JP5949516B2 - 半導体装置の製造方法 - Google Patents
半導体装置の製造方法 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP5949516B2 JP5949516B2 JP2012272987A JP2012272987A JP5949516B2 JP 5949516 B2 JP5949516 B2 JP 5949516B2 JP 2012272987 A JP2012272987 A JP 2012272987A JP 2012272987 A JP2012272987 A JP 2012272987A JP 5949516 B2 JP5949516 B2 JP 5949516B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- layer
- electrode layer
- semiconductor device
- manufacturing
- contact formation
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 title claims description 338
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 title claims description 146
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 claims description 198
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 claims description 105
- KDLHZDBZIXYQEI-UHFFFAOYSA-N Palladium Chemical compound [Pd] KDLHZDBZIXYQEI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 66
- 239000010936 titanium Substances 0.000 claims description 61
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 claims description 59
- 230000004888 barrier function Effects 0.000 claims description 48
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 47
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 claims description 47
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 claims description 43
- 229910052719 titanium Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 32
- RTAQQCXQSZGOHL-UHFFFAOYSA-N Titanium Chemical compound [Ti] RTAQQCXQSZGOHL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 30
- 229910045601 alloy Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 29
- 239000000956 alloy Substances 0.000 claims description 29
- 229910052782 aluminium Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 28
- XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N aluminium Chemical compound [Al] XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 28
- LEONUFNNVUYDNQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N vanadium atom Chemical compound [V] LEONUFNNVUYDNQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 25
- 239000010955 niobium Substances 0.000 claims description 24
- 239000010948 rhodium Substances 0.000 claims description 24
- PXHVJJICTQNCMI-UHFFFAOYSA-N Nickel Chemical compound [Ni] PXHVJJICTQNCMI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 23
- 229910052763 palladium Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 23
- ZOKXTWBITQBERF-UHFFFAOYSA-N Molybdenum Chemical compound [Mo] ZOKXTWBITQBERF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 19
- 229910052750 molybdenum Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 19
- 239000011733 molybdenum Substances 0.000 claims description 19
- 229910052735 hafnium Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 18
- VBJZVLUMGGDVMO-UHFFFAOYSA-N hafnium atom Chemical compound [Hf] VBJZVLUMGGDVMO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 18
- BASFCYQUMIYNBI-UHFFFAOYSA-N platinum Chemical compound [Pt] BASFCYQUMIYNBI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 18
- ATJFFYVFTNAWJD-UHFFFAOYSA-N Tin Chemical compound [Sn] ATJFFYVFTNAWJD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 16
- 229910052721 tungsten Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 16
- 229910052718 tin Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 15
- JMASRVWKEDWRBT-UHFFFAOYSA-N Gallium nitride Chemical compound [Ga]#N JMASRVWKEDWRBT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 12
- XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicon Chemical compound [Si] XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 12
- 229910008484 TiSi Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 12
- 229910052741 iridium Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 12
- GKOZUEZYRPOHIO-UHFFFAOYSA-N iridium atom Chemical compound [Ir] GKOZUEZYRPOHIO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 12
- 229910052758 niobium Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 12
- GUCVJGMIXFAOAE-UHFFFAOYSA-N niobium atom Chemical compound [Nb] GUCVJGMIXFAOAE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 12
- 229910052762 osmium Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 12
- SYQBFIAQOQZEGI-UHFFFAOYSA-N osmium atom Chemical compound [Os] SYQBFIAQOQZEGI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 12
- 229910052702 rhenium Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 12
- WUAPFZMCVAUBPE-UHFFFAOYSA-N rhenium atom Chemical compound [Re] WUAPFZMCVAUBPE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 12
- 229910052703 rhodium Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 12
- MHOVAHRLVXNVSD-UHFFFAOYSA-N rhodium atom Chemical compound [Rh] MHOVAHRLVXNVSD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 12
- VSZWPYCFIRKVQL-UHFFFAOYSA-N selanylidenegallium;selenium Chemical compound [Se].[Se]=[Ga].[Se]=[Ga] VSZWPYCFIRKVQL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 12
- 229910052710 silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 12
- 239000010703 silicon Substances 0.000 claims description 12
- 229910052715 tantalum Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 12
- GUVRBAGPIYLISA-UHFFFAOYSA-N tantalum atom Chemical compound [Ta] GUVRBAGPIYLISA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 12
- WFKWXMTUELFFGS-UHFFFAOYSA-N tungsten Chemical compound [W] WFKWXMTUELFFGS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 12
- 239000010937 tungsten Substances 0.000 claims description 12
- 229910052759 nickel Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 8
- 229910052697 platinum Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 6
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 claims description 5
- 229910001092 metal group alloy Inorganic materials 0.000 claims 1
- 239000010410 layer Substances 0.000 description 1057
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 87
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 43
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 43
- 238000005530 etching Methods 0.000 description 27
- 230000000052 comparative effect Effects 0.000 description 22
- 239000011229 interlayer Substances 0.000 description 20
- VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicium dioxide Chemical compound O=[Si]=O VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 18
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 description 12
- 230000002093 peripheral effect Effects 0.000 description 11
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 description 11
- MCMNRKCIXSYSNV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Zirconium dioxide Chemical compound O=[Zr]=O MCMNRKCIXSYSNV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 8
- 230000015556 catabolic process Effects 0.000 description 8
- 238000011156 evaluation Methods 0.000 description 7
- 235000012239 silicon dioxide Nutrition 0.000 description 7
- 239000000377 silicon dioxide Substances 0.000 description 7
- 238000009616 inductively coupled plasma Methods 0.000 description 5
- 238000000206 photolithography Methods 0.000 description 5
- HQVNEWCFYHHQES-UHFFFAOYSA-N silicon nitride Chemical compound N12[Si]34N5[Si]62N3[Si]51N64 HQVNEWCFYHHQES-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- VZSRBBMJRBPUNF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-(2,3-dihydro-1H-inden-2-ylamino)-N-[3-oxo-3-(2,4,6,7-tetrahydrotriazolo[4,5-c]pyridin-5-yl)propyl]pyrimidine-5-carboxamide Chemical compound C1C(CC2=CC=CC=C12)NC1=NC=C(C=N1)C(=O)NCCC(N1CC2=C(CC1)NN=N2)=O VZSRBBMJRBPUNF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 239000013078 crystal Substances 0.000 description 4
- 238000013461 design Methods 0.000 description 4
- 238000002474 experimental method Methods 0.000 description 4
- 238000000605 extraction Methods 0.000 description 4
- 201000002161 intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy Diseases 0.000 description 4
- 239000012299 nitrogen atmosphere Substances 0.000 description 4
- 239000002356 single layer Substances 0.000 description 4
- AFCARXCZXQIEQB-UHFFFAOYSA-N N-[3-oxo-3-(2,4,6,7-tetrahydrotriazolo[4,5-c]pyridin-5-yl)propyl]-2-[[3-(trifluoromethoxy)phenyl]methylamino]pyrimidine-5-carboxamide Chemical compound O=C(CCNC(=O)C=1C=NC(=NC=1)NCC1=CC(=CC=C1)OC(F)(F)F)N1CC2=C(CC1)NN=N2 AFCARXCZXQIEQB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 229910052581 Si3N4 Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 238000007796 conventional method Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 3
- 239000007772 electrode material Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000010931 gold Substances 0.000 description 3
- CJNBYAVZURUTKZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N hafnium(iv) oxide Chemical compound O=[Hf]=O CJNBYAVZURUTKZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- KRHYYFGTRYWZRS-UHFFFAOYSA-N Fluorane Chemical compound F KRHYYFGTRYWZRS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 230000002411 adverse Effects 0.000 description 2
- PNEYBMLMFCGWSK-UHFFFAOYSA-N aluminium oxide Inorganic materials [O-2].[O-2].[O-2].[Al+3].[Al+3] PNEYBMLMFCGWSK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000000460 chlorine Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910052593 corundum Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 238000006731 degradation reaction Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000008021 deposition Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000001312 dry etching Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000004904 shortening Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229910001845 yogo sapphire Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 229910018072 Al 2 O 3 Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- ZAMOUSCENKQFHK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Chlorine atom Chemical compound [Cl] ZAMOUSCENKQFHK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910002601 GaN Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910004298 SiO 2 Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000007864 aqueous solution Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000008901 benefit Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229910052801 chlorine Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000000470 constituent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000007789 gas Substances 0.000 description 1
- PCHJSUWPFVWCPO-UHFFFAOYSA-N gold Chemical compound [Au] PCHJSUWPFVWCPO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052737 gold Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 230000006872 improvement Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000005259 measurement Methods 0.000 description 1
- TWNQGVIAIRXVLR-UHFFFAOYSA-N oxo(oxoalumanyloxy)alumane Chemical compound O=[Al]O[Al]=O TWNQGVIAIRXVLR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- RVTZCBVAJQQJTK-UHFFFAOYSA-N oxygen(2-);zirconium(4+) Chemical compound [O-2].[O-2].[Zr+4] RVTZCBVAJQQJTK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910021420 polycrystalline silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229920005591 polysilicon Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000011135 tin Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052720 vanadium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 238000007740 vapor deposition Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000001039 wet etching Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910001928 zirconium oxide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/02—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/12—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by the materials of which they are formed
- H01L29/20—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by the materials of which they are formed including, apart from doping materials or other impurities, only AIIIBV compounds
- H01L29/2003—Nitride compounds
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/04—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof the devices having potential barriers, e.g. a PN junction, depletion layer or carrier concentration layer
- H01L21/18—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof the devices having potential barriers, e.g. a PN junction, depletion layer or carrier concentration layer the devices having semiconductor bodies comprising elements of Group IV of the Periodic Table or AIIIBV compounds with or without impurities, e.g. doping materials
- H01L21/28—Manufacture of electrodes on semiconductor bodies using processes or apparatus not provided for in groups H01L21/20 - H01L21/268
- H01L21/283—Deposition of conductive or insulating materials for electrodes conducting electric current
- H01L21/285—Deposition of conductive or insulating materials for electrodes conducting electric current from a gas or vapour, e.g. condensation
- H01L21/28506—Deposition of conductive or insulating materials for electrodes conducting electric current from a gas or vapour, e.g. condensation of conductive layers
- H01L21/28575—Deposition of conductive or insulating materials for electrodes conducting electric current from a gas or vapour, e.g. condensation of conductive layers on semiconductor bodies comprising AIIIBV compounds
- H01L21/28587—Deposition of conductive or insulating materials for electrodes conducting electric current from a gas or vapour, e.g. condensation of conductive layers on semiconductor bodies comprising AIIIBV compounds characterised by the sectional shape, e.g. T, inverted T
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/40—Electrodes ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/43—Electrodes ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by the materials of which they are formed
- H01L29/45—Ohmic electrodes
- H01L29/452—Ohmic electrodes on AIII-BV compounds
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/66—Types of semiconductor device ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/66007—Multistep manufacturing processes
- H01L29/66075—Multistep manufacturing processes of devices having semiconductor bodies comprising group 14 or group 13/15 materials
- H01L29/66227—Multistep manufacturing processes of devices having semiconductor bodies comprising group 14 or group 13/15 materials the devices being controllable only by the electric current supplied or the electric potential applied, to an electrode which does not carry the current to be rectified, amplified or switched, e.g. three-terminal devices
- H01L29/66409—Unipolar field-effect transistors
- H01L29/66477—Unipolar field-effect transistors with an insulated gate, i.e. MISFET
- H01L29/66674—DMOS transistors, i.e. MISFETs with a channel accommodating body or base region adjoining a drain drift region
- H01L29/66712—Vertical DMOS transistors, i.e. VDMOS transistors
- H01L29/66727—Vertical DMOS transistors, i.e. VDMOS transistors with a step of recessing the source electrode
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/66—Types of semiconductor device ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/66007—Multistep manufacturing processes
- H01L29/66075—Multistep manufacturing processes of devices having semiconductor bodies comprising group 14 or group 13/15 materials
- H01L29/66227—Multistep manufacturing processes of devices having semiconductor bodies comprising group 14 or group 13/15 materials the devices being controllable only by the electric current supplied or the electric potential applied, to an electrode which does not carry the current to be rectified, amplified or switched, e.g. three-terminal devices
- H01L29/66409—Unipolar field-effect transistors
- H01L29/66477—Unipolar field-effect transistors with an insulated gate, i.e. MISFET
- H01L29/66674—DMOS transistors, i.e. MISFETs with a channel accommodating body or base region adjoining a drain drift region
- H01L29/66712—Vertical DMOS transistors, i.e. VDMOS transistors
- H01L29/66734—Vertical DMOS transistors, i.e. VDMOS transistors with a step of recessing the gate electrode, e.g. to form a trench gate electrode
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/66—Types of semiconductor device ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/68—Types of semiconductor device ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor controllable by only the electric current supplied, or only the electric potential applied, to an electrode which does not carry the current to be rectified, amplified or switched
- H01L29/76—Unipolar devices, e.g. field effect transistors
- H01L29/772—Field effect transistors
- H01L29/78—Field effect transistors with field effect produced by an insulated gate
- H01L29/7801—DMOS transistors, i.e. MISFETs with a channel accommodating body or base region adjoining a drain drift region
- H01L29/7802—Vertical DMOS transistors, i.e. VDMOS transistors
- H01L29/7813—Vertical DMOS transistors, i.e. VDMOS transistors with trench gate electrode, e.g. UMOS transistors
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/40—Electrodes ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/401—Multistep manufacturing processes
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/40—Electrodes ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/41—Electrodes ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape, relative sizes or dispositions
- H01L29/417—Electrodes ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape, relative sizes or dispositions carrying the current to be rectified, amplified or switched
- H01L29/41725—Source or drain electrodes for field effect devices
- H01L29/41741—Source or drain electrodes for field effect devices for vertical or pseudo-vertical devices
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/40—Electrodes ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/41—Electrodes ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape, relative sizes or dispositions
- H01L29/417—Electrodes ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape, relative sizes or dispositions carrying the current to be rectified, amplified or switched
- H01L29/41725—Source or drain electrodes for field effect devices
- H01L29/41766—Source or drain electrodes for field effect devices with at least part of the source or drain electrode having contact below the semiconductor surface, e.g. the source or drain electrode formed at least partially in a groove or with inclusions of conductor inside the semiconductor
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Microelectronics & Electronic Packaging (AREA)
- Power Engineering (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Condensed Matter Physics & Semiconductors (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Computer Hardware Design (AREA)
- Ceramic Engineering (AREA)
- Manufacturing & Machinery (AREA)
- Electrodes Of Semiconductors (AREA)
Description
A−1.半導体装置の構成:
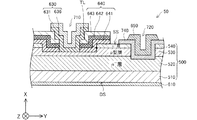
図1は、第1実施形態における半導体装置50の構成を模式的に示す断面図である。図1には、本実施形態における半導体装置50の断面の一部を示している。なお、図1は、半導体装置50の技術的特徴をわかりやすく示すための図であり、各部の寸法を正確に示すものではない。また、図1には、説明を容易にするために、相互に直交するXYZ軸が図示されている。以降の図についても同様である。
図2は、第1実施形態における半導体装置50の製造方法を示すフローチャートである。はじめに、n型基板510上に、結晶成長によってn−層520が形成され(ステップS210)、さらに結晶成長によってp型層530およびn+層540が形成される(ステップS220およびS230)。次に、ドライエッチングによって積層体500のソース側表面SS側にトレンチ720およびリセス710が形成され(ステップS232)、フォトリソグラフィによるレジストパタンへの電極材料蒸着およびリフトオフプロセスによって、n+層540上にソース電極層640が形成されると共に(ステップS240)、p型層530上にp電極層630が形成され(ステップS250)、各電極層と各半導体層との間のコンタクト抵抗低減のための熱処理が実行される(ステップS260)。このような製造方法によれば、p電極層630がソース電極層640上に積層され電極周辺部分が微細化された小型の半導体装置50を製造することができ、半導体装置50の製造コストを低減することができる。なお、本実施形態では、熱処理は、p電極層630およびソース電極層640に対して同時に行われる。このようにすれば、一度の熱処理によって、p電極層630およびソース電極層640の両方について、各半導体層と各電極層との間での良好なオーム性接触を実現することができる。
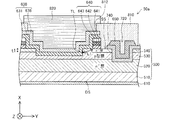
図3は、第1実施形態の変形例における半導体装置50aの構成を模式的に示す断面図である。第1実施形態の変形例における半導体装置50aは、ソース電極層640およびp電極層630の構成と層間絶縁膜810および配線電極層820を備える点とが図1に示した第1実施形態の半導体装置50と異なっており、その他の構成は第1実施形態の半導体装置50と同じである。
図5ないし図7は、第1実施形態(およびその変形例)の半導体装置の性能を評価するための実験結果の一例を示す説明図である。実験に使用した実施例および比較例における各電極層の構成は以下の通りである。
[実施例1−1]
・p電極層630
pコンタクト形成層631:(材料)パラジウム(Pd) (層厚)20nm
pキャップ層636:なし
・ソース電極層640
第1のnコンタクト形成層641:(材料)チタン(Ti) (層厚)17.5nm
第2のnコンタクト形成層642:(材料)アルミニウム(Al) (層厚)300nm
nバリア層643:(材料)パラジウム(Pd) (層厚)20nm
*この実施例では、1つのパラジウム層が、pコンタクト形成層631およびnバリア層643として機能する。
[実施例1−2]
・p電極層630
pコンタクト形成層631:(材料)パラジウム(Pd) (層厚)50nm
pキャップ層636:なし
・ソース電極層640
第1のnコンタクト形成層641:(材料)チタン(Ti) (層厚)17.5nm
第2のnコンタクト形成層642:(材料)アルミニウム(Al) (層厚)300nm
nバリア層643:(材料)パラジウム(Pd) (層厚)50nm
*この実施例では、1つのパラジウム層が、pコンタクト形成層631およびnバリア層643として機能する。
[実施例2]
・p電極層630
pコンタクト形成層631:(材料)パラジウム(Pd) (層厚)50nm
pキャップ層636:なし
・ソース電極層640
第1のnコンタクト形成層641:(材料)バナジウム(V) (層厚)17.5nm
第2のnコンタクト形成層642:(材料)アルミニウム(Al) (層厚)300nm
nバリア層643:(材料)モリブデン(Mo) (層厚)50nm
[比較例]
・ソース電極層640
第1のnコンタクト形成層641:(材料)チタン(Ti) (層厚)17.5nm
第2のnコンタクト形成層642:(材料)アルミニウム(Al) (層厚)300nm
nバリア層643:なし
*この比較例は、ソース電極層640単独の例(すなわち、ソース電極層640上にp電極層630が積層されていない例)
B−1.半導体装置の構成:
図8は、第2実施形態における半導体装置50bの構成を模式的に示す断面図である。第2実施形態における半導体装置50bは、ソース電極層640およびp電極層630の構成が図1に示した第1実施形態の半導体装置50と異なっており、その他の構成は第1実施形態の半導体装置50と同じである。
図9は、第2実施形態における半導体装置50bの製造方法を示すフローチャートである。第2実施形態における半導体装置50bの製造方法は、ソース電極層640およびp電極層630の形成順序が図2に示した第1実施形態の製造方法と異なっており、その他のステップは第1実施形態の製造方法と同じである。
図10は、第2実施形態の変形例における半導体装置50cの構成を模式的に示す断面図である。第2実施形態の変形例における半導体装置50cは、ソース電極層640およびp電極層630の構成と層間絶縁膜810および配線電極層820を備える点とが図8に示した第2実施形態の半導体装置50bと異なっており、その他の構成は第2実施形態の半導体装置50bと同じである。
図12ないし図14は、第2実施形態(およびその変形例)の半導体装置の性能を評価するための実験結果の一例を示す説明図である。実験に使用した実施例および比較例における各電極層の構成は以下の通りである。
[実施例1−1]
・p電極層630
pコンタクト形成層631:(材料)パラジウム(Pd) (層厚)20nm
pバリア層632:なし
・ソース電極層640
第1のnコンタクト形成層641:(材料)チタン(Ti) (層厚)17.5nm
第2のnコンタクト形成層642:(材料)アルミニウム(Al) (層厚)300nm
nキャップ層646:なし
[実施例1−2]
・p電極層630
pコンタクト形成層631:(材料)パラジウム(Pd) (層厚)50nm
pバリア層632:なし
・ソース電極層640
第1のnコンタクト形成層641:(材料)チタン(Ti) (層厚)17.5nm
第2のnコンタクト形成層642:(材料)アルミニウム(Al) (層厚)300nm
nキャップ層646:なし
[実施例2]
・p電極層630
pコンタクト形成層631:(材料)パラジウム(Pd) (層厚)50nm
pバリア層632:(材料)バナジウム(V) (層厚)17.5nm
・ソース電極層640
第1のnコンタクト形成層641:(材料)バナジウム(V) (層厚)17.5nm
第2のnコンタクト形成層642:(材料)アルミニウム(Al) (層厚)300nm
nキャップ層646:(材料)モリブデン(Mo) (層厚)50nm
*この実施例では、1つのバナジウム層が、pバリア層632および第1のnコンタクト形成層641として機能する。
[実施例3]
・p電極層630
pコンタクト形成層631:(材料)パラジウム(Pd) (層厚)50nm
pバリア層632:(材料)モリブデン(Mo) (層厚)50nm
・ソース電極層640
第1のnコンタクト形成層641:(材料)チタン(Ti) (層厚)17.5nm
第2のnコンタクト形成層642:(材料)アルミニウム(Al) (層厚)300nm
nキャップ層646:(材料)モリブデン(Mo) (層厚)50nm
[比較例]
・p電極層630
pコンタクト形成層631:(材料)パラジウム(Pd) (層厚)50nm
pバリア層632:なし
*この比較例は、p電極層630単独の例(すなわち、p電極層630上にソース電極層640が積層されていない例)
この発明は上記の実施形態に限られるものではなく、その要旨を逸脱しない範囲において種々の態様において実施することが可能であり、例えば次のような変形も可能である。
上記各実施形態では、半導体装置としてのトレンチ型MOSFETについて説明したが、本発明はそれ以外の半導体装置の製造方法にも適用可能である。例えば、本発明は、横型のMOSFETや絶縁ゲートバイポーラトランジスタ(IGBT)、(制御電極層としてのベース電極層を備える)バイポーラトランジスタの製造方法にも適用可能である。その他、本発明は、n型半導体層に形成された第1の電極層とp型半導体層に形成された第2の電極層とが互いに同電位で動作するような半導体装置全般の製造方法に適用可能である。
上記各実施形態における半導体装置の製造方法はあくまで一例であり、種々変形可能である。例えば、上記各実施形態では、p電極層630およびソース電極層640が形成された後にp電極層630およびソース電極層640の両方に対する熱処理(図2,4,6,8のステップS260)が行われるとしているが、p電極層630が形成された後に行われるp電極層630のための熱処理と、ソース電極層640が形成された後に行われるソース電極層のための熱処理とが、別々に行われるとしてもよい。このようにすれば、p電極層630とソース電極層640とのそれぞれについて熱処理条件を最適化することができる。
上記各実施形態では、ゲート絶縁膜740は二酸化ケイ素(SiO2)により形成されているとしているが、酸化アルミニウム(Al2O3)や窒化ケイ素(SiN)、酸化ハフニウム(HfO2)、酸化ジルコニウム(ZrO2)といった他の材料により形成されているとしてもよい。また、ゲート絶縁膜740は複数層構成であるとしてもよい。例えば、ゲート絶縁膜740は、SiO2の上にZrO2を設けたZrO2/SiO2構成をはじめ、HfO2/SiO2構成、Al2O3/SiO2構成、SiO2/SiN構成といった2層構成や、SiNの上にSiO2を設け、さらにその上にZrO2を設けたZrO2/SiO2/SiN構成をはじめ、HfO2/Al2O3/SiO2構成といった3層構成であるとしてもよい。
500…積層体
510…n型基板
520…n型半導体層(n−層)
530…p型半導体層(p型層)
540…第2のn型半導体層(n+層)
610…ドレイン電極層
630…p電極層
631…pコンタクト形成層
632…pバリア層
636…pキャップ層
640…ソース電極層
641…第1のnコンタクト形成層
642…第2のnコンタクト形成層
643…nバリア層
646…nキャップ層
650…ゲート電極層
710…リセス
720…トレンチ
740…ゲート絶縁膜
810…層間絶縁膜
812…コンタクトホール
820…配線電極層
Claims (26)
- 主として窒化ガリウム(GaN)により形成されたp型半導体層と、主として窒化ガリウム(GaN)により形成されると共に前記p型半導体層に接続されたn型半導体層と、前記n型半導体層に形成された第1の電極層と、前記p型半導体層に形成された第2の電極層と、を有し、前記第1の電極層と前記第2の電極層とは互いに同電位で動作するように電気的に接続されており、前記第1の電極層は前記第2の電極層における前記p型半導体層に接する表面とは反対側の表面の少なくとも一部に接続されている半導体装置の製造方法であって、
前記n型半導体層上に前記第1の電極層を形成する工程と、
前記p型半導体層上に前記第2の電極層を形成する工程と、
前記半導体層上に形成された前記第1の電極層と前記第2の電極層とに対して熱処理を行う工程と、を備え、
前記熱処理の温度は、摂氏400度以上650度以下であり、
前記p型半導体層上に形成される前記第2の電極層は、前記p型半導体層と接続される側に配置されたpコンタクト形成層を備え、
前記pコンタクト形成層は、ニッケル(Ni)、パラジウム(Pd)および白金(Pt)からなる群から選択された少なくとも1種の金属または前記選択された金属の合金を含み、
前記pコンタクト形成層の層厚は、3nm以上1000nm以下である、半導体装置の製造方法。 - 主として窒化ガリウム(GaN)により形成されたp型半導体層と、主として窒化ガリウム(GaN)により形成されると共に前記p型半導体層に接続されたn型半導体層と、前記n型半導体層に形成された第1の電極層と、前記p型半導体層に形成された第2の電極層と、を有し、前記第1の電極層と前記第2の電極層とは互いに同電位で動作するように電気的に接続されており、前記第2の電極層は前記第1の電極層における前記n型半導体層に接する表面とは反対側の表面の少なくとも一部に接続されている半導体装置の製造方法であって、
前記n型半導体層上に前記第1の電極層を形成する工程と、
前記p型半導体層上に前記第2の電極層を形成する工程と、
前記半導体層上に形成された前記第1の電極層と前記第2の電極層とに対して熱処理を行う工程と、を備える、半導体装置の製造方法。 - 請求項2に記載の半導体装置の製造方法であって、
前記熱処理の温度は、摂氏450度以上700度以下である、半導体装置の製造方法。 - 請求項1から請求項3までのいずれか一項に記載の半導体装置の製造方法であって、
前記熱処理を行う工程は、前記第1の電極層と前記第2の電極層との両方に対して同時に熱処理を行う工程である、半導体装置の製造方法。 - 請求項1から請求項3までのいずれか一項に記載の半導体装置の製造方法であって、
前記熱処理を行う工程は、
前記第1の電極層に対して第1の熱処理を行う工程と、
前記第2の電極層に対して第2の熱処理を行う工程と、を含む、半導体装置の製造方法。 - 請求項1から請求項5までのいずれか一項に記載の半導体装置の製造方法であって、
前記熱処理の継続時間は、1分間以上1時間間以下である、半導体装置の製造方法。 - 請求項1に記載の半導体装置の製造方法であって、
前記p型半導体層上に形成される前記第2の電極層は、前記pコンタクト形成層における前記p型半導体層と接続される側とは反対側に配置されたpバリア層を備え、
前記pバリア層は、ハフニウム(Hf)、バナジウム(V)、チタン(Ti)、モリブデン(Mo)、ニオブ(Nb)、ロジウム(Rh)、ケイ素(Si)、タンタル(Ta)、タングステン(W)、ジルコニウム(Zr)、イリジウム(Ir)、オスミウム(Os)、レニウム(Re)、TiSi、TiN、TiW、TaSiおよびTaNからなる群から選択された少なくとも1種の金属または前記選択された金属の合金を含む、半導体装置の製造方法。 - 請求項7に記載の半導体装置の製造方法であって、
前記pバリア層の層厚は、3nm以上1000nm以下である、半導体装置の製造方法。 - 請求項1、請求項7、または請求項8に記載の半導体装置の製造方法であって、
前記n型半導体層上に形成される前記第1の電極層は、前記n型半導体層と接続される側に配置された第1のnコンタクト形成層と、前記第1のnコンタクト形成層における前記n型半導体層と接続される側とは反対側に配置された第2のnコンタクト形成層と、を備え、
前記第1のnコンタクト形成層は、ハフニウム(Hf)、チタン(Ti)およびバナジウム(V)からなる群から選択された少なくとも1種の金属または前記選択された金属の合金を含む、半導体装置の製造方法。 - 請求項9に記載の半導体装置の製造方法であって、
前記第1のnコンタクト形成層の層厚は、3nm以上100nm以下である、半導体装置の製造方法。 - 請求項9または請求項10に記載の半導体装置の製造方法であって、
前記第2のnコンタクト形成層は、アルミニウム(Al)またはアルミニウム(Al)の合金を含む、半導体装置の製造方法。 - 請求項11に記載の半導体装置の製造方法であって、
前記第2のnコンタクト形成層の層厚は、100nm以上100μm以下である、半導体装置の製造方法。 - 請求項11または請求項12に記載の半導体装置の製造方法であって、
前記n型半導体層上に形成される前記第1の電極層は、前記第2のnコンタクト形成層における前記第1のnコンタクト形成層と接続される側とは反対側に配置されたnキャップ層を備え、
前記nキャップ層は、ハフニウム(Hf)、バナジウム(V)、チタン(Ti)、モリブデン(Mo)、ニオブ(Nb)、ロジウム(Rh)、ケイ素(Si)、タンタル(Ta)、タングステン(W)、ジルコニウム(Zr)、イリジウム(Ir)、オスミウム(Os)、レニウム(Re)、TiSi、TiN、TiW、TaSiおよびTaNからなる群から選択された少なくとも1種の金属または前記選択された金属の合金を含む、半導体装置の製造方法。 - 請求項13に記載の半導体装置の製造方法であって、
前記nキャップ層の層厚は、3nm以上100μm以下である、半導体装置の製造方法。 - 請求項7または請求項8に記載の半導体装置であって、
前記n型半導体層上に形成される前記第1の電極層は、前記n型半導体層と接続される側に配置された第1のnコンタクト形成層を備え、
前記pバリア層と前記第1のnコンタクト形成層とは、同一のプロセスにより形成される、半導体装置の製造方法。 - 請求項2または請求項3に記載の半導体装置の製造方法であって、
前記n型半導体層上に形成される前記第1の電極層は、前記n型半導体層と接続される側に配置された第1のnコンタクト形成層と、前記第1のnコンタクト形成層における前記n型半導体層と接続される側とは反対側に配置された第2のnコンタクト形成層と、を備え、
前記第1のnコンタクト形成層は、ハフニウム(Hf)、チタン(Ti)およびバナジウム(V)からなる群から選択された少なくとも1種の金属または前記選択された金属の合金を含む、半導体装置の製造方法。 - 請求項16に記載の半導体装置の製造方法であって、
前記第1のnコンタクト形成層の層厚は、3nm以上100nm以下である、半導体装置の製造方法。 - 請求項16または請求項17に記載の半導体装置の製造方法であって、
前記第2のnコンタクト形成層は、アルミニウム(Al)またはアルミニウム(Al)の合金を含む、半導体装置の製造方法。 - 請求項18に記載の半導体装置の製造方法であって、
前記第2のnコンタクト形成層の層厚は、100nm以上1000nm以下である、半導体装置の製造方法。 - 請求項18または請求項19に記載の半導体装置の製造方法であって、
前記n型半導体層上に形成される前記第1の電極層は、前記第2のnコンタクト形成層における前記第1のnコンタクト形成層と接続される側とは反対側に配置されたnバリア層を備え、
前記nバリア層は、ハフニウム(Hf)、バナジウム(V)、チタン(Ti)、モリブデン(Mo)、ニオブ(Nb)、ロジウム(Rh)、ケイ素(Si)、タンタル(Ta)、タングステン(W)、ジルコニウム(Zr)、イリジウム(Ir)、オスミウム(Os)、レニウム(Re)、TiSi、TiN、TiW、TaSiおよびTaNからなる群から選択された少なくとも1種の金属または前記選択された金属の合金を含む、半導体装置の製造方法。 - 請求項20に記載の半導体装置の製造方法であって、
前記nバリア層の層厚は、3nm以上1000nm以下である、半導体装置の製造方法。 - 請求項16から請求項21までのいずれか一項に記載の半導体装置の製造方法であって、
前記p型半導体層上に形成される前記第2の電極層は、前記p型半導体層と接続される側に配置されたpコンタクト形成層を備え、
前記pコンタクト形成層は、ニッケル(Ni)、パラジウム(Pd)および白金(Pt)からなる群から選択された少なくとも1種の金属または前記選択された金属の合金を含む、半導体装置の製造方法。 - 請求項22に記載の半導体装置の製造方法であって、
前記pコンタクト形成層の層厚は、3nm以上100μm以下である、半導体装置の製造方法。 - 請求項22または請求項23に記載の半導体装置の製造方法であって、
前記p型半導体層上に形成される前記第2の電極層は、前記pコンタクト形成層における前記p型半導体層と接続される側とは反対側に配置されたpキャップ層を備え、
前記pキャップ層は、ハフニウム(Hf)、バナジウム(V)、チタン(Ti)、モリブデン(Mo)、ニオブ(Nb)、ロジウム(Rh)、ケイ素(Si)、タンタル(Ta)、タングステン(W)、ジルコニウム(Zr)、イリジウム(Ir)、オスミウム(Os)、レニウム(Re)、TiSi、TiN、TiW、TaSiおよびTaNからなる群から選択された少なくとも1種の金属または前記選択された金属の合金を含む、半導体装置の製造方法。 - 請求項24に記載の半導体装置の製造方法であって、
前記pキャップ層の層厚は、3nm以上100μm以下である、半導体装置の製造方法。 - 請求項20または請求項21に記載の半導体装置の製造方法であって、
前記p型半導体層上に形成される前記第2の電極層は、前記p型半導体層と接続される側に配置されたpコンタクト形成層を備え、
前記nバリア層と前記pコンタクト形成層とは、同一のプロセスにより形成される、半導体装置の製造方法。
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012272987A JP5949516B2 (ja) | 2012-12-14 | 2012-12-14 | 半導体装置の製造方法 |
| US14/105,018 US9123635B2 (en) | 2012-12-14 | 2013-12-12 | Manufacturing method of semiconductor device |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012272987A JP5949516B2 (ja) | 2012-12-14 | 2012-12-14 | 半導体装置の製造方法 |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2014120542A JP2014120542A (ja) | 2014-06-30 |
| JP2014120542A5 JP2014120542A5 (ja) | 2015-02-05 |
| JP5949516B2 true JP5949516B2 (ja) | 2016-07-06 |
Family
ID=50929901
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012272987A Active JP5949516B2 (ja) | 2012-12-14 | 2012-12-14 | 半導体装置の製造方法 |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US9123635B2 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JP5949516B2 (ja) |
Families Citing this family (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP6007769B2 (ja) * | 2012-12-14 | 2016-10-12 | 豊田合成株式会社 | 半導体装置 |
| JP6369366B2 (ja) * | 2015-03-26 | 2018-08-08 | 豊田合成株式会社 | 半導体装置の製造方法 |
| JP6631853B2 (ja) * | 2015-09-25 | 2020-01-15 | パナソニックIpマネジメント株式会社 | 半導体装置 |
| JP6888224B2 (ja) * | 2017-10-16 | 2021-06-16 | 住友電工デバイス・イノベーション株式会社 | 半導体装置の製造方法 |
Family Cites Families (17)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2783349B2 (ja) | 1993-07-28 | 1998-08-06 | 日亜化学工業株式会社 | n型窒化ガリウム系化合物半導体層の電極及びその形成方法 |
| JP3620926B2 (ja) * | 1995-06-16 | 2005-02-16 | 豊田合成株式会社 | p伝導形3族窒化物半導体の電極及び電極形成方法及び素子 |
| JP3625377B2 (ja) * | 1998-05-25 | 2005-03-02 | ローム株式会社 | 半導体発光素子 |
| JP4003296B2 (ja) | 1998-06-22 | 2007-11-07 | 株式会社デンソー | 炭化珪素半導体装置及びその製造方法 |
| JP4645034B2 (ja) | 2003-02-06 | 2011-03-09 | 株式会社豊田中央研究所 | Iii族窒化物半導体を有する半導体素子 |
| JP4645753B2 (ja) | 2003-02-06 | 2011-03-09 | 株式会社豊田中央研究所 | Iii族窒化物半導体を有する半導体素子 |
| JP2008053449A (ja) | 2006-08-24 | 2008-03-06 | Rohm Co Ltd | 半導体装置およびその製造方法 |
| JP2008205175A (ja) | 2007-02-20 | 2008-09-04 | Rohm Co Ltd | 窒化物半導体素子の製造方法 |
| JP4478175B2 (ja) | 2007-06-26 | 2010-06-09 | 株式会社東芝 | 半導体装置 |
| JP2009094427A (ja) * | 2007-10-12 | 2009-04-30 | Eudyna Devices Inc | 発光素子の製造方法 |
| JP2009117820A (ja) * | 2007-10-16 | 2009-05-28 | Rohm Co Ltd | 窒化物半導体素子および窒化物半導体素子の製造方法 |
| JP5390983B2 (ja) * | 2008-08-08 | 2014-01-15 | 古河電気工業株式会社 | 電界効果トランジスタおよび電界効果トランジスタの製造方法 |
| JP5325534B2 (ja) | 2008-10-29 | 2013-10-23 | 株式会社東芝 | 窒化物半導体素子 |
| JP2010205918A (ja) * | 2009-03-03 | 2010-09-16 | Sumitomo Electric Ind Ltd | パワーデバイスおよびその製造方法 |
| JP5453892B2 (ja) * | 2009-04-15 | 2014-03-26 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | 窒化物半導体装置 |
| JP5144585B2 (ja) * | 2009-05-08 | 2013-02-13 | 住友電気工業株式会社 | 半導体装置およびその製造方法 |
| JP4737471B2 (ja) | 2009-10-08 | 2011-08-03 | 住友電気工業株式会社 | 半導体装置およびその製造方法 |
-
2012
- 2012-12-14 JP JP2012272987A patent/JP5949516B2/ja active Active
-
2013
- 2013-12-12 US US14/105,018 patent/US9123635B2/en active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2014120542A (ja) | 2014-06-30 |
| US9123635B2 (en) | 2015-09-01 |
| US20140167062A1 (en) | 2014-06-19 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5649347B2 (ja) | 半導体装置 | |
| US9559218B2 (en) | Semiconductor device and method of manufacturing the same | |
| JP6007769B2 (ja) | 半導体装置 | |
| JP6197427B2 (ja) | ショットキーバリアダイオード | |
| JP6269276B2 (ja) | 半導体装置、半導体装置の製造方法 | |
| JP5949516B2 (ja) | 半導体装置の製造方法 | |
| JP6007771B2 (ja) | 半導体装置 | |
| JP6149786B2 (ja) | 半導体装置および半導体装置の製造方法 | |
| JP6179445B2 (ja) | 縦型ショットキーバリアダイオード、縦型ショットキーバリアダイオードの製造方法 | |
| US10672876B2 (en) | Field-effect transistor having a bypass electrode connected to the gate electrode connection section | |
| JP6007770B2 (ja) | 半導体装置 | |
| JP2015204333A (ja) | 半導体装置および半導体装置の製造方法 | |
| JP6369366B2 (ja) | 半導体装置の製造方法 | |
| JP6176131B2 (ja) | 半導体装置の製造方法 | |
| JP2016162786A (ja) | 半導体装置およびその製造方法 | |
| JP6478395B2 (ja) | 半導体装置 | |
| JP5370026B2 (ja) | 半導体装置および半導体装置の製造方法 | |
| JP6237553B2 (ja) | 半導体装置およびその製造方法 | |
| US20150091062A1 (en) | Semiconductor element, semiconductor device, method for manufacturing semiconductor element, and method for manufacturing semiconductor device | |
| JP5765143B2 (ja) | 高電子移動度トランジスタとその製造方法 | |
| JP2020120110A (ja) | 半導体装置 | |
| JP2015204335A (ja) | 半導体装置および半導体装置の製造方法 | |
| JP5171996B2 (ja) | パワーデバイス | |
| JP2013211484A (ja) | 半導体装置の製造方法 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| RD04 | Notification of resignation of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7424 Effective date: 20140404 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20141211 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20150224 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20150821 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20150901 |
|
| A521 | Written amendment |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20151027 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20160510 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20160523 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 5949516 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |