EP3239378B1 - Procede et dispositif destines a la fabrication de tissus non-tisses a partir de filaments continus - Google Patents
Procede et dispositif destines a la fabrication de tissus non-tisses a partir de filaments continus Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP3239378B1 EP3239378B1 EP16167804.0A EP16167804A EP3239378B1 EP 3239378 B1 EP3239378 B1 EP 3239378B1 EP 16167804 A EP16167804 A EP 16167804A EP 3239378 B1 EP3239378 B1 EP 3239378B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- foraminous belt
- filaments
- air
- belt
- maximum
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title claims description 17
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 title claims description 5
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 title description 2
- 230000035699 permeability Effects 0.000 claims description 26
- 239000004745 nonwoven fabric Substances 0.000 claims description 24
- 238000001816 cooling Methods 0.000 claims description 19
- 238000000151 deposition Methods 0.000 claims description 15
- 238000009987 spinning Methods 0.000 claims description 8
- 238000000605 extraction Methods 0.000 claims description 6
- 239000002759 woven fabric Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- 230000008021 deposition Effects 0.000 claims 7
- 230000000087 stabilizing effect Effects 0.000 claims 1
- 239000003570 air Substances 0.000 description 64
- 239000004744 fabric Substances 0.000 description 18
- 238000003860 storage Methods 0.000 description 14
- 150000001875 compounds Chemical class 0.000 description 10
- 238000007789 sealing Methods 0.000 description 10
- 239000004033 plastic Substances 0.000 description 7
- 229920003023 plastic Polymers 0.000 description 7
- 238000007596 consolidation process Methods 0.000 description 6
- 239000000835 fiber Substances 0.000 description 6
- 238000000926 separation method Methods 0.000 description 6
- 238000005259 measurement Methods 0.000 description 4
- 239000012815 thermoplastic material Substances 0.000 description 4
- 239000012080 ambient air Substances 0.000 description 3
- 238000005056 compaction Methods 0.000 description 3
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 3
- 238000009941 weaving Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000007664 blowing Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000006073 displacement reaction Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000002347 injection Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000007924 injection Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000010410 layer Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000004750 melt-blown nonwoven Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229920000642 polymer Polymers 0.000 description 2
- -1 polypropylene Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 238000012935 Averaging Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000004698 Polyethylene Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000004743 Polypropylene Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000853 adhesive Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000001070 adhesive effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000015556 catabolic process Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000011258 core-shell material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000004049 embossing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000007788 liquid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920000573 polyethylene Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000002861 polymer material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920000098 polyolefin Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920001155 polypropylene Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 230000008092 positive effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000005855 radiation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000003566 sealing material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000007711 solidification Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000008023 solidification Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000002344 surface layer Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920001169 thermoplastic Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000004416 thermosoftening plastic Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000011144 upstream manufacturing Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D04—BRAIDING; LACE-MAKING; KNITTING; TRIMMINGS; NON-WOVEN FABRICS
- D04H—MAKING TEXTILE FABRICS, e.g. FROM FIBRES OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL; FABRICS MADE BY SUCH PROCESSES OR APPARATUS, e.g. FELTS, NON-WOVEN FABRICS; COTTON-WOOL; WADDING ; NON-WOVEN FABRICS FROM STAPLE FIBRES, FILAMENTS OR YARNS, BONDED WITH AT LEAST ONE WEB-LIKE MATERIAL DURING THEIR CONSOLIDATION
- D04H17/00—Felting apparatus
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D01—NATURAL OR MAN-MADE THREADS OR FIBRES; SPINNING
- D01D—MECHANICAL METHODS OR APPARATUS IN THE MANUFACTURE OF ARTIFICIAL FILAMENTS, THREADS, FIBRES, BRISTLES OR RIBBONS
- D01D5/00—Formation of filaments, threads, or the like
- D01D5/08—Melt spinning methods
- D01D5/088—Cooling filaments, threads or the like, leaving the spinnerettes
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D01—NATURAL OR MAN-MADE THREADS OR FIBRES; SPINNING
- D01D—MECHANICAL METHODS OR APPARATUS IN THE MANUFACTURE OF ARTIFICIAL FILAMENTS, THREADS, FIBRES, BRISTLES OR RIBBONS
- D01D10/00—Physical treatment of artificial filaments or the like during manufacture, i.e. during a continuous production process before the filaments have been collected
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D01—NATURAL OR MAN-MADE THREADS OR FIBRES; SPINNING
- D01D—MECHANICAL METHODS OR APPARATUS IN THE MANUFACTURE OF ARTIFICIAL FILAMENTS, THREADS, FIBRES, BRISTLES OR RIBBONS
- D01D11/00—Other features of manufacture
- D01D11/02—Opening bundles to space the threads or filaments from one another
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D01—NATURAL OR MAN-MADE THREADS OR FIBRES; SPINNING
- D01D—MECHANICAL METHODS OR APPARATUS IN THE MANUFACTURE OF ARTIFICIAL FILAMENTS, THREADS, FIBRES, BRISTLES OR RIBBONS
- D01D5/00—Formation of filaments, threads, or the like
- D01D5/08—Melt spinning methods
- D01D5/098—Melt spinning methods with simultaneous stretching
- D01D5/0985—Melt spinning methods with simultaneous stretching by means of a flowing gas (e.g. melt-blowing)
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D01—NATURAL OR MAN-MADE THREADS OR FIBRES; SPINNING
- D01D—MECHANICAL METHODS OR APPARATUS IN THE MANUFACTURE OF ARTIFICIAL FILAMENTS, THREADS, FIBRES, BRISTLES OR RIBBONS
- D01D5/00—Formation of filaments, threads, or the like
- D01D5/12—Stretch-spinning methods
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D03—WEAVING
- D03D—WOVEN FABRICS; METHODS OF WEAVING; LOOMS
- D03D13/00—Woven fabrics characterised by the special disposition of the warp or weft threads, e.g. with curved weft threads, with discontinuous warp threads, with diagonal warp or weft
- D03D13/008—Woven fabrics characterised by the special disposition of the warp or weft threads, e.g. with curved weft threads, with discontinuous warp threads, with diagonal warp or weft characterised by weave density or surface weight
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D04—BRAIDING; LACE-MAKING; KNITTING; TRIMMINGS; NON-WOVEN FABRICS
- D04H—MAKING TEXTILE FABRICS, e.g. FROM FIBRES OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL; FABRICS MADE BY SUCH PROCESSES OR APPARATUS, e.g. FELTS, NON-WOVEN FABRICS; COTTON-WOOL; WADDING ; NON-WOVEN FABRICS FROM STAPLE FIBRES, FILAMENTS OR YARNS, BONDED WITH AT LEAST ONE WEB-LIKE MATERIAL DURING THEIR CONSOLIDATION
- D04H3/00—Non-woven fabrics formed wholly or mainly of yarns or like filamentary material of substantial length
- D04H3/005—Synthetic yarns or filaments
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D04—BRAIDING; LACE-MAKING; KNITTING; TRIMMINGS; NON-WOVEN FABRICS
- D04H—MAKING TEXTILE FABRICS, e.g. FROM FIBRES OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL; FABRICS MADE BY SUCH PROCESSES OR APPARATUS, e.g. FELTS, NON-WOVEN FABRICS; COTTON-WOOL; WADDING ; NON-WOVEN FABRICS FROM STAPLE FIBRES, FILAMENTS OR YARNS, BONDED WITH AT LEAST ONE WEB-LIKE MATERIAL DURING THEIR CONSOLIDATION
- D04H3/00—Non-woven fabrics formed wholly or mainly of yarns or like filamentary material of substantial length
- D04H3/02—Non-woven fabrics formed wholly or mainly of yarns or like filamentary material of substantial length characterised by the method of forming fleeces or layers, e.g. reorientation of yarns or filaments
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D04—BRAIDING; LACE-MAKING; KNITTING; TRIMMINGS; NON-WOVEN FABRICS
- D04H—MAKING TEXTILE FABRICS, e.g. FROM FIBRES OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL; FABRICS MADE BY SUCH PROCESSES OR APPARATUS, e.g. FELTS, NON-WOVEN FABRICS; COTTON-WOOL; WADDING ; NON-WOVEN FABRICS FROM STAPLE FIBRES, FILAMENTS OR YARNS, BONDED WITH AT LEAST ONE WEB-LIKE MATERIAL DURING THEIR CONSOLIDATION
- D04H3/00—Non-woven fabrics formed wholly or mainly of yarns or like filamentary material of substantial length
- D04H3/08—Non-woven fabrics formed wholly or mainly of yarns or like filamentary material of substantial length characterised by the method of strengthening or consolidating
- D04H3/14—Non-woven fabrics formed wholly or mainly of yarns or like filamentary material of substantial length characterised by the method of strengthening or consolidating with bonds between thermoplastic yarns or filaments produced by welding
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D04—BRAIDING; LACE-MAKING; KNITTING; TRIMMINGS; NON-WOVEN FABRICS
- D04H—MAKING TEXTILE FABRICS, e.g. FROM FIBRES OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL; FABRICS MADE BY SUCH PROCESSES OR APPARATUS, e.g. FELTS, NON-WOVEN FABRICS; COTTON-WOOL; WADDING ; NON-WOVEN FABRICS FROM STAPLE FIBRES, FILAMENTS OR YARNS, BONDED WITH AT LEAST ONE WEB-LIKE MATERIAL DURING THEIR CONSOLIDATION
- D04H3/00—Non-woven fabrics formed wholly or mainly of yarns or like filamentary material of substantial length
- D04H3/08—Non-woven fabrics formed wholly or mainly of yarns or like filamentary material of substantial length characterised by the method of strengthening or consolidating
- D04H3/16—Non-woven fabrics formed wholly or mainly of yarns or like filamentary material of substantial length characterised by the method of strengthening or consolidating with bonds between thermoplastic filaments produced in association with filament formation, e.g. immediately following extrusion
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D10—INDEXING SCHEME ASSOCIATED WITH SUBLASSES OF SECTION D, RELATING TO TEXTILES
- D10B—INDEXING SCHEME ASSOCIATED WITH SUBLASSES OF SECTION D, RELATING TO TEXTILES
- D10B2401/00—Physical properties
- D10B2401/04—Heat-responsive characteristics
- D10B2401/041—Heat-responsive characteristics thermoplastic; thermosetting
Definitions
- the invention relates to a device for the production of nonwovens from continuous filaments, the filaments consist in particular of thermoplastic material, wherein at least one spinning device for spinning the filaments is present, wherein the filaments are cooled and stretched and wherein a storage device is provided for storing the drawn filaments ,
- the invention further relates to a process for the production of nonwovens from continuous filaments.
- - Endless filaments differ because of their quasi-endless length of staple fibers, which have much smaller lengths, for example, 10 mm to 60 mm.
- WO 03/038168 A1 describes in this context a woven screen belt for the storage of spunbonded webs, which consists of warp and weft threads and influenced by its special structure, the flow of air through the storage belt such that a uniform spunbond results and at the same time a low fiber breakdown is achieved.
- Another method is based on the use of a structured and partially air-permeable storage belt (EP 0 696 333 ).
- the storage belt is equipped with air-impermeable closing points and these closing points have protruding projections from the wire belt surface.
- the deposited filaments are preconsolidated on the storage belt with an adhesive - hot air-solidified, for example - and then the nonwoven fabric is peeled off.
- the structure of the web is achieved, as it were, by taking an impression of the locking point protrusions projecting from the depositing belt surface.
- WO 2004/061219 A1 a storage belt which is partially closed by application of a polymer material. The pattern thus produced on the tape can be transferred to products which are deposited on the tape.
- US 4,514,345 A relates to a deposit screen belt to which a shape excellent from the screen belt surface is applied so that a paper web deposited on the belt is patterned according to the shape.
- these known measures are often prone to interference and error and have not been proven in practice.
- the invention is the technical problem of providing a device of the type mentioned, with a non-woven with 3D structure can be produced in a simple and efficient manner, this fleece is characterized by an aesthetically flawless, reproducible 3D structure and also has a sufficiently soft grip.
- the invention is further based on the technical problem of specifying a corresponding method for producing the nonwoven and a corresponding nonwoven.
- the invention teaches an apparatus for producing continuous filament nonwovens, wherein the filaments consist in particular of thermoplastic material, wherein at least one spinning device for spinning the filaments is present, wherein the filaments are cooled and stretched and wherein a storage device is provided for depositing the drawn filaments to the nonwoven fabric, wherein the storage device is designed in the form of a sieve belt having a plurality of screen belt openings distributed over the screen belt surface, whereby air can be sucked through the screen belt surface or through the screen belt openings and for this purpose at least one suction fan is arranged below the screen belt, whereby a part of the screen belt openings is closed is trained.
- the device according to the invention is a spunbond apparatus, wherein a cooling device is provided for cooling the filaments and a stretching device for drawing the filaments.
- a cooling device is provided for cooling the filaments and a stretching device for drawing the filaments.
- the device according to the invention is a meltblown device.
- the air permeability of the unclosed screen belt is 300 to 1100 cfm (510 to 1870 m 3 / h), preferably 350 to 1050 cfm (595 to 1785 m 3 / h) and preferably 400 to 1000 cfm (680 to 1700 m 3 / h) and the air permeability of the partially closed screen belt according to the invention is 150 to 700 cfm (255 to 1190 m 3 / h), preferably 200 to 600 cfm (340 to 1020 m 3 / h) and preferably 250 to 500 cfm (425 to 850 m 3 / h). H).
- the air permeability of the partially closed screen belt is particularly preferably 300 to 500 cfm (510 to 850 m 3 / h) and very particularly preferably 350 to 500 cfm (595 to 850 m 3 / h).
- the uncovered screen belt means the screen belt used according to the invention with only open or unclosed screen belt openings.
- the unclosed screen belt serves only as a reference, since according to the invention a partially closed screen belt or a screen belt is used with partially closed Siebbandö réelleen. - It is understood that the air permeability of the unclosed screen belt is greater than the air permeability of the partially closed screen belt.
- the air permeability is given here in cfm (cubic foot / min).
- the measurement of the air permeability is preferably carried out on a circular area of 38.3 cm 2 at a pressure difference of 125 Pa.
- a plurality of individual measurements is carried out - recommended ten individual measurements - and the air permeability results then by averaging the individual measurements.
- the air permeability is measured according to ASTM D 737.
- the screen belt to intersect a woven fabric Has threads.
- the threads of the screen belt as plastic threads - in particular as monofilaments - and / or formed as metal threads.
- the fabric of the wire can be single-layered or multi-layered.
- the surface of the uppermost layer of the fabric is understood here to mean the surface of the sieve belt.
- the screen belt has only one layer of a fabric.
- a recommended embodiment of the device according to the invention is characterized in that the screen belt has a fabric of warp threads and weft threads delimiting the wire belt openings. It is recommended that the fabric of the screen belt has a weaving density of 20 to 75 warp threads / 25 mm and preferably from 30 to 55 warp threads / 25 mm and from 10 to 50 weft threads / 25 mm, preferably from 10 to 40 weft threads / 25 mm.
- a plurality or plurality of open Siebbandö Samuelen is distributed over the Siebbandober measurements and that also a plurality or a plurality of closed Siebbandö réelleen is distributed over the Siebbandober composition.
- a closed screen belt opening or several adjacent closed belt openings form a closure point of the screen belt. It is recommended that the diameter d or the smallest diameter d of a closure point of the screen belt is at least 1.5 mm, preferably at least 2 mm and not more than 8 mm, preferably not more than 9 mm and in particular not more than 10 mm.
- the ratio of the air permeability of the unclosed screen belt to the air permeability of the partially closed screen belt amounts to 1.2 to 4, preferably to 1.3 to 3.5, preferably to 1.5 to 3 and particularly preferably to 1.8 to 2.8.
- the closed Siebbandö réelleen or the closure sites require that the screen belt in contrast to the unclosed screen belt no longer has a homogeneous air permeability.
- the invention is based on the finding that the closure points of the air flowing inwards onto the sieve belt impose a lateral movement directly above the sieve belt.
- the filaments to be deposited contained in this air flow follow this lateral air displacement at least partially and are thereby preferably deposited on the open or unclosed areas of the screen belt. In this way, a fleece with different local basis weights or with a defined 3D structure is created.
- the closed Siebbandö réelleen or the closure sites are arranged distributed in a regular pattern on the wire.
- EmpfohleneIER have the Siebbandö réelleen or the closure points in at least one spatial direction at constant distances from each other.
- the closure points are punctiform.
- dot-shaped here means that the diameter is a closure point in all spatial directions similar or comparable or substantially the same.
- a proven embodiment is characterized in that the punctiform closure sites are distributed at regular intervals over the screen belt or over the screen belt surface.
- the smallest diameter d of these punctiform closure sites is at least 2 mm, preferably at least 2.5 mm and more preferably at least 3 mm and a maximum of 8 mm, preferably not more than 9 mm and very preferably not more than 10 mm.
- the closure points are formed linear. It is within the scope of the invention that the linear closure points are usually not exactly rectilinear or linear and that, in general, especially the edges of the linear closure points are not formed exactly straight or linear. According to a proven embodiment, the linear closure points have constant distances or substantially constant distances from one another. Conveniently, the linear closure points are arranged parallel or substantially parallel to one another. It is also within the scope of the invention that the linear closure points are each formed as broken lines and are arranged on a line linear closure point sections and the sections connecting line-shaped open Siebband Scheme Schemee.
- line-shaped closure points intersect, wherein preferably the linear closure points extending in one direction are arranged parallel to one another and wherein the linear closure points extending in a second direction are expediently (also) arranged parallel to one another.
- the line-shaped closure locations of a screen belt have different densities in different areas of the screen belt or the screen belt surface and / or have different widths (smallest diameters d).
- the linear closure points may also be curved or curved line-shaped closure sites.
- the width (smallest diameter d) of a linear closure point is preferably at least 1.5 mm, preferably at least 2 mm and recommended maximum 8 mm and in particular maximum 9 mm.
- point and line closure points can be combined.
- various geometric configurations for the closure points are conceivable and these different configurations can also be combined with each other.
- Open Siebband Schemee may be surrounded by closure sites or by closed Siebband Schemeen or vice versa.
- sealing materials made of plastic or of polymers are used to produce the closed Siebbandö réelleen or for generating the closure sites.
- molten or liquid plastic is expediently introduced into the fabric of the wire belt or introduced into the wire belt openings of the wire belt.
- the sealing compound may be photosensitive plastic or a photosensitive multi-component system which is first introduced into the fabric of the screen belt and then cured and cured in particular under the action of light and preferably under the action of UV radiation.
- the sealing compound penetrates into the mesh openings of the mesh fabric and that the closure pattern formed depend on the weave and weaving density.
- the mesh fabric is formed from monofilaments having a diameter of 0.2 to 0.9 mm, preferably 0.3 to 0.7 mm. It is recommended that a closure site is formed by closing the screen belt openings between at least 2 warp threads and / or weft threads, preferably between / over at least 3 warp threads and / or weft threads.
- a particularly recommended embodiment of the invention is characterized in that the sealing compound of the closure sites is arranged only in and / or below the screen belt surface and does not protrude beyond the screen belt surface.
- the sealing compound extends over the entire thickness or essentially over the entire thickness of the sieve belt or of the sieve belt fabric.
- the sealing compound of a closing point or of a closed sieve belt opening extends only over part of the thickness of the sieve belt fabric.
- the sealing compound of a closed Siebbandö réelle or a closure point extends from the screen belt surface downwards, in which case the sealing compound - as described above - either over the entire thickness of the screen belt or only over a part of the thickness of the screen belt can extend.
- the sealing compound is expediently arranged over at least 30%, preferably over at least 33%, of the thickness of the sieve belt or of the sieve belt fabric, the closure mass preferably extending from the sieve belt surface downwards, as noted above.
- At least 25%, preferably at least 30%, of the screen belt openings of the screen belt used in the invention are designed to be closed.
- a maximum of 67%, preferably not more than 60% of the Siebbandö Maschinentechnisch the screen belt formed sealed is provided.
- the sealing compound of the closure sites is arranged in and / or below the sieve belt surface of the sieve belt and does not project beyond the sieve belt surface or protrudes by a maximum of 1.0 mm, preferably by a maximum of 0.8 mm, very preferably by a maximum of 0.6 mm and especially preferably at a maximum of 0.3 mm to 0.6 mm beyond the screen belt surface.
- the closure points cause a lateral air movement of the air flowing through the filter belt and that due to this lateral movement the filaments contained in the air flow follow the flow and are therefore preferably deposited on the open wire belt regions.
- the invention is based on the finding that this displacement can be effectively enhanced if the sealing compound of the closure points protrudes upward beyond the screen belt surface. Over the resulting dome, the deposited filaments can slip into the adjacent open Siebband Scheme and the differences in the filament density or in the basis weight can be characterized even more pronounced.
- the invention is further based on the knowledge that the height of the region projecting out of the sieve belt is limited, since a region which protrudes too high is associated with a reduction in the stability of the filament deposit.
- the invention is based on the finding that a region projecting out of the screen belt surface is preferably intended to protrude from the screen belt surface by a maximum of 0.6 mm, very preferably by a maximum of 0.5 mm.
- the device according to the invention has at least one spinning device or spinnerette with which the endless filaments are spun.
- spunbond nonwovens are produced with the device according to the invention and insofar is the Device designed as a spunbond device.
- Monocomponent filaments and / or multicomponent filaments or bicomponent filaments are produced as continuous filaments.
- the multicomponent filaments or bicomponent filaments can be continuous filaments with a core-shell configuration or endless filaments with crimped potential, for example with side-side configuration.
- the continuous filaments produced by the device according to the invention or by the process according to the invention consist of at least one polyolefin, in particular of polypropylene and / or polyethylene.
- An apparatus according to the invention in the form of a spunbond apparatus has at least one cooling device for cooling the filaments and at least one drawing device for drawing the filaments.
- the aggregate of the cooling device and the drafting device is designed as a closed aggregate, with the exception of the supply of cooling air in the cooling device no further air supply takes place in the closed unit.
- This closed embodiment of the device according to the invention has proven particularly useful in connection with the screen belt used in the invention.
- a recommended embodiment of the invention is further characterized in that at least one diffuser is arranged between the drawing device and the depositing device or the screen belt.
- the continuous filaments emerging from the drawing device are passed through the diffuser and then deposited on the depositing device or on the screen belt.
- a particular embodiment variant of the invention is characterized in that at least two diffusers, preferably two diffusers in the filament flow direction, are arranged one behind the other between the drawing device and the screen belt. Conveniently, at least one secondary air inlet gap for the entry of ambient air is provided between the two diffusers.
- the embodiment with the at least one diffuser or with the at least two diffusers and the secondary air inlet gap has proven particularly useful in combination with the screen belt according to the invention.
- air is sucked through the screen belt or sucked through the screen belt in the filament flow direction.
- at least one suction fan is expediently provided below the screen belt.
- at least two, preferably at least three, and preferably three separate suction regions are arranged one behind the other in the conveying direction of the wire.
- a main suction area is preferably provided in which air is extracted with a higher suction speed than in the at least one further suction area or in the two further suction areas.
- the air is drawn through the screen belt at a suction rate of 5 to 30 m / s.
- a proven embodiment of the invention is characterized in that at least one further suction region is connected downstream of the main suction region in the conveying direction of the wire belt and that the suction speed of the air extracted in this further suction region is less than the suction speed in the suction line Main suction. It is recommended that a first suction region with respect to the conveying direction of the wire belt is arranged in front of the Hauptabsaug Colour and that a second suction region is arranged in the conveying direction of the wire belt behind the Hauptabsaug Scheme. Expediently, the extraction speed in the main suction area or in the storage area of the nonwoven is set so that it is greater than the extraction speeds in the two further extraction areas.
- the extraction speeds in the first and / or in the second suction region are, according to one embodiment of the invention, between 2 and 10 m / s, in particular between 2 and 5 m / s.
- a recommended embodiment of the invention is characterized in that the nonwoven fabric deposited on the screen belt is preconsolidated and is particularly preferably preconsolidated with the aid of at least one compaction roller as the preconsolidating device. Conveniently, the at least one compaction roller is formed heated. According to another embodiment of the invention, the preconsolidation of the web on the wire can also be done as a hot air hardening.
- a final consolidation of the nonwoven produced according to the invention is carried out.
- the final consolidation can also be carried out on the screen belt. According to the preferred embodiment explained below, however, the nonwoven fabric is removed from the wire belt and then subjected to final consolidation.
- the nonwoven web deposited on the screen belt has to be separated or removed again from the screen belt.
- a particularly preferred embodiment of the invention is characterized in that, for separating the nonwoven from the wire, air (dissolving air) is blown through the wire from below or in the direction of the underside of the nonwoven.
- a separate fan is provided for this purpose and it is recommended that the air injection takes place with respect to the conveying direction of the screen belt behind the at least one suction area or behind the suction areas and above all behind the storage area of the nonwoven.
- the separation of the web or the arrangement of the fan for separating the web from the wire in the conveying direction of the wire behind at least one Vorverfestists worn and in particular behind at least one Kompaktierwalze is arranged.
- the blowing in of the dissolving air in the conveying direction of the fleece strip takes place shortly before the position at which the filament deposit is removed from the sieve belt in any case.
- air or dissolving air is blown in at an air velocity of between 1 and 40 m / s for separating the nonwoven fabric.
- at least one supporting surface for the fleece acted upon by the release air is additionally provided above the sieve belt.
- this is an air-permeable or permeable support surface which is actively evacuated according to a variant embodiment.
- a support surface for example, a co-rotating permeable drum can be used, the surface of which is preferably formed by a metal fabric.
- a co-rotating additional screen belt arranged above the screen belt can be provided as a support surface.
- the support surface for example, designed as a drum or as additional screen belt support surface - is evacuated and is preferably sucked from above, so that the blown in from below Liereluft is sucked through the support surface.
- At least one injection gap arranged transversely to the conveying direction of the wire belt can be arranged below the wire belt.
- the gap width may be 3 to 30 mm. It is within the scope of the invention that the gap width of the Einblasspaltes is adjusted so that the deposited on the wire belt fleece for the separation of the web is just raised without being destroyed.
- the nonwoven - finally after a preconsolidation and preferably after separation from the wire belt - is finally solidified.
- the final consolidation can be carried out in particular with at least one calender or with at least one heated calender.
- the final solidification can also be carried out in other ways, for example as hydroentanglement, as mechanical needling or as hot air hardening.
- An embodiment of the invention is characterized in that a laminate of spunbond nonwovens and a meltblown nonwoven can be produced with a device according to the invention. It is therefore within the scope of the invention to use a spunbond meltblown spunbond device (SMS) device. In such a device, two spunbond beams and one meltblown beam are used to wind the individual webs. For such a combination, the device according to the invention and the inventive method has proven particularly useful.
- SMS spunbond meltblown spunbond device
- the endless filaments are preferably made of thermoplastic Consist of plastic or consist essentially. It is within the scope of the invention that the continuous filaments of this web have a denier of 0.9 to 10 denier.
- the filaments may also have a diameter of 0.5 to 5 microns.
- the nonwoven may be a spunbond nonwoven or a meltblown nonwoven. Particularly preferred is a spunbond nonwoven.
- the invention is based on the finding that a structured spunbonded fabric with locally different basis weights can be produced in a simple and cost-effective manner with the device according to the invention and with the method according to the invention.
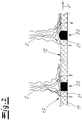
- the figures show a device according to the invention for producing nonwovens 1 from continuous filaments 2.
- these are spunbond devices for producing spunbonded nonwovens 1 or spunbonded nonwovens 1.
- the continuous filaments 2 are preferably made of thermoplastic material Plastic or substantially of thermoplastic material.
- the endless filaments 2 are spun with the aid of a spinning device designed as a spinnerette 3. Subsequently, the endless filaments 2 are cooled in a cooling device 4.
- This cooling device 4 preferably and in the exemplary embodiment has two cabin sections 4a, 4b arranged one above the other or in the filament flow direction, from which cooling air of different temperature is introduced into the filament flow space.
- the cooling device 4 is followed by a stretching device 5 downstream of the filament flow direction, and this stretching device 5 preferably has, in the exemplary embodiment, an intermediate channel 6 converging in the direction of flow of the endless filaments 2 and an adjoining drawing channel 7.
- this stretching device 5 preferably has, in the exemplary embodiment, an intermediate channel 6 converging in the direction of flow of the endless filaments 2 and an adjoining drawing channel 7.
- At least one diffuser 8, 9 adjoins the drawing device 5 in the filament flow direction.
- two mutually or successively arranged diffusers 8, 9 are provided. It is recommended that an ambient air inlet gap 10 for the entry of ambient air is provided between the two diffusers 8, 9. It is within the scope of the invention that the continuous filaments 2 are deposited on a depositing device in the form of a screen belt 11 following the diffusers 8, 9. Furthermore, it is within the scope of the invention that this is an endlessly circulating screen belt 11.
- the screen belt 11 has a screen belt surface 12 with a multiplicity of screen belt openings 13 distributed over the screen belt surface 12. According to the invention, air is sucked through the screen belt surface 12 or through the (open) screen belt openings 13.
- at least one exhaust fan is arranged below the screen belt 11.
- three separate suction regions 14, 15, 16 are arranged one behind the other in the conveying direction of the wire.
- a main suction area 15 is preferably provided, in which air is sucked through the sieve belt 11, for example at a suction speed or at a mean suction speed of 5 to 30 m / s.
- the suction speed in the main suction region 15 is set so that it is greater than the suction speed in the further suction regions 14 and 16.
- a first suction region 14 is connected upstream of the main suction region 15 and a second suction region 16 is the main suction region 15 downstream.
- a compacting device 18 with two compacting rollers 19, 20 for compacting or preconsolidating the nonwoven 1 is provided above the second suction region 16.
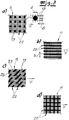
- a part of the screen belt openings 13 of the screen belt 11 is designed to be closed.
- closed Siebbandö Maschinenen 21 or closure points 22 result in the wire
- the closure points 22 are composed of a closed Siebbandö réelle 21 or from several adjacent closed Siebbandö réelleen 21.
- the air permeability of the unclosed screen belt 11 is greater than the air permeability of the provided with closed Siebbandö réelleen 21 screen belt 11.
- the ratio of the air permeability of the unclosed screen belt 11 to the air permeability of the partially closed screen belt 11 is preferably 1.2 to 3.
- the air permeability is measured in particular transversely to the screen belt surface 12 at a circular area of 38.3 cm 2 of the screen belt at a pressure difference of 125 Pa ,
- the screen belt 11 a fabric of the Siebbandö Stamm 13 delimiting warp threads 23 and weft threads 24.
- the diameter D or the smallest diameter D of a wire opening 13 may be 0.5 mm in the embodiment.
- the fabric of the wire 11 has a weaving density of 20 to 75 warp / 25 mm and 10 to 50 wefts / 25 mm.
- the closure points 22 in the wire 11 are punctiform and / or linear.
- the Fig. 3a shows the punctiform formation of closure points 22 in the wire 11.
- the (smallest) diameter d of such a point-like closure point 22 may be 2 mm in the embodiment.
- line-shaped closure points 22 are shown.
- the smallest width b of the linear closure points 22 may also be 2 mm in the exemplary embodiment.
- the Fig. 3c ) shows a further embodiment with broken line-shaped closure points 22.
- the line-shaped closure points 22 can be formed otherwise in a manner not shown as curved or arcuate lines.
- an additional embodiment with crossed line-shaped closure points 22 is shown.
- FIG. 3a), 3b) and 3d show, moreover, embodiments in which the closure points 22 is formed symmetrically with respect to the longitudinal direction or the conveying direction of the screen belt 11.
- the conveying direction F of the wire 11 is in the Fig. 3a) to 3d ) has been indicated by an arrow.
- the embodiment according to Fig. 3c ) asymmetrical with respect to the longitudinal direction or with respect to the conveying direction F of the screen belt 11.
- the embodiments symmetrical with respect to the longitudinal direction or conveying direction F are preferred within the scope of the invention.
- Fig. 4 is shown a particularly recommended embodiment of the device according to the invention.
- the continuous filaments 2 emerging from the diffuser 9 are deposited on the screen belt surface 12 in the depositing area 17 of the screen belt 11.
- Below the storage area 17 is the Hauptabsaug Colour 15 for the extraction of the process air through the wire 11 and through the Siebbandober Structure 12.
- Following the Hauptabsaug Scheme 15 of the second suction 16 is arranged, sucked in the process air with compared to Hauptabsaug Scheme 15 lower air velocity becomes.
- the compacting device 18 with the two compacting rollers 19, 20 is provided above the second suction region 16, the compacting device 18 with the two compacting rollers 19, 20 is provided. In the conveying direction of the web 1 then a separation region 25 is connected downstream.
- the nonwoven fabric 1 or the preconsolidated nonwoven fabric 1 is detached / separated from the wire belt 11 or from the wire belt surface 12.
- air is blown from below or in the direction of the underside of the web 1 through the wire 11.
- This is in the 4 and 5 has been clarified by corresponding arrows 26.
- the nonwoven fabric 1 acted upon by the release air is supported by an air-permeable or permeable drum 27 rotating in the conveying direction of the wire 11.
- the drum may, for example, be arranged at a distance of 0.5 to 5 mm above the screen belt surface 12.
- the surface of the drum 27 may be formed, for example in the form of a metal fabric.
- co-rotating additional screen belt (not shown) could be used.
- the Fig. 5 shows a further embodiment of a provided for supporting the treated with the release air fleece 1 drum 27.
- the drum 27 has a suction region 28 for receiving the release air and in addition is here in the direction of the wire 11 and Direction of the web 1 blown support air to prevent snagging of the endless filaments 2 and the web 1 on the drum 27.
- the support air is in Fig. 5 symbolized by an arrow 29.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Textile Engineering (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Nonwoven Fabrics (AREA)
- Spinning Methods And Devices For Manufacturing Artificial Fibers (AREA)
- Woven Fabrics (AREA)
- Absorbent Articles And Supports Therefor (AREA)
Claims (15)
- Dispositif, destiné à la fabrication de non-tissés (1) à partir de filaments continus (2), au moins un système de filage étant présent pour le filage des filaments (2), les filaments (2) étant refroidis et étirés et un système de dépose étant prévu pour déposer les filaments (2) étirés pour former le non-tissé (1),
le système de dépose étant réalisé sous la forme d'une bande de tamisage (11) dotée d'une pluralité d'orifices de bande de tamisage (13) distribués sur la surface de la bande de tamisage (12), de l'air étant susceptible d'être aspiré à travers la surface de la bande de tamisage (12) ou à travers les orifices de bande de tamisage (13) et à cet effet, de préférence une soufflante d'aspiration étant placée en-dessous de la bande de tamisage (11),
une partie des orifices de bande de tamisage (13) étant conçue en étant obturée, la perméabilité à l'air de la bande de tamisage non obturée étant de 300 à 1100 cfm (510 à 1870 m3/h), de préférence de 350 à 1050 cfm (595 à 1785 m3/h) et de manière préférentielle, de 400 à 1000 cfm (680 à 1700 m3/h), la perméabilité à l'air de la bande de tamisage partiellement obturée étant de 150 à 700 cfm (255 à 1190 m3/h), de préférence 250 à 600 cfm (425 à 1020 m3/h) et de manière préférentielle, de 350 à 500 cfm (595 à 850 m3/h)
et la masse d'obturation des zones obturées (22) étant placée dans et/ou en-dessous de la surface de la bande de tamisage (12) et ne saillant pas par-dessus la surface de la bande de tamisage (12) ou saillant au maximum de 1,0 mm, de manière préférentielle, au maximum de 0,8 mm, de manière très préférentielle, au maximum de 0,6 mm et de manière particulièrement préférentielle, au maximum de 0,3 à 0,6 mm par-dessus la surface de la bande de tamisage (12). - Dispositif selon la revendication 1, la bande de tamisage (11) comportant un tissu composé de fils de chaîne (23) et de fils de trame (24) délimitant les orifices de la bande de tamisage (13).
- Dispositif selon l'une quelconque des revendications 1 ou 2, le tissu de la bande de tamisage (11) présentant une densité de tissage de 20 à 75 fils de chaîne/25 mm et de préférence de 30 à 55 fils de chaîne/25 mm, ainsi que de 10 à 50 fils de trame/25 mm, de manière préférentielle, de 10 à 40 fils de trame/25 mm.
- Dispositif selon l'une quelconque des revendications 1 à 3, le plus petit diamètre d'une zone d'obturation (22) de la bande de tamisage (11) étant d'au moins 1,5 mm, de préférence d'au moins 2 mm et au maximum de 8 mm, de manière préférentielle, au maximum de 9 mm et notamment au maximum de 10 mm.
- Dispositif selon l'une quelconque des revendications 1 à 4, le rapport de la perméabilité à l'air de la bande de tamisage (11) non obturée à la perméabilité à l'air de la bande de tamisage partiellement obturée étant de 1,2 à 4, de préférence de 1,3 à 3,5, de manière préférentielle, de 1,5 à 3 et de manière particulièrement préférentielle, de 1,8 à 2,8.
- Dispositif selon l'une quelconque des revendications 1 à 5, les zones obturées (22) étant conçues en forme de points et/ou en forme de lignes.
- Dispositif selon l'une quelconque des revendications 1 à 6, les zones obturées (22) étant placées en étant distribuées selon un motif régulier sur la bande de tamisage (11).
- Dispositif selon l'une quelconque des revendications 1 à 7, au moins un système de refroidissement (4) pour refroidir les filaments (2) et au moins un système d'étirage (5) pour étirer les filaments (2) refroidis étant prévus, le groupe composé du système de refroidissement (4) et du système d'étirage (5) étant conçu sous la forme d'un groupe fermé et
à part l'alimentation de l'air de refroidissement dans le système de refroidissement (4), aucune alimentation d'air supplémentaire n'étant prévue à l'intérieur dudit groupe fermé. - Dispositif selon l'une quelconque des revendications 1 à 8, entre le système d'étirage (5) et le système de dépose étant placé au moins un diffuseur (8, 9) à l'aide duquel les filaments (2) peuvent être menés avant la dépose sur le système de dépose.
- Dispositif selon l'une quelconque des revendications 1 à 9, au moins un rouleau compacteur (19, 20) étant présent pour pré-consolider le non-tissé (1) déposé sur le système de dépose ou sur la bande de tamisage (11) et le rouleau compacteur (19, 20) étant conçu de préférence en étant chauffé.
- Procédé, destiné à la fabrication de non-tissés en filaments continus (2),- doté notamment d'un dispositif selon l'une quelconque des revendications 1 à 10- lors duquel les filaments continus (2) sont filés, puis refroidis par la suite et déposés ensuite sur un système de dépose prenant la forme d'une bande de tamisage (11) pourvue d'orifices de bande de tamisage (13) ouverts et obturés pour former le non-tissé (1), pour stabiliser le non-tissé (1) déposé sur la bande de tamisage (11), de l'air étant aspiré à travers la bande de tamisage (11) ou à travers la surface de la bande de tamisage (12), le rapport de la perméabilité à l'air de la bande de tamisage (11) pourvue exclusivement d'orifices de bande de tamisage (13) non obturés à la perméabilité à l'air de la bande de tamisage (11) pourvue en partie d'orifices de bande de tamisage obturés étant de 1,2 à 4, de préférence de 1,3 à 3,5, de manière préférentielle, de 1,5 à 3 et de manière particulièrement préférentielle, de 1,8 à 2,8 et la masse d'obturation des zones obturées (22) étant placée dans et/ou en-dessous de la surface de la bande de tamisage (12) et ne saillant pas par-dessus la surface de la bande de tamisage (12) ou saillant au maximum de 1,0 mm, de manière préférentielle, au maximum de 0,8 mm, de manière très préférentielle, au maximum de 0,6 mm et de manière particulièrement préférentielle, au maximum de 0,3 à 0,6 mm par-dessus la surface de la bande de tamisage (12).
- Procédé selon la revendication 11, les non-tissés (1) étant fabriqués sous la forme de non-tissés liés par filage.
- Procédé selon l'une quelconque des revendications 11 ou 12, dans la zone de dépose (17) du non-tissé (1), de l'air étant aspiré à une vitesse d'aspiration de 5 à 25 m/s à travers la bande de tamisage (11).
- Procédé selon l'une quelconque des revendications 11 à 13, lors duquel on soumet le non-tissé (1) à une pré-consolidation et il est recommandé de le soumettre à une consolidation finale.
- Procédé selon l'une quelconque des revendications 11 à 14, pour désolidariser le non-tissé (1) de la bande de tamisage (11), de l'air étant soufflé par le dessous ou dans la direction de la face inférieure du non-tissé (1) à travers la bande de tamisage (11).
Priority Applications (16)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| ES16167804T ES2720805T3 (es) | 2016-04-29 | 2016-04-29 | Dispositivo y procedimiento para fabricar no tejidos a base de filamentos continuos |
| SI201630251T SI3239378T1 (sl) | 2016-04-29 | 2016-04-29 | Naprava in postopek za izdelavo kopren iz brezkončnih filamentov |
| EP16167804.0A EP3239378B1 (fr) | 2016-04-29 | 2016-04-29 | Procede et dispositif destines a la fabrication de tissus non-tisses a partir de filaments continus |
| PL16167804T PL3239378T3 (pl) | 2016-04-29 | 2016-04-29 | Urządzenie i sposób do wytwarzania włóknin z włókien ciągłych |
| US15/493,170 US20170314163A1 (en) | 2016-04-29 | 2017-04-21 | Method and apparatus for making nonwoven from continuous filaments |
| BR102017008542-2A BR102017008542B1 (pt) | 2016-04-29 | 2017-04-25 | Dispositivo e método para a produção de não tecidos de filamentos contínuos |
| ARP170101067A AR108335A1 (es) | 2016-04-29 | 2017-04-26 | Dispositivo y procedimiento para la fabricación de telas no tejidas de filamentos sinfín |
| MYPI2017701469A MY174811A (en) | 2016-04-29 | 2017-04-26 | Method and apparatus for making nonwoven from continuous filaments |
| MX2017005446A MX2017005446A (es) | 2016-04-29 | 2017-04-26 | Dispositivo y procedimiento para la fabricacion de telas no tejidas de filamentos sinfin. |
| KR1020170054608A KR102148557B1 (ko) | 2016-04-29 | 2017-04-27 | 연속 필라멘트로부터 부직포를 제조하는 방법 및 그 장치 |
| CN201710291490.9A CN107326541B (zh) | 2016-04-29 | 2017-04-28 | 用于由连续长丝制造无纺布的设备和方法 |
| RU2017114956A RU2710674C2 (ru) | 2016-04-29 | 2017-04-28 | Устройство и способ изготовления нетканых материалов из элементарных волокон |
| JP2017089661A JP6968570B2 (ja) | 2016-04-29 | 2017-04-28 | 無端フィラメントから成る不織布を製造するための装置及び方法 |
| US17/213,873 US11655563B2 (en) | 2016-04-29 | 2021-03-26 | Apparatus for making nonwoven from continuous filaments |
| JP2021170481A JP7176076B2 (ja) | 2016-04-29 | 2021-10-18 | 無端フィラメントから成る不織布を製造するための装置及び方法 |
| US18/299,909 US20230250558A1 (en) | 2016-04-29 | 2023-04-13 | Methods of making a nonwoven from continuous filaments |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP16167804.0A EP3239378B1 (fr) | 2016-04-29 | 2016-04-29 | Procede et dispositif destines a la fabrication de tissus non-tisses a partir de filaments continus |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP3239378A1 EP3239378A1 (fr) | 2017-11-01 |
| EP3239378B1 true EP3239378B1 (fr) | 2019-02-13 |
Family
ID=55862667
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP16167804.0A Active EP3239378B1 (fr) | 2016-04-29 | 2016-04-29 | Procede et dispositif destines a la fabrication de tissus non-tisses a partir de filaments continus |
Country Status (13)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (3) | US20170314163A1 (fr) |
| EP (1) | EP3239378B1 (fr) |
| JP (2) | JP6968570B2 (fr) |
| KR (1) | KR102148557B1 (fr) |
| CN (1) | CN107326541B (fr) |
| AR (1) | AR108335A1 (fr) |
| BR (1) | BR102017008542B1 (fr) |
| ES (1) | ES2720805T3 (fr) |
| MX (1) | MX2017005446A (fr) |
| MY (1) | MY174811A (fr) |
| PL (1) | PL3239378T3 (fr) |
| RU (1) | RU2710674C2 (fr) |
| SI (1) | SI3239378T1 (fr) |
Families Citing this family (17)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN114775172A (zh) * | 2015-07-31 | 2022-07-22 | 宝洁公司 | 用于成型非织造布的成形带 |
| JP2018523556A (ja) | 2015-07-31 | 2018-08-23 | ザ プロクター アンド ギャンブル カンパニー | 成形された不織布を用いた吸収性物品のパッケージ |
| SI3239378T1 (sl) | 2016-04-29 | 2019-06-28 | Reifenhaeuser Gmbh & Co. Kg Maschinenfabrik | Naprava in postopek za izdelavo kopren iz brezkončnih filamentov |
| CN109322062B (zh) * | 2018-10-26 | 2021-02-02 | 大连民族大学 | 3d堆叠式多层电纺纤维逐层喷射方法 |
| WO2020112705A1 (fr) * | 2018-11-30 | 2020-06-04 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Bandes non-tissées de fibres continues liées par fluide traversant |
| CN113166988B (zh) | 2018-11-30 | 2023-04-07 | 宝洁公司 | 形成柔软且蓬松的非织造纤维网的方法 |
| EP3887584B1 (fr) | 2018-11-30 | 2022-08-24 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Procédés de production de bandes non tissées liées par un fluide traversant |
| EP3771760B1 (fr) * | 2019-07-30 | 2023-06-07 | Asahi Kasei Kabushiki Kaisha | Procédé et appareil de production d'un tissu non tissé en fibres synthétiques serties |
| ES2907976T3 (es) * | 2019-07-30 | 2022-04-27 | Reifenhaeuser Masch | Dispositivo y procedimiento para producir un material no tejido de fibras rizadas |
| DK3771762T3 (da) * | 2019-07-30 | 2021-08-30 | Reifenhaeuser Masch | Indretning og fremgangsmåde til fremstilling af et vliesstof af fibre |
| CN112176435A (zh) * | 2020-10-14 | 2021-01-05 | 安徽伯辉智能装备有限公司 | 一种熔喷非织造布生产用熔体冷却设备 |
| CN112481835B (zh) * | 2020-11-30 | 2022-08-23 | 厦门当盛新材料有限公司 | 一种聚乙烯膜的生产方法 |
| CN113481662A (zh) * | 2021-07-28 | 2021-10-08 | 浙江朝隆纺织机械股份有限公司 | 一种成网机抽吸风结构 |
| WO2023081745A1 (fr) | 2021-11-04 | 2023-05-11 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Courroie de structuration de matériau en bande, procédé de fabrication de matériau en bande structuré et matériau en bande structuré fabriqué par le procédé |
| CA3181031A1 (fr) | 2021-11-04 | 2023-05-04 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Courroie de structure de materiau en toile, methode de fabrication et methode d'utilisation |
| CA3181019A1 (fr) | 2021-11-04 | 2023-05-04 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Courroie de structure de materiau en toile, methode de fabrication et methode d'utilisation |
| CA3180938A1 (fr) | 2021-11-04 | 2023-05-04 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Courroie de structure de materiau en toile, methode de fabrication et methode d'utilisation |
Family Cites Families (186)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS4827070B1 (fr) | 1970-07-21 | 1973-08-18 | ||
| US4333979A (en) | 1980-08-18 | 1982-06-08 | Kimberly-Clark Corporation | Soft, bulky, lightweight nonwoven web and method of producing; the web has both fused spot bonds and patterned embossments |
| US4514345A (en) * | 1983-08-23 | 1985-04-30 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Method of making a foraminous member |
| US4741941A (en) * | 1985-11-04 | 1988-05-03 | Kimberly-Clark Corporation | Nonwoven web with projections |
| US4970104A (en) | 1988-03-18 | 1990-11-13 | Kimberly-Clark Corporation | Nonwoven material subjected to hydraulic jet treatment in spots |
| US5302220A (en) * | 1989-04-06 | 1994-04-12 | Chisso Corporation | Method for manufacturing bulky nonwoven fabrics |
| EP0418493A1 (fr) * | 1989-07-28 | 1991-03-27 | Fiberweb North America, Inc. | Une étoffe non-tissée composée combinée par hydroenchevêtrement et un procédé de sa fabrication |
| GB8921962D0 (en) | 1989-09-28 | 1989-11-15 | Browning Michael R S | Variable suspension system |
| DK0536320T3 (da) | 1990-06-29 | 1995-02-20 | Procter & Gamble | Papirfremstillingsbånd og fremgangsmåde til fremstilling af samme under anvendelse af forskellig belysningstransmissionsteknik |
| US5145727A (en) | 1990-11-26 | 1992-09-08 | Kimberly-Clark Corporation | Multilayer nonwoven composite structure |
| US5206023A (en) | 1991-01-31 | 1993-04-27 | Robert F. Shaw | Method and compositions for the treatment and repair of defects or lesions in cartilage |
| JP3171457B2 (ja) * | 1991-04-26 | 2001-05-28 | 日本フイルコン株式会社 | 突起を設けた不織布製造用ベルト及び模様を形成した不織布の製造方法 |
| US5399174A (en) | 1993-04-06 | 1995-03-21 | Kimberly-Clark Corporation | Patterned embossed nonwoven fabric, cloth-like liquid barrier material |
| US5599420A (en) | 1993-04-06 | 1997-02-04 | Kimberly-Clark Corporation | Patterned embossed nonwoven fabric, cloth-like liquid barrier material and method for making same |
| CA2105026C (fr) | 1993-04-29 | 2003-12-16 | Henry Louis Griesbach Iii | Non-tisse forme et sa methode de fabrication |
| DE69515896T2 (de) | 1994-11-02 | 2000-10-19 | Procter & Gamble | Verfahren zur herstellung von vliesstoffen |
| US5573719A (en) | 1994-11-30 | 1996-11-12 | Kimberly-Clark Corporation | Process of making highly absorbent nonwoven fabric |
| DE19518975C1 (de) | 1995-05-23 | 1996-06-13 | Freudenberg Carl Fa | Wischtuch |
| US5628097A (en) | 1995-09-29 | 1997-05-13 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Method for selectively aperturing a nonwoven web |
| US5995020A (en) | 1995-10-17 | 1999-11-30 | Pes, Inc. | Downhole power and communication system |
| US5858515A (en) | 1995-12-29 | 1999-01-12 | Kimberly-Clark Worldwide, Inc. | Pattern-unbonded nonwoven web and process for making the same |
| JPH1077566A (ja) | 1996-07-11 | 1998-03-24 | Uni Charm Corp | 不織布およびその製造方法 |
| BR9713568A (pt) | 1996-12-06 | 2000-03-14 | Bba Nonwovens Simpsonville Inc | Laminado de rede não-tecida tendo relativamente zonas hidrófilas e método relacionado para sua fabricação. |
| WO1998042289A1 (fr) | 1997-03-21 | 1998-10-01 | Kimberly-Clark Worldwide, Inc. | Voiles absorbants a zone double |
| US6383431B1 (en) | 1997-04-04 | 2002-05-07 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Method of modifying a nonwoven fibrous web for use as component of a disposable absorbent article |
| WO2000020675A1 (fr) | 1998-10-01 | 2000-04-13 | Kimberly-Clark Worldwide, Inc. | Voiles en non tisse a poids de base differentiel |
| US6673418B1 (en) | 1998-12-23 | 2004-01-06 | Mcneil-Ppc, Inc. | Absorbent product having a non-woven fabric cover with a three-dimensional profile region |
| US6331345B1 (en) | 1999-08-13 | 2001-12-18 | First Quality Nonwovens, Inc. | Nonwoven fabric with high CD elongation and method of making same |
| US6319455B1 (en) * | 1999-08-13 | 2001-11-20 | First Quality Nonwovens, Inc. | Nonwoven fabric with high CD elongation and method of making same |
| US6331268B1 (en) | 1999-08-13 | 2001-12-18 | First Quality Nonwovens, Inc. | Nonwoven fabric with high CD elongation and method of making same |
| WO2001027435A1 (fr) | 1999-10-13 | 2001-04-19 | Baker Hughes Incorporated | Appareil permettant le transfert d'energie electrique entre les elements rotatifs et non rotatifs des outils fond de trou |
| US6679332B2 (en) | 2000-01-24 | 2004-01-20 | Shell Oil Company | Petroleum well having downhole sensors, communication and power |
| DE10003684A1 (de) | 2000-01-28 | 2001-08-02 | Voith Paper Patent Gmbh | Maschine sowie Verfahren zur Herstellung einer Tissuebahn |
| US7589249B2 (en) | 2000-02-16 | 2009-09-15 | Mcneil-Ppc, Inc. | Multiple zone apertured web |
| JP3701208B2 (ja) | 2000-03-13 | 2005-09-28 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | 開孔シートとこの開孔シートを使用した吸収性物品および前記開孔シートの製造方法。 |
| US6632504B1 (en) | 2000-03-17 | 2003-10-14 | Bba Nonwovens Simpsonville, Inc. | Multicomponent apertured nonwoven |
| US20020119720A1 (en) | 2000-10-13 | 2002-08-29 | Arora Kelyn Anne | Abrasion resistant, soft nonwoven |
| JP3877953B2 (ja) | 2000-10-31 | 2007-02-07 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | 使い捨て着用物品の不織布製表面シート |
| US20030203196A1 (en) | 2000-11-27 | 2003-10-30 | Trokhan Paul Dennis | Flexible structure comprising starch filaments |
| DE10103627B4 (de) | 2001-01-27 | 2007-11-15 | Sandler Ag | Vliesstoff mit Struktur |
| DE10109304C5 (de) | 2001-02-26 | 2009-07-16 | Sandler Ag | Strukturiertes, voluminöses Metblown-Vlies |
| US6601706B2 (en) | 2001-04-19 | 2003-08-05 | Kimberly-Clark Worldwide, Inc. | Package for absorbent articles |
| US20020193032A1 (en) | 2001-06-01 | 2002-12-19 | Bba Nonwovens Simpsonville, Inc. | Nonwoven fabric with areas of differing basis weight |
| RU2526209C2 (ru) | 2001-08-14 | 2014-08-20 | МакНЕЙЛ-ППС, ИНК. | Полотно с отверстиями, имеющее множество зон |
| JP4707282B2 (ja) | 2001-08-21 | 2011-06-22 | 旭化成せんい株式会社 | 衛生材料用トップシート |
| JP4723808B2 (ja) * | 2001-10-29 | 2011-07-13 | アルバニー インターナショナル コーポレイション | 不織ファブリックの高速スパンボンド生産 |
| US20030093045A1 (en) | 2001-11-13 | 2003-05-15 | Erdman Carol L. | Absorbing article having zoned areas of hydrophilicity |
| US6921570B2 (en) | 2001-12-21 | 2005-07-26 | Kimberly-Clark Worldwide, Inc. | Pattern unbonded nonwoven web and process for making same |
| JP3611838B2 (ja) | 2001-12-28 | 2005-01-19 | 花王株式会社 | 吸収性物品用の表面シート |
| JP3625804B2 (ja) | 2002-02-25 | 2005-03-02 | 花王株式会社 | 立体シート材料 |
| DE60301802T2 (de) | 2002-02-25 | 2006-05-11 | Kao Corp. | Deckschicht für absorbierenden Artikel |
| EP1340842B2 (fr) | 2002-02-28 | 2010-12-08 | Reifenhäuser GmbH & Co. KG Maschinenfabrik | Appareil pour la fabrication en continu d'un voile de tissé-lié |
| US20030203691A1 (en) | 2002-04-30 | 2003-10-30 | Kimberly-Clark Worldwide, Inc. | Nonwoven materials having surface features |
| US20030203162A1 (en) | 2002-04-30 | 2003-10-30 | Kimberly-Clark Worldwide, Inc. | Methods for making nonwoven materials on a surface having surface features and nonwoven materials having surface features |
| US20030211802A1 (en) | 2002-05-10 | 2003-11-13 | Kimberly-Clark Worldwide, Inc. | Three-dimensional coform nonwoven web |
| US20040005457A1 (en) | 2002-07-03 | 2004-01-08 | Kimberly-Clark Worldwide, Inc. | Methods of improving the softness of fibers and nonwoven webs and fibers and nonwoven webs having improved softness |
| US20040059309A1 (en) | 2002-09-18 | 2004-03-25 | Nortman Brian Keith | Absorbent article with untreated hydrophobic target area |
| KR100752979B1 (ko) | 2002-09-26 | 2007-08-30 | 아사히 가세이 셍이 가부시키가이샤 | 스펀본드계 부직포 및 위생 재료 |
| US7067711B2 (en) | 2002-12-05 | 2006-06-27 | Uni-Charm Corporation | Elongated absorbent article |
| US8030535B2 (en) | 2002-12-18 | 2011-10-04 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Sanitary napkin for clean body benefit |
| US9844476B2 (en) | 2014-03-18 | 2017-12-19 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Sanitary napkin for clean body benefit |
| DE50201372D1 (de) | 2002-12-19 | 2004-11-25 | Reifenhaeuser Masch | Vorrichtung für die Ablage und Förderung einer Vliesbahn aus Kunststofffäden |
| US7005044B2 (en) | 2002-12-31 | 2006-02-28 | Albany International Corp. | Method of fabricating a belt and a belt used to make bulk tissue and towel, and nonwoven articles and fabrics |
| US8241543B2 (en) | 2003-08-07 | 2012-08-14 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Method and apparatus for making an apertured web |
| SE0303413D0 (sv) * | 2003-12-18 | 2003-12-18 | Sca Hygiene Prod Ab | a composite nonwoven material containing continuous filaments and short fibres |
| EP1778069A4 (fr) | 2004-08-17 | 2009-12-02 | Kenneth Binmoeller | Logement pour instrument endoscopique sterile |
| JP4580736B2 (ja) | 2004-11-18 | 2010-11-17 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | 吸液性芯材成型ドラム |
| RU2401892C2 (ru) * | 2004-12-17 | 2010-10-20 | Олбэни Интернэшнл Корп. | Образование рисунка на изделии спанбонд-мелтблаун-спанбонд (смс) |
| US8197455B2 (en) | 2004-12-21 | 2012-06-12 | Kimberly-Clark Worldwide, Inc. | Absorbent articles and/or packaging components each having different patterns in a single container |
| JP4870365B2 (ja) | 2005-02-23 | 2012-02-08 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | 生理用ナプキン |
| US20070045143A1 (en) | 2005-08-26 | 2007-03-01 | Clough Jane L | Package of flexible absorbent articles |
| US20070045144A1 (en) | 2005-08-31 | 2007-03-01 | Kimberly-Clark Worldwide, Inc. | Packaging component for personal care articles |
| AU2006301829A1 (en) | 2005-10-11 | 2007-04-19 | Johnson & Johnson Inc. | Rolled disposable absorbent article |
| RU2388860C2 (ru) | 2005-12-07 | 2010-05-10 | Ска Хайджин Продактс Аб | Нетканый материал и абсорбирующее изделие, включающее нетканый материал |
| US8853108B2 (en) | 2005-12-07 | 2014-10-07 | Sca Hygiene Products Ab | Nonwoven material and absorbing article comprising nonwoven material |
| WO2007120629A2 (fr) | 2006-04-10 | 2007-10-25 | First Quality Nonwovens, Inc. | Voile composite non-tissé/pâte co-attendri et procédé de production |
| US8129298B2 (en) | 2006-05-31 | 2012-03-06 | Mitsui Chemicals, Inc. | Nonwoven laminates and process for producing the same |
| JP5328089B2 (ja) | 2006-06-23 | 2013-10-30 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | 多層不織布及び多層不織布の製造方法 |
| JP5069890B2 (ja) | 2006-06-23 | 2012-11-07 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | 不織布 |
| JP5069891B2 (ja) | 2006-06-23 | 2012-11-07 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | 不織布 |
| JP5123505B2 (ja) | 2006-06-23 | 2013-01-23 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | 不織布 |
| JP5123513B2 (ja) | 2006-06-23 | 2013-01-23 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | 吸収体 |
| JP5328088B2 (ja) | 2006-06-23 | 2013-10-30 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | 不織布 |
| JP5154048B2 (ja) | 2006-06-23 | 2013-02-27 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | 不織布 |
| JP5123511B2 (ja) | 2006-06-23 | 2013-01-23 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | 不織布 |
| CN101448991B (zh) | 2006-06-23 | 2011-05-25 | 尤妮佳股份有限公司 | 无纺织物 |
| KR101395379B1 (ko) | 2006-06-23 | 2014-05-14 | 유니챰 가부시키가이샤 | 흡수성 물품 |
| JP5123512B2 (ja) | 2006-06-23 | 2013-01-23 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | 不織布 |
| JP5123497B2 (ja) | 2006-06-23 | 2013-01-23 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | 不織布、不織布製造方法及び不織布製造装置 |
| JP5054962B2 (ja) | 2006-11-06 | 2012-10-24 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | 吸収性物品 |
| DE502006007979D1 (de) * | 2006-12-06 | 2010-11-11 | Reifenhaeuser Gmbh & Co Kg | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur Herstellung eines Spinnvlieses |
| DE602006012527D1 (de) * | 2006-12-15 | 2010-04-08 | Fare Spa | Vorrichtung und Prozess zur Herstellung einer Spinnvliesmatte |
| DE102006062237A1 (de) | 2006-12-22 | 2008-06-26 | Voith Patent Gmbh | Maschine zur Herstellung einer Faserstoffbahn |
| PL1967628T5 (pl) * | 2007-03-08 | 2014-04-30 | Truetzschler Nonwovens Gmbh | Sposób i urządzenie do wytwarzania włókniny metodą "spod filiery" |
| US8273941B2 (en) | 2007-04-17 | 2012-09-25 | Uni-Charm Corporation | Nonwoven fabric, method for producing nonwoven fabric, and absorbent article |
| JP5053815B2 (ja) | 2007-12-03 | 2012-10-24 | 花王株式会社 | 吸収性物品 |
| JP5197147B2 (ja) | 2008-05-15 | 2013-05-15 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | 吸収性物品 |
| JP5269485B2 (ja) | 2008-05-30 | 2013-08-21 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | 凹凸模様を有する嵩高紙及びその製造方法 |
| US8058501B2 (en) | 2008-08-08 | 2011-11-15 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Regionalized topsheet |
| JP5596688B2 (ja) | 2008-09-11 | 2014-09-24 | オルバニー インターナショナル コーポレイション | ティッシュ、タオルおよび不織物製造のための流体透過性ベルト |
| WO2010074982A1 (fr) | 2008-12-23 | 2010-07-01 | 3M Innovative Properties Company | Toiles fibreuses non tissées à motifs et procédés pour les fabriquer et les utiliser |
| ES2879403T3 (es) | 2009-01-28 | 2021-11-22 | Albany Int Corp | Tela de fabricación de papel para producir productos de papel tisú y papel toalla, y sistema y método para obtener la tela. |
| US8906275B2 (en) | 2012-05-29 | 2014-12-09 | Nike, Inc. | Textured elements incorporating non-woven textile materials and methods for manufacturing the textured elements |
| US20100224356A1 (en) | 2009-03-06 | 2010-09-09 | Smith International, Inc. | Apparatus for electrical power and/or data transfer between rotating components in a drill string |
| US8975466B2 (en) | 2009-04-29 | 2015-03-10 | Eveready Battery Company, Inc. | Absorbent article including a plurality of longitudinally extending channels |
| JP5421676B2 (ja) | 2009-07-07 | 2014-02-19 | 花王株式会社 | 吸収性物品用の表面シート |
| JP5399174B2 (ja) | 2009-09-08 | 2014-01-29 | 株式会社オプトラン | 多源蒸着薄膜の組成制御方法および製造装置 |
| US8676549B2 (en) | 2009-09-29 | 2014-03-18 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Method of maximizing shipping efficiency of absorbent articles |
| CA2678090C (fr) | 2009-09-29 | 2011-05-10 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Produits absorbants comportant un emballage plus efficace |
| JP5421720B2 (ja) | 2009-10-09 | 2014-02-19 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | 不織布 |
| JP2011131044A (ja) | 2009-11-24 | 2011-07-07 | Kao Corp | 吸収性物品 |
| US8668975B2 (en) | 2009-11-24 | 2014-03-11 | Exxonmobil Chemical Patents Inc. | Fabric with discrete elastic and plastic regions and method for making same |
| KR101477881B1 (ko) | 2010-03-30 | 2014-12-30 | 미쓰이 가가쿠 가부시키가이샤 | 부직포 |
| WO2011155460A1 (fr) | 2010-06-10 | 2011-12-15 | 花王株式会社 | Procédé de production d'un produit absorbant |
| US10639212B2 (en) | 2010-08-20 | 2020-05-05 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Absorbent article and components thereof having improved softness signals, and methods for manufacturing |
| WO2012024576A1 (fr) | 2010-08-20 | 2012-02-23 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Article absorbant et ses composants dotés de signes de souplesse améliorés et procédés de fabrication |
| JP5729948B2 (ja) | 2010-08-31 | 2015-06-03 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | 不織布シート、その製造方法および吸収性物品 |
| JP5780731B2 (ja) | 2010-09-30 | 2015-09-16 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | 使い捨ておむつ |
| JP5773604B2 (ja) | 2010-09-30 | 2015-09-02 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | 吸収性物品および使い捨ておむつ |
| WO2012086730A1 (fr) | 2010-12-24 | 2012-06-28 | 花王株式会社 | Tissu non tissé et article absorbant utilisant ledit tissu |
| US20120238979A1 (en) | 2011-03-15 | 2012-09-20 | Paul Thomas Weisman | Structured Fibrous Web |
| US20120238982A1 (en) | 2011-03-15 | 2012-09-20 | Paul Thomas Weisman | Structured Fibrous Web |
| US20120316532A1 (en) | 2011-06-13 | 2012-12-13 | Mccormick Sarah Ann | Disposable Absorbent Article With Topsheet Having A Continuous, Bonded Pattern |
| JP5709685B2 (ja) | 2011-07-29 | 2015-04-30 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | 使い捨ておむつ |
| JP5717602B2 (ja) | 2011-09-30 | 2015-05-13 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | 積層不織布、及び当該積層不織布の製造方法 |
| BR112014009539A2 (pt) | 2011-10-19 | 2017-05-09 | Kao Corp | dispositivo de empilhamento de fibras |
| US20130112584A1 (en) | 2011-11-08 | 2013-05-09 | Seda Gaspari | Compact Tissue Dispenser |
| JP5743961B2 (ja) | 2011-12-09 | 2015-07-01 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | 透液性不織布 |
| JP5858776B2 (ja) | 2011-12-27 | 2016-02-10 | 花王株式会社 | 不織布 |
| MX342355B (es) | 2012-01-04 | 2016-09-23 | Procter & Gamble | Estructuras fibrosas que contienen activos con multiples regiones. |
| CA2860647C (fr) | 2012-01-04 | 2022-06-14 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Structures fibreuses contenant des principes actifs et presentant de multiples zones de densite differente |
| JP5925015B2 (ja) | 2012-03-30 | 2016-05-25 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | 吸収性物品 |
| EP2660377B1 (fr) | 2012-05-03 | 2014-04-09 | Chen-Cheng Huang | Procédé de fabrication d'un tissu non tissée gaufrée double face |
| JP5979983B2 (ja) | 2012-05-28 | 2016-08-31 | 大王製紙株式会社 | 吸収性物品及びその製造方法 |
| US10695250B2 (en) | 2012-07-24 | 2020-06-30 | Maquet (Suzhou) Co., Ltd. | Medical supply unit having an elbow joint part |
| EP2879637B1 (fr) | 2012-08-01 | 2020-08-19 | The Procter and Gamble Company | Structure de couche avec des attributs pour une souplesse tactile ameliorée |
| CN108210177A (zh) | 2012-08-13 | 2018-06-29 | 宝洁公司 | 带有视觉上不同的粘结部位的多层的非织造纤维网及制备方法 |
| EP2897563B1 (fr) | 2012-09-21 | 2018-10-24 | The Procter and Gamble Company | Article comprenant un non-tissés doux |
| JP5875157B2 (ja) | 2012-09-28 | 2016-03-02 | 花王株式会社 | 繊維シート |
| US20140127460A1 (en) | 2012-11-06 | 2014-05-08 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Article(s) with soft nonwoven web |
| JP6050659B2 (ja) | 2012-11-16 | 2016-12-21 | 花王株式会社 | 吸収性物品 |
| EP2740450A1 (fr) | 2012-12-10 | 2014-06-11 | The Procter & Gamble Company | C'ur absorbant à haute teneur en matériau superabsorbant |
| HUE044699T2 (hu) | 2012-12-10 | 2019-11-28 | Procter & Gamble | Folyadékgyûjtõ-eloszlató rendszerrel kiegészített nedvszívó termék |
| US8851161B2 (en) | 2013-01-22 | 2014-10-07 | Halliburton Energy Services, Inc. | Cross-communication between electronic circuits and electrical devices in well tools |
| DK2971315T3 (en) | 2013-03-12 | 2018-09-17 | Fitesa Nonwoven Inc | Stretchable nonwoven fabric |
| JP6044413B2 (ja) | 2013-03-26 | 2016-12-14 | 王子ホールディングス株式会社 | 吸収性物品のトップシート及びそれを用いた吸収性物品 |
| US9173782B2 (en) | 2013-03-28 | 2015-11-03 | Kimberly-Clark Worldwide, Inc. | Coordinated apertured and embossed topsheet layer materials, and absorbent articles containing such |
| US20140324009A1 (en) | 2013-04-29 | 2014-10-30 | Kimberly-Clark Worldwide, Inc. | Aperture-Patterned Fibrous Nonwoven Web |
| WO2014189905A1 (fr) | 2013-05-20 | 2014-11-27 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Bandes de non-tissé comprenant des sites de liaison visuellement distincts et procédé de fabrication associé |
| US20140358101A1 (en) | 2013-05-30 | 2014-12-04 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Nonwoven Web Material Having Enhanced Glide Softness And Good Strength Attributes, And Method For Manufacturing |
| JP2014234345A (ja) | 2013-05-30 | 2014-12-15 | スリーエム イノベイティブ プロパティズ カンパニー | スキンケア用シートおよびスキンケア製品 |
| ES2653574T3 (es) | 2013-07-02 | 2018-02-07 | Fitesa Germany Gmbh | Tela no tejida y procedimiento de formación de la misma |
| US10258516B2 (en) | 2013-07-31 | 2019-04-16 | Kimberly-Clark Worldwide, Inc. | Treated three-dimensional apertured liners |
| EP2886093B1 (fr) | 2013-12-19 | 2016-09-21 | The Procter and Gamble Company | Article absorbant comprenant une ou plusieurs zones colorées |
| WO2015112693A1 (fr) | 2014-01-24 | 2015-07-30 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Articles absorbants jetables comprenant une ou plusieurs compositions médicales pour la peau et procédés associés |
| CN203841923U (zh) | 2014-03-26 | 2014-09-24 | 厦门延江工贸有限公司 | 一种具有开孔结构的立体无纺布 |
| JP6289224B2 (ja) | 2014-04-04 | 2018-03-07 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | 不織布 |
| US10271997B2 (en) | 2014-04-08 | 2019-04-30 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Absorbent articles having substrates having zonal treatments |
| TWI616313B (zh) | 2014-04-18 | 2018-03-01 | Huang Zhen Zheng | Forming system for producing breathable film and finished product thereof |
| JP2017537677A (ja) | 2014-11-06 | 2017-12-21 | ザ プロクター アンド ギャンブル カンパニー | 予ひずみ状積層体及びその作製方法 |
| US10517775B2 (en) | 2014-11-18 | 2019-12-31 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Absorbent articles having distribution materials |
| WO2016108741A1 (fr) | 2015-01-02 | 2016-07-07 | Sca Hygiene Products Ab | Article absorbant |
| EP3058916B1 (fr) | 2015-02-17 | 2018-01-31 | The Procter and Gamble Company | Emballage pour articles absorbants formant un bassin tridimensionnel |
| CN108348372B (zh) * | 2015-07-31 | 2022-05-03 | 宝洁公司 | 成型非织造布 |
| CN114775172A (zh) * | 2015-07-31 | 2022-07-22 | 宝洁公司 | 用于成型非织造布的成形带 |
| JP2018523556A (ja) | 2015-07-31 | 2018-08-23 | ザ プロクター アンド ギャンブル カンパニー | 成形された不織布を用いた吸収性物品のパッケージ |
| US10858768B2 (en) | 2015-07-31 | 2020-12-08 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Shaped nonwoven |
| US10973702B2 (en) | 2015-08-26 | 2021-04-13 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Absorbent articles having three dimensional substrates and indicia |
| MX2018005816A (es) | 2015-11-12 | 2019-05-16 | Pfnonwovens Llc | Trama no tejida con resistencia mejorada a la abrasion y metodo para su fabricacion. |
| WO2017106080A1 (fr) | 2015-12-16 | 2017-06-22 | Avintiv Specialty Materials Inc. | Non-tissé souple et son procédé de fabrication |
| RU2703390C1 (ru) | 2015-12-17 | 2019-10-17 | Дзе Проктер Энд Гэмбл Компани | Формованный нетканый материал |
| JP6055074B1 (ja) | 2015-12-25 | 2016-12-27 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | 吸収性物品 |
| US10195091B2 (en) | 2016-03-11 | 2019-02-05 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Compositioned, textured nonwoven webs |
| SI3239378T1 (sl) | 2016-04-29 | 2019-06-28 | Reifenhaeuser Gmbh & Co. Kg Maschinenfabrik | Naprava in postopek za izdelavo kopren iz brezkončnih filamentov |
| US10888471B2 (en) | 2016-12-15 | 2021-01-12 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Shaped nonwoven |
| BR112019015923B1 (pt) | 2017-01-31 | 2023-12-26 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Não-tecido formatado, artigo absorvente e embalagem de artigo absorvente |
| JP7376354B2 (ja) | 2017-01-31 | 2023-11-08 | ザ プロクター アンド ギャンブル カンパニー | 成形不織布 |
| JP6946441B2 (ja) | 2017-01-31 | 2021-10-06 | ザ プロクター アンド ギャンブル カンパニーThe Procter & Gamble Company | 成形不織布及び成形不織布を含む物品 |
| JP7486317B2 (ja) | 2017-06-05 | 2024-05-17 | ザ プロクター アンド ギャンブル カンパニー | 排泄物の可視化が改善された構成可能な吸収性物品 |
| WO2019005906A1 (fr) | 2017-06-30 | 2019-01-03 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Non-tissé façonné |
| US10577722B2 (en) | 2017-06-30 | 2020-03-03 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Method for making a shaped nonwoven |
| RU2721351C1 (ru) | 2017-08-31 | 2020-05-19 | Као Корпорейшн | Нетканый материал |
| CN112423715B (zh) | 2018-06-26 | 2022-09-02 | 宝洁公司 | 具有经处理以减少表面活性剂迁移的顶片的吸收制品 |
| WO2020028734A1 (fr) | 2018-08-03 | 2020-02-06 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Bandes avec des compositions appliquées sur celles-ci |
| WO2020226951A1 (fr) | 2019-05-03 | 2020-11-12 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Bandes non tissées avec une ou plusieurs unités de répétition |
| US20210169710A1 (en) | 2019-12-10 | 2021-06-10 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Nonwoven webs with visually discernible patterns and improved texture perception |
-
2016
- 2016-04-29 SI SI201630251T patent/SI3239378T1/sl unknown
- 2016-04-29 PL PL16167804T patent/PL3239378T3/pl unknown
- 2016-04-29 ES ES16167804T patent/ES2720805T3/es active Active
- 2016-04-29 EP EP16167804.0A patent/EP3239378B1/fr active Active
-
2017
- 2017-04-21 US US15/493,170 patent/US20170314163A1/en not_active Abandoned
- 2017-04-25 BR BR102017008542-2A patent/BR102017008542B1/pt active IP Right Grant
- 2017-04-26 MY MYPI2017701469A patent/MY174811A/en unknown
- 2017-04-26 MX MX2017005446A patent/MX2017005446A/es unknown
- 2017-04-26 AR ARP170101067A patent/AR108335A1/es active IP Right Grant
- 2017-04-27 KR KR1020170054608A patent/KR102148557B1/ko active IP Right Grant
- 2017-04-28 CN CN201710291490.9A patent/CN107326541B/zh active Active
- 2017-04-28 JP JP2017089661A patent/JP6968570B2/ja active Active
- 2017-04-28 RU RU2017114956A patent/RU2710674C2/ru active
-
2021
- 2021-03-26 US US17/213,873 patent/US11655563B2/en active Active
- 2021-10-18 JP JP2021170481A patent/JP7176076B2/ja active Active
-
2023
- 2023-04-13 US US18/299,909 patent/US20230250558A1/en active Pending
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| None * |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| RU2710674C2 (ru) | 2019-12-30 |
| US20170314163A1 (en) | 2017-11-02 |
| JP2022009216A (ja) | 2022-01-14 |
| JP2017206803A (ja) | 2017-11-24 |
| CN107326541A (zh) | 2017-11-07 |
| US11655563B2 (en) | 2023-05-23 |
| JP6968570B2 (ja) | 2021-11-17 |
| MX2017005446A (es) | 2018-08-20 |
| RU2017114956A3 (fr) | 2019-07-17 |
| CN107326541B (zh) | 2024-02-06 |
| BR102017008542B1 (pt) | 2022-09-06 |
| US20230250558A1 (en) | 2023-08-10 |
| EP3239378A1 (fr) | 2017-11-01 |
| MY174811A (en) | 2020-05-15 |
| AR108335A1 (es) | 2018-08-08 |
| SI3239378T1 (sl) | 2019-06-28 |
| PL3239378T3 (pl) | 2019-07-31 |
| KR20170124095A (ko) | 2017-11-09 |
| RU2017114956A (ru) | 2018-10-30 |
| JP7176076B2 (ja) | 2022-11-21 |
| US20210214858A1 (en) | 2021-07-15 |
| ES2720805T3 (es) | 2019-07-24 |
| BR102017008542A2 (pt) | 2017-11-07 |
| KR102148557B1 (ko) | 2020-08-26 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP3239378B1 (fr) | Procede et dispositif destines a la fabrication de tissus non-tisses a partir de filaments continus | |
| EP1967628B2 (fr) | Procédé et dispositif de fabrication d'un textile non-tissé filé-lié | |
| EP2630287B1 (fr) | Procédé et dispositif de fabrication d'un non-tissé composite | |
| EP1726700B1 (fr) | Procédé et dispositif pour la fabrication d'un non-tissé | |
| DE1950669A1 (de) | Neuartiges Endlosfadenvlies | |
| EP1092054B1 (fr) | Procede de production d'un non-tisse a partir de fibres | |
| DE3151322C2 (de) | "Verfahren zur Herstellung von Polypropylen-Spinnvliesen mit niedrigem Fallkoeffizienten" | |
| EP2128320B1 (fr) | Procédé et dispositif destinés à la fabrication de tissus non tissés en filaments | |
| EP3289131B1 (fr) | Installation et procédé de consolidation et de structuration de fibres à un non-tissé | |
| DE102013111499A1 (de) | Voluminöses Vlieskomposit und Verfahren zur Herstellung desselben | |
| DE60014900T2 (de) | Vorrichtung zur herstellung einer faservliesbahn sowie verfahren zur durchführung dieser vorrichtung | |
| DE2448299A1 (de) | Mehrschichtige, bindefaedengebundene spinnvliese | |
| EP0598463A1 (fr) | Procédé et installation pour produire et coucher des faiseaux de filaments continus au moyen de force d'air | |
| EP3771763B1 (fr) | Dispositif et procédé de fabrication d'un non-tissé de fibres bouclées | |
| DE102007023174A1 (de) | Vorrichtung zum Behandeln und Verfestigen eines Verbunds | |
| EP0403840B1 (fr) | Matériau non tissé | |
| EP3382080B1 (fr) | Procédé et dispositif de fabrication d'un non-tissé à partir de fibres | |
| EP3771556B1 (fr) | Stratifié non-tissé et procédé de fabrication d'un stratifié non-tissé | |
| DE19956368C2 (de) | Verfahren zur Herstellung von schmelzgeblasenen Vliesstoffen, daraus hergestellte schmelzgeblasene Vliesstoffe und Verwendung der schmelzgeblasenen Vliesstoffe | |
| DE102009010935A1 (de) | Verbundvliesstoff sowie Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur Herstellung eines solchen Verbundvliesstoffes | |
| EP0480550B1 (fr) | Procédé et installation pour la production de non-tissés en filaments continus | |
| WO2008080382A1 (fr) | Procédé et dispositif de fabrication d'un non-tissé à une couche ou plusieurs couches | |
| DE10345953B4 (de) | Vliesstoff und Verfahren zur seiner Herstellung | |
| EP4001488B1 (fr) | Dispositif de fabrication de tissus non tissés à partir de filaments continus | |
| EP3974572B1 (fr) | Procédé de fabrication d'un agrégat non tissé et agrégat non tissé |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: EXAMINATION IS IN PROGRESS |
|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20170306 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Extension state: BA ME |
|
| GRAP | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR1 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: GRANT OF PATENT IS INTENDED |
|
| INTG | Intention to grant announced |
Effective date: 20180830 |
|
| GRAS | Grant fee paid |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR3 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: THE PATENT HAS BEEN GRANTED |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: NOT ENGLISH |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: EP Ref country code: AT Ref legal event code: REF Ref document number: 1096303 Country of ref document: AT Kind code of ref document: T Effective date: 20190215 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: LANGUAGE OF EP DOCUMENT: GERMAN |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R096 Ref document number: 502016003384 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: SE Ref legal event code: TRGR |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: NV Representative=s name: KELLER AND PARTNER PATENTANWAELTE AG, CH |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: NL Ref legal event code: FP |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: LT Ref legal event code: MG4D |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: ES Ref legal event code: FG2A Ref document number: 2720805 Country of ref document: ES Kind code of ref document: T3 Effective date: 20190724 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20190213 Ref country code: FI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20190213 Ref country code: NO Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20190513 Ref country code: PT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20190613 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GR Ref legal event code: EP Ref document number: 20190401363 Country of ref document: GR Effective date: 20190708 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: HR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20190213 Ref country code: RS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20190213 Ref country code: BG Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20190513 Ref country code: LV Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20190213 Ref country code: IS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20190613 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: EE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20190213 Ref country code: SK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20190213 Ref country code: AL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20190213 Ref country code: RO Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20190213 Ref country code: DK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20190213 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R097 Ref document number: 502016003384 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SM Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20190213 |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MC Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20190213 Ref country code: LU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20190429 |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed |
Effective date: 20191114 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20190429 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PFA Owner name: REIFENHAEUSER GMBH AND CO. KG MASCHINENFABRIK, DE Free format text: FORMER OWNER: REIFENHAEUSER GMBH AND CO. KG MASCHINENFABRIK, DE |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CY Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20190213 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R082 Ref document number: 502016003384 Country of ref document: DE Representative=s name: ANDREJEWSKI HONKE PATENT- UND RECHTSANWAELTE P, DE Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R081 Ref document number: 502016003384 Country of ref document: DE Owner name: THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY, CINCINNATI, US Free format text: FORMER OWNER: REIFENHAEUSER GMBH & CO. KG MASCHINENFABRIK, 53844 TROISDORF, DE |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: BE Ref legal event code: PD Owner name: THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY; US Free format text: DETAILS ASSIGNMENT: CHANGE OF OWNER(S), ASSIGNMENT; FORMER OWNER NAME: REIFENHAEUSER GMBH & CO. KG MASCHINENFABRIK Effective date: 20210608 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: HU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT; INVALID AB INITIO Effective date: 20160429 Ref country code: MT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20190213 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: NL Ref legal event code: PD Owner name: THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY; US Free format text: DETAILS ASSIGNMENT: CHANGE OF OWNER(S), ASSIGNMENT; FORMER OWNER NAME: REIFENHAEUSER GMBH & CO. KG MASCHINENFABRIK Effective date: 20210713 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: ES Ref legal event code: PC2A Owner name: THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY Effective date: 20210827 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: AT Ref legal event code: PC Ref document number: 1096303 Country of ref document: AT Kind code of ref document: T Owner name: THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY, US Effective date: 20210719 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: SI Ref legal event code: SP73 Owner name: THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY; US Effective date: 20210729 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: 732E Free format text: REGISTERED BETWEEN 20210916 AND 20210922 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20190213 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Payment date: 20230309 Year of fee payment: 8 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Payment date: 20230310 Year of fee payment: 8 Ref country code: PL Payment date: 20230315 Year of fee payment: 8 Ref country code: IT Payment date: 20230310 Year of fee payment: 8 Ref country code: BE Payment date: 20230315 Year of fee payment: 8 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: ES Payment date: 20230512 Year of fee payment: 8 Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20230307 Year of fee payment: 8 Ref country code: CZ Payment date: 20230419 Year of fee payment: 8 Ref country code: CH Payment date: 20230502 Year of fee payment: 8 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: TR Payment date: 20230427 Year of fee payment: 8 Ref country code: SI Payment date: 20230315 Year of fee payment: 8 Ref country code: AT Payment date: 20230327 Year of fee payment: 8 |
|
| P01 | Opt-out of the competence of the unified patent court (upc) registered |
Effective date: 20240221 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GR Payment date: 20240312 Year of fee payment: 9 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Payment date: 20240315 Year of fee payment: 9 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 20240307 Year of fee payment: 9 |