WO2015056526A1 - エンコーダ付組み合わせシールリング及びエンコーダ付転がり軸受ユニット - Google Patents
エンコーダ付組み合わせシールリング及びエンコーダ付転がり軸受ユニット Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2015056526A1 WO2015056526A1 PCT/JP2014/074930 JP2014074930W WO2015056526A1 WO 2015056526 A1 WO2015056526 A1 WO 2015056526A1 JP 2014074930 W JP2014074930 W JP 2014074930W WO 2015056526 A1 WO2015056526 A1 WO 2015056526A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- encoder
- peripheral surface
- ring
- slinger
- seal ring
- Prior art date
Links
- 230000002093 peripheral effect Effects 0.000 claims abstract description 96
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 24
- 238000005096 rolling process Methods 0.000 claims description 22
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 claims description 17
- 239000013013 elastic material Substances 0.000 claims description 8
- 238000007493 shaping process Methods 0.000 abstract description 2
- 238000007789 sealing Methods 0.000 description 14
- 229920001971 elastomer Polymers 0.000 description 11
- 238000005452 bending Methods 0.000 description 7
- 239000000696 magnetic material Substances 0.000 description 5
- 238000000465 moulding Methods 0.000 description 5
- 239000004033 plastic Substances 0.000 description 5
- 229920003002 synthetic resin Polymers 0.000 description 5
- 239000000057 synthetic resin Substances 0.000 description 5
- 238000000137 annealing Methods 0.000 description 4
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 4
- 239000003302 ferromagnetic material Substances 0.000 description 4
- 230000005415 magnetization Effects 0.000 description 4
- 239000000725 suspension Substances 0.000 description 4
- 238000004073 vulcanization Methods 0.000 description 4
- 238000004132 cross linking Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000001514 detection method Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 3
- 229910000859 α-Fe Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 229910001209 Low-carbon steel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 238000001746 injection moulding Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000005291 magnetic effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000002994 raw material Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000001105 regulatory effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000007711 solidification Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000008023 solidification Effects 0.000 description 2
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Substances O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229920000459 Nitrile rubber Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920000800 acrylic rubber Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 230000004323 axial length Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000005540 biological transmission Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000002425 crystallisation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000008025 crystallization Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000006866 deterioration Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000000428 dust Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000005489 elastic deformation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000000806 elastomer Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920001973 fluoroelastomer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 238000011010 flushing procedure Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000004519 grease Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000006247 magnetic powder Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000005389 magnetism Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229920000058 polyacrylate Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000002861 polymer material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000003566 sealing material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000006641 stabilisation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000011105 stabilization Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910001220 stainless steel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F16—ENGINEERING ELEMENTS AND UNITS; GENERAL MEASURES FOR PRODUCING AND MAINTAINING EFFECTIVE FUNCTIONING OF MACHINES OR INSTALLATIONS; THERMAL INSULATION IN GENERAL
- F16J—PISTONS; CYLINDERS; SEALINGS
- F16J15/00—Sealings
- F16J15/16—Sealings between relatively-moving surfaces
- F16J15/34—Sealings between relatively-moving surfaces with slip-ring pressed against a more or less radial face on one member
- F16J15/3492—Sealings between relatively-moving surfaces with slip-ring pressed against a more or less radial face on one member with monitoring or measuring means associated with the seal
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F16—ENGINEERING ELEMENTS AND UNITS; GENERAL MEASURES FOR PRODUCING AND MAINTAINING EFFECTIVE FUNCTIONING OF MACHINES OR INSTALLATIONS; THERMAL INSULATION IN GENERAL
- F16C—SHAFTS; FLEXIBLE SHAFTS; ELEMENTS OR CRANKSHAFT MECHANISMS; ROTARY BODIES OTHER THAN GEARING ELEMENTS; BEARINGS
- F16C33/00—Parts of bearings; Special methods for making bearings or parts thereof
- F16C33/72—Sealings
- F16C33/76—Sealings of ball or roller bearings
- F16C33/78—Sealings of ball or roller bearings with a diaphragm, disc, or ring, with or without resilient members
- F16C33/7816—Details of the sealing or parts thereof, e.g. geometry, material
- F16C33/783—Details of the sealing or parts thereof, e.g. geometry, material of the mounting region
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F16—ENGINEERING ELEMENTS AND UNITS; GENERAL MEASURES FOR PRODUCING AND MAINTAINING EFFECTIVE FUNCTIONING OF MACHINES OR INSTALLATIONS; THERMAL INSULATION IN GENERAL
- F16C—SHAFTS; FLEXIBLE SHAFTS; ELEMENTS OR CRANKSHAFT MECHANISMS; ROTARY BODIES OTHER THAN GEARING ELEMENTS; BEARINGS
- F16C19/00—Bearings with rolling contact, for exclusively rotary movement
- F16C19/02—Bearings with rolling contact, for exclusively rotary movement with bearing balls essentially of the same size in one or more circular rows
- F16C19/04—Bearings with rolling contact, for exclusively rotary movement with bearing balls essentially of the same size in one or more circular rows for radial load mainly
- F16C19/08—Bearings with rolling contact, for exclusively rotary movement with bearing balls essentially of the same size in one or more circular rows for radial load mainly with two or more rows of balls
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F16—ENGINEERING ELEMENTS AND UNITS; GENERAL MEASURES FOR PRODUCING AND MAINTAINING EFFECTIVE FUNCTIONING OF MACHINES OR INSTALLATIONS; THERMAL INSULATION IN GENERAL
- F16C—SHAFTS; FLEXIBLE SHAFTS; ELEMENTS OR CRANKSHAFT MECHANISMS; ROTARY BODIES OTHER THAN GEARING ELEMENTS; BEARINGS
- F16C33/00—Parts of bearings; Special methods for making bearings or parts thereof
- F16C33/72—Sealings
- F16C33/76—Sealings of ball or roller bearings
- F16C33/768—Sealings of ball or roller bearings between relatively stationary parts, i.e. static seals
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F16—ENGINEERING ELEMENTS AND UNITS; GENERAL MEASURES FOR PRODUCING AND MAINTAINING EFFECTIVE FUNCTIONING OF MACHINES OR INSTALLATIONS; THERMAL INSULATION IN GENERAL
- F16C—SHAFTS; FLEXIBLE SHAFTS; ELEMENTS OR CRANKSHAFT MECHANISMS; ROTARY BODIES OTHER THAN GEARING ELEMENTS; BEARINGS
- F16C33/00—Parts of bearings; Special methods for making bearings or parts thereof
- F16C33/72—Sealings
- F16C33/76—Sealings of ball or roller bearings
- F16C33/78—Sealings of ball or roller bearings with a diaphragm, disc, or ring, with or without resilient members
- F16C33/7816—Details of the sealing or parts thereof, e.g. geometry, material
- F16C33/782—Details of the sealing or parts thereof, e.g. geometry, material of the sealing region
- F16C33/7823—Details of the sealing or parts thereof, e.g. geometry, material of the sealing region of sealing lips
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F16—ENGINEERING ELEMENTS AND UNITS; GENERAL MEASURES FOR PRODUCING AND MAINTAINING EFFECTIVE FUNCTIONING OF MACHINES OR INSTALLATIONS; THERMAL INSULATION IN GENERAL
- F16C—SHAFTS; FLEXIBLE SHAFTS; ELEMENTS OR CRANKSHAFT MECHANISMS; ROTARY BODIES OTHER THAN GEARING ELEMENTS; BEARINGS
- F16C33/00—Parts of bearings; Special methods for making bearings or parts thereof
- F16C33/72—Sealings
- F16C33/76—Sealings of ball or roller bearings
- F16C33/78—Sealings of ball or roller bearings with a diaphragm, disc, or ring, with or without resilient members
- F16C33/7869—Sealings of ball or roller bearings with a diaphragm, disc, or ring, with or without resilient members mounted with a cylindrical portion to the inner surface of the outer race and having a radial portion extending inward
- F16C33/7879—Sealings of ball or roller bearings with a diaphragm, disc, or ring, with or without resilient members mounted with a cylindrical portion to the inner surface of the outer race and having a radial portion extending inward with a further sealing ring
- F16C33/7883—Sealings of ball or roller bearings with a diaphragm, disc, or ring, with or without resilient members mounted with a cylindrical portion to the inner surface of the outer race and having a radial portion extending inward with a further sealing ring mounted to the inner race and of generally L-shape, the two sealing rings defining a sealing with box-shaped cross-section
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F16—ENGINEERING ELEMENTS AND UNITS; GENERAL MEASURES FOR PRODUCING AND MAINTAINING EFFECTIVE FUNCTIONING OF MACHINES OR INSTALLATIONS; THERMAL INSULATION IN GENERAL
- F16C—SHAFTS; FLEXIBLE SHAFTS; ELEMENTS OR CRANKSHAFT MECHANISMS; ROTARY BODIES OTHER THAN GEARING ELEMENTS; BEARINGS
- F16C41/00—Other accessories, e.g. devices integrated in the bearing not relating to the bearing function as such
- F16C41/007—Encoders, e.g. parts with a plurality of alternating magnetic poles
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F16—ENGINEERING ELEMENTS AND UNITS; GENERAL MEASURES FOR PRODUCING AND MAINTAINING EFFECTIVE FUNCTIONING OF MACHINES OR INSTALLATIONS; THERMAL INSULATION IN GENERAL
- F16J—PISTONS; CYLINDERS; SEALINGS
- F16J15/00—Sealings
- F16J15/16—Sealings between relatively-moving surfaces
- F16J15/34—Sealings between relatively-moving surfaces with slip-ring pressed against a more or less radial face on one member
- F16J15/3436—Pressing means
- F16J15/3456—Pressing means without external means for pressing the ring against the face, e.g. slip-ring with a resilient lip
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F16—ENGINEERING ELEMENTS AND UNITS; GENERAL MEASURES FOR PRODUCING AND MAINTAINING EFFECTIVE FUNCTIONING OF MACHINES OR INSTALLATIONS; THERMAL INSULATION IN GENERAL
- F16C—SHAFTS; FLEXIBLE SHAFTS; ELEMENTS OR CRANKSHAFT MECHANISMS; ROTARY BODIES OTHER THAN GEARING ELEMENTS; BEARINGS
- F16C19/00—Bearings with rolling contact, for exclusively rotary movement
- F16C19/02—Bearings with rolling contact, for exclusively rotary movement with bearing balls essentially of the same size in one or more circular rows
- F16C19/14—Bearings with rolling contact, for exclusively rotary movement with bearing balls essentially of the same size in one or more circular rows for both radial and axial load
- F16C19/18—Bearings with rolling contact, for exclusively rotary movement with bearing balls essentially of the same size in one or more circular rows for both radial and axial load with two or more rows of balls
- F16C19/181—Bearings with rolling contact, for exclusively rotary movement with bearing balls essentially of the same size in one or more circular rows for both radial and axial load with two or more rows of balls with angular contact
- F16C19/183—Bearings with rolling contact, for exclusively rotary movement with bearing balls essentially of the same size in one or more circular rows for both radial and axial load with two or more rows of balls with angular contact with two rows at opposite angles
- F16C19/184—Bearings with rolling contact, for exclusively rotary movement with bearing balls essentially of the same size in one or more circular rows for both radial and axial load with two or more rows of balls with angular contact with two rows at opposite angles in O-arrangement
- F16C19/186—Bearings with rolling contact, for exclusively rotary movement with bearing balls essentially of the same size in one or more circular rows for both radial and axial load with two or more rows of balls with angular contact with two rows at opposite angles in O-arrangement with three raceways provided integrally on parts other than race rings, e.g. third generation hubs
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F16—ENGINEERING ELEMENTS AND UNITS; GENERAL MEASURES FOR PRODUCING AND MAINTAINING EFFECTIVE FUNCTIONING OF MACHINES OR INSTALLATIONS; THERMAL INSULATION IN GENERAL
- F16C—SHAFTS; FLEXIBLE SHAFTS; ELEMENTS OR CRANKSHAFT MECHANISMS; ROTARY BODIES OTHER THAN GEARING ELEMENTS; BEARINGS
- F16C2326/00—Articles relating to transporting
- F16C2326/01—Parts of vehicles in general
- F16C2326/02—Wheel hubs or castors
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a combined seal ring with an encoder for closing an opening end portion of a rolling bearing incorporated in a rotation support portion of various mechanical devices, and detecting a rotation speed of a rotating member supported by the rolling bearing, and the encoder
- the present invention relates to an improvement of a rolling bearing unit with an encoder provided with a combined seal ring. Specifically, a structure capable of ensuring the sealing performance of the fitting portion between the rotating cylindrical portion constituting the slinger and the outer peripheral surface of the inner diameter side race ring member is realized.
- a rotation support part of various machine devices for example, a wheel support rolling bearing unit for supporting a wheel of a vehicle (automobile) on a suspension device can be cited.
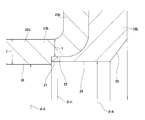
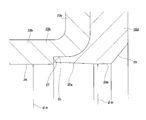
- a rolling bearing unit 1 with an encoder as shown in FIGS. 9 to 10 has been widely known (see, for example, Patent Documents 1 and 2).
- an outer ring 2 that is an outer diameter side race ring member and a hub 3 that is an inner diameter side race ring member are arranged concentrically with each other.
- each ball 6 is a rolling element.
- 6 are arranged in plural for both rows. The balls 6 and 6 are held by the cages 7 and 7 so as to freely roll.
- the hub 3 is rotatably supported on the inner diameter side of the outer ring 2 supported and fixed to the suspension device.
- both ends in the axial direction of the annular space 8 in which the balls 6 and 6 are installed are respectively formed by a seal ring 9 and a combined seal ring 10 with an encoder. It is clogged up around the perimeter.
- the seal ring 9 includes a metal core 11 made of a metal plate and a plurality of seal lips 12 made of an elastic material. And the metal core 11 is the outer end in the axial direction of the outer ring 2 (outside with respect to the axial direction means the left side of each figure on the outer side in the width direction of the vehicle body when assembled to the automobile.
- the center side in the width direction on the right side is referred to as the inside in the axial direction (the same applies throughout the present specification), and the end edge of each seal lip 12 is connected to the intermediate portion in the axial direction of the hub 3 with an interference fit.
- the outer peripheral surface is in sliding contact with the entire periphery.
- the combined seal ring 10 with an encoder includes a seal ring 14 and a slinger 15 that constitute the combined seal ring 13, and an encoder 16.
- the seal ring 14 includes a cored bar 17 having an L-shaped cross section and an annular shape as a whole, and an elastic material 18.
- the cored bar 17 is formed of a metal plate such as a mild steel plate and is formed in an annular shape as a whole with an L-shaped cross section.
- the metal core 17 is fixed to the inner peripheral surface of the inner end portion in the axial direction of the outer ring 2 by an interference fit, and from the outer end edge in the axial direction of the fixed cylindrical portion 19 toward the outer peripheral surface of the hub 3.
- a fixed annular portion 20 that is bent inward in the radial direction.
- the elastic member 18 is attached over the entire circumference of the core metal 17 and has one to a plurality of (three in the illustrated example) seal lips 21a to 21c.
- the elastic material 18 is made of rubber and is bonded to the core
- the slinger 15 includes a rotating cylindrical portion 22 that is fitted and fixed to the outer peripheral surface of the inner end portion in the axial direction of the hub 3 (the inner ring that constitutes the hub 3 together with the hub body), and the axial direction of the rotating cylindrical portion 22.
- a rotating ring portion 23 that is bent radially outward from the inner end edge toward the inner peripheral surface of the outer ring 2 is provided.
- the slinger 15 has smooth surfaces at the outer peripheral surface of the rotating cylindrical portion 22 and the axially outer surface of the rotating annular portion 23 where the tip edges of the seal lips 21a to 21c are slidably contacted.
- the encoder 16 is made of a permanent magnet such as a rubber magnet or a plastic magnet, and is magnetized in the axial direction.
- the magnetization direction is changed alternately and at equal intervals in the circumferential direction. Therefore, the south pole and the north pole are alternately arranged at equal intervals in the circumferential direction on the inner side surface in the axial direction of the encoder 16 that is the detection surface.
- the detection surface of the sensor is opposed to the detection surface of such an encoder 16 so that the rotational speed of the wheel rotating together with the hub 3 can be measured.
- the signal showing the measured rotational speed of a wheel is utilized for control of the travel stabilization apparatus of vehicles, such as an anti-lock brake system (ABS) and a traction control system (TCS).
- ABS anti-lock brake system
- TCS traction control system
- the combined seal ring 10 with the encoder can effectively prevent the entry of relatively large foreign matters such as dust, but sufficiently prevents the entry of rainwater, muddy water, and the like. Things are difficult.
- the combined seal ring 10 with an encoder is merely configured to externally fix the rotating cylindrical portion 22 of the slinger 15 to the outer peripheral surface of the inner end portion in the axial direction of the hub 3 and provide a structure for sealing the fitting portion. Not. Even when the rotating cylindrical portion 22 of the slinger 15 is externally fitted to the outer peripheral surface of the inner end portion in the axial direction of the hub 3, it is inevitable that a minute gap is generated in the fitting portion.
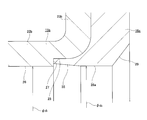
- Patent Document 3 proposes to use a combined seal ring 10a with an encoder as shown in FIG. 11 for the purpose of preventing rain water and the like from entering the annular space as described above.
- a lip portion 24 having an inner diameter smaller than the inner diameter of the rotating cylindrical portion 22a of the slinger 15a is provided on the inner peripheral edge of the encoder 16a. The lip portion 24 is elastically brought into contact with the outer peripheral surface of the hub 3a in a state where the rotating cylindrical portion 22a of the slinger 15a is fitted and fixed to the hub 3a.
- the sealing performance of the fitting portion between the rotating cylindrical portion 22a of the slinger 15a and the outer peripheral surface of the hub 3a is sufficiently ensured for the following reason. Things are difficult. That is, the material constituting the lip portion 24 is the same as that of the encoder 16a, and contains a large amount (for example, 80 to 90% by weight) of a ferromagnetic material such as ferrite in order to ensure sufficient magnetism. Compared to general sealing materials, it is difficult to elastically deform and is brittle.
- the encoder 16a arranges the slinger 15a in a molding die (mold), and fixes a permanent magnet material (high molecular material such as rubber or synthetic resin containing a ferromagnetic material) to the slinger 15a. (Fixed by vulcanization or injection molding).
- a permanent magnet material high molecular material such as rubber or synthetic resin containing a ferromagnetic material
- the encoder 16a is manufactured in this way, when the slinger 15a and the solidified permanent magnet material (unmagnetized encoder) are extracted from the mold, the portion to be the lip portion 24 has a large fastening margin. It must be greatly deformed accordingly (must be forcibly removed). Since it is difficult to greatly deform the portion to be the lip portion 24 in this way, it is difficult to ensure a large allowance for the lip portion 24.
- the rotating cylindrical portion 22a of the slinger 15a is fitted and fixed to the hub 3a by an interference fit, the rotating cylindrical portion 22a is elastically expanded in diameter, but the rotating cylindrical portion 22a and the rotating annular portion 23a are continuous. Therefore, the influence of the diameter expansion of the rotating cylindrical portion 22a is easily transmitted to the rotating annular portion 23a. For this reason, the diameter of the encoder 16a supported and fixed to the rotating ring portion 23a is also easily increased, and the amount of reduction in the tightening allowance of the lip portion 24 is increased.
- Japanese Unexamined Patent Publication No. 2008-233110 Japanese Unexamined Patent Publication No. 2009-185965 Japanese Unexamined Patent Publication No. 2007-52036
- the present invention provides a seal ring with an encoder and a rolling with an encoder that can improve the sealing performance of a fitting portion between a rotating cylindrical portion constituting a slinger and an outer peripheral surface of an inner diameter side race ring member. Invented to realize the structure of the bearing unit.
- the combined seal ring with an encoder of the present invention is an annular space that exists between the outer peripheral surface of the inner diameter side race ring member that rotates during use and the inner peripheral surface of the outer diameter side race ring member that does not rotate during use.
- a slinger externally fitted to the slinger, and an encoder supported and fixed to the slinger.
- the seal ring includes a cored bar and an elastic material having at least one seal lip attached to the entire circumference of the cored bar.
- the slinger is formed by bending a metal plate so as to have a substantially L-shaped cross section and is formed into an annular shape as a whole. And a rotating ring part that is bent radially outward from one axial end edge of the rotating cylindrical part.
- the encoder is made of a permanent magnet in which S poles and N poles are alternately arranged in the circumferential direction, and the whole is configured in a ring shape. Is supported and fixed to the side surface opposite to the side surface facing the.
- the inner peripheral surface of the rotating cylindrical portion includes a large diameter portion provided on one axial end side of the rotating cylindrical portion, and a small diameter portion provided on the remaining portion. Is a stepped cylindrical surface made continuous by a stepped portion.
- the encoder has no lip on its inner peripheral surface, and the molten permanent magnet is disposed in a state in which the slinger is disposed in the mold and a part of the mold is abutted against the stepped portion. It is assumed that the raw material ⁇ rubber mixed with a ferromagnetic material such as ferrite or a polymer material such as synthetic resin (for example, plastic) ⁇ is solidified and fixed to the slinger.
- the outer diameter of the outer peripheral surface of the inner diameter side race ring member for fitting and fixing the slinger is ⁇ D
- the inner diameter in the free state of the small diameter portion is ⁇ d1
- the encoder in the free state When the inner diameter is ⁇ d2, the relationship ⁇ d1 ⁇ ⁇ d2 ⁇ D is satisfied.
- the radial thickness (wall thickness) of the rotating cylindrical portion is set to the small diameter with respect to the axial direction. It is made smaller at the portion that matches the large diameter portion than the portion that matches the portion. Further, for example, as in the third aspect of the invention, at least a part of the inner circumferential surface of the encoder having the smallest inner diameter dimension is supported in the axial direction, and the encoder is supported in the rotating ring portion. It is located on the side farther from the fixed cylindrical part in the axial direction than the fixed side surface.
- the portion of the inner peripheral surface of the encoder having the smallest inner diameter dimension is a single cylindrical surface shape in which the inner diameter dimension ( ⁇ d2) does not change in the axial direction.
- the cylindrical surface portion is used.
- a rolling bearing unit with an encoder includes an inner diameter side bearing ring member (for example, a hub) having an inner ring raceway on an outer peripheral surface, an outer diameter side bearing ring member (for example, an outer ring) having an outer ring raceway on an inner peripheral surface, and the inner ring A plurality of rolling elements (eg, balls, cylindrical rollers, tapered rollers) provided between a raceway and the outer ring raceway, a peripheral surface of the inner diameter side raceway member, and the outer diameter side raceway ring member And a combination seal ring that closes the end opening of the annular space existing between the inner peripheral surface and the inner peripheral surface.
- the combined seal ring is the combined seal ring with an encoder according to any one of claims 1 to 4.
- the sealing performance of the fitting portion between the rotating cylindrical portion constituting the slinger and the outer peripheral surface of the inner diameter side race ring member is good.
- the inner peripheral surface of the rotating cylindrical portion constituting the slinger is a stepped portion between a large diameter portion provided at one axial end of the rotating cylindrical portion and a small diameter portion provided at the remaining portion.
- the stepped cylindrical surface is made continuous.
- this small diameter portion By elastically deforming the portion that matches the large diameter portion provided between the rotating ring portion and the rotating ring portion, it is possible to effectively prevent the influence of the expansion of the small diameter portion from being transmitted to the rotating ring portion.
- the rotating ring portion has a high rigidity in the radial direction because of its shape. Accordingly, since the encoder can be effectively prevented from expanding in diameter, the inner diameter dimension of the encoder can be maintained smaller than the outer diameter dimension of the outer peripheral surface of the inner diameter side race ring member to which the slinger is fitted and fixed. .
- the inner peripheral surface of the encoder can be brought into contact with the outer peripheral surface of the inner diameter side race ring member in a state where the entire periphery has a tightening allowance. Further, since an encoder made by solidifying a permanent magnet material is used, it is advantageous in increasing the tightening allowance. That is, the inner diameter dimension of the non-magnetized encoder after being taken out from the mold becomes smaller than the outer diameter dimension of the portion that forms the inner peripheral surface of the encoder in the inner surface of the mold as it solidifies.
- the margin can be increased even if the inner peripheral edge of the unmagnetized encoder is not deformed or the amount of deformation is kept small.
- the lip is not provided on the inner peripheral surface of the encoder, when the slinger is fitted and fixed to the inner ring-side raceway member, the inner diameter dimension is the smallest among the inner peripheral surfaces of the encoder. The adjacent portion including the formed portion is compressed in the radial direction by contact with the outer peripheral surface of the inner diameter side race ring member.
- the compressive force generated at the inner peripheral edge of the encoder in this way generates a greater compressive force than the compressive force generated based on the bending deformation of the lip. For this reason, even if the tightening allowance is small as compared with the case where the lip is provided, a sufficiently large tightening force can be generated by the inner peripheral surface of the encoder. As a result, according to the present invention, the sealing performance of the fitting portion between the rotating cylindrical portion constituting the slinger and the outer peripheral surface of the inner diameter side race ring member can be improved.
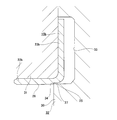
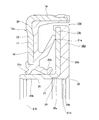
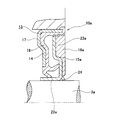
- the fragmentary sectional view which takes out and shows the combination seal ring with an encoder which shows the 1st example of embodiment of this invention.
- the enlarged view of the part corresponded to the A section of FIG.
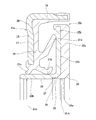
- the fragmentary sectional view which shows the state which set the slinger to the shaping
- the fragmentary sectional view which shows another example similarly.
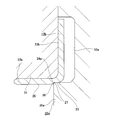
- the figure similar to FIG. 1 which shows the 2nd example of embodiment of this invention.
- the same figure as FIG. The figure similar to FIG. 1 which shows the 3rd example of embodiment of this invention.
- FIG. Sectional drawing which shows an example of the rolling bearing unit with an encoder known conventionally.
- the B section enlarged view of FIG. The fragmentary sectional view equivalent to FIG. 10 which shows the 2nd example of a conventional structure.
- FIGS. 1-10 A first example of the embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to FIGS.
- the feature of this example is the structure of the portion that improves the sealing performance of the fitting portion between the rotating cylindrical portion 22b of the slinger 15b and the outer peripheral surface of the hub 3 by using the inner peripheral edge portion of the encoder 16b. Since the configuration and operational effects of other parts, including the entire structure of the rolling bearing unit with encoder, are basically the same as those in the first example of the conventional structure described above, the same reference numerals are used for the equivalent parts. The overlapping illustrations and explanations will be omitted or simplified, and the following description will focus on the features of this example.
- the combined seal ring with an encoder 10b of this example is composed of a seal ring 14 and a slinger 15b that constitute the combined seal ring 13a, and an encoder 16b.
- the seal ring 14 includes a cored bar 17 and an elastic material 18.
- the metal core 17 is formed by bending a metal plate such as a mild steel plate by press working to form an annular shape with an L-shaped cross section.
- the cored bar 17 has a fixed cylindrical portion 19 that is fitted and fixed to the inner peripheral surface of the outer ring 2 that is the outer diameter side race ring member by an interference fit on the inner peripheral surface of the outer ring 2, and a diameter from the outer edge in the axial direction of the fixed cylindrical portion 19.
- a fixed ring portion 20 that is bent inward in the direction.
- the elastic member 18 is made of an elastomer such as rubber, and is attached over the entire circumference of the cored bar 17 and has three seal lips 21a to 21c.
- the slinger 15b is formed by bending a metal plate such as a ferritic stainless steel plate such as SUS430 by press working to form an annular shape with an L-shaped cross section.
- the slinger 15b includes a rotating cylindrical portion 22b that is fitted and fixed to the outer peripheral surface of the inner end portion in the axial direction of the hub 3 (the inner ring that constitutes the hub 3 together with the hub main body) that is an inner raceway member, and a rotating cylinder. And a rotating annular ring portion 23b that is bent radially outward from an axially inner end edge (corresponding to one axial end edge recited in the claims) of the portion 22b.
- the portions of the outer peripheral surface of the rotating cylindrical portion 22b and the outer surface in the axial direction of the rotating annular portion 23b that are in sliding contact with the tip edges of the seal lips 21a to 21c are smooth surfaces.
- the distal end edge of the outer seal lip 21a which is called the side lip, is arranged on the outermost radial direction and protrudes inward in the axial direction.
- 23b is slidably brought into contact with the outer circumferential surface of 23b.
- the leading edges of the remaining two intermediate and inner seal lips 21b and 21c are slidably contacted with the outer peripheral surface of the rotating cylindrical portion 22b over the entire circumference.
- the inner peripheral surface of the rotating cylindrical portion 22b is a stepped cylindrical surface.
- a large-diameter portion 25 is formed on the inner peripheral surface of the rotating cylindrical portion 22b on the inner end side in the axial direction of the rotating cylindrical portion 22b, and a smaller diameter is formed on the remaining portion (the axially outer end portion to the inner end portion).
- a portion 26 is formed.
- the large-diameter portion 25 and the small-diameter portion 26 are continued by an annular step portion 27.
- the radial thickness (wall thickness) of the rotating cylindrical portion 22b is made smaller at the portion (t) aligned with the large diameter portion 25 than at the portion (T) aligned with the small diameter portion 26 in the axial direction.
- a value 1 ⁇ 2 of the difference between the inner diameter dimension ( ⁇ d3) of the large diameter portion 25 and the inner diameter dimension ( ⁇ d1) of the small diameter portion 26 ⁇ ( ⁇ d3 ⁇ d1) / 2 ⁇ is set to about 1/10 to 1/4 of the wall thickness (T) of the metal plate (portion other than the large diameter portion 25) constituting the slinger 15b.
- the inner diameter dimension ( ⁇ d1) of the small diameter portion 26 of the rotating cylindrical portion 22b is set in the axial direction of the hub 3.
- the step portion 27 (and the large diameter portion 25) can be formed in advance when the slinger 15b is manufactured by press working, or when the encoder 16b is manufactured by using a molding die (32a) described later. Can also be processed.
- the encoder 16b is supported and fixed concentrically with the slinger 15b on the inner side surface in the axial direction of the rotating ring portion 23b of the slinger 15b (the side surface opposite to the side surface facing the seal lips 21a to 21c).
- the encoder 16b is made of a permanent magnet such as a rubber magnet or a plastic magnet.
- the encoder 16b has a ring shape as a whole, and is magnetized in the axial direction. The magnetization direction is changed alternately and at equal intervals in the circumferential direction. Therefore, the south pole and the north pole are alternately arranged at equal intervals in the circumferential direction on the inner side surface in the axial direction of the encoder 16b, which is the detected surface.
- the inner peripheral surface of the encoder 16b is formed in a single cylindrical surface cylindrical surface portion 28 formed in a range extending from the axial outer end portion to the inner end portion, and the axial inner end portion.
- the lip portion 24 (see FIG. 11) as in the case of the second example of the conventional structure described above is not provided.
- the axially inner half portion of the cylindrical surface portion 28 having the smallest inner diameter dimension is positioned axially inward from the axial inner surface of the rotating ring portion 23b. Yes.
- the inner diameter dimension ( ⁇ d2) of the cylindrical surface portion 28 in a free state before the slinger 15b is fitted and fixed to the hub 3 is smaller than the outer diameter dimension ( ⁇ D) of the inner end portion in the axial direction of the hub 3, and
- the inner diameter dimension ( ⁇ d1) of the small-diameter portion 26 is larger ( ⁇ d1 ⁇ d2 ⁇ D).
- the size of the interference when the slinger 15b is externally fixed to the hub 3 by interference fitting is about 0.15 to 0.3% of the outer diameter ( ⁇ D) of the hub 3 (0.997 ⁇ In many cases, ⁇ D ⁇ d1 ⁇ 0.9985 ⁇ ⁇ D) is set.
- the extent to which the inner diameter dimension ( ⁇ d2) of the encoder 16b is larger than the inner diameter dimension ( ⁇ d1) of the small diameter portion 26 (diameter difference ⁇ d2 ⁇ d1) is 0.05 to 0. 0 of the inner diameter dimension ( ⁇ d2) of the encoder 16b. It can be about 25% (0.995 ⁇ ⁇ d2 ⁇ d1 ⁇ 0.9975 ⁇ ⁇ d2).
- the encoder 16b having the above-described configuration is manufactured by using a molding die (die) 32 (32a) made of a metal and made up of a pair of upper die 30 (30a) and lower die 31.
- a molding die (die) 32 (32a) made of a metal and made up of a pair of upper die 30 (30a) and lower die 31.
- the slinger 15b is replaced with the annular cavity of the mold 32 as shown in FIG.
- the stepped portion 27 is disposed in a state where the corner portion 34 provided on the outer peripheral edge of the central portion of the upper mold 30 is abutted.
- the slinger 15b is replaced with the cavity 33a of the mold 32a as shown in FIG.
- the corner portion 34a provided at the outer peripheral edge of the central portion of the cemented carbide upper mold 30a is driven into the inner peripheral surface of the rotating cylindrical portion 22b, and the rotating cylindrical portion is plastically deformed.
- the step portion 27 and the large diameter portion 25 are formed on the inner peripheral surface of 22b (the remaining portion is the small diameter portion 26), and the corner portion 34a is abutted against the step portion 27.
- the reason why the corner portion 34 (34a) of the upper mold 30 (30a) abuts on the step portion 27 is to press the molten permanent magnet material into the cavity 33 (33a) as described below. This is to prevent the occurrence of flushing such that the permanent magnet material leaks to the portion of the inner peripheral surface of the rotating cylindrical portion 22b that does not need to be covered by the encoder 16b when it is fed in a state. As shown in FIG. 4, when the inner peripheral surface of the rotating cylindrical portion 22b of the slinger 15b is plastically deformed by the corner portion 34a of the upper mold 30a, the step portion of the inner peripheral surface of the rotating cylindrical portion 22b.
- a surplus part (burr) 36 protruding inward in the radial direction is formed in front of the portion 27 (axially outward). For this reason, in the case of this example, the plastic deformation amount (the radial dimension and the axial length of the part to be plastically deformed) so that the inner diameter dimension of the surplus portion 36 does not become smaller than the inner diameter dimension of the small diameter portion 26. Is regulated.
- a molten permanent magnet material ⁇ rubber or synthetic resin (plastic) or the like is placed in the cavity 33 (33a).
- a high-molecular material mixed with, for example, 80 to 90% by weight of a ferromagnetic material such as ferrite ⁇ is fed in a pressurized state.
- the magnetic strength after magnetization can be increased.
- the permanent magnet material is fixed to the inner side surface in the axial direction of the rotating ring portion 23b of the slinger 15b (adhered by vulcanization adhesion or injection molding).
- the slinger 15b and the non-magnetized encoder (solidified permanent magnet material) are extracted from the mold 32 (32a), and the non-magnetized encoder is subjected to an annealing process in which secondary heating is performed using a furnace such as an oven.
- a furnace such as an oven.
- the temperature is raised from room temperature to 150 to 200 ° C. over 3 to 4 hours, held at the increased temperature for 2 to 4 hours, and then cooled to room temperature over 3 to 5 hours).
- a synthetic resin when used as a permanent magnet material, crystallization is advanced to reduce residual stress, thereby obtaining dimensional stability and improving strength.
- the permanent magnet material is nitrile rubber
- the annealing process is less necessary than other types of rubber because most of the crosslinking is completed during vulcanization molding. Doing so increases cross-linking and improves strength. In the case of acrylic rubber or fluoro rubber, be sure to do it.
- the unmagnetized encoder is magnetized in the axial direction with the unmagnetized encoder facing a magnetized yoke (not shown).
- This kind of magnetizing work involves rotating the non-magnetized encoder as a magnetized yoke in addition to a circular magnet that simultaneously magnetizes (performs one-shot magnetization) the entire surface to be detected of the non-magnetized encoder.
- a rotary magnetizing type that sequentially magnetizes can also be used.
- an annular permanent magnet in which S poles and N poles are alternately arranged at equal intervals over the circumferential direction on the inner side surface in the axial direction, which is the detected surface.
- a manufactured encoder 16b is obtained.
- the encoder combined seal ring 10a of the present example having the above-described configuration is configured such that the fixed cylindrical portion 19 of the core metal 17 is fitted and fixed to the outer ring 2 that does not rotate even during use, and the rotary cylindrical portion 22b of the slinger 15b
- the small-diameter portion 26 is externally fixed to the hub 3 that rotates during use. In this state, the tip edges of the seal lips 21a to 21c are brought into sliding contact with the entire surface of the slinger 15b so as to close the axial inner end opening of the annular space 8 (see FIG. 9).
- the sealing performance of the fitting portion between the rotating cylindrical portion 22b of the slinger 15b and the outer peripheral surface of the hub 3 can be improved in a state where the combined seal ring with encoder 10a is assembled as described above. That is, in the case of this example, the inner peripheral surface of the rotating cylindrical portion 22b of the slinger 15b is a stepped cylindrical surface in which the large diameter portion 25 and the small diameter portion 26 are continuous by the step portion 27. For this reason, when the small diameter portion 26 is externally fixed to the outer peripheral surface of the hub 3 by an interference fit, even when the portion aligned with the small diameter portion 26 in the axial direction is elastically expanded, the small diameter portion 26 rotates.
- a portion having a smaller radial diameter than a portion matching the small-diameter portion 26 provided between the annular portion 23b and a portion matching the large-diameter portion 25 is elastically deformed, thereby reducing the small-diameter portion. It is possible to effectively prevent the influence of the 26 diameter expansion from being transmitted to the rotating ring portion 23b. Further, the rotating ring portion 23b has high radial rigidity due to its shape. Accordingly, since the encoder 16b can be effectively prevented from expanding in diameter, the inner diameter dimension of the encoder 16b can be kept smaller than the outer diameter dimension of the outer peripheral surface of the hub 3 where the slinger 15b is fitted and fixed.
- the axially inner half portion of the cylindrical surface portion 28 is positioned axially inward from the axially inner side surface of the rotating ring portion 23b. Since the axial distance to the inner half of the axial direction 28 is increased, the influence of the diameter expansion of the small diameter portion 26 can hardly be transmitted to the inner half of the cylindrical surface portion 28. For this reason, according to the structure of this example, the cylindrical surface portion 28 of the inner peripheral surface of the encoder 16b can be brought into contact with the outer peripheral surface of the hub 3 in a state of having a tightening margin on the entire periphery (particularly, In the case of this example, the tightening allowance of the inner half of the cylindrical surface portion 28 is larger than the allowance of the outer half of the axial direction).
- the encoder 16b is made by solidifying a permanent magnet material, it is advantageous in increasing the tightening allowance. That is, the inner diameter of the unmagnetized encoder after being taken out from the mold 32 (32a) is outside the portion of the inner surface of the mold 32 (32a) that forms the inner peripheral surface of the encoder 16b as the solidification occurs. It becomes smaller than the diameter dimension. Therefore, when the slinger 15b and the non-magnetized encoder are extracted from the mold 32 (32a), the inner margin of the non-magnetized encoder is not deformed or even if the deformation amount is kept small. Can be increased.
- rubber or synthetic resin which is a permanent magnet material
- rubber or synthetic resin which is a permanent magnet material
- the inner diameter is Although it is reduced by about 0.5 to 1%, the reduction ratio of the inner diameter is small in the case of containing about 80 to 90% by weight of a magnetic material and fixed to the slinger 15b. For this reason, the inner diameter dimension of the encoder 16b does not become smaller than the inner diameter dimension of the small diameter portion 26 (the relationship of ⁇ d1 ⁇ d2 is maintained).
- the tightening allowance can be further increased.
- the sealing performance of the fitting portion between the rotating cylindrical portion 22b of the slinger 15b and the outer peripheral surface of the hub 3 can be improved.
- Other configurations and operational effects are the same as those of the first example of the conventional structure described above.
- FIGS. 1-10 A second example of the embodiment of the present invention will be described with reference to FIGS.
- This example is suitable for the case where the content of the magnetic material is small (for example, 50 to 70% by weight) as compared with the case of the first example of the above-described embodiment as a permanent magnet material for manufacturing the encoder 16c.
- the inner peripheral surface of the encoder 16c is inclined in a direction in which the inner diameter dimension becomes smaller toward the inner side in the axial direction, and a partially conical cylindrical surface portion 35 provided at the outer end portion in the axial direction, and an intermediate portion in the axial direction. It is composed of a cylindrical surface portion 28a provided and a chamfered portion 29 provided at the inner end in the axial direction.
- the inner half in the axial direction of the cylindrical surface portion 28a having the smallest inner diameter dimension ( ⁇ d2) is positioned more inward in the axial direction than the inner side surface in the axial direction of the rotating ring portion 23b of the slinger 15b.
- the inner diameter dimension ( ⁇ d2) of the cylindrical surface portion 28a is regulated to be equal to or larger than the inner diameter dimension ( ⁇ d1) of the small diameter portion 26 of the rotating cylindrical portion 22b of the slinger 15b ( ⁇ d2 ⁇ ⁇ d1, in the illustrated example). ⁇ d2 ⁇ d1).
- the inner diameter of the encoder 16c (cylindrical surface portion 28a) is made smaller than that in the first example of the embodiment, so A large fastening margin can be secured, and the sealing performance of the fitting portion can be further improved.
- the inner peripheral edge portion (the portion corresponding to the cylindrical surface portion 28a) of the non-magnetized encoder is slightly deformed (elastic deformation).
- the content of the magnetic material in the permanent magnet material is kept low (easily elastically deformed), and the forming die (upper die) is pulled out by the partially conical cylindrical surface portion 35 (FIG. 5). , The right side of 6), such work can be performed substantially without any problem.
- the content of the magnetic material is small (for example, 50 to 70% by weight) as a permanent magnet material for manufacturing the encoder 16d.
- the structure is suitable for the case.
- the inner peripheral surface of the encoder 16d is inclined in a direction in which the inner diameter dimension becomes smaller toward the inner side in the axial direction, and is provided in a partially conical cylindrical surface portion 35a provided in the outer end portion in the axial direction, and in an intermediate portion in the axial direction. It is comprised from the cylindrical surface part 28b and the chamfering part 29 provided in the axial direction inner end part.
- the axial dimension of the partial conical cylindrical surface portion 35a is increased (the inclination angle is reduced) compared to the case of the second example of the embodiment, whereby the entire cylindrical surface portion 28b is It is located axially inward from the axial inner side surface of the rotating ring portion 23b of 15b.
- the cylindrical surface portion 28b of the inner peripheral surface of the encoder 16d is fastened to the outer peripheral surface of the hub 3 (see FIGS. 1 and 9) in the assembled state of the combined seal ring with encoder 10d. It is made to contact
- the small diameter portion 26 of the rotating cylindrical portion 22b of the slinger 15b is fitted and fixed to the hub 3 with an interference fit, thereby matching the small diameter portion 26 in the axial direction.
- the influence of the expansion of the small-diameter portion 26 is affected by the large axial distance from the small-diameter portion 26 to the cylindrical surface portion 28b and the presence of the highly rigid rotating ring portion 23b.
- a larger allowance can be secured for the cylindrical surface portion 28b with respect to the hub 3, and the sealing performance of the fitting portion can be further improved.
- the number of seal lips provided on the elastic material may be one (preferably only the side lips that are liable to cause change in tightening allowance), or two or three as in each example, Or more than that.
- the rolling bearing unit with an encoder of the present invention is not limited to a wheel bearing rolling bearing unit for supporting a vehicle wheel on a suspension device, and it is necessary to detect the rotational speed of a rotating member such as a machine tool or an industrial machine.
- a rolling bearing unit (rolling bearing) that constitutes a rotation support portion of various mechanical devices is also an object.
- the portion having the smallest inner diameter dimension among the inner peripheral surfaces of the encoder is configured by a single cylindrical surface cylindrical surface portion has been described. The shape of the part can be implemented without being limited to the cylindrical surface.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Rolling Contact Bearings (AREA)
- Sealing Of Bearings (AREA)
Abstract
スリンガ(15b)は、断面略L字形で、回転円筒部(22b)と、回転円筒部(22b)の軸方向内端縁から径方向外方に折れ曲がった回転円輪部(23b)と、を有する。回転円筒部(22b)の内周面を、回転円輪部(23b)に近い側の端部に設けた大径部(25)と、残部の小径部(26)と、を段差部(27)により連続させた段付円筒面とする。回転円輪部(23b)に支持するエンコーダ(16b)を、成形型を段差部(27)に突き当てた状態で、溶融した永久磁石素材を凝固させて造る。ハブ(3)の外径寸法をφDとし、小径部(26)の自由状態での内径寸法をφd1とし、エンコーダ(16b)の自由状態での内径寸法をφd2とした場合に、φd1≦φd2<φDの関係を満たす。
Description
この発明は、各種機械装置の回転支持部に組み込む転がり軸受の開口端部を塞ぐと共に、この転がり軸受に支持される回転部材の回転速度を検出する為のエンコーダ付組み合わせシールリング、及び、このエンコーダ付組み合わせシールリングを備えたエンコーダ付転がり軸受ユニットの改良に関する。具体的には、スリンガを構成する回転円筒部と内径側軌道輪部材の外周面との嵌合部の密封性を確保できる構造を実現するものである。各種機械装置の回転支持部としては、例えば車両(自動車)の車輪を懸架装置に支持する為の車輪支持用転がり軸受ユニット等が挙げられる。
自動車の車輪を懸架装置に対して回転自在に支持する為に、図9~10に示す様な、エンコーダ付転がり軸受ユニット1が従来から広く知られている(例えば特許文献1、2参照)。エンコーダ付転がり軸受ユニット1は、外径側軌道輪部材である外輪2と、内径側軌道輪部材であるハブ3とを、互いに同心に配置している。そして、外輪2の内周面に設けた複列の外輪軌道4、4と、ハブ3の外周面に設けた複列の内輪軌道5、5との間に、それぞれが転動体である玉6、6を、両列毎に複数個ずつ配置している。各玉6、6は、それぞれ保持器7、7により、転動自在に保持されている。この様な構成により、懸架装置に支持固定される外輪2の内径側にハブ3を、回転自在に支持している。
外輪2の内周面とハブ3の外周面との間で、各玉6、6を設置した環状空間8の軸方向両端開口は、それぞれシールリング9とエンコーダ付組み合わせシールリング10とにより、全周に亙り塞がれている。シールリング9は、金属板製の芯金11と弾性材製の複数本のシールリップ12とを備える。そして、芯金11を外輪2の軸方向外端部(軸方向に関して外とは、自動車への組み付け状態で車体の幅方向外側で、各図の左側を言う。これに対して、各図の右側である、幅方向中央側を、軸方向に関して内と言う。本明細書全体で同じ。)に締り嵌めで内嵌した状態で、各シールリップ12の先端縁をハブ3の軸方向中間部外周面に、全周に亙り摺接させている。
エンコーダ付組み合わせシールリング10は、組み合わせシールリング13を構成するシールリング14及びスリンガ15と、エンコーダ16とから成る。シールリング14は、断面L字形で全体が円環状の芯金17と、弾性材18とから成る。芯金17は、軟鋼板等の金属板により、断面L字形で全体を円環状に形成して成る。芯金17は、外輪2の軸方向内端部内周面に締り嵌めにより内嵌固定される固定円筒部19と、固定円筒部19の軸方向外端縁から、ハブ3の外周面に向け、径方向内方に折れ曲がった固定円輪部20とを有する。又、弾性材18は、芯金17の全周に亙って添着されたもので、1乃至複数本(図示の例では3本)のシールリップ21a~21cを有する。一般的には、弾性材18は、ゴム製とし、芯金17に対し焼き付けにより結合している。
一方、スリンガ15は、ハブ3(ハブ本体と共にこのハブ3を構成する内輪)の軸方向内端部外周面に締り嵌めにより外嵌固定される回転円筒部22と、回転円筒部22の軸方向内端縁から、外輪2の内周面に向け、径方向外方に折れ曲がった回転円輪部23とを備える。又、スリンガ15は、回転円筒部22の外周面及びこの回転円輪部23の軸方向外側面で、シールリップ21a~21cの先端縁を摺接させる部分を、それぞれ平滑面としている。
エンコーダ16は、ゴム磁石、プラスチック磁石等の永久磁石製であり、軸方向に着磁している。着磁方向は、円周方向に関して交互に且つ等間隔で変化させている。従って、被検出面であるエンコーダ16の軸方向内側面には、S極とN極とが、円周方向に関して交互に且つ等間隔で配置されている。この様なエンコーダ16の被検出面には、センサの検出部を対向させて、ハブ3と共に回転する車輪の回転速度を測定可能とする。そして、測定した車輪の回転速度を表す信号を、アンチロックブレーキシステム(ABS)やトラクションコントロールシステム(TCS)等、車両の走行安定化装置の制御に利用する。
上述した様な従来構造の第1例の場合、エンコーダ付組み合わせシールリング10は、塵芥等の比較的大きな異物の進入は有効に防止する事ができるが、雨水や泥水等の進入を十分に防ぐ事は難しい。即ち、エンコーダ付組み合わせシールリング10は、スリンガ15の回転円筒部22を、ハブ3の軸方向内端部外周面に外嵌固定しているだけであり、この嵌合部を密封する構造を設けていない。スリンガ15の回転円筒部22をハブ3の軸方向内端部外周面に締り嵌めで外嵌した状態でも、この嵌合部に微小隙間が生じる事は避けられない。この微小隙間に水分が侵入すると、両周面のうちの少なくとも一方の周面が腐食する事により当該部分の体積が増加し、この微小隙間が拡がる。そして、この拡がった隙間を通じて環状空間8内に水分が侵入する可能性がある。環状空間8内への水分の侵入は、グリースの劣化による軸受ユニットの耐久性低下の原因となり、好ましくない。この様に、従来構造のエンコーダ付組み合わせシールリング10によっては、嵌合部の密封性を十分に確保する事は難しい。
上述の様な雨水等の環状空間内への侵入を防ぐ事を目的として、例えば特許文献3には、図11に示す様なエンコーダ付組み合わせシールリング10aを使用する事が提案されている。この従来構造の第2例では、エンコーダ16aの内周縁部に、スリンガ15aの回転円筒部22aの内径寸法よりも小さな内径寸法を有するリップ部24を設けている。そして、スリンガ15aの回転円筒部22aをハブ3aに外嵌固定した状態で、リップ部24をこのハブ3aの外周面に弾性的に当接させている。
但し、上述した様な従来構造の第2例の場合にも、次の様な理由から、スリンガ15aの回転円筒部22aとハブ3aの外周面との嵌合部の密封性を十分に確保する事は難しい。即ち、リップ部24を構成する材料は、エンコーダ16aと同じであり、十分な磁性を確保する為に、フェライト等の強磁性材を多量(例えば80~90重量%)に含有している為、一般的なシール用の材料に比べて弾性変形しにくく脆い。一方、エンコーダ16aは、スリンガ15aを成形型(金型)内に配置し、永久磁石となるべき永久磁石素材(強磁性材を含有したゴム或いは合成樹脂等の高分子材料)をスリンガ15aに固定(加硫固定或いは射出成形により固定)する事により造られる。但し、この様にしてエンコーダ16aを造る場合には、成形型からスリンガ15a及び凝固した永久磁石素材(未着磁のエンコーダ)を抜き出す際に、リップ部24となるべき部分を、締め代の大きさに応じて大きく変形させなければならない(無理抜きしなければならない)。そして、リップ部24となるべき部分をこの様に大きく変形させる事は困難である為、このリップ部24の締め代を大きく確保する事は難しくなる。又、スリンガ15aの回転円筒部22aをハブ3aに締り嵌めで外嵌固定した場合、回転円筒部22aは弾性的に拡径するが、回転円筒部22aと回転円輪部23aとは連続する状態で設けられている為、回転円筒部22aの拡径の影響は、回転円輪部23aに伝わり易くなる。この為、回転円輪部23aに支持固定されたエンコーダ16aも拡径し易くなり、リップ部24の締め代の減少量が大きくなる。更に、リップ部24による密封構造の場合、自身の曲げ変形量の大きさが緊迫力の大きさに影響する為、締め代を大きく確保して曲げ変形量を増やさなければ、十分な緊迫力を確保できない。しかし、リップ部24を構成する材料が弾性変形しにくい為、たとえ締め代を確保できたとしても、十分な緊迫力を確保する事は難しい。この様に、従来構造の第2例の場合にも、スリンガ15aの回転円筒部22aとハブ3aの外周面との嵌合部の密封性を十分に確保する事は難しい。
本発明は、上述の様な事情に鑑みて、スリンガを構成する回転円筒部と内径側軌道輪部材の外周面との嵌合部の密封性を良好にできる、エンコーダ付シールリング及びエンコーダ付転がり軸受ユニットの構造を実現すべく発明したものである。
本発明のエンコーダ付組み合わせシールリングは、使用時に回転する内径側軌道輪部材の外周面と、使用時にも回転しない外径側軌道輪部材の内周面との間部分に存在する、環状空間の端部開口を塞ぐと共に、前記内径側軌道輪部材の回転速度を検出する為に使用するものであり、前記外径側軌道輪部材に内嵌固定されるシールリングと、前記内径側軌道輪部材に外嵌固定されるスリンガと、前記スリンガに支持固定されるエンコーダとを備える。
前記シールリングは、芯金と、前記芯金の全周に亙って添着された、少なくとも1本のシールリップを有する弾性材とを備える。
又、前記スリンガは、金属板を曲げ形成する事により、断面略L字形で全体を円環状に構成したものであり、前記内径側軌道輪部材に締り嵌めで外嵌固定される回転円筒部と、前記回転円筒部の軸方向一端縁から径方向外方に向けて折れ曲がった回転円輪部とを備える。
又、前記エンコーダは、円周方向に亙ってS極とN極とを交互に配置した永久磁石製で、全体を円輪状に構成したものであり、前記回転円輪部のうち前記シールリップと対向する側面とは反対側の側面に支持固定されている。
前記シールリングは、芯金と、前記芯金の全周に亙って添着された、少なくとも1本のシールリップを有する弾性材とを備える。
又、前記スリンガは、金属板を曲げ形成する事により、断面略L字形で全体を円環状に構成したものであり、前記内径側軌道輪部材に締り嵌めで外嵌固定される回転円筒部と、前記回転円筒部の軸方向一端縁から径方向外方に向けて折れ曲がった回転円輪部とを備える。
又、前記エンコーダは、円周方向に亙ってS極とN極とを交互に配置した永久磁石製で、全体を円輪状に構成したものであり、前記回転円輪部のうち前記シールリップと対向する側面とは反対側の側面に支持固定されている。
特に本発明のエンコーダ付組み合わせシールリングの場合には、前記回転円筒部の内周面を、前記回転円筒部の軸方向一端側に設けられた大径部と、残部に設けられた小径部とを、段差部により連続させた段付円筒面としている。
又、前記エンコーダを、その内周面にリップを有しておらず、前記スリンガを成形型内に、前記成形型の一部を前記段差部に突き当てて配置した状態で、溶融した永久磁石素材{フェライト等の強磁性材を混入したゴム或いは合成樹脂(例えばプラスチック)等の高分子材料}を凝固させ前記スリンガに固着して造られたものとしている。
更に、前記内径側軌道輪部材の外周面のうち前記スリンガを外嵌固定する部分の外径寸法をφDとし、前記小径部の自由状態での内径寸法をφd1とし、前記エンコーダの自由状態での内径寸法をφd2とした場合に、φd1≦φd2<φDの関係を満たしている。
又、前記エンコーダを、その内周面にリップを有しておらず、前記スリンガを成形型内に、前記成形型の一部を前記段差部に突き当てて配置した状態で、溶融した永久磁石素材{フェライト等の強磁性材を混入したゴム或いは合成樹脂(例えばプラスチック)等の高分子材料}を凝固させ前記スリンガに固着して造られたものとしている。
更に、前記内径側軌道輪部材の外周面のうち前記スリンガを外嵌固定する部分の外径寸法をφDとし、前記小径部の自由状態での内径寸法をφd1とし、前記エンコーダの自由状態での内径寸法をφd2とした場合に、φd1≦φd2<φDの関係を満たしている。
又、本発明のエンコーダ付組み合わせシールリングを実施する場合には、例えば請求項2に記載した発明の様に、前記回転円筒部の径方向厚さ寸法(肉厚)を、軸方向に関して前記小径部に整合する部分に比べて前記大径部に整合する部分で小さくする。
又、例えば請求項3に記載した発明の様に、前記エンコーダの内周面のうちで最も内径寸法が小さくなった部分の少なくとも軸方向一部を、前記回転円輪部のうち前記エンコーダを支持固定した側面よりも、軸方向に関して前記固定円筒部から離れた側に位置させる。
更に、例えば請求項4に記載した発明の様に、前記エンコーダの内周面のうちで最も内径寸法が小さくなった部分を、内径寸法(φd2)が軸方向に亙り変化しない単一円筒面状の円筒面部により構成する。
又、例えば請求項3に記載した発明の様に、前記エンコーダの内周面のうちで最も内径寸法が小さくなった部分の少なくとも軸方向一部を、前記回転円輪部のうち前記エンコーダを支持固定した側面よりも、軸方向に関して前記固定円筒部から離れた側に位置させる。
更に、例えば請求項4に記載した発明の様に、前記エンコーダの内周面のうちで最も内径寸法が小さくなった部分を、内径寸法(φd2)が軸方向に亙り変化しない単一円筒面状の円筒面部により構成する。
本発明のエンコーダ付転がり軸受ユニットは、外周面に内輪軌道を有する内径側軌道輪部材(例えばハブ)と、内周面に外輪軌道を有する外径側軌道輪部材(例えば外輪)と、前記内輪軌道と前記外輪軌道との間に転動自在に設けられた複数個の転動体(例えば玉、円筒ころ、円すいころ)と、前記内径側軌道輪部材の外周面と前記外径側軌道輪部材の内周面との間に存在する環状空間の端部開口を塞ぐ組み合わせシールリングとを備える。
そして特に、本発明のエンコーダ付転がり軸受ユニットの場合には、前記組み合わせシールリングを、請求項1~4のうちの何れか1項に記載したエンコーダ付組み合わせシールリングとしている。
そして特に、本発明のエンコーダ付転がり軸受ユニットの場合には、前記組み合わせシールリングを、請求項1~4のうちの何れか1項に記載したエンコーダ付組み合わせシールリングとしている。
上述の様に構成する本発明のエンコーダ付組み合わせシールリング及びエンコーダ付転がり軸受ユニットによれば、スリンガを構成する回転円筒部と内径側軌道輪部材の外周面との嵌合部の密封性を良好にできる。
即ち、本発明の場合には、スリンガを構成する回転円筒部の内周面を、この回転円筒部の軸方向一端側に設けられた大径部と残部に設けられた小径部とを段差部により連続させた段付円筒面としている。この為、回転円筒部のうちの小径部を、内径側軌道輪部材に締り嵌めで外嵌固定する事で、この小径部に整合する部分が弾性的に拡径した場合にも、この小径部と回転円輪部との間部分に設けられた大径部に整合する部分を弾性変形させる事で、この小径部の拡径の影響が回転円輪部にまで伝わる事を有効に防止できる。又、この回転円輪部は、その形状故に径方向に関する剛性は高い。従って、エンコーダが拡径する事を有効に防止できる為、このエンコーダの内径寸法を、内径側軌道輪部材の外周面のうちスリンガを外嵌固定する部分の外径寸法よりも小さい状態に維持できる。この為、本発明によれば、エンコーダの内周面を内径側軌道輪部材の外周面に対し全周に亙り締め代を有する状態で当接させる事ができる。
又、エンコーダとして、永久磁石素材を凝固させる事により造られたものを使用している為、締め代を増やす上で有利になる。即ち、成形型から取り出した後の未着磁エンコーダの内径寸法は、凝固に伴い、この成形型の内面のうちで、エンコーダの内周面を形成する部分の外径寸法よりも小さくなる。従って、成形型からスリンガ及び未着磁エンコーダを抜き出す際に、この未着磁エンコーダの内周縁部を、変形させないか、或いは、変形量を小さく抑えた場合にも、締め代を増やす事ができる。
更に、本発明の場合には、エンコーダの内周面にリップを設けていない為、スリンガを内径側軌道輪部材に外嵌固定した際に、エンコーダの内周面のうち、最も内径寸法が小さくなった部分を含むその近傍部分が、内径側軌道輪部材の外周面との当接により径方向に圧縮される。そして、この様にしてエンコーダの内周縁部に発生する圧縮力は、リップの曲げ変形に基づき発生する緊迫力に比べて大きな緊迫力を発生させる。この為、リップを設けた場合に比べて締め代の大きさが小さくても、エンコーダの内周面によって十分に大きな緊迫力を発生させる事ができる。
この結果、本発明によれば、スリンガを構成する回転円筒部と内径側軌道輪部材の外周面との嵌合部の密封性を良好にできる。
即ち、本発明の場合には、スリンガを構成する回転円筒部の内周面を、この回転円筒部の軸方向一端側に設けられた大径部と残部に設けられた小径部とを段差部により連続させた段付円筒面としている。この為、回転円筒部のうちの小径部を、内径側軌道輪部材に締り嵌めで外嵌固定する事で、この小径部に整合する部分が弾性的に拡径した場合にも、この小径部と回転円輪部との間部分に設けられた大径部に整合する部分を弾性変形させる事で、この小径部の拡径の影響が回転円輪部にまで伝わる事を有効に防止できる。又、この回転円輪部は、その形状故に径方向に関する剛性は高い。従って、エンコーダが拡径する事を有効に防止できる為、このエンコーダの内径寸法を、内径側軌道輪部材の外周面のうちスリンガを外嵌固定する部分の外径寸法よりも小さい状態に維持できる。この為、本発明によれば、エンコーダの内周面を内径側軌道輪部材の外周面に対し全周に亙り締め代を有する状態で当接させる事ができる。
又、エンコーダとして、永久磁石素材を凝固させる事により造られたものを使用している為、締め代を増やす上で有利になる。即ち、成形型から取り出した後の未着磁エンコーダの内径寸法は、凝固に伴い、この成形型の内面のうちで、エンコーダの内周面を形成する部分の外径寸法よりも小さくなる。従って、成形型からスリンガ及び未着磁エンコーダを抜き出す際に、この未着磁エンコーダの内周縁部を、変形させないか、或いは、変形量を小さく抑えた場合にも、締め代を増やす事ができる。
更に、本発明の場合には、エンコーダの内周面にリップを設けていない為、スリンガを内径側軌道輪部材に外嵌固定した際に、エンコーダの内周面のうち、最も内径寸法が小さくなった部分を含むその近傍部分が、内径側軌道輪部材の外周面との当接により径方向に圧縮される。そして、この様にしてエンコーダの内周縁部に発生する圧縮力は、リップの曲げ変形に基づき発生する緊迫力に比べて大きな緊迫力を発生させる。この為、リップを設けた場合に比べて締め代の大きさが小さくても、エンコーダの内周面によって十分に大きな緊迫力を発生させる事ができる。
この結果、本発明によれば、スリンガを構成する回転円筒部と内径側軌道輪部材の外周面との嵌合部の密封性を良好にできる。
[実施の形態の第1例]
本発明の実施の形態の第1例に就いて、図1~4により説明する。尚、本例の特徴は、スリンガ15bの回転円筒部22bとハブ3の外周面との嵌合部の密封性を、エンコーダ16bの内周縁部を利用して向上させる部分の構造にある。エンコーダ付転がり軸受ユニットの全体構造を含め、その他の部分の構成及び作用効果に就いては、前述した従来構造の第1例の場合と基本的には同じであるから、同等部分には同一符号を付して重複する図示並びに説明は省略若しくは簡略にし、以下、本例の特徴部分を中心に説明する。
本発明の実施の形態の第1例に就いて、図1~4により説明する。尚、本例の特徴は、スリンガ15bの回転円筒部22bとハブ3の外周面との嵌合部の密封性を、エンコーダ16bの内周縁部を利用して向上させる部分の構造にある。エンコーダ付転がり軸受ユニットの全体構造を含め、その他の部分の構成及び作用効果に就いては、前述した従来構造の第1例の場合と基本的には同じであるから、同等部分には同一符号を付して重複する図示並びに説明は省略若しくは簡略にし、以下、本例の特徴部分を中心に説明する。
本例のエンコーダ付組み合わせシールリング10bは、組み合わせシールリング13aを構成するシールリング14及びスリンガ15bと、エンコーダ16bとから成る。シールリング14は、芯金17と弾性材18とを備える。芯金17は、軟鋼板等の金属板をプレス加工により曲げ成形して、断面L字形で全体を円環状としたものである。芯金17は、外径側軌道輪部材である外輪2の軸方向内端部内周面に締り嵌めにより内嵌固定される固定円筒部19と、固定円筒部19の軸方向外端縁から径方向内方に向けて折れ曲がった固定円輪部20とを有する。又、弾性材18は、ゴムの如きエラストマー製で、芯金17の全周に亙って添着されており、3本のシールリップ21a~21cを有している。
スリンガ15bは、SUS430等のフェライト系ステンレス鋼板等の金属板をプレス加工により曲げ成形して、断面L字形で全体を円環状としたものである。スリンガ15bは、内径側軌道輪部材であるハブ3(ハブ本体と共にこのハブ3を構成する内輪)の軸方向内端部外周面に締り嵌めにより外嵌固定される回転円筒部22bと、回転円筒部22bの軸方向内端縁(特許請求の範囲に記載した軸方向一端縁に相当)から径方向外方に向けて折れ曲がった回転円輪部23bとを備える。又、スリンガ15bのうち、回転円筒部22bの外周面及び回転円輪部23bの軸方向外側面で、各シールリップ21a~21cの先端縁を摺接させる部分を、それぞれ平滑面としている。そして、各シールリップ21a~21cのうちで、最も径方向外側に配置され、軸方向内方に突出する状態で設けられた、サイドリップと呼ばれる外側シールリップ21aの先端縁を、回転円輪部23bの軸方向外側面に全周に亙り摺接させている。これに対して、残り2本の中間及び内側シールリップ21b、21cの先端縁を、回転円筒部22bの外周面に全周に亙り摺接させている。
特に本例の場合には、回転円筒部22bの内周面を段付円筒面としている。この為に、回転円筒部22bの内周面のうち、回転円筒部22bの軸方向内端側に大径部25を形成すると共に、残部(軸方向外端部乃至内端寄り部分)に小径部26を形成している。そして、これら大径部25と小径部26とを円輪状の段差部27により連続させている。又、回転円筒部22bの径方向厚さ寸法(肉厚)を、軸方向に関して小径部26に整合する部分(T)に比べて大径部25に整合する部分(t)で小さくしている(T>t)。又、回転円筒部22bをハブ3に外嵌固定する以前の自由状態で、大径部25の内径寸法(φd3)と小径部26の内径寸法(φd1)との差の1/2の値{(φd3-φd1)/2}を、スリンガ15bを構成する金属板(大径部25以外の部分)の肉厚(T)のおよそ1/10~1/4程度としている。又、本例の場合には、スリンガ15bをハブ3に対して締り嵌めで内嵌固定する為、回転円筒部22bのうちの小径部26の内径寸法(φd1)を、ハブ3の軸方向内端部の外径寸法(φD)よりも小さくしている(φd1<φD)。尚、段差部27(及び大径部25)は、スリンガ15bをプレス加工により造る際に予め形成しておく事もできるし、後述する成形型(32a)を利用してエンコーダ16bを製造する際に加工する事もできる。
エンコーダ16bは、スリンガ15bの回転円輪部23bの軸方向内側面(シールリップ21a~21cと対向する側面とは反対側の側面)に、スリンガ15bと同心に支持固定されている。又、エンコーダ16bは、ゴム磁石製又はプラスチック磁石製等の永久磁石製で、全体を円輪状に構成しており、軸方向に着磁されている。着磁方向は、円周方向に関して交互に且つ等間隔で変化させている。従って、被検出面であるエンコーダ16bの軸方向内側面には、S極とN極とが円周方向に関して交互に且つ等間隔で配置されている。
特に本例の場合には、エンコーダ16bの内周面を、軸方向外端部乃至内端寄り部分に亙る範囲に形成された単一円筒面状の円筒面部28と、軸方向内端部に形成された部分円すい筒面である面取り部29とから構成しており、前述した従来構造の第2例の場合の様なリップ部24(図11参照)は設けていない。又、エンコーダ16bの内周面において、最も内径寸法が小さくなった円筒面部28のうちの軸方向内半部を、回転円輪部23bの軸方向内側面よりも軸方向内方に位置させている。又、スリンガ15bをハブ3に外嵌固定する以前の自由状態での、円筒面部28の内径寸法(φd2)を、ハブ3の軸方向内端部の外径寸法(φD)よりも小さく、且つ、小径部26の内径寸法(φd1)よりも大きくしている(φd1<φd2<φD)。一般的に、スリンガ15bをハブ3に締り嵌めで外嵌固定する際の締め代の大きさは、ハブ3の外径寸法(φD)の0.15~0.3%程度(0.997×φD<φd1<0.9985×φD)に設定する場合が多い。この為、エンコーダ16bの内径寸法(φd2)を小径部26の内径寸法(φd1)よりも大きくする程度(径差φd2-φd1)は、エンコーダ16bの内径寸法(φd2)の0.05~0.25%程度(0.995×φd2<φd1<0.9975×φd2)とする事ができる。
上述の様な構成を有するエンコーダ16bは、それぞれが金属製で1対の上型30(30a)と下型31とから成る成形型(金型)32(32a)を利用して製造する。特に、回転円筒部22bの内周面に予め段差部27(及び大径部25)を形成している場合には、図3に示した様に、スリンガ15bを、成形型32の環状のキャビティ33内に、段差部27に上型30の中央部外周縁部に設けた角部34を突き当てた状態で配置する。これに対し、回転円筒部22bの内周面に段差部27(及び大径部25)を予め形成していない場合には、図4に示す様に、スリンガ15bを、成形型32aのキャビティ33a内にセットする際に、超硬製の上型30aの中央部外周縁部に設けた角部34aを回転円筒部22bの内周面に打ち込み、当該部分を塑性変形させる事で、回転円筒部22bの内周面に段差部27と大径部25を形成し(残部を小径部26とし)、段差部27に角部34aを突き当てる。この様に、この段差部27に上型30(30a)の角部34(34a)を突き当てる理由は、次述する様に、キャビティ33(33a)内に溶融した永久磁石素材を加圧した状態で送り込んだ際に、この永久磁石素材が、回転円筒部22bの内周面のうちでエンコーダ16bにより本来覆う必要のない部分にまで漏れ出すといった、フラッシングの発生を防止する為である。尚、図4に示した様に、スリンガ15bの回転円筒部22bの内周面を、上型30aの角部34aにより塑性変形させる場合には、回転円筒部22bの内周面のうち段差部27となる部分の前方(軸方向外方)に径方向内方に向けて突出した余肉部(バリ)36が形成される。この為、本例の場合には、余肉部36の内径寸法が、小径部26の内径寸法よりも小さくならない様に、塑性変形量(塑性変形させる部分の径方向寸法及び軸方向長さ)を規制している。
図3及び図4の何れの場合にも、キャビティ33(33a)にスリンガ15bを配置したならば、このキャビティ33(33a)内に、溶融した永久磁石素材{ゴム或いは合成樹脂(プラスチック)等の高分子材料中にフェライト等の強磁性材を例えば80~90重量%混入したもの}を加圧した状態で送り込む。この際、アキシアル方向に磁場を加えて、永久磁石素材中の磁性材を配向する事により、着磁後の磁気強度を高められる様にする。そして、この永久磁石素材を凝固させる事で、スリンガ15bの回転円輪部23bの軸方向内側面に固着させる(加硫接着或いは射出成形により接着させる)。
次いで、スリンガ15b及び未着磁エンコーダ(凝固した永久磁石素材)を、成形型32(32a)から抜き出し、この未着磁エンコーダに、オーブン等の炉を利用して二次加熱を行うアニーリング処理を施す(例えば室温から3~4時間かけて150~200℃まで昇温し、上昇した温度で2~4時間保持し、その後3~5時間かけて室温まで除冷する)。これにより、永久磁石素材としてゴムを使用している場合には、加硫を進行させて架橋を増やし、強度を向上させる。これに対し、永久磁石素材として合成樹脂を使用している場合には、結晶化を進め、残留応力を低減させて、寸法安定性を得ると共に強度を向上させる。尚、アニーリング処理は、例えば永久磁石素材がニトリルゴムである場合には、加硫成形時に架橋の大部分が完了する為、他の種類のゴムと比較して実施の必要性は低いが、実施する事で架橋を増やし強度の向上を図れる。アクリルゴムやフッ素ゴムの場合には、必ず実施するようにする。
アニーリング処理を施した後には、未着磁エンコーダを、図示しない着磁ヨークと対向させて、この未着磁エンコーダを軸方向に着磁する。この様な着磁作業は、着磁ヨークとして、未着磁エンコーダの被検出面を全周に亙り同時に着磁する(一発着磁を行う)円環状のもののほか、未着磁エンコーダを回転させながら、順次着磁を行う回転着磁式のものも使用できる。そして、この様な着磁作業により、被検出面である軸方向内側面に、円周方向に亙ってS極とN極とが交互に且つ等間隔で配置された、円輪状で永久磁石製のエンコーダ16bが得られる。
以上の様な構成を有する本例のエンコーダ付組み合わせシールリング10aは、芯金17の固定円筒部19を、使用時にも回転しない外輪2に内嵌固定し、スリンガ15bの回転円筒部22bのうちの小径部26を、使用時に回転するハブ3に外嵌固定する。そして、この状態で、各シールリップ21a~21cの先端縁を、スリンガ15bの表面に、それぞれ全周に亙り摺接させて、環状空間8(図9参照)の軸方向内端開口を塞ぐ。
特に本例の場合には、上述した様にエンコーダ付組み合わせシールリング10aを組み付けた状態で、スリンガ15bの回転円筒部22bとハブ3の外周面との嵌合部の密封性を良好にできる。
即ち、本例の場合には、スリンガ15bの回転円筒部22bの内周面を、大径部25と小径部26とを段差部27により連続させた段付円筒面としている。この為、小径部26を、ハブ3の外周面に締り嵌めで外嵌固定する事で、軸方向に関して小径部26に整合する部分が弾性的に拡径した場合にも、小径部26と回転円輪部23bとの間部分に設けられた、小径部26に整合する部分と比べて径方向厚さ寸法が小さくなった、大径部25に整合する部分を弾性変形させる事で、小径部26の拡径の影響が回転円輪部23bにまで伝わる事を有効に防止できる。又、回転円輪部23bは、その形状故に径方向に関する剛性が高い。従って、エンコーダ16bが拡径する事を有効に防止できる為、エンコーダ16bの内径寸法を、ハブ3の外周面のうちスリンガ15bを外嵌固定する部分の外径寸法よりも小さい状態に維持できる。又、本例の場合には、円筒面部28のうちの軸方向内半部を、回転円輪部23bの軸方向内側面よりも軸方向内方に位置させており、小径部26から円筒面部28のうちの軸方向内半部までの軸方向距離を大きくしている為、小径部26の拡径の影響が、円筒面部28の軸方向内半部にまで伝わりにくくできる。この為、本例の構造によれば、エンコーダ16bの内周面のうちの円筒面部28を、ハブ3の外周面に対し全周に亙り締め代を有する状態で当接させる事ができる(特に本例の場合には、円筒面部28のうちの軸方向内半部の締め代が軸方向外半部の締め代よりも大きくなる)。
即ち、本例の場合には、スリンガ15bの回転円筒部22bの内周面を、大径部25と小径部26とを段差部27により連続させた段付円筒面としている。この為、小径部26を、ハブ3の外周面に締り嵌めで外嵌固定する事で、軸方向に関して小径部26に整合する部分が弾性的に拡径した場合にも、小径部26と回転円輪部23bとの間部分に設けられた、小径部26に整合する部分と比べて径方向厚さ寸法が小さくなった、大径部25に整合する部分を弾性変形させる事で、小径部26の拡径の影響が回転円輪部23bにまで伝わる事を有効に防止できる。又、回転円輪部23bは、その形状故に径方向に関する剛性が高い。従って、エンコーダ16bが拡径する事を有効に防止できる為、エンコーダ16bの内径寸法を、ハブ3の外周面のうちスリンガ15bを外嵌固定する部分の外径寸法よりも小さい状態に維持できる。又、本例の場合には、円筒面部28のうちの軸方向内半部を、回転円輪部23bの軸方向内側面よりも軸方向内方に位置させており、小径部26から円筒面部28のうちの軸方向内半部までの軸方向距離を大きくしている為、小径部26の拡径の影響が、円筒面部28の軸方向内半部にまで伝わりにくくできる。この為、本例の構造によれば、エンコーダ16bの内周面のうちの円筒面部28を、ハブ3の外周面に対し全周に亙り締め代を有する状態で当接させる事ができる(特に本例の場合には、円筒面部28のうちの軸方向内半部の締め代が軸方向外半部の締め代よりも大きくなる)。
又、本例の場合には、エンコーダ16bとして、永久磁石素材を凝固させる事により造られたものを使用している為、締め代を増やす上で有利になる。
即ち、成形型32(32a)から取り出した後の未着磁エンコーダの内径寸法は、凝固に伴い、この成形型32(32a)の内面のうち、エンコーダ16bの内周面を形成する部分の外径寸法よりも小さくなる。従って、成形型32(32a)からスリンガ15b及び未着磁エンコーダを抜き出す際に、この未着磁エンコーダの内周縁部を、変形させないか、或いは、変形量を小さく抑えた場合にも、締め代を増やす事ができる。一般的に、永久磁石素材であるゴムや合成樹脂は、凝固によって体積が2~3%減少する為、磁性粉末を含有しておらず、スリンガ15bにも固着していない状態では、内径寸法は0.5~1%程度小さくなるが、磁性材を80~90重量%程度含有し、スリンガ15bに固着したものにあっては、内径寸法の縮小率は小さくなる。この為、エンコーダ16bの内径寸法が、小径部26の内径寸法よりも小さくなる事はない(φd1<φd2の関係は維持される)。又、本例の場合には、凝固した永久磁石素材に対して、前述した様なアニーリング処理を施している為、締め代をより増やす事ができる。
即ち、成形型32(32a)から取り出した後の未着磁エンコーダの内径寸法は、凝固に伴い、この成形型32(32a)の内面のうち、エンコーダ16bの内周面を形成する部分の外径寸法よりも小さくなる。従って、成形型32(32a)からスリンガ15b及び未着磁エンコーダを抜き出す際に、この未着磁エンコーダの内周縁部を、変形させないか、或いは、変形量を小さく抑えた場合にも、締め代を増やす事ができる。一般的に、永久磁石素材であるゴムや合成樹脂は、凝固によって体積が2~3%減少する為、磁性粉末を含有しておらず、スリンガ15bにも固着していない状態では、内径寸法は0.5~1%程度小さくなるが、磁性材を80~90重量%程度含有し、スリンガ15bに固着したものにあっては、内径寸法の縮小率は小さくなる。この為、エンコーダ16bの内径寸法が、小径部26の内径寸法よりも小さくなる事はない(φd1<φd2の関係は維持される)。又、本例の場合には、凝固した永久磁石素材に対して、前述した様なアニーリング処理を施している為、締め代をより増やす事ができる。
更に、本例の場合には、エンコーダ16bの内周面にリップを設けていない為、スリンガ15bをハブ3に外嵌固定した際に、エンコーダ16bの内周面のうちの円筒面部28の近傍部分(周辺部分)が、ハブ3の外周面との当接により径方向に圧縮される。そして、この様にしてエンコーダ16bの内周縁部に発生する圧縮力は、リップの曲げ変形に基づき発生する緊迫力に比べて十分に大きな緊迫力を発生させる。この為、本例の場合には、リップを設けた場合に比べて締め代の大きさが小さくても、エンコーダ16bの内周面によって十分に大きな緊迫力を発生させる事ができる。
この結果、本発明によれば、スリンガ15bの回転円筒部22bとハブ3の外周面との嵌合部の密封性を良好にできる。
その他の構成及び作用効果に就いては、前述した従来構造の第1例の場合と同様である。
この結果、本発明によれば、スリンガ15bの回転円筒部22bとハブ3の外周面との嵌合部の密封性を良好にできる。
その他の構成及び作用効果に就いては、前述した従来構造の第1例の場合と同様である。
[実施の形態の第2例]
本発明の実施の形態の第2例に就いて、図5~6により説明する。本例は、エンコーダ16cを造る為の永久磁石素材として、上述した実施の形態の第1例の場合に比べて、磁性材の含有量が少ない(例えば50~70重量%含有する)場合に適した構造である。具体的には、エンコーダ16cの内周面を、軸方向内側に向かう程内径寸法が小さくなる方向に傾斜した、軸方向外端部に設けられた部分円すい筒面部35と、軸方向中間部に設けられた円筒面部28aと、軸方向内端部に設けられた面取り部29とから構成している。そして、このうちの最も内径寸法(φd2)が小さくなった円筒面部28aの軸方向内半部を、スリンガ15bの回転円輪部23bの軸方向内側面よりも軸方向内方に位置させている。又、円筒面部28aの内径寸法(φd2)を、スリンガ15bの回転円筒部22bのうち、小径部26の内径寸法(φd1)以上になる様に規制している(φd2≧φd1、図示の例ではφd2≒φd1としている)。そして、エンコーダ付組み合わせシールリング10cの組み付け状態で、エンコーダ16cの内周面のうちの円筒面部28aを、ハブ3(図1、9参照)の外周面に対して締め代を有する状態で当接させている。
本発明の実施の形態の第2例に就いて、図5~6により説明する。本例は、エンコーダ16cを造る為の永久磁石素材として、上述した実施の形態の第1例の場合に比べて、磁性材の含有量が少ない(例えば50~70重量%含有する)場合に適した構造である。具体的には、エンコーダ16cの内周面を、軸方向内側に向かう程内径寸法が小さくなる方向に傾斜した、軸方向外端部に設けられた部分円すい筒面部35と、軸方向中間部に設けられた円筒面部28aと、軸方向内端部に設けられた面取り部29とから構成している。そして、このうちの最も内径寸法(φd2)が小さくなった円筒面部28aの軸方向内半部を、スリンガ15bの回転円輪部23bの軸方向内側面よりも軸方向内方に位置させている。又、円筒面部28aの内径寸法(φd2)を、スリンガ15bの回転円筒部22bのうち、小径部26の内径寸法(φd1)以上になる様に規制している(φd2≧φd1、図示の例ではφd2≒φd1としている)。そして、エンコーダ付組み合わせシールリング10cの組み付け状態で、エンコーダ16cの内周面のうちの円筒面部28aを、ハブ3(図1、9参照)の外周面に対して締め代を有する状態で当接させている。
以上の様な構成を有する本例の場合には、エンコーダ16c(円筒面部28a)の内径寸法を、実施の形態の第1例の場合に比べて小さくしている為、ハブ3の外周面に対する締め代を大きく確保でき、嵌合部の密封性の更なる向上を図れる。又、本例の場合には、スリンガ15b及び未着磁エンコーダを成形型から抜き出す際に、この未着磁エンコーダの内周縁部分(円筒面部28aに相当する部分)を僅かに変形(弾性変形)させる必要があるが、永久磁石素材中の磁性材の含有量を低く抑えている(弾性変形し易くなっている)と共に、成形型(上型)を部分円すい筒面部35により抜き方向(図5、6の右側)に案内できる為、この様な作業は実質上問題なく行える。
その他の構成及び作用効果に就いては、上述した実施の形態の第1例の場合と同様である。
その他の構成及び作用効果に就いては、上述した実施の形態の第1例の場合と同様である。
[実施の形態の第3例]
本発明の実施の形態の第3例に就いて、図7~8により説明する。本例の場合にも、上述した実施の形態の第2例の場合と同様に、エンコーダ16dを造る為の永久磁石素材として、磁性材の含有量が少ない(例えば50~70重量%含有する)場合に適した構造である。そして、エンコーダ16dの内周面を、軸方向内側に向かう程内径寸法が小さくなる方向に傾斜した、軸方向外端部に設けられた部分円すい筒面部35aと、軸方向中間部に設けられた円筒面部28bと、軸方向内端部に設けられた面取り部29とから構成している。特に本例の場合には、実施の形態の第2例の場合に比べて、部分円すい筒面部35aの軸方向寸法を大きくする(傾斜角度は小さくする)事で、円筒面部28b全体を、スリンガ15bの回転円輪部23bの軸方向内側面よりも軸方向内方に位置させている。そして、本例の場合にも、エンコーダ付組み合わせシールリング10dの組み付け状態で、エンコーダ16dの内周面のうちの円筒面部28bを、ハブ3(図1、9参照)の外周面に対して締め代を有する状態で当接させている。
本発明の実施の形態の第3例に就いて、図7~8により説明する。本例の場合にも、上述した実施の形態の第2例の場合と同様に、エンコーダ16dを造る為の永久磁石素材として、磁性材の含有量が少ない(例えば50~70重量%含有する)場合に適した構造である。そして、エンコーダ16dの内周面を、軸方向内側に向かう程内径寸法が小さくなる方向に傾斜した、軸方向外端部に設けられた部分円すい筒面部35aと、軸方向中間部に設けられた円筒面部28bと、軸方向内端部に設けられた面取り部29とから構成している。特に本例の場合には、実施の形態の第2例の場合に比べて、部分円すい筒面部35aの軸方向寸法を大きくする(傾斜角度は小さくする)事で、円筒面部28b全体を、スリンガ15bの回転円輪部23bの軸方向内側面よりも軸方向内方に位置させている。そして、本例の場合にも、エンコーダ付組み合わせシールリング10dの組み付け状態で、エンコーダ16dの内周面のうちの円筒面部28bを、ハブ3(図1、9参照)の外周面に対して締め代を有する状態で当接させている。
以上の様な構成を有する本例の場合には、スリンガ15bの回転円筒部22bの小径部26を、ハブ3に締り嵌めで外嵌固定する事で、軸方向に関して小径部26に整合する部分が弾性的に拡径した場合にも、小径部26から円筒面部28bまでの軸方向距離が大きい事と、剛性の高い回転円輪部23bの存在に基づき、小径部26の拡径の影響が、円筒面部28bにまで伝わる事を有効に防止できる。従って、ハブ3に対するこの円筒面部28bの締め代をより大きく確保できて、嵌合部の密封性の更なる向上を図れる。
その他の構成及び作用効果に就いては、前述した実施の形態の第1例及び第2例の場合と同様である。
その他の構成及び作用効果に就いては、前述した実施の形態の第1例及び第2例の場合と同様である。
本出願は、2013年10月16日出願の日本特許出願2013-215358に基づくものであり、その内容はここに参照として取り込まれる。
本発明を実施する場合に、弾性材に設けるシールリップの数は1本(好ましくは締め代の変化を生じ易いサイドリップのみ)でも良いし、2本或いは各例の場合の様に3本、又はそれ以上でも良い。更に、本発明のエンコーダ付転がり軸受ユニットは、自動車の車輪を懸架装置に支持する為の車輪支持用転がり軸受ユニットに限らず、工作機械、産業機械等、回転部材の回転速度を検出する必要がある、各種機械装置の回転支持部を構成する転がり軸受ユニット(転がり軸受)も対象になる。又、前述した実施の形態の各例では、エンコーダの内周面のうち最も内径寸法が小さくなった部分を、単一円筒面状の円筒面部により構成した場合に就いてのみ説明したが、当該部分の形状は、円筒面に限定されずに実施する事ができる。
1 エンコーダ付転がり軸受ユニット
2 外輪(外径側軌道輪部材)
3、3a ハブ(内径側軌道輪部材)
4 外輪軌道
5 内輪軌道
6 玉(転動体)
7 保持器
8 環状空間
9 シールリング
10、10a~10d エンコーダ付組み合わせシールリング
11 芯金
12 シールリップ
13、13a 組み合わせシールリング
14 シールリング
15、15a、15b スリンガ
16、16a~16d エンコーダ
17 芯金
18 弾性材
19 固定円筒部
20 固定円輪部
21a~21c シールリップ
22、22a、22b 回転円筒部
23、23a、23b 回転円輪部
24 リップ部
25 大径部
26 小径部
27 段差部
28、28a、28b 円筒面部
29 面取り部
30、30a 上型
31 下型
32、32a 成形型
33、33a キャビティ
34、34a 角部
35 部分円すい筒面部
36 余肉部
2 外輪(外径側軌道輪部材)
3、3a ハブ(内径側軌道輪部材)
4 外輪軌道
5 内輪軌道
6 玉(転動体)
7 保持器
8 環状空間
9 シールリング
10、10a~10d エンコーダ付組み合わせシールリング
11 芯金
12 シールリップ
13、13a 組み合わせシールリング
14 シールリング
15、15a、15b スリンガ
16、16a~16d エンコーダ
17 芯金
18 弾性材
19 固定円筒部
20 固定円輪部
21a~21c シールリップ
22、22a、22b 回転円筒部
23、23a、23b 回転円輪部
24 リップ部
25 大径部
26 小径部
27 段差部
28、28a、28b 円筒面部
29 面取り部
30、30a 上型
31 下型
32、32a 成形型
33、33a キャビティ
34、34a 角部
35 部分円すい筒面部
36 余肉部
Claims (5)
- 使用時に回転する内径側軌道輪部材の外周面と、使用時にも回転しない外径側軌道輪部材の内周面と、の間に存在する環状空間の端部開口を塞ぐと共に、前記内径側軌道輪部材の回転速度を検出する為に使用するものであり、
前記外径側軌道輪部材に内嵌固定されるシールリングと、前記内径側軌道輪部材に外嵌固定されるスリンガと、前記スリンガに支持固定されるエンコーダとを備え、
前記シールリングは、芯金と、前記芯金の全周に亙って添着された、少なくとも1本のシールリップを有する弾性材とを備えており、
前記スリンガは、金属板製の断面略L字形で、全体を円環状に構成したものであり、前記内径側軌道輪部材に締り嵌めで外嵌固定される回転円筒部と、前記回転円筒部の軸方向一端縁から径方向外方に向けて折れ曲がった回転円輪部とを備えており、
前記エンコーダは、円周方向に亙ってS極とN極とを交互に配置した永久磁石製で、全体を円輪状に構成したものであり、前記回転円輪部のうち前記シールリップと対向する側面とは反対側の側面に支持固定されている、
エンコーダ付組み合わせシールリングであって、
前記回転円筒部の内周面が、前記回転円筒部の軸方向一端側に設けられた大径部と、残部に設けられた小径部と、を段差部により連続させた段付円筒面であり、
前記エンコーダが、その内周面にリップを有しておらず、前記スリンガを成形型内に前記成形型の一部を前記段差部に突き当てて配置した状態で、溶融した永久磁石素材を凝固させ前記スリンガに固着して造られたものであり、
前記内径側軌道輪部材の外周面のうち前記スリンガを外嵌固定する部分の外径寸法をφDとし、前記小径部の自由状態での内径寸法をφd1とし、前記エンコーダの自由状態での内径寸法をφd2とした場合に、φd1≦φd2<φDの関係を満たす、
事を特徴とするエンコーダ付組み合わせシールリング。 - 前記回転円筒部の径方向厚さ寸法が、軸方向に関して前記小径部に整合する部分に比べて前記大径部に整合する部分で小さくなっている、請求項1に記載したエンコーダ付組み合わせシールリング。
- 前記エンコーダの内周面のうちで最も内径寸法が小さくなった部分の少なくとも軸方向一部が、前記回転円輪部のうち前記エンコーダを支持固定した側面よりも、軸方向に関して前記回転円筒部から離れた側に位置している、請求項1~2のうちの何れか1項に記載したエンコーダ付組み合わせシールリング。
- 前記エンコーダの内周面のうちで最も内径寸法が小さくなった部分が、内径寸法が軸方向に亙り変化しない円筒面部により構成されている、請求項1~3のうちの何れか1項に記載したエンコーダ付組み合わせシールリング。
- 外周面に内輪軌道を有する内径側軌道輪部材と、内周面に外輪軌道を有する外径側軌道輪部材と、前記内輪軌道と前記外輪軌道との間に転動自在に設けられた複数個の転動体と、前記内径側軌道輪部材の外周面と前記外径側軌道輪部材の内周面との間に存在する環状空間の端部開口を塞ぐ組み合わせシールリングとを備えたエンコーダ付転がり軸受ユニットであって、
前記組み合わせシールリングが、請求項1~4のうちの何れか1項に記載したエンコーダ付組み合わせシールリングである事を特徴とするエンコーダ付転がり軸受ユニット。
Priority Applications (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP14853823.4A EP3059465B1 (en) | 2013-10-16 | 2014-09-19 | Combination seal ring with encoder and roller bearing unit with encoder |
| CN201480057347.8A CN105637245B (zh) | 2013-10-16 | 2014-09-19 | 带编码器的组合密封圈和带编码器的滚动轴承单元 |
| US15/029,766 US9695943B2 (en) | 2013-10-16 | 2014-09-19 | Combined seal ring with encoder and rolling bearing unit with encoder |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013215358A JP6241188B2 (ja) | 2013-10-16 | 2013-10-16 | エンコーダ付組み合わせシールリング及びエンコーダ付転がり軸受ユニット |
| JP2013-215358 | 2013-10-16 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2015056526A1 true WO2015056526A1 (ja) | 2015-04-23 |
Family
ID=52827979
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2014/074930 WO2015056526A1 (ja) | 2013-10-16 | 2014-09-19 | エンコーダ付組み合わせシールリング及びエンコーダ付転がり軸受ユニット |
Country Status (5)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US9695943B2 (ja) |
| EP (1) | EP3059465B1 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JP6241188B2 (ja) |
| CN (1) | CN105637245B (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2015056526A1 (ja) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2016181515A1 (ja) * | 2015-05-12 | 2016-11-17 | 日本精工株式会社 | 磁気エンコーダ及び転がり軸受 |
Families Citing this family (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP6782600B2 (ja) * | 2016-10-04 | 2020-11-11 | ナブテスコ株式会社 | シール及びシール機構 |
| US11092467B2 (en) * | 2018-10-30 | 2021-08-17 | Stm Corporation | Elastic encoder and manufacturing method thereof |
| CN108759762B (zh) * | 2018-08-02 | 2023-10-03 | 中国工程物理研究院机械制造工艺研究所 | 一种内外双轴式自校准转台及使用方法 |
| CN112166268B (zh) * | 2018-08-28 | 2023-01-31 | Nok株式会社 | 树脂制盖中的密封结构 |
| CN112789421B (zh) * | 2018-09-28 | 2023-04-04 | 美国联合金属制品股份有限公司 | 具有聚四氟乙烯推力缓冲器的轴承密封件 |
| IT201800010424A1 (it) * | 2018-11-19 | 2020-05-19 | Skf Ab | Dispositivo di tenuta a labirinto |
| JP2024022915A (ja) | 2022-08-08 | 2024-02-21 | 中西金属工業株式会社 | 磁気エンコーダ、及び磁気エンコーダの製造方法 |
Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2005233923A (ja) * | 2004-01-22 | 2005-09-02 | Nsk Ltd | 転がり軸受 |
| JP2007052036A (ja) | 1993-01-19 | 2007-03-01 | Snr Roulements | コーダ内蔵密閉構造 |
| JP2007270992A (ja) * | 2006-03-31 | 2007-10-18 | Nok Corp | 密封装置 |
| JP2008233110A (ja) | 2004-08-23 | 2008-10-02 | Nsk Ltd | 磁気エンコーダの製造方法 |
| JP2009185965A (ja) | 2008-02-08 | 2009-08-20 | Nsk Ltd | 組み合わせシールリング付転がり軸受ユニット |
| JP2012093310A (ja) * | 2010-10-28 | 2012-05-17 | Jtekt Corp | パルサーリング、密封装置、及び転がり軸受 |
| JP2013104455A (ja) * | 2011-11-11 | 2013-05-30 | Nsk Ltd | エンコーダ付転がり軸受ユニット |
Family Cites Families (16)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2000289405A (ja) * | 1999-04-02 | 2000-10-17 | Nsk Ltd | エンコーダ付組み合わせシールリング |
| JP2002048247A (ja) * | 2000-08-01 | 2002-02-15 | Nok Corp | 回転検出可能な密封装置 |
| JP4997520B2 (ja) * | 2001-09-07 | 2012-08-08 | 株式会社ジェイテクト | パルサリングの製造方法 |
| JP2003089302A (ja) * | 2001-09-18 | 2003-03-25 | Ntn Corp | 磁気エンコーダおよびそれを備えた車輪用軸受 |
| US6789948B2 (en) * | 2001-09-25 | 2004-09-14 | Ntn Corporation | Magnetic encoder and wheel bearing assembly using the same |
| JP4372438B2 (ja) * | 2003-03-11 | 2009-11-25 | Ntn株式会社 | 車輪用軸受 |
| JP2005321307A (ja) * | 2004-05-10 | 2005-11-17 | Nsk Ltd | 磁気エンコーダ及び当該磁気エンコーダを備えた転がり軸受ユニット |
| JP4720400B2 (ja) * | 2005-09-22 | 2011-07-13 | 日本精工株式会社 | 組み合わせシールリング付車輪支持用転がり軸受ユニット及びその製造方法 |
| DE102005061168A1 (de) * | 2005-12-21 | 2007-08-09 | Schaeffler Kg | Radiallager mit einer Kassettendichtung, sowie Kassettendichtung |
| JP2007321881A (ja) * | 2006-06-01 | 2007-12-13 | Ntn Corp | 車輪用軸受装置 |
| JP5097489B2 (ja) * | 2007-09-21 | 2012-12-12 | Ntn株式会社 | 磁気エンコーダおよび転がり軸受 |
| JP5081553B2 (ja) * | 2007-09-27 | 2012-11-28 | Ntn株式会社 | 回転検出装置および回転検出装置付き軸受 |
| JP5285457B2 (ja) * | 2009-01-29 | 2013-09-11 | 株式会社ジェイテクト | 転がり軸受 |
| JP2010249168A (ja) * | 2009-04-13 | 2010-11-04 | Nok Corp | 密封装置 |
| EP2525110B1 (en) * | 2010-01-13 | 2019-10-30 | NSK Ltd. | Rolling bearing unit with combination seal ring, and method for manufacturing same |
| EP3026282B1 (en) * | 2014-11-28 | 2017-06-21 | Aktiebolaget SKF | Sealing device with an encoder for a wheel hub rolling bearing assembly connected to a constant velocity joint |
-
2013
- 2013-10-16 JP JP2013215358A patent/JP6241188B2/ja active Active
-
2014
- 2014-09-19 US US15/029,766 patent/US9695943B2/en active Active
- 2014-09-19 EP EP14853823.4A patent/EP3059465B1/en active Active
- 2014-09-19 CN CN201480057347.8A patent/CN105637245B/zh active Active
- 2014-09-19 WO PCT/JP2014/074930 patent/WO2015056526A1/ja active Application Filing
Patent Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007052036A (ja) | 1993-01-19 | 2007-03-01 | Snr Roulements | コーダ内蔵密閉構造 |
| JP2005233923A (ja) * | 2004-01-22 | 2005-09-02 | Nsk Ltd | 転がり軸受 |
| JP2008233110A (ja) | 2004-08-23 | 2008-10-02 | Nsk Ltd | 磁気エンコーダの製造方法 |
| JP2007270992A (ja) * | 2006-03-31 | 2007-10-18 | Nok Corp | 密封装置 |
| JP2009185965A (ja) | 2008-02-08 | 2009-08-20 | Nsk Ltd | 組み合わせシールリング付転がり軸受ユニット |
| JP2012093310A (ja) * | 2010-10-28 | 2012-05-17 | Jtekt Corp | パルサーリング、密封装置、及び転がり軸受 |
| JP2013104455A (ja) * | 2011-11-11 | 2013-05-30 | Nsk Ltd | エンコーダ付転がり軸受ユニット |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2016181515A1 (ja) * | 2015-05-12 | 2016-11-17 | 日本精工株式会社 | 磁気エンコーダ及び転がり軸受 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP3059465A1 (en) | 2016-08-24 |
| JP6241188B2 (ja) | 2017-12-06 |
| CN105637245A (zh) | 2016-06-01 |
| US9695943B2 (en) | 2017-07-04 |
| JP2015078732A (ja) | 2015-04-23 |
| EP3059465B1 (en) | 2018-12-12 |
| CN105637245B (zh) | 2018-08-28 |
| EP3059465A4 (en) | 2016-10-05 |
| US20160245409A1 (en) | 2016-08-25 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| WO2015056526A1 (ja) | エンコーダ付組み合わせシールリング及びエンコーダ付転がり軸受ユニット | |
| JP5040469B2 (ja) | 車輪支持装置の密封構造 | |
| JP6323046B2 (ja) | 回転速度検出装置付転がり軸受ユニット | |
| WO2011027781A1 (ja) | 回転速度検出装置付き車輪用軸受装置 | |
| JP2012087858A (ja) | 車輪用軸受装置 | |
| JP4720400B2 (ja) | 組み合わせシールリング付車輪支持用転がり軸受ユニット及びその製造方法 | |
| JP6260348B2 (ja) | 回転速度検出装置付転がり軸受ユニット | |
| WO2017150562A1 (ja) | 車輪用軸受装置 | |
| JP6256122B2 (ja) | 回転速度検出装置付転がり軸受ユニット | |
| JP4375790B2 (ja) | 回転速度検出装置付き車輪用軸受装置 | |
| JP2019052738A (ja) | ハブユニット軸受 | |
| JP4742796B2 (ja) | 回転検出装置付転がり軸受ユニット | |
| JP4628395B2 (ja) | 回転速度検出装置付き車輪用軸受装置 | |
| JP6012478B2 (ja) | 回転速度検出装置付き車輪用軸受装置 | |
| JP4260055B2 (ja) | 車輪用軸受装置 | |
| JP6417701B2 (ja) | 回転速度検出装置付転がり軸受ユニット | |
| JP2017203515A (ja) | エンコーダ付転がり軸受ユニット | |
| JP2015137738A (ja) | エンコーダ付車輪支持用軸受ユニット | |
| JP2017048892A (ja) | ハブユニット軸受 | |
| JP2021080996A (ja) | エンコーダ付きスリンガ及びその製造方法、並びに、ハブユニット軸受 | |
| JP5017951B2 (ja) | ハブユニット軸受 | |
| JP2015190474A (ja) | 回転速度検出装置付転がり軸受ユニット | |
| EP1983306B1 (en) | Rotor for rotary encoder and rolling bearing for wheel having same | |
| JP2007232606A (ja) | 車輪用軸受装置 | |
| JP2017190803A (ja) | ハブユニット軸受 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 14853823 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| REEP | Request for entry into the european phase |
Ref document number: 2014853823 Country of ref document: EP |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 2014853823 Country of ref document: EP |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 15029766 Country of ref document: US |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |