JP4123027B2 - 半導体装置の製造方法 - Google Patents
半導体装置の製造方法 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP4123027B2 JP4123027B2 JP2003095975A JP2003095975A JP4123027B2 JP 4123027 B2 JP4123027 B2 JP 4123027B2 JP 2003095975 A JP2003095975 A JP 2003095975A JP 2003095975 A JP2003095975 A JP 2003095975A JP 4123027 B2 JP4123027 B2 JP 4123027B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- semiconductor chip
- semiconductor
- back surface
- conductive wire
- insulating resin
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Fee Related
Links
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 title claims abstract description 511
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 title claims description 28
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 55
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 claims description 28
- 238000005520 cutting process Methods 0.000 claims description 7
- 238000005530 etching Methods 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000011347 resin Substances 0.000 description 92
- 229920005989 resin Polymers 0.000 description 92
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 28
- 238000007789 sealing Methods 0.000 description 14
- 239000010410 layer Substances 0.000 description 13
- 239000012790 adhesive layer Substances 0.000 description 11
- 229910000679 solder Inorganic materials 0.000 description 4
- VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicium dioxide Chemical compound O=[Si]=O VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 230000002159 abnormal effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000002347 injection Methods 0.000 description 3
- 239000007924 injection Substances 0.000 description 3
- 238000010521 absorption reaction Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000004026 adhesive bonding Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000003822 epoxy resin Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000000945 filler Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000000227 grinding Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000010030 laminating Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229920000647 polyepoxide Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 238000003825 pressing Methods 0.000 description 2
- XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N water Substances O XLYOFNOQVPJJNP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000004925 Acrylic resin Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920000178 Acrylic resin Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000004593 Epoxy Substances 0.000 description 1
- PEEHTFAAVSWFBL-UHFFFAOYSA-N Maleimide Chemical compound O=C1NC(=O)C=C1 PEEHTFAAVSWFBL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052581 Si3N4 Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910045601 alloy Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000000956 alloy Substances 0.000 description 1
- PNEYBMLMFCGWSK-UHFFFAOYSA-N aluminium oxide Inorganic materials [O-2].[O-2].[O-2].[Al+3].[Al+3] PNEYBMLMFCGWSK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000013459 approach Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000004760 aramid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920003235 aromatic polyamide Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000000919 ceramic Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000002131 composite material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000007598 dipping method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000011521 glass Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000009413 insulation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005304 joining Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000004973 liquid crystal related substance Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920001721 polyimide Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000009719 polyimide resin Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000007639 printing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000377 silicon dioxide Substances 0.000 description 1
- HQVNEWCFYHHQES-UHFFFAOYSA-N silicon nitride Chemical compound N12[Si]34N5[Si]62N3[Si]51N64 HQVNEWCFYHHQES-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052814 silicon oxide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 238000001721 transfer moulding Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L25/00—Assemblies consisting of a plurality of individual semiconductor or other solid state devices ; Multistep manufacturing processes thereof
- H01L25/50—Multistep manufacturing processes of assemblies consisting of devices, each device being of a type provided for in group H01L27/00 or H01L29/00
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L24/00—Arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies; Methods or apparatus related thereto
- H01L24/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L24/02—Bonding areas ; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L24/03—Manufacturing methods
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L24/00—Arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies; Methods or apparatus related thereto
- H01L24/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L24/02—Bonding areas ; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L24/04—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bonding areas prior to the connecting process
- H01L24/05—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bonding areas prior to the connecting process of an individual bonding area
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L24/00—Arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies; Methods or apparatus related thereto
- H01L24/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L24/26—Layer connectors, e.g. plate connectors, solder or adhesive layers; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L24/31—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the layer connectors after the connecting process
- H01L24/32—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the layer connectors after the connecting process of an individual layer connector
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L25/00—Assemblies consisting of a plurality of individual semiconductor or other solid state devices ; Multistep manufacturing processes thereof
- H01L25/03—Assemblies consisting of a plurality of individual semiconductor or other solid state devices ; Multistep manufacturing processes thereof all the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/00, or in a single subclass of H10K, H10N, e.g. assemblies of rectifier diodes
- H01L25/04—Assemblies consisting of a plurality of individual semiconductor or other solid state devices ; Multistep manufacturing processes thereof all the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/00, or in a single subclass of H10K, H10N, e.g. assemblies of rectifier diodes the devices not having separate containers
- H01L25/065—Assemblies consisting of a plurality of individual semiconductor or other solid state devices ; Multistep manufacturing processes thereof all the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/00, or in a single subclass of H10K, H10N, e.g. assemblies of rectifier diodes the devices not having separate containers the devices being of a type provided for in group H01L27/00
- H01L25/0657—Stacked arrangements of devices
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/02—Bonding areas; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/04—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bonding areas prior to the connecting process
- H01L2224/0401—Bonding areas specifically adapted for bump connectors, e.g. under bump metallisation [UBM]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/02—Bonding areas; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/04—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bonding areas prior to the connecting process
- H01L2224/04042—Bonding areas specifically adapted for wire connectors, e.g. wirebond pads
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/02—Bonding areas; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/04—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bonding areas prior to the connecting process
- H01L2224/05—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bonding areas prior to the connecting process of an individual bonding area
- H01L2224/0554—External layer
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/10—Bump connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/12—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors prior to the connecting process
- H01L2224/13—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors prior to the connecting process of an individual bump connector
- H01L2224/13001—Core members of the bump connector
- H01L2224/1302—Disposition
- H01L2224/13022—Disposition the bump connector being at least partially embedded in the surface
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/10—Bump connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/15—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors after the connecting process
- H01L2224/16—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors after the connecting process of an individual bump connector
- H01L2224/161—Disposition
- H01L2224/16151—Disposition the bump connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive
- H01L2224/16221—Disposition the bump connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked
- H01L2224/16225—Disposition the bump connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked the item being non-metallic, e.g. insulating substrate with or without metallisation
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/26—Layer connectors, e.g. plate connectors, solder or adhesive layers; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/31—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the layer connectors after the connecting process
- H01L2224/32—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the layer connectors after the connecting process of an individual layer connector
- H01L2224/321—Disposition
- H01L2224/32135—Disposition the layer connector connecting between different semiconductor or solid-state bodies, i.e. chip-to-chip
- H01L2224/32145—Disposition the layer connector connecting between different semiconductor or solid-state bodies, i.e. chip-to-chip the bodies being stacked
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/26—Layer connectors, e.g. plate connectors, solder or adhesive layers; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/31—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the layer connectors after the connecting process
- H01L2224/32—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the layer connectors after the connecting process of an individual layer connector
- H01L2224/321—Disposition
- H01L2224/32151—Disposition the layer connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive
- H01L2224/32221—Disposition the layer connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked
- H01L2224/32225—Disposition the layer connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked the item being non-metallic, e.g. insulating substrate with or without metallisation
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/26—Layer connectors, e.g. plate connectors, solder or adhesive layers; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/31—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the layer connectors after the connecting process
- H01L2224/32—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the layer connectors after the connecting process of an individual layer connector
- H01L2224/321—Disposition
- H01L2224/32151—Disposition the layer connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive
- H01L2224/32221—Disposition the layer connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked
- H01L2224/32245—Disposition the layer connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked the item being metallic
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/42—Wire connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/44—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors prior to the connecting process
- H01L2224/45—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors prior to the connecting process of an individual wire connector
- H01L2224/45001—Core members of the connector
- H01L2224/45099—Material
- H01L2224/451—Material with a principal constituent of the material being a metal or a metalloid, e.g. boron (B), silicon (Si), germanium (Ge), arsenic (As), antimony (Sb), tellurium (Te) and polonium (Po), and alloys thereof
- H01L2224/45117—Material with a principal constituent of the material being a metal or a metalloid, e.g. boron (B), silicon (Si), germanium (Ge), arsenic (As), antimony (Sb), tellurium (Te) and polonium (Po), and alloys thereof the principal constituent melting at a temperature of greater than or equal to 400°C and less than 950°C
- H01L2224/45124—Aluminium (Al) as principal constituent
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/42—Wire connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/44—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors prior to the connecting process
- H01L2224/45—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors prior to the connecting process of an individual wire connector
- H01L2224/45001—Core members of the connector
- H01L2224/45099—Material
- H01L2224/451—Material with a principal constituent of the material being a metal or a metalloid, e.g. boron (B), silicon (Si), germanium (Ge), arsenic (As), antimony (Sb), tellurium (Te) and polonium (Po), and alloys thereof
- H01L2224/45138—Material with a principal constituent of the material being a metal or a metalloid, e.g. boron (B), silicon (Si), germanium (Ge), arsenic (As), antimony (Sb), tellurium (Te) and polonium (Po), and alloys thereof the principal constituent melting at a temperature of greater than or equal to 950°C and less than 1550°C
- H01L2224/45144—Gold (Au) as principal constituent
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/42—Wire connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/47—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors after the connecting process
- H01L2224/48—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors after the connecting process of an individual wire connector
- H01L2224/4805—Shape
- H01L2224/4809—Loop shape
- H01L2224/48091—Arched
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/42—Wire connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/47—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors after the connecting process
- H01L2224/48—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors after the connecting process of an individual wire connector
- H01L2224/481—Disposition
- H01L2224/48151—Connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive
- H01L2224/48221—Connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked
- H01L2224/48225—Connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked the item being non-metallic, e.g. insulating substrate with or without metallisation
- H01L2224/48227—Connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked the item being non-metallic, e.g. insulating substrate with or without metallisation connecting the wire to a bond pad of the item
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/42—Wire connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/47—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors after the connecting process
- H01L2224/48—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors after the connecting process of an individual wire connector
- H01L2224/481—Disposition
- H01L2224/48151—Connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive
- H01L2224/48221—Connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked
- H01L2224/48245—Connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked the item being metallic
- H01L2224/48247—Connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked the item being metallic connecting the wire to a bond pad of the item
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/73—Means for bonding being of different types provided for in two or more of groups H01L2224/10, H01L2224/18, H01L2224/26, H01L2224/34, H01L2224/42, H01L2224/50, H01L2224/63, H01L2224/71
- H01L2224/732—Location after the connecting process
- H01L2224/73251—Location after the connecting process on different surfaces
- H01L2224/73265—Layer and wire connectors
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/80—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected
- H01L2224/83—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected using a layer connector
- H01L2224/8336—Bonding interfaces of the semiconductor or solid state body
- H01L2224/83365—Shape, e.g. interlocking features
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/91—Methods for connecting semiconductor or solid state bodies including different methods provided for in two or more of groups H01L2224/80 - H01L2224/90
- H01L2224/92—Specific sequence of method steps
- H01L2224/922—Connecting different surfaces of the semiconductor or solid-state body with connectors of different types
- H01L2224/9222—Sequential connecting processes
- H01L2224/92242—Sequential connecting processes the first connecting process involving a layer connector
- H01L2224/92247—Sequential connecting processes the first connecting process involving a layer connector the second connecting process involving a wire connector
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2225/00—Details relating to assemblies covered by the group H01L25/00 but not provided for in its subgroups
- H01L2225/03—All the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/648 and H10K99/00
- H01L2225/04—All the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/648 and H10K99/00 the devices not having separate containers
- H01L2225/065—All the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/648 and H10K99/00 the devices not having separate containers the devices being of a type provided for in group H01L27/00
- H01L2225/06503—Stacked arrangements of devices
- H01L2225/0651—Wire or wire-like electrical connections from device to substrate
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2225/00—Details relating to assemblies covered by the group H01L25/00 but not provided for in its subgroups
- H01L2225/03—All the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/648 and H10K99/00
- H01L2225/04—All the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/648 and H10K99/00 the devices not having separate containers
- H01L2225/065—All the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/648 and H10K99/00 the devices not having separate containers the devices being of a type provided for in group H01L27/00
- H01L2225/06503—Stacked arrangements of devices
- H01L2225/06555—Geometry of the stack, e.g. form of the devices, geometry to facilitate stacking
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2225/00—Details relating to assemblies covered by the group H01L25/00 but not provided for in its subgroups
- H01L2225/03—All the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/648 and H10K99/00
- H01L2225/04—All the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/648 and H10K99/00 the devices not having separate containers
- H01L2225/065—All the devices being of a type provided for in the same subgroup of groups H01L27/00 - H01L33/648 and H10K99/00 the devices not having separate containers the devices being of a type provided for in group H01L27/00
- H01L2225/06503—Stacked arrangements of devices
- H01L2225/06582—Housing for the assembly, e.g. chip scale package [CSP]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L24/00—Arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies; Methods or apparatus related thereto
- H01L24/73—Means for bonding being of different types provided for in two or more of groups H01L24/10, H01L24/18, H01L24/26, H01L24/34, H01L24/42, H01L24/50, H01L24/63, H01L24/71
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/02—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/06—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions
- H01L29/0657—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions characterised by the shape of the body
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01004—Beryllium [Be]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01005—Boron [B]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01006—Carbon [C]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01013—Aluminum [Al]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01029—Copper [Cu]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01033—Arsenic [As]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01079—Gold [Au]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01082—Lead [Pb]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/013—Alloys
- H01L2924/014—Solder alloys
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/10—Details of semiconductor or other solid state devices to be connected
- H01L2924/1015—Shape
- H01L2924/10155—Shape being other than a cuboid
- H01L2924/10158—Shape being other than a cuboid at the passive surface
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/10—Details of semiconductor or other solid state devices to be connected
- H01L2924/11—Device type
- H01L2924/12—Passive devices, e.g. 2 terminal devices
- H01L2924/1204—Optical Diode
- H01L2924/12042—LASER
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/15—Details of package parts other than the semiconductor or other solid state devices to be connected
- H01L2924/151—Die mounting substrate
- H01L2924/153—Connection portion
- H01L2924/1531—Connection portion the connection portion being formed only on the surface of the substrate opposite to the die mounting surface
- H01L2924/15311—Connection portion the connection portion being formed only on the surface of the substrate opposite to the die mounting surface being a ball array, e.g. BGA
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/15—Details of package parts other than the semiconductor or other solid state devices to be connected
- H01L2924/181—Encapsulation
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Microelectronics & Electronic Packaging (AREA)
- Power Engineering (AREA)
- Computer Hardware Design (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Condensed Matter Physics & Semiconductors (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Manufacturing & Machinery (AREA)
- Wire Bonding (AREA)
- Encapsulation Of And Coatings For Semiconductor Or Solid State Devices (AREA)
Description
【発明の属する技術分野】
本発明は、半導体装置、電子デバイス、電子機器および半導体装置の製造方法に関し、特に、半導体チップの積層構造に適用して好適なものである。
【0002】
【従来の技術】
従来の半導体装置では、例えば、特許文献1に開示されているように、半導体チップの3次元実装構造を実現するため、積層された半導体チップをワイヤボンド接続する方法があった。
図11は、従来の半導体装置の概略構成を示す断面図である。
【0003】
図11において、キャリア基板101の表面には導電性ワイヤ104d、105cを接続するランド102が設けられるとともに、キャリア基板101の裏面には突出電極103が設けられている。また、半導体チップ104a、105aには、導電性ワイヤ104d、105dを接続する電極パッド104b、105bがそれぞれ設けられている。そして、キャリア基板101上には、接着層104cを介して半導体チップ104aがフェースアップ実装されている。さらに、半導体チップ104a上には、接着層106b、106cが両面にそれぞれ設けられたミラーチップ106aを介して、半導体チップ105aがフェースアップ実装されている。ここで、ミラーチップ106aは、半導体チップ104aに設けられた電極パッド104bを避けるようにして、半導体チップ104a、105a間に配置されている。
【0004】
そして、キャリア基板101上に実装された半導体チップ104aは、導電性ワイヤ104dを介してキャリア基板101のランド102に電気的に接続されるとともに、ミラーチップ106aを介して半導体チップ104a上に積層された半導体チップ104bは、導電性ワイヤ105dを介してキャリア基板101のランド102に電気的に接続されている。そして、導電性ワイヤ104d、105dがそれぞれ接続された半導体チップ104a、105aは、封止樹脂107により封止されている。
【0005】
ここで、半導体チップ104a、105a間にミラーチップ106aを配置することにより、半導体チップ104a、105a間の間隔を増加させることができる。このため、下層の半導体チップ104aに接続される導電性ワイヤ104dが上層の半導体チップ105aに接触することを防止することができ、サイズが等しい半導体チップ104a、105aを積層した場合においても、下層の半導体チップ104aをワイヤボンド接続することが可能となる。
【0006】
【特許文献1】
特開2000−101016号公報
【0007】
【発明が解決しようとする課題】
しかしながら、図11の半導体装置では、下層の半導体チップ104aをワイヤボンド接続するために、半導体チップ104a、105a間にミラーチップ106aを配置する必要があり、工程数が増大するとともに、コストアップを招くという問題があった。
【0008】
そこで、本発明の目的は、工程数の増大を抑制しつつ、積層される半導体チップ間の間隔を増大させることが可能な半導体装置、電子デバイス、電子機器および半導体装置の製造方法を提供することである。
【0009】
【課題を解決するための手段】
上述した課題を解決するために、本発明の一態様に係る半導体装置によれば、導電性ワイヤ接続用の端子が設けられた基材と、前記基材上にフェースアップ実装され、導電性ワイヤにより前記基材に設けられた端子と電気的に接続された第1半導体チップと、裏面に突出部が形成され、前記突出部を介して前記第1半導体チップ上に固着された第2半導体チップとを備えることを特徴とする。
【0010】
これにより、第1半導体チップ上に第2半導体チップを積層することで、第1半導体チップと第2半導体チップと間の間隔を一定に保つことを可能としつつ、第1半導体チップと第2半導体チップとを固定することが可能となる。このため、工程数の増大を抑制しつつ、第1半導体チップと第2半導体チップと間の間隔を増大させることが可能となり、第1半導体チップと第2半導体チップとのサイズが等しい場合においても、第1半導体チップをワイヤボンド接続することが可能となる。
【0011】
また、本発明の一態様に係る半導体装置によれば、前記突出部を介して前記第1半導体チップ上に前記第2半導体チップを固着する絶縁性樹脂をさらに備えることを特徴とする。
これにより、絶縁性樹脂を介して第1半導体チップ上に第2半導体チップを積層することで、第1半導体チップと第2半導体チップとの間の絶縁性を確保することが可能となるとともに、工程数の増大を抑制しつつ、第1半導体チップ上に第2半導体チップを固着することが可能となる。
【0012】
また、本発明の一態様に係る半導体装置によれば、前記絶縁性樹脂にはフィラーが混入されていることを特徴とする。
これにより、絶縁性樹脂の吸水性を低下させることが可能となるとともに、絶縁性樹脂の線膨張係数を半導体チップに近づけることが可能となり、絶縁性樹脂による応力を緩和することを可能として、半導体装置の信頼性を向上させることが可能となる。
【0013】
また、本発明の一態様に係る半導体装置によれば、前記絶縁性樹脂は、前記突出部が設けられた段差部分の少なくとも一部の領域に充填されていることを特徴とする。
これにより、第2半導体チップの裏面に突出部を形成したために、第2半導体チップの端部が薄型化した場合においても、薄型化された第2半導体チップの端部を絶縁性樹脂で補強することができる。
【0014】
また、本発明の一態様に係る半導体装置によれば、導電性ワイヤ接続用の端子が設けられた基材と、前記基材上にフェースアップ実装された第1半導体チップと、前記第1半導体チップに設けられた第1電極パッドと、前記第1電極パッドと前記基材に設けられた端子とを電気的に接続する第1導電性ワイヤと、裏面に突出部が形成された第2半導体チップと、前記第2半導体チップに設けられた第2電極パッドと、前記第1半導体チップ上の第1導電性ワイヤを包み込むようにして、前記突出部を介して前記第1半導体チップを前記第2半導体チップ上に固着させる絶縁性樹脂と、前記第2電極パッドと前記基材に設けられた端子とを電気的に接続する第2導電性ワイヤと、前記第1導電性ワイヤが接続された第1半導体チップおよび前記第2導電性ワイヤが接続された第2半導体チップを封止する封止樹脂とを備えることを特徴とする。
【0015】
これにより、絶縁性樹脂を介して第1半導体チップ上に第2半導体チップを積層することで、第1半導体チップと第2半導体チップと間の間隔を一定に保つことを可能としつつ、第1半導体チップ上の第1導電性ワイヤを絶縁性樹脂で固定することが可能となる。このため、第1導電性ワイヤが接続された第1半導体チップが樹脂封止される場合においても、封止樹脂の注入圧力で第1導電性ワイヤが変形することを防止することが可能となり、工程数の増大を抑制しつつ、ワイヤボンド接続された第1半導体チップ上に第2半導体チップを積層することが可能となるとともに、第1導電性ワイヤの異常接触を防止することが可能となる。
【0016】
また、本発明の一態様に係る半導体装置によれば、導電性ワイヤ接続用の端子が設けられた基材と、前記基材上にフェースアップ実装された第1半導体チップと、前記第1半導体チップに設けられた第1電極パッドと、前記第1電極パッドと前記基材に設けられた端子とを電気的に接続する第1導電性ワイヤと、裏面に突出部が形成された第2半導体チップと、前記第2半導体チップに設けられた第2電極パッドと、少なくとも前記第2電極パッド下に存在するようにして前記第1半導体チップと前記第2半導体チップとの間に設けられ、前記突出部を介して前記第1半導体チップを前記第2半導体チップ上に固着させる絶縁性樹脂と、前記第2電極パッドと前記基材に設けられた端子とを電気的に接続する第2導電性ワイヤとを備えることを特徴とする。
【0017】
これにより、絶縁性樹脂を介して第1半導体チップ上に第2半導体チップを積層することで、第1半導体チップと第2半導体チップと間の間隔を一定に保つことを可能としつつ、第2電極パッドの形成領域を絶縁性樹脂で支えることが可能となる。このため、第2電極パッド上に第2導電性ワイヤが接続される場合においても、ワイヤボンド時の超音波振動で第2半導体チップが破壊されることを防止することが可能となり、工程数の増大を抑制しつつ、ワイヤボンド接続された第1半導体チップ上に第2半導体チップを積層することが可能となるとともに、ワイヤボンドを安定して行うことが可能となる。
【0018】
また、本発明の一態様に係る半導体装置によれば、前記突出部を含む第2半導体チップの裏面全体に形成された絶縁層をさらに備えることを特徴とする。
これにより、第1半導体チップに接続された第1導電性ワイヤの高さが高くなった場合においても、第1導電性ワイヤが第2半導体チップの裏面とショートすることを防止することができ、ワイヤボンド接続された第1半導体チップ上に第2半導体チップを安定して積層することが可能となる。
【0019】
また、本発明の一態様に係る半導体装置によれば、前記突出部の少なくとも一部の領域は、前記突出部の形成面に近づくにつれ広がる形状を有していることを特徴とする。
これにより、第2半導体チップの裏面に突出部を形成したために、第2半導体チップの端部が薄型化した場合においても、第2半導体チップの端部にかかる応力を効率よく逃がすことが可能となる。このため、第1導電性ワイヤが第2半導体チップの裏面に接触することを防止しつつ、第2半導体チップの端部の強度を向上させることが可能となる。
【0020】
また、本発明の一態様に係る半導体装置によれば、前記第2半導体チップのサイズは前記第1半導体チップのサイズよりも大きいことを特徴とする。
これにより、製造工程を複雑化させることなく、第1半導体チップから引き出された導電性ワイヤ上にも第2半導体チップを配置することが可能となり、半導体チップ実装時の省スペース化を図ることが可能となる。
【0021】
また、本発明の一態様に係る半導体装置によれば、導電性ワイヤ接続用の端子が設けられた基材と、前記基材上にフリップチップ実装された第1半導体チップと、接着層を介して前記第1半導体チップ上にフェースアップ実装された第2半導体チップと、前記基材に設けられた端子と前記第2半導体チップとを電気的に接続する第1導電性ワイヤと、裏面に突出部が形成され、前記突出部を介して前記第2半導体チップ上に固着された第3半導体チップと、前記基材に設けられた端子と前記第3半導体チップとを電気的に接続する第2導電性ワイヤとを備えることを特徴とする。
【0022】
これにより、第2半導体チップ上に第3半導体チップを積層することで、第2半導体チップと第3半導体チップと間の間隔を一定に保つことを可能としつつ、第2半導体チップと第3半導体チップとを固定することが可能となるとともに、高さの増大を抑制しつつ、第2半導体チップと基材との間に第1半導体チップを介装することが可能となる。このため、工程数の増大を抑制しつつ、ワイヤボンド接続された第2半導体チップ上に第3半導体チップを積層することが可能となるとともに、省スペース化を可能としつつ、半導体チップの積層数を増加させることが可能となる。
【0023】
また、本発明の一態様に係る電子デバイスによれば、導電性ワイヤ接続用の端子が設けられた基材と、前記基材上にフェースアップ実装され、導電性ワイヤにより前記基材に設けられた端子と電気的に接続された第1電子部品と、裏面に突出部が形成され、前記突出部を介して前記第1電子部品上に固着された第2電子部品とを備えることを特徴とする。
【0024】
これにより、第1電子部品上に第2電子部品を積層することで、第1電子部品と第2電子部品と間の間隔を一定に保つことを可能としつつ、第1電子部品と第2電子部品とを固定することが可能となる。このため、工程数の増大を抑制しつつ、第1電子部品と第2電子部品と間の間隔を増大させることが可能となり、第1電子部品と第2電子部品とのサイズが等しい場合においても、第1電子部品をワイヤボンド接続することが可能となる。
【0025】
また、本発明の一態様に係る電子機器によれば、導電性ワイヤ接続用の端子が設けられた基材と、前記基材上にフェースアップ実装され、導電性ワイヤにより前記基材に設けられた端子と電気的に接続された第1半導体チップと、裏面に突出部が形成され、前記突出部を介して前記第1半導体チップ上に固着された第2半導体チップと、前記基材を介して前記第1半導体チップおよび前記第2半導体チップに電気的に接続された電子部品とを備えることを特徴とする。
【0026】
これにより、工程数の増大を抑制しつつ、ワイヤボンド接続された半導体チップの積層構造を実現することが可能となり、電子機器のコストダウンを図ることが可能となる。
また、本発明の一態様に係る半導体装置の製造方法によれば、導電性ワイヤ接続用の端子が設けられた基材上に第1半導体チップをマウントする工程と、前記基材上にマウントされた第1半導体チップと前記基材に設けられた端子とを導電性ワイヤで接続する工程と、裏面に突出部が形成された第2半導体チップを前記第1半導体チップ上に固着する工程とを備えることを特徴とする。
【0027】
これにより、第1半導体チップに接続された導電性ワイヤが第2半導体チップに接触することを防止しつつ、ワイヤボンド接続された第1半導体チップ上に第2半導体チップを積層することが可能となり、ワイヤボンド接続された半導体チップの積層構造のコストダウンを図ることが可能となる。
また、本発明の一態様に係る半導体装置の製造方法によれば、導電性ワイヤ接続用の端子が設けられた基材上に第1半導体チップをマウントする工程と、前記基材上にマウントされた第1半導体チップと前記基材に設けられた端子とを導電性ワイヤで接続する工程と、前記第1半導体チップ上に絶縁性樹脂を配置する工程と、第2半導体チップの裏面に形成された突出部を前記絶縁性樹脂に押し当てることにより、前記第2半導体チップを前記第1半導体チップ上に固着する工程とを備えることを特徴とする。
【0028】
これにより、第1半導体チップ上に第2半導体チップを積層することで、絶縁性樹脂が突出部から食み出すことを可能としつつ、第1半導体チップ上に第2半導体チップを固着することが可能となる。このため、第1半導体チップ上に第2半導体チップを固着することを可能としつつ、突出部が設けられた第2半導体チップの裏面の段差部分に絶縁性樹脂を充填することが可能となり、工程数の増大を抑制しつつ、第2半導体チップの端部の強度を向上させることが可能となるとともに、第1導電性ワイヤが第1半導体チップの裏面に接触することを防止することが可能となる。
【0029】
また、本発明の一態様に係る半導体装置の製造方法によれば、表面がスクライブラインで区画されたウェハの裏面をハーフカットすることにより、前記スクライブラインに対向配置された溝を前記ウェハの裏面に形成する工程と、前記スクライブラインに沿って前記溝を切断することにより、裏面に突出部が形成された前記第2半導体チップを形成する工程とをさらに備えることを特徴とする。
【0030】
これにより、複数の半導体チップの裏面に突出部を一括形成することが可能となり、製造工程の煩雑化を抑制しつつ、ワイヤボンド接続された第1半導体チップ上に第2半導体チップを安定して積層することが可能となる。
また、本発明の一態様に係る半導体装置の製造方法によれば、前記ハーフカットは、先端が丸みを帯びたブレードによるダイシング、等方性エッチングまたはレーザ加工により行われることを特徴とする。
【0031】
これにより、半導体チップの裏面に形成される突出部にアール形状を持たせることを可能としつつ、半導体チップの裏面の突出部を一括形成することが可能となる。このため、半導体チップの裏面に突出部を形成したために、半導体チップの端部が薄型化した場合においても、製造工程の煩雑化を抑制しつつ、第2半導体チップの端部の強度を向上させることが可能となり、ワイヤボンド接続された半導体チップの積層構造を安定して製造することが可能となる。
【0032】
また、本発明の一態様に係る半導体装置の製造方法によれば、前記溝が形成されたウェハの裏面に絶縁膜を成膜する工程をさらに備えることを特徴とする。
これにより、突出部が形成される複数の半導体チップの裏面全体に絶縁膜を一括形成することが可能となる。このため、第1導電性ワイヤが第2半導体チップの裏面とショートすることを防止するために、各第2半導体チップに個別に絶縁膜を形成する必要がなくなり、製造工程の煩雑化を抑制しつつ、ワイヤボンド接続された第1半導体チップ上に第2半導体チップを安定して積層することが可能となる。
【0033】
【発明の実施の形態】
以下、本発明の実施形態に係る半導体装置およびその製造方法について図面を参照しながら説明する。
図1は、本発明の第1実施形態に係る半導体装置の概略構成を示す断面図である。
【0034】
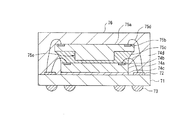
図1において、キャリア基板1の表面には導電性ワイヤ4d、5dを接続するランド2が設けられるとともに、キャリア基板1の裏面には突出電極3が設けられている。なお、キャリア基板1としては、例えば、両面基板、多層配線基板、ビルドアップ基板、テープ基板またはフィルム基板などを用いることができ、キャリア基板1の材質としては、例えば、ポリイミド樹脂、ガラスエポキシ樹脂、BTレジン、アラミドとエポキシのコンポジットまたはセラミックなどを用いることができる。また、突出電極3としては、例えば、Auバンプ、半田材などで被覆されたCuバンプやNiバンプ、あるいは半田ボールなどを用いることができる。
【0035】
また、半導体チップ4a、5aには、導電性ワイヤ4d、5dを接続する電極パッド4b、5bがそれぞれ設けられ、半導体チップ5aの裏面には、半導体チップ5aに一体的に形成された突出部5eが設けられている。なお、半導体チップ5aの厚みは、例えば、50〜200μm程度の範囲、突出部5eの高さは、例えば、30〜150μm程度の範囲に設定することができる。また、導電性ワイヤ4d、5dとしては、例えば、AuワイヤやAlワイヤなどを用いることができる。
【0036】
そして、キャリア基板1上には、接着層4cを介して半導体チップ4aがフェースアップ実装されている。さらに、半導体チップ4a上には、突出部5eを介して半導体チップ5aがフェースアップ実装され、突出部5eは、絶縁性樹脂5cにより半導体チップ4a上に固着されている。なお、絶縁性樹脂5cとしては、ペースト状樹脂またはシート状樹脂を用いることができ、例えば、エポキシ系樹脂、アクリル系樹脂またはマレイミド系樹脂などを用いることができる。また、絶縁性樹脂5cには、シリカやアルミナなどのフィラーが混入されるようにしてもよい。これにより、絶縁性樹脂5cの吸水性を低下させることが可能となるとともに、絶縁性樹脂5cの線膨張係数を半導体チップ4a、5aに近づけることが可能となり、絶縁性樹脂5cによる応力を緩和することを可能として、半導体装置の信頼性を向上させることが可能となる。
【0037】
そして、キャリア基板1上に実装された半導体チップ4aは、導電性ワイヤ4dを介してキャリア基板1のランド2に電気的に接続されるとともに、突出部5eを介して半導体チップ4a上に積層された半導体チップ5aは、導電性ワイヤ5dを介してキャリア基板1のランド2に電気的に接続されている。そして、導電性ワイヤ4d、5dがそれぞれ接続された半導体チップ4a、5aは、封止樹脂6により封止されている。
【0038】
ここで、突出部5eの高さは、半導体チップ4a上に半導体チップ5aを積層した場合、導電性ワイヤ4dが半導体チップ5aの裏面に接触しないように設定することができる。また、突出部5eは、半導体チップ4aに接続された導電性ワイヤ4dを避けるように、半導体チップ4a上に配置することができる。
これにより、半導体チップ4a上に半導体チップ5aを積層することで、半導体チップ5aの裏面に導電性ワイヤ4dが接触することを防止しつつ、半導体チップ4a、5aを固定することが可能となる。このため、半導体チップ4a、5aのサイズが等しい場合においても、工程数の増大を抑制しつつ、導電性ワイヤ4dが接続された半導体チップ4a上に半導体チップ5aを積層することが可能となる。
【0039】
また、絶縁性樹脂5cにより突出部5eを半導体チップ4a上に固着する場合、半導体チップ4a上に配置された絶縁性樹脂5cを突出部5eの周囲に食み出させることにより、突出部5eが形成された半導体チップ5aの裏面の段差部分に絶縁性樹脂5cを充填し、半導体チップ4a上の導電性ワイヤ4dを包み込ませることができる。
【0040】
これにより、半導体チップ4a、5a間の間隔を一定に保つことを可能としつつ、半導体チップ4a上の導電性ワイヤ4dを絶縁性樹脂5cで固定することが可能となる。このため、導電性ワイヤ4dが接続された半導体チップ4aが樹脂封止される場合においても、封止樹脂6の注入圧力で導電性ワイヤ4dが流されることを防止することが可能となり、工程数の増大を抑制しつつ、ワイヤボンド接続された半導体チップ4a上に半導体チップ5aを積層することが可能となるとともに、導電性ワイヤ4dの異常接触を防止することが可能となる。
【0041】
また、半導体チップ5aの電極パッド5b下にも絶縁性樹脂6が存在するように、半導体チップ4a、5a間に絶縁性樹脂6を充填することができる。これにより、半導体チップ4a、5a間の間隔を一定に保つことを可能としつつ、電極パッド5bの形成領域を絶縁性樹脂6で支えることが可能となる。このため、電極パッド5b上に導電性ワイヤ5dが接続される場合においても、ワイヤボンド時の超音波振動で半導体チップ5aが破壊されることを防止することが可能となり、工程数の増大を抑制しつつ、ワイヤボンド接続された半導体チップ4a上に半導体チップ5aを積層することが可能となるとともに、ワイヤボンドを安定して行うことが可能となる。
【0042】
図2は、図1の半導体装置の製造方法を示す断面図である。
図2(a)において、接着層4cを介し、半導体チップ4aをキャリア基板1上にフェースアップ実装する。そして、キャリア基板1上にフェースアップ実装された半導体チップ4aのワイヤボンドを行うことにより、ランド2と電極パッド4bとを導電性ワイヤ4dで接続する。
【0043】
次に、図2(b)に示すように、導電性ワイヤ4dが接続された半導体チップ4a上に絶縁性樹脂5cを配置する。なお、絶縁性樹脂5cを半導体チップ4a上に配置する場合、例えば、ディスペンサなどを用いることができる。
次に、図2(c)に示すように、突出部5eが形成された半導体チップ5aの裏面を絶縁性樹脂6に押し当てながら、半導体チップ5aを半導体チップ4a上にフェースアップ実装する。ここで、半導体チップ4a上に配置される絶縁性樹脂5cの量を調整し、半導体チップ5aを半導体チップ4a上に実装した際に、半導体チップ4a上に配置された絶縁性樹脂5cが突出部5eの周囲に食み出すようにすることができる。
【0044】
これにより、半導体チップ5aを半導体チップ4a上に実装することで、突出部5eが形成された半導体チップ5aの裏面の段差部分に絶縁性樹脂6を充填することができる。このため、工程数を増加させることなく、半導体チップ4a上の導電性ワイヤ4dを絶縁性樹脂6で包み込んだり、半導体チップ5aの電極パッド5b下を絶縁性樹脂6で補強したりすることができる。
【0045】
そして、突出部5eを介して半導体チップ5aが半導体チップ4a上に積層された状態で、絶縁性樹脂6を硬化させる。そして、半導体チップ4a上にフェースアップ実装された半導体チップ5aのワイヤボンドを行うことにより、ランド2と電極パッド5bとを導電性ワイヤ5dで接続する。ここで、電極パッド5bの配置位置に対応して、半導体チップ5aの裏面に絶縁性樹脂5cを充填することにより、半導体チップ5aの電極パッド5b下を絶縁性樹脂5cで補強することが可能となる。このため、電極パッド5b上に導電性ワイヤ5dが接続される場合においても、ワイヤボンド時の超音波振動で半導体チップ5aが破壊されることを防止することが可能となり、工程数の増大を抑制しつつ、ワイヤボンドを安定して行うことが可能となる。
【0046】
なお、絶縁性樹脂5cを介して半導体チップ4a上に半導体チップ5aを固着する場合、例えば、ACF(Anisotropic Conductive Film)接合、NCF(Nonconductive Film)接合、ACP(Anisotropic Conductive Paste)接合、NCP(Nonconductive Paste)接合などの接着剤接合を用いるようにしてもよい。
【0047】
次に、図1に示すように、トランスファーモールドなどの方法により、導電性ワイヤ4d、5dでそれぞれ接続された半導体チップ4a、5aを封止樹脂6で封止する。ここで、半導体チップ4a上の導電性ワイヤ4dが包み込まれるように、半導体チップ5aの裏面に絶縁性樹脂5cを充填することにより、半導体チップ4a上の導電性ワイヤ4dを絶縁性樹脂5cで固定することが可能となる。このため、導電性ワイヤ4dが接続された半導体チップ4aが樹脂封止される場合においても、封止樹脂6の注入圧力で導電性ワイヤ4dが流されることを防止することが可能となり、工程数の増大を抑制しつつ、ワイヤボンド接続された半導体チップ上4aに半導体チップ5aを積層することが可能となるとともに、導電性ワイヤ4dの異常接触を防止することが可能となる。
【0048】
なお、半導体チップ4a、5a間に絶縁性樹脂5cを設ける場合、絶縁性樹脂5cを半導体チップ4a上に配置する代わりに、印刷またはディッピングなどの方法により、突出部5eに絶縁性樹脂5cを付着させるようにしてもよい。
図3は、図1の半導体装置の突出部の製造方法を示す断面図である。
図3(a)において、半導体ウェハ11の表面はスクライブラインSB1〜SB4で区画され、スクライブラインSB1〜SB4で区画された各区画領域には、能動面がそれぞれ形成されるとともに、電極パッド12a〜12cがそれぞれ設けられている。そして、半導体ウェハ11上に形成された能動面を避けるようにして、半導体ウェハ11に開口部13を形成する。
【0049】
次に、図3(b)に示すように、開口部13が形成された半導体ウェハ11の裏面11´を研削することにより、半導体ウェハ11を薄型化し、開口部13を貫通させることで、貫通孔13´を半導体ウェハ11に形成する。なお、開口部13は予め貫通していてもよい。
次に、図3(c)に示すように、貫通孔13´が形成された半導体ウェハ11の能動面側にダイシングテープ14を貼り付ける。そして、貫通孔13´を参照しながらブレード15の位置合わせを行うことにより、ブレード15の中央がスクライブラインSB1〜SB4の位置に対応するように配置する。そして、ブレード15を用いて半導体ウェハ11の裏面をハーフカットすることにより、半導体ウェハ11の裏面に溝を形成し、スクライブラインSB1〜SB4で区画された各区画領域に突出部16a〜16cを形成する。なお、半導体ウェハ11の能動面側を見ながら、半導体ウェハ11の裏面でブレード15の位置合わせができるダイシング装置を用いる場合、貫通孔13´は必ずしも形成する必要はない。
【0050】
ここで、半導体ウェハ11の裏面に形成される溝の深さは、突出部16a〜16cが形成された半導体チップ11a〜11cを、ワイヤボンド接続された下層の半導体チップ上に積層した場合、下層の半導体チップに接続された導電性ワイヤが、半導体チップ11a〜11cの裏面に接触しないように設定することができる。また、ブレード15の幅は、下層の半導体チップに接続された導電性ワイヤを避けながら、突出部16a〜16cが形成された半導体チップ11a〜11cを下層の半導体チップ上に配置することができるように設定することができる。
【0051】
次に、図3(d)に示すように、突出部16a〜16cが形成された半導体ウェハ11からダイシングテープ14を剥がし、突出部16a〜16cを介して半導体ウェハ11の裏面側にダイシングテープ17に貼り付ける。
次に、図3(e)に示すように、ブレード15よりも幅の小さなブレード18を用い、スクライブラインSB1〜SB4に沿って半導体ウェハ11のフルカットを行うことにより、突出部16a〜16cが裏面にそれぞれ形成された半導体チップ11a〜11cを形成する。
【0052】
これにより、複数の半導体チップ11a〜11cの裏面に突出部16a〜16cをそれぞれ一括形成することが可能となり、製造工程の煩雑化を抑制しつつ、ワイヤボンド接続された下層の半導体チップ上に半導体チップ11a〜11cを安定して積層することが可能となる。
なお、突出部16a〜16cが設けられた半導体チップ11a〜11cを形成する場合、ブレード18によりスクライブラインSB1〜SB4に沿って半導体ウェハ11表面のハーフカッットを行った後、ブレード15により半導体ウェハ11の裏面のハーフカッットを行うようにしてもよい。
【0053】
図4は、本発明の第2実施形態に係る半導体装置の概略構成を示す断面図である。
図4において、キャリア基板21の表面には導電性ワイヤ24d、25dを接続するランド22が設けられるとともに、キャリア基板21の裏面には突出電極23が設けられている。また、半導体チップ24a、25aには、導電性ワイヤ24d、25dを接続する電極パッド24b、25bがそれぞれ設けられ、半導体チップ25aの裏面には、半導体チップ25aに一体的に形成された突出部25eが設けられている。そして、突出部25eを含む半導体チップ25aの裏面全体には絶縁層25eが形成されている。なお、絶縁層25fとしては、例えば、シリコン酸化膜やシリコン窒化膜などを用いることができる。
【0054】
ここで、突出部25eを含む半導体チップ25aの裏面全体に絶縁層25eを形成することにより、半導体チップ24aに接続された導電性ワイヤ24dの高さが高くなった場合においても、導電性ワイヤ24dが半導体チップ25aの裏面とショートすることを防止することができる。
そして、キャリア基板21上には、接着層24cを介して半導体チップ24aがフェースアップ実装されている。さらに、半導体チップ24a上には、突出部25eを介して半導体チップ25aがフェースアップ実装され、突出部25eは、絶縁性樹脂25cにより半導体チップ24a上に固着されている。ここで、絶縁性樹脂25cが突出部25eの周囲に食み出すようにすることにより、突出部25eが形成された半導体チップ25aの裏面の段差部分に絶縁性樹脂25cを充填し、半導体チップ24a上の導電性ワイヤ24dを絶縁性樹脂25cで包み込んだり、半導体チップ25aの電極パッド25b下を絶縁性樹脂25cで補強したりすることができる。
【0055】
そして、キャリア基板21上に実装された半導体チップ24aは、導電性ワイヤ24dを介してキャリア基板21のランド22に電気的に接続されるとともに、突出部25eを介して半導体チップ24a上に積層された半導体チップ25aは、導電性ワイヤ25dを介してキャリア基板21のランド22に電気的に接続されている。そして、導電性ワイヤ24d、25dがそれぞれ接続された半導体チップ24a、25aは封止樹脂26により封止されている。
【0056】
なお、突出部25eの高さは、半導体チップ24a上に半導体チップ25aを積層した場合、導電性ワイヤ24dが半導体チップ25aの裏面に接触しないように設定することができる。また、突出部25eは、半導体チップ24aに接続された導電性ワイヤ24dを避けるように、半導体チップ24a上に配置することができる。
【0057】
図5は、図4の半導体装置の突出部の製造方法を示す断面図である。
図5(a)において、半導体ウェハ31の表面はスクライブラインSB11〜SB14で区画され、スクライブラインSB11〜SB14で区画された各区画領域には、能動面がそれぞれ形成されるとともに、電極パッド32a〜32cがそれぞれ設けられている。また、半導体ウェハ31には、半導体ウェハ31上に形成された能動面を避けるようにして、貫通孔33が形成されている。
【0058】
そして、貫通孔33が形成された半導体ウェハ31の能動面側にダイシングテープ34を貼り付ける。そして、貫通孔33を参照しながらブレード35の位置合わせを行うことにより、ブレード35の中央がスクライブラインSB11〜SB14の位置に対応するように配置する。そして、ブレード35を用いて半導体ウェハ31の裏面をハーフカットすることにより、半導体ウェハ31の裏面に溝を形成し、スクライブラインSB11〜SB14で区画された各区画領域に突出部36a〜36cを形成する。
【0059】
ここで、半導体ウェハ31の裏面に形成される溝の深さは、突出部36a〜36cが形成された半導体チップ31a〜31cを、ワイヤボンド接続された下層の半導体チップ上に積層した場合、下層の半導体チップに接続された導電性ワイヤが、半導体チップ31a〜31cの裏面に接触しないように設定することができる。また、ブレード35の幅は、下層の半導体チップに接続された導電性ワイヤを避けながら、突出部36a〜36cが形成された半導体チップ31a〜31cを下層の半導体チップ上に配置することができるように設定することができる。
【0060】
次に、図5(b)に示すように、例えば、CVDなどの方法により、突出部36a〜36cの表面を含む半導体ウェハ31の裏面全体に絶縁層39を形成する。
次に、図5(c)に示すように、突出部36a〜36cが形成された半導体ウェハ31からダイシングテープ34を剥がし、突出部36a〜36cを介して半導体ウェハ31の裏面側にダイシングテープ37を貼り付ける。
【0061】
次に、図5(d)に示すように、ブレード35よりも幅の小さなブレード38を用い、スクライブラインSB11〜SB14に沿って半導体ウェハ31のフルカットを行うことにより、突出部36a〜36cおよび絶縁層39a〜39cがそれぞれ設けられた半導体チップ31a〜31cを形成する。
これにより、突出部36a〜36cがそれぞれ形成される複数の半導体チップ31a〜31cの裏面全体に絶縁層39a〜39cをそれぞれ一括形成することが可能となる。このため、下層の半導体チップに接続された導電性ワイヤが半導体チップ31a〜31cの裏面とショートすることを防止するために、各半導体チップ31a〜31cに個別に絶縁層39a〜39cを形成する必要がなくなり、製造工程の煩雑化を抑制しつつ、ワイヤボンド接続された下層の半導体チップ上に半導体チップ31a〜31cを安定して積層することが可能となる。
【0062】
図6は、本発明の第3実施形態に係る半導体装置の概略構成を示す断面図である。
図6(a)において、キャリア基板41の表面には導電性ワイヤ44d、45dを接続するランド42が設けられるとともに、キャリア基板41の裏面には突出電極43が設けられている。また、半導体チップ44a、45aには、導電性ワイヤ44d、45dを接続する電極パッド44b、45bがそれぞれ設けられ、半導体チップ45aの裏面には、半導体チップ45aに一体的に形成された突出部45eが設けられている。ここで、突出部45eの少なくとも一部の領域は、突出部45eの形成面に近づくにつれ広がる形状を有し、例えば、突出部45eにアール形状を持たせることができる。
【0063】
これにより、半導体チップ45aの裏面に突出部45eを形成したために、半導体チップ45aの端部が薄型化した場合においても、半導体チップ45aの端部にかかる応力を効率よく逃がすことが可能となる。このため、半導体チップ44aに接続された導電性ワイヤ44dが半導体チップ45aの裏面に接触することを防止しつつ、半導体チップ45aの端部の強度を向上させることが可能となり、ワイヤボンド時の超音波振動などで半導体チップ45aが破壊することを防止することができる。
【0064】
そして、キャリア基板41上には、接着層44cを介して半導体チップ44aがフェースアップ実装されている。さらに、半導体チップ44a上には、突出部45eを介して半導体チップ45aがフェースアップ実装され、突出部45eは、絶縁性樹脂45cにより半導体チップ44a上に固着されている。ここで、絶縁性樹脂45cが突出部45eの周囲に食み出すようにすることにより、突出部45eが形成された半導体チップ45aの裏面の段差部分に絶縁性樹脂45cを充填し、半導体チップ44a上の導電性ワイヤ44dを絶縁性樹脂45cで包み込んだり、半導体チップ45aの電極パッド45b下を絶縁性樹脂45cで補強したりすることができる。
【0065】
そして、キャリア基板41上に実装された半導体チップ44aは、導電性ワイヤ44dを介してキャリア基板41のランド42に電気的に接続されるとともに、突出部45eを介して半導体チップ44a上に積層された半導体チップ45aは、導電性ワイヤ45dを介してキャリア基板41のランド42に電気的に接続されている。そして、導電性ワイヤ44d、45dがそれぞれ接続された半導体チップ44a、45aは封止樹脂46により封止されている。
【0066】
ここで、突出部45eの高さは、半導体チップ44a上に半導体チップ45aを積層した場合、半導体チップ45aの裏面に導電性ワイヤ44dが接触しないように設定することができる。また、突出部45eは、半導体チップ44aに接続された導電性ワイヤ44dを避けるように、半導体チップ44a上に配置することができる。
【0067】
なお、図6(a)の実施形態では、突出部45eの少なくとも一部の領域にアール形状を持たせる方法について説明したが、図6(b)に示すように、電極パット51bが表面に形成された半導体チップ51aの裏面の少なくとも一部の領域に、傾斜面51cを設けるようにしてもよい。また、図6(c)に示すように、電極パット52bが表面に形成された半導体チップ52aの裏面の少なくとも一部の領域に、傾斜面52dを介して突出部52cを設けるようにしてもよい。また、図6(d)に示すように、電極パット53bが表面に形成された半導体チップ53aの裏面の少なくとも一部の領域に、平坦面53dを介して傾斜面が設けられた突出部53cを設けるようにしてもよい。
【0068】
図7は、図6の半導体装置の突出部の製造方法を示す断面図である。
図7(a)において、半導体ウェハ61の表面はスクライブラインSB21〜SB24で区画され、スクライブラインSB21〜SB24で区画された各区画領域には、能動面がそれぞれ形成されるとともに、電極パッド62a〜62cがそれぞれ設けられている。そして、半導体ウェハ61上に形成された能動面を避けるようにして、半導体ウェハ61に開口部63を形成する。
【0069】
次に、図7(b)に示すように、開口部63が形成された半導体ウェハ61の裏面61´を研削することにより、半導体ウェハ61を薄型化し、開口部63を貫通させることで、貫通孔63´を半導体ウェハ61に形成する。
次に、図7(c)に示すように、貫通孔63´が形成された半導体ウェハ61の能動面側にダイシングテープ64を貼り付ける。そして、貫通孔63´を参照しながらブレード65の位置合わせを行うことにより、ブレード65の中央がスクライブラインSB21〜SB24の位置に対応するように配置する。ここで、ブレード65の先端は、丸みを帯びた形状を持たせることができる。そして、ブレード65を用いて半導体ウェハ61の裏面をハーフカットすることにより、アール形状を有する溝を半導体ウェハ61の裏面に形成し、アール形状を有する突出部66a〜66cをスクライブラインSB21〜SB24で区画された各区画領域に形成する。
【0070】
ここで、半導体ウェハ61の裏面に形成される溝の深さは、突出部66a〜66cが形成された半導体チップ61a〜61cを、ワイヤボンド接続された下層の半導体チップ上に積層した場合、下層の半導体チップに接続された導電性ワイヤが、半導体チップ61a〜61cの裏面に接触しないように設定することができる。また、ブレード65の幅は、下層の半導体チップに接続された導電性ワイヤを避けながら、突出部66a〜66cが形成された半導体チップ61a〜61cを下層の半導体チップ上に配置することができるように設定することができる。
【0071】
次に、図7(d)に示すように、突出部66a〜66cが形成された半導体ウェハ61からダイシングテープ64を剥がし、突出部66a〜66cを介して半導体ウェハ61の裏面側にダイシングテープ67を貼り付ける。
次に、図7(e)に示すように、ブレード65よりも幅の小さなブレード68を用い、スクライブラインSB21〜SB24に沿って半導体ウェハ61のフルカットを行うことにより、アール形状を有する突出部66a〜66cが裏面にそれぞれ設けられた半導体チップ61a〜61cを形成する。
【0072】
これにより、半導体チップ61a〜61cの裏面に形成される突出部66a〜66cにアール形状をそれぞれ持たせることを可能としつつ、半導体チップ61a〜61cの裏面の突出部66a〜66cを一括形成することが可能となる。このため、半導体チップ61a〜61cの裏面に突出部66a〜66cを形成したために、半導体チップ61a〜61cの端部が薄型化した場合においても、製造工程の煩雑化を抑制しつつ、半導体チップ61a〜61cの端部の強度を向上させることが可能となり、ワイヤボンド接続された半導体チップの積層構造を安定して製造することが可能となる。
【0073】
なお、図7の実施形態では、先端が丸みを帯びたブレードによるダイシングを行うことにより、アール形状を有する突出部66a〜66cを形成する方法について説明したが、等方性エッチングまたはレーザ加工により、アール形状を有する突出部66a〜66cを形成するようにしてもよい。また、ブレードの先端の形状を適宜変更することにより、ブレードの先端の形状に合わせて突出部66a〜66cの形状を変更するようにしてもよい。
【0074】
図8は、本発明の第4実施形態に係る半導体装置の概略構成を示す断面図である。
図8において、キャリア基板71の表面には導電性ワイヤ74d、75dを接続するランド72が設けられるとともに、キャリア基板71の裏面には突出電極73が設けられている。また、半導体チップ74a、75aには、導電性ワイヤ74d、75dを接続する電極パッド74b、75bがそれぞれ設けられ、半導体チップ75aの裏面には、半導体チップ75aに一体的に形成された突出部75eが設けられている。また、半導体チップ75aのサイズは、半導体チップ74aのサイズよりも大きくすることができる。
【0075】
そして、キャリア基板71上には、接着層74cを介して半導体チップ74aがフェースアップ実装されている。さらに、半導体チップ74a上には、突出部75eを介して半導体チップ75aがフェースアップ実装され、突出部75eは、絶縁性樹脂75cにより半導体チップ74a上に固着されているとともに、半導体チップ75aの端部が、半導体チップ74aから引き出された導電性ワイヤ74d上に配置されている。これにより、製造工程を複雑化させることなく、導電性ワイヤ74dの配線領域上の空間を有効利用することが可能となり、半導体チップ75a実装時の省スペース化を図ることが可能となる。
【0076】
ここで、絶縁性樹脂75cが突出部75eの周囲に食み出すようにすることにより、突出部75eが形成された半導体チップ75aの裏面の段差部分に絶縁性樹脂75cを充填し、半導体チップ74a上の導電性ワイヤ74dを絶縁性樹脂75cで包み込んだり、半導体チップ75aの電極パッド75b下を絶縁性樹脂75cで補強したりすることができる。
【0077】
そして、キャリア基板71上に実装された半導体チップ74aは、導電性ワイヤ74dを介してキャリア基板71のランド72に電気的に接続されるとともに、突出部75eを介して半導体チップ74a上に積層された半導体チップ75aは、導電性ワイヤ75dを介してキャリア基板71のランド72に電気的に接続されている。そして、導電性ワイヤ74d、75dがそれぞれ接続された半導体チップ74a、75aは、封止樹脂76により封止されている。
【0078】
ここで、突出部75eの高さは、半導体チップ74a上に半導体チップ75aを積層した場合、半導体チップ75aの裏面に導電性ワイヤ74dが接触しないように設定することができる。また、突出部75eは、半導体チップ74aに接続された導電性ワイヤ74dを避けるように、半導体チップ74a上に配置することができる。
【0079】
図9は、本発明の第5実施形態に係る半導体装置の概略構成を示す断面図である。
図9において、リードフレーム81には、半導体チップ84aをダイボンドするダイパッド82が設けられるとともに、導電性ワイヤ84d、85dを接続するリード83が設けられている。また、半導体チップ84a、85aには、導電性ワイヤ84d、85dを接続する電極パッド84b、85bがそれぞれ設けられ、半導体チップ85aの裏面には、半導体チップ85aに一体的に形成された突出部85eが設けられている。
【0080】
そして、リードフレーム81のダイパッド82上には、接着層84cを介して半導体チップ84aがフェースアップ実装されている。さらに、半導体チップ84a上には、突出部85eを介して半導体チップ85aがフェースアップ実装され、突出部85eは、絶縁性樹脂85cにより半導体チップ84a上に固着されている。
【0081】
そして、ダイパッド82上にダイボンドされた半導体チップ84aは、導電性ワイヤ84dを介してリードフレーム81のリード83に電気的に接続されるとともに、突出部85eを介して半導体チップ84a上に積層された半導体チップ85aは、導電性ワイヤ85dを介してリードフレーム81のリード83に電気的に接続されている。そして、導電性ワイヤ84d、85dがそれぞれ接続された半導体チップ84a、85aは、封止樹脂86により封止されている。
【0082】
ここで、突出部85eの高さは、半導体チップ84a上に半導体チップ85aを積層した場合、導電性ワイヤ84dが半導体チップ85aの裏面に接触しないように設定することができる。また、突出部85eは、半導体チップ84aに接続された導電性ワイヤ84dを避けるように、半導体チップ84a上に配置することができる。また、絶縁性樹脂85cが突出部85eの周囲に食み出すようにすることにより、突出部85eが形成された半導体チップ85aの裏面の段差部分に絶縁性樹脂85cを充填し、半導体チップ84a上の導電性ワイヤ84dを絶縁性樹脂85cで包み込んだり、半導体チップ85aの電極パッド85b下を絶縁性樹脂85cで補強したりすることができる。
【0083】
これにより、半導体チップ84a、85aの積層構造をリードフレーム81にマウントする場合においても、半導体チップ85aの裏面に導電性ワイヤ84dが接触することを防止しつつ、導電性ワイヤ84dが接続された半導体チップ84a上に半導体チップ85aを積層することが可能となり、半導体装置のコストダウンを図ることが可能となる。
【0084】
図10は、本発明の第6実施形態に係る半導体装置の概略構成を示す断面図である。
図10において、キャリア基板91の表面には、導電性ワイヤ95d、96dを接続するランド92aが設けられるとともに、突出電極94cを接合するランド92bが設けられ、キャリア基板91の裏面には突出電極93が設けられている。また、半導体チップ94aには、突出電極94cが配置された電極パッド94bが設けられている。また、半導体チップ95a、96aには、導電性ワイヤ95d、96dを接続する電極パッド95b、96bがそれぞれ設けられ、半導体チップ96aの裏面には、半導体チップ96aに一体的に形成された突出部96eが設けられている。なお、突出電極93、94cとしては、例えば、Auバンプ、半田材などで被覆されたCuバンプやNiバンプ、あるいは半田ボールなどを用いることができる。
【0085】
そして、キャリア基板91上には、突出電極94cを介して半導体チップ94aがフリップチップ実装されている。なお、突出電極94cを介して半導体チップ94をキャリア基板91上にフリップチップ実装する場合、例えば、ACF接合、NCF接合、ACP接合、NCP接合などの接着剤接合を用いるようにしてもよく、半田接合や合金接合などの金属接合を用いるようにしてもよい。
【0086】
また、フリップチップ実装された半導体チップ94aの裏面上には、接着層95cを介して半導体チップ95aがフェースアップ実装されている。さらに、半導体チップ95a上には、突出部96eを介して半導体チップ96aがフェースアップ実装され、突出部96eは、絶縁性樹脂96cにより半導体チップ95a上に固着されている。
【0087】
そして、半導体チップ94aの裏面上に実装された半導体チップ95aは、導電性ワイヤ95dを介してキャリア基板91のランド92aに電気的に接続されるとともに、絶縁性樹脂97を介して半導体チップ95a上に積層された半導体チップ96aは、導電性ワイヤ96dを介してキャリア基板91のランド92aに電気的に接続されている。そして、フリップチップ実装された半導体チップ94aおよび導電性ワイヤ95d、96dがそれぞれ接続された半導体チップ95a、96aは、封止樹脂97により封止されている。
【0088】
ここで、突出部96eの高さは、半導体チップ95a上に半導体チップ96aを積層した場合、導電性ワイヤ95dが半導体チップ96aの裏面に接触しないように設定することができる。また、突出部96eは、半導体チップ95aに接続された導電性ワイヤ95dを避けるように、半導体チップ95a上に配置することができる。また、絶縁性樹脂96cが突出部96eの周囲に食み出すようにすることにより、突出部96eが形成された半導体チップ96aの裏面の段差部分に絶縁性樹脂96cを充填し、半導体チップ95a上の導電性ワイヤ95dを絶縁性樹脂96cで包み込んだり、半導体チップ96aの電極パッド96b下を絶縁性樹脂96cで補強したりすることができる。
【0089】
これにより、半導体チップ95a上に半導体チップ96aを積層することで、半導体チップ96aの裏面に導電性ワイヤ95dが接触することを防止しつつ、半導体チップ95a、96aを固定することが可能となるとともに、高さの増大を抑制しつつ、半導体チップ95aとキャリア基板91との間に半導体チップ94aを介装することが可能となる。このため、工程数の増大を抑制しつつ、ワイヤボンド接続された半導体チップ95a上に半導体チップ96aを積層することが可能となるとともに、省スペース化を可能としつつ、半導体チップ94a〜96aの積層数を増加させることが可能となる。
【0090】
なお、上述した半導体装置は、例えば、液晶表示装置、携帯電話、携帯情報端末、ビデオカメラ、デジタルカメラ、MD(Mini Disc)プレーヤなどの電子機器に適用することができ、電子機器の小型・軽量化を可能としつつ、電子機器のコストダウンを図ることができる。
【図面の簡単な説明】
【図1】 第1実施形態に係る半導体装置の概略構成を示す断面図。
【図2】 図1の半導体装置の製造方法を示す断面図。
【図3】 図1の半導体装置の製造方法を示す断面図。
【図4】 第2実施形態に係る半導体装置の概略構成を示す断面図。
【図5】 図4の半導体装置の製造方法を示す断面図。
【図6】 第3実施形態に係る半導体装置の概略構成を示す断面図。
【図7】 図6の半導体装置の製造方法を示す断面図。
【図8】 第4実施形態に係る半導体装置の概略構成を示す断面図。
【図9】 第5実施形態に係る半導体装置の概略構成を示す断面図。
【図10】 第6実施形態に係る半導体装置の概略構成を示す断面図。
【図11】 従来の半導体装置の概略構成を示す断面図。
【符号の説明】
1、21、41、71、91 キャリア基板、2、22、42、72、92a、92b ランド、3、23、43、73、93、94c 突出電極、4a、5a、11a〜11c、24a、25a、31a〜31c、44a、45a、51a、52a、53a、61a〜61c、74a、75a、84a、85a、94a、95a、96a 半導体チップ、4b、5b、12a〜12c、24b、25b、32a〜32c、44b、45b、51b、52b、53b、62a〜62c、74b、75b、84b、85b、94b、95b、96b 電極パッド、4c、24c、44c、74c、84c、95c 接着層、5c、25c、45c、75c、85c 絶縁性樹脂、4d、5d、24d、25d、44d、45d、74d、75d、84d、85d、95d、96d 導電性ワイヤ、5e、25e、16a〜16c、36a〜36c、45e、51c、52c、53c、66a〜66c、75e、85e、96e 突出部、6、46、76、86、97 封止樹脂、SB1〜SB4、SB11〜SB14、SB21〜SB24 スクライブライン、11、31、61 半導体ウェハ、11´、61´ 裏面、13、63 開口部、13´、33、63´ 貫通孔、14、17、34、37、64、67 ダイシングテープ、15、18、35、38、65、68 ブレード、25f、39、39a〜39c 絶縁層、52d 傾斜面、53d 平坦面、81 リードフレーム、82 ダイパッド、83 リード
Claims (2)
- 導電性ワイヤ接続用の端子が設けられた基材上に第1半導体チップをマウントする工程と、
前記基材上にマウントされた第1半導体チップと前記基材に設けられた端子とを導電性ワイヤで接続する工程と、
表面がスクライブラインで区画されたウェハの裏面をハーフカットすることにより、前記スクライブラインに対向配置された溝を前記ウェハの裏面に形成する工程と、
前記溝が形成されたウェハの裏面に、CVDにより絶縁膜を成膜する工程と、
前記スクライブラインに沿って前記溝を切断することにより、裏面に突出部が形成された第2半導体チップを形成する工程と、
前記第2半導体チップを前記第1半導体チップ上に固着する工程とを備えることを特徴とする半導体装置の製造方法。 - 前記ハーフカットは、先端が丸みを帯びたブレードによるダイシング、等方性エッチングまたはレーザ加工により行われることを特徴とする請求項1記載の半導体装置の製造方法。
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2003095975A JP4123027B2 (ja) | 2003-03-31 | 2003-03-31 | 半導体装置の製造方法 |
| US10/812,346 US20040245652A1 (en) | 2003-03-31 | 2004-03-29 | Semiconductor device, electronic device, electronic appliance, and method of manufacturing a semiconductor device |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2003095975A JP4123027B2 (ja) | 2003-03-31 | 2003-03-31 | 半導体装置の製造方法 |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2004303992A JP2004303992A (ja) | 2004-10-28 |
| JP2004303992A5 JP2004303992A5 (ja) | 2005-06-23 |
| JP4123027B2 true JP4123027B2 (ja) | 2008-07-23 |
Family
ID=33408173
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2003095975A Expired - Fee Related JP4123027B2 (ja) | 2003-03-31 | 2003-03-31 | 半導体装置の製造方法 |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US20040245652A1 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JP4123027B2 (ja) |
Families Citing this family (34)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US7116002B2 (en) * | 2004-05-10 | 2006-10-03 | Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company, Ltd. | Overhang support for a stacked semiconductor device, and method of forming thereof |
| US7588963B2 (en) * | 2004-06-30 | 2009-09-15 | Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company, Ltd. | Method of forming overhang support for a stacked semiconductor device |
| US7067927B1 (en) * | 2005-01-31 | 2006-06-27 | National Semiconductor Corporation | Die with integral pedestal having insulated walls |
| US7675153B2 (en) | 2005-02-02 | 2010-03-09 | Kabushiki Kaisha Toshiba | Semiconductor device having semiconductor chips stacked and mounted thereon and manufacturing method thereof |
| US20070152314A1 (en) * | 2005-12-30 | 2007-07-05 | Intel Corporation | Low stress stacked die packages |
| JP4577228B2 (ja) | 2006-02-09 | 2010-11-10 | セイコーエプソン株式会社 | 半導体装置および半導体装置の製造方法 |
| JP4876618B2 (ja) | 2006-02-21 | 2012-02-15 | セイコーエプソン株式会社 | 半導体装置および半導体装置の製造方法 |
| JP4719042B2 (ja) * | 2006-03-16 | 2011-07-06 | 株式会社東芝 | 半導体装置の製造方法 |
| TWI305400B (en) * | 2006-08-11 | 2009-01-11 | Advanced Semiconductor Eng | Chip package |
| US20080128879A1 (en) * | 2006-12-01 | 2008-06-05 | Hem Takiar | Film-on-wire bond semiconductor device |
| US20080131998A1 (en) * | 2006-12-01 | 2008-06-05 | Hem Takiar | Method of fabricating a film-on-wire bond semiconductor device |
| SG149724A1 (en) * | 2007-07-24 | 2009-02-27 | Micron Technology Inc | Semicoductor dies with recesses, associated leadframes, and associated systems and methods |
| JP5301126B2 (ja) | 2007-08-21 | 2013-09-25 | スパンション エルエルシー | 半導体装置及びその製造方法 |
| JP5486772B2 (ja) * | 2008-02-04 | 2014-05-07 | リンテック株式会社 | 半導体ウエハ及びその製造方法 |
| KR20100056247A (ko) * | 2008-11-19 | 2010-05-27 | 삼성전자주식회사 | 접착층을 구비하는 반도체 패키지 |
| US8174131B2 (en) * | 2009-05-27 | 2012-05-08 | Globalfoundries Inc. | Semiconductor device having a filled trench structure and methods for fabricating the same |
| US8058706B2 (en) * | 2009-09-08 | 2011-11-15 | Texas Instruments Incorporated | Delamination resistant packaged die having support and shaped die having protruding lip on support |
| US8687378B2 (en) * | 2011-10-17 | 2014-04-01 | Murata Manufacturing Co., Ltd. | High-frequency module |
| US20130157414A1 (en) * | 2011-12-20 | 2013-06-20 | Nxp B. V. | Stacked-die package and method therefor |
| KR20130090173A (ko) * | 2012-02-03 | 2013-08-13 | 삼성전자주식회사 | 반도체 패키지 |
| JP2014007228A (ja) * | 2012-06-22 | 2014-01-16 | Ps4 Luxco S A R L | 半導体装置及びその製造方法 |
| KR102116987B1 (ko) * | 2013-10-15 | 2020-05-29 | 삼성전자 주식회사 | 반도체 패키지 |
| US9524942B2 (en) * | 2013-12-18 | 2016-12-20 | Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company, Ltd. | Chip-on-substrate packaging on carrier |
| CN105023877B (zh) * | 2014-04-28 | 2019-12-24 | 联华电子股份有限公司 | 半导体晶片、封装结构与其制作方法 |
| TWI591707B (zh) * | 2014-06-05 | 2017-07-11 | 東琳精密股份有限公司 | 薄型化晶片之封裝結構及其製造方法 |
| JP6560496B2 (ja) * | 2015-01-26 | 2019-08-14 | 株式会社ジェイデバイス | 半導体装置 |
| US9893058B2 (en) * | 2015-09-17 | 2018-02-13 | Semiconductor Components Industries, Llc | Method of manufacturing a semiconductor device having reduced on-state resistance and structure |
| CN106683984A (zh) * | 2017-01-22 | 2017-05-17 | 合肥中感微电子有限公司 | 电池保护控制晶片的制作方法以及电池保护控制芯片以及用户设备 |
| KR102442622B1 (ko) * | 2017-08-03 | 2022-09-13 | 삼성전자주식회사 | 반도체 소자 패키지 |
| JP2020021908A (ja) * | 2018-08-03 | 2020-02-06 | キオクシア株式会社 | 半導体装置およびその製造方法 |
| JP7243016B2 (ja) * | 2019-01-30 | 2023-03-22 | 日清紡マイクロデバイス株式会社 | 半導体装置およびその製造方法 |
| KR20210058165A (ko) * | 2019-11-13 | 2021-05-24 | 삼성전자주식회사 | 반도체 패키지 |
| JP2022129462A (ja) * | 2021-02-25 | 2022-09-06 | キオクシア株式会社 | 半導体装置および半導体装置の製造方法 |
| CN112978393B (zh) * | 2021-04-13 | 2022-12-20 | 山东省科学院自动化研究所 | 烧结砖自动卸垛的辅助系统及方法 |
Family Cites Families (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR0158868B1 (ko) * | 1988-09-20 | 1998-12-01 | 미다 가쓰시게 | 반도체장치 |
| US5323060A (en) * | 1993-06-02 | 1994-06-21 | Micron Semiconductor, Inc. | Multichip module having a stacked chip arrangement |
| US6784541B2 (en) * | 2000-01-27 | 2004-08-31 | Hitachi, Ltd. | Semiconductor module and mounting method for same |
| US6340846B1 (en) * | 2000-12-06 | 2002-01-22 | Amkor Technology, Inc. | Making semiconductor packages with stacked dies and reinforced wire bonds |
| US20020096754A1 (en) * | 2001-01-24 | 2002-07-25 | Chen Wen Chuan | Stacked structure of integrated circuits |
| US7169685B2 (en) * | 2002-02-25 | 2007-01-30 | Micron Technology, Inc. | Wafer back side coating to balance stress from passivation layer on front of wafer and be used as die attach adhesive |
| US20040026768A1 (en) * | 2002-08-08 | 2004-02-12 | Taar Reginald T. | Semiconductor dice with edge cavities |
-
2003
- 2003-03-31 JP JP2003095975A patent/JP4123027B2/ja not_active Expired - Fee Related
-
2004
- 2004-03-29 US US10/812,346 patent/US20040245652A1/en not_active Abandoned
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2004303992A (ja) | 2004-10-28 |
| US20040245652A1 (en) | 2004-12-09 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP4123027B2 (ja) | 半導体装置の製造方法 | |
| JP5215244B2 (ja) | 半導体装置 | |
| TWI277187B (en) | Semiconductor device and manufacturing method for the same | |
| JP3481444B2 (ja) | 半導体装置及びその製造方法 | |
| JP3565334B2 (ja) | 半導体装置およびそれを用いる液晶モジュール、並びに半導体装置の製造方法 | |
| JP2003273317A (ja) | 半導体装置及びその製造方法 | |
| US7309648B2 (en) | Low profile, chip-scale package and method of fabrication | |
| US20020149097A1 (en) | Method and apparatus for package reduction in stacked chip and board assemblies | |
| JP2002359346A (ja) | 半導体装置および半導体チップの積層方法 | |
| JP2002368190A (ja) | 半導体装置およびその製造方法 | |
| JP2004363126A (ja) | 半導体装置、電子デバイス、電子機器および半導体装置の製造方法 | |
| JP4876618B2 (ja) | 半導体装置および半導体装置の製造方法 | |
| JP2004296897A (ja) | 半導体装置、電子デバイス、電子機器および半導体装置の製造方法 | |
| JP2013045863A (ja) | 半導体装置およびその製造方法 | |
| JP2001223326A (ja) | 半導体装置 | |
| JP2001298147A (ja) | 半導体装置及びその製造方法 | |
| JP4175138B2 (ja) | 半導体装置 | |
| JP2895920B2 (ja) | 半導体装置及びその製造方法 | |
| US7659620B2 (en) | Integrated circuit package employing a flexible substrate | |
| JP3892359B2 (ja) | 半導体チップの実装方法 | |
| JPH06120296A (ja) | 半導体集積回路装置 | |
| JP2001127244A (ja) | マルチチップ半導体装置およびその製造方法 | |
| JP2817425B2 (ja) | 半導体装置の実装方法 | |
| JP4141941B2 (ja) | 半導体装置 | |
| JP5223231B2 (ja) | 半導体装置 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20040924 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20040924 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20060919 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20060926 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20061121 |
|
| RD04 | Notification of resignation of power of attorney |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A7424 Effective date: 20070403 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20080408 |
|
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20080421 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20110516 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20120516 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20120516 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20130516 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| LAPS | Cancellation because of no payment of annual fees |