EP0967167B1 - Dispositif de transport de cahiers de feuilles, en particulier dispositif de pliage ainsi qu'une méthode de transport de cahier de feuilles, en particulier méthode de formation du pli - Google Patents
Dispositif de transport de cahiers de feuilles, en particulier dispositif de pliage ainsi qu'une méthode de transport de cahier de feuilles, en particulier méthode de formation du pli Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0967167B1 EP0967167B1 EP99111206A EP99111206A EP0967167B1 EP 0967167 B1 EP0967167 B1 EP 0967167B1 EP 99111206 A EP99111206 A EP 99111206A EP 99111206 A EP99111206 A EP 99111206A EP 0967167 B1 EP0967167 B1 EP 0967167B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- conveyor
- engaging
- sub
- conveying
- folding
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B65—CONVEYING; PACKING; STORING; HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL
- B65H—HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL, e.g. SHEETS, WEBS, CABLES
- B65H45/00—Folding thin material
- B65H45/12—Folding articles or webs with application of pressure to define or form crease lines
- B65H45/18—Oscillating or reciprocating blade folders
Definitions
- the invention relates to a device according to the preamble of claim 1 and a method according to the preamble of Claim 6.
- They are for transporting sheet layers suitable, e.g. contiguous over a connection, like an edge connection, hereinafter called fold, with each other are directly connected.
- the sheet layers like paper, then lie against each other with their inner sides and form an outside with facing outer surfaces. If folded, the insides go over the concave Inside of the fold and the outer surfaces over the convex curved outside of the fold in one piece.
- the sheet layers can be on either side of the connection or be multilayer on this. The insides are then through the innermost layer and the outsides through the outermost Location formed. In between there are other layers.
- Such too folding or folded sheets are e.g. to exercise books further processed.
- DE-PS 25 19 420 is a transport and folding device become known, on their characteristics and effects for inclusion in the present invention. With her can also stack thicker sheets without the risk of internal crushing high speed and easy to set up.
- US 1 693 147 describes a folding device with one on one Swiveling arm arranged folding sword that has a front folding edge projecting toothed sections and recessed smooth Has sections.
- the layer to be folded is passed through a folding gap between two transport rollers, which are set down so that they the folded position mainly in the area of the recessed leading edge of the folded sword to contact. This will create an undesirable friction between the Folding sword and, with the folded layer in between, the transport rollers avoided.
- the invention has for its object a device or a method to create, by which this effect is further improved. Although the Leaf layer is removed from the engagement member with little friction or the Working speed should be increased, a perfect folding result sought.
- means are provided by which the sheet layer is so attached to the Conveyor is passed that the shear force acting on the outside not or only insignificantly or negligibly on the engaging member is transmitted.
- This transverse force expediently acts on everyone Leaf layers so clamping that they do not oppose each other under the Can shift conveying force, the direction of which is transverse to the transverse force.
- the Sheet layers become only by frictional intervention in the outside transported. The transfer of the frictional pressure to the contact between Leaf position and engagement member is significantly reduced or eliminated.
- the force attack for feeding the sheet layer into the conveying engagement can be in the area an opening or interruption of the engagement member also upstream from Conveyors are made on the outside.
- this opening is useful on Provided end of the engagement member as an open cutout in the area in which the conveyor engages in the outside of the sheet layer. This presses the conveyor the sheet layers with their insides in the opening immediately against each other and not against the engaging member.
- the training according to the invention is useful wherever sheet layers to be removed from an engagement member with reduced friction. Regardless of the training described, it is also advantageous to like the conveyor is pressing and running on the outside of the sheet layer form the attacking member so that its in the transport or running direction front area exerts the greatest pressing force. Immediately behind it subsequent areas of the pressing surface exert a lower pressing force, e.g. while the pressing surface rolls on the outer surface of the sheet layer.
- the Transverse displacement of the conveyor, the pressing surfaces or the like electronic or hydraulic or pneumatic Control means conceivable, but mechanical are expedient Control means provided.
- These can be a cam control include. Those guided on the cam or cam bodies Runners are connected to each other via transmission drives controlling link connected to the drive.
- the transmission drive can include levers or push and pull rods with joints or only be formed by such.
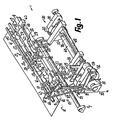
- the device 1 is used for fully automated implementation of the method according to the invention.
- a sheet layer is like a stack of ten or more papers sheets on top of each other, forming a fold 3 folded over 180 °.
- the two fold legs of the same size then lie against each other with their inner surfaces and merge into each other on the inside 4 of the fold 3, so that they form outer sides 5 facing away from each other.
- at the fold becomes the layer 2 perpendicular to its spread Level 10 in the direction 6 or 16 compared to a stationary one Device rack 7 from a table 8 at right angles moved away.
- the upper table surface is the spread, flat layer 2 parallel to level 10 by means of funding supplied that the fold zone congruent with the Table 8 penetrating gap 9 is.
- this layer 2 of the table surface 10 in the area of Fold zone lifted vertically upwards.
- the fold 3 and the Layer legs are then symmetrical to or on both sides of the Folding plane 11, which is perpendicular to plane 10.
- the one to fold 3 parallel length of layer 2 is useful, i.e. to a Many times larger than the booklets to be produced.
- Level 10 parallel level 12, in which the outer sides 5 for the further transport in direction 6 or 16 can be detected.
- a level 13 that is at least as far as level 12 or slightly further from level 10 the inside 4 by pressure directly in the direction 16 loaded.
- a level 14 which closer to level 10 than level 12, 13 which Layer legs parallel at a small distance from each other held.
- Levels 10 and 12 to 14 are parallel.
- the fold 3 or the immediately adjacent to it subsequent layer legs pressed.
- the Layer legs in the press area up to the inside 4 and over their entire length continuously spaced from each other held.
- the pressure against level 11 is carried out in one pass in direction 6 through level 15.
- the glide Lay leg under curve on the table surface and lift until they are level.
- the pressing is finished shortly before the fold 3 reaches one of the parallel planes 12 to 15.
- the Layer legs are then free from the pressing contact.
- the Pressing is only carried out using a smaller area of the height of the ply legs and during these still touch level 10. This also applies to that Reach levels 12 to 13.
- the maximum pressing from level 12 and across to level 11 Funding intervention takes place only in sections of the length of the Layer 2. These sections are shorter than the ones in between lying longitudinal sections in which the pressure of the conveyor intervention on the other hand, is reduced or completely avoided. in the Area of these longitudinal sections touch the inside the layer leg therefore until level 12 or 13 not, but only immediately afterwards. While the Pressure between and at a distance from both levels 10, 14 by an arc movement in the direction 18 across the planes 10 and 12 to 14, the fold pressure of the layer 2 between levels 12 to 14 by moving in the direction 19 transversely to level 11.
- the direction 19 can be parallel to levels 10 and 12 to 14 or in an arch path lie, which are steeper than the direction of level 11 18 is.
- a plate-shaped engagement member or folding sword 20 is provided. It is in the Level 11, in the starting position completely below level 10 and is then moved through the gap 9 in the direction 16. there it will on the lateral boundary surfaces of the gap 9th and table 8 slidably guided. Here it lies above the entire length on the inside 4 with one on both sides end edge flanked at an angle and at an acute angle.
- the sword 20 promotes the situation 2 through the press 22 and up to Level 14.
- the sword 20 is only on the longitudinal areas mentioned the inside 4, but not in between Partial areas.
- the sword 20 is in two combs or sub-members 23, 24 of equal length divided. They have between levels 10 and 12 to 14 same cross sections and are always on the same level.
- Each sub-link 23, 24 consists of next to each other at a distance lying arms or strips of sheet metal that point towards 6, 16 protrude freely up to their pointed ends 25 or 26. Both side edges of each link 24 facing away from one another are on two mutually facing side edges of two neighboring Links 23 slidably guided. The same width among themselves the arm 23 is twice as large or larger than that between each other equal width of each of the arms 24. The two laterally outermost arms 23 are opposite the other arms 23, 24 narrower.
- the end edges 26 of all lie up to level 14 Links 24 in a line with and immediately after to the also rectilinear end edges 25 of all links 23. Then the links 24 stop moving in the direction 16, while the links 23 up to level 12 or 13 in the direction 16 continue to run.
- the Carriages 28, 29 lie below level 10 or table 8.
- the carriage 28 is on a linear guide 31 of the frame 7 in the direction 16 to and fro stored.
- the carriage 29 is on a linear guide 32 of the carriage 28 back and forth in the same direction 16 slidably guided.
- the slides 28, 29 are common as well as independently in and against direction 16 displaceable, whereby the position control of the ends 25, 26 is effected.
- the upper end of the guide 31 can Wear table 8.
- the transporter 21 has a position 2 for the entry mouth 33 constantly widened in the direction of 6. It extends between level 10 and level 12 or 14. In level 12 the narrowest area of the mouth 33 reached. It is bounded by driving surfaces 34 which are in Walk towards 6 and frictionally into the outside 5 intervene only in the area of the mentioned sections. In Direction 6 from level 12, these surfaces 34 delimit one Constantly wide, but elastically expandable conveyor gap 35 for position 2.
- the mouth 33 is up to level 12 from circular deflections on both sides of level 11, flanked like rollers 36, each over an endless Conveyor belt 37 rotates continuously. The bands 37 limit this Mouth 33 and with the surfaces 34 the gap 35.
- the opposing rollers 36 are on separate Carriers 38 suspended rotatably, which on both sides of the Level 11 can be pivoted about separate axes 39 in the direction 19 are. The distance between these fixed as well as above the axes of the rollers 39 are always larger than the distance between the roller axes.
- One each Conveying gap 33 to 35 lies in the area of an arm 24 or the associated gap 27.
- On each side of level 11 are the holder 38 of all rollers 36 along the same axis 39 and attached rotatably adjustable.
- Opposing beams 38 or axes 39 are directly opposed to each other drive-connected. This drive connection 40 can be form-fitting, e.g. by two arranged on the axes 39, equally large gears are formed.
- the press 22 has one on each side of the level 11 plate or strip-shaped ram 41.
- Everyone Stamp 41 forms with its edge surface closest to level 11 a convexly curved pressing surface 42. It goes over the total working width of the device 1 or 20 or 21 or 22 continuously through and lies like the stamp 41 in the Distance from levels 10 and 12 to 14.
- the end edges of each Stamp 41 are movably attached to two carriers 43, which in turn is fixed on an axis or shaft 46 are.
- the axes 46 are equidistant from the plane 11 and lie in the level 15 in the middle between the Levels 10, 14.
- Each axis 46 lies in the central plane of the associated surface 42 or plate 41 and at a distance behind the longitudinal edge facing away from surface 42 Plate 41.
- the surfaces 42 lie with Distance from and between levels 10, 15 and in the end position at a distance from and between levels 12 to 14 and 15.
- the foremost end and longitudinal edge 47 in direction 18 each surface 42 describes the movement between the two positions about the axis 46 an arc path 17, of which is the upstream surface areas 42 are permanently set back.
- Form in the starting position therefore the surfaces 42 a funnel-shaped up to these edges 47 narrowed mouth for the fold 3, which is at a distance of and is immediately adjacent to level 10.
- the transport of the unfolded layers 2 over the withdrawn Sword 20 and all movements described and the Removal is synchronized by a controller 30 and like this powered by a common motor.
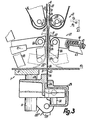
- the Control 30 points below the table 8 and laterally adjacent to level 11, a camshaft 48 and above lying and further away from level 11 a control shaft 49 on. Circumferential cams are rotatably fixed on the rotatable shaft 48 50 to 52 and 54 arranged.
- On the other side of the Level 11 is one in height between the waves 48, 49 Intermediate shaft 53 to limit the stroke of the links 24 to provided for level 14.
- the facilities 20 to 21 will be controlled by the cams moved via a linkage 55.
- Levers are fixed on the shaft 49 in a rotationally fixed manner at a distance from one another 56 arranged, which protrude freely in the direction of level 11.
- Rod 57 At the end of each lever 56 is one perpendicular to level 10 Rod 57 with its lower end pivoted, the upper end articulated to the underside of the carriage 28 is.
- rod 57 on each Transmission link 56 a rod in the form of a toggle lever 58 hinged, the upper end of which is at the bottom of the carriage 29 or above is pivoted.
- the stretched Position namely at the stroke up to approximately level 14 also both knee arms of lever 58 at right angles to level 10.
- Control member such as a rod 59, the effective length of rod 58 changed.
- the cam plate 50 is used to jointly pivot the Wave 49 and transmission organs 56 to 59, 69, for what you run a runner 60.
- a corresponding runner 61 is guided on the cam 51 to the conveyor 21 Intermediate organs 71, 65, 67, 39, 38 to operate.
- a runner 62 is guided to the press 22nd to operate via intermediate organs 72, 66, 68, 46, 43.
- a runner 64 is guided on the cam disk 54 in order to the carriage 29 via transmission members 74, 75, 63, 59, 58 to operate or the carriage 28, 29 or the partial links 23, 24 to move against each other.
- the pontics include an obtuse angle lever arranged on the axis 53 63, on its upward arm the rod 59 is articulated. In the middle between its two end positions the effective axial plane of this arm is at right angles to level 10.
- the rotor 60 is mounted on the free end of a lever 70, which, like the lever 56, is arranged on the shaft 49 in a rotationally fixed manner is.
- the runners 61, 62, 64 are each on an associated Lever 71, 72, 74 mounted, which in turn is rotatable on the Shaft 49 is mounted.
- All levers 70 to 72, 74 project from the shaft 49 against level 11.
- the effective axial plane of each of these Lever and the lever 56 is in the associated middle position perpendicular to level 11. All levers are independent from each other down or against the corresponding cam Springs 73 spring-loaded.
- lever 71 On the lever 71 is an acute angle to the plane 11 Rod 65 articulated with its lower end. It prevails level 10 and is at its upper end on a lever 67 articulated, which is directed away from level 11 of the shaft 39 which is arranged on that of the Waves 48, 49 facing away from level 11.
- the effective axial plane of this lever 67 is in the central position of the pliers 21 at right angles to level 11.
- the rotor 61 lies between the lower linkage of the rod 65 and the Wave 49.
- At the free end of the lever 72 are separate Rods 66 articulated with their lower ends so that their common pivot axis coaxial to the associated pivot axes of the rods 57, 58 may lie because of these articulation points have the same radial distances from the axis 49.
- the Bars 66 diverge at an acute angle, push through level 10 and are at their upper ends to each other facing ends of levers 68 articulated separately.
- Each lever 68 is firmly seated on the associated shaft 46 and protrudes freely against level 11. In the middle position mentioned the press 22, the levers 68 are at right angles to the Level 11. The axis of the joint between rod 66 and lever 68 lies below the central plane parallel to it Surface 42 and in a parallel to plane 11 and common Axial plane with the associated deflection 36, if this 2 and 3 is closest to level 11.
- the axis of each of the rotating bodies or joints 36, 38 to 41, 43, 46, 48 to 54 and 56 to 75 lies parallel to the Levels 10 and 11.
- the axes of the shafts 39, 46, 48, 49, 53 are permanently provided on frame 7.
- the device 1 works according to the following method:
- the shaft 48 with the non-rotatably arranged cams 50 to 52, 54 continuously rotates according to FIGS. 1 and 2 Clockwise towards 76.
- This will make the sled 28, 29 with the sword parts 23, 24 reversing over a adjustable stroke between their upper and lower end positions with constantly changing speeds back and forth reciprocated.
- Below the level 14 are the ends 25, 26 or the tops of the slides 28, 29 always on aligned at the same height.
- the press 22 lowered to its starting position. She achieves this when the sword 20 has reached its lower turning point or shortly after it started moving upwards. in the mouth 33 begins at the same moment or shortly before to open.
- the lever 58 is in its extended position, so that the edges 25, 26 are aligned.
- the spread layer 2 is over him fed and immediately detected by the edge 25, 26.
- the layer 2 is forming the fold 3 up to the area of the surfaces 42 still standing in the initial position, which in the upper end position according to FIG. 3 the transition forms between the inlet and the outlet mouth.
- This The area is closer to the edge 47 than from the lower end of the Areas 42. The areas run when this area is reached 42 in sync with the fold 3 and roll it against the sloping flanks of the ends 25, 26.
- roller pressure takes the center position of the stamp 41 of the surfaces 42 steadily again up to their upper end position until they detach completely from the layer legs and from the aligned ends 25, 26 are run through. In this Position the surfaces 42 until the return stroke explained of the sword 20 held continuously.
- the upward movement of the sword 20 is faster than in the first stroke part while the ends 25, 26 pass through the press 22 and then faster again.
- the shortening can be similar lever 58 at the beginning be faster than towards the end.
- the Coordination of the movements is based on the curve shapes Fig. 2 can be seen.
- the control of the relative movement of the slide 29 without possibly conceivable elastic stops causes a damping of Mass forces, so that even at high running speed low-impact and low-vibration work is guaranteed. It Up to a hundred or more folds or Lift cycles or full rotations of the shaft 48 are performed. Through to level 11 or to levels 10, 11 right-angled mid-plane symmetrical formation of many Parts, these can be placed equally on both sides of the plane 11 can be used optionally. This applies e.g. for the units 36, 38, 39, the units 41 to 45 or their separate reference numerals provided for or Bars 66. The entire control 30 is space-saving below the table 8 provided so that the level 10 only of the rods 65, 66 is penetrated upwards.
- a device 77 is provided through which a Avoid overloading the device 1 or for adjustment Control connections can be interrupted.
- the facility 77 forms a disengageable drive connection or Coupling between the unit 60, 70 on the one hand and the Linkage 55 or the levers 56 on the other hand.
- the Intervention is form-fitting, but in such a way that it is exceeded a predetermined driving force against a spring force disengages by itself.
- the counter member 79 is mounted on the axis 49 or lever non-rotatably connected to lever 56, which protrudes freely to level 11 and driver 78.
- the Driver 78 is due to the shorter, downward Arm formed by a two-armed lever, the top of which directed longer arm with an actuator one Controller 80 is connected. With the controller 80, the Tripping force of the device 77 or the spring force mentioned can be changed continuously. Is the control rod 80 e.g. With a pneumatic cylinder with the same axis as it or its Piston rod connected, the clutch 77 can also be arbitrarily engaged and disengaged. That cylinder or drive is attached to a carrier or pivotable stored, which on the axis 49 or on their bearings is arranged.
Landscapes
- Folding Of Thin Sheet-Like Materials, Special Discharging Devices, And Others (AREA)
- Making Paper Articles (AREA)
Claims (8)
- Dispositif de transport pour cahiers de feuilles (2) présentant une jonction (3), tel qu'un pli, avec une face intérieure (4) et une face extérieure (5), notamment dispositif de pliage pour la formation du pli (3), avec un bâti de dispositif (7), un élément d'engagement (20) étant prévu pour l'engagement dans un plan d'engagement (11) ainsi que dans un domaine d'engagement (10, de 12 à 15) à la face intérieure (4) de la jonction (3) et un moyen de transport (21) pour lever le cahier de feuilles (2) dans une direction de marche (6, 16) par une prise à la face extérieure (5) du cahier de feuilles (2) dans un domaine d'engagement (de 12 à 14), des moyens étant prévus pour l'engagement de transport dans le cahier de feuilles (2) essentiellement à l'extérieur de la zone d'engagement de l'élément d'engagement (20) conduisant encore le cahier de feuilles (2) et l'élément d'engagement (20) présentant une ouverture (27) pour l'engagement du moyen de transport (21), en ce que l'élément d'engagement (20) présente deux éléments partiels (23, 24) s'engageant dans le cahier de feuilles (2), caractérisé en ce que un premier élément entré les éléments partiels peut être déplacé par rapport à un deuxième élément partiel de telle manière, que des sections d'arête (25, 26) du premier et du deuxième élément partiel peuvent être déplacées en direction de transport en sens de marche (6) l'une contre l'autre pour la formation de l'ouverture (27) et que dans une position relative elles sont alignées de manière au moins approximative.
- Dispositif de transport d'après la revendication 1, caractérisé au moins par une des caractéristiques suivantes :a) l'élément d'engagement (20) et le moyen de transport (21) peuvent être rapprochés l'un à l'autre de manière réversible dans le sens de marche (6),b) le premier élément partiel (23) peut être déplacé plus loin dans le domaine d'engagement (12, 13) du moyen de transport (21) que le deuxième élément partiel (24),c) le deuxième élément partiel (24) se trouve toujours à l'extérieur du domaine d'engagement (12, 13); dans une position terminale (14) il s'étend cependant jusqu'à proximité immédiate du domaine d'engagement (12, 13),d) l'élément d'engagement (20) est une lame de pliage en forme de plaque pour le pliage du cahier de feuilles (2) pendant un mouvement de pliage (16) et il forme un interstice (27) pour l'engagement du moyen de transport (21),e) les deux éléments partiels (23, 24) se trouvent dans un même plan et il se font la suite de manière directe par des arêtes latérales,f) au moins un des éléments partiels (23, 24) est formé par des bras, qui sont situés avec un certain écart l'un à côté de l'autre et qui saillent librement contre le domaine d'engagement (12, 13), entre lesquels s'engage l'autre élément partiel (24, 23),g) une presse de pliage (22) devance le moyen de transport (21),h) la presse de pliage (22) est réalisée en tant que presse à rouleaux avec un fente de pressage qui se rapproche au domaine d'engagement (12, 13) avec l'élément d'engagement (20), eti) les deux éléments partiels (23, 24) peuvent être déplacés à travers la fente de pressage et/ou à travers une surface de table (10) fixe, logeant les cahiers de feuilles (2).
- Dispositif de transport d'après une des revendications précédentes, caractérisé en ce qu'au moins une surface de pressage (34, 42) d'une presse de pliage (21, 22) peut être pivotée autour d'un axe de pressage (39, 46) et qu'elle exerce la plus grande force de pressage dans le domaine essentiellement le plus avancé en direction du mouvement de pressage (19, 18), en ce que notamment un élément de pressage (41) de la presse de pliage (22) est une tige allongée à peu près parallèle à la direction longitudinale dé la jonction de bords (3) et logée à des supports de presse (43) faisant la suite latéralement et pouvant être déplacés en direction à peu près parallèle à la pression de compression, et en ce que de préférence un actionnement (66, 72) pour la surface de pressage (42) s'engage à une distance de celle-ci correspondant tout au plus à la hauteur de la surface de pressage (42).
- Dispositif de transport d'après une des revendications précédentes, caractérisé en ce que les moyens pour le déplacement transversal (19) d'au moins un élément de transport (36, 37) du moyen de transport (21) sont réalisés de manière relative par rapport au plan d'engagement (11) ou encore que le déplacement transversal (19) commandé par moteur est prévu de manière indépendante du mouvement de transport (6), en ce que notamment le moyen de transport (21) est réalisé en tant que davier ou encore pince motorisée distincte de la presse de pliage (22), et en ce que de préférence des moyens de commande (30) tels qu'une commande à cames sont prévus pour le mouvement synchronisé de l'élément d'engagement (20), du moyen de transport (21) et/ou de la presse de pliage (22), les moyen de commande (30) présentant notamment à proximité d'un arbre à cames (48) un arbre de commande (49) étant rotatif pour le déplacement synchrone des éléments partiels (23, 24) et qu'un curseur de came (64 ou encore 61) est logé de manière mobile pour permettre un mouvement relatif réciproque des éléments partiels (23, 24) et/ou pour permettre l'ouverture du moyen de transport (21).
- Dispositif de transport d'après une des revendications précédentes, caractérisé en ce que deux éléments de transport (37) du moyen de transport (21) situés sur les deux côtés du plan d'engagement (11) sont directement raccordés à entraínement entre eux pour un déplacement transversal (19) opposé, en ce que notamment le moyen de transport (21) est chargé par ressort contre le plan d'engagement (11), et en ce que de préférence un élément de transport (37) s'engageant sur le pli (3) est logé de manière à pivoter autour d'un axe de guidage (39) situé à une certaine distance de l'élément d'engagement (20).
- Procédé pour le transport de cahiers de feuilles (2) qui présentent une jonction de bords (3), telle qu'un pli, avec une face intérieure (4) et une face extérieure (5), notamment pour la formation du pli, le cahier de feuilles (2) étant déplacé par rapport à un moyen de transport (21) par un élément d'engagement (20) situé à la face intérieure (4) dans une zone d'engagement, mis en prise pour le transport dans une zone d'engagement de sa face extérieure (5) par un moyen de transport (21) et enlevé, caractérisé en ce qu'avant l'engagement de transport l'élément d'engagement (20) est adjacent en étant quasiment aligné avec la face intérieure (4) de la jonction de bords (3) et que pendant l'engagement de transport il est gardé de manière rétractée par compartiments par rapport à la face intérieure (4) de la jonction de bords (3).
- Procédé d'après la revendication 6, caractérisé en ce que par l'élément d'engagement (20) la jonction de bords (3) est poussée dans le moyen de transport (21) seulement par domaines situés dans sa direction longitudinale à proximité du point d'engagement de transport et notamment par contact direct au raccord de bords (3), et en ce que de préférence la jonction de bords (3) est préalablement poussée dans la presse de pliage (22) par l'élément d'engagement (20) essentiellement par la jonction de bords (3) ou encore dans le domaine de son point d'engagement suivant.
- Procédé d'après une des revendications de 6 à 7, caractérisé en ce que par le moyen de transport (21) on saisit la face extérieure (5) du cahier de feuilles (2) par un mouvement de pinçage (19) de fermeture pour l'engagement de transport, notamment pendant que la jonction de bords (3) atteint le moyen de transport (21), et en ce que de préférence le mouvement de pinçage est commandé de manière forcée à engagement positif.
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE19828300 | 1998-06-25 | ||
| DE19828300A DE19828300A1 (de) | 1998-06-25 | 1998-06-25 | Transportvorrichtung für Blattlagen, insbesondere Falzvorrichtung, sowie Verfahren zum Transportieren von Blattlagen, insbesondere zum Herstellen des Falzes |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0967167A1 EP0967167A1 (fr) | 1999-12-29 |
| EP0967167B1 true EP0967167B1 (fr) | 2003-09-03 |
Family
ID=7871969
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP99111206A Expired - Lifetime EP0967167B1 (fr) | 1998-06-25 | 1999-06-09 | Dispositif de transport de cahiers de feuilles, en particulier dispositif de pliage ainsi qu'une méthode de transport de cahier de feuilles, en particulier méthode de formation du pli |
Country Status (5)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US6511407B2 (fr) |
| EP (1) | EP0967167B1 (fr) |
| JP (1) | JP2000026020A (fr) |
| AT (1) | ATE248764T1 (fr) |
| DE (2) | DE19828300A1 (fr) |
Families Citing this family (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ES1049614Y (es) * | 2001-07-16 | 2002-04-16 | Mias Juan Marce | Dispositivo plegador de formatos de papel plegado. |
| US6981938B2 (en) * | 2003-08-15 | 2006-01-03 | Xerox Corporation | Booklet maker with crease rolls having a slip clutch |
| US7798950B2 (en) * | 2007-11-27 | 2010-09-21 | Ricoh Company, Limited | Sheet finisher, image forming apparatus, and sheet processing method |
| US20110218092A1 (en) * | 2010-03-05 | 2011-09-08 | Kabushiki Kaisha Toshiba | Sheet folding mechanism, sheet post-processing apparatus and method thereof |
| JP5561597B2 (ja) * | 2010-06-02 | 2014-07-30 | 株式会社リコー | 用紙折り装置 |
| JP5640757B2 (ja) * | 2011-01-18 | 2014-12-17 | 株式会社リコー | シート折り装置及び画像形成システム |
| JP6146650B2 (ja) * | 2013-01-28 | 2017-06-14 | 株式会社リコー | シート処理装置及び画像形成システム |
Family Cites Families (12)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE365688C (de) * | 1920-11-02 | 1922-12-20 | Gandenbergersche Maschinenfabr | Falzvorrichtung fuer Druckmaschinen |
| US1693147A (en) * | 1927-07-01 | 1928-11-27 | Chambers Brothers Co | Sheet folding |
| GB1208728A (en) | 1966-12-19 | 1970-10-14 | Weir Henry J | Laundry folding device |
| FR2262593B1 (fr) | 1974-02-28 | 1976-12-10 | Martin Sa | |
| DD114580A1 (fr) * | 1974-03-07 | 1975-08-12 | ||
| DE2519420C3 (de) * | 1975-04-30 | 1981-11-26 | Bielomatik Leuze Gmbh + Co, 7442 Neuffen | Falzvorrichtung |
| FR2412485A2 (fr) * | 1977-12-26 | 1979-07-20 | Duflot Rene | Machine a plier des nappes de tissu, telles que des draps |
| FR2497782B1 (fr) | 1981-01-09 | 1985-08-02 | Mabotex | Machine automatique de coupe, de pliage et de conditionnement des feuilles de materiaux souples, debitees en bandes enroulees |
| FR2639928B1 (fr) * | 1988-12-01 | 1991-03-29 | Marion Louis | Procede et dispositif de pliage de bandes de materiaux textiles, notamment de compresses |
| DE4101399A1 (de) * | 1991-01-18 | 1992-07-23 | Kodak Ag | Vorrichtung zum falten von blaettern |
| DE59300080D1 (de) | 1993-02-18 | 1995-03-23 | Jensen Ag Burgdorf | Falteinrichtung zum automatischen Falten von Wäschestücken. |
| JP2786617B2 (ja) | 1996-05-16 | 1998-08-13 | 三菱重工業株式会社 | 折機のシート等の搬送装置 |
-
1998
- 1998-06-25 DE DE19828300A patent/DE19828300A1/de not_active Withdrawn
-
1999
- 1999-06-09 AT AT99111206T patent/ATE248764T1/de not_active IP Right Cessation
- 1999-06-09 EP EP99111206A patent/EP0967167B1/fr not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1999-06-09 DE DE59906825T patent/DE59906825D1/de not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 1999-06-23 JP JP11177236A patent/JP2000026020A/ja active Pending
-
2001
- 2001-09-10 US US09/950,260 patent/US6511407B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| ATE248764T1 (de) | 2003-09-15 |
| US20020082151A1 (en) | 2002-06-27 |
| DE59906825D1 (de) | 2003-10-09 |
| JP2000026020A (ja) | 2000-01-25 |
| US6511407B2 (en) | 2003-01-28 |
| EP0967167A1 (fr) | 1999-12-29 |
| DE19828300A1 (de) | 1999-12-30 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| DE3512737C2 (de) | Aufgeber von Heftlagen, Bogen und ähnlichen Erzeugnissen für Zuführvorrichtungen in Packmaschinen, Buchbindereimaschinen u.dgl. | |
| DE19814917C2 (de) | Anlage zum Falten eines Textilbahnabschnitts | |
| DE1930128C2 (de) | Vorrichtung zur Ausrichtung eines Stapels von Bogen zum Heften | |
| EP1242300B1 (fr) | Cylindres permettant de guider des bandes papier | |
| DE4211219C2 (de) | Anordnung zur Handhabung von Flachmaterial | |
| DE3145490A1 (de) | Kunststoffschweissgeraet zum verschliessen von beuteln aus thermoplastischen kunststoffolien o.dgl. | |
| EP0522319A1 (fr) | Procédé et dispositif pour ouvrir des articles flexible pliés hors du centre | |
| DE2058606C3 (de) | Vorrichtung zum kontinuierlichen Fördern und Ausrichten von vereinzelten Bogen | |
| EP0967167B1 (fr) | Dispositif de transport de cahiers de feuilles, en particulier dispositif de pliage ainsi qu'une méthode de transport de cahier de feuilles, en particulier méthode de formation du pli | |
| DE1277140B (de) | Vorrichtung zum Stapeln und Transportieren von flachen Gegenstaenden, insbesondere Papiertuechern | |
| DE2335358C3 (de) | Automatische Maschine zum Transport und Aufnähen der Signaturen in Büchern | |
| DE1586347B1 (de) | Vorrichtung zum Drehen von flachliegend voranbewegten Werkstuecken in ihrer Bewegungsebene | |
| DE2214656C2 (de) | Vorrichtung zum Überführen eines Eingangsstromes aus aneinander anliegenden Gegenständen in einen Ausgangsstrom unter Abstand aufeinanderfolgender Gegenstände | |
| DE2519420B2 (de) | Falzvorrichtung | |
| DE60318360T2 (de) | Rill- und Falzmaschine für Kartonplatten | |
| DE1561141B2 (de) | Vorrichtung zum einfuehren von beilagen in gefaltete druckerzeugnisse | |
| EP1334940B1 (fr) | Dispositif de pliage longitudinal | |
| EP2102085B1 (fr) | Dispositif de transport | |
| EP2711164B1 (fr) | Dispositif et procédé destinés à ouvrir une zone d'extrémité d'un corps de sachet tubulaire | |
| EP0207271B1 (fr) | Dispositif pour comprimer le pli d'articles imprimés transportés sur un convoyeur | |
| DE3335583C2 (fr) | ||
| DE19621586C2 (de) | Vorrichtung zum Übergeben von Zetteln von einem rotierend angetriebenen ersten Zylinder an einen rotierend angetriebenen zweiten Zylinder | |
| AT406755B (de) | Vorrichtung zum öffnen von schlauchförmigen sackkörpern | |
| DE2220567A1 (de) | Verfahren und vorrichtung zum buchbinden | |
| DE2243594C2 (de) | Mehrfachfalt vorrichtung |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AT CH DE FR GB IT LI |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Free format text: AL;LT;LV;MK;RO;SI |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20000531 |
|
| AKX | Designation fees paid |
Free format text: AT CH DE FR GB IT LI |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 20020506 |
|
| GRAH | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS IGRA |
|
| GRAS | Grant fee paid |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR3 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AT CH DE FR GB IT LI |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: NOT ENGLISH |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: EP |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: NV Representative=s name: WILLIAM BLANC & CIE CONSEILS EN PROPRIETE INDUSTRI |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 59906825 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 20031009 Kind code of ref document: P |
|
| GBT | Gb: translation of ep patent filed (gb section 77(6)(a)/1977) | ||
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AT Payment date: 20040611 Year of fee payment: 6 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Payment date: 20040618 Year of fee payment: 6 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CH Payment date: 20040623 Year of fee payment: 6 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 20040629 Year of fee payment: 6 |
|
| ET | Fr: translation filed | ||
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20040709 Year of fee payment: 6 |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed |
Effective date: 20040604 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20050609 Ref country code: AT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20050609 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20050630 Ref country code: CH Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20050630 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20060103 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20060228 |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 20050609 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: ST Effective date: 20060228 |