JP4653735B2 - デュアルメタルゲート構造を形成するためのプロセス - Google Patents
デュアルメタルゲート構造を形成するためのプロセス Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP4653735B2 JP4653735B2 JP2006509809A JP2006509809A JP4653735B2 JP 4653735 B2 JP4653735 B2 JP 4653735B2 JP 2006509809 A JP2006509809 A JP 2006509809A JP 2006509809 A JP2006509809 A JP 2006509809A JP 4653735 B2 JP4653735 B2 JP 4653735B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- layer
- metal
- region
- gate
- containing layer
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 title claims description 40
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 title claims description 40
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title claims description 14
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 title claims description 11
- 230000009977 dual effect Effects 0.000 title claims description 4
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 claims description 19
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 claims description 17
- XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicon Chemical compound [Si] XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 15
- 229910052710 silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 15
- 239000010703 silicon Substances 0.000 claims description 15
- NRTOMJZYCJJWKI-UHFFFAOYSA-N Titanium nitride Chemical compound [Ti]#N NRTOMJZYCJJWKI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 14
- 238000004140 cleaning Methods 0.000 claims description 9
- 238000001039 wet etching Methods 0.000 claims description 9
- 241000252506 Characiformes Species 0.000 claims description 8
- 229910052581 Si3N4 Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 8
- HWEYZGSCHQNNEH-UHFFFAOYSA-N silicon tantalum Chemical compound [Si].[Ta] HWEYZGSCHQNNEH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 8
- VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicium dioxide Chemical compound O=[Si]=O VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 7
- 229910052814 silicon oxide Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 7
- QAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-N Sulfuric acid Chemical compound OS(O)(=O)=O QAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 6
- 238000001312 dry etching Methods 0.000 claims description 6
- MHAJPDPJQMAIIY-UHFFFAOYSA-N Hydrogen peroxide Chemical compound OO MHAJPDPJQMAIIY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 5
- 239000007864 aqueous solution Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- 230000000873 masking effect Effects 0.000 claims 5
- 238000005530 etching Methods 0.000 description 19
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 9
- 238000001020 plasma etching Methods 0.000 description 9
- 229920002120 photoresistant polymer Polymers 0.000 description 8
- 229910052736 halogen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 6
- 150000002367 halogens Chemical class 0.000 description 6
- 229910021420 polycrystalline silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 6
- 229920005591 polysilicon Polymers 0.000 description 6
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 5
- 229910021332 silicide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 5
- FVBUAEGBCNSCDD-UHFFFAOYSA-N silicide(4-) Chemical group [Si-4] FVBUAEGBCNSCDD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- 150000002739 metals Chemical class 0.000 description 4
- 230000008901 benefit Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000007796 conventional method Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 3
- 239000000243 solution Substances 0.000 description 3
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 2
- HQVNEWCFYHHQES-UHFFFAOYSA-N silicon nitride Chemical compound N12[Si]34N5[Si]62N3[Si]51N64 HQVNEWCFYHHQES-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 125000006850 spacer group Chemical group 0.000 description 2
- 229910045601 alloy Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000000956 alloy Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000004020 conductor Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000007812 deficiency Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000002019 doping agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000011810 insulating material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000012212 insulator Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000001459 lithography Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000009467 reduction Effects 0.000 description 1
- WFKWXMTUELFFGS-UHFFFAOYSA-N tungsten Chemical compound [W] WFKWXMTUELFFGS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052721 tungsten Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000010937 tungsten Substances 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/70—Manufacture or treatment of devices consisting of a plurality of solid state components formed in or on a common substrate or of parts thereof; Manufacture of integrated circuit devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/77—Manufacture or treatment of devices consisting of a plurality of solid state components or integrated circuits formed in, or on, a common substrate
- H01L21/78—Manufacture or treatment of devices consisting of a plurality of solid state components or integrated circuits formed in, or on, a common substrate with subsequent division of the substrate into plural individual devices
- H01L21/82—Manufacture or treatment of devices consisting of a plurality of solid state components or integrated circuits formed in, or on, a common substrate with subsequent division of the substrate into plural individual devices to produce devices, e.g. integrated circuits, each consisting of a plurality of components
- H01L21/822—Manufacture or treatment of devices consisting of a plurality of solid state components or integrated circuits formed in, or on, a common substrate with subsequent division of the substrate into plural individual devices to produce devices, e.g. integrated circuits, each consisting of a plurality of components the substrate being a semiconductor, using silicon technology
- H01L21/8232—Field-effect technology
- H01L21/8234—MIS technology, i.e. integration processes of field effect transistors of the conductor-insulator-semiconductor type
- H01L21/823468—MIS technology, i.e. integration processes of field effect transistors of the conductor-insulator-semiconductor type with a particular manufacturing method of the gate sidewall spacers, e.g. double spacers, particular spacer material or shape
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/70—Manufacture or treatment of devices consisting of a plurality of solid state components formed in or on a common substrate or of parts thereof; Manufacture of integrated circuit devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/77—Manufacture or treatment of devices consisting of a plurality of solid state components or integrated circuits formed in, or on, a common substrate
- H01L21/78—Manufacture or treatment of devices consisting of a plurality of solid state components or integrated circuits formed in, or on, a common substrate with subsequent division of the substrate into plural individual devices
- H01L21/82—Manufacture or treatment of devices consisting of a plurality of solid state components or integrated circuits formed in, or on, a common substrate with subsequent division of the substrate into plural individual devices to produce devices, e.g. integrated circuits, each consisting of a plurality of components
- H01L21/822—Manufacture or treatment of devices consisting of a plurality of solid state components or integrated circuits formed in, or on, a common substrate with subsequent division of the substrate into plural individual devices to produce devices, e.g. integrated circuits, each consisting of a plurality of components the substrate being a semiconductor, using silicon technology
- H01L21/8232—Field-effect technology
- H01L21/8234—MIS technology, i.e. integration processes of field effect transistors of the conductor-insulator-semiconductor type
- H01L21/823437—MIS technology, i.e. integration processes of field effect transistors of the conductor-insulator-semiconductor type with a particular manufacturing method of the gate conductors, e.g. particular materials, shapes
- H01L21/82345—MIS technology, i.e. integration processes of field effect transistors of the conductor-insulator-semiconductor type with a particular manufacturing method of the gate conductors, e.g. particular materials, shapes gate conductors with different gate conductor materials or different gate conductor implants, e.g. dual gate structures
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/70—Manufacture or treatment of devices consisting of a plurality of solid state components formed in or on a common substrate or of parts thereof; Manufacture of integrated circuit devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/77—Manufacture or treatment of devices consisting of a plurality of solid state components or integrated circuits formed in, or on, a common substrate
- H01L21/78—Manufacture or treatment of devices consisting of a plurality of solid state components or integrated circuits formed in, or on, a common substrate with subsequent division of the substrate into plural individual devices
- H01L21/82—Manufacture or treatment of devices consisting of a plurality of solid state components or integrated circuits formed in, or on, a common substrate with subsequent division of the substrate into plural individual devices to produce devices, e.g. integrated circuits, each consisting of a plurality of components
- H01L21/822—Manufacture or treatment of devices consisting of a plurality of solid state components or integrated circuits formed in, or on, a common substrate with subsequent division of the substrate into plural individual devices to produce devices, e.g. integrated circuits, each consisting of a plurality of components the substrate being a semiconductor, using silicon technology
- H01L21/8232—Field-effect technology
- H01L21/8234—MIS technology, i.e. integration processes of field effect transistors of the conductor-insulator-semiconductor type
- H01L21/823462—MIS technology, i.e. integration processes of field effect transistors of the conductor-insulator-semiconductor type with a particular manufacturing method of the gate insulating layers, e.g. different gate insulating layer thicknesses, particular gate insulator materials or particular gate insulator implants
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Condensed Matter Physics & Semiconductors (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Manufacturing & Machinery (AREA)
- Computer Hardware Design (AREA)
- Microelectronics & Electronic Packaging (AREA)
- Power Engineering (AREA)
- Metal-Oxide And Bipolar Metal-Oxide Semiconductor Integrated Circuits (AREA)
- Electrodes Of Semiconductors (AREA)
- Thin Film Transistor (AREA)
Description
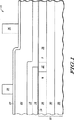
図中の要素が明瞭化及び簡略化のために示され、実寸で図示される必要のないことは当業者にとって明らかである。例えば、本発明の実施形態に対する理解をより深めるため、図中の要素のうち、いくつかの寸法が、他の要素に比べて誇張されている。
Claims (2)
- デュアルメタルゲート構造を形成するためのプロセスであって、
第1領域と第2領域とを有し、前記第1領域はN型を有し、前記第2領域はP型を有する半導体基板を提供するステップと、
前記半導体基板の前記第1領域と前記第2領域とを覆う誘電体層を形成するステップであって、前記誘電体層は酸窒化シリコン又は酸化シリコンからなるステップと、
前記誘電体層上に設けられ、前記半導体基板の前記第1領域を覆う第1メタル含有層を形成するステップであって、前記第1メタル含有層は窒化チタンからなるステップと、
前記第1メタル含有層と前記誘電体層とを覆うと共に、前記半導体基板の前記第2領域上に設けられた前記誘電体層の一部と直接接する第2メタル含有層を形成するステップであって、前記第2メタル含有層は窒化タンタルシリコンからなるステップと、
前記第2メタル含有層上にパターン化されたマスキング層を形成するステップと、
前記パターン化されたマスキング層を用いて前記第2メタル含有層をドライエッチングし、第2ゲート層を形成すると共に前記第1メタル含有層上に第1ゲート層の上部を形成するステップと、
前記第1ゲート層の上部をマスクとして用いて前記第1メタル含有層の少なくとも一部をウェットエッチングし、前記第1ゲート層の下部を形成するステップであって、前記ウェットエッチングは、硫酸及び過酸化水素の水溶液を用いたピラニア洗浄であるステップと
を備えるプロセス。 - デュアルメタルゲート構造を形成するためのプロセスであって、
第1領域と第2領域とを有し、前記第1領域はN領域であり、前記第2領域はP領域である半導体基板を提供するステップと、
前記半導体基板の前記第1領域と前記第2領域とを覆うゲート誘電体層を形成するステップであって、前記ゲート誘電体層は酸窒化シリコン又は酸化シリコンからなるステップと、
前記ゲート誘電体層上に設けられ、前記半導体基板の前記第1領域を覆う第1メタル含有層を形成するステップであって、前記第1メタル含有層は窒化チタンからなるステップと、
前記第1メタル含有層と前記ゲート誘電体層とを覆うように設けられ、前記半導体基板の前記第2領域を覆う前記ゲート誘電体層の一部と直接接する第2メタル含有層を形成するステップであって、前記第2メタル含有層は窒化タンタルシリコンからなるステップと、
前記第2メタル含有層上にパターン化されたマスキング層を形成するステップと、
前記パターン化されたマスキング層を用いて前記第2メタル含有層をドライエッチングし、第2ゲート層を形成すると共に前記第1メタル含有層上に第1ゲート層の上部を形成するステップと、
前記パターン化されたマスキング層を用いて前記第1メタル含有層の少なくとも一部をウェットエッチングし、前記第1ゲート層の下部を形成するステップであって、前記ウェットエッチングは、硫酸及び過酸化水素の水溶液を用いたピラニア洗浄であるステップと
を備えるプロセス。
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US10/410,043 US6790719B1 (en) | 2003-04-09 | 2003-04-09 | Process for forming dual metal gate structures |
| PCT/US2004/010814 WO2004093182A1 (en) | 2003-04-09 | 2004-04-08 | Process for forming dual metal gate structures |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2006523037A JP2006523037A (ja) | 2006-10-05 |
| JP2006523037A5 JP2006523037A5 (ja) | 2007-06-07 |
| JP4653735B2 true JP4653735B2 (ja) | 2011-03-16 |
Family
ID=32927360
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2006509809A Expired - Fee Related JP4653735B2 (ja) | 2003-04-09 | 2004-04-08 | デュアルメタルゲート構造を形成するためのプロセス |
Country Status (6)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US6790719B1 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JP4653735B2 (ja) |
| KR (1) | KR101159339B1 (ja) |
| CN (1) | CN100487880C (ja) |
| TW (1) | TWI342044B (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2004093182A1 (ja) |
Families Citing this family (48)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP3790237B2 (ja) * | 2003-08-26 | 2006-06-28 | 株式会社東芝 | 半導体装置の製造方法 |
| US7125775B1 (en) * | 2004-03-18 | 2006-10-24 | Integrated Device Technology, Inc. | Method for forming hybrid device gates |
| US7030001B2 (en) * | 2004-04-19 | 2006-04-18 | Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. | Method for forming a gate electrode having a metal |
| DE102004026232B4 (de) * | 2004-05-28 | 2006-05-04 | Infineon Technologies Ag | Verfahren zum Ausbilden einer integrierten Halbleiterschaltungsanordnung |
| KR100602122B1 (ko) * | 2004-12-03 | 2006-07-19 | 동부일렉트로닉스 주식회사 | 반도체 소자의 제조방법 |
| US7109079B2 (en) * | 2005-01-26 | 2006-09-19 | Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. | Metal gate transistor CMOS process and method for making |
| JP4764030B2 (ja) | 2005-03-03 | 2011-08-31 | 株式会社東芝 | 半導体装置及びその製造方法 |
| JP4626411B2 (ja) * | 2005-06-13 | 2011-02-09 | ソニー株式会社 | 半導体装置および半導体装置の製造方法 |
| US20070048920A1 (en) * | 2005-08-25 | 2007-03-01 | Sematech | Methods for dual metal gate CMOS integration |
| US7332433B2 (en) * | 2005-09-22 | 2008-02-19 | Sematech Inc. | Methods of modulating the work functions of film layers |
| JP4723975B2 (ja) | 2005-10-25 | 2011-07-13 | 株式会社東芝 | 半導体装置およびその製造方法 |
| JP2007123548A (ja) * | 2005-10-28 | 2007-05-17 | Renesas Technology Corp | 半導体装置の製造方法 |
| KR100827435B1 (ko) * | 2006-01-31 | 2008-05-06 | 삼성전자주식회사 | 반도체 소자에서 무산소 애싱 공정을 적용한 게이트 형성방법 |
| US20070178634A1 (en) * | 2006-01-31 | 2007-08-02 | Hyung Suk Jung | Cmos semiconductor devices having dual work function metal gate stacks |
| JP4929867B2 (ja) * | 2006-06-19 | 2012-05-09 | 富士通セミコンダクター株式会社 | 半導体装置の製造方法 |
| KR100835430B1 (ko) * | 2007-05-21 | 2008-06-04 | 주식회사 동부하이텍 | 반도체 소자의 듀얼 게이트 전극 형성 방법 |
| US7696036B2 (en) * | 2007-06-14 | 2010-04-13 | International Business Machines Corporation | CMOS transistors with differential oxygen content high-k dielectrics |
| US7666730B2 (en) * | 2007-06-29 | 2010-02-23 | Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. | Method for forming a dual metal gate structure |
| KR100903383B1 (ko) * | 2007-07-31 | 2009-06-23 | 주식회사 하이닉스반도체 | 일함수가 조절된 게이트전극을 구비한 트랜지스터 및 그를구비하는 메모리소자 |
| JP2009044051A (ja) * | 2007-08-10 | 2009-02-26 | Panasonic Corp | 半導体装置及びその製造方法 |
| US20090206416A1 (en) * | 2008-02-19 | 2009-08-20 | International Business Machines Corporation | Dual metal gate structures and methods |
| US7691701B1 (en) | 2009-01-05 | 2010-04-06 | International Business Machines Corporation | Method of forming gate stack and structure thereof |
| DE102009039418B4 (de) * | 2009-08-31 | 2013-08-22 | GLOBALFOUNDRIES Dresden Module One Ltd. Liability Company & Co. KG | Einstellung der Austrittsarbeit in Gate-Stapeln mit großem ε, die Gatedielektrika mit unterschiedlicher Dicke enthalten |
| US8435878B2 (en) | 2010-04-06 | 2013-05-07 | International Business Machines Corporation | Field effect transistor device and fabrication |
| US8211775B1 (en) | 2011-03-09 | 2012-07-03 | United Microelectronics Corp. | Method of making transistor having metal gate |
| US8519487B2 (en) | 2011-03-21 | 2013-08-27 | United Microelectronics Corp. | Semiconductor device |
| US9384962B2 (en) | 2011-04-07 | 2016-07-05 | United Microelectronics Corp. | Oxygen treatment of replacement work-function metals in CMOS transistor gates |
| US8530980B2 (en) | 2011-04-27 | 2013-09-10 | United Microelectronics Corp. | Gate stack structure with etch stop layer and manufacturing process thereof |
| US8673758B2 (en) | 2011-06-16 | 2014-03-18 | United Microelectronics Corp. | Structure of metal gate and fabrication method thereof |
| US9490342B2 (en) | 2011-06-16 | 2016-11-08 | United Microelectronics Corp. | Method for fabricating semiconductor device |
| US8536038B2 (en) | 2011-06-21 | 2013-09-17 | United Microelectronics Corp. | Manufacturing method for metal gate using ion implantation |
| US8486790B2 (en) | 2011-07-18 | 2013-07-16 | United Microelectronics Corp. | Manufacturing method for metal gate |
| US8551876B2 (en) | 2011-08-18 | 2013-10-08 | United Microelectronics Corp. | Manufacturing method for semiconductor device having metal gate |
| US8872286B2 (en) | 2011-08-22 | 2014-10-28 | United Microelectronics Corp. | Metal gate structure and fabrication method thereof |
| US8691681B2 (en) | 2012-01-04 | 2014-04-08 | United Microelectronics Corp. | Semiconductor device having a metal gate and fabricating method thereof |
| US8860181B2 (en) | 2012-03-07 | 2014-10-14 | United Microelectronics Corp. | Thin film resistor structure |
| US9105623B2 (en) | 2012-05-25 | 2015-08-11 | United Microelectronics Corp. | Semiconductor device having metal gate and manufacturing method thereof |
| US8975666B2 (en) | 2012-08-22 | 2015-03-10 | United Microelectronics Corp. | MOS transistor and process thereof |
| US9054172B2 (en) | 2012-12-05 | 2015-06-09 | United Microelectrnics Corp. | Semiconductor structure having contact plug and method of making the same |
| US8735269B1 (en) | 2013-01-15 | 2014-05-27 | United Microelectronics Corp. | Method for forming semiconductor structure having TiN layer |
| US9653300B2 (en) | 2013-04-16 | 2017-05-16 | United Microelectronics Corp. | Structure of metal gate structure and manufacturing method of the same |
| US9159798B2 (en) | 2013-05-03 | 2015-10-13 | United Microelectronics Corp. | Replacement gate process and device manufactured using the same |
| US9196542B2 (en) | 2013-05-22 | 2015-11-24 | United Microelectronics Corp. | Method for manufacturing semiconductor devices |
| US8921947B1 (en) | 2013-06-10 | 2014-12-30 | United Microelectronics Corp. | Multi-metal gate semiconductor device having triple diameter metal opening |
| US20150069534A1 (en) | 2013-09-11 | 2015-03-12 | United Microelectronics Corp. | Semiconductor device and method for fabricating the same |
| US9105720B2 (en) | 2013-09-11 | 2015-08-11 | United Microelectronics Corp. | Semiconductor device having metal gate and manufacturing method thereof |
| US9196546B2 (en) | 2013-09-13 | 2015-11-24 | United Microelectronics Corp. | Metal gate transistor |
| US9231071B2 (en) | 2014-02-24 | 2016-01-05 | United Microelectronics Corp. | Semiconductor structure and manufacturing method of the same |
Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002083812A (ja) * | 1999-06-29 | 2002-03-22 | Semiconductor Energy Lab Co Ltd | 配線材料およびこれを用いた配線を備えた半導体装置およびその作製方法 |
| JP2002359295A (ja) * | 2001-04-11 | 2002-12-13 | Samsung Electronics Co Ltd | デュアルゲートを有するcmos型半導体装置形成方法 |
Family Cites Families (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US6004869A (en) | 1997-04-25 | 1999-12-21 | Micron Technology, Inc. | Method for making a low resistivity electrode having a near noble metal |
| US6171959B1 (en) * | 1998-01-20 | 2001-01-09 | Motorola, Inc. | Method for making a semiconductor device |
| US6166417A (en) * | 1998-06-30 | 2000-12-26 | Intel Corporation | Complementary metal gates and a process for implementation |
| US6171910B1 (en) * | 1999-07-21 | 2001-01-09 | Motorola Inc. | Method for forming a semiconductor device |
| US6214681B1 (en) * | 2000-01-26 | 2001-04-10 | Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. | Process for forming polysilicon/germanium thin films without germanium outgassing |
| US6444512B1 (en) | 2000-06-12 | 2002-09-03 | Motorola, Inc. | Dual metal gate transistors for CMOS process |
-
2003
- 2003-04-09 US US10/410,043 patent/US6790719B1/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
-
2004
- 2004-04-08 KR KR1020057019065A patent/KR101159339B1/ko not_active IP Right Cessation
- 2004-04-08 WO PCT/US2004/010814 patent/WO2004093182A1/en active Application Filing
- 2004-04-08 CN CNB2004800094963A patent/CN100487880C/zh not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2004-04-08 JP JP2006509809A patent/JP4653735B2/ja not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2004-04-09 TW TW093110018A patent/TWI342044B/zh not_active IP Right Cessation
Patent Citations (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2002083812A (ja) * | 1999-06-29 | 2002-03-22 | Semiconductor Energy Lab Co Ltd | 配線材料およびこれを用いた配線を備えた半導体装置およびその作製方法 |
| JP2002359295A (ja) * | 2001-04-11 | 2002-12-13 | Samsung Electronics Co Ltd | デュアルゲートを有するcmos型半導体装置形成方法 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| KR20050120785A (ko) | 2005-12-23 |
| JP2006523037A (ja) | 2006-10-05 |
| KR101159339B1 (ko) | 2012-06-25 |
| US6790719B1 (en) | 2004-09-14 |
| TW200507099A (en) | 2005-02-16 |
| CN1771590A (zh) | 2006-05-10 |
| CN100487880C (zh) | 2009-05-13 |
| WO2004093182A1 (en) | 2004-10-28 |
| TWI342044B (en) | 2011-05-11 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP4653735B2 (ja) | デュアルメタルゲート構造を形成するためのプロセス | |
| TWI523153B (zh) | 製造分離閘記憶體單元之方法 | |
| KR100374916B1 (ko) | 집적회로제조방법및집적회로형성방법 | |
| US7396711B2 (en) | Method of fabricating a multi-cornered film | |
| KR100781033B1 (ko) | 반도체 소자의 제조방법 | |
| US6846716B2 (en) | Integrated circuit device and method therefor | |
| KR20050026319A (ko) | 리세스 채널을 가지는 트랜지스터 제조 방법 | |
| US9379222B2 (en) | Method of making a split gate non-volatile memory (NVM) cell | |
| JP2005072578A (ja) | 半導体装置及び半導体装置の製造方法 | |
| JP2005116633A (ja) | 半導体装置及びその製造方法 | |
| US20070004128A1 (en) | Method for fabricating semiconductor device with recess gate | |
| KR100469913B1 (ko) | 반도체소자의 제조방법 | |
| JP2009535817A (ja) | 溝型半導体デバイスの製造のためのマスク構造 | |
| KR100327428B1 (ko) | 반도체 소자의 제조 방법 | |
| KR100537275B1 (ko) | 반도체 소자 제조방법 | |
| US7491644B2 (en) | Manufacturing process for a transistor made of thin layers | |
| KR100827514B1 (ko) | 반도체 소자 및 반도체 소자의 형성 방법 | |
| US20050156229A1 (en) | Integrated circuit device and method therefor | |
| KR100533394B1 (ko) | 트랜지스터 제조 방법 | |
| KR100214534B1 (ko) | 반도체소자의 소자격리구조 형성방법 | |
| KR100596802B1 (ko) | 반도체 소자의 제조방법 | |
| JPH03278543A (ja) | 電界効果トランジスタの製造方法 | |
| JP2006295170A (ja) | ゲート電極積層およびゲート電極積層を用いる方法 | |
| JP2001015587A (ja) | 半導体装置の製造方法 | |
| KR20030051038A (ko) | 반도체 소자의 제조 방법 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20070409 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20070409 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20090331 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20090407 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20090626 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20091222 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20100319 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20101124 |
|
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20101217 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 4653735 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20131224 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| S533 | Written request for registration of change of name |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R313533 |
|
| R350 | Written notification of registration of transfer |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R350 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |