JP6549451B2 - 半導体集積回路装置および電子装置 - Google Patents
半導体集積回路装置および電子装置 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP6549451B2 JP6549451B2 JP2015172625A JP2015172625A JP6549451B2 JP 6549451 B2 JP6549451 B2 JP 6549451B2 JP 2015172625 A JP2015172625 A JP 2015172625A JP 2015172625 A JP2015172625 A JP 2015172625A JP 6549451 B2 JP6549451 B2 JP 6549451B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- circuit
- current
- drive
- power semiconductor
- current detection
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H02—GENERATION; CONVERSION OR DISTRIBUTION OF ELECTRIC POWER
- H02P—CONTROL OR REGULATION OF ELECTRIC MOTORS, ELECTRIC GENERATORS OR DYNAMO-ELECTRIC CONVERTERS; CONTROLLING TRANSFORMERS, REACTORS OR CHOKE COILS
- H02P27/00—Arrangements or methods for the control of AC motors characterised by the kind of supply voltage
- H02P27/04—Arrangements or methods for the control of AC motors characterised by the kind of supply voltage using variable-frequency supply voltage, e.g. inverter or converter supply voltage
- H02P27/06—Arrangements or methods for the control of AC motors characterised by the kind of supply voltage using variable-frequency supply voltage, e.g. inverter or converter supply voltage using dc to ac converters or inverters
- H02P27/08—Arrangements or methods for the control of AC motors characterised by the kind of supply voltage using variable-frequency supply voltage, e.g. inverter or converter supply voltage using dc to ac converters or inverters with pulse width modulation
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H02—GENERATION; CONVERSION OR DISTRIBUTION OF ELECTRIC POWER
- H02M—APPARATUS FOR CONVERSION BETWEEN AC AND AC, BETWEEN AC AND DC, OR BETWEEN DC AND DC, AND FOR USE WITH MAINS OR SIMILAR POWER SUPPLY SYSTEMS; CONVERSION OF DC OR AC INPUT POWER INTO SURGE OUTPUT POWER; CONTROL OR REGULATION THEREOF
- H02M7/00—Conversion of ac power input into dc power output; Conversion of dc power input into ac power output
- H02M7/42—Conversion of dc power input into ac power output without possibility of reversal
- H02M7/44—Conversion of dc power input into ac power output without possibility of reversal by static converters
- H02M7/48—Conversion of dc power input into ac power output without possibility of reversal by static converters using discharge tubes with control electrode or semiconductor devices with control electrode
- H02M7/53—Conversion of dc power input into ac power output without possibility of reversal by static converters using discharge tubes with control electrode or semiconductor devices with control electrode using devices of a triode or transistor type requiring continuous application of a control signal
- H02M7/537—Conversion of dc power input into ac power output without possibility of reversal by static converters using discharge tubes with control electrode or semiconductor devices with control electrode using devices of a triode or transistor type requiring continuous application of a control signal using semiconductor devices only, e.g. single switched pulse inverters
- H02M7/5387—Conversion of dc power input into ac power output without possibility of reversal by static converters using discharge tubes with control electrode or semiconductor devices with control electrode using devices of a triode or transistor type requiring continuous application of a control signal using semiconductor devices only, e.g. single switched pulse inverters in a bridge configuration
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01R—MEASURING ELECTRIC VARIABLES; MEASURING MAGNETIC VARIABLES
- G01R19/00—Arrangements for measuring currents or voltages or for indicating presence or sign thereof
- G01R19/165—Indicating that current or voltage is either above or below a predetermined value or within or outside a predetermined range of values
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60L—PROPULSION OF ELECTRICALLY-PROPELLED VEHICLES; SUPPLYING ELECTRIC POWER FOR AUXILIARY EQUIPMENT OF ELECTRICALLY-PROPELLED VEHICLES; ELECTRODYNAMIC BRAKE SYSTEMS FOR VEHICLES IN GENERAL; MAGNETIC SUSPENSION OR LEVITATION FOR VEHICLES; MONITORING OPERATING VARIABLES OF ELECTRICALLY-PROPELLED VEHICLES; ELECTRIC SAFETY DEVICES FOR ELECTRICALLY-PROPELLED VEHICLES
- B60L15/00—Methods, circuits, or devices for controlling the traction-motor speed of electrically-propelled vehicles
- B60L15/02—Methods, circuits, or devices for controlling the traction-motor speed of electrically-propelled vehicles characterised by the form of the current used in the control circuit
- B60L15/08—Methods, circuits, or devices for controlling the traction-motor speed of electrically-propelled vehicles characterised by the form of the current used in the control circuit using pulses
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60L—PROPULSION OF ELECTRICALLY-PROPELLED VEHICLES; SUPPLYING ELECTRIC POWER FOR AUXILIARY EQUIPMENT OF ELECTRICALLY-PROPELLED VEHICLES; ELECTRODYNAMIC BRAKE SYSTEMS FOR VEHICLES IN GENERAL; MAGNETIC SUSPENSION OR LEVITATION FOR VEHICLES; MONITORING OPERATING VARIABLES OF ELECTRICALLY-PROPELLED VEHICLES; ELECTRIC SAFETY DEVICES FOR ELECTRICALLY-PROPELLED VEHICLES
- B60L3/00—Electric devices on electrically-propelled vehicles for safety purposes; Monitoring operating variables, e.g. speed, deceleration or energy consumption
- B60L3/0023—Detecting, eliminating, remedying or compensating for drive train abnormalities, e.g. failures within the drive train
- B60L3/0061—Detecting, eliminating, remedying or compensating for drive train abnormalities, e.g. failures within the drive train relating to electrical machines
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60L—PROPULSION OF ELECTRICALLY-PROPELLED VEHICLES; SUPPLYING ELECTRIC POWER FOR AUXILIARY EQUIPMENT OF ELECTRICALLY-PROPELLED VEHICLES; ELECTRODYNAMIC BRAKE SYSTEMS FOR VEHICLES IN GENERAL; MAGNETIC SUSPENSION OR LEVITATION FOR VEHICLES; MONITORING OPERATING VARIABLES OF ELECTRICALLY-PROPELLED VEHICLES; ELECTRIC SAFETY DEVICES FOR ELECTRICALLY-PROPELLED VEHICLES
- B60L3/00—Electric devices on electrically-propelled vehicles for safety purposes; Monitoring operating variables, e.g. speed, deceleration or energy consumption
- B60L3/12—Recording operating variables ; Monitoring of operating variables
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60L—PROPULSION OF ELECTRICALLY-PROPELLED VEHICLES; SUPPLYING ELECTRIC POWER FOR AUXILIARY EQUIPMENT OF ELECTRICALLY-PROPELLED VEHICLES; ELECTRODYNAMIC BRAKE SYSTEMS FOR VEHICLES IN GENERAL; MAGNETIC SUSPENSION OR LEVITATION FOR VEHICLES; MONITORING OPERATING VARIABLES OF ELECTRICALLY-PROPELLED VEHICLES; ELECTRIC SAFETY DEVICES FOR ELECTRICALLY-PROPELLED VEHICLES
- B60L50/00—Electric propulsion with power supplied within the vehicle
- B60L50/50—Electric propulsion with power supplied within the vehicle using propulsion power supplied by batteries or fuel cells
- B60L50/51—Electric propulsion with power supplied within the vehicle using propulsion power supplied by batteries or fuel cells characterised by AC-motors
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60L—PROPULSION OF ELECTRICALLY-PROPELLED VEHICLES; SUPPLYING ELECTRIC POWER FOR AUXILIARY EQUIPMENT OF ELECTRICALLY-PROPELLED VEHICLES; ELECTRODYNAMIC BRAKE SYSTEMS FOR VEHICLES IN GENERAL; MAGNETIC SUSPENSION OR LEVITATION FOR VEHICLES; MONITORING OPERATING VARIABLES OF ELECTRICALLY-PROPELLED VEHICLES; ELECTRIC SAFETY DEVICES FOR ELECTRICALLY-PROPELLED VEHICLES
- B60L7/00—Electrodynamic brake systems for vehicles in general
- B60L7/10—Dynamic electric regenerative braking
- B60L7/14—Dynamic electric regenerative braking for vehicles propelled by ac motors
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H02—GENERATION; CONVERSION OR DISTRIBUTION OF ELECTRIC POWER
- H02P—CONTROL OR REGULATION OF ELECTRIC MOTORS, ELECTRIC GENERATORS OR DYNAMO-ELECTRIC CONVERTERS; CONTROLLING TRANSFORMERS, REACTORS OR CHOKE COILS
- H02P27/00—Arrangements or methods for the control of AC motors characterised by the kind of supply voltage
- H02P27/04—Arrangements or methods for the control of AC motors characterised by the kind of supply voltage using variable-frequency supply voltage, e.g. inverter or converter supply voltage
- H02P27/06—Arrangements or methods for the control of AC motors characterised by the kind of supply voltage using variable-frequency supply voltage, e.g. inverter or converter supply voltage using dc to ac converters or inverters
- H02P27/08—Arrangements or methods for the control of AC motors characterised by the kind of supply voltage using variable-frequency supply voltage, e.g. inverter or converter supply voltage using dc to ac converters or inverters with pulse width modulation
- H02P27/085—Arrangements or methods for the control of AC motors characterised by the kind of supply voltage using variable-frequency supply voltage, e.g. inverter or converter supply voltage using dc to ac converters or inverters with pulse width modulation wherein the PWM mode is adapted on the running conditions of the motor, e.g. the switching frequency
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H02—GENERATION; CONVERSION OR DISTRIBUTION OF ELECTRIC POWER
- H02P—CONTROL OR REGULATION OF ELECTRIC MOTORS, ELECTRIC GENERATORS OR DYNAMO-ELECTRIC CONVERTERS; CONTROLLING TRANSFORMERS, REACTORS OR CHOKE COILS
- H02P29/00—Arrangements for regulating or controlling electric motors, appropriate for both AC and DC motors
- H02P29/02—Providing protection against overload without automatic interruption of supply
- H02P29/032—Preventing damage to the motor, e.g. setting individual current limits for different drive conditions
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H03—ELECTRONIC CIRCUITRY
- H03K—PULSE TECHNIQUE
- H03K17/00—Electronic switching or gating, i.e. not by contact-making and –breaking
- H03K17/08—Modifications for protecting switching circuit against overcurrent or overvoltage
- H03K17/082—Modifications for protecting switching circuit against overcurrent or overvoltage by feedback from the output to the control circuit
- H03K17/0828—Modifications for protecting switching circuit against overcurrent or overvoltage by feedback from the output to the control circuit in composite switches
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60L—PROPULSION OF ELECTRICALLY-PROPELLED VEHICLES; SUPPLYING ELECTRIC POWER FOR AUXILIARY EQUIPMENT OF ELECTRICALLY-PROPELLED VEHICLES; ELECTRODYNAMIC BRAKE SYSTEMS FOR VEHICLES IN GENERAL; MAGNETIC SUSPENSION OR LEVITATION FOR VEHICLES; MONITORING OPERATING VARIABLES OF ELECTRICALLY-PROPELLED VEHICLES; ELECTRIC SAFETY DEVICES FOR ELECTRICALLY-PROPELLED VEHICLES
- B60L2210/00—Converter types
- B60L2210/40—DC to AC converters
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60L—PROPULSION OF ELECTRICALLY-PROPELLED VEHICLES; SUPPLYING ELECTRIC POWER FOR AUXILIARY EQUIPMENT OF ELECTRICALLY-PROPELLED VEHICLES; ELECTRODYNAMIC BRAKE SYSTEMS FOR VEHICLES IN GENERAL; MAGNETIC SUSPENSION OR LEVITATION FOR VEHICLES; MONITORING OPERATING VARIABLES OF ELECTRICALLY-PROPELLED VEHICLES; ELECTRIC SAFETY DEVICES FOR ELECTRICALLY-PROPELLED VEHICLES
- B60L2240/00—Control parameters of input or output; Target parameters
- B60L2240/40—Drive Train control parameters
- B60L2240/42—Drive Train control parameters related to electric machines
- B60L2240/427—Voltage
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60L—PROPULSION OF ELECTRICALLY-PROPELLED VEHICLES; SUPPLYING ELECTRIC POWER FOR AUXILIARY EQUIPMENT OF ELECTRICALLY-PROPELLED VEHICLES; ELECTRODYNAMIC BRAKE SYSTEMS FOR VEHICLES IN GENERAL; MAGNETIC SUSPENSION OR LEVITATION FOR VEHICLES; MONITORING OPERATING VARIABLES OF ELECTRICALLY-PROPELLED VEHICLES; ELECTRIC SAFETY DEVICES FOR ELECTRICALLY-PROPELLED VEHICLES
- B60L2240/00—Control parameters of input or output; Target parameters
- B60L2240/40—Drive Train control parameters
- B60L2240/42—Drive Train control parameters related to electric machines
- B60L2240/429—Current
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01R—MEASURING ELECTRIC VARIABLES; MEASURING MAGNETIC VARIABLES
- G01R19/00—Arrangements for measuring currents or voltages or for indicating presence or sign thereof
- G01R19/165—Indicating that current or voltage is either above or below a predetermined value or within or outside a predetermined range of values
- G01R19/16533—Indicating that current or voltage is either above or below a predetermined value or within or outside a predetermined range of values characterised by the application
- G01R19/16538—Indicating that current or voltage is either above or below a predetermined value or within or outside a predetermined range of values characterised by the application in AC or DC supplies
- G01R19/16547—Indicating that current or voltage is either above or below a predetermined value or within or outside a predetermined range of values characterised by the application in AC or DC supplies voltage or current in AC supplies
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01R—MEASURING ELECTRIC VARIABLES; MEASURING MAGNETIC VARIABLES
- G01R31/00—Arrangements for testing electric properties; Arrangements for locating electric faults; Arrangements for electrical testing characterised by what is being tested not provided for elsewhere
- G01R31/26—Testing of individual semiconductor devices
- G01R31/2607—Circuits therefor
- G01R31/2608—Circuits therefor for testing bipolar transistors
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G01—MEASURING; TESTING
- G01R—MEASURING ELECTRIC VARIABLES; MEASURING MAGNETIC VARIABLES
- G01R31/00—Arrangements for testing electric properties; Arrangements for locating electric faults; Arrangements for electrical testing characterised by what is being tested not provided for elsewhere
- G01R31/40—Testing power supplies
- G01R31/42—AC power supplies
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H03—ELECTRONIC CIRCUITRY
- H03K—PULSE TECHNIQUE
- H03K17/00—Electronic switching or gating, i.e. not by contact-making and –breaking
- H03K17/04—Modifications for accelerating switching
- H03K17/042—Modifications for accelerating switching by feedback from the output circuit to the control circuit
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02T—CLIMATE CHANGE MITIGATION TECHNOLOGIES RELATED TO TRANSPORTATION
- Y02T10/00—Road transport of goods or passengers
- Y02T10/60—Other road transportation technologies with climate change mitigation effect
- Y02T10/64—Electric machine technologies in electromobility
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02T—CLIMATE CHANGE MITIGATION TECHNOLOGIES RELATED TO TRANSPORTATION
- Y02T10/00—Road transport of goods or passengers
- Y02T10/60—Other road transportation technologies with climate change mitigation effect
- Y02T10/70—Energy storage systems for electromobility, e.g. batteries
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02T—CLIMATE CHANGE MITIGATION TECHNOLOGIES RELATED TO TRANSPORTATION
- Y02T10/00—Road transport of goods or passengers
- Y02T10/60—Other road transportation technologies with climate change mitigation effect
- Y02T10/72—Electric energy management in electromobility
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Power Engineering (AREA)
- Transportation (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Sustainable Development (AREA)
- Sustainable Energy (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Power Conversion In General (AREA)
- Inverter Devices (AREA)
Description
その他の課題と新規な特徴は、本明細書の記述および添付図面から明らかになるであろう。
すなわち、半導体集積回路装置は電力用半導体装置のセンス電流から検出した通常電流に基づいて駆動回路の駆動能力を制御する駆動能力制御回路を備える。
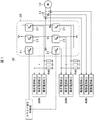
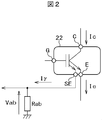
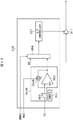
図1は比較例に係る電動機システムの一部を示すブロック図である。図2はIGBTのセンス電流を説明するための図である。電動機システム1Rは三相モータ10とインバータ回路20とドライバIC30Rと制御回路40Rとを備える。三相モータ10は3個の変流器(コイル)11を備える。なお、2つの位相電流検出ができれば、各相の電流計算は可能であるので、変流器は2個でもよい。インバータ回路20は6個の電力用半導体装置21によって三相ブリッジ構成する。図2に示すように、電力用半導体装置21はスイッチングトランジスタであるIGBT22を備え、IGBT22はゲート端子Gとコレクタ端子Cと駆動電流を流すエミッタ端子Eとセンス電流を流す電流検出端子SEとを備える。ドライバIC30Rは電力用半導体21を駆動し、制御回路40はドライバIC30を制御する。
(1)各位相のモータ駆動電流を変流器11、制御回路40のA/D変換器などを使ってモニタし、通常電流検出用としてモータ駆動制御に利用する。
(2)センス電流をドライバIC30での電圧比較回路やA/D変換器などを使ってモニタし、主に過電流検出用として異常電流時にドライバ信号を遮断するために利用する。
Vab=(1600A/4000)×5Ω=2V
一方で通常動作における電流検出電圧(Vn)は、下記のとおりである。
Vn=(400/4000)×5Ω=0.5V
さらに、モータの低速領域では駆動電流は小さくなるためダイナミックレンジは非常に小さいものになる。
図14は実施形態に係る半導体集積回路装置を説明するためのブロック図である。半導体集積回路装置30は、電力用半導体装置21を駆動する駆動回路31と、駆動回路31の駆動能力を制御する駆動能力制御回路34と、を備える。駆動回路31は、電力用半導体装置21のセンス電流から検出した異常電流に基づいて電力用半導体装置21の駆動を停止する。駆動能力制御回路34は、電力用半導体装置21のセンス電流から検出した通常電流に基づいて駆動回路31の駆動能力を制御する。
電力用半導体装置の駆動能力が向上し、例えばモータを高トルクで駆動することが可能になる。
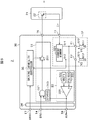
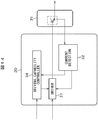
図3は実施例1に係る電動機システムの構成を示すブロック図である。図3の電動機システム1は三相モータ10と電力用半導体装置を6個用いたインバータ回路20と6個のドライバIC30と制御回路40と直流電源50とを備える。インバータ回路20、6個のドライバIC30および制御回路40で構成される部分を電子装置2という。インバータ回路20は、車両等の駆動時には直流電源(DC)50の電圧から、三相モータ10の各相に電流を流すように、インバータ回路20内部のスイッチングトランジスタ22をON/OFF制御し、このスイッチングの周波数により車両等の速度を変化させる。また、車両等の制動時には、三相モータ10の各相に生じる電圧に同期してスイッチングトランジスタ22をON/OFF制御し、いわゆる整流動作を行い、直流電圧に変換して回生を行う。
図4は図3の電動機システムの一部である電子装置を示すブロック図である。ドライバIC30は駆動回路31と電流検出回路32と保護検出回路33とアイソレータ34とドライブ能力制御回路35とを備える。電流検出回路32は異常電流を検出する電流増幅回路(CURRENT AMP)32−1と通常電流を検出する電流増幅回路32−2を備える。電流増幅回路(CURRENT AMP)32−1はセンス電流を電圧(V1)に変換し、保護検出回路33はその電圧に基づいて異常電流を検出して駆動回路31に送られIGBT22の駆動信号を遮断するとともに、アイソレータ34、制御回路40のI/Oインタフェース44を介してCPU41に送られる。電流増幅回路32−2は通常電流を電圧(V2)に変換し、ドライブ能力制御回路35に送られ駆動回路31の駆動能力を制御する。なお、アイソレータ34はドライバIC30と制御回路40との間を伝送する信号を磁気結合によって伝達する。アイソレータ34は配線で形成されたオンチップトランスを層間膜で絶縁することにより構成される。
V1=Iγ1×RS1
V2=Iγ2×RS2
となる。
トランジスタQ2の電流をIγ×1
トランジスタQ3の電流をIγ×10
とすることができる。
V3はV2が小さいときはV3が大きくなり、V2が大きいときはV3が小さくなる。
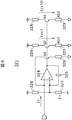
図13は図11のドライブ能力制御部を説明するためのブロック図である。実施例1の基準電圧(VREF2)を調整可能な機能を有し、その他の構成は実施例1と同様である。制御回路40BはA/D変換器36を経由して得られた電圧(Vn)に基づいて制御信号(RVC)を生成する。ドライブ能力制御回路35Cの基準電圧生成回路355Cの基準電圧(VREF2)は可変であり、端子T8から入力される制御信号(RVC)に基づいて基準電圧の調整が可能とされる。通常電流検出用電圧(Vn)のフィードバックゲインを調整できる機能(基準電圧生成回路355Cの基準電圧(VREF2)を調整できる機能)を有することで、通常電流検出用抵抗322の抵抗値(RS2)のバラツキにあわせて、当該ゲインを調整することで、精度の高い駆動能力制御が可能となる。
10・・・三相モータ
11・・・変流器
20・・・インバータ回路
21・・・電力用半導体装置
22・・・IGBT
30・・・ドライバIC
31・・・駆動回路
311・・・ドライバ
312・・・ANDゲート
313・・・状態保持回路
32・・・電流検出回路
321・・・カレントミラー回路
322・・・異常電流検出抵抗
323・・・通常電流検出抵抗
33・・・保護検出回路
331・・・コンパレータ
332・・・基準電圧
333・・・フィルタ回路
34・・・アイソレータ
35・・・ドライブ能力制御回路
351・・・増幅回路
352・・・オペアンプ
353・・・抵抗
354・・・抵抗
355・・・基準電圧生成回路
356・・・切替回路
357・・・電圧または電流制御回路
40・・・制御回路
41・・・CPU
42・・・PWM回路
43・・・I/Oインタフェース
44・・・I/Oインタフェース
Claims (6)
- 電力用半導体装置を駆動する駆動回路と、
前記駆動回路の駆動能力を制御する駆動能力制御回路と、
前記電力用半導体装置のセンス電流に基づいて異常電流検出用電圧を出力する第1の電流検出回路と、
前記電力用半導体装置の前記センス電流に基づいて通常電流検出用電圧を出力する第2の電流検出回路と、
前記電力用半導体装置の異常電流検出用抵抗を外部に接続するための第1の端子と、
前記電力用半導体装置の通常電流検出用抵抗を外部に接続するための第2の端子と、
を備え、
前記駆動回路は、前記電力用半導体装置の前記センス電流から検出した異常電流に基づいて前記電力用半導体装置の駆動を停止するよう構成され、
前記駆動能力制御回路は、前記電力用半導体装置の前記センス電流から検出した通常電流に基づいて前記駆動回路の駆動能力を制御するよう構成され、
前記第1の電流検出回路および前記第2の電流検出回路はカレントミラー回路で構成される半導体集積回路装置。 - 電力用半導体装置を駆動する駆動回路と、
前記駆動回路の駆動能力を制御する駆動能力制御回路と、
前記電力用半導体装置のセンス電流に基づいて異常電流検出用電圧を出力する第1の電流検出回路と、
前記電力用半導体装置の前記センス電流に基づいて通常電流検出用電圧を出力する第2の電流検出回路と、
を備え、
前記駆動回路は、前記電力用半導体装置の前記センス電流から検出した異常電流に基づいて前記電力用半導体装置の駆動を停止するよう構成され、
前記駆動能力制御回路は、前記電力用半導体装置の前記センス電流から検出した通常電流に基づいて前記駆動回路の駆動能力を制御するよう構成され、
前記駆動能力制御回路は、
前記通常電流検出用電圧に基づいた電圧を生成する回路と、
前記電圧に基づいて前記駆動回路の電圧または電流を制御する制御回路と、
を備え、
前記回路は、
オペアンプとループ抵抗を有する増幅回路と、
基準電圧を生成する回路と、
を備え、
前記ループ抵抗の抵抗値または前記基準電圧は制御信号に基づいて変更することが可能である半導体集積回路装置。 - 請求項2の半導体集積回路装置において、さらに、
前記通常電流検出用電圧を変換するA/D変換回路と、
前記A/D変換回路の出力を出力する端子と、
前記A/D変換回路の出力に基づいて生成された前記制御信号を入力する端子と、
を備える半導体集積回路装置。 - 電力用半導体装置と、
第1の半導体集積回路装置と、
第2の半導体集積回路装置と、
を備え、
前記電力用半導体装置は、
負荷を駆動するための電流を供給する第1の端子と、
駆動電流をモニタするための電流を供給する第2の端子と、
を備え、
前記第1の半導体集積回路装置は、
前記電力用半導体装置を駆動する駆動回路と、
前記駆動回路の駆動能力を制御する駆動能力制御回路と、
前記第2の端子からの電流に基づいて異常電流検出用電圧を出力する第1の電流検出回路と、
前記第2の端子からの電流に基づいて通常電流検出用電圧を出力する第2の電流検出回路と、
前記電力用半導体装置の異常電流検出用抵抗を外部に接続するための第4の端子と、
前記電力用半導体装置の通常電流検出用抵抗を外部に接続するための第5の端子と、
を備え、
前記駆動回路は、前記電力用半導体装置のセンス電流から検出した異常電流に基づいて前記電力用半導体装置の駆動を停止するよう構成され、
前記駆動能力制御回路は、前記電力用半導体装置のセンス電流から検出した通常電流に基づいて前記駆動回路の駆動能力を制御するよう構成され、
前記第1の電流検出回路および前記第2の電流検出回路は、カレントミラー回路で構成され、
前記カレントミラー回路は前記第4の端子および第5の端子に接続される電子装置。 - 電力用半導体装置と、
第1の半導体集積回路装置と、
第2の半導体集積回路装置と、
を備え、
前記電力用半導体装置は、
負荷を駆動するための電流を供給する第1の端子と、
駆動電流をモニタするための電流を供給する第2の端子と、
を備え、
前記第1の半導体集積回路装置は、
前記電力用半導体装置を駆動する駆動回路と、
前記駆動回路の駆動能力を制御する駆動能力制御回路と、
前記第2の端子からの電流に基づいて異常電流検出用電圧を出力する第1の電流検出回路と、
前記第2の端子からの電流に基づいて通常電流検出用電圧を出力する第2の電流検出回路と、
を備え、
前記駆動回路は、前記電力用半導体装置のセンス電流から検出した異常電流に基づいて前記電力用半導体装置の駆動を停止すよう構成され、
前記駆動能力制御回路は、前記電力用半導体装置のセンス電流から検出した通常電流に基づいて前記駆動回路の駆動能力を制御するよう構成され、
前記駆動能力制御回路は、
前記通常電流検出用電圧に基づいた電圧を生成する回路と、
前記電圧に基づいて前記駆動回路の電圧または電流を制御する制御回路と、
を備え、
前記回路は、
オペアンプとループ抵抗を有する増幅回路と、
基準電圧を生成する回路と、
を備え、
前記ループ抵抗の抵抗値または前記基準電圧は制御信号に基づいて変更することが可能である電子装置。 - 請求項5の電子装置において、
前記第1の半導体集積回路装置は、さらに前記通常電流検出用電圧を変換するA/D変換回路を備え、
前記第2の半導体集積回路装置は、前記前記A/D変換回路の出力に基づいて前記制御信号を生成するCPUを備える電子装置。
Priority Applications (4)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2015172625A JP6549451B2 (ja) | 2015-09-02 | 2015-09-02 | 半導体集積回路装置および電子装置 |
| US15/216,859 US9835658B2 (en) | 2015-09-02 | 2016-07-22 | Semiconductor integrated circuit device and electronic device for driving a power semiconductor device |
| CN201610670696.8A CN106487264B (zh) | 2015-09-02 | 2016-08-15 | 驱动功率半导体器件的半导体集成电路器件及电子器件 |
| US15/797,757 US10324114B2 (en) | 2015-09-02 | 2017-10-30 | Semiconductor integrated circuit device and electronic device for driving a power semiconductor device |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2015172625A JP6549451B2 (ja) | 2015-09-02 | 2015-09-02 | 半導体集積回路装置および電子装置 |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2017050984A JP2017050984A (ja) | 2017-03-09 |
| JP2017050984A5 JP2017050984A5 (ja) | 2018-07-05 |
| JP6549451B2 true JP6549451B2 (ja) | 2019-07-24 |
Family
ID=58103744
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2015172625A Active JP6549451B2 (ja) | 2015-09-02 | 2015-09-02 | 半導体集積回路装置および電子装置 |
Country Status (3)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (2) | US9835658B2 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JP6549451B2 (ja) |
| CN (1) | CN106487264B (ja) |
Families Citing this family (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2018093684A (ja) * | 2016-12-07 | 2018-06-14 | ルネサスエレクトロニクス株式会社 | 半導体装置および電力変換装置 |
| WO2019049698A1 (ja) * | 2017-09-08 | 2019-03-14 | パナソニックIpマネジメント株式会社 | 電力変換回路および電力変換装置 |
| DE102019119973B3 (de) * | 2019-07-24 | 2021-01-21 | Infineon Technologies Ag | Intelligenter elektronischer schalter |
| KR20210015261A (ko) * | 2019-08-01 | 2021-02-10 | 현대자동차주식회사 | 인버터용 스위칭소자의 과전류 검출기준 보상 시스템 및 이를 이용한 과전류 검출 시스템 |
| CN111653852B (zh) * | 2020-05-19 | 2021-06-11 | 南京理工大学 | 片上基于变压器的传输零点可调滤波器 |
| DE102020123149A1 (de) | 2020-09-04 | 2022-03-10 | Infineon Technologies Ag | Ansteuerschaltung für elektronischen schalter |
Family Cites Families (19)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS6395728A (ja) * | 1986-10-13 | 1988-04-26 | Fuji Electric Co Ltd | Igbtの過電流保護回路 |
| US5061863A (en) * | 1989-05-16 | 1991-10-29 | Kabushiki Kaisha Toyoda Jidoshokki Seisakusho | Transistor provided with a current detecting function |
| JP2800277B2 (ja) * | 1989-06-26 | 1998-09-21 | 株式会社豊田自動織機製作所 | 半導体素子駆動回路 |
| JP3125622B2 (ja) * | 1995-05-16 | 2001-01-22 | 富士電機株式会社 | 半導体装置 |
| JP2000323974A (ja) * | 1999-05-12 | 2000-11-24 | Fuji Electric Co Ltd | 半導体素子の短絡保護回路 |
| US6717785B2 (en) * | 2000-03-31 | 2004-04-06 | Denso Corporation | Semiconductor switching element driving circuit |
| JP2006187101A (ja) * | 2004-12-27 | 2006-07-13 | Nissan Motor Co Ltd | 電圧駆動素子の駆動方法 |
| JP4619812B2 (ja) * | 2005-02-16 | 2011-01-26 | 株式会社東芝 | ゲート駆動回路 |
| DE602005018201D1 (de) * | 2005-08-17 | 2010-01-21 | Infineon Technologies Ag | Verfahren und Treiberschaltung für die Steuerung eines MOS Leistungshalbleiters |
| JP2007228447A (ja) * | 2006-02-27 | 2007-09-06 | Hitachi Ltd | スイッチング素子のゲート駆動回路 |
| JP5443946B2 (ja) | 2009-11-02 | 2014-03-19 | 株式会社東芝 | インバータ装置 |
| JP5678498B2 (ja) * | 2010-07-15 | 2015-03-04 | 富士電機株式会社 | 電力用半導体素子のゲート駆動回路 |
| US8633755B2 (en) * | 2010-11-22 | 2014-01-21 | Denso Corporation | Load driver with constant current variable structure |
| JP5783121B2 (ja) * | 2012-04-09 | 2015-09-24 | 株式会社デンソー | 駆動対象スイッチング素子の駆動装置 |
| CN104170255B (zh) * | 2012-06-22 | 2017-09-19 | 富士电机株式会社 | 过电流检测装置及使用其的智能功率模块 |
| US8703091B2 (en) * | 2012-07-31 | 2014-04-22 | Uht Unitech Co., Ltd. | High modulus graphite fiber and manufacturing method thereof |
| US9461640B2 (en) * | 2012-12-21 | 2016-10-04 | Mitsubishi Electric Corporation | Switching element drive circuit, power module, and automobile |
| JP6065597B2 (ja) * | 2013-01-16 | 2017-01-25 | 富士電機株式会社 | 電力変換装置 |
| JP6197685B2 (ja) * | 2014-02-19 | 2017-09-20 | 株式会社デンソー | ゲート駆動回路 |
-
2015
- 2015-09-02 JP JP2015172625A patent/JP6549451B2/ja active Active
-
2016
- 2016-07-22 US US15/216,859 patent/US9835658B2/en active Active
- 2016-08-15 CN CN201610670696.8A patent/CN106487264B/zh active Active
-
2017
- 2017-10-30 US US15/797,757 patent/US10324114B2/en active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| US20170063367A1 (en) | 2017-03-02 |
| CN106487264A (zh) | 2017-03-08 |
| US20180067150A1 (en) | 2018-03-08 |
| US10324114B2 (en) | 2019-06-18 |
| CN106487264B (zh) | 2020-08-28 |
| JP2017050984A (ja) | 2017-03-09 |
| US9835658B2 (en) | 2017-12-05 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP6549451B2 (ja) | 半導体集積回路装置および電子装置 | |
| CN106953503B (zh) | 半导体集成电路器件和电子器件 | |
| JP5556353B2 (ja) | モータ電流検出器及びモータ制御装置 | |
| WO2009128536A1 (ja) | 温度検出回路 | |
| US20100013422A1 (en) | Motor driving apparatus and control method thereof | |
| JP5716158B2 (ja) | モータ電流検出用ic、およびこれを用いた電流検出器またはモータ制御装置 | |
| JP2009303338A (ja) | モータ駆動装置と制御方法 | |
| JP6621530B2 (ja) | 電流検出装置 | |
| WO2015097836A1 (ja) | 電力変換装置および電力変換装置の制御方法 | |
| US10658947B2 (en) | Semiconductor device, power module, and control method of power conversion device | |
| TWI469498B (zh) | 用於檢測馬達電流之ic及使用其之馬達電流檢測器或馬達控制裝置 | |
| JP2015033149A (ja) | 半導体素子の駆動装置及びそれを用いた電力変換装置 | |
| JP2007259690A (ja) | パワーモジュール | |
| JP4862319B2 (ja) | 保護回路を備えた半導体装置 | |
| JP5477159B2 (ja) | モータ電流検出用ic、およびこれを用いた電流検出器またはモータ制御装置 | |
| US10720871B2 (en) | Driving circuit and motor | |
| JP2022015787A (ja) | 半導体モジュール | |
| JP2019146354A (ja) | インバータ用ゲート駆動回路及び車載用電子制御装置 | |
| JP6025057B2 (ja) | パワー素子の温度検出装置 | |
| JP5050900B2 (ja) | 電力変換回路の駆動装置、及び電力変換装置 | |
| JP2016093074A (ja) | インバータシステム | |
| JP4869753B2 (ja) | インバータ | |
| JP2005102443A (ja) | 電力変換装置の出力電圧検出方法 | |
| JP2019140845A (ja) | モータ駆動回路、ファンモータ、駆動制御回路及びモータシステム | |
| JP2020005436A (ja) | 電力用半導体装置及び電力変換装置 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20180524 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20180524 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20190308 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20190319 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20190516 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20190625 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20190627 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 6549451 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |