JP5714200B2 - 改良電気活性ポリマ - Google Patents
改良電気活性ポリマ Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP5714200B2 JP5714200B2 JP2001510924A JP2001510924A JP5714200B2 JP 5714200 B2 JP5714200 B2 JP 5714200B2 JP 2001510924 A JP2001510924 A JP 2001510924A JP 2001510924 A JP2001510924 A JP 2001510924A JP 5714200 B2 JP5714200 B2 JP 5714200B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- polymer
- generator
- electrodes
- electroactive
- deformation
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
- 229920001746 electroactive polymer Polymers 0.000 title claims abstract description 137
- 229920000642 polymer Polymers 0.000 claims abstract description 555
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 51
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 44
- 239000010410 layer Substances 0.000 claims description 157
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 claims description 71
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 claims description 47
- 230000005684 electric field Effects 0.000 claims description 46
- 230000004044 response Effects 0.000 claims description 45
- 239000000654 additive Substances 0.000 claims description 19
- 230000008602 contraction Effects 0.000 claims description 19
- 230000015556 catabolic process Effects 0.000 claims description 18
- 238000006073 displacement reaction Methods 0.000 claims description 14
- 229920000058 polyacrylate Polymers 0.000 claims description 14
- 229920000800 acrylic rubber Polymers 0.000 claims description 11
- 230000000996 additive effect Effects 0.000 claims description 11
- 239000012790 adhesive layer Substances 0.000 claims description 10
- 229920002379 silicone rubber Polymers 0.000 claims description 10
- 229920001577 copolymer Polymers 0.000 claims description 6
- 230000007547 defect Effects 0.000 claims description 5
- 239000004014 plasticizer Substances 0.000 claims description 5
- 239000003963 antioxidant agent Substances 0.000 claims description 4
- 230000003078 antioxidant effect Effects 0.000 claims description 3
- 230000003014 reinforcing effect Effects 0.000 claims description 2
- 239000010419 fine particle Substances 0.000 claims 1
- 230000001737 promoting effect Effects 0.000 claims 1
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 abstract description 42
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 54
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 54
- 230000001965 increasing effect Effects 0.000 description 26
- OKTJSMMVPCPJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N Carbon Chemical compound [C] OKTJSMMVPCPJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 25
- 238000009826 distribution Methods 0.000 description 25
- XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicon Chemical compound [Si] XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 22
- 239000010703 silicon Substances 0.000 description 22
- 229910052710 silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 22
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 description 21
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 description 20
- 239000004519 grease Substances 0.000 description 19
- 230000033001 locomotion Effects 0.000 description 17
- 238000005452 bending Methods 0.000 description 16
- 229910052799 carbon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 15
- PCHJSUWPFVWCPO-UHFFFAOYSA-N gold Chemical compound [Au] PCHJSUWPFVWCPO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 14
- 229910052737 gold Inorganic materials 0.000 description 14
- 239000010931 gold Substances 0.000 description 14
- 210000003205 muscle Anatomy 0.000 description 14
- 230000007423 decrease Effects 0.000 description 11
- 238000004528 spin coating Methods 0.000 description 11
- 239000010409 thin film Substances 0.000 description 11
- NIXOWILDQLNWCW-UHFFFAOYSA-N acrylic acid group Chemical group C(C=C)(=O)O NIXOWILDQLNWCW-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 10
- 239000002861 polymer material Substances 0.000 description 10
- 239000007787 solid Substances 0.000 description 10
- 229920002633 Kraton (polymer) Polymers 0.000 description 9
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 9
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 9
- 230000003287 optical effect Effects 0.000 description 9
- 238000001020 plasma etching Methods 0.000 description 9
- BQCADISMDOOEFD-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silver Chemical compound [Ag] BQCADISMDOOEFD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 8
- 229920002120 photoresistant polymer Polymers 0.000 description 8
- 230000009471 action Effects 0.000 description 7
- 230000008901 benefit Effects 0.000 description 7
- 239000000919 ceramic Substances 0.000 description 7
- 229920001971 elastomer Polymers 0.000 description 7
- 230000006870 function Effects 0.000 description 7
- 239000007789 gas Substances 0.000 description 7
- 239000007788 liquid Substances 0.000 description 7
- 229910052709 silver Inorganic materials 0.000 description 7
- 239000004332 silver Substances 0.000 description 7
- 239000000725 suspension Substances 0.000 description 7
- 239000002033 PVDF binder Substances 0.000 description 6
- 230000004888 barrier function Effects 0.000 description 6
- 239000003795 chemical substances by application Substances 0.000 description 6
- 230000008878 coupling Effects 0.000 description 6
- 238000010168 coupling process Methods 0.000 description 6
- 238000005859 coupling reaction Methods 0.000 description 6
- 238000013461 design Methods 0.000 description 6
- 239000012528 membrane Substances 0.000 description 6
- 239000002480 mineral oil Substances 0.000 description 6
- 235000010446 mineral oil Nutrition 0.000 description 6
- 239000000178 monomer Substances 0.000 description 6
- 239000002245 particle Substances 0.000 description 6
- 229920002635 polyurethane Polymers 0.000 description 6
- 239000004814 polyurethane Substances 0.000 description 6
- 229920002981 polyvinylidene fluoride Polymers 0.000 description 6
- XOJVVFBFDXDTEG-UHFFFAOYSA-N Norphytane Natural products CC(C)CCCC(C)CCCC(C)CCCC(C)C XOJVVFBFDXDTEG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- 239000000853 adhesive Substances 0.000 description 5
- 230000001070 adhesive effect Effects 0.000 description 5
- 239000011230 binding agent Substances 0.000 description 5
- 239000002131 composite material Substances 0.000 description 5
- 239000004020 conductor Substances 0.000 description 5
- 230000003247 decreasing effect Effects 0.000 description 5
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 description 5
- 229910002804 graphite Inorganic materials 0.000 description 5
- 239000010439 graphite Substances 0.000 description 5
- BNIXVQGCZULYKV-UHFFFAOYSA-N pentachloroethane Chemical compound ClC(Cl)C(Cl)(Cl)Cl BNIXVQGCZULYKV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- 229920006254 polymer film Polymers 0.000 description 5
- 239000002904 solvent Substances 0.000 description 5
- 238000005507 spraying Methods 0.000 description 5
- 239000000126 substance Substances 0.000 description 5
- WYURNTSHIVDZCO-UHFFFAOYSA-N Tetrahydrofuran Chemical compound C1CCOC1 WYURNTSHIVDZCO-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- -1 aliphatic acrylates Chemical class 0.000 description 4
- 229910052782 aluminium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 4
- XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N aluminium Chemical compound [Al] XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 239000006229 carbon black Substances 0.000 description 4
- 239000002041 carbon nanotube Substances 0.000 description 4
- 229910021393 carbon nanotube Inorganic materials 0.000 description 4
- 239000003575 carbonaceous material Substances 0.000 description 4
- 238000004891 communication Methods 0.000 description 4
- 230000006378 damage Effects 0.000 description 4
- 239000010408 film Substances 0.000 description 4
- 239000006260 foam Substances 0.000 description 4
- 230000007246 mechanism Effects 0.000 description 4
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 description 4
- 229920003229 poly(methyl methacrylate) Polymers 0.000 description 4
- 229920002959 polymer blend Polymers 0.000 description 4
- 230000002829 reductive effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- 239000005060 rubber Substances 0.000 description 4
- 239000003351 stiffener Substances 0.000 description 4
- 229920000468 styrene butadiene styrene block copolymer Polymers 0.000 description 4
- 238000012546 transfer Methods 0.000 description 4
- 238000004804 winding Methods 0.000 description 4
- 229920002799 BoPET Polymers 0.000 description 3
- 241001070941 Castanea Species 0.000 description 3
- 235000014036 Castanea Nutrition 0.000 description 3
- PEDCQBHIVMGVHV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Glycerine Chemical compound OCC(O)CO PEDCQBHIVMGVHV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- KFZMGEQAYNKOFK-UHFFFAOYSA-N Isopropanol Chemical compound CC(C)O KFZMGEQAYNKOFK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 239000005041 Mylar™ Substances 0.000 description 3
- FACXGONDLDSNOE-UHFFFAOYSA-N buta-1,3-diene;styrene Chemical group C=CC=C.C=CC1=CC=CC=C1.C=CC1=CC=CC=C1 FACXGONDLDSNOE-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 3
- 230000006835 compression Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000007906 compression Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000000151 deposition Methods 0.000 description 3
- 239000002270 dispersing agent Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000000806 elastomer Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000007772 electrode material Substances 0.000 description 3
- 150000002739 metals Chemical class 0.000 description 3
- 238000000059 patterning Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000000206 photolithography Methods 0.000 description 3
- 229920005596 polymer binder Polymers 0.000 description 3
- 239000002491 polymer binding agent Substances 0.000 description 3
- 239000004926 polymethyl methacrylate Substances 0.000 description 3
- 229920001296 polysiloxane Polymers 0.000 description 3
- NLKNQRATVPKPDG-UHFFFAOYSA-M potassium iodide Chemical compound [K+].[I-] NLKNQRATVPKPDG-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 3
- 238000005086 pumping Methods 0.000 description 3
- 229910001285 shape-memory alloy Inorganic materials 0.000 description 3
- 239000002520 smart material Substances 0.000 description 3
- FVAUCKIRQBBSSJ-UHFFFAOYSA-M sodium iodide Chemical compound [Na+].[I-] FVAUCKIRQBBSSJ-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 3
- 229920002725 thermoplastic elastomer Polymers 0.000 description 3
- SMZOUWXMTYCWNB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-(2-methoxy-5-methylphenyl)ethanamine Chemical compound COC1=CC=C(C)C=C1CCN SMZOUWXMTYCWNB-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- DXPPIEDUBFUSEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 6-methylheptyl prop-2-enoate Chemical compound CC(C)CCCCCOC(=O)C=C DXPPIEDUBFUSEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 241001465677 Ancylostomatoidea Species 0.000 description 2
- DKPFZGUDAPQIHT-UHFFFAOYSA-N Butyl acetate Natural products CCCCOC(C)=O DKPFZGUDAPQIHT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000004215 Carbon black (E152) Substances 0.000 description 2
- 241000251730 Chondrichthyes Species 0.000 description 2
- 239000004642 Polyimide Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000004026 adhesive bonding Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000005266 casting Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000012512 characterization method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000011248 coating agent Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000000576 coating method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000007796 conventional method Methods 0.000 description 2
- JHIVVAPYMSGYDF-UHFFFAOYSA-N cyclohexanone Chemical compound O=C1CCCCC1 JHIVVAPYMSGYDF-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 238000011161 development Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000003618 dip coating Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000007598 dipping method Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000000839 emulsion Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000005530 etching Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000012530 fluid Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229920001973 fluoroelastomer Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 230000009477 glass transition Effects 0.000 description 2
- FUZZWVXGSFPDMH-UHFFFAOYSA-N hexanoic acid Chemical compound CCCCCC(O)=O FUZZWVXGSFPDMH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229930195733 hydrocarbon Natural products 0.000 description 2
- 150000002430 hydrocarbons Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- 238000010030 laminating Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229920000126 latex Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 238000013017 mechanical damping Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229920003023 plastic Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 239000004033 plastic Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229920001721 polyimide Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 239000000843 powder Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000002787 reinforcement Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000002441 reversible effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 150000003839 salts Chemical class 0.000 description 2
- HBMJWWWQQXIZIP-UHFFFAOYSA-N silicon carbide Chemical compound [Si+]#[C-] HBMJWWWQQXIZIP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229920002545 silicone oil Polymers 0.000 description 2
- 239000002356 single layer Substances 0.000 description 2
- YLQBMQCUIZJEEH-UHFFFAOYSA-N tetrahydrofuran Natural products C=1C=COC=1 YLQBMQCUIZJEEH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- FHCPAXDKURNIOZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N tetrathiafulvalene Chemical compound S1C=CSC1=C1SC=CS1 FHCPAXDKURNIOZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 238000012876 topography Methods 0.000 description 2
- GOXQRTZXKQZDDN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-Ethylhexyl acrylate Chemical compound CCCCC(CC)COC(=O)C=C GOXQRTZXKQZDDN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- WDQMWEYDKDCEHT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 2-ethylhexyl 2-methylprop-2-enoate Chemical compound CCCCC(CC)COC(=O)C(C)=C WDQMWEYDKDCEHT-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- NQSLZEHVGKWKAY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 6-methylheptyl 2-methylprop-2-enoate Chemical compound CC(C)CCCCCOC(=O)C(C)=C NQSLZEHVGKWKAY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- CUXGDKOCSSIRKK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 7-methyloctyl prop-2-enoate Chemical compound CC(C)CCCCCCOC(=O)C=C CUXGDKOCSSIRKK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- QTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-M Acetate Chemical compound CC([O-])=O QTBSBXVTEAMEQO-UHFFFAOYSA-M 0.000 description 1
- NLZUEZXRPGMBCV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Butylhydroxytoluene Chemical compound CC1=CC(C(C)(C)C)=C(O)C(C(C)(C)C)=C1 NLZUEZXRPGMBCV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 241001092081 Carpenteria Species 0.000 description 1
- LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Ethanol Chemical compound CCO LFQSCWFLJHTTHZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000004606 Fillers/Extenders Substances 0.000 description 1
- PXGOKWXKJXAPGV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Fluorine Chemical compound FF PXGOKWXKJXAPGV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 108010010803 Gelatin Proteins 0.000 description 1
- 239000013032 Hydrocarbon resin Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000004820 Pressure-sensitive adhesive Substances 0.000 description 1
- 241000555745 Sciuridae Species 0.000 description 1
- 239000004809 Teflon Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920006362 Teflon® Polymers 0.000 description 1
- RTAQQCXQSZGOHL-UHFFFAOYSA-N Titanium Chemical compound [Ti] RTAQQCXQSZGOHL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000009825 accumulation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000002253 acid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000003522 acrylic cement Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920006397 acrylic thermoplastic Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 230000003213 activating effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000002998 adhesive polymer Substances 0.000 description 1
- 125000001931 aliphatic group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 230000004075 alteration Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000013459 approach Methods 0.000 description 1
- QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N atomic oxygen Chemical compound [O] QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229920005601 base polymer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 230000006399 behavior Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000002457 bidirectional effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229920001400 block copolymer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000003990 capacitor Substances 0.000 description 1
- OKTJSMMVPCPJKN-YPZZEJLDSA-N carbon-10 atom Chemical compound [10C] OKTJSMMVPCPJKN-YPZZEJLDSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000005119 centrifugation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000013626 chemical specie Substances 0.000 description 1
- 210000004081 cilia Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 238000004140 cleaning Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000002485 combustion reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000013065 commercial product Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000003750 conditioning effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229920001940 conductive polymer Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 238000005336 cracking Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000004132 cross linking Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000013078 crystal Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000001186 cumulative effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000005520 cutting process Methods 0.000 description 1
- FWLDHHJLVGRRHD-UHFFFAOYSA-N decyl prop-2-enoate Chemical compound CCCCCCCCCCOC(=O)C=C FWLDHHJLVGRRHD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000005489 elastic deformation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000005611 electricity Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010894 electron beam technology Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000008030 elimination Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000003379 elimination reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000002708 enhancing effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000007613 environmental effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000000945 filler Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052731 fluorine Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000011737 fluorine Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000446 fuel Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000499 gel Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000008273 gelatin Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920000159 gelatin Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 235000019322 gelatine Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 235000011852 gelatine desserts Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000011521 glass Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000003292 glue Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052736 halogen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 150000002367 halogens Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- LNMQRPPRQDGUDR-UHFFFAOYSA-N hexyl prop-2-enoate Chemical compound CCCCCCOC(=O)C=C LNMQRPPRQDGUDR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229920006270 hydrocarbon resin Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 230000002209 hydrophobic effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000005468 ion implantation Methods 0.000 description 1
- 150000002500 ions Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- PBOSTUDLECTMNL-UHFFFAOYSA-N lauryl acrylate Chemical compound CCCCCCCCCCCCOC(=O)C=C PBOSTUDLECTMNL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000031700 light absorption Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000000873 masking effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000004377 microelectronic Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229920001206 natural gum Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229910001000 nickel titanium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- HLXZNVUGXRDIFK-UHFFFAOYSA-N nickel titanium Chemical compound [Ti].[Ti].[Ti].[Ti].[Ti].[Ti].[Ti].[Ti].[Ti].[Ti].[Ti].[Ni].[Ni].[Ni].[Ni].[Ni].[Ni].[Ni].[Ni].[Ni].[Ni].[Ni].[Ni].[Ni].[Ni] HLXZNVUGXRDIFK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000002736 nonionic surfactant Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000003921 oil Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052760 oxygen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000001301 oxygen Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000004806 packaging method and process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000036961 partial effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000000049 pigment Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920005597 polymer membrane Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920006264 polyurethane film Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 230000002040 relaxant effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000008439 repair process Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000010076 replication Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000011160 research Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000035945 sensitivity Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229910010271 silicon carbide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000004945 silicone rubber Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000009518 sodium iodide Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000007921 spray Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000004544 sputter deposition Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000006467 substitution reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000004381 surface treatment Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000008961 swelling Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000000057 synthetic resin Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920003002 synthetic resin Polymers 0.000 description 1
- ISXSCDLOGDJUNJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N tert-butyl prop-2-enoate Chemical compound CC(C)(C)OC(=O)C=C ISXSCDLOGDJUNJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- PCCVSPMFGIFTHU-UHFFFAOYSA-N tetracyanoquinodimethane Chemical compound N#CC(C#N)=C1C=CC(=C(C#N)C#N)C=C1 PCCVSPMFGIFTHU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- TXEYQDLBPFQVAA-UHFFFAOYSA-N tetrafluoromethane Chemical compound FC(F)(F)F TXEYQDLBPFQVAA-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 230000009466 transformation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000007704 transition Effects 0.000 description 1
- 150000003673 urethanes Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 238000005406 washing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000001039 wet etching Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H02—GENERATION; CONVERSION OR DISTRIBUTION OF ELECTRIC POWER
- H02N—ELECTRIC MACHINES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H02N11/00—Generators or motors not provided for elsewhere; Alleged perpetua mobilia obtained by electric or magnetic means
- H02N11/006—Motors
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F02—COMBUSTION ENGINES; HOT-GAS OR COMBUSTION-PRODUCT ENGINE PLANTS
- F02G—HOT GAS OR COMBUSTION-PRODUCT POSITIVE-DISPLACEMENT ENGINE PLANTS; USE OF WASTE HEAT OF COMBUSTION ENGINES; NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- F02G1/00—Hot gas positive-displacement engine plants
- F02G1/04—Hot gas positive-displacement engine plants of closed-cycle type
- F02G1/043—Hot gas positive-displacement engine plants of closed-cycle type the engine being operated by expansion and contraction of a mass of working gas which is heated and cooled in one of a plurality of constantly communicating expansible chambers, e.g. Stirling cycle type engines
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F04—POSITIVE - DISPLACEMENT MACHINES FOR LIQUIDS; PUMPS FOR LIQUIDS OR ELASTIC FLUIDS
- F04B—POSITIVE-DISPLACEMENT MACHINES FOR LIQUIDS; PUMPS
- F04B35/00—Piston pumps specially adapted for elastic fluids and characterised by the driving means to their working members, or by combination with, or adaptation to, specific driving engines or motors, not otherwise provided for
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F04—POSITIVE - DISPLACEMENT MACHINES FOR LIQUIDS; PUMPS FOR LIQUIDS OR ELASTIC FLUIDS
- F04B—POSITIVE-DISPLACEMENT MACHINES FOR LIQUIDS; PUMPS
- F04B35/00—Piston pumps specially adapted for elastic fluids and characterised by the driving means to their working members, or by combination with, or adaptation to, specific driving engines or motors, not otherwise provided for
- F04B35/04—Piston pumps specially adapted for elastic fluids and characterised by the driving means to their working members, or by combination with, or adaptation to, specific driving engines or motors, not otherwise provided for the means being electric
- F04B35/045—Piston pumps specially adapted for elastic fluids and characterised by the driving means to their working members, or by combination with, or adaptation to, specific driving engines or motors, not otherwise provided for the means being electric using solenoids
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F04—POSITIVE - DISPLACEMENT MACHINES FOR LIQUIDS; PUMPS FOR LIQUIDS OR ELASTIC FLUIDS
- F04B—POSITIVE-DISPLACEMENT MACHINES FOR LIQUIDS; PUMPS
- F04B43/00—Machines, pumps, or pumping installations having flexible working members
- F04B43/02—Machines, pumps, or pumping installations having flexible working members having plate-like flexible members, e.g. diaphragms
- F04B43/04—Pumps having electric drive
- F04B43/043—Micropumps
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H02—GENERATION; CONVERSION OR DISTRIBUTION OF ELECTRIC POWER
- H02N—ELECTRIC MACHINES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H02N2/00—Electric machines in general using piezoelectric effect, electrostriction or magnetostriction
- H02N2/02—Electric machines in general using piezoelectric effect, electrostriction or magnetostriction producing linear motion, e.g. actuators; Linear positioners ; Linear motors
- H02N2/021—Electric machines in general using piezoelectric effect, electrostriction or magnetostriction producing linear motion, e.g. actuators; Linear positioners ; Linear motors using intermittent driving, e.g. step motors, piezoleg motors
- H02N2/023—Inchworm motors
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04R—LOUDSPEAKERS, MICROPHONES, GRAMOPHONE PICK-UPS OR LIKE ACOUSTIC ELECTROMECHANICAL TRANSDUCERS; DEAF-AID SETS; PUBLIC ADDRESS SYSTEMS
- H04R19/00—Electrostatic transducers
- H04R19/02—Loudspeakers
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H10—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES; ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H10N—ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H10N30/00—Piezoelectric or electrostrictive devices
- H10N30/20—Piezoelectric or electrostrictive devices with electrical input and mechanical output, e.g. functioning as actuators or vibrators
- H10N30/204—Piezoelectric or electrostrictive devices with electrical input and mechanical output, e.g. functioning as actuators or vibrators using bending displacement, e.g. unimorph, bimorph or multimorph cantilever or membrane benders
- H10N30/2041—Beam type
- H10N30/2042—Cantilevers, i.e. having one fixed end
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H10—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES; ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H10N—ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H10N30/00—Piezoelectric or electrostrictive devices
- H10N30/20—Piezoelectric or electrostrictive devices with electrical input and mechanical output, e.g. functioning as actuators or vibrators
- H10N30/204—Piezoelectric or electrostrictive devices with electrical input and mechanical output, e.g. functioning as actuators or vibrators using bending displacement, e.g. unimorph, bimorph or multimorph cantilever or membrane benders
- H10N30/2047—Membrane type
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H10—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES; ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H10N—ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H10N30/00—Piezoelectric or electrostrictive devices
- H10N30/20—Piezoelectric or electrostrictive devices with electrical input and mechanical output, e.g. functioning as actuators or vibrators
- H10N30/206—Piezoelectric or electrostrictive devices with electrical input and mechanical output, e.g. functioning as actuators or vibrators using only longitudinal or thickness displacement, e.g. d33 or d31 type devices
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H10—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES; ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H10N—ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H10N30/00—Piezoelectric or electrostrictive devices
- H10N30/30—Piezoelectric or electrostrictive devices with mechanical input and electrical output, e.g. functioning as generators or sensors
- H10N30/308—Membrane type
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H10—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES; ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H10N—ELECTRIC SOLID-STATE DEVICES NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- H10N30/00—Piezoelectric or electrostrictive devices
- H10N30/80—Constructional details
- H10N30/85—Piezoelectric or electrostrictive active materials
- H10N30/857—Macromolecular compositions
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F02—COMBUSTION ENGINES; HOT-GAS OR COMBUSTION-PRODUCT ENGINE PLANTS
- F02G—HOT GAS OR COMBUSTION-PRODUCT POSITIVE-DISPLACEMENT ENGINE PLANTS; USE OF WASTE HEAT OF COMBUSTION ENGINES; NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- F02G2243/00—Stirling type engines having closed regenerative thermodynamic cycles with flow controlled by volume changes
- F02G2243/30—Stirling type engines having closed regenerative thermodynamic cycles with flow controlled by volume changes having their pistons and displacers each in separate cylinders
- F02G2243/50—Stirling type engines having closed regenerative thermodynamic cycles with flow controlled by volume changes having their pistons and displacers each in separate cylinders having resonance tubes
- F02G2243/52—Stirling type engines having closed regenerative thermodynamic cycles with flow controlled by volume changes having their pistons and displacers each in separate cylinders having resonance tubes acoustic
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F05—INDEXING SCHEMES RELATING TO ENGINES OR PUMPS IN VARIOUS SUBCLASSES OF CLASSES F01-F04
- F05C—INDEXING SCHEME RELATING TO MATERIALS, MATERIAL PROPERTIES OR MATERIAL CHARACTERISTICS FOR MACHINES, ENGINES OR PUMPS OTHER THAN NON-POSITIVE-DISPLACEMENT MACHINES OR ENGINES
- F05C2225/00—Synthetic polymers, e.g. plastics; Rubber
- F05C2225/08—Thermoplastics
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F25—REFRIGERATION OR COOLING; COMBINED HEATING AND REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS; HEAT PUMP SYSTEMS; MANUFACTURE OR STORAGE OF ICE; LIQUEFACTION SOLIDIFICATION OF GASES
- F25B—REFRIGERATION MACHINES, PLANTS OR SYSTEMS; COMBINED HEATING AND REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS; HEAT PUMP SYSTEMS
- F25B9/00—Compression machines, plants or systems, in which the refrigerant is air or other gas of low boiling point
- F25B9/14—Compression machines, plants or systems, in which the refrigerant is air or other gas of low boiling point characterised by the cycle used, e.g. Stirling cycle
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04R—LOUDSPEAKERS, MICROPHONES, GRAMOPHONE PICK-UPS OR LIKE ACOUSTIC ELECTROMECHANICAL TRANSDUCERS; DEAF-AID SETS; PUBLIC ADDRESS SYSTEMS
- H04R23/00—Transducers other than those covered by groups H04R9/00 - H04R21/00
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y10—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC
- Y10S—TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y10S310/00—Electrical generator or motor structure
- Y10S310/80—Piezoelectric polymers, e.g. PVDF
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Acoustics & Sound (AREA)
- Combustion & Propulsion (AREA)
- Spectroscopy & Molecular Physics (AREA)
- General Electrical Machinery Utilizing Piezoelectricity, Electrostriction Or Magnetostriction (AREA)
- Micromachines (AREA)
- Reciprocating Pumps (AREA)
- Processes Of Treating Macromolecular Substances (AREA)
- Addition Polymer Or Copolymer, Post-Treatments, Or Chemical Modifications (AREA)
- Polyesters Or Polycarbonates (AREA)
Description
添付の図面に関連して行う以下の説明から、本発明のさらなる特徴および利点が明らかになる。
電気活性ポリマは、電気エネルギによって作動されると変形を生じる。一実施形態において、電気活性ポリマは、2つの電極間の絶縁誘電体として作用し且つ2つの電極間に電圧差を加えると変形するようなポリマを指す。本発明の一態様は、電気エネルギと機械エネルギとの間の変換を改善するようにプリストレインされたポリマに関する。このプリストレインによって、電気活性ポリマの機械応答が、プリストレインされていない電気活性ポリマのそれに比べて改善される。機械応答の改善によって、例えば変形や作動圧力などの、より大きな機械的作用を電気活性ポリマに加えることが可能になる。例えば、本発明によるプリストレインドポリマには、少なくとも約200%の線ひずみと、少なくとも約300%の面ひずみと、を加えることが可能である。このプリストレインは、ポリマの方向によって大きさが異なる。プリストレインの方向による可変性、ポリマを制約する様々な方法、電気活性ポリマのミクロおよびマクロのレベルへの拡張性、そしてポリマの様々な指向方向を組み合わせる(例えば個々のポリマ層を巻いたり積層させたりする)ことによって、電気エネルギを機械的作用に変換させる様々なアクチュエータを実現することが可能になる。このようなアクチュエータは、広い用途において使用することができる。
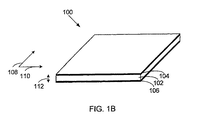
図1Aおよび図1Bは、トランスデューサ100を、本発明の一実施形態にしたがって示した上面図である。トランスデューサ100は、電気エネルギと機械エネルギとの間の変換を行うためのポリマ102を備える。電気活性ポリマ102の上面および下面には、トップ電極104およびボトム電極106がそれぞれ取り付けられており、ポリマ102の一部分に電圧差を提供する。ポリマ102は、トップ電極104およびボトム電極106によって提供される電場の変化によって変形する。電極104,106によって提供される電場の変化に応じたトランスデューサ100の変形は、作動と称される。ポリマ102のサイズが変化するのにともなって、この変形を使用して機械的作用を生じることができる。
プリストレインドポリマの変形を様々な形で使用することによって、機械エネルギを生成または受けることができる。一般に、本発明による電気活性ポリマは、プリストレインドポリマによって改良された従来のアクチュエータおよびジェネレータや、1つまたはそれ以上のプリストレインドポリマのために特別に設計されたカスタムアクチュエータおよびカスタムジェネレータを含む、様々な形のアクチュエータおよびジェネレータにおいて使用して良い。従来のアクチュエータおよびジェネレータは、エクステンダ、曲がり梁、スタック、ダイヤフラム等などを含む。以下では、本発明にしたがった、幾つかの代表的なカスタムアクチュエータおよびジェネレータに関して説明する。
本発明にしたがったトランスデューサは、電気エネルギと機械エネルギとの間でエネルギの変換を行う。トランスデューサの性能は、トランスデューサ自体の観点から見て特徴付けられる。すなわち、アクチュエータにおけるトランスデューサの性能か、または特定の1用途におけるトランスデューサの性能(例えば、1モータ内に実装されたトランスデューサの数)によって特徴付けられて良い。プリストレインされた本発明にしたがった電気活性ポリマによって、トランスデューサの性能は大きく向上される。
上述のように、本発明のトランスデューサは、電気活性ポリマを作動させるための1つ以上の電極を備えることが好ましい。概して、本発明での使用に適した電極は、時間的に一定もしくは変化する適切な電圧を電気活性ポリマに供給し、電気活性ポリマから受け取ることができれば、どのような形態および材料であっても良い。一実施形態では、電極は、ポリマの表面に接着されている。ポリマに接着する電極は、適合性で、ポリマの形状変化に適合することが好ましい。電極は、電気活性ポリマの一部分にのみ適用可能であり、電極の形状にしたがってアクティブ領域を規定する。
本発明は、ミクロおよびマクロスケール両方で、非常に様々なアクチュエータ設計に実装可能なトランスデューサを含むため、本発明は、電気的エネルギと機械的エネルギの変換を必要とする幅広い用途に用いることが可能である。以下は、上述のアクチュエータの一部に関するいくつかの代表的な用途である。一般に、本発明のトランスデューサとアクチュエータは、電気的エネルギと機械的エネルギの変換を必要とする任意の用途に用いることができる。これらの用途は、ロボット工学、センサ、モータ、玩具、マイクロアクチュエータ、ポンプ、ジェネレータなどである。
プリストレインドポリマは、幅広い材料の様々なアクチュエータの設計において、そして多様な用途において、ミクロおよびマクロのスケールの両方で実装可能なため、本発明において使用される製造プロセスも、実に多様である。本発明の一形態は、1つまたはそれ以上のプリストレインポリマを有した電気機械デバイスを製造する方法を提供する。
本発明は、いくつかの好ましい実施形態に即して説明され、簡単のために省略したが、本発明の範囲内の変更、置換、等価物が存在する。例えば、本発明は、様々な多数の応用材料の電極に即して説明されたが、本発明は、これらの材料に限定されず、空気を電極として備える場合もある。さらに、本発明は、特定の性能範囲を持ついくつかの好ましいポリマの材料および形状寸法に即して説明されたが、本発明は、これらの材料および形状寸法に限定されず、挙げられた範囲外の性能を持つ場合もある。したがって、本発明の範囲は、添付の請求項を参照して決定されるべきである。
102 ポリマ
104 トップ電極
106 ボトム電極
108 方向
110 方向
130 ダイヤフラムデバイス
131 プリストレインドポリマ
132 フレーム
133 アパチャ
134 電極
136 電極
137 高さ
139 穴の直径
141 下面側
143 矢印
147 角度
150 テクスチャ加工された表面
152 電気活性ポリマ
154 表面の波
155 方向
156 剛性材料
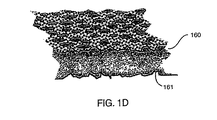
160 電気活性ポリマ
161 粗面
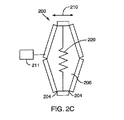
200 バウデバイス
202 フレーム
204 剛体部材
205 ジョイント
206 ポリマ
207 電極
208 方向
210 方向
211 負荷
220 バネ
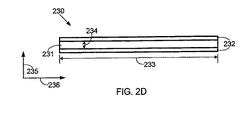
230 直線運動デバイス
231 ポリマ
232 剛体部材
233 長さ
234 幅
235 方向
236 方向
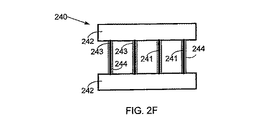
240 多層デバイス
241 プリストレインドポリマ
242 剛性フレーム
243 電極
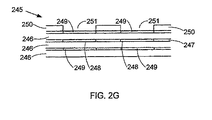
244 電極
245 多層ダイヤフラムデバイス
246 ポリマ層
247 接着層
248 電極
249 電極
250 プレート
251 穴
255 線形アクチュエータ
256 ダイヤフラム
257 出力シャフト
258 アパチャ
259 矢印
260 バネ要素
261 フレーム
262 シャクトリムシ型アクチュエータ
263 ポリマ
264 静電クランプ
265 静電クランプ
266 ボディ
267 接続領域
268 金属面
269 絶縁接着剤
270 伸張膜デバイス
271 剛性フレーム
272 穴
273 プリストレインドポリマ
274 剛体バー
275 電極対
276 電極対
279 ストローク
280 曲がり梁デバイス
282 剛体サポート
281 ポリマ
283 薄膜材料
284 電極
285 電極
286 上面
287 下面
288 自由端
290 曲がり梁デバイス
291 プリストレインドポリマ
292 プリストレインドポリマ
293 電極
294 電極
295 電極
296 剛体サポート
297 半径方向
298 直線方向
299 自由端
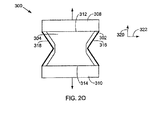
300 デバイス
302 ポリマ
304 電極
308 剛体部材
310 剛体部材
312 エッジ
314 エッジ
316 湾曲部分
318 湾曲部分
320 方向
322 方向
500 ポリマ
501 構造化電極
502 金属トレース
503 電荷分布層
506 適合的な方向
510 プリストレイン
512 金属トレース
514 方向
516 方向
520 テクスチャ加工された電極
521 テクスチャ加工された電極
522 ポリマ
526 方向
540 ダイヤフラムポンプ
542 ダイヤフラムポンプ
544 プリストレインドポリマ
545 フレーム
546 プリストレインドポリマ
547 フレーム
548 穴
550 穴
551 空洞
552 空洞
553 プランジャ
555 1方向バルブ
556 1方向バルブ
558 1方向バルブ
560 曲げバネ
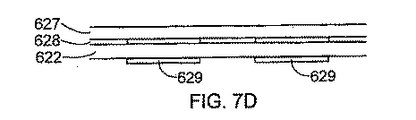
622 プリストレインドポリマ
624 剛体基板
625 電極
626 露出面
627 固形部材
628 接着剤
629 電極
630 電気活性ポリマ層
631 剛体基板
632 接着層
633 電極
634 利用可能な面
635 ポリマ層
636 穴
640 電気機械デバイス
Claims (39)
- 機械エネルギと電気エネルギとの間の変換を行うジェネレータであって、
少なくとも2つの電極と、
第1の部分に加えられた変形に応じて電場の変化を生じるように構成され、弾性的にプリストレインされている、100Mpa未満の弾性率を有する電気活性ポリマと、
を備えるジェネレータ。
- 請求項1記載のジェネレータであって、
前記ジェネレータは、前記変形に先立ってプリストレインされているジェネレータ。
- 請求項2記載のジェネレータであって、
前記少なくとも2つの電極は、前記プリストレインの結果として生じる弾性復元応力よりも小さい電場による応力を前記電気活性ポリマ内に生じさせる電圧を印加するために用いられるジェネレータ。
- 請求項2記載のジェネレータであって、
前記変形は、1方向への収縮であるジェネレータ。
- 請求項4記載のジェネレータであって、
電気エネルギは、前記収縮時に前記少なくとも2つの電極を介して出力されるジェネレータ。
- 請求項1記載のジェネレータであって、さらに、
前記変形を提供する機械的入力を備えるジェネレータ。
- 請求項1記載のジェネレータであって、
前記電気活性ポリマは一定の厚さを有し、前記変形は前記ポリマの前記厚さに垂直な面積の増大を含むジェネレータ。
- 請求項1記載のジェネレータであって、
前記プリストレインは、第1の方向と直交する第2の方向に加えられるプリストレインを超える大きさで前記第1の方向に加えられるジェネレータ。
- 請求項8記載のジェネレータであって、
前記第1の方向に加えられる前記プリストレインは、前記第2の方向への変形から生じる電場の変化を強化させるために使用されるジェネレータ。
- 請求項1記載のジェネレータであって、
前記電気活性ポリマは、シリコンエラストマ、アクリルエラストマ、PVDFコポリマ、およびこれらの組み合わせからなる群より選択される材料を備えるジェネレータ。
- 請求項1記載のジェネレータであって、
前記少なくとも2つの電極の1つは、前記電気活性ポリマの変形に伴って形状を変化させるジェネレータ。
- 請求項1記載のジェネレータであって、さらに、
バイアス圧力が加えられるジェネレータ。
- 請求項1記載のジェネレータであって、
第1の方向への機械エネルギを電気エネルギに変換させ、
前記電気活性ポリマは、前記第1の方向への前記変形に応じて前記電場の変化を生じるように構成され、
前記ジェネレータの前記ポリマに結合され、前記ジェネレータに関して機械エネルギから電気エネルギへの変換を促進させる可撓性フレームと
を備えるジェネレータ。
- 請求項1記載のジェネレータであって、
第1の方向への機械エネルギを電気エネルギに変換させ、
前記電気活性ポリマは、前記第1の方向への前記変形に応じて前記電場の変化を生じるように構成され、
前記ジェネレータに結合され、前記第1の方向と直交する第2の方向への変位を実質的に阻止する少なくとも1つの剛性部材と
を備えるジェネレータ。
- 請求項14記載のジェネレータであって、
前記電気活性ポリマは、ある1方向にだけ別の1方向よりも大きく変形し得るジェネレータ。
- 請求項1記載のジェネレータであって、
前記電気活性ポリマは添加物を含む、
ジェネレータ。
- 請求項16記載のジェネレータであって、
前記添加物は、電気活性ポリマの絶縁破壊強度、最大の線ひずみ、誘電率、弾性率、応答時間、および作動電圧のうち少なくとも1つを改善させるジェネレータ。
- 請求項16記載のジェネレータであって、
前記添加物は、可塑剤、抗酸化剤、高誘電率微粒子のうち少なくとも1つを備えるジェネレータ。
- 請求項16記載のジェネレータであって、
前記添加物は、前記電気活性ポリマの能力のうち、機械エネルギと電気エネルギとの間の変換を行う能力と、接着の能力と、のうちいずれか1つを向上させるジェネレータ。
- 請求項1記載のジェネレータはさらに、
前記電気活性ポリマの1つの少なくとも一部分および前記少なくとも2つの電極に重ね合わされ、前記ポリマおよび/または前記少なくとも2つの電極の1つに機械的に結合された層であって、第1の電極の一部分に積層され、前記第1の電極を外側から機械的に保護する層を備える、ジェネレータ。
- 請求項1記載のジェネレータはさらに、
前記電気活性ポリマの1つの少なくとも一部分および前記少なくとも2つの電極に重ね合わされ、前記ポリマおよび/または前記少なくとも2つの電極の1つに機械的に結合された層であって、変形の最中に、より均一に前記電気活性ポリマに負荷を分布させる層を備える、ジェネレータ。
- 請求項1記載のジェネレータはさらに、
前記電気活性ポリマの1つの少なくとも一部分および前記少なくとも2つの電極に重ね合わされ、前記ポリマおよび/または前記少なくとも2つの電極の1つに機械的に結合された層であって、前記電気活性ポリマよりも大きい剛性を有する層を備える、ジェネレータ。
- 請求項1記載のジェネレータであって、
前記少なくとも2つの電極は第1の電極と前記第2の電極とを備え、
前記電気活性ポリマの1つの少なくとも一部分および前記少なくとも2つの電極に重ね合わされ、前記ポリマおよび/または前記少なくとも2つの電極の1つに機械的に結合された層であって、前記第1および第2の電極の間の部分に積層される層を備える、ジェネレータ。
- 請求項23記載のジェネレータであって、
前記層は、前記ジェネレータの破壊強度を増大させるジェネレータ。
- 請求項1記載のジェネレータはさらに、
前記電気活性ポリマの1つの少なくとも一部分および前記少なくとも2つの電極に重ね合わされ、前記ポリマおよび/または前記少なくとも2つの電極の1つに機械的に結合された層であって、前記電気活性ポリマの製造欠陥を補償するために使用される層を備える、ジェネレータ。
- 請求項1記載のジェネレータはさらに、
前記電気活性ポリマの1つの少なくとも一部分および前記少なくとも2つの電極に重ね合わされ、前記ポリマおよび/または前記少なくとも2つの電極の1つに機械的に結合された層であって、変形の最中におけるポリマの均一性を高める層を備える、ジェネレータ。
- 請求項1記載のジェネレータはさらに、
前記電気活性ポリマの1つの少なくとも一部分および前記少なくとも2つの電極に重ね合わされ、前記ポリマおよび/または前記少なくとも2つの電極の1つに機械的に結合された層であって、前記ジェネレータの機械的性質を改善する補強用の層を備える、ジェネレータ。
- 請求項1記載のジェネレータはさらに、
前記電気活性ポリマの1つの少なくとも一部分および前記少なくとも2つの電極に重ね合わされ、前記ポリマおよび/または前記少なくとも2つの電極の1つに機械的に結合された層を備え、前記層は接着層を使用して接着される、ジェネレータ。
- 請求項1記載のジェネレータであって、
前記電気活性ポリマは巻かれるまたは折られるジェネレータ。
- 請求項29記載のジェネレータであって、
前記少なくとも2つの電極は、接地され外側に露出された電極を含むジェネレータ。
- 電気エネルギと機械エネルギとの間で変換を行うためのデバイスであって、
少なくとも1つの請求項1に記載のジェネレータと、
前記電気活性ポリマの第2の部分に結合され、電気エネルギと機械エネルギとの間の変換を改善させる少なくとも1つの湾曲部分と、
を備えるデバイス。
- 請求項31記載のデバイスであって、さらに、
前記電気活性ポリマの第3の部分に取り付けられた第1の剛性部材と、前記電気活性ポリマの第4の部分に取り付けられた第2の剛性部材と、を備えるデバイス。
- 請求項32記載のデバイスであって、さらに、
電気エネルギと機械エネルギとの間で変換を行うための第2のデバイスを備え、
前記第1および第2の剛性部材は、前記デバイスと前記第2のデバイスとを並列に繋ぐために、前記デバイスを、前記第2のデバイスに機械的に結合する、デバイス。
- 電気エネルギと第1の方向への機械エネルギとの間で変換を行うためのデバイスであって、
少なくとも1つの請求項1に記載のジェネレータと、
前記電気活性ポリマの相対する2面に結合され、前記電気エネルギと前記第1の方向への機械エネルギとの間の変換を改善させる1対の湾曲部分と、
を備えるデバイス。
- 請求項34記載のデバイスであって、
前記1対の湾曲部分は、前記第1の方向と直交する第2の方向へのポリマの変形を前記第1の方向への変位へと結合させるデバイス。
- 電気エネルギと機械エネルギとの間で変換を行うためのデバイスであって、
少なくとも1つの請求項1に記載のジェネレータと、
前記電気活性ポリマの第2の部分に取り付けられ、少なくとも1つの非円形のアパチャを備えたフレームと、
を備え、
前記電極は、前記電気活性ポリマの前記第1の部分に取り付けられるデバイス。
- 請求項36記載のデバイスであって、
前記非円形のアパチャはスロットであるデバイス。
- 請求項36記載のデバイスであって、さらに、
前記電気活性ポリマの下面側にバイアス圧力が加えられるデバイス。
- 機械エネルギと電気エネルギとの間の変換を行うセンサであって、
少なくとも2つの電極と、
第1の部分に加えられた変形に応じて電場の変化を生じるように構成され、弾性的にプリストレインされている、100Mpa未満の弾性率を有する電気活性ポリマと、
を備えるセンサ。
Applications Claiming Priority (15)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US14455699P | 1999-07-20 | 1999-07-20 | |
| US60/144,556 | 1999-07-20 | ||
| US15332999P | 1999-09-10 | 1999-09-10 | |
| US60/153,329 | 1999-09-10 | ||
| US16132599P | 1999-10-25 | 1999-10-25 | |
| US60/161,325 | 1999-10-25 | ||
| US18140400P | 2000-02-09 | 2000-02-09 | |
| US60/181,404 | 2000-02-09 | ||
| US18421700P | 2000-02-23 | 2000-02-23 | |
| US60/184,217 | 2000-02-23 | ||
| US18780900P | 2000-03-08 | 2000-03-08 | |
| US60/187,809 | 2000-03-08 | ||
| US19223700P | 2000-03-27 | 2000-03-27 | |
| US60/192,237 | 2000-03-27 | ||
| PCT/US2000/019951 WO2001006575A1 (en) | 1999-07-20 | 2000-07-20 | Improved electroactive polymers |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2003505865A JP2003505865A (ja) | 2003-02-12 |
| JP2003505865A5 JP2003505865A5 (ja) | 2005-12-22 |
| JP5714200B2 true JP5714200B2 (ja) | 2015-05-07 |
Family
ID=27568972
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2001510924A Expired - Lifetime JP5714200B2 (ja) | 1999-07-20 | 2000-07-20 | 改良電気活性ポリマ |
Country Status (7)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (2) | US7034432B1 (ja) |
| EP (1) | EP1212800B1 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JP5714200B2 (ja) |
| AT (1) | ATE381116T1 (ja) |
| AU (1) | AU6230800A (ja) |
| DE (1) | DE60037433T2 (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2001006575A1 (ja) |
Cited By (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2017154303A1 (ja) * | 2016-03-11 | 2017-09-14 | 株式会社リコー | 非常停止用感圧センサ、安全装置及び安全システム |
| KR20180097743A (ko) * | 2016-01-29 | 2018-08-31 | 가부시키가이샤 리코 | 감압 센서, 파지 장치 및 로봇 |
| US11581823B2 (en) | 2020-02-20 | 2023-02-14 | Toyota Jidosha Kabushiki Kaisha | Actuator and actuator manufacturing method |
| US11601072B2 (en) | 2020-10-12 | 2023-03-07 | Toyota Jidosha Kabushiki Kaisha | Actuator |
| US11730059B2 (en) | 2021-04-12 | 2023-08-15 | Toyota Jidosha Kabushiki Kaisha | Actuator |
| US11824467B2 (en) | 2021-05-21 | 2023-11-21 | Toyota Jidosha Kabushiki Kaisha | Actuator |
| US11825747B2 (en) | 2021-04-12 | 2023-11-21 | Toyota Jidosha Kabushiki Kaisha | Actuator |
| US11888413B2 (en) | 2019-07-22 | 2024-01-30 | Toyota Jidosha Kabushiki Kaisha | Actuator |
Families Citing this family (265)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US7052594B2 (en) | 2002-01-31 | 2006-05-30 | Sri International | Devices and methods for controlling fluid flow using elastic sheet deflection |
| US6812624B1 (en) * | 1999-07-20 | 2004-11-02 | Sri International | Electroactive polymers |
| US7320457B2 (en) | 1997-02-07 | 2008-01-22 | Sri International | Electroactive polymer devices for controlling fluid flow |
| US6586859B2 (en) | 2000-04-05 | 2003-07-01 | Sri International | Electroactive polymer animated devices |
| US6899137B2 (en) * | 1999-06-28 | 2005-05-31 | California Institute Of Technology | Microfabricated elastomeric valve and pump systems |
| US7144616B1 (en) * | 1999-06-28 | 2006-12-05 | California Institute Of Technology | Microfabricated elastomeric valve and pump systems |
| US8550119B2 (en) * | 1999-06-28 | 2013-10-08 | California Institute Of Technology | Microfabricated elastomeric valve and pump systems |
| KR100865105B1 (ko) | 1999-06-28 | 2008-10-24 | 캘리포니아 인스티튜트 오브 테크놀로지 | 마이크로 가공된 탄성중합체 밸브 및 펌프 시스템 |
| US7608989B2 (en) | 1999-07-20 | 2009-10-27 | Sri International | Compliant electroactive polymer transducers for sonic applications |
| WO2001006579A2 (en) * | 1999-07-20 | 2001-01-25 | Sri International | Pre-strained electroactive polymers |
| US6664718B2 (en) | 2000-02-09 | 2003-12-16 | Sri International | Monolithic electroactive polymers |
| US6806621B2 (en) * | 2001-03-02 | 2004-10-19 | Sri International | Electroactive polymer rotary motors |
| US7537197B2 (en) * | 1999-07-20 | 2009-05-26 | Sri International | Electroactive polymer devices for controlling fluid flow |
| ATE381116T1 (de) * | 1999-07-20 | 2007-12-15 | Stanford Res Inst Int | Elektroaktive polymergeneratoren |
| US6264695B1 (en) * | 1999-09-30 | 2001-07-24 | Replication Medical, Inc. | Spinal nucleus implant |
| US6911764B2 (en) | 2000-02-09 | 2005-06-28 | Sri International | Energy efficient electroactive polymers and electroactive polymer devices |
| US6768246B2 (en) | 2000-02-23 | 2004-07-27 | Sri International | Biologically powered electroactive polymer generators |
| WO2002023163A1 (en) | 2000-09-15 | 2002-03-21 | California Institute Of Technology | Microfabricated crossflow devices and methods |
| US7548015B2 (en) * | 2000-11-02 | 2009-06-16 | Danfoss A/S | Multilayer composite and a method of making such |
| US7518284B2 (en) * | 2000-11-02 | 2009-04-14 | Danfoss A/S | Dielectric composite and a method of manufacturing a dielectric composite |
| US8181338B2 (en) | 2000-11-02 | 2012-05-22 | Danfoss A/S | Method of making a multilayer composite |
| DE10054247C2 (de) * | 2000-11-02 | 2002-10-24 | Danfoss As | Betätigungselement und Verfahren zu seiner Herstellung |
| US7166953B2 (en) | 2001-03-02 | 2007-01-23 | Jon Heim | Electroactive polymer rotary clutch motors |
| US6960437B2 (en) | 2001-04-06 | 2005-11-01 | California Institute Of Technology | Nucleic acid amplification utilizing microfluidic devices |
| US7233097B2 (en) | 2001-05-22 | 2007-06-19 | Sri International | Rolled electroactive polymers |
| US7034802B1 (en) * | 2001-08-30 | 2006-04-25 | Palm, Incorporated | Implementation of electronic muscles in a portable computer as user input/output devices |
| US7075162B2 (en) | 2001-08-30 | 2006-07-11 | Fluidigm Corporation | Electrostatic/electrostrictive actuation of elastomer structures using compliant electrodes |
| WO2003031066A1 (en) | 2001-10-11 | 2003-04-17 | California Institute Of Technology | Devices utilizing self-assembled gel and method of manufacture |
| US8440093B1 (en) | 2001-10-26 | 2013-05-14 | Fuidigm Corporation | Methods and devices for electronic and magnetic sensing of the contents of microfluidic flow channels |
| AUPR907101A0 (en) | 2001-11-23 | 2001-12-20 | University Of Wollongong, The | An electromechanical actuator and methods of providing same |
| US7691333B2 (en) | 2001-11-30 | 2010-04-06 | Fluidigm Corporation | Microfluidic device and methods of using same |
| EP1463796B1 (en) | 2001-11-30 | 2013-01-09 | Fluidigm Corporation | Microfluidic device and methods of using same |
| DE60224844T2 (de) | 2001-12-21 | 2009-01-08 | Danfoss A/S | Dielektrisches betätigungsglied oder sensorstruktur und herstellungsverfahren |
| EP1481467B1 (en) * | 2002-03-05 | 2010-06-09 | Sri International | Electroactive polymer devices for controlling fluid flow |
| JP2005522162A (ja) | 2002-03-18 | 2005-07-21 | エスアールアイ インターナショナル | 流体を移動させる電気活性ポリマーデバイス |
| WO2003085379A2 (en) | 2002-04-01 | 2003-10-16 | Fluidigm Corporation | Microfluidic particle-analysis systems |
| US7411331B2 (en) | 2002-05-10 | 2008-08-12 | Massachusetts Institute Of Technology | Dielectric elastomer actuated systems and methods |
| US7362889B2 (en) | 2002-05-10 | 2008-04-22 | Massachusetts Institute Of Technology | Elastomeric actuator devices for magnetic resonance imaging |
| EP1540807B1 (en) * | 2002-09-20 | 2013-01-09 | Danfoss A/S | Elastomer actuator and method of making the actuator |
| US7143785B2 (en) | 2002-09-25 | 2006-12-05 | California Institute Of Technology | Microfluidic large scale integration |
| WO2004040001A2 (en) | 2002-10-02 | 2004-05-13 | California Institute Of Technology | Microfluidic nucleic acid analysis |
| US20040068224A1 (en) * | 2002-10-02 | 2004-04-08 | Couvillon Lucien Alfred | Electroactive polymer actuated medication infusion pumps |
| US20040230090A1 (en) * | 2002-10-07 | 2004-11-18 | Hegde Anant V. | Vascular assist device and methods |
| DE60328913D1 (de) | 2002-12-12 | 2009-10-01 | Danfoss As | Berührungssensorelement und sensorgruppe |
| ES2309502T3 (es) * | 2003-02-24 | 2008-12-16 | Danfoss A/S | Vendaje de compresion elastico electroactivo. |
| WO2004077654A1 (ja) * | 2003-02-28 | 2004-09-10 | Eamex Corporation | アクチュエータ素子 |
| US20050012434A1 (en) * | 2003-03-26 | 2005-01-20 | Continuum Photonics, Inc. | Robust piezoelectric power generation module |
| US7476363B2 (en) | 2003-04-03 | 2009-01-13 | Fluidigm Corporation | Microfluidic devices and methods of using same |
| US7666361B2 (en) | 2003-04-03 | 2010-02-23 | Fluidigm Corporation | Microfluidic devices and methods of using same |
| US20050145496A1 (en) | 2003-04-03 | 2005-07-07 | Federico Goodsaid | Thermal reaction device and method for using the same |
| US7604965B2 (en) | 2003-04-03 | 2009-10-20 | Fluidigm Corporation | Thermal reaction device and method for using the same |
| US8828663B2 (en) | 2005-03-18 | 2014-09-09 | Fluidigm Corporation | Thermal reaction device and method for using the same |
| AU2004240944A1 (en) | 2003-05-20 | 2004-12-02 | Fluidigm Corporation | Method and system for microfluidic device and imaging thereof |
| EP1667829A4 (en) | 2003-07-28 | 2008-12-10 | Fluidigm Corp | IMAGE PROCESSING SYSTEM AND SYSTEM FOR MICROFLUID DEVICES |
| US7413712B2 (en) | 2003-08-11 | 2008-08-19 | California Institute Of Technology | Microfluidic rotary flow reactor matrix |
| US6876125B2 (en) | 2003-08-26 | 2005-04-05 | Delphi Technologies, Inc. | Elastomeric polyphosphazene transducers, methods of making, and methods of use thereof |
| WO2005081676A2 (en) | 2003-08-29 | 2005-09-09 | Sri International | Electroactive polymer pre-strain |
| JP4875982B2 (ja) | 2003-09-03 | 2012-02-15 | エスアールアイ インターナショナル | 表面変形電気活性ポリマートランスデューサ |
| US7557433B2 (en) | 2004-10-25 | 2009-07-07 | Mccain Joseph H | Microelectronic device with integrated energy source |
| JP4038685B2 (ja) * | 2003-12-08 | 2008-01-30 | 独立行政法人科学技術振興機構 | アクチュエータ素子 |
| CN1910810B (zh) * | 2004-02-05 | 2010-04-21 | 松下电器产业株式会社 | 促动器及促动器用平板状电极支撑体的制造方法 |
| WO2005089176A2 (en) * | 2004-03-12 | 2005-09-29 | Sri International | Mechanical meta-materials |
| US7392876B2 (en) * | 2004-06-09 | 2008-07-01 | General Motors Corporation | Hood assembly utilizing active materials based mechanisms |
| JP2008510590A (ja) * | 2004-08-25 | 2008-04-10 | パヴァド・メディカル・インコーポレーテッド | 人工括約筋 |
| FR2875607B1 (fr) * | 2004-09-20 | 2006-11-24 | Cit Alcatel | Miroir a deformation locale par variation d'epaisseur d'un materiau electro-actif controlee par effet electrique |
| KR100616626B1 (ko) * | 2004-10-22 | 2006-08-28 | 삼성전기주식회사 | 고체 전기활성 구동기 및 그 제조방법 |
| WO2007015710A2 (en) * | 2004-11-09 | 2007-02-08 | Board Of Regents, The University Of Texas System | The fabrication and application of nanofiber ribbons and sheets and twisted and non-twisted nanofiber yarns |
| US7844549B2 (en) * | 2005-03-14 | 2010-11-30 | Mark Strickland | File sharing methods and systems |
| US7626319B2 (en) * | 2005-03-21 | 2009-12-01 | Artificial Muscle, Inc. | Three-dimensional electroactive polymer actuated devices |
| US7521840B2 (en) * | 2005-03-21 | 2009-04-21 | Artificial Muscle, Inc. | High-performance electroactive polymer transducers |
| US20070200457A1 (en) * | 2006-02-24 | 2007-08-30 | Heim Jonathan R | High-speed acrylic electroactive polymer transducers |
| US8054566B2 (en) * | 2005-03-21 | 2011-11-08 | Bayer Materialscience Ag | Optical lens displacement systems |
| US7595580B2 (en) * | 2005-03-21 | 2009-09-29 | Artificial Muscle, Inc. | Electroactive polymer actuated devices |
| US7915789B2 (en) | 2005-03-21 | 2011-03-29 | Bayer Materialscience Ag | Electroactive polymer actuated lighting |
| US7521847B2 (en) * | 2005-03-21 | 2009-04-21 | Artificial Muscle, Inc. | High-performance electroactive polymer transducers |
| US7750532B2 (en) * | 2005-03-21 | 2010-07-06 | Artificial Muscle, Inc. | Electroactive polymer actuated motors |
| WO2006121818A2 (en) * | 2005-05-05 | 2006-11-16 | Rodrigo Alvarez Icaza Rivera | Dielectric elastomer fiber transducers |
| CN101053147B (zh) * | 2005-08-05 | 2012-05-02 | 松下电器产业株式会社 | 聚合物驱动器 |
| US7443082B2 (en) | 2006-03-03 | 2008-10-28 | Basf Corporation | Piezoelectric polymer composite article and system |
| US7585122B2 (en) * | 2006-03-15 | 2009-09-08 | Nokia Corporation | Aperture construction for a mobile camera |
| US7538445B2 (en) * | 2006-05-05 | 2009-05-26 | Sri International | Wave powered generation |
| US7557456B2 (en) | 2006-05-05 | 2009-07-07 | Sri International | Wave powered generation using electroactive polymers |
| JP2009539143A (ja) * | 2006-06-01 | 2009-11-12 | ライト レゾナンス テクノロジーズ リミテッド ライアビリティー カンパニー | 光フィルタ/モジュレータ及びフィルタ/モジュレータのアレイ |
| US7554787B2 (en) * | 2006-06-05 | 2009-06-30 | Sri International | Wall crawling devices |
| JP2008087110A (ja) * | 2006-10-02 | 2008-04-17 | Toyota Motor Corp | ロボットの関節構造 |
| US7880371B2 (en) | 2006-11-03 | 2011-02-01 | Danfoss A/S | Dielectric composite and a method of manufacturing a dielectric composite |
| US7732999B2 (en) | 2006-11-03 | 2010-06-08 | Danfoss A/S | Direct acting capacitive transducer |
| WO2008063590A1 (en) * | 2006-11-24 | 2008-05-29 | North Carolina State University | Electroactive nanostructured polymers as tunable organic actuators |
| KR100889752B1 (ko) * | 2006-12-05 | 2009-03-24 | 한국전자통신연구원 | 이종 접합막 및 그의 제조 방법 |
| US7492076B2 (en) * | 2006-12-29 | 2009-02-17 | Artificial Muscle, Inc. | Electroactive polymer transducers biased for increased output |
| FR2911733B1 (fr) * | 2007-01-22 | 2009-02-20 | Siemens Vdo Automotive Sas | Generateur electrique utilisant un polymere electroactif |
| US7508085B2 (en) * | 2007-02-24 | 2009-03-24 | Phillip Reed Martineau | Flexible member energy conversion device |
| US7729068B2 (en) | 2007-02-27 | 2010-06-01 | Konica Minolta Holdings, Inc. | Polymer actuator and optical unit |
| US7977923B2 (en) * | 2007-03-09 | 2011-07-12 | Sri International | Circuits for electroactive polymer generators |
| US7804227B2 (en) * | 2007-03-16 | 2010-09-28 | Sri International | Tear resistant electroactive polymer transducers |
| US8432057B2 (en) * | 2007-05-01 | 2013-04-30 | Pliant Energy Systems Llc | Pliant or compliant elements for harnessing the forces of moving fluid to transport fluid or generate electricity |
| US7696634B2 (en) * | 2007-05-01 | 2010-04-13 | Pliant Energy Systems Llc | Pliant mechanisms for extracting power from moving fluid |
| KR101210116B1 (ko) * | 2007-05-31 | 2012-12-07 | 아트피셜 머슬, 인코퍼레이션 | 유연한 전기활성 물질을 이용한 광학 시스템 |
| JPWO2009001769A1 (ja) * | 2007-06-27 | 2010-08-26 | アルプス電気株式会社 | 電歪アクチュエータモジュール |
| EP2174360A4 (en) | 2007-06-29 | 2013-12-11 | Artificial Muscle Inc | CONVERTER WITH ELECTROACTIVE POLYMER FOR SENSOR REVIEW APPLICATIONS |
| US8076825B1 (en) | 2007-07-12 | 2011-12-13 | Louisiana Tech University Foundation, Inc. | Electret film generator |
| US8354774B2 (en) | 2007-08-17 | 2013-01-15 | Kuraray Co., Ltd. | Dielectric material for polymeric actuator, and polymeric actuator using the same |
| US9370640B2 (en) | 2007-09-12 | 2016-06-21 | Novasentis, Inc. | Steerable medical guide wire device |
| CN101743782A (zh) * | 2007-09-19 | 2010-06-16 | 富士电机控股株式会社 | 色变换滤光片、以及色变换滤光片和有机el显示器的制造方法 |
| US20090092807A1 (en) * | 2007-10-09 | 2009-04-09 | The Hong Kong Polytechnic University | Two-way shape memory composite polymer and methods of making |
| JP5247123B2 (ja) * | 2007-11-15 | 2013-07-24 | 豊田合成株式会社 | アクチュエータ |
| SG186011A1 (en) * | 2007-11-21 | 2012-12-28 | Artificial Muscle Inc | Electroactive polymer transducers for tactile feedback devices |
| DE102007059858A1 (de) * | 2007-12-12 | 2009-06-18 | Bayer Materialscience Ag | Energiewandler hergestellt aus filmbildenden wässrigen Polymer-Dispersionen, insbesondere Polyurethan-Dispersionen |
| US8851442B2 (en) * | 2008-01-22 | 2014-10-07 | Honeywell International Inc. | Aerogel-bases mold for MEMS fabrication and formation thereof |
| US20090259093A1 (en) * | 2008-04-14 | 2009-10-15 | Bhat Nikhil D | Artificial sphincter with piezoelectric actuator |
| FR2931548B1 (fr) * | 2008-05-26 | 2010-06-18 | Continental Automotive France | Procede de determination de la hauteur de caisse d'un vehicule automobile |
| US8120195B2 (en) * | 2008-07-23 | 2012-02-21 | Single Buoy Moorings, Inc. | Wave energy converter |
| EP2154167A1 (de) | 2008-07-30 | 2010-02-17 | Bayer MaterialScience AG | Elektromechanischer Wandler mit einem Polymerelement auf Polyisocyanat-Basis |
| WO2010020960A1 (en) | 2008-08-20 | 2010-02-25 | Braun Gmbh | Electro-polymer motor |
| DE202009001086U1 (de) * | 2009-01-29 | 2009-04-30 | Gröger, Achim | Künstlicher Muskel |
| FR2936650B1 (fr) * | 2008-09-26 | 2011-03-11 | Commissariat Energie Atomique | Transducteur a polymere electroactif |
| EP2182559A1 (de) * | 2008-10-30 | 2010-05-05 | Bayer MaterialScience AG | Energiewandler auf Basis von Polyurethan-Lösungen |
| US8222799B2 (en) * | 2008-11-05 | 2012-07-17 | Bayer Materialscience Ag | Surface deformation electroactive polymer transducers |
| EP2239793A1 (de) | 2009-04-11 | 2010-10-13 | Bayer MaterialScience AG | Elektrisch schaltbarer Polymerfilmaufbau und dessen Verwendung |
| EP2282048A1 (de) | 2009-07-02 | 2011-02-09 | Bayer MaterialScience AG | Verfahren Gewinnung von elektrischer Energie aus der Bewegungsenergie von Wasserwellen |
| WO2011005123A1 (en) | 2009-07-07 | 2011-01-13 | Auckland Uniservices Limited | Transformer and priming circuit therefor |
| EP2280034A1 (de) | 2009-07-31 | 2011-02-02 | Bayer MaterialScience AG | Elektromechanischer Wandler mit einem Polymerelement auf Basis einer Mischung aus Polyisocyanat und Isocyanat-funktionellem Prepolymer und einer Verbindung mit mindestens zwei isocyanatreaktiven Hydroxygruppen |
| US20110032103A1 (en) * | 2009-08-07 | 2011-02-10 | Bhat Nikhil | Motion detection system |
| TWI388813B (zh) * | 2009-08-31 | 2013-03-11 | Universal Cement Corp | 壓力感測器以及具有壓力感測器之拳擊機 |
| JP5558876B2 (ja) | 2009-09-18 | 2014-07-23 | 東海ゴム工業株式会社 | 誘電膜、およびその製造方法、並びにそれを用いたトランスデューサ |
| DE102009054035A1 (de) | 2009-11-20 | 2011-05-26 | Robert Bosch Gmbh | Energietransformer mit elektroaktivem Polymerfolienkörper |
| EP2330649A1 (de) * | 2009-12-04 | 2011-06-08 | Bayer MaterialScience AG | Elektromechanischer Wandler, umfassend ein Polyurethanpolymer mit Polytetramethylenglykolether-Einheiten |
| DE102009059024A1 (de) | 2009-12-18 | 2011-06-22 | Robert Bosch GmbH, 70469 | Energietransformer mit elektroaktivem Polymer |
| US8325458B2 (en) | 2010-02-10 | 2012-12-04 | Sri International | Electroadhesive gripping |
| JP5729701B2 (ja) * | 2010-02-18 | 2015-06-03 | 高圧ガス工業株式会社 | 複合誘電体素子 |
| US8193655B2 (en) * | 2010-03-10 | 2012-06-05 | Allan Roberts | System for converting ocean wave energy to electric power |
| WO2011113883A1 (en) | 2010-03-17 | 2011-09-22 | Bayer Materialscience Ag | Statistic analysis of audio signals for generation of discernable feedback |
| US9401668B2 (en) * | 2010-03-19 | 2016-07-26 | Sri International | Materials for electroadhesion and electrolaminates |
| DE102010034313A1 (de) | 2010-03-24 | 2011-09-29 | J. Eberspächer GmbH & Co. KG | Haltevorrichtung |
| KR101095024B1 (ko) * | 2010-04-27 | 2011-12-20 | 한국과학기술연구원 | 고분자 복합체 액츄에이터 |
| TWI485896B (zh) * | 2010-05-06 | 2015-05-21 | Hon Hai Prec Ind Co Ltd | 電致動結構及電致動元件 |
| EP2400573A1 (de) | 2010-06-23 | 2011-12-28 | Bayer MaterialScience AG | Elektromechanischer Wandler, Verfahren zu dessen Herstellung und Verwendung desselben |
| EP2416205A1 (de) | 2010-08-04 | 2012-02-08 | Bayer MaterialScience AG | Schaltbare Lummer-Gehrcke-Platte |
| EP2416111A1 (de) | 2010-08-04 | 2012-02-08 | Bayer MaterialScience AG | Schaltbares optisches Element für ein Interferometer |
| EP2416206A1 (de) | 2010-08-04 | 2012-02-08 | Bayer MaterialScience AG | Schaltbares Interferometer |
| EP2416207A1 (de) | 2010-08-04 | 2012-02-08 | Bayer MaterialScience AG | Schaltbares optisches Modulationssystem |
| CN103119075B (zh) | 2010-08-09 | 2014-12-10 | 拜耳知识产权有限责任公司 | 包含具有聚酯和/或聚碳酸酯单元的聚氨酯聚合物的机电转换器 |
| EP2418231A1 (de) | 2010-08-09 | 2012-02-15 | Bayer MaterialScience AG | Elektromechanischer Wandler, umfassend ein Polyurethanpolymer mit Polycarbonat-Einheiten |
| EP2418230A1 (de) | 2010-08-09 | 2012-02-15 | Bayer MaterialScience AG | Elektromechanischer Wandler, umfassend ein Polyurethanpolymer mit Polyester-Einheiten |
| US20120050335A1 (en) * | 2010-08-25 | 2012-03-01 | Universal Cement Corporation | Zooming system for a display |
| WO2012055436A1 (en) | 2010-10-27 | 2012-05-03 | Advanced Bionics Ag | Implantable actuator for hearing stimulation |
| KR101703281B1 (ko) * | 2010-12-07 | 2017-02-06 | 삼성전자주식회사 | 다층 전기활성 폴리머 디바이스 및 그 제조방법 |
| EP2468496A1 (de) * | 2010-12-22 | 2012-06-27 | Bayer MaterialScience AG | Umhüllter Artikel |
| EP2662558A3 (en) | 2011-01-10 | 2015-01-14 | Benjamin Filardo | Mechanisms for creating undulating motion, such as for propulsion and for harnessing the energy of moving fluid |
| WO2012118916A2 (en) * | 2011-03-01 | 2012-09-07 | Bayer Materialscience Ag | Automated manufacturing processes for producing deformable polymer devices and films |
| CN103563236A (zh) * | 2011-03-09 | 2014-02-05 | 拜耳知识产权有限责任公司 | 电活性聚合物能量转换器 |
| CN103703404A (zh) | 2011-03-22 | 2014-04-02 | 拜耳知识产权有限责任公司 | 电活化聚合物致动器双凸透镜系统 |
| WO2012129541A2 (en) | 2011-03-23 | 2012-09-27 | Sri International | Active electroadhesive cleaning |
| US20120248942A1 (en) | 2011-04-01 | 2012-10-04 | Bayer Materialscience Ag | Electromechanical converter, method for its production and use thereof |
| EP2506325A1 (de) | 2011-04-01 | 2012-10-03 | Bayer Material Science AG | Elektromechanischer Wandler, Verfahren zu dessen Herstellung und Verwendung desselben |
| EP2509127A1 (de) | 2011-04-07 | 2012-10-10 | Bayer Material Science AG | Verwendung von thermoplastischen Polyurethanen zur Wandlung von mechanischer Energie in elektrische Energie |
| EP2509126A1 (de) | 2011-04-07 | 2012-10-10 | Bayer Material Science AG | Verwendung von thermoplastischen Polyurethanen zur Erzeugung elektrischer Energie aus Wellenenergie |
| EP2511314A1 (de) | 2011-04-12 | 2012-10-17 | Bayer MaterialScience AG | Polyurethanpolymer und dessen Verwendung in elektromechanischen Wandlern |
| EP2511352A1 (de) | 2011-04-13 | 2012-10-17 | Bayer Materialscience AG | Siebdruckverfahren mit zu einem Polyurethanpolymer reagierender Drucktinte |
| US8749081B2 (en) * | 2011-05-09 | 2014-06-10 | Phillip Reed Martineau | Moving fluid energy conversion device |
| CN103535053B (zh) | 2011-05-17 | 2017-03-29 | 株式会社村田制作所 | 平面型扬声器以及av设备 |
| DE102011077583A1 (de) * | 2011-06-16 | 2012-12-20 | Robert Bosch Gmbh | Relativverschiebung erleichternde Oberflächen bei EAP-Generatoren |
| DK2757950T3 (da) | 2011-09-22 | 2020-02-10 | Region Nordjylland Aalborg Sygehus | Fremgangsmåde, indretning og computerprogram til bestemmelse af strækværdier |
| US20130186699A1 (en) | 2012-01-23 | 2013-07-25 | Sri International | High voltage converters for electrostatic applications |
| TW201343699A (zh) | 2012-02-01 | 2013-11-01 | 拜耳智慧財產有限公司 | 包含具有聚酯單元及/或聚碳酸酯單元之聚胺基甲酸酯之機電轉換器 |
| US8692442B2 (en) | 2012-02-14 | 2014-04-08 | Danfoss Polypower A/S | Polymer transducer and a connector for a transducer |
| US8891222B2 (en) | 2012-02-14 | 2014-11-18 | Danfoss A/S | Capacitive transducer and a method for manufacturing a transducer |
| JP5308603B1 (ja) * | 2012-02-15 | 2013-10-09 | バンドー化学株式会社 | 圧電素子、アクチュエータ素子、アクチュエータ、発電素子、発電デバイス及び可撓性シート |
| US9048761B1 (en) * | 2012-03-06 | 2015-06-02 | The United States Of America As Represented By The Secretary Of The Navy | Energy harvesting device using auxetic materials |
| DE102012212222B4 (de) * | 2012-03-12 | 2018-05-30 | Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft zur Förderung der angewandten Forschung e.V. | Dielektrisches Elastomer auf Fluorosilicon-Basis und Verfahren zu seiner Herstellung |
| JP5946299B2 (ja) * | 2012-03-13 | 2016-07-06 | 国立大学法人信州大学 | コロッサル誘電性を持つゲル状ポリマーデバイス及びその製造方法 |
| EP2828901B1 (en) | 2012-03-21 | 2017-01-04 | Parker Hannifin Corporation | Roll-to-roll manufacturing processes for producing self-healing electroactive polymer devices |
| CN103946927A (zh) * | 2012-03-29 | 2014-07-23 | 东海橡塑工业株式会社 | 导电性组合物和导电膜 |
| US20130300571A1 (en) * | 2012-04-18 | 2013-11-14 | Farrokh Mohamadi | Interrogation of active and passive proppants for real-time monitoring of fractured wells |
| WO2013166329A2 (en) | 2012-05-02 | 2013-11-07 | Sri International | Electroadhesive handling and manipulation |
| WO2013166317A2 (en) | 2012-05-02 | 2013-11-07 | Sri International | Handling and sorting materials using electroadhesion |
| US9735706B2 (en) * | 2012-05-10 | 2017-08-15 | Single Buoy Moorings Inc. | Method and system for harvesting energy using an EAP based deformable body |
| DE102012208557A1 (de) | 2012-05-22 | 2013-11-28 | Robert Bosch Gmbh | Generatoren aus elektroaktiven Polymeren (EAP) in Differenzanordnung |
| EP2856527A4 (en) * | 2012-06-01 | 2016-05-04 | Univ Syddansk | ULTRASONIC TRANSDUCER USING DIELECTRIC ELASTOMER AS ACTIVE LAYER |
| JP5916950B2 (ja) | 2012-06-11 | 2016-05-11 | エスアールアイ インターナショナルSRI International | 電気吸着表面クリーナ |
| KR20150031285A (ko) | 2012-06-18 | 2015-03-23 | 바이엘 인텔렉쳐 프로퍼티 게엠베하 | 연신 공정을 위한 연신 프레임 |
| US9705068B2 (en) | 2012-06-19 | 2017-07-11 | Novasentis, Inc. | Ultra-thin inertial actuator |
| KR20150023462A (ko) | 2012-06-27 | 2015-03-05 | 바이엘 머티리얼사이언스 아게 | 유전체 폴리우레탄 필름 |
| JP2015533671A (ja) | 2012-07-03 | 2015-11-26 | バイエル・マテリアルサイエンス・アクチェンゲゼルシャフトBayer MaterialScience AG | 多層誘電性ポリウレタンフィルム系を製造するための方法 |
| US9183710B2 (en) | 2012-08-03 | 2015-11-10 | Novasentis, Inc. | Localized multimodal electromechanical polymer transducers |
| DE102012016378B4 (de) * | 2012-08-13 | 2020-06-18 | Technische Universität Dresden | Dielektrischer Elastomeraktor und Verfahren zu seiner Herstellung |
| CA2885228C (en) | 2012-09-17 | 2021-07-20 | President And Fellows Of Harvard College | Soft exosuit for assistance with human motion |
| CN205129876U (zh) | 2012-10-12 | 2016-04-06 | Sri国际公司 | 电粘附性抓持系统 |
| WO2014059325A1 (en) | 2012-10-12 | 2014-04-17 | Sri International | Vacuum augmented electroadhesive device |
| WO2014066576A1 (en) | 2012-10-24 | 2014-05-01 | Bayer Intellectual Property Gmbh | Polymer diode |
| US9851708B2 (en) * | 2012-11-06 | 2017-12-26 | Koninklijke Philips N.V. | Sensor for moving equipment |
| US9269885B2 (en) | 2012-11-21 | 2016-02-23 | Novasentis, Inc. | Method and localized haptic response system provided on an interior-facing surface of a housing of an electronic device |
| US9053617B2 (en) | 2012-11-21 | 2015-06-09 | Novasentis, Inc. | Systems including electromechanical polymer sensors and actuators |
| US9357312B2 (en) | 2012-11-21 | 2016-05-31 | Novasentis, Inc. | System of audio speakers implemented using EMP actuators |
| US9164586B2 (en) | 2012-11-21 | 2015-10-20 | Novasentis, Inc. | Haptic system with localized response |
| US9170650B2 (en) | 2012-11-21 | 2015-10-27 | Novasentis, Inc. | EMP actuators for deformable surface and keyboard application |
| US20150319514A1 (en) | 2012-12-07 | 2015-11-05 | Roger N. Hitchcock | Electroactive polymer actuated aperture |
| US10329393B2 (en) | 2012-12-12 | 2019-06-25 | Eastman Chemical Company | Copolysters plasticized with polymeric plasticizer for shrink film applications |
| DE102012024333B4 (de) * | 2012-12-13 | 2022-11-03 | Festo Se & Co. Kg | Ventileinrichtung |
| US10088936B2 (en) * | 2013-01-07 | 2018-10-02 | Novasentis, Inc. | Thin profile user interface device and method providing localized haptic response |
| JP6047405B2 (ja) * | 2013-01-08 | 2016-12-21 | 住友理工株式会社 | バルブ |
| TW201502859A (zh) | 2013-01-28 | 2015-01-16 | Bayer Materialscience Ag | 電活性聚合物致動器及其回饋系統 |
| EP2954568B1 (en) * | 2013-02-07 | 2017-01-04 | Danfoss A/S | All compliant electrode |
| WO2014131895A1 (de) | 2013-02-28 | 2014-09-04 | Bayer Materialscience Ag | Verfahren zur herstellung eines mehrschichtigen dielektrischen polyurethanfilmsystems |
| WO2015020698A2 (en) | 2013-03-15 | 2015-02-12 | Bayer Materialscience Ag | Electroactive polymer actuated air flow thermal management module |
| WO2014160757A2 (en) | 2013-03-26 | 2014-10-02 | Bayer Materialscience Ag | Independent tunig of audio devices employing electroactive polymer actuators |
| WO2014194257A1 (en) | 2013-05-31 | 2014-12-04 | President And Fellows Of Harvard College | Soft exosuit for assistance with human motion |
| CN103280523B (zh) * | 2013-06-18 | 2015-03-25 | 厦门乃尔电子有限公司 | 高温压电元件电极制作方法及压电元件结构 |
| US9142754B2 (en) * | 2013-07-12 | 2015-09-22 | Novasentis, Inc. | Electromechanical polymer-based linear resonant actuator |
| US10125758B2 (en) | 2013-08-30 | 2018-11-13 | Novasentis, Inc. | Electromechanical polymer pumps |
| US9833596B2 (en) | 2013-08-30 | 2017-12-05 | Novasentis, Inc. | Catheter having a steerable tip |
| US9507468B2 (en) | 2013-08-30 | 2016-11-29 | Novasentis, Inc. | Electromechanical polymer-based sensor |
| JP6343618B2 (ja) | 2013-10-01 | 2018-06-13 | 住友理工株式会社 | 搬送装置 |
| JP6037039B2 (ja) * | 2013-10-08 | 2016-11-30 | 株式会社村田製作所 | 触覚提示装置 |
| US9666391B2 (en) | 2013-10-22 | 2017-05-30 | Novasentis, Inc. | Retractable snap domes |
| DE102013222553B4 (de) * | 2013-11-06 | 2018-02-08 | Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt e.V. | Verfahren zur Herstellung von elektroaktiven Polymeraktuatoren |
| EP4104757B1 (en) | 2013-12-09 | 2024-10-02 | President and Fellows of Harvard College | Assistive flexible suits, flexible suit systems, and methods for making and control thereof to assist human mobility |
| US10278883B2 (en) | 2014-02-05 | 2019-05-07 | President And Fellows Of Harvard College | Systems, methods, and devices for assisting walking for developmentally-delayed toddlers |
| WO2015142911A1 (en) | 2014-03-17 | 2015-09-24 | Grabit, Inc. | Electroadhesive gripping system with smart brake and metering |
| WO2015157731A1 (en) | 2014-04-10 | 2015-10-15 | President And Fellows Of Harvard College | Orthopedic device including protruding members |
| WO2015164264A1 (en) | 2014-04-21 | 2015-10-29 | Grabit, Inc. | Automated item handling with reconfigurable totes |
| WO2015166700A1 (ja) * | 2014-04-30 | 2015-11-05 | 株式会社 村田製作所 | 導電パターン付絶縁基材 |
| US9652946B2 (en) | 2014-05-02 | 2017-05-16 | Novasentis, Inc. | Hands-free, wearable vibration devices and method |
| EP3143061A1 (de) | 2014-05-12 | 2017-03-22 | Covestro Deutschland AG | Dielektrische eap folien mit niedrigem glaspunkt auf der basis von polyesterpolyolen |
| DE102014212939A1 (de) | 2014-07-03 | 2016-01-07 | Robert Bosch Gmbh | Vorrichtung und Verfahren zum Gewinnen von elektrischer Nutzleistung |
| KR101988876B1 (ko) * | 2014-07-15 | 2019-06-13 | 전자부품연구원 | 액체를 이용한 전극 적층 구조 에너지 전환 장치 |
| US9951757B2 (en) * | 2014-07-31 | 2018-04-24 | Battelle Memorial Institute | Increased force generation in electroactive polymers |
| US9576446B2 (en) | 2014-08-07 | 2017-02-21 | Novasentis, Inc. | Ultra-thin haptic switch with lighting |
| US9972768B2 (en) | 2014-08-15 | 2018-05-15 | Novasentis, Inc. | Actuator structure and method |
| JP2016046953A (ja) * | 2014-08-25 | 2016-04-04 | ソニー株式会社 | トランスデューサおよび電子機器 |
| WO2016089466A2 (en) | 2014-09-19 | 2016-06-09 | President And Fellows Of Harvard College | Soft exosuit for assistance with human motion |
| EP3037449A1 (de) | 2014-12-22 | 2016-06-29 | Covestro Deutschland AG | Dipol-modifiziertes Polyurethan, Verfahren zu dessen Herstellung und Verwendung zur Herstellung von elektroaktiven Polyurethan-basierten Gießelastomerfolien |
| US11278455B2 (en) * | 2014-12-29 | 2022-03-22 | ElastiMed Ltd. | Methods for maintaining an electro-active polymer in a pre-stretch state |
| EP3041059B1 (en) * | 2014-12-31 | 2019-09-11 | LG Display Co., Ltd. | Multilayer actuator and display device comprising the same |
| US10119532B2 (en) * | 2015-02-16 | 2018-11-06 | Hamilton Sundstrand Corporation | System and method for cooling electrical components using an electroactive polymer actuator |
| RU2705647C2 (ru) * | 2015-03-31 | 2019-11-11 | Конинклейке Филипс Н.В. | Исполнительное или сенсорное устройство на основе электроактивного полимера |
| JP6547674B2 (ja) | 2015-05-15 | 2019-07-24 | 信越化学工業株式会社 | 光硬化性組成物及びこれを含む硬化物 |
| US9773969B2 (en) | 2015-05-28 | 2017-09-26 | The Board Of Trustees Of The Leland Stanford Junior University | Electrostrictive element manufacturing method |
| US10020440B2 (en) | 2015-05-28 | 2018-07-10 | Honda Motor Co., Ltd. | Electrostrictive element and manufacturing method therefor |
| US10020439B2 (en) | 2015-05-28 | 2018-07-10 | Honda Motor Co., Ltd. | Electrostrictive element |
| US9871183B2 (en) | 2015-05-28 | 2018-01-16 | The Board Of Trustees Of The Leland Stanford Junior University | Electrostrictive element |
| EP3098248A1 (de) | 2015-05-29 | 2016-11-30 | Covestro Deutschland AG | Polymeres, nicht angebundenes additiv zur erhöhung der dielektrizitätskonstante in elektroaktiven polyurethan polymeren |
| EP3344872B1 (en) * | 2015-08-31 | 2019-06-19 | Koninklijke Philips N.V. | Actuator or sensor device based on an electroactive or photoactive polymer |
| MX2018008580A (es) | 2016-01-12 | 2019-09-02 | Grabit Inc | Metodos y sistemas para la manipulacion basada en la electroadhesion y la liberacion mecanica en la fabricacion. |
| US11590046B2 (en) | 2016-03-13 | 2023-02-28 | President And Fellows Of Harvard College | Flexible members for anchoring to the body |
| DE102016208515A1 (de) | 2016-05-18 | 2017-11-23 | Bayerische Motoren Werke Aktiengesellschaft | Anbauelement, System und Verfahren zur Herstellung eines Anbauelements |
| US10190570B1 (en) | 2016-06-30 | 2019-01-29 | Pliant Energy Systems Llc | Traveling wave propeller, pump and generator apparatuses, methods and systems |
| US10519926B2 (en) | 2016-06-30 | 2019-12-31 | Pliant Energy Systems Llc | Traveling wave propeller, pump and generator apparatuses, methods and systems |
| US11795900B2 (en) | 2016-06-30 | 2023-10-24 | Pliant Energy Systems Llc | Vehicle with traveling wave thrust module apparatuses, methods and systems |
| US11209022B2 (en) | 2016-06-30 | 2021-12-28 | Pliant Energy Systems Llc | Vehicle with traveling wave thrust module apparatuses, methods and systems |
| US11498203B2 (en) | 2016-07-22 | 2022-11-15 | President And Fellows Of Harvard College | Controls optimization for wearable systems |
| DE102016213816B4 (de) * | 2016-07-27 | 2018-06-07 | Fraunhofer-Gesellschaft zur Förderung der angewandten Forschung e.V. | Vorrichtung und Verfahren zur Umwandlung der kinetischen Energie eines strömenden Mediums in elektrische Energie |
| JP6300865B2 (ja) * | 2016-08-09 | 2018-03-28 | バンドー化学株式会社 | トランスデューサ用可撓性シート |
| DE102016009832A1 (de) * | 2016-08-15 | 2018-02-15 | Drägerwerk AG & Co. KGaA | Fluidisches Stellglied, insbesondere Ventil, und Verfahren zum Betrieb eines fluidischen Stellglieds |
| WO2018124308A1 (ja) * | 2016-12-29 | 2018-07-05 | ソニー株式会社 | アクチュエータおよびその製造方法 |
| US11014804B2 (en) | 2017-03-14 | 2021-05-25 | President And Fellows Of Harvard College | Systems and methods for fabricating 3D soft microstructures |
| GB2565078B (en) * | 2017-07-31 | 2020-05-20 | Camlin Tech Limited | Hybrid switching device and hybrid actuator incorporating same |
| DE102018218637B3 (de) * | 2018-10-31 | 2020-02-20 | Festo Ag & Co. Kg | Elektroaktive Polymeraktuatoreinrichtung |
| US20210384408A1 (en) * | 2018-10-31 | 2021-12-09 | Seiki Chiba | Dielectric elastomer transducer |
| JP2020080633A (ja) * | 2018-11-14 | 2020-05-28 | 株式会社デンソー | アクチュエータ装置およびそのアクチュエータ装置の製造方法 |
| WO2020190732A1 (en) * | 2019-03-15 | 2020-09-24 | Massachusetts Institute Of Technology | Microscale and nanoscale structured electromechanical transducers employing compliant dielectric spacers |
| CN110757434B (zh) * | 2019-11-06 | 2022-06-24 | 中国科学院宁波材料技术与工程研究所 | 基于介电弹性体与可调刚度智能流体的人工肌肉及其制法 |
| DE102020203830A1 (de) | 2020-03-25 | 2021-09-30 | Te Connectivity Germany Gmbh | Aktuationsvorrichtung, insbesondere für ein Relais |
| US11827459B2 (en) | 2020-10-16 | 2023-11-28 | Artimus Robotics Inc. | Control of conveyor systems using hydraulically amplified self-healing electrostatic (HASEL) actuators |
| US11353009B1 (en) | 2021-03-30 | 2022-06-07 | Toyota Motor Engineering & Manufacturing North America, Inc. | Intermuscular ridged boards for artificial muscle devices under heavy lift conditions |
Family Cites Families (64)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US444372A (en) * | 1891-01-06 | Pipe-wrench | ||
| DE1967130C2 (de) * | 1968-01-25 | 1982-04-01 | Pioneer Electronic Corp., Tokyo | Mechanisch-elektrisch bzw. elektrisch-mechanischer Wandler |
| JPS5318893B2 (ja) * | 1971-12-03 | 1978-06-17 | ||
| US3816774A (en) * | 1972-01-28 | 1974-06-11 | Victor Company Of Japan | Curved piezoelectric elements |
| FR2409654B1 (fr) | 1977-11-17 | 1985-10-04 | Thomson Csf | Dispositif transducteur piezoelectrique et son procede de fabrication |
| JPS5569902A (en) * | 1978-11-21 | 1980-05-27 | Kureha Chemical Ind Co Ltd | Preparing piezoelectric* electrically scorchable film |
| FR2477822A1 (fr) * | 1980-03-04 | 1981-09-11 | Thomson Csf | Transducteur electromecanique a suspension active et son procede de fabrication |
| US4342936A (en) * | 1980-12-19 | 1982-08-03 | Eastman Kodak Company | High deflection bandwidth product polymeric piezoelectric flexure mode device and method of making same |
| FR2511570A1 (fr) * | 1981-08-11 | 1983-02-18 | Thomson Csf | Transducteur electroacoustique a polymere piezoelectrique |
| US4877988A (en) | 1982-03-01 | 1989-10-31 | Battelle Memorial Institute | Piezoelectric and pyroelectric polymers |
| US4442372A (en) | 1982-11-22 | 1984-04-10 | Walton Energy Systems Co. | Piezo electric apparatus for generating electricity |
| JPS59126689A (ja) | 1983-01-10 | 1984-07-21 | Toshio Sugita | 太陽熱機関と圧電素子による高電圧発生装置 |
| US4609845A (en) * | 1984-07-06 | 1986-09-02 | Raychem Corporation | Stretched piezoelectric polymer coaxial cable |
| JPS6247179A (ja) * | 1985-08-27 | 1987-02-28 | Asahi Chem Ind Co Ltd | 圧電性フイルムおよびその製造方法 |
| JPH0632549B2 (ja) * | 1986-03-31 | 1994-04-27 | 日本特殊陶業株式会社 | 圧電送受波器 |
| DE3618106A1 (de) | 1986-05-30 | 1987-12-03 | Siemens Ag | Piezoelektrisch betriebene fluidpumpe |
| US4733121A (en) | 1986-10-14 | 1988-03-22 | Hebert Alvin J | Solid state heat to electricity converter |
| US4868447A (en) | 1987-09-11 | 1989-09-19 | Cornell Research Foundation, Inc. | Piezoelectric polymer laminates for torsional and bending modal control |
| FR2657552B1 (fr) * | 1990-01-30 | 1994-10-21 | Elf Aquitaine | Procede et dispositif de decoupe d'un ensemble multicouche constitue d'une pluralite de couches minces. |
| US5229979A (en) | 1990-12-14 | 1993-07-20 | Rutgers, The State University Of New Jersey | Electrostrictive driving device, process for sonic wave projection and polymer materials for use therein |
| JPH04353279A (ja) | 1991-05-30 | 1992-12-08 | Mitsubishi Materials Corp | 圧電ダイヤフラムポンプ |
| JPH05202707A (ja) | 1992-01-29 | 1993-08-10 | Suzuki Motor Corp | エンジンの動弁装置 |
| US5356500A (en) * | 1992-03-20 | 1994-10-18 | Rutgers, The State University Of New Jersey | Piezoelectric laminate films and processes for their manufacture |
| US5430565A (en) * | 1992-06-02 | 1995-07-04 | Fuji Photo Film Co., Ltd. | Uniaxially stretched negative birefringent film and liquid crystal display having the same |
| US5678571A (en) | 1994-05-23 | 1997-10-21 | Raya Systems, Inc. | Method for treating medical conditions using a microprocessor-based video game |
| US5913310A (en) | 1994-05-23 | 1999-06-22 | Health Hero Network, Inc. | Method for diagnosis and treatment of psychological and emotional disorders using a microprocessor-based video game |
| AU6235094A (en) | 1993-02-12 | 1994-08-29 | Ohio University | Microminiature stirling cycle cryocoolers and engines |
| US5642015A (en) | 1993-07-14 | 1997-06-24 | The University Of British Columbia | Elastomeric micro electro mechanical systems |
| US5835453A (en) | 1993-07-20 | 1998-11-10 | The United States Of America As Represented By The Secretary Of The Navy | Electrostrictive acoustic projector and polymers used therein |
| US5377258A (en) | 1993-08-30 | 1994-12-27 | National Medical Research Council | Method and apparatus for an automated and interactive behavioral guidance system |
| JPH07111785A (ja) | 1993-10-13 | 1995-04-25 | Toshiba Corp | ワイヤレスアクチュエータ |
| US5660176A (en) | 1993-12-29 | 1997-08-26 | First Opinion Corporation | Computerized medical diagnostic and treatment advice system |
| US5869189A (en) * | 1994-04-19 | 1999-02-09 | Massachusetts Institute Of Technology | Composites for structural control |
| US5440194A (en) * | 1994-05-13 | 1995-08-08 | Beurrier; Henry R. | Piezoelectric actuators |
| GB9410658D0 (en) | 1994-05-27 | 1994-07-13 | Electrosols Ltd | Dispensing device |
| JP3545414B2 (ja) | 1994-07-29 | 2004-07-21 | ミネソタ マイニング アンド マニュファクチャリング カンパニー | 架橋結合された粘弾性高分子材料に硬化可能なシロップ |
| US5751090A (en) * | 1995-05-17 | 1998-05-12 | Burleigh Instruments Inc | Peristaltic driver apparatus |
| US5703474A (en) | 1995-10-23 | 1997-12-30 | Ocean Power Technologies | Power transfer of piezoelectric generated energy |
| US5977685A (en) | 1996-02-15 | 1999-11-02 | Nitta Corporation | Polyurethane elastomer actuator |
| WO1997036365A1 (en) * | 1996-03-26 | 1997-10-02 | Stefan Johansson | An actuator motor and a method for fabrication of such an actuator |
| US6812624B1 (en) * | 1999-07-20 | 2004-11-02 | Sri International | Electroactive polymers |
| US6543110B1 (en) * | 1997-02-07 | 2003-04-08 | Sri International | Electroactive polymer fabrication |
| US6545384B1 (en) * | 1997-02-07 | 2003-04-08 | Sri International | Electroactive polymer devices |
| US6781284B1 (en) * | 1997-02-07 | 2004-08-24 | Sri International | Electroactive polymer transducers and actuators |
| US6376971B1 (en) * | 1997-02-07 | 2002-04-23 | Sri International | Electroactive polymer electrodes |
| US6060811A (en) | 1997-07-25 | 2000-05-09 | The United States Of America As Represented By The United States National Aeronautics And Space Administration | Advanced layered composite polylaminate electroactive actuator and sensor |
| WO1999007997A1 (en) | 1997-08-11 | 1999-02-18 | Massachusetts Institute Of Technology | Conducting polymer driven rotary motor |
| WO1999017929A1 (en) | 1997-10-03 | 1999-04-15 | The Trustees Of The University Of Pennsylvania | Polymeric electrostrictive systems |
| RU2150170C1 (ru) | 1997-10-30 | 2000-05-27 | Нунупаров Мартын Сергеевич | Способ питания электронной системы и устройство для его осуществления |
| US6682500B2 (en) * | 1998-01-29 | 2004-01-27 | David Soltanpour | Synthetic muscle based diaphragm pump apparatuses |
| US6249076B1 (en) | 1998-04-14 | 2001-06-19 | Massachusetts Institute Of Technology | Conducting polymer actuator |
| US6165126A (en) | 1998-08-14 | 2000-12-26 | Scientific Learning Corporation | Remediation of depression through computer-implemented interactive behavioral training |
| US6184608B1 (en) | 1998-12-29 | 2001-02-06 | Honeywell International Inc. | Polymer microactuator array with macroscopic force and displacement |
| ATE381116T1 (de) * | 1999-07-20 | 2007-12-15 | Stanford Res Inst Int | Elektroaktive polymergeneratoren |
| DE19952062A1 (de) | 1999-10-28 | 2000-05-04 | Michael Johannes Jensen | Rauschenergieumwandler |
| JP3501216B2 (ja) | 2000-03-31 | 2004-03-02 | 慶和 劉 | 電歪伸縮材を利用した駆動装置 |
| DE10054246C2 (de) | 2000-11-02 | 2002-09-26 | Danfoss As | Betätigungselement |
| DE10054247C2 (de) | 2000-11-02 | 2002-10-24 | Danfoss As | Betätigungselement und Verfahren zu seiner Herstellung |
| DE60224844T2 (de) | 2001-12-21 | 2009-01-08 | Danfoss A/S | Dielektrisches betätigungsglied oder sensorstruktur und herstellungsverfahren |
| AU2002351735A1 (en) | 2001-12-21 | 2003-07-15 | Danfoss A/S | Position sensor comprising elastomeric material |
| EP1540807B1 (en) | 2002-09-20 | 2013-01-09 | Danfoss A/S | Elastomer actuator and method of making the actuator |
| DE60328913D1 (de) | 2002-12-12 | 2009-10-01 | Danfoss As | Berührungssensorelement und sensorgruppe |
| ES2309502T3 (es) | 2003-02-24 | 2008-12-16 | Danfoss A/S | Vendaje de compresion elastico electroactivo. |
| WO2004074797A1 (en) | 2003-02-24 | 2004-09-02 | Danfoss A/S | Structure for shear force sensing |
-
2000
- 2000-07-20 AT AT00948873T patent/ATE381116T1/de not_active IP Right Cessation
- 2000-07-20 US US09/619,848 patent/US7034432B1/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2000-07-20 JP JP2001510924A patent/JP5714200B2/ja not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2000-07-20 WO PCT/US2000/019951 patent/WO2001006575A1/en active IP Right Grant
- 2000-07-20 AU AU62308/00A patent/AU6230800A/en not_active Abandoned
- 2000-07-20 DE DE60037433T patent/DE60037433T2/de not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2000-07-20 EP EP00948873A patent/EP1212800B1/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
-
2006
- 2006-01-24 US US11/339,078 patent/US7368862B2/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
Cited By (13)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US10442091B2 (en) | 2016-01-29 | 2019-10-15 | Ricoh Company, Ltd. | Pressure-sensitive sensor, gripping device, and robot |
| KR20180097743A (ko) * | 2016-01-29 | 2018-08-31 | 가부시키가이샤 리코 | 감압 센서, 파지 장치 및 로봇 |
| KR102176966B1 (ko) * | 2016-01-29 | 2020-11-10 | 가부시키가이샤 리코 | 감압 센서, 파지 장치 및 로봇 |
| JPWO2017130591A1 (ja) * | 2016-01-29 | 2018-10-18 | 株式会社リコー | 感圧センサ、把持装置及びロボット |
| US11534929B2 (en) | 2016-03-11 | 2022-12-27 | Ricoh Company, Ltd. | Emergency stop pressure sensor, safety device, and safety system |
| JPWO2017154303A1 (ja) * | 2016-03-11 | 2018-09-20 | 株式会社リコー | 非常停止用感圧センサ、安全装置及び安全システム |
| WO2017154303A1 (ja) * | 2016-03-11 | 2017-09-14 | 株式会社リコー | 非常停止用感圧センサ、安全装置及び安全システム |
| US11888413B2 (en) | 2019-07-22 | 2024-01-30 | Toyota Jidosha Kabushiki Kaisha | Actuator |
| US11581823B2 (en) | 2020-02-20 | 2023-02-14 | Toyota Jidosha Kabushiki Kaisha | Actuator and actuator manufacturing method |
| US11601072B2 (en) | 2020-10-12 | 2023-03-07 | Toyota Jidosha Kabushiki Kaisha | Actuator |
| US11730059B2 (en) | 2021-04-12 | 2023-08-15 | Toyota Jidosha Kabushiki Kaisha | Actuator |
| US11825747B2 (en) | 2021-04-12 | 2023-11-21 | Toyota Jidosha Kabushiki Kaisha | Actuator |
| US11824467B2 (en) | 2021-05-21 | 2023-11-21 | Toyota Jidosha Kabushiki Kaisha | Actuator |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP1212800A4 (en) | 2004-09-15 |
| US7368862B2 (en) | 2008-05-06 |
| EP1212800A1 (en) | 2002-06-12 |
| JP2003505865A (ja) | 2003-02-12 |
| EP1212800B1 (en) | 2007-12-12 |
| DE60037433D1 (de) | 2008-01-24 |
| WO2001006575A1 (en) | 2001-01-25 |
| AU6230800A (en) | 2001-02-05 |
| US7034432B1 (en) | 2006-04-25 |
| US20060238066A1 (en) | 2006-10-26 |
| DE60037433T2 (de) | 2008-12-04 |
| ATE381116T1 (de) | 2007-12-15 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5714200B2 (ja) | 改良電気活性ポリマ | |
| JP5937044B2 (ja) | トランスデューサ、アクチュエータ、及び、トランスデューサを製造する方法 | |
| US7049732B2 (en) | Electroactive polymers | |
| US6545384B1 (en) | Electroactive polymer devices | |
| US6781284B1 (en) | Electroactive polymer transducers and actuators | |
| US6583533B2 (en) | Electroactive polymer electrodes | |
| US6543110B1 (en) | Electroactive polymer fabrication | |
| JP5512834B2 (ja) | 電気活性ポリマーの予歪み |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20041110 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20070710 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20110621 |
|
| A601 | Written request for extension of time |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A601 Effective date: 20110920 |
|
| A602 | Written permission of extension of time |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A602 Effective date: 20110929 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20111219 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20120814 |
|
| A601 | Written request for extension of time |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A601 Effective date: 20121113 |
|
| A602 | Written permission of extension of time |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A602 Effective date: 20121217 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20130213 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A821 Effective date: 20130213 |
|
| A02 | Decision of refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A02 Effective date: 20130820 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20131220 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A821 Effective date: 20131225 |
|
| A911 | Transfer to examiner for re-examination before appeal (zenchi) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A911 Effective date: 20140319 |
|
| A912 | Re-examination (zenchi) completed and case transferred to appeal board |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A912 Effective date: 20140516 |
|
| A601 | Written request for extension of time |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A601 Effective date: 20141218 |
|
| A602 | Written permission of extension of time |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A602 Effective date: 20141224 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20150116 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20150311 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 5714200 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| EXPY | Cancellation because of completion of term |