WO2018168298A1 - 投薬支援装置、方法及びプログラム - Google Patents
投薬支援装置、方法及びプログラム Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2018168298A1 WO2018168298A1 PCT/JP2018/004911 JP2018004911W WO2018168298A1 WO 2018168298 A1 WO2018168298 A1 WO 2018168298A1 JP 2018004911 W JP2018004911 W JP 2018004911W WO 2018168298 A1 WO2018168298 A1 WO 2018168298A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- medication
- information
- blood pressure
- patient
- network
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Ceased
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G16—INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR SPECIFIC APPLICATION FIELDS
- G16H—HEALTHCARE INFORMATICS, i.e. INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR THE HANDLING OR PROCESSING OF MEDICAL OR HEALTHCARE DATA
- G16H40/00—ICT specially adapted for the management or administration of healthcare resources or facilities; ICT specially adapted for the management or operation of medical equipment or devices
- G16H40/20—ICT specially adapted for the management or administration of healthcare resources or facilities; ICT specially adapted for the management or operation of medical equipment or devices for the management or administration of healthcare resources or facilities, e.g. managing hospital staff or surgery rooms
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G16—INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR SPECIFIC APPLICATION FIELDS
- G16H—HEALTHCARE INFORMATICS, i.e. INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR THE HANDLING OR PROCESSING OF MEDICAL OR HEALTHCARE DATA
- G16H20/00—ICT specially adapted for therapies or health-improving plans, e.g. for handling prescriptions, for steering therapy or for monitoring patient compliance
- G16H20/10—ICT specially adapted for therapies or health-improving plans, e.g. for handling prescriptions, for steering therapy or for monitoring patient compliance relating to drugs or medications, e.g. for ensuring correct administration to patients
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B5/00—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons
- A61B5/0002—Remote monitoring of patients using telemetry, e.g. transmission of vital signals via a communication network
- A61B5/0004—Remote monitoring of patients using telemetry, e.g. transmission of vital signals via a communication network characterised by the type of physiological signal transmitted
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B5/00—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons
- A61B5/02—Detecting, measuring or recording for evaluating the cardiovascular system, e.g. pulse, heart rate, blood pressure or blood flow
- A61B5/021—Measuring pressure in heart or blood vessels
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B5/00—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons
- A61B5/48—Other medical applications
- A61B5/4833—Assessment of subject's compliance to treatment
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61B—DIAGNOSIS; SURGERY; IDENTIFICATION
- A61B5/00—Measuring for diagnostic purposes; Identification of persons
- A61B5/74—Details of notification to user or communication with user or patient; User input means
- A61B5/742—Details of notification to user or communication with user or patient; User input means using visual displays
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G16—INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR SPECIFIC APPLICATION FIELDS
- G16H—HEALTHCARE INFORMATICS, i.e. INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR THE HANDLING OR PROCESSING OF MEDICAL OR HEALTHCARE DATA
- G16H40/00—ICT specially adapted for the management or administration of healthcare resources or facilities; ICT specially adapted for the management or operation of medical equipment or devices
- G16H40/60—ICT specially adapted for the management or administration of healthcare resources or facilities; ICT specially adapted for the management or operation of medical equipment or devices for the operation of medical equipment or devices
- G16H40/63—ICT specially adapted for the management or administration of healthcare resources or facilities; ICT specially adapted for the management or operation of medical equipment or devices for the operation of medical equipment or devices for local operation
Definitions
- the present disclosure relates to a medication support apparatus, method, and program for supporting a doctor's medication work, for example.
- doctors prescribe antihypertensive drugs to patients based on the results of examinations, patients take prescribed antihypertensive drugs, and use a sphygmomanometer to monitor blood pressure at a set time every day. It is common to measure and report this measurement result to a doctor at the next visit.
- a system has been proposed in which a remote patient is treated using a network.
- a patient transfers vital measurement information such as blood pressure to a server via the Internet and registers it on a homepage, and a doctor browses vital measurement data registered on the homepage of the server from his / her terminal and The comment is sent to the patient's vital measurement device at the next vital measurement (see, for example, JP-A-2002-312487).
- a doctor grasps a patient's treatment performance using only a blood pressure value reported or measured by a patient as a judgment material, regardless of whether it is outpatient medical treatment or remote medical treatment. For this reason, for example, when a patient's blood pressure rises or falls and it is necessary to change the prescription of antihypertensive drugs accordingly, it is necessary to check the prescription of past medication by browsing the patient's medical chart one by one was there. In addition, when changing the prescription of medication, it is necessary to check whether or not the patient has taken antihypertensive drugs as prescribed, but the patient generally reports the oral status to the doctor at the time of medical treatment. Therefore, the doctor may not be able to accurately determine the relationship between the change in blood pressure value and the medication situation.
- One aspect of the present invention is to enable presentation of information representing at least the transition of blood pressure or the relationship between medication status and medication without generation by the prescriber's terminal, whereby the processing load on the prescriber's terminal is increased. It is intended to provide a technology that keeps low. In addition, for the prescriber, the patient's past blood pressure change can be grasped in association with the type and amount of the medicine prescribed in the past, thereby making it possible to efficiently and accurately determine the medication for the patient. It is intended to provide such a technology.
- a first aspect of the present invention is a medication support apparatus capable of communicating via a network between a first terminal used by a doctor and a second terminal including a sphygmomanometer used by a patient.
- the type and amount of the medicine included in the acquired medication information and the transition of the blood pressure value based on the acquired blood pressure measurement information are displayed for each patient by the display information generation unit.
- the medication treatment result information to be displayed in association with each other in time series is generated.
- the medication treatment performance information corresponding to the said patient is transmitted to the said 1st terminal of the request origin via the said network. It is what I did.
- the medication support apparatus for each patient, the kind and amount of the medicine included in the medication information obtained from the prescriber's terminal such as a doctor, and the patient's terminal.
- Medication treatment result information for displaying the transition of blood pressure values based on blood pressure measurement information in association with each other on a time series is generated, and this medication treatment result information is transmitted to the requesting prescriber's terminal, Presented. For this reason, it becomes possible to present the medication treatment result information without generating the terminal on the prescriber side, thereby reducing the processing load on the terminal on the prescriber side.
- prescribers such as doctors prescribe changes in past blood pressure values of the patient by simply listing the display of medication treatment results information when performing outpatient treatment or telemedicine for the patient. It can be grasped in association with the type and amount of the drug. Accordingly, it is possible to efficiently and accurately determine whether or not a patient needs medication, that is, whether or not to change the medicine.
- the display information generation unit detects a change exceeding a preset amount of the blood pressure value from the change of the blood pressure value based on the blood pressure measurement information, and displays information indicating the content of the change. Medication treatment result information for adding and displaying the corresponding position on the time series of the graph representing the transition of the blood pressure is generated.
- a change exceeding the preset amount of the blood pressure value is detected from the blood pressure value transition based on the blood pressure measurement information, and the information representing the content of the change represents the blood pressure transition.
- the time position is displayed in association with the graph. For this reason, the doctor can recognize the abnormal fluctuation of the blood pressure value at a glance, thereby making it possible to more efficiently and accurately determine the medication.
- the display information generation unit displays the type of drug included in the medication information as a block having a different color or gray scale, and displays the amount of the drug by the number of stacked blocks. Information on medication treatment results is generated.
- the type of medicine is displayed as a block having a different color or gray scale, and the amount of the medicine is displayed by the number of stacked blocks. For this reason, it is possible to easily and accurately grasp the type and amount of a medicine that has been dispensed in the past based on the color and number of blocks, thereby making it possible to determine the dosage more efficiently and accurately.
- the fourth aspect of the present invention further includes a medication information acquisition unit that acquires medication information representing a medication status of the patient from the second terminal via the network. Then, the display information generating unit generates medication adherence information indicating the status of internal compliance based on the acquired medication information, and the generated medication adherence information includes the type and amount of the medication and the blood pressure value. Medication treatment result information to be displayed in association with information representing the transition of the time series in time series.
- the medication adherence information indicating the status of compliance with internal use is generated based on the medication information acquired from the terminal of the patient, and the medication adherence information includes the type and amount of the drug and the blood pressure value. Is displayed in association with the transition of the time series. For this reason, transition of blood pressure and medication adherence can be taken into consideration in the judgment requirements for medication to the patient, thereby making it possible to more accurately judge medication.
- the fifth aspect of the present invention further includes an activity amount information acquisition unit that acquires activity amount information representing the activity amount of the patient from the second terminal via the network. Then, the display information generation unit generates information indicating the transition of activity based on the acquired activity information, and the information indicating the transition of the generated activity is determined based on the type and amount of the drug and The medication treatment result information for displaying the blood pressure value transition and the time series in association with each other is generated.
- information indicating the transition of the activity amount is generated based on the activity amount information acquired from the patient's terminal, and the information indicating the transition of the activity amount is the type and amount of the drug.
- the blood pressure values are displayed in association with the transition of the blood pressure values over time. For this reason, it is possible to consider the amount of activity in the requirements for determination of medication for the patient, thereby making it possible to more accurately determine the medication.
- the medicine to be prescribed to the patient with reference to at least the medication treatment result information corresponding to the patient is generated, and the generated medication guide information is transmitted to the first terminal that is the request source via the network.
- medication guide information representing a candidate for prescription of the type and amount of a drug is generated in consideration of at least medication treatment result information corresponding to a patient to be treated. , Displayed on the doctor's terminal. Therefore, the doctor can determine the content of medication with reference to the medication guide information when he / she is not sure about the type and amount of the medicine to be prescribed.
- a network between a first terminal used by a drug prescriber and a second terminal connected to a blood pressure monitor or incorporating a blood pressure monitor and used by a patient.
- a medication support apparatus capable of communicating via the first terminal, obtaining medication information including the type and amount of the medicine prescribed for the patient via the network, and from the second terminal.
- the blood pressure measurement information of the patient obtained by the sphygmomanometer is acquired via the network, and the medication information representing the status of the patient's medication is obtained via the network.
- the medication adherence information representing the status of internal compliance is generated based on the obtained medication information, and the type of medication included in the created medication adherence information and the obtained medication information And dosage information are generated in order to display them in association with each other in a time series based on information indicating the medication date and time and the medication date and time included in the medication information and medication information, respectively.
- the result information is transmitted to the requesting first terminal via the network.
- the medication adherence information indicating the status of internal compliance is generated based on the medication information acquired from the patient's terminal, and the medication adherence information shows the transition of the type and amount of the drug.
- the information to be displayed is displayed in association with the time series. For this reason, it is possible to consider the medication adherence in the requirements for determining the medication for the patient, and thus the medication can be determined in consideration of the patient's medication status.
- information representing at least the transition of blood pressure or the relationship between the medication situation and medication can be presented without the prescriber's terminal generating it, thereby the prescriber's terminal It is possible to provide a technique that keeps the processing load of the system low. In addition, it is possible for the prescriber to easily and accurately confirm at least the transition of blood pressure or the situation of medication and medication, thereby providing a technique that enables accurate medication.
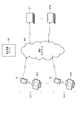
- FIG. 1 is a diagram showing the overall configuration of a system including a medication support apparatus according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
- FIG. 2 is a block diagram showing a functional configuration of the medication support apparatus according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
- FIG. 3 is a flowchart showing a processing procedure and processing contents of medication support control by the medication support device shown in FIG.
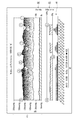
- FIG. 4 is a diagram showing an example of medication treatment result display data generated by the medication support control shown in FIG.
- FIG. 5 is a diagram showing another example of medication treatment result display data generated by the medication support control shown in FIG.
- FIG. 1 is a diagram showing an overall configuration of a medication support system according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
- SV is a medication support server that functions as a medication support device
- DT1 to DTm are first terminals used by doctors (hereinafter also referred to as doctor terminals)
- UT1 to UTn are second terminals used by patients (hereinafter referred to as doctor terminals). Also referred to as a patient terminal).
- the medication support server SV, the doctor terminals DT1 to DTm, and the patient terminals UT1 to UTn can communicate with each other via the communication network NW.
- the doctor terminals DT1 to DTm are composed of, for example, a stationary personal computer, a portable notebook personal computer, or a tablet terminal.
- the doctor terminals DT1 to DTm are provided with at least a browser, and by using this browser, the medication support server SV can be accessed.
- the patient terminals UT1 to UTn include blood pressure monitors BT1 to BTn and portable information terminals IT1 to ITn.
- the sphygmomanometers BT1 to BTn are mounted on a patient's wrist, for example, measure blood pressure by a patient's operation or a preset timing or time interval, for example, by an oscillometric method, and the blood pressure data is transmitted by a wireless interface. Wireless transmission is performed to the portable information terminals IT1 to ITn.
- the blood pressure monitors BT1 to BTn are measured in a spot-like manner using the Beat by Beat method for measuring every beat of the heartbeat or the Pulse Transit Time (PTT) method to estimate blood pressure fluctuation and using the estimated fluctuation as a trigger.
- PTT Pulse Transit Time
- the sphygmomanometers BT1 to BTn are not limited to the type attached to the wrist, but may be a type in which the cuff is wound around the upper arm or the like or a stationary type.
- the portable information terminals IT1 to ITn are, for example, smartphones or tablet terminals.
- the portable information terminals IT1 to ITn have a blood pressure data transfer unit and a patient data transmission unit.
- the blood pressure data transfer unit receives the patient's blood pressure data transmitted from the sphygmomanometers BT1 to BTn, and transfers the blood pressure data to the medication support server SV via the communication network NW.
- the patient data transmission unit sends information representing the medication status manually input by the patient, information representing the amount of activity, information representing the weight of the patient, and information representing the food intake status via the communication network NW. Send to SV.
- a wireless interface used between the sphygmomanometers BT1 to BTn and the portable information terminals IT1 to ITn an interface employing a short-range wireless data communication standard such as Bluetooth (registered trademark) is used.
- portable information terminals IT1 to ITn transmit blood pressure values manually input by the patient and information indicating the measurement date and time to medication support server SV.
- the wearable terminal When the portable information terminals IT1 to ITn are wearable terminals that are worn on the patient's wrist, the wearable terminal includes a blood pressure measurement unit, an activity amount measurement unit, a step count measurement unit, a sleep state measurement unit, temperature, humidity, atmospheric pressure, and the like. An environmental measurement unit is provided. Then, the wearable terminal automatically transmits the measurement data respectively measured by each of the measurement units at a preset timing or periodically by the wearable terminal. The above activities, steps, and sleep state can be calculated based on the measurement data of the 3-axis accelerometer, and the temperature, humidity, and barometric pressure are measured from the thermometer, hygrometer, and barometer, respectively. Can be sought.
- the portable information terminals IT1 to ITn are able to check the blood pressure, activity amount, number of steps, sleep state, environment, etc.
- Each measurement data can be provided to the application program.
- the provision of the measurement data can be realized by providing a data connection function in the portable information terminals IT1 to ITn.
- the data connect function for example, performs authentication between the application program and each measurement data or its measurement unit, and when the application program has a qualification to use each measurement data, Transfer to application program.
- the data connect function may have a function of converting each measurement data into a data format that can be handled by the application program.
- the medication support server SV is composed of a server computer and is configured as follows.
- FIG. 2 is a block diagram showing the functional configuration.
- the medication support server SV includes a control unit 1, a storage unit 2, and a communication interface unit 3.
- the communication interface unit 3 performs data communication with the doctor terminals DT1 to DTm and the portable information terminals IT1 to ITn through the communication network NW under the control of the control unit 1.
- the communication protocol uses a protocol defined by the communication network NW. Specifically, TCP / IP (Transmission Protocol / Internet / protocol), UDP / IP (User Datagram Protocol / Internet protocol) or the like is used.
- the storage unit 2 is a nonvolatile memory such as HDD (Hard Disk Drive) or SSD (Solid State Device) that can be written and read at any time, and a volatile memory that can be written and read as RAM (Random Access Memory).
- a medication database 21 a blood pressure database 22, a medication database 23, a patient life information database 24, and a medication treatment are used.
- a track record information database 25 a database necessary for implementing the first embodiment of the present invention.
- the storage unit 2 is also provided with a storage area as a program memory.
- the medication database 21 stores drug information, medication guide information, and medication management information.
- the drug information includes information on the type (class) of the drug and indications and contraindications for each type.
- the medication guide information indicates the type and amount of drug to be prescribed to the patient, depending on the combination of the type and amount of antihypertensive drugs being prescribed, the change in blood pressure, the change in activity, and the weight of the patient. Several candidates are prepared.
- the medication management information associates the type and amount of the medicine prescribed to the patient with the prescription date, and is created for each patient.
- the blood pressure database 22 is used to store information representing the transition of blood pressure data for each patient.
- the medication database 23 is used to store information representing the medication history for each patient.
- the patient life information database 24 is used to store information representing the amount of activity, weight, and food intake status for each patient, that is, patient life information.
- the medication treatment result information database 25 is used for storing medication treatment result information generated by the control unit 1 described later for each patient.
- the control unit 1 includes a hardware processor and a working memory. As processing functions necessary for carrying out the first embodiment of the present invention, a medication management unit 11, a blood pressure transition management unit 12, a medication history management Unit 13, patient life information management unit 14, and medication treatment result information generation unit 15. These processing functions are realized by causing the hardware processor to execute a program stored in the program memory of the storage unit 2.
- the medication management unit 11 includes a medication guide transmission unit and a medication information management unit.
- the medication guide transmission unit receives a medication guide transmission request from the doctor terminals DT1 to DTm
- the medication guide transmission unit reads the medication treatment result information of the corresponding patient from the medication treatment result information database 25. Then, based on the medication treatment result information, a candidate for prescription of the type and amount of the medicine is selected from the medication database 21, and processing is performed for sending this as medication guide information to the requesting doctor terminals DT1 to DTm.
- the medication information management unit extracts the medication information (prescription information) from the electronic medical record data, and the prescription information is extracted.
- a process of adding to the medication management information of the corresponding patient stored in the medication database 21 together with information representing the medication date and time is performed.
- the blood pressure transition management unit 12 stores the blood pressure data in the blood pressure database 22 in association with patient identification information together with information indicating the measurement date and time. That is, the blood pressure transition management unit 12 stores information representing the blood pressure transition of each patient while updating the information.
- the medication history management unit 13 takes the information indicating the status of the medication in association with the identification information of the patient together with the information indicating the measurement date and time.
- the medication adherence is calculated based on information stored in the database 23 and indicating the stored medication situation.
- the patient life information management unit 14 measures or inputs information indicating the amount of activity, body weight, and food intake status each time information indicating the amount of activity, weight, and food intake status is sent from the patient terminals UT1 to UTn. Along with information representing the date and time, it is stored in the medication database 23 as patient life information in a state associated with patient identification information.
- the medication treatment result information generating unit 15 performs medication management information, blood pressure transition information, medication adherence information from the medication database 21, blood pressure database 22, medication database 23, and patient life information database 24 for each patient in a predetermined cycle. And read patient life information. Then, based on each read information, information representing the medication treatment result is generated, and the generated medication treatment result information is stored in the medication treatment result information database 25 in association with the identification information of the patient.
- the medication treatment result information generating unit 15 reads out the medication treatment result information of the patient designated by the request from the medication treatment result information database 25, The medication treatment result information is transmitted to the requesting doctor terminals DT1 to DTm.
- FIG. 3 is a flowchart showing the processing procedure and processing contents of the medication support server SV.
- a drug hypertensive drug
- the explanation is based on the assumption that the information and the patient life information such as the amount of activity, weight, and food intake are received.
- the medication support server SV performs medication treatment based on the type and amount of antihypertensive drugs being prescribed, received blood pressure data, information on medication status, and patient life information. Result information is generated and stored in the medication treatment result information database 25. A specific example of medication treatment result information will be described in detail later.
- the doctor designates the patient identification information at his / her doctor terminal DT1 to DTm and sends the medication guide Enter the request. Then, a medication guide transmission request including patient identification information is transmitted from the doctor terminals DT1 to DTm to the medication support server SV.
- the medication support server SV monitors reception of a medication guide transmission request in step S10 in a standby state. In this state, when a medication guide transmission request is received, medication guide information is generated as follows under the control of the medication management unit 11 in step S11.
- the medication management unit 11 reads the corresponding medication treatment result information from the medication treatment result information database 25 based on the identification information of the designated patient. Then, the medication database 21 is searched based on the medication treatment result information. At this time, the prescription of the type and amount of the antihypertensive drug set in advance corresponding to the combination of the type and amount of the antihypertensive drug in the prescription, the change in blood pressure value, the change in the activity amount, and the weight of the patient is stored in the medication database 21 A plurality of candidates are stored. For this reason, from the medication database 21, candidates for prescriptions of types and amounts of antihypertensive drugs corresponding to the medication treatment performance information of the patient are read out.
- 1 unit (1 tablet) of ACE inhibitor (Angiotensin Converting-Enzyme Inhibitor) and Ca antagonist (Calcium Channel ⁇ ⁇ ⁇ ⁇ Blocker: CCB) is prescribed, and its medication adherence (Adherence) and activity amount
- ACE inhibitor Angiotensin Converting-Enzyme Inhibitor
- Ca antagonist Calcium Channel ⁇ ⁇ ⁇ ⁇ Blocker: CCB
- a prescription candidate “add 1 unit of diuretic (DIU)” is read.
- a prescription candidate “add 2 units of diuretic (DIU)” is read.
- Hypertension treatment guidelines define prescription plans that indicate the types and amounts of drugs that should be prescribed to patients at each stage of medical care. For example, for hypertension, blood pressure levels and their transition (medication effect), presence of complications It is determined in consideration of the patient's weight and the like.
- the hypertension treatment guideline is described in, for example, Japanese hypertension treatment guideline 2014 (JSH2014).
- the medication management unit 11 transmits the prescription candidate of the read type and amount of the antihypertensive drug to the requesting doctor terminals DT1 to DTm as medication guide information.
- the medication guide information is displayed on the doctor terminals DT1 to DTm.
- the doctor refers to the displayed medication guide information and further determines whether or not to change the prescription of the antihypertensive drug, taking into consideration the presence or absence of side effects due to the ACE inhibitor.
- the doctor terminals DT1 to DTm transmit the prescription content determined by the doctor to the medication support server SV, and the medication management unit 11 of the medication support server SV stores it in the medication database 21 based on the prescription content determined by the doctor.
- the content of the corresponding medication guide information may be updated.
- the medication management unit 11 may add the prescription content determined by the doctor as a new candidate without updating the content of the medication guide information.
- the doctor transmits the data of the electronic medical record from his / her doctor terminals DT1 to DTm to the medication support server SV.
- the medication support server SV monitors reception of electronic medical record data in step S12 in the standby state.
- the medication support server SV stores the received electronic medical record data in the medication database 21 in association with the patient identification information in step S13 under the control of the medication management unit 11.
- step S14 the medication management unit 11 extracts medication information from the electronic medical record data, that is, prescription information indicating the type and amount of the medicine prescribed to the patient, and the extracted prescription information is stored in the medication database 21. To the medication management information of the corresponding patient. Thereafter, each time electronic medical record data is received from the doctor terminals DT1 to DTm, the medication management unit 11 repeatedly executes the processes in steps S12 to S14.
- Blood pressure data management In the patient terminals UT1 to UTn, blood pressure in the patient's home or office is measured at regular time intervals by the blood pressure monitors BT1 to BTn. The measured blood pressure data is transmitted from the blood pressure monitors BT1 to BTn to the portable information terminals IT1 to ITn, and is transmitted from the portable information terminals IT1 to ITn to the medication support server SV.
- the medication support server SV monitors the reception of blood pressure data in step S15 in the standby state.
- the blood pressure transition management unit 12 receives the blood pressure data in step S16, and then transmits the blood pressure data together with information indicating the measurement date and time.
- the blood pressure database 22 is additionally stored in association with the identification information.
- the blood pressure transition management unit 12 calculates, for example, the weekly average of blood pressure values measured during the period for each week based on the blood pressure data stored in the blood pressure database 22, and the calculation The value is stored in the blood pressure database 22 as blood pressure transition information of the corresponding patient.
- the blood pressure transition management unit 12 compares the blood pressure average value of this week with the blood pressure average value of the previous week based on the blood pressure transition information, and determines whether or not the amount of change is equal to or greater than a threshold value.
- the change amount threshold is set to a value medically defined as an abnormal blood pressure change.
- the blood pressure transition management unit 12 adds information indicating the amount of change and the direction of change (increase / decrease) to the blood pressure average value for this week.
- the blood pressure transition management unit 12 repeatedly executes the processes in steps S15 to S17.
- the medication support server SV monitors reception of medication input data in step S18 in the standby state.
- the medication history management unit 13 receives the medication input data in step S19, and then associates it with the patient identification information in the medication database 23. Add additional memory.
- step S20 the medication history management unit 13 calculates, for example, a medication adherence representing the degree of execution of the medication during the period based on the medication input data stored in the medication database 23.
- the medication adherence information is stored in the medication database 23.
- the medication history management unit 13 repeatedly executes the processes in steps S18 to S20.
- the activity amount data is represented by, for example, the number of steps measured by a pedometer or the amount of movement measured by an acceleration sensor.
- the portable information terminals IT1 to ITn transmit the inputted information to the medication support server SV as patient life information.
- the activity amount data can be measured by an activity amount measurement application, and the measurement data can be automatically transmitted in addition to the manual input by the patient.
- the medication support server SV monitors reception of patient life information in step S21 in the standby state. Then, when patient life information is sent from the patient's portable information terminals IT1 to ITn, the patient life information management unit 14 receives the patient life information in step S22, and then associates it with the patient identification information in the patient life information database 24. Add to memory.
- step S23 the patient life information management unit 14 calculates the weekly average of the activity amount and the weight included in the period for each week for each patient, and stores the result in the patient life information database 24. Thereafter, each time new patient life information is received, the patient life information management unit 14 repeatedly executes the processes in steps S21 to S23.
- the medication support server SV monitors whether or not the timing of producing medication treatment result information has come in step S24 in the standby state.
- the generation timing is set every week, for example.
- the medication support server SV activates the medication treatment result information generation unit 15 at step S25 each time the generation timing comes. Then, under the control of the medication treatment result information generating unit 15, the medication treatment result information is generated as follows, and the result is stored in the medication treatment result information database 25 in association with the patient identification information.
- FIG. 4 is a diagram showing an example.
- the blood pressure (BP) transition 41, the activity change 42, and the medication adherence 43 are all represented by a line graph.
- a band-like region indicating the hypertension stage is displayed, so that it can be confirmed at a glance whether or not the patient's blood pressure change is included in the hypertension stage.
- the abnormal value and information indicating the change amount and the change direction are superimposed and displayed at the time position where the abnormal value (outlier value) of the blood pressure is measured.
- the doctor can check at a glance the abnormal value of blood pressure and the amount and direction of change thereof in association with the measurement date and time.
- the activity amount change 42 is displayed as, for example, the activity amount converted into the weekly average value of the travel distance km.
- the weekly average value of the degree of medication taken is displayed in%.
- other indicators related to the activity amount for example, the weight, the movement distance itself, or the number of steps may be displayed.
- the type of antihypertensive drug is represented as a block having a different color or gray scale, and the amount of the antihypertensive drug is represented by the number of stacked blocks.
- the amount of the antihypertensive drug is represented by the number of stacked blocks.
- one tablet of each ACE inhibitor and Ca antagonist (CCB) was prescribed until February 15, 2016. However, since the blood pressure value increased, February 15, 2016 This shows that one tablet of diuretic (DIU) was added in addition to the ACE inhibitor and Ca antagonist (CCB) from the day until February 29 of the same year.
- DIU diuretic
- an ⁇ blocker (AB) was further added. Shows the case.
- the amount of Ca antagonist (CCB) is increased to two tablets, it is displayed in a state where two blocks of Ca antagonist (CCB) are stacked.
- the block may have any closed shape, and may have any shape such as a rectangle, a circle, or a cube.
- the medication treatment result information generating unit 15 is configured for each of medication management information, blood pressure transition information, medication adherence information, and patient life information read from the medication database 21, blood pressure database 22, medication database 23, and patient life information database 24, respectively. , Calculate achievement score against target value in weekly units.
- BP blood pressure
- body weight if the target value is X_target, the latest measurement value is X_now, and the past measurement value is X_prev, both are 1- (X_target-X_now) / ( X_target-X_prev) Is calculated as
- the medication treatment result information generating unit 15 calculates the achievement score by category for this week, that is, blood pressure (Blood Pressure: BP) achievement score X1, body weight (Body Fat) achievement score X2, medication adherence (Adherence) achievement score X3, Activity achievement score X4, meal achievement status (meal) achievement score X5, each achievement score of the previous week, and each achievement of other patient groups this week Displayed side by side with the average score.
- the calculated overall achievement score X is displayed in a semicircular graph.
- FIG. 5 shows an example thereof.
- 46 indicates an achievement score for each category
- 47 in the figure indicates an overall achievement score X.
- each piece of information shown in FIGS. 4 and 5 may be configured as display data for another page, but may be configured to be display data for one page in order to improve the listability.
- the indicators such as the displayed blood pressure (BP) transition 41, activity change 42, medication adherence 43 and medication management information 44 are displayed on the doctor terminals DT1 to DTn by the doctor.
- the placement relationship can be switched by operating and dragging. That is, the display screen of the medication treatment result information can be customized to a screen that is easy for a doctor to see according to his / her wishes.
- the display screen should be customized according to the doctor's operation. Can do.
- the doctor selects the icon 45 indicating the type (class) of the antihypertensive drug displayed at the bottom of the medication management information 44 by clicking, the display of the corresponding antihypertensive drug in the medication management information 44 by the doctor terminals DT1 to DTn. Can be switched on / off. Further, according to the selection operation of the antihypertensive drug, only the medication adherence corresponding to the selected antihypertensive drug is displayed in the display area of the medication adherence (Adherence) 43 by the doctor terminals DT1 to DTn. For this reason, the doctor can confirm the medication adherence (Adherence) for every antihypertensive drug.
- the medication support server SV has a blood pressure (BP) change 41, an activity change 42, a medication adherence 43, and medication management information 44. Is generated in such a manner that the time-positions are displayed in association with each other on the same time series, and the results of the medication treatment are transmitted to the doctor terminals DT1 to DTm for display. Therefore, the doctor terminals DT1 to DTm can display the medication treatment result information as it is by receiving it without performing the process of generating the medication treatment result information within the terminal. That is, the doctor terminals DT1 to DTm can present medication treatment result information to the patient with a light processing load without installing a new application.
- BP blood pressure
- the doctor when a doctor performs outpatient treatment or telemedicine for a patient, the doctor simply displays a list of medication treatment result information displayed on the doctor terminals DT1 to DTm, and displays the past blood pressure value of the patient in the past. It is possible to grasp at a glance in association with the type and amount of the antihypertensive drug prescribed in the above, thereby making it possible to accurately determine the medication.
- doctors can take medication adherence and activity into consideration for medication decisions for patients by looking at information on medication treatment results, thereby further identifying the necessity and details of changes in antihypertensive drugs. Can be performed.
- the medication support server SV displays information indicating the abnormal value, the amount of change from the previous measurement value, and the direction of change, as a line graph representing the change in blood pressure.
- the medication treatment result information superimposed on the corresponding time position is generated, and this medication treatment result information is displayed on the doctor terminals DT1 to DTm. For this reason, the doctor can recognize abnormal fluctuations in blood pressure values at a glance by looking at the medication treatment result information displayed on the doctor terminals DT1 to DTm, thereby making the judgment of medication more efficiently and accurately. It becomes possible.
- the medication support server SV generates medication treatment result information that represents the type of antihypertensive drug as a block having a different color or gray scale, and the amount of the antihypertensive agent represented by the number of stacked blocks. Displayed on the doctor terminals DT1 to DTm. For this reason, doctors can easily and accurately grasp the type and amount of antihypertensive drugs prescribed by the color and number of blocks by looking at the medication treatment results information displayed on the doctor terminals DT1 to DTm. It becomes possible to determine the next medication more efficiently and accurately.
- the medication support server SV when a plurality of types of antihypertensive drugs are prescribed at the same time, the medication support server SV generates medicinal treatment result information in which the display positions of the blocks are sorted according to the selection order of the antihypertensive drugs.
- the result information is displayed on the doctor terminals DT1 to DTm. For this reason, the doctor can confirm the selection order of antihypertensive drugs at a glance, and can determine the next medication more accurately.
- the medication support server SV considers the medication treatment result information corresponding to the patient to be treated in accordance with the request information sent from the doctor terminals DT1 to DTm in response to the doctor's request, and prescribes the type and amount of antihypertensive drugs. Is generated, and this medication treatment result information is displayed on the doctor terminals DT1 to DTm. Therefore, the doctor can determine the content of medication with reference to the medication guide information when he / she is not sure about the type and amount of the medicine to be prescribed.
- the medication support server SV sets the granularity of the time axis in the medication treatment result information to “week” has been described as an example, but the granularity of the time axis is “day” or “month”. May be set. Further, the time axis granularity may be arbitrarily set by the doctor at the doctor terminals DT1 to DTm.
- the medication support server SV displays the blood pressure (Blood Pressure: BP) transition 41, activity change 42, medication adherence (Adherence) 43, and medication management information 44 in the medication treatment result information. It is arbitrarily changed and set according to a request from a doctor or the like sent from DT1 to DTm. Furthermore, when the medication support server SV generates the medication management information 44, the shape of the block for displaying one unit of the antihypertensive drug is not limited to a square but a circle or a capsule that is reminiscent of a general tablet shape. The type of antihypertensive drug may be different from the shape of the block in addition to the color and gray scale.
- the medication support server SV when the medication support server SV generates medication treatment result information, the blood pressure (Blood Pressure: BP) transition 41, the activity amount (Activity) change 42, the medication adherence (Adherence) 43 and the medication management information 44 are associated in time series, but only the medication adherence (Adherence) 43 and the medication management information 44 may be displayed in association with each other in time series. In this way, the medication adherence information is displayed in association with the information indicating the transition of the type and amount of the drug on the time series. For this reason, it is possible to consider the medication adherence in the requirements for determining the medication for the patient, and thus the medication can be determined in consideration of the patient's medication status.
- BP Blood Pressure
- Activity activity amount
- the medication support server SV displays the display screen indicating the medication candidates and the like on the doctor terminals DT1 to DTm
- the doctor terminal instead of the doctor terminal, other prescribers such as pharmacists You may make it display the said display screen on the terminal to be used.
- the configuration and installation location of the medication support apparatus, the procedure and contents of the medication support process, and the like can be variously modified without departing from the scope of the present invention.
- this invention is not limited to the said embodiment, In the implementation stage, it can change variously in the range which does not deviate from the summary.
- the embodiments may be appropriately combined as much as possible, and in that case, the combined effect can be obtained.
- the above embodiments include inventions at various stages, and various inventions can be extracted by appropriately combining a plurality of disclosed constituent elements.
- a medication support apparatus configured to transmit the generated medication treatment result information to the requesting first terminals (DT1 to DTm) via the network (NW).
- the hardware processor (1) From the first terminal (DT1 to DTm), obtain medication information including the type and amount of medicine prescribed for the patient via the network (NW), From the second terminal (UT1 to UTn), obtain blood pressure measurement information of the patient obtained by the blood pressure monitor (BT1 to BTn) via the network (NW), From the second terminal (UT1 to UTn), obtain medication information indicating the medication status of the patient via the network (NW), For each patient, medication adherence information representing the status of internal compliance is generated based on the obtained medication information, and the type and amount of medication included
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Medical Informatics (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Heart & Thoracic Surgery (AREA)
- Molecular Biology (AREA)
- Surgery (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- Pathology (AREA)
- Biophysics (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Primary Health Care (AREA)
- Epidemiology (AREA)
- General Business, Economics & Management (AREA)
- Business, Economics & Management (AREA)
- Physiology (AREA)
- Cardiology (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Bioinformatics & Cheminformatics (AREA)
- Medicinal Chemistry (AREA)
- Vascular Medicine (AREA)
- Medical Treatment And Welfare Office Work (AREA)
- Measuring Pulse, Heart Rate, Blood Pressure Or Blood Flow (AREA)
- Measuring And Recording Apparatus For Diagnosis (AREA)
Priority Applications (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE112018001359.6T DE112018001359T5 (de) | 2017-03-14 | 2018-02-13 | Arzneimittelverschreibungsunterstützungsvorrichtung, verfahren und programmfeld |
| CN201880017739.XA CN110402465B (zh) | 2017-03-14 | 2018-02-13 | 给药辅助装置、方法以及记录介质 |
| US16/554,918 US20190385723A1 (en) | 2017-03-14 | 2019-08-29 | Medication support apparatus, method, and program |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2017049176A JP6868423B2 (ja) | 2017-03-14 | 2017-03-14 | 投薬支援装置、方法及びプログラム |
| JP2017-049176 | 2017-03-14 |
Related Child Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| US16/554,918 Continuation US20190385723A1 (en) | 2017-03-14 | 2019-08-29 | Medication support apparatus, method, and program |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2018168298A1 true WO2018168298A1 (ja) | 2018-09-20 |
Family
ID=63523006
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2018/004911 Ceased WO2018168298A1 (ja) | 2017-03-14 | 2018-02-13 | 投薬支援装置、方法及びプログラム |
Country Status (5)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US20190385723A1 (enExample) |
| JP (1) | JP6868423B2 (enExample) |
| CN (1) | CN110402465B (enExample) |
| DE (1) | DE112018001359T5 (enExample) |
| WO (1) | WO2018168298A1 (enExample) |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN113544791A (zh) * | 2019-03-25 | 2021-10-22 | 欧姆龙健康医疗事业株式会社 | 服药情况管理装置、方法以及程序 |
| CN113557573A (zh) * | 2019-03-25 | 2021-10-26 | 欧姆龙健康医疗事业株式会社 | 服药辅助信息提供装置、方法以及程序 |
Families Citing this family (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20230214465A1 (en) * | 2020-05-28 | 2023-07-06 | Nec Corporation | Medical information control apparatus, system, method, and non-transitory computer readable medium storing program |
| US20220344046A1 (en) * | 2021-04-26 | 2022-10-27 | New Pill Technologies, Inc. | Methods, systems, apparatuses, and devices for facilitating managing administering of psychedelic drugs to users |
| JP7707655B2 (ja) * | 2021-05-25 | 2025-07-15 | オムロンヘルスケア株式会社 | 生体情報処理システム、生体情報処理装置、生体情報処理方法及びプログラム |
| JP7760906B2 (ja) * | 2021-12-15 | 2025-10-28 | オムロンヘルスケア株式会社 | 診療支援システム、診療支援装置及びプログラム |
| US20250069720A1 (en) * | 2022-01-05 | 2025-02-27 | Sony Group Corporation | Information processing device, information processing method, and program therefor |
| JP2023134034A (ja) * | 2022-03-14 | 2023-09-27 | コニカミノルタ株式会社 | 制御プログラム、情報処理装置、医療従事者用端末、情報処理システム、及び医療従事者用システム |
| JP2025135179A (ja) * | 2024-03-05 | 2025-09-18 | オムロンヘルスケア株式会社 | 端末装置 |
Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013109661A (ja) * | 2011-11-22 | 2013-06-06 | Sharp Corp | 認知症ケア支援方法、認知症情報出力装置、認知症ケア支援システム、及びコンピュータプログラム |
| JP2015162172A (ja) * | 2014-02-28 | 2015-09-07 | シャープ株式会社 | 服薬支援装置 |
| US20150289821A1 (en) * | 2014-04-10 | 2015-10-15 | Dexcom, Inc. | Glycemic urgency assessment and alerts interface |
| JP2016085481A (ja) * | 2014-09-01 | 2016-05-19 | 和貴 吉永 | 電子お薬ケースおよび連動システム |
| JP2016099656A (ja) * | 2014-11-18 | 2016-05-30 | 富士フイルム株式会社 | 情報収集装置、情報収集装置の作動方法および作動プログラム、並びに情報収集システム |
| JP2016218536A (ja) * | 2015-05-15 | 2016-12-22 | コニカミノルタ株式会社 | 診療支援システム、サーバー装置及びプログラム |
Family Cites Families (10)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20020087054A1 (en) * | 2001-01-03 | 2002-07-04 | Wen-Guai Lin | System and a method for monitoring the effectiveness of a medical treatment |
| SG195535A1 (en) * | 2008-07-08 | 2013-12-30 | Proteus Digital Health Inc | Ingestible event marker data framework |
| HK1224390A1 (zh) * | 2013-10-25 | 2017-08-18 | 阿瑞斯贸易股份公司 | 报告对处置方案的依从性的患者护理系统 |
| CN104970965A (zh) * | 2014-04-10 | 2015-10-14 | 贝思亲健康科技股份有限公司 | 智能型药盒装置 |
| US20160154945A1 (en) * | 2014-12-01 | 2016-06-02 | Lg Cns Co., Ltd. | Method and system for changing medicine-taking schedule |
| JP6116769B2 (ja) * | 2015-05-01 | 2017-04-19 | 株式会社キュア・アップ | 禁煙患者のためのプログラム、装置、システム及び方法 |
| CN105069730A (zh) * | 2015-08-26 | 2015-11-18 | 深圳感讯科技有限公司 | 基于云计算的健康管理系统与方法 |
| JP5940723B1 (ja) * | 2015-10-29 | 2016-06-29 | 株式会社ノアコンツェル | 投薬支援システム |
| JP5998269B1 (ja) * | 2015-12-15 | 2016-09-28 | クラリオン株式会社 | 服薬支援システム |
| JP6038376B1 (ja) * | 2016-07-04 | 2016-12-07 | 裕一 木村 | 診療データ統合装置、診療データ統合装置による診療データ統合方法及び診療データ統合装置で実行されるためのコンピュータプログラムを記録したコンピュータ読み取り可能な記録媒体 |
-
2017
- 2017-03-14 JP JP2017049176A patent/JP6868423B2/ja active Active
-
2018
- 2018-02-13 DE DE112018001359.6T patent/DE112018001359T5/de active Pending
- 2018-02-13 WO PCT/JP2018/004911 patent/WO2018168298A1/ja not_active Ceased
- 2018-02-13 CN CN201880017739.XA patent/CN110402465B/zh active Active
-
2019
- 2019-08-29 US US16/554,918 patent/US20190385723A1/en not_active Abandoned
Patent Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013109661A (ja) * | 2011-11-22 | 2013-06-06 | Sharp Corp | 認知症ケア支援方法、認知症情報出力装置、認知症ケア支援システム、及びコンピュータプログラム |
| JP2015162172A (ja) * | 2014-02-28 | 2015-09-07 | シャープ株式会社 | 服薬支援装置 |
| US20150289821A1 (en) * | 2014-04-10 | 2015-10-15 | Dexcom, Inc. | Glycemic urgency assessment and alerts interface |
| JP2016085481A (ja) * | 2014-09-01 | 2016-05-19 | 和貴 吉永 | 電子お薬ケースおよび連動システム |
| JP2016099656A (ja) * | 2014-11-18 | 2016-05-30 | 富士フイルム株式会社 | 情報収集装置、情報収集装置の作動方法および作動プログラム、並びに情報収集システム |
| JP2016218536A (ja) * | 2015-05-15 | 2016-12-22 | コニカミノルタ株式会社 | 診療支援システム、サーバー装置及びプログラム |
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN113544791A (zh) * | 2019-03-25 | 2021-10-22 | 欧姆龙健康医疗事业株式会社 | 服药情况管理装置、方法以及程序 |
| CN113557573A (zh) * | 2019-03-25 | 2021-10-26 | 欧姆龙健康医疗事业株式会社 | 服药辅助信息提供装置、方法以及程序 |
| US12136476B2 (en) | 2019-03-25 | 2024-11-05 | Omron Healthcare Co., Ltd. | Medication assistance information providing device, method, and non-transitory recording medium recording program |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP6868423B2 (ja) | 2021-05-12 |
| JP2018151993A (ja) | 2018-09-27 |
| CN110402465A (zh) | 2019-11-01 |
| DE112018001359T5 (de) | 2019-11-21 |
| CN110402465B (zh) | 2023-05-02 |
| US20190385723A1 (en) | 2019-12-19 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| WO2018168298A1 (ja) | 投薬支援装置、方法及びプログラム | |
| JP7124453B2 (ja) | 投薬管理装置、投薬管理方法及び投薬管理プログラム | |
| Suh et al. | A remote patient monitoring system for congestive heart failure | |
| CN106102571B (zh) | 患者监控器和介入/事件时间线 | |
| US7860731B2 (en) | Monitoring and feedback wireless medical system and method | |
| US20140235293A1 (en) | Personal Health Monitoring System | |
| JP2025169408A (ja) | ウェアラブル装置を利用した甲状腺機能亢進症の予測システム及び予測コンピュータプログラム | |
| US20180286502A1 (en) | Patient data management | |
| US20210118539A1 (en) | Medication management device, medication management method, and non-transitory computer-readable storage medium storing medication management program | |
| CA3104720A1 (en) | Mobile electrocardiogram system | |
| JP7119707B2 (ja) | 診断支援装置、診断支援方法及び診断支援プログラム | |
| JPWO2021044520A1 (ja) | ソフトウェア、健康状態判定装置及び健康状態判定方法 | |
| JP2018156149A (ja) | 投薬支援装置、方法およびプログラム | |
| JP2019032775A (ja) | データ処理装置、データ処理方法及びデータ処理プログラム | |
| US20240194314A1 (en) | Medical care assistance system, medical care assistance device, and program | |
| WO2018235652A1 (ja) | 健康管理装置、健康管理方法、および健康管理プログラム | |
| CN113544791B (zh) | 服药情况管理装置、方法以及记录有程序的计算机可读记录介质 | |
| WO2007082930A1 (en) | A system and method for hypertension management | |
| US11783930B2 (en) | Information processing device, method, and non-transitory computer-readable storage medium storing program | |
| JP7707655B2 (ja) | 生体情報処理システム、生体情報処理装置、生体情報処理方法及びプログラム | |
| US20240185982A1 (en) | Medical care assistance system, medical care assistance device, and recording medium | |
| US20250218586A1 (en) | Systems and methods to monitor patient devices | |
| JP2025069586A (ja) | 情報処理装置及びプログラム | |
| JP2023010391A (ja) | 診療支援システム、診療支援装置、診療支援方法及びプログラム | |
| Blackman et al. | Wearable Devices and Mobile Technology in Clinical Trials |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 18767555 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 18767555 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |