WO2011155284A1 - 吸収性物品 - Google Patents
吸収性物品 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2011155284A1 WO2011155284A1 PCT/JP2011/060985 JP2011060985W WO2011155284A1 WO 2011155284 A1 WO2011155284 A1 WO 2011155284A1 JP 2011060985 W JP2011060985 W JP 2011060985W WO 2011155284 A1 WO2011155284 A1 WO 2011155284A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- sheet
- absorbent
- sanitary napkin
- heat
- absorbent article
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Ceased
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61F—FILTERS IMPLANTABLE INTO BLOOD VESSELS; PROSTHESES; DEVICES PROVIDING PATENCY TO, OR PREVENTING COLLAPSING OF, TUBULAR STRUCTURES OF THE BODY, e.g. STENTS; ORTHOPAEDIC, NURSING OR CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES; FOMENTATION; TREATMENT OR PROTECTION OF EYES OR EARS; BANDAGES, DRESSINGS OR ABSORBENT PADS; FIRST-AID KITS
- A61F13/00—Bandages or dressings; Absorbent pads
- A61F13/15—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators
- A61F13/53—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators characterised by the absorbing medium
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61F—FILTERS IMPLANTABLE INTO BLOOD VESSELS; PROSTHESES; DEVICES PROVIDING PATENCY TO, OR PREVENTING COLLAPSING OF, TUBULAR STRUCTURES OF THE BODY, e.g. STENTS; ORTHOPAEDIC, NURSING OR CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES; FOMENTATION; TREATMENT OR PROTECTION OF EYES OR EARS; BANDAGES, DRESSINGS OR ABSORBENT PADS; FIRST-AID KITS
- A61F13/00—Bandages or dressings; Absorbent pads
- A61F13/15—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators
- A61F13/45—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators characterised by the shape
- A61F13/47—Sanitary towels, incontinence pads or napkins
- A61F13/475—Sanitary towels, incontinence pads or napkins characterised by edge leakage prevention means
- A61F13/4751—Sanitary towels, incontinence pads or napkins characterised by edge leakage prevention means the means preventing fluid flow in a transversal direction
- A61F13/4756—Sanitary towels, incontinence pads or napkins characterised by edge leakage prevention means the means preventing fluid flow in a transversal direction the means consisting of grooves, e.g. channels, depressions or embossments, resulting in a heterogeneous surface level
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61F—FILTERS IMPLANTABLE INTO BLOOD VESSELS; PROSTHESES; DEVICES PROVIDING PATENCY TO, OR PREVENTING COLLAPSING OF, TUBULAR STRUCTURES OF THE BODY, e.g. STENTS; ORTHOPAEDIC, NURSING OR CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES; FOMENTATION; TREATMENT OR PROTECTION OF EYES OR EARS; BANDAGES, DRESSINGS OR ABSORBENT PADS; FIRST-AID KITS
- A61F13/00—Bandages or dressings; Absorbent pads
- A61F13/15—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators
- A61F13/51—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators characterised by the outer layers of the pads
- A61F13/511—Topsheet, i.e. the permeable cover or layer facing the skin
- A61F13/51104—Topsheet, i.e. the permeable cover or layer facing the skin the top sheet having a three-dimensional cross-section, e.g. corrugations, embossments, recesses or projections
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61F—FILTERS IMPLANTABLE INTO BLOOD VESSELS; PROSTHESES; DEVICES PROVIDING PATENCY TO, OR PREVENTING COLLAPSING OF, TUBULAR STRUCTURES OF THE BODY, e.g. STENTS; ORTHOPAEDIC, NURSING OR CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES; FOMENTATION; TREATMENT OR PROTECTION OF EYES OR EARS; BANDAGES, DRESSINGS OR ABSORBENT PADS; FIRST-AID KITS
- A61F13/00—Bandages or dressings; Absorbent pads
- A61F13/15—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators
- A61F13/51—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators characterised by the outer layers of the pads
- A61F13/511—Topsheet, i.e. the permeable cover or layer facing the skin
- A61F13/513—Topsheet, i.e. the permeable cover or layer facing the skin characterised by its function or properties, e.g. stretchability, breathability, rewet, visual effect; having areas of different permeability
- A61F13/51305—Topsheet, i.e. the permeable cover or layer facing the skin characterised by its function or properties, e.g. stretchability, breathability, rewet, visual effect; having areas of different permeability having areas of different permeability
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61F—FILTERS IMPLANTABLE INTO BLOOD VESSELS; PROSTHESES; DEVICES PROVIDING PATENCY TO, OR PREVENTING COLLAPSING OF, TUBULAR STRUCTURES OF THE BODY, e.g. STENTS; ORTHOPAEDIC, NURSING OR CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES; FOMENTATION; TREATMENT OR PROTECTION OF EYES OR EARS; BANDAGES, DRESSINGS OR ABSORBENT PADS; FIRST-AID KITS
- A61F13/00—Bandages or dressings; Absorbent pads
- A61F13/15—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators
- A61F13/51—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators characterised by the outer layers of the pads
- A61F13/515—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators characterised by the outer layers of the pads characterised by the interconnection of the topsheet and the backsheet
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61F—FILTERS IMPLANTABLE INTO BLOOD VESSELS; PROSTHESES; DEVICES PROVIDING PATENCY TO, OR PREVENTING COLLAPSING OF, TUBULAR STRUCTURES OF THE BODY, e.g. STENTS; ORTHOPAEDIC, NURSING OR CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES; FOMENTATION; TREATMENT OR PROTECTION OF EYES OR EARS; BANDAGES, DRESSINGS OR ABSORBENT PADS; FIRST-AID KITS
- A61F13/00—Bandages or dressings; Absorbent pads
- A61F13/15—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators
- A61F13/53—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators characterised by the absorbing medium
- A61F13/539—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators characterised by the absorbing medium characterised by the connection of the absorbent layers with each other or with the outer layers
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61F—FILTERS IMPLANTABLE INTO BLOOD VESSELS; PROSTHESES; DEVICES PROVIDING PATENCY TO, OR PREVENTING COLLAPSING OF, TUBULAR STRUCTURES OF THE BODY, e.g. STENTS; ORTHOPAEDIC, NURSING OR CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES; FOMENTATION; TREATMENT OR PROTECTION OF EYES OR EARS; BANDAGES, DRESSINGS OR ABSORBENT PADS; FIRST-AID KITS
- A61F13/00—Bandages or dressings; Absorbent pads
- A61F13/15—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators
- A61F13/53—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators characterised by the absorbing medium
- A61F2013/530131—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators characterised by the absorbing medium being made in fibre but being not pulp
- A61F2013/530226—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators characterised by the absorbing medium being made in fibre but being not pulp with polymeric fibres
Definitions
- the present invention relates to absorbent articles such as sanitary napkins and panty liners.
- Patent Document 1 describes a napkin in which a compression groove is provided in a mesh pattern on the upper surface of an absorption part.
- the sanitary napkin described in Patent Document 1 is provided with a compression groove in a mesh pattern, so that menstrual blood hardly spreads on the surface and menstrual leakage does not easily occur. Since the so-called second sheet is not arranged on the sanitary napkin, it is difficult to instantaneously absorb menstrual blood from the surface of the sanitary napkin.
- Patent Document 2 discloses a relatively thin sanitary napkin in which a liquid-permeable wiping acquisition sheet, which is a spunlace nonwoven fabric sheet made of rayon and polyester fibers, is disposed between a top sheet and an absorbent core. Is described. Further, for example, in Patent Document 3, an absorption composed of a body-capturing distribution layer on the upper sheet side and a liquid storage layer on the rear sheet side between the liquid-permeable upper sheet and the liquid-impermeable rear sheet. An absorbent article having a body core disposed therein is described, wherein the body-capturing distribution layer is described as a web made of hydrophilic cellulose fibers obtained by stiffening wood pulp fibers with an interfiber chemical stiffener. Yes.
- the sanitary napkin of Patent Document 2 is provided with a liquid permeable wiping acquisition sheet, which is a so-called second sheet, so that the body fluid can be dispersed in the lateral direction, and from the top sheet of the sanitary napkin instantly. Can absorb menstrual blood.
- seat which the sanitary napkin of patent document 2 contains the rayon which is a semi-synthetic fiber it is easy to produce the liquid residue of a bodily fluid, and an absorbent material from a liquid-permeable wiping acquisition sheet
- the absorbent article of Patent Document 3 is certainly provided with a body-capturing distribution layer that is a so-called second sheet, so that body fluid can be quickly collected and temporarily retained, and the absorbent article Body fluid can be instantaneously absorbed from the upper sheet.
- the body-capturing / distributing layer of the absorbent article of Patent Document 3 is a web made of hydrophilic cellulose fibers, it retains the body fluid and, like the sanitary napkin of Patent Document 2, The rest tends to occur, and it takes time to transfer the body fluid from the body-capturing distribution layer to the liquid storage layer.
- the present invention relates to providing an absorbent article in which bodily fluid is difficult to spread on the surface, the remaining amount of bodily fluid other than the absorber is reduced, and the transition time of the bodily fluid to the absorber can be shortened.
- the present invention provides a surface sheet disposed on the skin contact surface side, a back sheet disposed on the non-skin contact surface side, an absorber disposed between these sheets, and the absorber and the surface sheet. It is an absorptive article provided with the second sheet arranged between. In the absorbent article, the top sheet and the second sheet are partially fixed.
- the surface sheet has a large number of partitioned regions partitioned by linear embossing, and in the pore size distribution measurement with a pore size of 1 to 600 ⁇ m using a mercury porosimeter, the pore volume of the region having a pore size of 100 ⁇ m or less is all pores.
- the sheet is 10% or less of the capacity.
- the second sheet is a sheet in which the constituent fibers are synthetic fibers, the thickness is 0.15 to 0.4 mm, and the liquid holding amount is 60 g / m 2 or less.
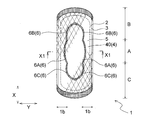
- FIG. 1 is a plan view of a sanitary napkin according to an embodiment of the absorbent article of the present invention as viewed from the top sheet side.
- FIG. 2 is a perspective view showing an embodiment of the top sheet of the sanitary napkin shown in FIG.
- FIG. 3 is an enlarged plan view showing a part on the skin contact surface side of the top sheet shown in FIG. 4 is a cross-sectional view taken along line XX of FIG.
- FIG. 5 is an enlarged cross-sectional view of a main part in which the main part in FIG.
- the absorbent article of one embodiment of the present invention is a sanitary napkin 1 and, as shown in FIGS. 1 and 4, a surface sheet 2 disposed on the skin contact surface side and a non-skin contact surface side. And the second sheet 5 disposed between the absorber 4 and the top sheet 2. The second sheet 5 is disposed between the top sheet 2 and the back sheet 3.
- the "skin contact surface side” is the surface side disposed on the skin side of the wearer when worn, among the front and back sides of the constituent members of the sanitary napkin 1,
- the “non-skin contact surface side” is a surface side arranged on the opposite side to the wearer's skin side when worn.
- the “Y direction” shown in the figure is a direction along the longitudinal direction of the sanitary napkin 1
- the “X direction” is a direction perpendicular to the Y direction and is a direction along the width direction of the sanitary napkin 1. It is.
- the present embodiment includes a rectangular absorbent body 4 that is long in the same direction as the front-rear direction at the time of mounting, and a second seat 5 that is substantially the same shape and size as the absorbent body 4. ing.
- a second sheet 5 is disposed on the skin contact surface side of the absorbent body 4.
- the top sheet 2 covers the entire area on the skin contact surface side of the rectangular second sheet 5, and the longitudinal direction (Y direction) of the absorber 4 and the second sheet 5. It has the part extended outward from both ends and both sides. As shown in FIGS.
- the back sheet 3 covers the entire area on the non-skin contact surface side of the absorbent body 4, both ends in the longitudinal direction (Y direction) of the absorbent body 4 and the second sheet 5, and It has a portion extending outward from both sides.
- the top sheet 2 and the back sheet 3 are fused (heat-embossed, super-exposed) at portions extending outward from both ends in the longitudinal direction (Y direction) of the absorber 4 and the second sheet 5.
- the portions that extend outward from both sides in the longitudinal direction (Y direction) of the absorber 4 and the second sheet 5 are fixed with an adhesive.
- the absorber 4 and the second sheet 5 are sandwiched between the top sheet 2 and the back sheet 3.
- the topsheet 2 of the sanitary napkin 1 has a large number of partitioned regions 22 partitioned by linear embosses 21 as shown in FIG. Since the topsheet 2 has the partition region 22 in this way, the wearer's bodily fluid absorbed in one partition region 22 diffuses to another partition region 22 adjacent beyond the partition region 22. hard.
- linear embossing means that the embossed shape is not limited to a straight line in a plan view but includes a curved line, and the embossed shape is a continuous line and includes an intermittent line such as a broken line. There is nothing. However, even if it is an intermittent line, if it is an interval of less than 1 mm, it is included because it has substantially the same effect as a continuous line.
- the partitioned area 22 may have a rectangular or curved shape other than the rhombus lattice pattern. A lattice pattern is particularly preferred.
- the surface sheet 2 of the present embodiment includes a plurality of first linear embosses 21 a formed in parallel with each other at predetermined intervals as linear embosses 21, and in parallel with each other.
- the groove width W1 of the first linear emboss 21a and the groove width of the second linear emboss 21b are the same, and the interval W2 between the adjacent first linear embosses 21a and the adjacent second linear emboss 21b. The interval between them is the same.
- the groove width W1 of the first linear emboss 21a is 0.1 to 1.5 mm, particularly 0.3 to 0.00 mm, from the viewpoint of securely fixing the constituent fibers in the linear emboss. It is preferably 9 mm. Further, the distance W2 between the first linear embosses 21a is preferably 2 to 14 mm, particularly 2 to 8 mm, from the viewpoint of achieving both liquid permeation and liquid suction.
- the groove width W1 and the interval W2 are measured in a direction perpendicular to the line. The width of the line may change from the intersection, but W1 is measured at the intersection and the midpoint of the intersection. W2 is measured by a line connecting opposite sides of the partition region 22.
- the surface sheet 2 of this embodiment forms the linear embossing 21 by performing a heat embossing from the non-skin contact surface side turned to a wearer's skin side when it is integrated in the sanitary napkin 1.
- the portion where the linear emboss 21 is formed is a recess.
- constituent fibers to be described later are heat-sealed in the thickness direction. Since the linear emboss 21 is formed in a lattice pattern by the first linear emboss 21a and the second linear emboss 21b, the surface sheet 2 is partitioned by the linear emboss 21. Regions 22, 22 ... are formed.
- Each partition region 22 is a region surrounded by a linear emboss 21 around each periphery, and has a rhombus shape in plan view. The central portion of each partition region 22 is raised relative to the linear emboss 21 (concave portion) surrounding the partition region 22 to form a convex portion.
- the surface sheet 2 of the present invention a sheet having high permeability is used. It has been found that good liquid permeability is exhibited when there are few voids, particularly pore regions, caused by fiber distribution in the sheet. Specifically, in pore diameter distribution measurement of pore diameters of 1 to 600 ⁇ m with a mercury porosimeter, It is preferable that the pore volume in a region having a pore diameter of 100 ⁇ m or less is a sheet having 10% or less of the total pore volume, and that the pore volume is 8% or less of the total pore volume, preferably 6% or less. More preferably, the sheet is Thus, the lower limit of the pore capacity in the region having a pore diameter of 100 ⁇ m or less is not particularly limited, and the smaller the better.
- the pore size distribution of the surface sheet 2 is measured using a mercury porosimeter (Shimadzu Corporation) in accordance with the mercury intrusion method (JIS R 1655).
- the mercury intrusion method is a method for obtaining information on the physical shape of the topsheet 2 by measuring the size (pores) between the constituent fibers of the topsheet 2 and the volume thereof.
- the principle of the mercury intrusion method is to apply a pressure to mercury to inject it into the pores of the object to be measured, and to measure the relationship between the pressure applied at that time and the volume of mercury that has been pushed in (intruded).
- a method for measuring the pore size distribution of the top sheet 2 using a mercury porosimeter will be described.
- the surface sheet 2 is taken out from the sanitary napkin 1 (absorbent article).
- the taken surface sheet 2 is cut into 24 mm ⁇ 15 mm.
- a total of 3 sheets are cut, and the cut samples are set in a sample cell of a mercury porosimeter (Shimadzu Corporation) so as not to overlap each other, and a pore size distribution with a pore size of 1 to 600 ⁇ m is measured.
- the total pore volume over a pore diameter of 1 to 600 ⁇ m is defined as the total pore volume, and the pore volume in the region with a pore diameter of 100 ⁇ m or less.
- the ratio to the total pore volume is determined.
- the ratio of the pore volume in the region having a pore diameter of 1 to 100 ⁇ m to the total pore volume is determined.
- Air-through nonwoven fabric composed only of non-heat-stretched fibers of 4 dtex or more, Air-through nonwoven fabric composed of heat-stretched fibers of 3.3 dtex or more, Air composed of non-heat-stretched fibers and heat-stretched fibers of 3.3 dtex or more A through nonwoven fabric is mentioned, and an air through nonwoven fabric composed of non-heat-stretched fibers and heat-stretched fibers of 3.3 dtex or more is preferable from the viewpoint of achieving both absorbency and texture.
- the topsheet 2 is an air-through nonwoven fabric containing thermally stretched fibers
- the topsheet 2 has the length of the thermally stretched fibers extended by heating in the partitioned region 22, and the inside of the partitioned region 22
- the crossing point of the crossed heat-stretched fibers indicates a non-woven fabric joined by thermal fusion.
- the heat-extending fiber is a heat-fusible fiber that is bonded by heat fusion
- the heat fusion is, for example, air-through heat fusion.
- the heat-fusible fiber as the heat-stretching fiber is preferably a heat-stretchable composite fiber comprising a heat-fusible component and a high-melting component having a higher melting point than the heat-fusible component.
- the heat fusion component and the high melting point component are preferably thermoplastic resins.
- the heat fusion component include polyethylene, polypropylene, polybutene-1, polypentene-1, or a random or block copolymer thereof.
- the high melting point component include polyesters such as polyethylene terephthalate and polybutylene terephthalate, and polyamides such as nylon-6 and nylon-66.
- Preferred combinations of the heat fusion component and the high melting point component include polyethylene and polyethylene terephthalate, polyethylene and polypropylene, low melting point polyethylene terephthalate and polyethylene terephthalate, polyethylene and polybutylene terephthalate, etc., but are not limited thereto. Absent.
- the core-sheath type composite fiber may be a concentric type, an eccentric type, or a fiber having a core component exposed at a part of the entire circumference of the fiber.
- the heat-extensible composite fiber is a fiber whose length is extended by heating, and is a fiber that extends at a temperature of 90 ° C. or higher, preferably 110 ° C. to 130 ° C.
- the heat-extensible conjugate fiber can be formed at the time of manufacturing the topsheet 2 to form irregularities with large undulations on the topsheet 2. Therefore, after the surface sheet 2 is completed, many of them are in an extended state, and do not mean fibers that are further extended from the state.
- the heat-extensible composite fiber after extension is also included in the heat-extensible composite fiber.
- the heat-extensible conjugate fiber examples include a fiber that changes in the crystalline state of the resin by heating, or a fiber that has been crimped and has an apparent length that is released by crimping. Etc.
- the stretch ratio at a temperature 10 ° C. higher than the softening point of the heat-fusible component and 10 ° C. lower than the melting point is 5 to 40%, particularly 10 to 30%. It is preferable from the point that a part and an uneven
- Preferred examples of the heat-extensible conjugate fiber are described in paragraphs [0024] to [0040] of JP-A-2005-350836.
- the ratio of the heat-stretchable conjugate fiber is that of the topsheet 2 from the viewpoint of exhibiting texture, concealment and high permeability
- the content of the constituent fibers is preferably 40 to 100% by mass, more preferably 70 to 100% by mass, and particularly preferably 95 to 100% by mass.
- the fiber to be blended in addition to the heat-extensible composite fiber include a fiber (non-composite fiber) made of a thermoplastic resin.
- the basis weight is preferably 20 to 50 g / m 2 .
- the topsheet 2 is an air-through nonwoven fabric composed only of heat-bonded fibers (non-heat-stretched fibers) of 4.4 dtex or more (preferably 4.4 to 10 dtex), it is a synthetic fiber such as polyethylene, A fiber made of a resin such as a polyester such as polypropylene, polyethylene terephthalate, polybutylene terephthalate, or a polyamide such as nylon-6 or nylon-66 may be used alone or in combination of two or more.
- the basis weight is preferably 20 to 50 g / m 2 .
- the second sheet 5 of the sanitary napkin 1 is composed of synthetic fibers.
- the synthetic fiber constituting the second sheet 5 is preferably a weakly hydrophilic fiber from the viewpoint of mechanical compatibility while keeping the diffusibility low.
- the synthetic fibers constituting the second sheet 5 fibers made of resin such as polyethylene, polypropylene, polyethylene terephthalate, polybutylene terephthalate, etc., polyamides such as nylon-6 and nylon-66, etc. are used alone or in two kinds The above can be mixed and formed.
- mixing mentioned here includes using 2 or more types of resin from which melting
- the second sheet 5 is a sheet having high permeability and moderate diffusivity, its thickness is 0.15 to 0.4 mm. From the viewpoint of suppressing the body fluid retention capacity and exhibiting high permeability.
- the thickness is preferably 0.15 to 0.4 mm, more preferably 0.2 to 0.3 mm. The thickness is measured under a 0.5 kPa load from the viewpoint of considering the wearing state.
- the liquid holding amount is a sheet having a liquid holding amount of 60 g / m 2 or less, but 35 g / m from the viewpoint of exhibiting high permeability.
- a sheet of 2 or less is preferable, and a sheet of 25 g / m 2 to 5 g / m 2 is more preferable.
- the lower limit of the liquid holding amount of the second sheet 5 is as low as possible.
- the liquid holding amount of the second sheet 5 is measured by the following measuring method.
- the intersecting points of the crossed synthetic fibers are joined by air-through heat fusion.
- An air-through nonwoven fabric that has been used can be preferably used.
- a point bond nonwoven fabric, a spunbond nonwoven fabric, a spunlace nonwoven fabric, or the like may be used as long as the thickness requirement and the liquid holding amount requirement are satisfied.
- the basis weight is preferably 15 to 40 g / m 2 .
- the top sheet 2 and the second sheet 5 of the sanitary napkin 1 are partially fixed.
- the second sheet 5 and the absorber 4 are also partially fixed as will be described later.
- Partially fixed means that there are fixed portions consisting of dots and lines, and the fixed portions are distributed over the entire sheet surface and do not need to be evenly distributed. Means no.
- the area of the fixed part is preferably about 10 to 60% of the total area of the fixed sheet.
- the topsheet 2 and the second sheet 5 are partially fixed by applying an adhesive intermittently or intermittently heat-sealing.
- the adhesive When the adhesive is applied intermittently, the adhesive is applied intermittently using a known means such as a slot coat gun, spirally applied using a spiral spray gun, or spray gun.
- a known means such as a slot coat gun, spirally applied using a spiral spray gun, or spray gun.
- a hot melt adhesive is preferably used as the adhesive to be applied.
- hot melt adhesive examples include styrene and olefin.
- Styrene-based hot melt adhesives include styrene-butadiene-styrene copolymer (SBS), styrene-isoprene-styrene copolymer (SIS), and styrene-ethylene-butylene-styrene copolymer that is a hydrogenated product of SBS. (SEBS) and blended hot melt adhesives in which two or more of these are blended can be used.
- SBS styrene-butadiene-styrene copolymer
- SIS styrene-isoprene-styrene copolymer
- SEBS blended hot melt adhesives in which two or more of these are blended can be used.
- a blended hot melt adhesive of SIS and SBS or a blended hot melt adhesive of SIS and SEBS is particularly preferably used in the present invention.
- the application amount of the hot melt adhesive is preferably 3 to 10 g / m 2 .
- a laminated sheet of the top sheet 2 and the second sheet 5 is formed with a hot embossing roll and a flat roll.
- the top sheet 2 and the second sheet 5 are partially fused by being conveyed and embossed.
- the interval between the plurality of fusion points formed by fusion is 5 to 5 from the viewpoint of maintaining appropriate permeability between the top sheet 2 and the second sheet 5 and maintaining appropriate fluid permeability. It is preferably 15 mm.
- the absorbent article of the present embodiment is a sanitary napkin 1, and since the product itself is required to be thin, the absorbent body 4 is formed from a multi-layered absorbent sheet 40.
- the absorbent sheet 40 is an absorbent sheet having a multi-surface shape and a superabsorbent polymer.
- the absorbent sheet 40 for example, an absorbent sheet produced by the method described in JP-A-8-246395, pulverized pulp supplied on an air stream and a water-absorbing polymer are deposited, and then an adhesive (for example, vinyl acetate) is deposited.
- An absorbent sheet obtained by blending a superabsorbent polymer therein can be used.
- These absorbent sheets can be cut into a predetermined shape and used as an absorbent sheet.
- a plurality of absorbent sheets are bonded together to form a multilayer sheet, or a single absorbent sheet is folded and the layers are bonded to form a multilayer sheet, and the multilayer sheet thus obtained is used as the absorbent sheet.
- an absorption core which is used for absorbent articles such as sanitary napkins, and is composed of absorbent polymer particles and a fiber material is coated with tissue paper.
- the body can also be used.
- the absorbent sheet 40 of the sanitary napkin 1 uses a known thin and highly absorbent sheet described in JP-A-8-246395 from the viewpoint of increasing absorbability and reducing thickness. I can do it.
- the obtained absorbent sheet is wet or dried, it is wetted again, and the wet absorbent sheet is pressed onto the roll surface of a heated cylindrical so-called Yankee dryer, and dried. Then, a crepe treatment is performed to peel off the dried absorbent sheet from the Yankee dryer through a blade. By performing the crepe treatment in this way, a large number of wrinkles that can be visually observed are formed on the surface of the absorbent sheet, and the surface of the absorbent sheet 40 becomes multi-fed.
- the distance between the ridges is preferably 0.2 mm to 2 mm.
- the sanitary napkin 1 of the present embodiment is a sectional area of the top sheet 2 in a cross-sectional view of the sanitary napkin 1 from the viewpoint of facilitating the absorption of the body fluid that has passed through the top sheet 2 and the second sheet 5.
- 22 is preferably 20 to 180 times, more preferably 25 to 160 times the distance between the fibers of the constituent fibers on the skin contact surface 40a of the absorbent sheet 40.
- the cross-sectional view of the sanitary napkin 1 shown in FIG. 4 shows a cross-sectional view taken along the line X1-X1 shown in FIG. 1, and the cross-sectional view of the sanitary napkin 1 shown in FIG. A cross-sectional view is shown.
- the X1-X1 line is a straight line extending in the X direction passing through the center of the sanitary napkin 1.
- the average distance in the width direction of the partition region 22 of the surface sheet 2 is determined by observing the cross section of the surface sheet 2 using a scanning electron microscope (SEM), and the first linear emboss 21a forming the partition region 22 Between the second linear emboss 21b, more specifically, between the X-direction center point in the groove of the first linear emboss 21a and the X-direction center point in the groove of the second linear emboss 21b. It is obtained by measuring. The number of measurement points is 10, and the average value is defined as the average interval in the width direction (X direction) of the partition region 22.
- the interfiber distance between the constituent fibers on the skin contact surface 40a of the absorbent sheet 40 is measured by observing the skin contact surface 40a using a scanning electron microscope (SEM). The number of measurement locations is 10, and the average value is the inter-fiber distance of the constituent fibers on the skin contact surface 40a.
- the sanitary napkin 1 of the present embodiment has a leak-proof groove 6 formed by integrally compressing the top sheet 2, the second sheet 5 and the absorbent body 4. Are provided on both surfaces 1b and 1b in the longitudinal direction (Y direction) of the sanitary napkin 1.
- the both sides of the topsheet 2 in the excretory part region A in contact with the body fluid excretion part of the wearer are convex outward in the X direction in plan view.
- a pair of leak-proof grooves 6A, 6A that are curved are formed, and each of the front region B extending in front of the excretory region A and the rear region C extending in the rear of the excretory region A is viewed in plan view.
- a pair of leak-proof grooves 6B, 6B and a pair of leak-proof grooves 6C, 6C that are convexly curved outward in the X direction are formed.
- the leak-proof groove 6 of the present embodiment is formed by connecting the leak-proof groove 6 ⁇ / b> A, the leak-proof groove 6 ⁇ / b> B, and the leak-proof groove 6 ⁇ / b> C to form an annular circumferential groove.
- the sanitary napkin 1 has the top sheet 2 and the second sheet 5 partially fixed, and in the present embodiment, as shown in FIG. These are partially fixed by the leak-proof groove 6. That is, the second sheet 5 and the absorber 4 are not fixed except for the leak-proof groove 6.
- the top sheet 2 and the second sheet 5 are partially fixed by intermittently applying an adhesive or intermittently heat-sealing.
- the surface sheet 2 and the second sheet 5 are intermittently fixed at the position of the linear emboss 21 (concave portion) forming the region 22.
- the crepe process is performed on the skin contact surface 40a of the absorber 4 as mentioned above, the uneven
- the top sheet 2 and the back sheet 3 any sheet can be used without particular limitation as long as it is normally used for absorbent articles such as sanitary napkins and panty liners.
- the top sheet 2 can be a hydrophilic and liquid permeable nonwoven fabric, an apertured film, or a laminate thereof
- the back sheet 3 can be a liquid impermeable or water repellent resin film, A laminate of a resin film and a non-woven fabric can be used.
- Examples of the processing method for forming the leak-proof groove 6 include embossing, heat embossing, ultrasonic embossing, and a combination thereof.
- the sanitary napkin 1 of the present embodiment has a large number of partitioned regions 22 partitioned by linear embosses 21 as shown in FIGS. 1 and 4, and is difficult to diffuse, and the pore size distribution measurement using a mercury porosimeter
- the top sheet 2 having high permeability satisfying the predetermined requirements, and the second sheet 5 having high permeability that is composed of the synthetic fiber and has low diffusibility, and the thickness and liquid holding amount satisfy the predetermined requirements.
- the sanitary napkin 1 of the present embodiment is formed by partially adhering the top sheet 2 and the second sheet 5 having low diffusibility and high permeability.
- the body fluid excreted from the wearer at the time of use is difficult to spread on the surface of the surface sheet 2, and the remaining body fluid is reduced by the surface sheet 2 and the second sheet 5 other than the absorber 4, and also the body fluid absorber 4
- the transition time can be shortened.
- the sanitary napkin 1 of this embodiment is provided with the absorption sheet 40 to which the creping process was performed, as shown in FIG. 5, and the second sheet 5 and the absorption sheet 40 are located at portions other than the leak-proof groove 6. Since it is not fixed, a space is formed between the uneven shape of the skin contact surface 40 a of the absorbent sheet 40 and the second sheet 5. Accordingly, the body fluid that has passed through the top sheet 2 and the second sheet 5 is likely to diffuse between the second sheet 5 and the absorbent sheet 40, so that a large amount of body fluid excreted from the surface of the top sheet 2 can be instantaneously transferred. The body fluid that has been transferred and diffused can be absorbed while effectively utilizing the absorption area of the absorbent sheet 40.
- the liquid diffusion area of the absorbent body 4 is 1.6 times the liquid diffusion area of the topsheet 2 in the measurement of liquid diffusibility in the state of an absorbent article (sanitary napkin 1). It is preferable that it is above, and it is preferable that it is twice or more.
- the liquid diffusion area, which is an index of liquid diffusibility, is measured by the following measurement method.
- the top sheet 2 and the second sheet 5 are quickly removed from the sanitary napkin 1, and the diffusion area of the absorbent body 4 is measured.
- the diffusion state immediately after dropping is recorded by various cameras (preferably one whose imaging data is digitized), the diffusion contour is marked, and the image analysis device (manufactured by NEXUS: Their diffusion areas are determined using NEW QUEBE Ver. 4.20).
- the absorbent article of the present invention is not limited to the sanitary napkin of the above-described embodiment, and can be appropriately changed.
- the sanitary napkin 1 includes the leak-proof groove 6 as shown in FIGS. 1 and 4, but may not be provided.
- the leak-proof groove 6 is not provided, the second sheet 5 and the absorbent body 4 are partially bonded by an adhesive or heat fusion in the same manner as the method of partially fixing the top sheet 2 and the second sheet 5. It is preferable that it is fixed to.
- the absorbent article of the present invention may be a panty liner, an incontinence pad, a disposable diaper or the like in addition to the sanitary napkin of the above embodiment.
- Example 1 A sanitary napkin shown in FIG. 1 was prepared and used as a sample of Example 1.
- the material used was a commercially available sanitary napkin (Laurie Super Slim Guard manufactured by Kao Corporation). However, the surface sheet of the sanitary napkin and the second sheet between the surface sheet and the absorber are not used, and instead, the surface sheet and the second sheet prepared as follows are used.
- the sanitary napkin of Example 1 was obtained.
- a core-sheath type composite fiber (core is polypropylene and sheath is polyethylene) having a fiber diameter of 4.0 dtex elongation rate of 6% and a non-extendable core-sheath type composite fiber (core is polyethylene terephthalate, sheath is 3.3 dtex) Polyethylene) is passed through a card machine at a ratio of 50 wt% to form a web, and the web is introduced into a heat embossing device, and linear emboss 21 (first linear emboss 21a and second linear A plurality of embosses 21b) were formed.
- the web was introduced into a hot air spraying apparatus, and hot air treatment was performed by air-through processing to obtain a surface sheet having partitioned regions 22 partitioned by linear embosses 21.
- the formation pattern of the linear embossing 21 of the obtained surface sheet is the pattern shown in FIG. 3, and the width W1 of each of the first and second linear embossing 21a and 21b is 0.5 mm, The distance between the embosses 21a and the distance W2 between the second linear embosses 21b were 6 mm, and the angle ⁇ between the first linear emboss 21a and the second linear emboss 21b was 56 °.
- the pore size distribution of the produced surface sheet was measured based on the above-mentioned [Method for measuring the pore size distribution of the surface sheet]
- the pore volume in the region having a pore diameter of 100 ⁇ m or less was 8% of the total pore volume.
- the basis weight of the resulting surface sheet was 25 g / m 2.
- a synthetic fiber made of a polyethylene / polyethylene terephthalate composite resin having a fiber diameter of 2.2 dtex is passed through a card machine to form a web, the web is introduced into a hot air blowing device, hot air treatment is performed by air-through processing, and then roll embossing is performed.
- a second sheet was obtained.
- the obtained second sheet had a thickness of 0.2 mm and a liquid holding amount of 26 g / m 2 .
- the basis weight of the obtained second sheet was 25 g / m 2 .
- a SEBS-based hot melt adhesive was applied between the prepared topsheet and the prepared second sheet, and the prepared topsheet and the prepared second sheet were partially fixed.
- the amount of hot melt adhesive applied was 5 g / m 2 .
- Example 2 The topsheet used in Example 1 described above was changed to a topsheet produced as follows, and the absorbent sheet was a wet state using a commercially available napkin (Laurier Super Slim Guard manufactured by Kao Corporation). A sanitary napkin of Example 2 was obtained in the same manner as in Example 1 described above, except that a crepe was used and a wrinkle at 1 mm intervals could be visually confirmed.
- a commercially available napkin Laurier Super Slim Guard manufactured by Kao Corporation
- the pore size distribution of the produced surface sheet was measured based on the above-mentioned [Method for measuring the pore size distribution of the surface sheet]
- the pore volume in the region having a pore diameter of 100 ⁇ m or less was 5% of the total pore volume.
- the basis weight of the resulting surface sheet was 25 g / m 2.
- Comparative Example 1 A sanitary napkin of Comparative Example 1 was obtained in the same manner as in Example 1 except that the surface sheet used in Example 1 was changed to the surface sheet produced as follows.
- the pore size distribution of the produced surface sheet was measured based on the above-mentioned [Method for measuring the pore size distribution of the surface sheet]
- the pore volume in the region having a pore diameter of 100 ⁇ m or less was 35% of the total pore volume.
- the basis weight of the resulting surface sheet was 25 g / m 2.
- Example 2 The surface sheet used in Example 1 described above is changed from a surface sheet having a basis weight of 25 g / m 2 to a surface sheet having a basis weight of 30 g / m 2 , and the second sheet used in Example 1 is not used. In the same manner, a sanitary napkin of Comparative Example 2 was obtained.
- the pore size distribution of the produced surface sheet was measured based on the above-mentioned [Method for measuring the pore size distribution of the surface sheet]
- the pore volume in the region having a pore diameter of 100 ⁇ m or less was 8% of the total pore volume.
- the measurement is performed under the temperature and humidity conditions using an absorbent article (sanitary napkin 1) that has been left for one day or longer in an environment of 20 ° C. and 65% RH.
- sanitary napkin 1 Place sanitary napkin 1 horizontally, place an acrylic plate injector (having a hole with a diameter of 10 mm) on it, apply a load of 5 g / cm 2 , and equine blood (manufactured by Nippon Biotest Co., Ltd.) 3 g of 3 hours after dropping 3 g of horse blood (manufactured by Nippon Biotest Co., Ltd.) from the same position 3 minutes later, the time taken for the horse blood to completely transfer from the surface sheet to the absorber visually Was measured as the body fluid absorption time of the sanitary napkin.
- Example 1 and Example 2 From the results shown in Table 1, in the samples of Example 1 and Example 2, the diffusion area of the surface sheet is narrower than the diffusion area of the absorber compared to the samples of Comparative Example 1 and Comparative Example 2, and the liquid residue of the surface sheet The amount was found to be small. In addition, it was found that the samples of Example 1 and Example 2 also had a shorter body fluid absorption time than the samples of Comparative Example 1 and Comparative Example 2.
- the absorbent article of the present invention it is difficult for the body fluid to spread on the surface, the remaining amount of the body fluid other than the absorber can be reduced, and the transition time of the body fluid to the absorber can be shortened.
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Epidemiology (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Heart & Thoracic Surgery (AREA)
- Vascular Medicine (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Fluid Mechanics (AREA)
- Absorbent Articles And Supports Therefor (AREA)
- Laminated Bodies (AREA)
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR1020127025297A KR101786474B1 (ko) | 2010-06-10 | 2011-05-12 | 흡수성 물품 |
| CN201180016875.5A CN102834080B (zh) | 2010-06-10 | 2011-05-12 | 吸收性物品 |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2010132804A JP5513267B2 (ja) | 2010-06-10 | 2010-06-10 | 吸収性物品 |
| JP2010-132804 | 2010-06-10 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2011155284A1 true WO2011155284A1 (ja) | 2011-12-15 |
Family
ID=45097896
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2011/060985 Ceased WO2011155284A1 (ja) | 2010-06-10 | 2011-05-12 | 吸収性物品 |
Country Status (5)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP5513267B2 (enExample) |
| KR (1) | KR101786474B1 (enExample) |
| CN (1) | CN102834080B (enExample) |
| TW (1) | TWI555517B (enExample) |
| WO (1) | WO2011155284A1 (enExample) |
Cited By (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2018166939A (ja) * | 2017-03-30 | 2018-11-01 | 花王株式会社 | 吸収性物品 |
| EP3434240A4 (en) * | 2016-03-24 | 2019-12-25 | Daio Paper Corporation | SUCTIONABLE ARTICLE |
| WO2020167171A1 (en) | 2019-02-15 | 2020-08-20 | Essity Hygiene And Health Aktiebolag | Absorbent article |
| WO2020167172A1 (en) | 2019-02-15 | 2020-08-20 | Essity Hygiene And Health Aktiebolag | Absorbent article with embossed surface layer |
| EP3711729B1 (en) | 2019-03-21 | 2020-12-16 | Ontex BV | Absorbent articles |
| US11149360B2 (en) | 2017-06-30 | 2021-10-19 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Method for making a shaped nonwoven |
| US11160694B2 (en) * | 2017-01-31 | 2021-11-02 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Three-dimensional substrates and absorbent articles having the same |
| US11214893B2 (en) | 2017-06-30 | 2022-01-04 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Shaped nonwoven |
Families Citing this family (15)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP5579337B1 (ja) | 2013-06-11 | 2014-08-27 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | 吸収体、及び当該吸収体を含む吸収性物品 |
| CN105683226B (zh) * | 2013-08-26 | 2018-08-17 | 巴斯夫欧洲公司 | 流体吸收制品 |
| JP2015154881A (ja) * | 2014-02-21 | 2015-08-27 | 日本製紙クレシア株式会社 | 吸収性物品 |
| JP6320184B2 (ja) * | 2014-06-11 | 2018-05-09 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | 吸収性物品 |
| CN106361503A (zh) * | 2015-07-21 | 2017-02-01 | 佛山市啟盛卫生用品有限公司 | 一种带压花锁水凹槽结构的婴儿纸尿裤 |
| JP6629542B2 (ja) * | 2015-08-04 | 2020-01-15 | 花王株式会社 | 吸収性物品 |
| JP6207557B2 (ja) * | 2015-08-27 | 2017-10-04 | 大王製紙株式会社 | 吸収性物品 |
| JP2018528015A (ja) * | 2015-09-22 | 2018-09-27 | ザ プロクター アンド ギャンブル カンパニー | 湾曲したチャネルを有する吸収性物品 |
| JP6242423B2 (ja) | 2016-03-29 | 2017-12-06 | 大王製紙株式会社 | 吸収性物品 |
| JP6259540B2 (ja) * | 2016-06-03 | 2018-01-10 | 花王株式会社 | 生理用吸収性物品 |
| WO2017209076A1 (ja) * | 2016-06-03 | 2017-12-07 | 花王株式会社 | 生理用吸収性物品 |
| JP7018863B2 (ja) * | 2018-10-09 | 2022-02-14 | ユニ・チャーム株式会社 | 吸収性物品 |
| JP2020116153A (ja) * | 2019-01-24 | 2020-08-06 | 株式会社リブドゥコーポレーション | 吸収性物品 |
| JP2022067373A (ja) * | 2020-10-20 | 2022-05-06 | 日本製紙クレシア株式会社 | 吸収性物品 |
| JP7256836B2 (ja) * | 2021-03-25 | 2023-04-12 | 花王株式会社 | 吸収性物品 |
Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004073759A (ja) * | 2002-06-21 | 2004-03-11 | Uni Charm Corp | 吸収性物品 |
| JP2004141619A (ja) * | 2002-06-14 | 2004-05-20 | Uni Charm Corp | 吸収性物品 |
| JP2005350836A (ja) * | 2004-06-14 | 2005-12-22 | Kao Corp | 立体賦形不織布 |
| JP2006521168A (ja) * | 2003-03-14 | 2006-09-21 | エスシーエー・ハイジーン・プロダクツ・アーベー | 改良された表面材料を有する吸収物品 |
| JP3940099B2 (ja) * | 2003-06-16 | 2007-07-04 | 大王製紙株式会社 | 吸収性物品 |
| JP2008136563A (ja) * | 2006-11-30 | 2008-06-19 | Daio Paper Corp | 吸収性物品 |
| JP2009148322A (ja) * | 2007-12-19 | 2009-07-09 | Kao Corp | 低拡散性透過紙及びそれを用いた吸収性物品 |
Family Cites Families (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP3611838B2 (ja) * | 2001-12-28 | 2005-01-19 | 花王株式会社 | 吸収性物品用の表面シート |
| JP4535984B2 (ja) * | 2005-11-08 | 2010-09-01 | 花王株式会社 | 凹凸構造体の製造方法 |
| JP5507193B2 (ja) * | 2008-10-15 | 2014-05-28 | 花王株式会社 | 吸収性物品の表面シート |
-
2010
- 2010-06-10 JP JP2010132804A patent/JP5513267B2/ja active Active
-
2011
- 2011-05-12 WO PCT/JP2011/060985 patent/WO2011155284A1/ja not_active Ceased
- 2011-05-12 CN CN201180016875.5A patent/CN102834080B/zh active Active
- 2011-05-12 KR KR1020127025297A patent/KR101786474B1/ko not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2011-05-18 TW TW100117452A patent/TWI555517B/zh active
Patent Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2004141619A (ja) * | 2002-06-14 | 2004-05-20 | Uni Charm Corp | 吸収性物品 |
| JP2004073759A (ja) * | 2002-06-21 | 2004-03-11 | Uni Charm Corp | 吸収性物品 |
| JP2006521168A (ja) * | 2003-03-14 | 2006-09-21 | エスシーエー・ハイジーン・プロダクツ・アーベー | 改良された表面材料を有する吸収物品 |
| JP3940099B2 (ja) * | 2003-06-16 | 2007-07-04 | 大王製紙株式会社 | 吸収性物品 |
| JP2005350836A (ja) * | 2004-06-14 | 2005-12-22 | Kao Corp | 立体賦形不織布 |
| JP2008136563A (ja) * | 2006-11-30 | 2008-06-19 | Daio Paper Corp | 吸収性物品 |
| JP2009148322A (ja) * | 2007-12-19 | 2009-07-09 | Kao Corp | 低拡散性透過紙及びそれを用いた吸収性物品 |
Cited By (18)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP3434240A4 (en) * | 2016-03-24 | 2019-12-25 | Daio Paper Corporation | SUCTIONABLE ARTICLE |
| US11395772B2 (en) | 2016-03-24 | 2022-07-26 | Daio Paper Corporation | Absorbent article |
| US11160694B2 (en) * | 2017-01-31 | 2021-11-02 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Three-dimensional substrates and absorbent articles having the same |
| JP2018166939A (ja) * | 2017-03-30 | 2018-11-01 | 花王株式会社 | 吸収性物品 |
| US11634838B2 (en) | 2017-06-30 | 2023-04-25 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Shaped nonwoven |
| US11746441B2 (en) | 2017-06-30 | 2023-09-05 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Method for making a shaped nonwoven |
| US12460321B2 (en) | 2017-06-30 | 2025-11-04 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Shaped nonwoven |
| US11214893B2 (en) | 2017-06-30 | 2022-01-04 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Shaped nonwoven |
| US11149360B2 (en) | 2017-06-30 | 2021-10-19 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Method for making a shaped nonwoven |
| US12146240B2 (en) | 2017-06-30 | 2024-11-19 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Method for making a shaped nonwoven |
| US11939701B2 (en) | 2017-06-30 | 2024-03-26 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Shaped nonwoven |
| WO2020167172A1 (en) | 2019-02-15 | 2020-08-20 | Essity Hygiene And Health Aktiebolag | Absorbent article with embossed surface layer |
| WO2020167171A1 (en) | 2019-02-15 | 2020-08-20 | Essity Hygiene And Health Aktiebolag | Absorbent article |
| AU2019429116B2 (en) * | 2019-02-15 | 2022-09-22 | Essity Hygiene And Health Aktiebolag | Absorbent article with embossed surface layer |
| EP3923889A4 (en) * | 2019-02-15 | 2022-09-07 | Essity Hygiene and Health Aktiebolag | ABSORBENT ARTICLE WITH EMBOSSED SURFACE LAYER |
| EP3923889B1 (en) | 2019-02-15 | 2024-04-03 | Essity Hygiene and Health Aktiebolag | Absorbent article with embossed surface layer |
| EP3923890A4 (en) * | 2019-02-15 | 2022-09-07 | Essity Hygiene and Health Aktiebolag | ABSORBENT ARTICLE |
| EP3711729B1 (en) | 2019-03-21 | 2020-12-16 | Ontex BV | Absorbent articles |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| KR20130080424A (ko) | 2013-07-12 |
| JP5513267B2 (ja) | 2014-06-04 |
| CN102834080A (zh) | 2012-12-19 |
| KR101786474B1 (ko) | 2017-11-15 |
| TW201143727A (en) | 2011-12-16 |
| JP2011255023A (ja) | 2011-12-22 |
| CN102834080B (zh) | 2015-12-02 |
| TWI555517B (zh) | 2016-11-01 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5513267B2 (ja) | 吸収性物品 | |
| JP2011255023A5 (enExample) | ||
| JP6005019B2 (ja) | 吸収性物品 | |
| JP6169338B2 (ja) | 吸収体及びこれを用いた吸収性物品 | |
| CN104023684B (zh) | 吸收性物品 | |
| JP6273101B2 (ja) | 不織布 | |
| TWI231754B (en) | Absorbent article | |
| JP2010148730A (ja) | 吸収性物品の表面シート | |
| JP7145940B2 (ja) | 吸収性物品用の層 | |
| CN102046122A (zh) | 吸收性物品及卫生巾 | |
| JP5792997B2 (ja) | 吸収性物品 | |
| JP4275421B2 (ja) | 吸収性物品 | |
| JP6499433B2 (ja) | 吸収性物品 | |
| JP6172809B2 (ja) | 吸収性物品 | |
| JP6231868B2 (ja) | 吸収性物品の表面シート及びそれを備えた吸収性物品 | |
| JP2017221277A (ja) | 吸収性物品 | |
| JP2012090689A (ja) | 吸収性物品 | |
| JP6982101B2 (ja) | 吸収性物品 | |
| JP5688265B2 (ja) | 吸収性物品 | |
| JP2017086621A (ja) | 吸収性物品 | |
| JP2007159943A (ja) | 使い捨ておむつ | |
| JP2007175093A (ja) | 吸収性物品 | |
| JP3210463U (ja) | 不織布、それを用いた吸収性物品の表面シート、及びそれを用いた吸収性物品 | |
| JP6405221B2 (ja) | 吸収性物品 | |
| JP2008132240A (ja) | 吸収性物品 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 201180016875.5 Country of ref document: CN |
|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 11792242 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 20127025297 Country of ref document: KR Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 1201005010 Country of ref document: TH |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 11792242 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |