WO2014030309A1 - 配線基板 - Google Patents
配線基板 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2014030309A1 WO2014030309A1 PCT/JP2013/004722 JP2013004722W WO2014030309A1 WO 2014030309 A1 WO2014030309 A1 WO 2014030309A1 JP 2013004722 W JP2013004722 W JP 2013004722W WO 2014030309 A1 WO2014030309 A1 WO 2014030309A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- base layer
- wiring board
- layer
- insulating layer
- wall surface
- Prior art date
Links
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 title abstract description 11
- 230000003746 surface roughness Effects 0.000 claims description 5
- 239000010410 layer Substances 0.000 description 79
- 239000004020 conductor Substances 0.000 description 18
- 229920005989 resin Polymers 0.000 description 11
- 239000011347 resin Substances 0.000 description 11
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 description 11
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 6
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 5
- 239000011810 insulating material Substances 0.000 description 4
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 description 4
- 230000004048 modification Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000012986 modification Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000007747 plating Methods 0.000 description 3
- 229910000679 solder Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 239000003822 epoxy resin Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000002093 peripheral effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000000016 photochemical curing Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229920000647 polyepoxide Polymers 0.000 description 2
- RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Copper Chemical compound [Cu] RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000007864 aqueous solution Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052802 copper Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000010949 copper Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000005530 etching Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000835 fiber Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000003365 glass fiber Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000009413 insulation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000007788 liquid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000011368 organic material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000002265 prevention Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000002356 single layer Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000001029 thermal curing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229920001187 thermosetting polymer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000011800 void material Substances 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L23/00—Details of semiconductor or other solid state devices
- H01L23/12—Mountings, e.g. non-detachable insulating substrates
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H05—ELECTRIC TECHNIQUES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H05K—PRINTED CIRCUITS; CASINGS OR CONSTRUCTIONAL DETAILS OF ELECTRIC APPARATUS; MANUFACTURE OF ASSEMBLAGES OF ELECTRICAL COMPONENTS
- H05K3/00—Apparatus or processes for manufacturing printed circuits
- H05K3/30—Assembling printed circuits with electric components, e.g. with resistor
- H05K3/32—Assembling printed circuits with electric components, e.g. with resistor electrically connecting electric components or wires to printed circuits
- H05K3/34—Assembling printed circuits with electric components, e.g. with resistor electrically connecting electric components or wires to printed circuits by soldering
- H05K3/3452—Solder masks
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/04—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof the devices having potential barriers, e.g. a PN junction, depletion layer or carrier concentration layer
- H01L21/50—Assembly of semiconductor devices using processes or apparatus not provided for in a single one of the subgroups H01L21/06 - H01L21/326, e.g. sealing of a cap to a base of a container
- H01L21/56—Encapsulations, e.g. encapsulation layers, coatings
- H01L21/563—Encapsulation of active face of flip-chip device, e.g. underfilling or underencapsulation of flip-chip, encapsulation preform on chip or mounting substrate
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L23/00—Details of semiconductor or other solid state devices
- H01L23/12—Mountings, e.g. non-detachable insulating substrates
- H01L23/13—Mountings, e.g. non-detachable insulating substrates characterised by the shape
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L24/00—Arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies; Methods or apparatus related thereto
- H01L24/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L24/26—Layer connectors, e.g. plate connectors, solder or adhesive layers; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L24/31—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the layer connectors after the connecting process
- H01L24/32—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the layer connectors after the connecting process of an individual layer connector
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L24/00—Arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies; Methods or apparatus related thereto
- H01L24/73—Means for bonding being of different types provided for in two or more of groups H01L24/10, H01L24/18, H01L24/26, H01L24/34, H01L24/42, H01L24/50, H01L24/63, H01L24/71
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L24/00—Arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies; Methods or apparatus related thereto
- H01L24/80—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected
- H01L24/83—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected using a layer connector
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H05—ELECTRIC TECHNIQUES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H05K—PRINTED CIRCUITS; CASINGS OR CONSTRUCTIONAL DETAILS OF ELECTRIC APPARATUS; MANUFACTURE OF ASSEMBLAGES OF ELECTRICAL COMPONENTS
- H05K1/00—Printed circuits
- H05K1/02—Details
- H05K1/11—Printed elements for providing electric connections to or between printed circuits
- H05K1/111—Pads for surface mounting, e.g. lay-out
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H05—ELECTRIC TECHNIQUES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H05K—PRINTED CIRCUITS; CASINGS OR CONSTRUCTIONAL DETAILS OF ELECTRIC APPARATUS; MANUFACTURE OF ASSEMBLAGES OF ELECTRICAL COMPONENTS
- H05K3/00—Apparatus or processes for manufacturing printed circuits
- H05K3/22—Secondary treatment of printed circuits
- H05K3/28—Applying non-metallic protective coatings
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/10—Bump connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/11—Manufacturing methods
- H01L2224/116—Manufacturing methods by patterning a pre-deposited material
- H01L2224/1161—Physical or chemical etching
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/10—Bump connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/12—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors prior to the connecting process
- H01L2224/13—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors prior to the connecting process of an individual bump connector
- H01L2224/13001—Core members of the bump connector
- H01L2224/13099—Material
- H01L2224/131—Material with a principal constituent of the material being a metal or a metalloid, e.g. boron [B], silicon [Si], germanium [Ge], arsenic [As], antimony [Sb], tellurium [Te] and polonium [Po], and alloys thereof
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/10—Bump connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/12—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors prior to the connecting process
- H01L2224/13—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors prior to the connecting process of an individual bump connector
- H01L2224/13001—Core members of the bump connector
- H01L2224/13099—Material
- H01L2224/131—Material with a principal constituent of the material being a metal or a metalloid, e.g. boron [B], silicon [Si], germanium [Ge], arsenic [As], antimony [Sb], tellurium [Te] and polonium [Po], and alloys thereof
- H01L2224/13101—Material with a principal constituent of the material being a metal or a metalloid, e.g. boron [B], silicon [Si], germanium [Ge], arsenic [As], antimony [Sb], tellurium [Te] and polonium [Po], and alloys thereof the principal constituent melting at a temperature of less than 400°C
- H01L2224/13113—Bismuth [Bi] as principal constituent
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/10—Bump connectors; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/15—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors after the connecting process
- H01L2224/16—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors after the connecting process of an individual bump connector
- H01L2224/161—Disposition
- H01L2224/16151—Disposition the bump connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive
- H01L2224/16221—Disposition the bump connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked
- H01L2224/16225—Disposition the bump connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked the item being non-metallic, e.g. insulating substrate with or without metallisation
- H01L2224/16238—Disposition the bump connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked the item being non-metallic, e.g. insulating substrate with or without metallisation the bump connector connecting to a bonding area protruding from the surface of the item
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/26—Layer connectors, e.g. plate connectors, solder or adhesive layers; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/28—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the layer connectors prior to the connecting process
- H01L2224/29—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the layer connectors prior to the connecting process of an individual layer connector
- H01L2224/29001—Core members of the layer connector
- H01L2224/29099—Material
- H01L2224/2919—Material with a principal constituent of the material being a polymer, e.g. polyester, phenolic based polymer, epoxy
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/26—Layer connectors, e.g. plate connectors, solder or adhesive layers; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L2224/31—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the layer connectors after the connecting process
- H01L2224/32—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the layer connectors after the connecting process of an individual layer connector
- H01L2224/321—Disposition
- H01L2224/32151—Disposition the layer connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive
- H01L2224/32221—Disposition the layer connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked
- H01L2224/32225—Disposition the layer connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked the item being non-metallic, e.g. insulating substrate with or without metallisation
- H01L2224/32237—Disposition the layer connector connecting between a semiconductor or solid-state body and an item not being a semiconductor or solid-state body, e.g. chip-to-substrate, chip-to-passive the body and the item being stacked the item being non-metallic, e.g. insulating substrate with or without metallisation the layer connector connecting to a bonding area disposed in a recess of the surface of the item
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/73—Means for bonding being of different types provided for in two or more of groups H01L2224/10, H01L2224/18, H01L2224/26, H01L2224/34, H01L2224/42, H01L2224/50, H01L2224/63, H01L2224/71
- H01L2224/732—Location after the connecting process
- H01L2224/73201—Location after the connecting process on the same surface
- H01L2224/73203—Bump and layer connectors
- H01L2224/73204—Bump and layer connectors the bump connector being embedded into the layer connector
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/80—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected
- H01L2224/81—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected using a bump connector
- H01L2224/8119—Arrangement of the bump connectors prior to mounting
- H01L2224/81193—Arrangement of the bump connectors prior to mounting wherein the bump connectors are disposed on both the semiconductor or solid-state body and another item or body to be connected to the semiconductor or solid-state body
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/80—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected
- H01L2224/81—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected using a bump connector
- H01L2224/8138—Bonding interfaces outside the semiconductor or solid-state body
- H01L2224/81385—Shape, e.g. interlocking features
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/80—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected
- H01L2224/81—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected using a bump connector
- H01L2224/8138—Bonding interfaces outside the semiconductor or solid-state body
- H01L2224/81399—Material
- H01L2224/814—Material with a principal constituent of the material being a metal or a metalloid, e.g. boron [B], silicon [Si], germanium [Ge], arsenic [As], antimony [Sb], tellurium [Te] and polonium [Po], and alloys thereof
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/80—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected
- H01L2224/81—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected using a bump connector
- H01L2224/8138—Bonding interfaces outside the semiconductor or solid-state body
- H01L2224/81399—Material
- H01L2224/814—Material with a principal constituent of the material being a metal or a metalloid, e.g. boron [B], silicon [Si], germanium [Ge], arsenic [As], antimony [Sb], tellurium [Te] and polonium [Po], and alloys thereof
- H01L2224/81438—Material with a principal constituent of the material being a metal or a metalloid, e.g. boron [B], silicon [Si], germanium [Ge], arsenic [As], antimony [Sb], tellurium [Te] and polonium [Po], and alloys thereof the principal constituent melting at a temperature of greater than or equal to 950°C and less than 1550°C
- H01L2224/81447—Copper [Cu] as principal constituent
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/80—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected
- H01L2224/81—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected using a bump connector
- H01L2224/818—Bonding techniques
- H01L2224/81801—Soldering or alloying
- H01L2224/81815—Reflow soldering
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/80—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected
- H01L2224/83—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected using a layer connector
- H01L2224/831—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected using a layer connector the layer connector being supplied to the parts to be connected in the bonding apparatus
- H01L2224/83102—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected using a layer connector the layer connector being supplied to the parts to be connected in the bonding apparatus using surface energy, e.g. capillary forces
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/80—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected
- H01L2224/83—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected using a layer connector
- H01L2224/8338—Bonding interfaces outside the semiconductor or solid-state body
- H01L2224/83385—Shape, e.g. interlocking features
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2224/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies and methods related thereto as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2224/80—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected
- H01L2224/83—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected using a layer connector
- H01L2224/838—Bonding techniques
- H01L2224/8385—Bonding techniques using a polymer adhesive, e.g. an adhesive based on silicone, epoxy, polyimide, polyester
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L24/00—Arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies; Methods or apparatus related thereto
- H01L24/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L24/10—Bump connectors ; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L24/11—Manufacturing methods
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L24/00—Arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies; Methods or apparatus related thereto
- H01L24/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L24/10—Bump connectors ; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L24/12—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors prior to the connecting process
- H01L24/13—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors prior to the connecting process of an individual bump connector
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L24/00—Arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies; Methods or apparatus related thereto
- H01L24/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L24/10—Bump connectors ; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L24/15—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors after the connecting process
- H01L24/16—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the bump connectors after the connecting process of an individual bump connector
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L24/00—Arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies; Methods or apparatus related thereto
- H01L24/01—Means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected, e.g. chip-to-package, die-attach, "first-level" interconnects; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L24/26—Layer connectors, e.g. plate connectors, solder or adhesive layers; Manufacturing methods related thereto
- H01L24/28—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the layer connectors prior to the connecting process
- H01L24/29—Structure, shape, material or disposition of the layer connectors prior to the connecting process of an individual layer connector
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L24/00—Arrangements for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies; Methods or apparatus related thereto
- H01L24/80—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected
- H01L24/81—Methods for connecting semiconductor or other solid state bodies using means for bonding being attached to, or being formed on, the surface to be connected using a bump connector
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/15—Details of package parts other than the semiconductor or other solid state devices to be connected
- H01L2924/151—Die mounting substrate
- H01L2924/1515—Shape
- H01L2924/15153—Shape the die mounting substrate comprising a recess for hosting the device
- H01L2924/15155—Shape the die mounting substrate comprising a recess for hosting the device the shape of the recess being other than a cuboid
- H01L2924/15156—Side view
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/30—Technical effects
- H01L2924/35—Mechanical effects
- H01L2924/351—Thermal stress
- H01L2924/3512—Cracking
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L2924/00—Indexing scheme for arrangements or methods for connecting or disconnecting semiconductor or solid-state bodies as covered by H01L24/00
- H01L2924/30—Technical effects
- H01L2924/38—Effects and problems related to the device integration
- H01L2924/384—Bump effects
- H01L2924/3841—Solder bridging
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H05—ELECTRIC TECHNIQUES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H05K—PRINTED CIRCUITS; CASINGS OR CONSTRUCTIONAL DETAILS OF ELECTRIC APPARATUS; MANUFACTURE OF ASSEMBLAGES OF ELECTRICAL COMPONENTS
- H05K2201/00—Indexing scheme relating to printed circuits covered by H05K1/00
- H05K2201/10—Details of components or other objects attached to or integrated in a printed circuit board
- H05K2201/10613—Details of electrical connections of non-printed components, e.g. special leads
- H05K2201/10954—Other details of electrical connections
- H05K2201/10977—Encapsulated connections
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H05—ELECTRIC TECHNIQUES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H05K—PRINTED CIRCUITS; CASINGS OR CONSTRUCTIONAL DETAILS OF ELECTRIC APPARATUS; MANUFACTURE OF ASSEMBLAGES OF ELECTRICAL COMPONENTS
- H05K2203/00—Indexing scheme relating to apparatus or processes for manufacturing printed circuits covered by H05K3/00
- H05K2203/05—Patterning and lithography; Masks; Details of resist
- H05K2203/0562—Details of resist
- H05K2203/0594—Insulating resist or coating with special shaped edges
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H05—ELECTRIC TECHNIQUES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H05K—PRINTED CIRCUITS; CASINGS OR CONSTRUCTIONAL DETAILS OF ELECTRIC APPARATUS; MANUFACTURE OF ASSEMBLAGES OF ELECTRICAL COMPONENTS
- H05K2203/00—Indexing scheme relating to apparatus or processes for manufacturing printed circuits covered by H05K3/00
- H05K2203/05—Patterning and lithography; Masks; Details of resist
- H05K2203/0562—Details of resist
- H05K2203/0597—Resist applied over the edges or sides of conductors, e.g. for protection during etching or plating
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H05—ELECTRIC TECHNIQUES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H05K—PRINTED CIRCUITS; CASINGS OR CONSTRUCTIONAL DETAILS OF ELECTRIC APPARATUS; MANUFACTURE OF ASSEMBLAGES OF ELECTRICAL COMPONENTS
- H05K3/00—Apparatus or processes for manufacturing printed circuits
- H05K3/30—Assembling printed circuits with electric components, e.g. with resistor
- H05K3/32—Assembling printed circuits with electric components, e.g. with resistor electrically connecting electric components or wires to printed circuits
- H05K3/34—Assembling printed circuits with electric components, e.g. with resistor electrically connecting electric components or wires to printed circuits by soldering
- H05K3/341—Surface mounted components
- H05K3/3431—Leadless components
- H05K3/3436—Leadless components having an array of bottom contacts, e.g. pad grid array or ball grid array components
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a wiring board.
- a wiring board that is configured so that a semiconductor chip can be mounted is known (see, for example, Patent Documents 1 and 2).
- connection terminals configured to be connectable to the semiconductor chip are formed.
- Patent Document 1 in order to prevent an electrical short circuit between connection terminals due to a plating material, an insulating layer having an opening exposing a plurality of connection terminals is formed, and insulation is performed between the plurality of connection terminals in the openings. It is described that a plurality of connection terminals are plated after an object is formed.
- Patent Document 2 describes that in order to prevent an electrical short circuit between connection terminals due to solder, the insulating layer formed between the connection terminals is thinned to be equal to or less than the thickness of the connection terminals.
- connection terminal of the wiring board is soldered to the semiconductor chip, and a liquid curable property called underfill is formed in the gap between the wiring board and the semiconductor chip around the connection terminal.
- the resin is filled (see, for example, Patent Document 3).
- the present invention has been made to solve the above-described problems, and can be realized as the following modes.
- a wiring board includes an insulating base layer; an insulating layer stacked on the base layer, a first surface on which an opening is formed, and the base layer side with respect to the first surface inside the opening.
- An insulating layer having an indented second surface and a wall surface connecting the first surface and the second surface along a stacking direction of the insulating layer with respect to the base layer inside the opening; 2 is a wiring board including a conductive connection terminal exposed from the surface, wherein the second surface has a deepest portion located closest to the base layer on the second surface, and is convex to the base layer side.
- the curved shape of the second surface improves the flowability of the underfill, and the space on the second surface on the wall surface side from the deepest portion becomes narrower toward the wall surface. The formation of voids in the region from the second surface to the wall surface can be suppressed.
- the deepest portion may include a connection portion connected to the connection terminal in the second surface. According to the wiring board of this embodiment, the flowability of the underfill can be further improved as compared with the case where the deepest part is away from the connection terminal.
- the insulating layer may further include a curved surface that curves and connects the first surface and the wall surface outwardly. According to the wiring board of this embodiment, it is possible to improve the pouring property of the underfill onto the second surface as compared with the case where the space between the first surface and the wall surface is angular.
- the surface roughness of the second surface may be rougher than that of the first surface.
- the underfill can be spread to each part on the second surface using the capillary phenomenon without hindering the flowability of the underfill.
- the present invention can be realized in various forms other than the wiring board.
- it is realizable with forms, such as an apparatus provided with a wiring board, and a manufacturing method of a wiring board.
- FIG. 1 is a partial cross-sectional view schematically showing the configuration of the wiring board 10 in the first embodiment.
- the wiring substrate 10 is a plate-like member that is formed using an organic material and is also called an organic substrate (organic substrate).
- the wiring substrate 10 is a flip chip mounting substrate configured to be capable of mounting a semiconductor chip (not shown).
- the wiring board 10 includes a base layer 120, a conductor layer 130, and an insulating layer 140.
- the wiring substrate 10 is formed by forming a conductor layer 130 on a base layer 120 and further forming an insulating layer 140 thereon.
- the wiring board 10 may have a multilayer structure in which a plurality of conductor layers and a plurality of insulating layers are alternately stacked on the base layer 120, and such a multilayer structure is provided on both surfaces of the base layer 120. You may have each.
- FIG. 1 shows XYZ axes orthogonal to each other.
- the axis along the stacking direction of the insulating layer 140 with respect to the base layer 120 is taken as the Z axis.
- the + Z-axis direction from the base layer 120 toward the insulating layer 140 is defined as the ⁇ Z-axis direction.
- two axes along the layer surface direction orthogonal to the Z axis are defined as an X axis and a Y axis.
- the + X-axis direction is from the left side to the right side, and the opposite direction to the + X-axis direction is the ⁇ X-axis direction.
- the + Y-axis direction is from the front of the paper to the back of the paper, and the opposite direction of the + Y-axis is the ⁇ Y-axis direction.
- the base layer 120 of the wiring board 10 is a plate-like member made of an insulating material.
- the insulating material of the base layer 120 is a thermosetting resin, such as a bismaleimide-triazine resin (BT) or an epoxy resin.
- the insulating material of the base layer 120 may be a fiber reinforced resin (eg, a glass fiber reinforced epoxy resin).
- a through hole, a through hole conductor, or the like may be formed inside the base layer 120 to constitute part of the wiring connected to the conductor layer 130.
- the conductor layer 130 of the wiring board 10 is a conductor pattern made of a conductive material formed on the base layer 120.
- the conductor layer 130 is formed by etching a copper plating layer formed on the surface of the base layer 120 into a desired shape.
- the conductor layer 130 includes connection terminals 132 and internal wiring 136.
- the connection terminal 132 of the conductor layer 130 is a conductor pattern exposed from the insulating layer 140, and is configured to be connectable to a semiconductor chip (not shown).
- the internal wiring 136 of the conductor layer 130 is a conductor pattern covered with the insulating layer 140.
- the insulating layer 140 of the wiring board 10 is a layer made of an insulating material also called a solder resist.
- the insulating layer 140 has a first surface 141, a second surface 142, and a wall surface 148.
- the first surface 141 of the insulating layer 140 is the surface of the insulating layer 140 in which the opening 150 is formed.
- the first surface 141 is a surface facing the + Z-axis direction side along the X-axis and the Y-axis, and constitutes the surface of the insulating layer 140 on the + Z-axis direction side.
- the second surface 142 of the insulating layer 140 is the surface of the insulating layer 140 that is recessed toward the base layer 120 with respect to the first surface 141 inside the opening 150.
- the connection terminal 132 of the conductor layer 130 is exposed from the second surface 142, and in the present embodiment, the connection terminal 132 protrudes from the second surface 142 in the + Z-axis direction side.
- the second surface 142 is a surface that curves convexly toward the base layer 120 side (the ⁇ Z-axis direction side) and connects the wall surface 148 and the connection terminal 132, and the insulating layer 140 is formed inside the opening 150.
- the surface on the + Z-axis direction side is configured.
- the second surface 142 has a deepest portion DP located closest to the base layer 120 ( ⁇ Z axis direction side) on the second surface 142.
- the relation of L1> L2 is satisfied.
- a corner 145 where the second surface 142 and the wall surface 148 are connected is a base point having a length L1.
- the connection portion 143 connected to the connection terminal 132 in the second surface 142 is a base point having a length L2.
- the surface roughness of the second surface 142 is rougher than that of the first surface 141.
- the center line average roughness Ra of the second surface 142 is 0.06 to 0.8 ⁇ m (micrometer), and the ten-point average roughness Rz of the second surface 142 is 1.0 to 9. 0.0 ⁇ m.
- the center line average roughness Ra of the first surface 141 is 0.02 to 0.25 ⁇ m, and the ten-point average roughness Rz of the first surface 141 is 0.6 to 5.0 ⁇ m.
- the wall surface 148 of the insulating layer 140 is a surface connecting the first surface 141 and the second surface 142 along the stacking direction (Z-axis direction) inside the opening 150.
- the wall surface 148 is connected to the first surface 141 in an angular shape as shown in FIG.
- the insulating layer 140 is formed by applying a photocurable insulating resin on the base layer 120 on which the conductor layer 130 is formed, and then exposing and developing.
- the opening 150 in the insulating layer 140 corresponds to a masked portion at the time of exposure, and the uncured portion is washed away at the time of development, whereby the second surface 142 and the wall surface 148 in the insulating layer 140 are formed.
- the first surface 141, the second surface 142, and the wall surface 148 of the insulating layer 140 are integrally formed as a portion constituting a single layer.
- the shape of the second surface 142 and the wall surface 148 adjusts the material of the photocurable insulating resin, the shape of the mask at the time of exposure, the intensity of irradiation light at the time of exposure, the irradiation time, the irradiation angle, and the like. It is realized by doing.
- connection terminal 132 is illustrated between the wall surface 148 on the + X axis direction side and the wall surface 148 on the ⁇ X axis direction side, but in another embodiment, the wall surface 148 on the + X axis direction side and the ⁇ Two or more connection terminals 132 may be provided between the wall surface 148 on the X-axis direction side.
- connection terminal 132 and the insulating layer 140 may be configured in the Y-axis direction as in the X-axis direction.
- the flow of the underfill is improved by the curved shape of the second surface 142 that satisfies L1> L2, and the second surface 142 on the wall surface 148 side of the deepest portion DP is improved. Since the space becomes narrower toward the wall surface 148, formation of voids at the corners 145 from the second surface 142 to the wall surface 148 can be suppressed. Further, since the surface roughness of the second surface 142 is rougher than that of the first surface 141, the underfill is spread to each part on the second surface 142 by utilizing capillary action without hindering the flowability of the underfill. Can be made.
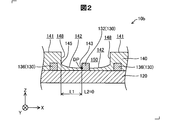
- FIG. 2 is a partial cross-sectional view schematically showing the configuration of the wiring board 10b in the second embodiment.
- the same components as those in the first embodiment are denoted by the same reference numerals and the description thereof is omitted.
- the wiring board 10b of the second embodiment is the same as that of the first embodiment except that the shape of the second surface 142 is different.
- the deepest portion DP of the second surface 142 is located between the connection portion 143 and the corner portion 145, but in the second embodiment, the deepest portion DP of the second surface 142 is the second surface.
- 142 is located in the connection part 143 connected to the connection terminal 132. That is, the deepest part DP includes the connection part 143.
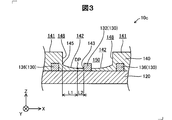
- FIG. 3 is a partial cross-sectional view schematically showing the configuration of the wiring board 10c in the third embodiment.
- the same components as those in the first embodiment are denoted by the same reference numerals and the description thereof is omitted.
- the wiring board 10c of the third embodiment is the same as that of the first embodiment except that the shape of the second surface 142 is different.
- the deepest portion DP of the second surface 142 is the first point located closest to the base layer 120 ( ⁇ Z axis direction side) on the second surface 142 in the middle from the wall surface 148 to the connection portion 143. .
- the second surface 142 protrudes in the + Z-axis direction from the deepest portion DP toward the connection portion 143.
- the second surface 142 is connected from the deepest portion DP. It has a shape parallel to the X axis toward the portion 143.
- the relationship between the length L1 and the length L2 satisfies L1> L2, as in the first embodiment.
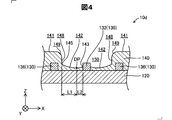
- FIG. 4 is a partial cross-sectional view schematically showing the configuration of the wiring board 10d in the fourth embodiment.
- the same components as those in the first embodiment are denoted by the same reference numerals and the description thereof is omitted.
- the wiring board 10d of the fourth embodiment is the same as that of the first embodiment except that the wiring board 10d has a curved surface 149 that curves and connects the first surface 141 and the wall surface 148 outwardly.
- the shape of the curved surface 149 is the same as that of the second surface 142 and the wall surface 148, the material of the photocurable insulating resin, the shape of the mask at the time of exposure, the intensity of irradiation light at the time of exposure, and the irradiation This is realized by adjusting time and irradiation angle.
- the fourth embodiment described above it is possible to suppress the formation of voids in the corners 145 extending from the second surface 142 to the wall surface 148, as in the first embodiment.
- the curved surface 149 is formed between the first surface 141 and the wall surface 148, compared with the case where the space between the first surface 141 and the wall surface 148 is angular as in the first embodiment, The pouring property of the underfill onto the second surface 142 can be improved.
- the curved surface 149 of the fourth embodiment may be applied to the wiring board 10b of the second embodiment and the wiring board 10c of the third embodiment.
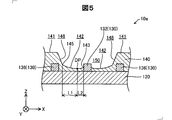
- FIG. 5 is a partial cross-sectional view schematically showing the configuration of the wiring board 10e in the fifth embodiment.
- the same components as those in the first embodiment are denoted by the same reference numerals and the description thereof is omitted.
- the wiring board 10e of the fifth embodiment is the same as that of the first embodiment except that the + Z-axis direction side of the wall surface 148 is inclined toward the outer peripheral side of the opening 150.
- the shape of the wall surface 148 in the fifth embodiment adjusts the material of the photocurable insulating resin, the shape of the mask at the time of exposure, the intensity of irradiation light at the time of exposure, the irradiation time, the irradiation angle, and the like. It is realized by doing.
- the space between the first surface 141 and the wall surface 148 is angular, but in other embodiments, the curved surface 149 is interposed between the first surface 141 and the wall surface 148 as in the fourth embodiment. May be formed.
- the shape of the second surface 142 is the same as that of the first embodiment, but in other embodiments, it may be the same as that of the second embodiment or the same as that of the third embodiment. May be.
- the fifth embodiment described above it is possible to suppress the formation of voids in the corners 145 extending from the second surface 142 to the wall surface 148, as in the first embodiment. Further, since the + Z-axis direction side of the wall surface 148 is inclined toward the outer peripheral side of the opening 150, the underfill flowability can be further improved.
- the second surface 142 and the wall surface 148 of the insulating layer 140 may be formed through the following steps.
- Step 1. A photocurable insulating resin, which is a material of the insulating layer 140, is applied or laminated on the base layer 120 on which the conductor layer 130 is formed. 2. After performing step 1, pattern exposure step for photocurable insulating resin on base layer 120; 3. After performing step 2, the uncured portion of the photocurable insulating resin on the base layer 120 is removed by a development process using an alkaline aqueous solution so that the connection terminal 132 is exposed from the insulating layer 140.
- the insulating layer 140 is cured by heating (thermal curing) and the insulating layer 140 is cured by ultraviolet rays (photocuring).
- the integrated light quantity in the photocuring of step 4 is 500 mJ / cm 2 (mm cm) is preferably at least 2,500 mJ / cm 2 or less per Joule, more preferably 1000 mJ / cm 2 or more 2000 mJ / cm 2 or less.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Microelectronics & Electronic Packaging (AREA)
- Computer Hardware Design (AREA)
- Power Engineering (AREA)
- Manufacturing & Machinery (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Condensed Matter Physics & Semiconductors (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Wire Bonding (AREA)
- Non-Metallic Protective Coatings For Printed Circuits (AREA)
- Internal Circuitry In Semiconductor Integrated Circuit Devices (AREA)
Abstract
Description
図1は、第1実施形態における配線基板10の構成を模式的に示す部分断面図である。配線基板10は、有機材料を用いて形成され、有機基板(オーガニック基板)とも呼ばれる板状の部材である。配線基板10は、半導体チップ(図示しない)を実装可能に構成されたフリップチップ実装基板である。
図2は、第2実施形態における配線基板10bの構成を模式的に示す部分断面図である。第2実施形態の説明において、第1実施形態と同様の構成については同一符号を付すと共に説明を省略する。
図3は、第3実施形態における配線基板10cの構成を模式的に示す部分断面図である。第3実施形態の説明において、第1実施形態と同様の構成については同一符号を付すと共に説明を省略する。
図4は、第4実施形態における配線基板10dの構成を模式的に示す部分断面図である。第4実施形態の説明において、第1実施形態と同様の構成については同一符号を付すと共に説明を省略する。
図5は、第5実施形態における配線基板10eの構成を模式的に示す部分断面図である。第5実施形態の説明において、第1実施形態と同様の構成については同一符号を付すと共に説明を省略する。
本発明は、上述の実施形態や実施例、変形例に限られるものではなく、その趣旨を逸脱しない範囲において種々の構成で実現することができる。例えば、発明の概要の欄に記載した各形態中の技術的特徴に対応する実施形態、実施例、変形例中の技術的特徴は、上述の課題の一部または全部を解決するために、あるいは、上述の効果の一部または全部を達成するために、適宜、差し替えや、組み合わせを行うことが可能である。また、その技術的特徴が本明細書中に必須なものとして説明されていなければ、適宜、削除することが可能である。
工程1.導体層130が形成された基層120上に、絶縁層140の材料である光硬化型絶縁性樹脂を、塗布またはラミネート加工
工程2.工程1を行った後、基層120上の光硬化型絶縁性樹脂に対してパターン露光
工程3.工程2を行った後、絶縁層140から接続端子132が露出するように、アルカリ水溶液を用いた現像処理によって、基層120上の光硬化型絶縁性樹脂における未硬化部分を除去
工程4.工程3を行った後、加熱による絶縁層140の硬化(熱硬化)と、紫外線による絶縁層140の硬化(光硬化)とを実施
工程4の光硬化における積算光量は、500mJ/cm2(ミリジュール毎平方センチメートル)以上2500mJ/cm2以下が好ましく、1000mJ/cm2以上2000mJ/cm2以下がさらに好ましい。
120…基層
130…導体層
132…接続端子
136…内部配線
140…絶縁層
141…第1表面
142…第2表面
143…接続部
145…隅部
148…壁面
149…湾曲面
150…開口部
DP…最深部
Claims (4)
- 絶縁性の基層と、
前記基層に積層された絶縁層であって、
開口部が形成された第1表面と、
前記開口部の内側において前記第1表面に対して前記基層側に窪んだ第2表面と、
前記開口部の内側において前記基層に対する前記絶縁層の積層方向に沿って前記第1表面と前記第2表面との間を繋ぐ壁面と
を有する絶縁層と、
前記第2表面から露出した導電性の接続端子と
を備える配線基板であって、
前記第2表面は、前記第2表面において最も前記基層側に位置する最深部を有し、前記基層側に凸状に湾曲して前記壁面と前記接続端子との間を繋ぐ面であり、
前記積層方向に直交する層面方向に沿った前記壁面と前記最深部との間の長さL1と、前記層面方向に沿った前記最深部と前記接続端子との間の長さL2との関係は、L1>L2を満たすことを特徴とする配線基板。 - 前記最深部は、前記第2表面のうち前記接続端子と接続する接続部を含むことを特徴とする請求項1に記載の配線基板。
- 前記絶縁層は、更に、前記第1表面と前記壁面との間を外側に凸状に湾曲して繋ぐ湾曲面を有することを特徴とする請求項1または請求項2に記載の配線基板。
- 前記第2表面の表面粗さは、前記第1表面よりも粗いことを特徴とする請求項1から請求項3のいずれか一項に記載の配線基板。
Priority Applications (6)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP13831747.4A EP2750172A4 (en) | 2012-08-24 | 2013-08-05 | WIRING SUBSTRATE |
| KR1020147010585A KR101603453B1 (ko) | 2012-08-24 | 2013-08-05 | 배선기판 |
| JP2013554712A JP5523641B1 (ja) | 2012-08-24 | 2013-08-05 | 配線基板 |
| US14/352,299 US20140284081A1 (en) | 2012-08-24 | 2013-08-05 | Wiring substrate |
| CN201380003704.8A CN103907180B (zh) | 2012-08-24 | 2013-08-05 | 布线基板 |
| TW102129936A TW201419949A (zh) | 2012-08-24 | 2013-08-22 | 配線基板 |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012-184962 | 2012-08-24 | ||
| JP2012184962 | 2012-08-24 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2014030309A1 true WO2014030309A1 (ja) | 2014-02-27 |
Family
ID=50149640
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2013/004722 WO2014030309A1 (ja) | 2012-08-24 | 2013-08-05 | 配線基板 |
Country Status (7)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US20140284081A1 (ja) |
| EP (1) | EP2750172A4 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JP5523641B1 (ja) |
| KR (1) | KR101603453B1 (ja) |
| CN (1) | CN103907180B (ja) |
| TW (1) | TW201419949A (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2014030309A1 (ja) |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2015207676A (ja) * | 2014-04-22 | 2015-11-19 | 京セラサーキットソリューションズ株式会社 | 配線基板およびその製造方法 |
| JP2017098306A (ja) * | 2015-11-18 | 2017-06-01 | 新光電気工業株式会社 | 配線基板、半導体装置及び配線基板の製造方法 |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US9620446B2 (en) * | 2014-12-10 | 2017-04-11 | Shinko Electric Industries Co., Ltd. | Wiring board, electronic component device, and method for manufacturing those |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007103648A (ja) | 2005-10-04 | 2007-04-19 | Hitachi Chem Co Ltd | プリント配線板、半導体チップ搭載基板、半導体パッケージ、プリント配線板の製造方法、及び半導体チップ搭載基板の製造方法 |
| JP2010153495A (ja) | 2008-12-24 | 2010-07-08 | Shinko Electric Ind Co Ltd | 半導体装置 |
| JP2011077191A (ja) * | 2009-09-29 | 2011-04-14 | Mitsubishi Paper Mills Ltd | ソルダーレジストの形成方法 |
| JP2011192692A (ja) | 2010-03-12 | 2011-09-29 | Mitsubishi Paper Mills Ltd | ソルダーレジストパターンの形成方法 |
Family Cites Families (11)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TW318321B (ja) * | 1995-07-14 | 1997-10-21 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | |
| JP3346263B2 (ja) * | 1997-04-11 | 2002-11-18 | イビデン株式会社 | プリント配線板及びその製造方法 |
| US5889655A (en) * | 1997-11-26 | 1999-03-30 | Intel Corporation | Integrated circuit package substrate with stepped solder mask openings |
| JP3922151B2 (ja) * | 2002-09-27 | 2007-05-30 | ブラザー工業株式会社 | フレキシブル配線基板の接続構造および接続方法 |
| TWI231028B (en) * | 2004-05-21 | 2005-04-11 | Via Tech Inc | A substrate used for fine-pitch semiconductor package and a method of the same |
| DE102005014665A1 (de) * | 2005-03-29 | 2006-11-02 | Infineon Technologies Ag | Substrat zur Herstellung einer Lötverbindung mit einem zweiten Substrat |
| KR100850243B1 (ko) * | 2007-07-26 | 2008-08-04 | 삼성전기주식회사 | 인쇄회로기판 및 그 제조방법 |
| US8222538B1 (en) * | 2009-06-12 | 2012-07-17 | Amkor Technology, Inc. | Stackable via package and method |
| JP5479233B2 (ja) * | 2010-06-04 | 2014-04-23 | 新光電気工業株式会社 | 配線基板及びその製造方法 |
| CN102480849B (zh) * | 2010-11-29 | 2014-09-24 | 宏恒胜电子科技(淮安)有限公司 | 电路板及其制作方法 |
| JP2013062472A (ja) * | 2011-09-15 | 2013-04-04 | Toppan Printing Co Ltd | 半導体パッケージおよびその製造方法 |
-
2013
- 2013-08-05 CN CN201380003704.8A patent/CN103907180B/zh not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2013-08-05 WO PCT/JP2013/004722 patent/WO2014030309A1/ja active Application Filing
- 2013-08-05 US US14/352,299 patent/US20140284081A1/en not_active Abandoned
- 2013-08-05 JP JP2013554712A patent/JP5523641B1/ja not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2013-08-05 KR KR1020147010585A patent/KR101603453B1/ko active IP Right Grant
- 2013-08-05 EP EP13831747.4A patent/EP2750172A4/en not_active Withdrawn
- 2013-08-22 TW TW102129936A patent/TW201419949A/zh not_active IP Right Cessation
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2007103648A (ja) | 2005-10-04 | 2007-04-19 | Hitachi Chem Co Ltd | プリント配線板、半導体チップ搭載基板、半導体パッケージ、プリント配線板の製造方法、及び半導体チップ搭載基板の製造方法 |
| JP2010153495A (ja) | 2008-12-24 | 2010-07-08 | Shinko Electric Ind Co Ltd | 半導体装置 |
| JP2011077191A (ja) * | 2009-09-29 | 2011-04-14 | Mitsubishi Paper Mills Ltd | ソルダーレジストの形成方法 |
| JP2011192692A (ja) | 2010-03-12 | 2011-09-29 | Mitsubishi Paper Mills Ltd | ソルダーレジストパターンの形成方法 |
Non-Patent Citations (1)
| Title |
|---|
| See also references of EP2750172A4 * |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2015207676A (ja) * | 2014-04-22 | 2015-11-19 | 京セラサーキットソリューションズ株式会社 | 配線基板およびその製造方法 |
| JP2017098306A (ja) * | 2015-11-18 | 2017-06-01 | 新光電気工業株式会社 | 配線基板、半導体装置及び配線基板の製造方法 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| TWI562686B (ja) | 2016-12-11 |
| EP2750172A4 (en) | 2015-05-06 |
| CN103907180B (zh) | 2016-08-31 |
| US20140284081A1 (en) | 2014-09-25 |
| JP5523641B1 (ja) | 2014-06-18 |
| KR101603453B1 (ko) | 2016-03-14 |
| CN103907180A (zh) | 2014-07-02 |
| TW201419949A (zh) | 2014-05-16 |
| EP2750172A1 (en) | 2014-07-02 |
| KR20140069213A (ko) | 2014-06-09 |
| JPWO2014030309A1 (ja) | 2016-07-28 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP6373574B2 (ja) | 回路基板及びその製造方法 | |
| TWI526128B (zh) | 多層基板及其製造方法 | |
| WO2014030355A1 (ja) | 配線基板 | |
| JP5093353B2 (ja) | 部品内蔵モジュールの製造方法及び部品内蔵モジュール | |
| KR101472672B1 (ko) | 전자부품 내장 인쇄회로기판 및 그 제조방법 | |
| KR102078009B1 (ko) | 인쇄회로기판 및 그 제조방법 | |
| JP5523641B1 (ja) | 配線基板 | |
| JP5462404B1 (ja) | 部品内蔵基板及び部品内蔵基板用コア基材 | |
| TWI586232B (zh) | 印刷電路板及其製造方法 | |
| JP2011029623A (ja) | 部品内蔵基板、その部品内蔵基板を用いたモジュール部品および部品内蔵基板の製造方法 | |
| TWI573502B (zh) | 基板結構及其製作方法 | |
| JP5491605B1 (ja) | 配線基板 | |
| KR20170038535A (ko) | 인쇄회로기판 및 그 제조방법 | |
| JP2014044979A (ja) | 配線基板 | |
| CN118872388A (zh) | 布线基板 | |
| KR101497268B1 (ko) | 회로 기판 및 회로 기판 제조방법 | |
| JP2014036183A (ja) | 電子部品実装基板の製造方法 | |
| JP2012069629A (ja) | プリント配線板の製造方法 | |
| JP2005197460A (ja) | プリント配線板及びその製造方法 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 2013554712 Country of ref document: JP Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 13831747 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 14352299 Country of ref document: US |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 20147010585 Country of ref document: KR Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |