CN1048821C - 形成半导体器件隔离的方法 - Google Patents
形成半导体器件隔离的方法 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN1048821C CN1048821C CN96101498A CN96101498A CN1048821C CN 1048821 C CN1048821 C CN 1048821C CN 96101498 A CN96101498 A CN 96101498A CN 96101498 A CN96101498 A CN 96101498A CN 1048821 C CN1048821 C CN 1048821C
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- substrate
- insulating barrier
- transition metal
- metal pad
- groove
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 33
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 title claims abstract description 13
- 238000002955 isolation Methods 0.000 title description 5
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 claims description 62
- 230000004888 barrier function Effects 0.000 claims description 41
- 229910052723 transition metal Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 31
- 150000003624 transition metals Chemical class 0.000 claims description 31
- XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicon Chemical compound [Si] XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 22
- 229910052710 silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 22
- 239000010703 silicon Substances 0.000 claims description 22
- 150000004767 nitrides Chemical class 0.000 claims description 17
- 150000002500 ions Chemical class 0.000 claims description 14
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 claims description 13
- 229920002120 photoresistant polymer Polymers 0.000 claims description 11
- 238000009792 diffusion process Methods 0.000 claims description 9
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 claims description 5
- 229910021332 silicide Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 5
- FVBUAEGBCNSCDD-UHFFFAOYSA-N silicide(4-) Chemical compound [Si-4] FVBUAEGBCNSCDD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 5
- 230000007797 corrosion Effects 0.000 claims description 3
- 238000005260 corrosion Methods 0.000 claims description 3
- 229910052750 molybdenum Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 3
- 229910052758 niobium Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 3
- 229910052715 tantalum Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 3
- 229910052719 titanium Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 3
- 229910052721 tungsten Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 3
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 claims 2
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 claims 2
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 abstract description 5
- 241000293849 Cordylanthus Species 0.000 abstract 1
- 230000010354 integration Effects 0.000 abstract 1
- 125000006850 spacer group Chemical group 0.000 abstract 1
- 210000003323 beak Anatomy 0.000 description 6
- NBIIXXVUZAFLBC-UHFFFAOYSA-N Phosphoric acid Chemical compound OP(O)(O)=O NBIIXXVUZAFLBC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 229910021420 polycrystalline silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 4
- 229920005591 polysilicon Polymers 0.000 description 4
- 238000005530 etching Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000003647 oxidation Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000007254 oxidation reaction Methods 0.000 description 3
- 229910000147 aluminium phosphate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000011248 coating agent Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000000576 coating method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000013078 crystal Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000008021 deposition Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000005468 ion implantation Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000001259 photo etching Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000005498 polishing Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000007547 defect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000003292 glue Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000002513 implantation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000011259 mixed solution Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000005192 partition Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000007634 remodeling Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000000717 retained effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000005728 strengthening Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000001039 wet etching Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/70—Manufacture or treatment of devices consisting of a plurality of solid state components formed in or on a common substrate or of parts thereof; Manufacture of integrated circuit devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/71—Manufacture of specific parts of devices defined in group H01L21/70
- H01L21/76—Making of isolation regions between components
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/70—Manufacture or treatment of devices consisting of a plurality of solid state components formed in or on a common substrate or of parts thereof; Manufacture of integrated circuit devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/71—Manufacture of specific parts of devices defined in group H01L21/70
- H01L21/76—Making of isolation regions between components
- H01L21/762—Dielectric regions, e.g. EPIC dielectric isolation, LOCOS; Trench refilling techniques, SOI technology, use of channel stoppers
- H01L21/76294—Dielectric regions, e.g. EPIC dielectric isolation, LOCOS; Trench refilling techniques, SOI technology, use of channel stoppers using selective deposition of single crystal silicon, i.e. SEG techniques
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/70—Manufacture or treatment of devices consisting of a plurality of solid state components formed in or on a common substrate or of parts thereof; Manufacture of integrated circuit devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/71—Manufacture of specific parts of devices defined in group H01L21/70
- H01L21/76—Making of isolation regions between components
- H01L21/762—Dielectric regions, e.g. EPIC dielectric isolation, LOCOS; Trench refilling techniques, SOI technology, use of channel stoppers
- H01L21/76224—Dielectric regions, e.g. EPIC dielectric isolation, LOCOS; Trench refilling techniques, SOI technology, use of channel stoppers using trench refilling with dielectric materials
- H01L21/76237—Dielectric regions, e.g. EPIC dielectric isolation, LOCOS; Trench refilling techniques, SOI technology, use of channel stoppers using trench refilling with dielectric materials introducing impurities in trench side or bottom walls, e.g. for forming channel stoppers or alter isolation behavior
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Condensed Matter Physics & Semiconductors (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Manufacturing & Machinery (AREA)
- Computer Hardware Design (AREA)
- Microelectronics & Electronic Packaging (AREA)
- Power Engineering (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Crystallography & Structural Chemistry (AREA)
- Element Separation (AREA)
- Local Oxidation Of Silicon (AREA)
Abstract
本发明提供一种不用LOCOS工艺形成场氧化层的方法。据此,本发明特别有效地增加有源区,改善半导体器件的集成度和防止鸟嘴发生。而且由于本发明场氧化层的宽度与绝缘层侧壁上的垫的宽度相同,从而使场氧化层的面积可以减至最小。
Description
本发明涉及一种形成半导体器件隔离的方法,尤其涉及通过减小鸟嘴来增加较大规模集成电路的有源区的方法。
通常采用LOCOS(硅局部氧化)法来形成集成电路的场氧化层,然而,LOCOS工艺增加了鸟嘴的尺寸,造成了半导体器件有源区的减小。
下面参照图1对常规的场氧化层形成方法进行详细地描述。
首先,图1表示的是能够较多减小鸟嘴的PBL工艺(多晶硅阻挡LOCOS)。
如图1所示,基底氧化层12在硅衬底11上形成,多晶硅层13、氮化物层14和光刻胶层(未示出)依次在基底氧化层12上形成。由预先确定的光刻掩膜确定了场区后,蚀刻氮化物层14和多晶硅层13的部分,使之露出硅衬底区的一部分,用热氧化工艺在露出的硅衬底上形成场氧化层15。
然而,在对露出的硅衬底11施行热氧化工艺形成场氧化层时,不管多晶硅层13的消耗量如何,都要沿多晶硅层13和硅衬底11的界面形成鸟嘴。由于鸟嘴尺寸的增加导致了半导体器件有源区的减小,要高度集成器件是很困难的。
美国专利5,256,591描述了一种采用槽来形成半导体器件的隔离区的方法,能够避免在槽形成时产生晶体缺陷和微填充效应(microloading effect)。但是,该专利并未解决上述LOCOS法中存在的问题。
本发明的一个目的是提供一种由增加半导体器件的有源区来形成较大规模集成电路的隔离方法。
本发明的一个方面是,提供一种隔离半导体器件的方法,该方法包括以下步骤:形成第一绝缘层,暴露衬底的场区;在所说衬底和所说第一绝缘层的侧壁上形成过渡金属垫;在整个生成结构上形成第二绝缘层;热处理所说衬底,将所说过渡金属垫的离子扩散进所说衬底;抛光所说第二绝缘层直至露出过渡金属垫,保留其一部分不被除去;除去所说过渡金属垫和所说过渡金属垫下面的离子扩散衬底,在所说衬底上形成一槽;在整个生成结构上形成第三绝缘层,填充所说槽;在所说第三绝缘层和所说场区上形成光刻胶图形;用所说光刻胶图形作蚀刻阻挡物蚀刻所说第三绝缘层;除去所说光剂胶图形和所说第一绝缘层,露出所说衬底的一部分;在所说露出的衬底上形成外延层,用作有源区。
本发明的另一方面是,提供一种隔离半导体器件的方法,该方法包括以下步骤:形成露出衬底的一部分的第一绝缘层;在所说衬底和所说第一绝缘层的侧壁上形成过渡金属垫;在整个生成结构上形成第二绝缘层;热处理所说衬底,将所说过渡金属垫的离子扩散进所说衬底;抛光所说第二绝缘层,以便露出所说过渡金属垫,保留其上的一部分不被除去;通过除去所说过渡金属垫和其下的经离子扩散过的衬底,在所说衬底上形成一槽;在整个生成结构上形成第三绝缘层,填充所说槽;抛光该多层叠层直至第一绝缘层和第二绝缘层的整个上表面全部露出为止,再施行平面化工艺;通过除去所说第二绝缘层和留下而未被除去的所说第一绝缘层,露出部分衬底,这样所说衬底就被暴露出来;在所说露出的衬底上形成外延层,用作有源区。
由参照附图对实施例所作的下列描述可以清楚地看出本发明的其它目的和方面,其中:
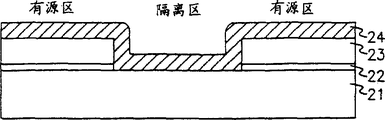
图1是采用PBL工艺所形成的常规场氧化层的横截面图;
图2A至2F是根据本发明的实施例的场氧化层的横截面图;和
图3A至3F是根据本发明的另一实施例的场氧化层的横截面图。
下文将参照图2A至2F描述本发明的一个实施例。
如图2A所示,在硅衬底21上依次淀积基底氧化层22和氧化物层23,它们的厚度分别为100-200A,和1000-1300A。使用具有场图形的掩膜选择性蚀刻氮化物层23和基底氧化层22,露出硅衬底的一部分。在整个生成结构上淀积一厚度大约为1000A的过渡金属24,如W、Ti、Ta,Mo和Nb。
如图2B所示,采用各向同性腐蚀工艺腐蚀过渡金属24,在氮化物23的侧壁上和基底氧化层22上形成过渡金属垫24′,并在整个生成结构上淀积厚度约为1000~1500A的氮化物层。在900~1000℃下对晶片热处理,使过渡金属24的离子扩散进硅衬底21,然后在硅衬底21里形成硅化物层26。
如图2C所示,用化学和机械抛光的手段除去晶片上层结构,直至露出过渡金属垫24′为止。用HNO3与HF的混合溶液除去过渡金属垫24′和硅化物层26之后,施行沟道阻塞离子注入工艺以增加隔离效果。例如,以10~50 kev的能量和1×1012~1×1018原子/cm2的注入剂量将BF2离子注入暴露的衬底。根据本发明的特征,也可以省去沟道阻塞离子注入工艺。
如图2D所示,在整个生成结构上淀积厚度大约1000~2000A的正硅酸乙脂(TEOS)层27,及在TEOS层27上形成光刻胶图形28。使用与用来选择性蚀刻如图2A所示的氮化物层23和基底氧化层22的光刻掩膜相反的光刻掩膜来形成光刻胶图形28。也就是说,如果形成如图2A所示的场区所用的光刻胶层是正的,那么图2D中的光刻胶图形就是负的,图2A和2D可以用相同的光刻膜掩膜。
接下来,如图2E所示,由光刻胶层28作蚀刻阻挡层湿法腐蚀TEOS层27。
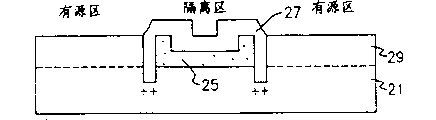
最后,如图2F所示,用磷酸除去基底氧化层22上的氮化物层23,利用各向同性腐蚀工艺除去基底氧化层22,便露出了硅衬底21的有源区。在暴露的硅衬底21上形成外延层29,用氮化物层25和TEOS层27作场氧化层,用外延层29作有源区。
下面参照附图3A至3F描述本发明的另一个实施例。
首先按照与图2A至2C所示的相同的方法形成图3A至3C所示的结构,因此,这里不再详细描述,在图2A至2C和3A至3C中相同的附图标记代表相同的部件。
然而,值得注意的是,在图3A中,所有由选择性腐蚀氮化物层而露出的硅衬底21的全部表面和基底氧化层22都不构成场氧化区。即,用除去过渡金属垫24′和硅化物层26而形成的一些槽39有助于构成场氧化层,在图3F中将详细描述场氧化层。
如图3D所示,在如图3C所示的为增强隔离效果对硅衬底21进行离子注入后,在整个生成结构上淀积TEOS层37,填充这些槽39。
接下来,如图3E所示,采用化学和机械抛光的方法,除去生成结构的上层部分,抛光至露出氮化物层35为止。此时,除出氮化物层35的垂直部分,将氧化物23的一部分的氮化物层33保留在基底氧化层22上,对晶片施行平面化工艺。
最后,如图3F所示,用磷酸除去基底氧化物层22上的氮化物层33,再用各向同性腐蚀工艺除去基底氧化层22,这样就露出了硅衬底21的有源区。由此,在硅衬底21的露出部分上形成的外延层39作有源区。而且,因为外延层39是在由该TEOS层37分成的两部分之间的硅衬底21的部位上形成,所以,图3F所示的有源区的面积比图2F中所示的要宽阔。
由上面的描述可清楚地看出,本发明能极有效地增加有源区,并改善半导体器件的集成度和防止鸟嘴发生。而且,在本发明的另一个实施例中,由于场氧化层的宽度与过渡金属垫的宽度相同,所以场氧化层的面积可以减到最小。
尽管为了说明本发明,而公开了一些优选实施例,但是,本领域的技术人员将会发现,可对本发明进行各种改型增加及替换。但这些均不脱离本发明权利要求书中所要求保护的本发明的范围和精神。
Claims (16)
1.一种形成半导体器件隔离的方法,包括以下步骤:
形成第一绝缘层,暴露出衬底的场区;
在所说衬底和所说第一绝缘层的侧壁上形成过渡金属垫;
其特征在于,还包括以下步骤:
在整个生成结构上形成第二绝缘层;
热处理所说衬底,将所说过渡金属垫离子扩散进所说衬底中;
抛光所说第二绝缘层直到露出所说过渡金属垫为止,保留下来的一部分金属垫不除去;
除去所说过渡金属垫和过渡金属垫下面的离子扩散过的衬底,在所说衬底中形成一槽;
在整个生成结构上形成第三绝缘层,填充所说槽;
在所说第三绝缘层和所说场区上形成光刻胶图形;
用所说光刻胶图形作腐蚀阻挡层,腐蚀所说第三绝缘层;
除去所说光刻胶图形和所说第一绝缘层,露出所说衬底的一部分;和
在所说衬底暴露部分上形成外延层用作有源区。
2.根据权利要求1的方法,其特征在于,在所说衬底中形成槽的步骤还包括给所说槽注入沟道阻塞离子的步骤。
3.根据权利要求1的方法,其特征在于,所说第一绝缘层是由基底氧化层和氮化物层形成的。
4.根据权利要求1的方法,其特征在于,所说衬底为硅衬底。
5.根据权利要求4的方法,其特征在于,从所说过渡金属垫扩散进所说衬底的所说离子在所说硅衬底上形成了硅化物层。
6.根据权利要求1的方法,其特征在于,所说第二绝缘层是氮化物层。
7.根据权利要求1的方法,其特征在于,所说第三绝缘层是正硅酸乙脂层。
8.根据权利要求1的方法,其特征在于,所说过渡金属是W、Ti、Ta、Mo或Nb之一。
9.一种形成半导体器件隔离的方法,包括以下步骤:
形成第一绝缘层,露出衬底的一部分;
在所说衬底和所说第一绝缘层的侧壁上形成过渡金属垫;
其特征在于,还包括以下步骤:
在整个生成结构上形成第二绝缘层;
热处理所说衬底,将所说过渡金属垫离子扩散进所说衬底中;
抛光所说第二绝缘层,露出所说过渡金属垫,保留下来的该金属垫的一部分不除去;
除去所说过渡金属垫和过渡金属垫下的离子扩散过的衬底,在所说衬底中形成槽;
在整个生成结构上形成第三绝缘层,填充所说槽;
抛光该多层叠层直到所说第一绝缘层和第二绝缘层的整个上表面全部露出为止,再施行平面化工艺;
除去保留下来而未被除去的所说第二绝缘层和第一绝缘层,露出所说衬底的一部分,这样暴露所说衬底;以及
在所说暴露的衬底上形成外延层用作有源层。
10.根据权利要求9的方法,其特征在于,在所说衬底上形成槽的步骤还包括向所说槽注入沟道阻塞离子的步骤。
11.根据权利要求9的方法,其特征在于,所说第一绝缘层是由基底氧化层和氮化物层组成。
12.根据权利要求9的方法,其特征在于,所说衬底是硅衬底。
13.根据权利要求12的方法,其特征在于,从所说过渡金属垫扩散到所说衬底的所说离子在所说硅衬底上形成了硅化物层。
14.根据权利要求9的方法,其特征在于,所说第二绝缘层是氮化物层。
15.根据权利要求9的方法,其特征在于,所说第三绝缘层是正硅酸乙脂层。
16.根据权利要求9的方法,其特征在于,所说过渡金属是W、Ti、Ta、Mo或Nb之一。
Applications Claiming Priority (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR3727/95 | 1995-02-24 | ||
| KR1019950003727A KR100190367B1 (ko) | 1995-02-24 | 1995-02-24 | 소자분리막형성방법 |
| KR3727/1995 | 1995-02-24 |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN1134038A CN1134038A (zh) | 1996-10-23 |
| CN1048821C true CN1048821C (zh) | 2000-01-26 |
Family
ID=19408771
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN96101498A Expired - Fee Related CN1048821C (zh) | 1995-02-24 | 1996-02-24 | 形成半导体器件隔离的方法 |
Country Status (5)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US5668043A (zh) |
| JP (1) | JP2788889B2 (zh) |
| KR (1) | KR100190367B1 (zh) |
| CN (1) | CN1048821C (zh) |
| TW (1) | TW301022B (zh) |
Families Citing this family (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TW365047B (en) * | 1996-10-04 | 1999-07-21 | Winbond Electronics Corp | Manufacturing method for simultaneously forming trenches of different depths |
| US6686283B1 (en) * | 1999-02-05 | 2004-02-03 | Texas Instruments Incorporated | Shallow trench isolation planarization using self aligned isotropic etch |
| US6306723B1 (en) | 2000-03-13 | 2001-10-23 | Chartered Semiconductor Manufacturing Ltd. | Method to form shallow trench isolations without a chemical mechanical polish |
| CN110223916B (zh) * | 2019-05-06 | 2022-03-08 | 瑞声科技(新加坡)有限公司 | 一种硅晶片的加工方法 |
Citations (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5256591A (en) * | 1991-01-07 | 1993-10-26 | Gold Star Electron Co., Ltd. | Method for forming isolation region in semiconductor device using trench |
Family Cites Families (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS5766627A (en) * | 1980-10-13 | 1982-04-22 | Toshiba Corp | Manufacture of semiconductor device |
| JPS5893220A (ja) * | 1981-11-30 | 1983-06-02 | Toshiba Corp | 半導体単結晶膜の製造方法 |
| JPH01321629A (ja) * | 1988-06-23 | 1989-12-27 | Nec Corp | 薄膜形成方法 |
-
1995
- 1995-02-24 KR KR1019950003727A patent/KR100190367B1/ko not_active IP Right Cessation
-
1996
- 1996-02-22 US US08/605,691 patent/US5668043A/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1996-02-24 CN CN96101498A patent/CN1048821C/zh not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 1996-02-24 TW TW085102096A patent/TW301022B/zh active
- 1996-02-26 JP JP8038523A patent/JP2788889B2/ja not_active Expired - Fee Related
Patent Citations (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5256591A (en) * | 1991-01-07 | 1993-10-26 | Gold Star Electron Co., Ltd. | Method for forming isolation region in semiconductor device using trench |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| US5668043A (en) | 1997-09-16 |
| JPH08264634A (ja) | 1996-10-11 |
| CN1134038A (zh) | 1996-10-23 |
| JP2788889B2 (ja) | 1998-08-20 |
| KR960032673A (ko) | 1996-09-17 |
| TW301022B (zh) | 1997-03-21 |
| KR100190367B1 (ko) | 1999-06-01 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| KR100433091B1 (ko) | 반도체소자의 도전배선 형성방법 | |
| KR20020011257A (ko) | 트렌치 소자 분리형 반도체 장치 및 그 형성방법 | |
| JP3953726B2 (ja) | 面取りが形成された金属シリサイド層を備えた半導体素子の製造方法 | |
| KR19980018004A (ko) | 반도체 장치 및 그 제조 방법 | |
| CN1048821C (zh) | 形成半导体器件隔离的方法 | |
| KR100529391B1 (ko) | 반도체 메모리 장치 및 그 제조 방법 | |
| JPH05335578A (ja) | 薄膜トランジスタの製造方法 | |
| KR19980036490A (ko) | 반도체소자의 트렌치 및 이의 형성방법 | |
| KR20000003920A (ko) | 반도체 장치 제조 방법 | |
| KR100232198B1 (ko) | 반도체소자의 격리영역 형성방법 | |
| KR100235960B1 (ko) | 반도체소자의 도전 라인 형성방법 | |
| KR100245136B1 (ko) | 반도체 소자의 자기정렬 콘택형성방법 | |
| KR100326262B1 (ko) | 반도체장치제조방법 | |
| KR100367694B1 (ko) | 반도체소자의콘택제조방법 | |
| KR100204022B1 (ko) | 반도체 소자의 소자분리막 형성방법 | |
| US6833315B1 (en) | Removing silicon oxynitride of polysilicon gates in fabricating integrated circuits | |
| KR20020058512A (ko) | 반도체 소자의 제조 방법 | |
| KR100312987B1 (ko) | 반도체소자의소자분리막제조방법 | |
| KR100209279B1 (ko) | 반도체 소자의 콘택홀 형성방법 | |
| KR100252908B1 (ko) | 반도체소자의 격리영역 형성방법 | |
| KR0147427B1 (ko) | 미세 반도체 소자의 소자분리막 형성 방법 | |
| KR100265835B1 (ko) | 반도체소자의금속배선형성방법 | |
| KR100192369B1 (ko) | 반도체소자 평탄화 형성방법 | |
| KR100226735B1 (ko) | 격리막 형성 방법 | |
| KR101035644B1 (ko) | 반도체 소자의 제조방법 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| C06 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| C10 | Entry into substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| C14 | Grant of patent or utility model | ||
| GR01 | Patent grant | ||
| C56 | Change in the name or address of the patentee |
Owner name: HYNIX SEMICONDUCTOR INC. Free format text: FORMER NAME OR ADDRESS: HYUNDAI ELECTRONICS INDUSTRIES CO., LTD. |
|
| CP01 | Change in the name or title of a patent holder |
Address after: Gyeonggi Do, South Korea Patentee after: Hairyoksa Semiconductor Co., Ltd. Address before: Gyeonggi Do, South Korea Patentee before: Hyundai Electronics Industries Co., Ltd. |
|
| C19 | Lapse of patent right due to non-payment of the annual fee | ||
| CF01 | Termination of patent right due to non-payment of annual fee |