JP5780682B2 - 低温基板上の薄膜の側方熱処理を提供する方法 - Google Patents
低温基板上の薄膜の側方熱処理を提供する方法 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP5780682B2 JP5780682B2 JP2013514223A JP2013514223A JP5780682B2 JP 5780682 B2 JP5780682 B2 JP 5780682B2 JP 2013514223 A JP2013514223 A JP 2013514223A JP 2013514223 A JP2013514223 A JP 2013514223A JP 5780682 B2 JP5780682 B2 JP 5780682B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- thin film
- substrate
- film
- traces
- absorption
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 239000010409 thin film Substances 0.000 title claims description 79
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title claims description 67
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 title claims description 64
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 title claims description 27
- 238000010521 absorption reaction Methods 0.000 claims description 83
- 239000010408 film Substances 0.000 claims description 83
- 238000009792 diffusion process Methods 0.000 claims description 27
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 claims description 15
- 239000000919 ceramic Substances 0.000 claims description 10
- 238000000059 patterning Methods 0.000 claims description 6
- 238000000151 deposition Methods 0.000 claims description 4
- 230000001678 irradiating effect Effects 0.000 claims description 4
- 230000002745 absorbent Effects 0.000 claims description 3
- 239000002250 absorbent Substances 0.000 claims description 3
- 229910021417 amorphous silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 18
- 230000005855 radiation Effects 0.000 description 16
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 description 12
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 8
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 8
- 239000012528 membrane Substances 0.000 description 7
- PCHJSUWPFVWCPO-UHFFFAOYSA-N gold Chemical compound [Au] PCHJSUWPFVWCPO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- 239000010931 gold Substances 0.000 description 6
- 229910052737 gold Inorganic materials 0.000 description 6
- 238000000576 coating method Methods 0.000 description 5
- 239000004642 Polyimide Substances 0.000 description 4
- 238000000137 annealing Methods 0.000 description 4
- 229920001721 polyimide Polymers 0.000 description 4
- 238000001237 Raman spectrum Methods 0.000 description 3
- 229910052454 barium strontium titanate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 239000011248 coating agent Substances 0.000 description 3
- 238000001723 curing Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000010894 electron beam technology Methods 0.000 description 3
- 239000010419 fine particle Substances 0.000 description 3
- 229920000642 polymer Polymers 0.000 description 3
- VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N silicon dioxide Inorganic materials O=[Si]=O VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicon Chemical compound [Si] XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000005388 borosilicate glass Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000005669 field effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000006698 induction Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000002347 injection Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000007924 injection Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000002955 isolation Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229910044991 metal oxide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 150000004706 metal oxides Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 230000003071 parasitic effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000002245 particle Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910052710 silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000010703 silicon Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000007740 vapor deposition Methods 0.000 description 2
- BQCADISMDOOEFD-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silver Chemical compound [Ag] BQCADISMDOOEFD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000002411 adverse Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229910021419 crystalline silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 238000002425 crystallisation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000008025 crystallization Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000007872 degassing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000003989 dielectric material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000002019 doping agent Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000001035 drying Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000005684 electric field Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000001017 electron-beam sputter deposition Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000011521 glass Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000000977 initiatory effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000011159 matrix material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910021424 microcrystalline silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 238000004377 microelectronic Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000005543 nano-size silicon particle Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000002105 nanoparticle Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000035699 permeability Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000004033 plastic Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920003207 poly(ethylene-2,6-naphthalate) Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000004417 polycarbonate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920000515 polycarbonate Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000011112 polyethylene naphthalate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920000139 polyethylene terephthalate Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000005020 polyethylene terephthalate Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000006116 polymerization reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000003672 processing method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000010926 purge Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000010453 quartz Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000377 silicon dioxide Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052709 silver Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000004332 silver Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000005245 sintering Methods 0.000 description 1
- HUAUNKAZQWMVFY-UHFFFAOYSA-M sodium;oxocalcium;hydroxide Chemical compound [OH-].[Na+].[Ca]=O HUAUNKAZQWMVFY-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/04—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof the devices having potential barriers, e.g. a PN junction, depletion layer or carrier concentration layer
- H01L21/18—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof the devices having potential barriers, e.g. a PN junction, depletion layer or carrier concentration layer the devices having semiconductor bodies comprising elements of Group IV of the Periodic Table or AIIIBV compounds with or without impurities, e.g. doping materials
- H01L21/26—Bombardment with radiation
- H01L21/263—Bombardment with radiation with high-energy radiation
- H01L21/268—Bombardment with radiation with high-energy radiation using electromagnetic radiation, e.g. laser radiation
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/04—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof the devices having potential barriers, e.g. a PN junction, depletion layer or carrier concentration layer
- H01L21/34—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof the devices having potential barriers, e.g. a PN junction, depletion layer or carrier concentration layer the devices having semiconductor bodies not provided for in groups H01L21/0405, H01L21/0445, H01L21/06, H01L21/16 and H01L21/18 with or without impurities, e.g. doping materials
- H01L21/42—Bombardment with radiation
- H01L21/423—Bombardment with radiation with high-energy radiation
- H01L21/428—Bombardment with radiation with high-energy radiation using electromagnetic radiation, e.g. laser radiation
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B29—WORKING OF PLASTICS; WORKING OF SUBSTANCES IN A PLASTIC STATE IN GENERAL
- B29C—SHAPING OR JOINING OF PLASTICS; SHAPING OF MATERIAL IN A PLASTIC STATE, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; AFTER-TREATMENT OF THE SHAPED PRODUCTS, e.g. REPAIRING
- B29C35/00—Heating, cooling or curing, e.g. crosslinking or vulcanising; Apparatus therefor
- B29C35/02—Heating or curing, e.g. crosslinking or vulcanizing during moulding, e.g. in a mould
- B29C35/0266—Local curing
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B29—WORKING OF PLASTICS; WORKING OF SUBSTANCES IN A PLASTIC STATE IN GENERAL
- B29C—SHAPING OR JOINING OF PLASTICS; SHAPING OF MATERIAL IN A PLASTIC STATE, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; AFTER-TREATMENT OF THE SHAPED PRODUCTS, e.g. REPAIRING
- B29C35/00—Heating, cooling or curing, e.g. crosslinking or vulcanising; Apparatus therefor
- B29C35/02—Heating or curing, e.g. crosslinking or vulcanizing during moulding, e.g. in a mould
- B29C35/0272—Heating or curing, e.g. crosslinking or vulcanizing during moulding, e.g. in a mould using lost heating elements, i.e. heating means incorporated and remaining in the formed article
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02104—Forming layers
- H01L21/02365—Forming inorganic semiconducting materials on a substrate
- H01L21/02367—Substrates
- H01L21/0237—Materials
- H01L21/02422—Non-crystalline insulating materials, e.g. glass, polymers
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02104—Forming layers
- H01L21/02365—Forming inorganic semiconducting materials on a substrate
- H01L21/02436—Intermediate layers between substrates and deposited layers
- H01L21/02439—Materials
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02104—Forming layers
- H01L21/02365—Forming inorganic semiconducting materials on a substrate
- H01L21/02518—Deposited layers
- H01L21/02521—Materials
- H01L21/02524—Group 14 semiconducting materials
- H01L21/02532—Silicon, silicon germanium, germanium
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02104—Forming layers
- H01L21/02365—Forming inorganic semiconducting materials on a substrate
- H01L21/02656—Special treatments
- H01L21/02664—Aftertreatments
- H01L21/02667—Crystallisation or recrystallisation of non-monocrystalline semiconductor materials, e.g. regrowth
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02104—Forming layers
- H01L21/02365—Forming inorganic semiconducting materials on a substrate
- H01L21/02656—Special treatments
- H01L21/02664—Aftertreatments
- H01L21/02667—Crystallisation or recrystallisation of non-monocrystalline semiconductor materials, e.g. regrowth
- H01L21/02675—Crystallisation or recrystallisation of non-monocrystalline semiconductor materials, e.g. regrowth using laser beams
- H01L21/02686—Pulsed laser beam
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02104—Forming layers
- H01L21/02365—Forming inorganic semiconducting materials on a substrate
- H01L21/02656—Special treatments
- H01L21/02664—Aftertreatments
- H01L21/02667—Crystallisation or recrystallisation of non-monocrystalline semiconductor materials, e.g. regrowth
- H01L21/02689—Crystallisation or recrystallisation of non-monocrystalline semiconductor materials, e.g. regrowth using particle beams
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L27/00—Devices consisting of a plurality of semiconductor or other solid-state components formed in or on a common substrate
- H01L27/02—Devices consisting of a plurality of semiconductor or other solid-state components formed in or on a common substrate including semiconductor components specially adapted for rectifying, oscillating, amplifying or switching and having potential barriers; including integrated passive circuit elements having potential barriers
- H01L27/12—Devices consisting of a plurality of semiconductor or other solid-state components formed in or on a common substrate including semiconductor components specially adapted for rectifying, oscillating, amplifying or switching and having potential barriers; including integrated passive circuit elements having potential barriers the substrate being other than a semiconductor body, e.g. an insulating body
- H01L27/1214—Devices consisting of a plurality of semiconductor or other solid-state components formed in or on a common substrate including semiconductor components specially adapted for rectifying, oscillating, amplifying or switching and having potential barriers; including integrated passive circuit elements having potential barriers the substrate being other than a semiconductor body, e.g. an insulating body comprising a plurality of TFTs formed on a non-semiconducting substrate, e.g. driving circuits for AMLCDs
- H01L27/1259—Multistep manufacturing methods
- H01L27/127—Multistep manufacturing methods with a particular formation, treatment or patterning of the active layer specially adapted to the circuit arrangement
- H01L27/1274—Multistep manufacturing methods with a particular formation, treatment or patterning of the active layer specially adapted to the circuit arrangement using crystallisation of amorphous semiconductor or recrystallisation of crystalline semiconductor
- H01L27/1281—Multistep manufacturing methods with a particular formation, treatment or patterning of the active layer specially adapted to the circuit arrangement using crystallisation of amorphous semiconductor or recrystallisation of crystalline semiconductor by using structural features to control crystal growth, e.g. placement of grain filters
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L27/00—Devices consisting of a plurality of semiconductor or other solid-state components formed in or on a common substrate
- H01L27/02—Devices consisting of a plurality of semiconductor or other solid-state components formed in or on a common substrate including semiconductor components specially adapted for rectifying, oscillating, amplifying or switching and having potential barriers; including integrated passive circuit elements having potential barriers
- H01L27/12—Devices consisting of a plurality of semiconductor or other solid-state components formed in or on a common substrate including semiconductor components specially adapted for rectifying, oscillating, amplifying or switching and having potential barriers; including integrated passive circuit elements having potential barriers the substrate being other than a semiconductor body, e.g. an insulating body
- H01L27/1214—Devices consisting of a plurality of semiconductor or other solid-state components formed in or on a common substrate including semiconductor components specially adapted for rectifying, oscillating, amplifying or switching and having potential barriers; including integrated passive circuit elements having potential barriers the substrate being other than a semiconductor body, e.g. an insulating body comprising a plurality of TFTs formed on a non-semiconducting substrate, e.g. driving circuits for AMLCDs
- H01L27/1259—Multistep manufacturing methods
- H01L27/127—Multistep manufacturing methods with a particular formation, treatment or patterning of the active layer specially adapted to the circuit arrangement
- H01L27/1274—Multistep manufacturing methods with a particular formation, treatment or patterning of the active layer specially adapted to the circuit arrangement using crystallisation of amorphous semiconductor or recrystallisation of crystalline semiconductor
- H01L27/1285—Multistep manufacturing methods with a particular formation, treatment or patterning of the active layer specially adapted to the circuit arrangement using crystallisation of amorphous semiconductor or recrystallisation of crystalline semiconductor using control of the annealing or irradiation parameters, e.g. using different scanning direction or intensity for different transistors
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/66—Types of semiconductor device ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/66007—Multistep manufacturing processes
- H01L29/66075—Multistep manufacturing processes of devices having semiconductor bodies comprising group 14 or group 13/15 materials
- H01L29/66227—Multistep manufacturing processes of devices having semiconductor bodies comprising group 14 or group 13/15 materials the devices being controllable only by the electric current supplied or the electric potential applied, to an electrode which does not carry the current to be rectified, amplified or switched, e.g. three-terminal devices
- H01L29/66409—Unipolar field-effect transistors
- H01L29/66477—Unipolar field-effect transistors with an insulated gate, i.e. MISFET
- H01L29/66742—Thin film unipolar transistors
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/66—Types of semiconductor device ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/66007—Multistep manufacturing processes
- H01L29/66075—Multistep manufacturing processes of devices having semiconductor bodies comprising group 14 or group 13/15 materials
- H01L29/66227—Multistep manufacturing processes of devices having semiconductor bodies comprising group 14 or group 13/15 materials the devices being controllable only by the electric current supplied or the electric potential applied, to an electrode which does not carry the current to be rectified, amplified or switched, e.g. three-terminal devices
- H01L29/66409—Unipolar field-effect transistors
- H01L29/66477—Unipolar field-effect transistors with an insulated gate, i.e. MISFET
- H01L29/66742—Thin film unipolar transistors
- H01L29/6675—Amorphous silicon or polysilicon transistors
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/66—Types of semiconductor device ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/66007—Multistep manufacturing processes
- H01L29/66075—Multistep manufacturing processes of devices having semiconductor bodies comprising group 14 or group 13/15 materials
- H01L29/66227—Multistep manufacturing processes of devices having semiconductor bodies comprising group 14 or group 13/15 materials the devices being controllable only by the electric current supplied or the electric potential applied, to an electrode which does not carry the current to be rectified, amplified or switched, e.g. three-terminal devices
- H01L29/66409—Unipolar field-effect transistors
- H01L29/66477—Unipolar field-effect transistors with an insulated gate, i.e. MISFET
- H01L29/66742—Thin film unipolar transistors
- H01L29/6675—Amorphous silicon or polysilicon transistors
- H01L29/66757—Lateral single gate single channel transistors with non-inverted structure, i.e. the channel layer is formed before the gate
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/66—Types of semiconductor device ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/68—Types of semiconductor device ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor controllable by only the electric current supplied, or only the electric potential applied, to an electrode which does not carry the current to be rectified, amplified or switched
- H01L29/76—Unipolar devices, e.g. field effect transistors
- H01L29/772—Field effect transistors
- H01L29/78—Field effect transistors with field effect produced by an insulated gate
- H01L29/786—Thin film transistors, i.e. transistors with a channel being at least partly a thin film
- H01L29/78603—Thin film transistors, i.e. transistors with a channel being at least partly a thin film characterised by the insulating substrate or support
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B29—WORKING OF PLASTICS; WORKING OF SUBSTANCES IN A PLASTIC STATE IN GENERAL
- B29C—SHAPING OR JOINING OF PLASTICS; SHAPING OF MATERIAL IN A PLASTIC STATE, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; AFTER-TREATMENT OF THE SHAPED PRODUCTS, e.g. REPAIRING
- B29C35/00—Heating, cooling or curing, e.g. crosslinking or vulcanising; Apparatus therefor
- B29C35/02—Heating or curing, e.g. crosslinking or vulcanizing during moulding, e.g. in a mould
- B29C35/08—Heating or curing, e.g. crosslinking or vulcanizing during moulding, e.g. in a mould by wave energy or particle radiation
- B29C35/0805—Heating or curing, e.g. crosslinking or vulcanizing during moulding, e.g. in a mould by wave energy or particle radiation using electromagnetic radiation
- B29C2035/0855—Heating or curing, e.g. crosslinking or vulcanizing during moulding, e.g. in a mould by wave energy or particle radiation using electromagnetic radiation using microwave
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B29—WORKING OF PLASTICS; WORKING OF SUBSTANCES IN A PLASTIC STATE IN GENERAL
- B29C—SHAPING OR JOINING OF PLASTICS; SHAPING OF MATERIAL IN A PLASTIC STATE, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; AFTER-TREATMENT OF THE SHAPED PRODUCTS, e.g. REPAIRING
- B29C35/00—Heating, cooling or curing, e.g. crosslinking or vulcanising; Apparatus therefor
- B29C35/02—Heating or curing, e.g. crosslinking or vulcanizing during moulding, e.g. in a mould
- B29C35/08—Heating or curing, e.g. crosslinking or vulcanizing during moulding, e.g. in a mould by wave energy or particle radiation
- B29C35/0866—Heating or curing, e.g. crosslinking or vulcanizing during moulding, e.g. in a mould by wave energy or particle radiation using particle radiation
- B29C2035/0877—Heating or curing, e.g. crosslinking or vulcanizing during moulding, e.g. in a mould by wave energy or particle radiation using particle radiation using electron radiation, e.g. beta-rays
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B29—WORKING OF PLASTICS; WORKING OF SUBSTANCES IN A PLASTIC STATE IN GENERAL
- B29C—SHAPING OR JOINING OF PLASTICS; SHAPING OF MATERIAL IN A PLASTIC STATE, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR; AFTER-TREATMENT OF THE SHAPED PRODUCTS, e.g. REPAIRING
- B29C35/00—Heating, cooling or curing, e.g. crosslinking or vulcanising; Apparatus therefor
- B29C35/02—Heating or curing, e.g. crosslinking or vulcanizing during moulding, e.g. in a mould
- B29C35/08—Heating or curing, e.g. crosslinking or vulcanizing during moulding, e.g. in a mould by wave energy or particle radiation
- B29C35/0805—Heating or curing, e.g. crosslinking or vulcanizing during moulding, e.g. in a mould by wave energy or particle radiation using electromagnetic radiation
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Power Engineering (AREA)
- Microelectronics & Electronic Packaging (AREA)
- Condensed Matter Physics & Semiconductors (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Computer Hardware Design (AREA)
- Manufacturing & Machinery (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Crystallography & Structural Chemistry (AREA)
- Ceramic Engineering (AREA)
- Optics & Photonics (AREA)
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery (AREA)
- Thermal Sciences (AREA)
- Materials Engineering (AREA)
- Electromagnetism (AREA)
- Toxicology (AREA)
- High Energy & Nuclear Physics (AREA)
- Recrystallisation Techniques (AREA)
- Thin Film Transistor (AREA)
- Electrodes Of Semiconductors (AREA)
- Physical Vapour Deposition (AREA)
- Formation Of Insulating Films (AREA)
Description
本願は、米国特許法§119(e)(1)の下、2010年6月2日に出願された米国仮特許出願第61/350,765号への優先権を主張し、この米国仮特許出願の内容は、本明細書中に参考として援用される。
1.技術分野
本発明は、概して、基板上の薄膜を硬化させるための方法に関し、具体的には、低温基板上の薄膜を熱的に処理するための方法に関する。
一般に、熱処理とは、焼結、焼き鈍し、硬化、乾燥、結晶化、重合、化学反応開始および変調、ドーパント送り込み、ガス抜き等を包含する。半導体薄膜の熱処理は、典型的には、高温環境において行なわれる。例えば、非晶質シリコン(a−Si)は、1100℃で焼き鈍しされ、シリコンナノ粒子膜は、900℃で焼結される。したがって、処理半導体薄膜のための高温要件は、多くの場合、半導体薄膜を担持するための選択肢基板として、焼成セラミックまたは石英等、高温基板の使用を余儀なくする。
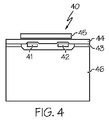
本発明の好ましい実施形態によると、離間した2つの吸収トレースが、基板の上部に位置する薄膜と接触される。パルス放射が、2つの吸収トレースを加熱するために利用され、2つの吸収トレースからの熱が、続いて、薄膜の平面において、2つの吸収トレース間の薄膜へと伝導され、薄膜を熱的に処理する。
本発明は、例えば、以下を提供する。
(項目1)
超薄膜を熱的に処理するための方法であって、
超薄膜の上部に2つの吸収トレースをパターン化するステップであって、上記薄膜は、基板の上部に位置する、ステップと、
少なくとも1つの電磁パルスで上記2つの吸収トレースを照射し、上記2つの吸収トレースを加熱するステップと、
上記2つの吸収トレースからの熱によって、上記超薄膜を熱的に処理するステップと、
を備える、方法。
(項目2)
上記基板は、450℃未満の最大作業温度を有する、項目1に記載の装置。
(項目3)
上記2つの吸収トレースは、上記超薄膜よりも上記電磁パルスに吸収性である材料から作製される、項目1に記載の方法。
(項目4)
上記2つの吸収トレースは、金属から作製される、項目1に記載の装置。
(項目5)
上記2つの吸収トレースは、セラミックから作製される、項目1に記載の方法。
(項目6)
上記超薄膜と上記基板との間に、熱拡散層を提供するステップをさらに含む、項目1に記載の方法。
(項目7)
上記電磁パルスは、閃光灯から提供される、項目1に記載の方法。
(項目8)
上記電磁パルスは、指向性プラズマアークから提供される、項目1に記載の方法。
(項目9)
薄膜トランジスタを加工するための方法であって、
超薄膜に隣接する2つの吸収トレースをパターン化するステップであって、上記薄膜は、基板の上部に位置する、ステップと、
少なくとも1つの電磁パルスで上記2つの吸収トレースを照射し、上記2つの吸収トレースを加熱し、上記2つの吸収トレースからの熱によって、上記超薄膜を熱的に処理するステップと、
上記2つの吸収トレースおよび上記超薄膜上に誘電層を蒸着させるステップと、
上記誘電層の上部に伝導性トレースを蒸着させることによって、ゲートを形成するステップと、
を備える、方法。
(項目10)
上記基板は、450℃未満の最大作業温度を有する、項目9に記載の方法。
(項目11)
、 上記2つの吸収トレースは、上記超薄膜よりも上記電磁パルスに吸収性である材料から作製される、項目9に記載の方法。
(項目12)
上記2つの吸収トレースは、金属から作製される、項目9に記載の方法。
(項目13)
上記2つの吸収トレースは、セラミックから作製される、項目9に記載の方法。
(項目14)
上記超薄膜と上記基板との間に、熱拡散層を提供するステップをさらに含む、項目9に記載の方法。
(項目15)
上記熱拡散層と上記基板との間に、高温低熱伝導性膜を提供するステップをさらに含む、項目14に記載の方法。
(項目16)
上記電磁パルスは、閃光灯から提供される、項目9に記載の方法。
(項目17)
上記電磁パルスは、指向性プラズマアークから提供される、項目9に記載の方法。
パルス放射熱処理技法を使用して、基板上の薄膜を熱的に処理する時、閃光灯、指向性プラズマアーク(DPA;directed plasma arc)、レーザ、マイクロ波、誘導加熱器、または電子ビームから放出されるパルス放射は、その基板にわたって、薄膜を選択的に加熱する能力を有する。加えて、基板の熱容量は、薄膜のものより遥かに大きく、加熱時間は、基板の熱平衡時間より遥かに短いため、基板は、熱処理直後に薄膜を急速冷却するために、放熱板としての役割を果たすことができる。
Claims (14)
- 超薄膜を熱的に処理するための方法であって、
超薄膜の上部に2つの吸収トレースをパターン化するステップであって、前記2つの吸収トレースは、セラミックから作製されており、前記薄膜は、基板の上部に位置する、ステップと、
少なくとも1つの電磁パルスで前記2つの吸収トレースを照射し、前記2つの吸収トレースを加熱するステップと、
前記2つの吸収トレースからの熱によって、前記超薄膜を熱的に処理するステップと、
を備える、方法。 - 前記基板は、450℃未満の最大作業温度を有する、請求項1に記載の装置。
- 前記2つの吸収トレースは、前記超薄膜よりも前記電磁パルスに吸収性である材料から作製される、請求項1に記載の方法。
- 前記超薄膜と前記基板との間に、熱拡散層を提供するステップをさらに含む、請求項1に記載の方法。
- 前記電磁パルスは、閃光灯から提供される、請求項1に記載の方法。
- 前記電磁パルスは、指向性プラズマアークから提供される、請求項1に記載の方法。
- 薄膜トランジスタを加工するための方法であって、
超薄膜に隣接する2つの吸収トレースをパターン化するステップであって、前記2つの吸収トレースは、セラミックから作製されており、前記薄膜は、基板の上部に位置する、ステップと、
少なくとも1つの電磁パルスで前記2つの吸収トレースを照射し、前記2つの吸収トレースを加熱し、前記2つの吸収トレースからの熱によって、前記超薄膜を熱的に処理するステップと、
前記2つの吸収トレースおよび前記超薄膜上に誘電層を蒸着させるステップと、
前記誘電層の上部に伝導性トレースを蒸着させることによって、ゲートを形成するステップと、
を備える、方法。 - 前記基板は、450℃未満の最大作業温度を有する、請求項7に記載の方法。
- 前記2つの吸収トレースは、前記超薄膜よりも前記電磁パルスに吸収性である材料から作製される、請求項7に記載の方法。
- 前記超薄膜と前記基板との間に、熱拡散層を提供するステップをさらに含む、請求項7に記載の方法。
- 前記熱拡散層と前記基板との間に、高温低熱伝導性膜を提供するステップをさらに含む、請求項10に記載の方法。
- 前記電磁パルスは、閃光灯から提供される、請求項7に記載の方法。
- 前記電磁パルスは、指向性プラズマアークから提供される、請求項7に記載の方法。
- 前記2つの吸収トレースは、前記薄膜トランジスタのソースおよびドレインを形成する、請求項7〜13のいずれか一項に記載の方法。
Applications Claiming Priority (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US35076510P | 2010-06-02 | 2010-06-02 | |
| US61/350,765 | 2010-06-02 | ||
| PCT/US2011/038937 WO2011153357A1 (en) | 2010-06-02 | 2011-06-02 | Method for providing lateral thermal processing of thin films on low-temperature substrates |
Related Child Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2015106595A Division JP6359484B2 (ja) | 2010-06-02 | 2015-05-26 | 低温基板上の薄膜の側方熱処理を提供する方法 |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2014505348A JP2014505348A (ja) | 2014-02-27 |
| JP5780682B2 true JP5780682B2 (ja) | 2015-09-16 |
Family
ID=45064782
Family Applications (4)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013514223A Active JP5780682B2 (ja) | 2010-06-02 | 2011-06-02 | 低温基板上の薄膜の側方熱処理を提供する方法 |
| JP2015106595A Active JP6359484B2 (ja) | 2010-06-02 | 2015-05-26 | 低温基板上の薄膜の側方熱処理を提供する方法 |
| JP2016157478A Withdrawn JP2016195285A (ja) | 2010-06-02 | 2016-08-10 | 低温基板上の薄膜の側方熱処理を提供する方法 |
| JP2018241034A Pending JP2019071453A (ja) | 2010-06-02 | 2018-12-25 | 低温基板上の薄膜の側方熱処理を提供する方法 |
Family Applications After (3)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2015106595A Active JP6359484B2 (ja) | 2010-06-02 | 2015-05-26 | 低温基板上の薄膜の側方熱処理を提供する方法 |
| JP2016157478A Withdrawn JP2016195285A (ja) | 2010-06-02 | 2016-08-10 | 低温基板上の薄膜の側方熱処理を提供する方法 |
| JP2018241034A Pending JP2019071453A (ja) | 2010-06-02 | 2018-12-25 | 低温基板上の薄膜の側方熱処理を提供する方法 |
Country Status (7)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (3) | US8557642B2 (ja) |
| EP (1) | EP2576860B1 (ja) |
| JP (4) | JP5780682B2 (ja) |
| KR (2) | KR101655879B1 (ja) |
| CN (2) | CN104992901B (ja) |
| CA (1) | CA2801900C (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2011153357A1 (ja) |
Families Citing this family (13)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US11155493B2 (en) | 2010-01-16 | 2021-10-26 | Cardinal Cg Company | Alloy oxide overcoat indium tin oxide coatings, coated glazings, and production methods |
| US10060180B2 (en) | 2010-01-16 | 2018-08-28 | Cardinal Cg Company | Flash-treated indium tin oxide coatings, production methods, and insulating glass unit transparent conductive coating technology |
| US10000965B2 (en) | 2010-01-16 | 2018-06-19 | Cardinal Cg Company | Insulating glass unit transparent conductive coating technology |
| US10000411B2 (en) | 2010-01-16 | 2018-06-19 | Cardinal Cg Company | Insulating glass unit transparent conductivity and low emissivity coating technology |
| US9862640B2 (en) | 2010-01-16 | 2018-01-09 | Cardinal Cg Company | Tin oxide overcoat indium tin oxide coatings, coated glazings, and production methods |
| US9639001B2 (en) * | 2014-02-04 | 2017-05-02 | Raytheon Company | Optically transitioned metal-insulator surface |
| US9728668B2 (en) | 2014-02-04 | 2017-08-08 | Raytheon Company | Integrated photosensitive film and thin LED display |
| WO2016040913A2 (en) | 2014-09-12 | 2016-03-17 | Board Of Regents, The University Of Texas System | Photonic curing of nanocrystal films for photovoltaics |
| WO2019143358A1 (en) * | 2018-01-19 | 2019-07-25 | Ncc Nano, Llc | Method for curing solder paste on a thermally fragile substrate |
| US11028012B2 (en) | 2018-10-31 | 2021-06-08 | Cardinal Cg Company | Low solar heat gain coatings, laminated glass assemblies, and methods of producing same |
| JP7203417B2 (ja) * | 2019-01-31 | 2023-01-13 | 株式会社ブイ・テクノロジー | レーザアニール方法、レーザアニール装置、およびtft基板 |
| EP3928966A1 (en) | 2020-06-26 | 2021-12-29 | Carl Zeiss Vision International GmbH | Method for manufacturing a coated lens |
| TW202236550A (zh) | 2020-11-25 | 2022-09-16 | 美商應用材料股份有限公司 | 用於低溫處理的補充能量 |
Family Cites Families (25)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5302230A (en) | 1980-02-27 | 1994-04-12 | Ricoh Company, Ltd. | Heat treatment by light irradiation |
| EP0169485B1 (en) * | 1984-07-17 | 1991-12-04 | Nec Corporation | Method and apparatus for inducing photochemical reaction |
| JPH0715881B2 (ja) * | 1984-12-20 | 1995-02-22 | ソニー株式会社 | 半導体薄膜の熱処理方法 |
| JPH0727198B2 (ja) * | 1987-02-18 | 1995-03-29 | キヤノン株式会社 | 多層膜反射型マスク |
| JPH02275641A (ja) * | 1989-04-17 | 1990-11-09 | Seiko Epson Corp | 半導体装置の製造方法 |
| US5180226A (en) * | 1991-10-30 | 1993-01-19 | Texas Instruments Incorporated | Method and apparatus for precise temperature measurement |
| CA2137632A1 (en) * | 1993-12-17 | 1995-06-18 | Douglas S. Dunn | Ablative flashlamp imaging |
| JPH09116158A (ja) * | 1995-10-17 | 1997-05-02 | Hitachi Ltd | 軽量基板薄膜半導体装置および液晶表示装置 |
| US5950078A (en) * | 1997-09-19 | 1999-09-07 | Sharp Laboratories Of America, Inc. | Rapid thermal annealing with absorptive layers for thin film transistors on transparent substrates |
| US6159832A (en) * | 1998-03-18 | 2000-12-12 | Mayer; Frederick J. | Precision laser metallization |
| JP3586558B2 (ja) * | 1998-04-17 | 2004-11-10 | 日本電気株式会社 | 薄膜の改質方法及びその実施に使用する装置 |
| TW457553B (en) * | 1999-01-08 | 2001-10-01 | Sony Corp | Process for producing thin film semiconductor device and laser irradiation apparatus |
| JP3980465B2 (ja) | 2001-11-09 | 2007-09-26 | 株式会社半導体エネルギー研究所 | 半導体装置の作製方法 |
| US7364952B2 (en) * | 2003-09-16 | 2008-04-29 | The Trustees Of Columbia University In The City Of New York | Systems and methods for processing thin films |
| JP2005150608A (ja) * | 2003-11-19 | 2005-06-09 | Seiko Epson Corp | ガラス基板の光処理方法およびデバイス |
| TW200541079A (en) * | 2004-06-04 | 2005-12-16 | Adv Lcd Tech Dev Ct Co Ltd | Crystallizing method, thin-film transistor manufacturing method, thin-film transistor, and display device |
| JP2006066902A (ja) * | 2004-07-28 | 2006-03-09 | Advanced Lcd Technologies Development Center Co Ltd | 半導体装置の製造方法 |
| US20070037346A1 (en) * | 2005-02-22 | 2007-02-15 | Grant Robert W | Rapid thermal annealing of targeted thin film layers |
| US7943447B2 (en) * | 2007-08-08 | 2011-05-17 | Ramesh Kakkad | Methods of fabricating crystalline silicon, thin film transistors, and solar cells |
| JP5447909B2 (ja) * | 2008-04-25 | 2014-03-19 | 株式会社日本製鋼所 | 薄膜材料の結晶化方法及びその装置 |
| US8410712B2 (en) * | 2008-07-09 | 2013-04-02 | Ncc Nano, Llc | Method and apparatus for curing thin films on low-temperature substrates at high speeds |
| JP5167050B2 (ja) * | 2008-09-30 | 2013-03-21 | ルネサスエレクトロニクス株式会社 | 半導体装置の製造方法およびマスクの製造方法 |
| US20100170566A1 (en) * | 2009-01-06 | 2010-07-08 | Arthur Don Harmala | Apparatus and method for manufacturing polymer solar cells |
| JP2010219207A (ja) * | 2009-03-16 | 2010-09-30 | Sony Corp | 金属−絶縁体相転移材料を用いた機能要素の形成方法及びこれによって形成された機能要素、並びに機能デバイスの製造方法及びこれによって製造された機能デバイス |
| JP7027198B2 (ja) | 2018-03-06 | 2022-03-01 | 株式会社Screenホールディングス | 基板処理装置 |
-
2011
- 2011-06-02 KR KR1020157035388A patent/KR101655879B1/ko active IP Right Grant
- 2011-06-02 CN CN201510261174.8A patent/CN104992901B/zh active Active
- 2011-06-02 US US13/152,065 patent/US8557642B2/en active Active
- 2011-06-02 CA CA2801900A patent/CA2801900C/en active Active
- 2011-06-02 JP JP2013514223A patent/JP5780682B2/ja active Active
- 2011-06-02 CN CN201180037944.0A patent/CN103038389B/zh active Active
- 2011-06-02 WO PCT/US2011/038937 patent/WO2011153357A1/en active Application Filing
- 2011-06-02 KR KR1020127034243A patent/KR101648101B1/ko active IP Right Grant
- 2011-06-02 EP EP11790412.8A patent/EP2576860B1/en not_active Not-in-force
-
2013
- 2013-09-11 US US14/024,243 patent/US9006047B2/en active Active
-
2015
- 2015-03-02 US US14/635,729 patent/US10553450B2/en active Active
- 2015-05-26 JP JP2015106595A patent/JP6359484B2/ja active Active
-
2016
- 2016-08-10 JP JP2016157478A patent/JP2016195285A/ja not_active Withdrawn
-
2018
- 2018-12-25 JP JP2018241034A patent/JP2019071453A/ja active Pending
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| US20140017857A1 (en) | 2014-01-16 |
| KR101648101B1 (ko) | 2016-08-16 |
| KR20160003297A (ko) | 2016-01-08 |
| CN103038389B (zh) | 2015-06-17 |
| JP2015149513A (ja) | 2015-08-20 |
| CN104992901A (zh) | 2015-10-21 |
| CN104992901B (zh) | 2017-03-15 |
| US10553450B2 (en) | 2020-02-04 |
| JP2019071453A (ja) | 2019-05-09 |
| EP2576860A4 (en) | 2015-04-08 |
| JP2016195285A (ja) | 2016-11-17 |
| CA2801900A1 (en) | 2011-12-08 |
| JP6359484B2 (ja) | 2018-07-18 |
| CA2801900C (en) | 2018-03-13 |
| EP2576860A1 (en) | 2013-04-10 |
| KR101655879B1 (ko) | 2016-09-08 |
| US9006047B2 (en) | 2015-04-14 |
| CN103038389A (zh) | 2013-04-10 |
| WO2011153357A1 (en) | 2011-12-08 |
| JP2014505348A (ja) | 2014-02-27 |
| US20150311092A1 (en) | 2015-10-29 |
| KR20130086547A (ko) | 2013-08-02 |
| EP2576860B1 (en) | 2017-08-09 |
| US8557642B2 (en) | 2013-10-15 |
| US20110300676A1 (en) | 2011-12-08 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP6359484B2 (ja) | 低温基板上の薄膜の側方熱処理を提供する方法 | |
| Lin et al. | Deep ultraviolet laser direct write for patterning sol-gel InGaZnO semiconducting micro/nanowires and improving field-effect mobility | |
| US7824957B2 (en) | Method for producing semiconductor device | |
| TWI399810B (zh) | 無機半導體膜及其製造方法 | |
| JP5467238B2 (ja) | 半導体の熱処理方法 | |
| JP2015149513A5 (ja) | ||
| WO2006094231A1 (en) | System and method for forming conductive material on a substrate | |
| Dellis et al. | Rapid laser-induced photochemical conversion of sol–gel precursors to In 2 O 3 layers and their application in thin-film transistors | |
| Li et al. | Precise Patterning of Large‐Scale TFT Arrays Based on Solution‐Processed Oxide Semiconductors: A Comparative Study of Additive and Subtractive Approaches | |
| Gokhale et al. | Controlling the crack formation in inkjet-printed silver nanoparticle thin-films for high resolution patterning using intense pulsed light treatment | |
| Weidling et al. | Large-area photonic lift-off process for flexible thin-film transistors | |
| WO2006098513A1 (ja) | 熱処理方法及び半導体の結晶化方法 | |
| Trifunovic et al. | Solution-based polycrystalline silicon transistors produced on a paper substrate | |
| CN117153694A (zh) | 一种高迁移率应变二维材料晶体管及其制备方法 | |
| KR101992480B1 (ko) | 저온 용액공정을 이용한 산화물 반도체의 제조방법 및 산화물 반도체 | |
| JP2011192908A (ja) | ポリシリコン膜の製造方法、太陽電池及び電子デバイス | |
| Noh et al. | Pulse thermal processing for low thermal budget integration of IGZO thin film transistors | |
| TWI587422B (zh) | 晶圓微波退火之晶圓承載結構及其應用 | |
| KR100920388B1 (ko) | 무감광 리소그래피에 의한 박막 패터닝 방법 | |
| Turkani et al. | Large-area photonic lift-off process for flexible thin-film transistors | |
| WO2006092936A1 (ja) | 半導体薄膜または半導体ウエハの電磁誘導加熱法 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20140306 |
|
| A977 | Report on retrieval |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A971007 Effective date: 20150305 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20150311 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20150526 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20150710 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20150713 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 5780682 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |