JP2010010330A - 半導体装置 - Google Patents
半導体装置 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP2010010330A JP2010010330A JP2008166991A JP2008166991A JP2010010330A JP 2010010330 A JP2010010330 A JP 2010010330A JP 2008166991 A JP2008166991 A JP 2008166991A JP 2008166991 A JP2008166991 A JP 2008166991A JP 2010010330 A JP2010010330 A JP 2010010330A
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- electrode lead
- semiconductor device
- sealing resin
- semiconductor element
- semiconductor
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L23/00—Details of semiconductor or other solid state devices
- H01L23/28—Encapsulations, e.g. encapsulating layers, coatings, e.g. for protection
- H01L23/31—Encapsulations, e.g. encapsulating layers, coatings, e.g. for protection characterised by the arrangement or shape
- H01L23/3107—Encapsulations, e.g. encapsulating layers, coatings, e.g. for protection characterised by the arrangement or shape the device being completely enclosed
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L23/00—Details of semiconductor or other solid state devices
- H01L23/34—Arrangements for cooling, heating, ventilating or temperature compensation ; Temperature sensing arrangements
- H01L23/36—Selection of materials, or shaping, to facilitate cooling or heating, e.g. heatsinks
- H01L23/373—Cooling facilitated by selection of materials for the device or materials for thermal expansion adaptation, e.g. carbon
- H01L23/3735—Laminates or multilayers, e.g. direct bond copper ceramic substrates
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L23/00—Details of semiconductor or other solid state devices
- H01L23/48—Arrangements for conducting electric current to or from the solid state body in operation, e.g. leads, terminal arrangements ; Selection of materials therefor
- H01L23/488—Arrangements for conducting electric current to or from the solid state body in operation, e.g. leads, terminal arrangements ; Selection of materials therefor consisting of soldered or bonded constructions
- H01L23/495—Lead-frames or other flat leads
- H01L23/49517—Additional leads
- H01L23/49524—Additional leads the additional leads being a tape carrier or flat leads
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L23/00—Details of semiconductor or other solid state devices
- H01L23/48—Arrangements for conducting electric current to or from the solid state body in operation, e.g. leads, terminal arrangements ; Selection of materials therefor
- H01L23/488—Arrangements for conducting electric current to or from the solid state body in operation, e.g. leads, terminal arrangements ; Selection of materials therefor consisting of soldered or bonded constructions
- H01L23/495—Lead-frames or other flat leads
- H01L23/49517—Additional leads
- H01L23/49531—Additional leads the additional leads being a wiring board
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L23/00—Details of semiconductor or other solid state devices
- H01L23/48—Arrangements for conducting electric current to or from the solid state body in operation, e.g. leads, terminal arrangements ; Selection of materials therefor
- H01L23/488—Arrangements for conducting electric current to or from the solid state body in operation, e.g. leads, terminal arrangements ; Selection of materials therefor consisting of soldered or bonded constructions
- H01L23/498—Leads, i.e. metallisations or lead-frames on insulating substrates, e.g. chip carriers
- H01L23/49811—Additional leads joined to the metallisation on the insulating substrate, e.g. pins, bumps, wires, flat leads
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/34—Strap connectors, e.g. copper straps for grounding power devices; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/36—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the strap connectors prior to the connecting process
- H01L2224/37—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the strap connectors prior to the connecting process of an individual strap connector
- H01L2224/37001—Core members of the connector
- H01L2224/3701—Shape
- H01L2224/37011—Shape comprising apertures or cavities
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/34—Strap connectors, e.g. copper straps for grounding power devices; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/39—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the strap connectors after the connecting process
- H01L2224/40—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the strap connectors after the connecting process of an individual strap connector
- H01L2224/401—Disposition
- H01L2224/40151—Connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive
- H01L2224/40221—Connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked
- H01L2224/40225—Connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked the item being non-metallic, e.g. insulating substrate with or without metallisation
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/42—Wire connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/44—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors prior to the connecting process
- H01L2224/45—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the wire connectors prior to the connecting process of an individual wire connector
- H01L2224/45001—Core members of the connector
- H01L2224/45099—Material
- H01L2224/451—Material with a principal constituent of the material being a metal or a metalloid, e.g. boron (B), silicon (Si), germanium (Ge), arsenic (As), antimony (Sb), tellurium (Te) and polonium (Po), and alloys thereof
- H01L2224/45117—Material with a principal constituent of the material being a metal or a metalloid, e.g. boron (B), silicon (Si), germanium (Ge), arsenic (As), antimony (Sb), tellurium (Te) and polonium (Po), and alloys thereof the principal constituent melting at a temperature of greater than or equal to 400°C and less than 950°C
- H01L2224/45124—Aluminium (Al) as principal constituent
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/80—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected
- H01L2224/84—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected using a strap connector
- H01L2224/848—Bonding techniques
- H01L2224/84801—Soldering or alloying
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L25/00—Assemblies consisting of a plurality of semiconductor or other solid state devices
- H01L25/03—Assemblies consisting of a plurality of semiconductor or other solid state devices all the devices being of a type provided for in a single subclass of subclasses H10B, H10D, H10F, H10H, H10K or H10N, e.g. assemblies of rectifier diodes
- H01L25/04—Assemblies consisting of a plurality of semiconductor or other solid state devices all the devices being of a type provided for in a single subclass of subclasses H10B, H10D, H10F, H10H, H10K or H10N, e.g. assemblies of rectifier diodes the devices not having separate containers
- H01L25/07—Assemblies consisting of a plurality of semiconductor or other solid state devices all the devices being of a type provided for in a single subclass of subclasses H10B, H10D, H10F, H10H, H10K or H10N, e.g. assemblies of rectifier diodes the devices not having separate containers the devices being of a type provided for in group subclass H10D
- H01L25/072—Assemblies consisting of a plurality of semiconductor or other solid state devices all the devices being of a type provided for in a single subclass of subclasses H10B, H10D, H10F, H10H, H10K or H10N, e.g. assemblies of rectifier diodes the devices not having separate containers the devices being of a type provided for in group subclass H10D the devices being arranged next to each other
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/0001—Technical content checked by a classifier
- H01L2924/00014—Technical content checked by a classifier the subject-matter covered by the group, the symbol of which is combined with the symbol of this group, being disclosed without further technical details
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01005—Boron [B]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01006—Carbon [C]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01013—Aluminum [Al]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01014—Silicon [Si]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01019—Potassium [K]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01029—Copper [Cu]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01033—Arsenic [As]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/0106—Neodymium [Nd]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01068—Erbium [Er]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01074—Tungsten [W]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/01—Chemical elements
- H01L2924/01082—Lead [Pb]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/15—Details of package parts other than the semiconductor or other solid state devices to be connected
- H01L2924/181—Encapsulation
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/19—Details of hybrid assemblies other than the semiconductor or other solid state devices to be connected
- H01L2924/1901—Structure
- H01L2924/1904—Component type
- H01L2924/19043—Component type being a resistor
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/30—Technical effects
- H01L2924/35—Mechanical effects
- H01L2924/351—Thermal stress
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Condensed Matter Physics & Semiconductors (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Computer Hardware Design (AREA)
- Microelectronics & Electronic Packaging (AREA)
- Power Engineering (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Ceramic Engineering (AREA)
- Materials Engineering (AREA)
- Structures Or Materials For Encapsulating Or Coating Semiconductor Devices Or Solid State Devices (AREA)
Abstract
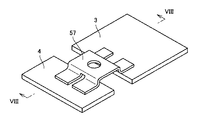
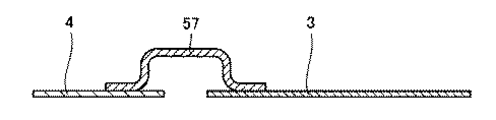
【解決手段】半導体装置は、基板11と、半導体素子4と、電極リード51と、封止樹脂部とを有する。基板11は、回路パターン3が形成された主面を有する。半導体素子4は、第1および第2の面を有し、第1の面と主面とが互いに面するように基板上に配置されている。電極リード51は、回路パターン3に接合された一方端と、第2の面にハンダ接合された他方端とを有する。他方端は、互いに分割された複数の部分を有する。封止樹脂部は、半導体素子4および電極リード51を封止している。
【選択図】図2
Description
(実施の形態1)
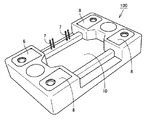
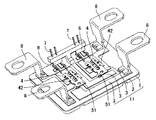
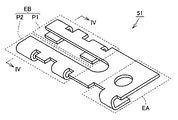
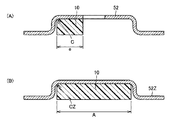
図1は、本発明の実施の形態1における半導体装置の構成を概略的に示す斜視図である。図2は、本発明の実施の形態1における半導体装置の封止樹脂部の内部の構成を概略的に示す斜視図である。図3は、本発明の実施の形態1における半導体装置の電極リードの構成を概略的に示す斜視図である。図4は、図3の線IV−IVに沿った概略断面図である。
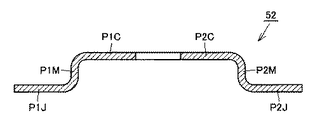
図9は、本発明の実施の形態2における半導体装置の電極リードの構成を概略的に示す斜視図である。図10は、図9の線X−Xに沿った概略断面図である。
Claims (3)
- 回路パターンが形成された主面を有する基板と、
第1および第2の面を有し、前記第1の面と前記主面とが互いに面するように前記基板上に配置された半導体素子と、
前記回路パターンに接合された一方端と、前記第2の面にハンダ接合された他方端とを有する電極リードとを備え、
前記他方端は、互いに分割された複数の部分を有し、
前記半導体素子および前記電極リードを封止する封止樹脂部をさらに備えた、半導体装置。 - 前記複数の部分の各々は、前記第2の面に接合された接合部と、前記接合部に対して前記第2の面に直交する方向に間隔を空けて配置された配線部と、前記接合部と前記配線部とを繋ぐ連結部とを有する、請求項1に記載の半導体装置。
- 前記封止樹脂部のうち前記第2の面の法線方向において前記複数の部分によって前記第2の面から隔てられている領域は、前記第2の面の法線方向に沿って前記複数の部分から露出されている、請求項1に記載の半導体装置。
Priority Applications (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008166991A JP4666185B2 (ja) | 2008-06-26 | 2008-06-26 | 半導体装置 |
| US12/203,524 US7768118B2 (en) | 2008-06-26 | 2008-09-03 | Semiconductor device |
| DE102008050852.7A DE102008050852B4 (de) | 2008-06-26 | 2008-10-08 | Halbleitervorrichtung mit abdichtendem Harzabschnitt |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008166991A JP4666185B2 (ja) | 2008-06-26 | 2008-06-26 | 半導体装置 |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2010010330A true JP2010010330A (ja) | 2010-01-14 |
| JP4666185B2 JP4666185B2 (ja) | 2011-04-06 |
Family
ID=41396874
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008166991A Active JP4666185B2 (ja) | 2008-06-26 | 2008-06-26 | 半導体装置 |
Country Status (3)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US7768118B2 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JP4666185B2 (ja) |
| DE (1) | DE102008050852B4 (ja) |
Cited By (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2015125772A1 (ja) * | 2014-02-24 | 2015-08-27 | 三菱電機株式会社 | 電極リードおよび半導体装置 |
| CN110574159A (zh) * | 2017-05-11 | 2019-12-13 | 三菱电机株式会社 | 功率模块、电力变换装置以及功率模块的制造方法 |
| CN112236860A (zh) * | 2018-06-12 | 2021-01-15 | 三菱电机株式会社 | 功率半导体模块以及电力变换装置 |
| WO2021157045A1 (ja) * | 2020-02-07 | 2021-08-12 | 三菱電機株式会社 | 半導体装置および半導体装置の製造方法 |
| JP2024102810A (ja) * | 2023-01-19 | 2024-07-31 | ジェイエムジェイ コリア カンパニー リミテッド | 半導体パッケージ及びその製造方法 |
| WO2025088687A1 (ja) * | 2023-10-24 | 2025-05-01 | 三菱電機株式会社 | 半導体装置 |
| US12315838B2 (en) | 2020-03-13 | 2025-05-27 | Fuji Electric Co., Ltd. | Wiring structure and semiconductor module |
Families Citing this family (13)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP5380376B2 (ja) * | 2010-06-21 | 2014-01-08 | 日立オートモティブシステムズ株式会社 | パワー半導体装置 |
| USD653634S1 (en) * | 2010-10-28 | 2012-02-07 | Fuji Electric Co., Ltd. | Semiconductor |
| USD653633S1 (en) * | 2010-12-14 | 2012-02-07 | Fuji Electric Co., Ltd. | Semiconductor |
| JP2013016629A (ja) | 2011-07-04 | 2013-01-24 | Mitsubishi Electric Corp | 半導体モジュール |
| EP2930747A1 (en) * | 2014-04-07 | 2015-10-14 | Nxp B.V. | Lead for connection to a semiconductor device |
| JP6451747B2 (ja) * | 2014-11-28 | 2019-01-16 | 富士電機株式会社 | 半導体装置 |
| USD774479S1 (en) * | 2014-11-28 | 2016-12-20 | Fuji Electric Co., Ltd. | Semiconductor module |
| JP6485257B2 (ja) * | 2015-07-01 | 2019-03-20 | 富士電機株式会社 | 半導体装置及び半導体装置の製造方法 |
| JP7001960B2 (ja) * | 2018-03-23 | 2022-01-20 | 株式会社オートネットワーク技術研究所 | 回路構成体 |
| CN115101498B (zh) * | 2022-05-18 | 2025-03-14 | 华为数字能源技术有限公司 | 功率模块、电源系统、车辆及光伏系统 |
| DE102022207848A1 (de) | 2022-07-29 | 2023-11-16 | Vitesco Technologies Germany Gmbh | Kontaktierungselement für Leistungshalbleitermodule, Leistungshalbleitermodul und Inverter mit einem Kontaktierungselement |
| EP4362087A1 (en) * | 2022-10-28 | 2024-05-01 | Infineon Technologies AG | Power semiconductor module arrangement |
| DE102022133982A1 (de) * | 2022-12-19 | 2024-06-20 | Semikron Danfoss GmbH | Leistungsmodul |
Citations (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH04336460A (ja) * | 1991-05-14 | 1992-11-24 | Fuji Electric Co Ltd | 半導体装置 |
| JPH04354362A (ja) * | 1991-05-31 | 1992-12-08 | Nippondenso Co Ltd | 電気溶接に適したリード及び端子の構造 |
| JPH10335553A (ja) * | 1997-05-28 | 1998-12-18 | Samsung Electro Mech Co Ltd | 圧電素子3端子部品を有する電子部品 |
| JP2002100716A (ja) * | 2000-09-21 | 2002-04-05 | Toshiba Corp | 半導体装置の製造方法および半導体装置 |
| JP2003258179A (ja) * | 2002-02-28 | 2003-09-12 | Sanyo Electric Co Ltd | 半導体装置およびその製造方法 |
| JP2004228461A (ja) * | 2003-01-27 | 2004-08-12 | Mitsubishi Electric Corp | 半導体装置 |
| JP2006202885A (ja) * | 2005-01-19 | 2006-08-03 | Mitsubishi Electric Corp | 半導体装置 |
| JP2007103810A (ja) * | 2005-10-07 | 2007-04-19 | Mitsubishi Electric Corp | 半導体装置およびその製造方法 |
| JP2007266608A (ja) * | 2006-03-29 | 2007-10-11 | Infineon Technologies Ag | 半導体モジュール |
| JP2009141080A (ja) * | 2007-12-05 | 2009-06-25 | Toshiba Corp | リードフレームおよび半導体装置 |
Family Cites Families (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2725954B2 (ja) * | 1992-07-21 | 1998-03-11 | 三菱電機株式会社 | 半導体装置およびその製造方法 |
| US5956231A (en) * | 1994-10-07 | 1999-09-21 | Hitachi, Ltd. | Semiconductor device having power semiconductor elements |
| US5705848A (en) * | 1995-11-24 | 1998-01-06 | Asea Brown Boveri Ag | Power semiconductor module having a plurality of submodules |
| JP2002359334A (ja) | 2001-05-31 | 2002-12-13 | Toyota Industries Corp | 半導体装置の端子構造 |
| JP2003264265A (ja) | 2002-03-08 | 2003-09-19 | Mitsubishi Electric Corp | 電力用半導体装置 |
| JP4455488B2 (ja) | 2005-12-19 | 2010-04-21 | 三菱電機株式会社 | 半導体装置 |
| JP4349364B2 (ja) | 2005-12-26 | 2009-10-21 | 三菱電機株式会社 | 半導体装置 |
| JP2007235004A (ja) * | 2006-03-03 | 2007-09-13 | Mitsubishi Electric Corp | 半導体装置 |
-
2008
- 2008-06-26 JP JP2008166991A patent/JP4666185B2/ja active Active
- 2008-09-03 US US12/203,524 patent/US7768118B2/en active Active
- 2008-10-08 DE DE102008050852.7A patent/DE102008050852B4/de active Active
Patent Citations (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH04336460A (ja) * | 1991-05-14 | 1992-11-24 | Fuji Electric Co Ltd | 半導体装置 |
| JPH04354362A (ja) * | 1991-05-31 | 1992-12-08 | Nippondenso Co Ltd | 電気溶接に適したリード及び端子の構造 |
| JPH10335553A (ja) * | 1997-05-28 | 1998-12-18 | Samsung Electro Mech Co Ltd | 圧電素子3端子部品を有する電子部品 |
| JP2002100716A (ja) * | 2000-09-21 | 2002-04-05 | Toshiba Corp | 半導体装置の製造方法および半導体装置 |
| JP2003258179A (ja) * | 2002-02-28 | 2003-09-12 | Sanyo Electric Co Ltd | 半導体装置およびその製造方法 |
| JP2004228461A (ja) * | 2003-01-27 | 2004-08-12 | Mitsubishi Electric Corp | 半導体装置 |
| JP2006202885A (ja) * | 2005-01-19 | 2006-08-03 | Mitsubishi Electric Corp | 半導体装置 |
| JP2007103810A (ja) * | 2005-10-07 | 2007-04-19 | Mitsubishi Electric Corp | 半導体装置およびその製造方法 |
| JP2007266608A (ja) * | 2006-03-29 | 2007-10-11 | Infineon Technologies Ag | 半導体モジュール |
| JP2009141080A (ja) * | 2007-12-05 | 2009-06-25 | Toshiba Corp | リードフレームおよび半導体装置 |
Cited By (13)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2015125772A1 (ja) * | 2014-02-24 | 2015-08-27 | 三菱電機株式会社 | 電極リードおよび半導体装置 |
| CN110574159B (zh) * | 2017-05-11 | 2023-04-04 | 三菱电机株式会社 | 功率模块、电力变换装置以及功率模块的制造方法 |
| CN110574159A (zh) * | 2017-05-11 | 2019-12-13 | 三菱电机株式会社 | 功率模块、电力变换装置以及功率模块的制造方法 |
| CN112236860A (zh) * | 2018-06-12 | 2021-01-15 | 三菱电机株式会社 | 功率半导体模块以及电力变换装置 |
| CN112236860B (zh) * | 2018-06-12 | 2024-04-16 | 三菱电机株式会社 | 功率半导体模块以及电力变换装置 |
| JP7267469B2 (ja) | 2020-02-07 | 2023-05-01 | 三菱電機株式会社 | 半導体装置および半導体装置の製造方法 |
| JPWO2021157045A1 (ja) * | 2020-02-07 | 2021-08-12 | ||
| WO2021157045A1 (ja) * | 2020-02-07 | 2021-08-12 | 三菱電機株式会社 | 半導体装置および半導体装置の製造方法 |
| US12334407B2 (en) | 2020-02-07 | 2025-06-17 | Mitsubishi Electric Corporation | Semiconductor device and method of manufacturing semiconductor device |
| US12315838B2 (en) | 2020-03-13 | 2025-05-27 | Fuji Electric Co., Ltd. | Wiring structure and semiconductor module |
| JP2024102810A (ja) * | 2023-01-19 | 2024-07-31 | ジェイエムジェイ コリア カンパニー リミテッド | 半導体パッケージ及びその製造方法 |
| JP7681920B2 (ja) | 2023-01-19 | 2025-05-23 | ジェイエムジェイ コリア カンパニー リミテッド | 半導体パッケージ及びその製造方法 |
| WO2025088687A1 (ja) * | 2023-10-24 | 2025-05-01 | 三菱電機株式会社 | 半導体装置 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| US7768118B2 (en) | 2010-08-03 |
| US20090321900A1 (en) | 2009-12-31 |
| JP4666185B2 (ja) | 2011-04-06 |
| DE102008050852B4 (de) | 2015-06-03 |
| DE102008050852A1 (de) | 2010-01-07 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP4666185B2 (ja) | 半導体装置 | |
| JP6012533B2 (ja) | 電力用半導体装置 | |
| US9293400B2 (en) | Package with terminal pins with lateral reversal point and laterally exposed free end | |
| US20070262409A1 (en) | Lead frame and semiconductor device using the same | |
| US10163752B2 (en) | Semiconductor device | |
| CN103378042A (zh) | 半导体封装模块 | |
| JP4686248B2 (ja) | 光半導体装置、及び光半導体装置製造方法 | |
| JP2020038914A (ja) | 半導体装置 | |
| US11094615B2 (en) | Semiconductor apparatus including leads and bonding wires | |
| CN110933900B (zh) | 电气设备和散热器 | |
| JP5481104B2 (ja) | 半導体装置 | |
| US20090130908A1 (en) | Memory module, socket and mounting method providing improved heat dissipating characteristics | |
| BR102018013849A2 (pt) | Módulo semicondutor | |
| JP2006332573A (ja) | パワーモジュールのパッケージ構造 | |
| CN100461404C (zh) | 半导体器件 | |
| JP5098301B2 (ja) | 電力用半導体装置 | |
| JP5273265B2 (ja) | 電力用半導体装置 | |
| CN111466158A (zh) | 用于电机的控制器 | |
| CN110444536A (zh) | 一种电力用逆变电路装置 | |
| JP6292066B2 (ja) | 電力用半導体装置 | |
| JP7543735B2 (ja) | 半導体モジュール | |
| CN104064538B (zh) | 具有构造为膜复合物的连接装置的功率组件 | |
| CN107431055A (zh) | 半导体装置 | |
| JP7050487B2 (ja) | 電子デバイス | |
| JP5180495B2 (ja) | 半導体装置およびその製造方法 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20100512 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20100914 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20101111 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20101214 |
|
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20101228 |
|
| FPAY | Renewal fee payment (event date is renewal date of database) |
Free format text: PAYMENT UNTIL: 20140121 Year of fee payment: 3 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 Ref document number: 4666185 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |