EP3551446B1 - Sackherstellvorrichtung und verfahren - Google Patents
Sackherstellvorrichtung und verfahren Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP3551446B1 EP3551446B1 EP17828860.1A EP17828860A EP3551446B1 EP 3551446 B1 EP3551446 B1 EP 3551446B1 EP 17828860 A EP17828860 A EP 17828860A EP 3551446 B1 EP3551446 B1 EP 3551446B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- bag
- film
- welding
- sack
- longitudinal section
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 title claims description 24
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title claims description 16
- 238000003466 welding Methods 0.000 claims description 106
- 238000005520 cutting process Methods 0.000 claims description 60
- 238000003860 storage Methods 0.000 claims description 8
- 230000004308 accommodation Effects 0.000 claims 1
- 239000003795 chemical substances by application Substances 0.000 description 7
- 238000007789 sealing Methods 0.000 description 6
- 239000011888 foil Substances 0.000 description 5
- 239000013590 bulk material Substances 0.000 description 4
- 239000002245 particle Substances 0.000 description 4
- 235000013305 food Nutrition 0.000 description 3
- 230000006835 compression Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000007906 compression Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000011161 development Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000018109 developmental process Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000006073 displacement reaction Methods 0.000 description 2
- 208000031872 Body Remains Diseases 0.000 description 1
- 241000252254 Catostomidae Species 0.000 description 1
- 241000196324 Embryophyta Species 0.000 description 1
- WQZGKKKJIJFFOK-GASJEMHNSA-N Glucose Natural products OC[C@H]1OC(O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1O WQZGKKKJIJFFOK-GASJEMHNSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229920002472 Starch Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 239000004809 Teflon Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920006362 Teflon® Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 230000003213 activating effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 235000008452 baby food Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 230000001351 cycling effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000001419 dependent effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000008121 dextrose Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000428 dust Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000945 filler Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000005429 filling process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000834 fixative Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000012212 insulator Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000013336 milk Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 239000008267 milk Substances 0.000 description 1
- 210000004080 milk Anatomy 0.000 description 1
- 230000003287 optical effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000000843 powder Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000003825 pressing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000007787 solid Substances 0.000 description 1
- 125000006850 spacer group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 239000008107 starch Substances 0.000 description 1
- 235000019698 starch Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 238000002604 ultrasonography Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000011144 upstream manufacturing Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B31—MAKING ARTICLES OF PAPER, CARDBOARD OR MATERIAL WORKED IN A MANNER ANALOGOUS TO PAPER; WORKING PAPER, CARDBOARD OR MATERIAL WORKED IN A MANNER ANALOGOUS TO PAPER
- B31B—MAKING CONTAINERS OF PAPER, CARDBOARD OR MATERIAL WORKED IN A MANNER ANALOGOUS TO PAPER
- B31B70/00—Making flexible containers, e.g. envelopes or bags
- B31B70/14—Cutting, e.g. perforating, punching, slitting or trimming
- B31B70/16—Cutting webs
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B65—CONVEYING; PACKING; STORING; HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL
- B65B—MACHINES, APPARATUS OR DEVICES FOR, OR METHODS OF, PACKAGING ARTICLES OR MATERIALS; UNPACKING
- B65B43/00—Forming, feeding, opening or setting-up containers or receptacles in association with packaging
- B65B43/04—Forming flat bags from webs
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B31—MAKING ARTICLES OF PAPER, CARDBOARD OR MATERIAL WORKED IN A MANNER ANALOGOUS TO PAPER; WORKING PAPER, CARDBOARD OR MATERIAL WORKED IN A MANNER ANALOGOUS TO PAPER
- B31B—MAKING CONTAINERS OF PAPER, CARDBOARD OR MATERIAL WORKED IN A MANNER ANALOGOUS TO PAPER
- B31B50/00—Making rigid or semi-rigid containers, e.g. boxes or cartons
- B31B50/14—Cutting, e.g. perforating, punching, slitting or trimming
- B31B50/16—Cutting webs
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B31—MAKING ARTICLES OF PAPER, CARDBOARD OR MATERIAL WORKED IN A MANNER ANALOGOUS TO PAPER; WORKING PAPER, CARDBOARD OR MATERIAL WORKED IN A MANNER ANALOGOUS TO PAPER
- B31B—MAKING CONTAINERS OF PAPER, CARDBOARD OR MATERIAL WORKED IN A MANNER ANALOGOUS TO PAPER
- B31B70/00—Making flexible containers, e.g. envelopes or bags
- B31B70/006—Controlling; Regulating; Measuring; Safety measures
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B31—MAKING ARTICLES OF PAPER, CARDBOARD OR MATERIAL WORKED IN A MANNER ANALOGOUS TO PAPER; WORKING PAPER, CARDBOARD OR MATERIAL WORKED IN A MANNER ANALOGOUS TO PAPER
- B31B—MAKING CONTAINERS OF PAPER, CARDBOARD OR MATERIAL WORKED IN A MANNER ANALOGOUS TO PAPER
- B31B70/00—Making flexible containers, e.g. envelopes or bags
- B31B70/02—Feeding or positioning sheets, blanks or webs
- B31B70/10—Feeding or positioning webs
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B31—MAKING ARTICLES OF PAPER, CARDBOARD OR MATERIAL WORKED IN A MANNER ANALOGOUS TO PAPER; WORKING PAPER, CARDBOARD OR MATERIAL WORKED IN A MANNER ANALOGOUS TO PAPER
- B31B—MAKING CONTAINERS OF PAPER, CARDBOARD OR MATERIAL WORKED IN A MANNER ANALOGOUS TO PAPER
- B31B70/00—Making flexible containers, e.g. envelopes or bags
- B31B70/60—Uniting opposed surfaces or edges; Taping
- B31B70/64—Uniting opposed surfaces or edges; Taping by applying heat or pressure
- B31B70/642—Uniting opposed surfaces or edges; Taping by applying heat or pressure using sealing jaws or sealing dies
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B31—MAKING ARTICLES OF PAPER, CARDBOARD OR MATERIAL WORKED IN A MANNER ANALOGOUS TO PAPER; WORKING PAPER, CARDBOARD OR MATERIAL WORKED IN A MANNER ANALOGOUS TO PAPER
- B31B—MAKING CONTAINERS OF PAPER, CARDBOARD OR MATERIAL WORKED IN A MANNER ANALOGOUS TO PAPER
- B31B70/00—Making flexible containers, e.g. envelopes or bags
- B31B70/60—Uniting opposed surfaces or edges; Taping
- B31B70/64—Uniting opposed surfaces or edges; Taping by applying heat or pressure
- B31B70/645—Making seals transversally to the direction of movement
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B65—CONVEYING; PACKING; STORING; HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL
- B65B—MACHINES, APPARATUS OR DEVICES FOR, OR METHODS OF, PACKAGING ARTICLES OR MATERIALS; UNPACKING
- B65B1/00—Packaging fluent solid material, e.g. powders, granular or loose fibrous material, loose masses of small articles, in individual containers or receptacles, e.g. bags, sacks, boxes, cartons, cans, or jars
- B65B1/02—Machines characterised by the incorporation of means for making the containers or receptacles
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B65—CONVEYING; PACKING; STORING; HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL
- B65B—MACHINES, APPARATUS OR DEVICES FOR, OR METHODS OF, PACKAGING ARTICLES OR MATERIALS; UNPACKING
- B65B1/00—Packaging fluent solid material, e.g. powders, granular or loose fibrous material, loose masses of small articles, in individual containers or receptacles, e.g. bags, sacks, boxes, cartons, cans, or jars
- B65B1/04—Methods of, or means for, filling the material into the containers or receptacles
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B65—CONVEYING; PACKING; STORING; HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL
- B65B—MACHINES, APPARATUS OR DEVICES FOR, OR METHODS OF, PACKAGING ARTICLES OR MATERIALS; UNPACKING
- B65B41/00—Supplying or feeding container-forming sheets or wrapping material
- B65B41/12—Feeding webs from rolls
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B65—CONVEYING; PACKING; STORING; HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL
- B65B—MACHINES, APPARATUS OR DEVICES FOR, OR METHODS OF, PACKAGING ARTICLES OR MATERIALS; UNPACKING
- B65B51/00—Devices for, or methods of, sealing or securing package folds or closures; Devices for gathering or twisting wrappers, or necks of bags
- B65B51/10—Applying or generating heat or pressure or combinations thereof
- B65B51/26—Devices specially adapted for producing transverse or longitudinal seams in webs or tubes
- B65B51/30—Devices, e.g. jaws, for applying pressure and heat, e.g. for subdividing filled tubes
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B65—CONVEYING; PACKING; STORING; HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL
- B65B—MACHINES, APPARATUS OR DEVICES FOR, OR METHODS OF, PACKAGING ARTICLES OR MATERIALS; UNPACKING
- B65B61/00—Auxiliary devices, not otherwise provided for, for operating on sheets, blanks, webs, binding material, containers or packages
- B65B61/005—Auxiliary devices, not otherwise provided for, for operating on sheets, blanks, webs, binding material, containers or packages for removing material by cutting
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B65—CONVEYING; PACKING; STORING; HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL
- B65D—CONTAINERS FOR STORAGE OR TRANSPORT OF ARTICLES OR MATERIALS, e.g. BAGS, BARRELS, BOTTLES, BOXES, CANS, CARTONS, CRATES, DRUMS, JARS, TANKS, HOPPERS, FORWARDING CONTAINERS; ACCESSORIES, CLOSURES, OR FITTINGS THEREFOR; PACKAGING ELEMENTS; PACKAGES
- B65D31/00—Bags or like containers made of paper and having structural provision for thickness of contents
- B65D31/10—Bags or like containers made of paper and having structural provision for thickness of contents with gusseted sides
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B31—MAKING ARTICLES OF PAPER, CARDBOARD OR MATERIAL WORKED IN A MANNER ANALOGOUS TO PAPER; WORKING PAPER, CARDBOARD OR MATERIAL WORKED IN A MANNER ANALOGOUS TO PAPER
- B31B—MAKING CONTAINERS OF PAPER, CARDBOARD OR MATERIAL WORKED IN A MANNER ANALOGOUS TO PAPER
- B31B2155/00—Flexible containers made from webs
- B31B2155/003—Flexible containers made from webs starting from tubular webs
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B31—MAKING ARTICLES OF PAPER, CARDBOARD OR MATERIAL WORKED IN A MANNER ANALOGOUS TO PAPER; WORKING PAPER, CARDBOARD OR MATERIAL WORKED IN A MANNER ANALOGOUS TO PAPER
- B31B—MAKING CONTAINERS OF PAPER, CARDBOARD OR MATERIAL WORKED IN A MANNER ANALOGOUS TO PAPER
- B31B2160/00—Shape of flexible containers
- B31B2160/20—Shape of flexible containers with structural provision for thickness of contents
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B31—MAKING ARTICLES OF PAPER, CARDBOARD OR MATERIAL WORKED IN A MANNER ANALOGOUS TO PAPER; WORKING PAPER, CARDBOARD OR MATERIAL WORKED IN A MANNER ANALOGOUS TO PAPER
- B31B—MAKING CONTAINERS OF PAPER, CARDBOARD OR MATERIAL WORKED IN A MANNER ANALOGOUS TO PAPER
- B31B70/00—Making flexible containers, e.g. envelopes or bags
- B31B70/14—Cutting, e.g. perforating, punching, slitting or trimming
- B31B70/148—Cutting-out portions from the sides of webs or sheets
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B65—CONVEYING; PACKING; STORING; HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL
- B65B—MACHINES, APPARATUS OR DEVICES FOR, OR METHODS OF, PACKAGING ARTICLES OR MATERIALS; UNPACKING
- B65B1/00—Packaging fluent solid material, e.g. powders, granular or loose fibrous material, loose masses of small articles, in individual containers or receptacles, e.g. bags, sacks, boxes, cartons, cans, or jars
- B65B1/20—Reducing volume of filled material
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B65—CONVEYING; PACKING; STORING; HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL
- B65B—MACHINES, APPARATUS OR DEVICES FOR, OR METHODS OF, PACKAGING ARTICLES OR MATERIALS; UNPACKING
- B65B51/00—Devices for, or methods of, sealing or securing package folds or closures; Devices for gathering or twisting wrappers, or necks of bags
- B65B51/10—Applying or generating heat or pressure or combinations thereof
- B65B51/14—Applying or generating heat or pressure or combinations thereof by reciprocating or oscillating members
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a sack manufacturing device and a method for manufacturing open-mouth sacks and open-mouth sacks manufactured therewith.
- a bag-making device is used in particular on or for an FFS system (Form-Fill-Seal) in order to produce the open-mouth bags required for filling bulk goods into open-mouth bags on site. It is also possible to produce sacks in advance with the sack manufacturing device according to the invention and to store them temporarily for later use.
- FFS system Form-Fill-Seal
- foodstuffs are filled into the open-mouth bags produced.
- Powdered foodstuffs such as milk powder, dextrose, starch, etc., are particularly preferably filled into the open-mouth bags.
- high hygienic standards must be observed.
- dirt particles as possible should be able to adhere to sacks filled with food.
- a tubular film In the production of open-mouth bags, a tubular film is usually used, which is transported in one transport direction. At a bottom seam welding station, a bottom seam is first introduced into the tubular film. The tubular film is then indexed by one sack length and the next bottom seam is introduced into the tubular film, while at the same time just below the tubular film is cut through at the bottom seam, creating the first open sack. The open-mouth bag is then filled with the product from above and the head end is welded using a welding device.
- the process works in principle, but has the disadvantage that there is at least a small overhang of the film at the bottom seam.
- the two layers of the excess film together form a receiving space or several receiving spaces or cavities on or in which dirt particles or the bulk material to be filled can become lodged, so that perfect hygiene conditions are not present.
- Another possibility is to use a second bottom seam welding station later in the transport direction, in addition to the first bottom seam welding station, which welds the excess film together.
- this increases the effort considerably and also reduces the performance of the system.
- EP 0 844 070 A1 , the DE 24 59 725 A1 and the WO 2011/037528 A1 disclose known methods for producing containers from film tubes.
- the bag-making device serves to produce open-mouth bags and includes a storage device with a supply of bag film.
- a control device is used for control.
- at least one transport device is provided for transporting the sack film and/or the sack body along a (predefined) transport path.
- At least) one welding device with welding means is provided for introducing (at least) one bottom seam into the sack film.
- at least) one cutting device is provided with (at least) one cutting means for cutting off a predetermined film length of the sack film to form a sack body of an open sack.
- the control device is set up and designed to control the transport device in such a way that a relative movement of the sack body and the sack film relative to one another is effected and a distance is created between the sack body and the sack film before the bottom seam is introduced.
- the control device is set up and designed to control the transport device and the welding means in such a way that the welding means extend beyond the bottom end in the longitudinal direction of the sack film of the sack body during welding, with the cutting means being in the same longitudinal section as the welding means when cutting.
- the longitudinal section defined by a length of the welding agent along the transport path.
- the cutting means is arranged and effective at least when cutting the sack film within a longitudinal section of the transport path in which (longitudinal section) the welding means are arranged and effective during welding.
- the bag making device according to the invention has many advantages.
- a significant advantage of the bag-making device according to the invention is that the welding means extend at least to the bottom end of the bag body when welding the bottom seam. This can be ensured by the cutting means being in the same longitudinal section as the welding means when cutting.
- the or at least one transport device ensures that there is a distance between the sack body and the sack film during the welding, which distance prevents the front end of the sack film from being welded.
- the bag film is preferably moved back in order to produce the (predetermined) distance after cutting and before welding.
- the cutting device and the welding device are arranged and effective in an overlapping longitudinal section of the transport track.
- an edge-tight weld is particularly preferably achieved. This can be ensured in that the welding means protrude beyond the end of the film and thus weld the film up to and including the bottom end.
- the bag body is fully welded within the bottom seam up to the bottom end. Then there are not two layers of film sticking out at the end, on which and between which dust can accumulate. In this way, a weld seam is produced without an external film overhang.
- the (separated) sack body to be moved further by the (predetermined) distance (along the transport path) relative to the sack film, while the sack film z. B. is not moved forward. Then the sack body is advanced by the predetermined distance until the bottom end reaches the welding means and during welding an edge-tight weld of the bottom seam or a full-surface bottom seam extending to the bottom end of the sack body is produced.
- the desired distance between the sack body and the sack film is created by a relative movement of the sack body and the sack film relative to one another before the bottom seam is introduced. This free space is so large that the front end of the sack film is not sealed.
- the distance is in particular greater than 2 mm and preferably greater than 5 mm or 10 mm.
- the distance can also be larger and z. B. 15 mm or 20 mm or 30 mm or 300 mm or 500 mm or more. In principle, the distance is arbitrary, as long as it is ensured that the welding means completely weld the bottom end up to the edge.
- the welding device preferably comprises welding jaws and in particular two welding jaws as the welding means.
- the sealing jaws preferably extend transversely across the sack film and more particularly outwards on both sides.
- At least) one fixing means is preferably provided for fixing the sack film to the transport path in front of the longitudinal section.
- (at least) one fixing means is provided for fixing the sack film to the transport track after the longitudinal section.
- a fixing means can be formed, for example, by a tube or a profile.
- a rubber covering or the like can be formed on the profile or tube, for example, in order to securely fix the sack film.
- the fixative can spot the sack film fix. It is possible and preferred for the fixing means to fix the sack film in a linear or planar manner, so that one or every (even only slight) local displacement of the sack film is prevented.
- the longitudinal section is preferably defined by a length of the welding means along the transport path or in the transport direction.
- the two welding means are preferably essentially identical or have a mirror-symmetrical or point-symmetrical structure.
- the two welding means preferably have at least substantially the same dimensions. However, it is also possible for the two welding means to have different lengths in the direction of the transport track. Then the longitudinal section is defined by the shorter length of the two welding means or by the overlapping length of the two welding means.
- the longitudinal section extends over a length of more than 5 mm or more than 10 mm.
- the longitudinal section can in particular extend over a length of between 2 mm and 50 mm and preferably between 5 mm and 30 mm.
- a length of the longitudinal section depends in particular on the dimensions of the open bag.
- the welding means extend beyond the bottom end of the bag body (in the longitudinal direction of the bag film) during welding. This enables and ensures that the bottom end of the sack body is sealed with a welded edge. This reliably avoids excess film at the bottom seam.
- a seam length of the bottom seam is preferably shorter than the longitudinal section. Seam lengths of between 2 mm and 15 mm and in particular between 3 mm and 10 mm are particularly preferred. With large open-mouth bags, the seam length can also be longer.
- the bag film is designed as a tubular film
- the Storage device includes a receptacle for (at least) a film roll and in particular hose roll. It is also conceivable to produce the open-mouth bags from a web of film that is folded over and longitudinally welded.
- the sack-making device comprises at least one corner seam welding device in order to introduce corner seams into the sack film, so that cuboid sacks are obtained in the filled state. It is also possible to do without a corner seam welding device or to use a film roll with prefabricated corner welding.
- the bag-making device comprises at least one film store with a movable or pivotable tension roller. It is also possible that two or more tension rollers are provided.
- the idler pulley or pulleys may be biased by a weight or spring or the like.
- the film accumulator can accommodate a portion of a sack length or a sack length or more to allow semi-continuous operation or continuous operation or continuous rotation of the film roll or tube roll on the storage facility.
- the film roll hose roll
- an attachment device is included in order to attach an open-mouth bag to a filling spout of a filling system. It is also possible that two or more hitch devices are provided.
- the method according to the invention is used to produce open-mouth bags from a supply of bag film, with the bag film being transported along a transport path and with (at least) one cutting means of a cutting device cutting off a predetermined length of film from the bag film in order to to form a bag body of an open-mouth bag.
- the sack film is moved relative to the sack body.
- a bottom seam is applied to the bottom end of the bag body by welding with welding means to form a mouth bag.
- the sack film is pulled back from the severed sack body before the bottom end is sealed.
- the welding means extend beyond the bottom end in the longitudinal direction of the bag film of the bag body during welding, the cutting means being located in the same longitudinal section as the welding means during cutting. In this case, the longitudinal section is defined by a length of the welding means along the transport path.
- the method according to the invention also has many advantages. With the method, open-mouth bags can be produced that meet high hygienic standards.
- the sack film is pulled back from the severed sack body, in particular in a defined manner, before the bottom end is sealed. It is also possible that the sack film is pulled back from the separated sack body in an undefined manner, for example by activating the associated drive for a certain period of time or the like.
- an optical sensor or the like can again detect the front edge of the sack film and thus enable a defined positioning of the front edge of the sack film.
- edge sealing of the bottom seam can be ensured while at the same time ensuring that the front end of the sack film is not welded, which forms the head end of the next open mouth sack.
- the foil or the bag body is fixed before the bag body is separated.
- the sack film is fixed in the area of the sack body and also the sack film in front of it.
- Such a fixation can take place, for example, by pressing onto the bag film from above with suitable fixing means or a tube or a rail or the like, so that the bag film is held in a defined manner. Then no undesired displacement of the sack body or the sack film can occur when the sack body is separated.
- the fixing of the sack film in front of the sack body is preferably canceled before the sack film is pulled back.
- the sack body remains fixed while the sack film is being pulled back.
- the welding means reaches at least the bottom end of the bag body when welding.
- the welding means project beyond the bottom end of the bag body during welding.
- the bottom seam of the bag body is welded edge-tight up to the bottom end. Welding is preferably carried out over the entire surface within the bottom seam.
- An open sack according to the application is produced using one of the methods described above and comprises a sack body consisting at least partially of sack film, with a bottom end of the sack body being closed by a bottom seam.
- the open-mouth bag can, in particular, comprise an edge-tight welded seam (extending as far as the bottom end) at the bottom seam.
- a bag filled with bulk material and closed at the head end can also have a top seam that is sealed at the edges.
- the bag body of the open-mouth bag can include side folds and/or welded corners.
- the invention provides an advantageous bag manufacturing device, an advantageous method and advantageous open-mouth bags, so that hygienic filling of bulk goods and in particular powdered foodstuffs into open-mouth bags is made possible.
- the finished open-mouth bags do not have any overhanging film at the bottom seam where particles or dirt can get stuck.
- the bag film is fed up to about one bag length beyond the cutting plane of the cutting device.
- the fixing means designed, for example, as a pressure bracket.
- the sack body is then cut off the sack film with the cutting device.
- This is followed by a loosening of the fixing means or press bracket which is in contact with the sack film, while the other press bracket is still fixing the sack body.
- the sack film is then pulled back a little, to the extent that the front end of the sack film is no longer in the effective range of the welding device for the bottom seam.
- the returned length of sack film is buffered by the film store.
- the bottom seam is then welded, with the welding means completely covering the bottom end and even extending beyond it, so that the bottom seam is welded edge-tight to the very end. This means that the foil layers lying on top of one another are completely welded to one another right to the very end.
- the finished sack body is transported further with the open side to the front in the transport direction of the transport line.
- the sack film is then advanced again so that a (new) sack body is again completely in front of the cutting plane.
- the feed of the sack film can be sensor-controlled or, for example, via a servo drive or the like, so that a precisely defined positioning of the sack film is possible.
- the bag-making device can include a film store so that continuous operation of the film roll or hose roll is possible. However, it is also possible that a start/stop operation of the film or tube roll is provided.
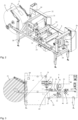
- figure 1 shows a schematic perspective view of a filling system 100, which has a preliminary silo 104 and a coarse flow 101 and a fine flow 102 to fill bulk goods and in particular powdered food into open-mouth bags.
- the filling system 100 comprises a sack manufacturing device 1.
- the sack manufacturing device 1 is connected upstream of the actual filling and manufactures individual open-mouth sacks 2 from a film roll or here hose roll 21 with sack film 5 wound up (cf figure 4 ) which, after being attached with the attachment device 26, are filled with the bulk material to be filled via the filling spout 110 of the filling system 100.
- the filling system here comprises rotating filling nozzles 110 which are rotated in cycles to the individual stations. After attachment to a first filling spout, filling takes place in the coarse flow at the next station, before filling takes place in the fine flow after further cycling. At least one compression device is provided both at the station with the filling in the coarse flow and at the station for filling with the fine flow, in order to bring about a compression of the bulk material in the open-mouth bag during the filling process. At the fourth station, the sack is transported away at the sack discharge 105 .
- the bag-making device 1 comprises a frame 30 on which a storage device 3 with the supply 4 is also arranged.
- the supply 4 here consists of the tube roll 21, on which the sack film 5, which is designed here as a tube film, is stored wound up.
- the tubular film 5 is transported along the transport track 7 by means of at least one transport device 6 .
- the transport device consists of one or two driven transport rollers, which transport the tubular film along the transport path 7 in a targeted manner.
- a corner seam welding device 22 can be provided in order to introduce corner welds 28 into the tubular film, which in the filled sack are connected to the side gussets 27 (compare figure 4 ) ensure a cuboid filled sack.
- Deflection rollers 31 are used to deflect the sack film 5 .
- the film store 24 can also include several tensioning rollers 25 so that continuous rotation of the hose roller 21 is made possible while the open-mouth bag 2 is being produced in the bag-making device 1 .
- the foil length withdrawn before the welding can be temporarily stored in the foil store.
- FIG. 12 shows a schematic perspective view of the bag manufacturing device 1.
- FIG figure 1 The imprints 33 shown by way of example on the hose reel 21, which are printed on the tubular film 5 of the hose reel 21 at a distance of one sack length, are clearly visible.
- the bag film 5 is transported along the transport path 7 by means of the transport device 6 and is deflected at the deflection roller 31 .
- the sack film 5 then comes to the corner seam welding device 22, with which the corner seams or the corner welds 28 (cf figure 4 ) are introduced into the bag film. Whenever this is desired. Without corner welds, so-called pillow-shaped bags form after filling. With corner seam welds, more box-shaped sacks are formed. In combination with peelable two-layer films as the sack wall, sacks that meet high hygienic requirements are created.
- the transport device 6 here comprises a driven roller, with which the sack film 5 is transported along the transport track 7 .
- Another transport device 45 in the form of a drive unit 45 is in 3 to recognize.
- the tensioning roller 25 of the film store 24 can be seen in the lower area of the sack manufacturing device 1 .
- the bag film 5 is transported horizontally along the transport direction of the transport track 7 , so that the bag film 5 is transported horizontally through the welding device 8 .
- the welding device 8 With the welding device 8, a bottom seam 11 is sewn into the bag body 16 (same figure 4 ) brought in.
- the attachment device 26 serves to pick up the open bag 2 lying at the front end and to bring it from the lying position into a hanging position by pivoting about the horizontal axis shown.
- the front open end 40 of the open-mouth bag 2 is opened by the suckers, so that the open-mouth bag 2 is attached to a filling spout 110 of a filling system.
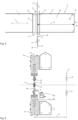
- figure 3 shows a longitudinal section through the sack manufacturing device 1 figure 2 .
- the sack film 5 unwound from the roll 21 is deflected by the deflection roll 31 and guided through the corner seam welding device 22, where corner welds 28 ( 4 ) are introduced into the bag film 5.
- the transport device 6 follows here with the drive unit 42, which ensures that the sack film 5 is transported.
- the sack film is then transported through the welding device 8 to such an extent that the sack film is exactly one sack length in front of a cutting plane 50 ( 4 ) one here not shown cutting device 12 extends.
- the cutter 12 is with respect to the Figures 4 to 7 explained in more detail.
- Fixing means 18 and 19 are used to fix the sack film in front of and behind the welding device 8 .
- the welding device 8 comprises welding means 9 and 10 which can be moved towards and away from one another via cylinders 35 and 36 .
- figure 4 shows a schematic plan view of the sack film and the cutting device 12.
- the sack film is advanced to the front end at the head end 39 shown here.
- the sack film 5 is then through the in figure 3 Fixing means 18 and 19 shown fixed.
- the cutting device 12 is then activated and is moved here transversely to the sack film 5 so that the cutting means 14 separates the sack body 16 from the sack film 5 .
- the cutting device 12 is located on the other long side of the sack film 5 in the position shown in dashed lines.
- the cutting device is then moved in the opposite direction and cuts the sack film 5 in the cutting plane 50 with the cutting means 13.
- the sack film 5 is pulled back via the transport device, resulting in a distance 37 from the bottom end of the sack body 16 to the front end 41 of the sack film 5 .
- This distance 37 is dimensioned in such a way that the now front end 41 of the sack film 5 is located outside of the longitudinal section 17 .
- the longitudinal section 17 is defined in particular by the longitudinal overlap of the welding means of the welding device 8, which are preferably designed as welding jaws. The mutually interacting welding means are moved to each other for welding and act in the longitudinal section 17. There they weld to each other lying layers of the bag film 5 together.
- the longitudinal section 17 is dimensioned in such a way and the bottom end 23 of the bag body 16 is also arranged in such a way that the layers of the bag film are completely welded to one another at the bottom end 23 .
- the result is an edge-tight weld, so that there is no longer any unwelded film protrusion at the weld seam. This enables a high level of hygiene. Particles and dirt cannot be deposited and collected between a film overhang of several layers, since all layers are tightly welded together up to the outermost edge.
- the bag body 16 of the open bag 2 can be transported further in the direction of the filling system or, alternatively, can be fed to a store, for example.
- the now front end 41 of the sack film 5 is then transported further by the distance 37 plus a sack length 15 in the direction of the transport path 7, so that the front end of the sack film 5 is then in the illustrated position of the top end 39. Abutting the front free end 41 on the transport surface can, for. B. be prevented by ramps that are not visible here.
- the fixing means 18 and 19 then fix the sack film 5 in place.
- the next sack body 16 is then cut off by the cutting device 12 .
- the sack body 16 is then further fixed with the front fixing means, while the rear fixing means is released and the sack film 5 is pulled back by the distance 37 so that the next bottom end 23 can be provided with a bottom seam 11 that is sealed at the edge.
- the cutting device and in particular the cutting means 13 and 14 are located in the cutting plane 50 which is located within the longitudinal section 17 .
- the welding agents act Welding device 8.
- the bottom seam 11 has a seam length 38 that ensures sufficient stability.
- the bag body 16 that has been cut off is transported with the drive unit 45 (as a further transport device) via the transport surface 46 to the attachment device 26 (cf. 3 ).
- FIG 5 shows a schematic cross section through the welding device 8 and the cutting device 12 of the bag manufacturing device 1 figure 2 .
- the sealing jaw 9 is moved by the cylinder 35 from the spaced position shown here into a welding position, not shown here, in which the sealing jaws 9 and 10 are in direct contact with the sack film 5 located between them.
- the length 20 of the welding means 9 and 10 defines the longitudinal section 17. Within the longitudinal section 17 is the cutting plane 50.
- the cutting means 13 and 14 are there at least when they are performing a cutting operation. It is also conceivable that the cutting means 13 and 14 and also the welding means 9 and 10 are in other planes and positions when they are not active. In any case, it is important that in the welding position there is a longitudinal section 17 within which the cutting plane of the cutting means 13 and 14 is located.
- the welding jaws 9 and 10 can be coated on the upper side with Teflon, for example, and applied to an insulator. However, it is also possible for a coated welding band or other suitable welding devices such as ultrasound, permanently heated welding jaws, etc. to be used.
- the welding means 9 and 10 shown in dashed lines, of a welding device to be offset forward by a predetermined distance 37 in the transport direction of the film.
- those drawn in solid are Welding agent 9 and 10 not necessary.
- the bottom seam 11 is then introduced into the bottom end 23 by means of the welding jaws 9 and 10 shown in dashed lines, with the welding means also projecting beyond the bottom end 23 during the welding in this variant.
- a weld seam is thus introduced into the bottom end, which welds the bag body over the entire area in the area of the bottom seam and up to the absolute bottom end 23 .
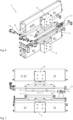
- FIG 6 shows a schematic perspective view of the welding device 8 and also the fixing means 18 and 19, which can be moved between the fixing and the releasing position via one of the cylinders 44 in each case.
- One or more adjustable spacers or adjustment sleeves can be provided to make the appropriate adjustments and allow for fine adjustment.
- the fixing means 18 and 19 here each comprise a linkage and a mechanism on which a fixing means, here tubular, is provided at the end for direct contact with the sack film or the sack body.
- figure 7 shows a view of figure 6 , whereby the cutting device 12 can also be seen on the side here, which is arranged so that it can be moved laterally transversely to the longitudinal extent of the bag film 5 .
- the invention provides an advantageous bag manufacturing device and an advantageous method for manufacturing open-mouth bags, with which a high standard of hygiene can be achieved.
- the manufacture of the sacks is efficient and does not require a great deal of equipment, although the bags can be sealed edge-tight.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Making Paper Articles (AREA)
- Containers And Plastic Fillers For Packaging (AREA)
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE102016123805.8A DE102016123805A1 (de) | 2016-12-08 | 2016-12-08 | Sackherstellvorrichtung und Verfahren |
| PCT/EP2017/082003 WO2018104515A1 (de) | 2016-12-08 | 2017-12-08 | Sackherstellvorrichtung und verfahren |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP3551446A1 EP3551446A1 (de) | 2019-10-16 |
| EP3551446B1 true EP3551446B1 (de) | 2023-07-19 |
Family
ID=60957254
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP17828860.1A Active EP3551446B1 (de) | 2016-12-08 | 2017-12-08 | Sackherstellvorrichtung und verfahren |
Country Status (7)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (2) | US11643234B2 (es) |
| EP (1) | EP3551446B1 (es) |
| CN (1) | CN110049861B (es) |
| CA (1) | CA3044550A1 (es) |
| DE (1) | DE102016123805A1 (es) |
| ES (1) | ES2959989T3 (es) |
| WO (1) | WO2018104515A1 (es) |
Families Citing this family (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN110254823B (zh) * | 2019-08-07 | 2021-11-09 | 广州市九科精细化工有限公司 | 一种用于条形软包装的全自动液体物料灌装包装工艺 |
| CN112224528B (zh) * | 2020-09-15 | 2022-04-19 | 北京三快在线科技有限公司 | 外带物品打包机及其打包袋制作模块 |
| JP2022160260A (ja) * | 2021-04-06 | 2022-10-19 | 住友化学株式会社 | 包装体 |
| CN113635610B (zh) * | 2021-10-13 | 2022-02-22 | 徐州鑫峰塑业有限公司 | 一种塑料袋封口装置 |
Family Cites Families (21)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BE789622A (fr) * | 1971-11-12 | 1973-02-01 | Fmc Corp | Procede et appareil pour fabriquer des sacs en matiere thermoplastique soudes a leur extremite inferieure |
| DE2459725A1 (de) * | 1974-12-18 | 1976-07-01 | Librawerk Pelz & Nagel Kg | Vorrichtung zum beschicken einer beutel- und sackfuelleinrichtung |
| BR8101449A (pt) * | 1981-03-12 | 1981-07-07 | Copia C Santos | Aperfeicoamentos em cabecote para maquina de fabricar sacos plasticos |
| US4617683A (en) * | 1984-01-30 | 1986-10-14 | Minigrip, Inc. | Reclosable bag, material, and method of and means for making same |
| US4546596A (en) * | 1984-05-08 | 1985-10-15 | Hayssen Manufacturing Company | Method of and apparatus for forming, filling and sealing packages |
| US5041070A (en) * | 1988-07-29 | 1991-08-20 | Amplas, Inc. | Intermittent web feed apparatus |
| ES2364690T3 (es) * | 1995-08-09 | 2011-09-12 | James Worth Yeager | Bolsa que se puede volver a cerrar. |
| EP0844070A1 (en) * | 1996-11-26 | 1998-05-27 | Kraft Foods, Inc. | Method and apparatus for obtaining individual web sections |
| DE10039105A1 (de) * | 2000-08-07 | 2002-02-21 | Deltapack Verpackungsmaschinen | Verfahren zur Herstellung von Schlauchbeuteln aus Folien |
| CA2360653C (en) * | 2000-11-02 | 2010-01-26 | Advanced Poly-Packaging, Inc. | Pre-opened resealable bags |
| US20060222430A1 (en) * | 2005-04-01 | 2006-10-05 | Duckett Jeanne F | Linerless web feeding method and system |
| MX2008009071A (es) | 2006-01-13 | 2009-05-13 | Cmd Corp | Metodo y aparato para fabricar bolsas. |
| CN1915658A (zh) | 2006-08-15 | 2007-02-21 | 山东新华医疗器械股份有限公司 | 粉液双腔软袋外保护铝箔贴覆焊接机 |
| SE534193C2 (sv) * | 2009-09-23 | 2011-05-31 | Ecolean Res & Dev As | Anordning för framställning av förpackningar samt fyllmaskin för fyllning av nämnda förpackning |
| DE102010049369A1 (de) * | 2010-10-26 | 2012-04-26 | Haver & Boecker Ohg | Sack und Verfahren zum Füllen eines Sacks |
| JP6163069B2 (ja) * | 2013-09-19 | 2017-07-12 | 株式会社イシダ | 製袋包装機 |
| CN104691804B (zh) * | 2015-03-13 | 2016-09-28 | 益盐堂(应城)健康盐制盐有限公司 | 一种膜片式包装袋的包装装置 |
| CN104985864B (zh) * | 2015-08-08 | 2017-10-31 | 洪东坡 | 一种结构改良的制袋机 |
| CN105415747B (zh) | 2015-11-25 | 2018-01-23 | 蚌埠市众邦包装厂 | 一种自动上下料的包装带加工控制系统 |
| CN106182892A (zh) | 2016-08-30 | 2016-12-07 | 浙江品诚包装有限公司 | 一种包装袋制备装置 |
| US10745227B1 (en) * | 2016-10-28 | 2020-08-18 | Quality Packaging Corp. | Packaging apparatus |
-
2016
- 2016-12-08 DE DE102016123805.8A patent/DE102016123805A1/de active Pending
-
2017
- 2017-12-08 US US16/466,504 patent/US11643234B2/en active Active
- 2017-12-08 CA CA3044550A patent/CA3044550A1/en active Pending
- 2017-12-08 EP EP17828860.1A patent/EP3551446B1/de active Active
- 2017-12-08 ES ES17828860T patent/ES2959989T3/es active Active
- 2017-12-08 CN CN201780074857.XA patent/CN110049861B/zh active Active
- 2017-12-08 WO PCT/EP2017/082003 patent/WO2018104515A1/de unknown
-
2023
- 2023-03-07 US US18/118,347 patent/US20230249861A1/en active Pending
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CA3044550A1 (en) | 2018-06-14 |
| US11643234B2 (en) | 2023-05-09 |
| EP3551446A1 (de) | 2019-10-16 |
| US20200262594A1 (en) | 2020-08-20 |
| ES2959989T3 (es) | 2024-02-29 |
| CN110049861A (zh) | 2019-07-23 |
| US20230249861A1 (en) | 2023-08-10 |
| CN110049861B (zh) | 2021-09-24 |
| WO2018104515A1 (de) | 2018-06-14 |
| DE102016123805A1 (de) | 2018-06-14 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP1060072B1 (de) | Vorrichtung zum herstellen von schlauchbeutelpackungen | |
| EP3551446B1 (de) | Sackherstellvorrichtung und verfahren | |
| EP1773576B1 (de) | Verfahren und vorrichtung zur herstellung und befüllung von säcken | |
| DE69813292T2 (de) | Beutel mit transversalen Verschlussprofilen und Verschlussmittel zu dessen Herstellung | |
| DE69629424T2 (de) | System und Verfahren zum Einfüllen von festen Gegenständen | |
| EP2739455B1 (de) | Verfahren und vorrichtung zum herstellen, befüllen und verschliessen von säcken sowie ein sack | |
| DE2925440A1 (de) | Mehrwandiger beutel sowie verfahren und vorrichtung zur herstellung eines mehrwandigen beutels | |
| EP2049327A1 (de) | Verfahren zum herstellen von verpackungsbeuteln mit verstärktem bodenbereich sowie vorrichtung zur durchführung des verfahrens | |
| DE112012004380T5 (de) | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur Entfaltung gefalteter Kunststofffolie zur Verwendung in der Formung eines Verpackungsrohrs | |
| WO2004071752A1 (de) | Verfahren zur herstellung von säcken | |
| EP3162730B1 (de) | Verfahren und vorrichtung zum herstellen von beuteln aus folie | |
| WO2018060277A1 (de) | Kunststoffsack, insbesondere ffs-sack, sowie verfahren und vorrichtung zur herstellung und zum befüllen eines sacks | |
| DE102011006930B4 (de) | Schweißvorrichtung | |
| DE60318887T2 (de) | Flexible verpackung | |
| DE2307354B2 (de) | Verfahren und vorrichtung zum verschliessen von schlauchbeuteln mit einem clip-verschluss | |
| EP2314510B1 (de) | Horizontalschlauchbeutelverpackungsmaschine | |
| DE2440491A1 (de) | Quadratischer behaelter und vorrichtung zu seiner herstellung | |
| DE102013100131A1 (de) | Verfahren zum Herstellen von Säcken | |
| EP3643635A1 (de) | Unbefüllter, unverschlossener seitenfaltenverpackungsbeutel | |
| DE102020208644B4 (de) | Vorrichtung und Verfahren zur Anordnung von Produkten im Bereich einer Quersiegeleinrichtung einer Schlauchbeutelverpackungsmaschine | |
| EP1597054A2 (de) | Schlauch sowie vorrichtung und verfahren zur herstellung desselben | |
| EP3452277A1 (de) | Transporteinrichtung und verfahren zum transport von säcken oder beuteln sowie vorrichtung zur herstellung von säcken oder beuteln | |
| DE3740058C2 (es) | ||
| DE10121525A1 (de) | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zum Herstellen von mit Wiederverschlußstreifen ausgestatteten Beutelpackungen | |
| DE60036497T2 (de) | Versiegelte Packung für flüssige Nahrungsmittel und Verfahren zu ihrer Herstellung |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: UNKNOWN |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: THE INTERNATIONAL PUBLICATION HAS BEEN MADE |
|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: REQUEST FOR EXAMINATION WAS MADE |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20190704 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Extension state: BA ME |
|
| DAV | Request for validation of the european patent (deleted) | ||
| DAX | Request for extension of the european patent (deleted) | ||
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: EXAMINATION IS IN PROGRESS |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 20220523 |
|
| GRAP | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR1 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: GRANT OF PATENT IS INTENDED |
|
| INTG | Intention to grant announced |
Effective date: 20230213 |
|
| GRAS | Grant fee paid |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR3 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: THE PATENT HAS BEEN GRANTED |
|
| P01 | Opt-out of the competence of the unified patent court (upc) registered |
Effective date: 20230515 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: NOT ENGLISH |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: EP |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R096 Ref document number: 502017015082 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: LANGUAGE OF EP DOCUMENT: GERMAN |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: NL Ref legal event code: FP |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: LT Ref legal event code: MG9D |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20231020 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 20231002 Year of fee payment: 7 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20231119 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20230719 Ref country code: RS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20230719 Ref country code: PT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20231120 Ref country code: NO Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20231019 Ref country code: LV Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20230719 Ref country code: LT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20230719 Ref country code: IS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20231119 Ref country code: HR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20230719 Ref country code: GR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20231020 Ref country code: FI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20230719 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Payment date: 20231226 Year of fee payment: 7 Ref country code: IT Payment date: 20231025 Year of fee payment: 7 Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20231002 Year of fee payment: 7 Ref country code: AT Payment date: 20231211 Year of fee payment: 7 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: PL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20230719 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BE Payment date: 20231130 Year of fee payment: 7 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: ES Ref legal event code: FG2A Ref document number: 2959989 Country of ref document: ES Kind code of ref document: T3 Effective date: 20240229 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: ES Payment date: 20240103 Year of fee payment: 7 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SM Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20230719 Ref country code: RO Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20230719 Ref country code: EE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20230719 Ref country code: DK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20230719 Ref country code: CZ Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20230719 Ref country code: SK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20230719 |