cooling is delayed, so that sink marks Z are generated.
- the first outer mold 14a from which the first inner mold 14b has been removed and the second inner mold 15b from which the second outer mold 15a has been removed are molded. Match. At this time, an injection space 16 is formed between the outer portion 1a and the inner portion 1b. Then, the resin material R is injected into the injection space 16 (tertiary injection process P5), and the canopy 1 is completed (see FIG. 15F).
- the sink material Z is induced on the inner peripheral surface of the outer portion 1a and the outer peripheral surface of the inner portion 1b, and then the resin material R is injected between these both surfaces.
- the resin material R is injected between these both surfaces.
- the material of the resin material R injected in the primary injection process to the tertiary injection process is not necessarily the same material.
- the material and characteristics of the resin material R injected in each of the injection processes P1, P3, and P5 the strength characteristics of the canopy 1 and the performance for suppressing optical distortion can be arbitrarily set.
- the injection molding apparatuses 2A to 2E and the injection molding method for transparent resin molded products according to the present invention the occurrence of defects such as bubbles, weld lines, sink marks and the like can be prevented, and the yield of transparent resin molded products can be increased. This can improve the manufacturing cost.
- the present invention is not limited to the configurations of the first to fifth embodiments described above, and can be appropriately modified or improved without departing from the gist of the present invention. Embodiments with or without modifications are also included in the scope of the right of the present invention.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Manufacturing & Machinery (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Moulds For Moulding Plastics Or The Like (AREA)
- Injection Moulding Of Plastics Or The Like (AREA)
Abstract
気泡、ウェルドライン、ヒケ等の欠陥の発生を防止し、透明樹脂成型品の歩留りを向上させて製造コストダウンを図る。透明樹脂成形品の射出成形装置(2A)は、透明樹脂成形品を射出成形するための成形型(3)と、この成形型(3)の周縁部に設けられ、成形型(3)の内部に樹脂材料(R)を射出する入口となるゲート(5)とを具備しており、成形型(3)の厚み寸法(Ta)が15~25mmの範囲のものにおいて、ゲート(5)の直径寸法(D)と成形型(3)の厚み寸法(Ta)との比率が1:6~1:3の範囲内に設定されている。
Description
本発明は、透明樹脂成形品の射出成形装置および射出成形方法に関するものである。
透明樹脂成形品の射出成形方法として、下記の特許文献1,2に開示されているものが知られている。
特許文献1に開示されている透明樹脂部材の製造方法は、同文献の図2~図4に示されるように、凸形状を有するポリカーボネート製の中間成形品2を、この中間成形品2の外観形状と同じ形状のキャビィティ面60a,61aを持つ下型60および上型61からなる成形型6の内部に配置して型締めし、中間成形品2とキャビィティ面60a,61aとの間の空隙に透明なアクリル樹脂を流し込み、これによってポリカーボネート製の中間成形品2の両面にアクリル樹脂が積層されたキャノピー1を成形するものである。
特許文献1に開示されている透明樹脂部材の製造方法は、同文献の図2~図4に示されるように、凸形状を有するポリカーボネート製の中間成形品2を、この中間成形品2の外観形状と同じ形状のキャビィティ面60a,61aを持つ下型60および上型61からなる成形型6の内部に配置して型締めし、中間成形品2とキャビィティ面60a,61aとの間の空隙に透明なアクリル樹脂を流し込み、これによってポリカーボネート製の中間成形品2の両面にアクリル樹脂が積層されたキャノピー1を成形するものである。
また、特許文献2に開示されているコンタクトレンズ材の製造方法は、同文献の図8,図9に示されるように、コンタクトレンズ材を製造するための第1の樹脂型、第2の樹脂型を射出成形し、 成形された第1の樹脂型、第2の樹脂型のいずれか一方にコンタクトレンズ材成形用材料を供給し、第1の樹脂型と第2の樹脂型を型合わせすることにより、コンタクトレンズ成形キャビテイを形成し、該キャビテイに充填された成形材料を成形することにより、目的とするコンタクトレンズ材を得るものである。
透明樹脂成形品の射出成形時における課題として、
A.気泡の混入
B.複数のゲート(射出孔)から成形型内に射出された樹脂同士が型内で隣接する際におけるウェルドライン(湯ざかい)の発生
C.樹脂材料の硬化時に体積が縮小することによるヒケ(凹み)の発生
が挙げられる。
A.気泡の混入
B.複数のゲート(射出孔)から成形型内に射出された樹脂同士が型内で隣接する際におけるウェルドライン(湯ざかい)の発生
C.樹脂材料の硬化時に体積が縮小することによるヒケ(凹み)の発生
が挙げられる。
特許文献1,2における透明樹脂成形品の製造方法は、いずれも成形品の厚さが1mm以下~8mm程度と比較的薄く、大きさも小さいものを成形する方法であるため、上記A~Cの課題は発生しにくいので大きな問題となりにくい。しかし、航空機のキャノピーのように、厚さが20mm程度ある厚肉で大型の透明樹脂成形品の場合は上記課題A~Cが顕著になる。
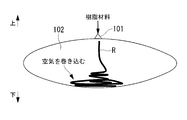
即ち、図16に示すように、ゲート101から成形型102内に樹脂材料Rが射出される際に、ゲート101の直径寸法Xに対して成形型102の厚み寸法Yが大きいために、射出された樹脂材料Rが成形型の内部に線状に押し出され、そのまま落下して積み上がってしまい、これによって多量の気泡が混入してしまう。
また、航空機のキャノピーを樹脂成形する場合、従来では図17に示すように、成形型102を横倒しの姿勢に保ち、その最上部にゲート101を形成するか、あるいは図18に示すように、成形型102の前後両端にゲート101を形成して樹脂材料Rを射出する。ところが、このような位置から成形型102の内部に樹脂材料Rを射出すると、成形型102の内部空間が広いために、ゲート101から射出された樹脂材料Rが成形型102の内壁に付着せずに落下し、図16の場合と同様に線状に押し出されて積み上がり、多量の気泡が混入してしまう。
さらに、全長が3m以上にも及ぶキャノピーの成形型102には、単一のゲートのみから樹脂材料Rを射出するのは容量的に困難なので、図19に示すように複数のゲート101(多点ゲート)を設けて樹脂材料Rを射出することになる。しかし、このような多点ゲート101から樹脂材料Rを射出すると、成形型102の内部で各ゲート101から射出された樹脂材料Rが互いに接する境界面(湯ざかい)が可視的に残存する、所謂ウェルドラインWが発生してしまう。このウェルドラインWは光学歪みを伴うため、航空機のキャノピーにおいては重大な欠陥となる。
また、一般に、樹脂材料は、硬化する際に体積が減少するため、樹脂成形品の表面が凹む、所謂ヒケと呼ばれる欠陥が発生しやすい。これは厚肉な成形品において顕著になる。ヒケは透明な成形品においては光学歪みの原因になるため、航空機のキャノピーの場合には成形品の表裏を研磨してヒケを消去する必要が生じ、この研磨作業が成形品の製造コストを上昇させる原因となっている。
本発明は、このような事情に鑑みてなされたものであって、気泡、ウェルドライン、ヒケ等の欠陥の発生を防止し、透明樹脂成型品の歩留りを向上させて製造コストダウンを図ることのできる透明樹脂成形品の射出成形装置および射出成形方法を提供することを目的とする。
上記課題を解決するために、本発明は以下の手段を採用する。
即ち、本発明の第1の態様に係る透明樹脂成形品の射出成形装置は、透明樹脂成形品を射出成形するための成形型と、前記成形型の周縁部に設けられ、前記成形型の内部に樹脂材料を射出する入口となるゲートと、を具備したものであって、前記成形型の厚み寸法が15~25mmの範囲のものにおいて、前記ゲートの直径寸法と前記成形型の厚み寸法との比率が1:6~1:3の範囲内に設定されている。
また、本発明の第1の態様に係る透明樹脂成形品の射出成形方法は、透明樹脂成形品を射出成形するための成形型と、前記成形型の周縁部に設けられ、前記成形型の内部に樹脂材料を射出する入口となるゲートと、を使用する射出成形方法であって、前記成形型の厚み寸法が15~25mmの範囲のものにおいて、前記ゲートの直径寸法と前記成形型の厚み寸法との比率を1:6~1:3の範囲内に設定して射出成型する。
上記の射出成形装置および射出成形方法によれば、ゲートの直径寸法と成形型の厚み寸法との比率が適正化されるため、ゲートから成形型の内部に射出された樹脂材料が成形型の内部に線状に押し出されて積み上がってしまうことがなく、射出された樹脂材料は成形型の内部をファウンテンフロー状に流れる。このため、樹脂材料に気泡が混入しなくなり、気泡の混入による欠陥の発生を防止して成形品の歩留りを向上させ、製造コストダウンを図ることができる。
また、本発明の第2の態様に係る透明樹脂成形品の射出成形装置は、凹形状の透明樹脂成形品を射出成形するための成形型と、前記成形型の内部に樹脂材料を射出する入口となるゲートと、を具備したものであって、前記ゲートは前記成形型の周縁部に設けられ、前記成形型は、その凹形状の開放面の角度が、前記ゲートが前記成形型の下部に位置するように保たれ、前記ゲートによって前記成形型の内部の下部から上方に向かって樹脂材料が射出される。
また、本発明の第2の態様に係る透明樹脂成形品の射出成形方法は、凹形状の透明樹脂成形品を射出成形するための成形型と、前記成形型の内部に樹脂材料を射出する入口となるゲートと、を使用する射出成形方法であって、前記成形型を、その凹形状の開放面が略鉛直となる姿勢に保ち、前記開放面の周縁部の下部に前記ゲートを設け、このゲートによって前記成形型の内部の下部から上方に向かって樹脂材料を射出する。
上記の射出成形装置および射出成形方法によれば、成形型の下部に位置するゲートから樹脂材料が成形型の内部に射出され、樹脂材料が成形型の内部を上方に向かって充填されてゆく。このため、ゲートから成形型の内部に射出される樹脂材料が、線状に押し出されて成形型の底部に落下して積み上がってしまうようなことがなく、成形品に気泡が混入する欠陥の発生を防止することができる。
上記構成の射出成形装置において、前記成形型の前記開放面の少なくとも下側の縁部に沿って、前記成形型の厚み寸法よりも大きな内幅を持つ樹脂材料プールを並設し、この樹脂材料プールと、前記成形型の下側の縁部との間を長手方向に沿って連続的に連通させ、前記樹脂材料プールの長手方向に沿って前記ゲートを複数箇所に設けてもよい。
同じく、上記構成の射出成形方法において、前記成形型の前記開放面の少なくとも下側の縁部に沿って、前記成形型の厚み寸法よりも大きな内幅を持つ樹脂材料プールを並設し、この樹脂材料プールと、前記成形型の下側の縁部との間を長手方向に沿って連続的に連通させるとともに、前記樹脂材料プールの長手方向に沿って前記ゲートを複数箇所に設け、前記複数のゲートから前記樹脂材料プールの内部に射出した前記樹脂材料を、前記樹脂材料プールの内部で流動および混合させてから前記成形型の内部に充填するようにしてもよい。
上記の射出成形装置および射出成形方法によれば、成形型の下部に、成形型の厚み寸法よりも大きな内幅を持つ樹脂材料プールが形成され、この樹脂材料プールに複数個所設けられたゲートから樹脂材料が射出される。複数のゲートから樹脂材料プールの内部に射出された樹脂材料は、まず樹脂材料プールの内部で流通することにより、互いに混ざり合う。そして、混ざり合った樹脂材料が樹脂材料プールから成形型の下側の縁部に沿って幅広く射出される。このため、複数のゲート(多点ゲート)から射出された樹脂材料が、成形型の内部で境界面(ウェルドライン)を形成するといった欠陥の発生を防止することができる。
さらに、上記の射出成形装置および射出成形方法において、前記成形型の前記開放面の下側の縁部と前記樹脂材料プールの内部とを接続する接続通路の通路幅を、前記成形型の凹形状の断面アーチ長さが長くなるにつれて大きくするのが好ましい。
上記の射出成形装置および射出成形方法によれば、樹脂材料プールから成形型に樹脂が射出される際に、成形型の凹形状の断面アーチ長さが長い位置では多くの樹脂材料が射出され、断面アーチ長さが短い位置では少ない樹脂材料が射出される。これにより、凹形状の一端から他端まで樹脂材料が充填される速度が成形型の全域に亘って均等になる。このため、成形型の内部で樹脂材料の到着速度に差が発生することに起因する境界面(ウェルドライン)の生成といった欠陥の発生を防止することができる。
また、本発明の第3の態様に係る透明樹脂成形品の射出成形装置は、凹形状の透明樹脂成形品を射出成形するための成形型を備えたものであって、前記成形型は、第1の外型と第1の内型との間で前記透明樹脂成形品の板厚方向中間部から外表面までの外側部分を射出成形する外側部分成形型と、第2の外型と第2の内型との間で前記透明樹脂成形品の板厚方向中間部から内表面までの内側部分を射出成形する内側部分成形型と、を備え、前記第1の外型と前記第2の内型とは型合わせ可能であり、前記外側部分成形型の射出成形後に前記第1の内型を取り外された前記第1の外型と、前記内側部分成形型の射出成形後に前記第2の外型を取り外された前記第2の内型とが型合わせされた状態で、前記外側部分と前記内側部分との間に樹脂材料を射出可能な射出空間が形成される。
同じく、本発明の第3の態様に係る透明樹脂成形品の射出成形方法は、凹形状の透明樹脂成形品を射出成形するための方法であって、前記透明樹脂成形品の板厚方向中間部から外表面までの外側部分を、第1の外型と第1の内型との間に射出成形する一次射出工程と、前記外側部分の射出成形後に前記第1の外型を残して前記第1の内型を取り外し、前記外側部分の前記内周面にヒケを誘発させる一次硬化工程と、前記透明樹脂成形品の板厚方向中間部から内表面までの内側部分を、第2の外型と第2の内型との間に射出成形する二次射出工程と、前記内側部分の射出成形後に前記第2の内型を残して前記第2の外型を取り外し、前記内側部分の前記外周面にヒケを誘発させる二次硬化工程と、前記一次硬化工程後の前記第1の外型と前記二次硬化工程後の前記第2の内型とを型合わせして前記外側部分と前記内側部分との間に形成される射出空間に樹脂材料を射出する三次射出工程と、を備えてなる。
上記の射出成形装置および射出成形方法によれば、外側部分成形型の第1の外型と第1の内型とによって凹形状の透明樹脂成形品の板厚方向中間部から外表面までの外側部分が射出成形される(一次射出工程)。また、内側部分成形型の第2の外型と第2の内型とによって凹形状の透明樹脂成形品の板厚方向中間部から内表面までの内側部分が射出成形される(二次射出工程)。
そして、外側部分の成形後に第1の内型を取り外すことにより、外側部分の内周面にヒケを誘発させ(一次硬化工程)、内側部分の成形後に第2の外型を取り外すことにより、内側部分の外周面にヒケを誘発させる(二次硬化工程)。その後、外側部分を成形した第1の外型と、内側部分を成形した第2の内型とを型合わせし、外側部分と内側部分との間(射出空間)に樹脂材料を射出する(三次射出工程)。
このように、外側部分の内周面と、内側部分の外周面とにヒケを誘発させてから、これら両面の間に樹脂材料を射出することにより、凹形状の透明樹脂成形品の表裏面にヒケが発生する欠陥を確実に防止することができる。
以上のように、本発明に係る透明樹脂成形品の射出成形装置および射出成形方法によれば、気泡、ウェルドライン、ヒケ等の欠陥の発生を防止し、透明樹脂成型品の歩留りを向上させて製造コストダウンを図ることができる。
以下に、本発明に係る透明樹脂成形品の射出成形装置および射出成形方法の複数の実施形態について、図面を参照しながら説明する。
図1は、透明樹脂成形品の一例を示す航空機のキャノピーの斜視図である。このキャノピー1は、前後方向に沿って長く延び、上方に向かって凸となる凹形状(椀形状)であり、その全長が例えば3m以上の大型な樹脂成形品である。キャノピー1はアクリルやポリカーボネート等に透明樹脂材料によって一体に射出成形され、その厚みが15~25mmの範囲に設定されている。
[第1実施形態]
図2は、本発明の第1実施形態に係るキャノピー1の射出成形装置2A(成形型3)の側面図であり、図3は図2のIII-III線に沿う縦断面図である。なお、これらの図は、成形型3の内部空間だけを概念的に示したものである。成形型3は、その凹形状の開放面4(図3参照)が略鉛直となる横倒しの姿勢に保たれている。
図2は、本発明の第1実施形態に係るキャノピー1の射出成形装置2A(成形型3)の側面図であり、図3は図2のIII-III線に沿う縦断面図である。なお、これらの図は、成形型3の内部空間だけを概念的に示したものである。成形型3は、その凹形状の開放面4(図3参照)が略鉛直となる横倒しの姿勢に保たれている。
射出成形装置2Aは、成形型3と、この成形型3の内部に樹脂材料を射出する入口となるゲート5とを備えている。ゲート5は、例えば成形型3の周縁部の最上部に1箇所設けられている。このゲート5から射出された樹脂材料が成形型3の内部に充填され、硬化することによってキャノピー1が成形される。
図4は、図3のIV部を拡大して成形型3とゲート5の接続部を示した縦断面図である。前述のように、成形型3の厚み寸法Taは15~25mmの範囲に設定されている。これに対してゲート5の直径寸法Dは、厚み寸法Taとの比率が1:6~1:3の範囲内となるように設定するのが好ましい。例えば、厚み寸法Taが20mmである場合は、直径寸法Dを3.3mm~6.7mmの範囲とするのが好ましい。
発明者らの実験では、ゲート5の直径寸法Dと成形型3の厚み寸法Taとの比率が1:3の時に、DとTaとの比率が適正化されて最も良好な射出成形が行えることが確認された。即ち、ゲート5から成形型3の内部に射出された樹脂材料が、図16に示す従来のように線状に押し出されて成形型3の底部に落下して積み上がってしまうことがなくなり、成形型3の内部をファウンテンフロー状に流れるようになって、樹脂材料に気泡が混入しなくなる。しかし、DがTaに対して1:3よりも大きくなってしまうと、樹脂材料の流動性が低下し、成形型3への樹脂材料の充填不良が発生する虞がある。
以上のように、この射出成形装置2Aおよび射出成形方法によれば、ゲート5の直径寸法Dと成形型3の厚み寸法Taとの比率を1:6~1:3の範囲内に設定することにより、気泡の混入による欠陥の発生を防止して成形品であるキャノピー1の歩留りを向上させ、製造コストダウンを図ることができる。
[第2実施形態]
図5は、本発明の第2実施形態を示す射出成形装置2B(成形型3)の側面図であり、図6は図5のVI-VI線に沿う縦断面図である。この射出成形装置2Bにおいても、成形型3は、その凹形状の開放面4(図6参照)が略鉛直となる横倒しの姿勢に保たれている。
図5は、本発明の第2実施形態を示す射出成形装置2B(成形型3)の側面図であり、図6は図5のVI-VI線に沿う縦断面図である。この射出成形装置2Bにおいても、成形型3は、その凹形状の開放面4(図6参照)が略鉛直となる横倒しの姿勢に保たれている。
この成形型3に樹脂材料を射出するゲート5は、成形型3の周縁部の最下部に1箇所設けられている。このゲート5によって成形型3の内部の最下部から上方に向かって樹脂材料Rが射出されるようになっている。
この射出成形装置2Bによれば、成形型3の最下部に位置するゲート5から樹脂材料Rが成形型3の内部に射出され、樹脂材料Rが成形型3の内部を最下部から上方に向かって充填されてゆく。このため、ゲート5から成形型3の内部に射出された樹脂材料Rが、図17、図18に示す従来のように線状に押し出されてそのまま落下し、成形型3の底部に積み上がってしまうようなことがない。したがって、成形品に気泡が混入する欠陥を防止することができる。
なお、成形型3の開放面4は必ずしも厳密に鉛直である必要はなく、ゲート5が成形型3の最下部に位置し、ここから射出された樹脂材料Rが、成形型3の内部で垂れることなく、成形型3の内部に下方から順次充填されていく角度であればよい。
[第3実施形態]
図7は、本発明の第3実施形態を示す射出成形装置2C(成形型3)の平面図であり、図8は図7のVIII矢視による側面図、図9は図8のIX-IX線に沿う縦断面図である。この射出成形装置2Cにおいても、成形型3は、その凹形状の開放面4(図9参照)が略鉛直となる横倒しの姿勢に保たれているが、必ずしも略鉛直出なくてもよく、下記のゲート5が成形型3の最下部に位置する角度であればよい。
図7は、本発明の第3実施形態を示す射出成形装置2C(成形型3)の平面図であり、図8は図7のVIII矢視による側面図、図9は図8のIX-IX線に沿う縦断面図である。この射出成形装置2Cにおいても、成形型3は、その凹形状の開放面4(図9参照)が略鉛直となる横倒しの姿勢に保たれているが、必ずしも略鉛直出なくてもよく、下記のゲート5が成形型3の最下部に位置する角度であればよい。
この射出成形装置2Cでは、成形型3の上下両側の縁部に沿って樹脂材料プール7,8が並設されている。これらの樹脂材料プール7,8は、図9に示すように、それぞれ成形型3の厚み寸法Taよりも大きな内幅Tb,Tcを持っている。なお、各樹脂材料プール7,8は、成形型3の外周形状に合わせて湾曲しているが、直線状に形成してもよい。
上下の樹脂材料プール7,8と、成形型3の上下両側の縁部との間は、それぞれ接続通路9,10で接続されている。図9に示すように、各接続通路9,10の通路幅Td,Teの大きさは、樹脂材料プール7,8の内幅Tb,Tcよりも小さくなっている。また、接続通路9,10の通路幅Td,Teと、成形型3の厚み寸法Taとの比率は、第1実施形態の射出成形装置2Aにおけるゲート5の直径寸法Dと成形型3の厚み寸法Taとの比率のように、1:6~1:3の範囲内に設定するのが好ましい。例えば、成形型3の厚み寸法Taが20mmである場合は、通路幅Td,Teの直径寸法Dを3.3mm~6.7mmの範囲とする。
これらの接続通路9,10により、成形型3の上下両側の縁部と樹脂材料プール7,8の内部とが長手方向に沿って連続的に接続されている。言い換えると、接続通路9,10は、成形型3の縁部と樹脂材料プール7,8との間を接続する狭いスリット状の通路である。そして、下側の樹脂材料プール8に、その長手方向に沿って複数(例えば4点)のゲート5が設けられている。
このように構成された射出成形装置2Cにおいて、複数のゲート5から樹脂材料プール8の内部に射出された樹脂材料Rは、図8に示すように、まず樹脂材料プール8の内部で合流し、相互に流通することにより、互いに混ざり合う。そして、図10にも示すように、混ざり合った樹脂材料Rが、幅の狭いスリット状の接続通路10を通ることにより面状に押し出され、成形型3の下側の縁部に沿って幅広く一斉に射出される。成形型3の内部に行き渡った樹脂材料Rの余剰分は、接続通路9を通って樹脂材料プール7に流出する。
このように、風数の複数のゲート5(多点ゲート)から射出された樹脂材料Rが、樹脂材料プール8の内部で一旦合流してからスリット状の接続通路10を通って面状になって成形型3の下側の縁部から充填されるため、樹脂材料Rが成形型3の内部で境界面(ウェルドライン)を形成することがない。したがって、成形品にウェルドラインができる欠陥を効果的に防止することができる。
[第4実施形態]
図11は、本発明の第4実施形態を示す射出成形装置2D(成形型3)の平面図であり、図12(a),(b)は、それぞれ図11のXIIa-XIIa線、XIIb-XIIb線に沿う縦断面図である。この射出成形装置2Dは、第3実施形態の射出成形装置2Cとほぼ同じ構成であるが、その接続通路9,10の通路幅Tfが、成形型3の凹形状の断面アーチ長さL(図12参照)が長くなるにつれて大きくなるように設定されている。即ち、接続通路9,10は、成形型3の前後方向の中間部では通路幅Tfが大きく、前後方向の両端部に行くにしたがって通路幅Tfが小さくなるテーパー状のスリットになっている。
図11は、本発明の第4実施形態を示す射出成形装置2D(成形型3)の平面図であり、図12(a),(b)は、それぞれ図11のXIIa-XIIa線、XIIb-XIIb線に沿う縦断面図である。この射出成形装置2Dは、第3実施形態の射出成形装置2Cとほぼ同じ構成であるが、その接続通路9,10の通路幅Tfが、成形型3の凹形状の断面アーチ長さL(図12参照)が長くなるにつれて大きくなるように設定されている。即ち、接続通路9,10は、成形型3の前後方向の中間部では通路幅Tfが大きく、前後方向の両端部に行くにしたがって通路幅Tfが小さくなるテーパー状のスリットになっている。
この射出成形装置2Dにおいて、複数のゲート5から樹脂材料プール8の内部に射出された樹脂材料Rは、第3実施形態の射出成形装置2Cと同じく、樹脂材料プール8の内部で合流してから接続通路10を通って成形型3の内部に射出される。
その際に、図13および図14に示すように、成形型3の凹形状の断面アーチ長さLが長い位置(長手方向中央部付近)では樹脂材料Rの射出量が多くなり、断面アーチ長さLが短い位置(長手方向両端部付近)では樹脂材料Rの射出量が少なくなる。
これにより、成形型3の凹形状の一端から他端まで樹脂材料Rが充填される速度が成形型3の長さ方向の全長に亘って均等になる。このため、成形型3の内部で樹脂材料Rの到着速度に差が発生することに起因する境界面(ウェルドライン)の生成を防止することができる。
[第5実施形態]
図15(a)~図15(f)は、本発明の第5実施形態を示す射出成形装置2Eの縦断面図である。この射出成形装置2Eは、前述したキャノピー1(図15(f)参照)のような凹形状の透明樹脂成形品を射出成形するための成形型13を備えている。
図15(a)~図15(f)は、本発明の第5実施形態を示す射出成形装置2Eの縦断面図である。この射出成形装置2Eは、前述したキャノピー1(図15(f)参照)のような凹形状の透明樹脂成形品を射出成形するための成形型13を備えている。
成形型13は、外側部分成形型14と内側部分成形型15とを備えている。外側部分成形型14は、キャノピー1の板厚方向中間部から外表面までの外側部分1aを射出成形する型であり、内側部分成形型15は、キャノピー1の板厚方向中間部から内表面までの内側部分1bを射出成形する型である。
外側部分成形型14は、第1の外型14aと第1の内型14bとを備えており、内側部分成形型15は、第2の外型15aと第2の内型15bとを備えている。そして、第1の外型14aと第2の内型15bとは型合わせ可能である(図15(e)参照)。
この射出成形装置2Eによってキャノピー1を射出成形する手順は次の通りである。
まず、図15(a)に示すように、外側部分成形型14の第1の外型14aと第1の内型14bとの間に樹脂材料Rを射出してキャノピー1の外側部分1aを射出成形する(一次射出工程P1)。
次に、図15(b)に示すように、第1の外型14aを残して第1の内型14bを取り外し、外側部分1aの内周面にヒケZ(凹み)を誘発させる(一次硬化工程P2)。即ち、射出成形された外側部分1aの外周面は、第1の外型14aに接しているために急速に冷却されてヒケが生じないが、外側部分1aの内周面は、第1の内型14bを取り外されることにより空気に保温され、冷却が遅れるためにヒケZが発生する。
また、上記の外側部分1aの射出成型と平行して、図15(c)に示すように、内側部分成形型15の第2の外型15aと第2の内型15bとの間に樹脂材料Rを射出してキャノピー1の内側部分1bを射出成形する(二次射出工程P3)。
次に、図15(d)に示すように、第2の内型15bを残して第2の外型15aを取り外し、内側部分1bの外周面にヒケZ(凹み)を誘発させる(二次硬化工程P4)。即ち、射出成形された内側部分1bの内周面は、第2の内型15bに接しているために急速に冷却されてヒケが生じないが、内側部分1bの外周面は、第2の外型15aを取り外されることにより空気に保温され、冷却が遅れるためにヒケZが発生する。
次に、図15(e)に示すように、第1の内型14bを取り外された第1の外型14aと、第2の外型15aを取り外された第2の内型15bとを型合わせする。この時、外側部分1aと内側部分1bとの間に射出空間16が形成される。そして、この射出空間16に樹脂材料Rを射出し(三次射出工程P5)、キャノピー1が完成する(図15(f)参照)。
このような射出成形装置2Eおよび射出成形方法によれば、外側部分1aの内周面と、内側部分1bの外周面とにヒケZを誘発させてから、これら両面の間に樹脂材料Rを射出することにより、キャノピー1の表裏面にヒケが発生する欠陥を確実に防止することができる。したがって、従来必要とされていた、キャノピー1の成形後にヒケを消去する研磨工程を省くことができ、これによって多大な製造コストダウンと品質向上に貢献することができる。
なお、一次射出工程~三次射出工程で射出する樹脂材料Rの材質は、必ずしも同じ材質でなくてもよい。これら各射出工程P1,P3,P5で射出する樹脂材料Rの材質や特性等を異ならせることにより、キャノピー1の強度特性や光学歪みを抑制する性能等を任意に設定することができる。
以上のように、本発明に係る透明樹脂成形品の射出成形装置2A~2Eおよび射出成形方法によれば、気泡、ウェルドライン、ヒケ等の欠陥の発生を防止し、透明樹脂成型品の歩留りを向上させて製造コストダウンを図ることができる。
なお、本発明は、上記の第1~第5実施形態の構成のみに限定されるものではなく、本発明の要旨を逸脱しない範囲内において適宜変更や改良を加えることができ、このように変更や改良を加えた実施形態も本発明の権利範囲に含まれるものとする。
1 キャノピー(凹形状の透明樹脂成形品)
1a 外側部分
1b 内側部分
2A,2B,2C,2D,2E 射出成形装置
3,13 成形型
4 開放面
5 ゲート
7,8 樹脂材料プール
9,10 接続通路
14 外側部分成形型
14a 第1の外型
14b 第1の内型
15 内側部分成形型
15a 第2の外型
15b 第2の内型
16 射出空間
D ゲートの直径寸法
L 成形型の凹形状の断面アーチ長さ
P1 一次射出工程
P2 一次硬化工程
P3 二次射出工程
P4 二次硬化工程
P5 三次射出工程
R 樹脂材料
Ta 成形型の厚み寸法
Tb,Tc 樹脂材料プールの内幅
Td,Te,Tf 接続通路の通路幅
1a 外側部分
1b 内側部分
2A,2B,2C,2D,2E 射出成形装置
3,13 成形型
4 開放面
5 ゲート
7,8 樹脂材料プール
9,10 接続通路
14 外側部分成形型
14a 第1の外型
14b 第1の内型
15 内側部分成形型
15a 第2の外型
15b 第2の内型
16 射出空間
D ゲートの直径寸法
L 成形型の凹形状の断面アーチ長さ
P1 一次射出工程
P2 一次硬化工程
P3 二次射出工程
P4 二次硬化工程
P5 三次射出工程
R 樹脂材料
Ta 成形型の厚み寸法
Tb,Tc 樹脂材料プールの内幅
Td,Te,Tf 接続通路の通路幅
Claims (10)
- 透明樹脂成形品を射出成形するための成形型と、
前記成形型の周縁部に設けられ、前記成形型の内部に樹脂材料を射出する入口となるゲートと、
を具備した透明樹脂成形品の射出成形装置であって、
前記成形型の厚み寸法が15~25mmの範囲のものにおいて、前記ゲートの直径寸法と前記成形型の厚み寸法との比率が1:6~1:3の範囲内に設定された透明樹脂成形品の射出成形装置。 - 凹形状の透明樹脂成形品を射出成形するための成形型と、
前記成形型の内部に樹脂材料を射出する入口となるゲートと、
を具備した透明樹脂成形品の射出成形装置であって、
前記ゲートは前記成形型の周縁部に設けられ、
前記成形型は、その凹形状の開放面の角度が、前記ゲートが前記成形型の下部に位置するように保たれ、
前記ゲートによって前記成形型の内部の下部から上方に向かって樹脂材料が射出される透明樹脂成形品の射出成形装置。 - 前記成形型の前記開放面の少なくとも下側の縁部に沿って、前記成形型の厚み寸法よりも大きな内幅を持つ樹脂材料プールを並設し、この樹脂材料プールと、前記成形型の下側の縁部との間を長手方向に沿って連続的に連通させ、前記樹脂材料プールの長手方向に沿って前記ゲートを複数箇所に設けた請求項2に記載の透明樹脂成形品の射出成形装置。
- 前記成形型の前記開放面の下側の縁部と前記樹脂材料プールの内部とを接続する接続通路の通路幅が、前記成形型の凹形状の断面アーチ長さが長くなるにつれて大きくなっている請求項3に記載の透明樹脂成形品の射出成形装置。
- 凹形状の透明樹脂成形品を射出成形するための成形型を備えた透明樹脂成形品の射出成形装置であって、
前記成形型は、
第1の外型と第1の内型との間で前記透明樹脂成形品の板厚方向中間部から外表面までの外側部分を射出成形する外側部分成形型と、
第2の外型と第2の内型との間で前記透明樹脂成形品の板厚方向中間部から内表面までの内側部分を射出成形する内側部分成形型と、
を備え、
前記第1の外型と前記第2の内型とは型合わせ可能であり、
前記外側部分成形型の射出成形後に前記第1の内型を取り外された前記第1の外型と、前記内側部分成形型の射出成形後に前記第2の外型を取り外された前記第2の内型とが型合わせされた状態で、前記外側部分と前記内側部分との間に樹脂材料を射出可能な射出空間が形成される透明樹脂成形品の射出成形装置。 - 透明樹脂成形品を射出成形するための成形型と、
前記成形型の周縁部に設けられ、前記成形型の内部に樹脂材料を射出する入口となるゲートと、
を使用する透明樹脂成形品の射出成形方法であって、
前記成形型の厚み寸法が15~25mmの範囲のものにおいて、前記ゲートの直径寸法と前記成形型の厚み寸法との比率を1:6~1:3の範囲内に設定して射出成型する透明樹脂成形品の射出成形方法。 - 凹形状の透明樹脂成形品を射出成形するための成形型と、
前記成形型の内部に樹脂材料を射出する入口となるゲートと、
を使用する透明樹脂成形品の射出成形方法であって、
前記成形型を、その凹形状の開放面が略鉛直となる姿勢に保ち、
前記開放面の周縁部の下部に前記ゲートを設け、このゲートによって前記成形型の内部の下部から上方に向かって樹脂材料を射出する透明樹脂成形品の射出成形方法。 - 前記成形型の前記開放面の少なくとも下側の縁部に沿って、前記成形型の厚み寸法よりも大きな内幅を持つ樹脂材料プールを並設し、この樹脂材料プールと、前記成形型の下側の縁部との間を長手方向に沿って連続的に連通させるとともに、
前記樹脂材料プールの長手方向に沿って前記ゲートを複数箇所に設け、
前記複数のゲートから前記樹脂材料プールの内部に射出した前記樹脂材料を、前記樹脂材料プールの内部で流動および混合させてから前記成形型の内部に充填する請求項7に記載の透明樹脂成形品の射出成形方法。 - 前記成形型の前記開放面の下側の縁部と前記樹脂材料プールの内部とを接続する接続通路の通路幅を、前記成形型の凹形状の断面アーチ長さが長い位置では大きくし、前記断面アーチ長さが短い位置では小さくした請求項8に記載の透明樹脂成形品の射出成形方法。
- 凹形状の透明樹脂成形品を射出成形するための射出成形方法であって、
前記透明樹脂成形品の板厚方向中間部から外表面までの外側部分を、第1の外型と第1の内型との間に射出成形する一次射出工程と、
前記外側部分の射出成形後に前記第1の外型を残して前記第1の内型を取り外し、前記外側部分の前記内周面にヒケを誘発させる一次硬化工程と、
前記透明樹脂成形品の板厚方向中間部から内表面までの内側部分を、第2の外型と第2の内型との間に射出成形する二次射出工程と、
前記内側部分の射出成形後に前記第2の内型を残して前記第2の外型を取り外し、前記内側部分の前記外周面にヒケを誘発させる二次硬化工程と、
前記一次硬化工程後の前記第1の外型と前記二次硬化工程後の前記第2の内型とを型合わせして前記外側部分と前記内側部分との間に形成される射出空間に樹脂材料を射出する三次射出工程と、
を備えてなる透明樹脂成形品の射出成形方法。
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US14/392,280 US10589448B2 (en) | 2013-09-30 | 2014-08-20 | Injection molding method and injection molding device for transparent resin molded article |
| US15/952,825 US10759098B2 (en) | 2013-09-30 | 2018-04-13 | Injection molding method and injection molding device for transparent resin molded article |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013204665A JP6309235B2 (ja) | 2013-09-30 | 2013-09-30 | 透明樹脂成形品の射出成形装置および射出成形方法 |
| JP2013-204665 | 2013-09-30 |
Related Child Applications (2)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| US14/392,280 A-371-Of-International US10589448B2 (en) | 2013-09-30 | 2014-08-20 | Injection molding method and injection molding device for transparent resin molded article |
| US15/952,825 Division US10759098B2 (en) | 2013-09-30 | 2018-04-13 | Injection molding method and injection molding device for transparent resin molded article |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2015045677A1 true WO2015045677A1 (ja) | 2015-04-02 |
Family
ID=52742831
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2014/071698 WO2015045677A1 (ja) | 2013-09-30 | 2014-08-20 | 透明樹脂成形品の射出成形装置および射出成形方法 |
Country Status (3)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (2) | US10589448B2 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JP6309235B2 (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2015045677A1 (ja) |
Families Citing this family (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP5972337B2 (ja) * | 2014-10-27 | 2016-08-17 | 日本特殊陶業株式会社 | スパークプラグ用絶縁体の製造方法 |
| TR201717944A2 (ja) * | 2017-11-15 | 2019-06-21 | Arcelik As |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS62180511U (ja) * | 1986-05-07 | 1987-11-16 | ||
| JPH11198184A (ja) * | 1998-01-16 | 1999-07-27 | Sekisui Chem Co Ltd | ホットランナ金型のゲート径の決定方法 |
| JP2000006203A (ja) * | 1998-06-29 | 2000-01-11 | Victor Co Of Japan Ltd | 光情報記録媒体用射出成形金型 |
| JP2004243590A (ja) * | 2003-02-12 | 2004-09-02 | Nippon Zeon Co Ltd | 射出成形用金型、成形体の製造方法及び導光板 |
| JP2004359221A (ja) * | 2003-05-30 | 2004-12-24 | Boeing Co:The | ウインドシールドアセンブリ、乗物および商用の航空機 |
Family Cites Families (28)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US4277435A (en) * | 1979-03-28 | 1981-07-07 | Logic Devices, Inc. | Plastic tumbler and method and apparatus for making same |
| JPS5995125A (ja) * | 1982-11-25 | 1984-06-01 | Toshiba Chem Corp | 射出成形ハ−ドコ−ト処理したウインドシ−ルド |
| JPS62180511A (ja) | 1986-02-05 | 1987-08-07 | Hitachi Ltd | 薄膜磁気ヘツドの製造方法 |
| JPS6450929A (en) | 1987-08-22 | 1989-02-27 | Bridgestone Corp | Sample device of test piece from sheet-like material |
| JPH04169298A (ja) | 1990-10-05 | 1992-06-17 | Michael John Williams | 石様表面を有する製品およびその製造方法 |
| JP3382281B2 (ja) * | 1993-01-22 | 2003-03-04 | 株式会社太洋工作所 | 熱可塑性樹脂射出成形用金型 |
| JP3130181B2 (ja) | 1993-07-08 | 2001-01-31 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | 透明樹脂部材の製造方法 |
| JP3512595B2 (ja) * | 1996-11-07 | 2004-03-29 | 株式会社リコー | プラスチック成形品の成形方法およびプラスチック成形品の成形用金型 |
| JPH07148765A (ja) * | 1993-11-30 | 1995-06-13 | Sekisui Chem Co Ltd | 射出成形方法及びその成形品 |
| JPH1029228A (ja) * | 1996-05-14 | 1998-02-03 | Nippon Zeon Co Ltd | 反応射出成形方法と金型装置 |
| JP3242077B2 (ja) | 1998-09-25 | 2001-12-25 | 株式会社日本製鋼所 | 内部が軟質材からなる3層構造物の成形方法および成形用金型 |
| JP4169298B2 (ja) | 1998-10-02 | 2008-10-22 | スタンレー電気株式会社 | 前照灯用レンズの製造方法 |
| JP2000355624A (ja) | 1999-06-14 | 2000-12-26 | Toyobo Co Ltd | ポリエステル樹脂およびその透明肉厚成形品 |
| JP2001030287A (ja) | 1999-07-22 | 2001-02-06 | Bridgestone Corp | プラスチック製光学部品の製造方法 |
| JP4183418B2 (ja) * | 1999-09-01 | 2008-11-19 | 株式会社トーメー | コンタクトレンズ材の製造方法及び装置並びにそれに用いられる射出成形用金型 |
| JP2002321256A (ja) * | 2001-04-23 | 2002-11-05 | Polyplastics Co | 発泡射出成形用金型及び発泡成形品 |
| DK176335B1 (da) * | 2001-11-13 | 2007-08-20 | Siemens Wind Power As | Fremgangsmåde til fremstilling af vindmöllevinger |
| US20040159745A1 (en) * | 2003-02-13 | 2004-08-19 | Wood Jeffrey H. | Attachment apparatus for injection-molded frameless canopies |
| US6796528B2 (en) * | 2003-02-13 | 2004-09-28 | The Boeing Company | Attachment apparatus for injected-molded canopies |
| JP4730307B2 (ja) * | 2004-10-29 | 2011-07-20 | コニカミノルタオプト株式会社 | プラスチックレンズの製造装置 |
| JP4429153B2 (ja) * | 2004-12-10 | 2010-03-10 | 三菱エンジニアリングプラスチックス株式会社 | 射出成形品の成形方法 |
| JP2007038535A (ja) * | 2005-08-03 | 2007-02-15 | Kuraray Co Ltd | 板状樹脂成形品の製造方法 |
| JP2007118214A (ja) | 2005-10-25 | 2007-05-17 | Sumitomo Heavy Ind Ltd | 積層射出成形機および積層射出成形方法 |
| JP2007283715A (ja) * | 2006-04-19 | 2007-11-01 | Nissan Motor Co Ltd | 樹脂板の射出圧縮成形装置及びその装置を用いて部品と一体化した樹脂板を製造する方法 |
| JP2008238653A (ja) | 2007-03-28 | 2008-10-09 | Oshima Denki Seisakusho:Kk | レンズ体およびその製造方法 |
| JP2010137539A (ja) * | 2008-11-17 | 2010-06-24 | Ricoh Co Ltd | 金型装置、樹脂成形方法および樹脂成形品 |
| JP5365916B2 (ja) | 2009-05-29 | 2013-12-11 | 株式会社吉野工業所 | 合成樹脂製厚肉成形品 |
| JP5855951B2 (ja) * | 2012-01-18 | 2016-02-09 | 三菱エンジニアリングプラスチックス株式会社 | 射出成形体の製造方法 |
-
2013
- 2013-09-30 JP JP2013204665A patent/JP6309235B2/ja active Active
-
2014
- 2014-08-20 WO PCT/JP2014/071698 patent/WO2015045677A1/ja active Application Filing
- 2014-08-20 US US14/392,280 patent/US10589448B2/en active Active
-
2018
- 2018-04-13 US US15/952,825 patent/US10759098B2/en active Active
Patent Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS62180511U (ja) * | 1986-05-07 | 1987-11-16 | ||
| JPH11198184A (ja) * | 1998-01-16 | 1999-07-27 | Sekisui Chem Co Ltd | ホットランナ金型のゲート径の決定方法 |
| JP2000006203A (ja) * | 1998-06-29 | 2000-01-11 | Victor Co Of Japan Ltd | 光情報記録媒体用射出成形金型 |
| JP2004243590A (ja) * | 2003-02-12 | 2004-09-02 | Nippon Zeon Co Ltd | 射出成形用金型、成形体の製造方法及び導光板 |
| JP2004359221A (ja) * | 2003-05-30 | 2004-12-24 | Boeing Co:The | ウインドシールドアセンブリ、乗物および商用の航空機 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| US10589448B2 (en) | 2020-03-17 |
| JP2015066874A (ja) | 2015-04-13 |
| US20160263797A1 (en) | 2016-09-15 |
| US20180229409A1 (en) | 2018-08-16 |
| JP6309235B2 (ja) | 2018-04-11 |
| US10759098B2 (en) | 2020-09-01 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| US10759098B2 (en) | Injection molding method and injection molding device for transparent resin molded article | |
| JP4679203B2 (ja) | 樹脂製リング形状品の射出成形型 | |
| TW200902287A (en) | Injection molding die | |
| JP6195324B2 (ja) | 透明樹脂成形品の射出成形方法 | |
| JP2012240385A (ja) | 射出成形金型 | |
| CN103963230A (zh) | 一种精密小型塑料件的注塑工艺及模具 | |
| JP2011126195A (ja) | 射出成形用金型 | |
| WO2024032024A1 (zh) | 注塑产品模具、注塑产品模具加工方法及注塑产品 | |
| US8083516B2 (en) | Mold having air-venting grooves | |
| JP2011240683A (ja) | 射出成型用金型 | |
| CN107225732A (zh) | 一种钥匙按钮注塑模具的模仁 | |
| CN202169676U (zh) | 注塑模具的潜浇口 | |
| CN214562615U (zh) | 一种全局相机壳体盖板成型模具 | |
| KR102048571B1 (ko) | 사각 성형물 제조용 금형장치 | |
| CN104924529A (zh) | 方便注塑底脚的托盘模具 | |
| JP2015066874A5 (ja) | ||
| JP6189371B2 (ja) | 中空成形品の成形方法 | |
| CN104107895A (zh) | 金属模具 | |
| CN109648888B (zh) | 一种复合材料空腔盒段液态成型方法 | |
| CN103950160B (zh) | 电动车座桶注塑模具母模板分体结构 | |
| CN107244045A (zh) | 一种钥匙按钮注塑模具的公模仁 | |
| CN215791436U (zh) | 一种汽车注塑件生产用模具 | |
| Rahman et al. | Optimizing the Die Design Parameters for FRP Components Produced in Injection Molding using Mold Flow Analysis | |
| CN105172068B (zh) | 模具内部水口剪切结构、灌胶注塑模具和注塑方法 | |
| CN109501157A (zh) | 一种侧键注塑装置及方法 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 14849037 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 14392280 Country of ref document: US |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 14849037 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |