JP6443362B2 - 半導体装置 - Google Patents
半導体装置 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP6443362B2 JP6443362B2 JP2016041427A JP2016041427A JP6443362B2 JP 6443362 B2 JP6443362 B2 JP 6443362B2 JP 2016041427 A JP2016041427 A JP 2016041427A JP 2016041427 A JP2016041427 A JP 2016041427A JP 6443362 B2 JP6443362 B2 JP 6443362B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- substrate
- protective film
- slit
- hole
- insulating film
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 title claims description 41
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 claims description 107
- 230000001681 protective effect Effects 0.000 claims description 71
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 claims description 4
- 230000000149 penetrating effect Effects 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000010410 layer Substances 0.000 description 61
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 12
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 12
- 230000035515 penetration Effects 0.000 description 7
- BOTDANWDWHJENH-UHFFFAOYSA-N Tetraethyl orthosilicate Chemical compound CCO[Si](OCC)(OCC)OCC BOTDANWDWHJENH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 6
- 239000012535 impurity Substances 0.000 description 5
- 229920002120 photoresistant polymer Polymers 0.000 description 5
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 4
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 description 4
- 239000011347 resin Substances 0.000 description 4
- 229920005989 resin Polymers 0.000 description 4
- XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicon Chemical compound [Si] XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 238000001312 dry etching Methods 0.000 description 3
- 229910052710 silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 239000010703 silicon Substances 0.000 description 3
- 238000005229 chemical vapour deposition Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000007423 decrease Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000005259 measurement Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000003921 oil Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000003071 parasitic effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Copper Chemical compound [Cu] RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000000853 adhesive Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000001070 adhesive effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000000956 alloy Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910045601 alloy Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 230000004888 barrier function Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000012141 concentrate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052802 copper Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000010949 copper Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000007547 defect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000009792 diffusion process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000012212 insulator Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000010884 ion-beam technique Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000002955 isolation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000007257 malfunction Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000007769 metal material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000000059 patterning Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000035699 permeability Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000009467 reduction Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000007789 sealing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000004544 sputter deposition Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000002344 surface layer Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000007740 vapor deposition Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L23/00—Details of semiconductor or other solid state devices
- H01L23/28—Encapsulations, e.g. encapsulating layers, coatings, e.g. for protection
- H01L23/31—Encapsulations, e.g. encapsulating layers, coatings, e.g. for protection characterised by the arrangement or shape
- H01L23/3157—Partial encapsulation or coating
- H01L23/3192—Multilayer coating
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01L—MEASURING FORCE, STRESS, TORQUE, WORK, MECHANICAL POWER, MECHANICAL EFFICIENCY, OR FLUID PRESSURE
- G01L9/00—Measuring steady of quasi-steady pressure of fluid or fluent solid material by electric or magnetic pressure-sensitive elements; Transmitting or indicating the displacement of mechanical pressure-sensitive elements, used to measure the steady or quasi-steady pressure of a fluid or fluent solid material, by electric or magnetic means
- G01L9/0041—Transmitting or indicating the displacement of flexible diaphragms
- G01L9/0042—Constructional details associated with semiconductive diaphragm sensors, e.g. etching, or constructional details of non-semiconductive diaphragms
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01L—MEASURING FORCE, STRESS, TORQUE, WORK, MECHANICAL POWER, MECHANICAL EFFICIENCY, OR FLUID PRESSURE
- G01L9/00—Measuring steady of quasi-steady pressure of fluid or fluent solid material by electric or magnetic pressure-sensitive elements; Transmitting or indicating the displacement of mechanical pressure-sensitive elements, used to measure the steady or quasi-steady pressure of a fluid or fluent solid material, by electric or magnetic means
- G01L9/0041—Transmitting or indicating the displacement of flexible diaphragms
- G01L9/0051—Transmitting or indicating the displacement of flexible diaphragms using variations in ohmic resistance
- G01L9/0052—Transmitting or indicating the displacement of flexible diaphragms using variations in ohmic resistance of piezoresistive elements
- G01L9/0054—Transmitting or indicating the displacement of flexible diaphragms using variations in ohmic resistance of piezoresistive elements integral with a semiconducting diaphragm
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02104—Forming layers
- H01L21/02107—Forming insulating materials on a substrate
- H01L21/02109—Forming insulating materials on a substrate characterised by the type of layer, e.g. type of material, porous/non-porous, pre-cursors, mixtures or laminates
- H01L21/02112—Forming insulating materials on a substrate characterised by the type of layer, e.g. type of material, porous/non-porous, pre-cursors, mixtures or laminates characterised by the material of the layer
- H01L21/02123—Forming insulating materials on a substrate characterised by the type of layer, e.g. type of material, porous/non-porous, pre-cursors, mixtures or laminates characterised by the material of the layer the material containing silicon
- H01L21/02126—Forming insulating materials on a substrate characterised by the type of layer, e.g. type of material, porous/non-porous, pre-cursors, mixtures or laminates characterised by the material of the layer the material containing silicon the material containing Si, O, and at least one of H, N, C, F, or other non-metal elements, e.g. SiOC, SiOC:H or SiONC
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02104—Forming layers
- H01L21/02107—Forming insulating materials on a substrate
- H01L21/02109—Forming insulating materials on a substrate characterised by the type of layer, e.g. type of material, porous/non-porous, pre-cursors, mixtures or laminates
- H01L21/02112—Forming insulating materials on a substrate characterised by the type of layer, e.g. type of material, porous/non-porous, pre-cursors, mixtures or laminates characterised by the material of the layer
- H01L21/02123—Forming insulating materials on a substrate characterised by the type of layer, e.g. type of material, porous/non-porous, pre-cursors, mixtures or laminates characterised by the material of the layer the material containing silicon
- H01L21/0217—Forming insulating materials on a substrate characterised by the type of layer, e.g. type of material, porous/non-porous, pre-cursors, mixtures or laminates characterised by the material of the layer the material containing silicon the material being a silicon nitride not containing oxygen, e.g. SixNy or SixByNz
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02104—Forming layers
- H01L21/02107—Forming insulating materials on a substrate
- H01L21/02225—Forming insulating materials on a substrate characterised by the process for the formation of the insulating layer
- H01L21/0226—Forming insulating materials on a substrate characterised by the process for the formation of the insulating layer formation by a deposition process
- H01L21/02263—Forming insulating materials on a substrate characterised by the process for the formation of the insulating layer formation by a deposition process deposition from the gas or vapour phase
- H01L21/02271—Forming insulating materials on a substrate characterised by the process for the formation of the insulating layer formation by a deposition process deposition from the gas or vapour phase deposition by decomposition or reaction of gaseous or vapour phase compounds, i.e. chemical vapour deposition
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/027—Making masks on semiconductor bodies for further photolithographic processing not provided for in group H01L21/18 or H01L21/34
- H01L21/0271—Making masks on semiconductor bodies for further photolithographic processing not provided for in group H01L21/18 or H01L21/34 comprising organic layers
- H01L21/0273—Making masks on semiconductor bodies for further photolithographic processing not provided for in group H01L21/18 or H01L21/34 comprising organic layers characterised by the treatment of photoresist layers
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/04—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof the devices having potential barriers, e.g. a PN junction, depletion layer or carrier concentration layer
- H01L21/18—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof the devices having potential barriers, e.g. a PN junction, depletion layer or carrier concentration layer the devices having semiconductor bodies comprising elements of Group IV of the Periodic Table or AIIIBV compounds with or without impurities, e.g. doping materials
- H01L21/26—Bombardment with radiation
- H01L21/263—Bombardment with radiation with high-energy radiation
- H01L21/265—Bombardment with radiation with high-energy radiation producing ion implantation
- H01L21/266—Bombardment with radiation with high-energy radiation producing ion implantation using masks
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/04—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof the devices having potential barriers, e.g. a PN junction, depletion layer or carrier concentration layer
- H01L21/18—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof the devices having potential barriers, e.g. a PN junction, depletion layer or carrier concentration layer the devices having semiconductor bodies comprising elements of Group IV of the Periodic Table or AIIIBV compounds with or without impurities, e.g. doping materials
- H01L21/30—Treatment of semiconductor bodies using processes or apparatus not provided for in groups H01L21/20 - H01L21/26
- H01L21/302—Treatment of semiconductor bodies using processes or apparatus not provided for in groups H01L21/20 - H01L21/26 to change their surface-physical characteristics or shape, e.g. etching, polishing, cutting
- H01L21/306—Chemical or electrical treatment, e.g. electrolytic etching
- H01L21/3065—Plasma etching; Reactive-ion etching
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/04—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof the devices having potential barriers, e.g. a PN junction, depletion layer or carrier concentration layer
- H01L21/18—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof the devices having potential barriers, e.g. a PN junction, depletion layer or carrier concentration layer the devices having semiconductor bodies comprising elements of Group IV of the Periodic Table or AIIIBV compounds with or without impurities, e.g. doping materials
- H01L21/30—Treatment of semiconductor bodies using processes or apparatus not provided for in groups H01L21/20 - H01L21/26
- H01L21/31—Treatment of semiconductor bodies using processes or apparatus not provided for in groups H01L21/20 - H01L21/26 to form insulating layers thereon, e.g. for masking or by using photolithographic techniques; After treatment of these layers; Selection of materials for these layers
- H01L21/3105—After-treatment
- H01L21/311—Etching the insulating layers by chemical or physical means
- H01L21/31105—Etching inorganic layers
- H01L21/31111—Etching inorganic layers by chemical means
- H01L21/31116—Etching inorganic layers by chemical means by dry-etching
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/04—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof the devices having potential barriers, e.g. a PN junction, depletion layer or carrier concentration layer
- H01L21/18—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof the devices having potential barriers, e.g. a PN junction, depletion layer or carrier concentration layer the devices having semiconductor bodies comprising elements of Group IV of the Periodic Table or AIIIBV compounds with or without impurities, e.g. doping materials
- H01L21/30—Treatment of semiconductor bodies using processes or apparatus not provided for in groups H01L21/20 - H01L21/26
- H01L21/31—Treatment of semiconductor bodies using processes or apparatus not provided for in groups H01L21/20 - H01L21/26 to form insulating layers thereon, e.g. for masking or by using photolithographic techniques; After treatment of these layers; Selection of materials for these layers
- H01L21/3205—Deposition of non-insulating-, e.g. conductive- or resistive-, layers on insulating layers; After-treatment of these layers
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/04—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof the devices having potential barriers, e.g. a PN junction, depletion layer or carrier concentration layer
- H01L21/18—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof the devices having potential barriers, e.g. a PN junction, depletion layer or carrier concentration layer the devices having semiconductor bodies comprising elements of Group IV of the Periodic Table or AIIIBV compounds with or without impurities, e.g. doping materials
- H01L21/30—Treatment of semiconductor bodies using processes or apparatus not provided for in groups H01L21/20 - H01L21/26
- H01L21/324—Thermal treatment for modifying the properties of semiconductor bodies, e.g. annealing, sintering
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/04—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof the devices having potential barriers, e.g. a PN junction, depletion layer or carrier concentration layer
- H01L21/50—Assembly of semiconductor devices using processes or apparatus not provided for in a single one of the subgroups H01L21/06 - H01L21/326, e.g. sealing of a cap to a base of a container
- H01L21/56—Encapsulations, e.g. encapsulation layers, coatings
- H01L21/565—Moulds
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/70—Manufacture or treatment of devices consisting of a plurality of solid state components formed in or on a common substrate or of parts thereof; Manufacture of integrated circuit devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/71—Manufacture of specific parts of devices defined in group H01L21/70
- H01L21/768—Applying interconnections to be used for carrying current between separate components within a device comprising conductors and dielectrics
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/70—Manufacture or treatment of devices consisting of a plurality of solid state components formed in or on a common substrate or of parts thereof; Manufacture of integrated circuit devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/71—Manufacture of specific parts of devices defined in group H01L21/70
- H01L21/768—Applying interconnections to be used for carrying current between separate components within a device comprising conductors and dielectrics
- H01L21/76801—Applying interconnections to be used for carrying current between separate components within a device comprising conductors and dielectrics characterised by the formation and the after-treatment of the dielectrics, e.g. smoothing
- H01L21/76802—Applying interconnections to be used for carrying current between separate components within a device comprising conductors and dielectrics characterised by the formation and the after-treatment of the dielectrics, e.g. smoothing by forming openings in dielectrics
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/70—Manufacture or treatment of devices consisting of a plurality of solid state components formed in or on a common substrate or of parts thereof; Manufacture of integrated circuit devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/71—Manufacture of specific parts of devices defined in group H01L21/70
- H01L21/768—Applying interconnections to be used for carrying current between separate components within a device comprising conductors and dielectrics
- H01L21/76898—Applying interconnections to be used for carrying current between separate components within a device comprising conductors and dielectrics formed through a semiconductor substrate
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L23/00—Details of semiconductor or other solid state devices
- H01L23/28—Encapsulations, e.g. encapsulating layers, coatings, e.g. for protection
- H01L23/31—Encapsulations, e.g. encapsulating layers, coatings, e.g. for protection characterised by the arrangement or shape
- H01L23/3157—Partial encapsulation or coating
- H01L23/3171—Partial encapsulation or coating the coating being directly applied to the semiconductor body, e.g. passivation layer
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L23/00—Details of semiconductor or other solid state devices
- H01L23/48—Arrangements for conducting electric current to or from the solid state body in operation, e.g. leads, terminal arrangements ; Selection of materials therefor
- H01L23/481—Internal lead connections, e.g. via connections, feedthrough structures
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L23/00—Details of semiconductor or other solid state devices
- H01L23/52—Arrangements for conducting electric current within the device in operation from one component to another, i.e. interconnections, e.g. wires, lead frames
- H01L23/522—Arrangements for conducting electric current within the device in operation from one component to another, i.e. interconnections, e.g. wires, lead frames including external interconnections consisting of a multilayer structure of conductive and insulating layers inseparably formed on the semiconductor body
- H01L23/528—Geometry or layout of the interconnection structure
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L23/00—Details of semiconductor or other solid state devices
- H01L23/58—Structural electrical arrangements for semiconductor devices not otherwise provided for, e.g. in combination with batteries
- H01L23/60—Protection against electrostatic charges or discharges, e.g. Faraday shields
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/66—Types of semiconductor device ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/84—Types of semiconductor device ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor controllable by variation of applied mechanical force, e.g. of pressure
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2223/00—Details relating to semiconductor or other solid state devices covered by the group H01L23/00
- H01L2223/544—Marks applied to semiconductor devices or parts
- H01L2223/54426—Marks applied to semiconductor devices or parts for alignment
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L23/00—Details of semiconductor or other solid state devices
- H01L23/544—Marks applied to semiconductor devices or parts, e.g. registration marks, alignment structures, wafer maps
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Power Engineering (AREA)
- Microelectronics & Electronic Packaging (AREA)
- Condensed Matter Physics & Semiconductors (AREA)
- Computer Hardware Design (AREA)
- Manufacturing & Machinery (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- High Energy & Nuclear Physics (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Analytical Chemistry (AREA)
- Geometry (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Toxicology (AREA)
- Plasma & Fusion (AREA)
- Ceramic Engineering (AREA)
- General Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Inorganic Chemistry (AREA)
- Pressure Sensors (AREA)
- Measuring Fluid Pressure (AREA)
- Internal Circuitry In Semiconductor Integrated Circuit Devices (AREA)
Description
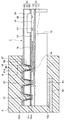
第1実施形態について図面を参照しつつ説明する。本実施形態では、半導体装置を圧力センサに適用した例について説明する。なお、この半導体装置としての圧力センサは、例えば、自動車に搭載され、オイルポンプから排出されたオイルの圧力を検出する圧力センサとして適用されると好適である。
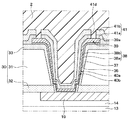
第2実施形態について説明する。本実施形態は、第1実施形態に対してスリット41dを形成する場所を変更したものであり、その他に関しては第1実施形態と同様であるため、ここでは説明を省略する。
第3実施形態について説明する。本実施形態は、第1実施形態に対して保護膜41の形状を変更したものであり、その他に関しては第1実施形態と同様であるため、ここでは説明を省略する。
本発明は上記した実施形態に限定されるものではなく、特許請求の範囲に記載した範囲内において適宜変更が可能である。
10a 一面
19〜21 接続部
30 第2基板
30a 一面
30b 他面
36 貫通孔
38 貫通電極
41 保護膜
41d スリット
Claims (5)
- 一面(10a)を有し、前記一面側に複数の接続部(19〜21)が形成された第1基板(10)と、
一面(30a)および当該一面と反対側の他面(30b)を有し、当該一面が前記第1基板の一面と接合されることで前記第1基板上に積層され、前記複数の接続部をそれぞれ露出させる複数の貫通孔(36)が前記第1基板との積層方向に沿って形成された第2基板(30)と、
前記複数の貫通孔のそれぞれに配置され、前記複数の接続部とそれぞれ電気的に接続される複数の貫通電極(38)と、
前記複数の貫通電極を一体的に覆う保護膜(41)と、を備え、
前記貫通電極および前記保護膜は、前記貫通孔の壁面に沿った形状で配置されており、
前記保護膜は、前記第1基板の一面に対する法線方向から視たとき、前記複数の貫通孔の開口部をそれぞれ囲む複数の枠状のスリット(41d)が形成され、前記スリットよりも内縁側の領域と前記スリットよりも外縁側の領域とが前記スリットによって分離されている半導体装置。 - 前記第2基板の他面上には、前記貫通電極と電気的に接続される配線層(39)が形成されており、
前記スリットは、前記保護膜を貫通して前記配線層を枠状に露出させる状態で形成されている請求項1に記載の半導体装置。 - 前記第2基板の他面上には、前記貫通電極と電気的に接続される配線層(39)が形成されており、
前記スリットは、前記貫通孔の開口部と共に、前記配線層を囲む状態で形成されている請求項1に記載の半導体装置。 - 前記第2基板は、前記他面側に絶縁膜(33)を有し、
前記配線層は、前記絶縁膜上に形成されており、
前記保護膜は、前記貫通電極と共に前記配線層を覆い、かつ前記絶縁膜と当接する部分が当該絶縁膜と同じ材料で構成されており、
前記保護膜および前記絶縁膜は、前記スリットが前記保護膜および前記絶縁膜を貫通して形成されることにより、前記スリットよりも内縁側の領域と前記スリットよりも外縁側の領域とに分離されている請求項3に記載の半導体装置。 - 前記貫通孔の底面と側面との間の境界部分上に配置された保護膜には、1240MPa以上の応力が印加される請求項1ないし4のいずれか1つに記載の半導体装置。
Priority Applications (4)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2016041427A JP6443362B2 (ja) | 2016-03-03 | 2016-03-03 | 半導体装置 |
| CN201780014552.XA CN108701615B (zh) | 2016-03-03 | 2017-02-23 | 半导体装置 |
| PCT/JP2017/006898 WO2017150343A1 (ja) | 2016-03-03 | 2017-02-23 | 半導体装置 |
| US16/078,131 US10468322B2 (en) | 2016-03-03 | 2017-02-23 | Semiconductor device capable of suppressing cracks of through-hole protective film and short circuit of adjacent through-electrodes |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2016041427A JP6443362B2 (ja) | 2016-03-03 | 2016-03-03 | 半導体装置 |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2017157751A JP2017157751A (ja) | 2017-09-07 |
| JP2017157751A5 JP2017157751A5 (ja) | 2018-06-14 |
| JP6443362B2 true JP6443362B2 (ja) | 2018-12-26 |
Family
ID=59742860
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2016041427A Active JP6443362B2 (ja) | 2016-03-03 | 2016-03-03 | 半導体装置 |
Country Status (4)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US10468322B2 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JP6443362B2 (ja) |
| CN (1) | CN108701615B (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2017150343A1 (ja) |
Families Citing this family (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2019067937A (ja) | 2017-10-02 | 2019-04-25 | ソニーセミコンダクタソリューションズ株式会社 | 半導体装置、半導体装置の製造方法、及び、電子機器 |
| JP7340965B2 (ja) | 2019-06-13 | 2023-09-08 | キヤノン株式会社 | 半導体装置およびその製造方法 |
| EP3790046A1 (en) * | 2019-09-03 | 2021-03-10 | Ams Ag | Through-substrate via and method for manufacturing a through-substrate via |
Family Cites Families (19)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP4088120B2 (ja) * | 2002-08-12 | 2008-05-21 | 株式会社ルネサステクノロジ | 半導体装置 |
| JP4966487B2 (ja) * | 2004-09-29 | 2012-07-04 | オンセミコンダクター・トレーディング・リミテッド | 半導体装置及びその製造方法 |
| JP4937842B2 (ja) * | 2007-06-06 | 2012-05-23 | ルネサスエレクトロニクス株式会社 | 半導体装置およびその製造方法 |
| KR100945504B1 (ko) | 2007-06-26 | 2010-03-09 | 주식회사 하이닉스반도체 | 스택 패키지 및 그의 제조 방법 |
| US8334599B2 (en) * | 2008-08-21 | 2012-12-18 | Qimonda Ag | Electronic device having a chip stack |
| JP5146307B2 (ja) * | 2008-12-26 | 2013-02-20 | パナソニック株式会社 | 半導体装置 |
| JP4659875B2 (ja) * | 2008-11-25 | 2011-03-30 | パナソニック株式会社 | 半導体装置 |
| WO2010061551A1 (ja) | 2008-11-25 | 2010-06-03 | パナソニック株式会社 | 半導体装置および電子機器 |
| JP2011165983A (ja) | 2010-02-10 | 2011-08-25 | Seiko Epson Corp | 配線基板の製造方法、導体パターン形成用インクセットおよび配線基板 |
| JP5622433B2 (ja) * | 2010-04-28 | 2014-11-12 | ルネサスエレクトロニクス株式会社 | 半導体装置およびその製造方法 |
| JP2012009473A (ja) | 2010-06-22 | 2012-01-12 | Panasonic Corp | 半導体装置及びその製造方法 |
| EP2463896B1 (en) | 2010-12-07 | 2020-04-15 | IMEC vzw | Method for forming through-substrate vias surrounded by isolation trenches with an airgap and corresponding device |
| JP2012253182A (ja) * | 2011-06-02 | 2012-12-20 | Panasonic Corp | 半導体装置及びその製造方法 |
| JP2013098308A (ja) | 2011-10-31 | 2013-05-20 | Elpida Memory Inc | 半導体ウェハ、半導体装置及びその製造方法 |
| JP5948924B2 (ja) * | 2012-02-09 | 2016-07-06 | セイコーエプソン株式会社 | 半導体装置、半導体装置の製造方法、回路装置、回路装置の製造方法、電子機器 |
| KR102094924B1 (ko) * | 2013-06-27 | 2020-03-30 | 삼성전자주식회사 | 관통전극을 갖는 반도체 패키지 및 그 제조방법 |
| JP6098412B2 (ja) * | 2013-07-23 | 2017-03-22 | 株式会社デンソー | 半導体装置 |
| JP5783297B2 (ja) | 2013-08-06 | 2015-09-24 | 株式会社デンソー | 力学量センサ |
| JP6335099B2 (ja) * | 2014-11-04 | 2018-05-30 | 東芝メモリ株式会社 | 半導体装置および半導体装置の製造方法 |
-
2016
- 2016-03-03 JP JP2016041427A patent/JP6443362B2/ja active Active
-
2017
- 2017-02-23 WO PCT/JP2017/006898 patent/WO2017150343A1/ja active Application Filing
- 2017-02-23 CN CN201780014552.XA patent/CN108701615B/zh active Active
- 2017-02-23 US US16/078,131 patent/US10468322B2/en active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN108701615B (zh) | 2022-09-16 |
| US10468322B2 (en) | 2019-11-05 |
| WO2017150343A1 (ja) | 2017-09-08 |
| JP2017157751A (ja) | 2017-09-07 |
| CN108701615A (zh) | 2018-10-23 |
| US20190051575A1 (en) | 2019-02-14 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP4793496B2 (ja) | 半導体装置およびその製造方法 | |
| JP5935352B2 (ja) | Son構造を有する物理量センサの製造方法。 | |
| US9422152B2 (en) | Hybridly integrated module having a sealing structure | |
| JP5783297B2 (ja) | 力学量センサ | |
| JP2008020433A (ja) | 力学量センサ | |
| JP5545281B2 (ja) | 力学量センサ | |
| JP5874609B2 (ja) | 半導体装置およびその製造方法 | |
| JP6443362B2 (ja) | 半導体装置 | |
| JP4933934B2 (ja) | 半導体装置及び半導体装置の製造方法 | |
| JP6176286B2 (ja) | 半導体装置およびその製造方法 | |
| JP2012028900A (ja) | コンデンサマイクロホン | |
| JP5392296B2 (ja) | 半導体装置およびその製造方法 | |
| JP4807080B2 (ja) | 半導体装置の製造方法 | |
| JP6287600B2 (ja) | 温度センサ | |
| JP2014102225A (ja) | 物理量センサおよびその製造方法 | |
| JP6142736B2 (ja) | 半導体圧力センサ | |
| JP6142735B2 (ja) | 半導体圧力センサ | |
| JP5955024B2 (ja) | Memsモジュール及びその製造方法 | |
| JP5884667B2 (ja) | 半導体装置の製造方法 | |
| JP2020199591A (ja) | 半導体装置およびその製造方法 | |
| JP2018004448A (ja) | 半導体装置 | |
| JP6237515B2 (ja) | 圧力センサおよびその製造方法 | |
| JP2014232090A (ja) | 物理量センサ | |
| WO2018003353A1 (ja) | 半導体装置 | |
| JP2014169915A (ja) | 半導体圧力センサの製造方法 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20180425 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20180425 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20181030 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20181112 |
|
| R151 | Written notification of patent or utility model registration |
Ref document number: 6443362 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R151 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |