EP1639907B1 - Vorrichtung zur Übergabe stabförmiger Artikel - Google Patents
Vorrichtung zur Übergabe stabförmiger Artikel Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP1639907B1 EP1639907B1 EP05090268A EP05090268A EP1639907B1 EP 1639907 B1 EP1639907 B1 EP 1639907B1 EP 05090268 A EP05090268 A EP 05090268A EP 05090268 A EP05090268 A EP 05090268A EP 1639907 B1 EP1639907 B1 EP 1639907B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- adjusting
- receptacles
- conveying means
- disc
- elements
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 230000008878 coupling Effects 0.000 claims description 13
- 238000010168 coupling process Methods 0.000 claims description 13
- 238000005859 coupling reaction Methods 0.000 claims description 13
- 230000007246 mechanism Effects 0.000 claims description 5
- 238000007599 discharging Methods 0.000 claims 1
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 abstract description 6
- 235000019504 cigarettes Nutrition 0.000 abstract description 2
- 230000008859 change Effects 0.000 description 14
- 230000005540 biological transmission Effects 0.000 description 2
- 238000009434 installation Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000001360 synchronised effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 241000208125 Nicotiana Species 0.000 description 1
- 235000002637 Nicotiana tabacum Nutrition 0.000 description 1
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000003247 decreasing effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000001419 dependent effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000006073 displacement reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000009467 reduction Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000011144 upstream manufacturing Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A24—TOBACCO; CIGARS; CIGARETTES; SIMULATED SMOKING DEVICES; SMOKERS' REQUISITES
- A24C—MACHINES FOR MAKING CIGARS OR CIGARETTES
- A24C5/00—Making cigarettes; Making tipping materials for, or attaching filters or mouthpieces to, cigars or cigarettes
- A24C5/32—Separating, ordering, counting or examining cigarettes; Regulating the feeding of tobacco according to rod or cigarette condition
- A24C5/322—Transporting cigarettes during manufacturing
- A24C5/326—Transporting cigarettes during manufacturing with lateral transferring means
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A24—TOBACCO; CIGARS; CIGARETTES; SIMULATED SMOKING DEVICES; SMOKERS' REQUISITES
- A24D—CIGARS; CIGARETTES; TOBACCO SMOKE FILTERS; MOUTHPIECES FOR CIGARS OR CIGARETTES; MANUFACTURE OF TOBACCO SMOKE FILTERS OR MOUTHPIECES
- A24D3/00—Tobacco smoke filters, e.g. filter-tips, filtering inserts; Filters specially adapted for simulated smoking devices; Mouthpieces for cigars or cigarettes
- A24D3/02—Manufacture of tobacco smoke filters
- A24D3/0275—Manufacture of tobacco smoke filters for filters with special features
- A24D3/0287—Manufacture of tobacco smoke filters for filters with special features for composite filters
Definitions
- the invention relates to a device for transferring rod-shaped articles, in particular filter rods, from a device for Queraxialen promotion of the article on a device for longitudinal axial promotion of the article or vice versa, wherein the transport directions of the devices extend transversely to each other, comprising a rotatably driven conveying means with at least one receptacle wherein each receptacle is adapted to receive at least one article from the device for transversely conveying the articles and delivering the or each article received to the longitudinal axial conveying device or vice versa.
- the rod-shaped articles may e.g. Filter, filter segments or segment groups and cigarettes or the like.
- the generic device is used.
- each filter usually consists of one or more components, the so-called segments, which are surrounded by wrapping material.
- filters have a different length and / or a different diameter.
- filters have often consisted of a single component.
- the filter is usually formed of several components. This results in different filter lengths, which are usually in a range of about 21 to 27 mm. Other lengths are also standard. Furthermore, it can also lead to changes in diameter.
- Filter or the filter material or the filter segments are prepared in single or multiple use length or segment groups of different lengths and transported transversely in the direction of the generic device. By means of the latter device, the articles are converted to the device for longitudinal axial promotion, the actual stranding machine. On the stranding machine, the individual or group-wise assembled filter segments are surrounded with wrapping paper and cut into the final filter.
- a filter length or the length of the filter segments or segment groups is also referred to as format.
- a format change is necessary. That is, the production must be switched from a first length to a second length other than the first length in order to achieve optimum utilization of the productivity of the device as well as the upstream and downstream devices.
- this change makes a change in the diameter of the conveyor or a change in the described by rotating rotating recordings necessary to optimally adapt the device to the respective desired cut length of the filter. In today's devices, this requires the replacement of the entire conveyor.
- Each format has its own separate funding, which must be exchanged at machine standstill. The format change leads to considerable installation effort, which leads as well as the machine downtime at increased costs.
- This object is achieved by a device having the features mentioned in that the formed by the or each recording run L is variable. This makes it possible in a simple manner to adapt the funding to the respective format to be processed. Within a certain range is the Device suitable for transferring different formats. In other words, covers a single funding from the usual formats, so that a constant exchange of funds can be avoided. This saves installation effort and thus costs.
- the or each receptacle for changing the running circle L is radially adjustable.
- radially adjustable means in addition to the actual radially directed movement also pivoting, tilting, rocking or other movements that result in a radial adjustment of the running circle L.
- a plurality of receptacles are distributed uniformly over the circumference of the conveying means, wherein all receptacles are designed to be radially adjustable during operation of the device.
- the devices shown are used for transferring rod-shaped articles from a device for the cross-axial promotion of the article on a device for longitudinal axial promotion of the article.
- the devices may equally be adapted and used for transfer from a longitudinal axial conveying device to a transverse axial conveying device.
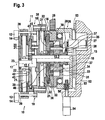
- FIGS. 1 and 2 show a first embodiment of a device 10 for transferring rod-shaped articles.
- the apparatus 10 is typically between a device (not shown) for transversely conveying the articles, for example a device for assembling groups of filter segments for the production of multi-segment filters, and a device (also not shown) for the longitudinal axial conveying of the articles, for example a strand-forming device, arranged.
- the device 10 essentially comprises a conveying means 11, which has at least one, but preferably a plurality of receptacles 12.
- the receptacles 12 are used to remove at least one article from the device for Queraxialen promotion and delivery of the or each recorded article to the device for longitudinal axial promotion.
- the conveyor 11 is driven to rotate about an axis 13.
- Several, preferably twelve receptacles 12 are distributed uniformly over the circumference of the conveyor 11, wherein all receptacles 12 are synchronously radially adjustable during operation of the device 10.
- Each receptacle 12 is pivotally mounted on the conveyor 11, so that format holder 14, which are associated with each receptacle 12, preferably in each Position, but in particular at the time of taking up the articles and submitting the articles, in parallel to the articles. This is usually the horizontal position.
- the format holder 14 are adapted to the respective format to be transferred, in particular as regards the length and the diameter of the article.
- the format holder 14 may be formed to receive a single article, but also to receive a plurality of parallel juxtaposed articles.
- the receptacles 12 are designed to be variable. The adjustment to different diameters can be done manually or automatically.
- the or each receptacle 12 is designed to change the running circle L radially adjustable. The radial adjustment can be achieved by linear and / or circular or arcuate and / or pivoting, rocking or otherwise known and usual movement arrangements.
- the conveyor 11 has two discs 15 and 16, which are positioned centrally on the common axis 13.
- the preferably integrally formed axis 13 is formed offset in parallel, that is, that it has two sections 13.1 and 13.2, which are arranged offset to one another.
- the sections 13.1 and 13.2 or the axes of rotation 17 and 18 of the sections 13.1 and 13.2 are parallel to each other.
- the outer disc 15, which is arranged at the free end 23 of the axis 13, more precisely of the portion 13.1, in the described embodiment, thus facing the device for longitudinal axial promotion, is disposed on the portion 13.1 and rotated about the rotation axis 17.
- the inner disc 16th is arranged on the section 13.2 and rotates about the axis of rotation 18.
- the discs 15, 16 are arranged parallel and axially offset from one another. Both discs 15, 16 are coupled to each other via hinge elements 19 and thereby in operative connection, such that they rotate at the same speed about the axes of rotation 17, 18.
- the receptacles 12 are assigned to the front disk 15. More specifically, the receptacles are arranged at free ends 20 of the hinge elements 19 which protrude from the disc 15.
- the discs 15, 16 have the same diameter in the embodiment shown. However, the diameters can also be different.
- Each disk 15, 16 has adjusting elements 21.
- the adjusting elements 21 are arranged in the region of the circumference of the respective disk 15 or 16.
- the number of actuators 21 per disc 15, 16 preferably corresponds to the number of receptacles 12.
- the actuators 21 are segmented, i. that each actuator 21 is formed separately from the adjacent actuator 21.
- Each receptacle 12 is associated with a pair of control elements.
- the pair of control elements is formed from an actuating element 21 of the disk 15 and a corresponding actuating element 21 of the disk 16.
- the adjusting elements 21 of a pair of adjusting elements are arranged one behind the other in front view.
- the connection between the discs 15, 16 or between the adjusting elements 21 of each pair of adjusting elements is made by the hinge elements 19, which are the same as the axis 13 offset parallel or formed angled.
- the hinge elements 19 are mounted in the adjusting elements 21, so that the arranged on the hinge elements 19 receptacles 12 despite rotation of the discs 15, 16 are always in the same position with respect to the orientation to the articles.
- the adjusting elements 21 are arranged in recesses 22 of the discs 15, 16.
- the conveyor 11 or more precisely the discs 15, 16 are driven in rotation by means of a drive 24.
- the drive 24 is connected via a toothed belt 25 or other common Ubertragungs institute in operative connection with one of the discs 15, 16, preferably the inner disc 16.
- the rotation of the disc 16 on the disc 15 is transferable. Both discs 15, 16 rotate at the same speed.
- an additional movement can be superimposed on the rotational movement of the disks 15, 16.
- FIGS. 3 to 7 All shown embodiments according to the FIGS. 3 to 7 are basically constructed on the same principle as the previously described embodiment of FIGS. 1 and 2 , so that a renewed description is omitted.
- the same reference numbers are used for the same parts.
- the different embodiments differ in the formation of the mechanism for adjusting the running circle formed by the receptacles 12. In other words, various possibilities are explained below, as the actual rotational movement of the conveyor 11, namely the discs 15, 16, an additional adjusting movement can be superimposed.
- the conveyor 11 for superimposing an additional movement associated with a transmission, in particular an addition gear 26.
- the addition gear 26 is connected to an actuator 27 in operative connection and driven by this.
- the operative connection between the actuator 27 and the addition gear 26 is made by a toothed belt 28 or other common transmission elements.
- the addition gear 26 essentially comprises two planetary gear 29, 30, which are connected in parallel. Both planetary gear 29, 30 have a ring gear 31, 32, a set of planetary gears 33, 34 and a sun gear 35, 36.
- Each set planetary gears 33, 34 comprises a plurality of planetary gears, wherein in the embodiment shown two planetary gears are provided.
- a planetary gear of the set 33 is connected to a planetary gear of the set 34 via an axis 37.
- the driven by the actuator 27 sun gear 35 is centrally positioned or mounted on the axis 13.
- the sun gear 36 is rotatably mounted on the axis 13.
- the planetary gears 33 associated ring gear 31 is an integral part of the disc 16.
- the ring gear 32 is also formed as a thumbwheel 38.
- the conveyor 11 is associated with at least one thumbwheel. Preferably, however, each disc 15, 16 on a thumbwheel.
- the disk 15 is associated with the thumbwheel 39.
- the disk 16 is associated with the thumbwheel 38.
- Both adjusting wheels 38, 39 each have a plan curve 40, 41. Plankurven 40, 41 extend, starting from the axis 13 spirally outwards to the periphery of the discs 15, 16.
- the pins 42 of all control elements 21 are in the plan curves 40, 41, which can also be referred to as cams or control curves out.
- the pins 42 of the adjusting elements 21, which are associated with the disc 16, are the Plankurve 40 associated with the setting wheel 38.
- the pins 42 of the adjusting elements 21, which are associated with the disc 15, the plan curve 41 of the setting wheel 39 are assigned.
- the adjusting wheels 38, 39 are verkuppelt each other by means of suitable coupling elements, preferably Schmidt couplings 43, for carrying out a synchronous movement.
- suitable coupling elements preferably Schmidt couplings 43
- Other known types of couplings, such as Oldham couplings or drive shafts or other conventional coupling elements are also used.
- the operation of the embodiment according to the FIGS. 1 and 2 as well as the embodiment of the FIG. 3 , which only by the height adjustment, which will be described below, of the embodiment according to FIG. 1 and 2 different, is as follows:
- the conveying means 11 or discs 15, 16 rotate at the same speed and at one pick-up point remove the article (s) from a first device and deliver it at a delivery point to a second device.
- the rotation of the discs 15, 16 is superimposed on a further movement in order to adapt the conveyor 11 to the new format.
- the actuator 27 is actuated.
- the rotation of the sun gear 35 is transmitted via the planetary gear sets 33, 34 to the ring gear 32 and the setting wheel 38 and through the clutch 43 to the setting wheel 39.
- the rotation of the adjusting wheels 38, 39 then causes the radial adjustment of the adjusting elements 21, because by the rotating adjusting wheels 38, 39 and thereby changing plan curves 40, 41, the positions of the pins 42 with respect to the axis change Depending on the direction of rotation of the actuator 27, the arranged on the adjusting elements 21 receptacles 12 move radially outward inside, so that the running circle L is thus increased or decreased.
- each wheel 15, 16 is associated with a setting wheel 44, 45.
- the disk 16 is associated with the thumbwheel 44.
- the disc 15 is associated with the setting wheel 45.
- the thumbwheel 44 is an integral part of the ring gear 32.
- the thumbwheel 44 is further assigned a bevel gear 46.
- the thumbwheel 45 is connected via suitable couplings 47 corresponding to the couplings 43, with the thumbwheel 44.
- the thumbwheel 45 is also assigned a bevel gear 48.
- each actuator 21 has a spindle 49.
- Each of the spindles 49 is aligned radially to the axis 13 and provided with a bevel gear 50 for producing the operative connection with one of the two adjusting wheels 44, 45.
- the bevel gears 50 with the bevel gears 46 and 48, respectively.
- the spindles 49 run in threaded guides S1, which has each actuator 21.
- the actuator 27 For superposition of the adjusting movement of the actuator 27 is actuated.
- the rotation of the sun gear 35 is transmitted via the planetary gearsets 33, 34 to the ring gear 32 and the thumbwheel 44 and through the clutch 47 to the thumbwheel 45.
- the rotation of the adjusting wheels 44, 45 then causes the radial adjustment of the adjusting elements 21.
- the adjusting elements 21 run with their threaded guides 51 quasi on the spindles 49 depending on the direction of rotation of the adjusting wheels 44, 45 up and down or radially outward or inward. Accordingly, the receptacles 12 move in the radial direction to change the diameter of the running circle L.
- the entire unit of conveyor 11, adder 26 and clutch (s) 43 and 47 is disposed on a frame 52 and guided on or in linear guides 53.
- an actuator 54 the entire unit is designed to be height adjustable. The height adjustment serves to compensate for the change in diameter of the conveyor 11 or to compensate for the radial displacement of the receptacles 12.
- the actuator 27 and the actuator 54 are formed as a single actuator.
- the common actuator is still in operative connection with a gear arrangement 55.
- the actuators 27 and 54 are formed separately from each other.
- the actuator 54 drives therein a spindle 56, which leads to adjust the height position of the unit along the linear guides 53.
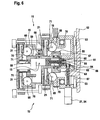
- the change of the running circle L is in the embodiment according to the FIGS. 6 and 7 achieved by a pinion arrangement.
- the conveyor 11 is at least one Assigned adjusting wheel.
- each wheel 15, 16 is associated with a setting wheel 57, 58, wherein the setting wheel 57 of the disc 16 and the setting wheel 58 of the disc 15 is associated.
- the adjusting wheels 57, 58 have a groove 59 which is formed ste Trentslos.
- the adjusting wheels 57, 58 are in the operation of a rack according to and in the axial direction of the axis 13 movable. In other words, replace the adjusting wheels 57, 58 in a number of twelve shots 12 twelve racks.
- the setting wheel 57 is for this purpose with a driver element 60 in conjunction, which is arranged on a sleeve 61.
- the sleeve 61 is arranged on a spindle 62 which is rotatable but in the axial direction but stationary in the region of the axis 13, preferably in a recess 63 of the axis 13 is arranged in its longitudinal extent.
- a bevel gear 65 is arranged, which is in engagement with a bevel gear 66 of a further spindle 67.
- the spindle 67 is rotatably driven by means of the actuator 27, which is also the actuator 54 for height adjustment at the same time.
- the setting wheel 58 is connected via a coupling 68 which corresponds to the clutch 43 of the embodiment described above, in operative connection with the setting wheel 57, so that the axial movement of the setting wheel 58 can be transferred to the setting wheel 57.
- Each actuator 21 is associated with a pinion 69 having a groove 70 which corresponds to the groove 59 of the adjusting wheels 57, 58.
- the adjusting elements 21 also have a groove 71.
- the pinions 69 thus serve to produce an operative connection between the adjusting wheels 57, 58, on the one hand, and the adjusting elements 21, on the other hand.
- the device 10 according to FIGS. 6 and 7 functions in principle as follows:
- the axial movement of the adjusting elements 21 leads for changing the position of the receptacles 12, which describe the running circle L. Adjusted to the change of the running circle L, the height of the unit of conveying means 11, adjusting wheels 57, 58 and coupling (s) 68 is adapted by the spindle 67.
- the device 10 may be associated with a control, such that an adjustment of the device 10, so in particular a radial adjustment of the receptacles 12 and an adjustment of the height of the entire unit by means of "push of a button" automatically coordinated feasible.
- the drive 24 and the actuators 27 and 54 are connected to the controller.
Landscapes
- Specific Conveyance Elements (AREA)
- Manufacturing Of Cigar And Cigarette Tobacco (AREA)
- Chain Conveyers (AREA)
- Attitude Control For Articles On Conveyors (AREA)
- Cigarettes, Filters, And Manufacturing Of Filters (AREA)
- Retarders (AREA)
- Heat Treatment Of Articles (AREA)
Description
- Die Erfindung betrifft eine Vorrichtung zur Übergabe stabförmiger Artikel, insbesondere Filterstäbe, von einer Vorrichtung zur queraxialen Förderung der Artikel auf eine Vorrichtung zur längsaxialen Förderung der Artikel oder umgekehrt, wobei die Transportrichtungen der Vorrichtungen quer zueinander verlaufen, umfassend ein rotierend antreibbares Fördermittel mit mindestens einer Aufnahme, wobei jede Aufnahme zur Abnahme mindestens eines Artikels von der Vorrichtung zur queraxialen Förderung der Artikel und Abgabe des oder jedes aufgenommenen Artikels auf die Vorrichtung zur längsaxialen Förderung oder umgekehrt ausgebildet ist.
- Derartige Vorrichtung kommen insbesondere in der tabakverarbeitenden Industrie zum Einsatz. Die stabförmigen Artikel können z.B. Filter, Filtersegmente oder Segmentgruppen sowie Zigaretten oder dergleichen sein. Bei der Bearbeitung bzw. Herstellung solcher Artikel ist es aufgrund von winklig angeordneten Maschinen und Vorrichtungen erforderlich, die Artikel von einer queraxialen Förderung auf eine längsaxiale Förderung oder umgekehrt umzusetzen. Hierzu dient die gattungsgemäße Vorrichtung.
- Die genannte Vorrichtung muß jedoch an die jeweilige Länge und/oder den jeweiligen Durchmesser der umzusetzenden Artikel angepaßt werden, um eine optimale Produktivität zu erzielen. Dies wird im folgenden am Beispiel der Herstellung von Filtern erläutert. Jeder Filter besteht üblicherweise aus einer oder mehreren Komponenten, den sogenannten Segmenten, die mit Umhüllungsmaterial umgeben werden. Filter weisen je nach Anforderung und/oder Kundenwunsch eine unterschiedliche Länge und/oder einen unterschiedlichen Durchmesser auf. In der Vergangenheit haben Filter oftmals aus einer einzigen Komponente bestanden.
- Heutzutage ist der Filter üblicherweise aus mehreren Komponenten gebildet. Dabei entstehen unterschiedliche Filterlängen, die in der Regel in einem Bereich von etwa 21 bis 27 mm liegen. Andere Längen sind jedoch ebenfalls Standard. Des weiteren kann es auch zu Durchmesserveränderungen kommen. Filter bzw. das Filtermaterial oder die Filtersegmente werden in einfacher oder mehrfacher Gebrauchslänge oder in Segmentgruppen unterschiedlicher Länge vorbereitet und queraxial in Richtung der gattungsgemäßen Vorrichtung transportiert. Mittels der letztgenannten Vorrichtung werden die Artikel auf die Vorrichtung zur längsaxialen Förderung, die eigentliche Strangmaschine umgesetzt. Auf der Strangmaschine werden die einzelnen oder gruppenweise zusammengesetzten Filtersegmente mit Umhüllungspapier umgeben und in die endgültigen Filter geschnitten.
- Eine Filterlänge bzw. die Länge der Filtersegmente oder Segmentgruppen wird auch als Format bezeichnet. Bei der Herstellung kommt es häufig vor, daß ein Formatwechsel notwendig ist. D.h., daß die Produktion von einer ersten Länge auf eine zweite Länge, die von der ersten Länge abweicht, umgestellt werden muß, um eine optimale Ausnutzung der Produktivität der Vorrichtung sowie der vor- und nachgeschalteten Vorrichtungen zu erreichen. Diese Umstellung macht jedoch eine Veränderung des Durchmessers des Fördermittels bzw. eine Veränderung des durch die rotierend umlaufenden Aufnahmen beschriebenen Laufkreises notwendig, um die Einrichtung an die jeweils gewünschte Schnittlänge der Filter optimal anzupassen. Bei heutigen Vorrichtungen erfordert dies den Austausch des gesamten Fördermittels. Für jedes Format existiert ein eigenes separates Fördermittel, das bei Maschinenstillstand ausgetauscht werden muß. Der Formatwechsel führt zu erheblichem Montageaufwand, der ebenso wie der Maschinenstillstand zu erhöhten Kosten führt.
- Es ist daher Aufgabe der vorliegenden Erfindung, eine Vorrichtung zu schaffen, die einen Formatwechsel mit reduziertem Aufwand gewährleistet.
- Diese Aufgabe wird durch eine Vorrichtung mit den eingangs genannten Merkmalen dadurch gelöst, daß der durch die oder jede Aufnahme gebildete Laufkreis L variabel ausgebildet ist. Dadurch ist es auf einfache Weise möglich, das Fördermittel an das jeweils zu bearbeitende Format anzupassen. Innerhalb einer gewissen Bandbreite ist die Einrichtung zur Übergabe unterschiedlicher Formate geeignet. Mit anderen Worten deckt ein einziges Fördermittel die gängigen Formate ab, so daß ein ständiger Austausch der Fördermittel vermieden werden kann. Das erspart Montageaufwand und damit Kosten.
- In einer vorteilhaften Ausgestaltung der Erfindung ist die oder jede Aufnahme zur Veränderung des Laufkreises L radial verstellbar ausgebildet. Dadurch läßt sich auf besonders einfache Weise eine Anpassung des Durchmessers des Laufkreises L bei konstanter Anzahl der Aufnahmen erreichen. Radial verstellbar meint in diesem Zusammenhang neben der tatsächlichen radialgerichteten Bewegung auch Schwenk-, Kipp-, Wipp- oder anderweitige Bewegungen, die in einer radialen Verstellung des Laufkreises L resultieren.
- In einer bevorzugten Ausführungsform der Erfindung sind mehrere Aufnahmen gleichmäßig über den Umfang des Fördermittels verteilt angeordnet, wobei sämtliche Aufnahmen synchron während des Betriebs der Vorrichtung radial verstellbar ausgebildet sind. Mit dieser Ausführung ist eine on-line-Anpassung des Fördermittels an unterschiedliche Formate möglich, wodurch ein Maschinenstillstand verhindert wird. Dies führt zu einer erhöhten Flexibilität der Vorrichtung sowie zu einer Kostensenkung.
- Weitere bevorzugte und vorteilhafte Merkmale und Ausführungsformen ergeben sich aus den Unteransprüchen und der Beschreibung. Besonders bevorzugte Ausführungsformen der Erfindung sowie das Verfahrensprinzip werden im folgenden anhand der beigefügten Zeichnung näher erläutert. In der Zeichnung zeigt:
- Fig. 1
- eine Seitenansicht einer ersten Ausführungsform der Vorrichtung zur Übergabe stabförmiger Artikel im Schnitt,
- Fig. 2
- eine Vorderansicht der Vorrichtung gemäß
Figur 1 , - Fig.
- 3 eine Variante der ersten Ausführungsform gemäß
Figur 1 im Schnitt, - Fig. 4
- eine Seitenansicht einer weiteren Ausführungsform der Vorrichtung zur Übergabe stabförmiger Artikel im Schnitt,
- Fig. 5
- eine Vorderansicht der Ausführungsform gemäß
Figur 4 , - Fig. 6
- eine Seitenansicht einer weiteren Ausführungsform der Vorrichtung zur Übergabe stabförmiger Artikel im Schnitt, und
- Fig. 7
- eine Vorderansicht der Ausführungsform gemäß
Figur 6 . - Die gezeigten Vorrichtungen dienen zur Übergabe stabförmiger Artikel von einer Vorrichtung zur queraxialen Förderung der Artikel auf eine Vorrichtung zur längsaxialen Förderung der Artikel. Die Vorrichtungen können jedoch in gleicher Weise für die Übergabe von einer Vorrichtung zur längsaxialen Förderung auf eine Vorrichtung zur queraxialen Förderung ausgebildet sein und eingesetzt werden.
- Die
Figuren 1 und2 zeigen eine erste Ausführungsform einer Vorrichtung 10 zur Übergabe stabförmiger Artikel. Die Vorrichtung 10 ist üblicherweise zwischen einer (nicht dargestellten) Vorrichtung zur queraxialen Förderung der Artikel, beispielsweise einer Einrichtung zum Zusammenstellen von Gruppen von Filtersegmenten zur Herstellung von Multisegmentfiltern, und einer (ebenfalls nicht dargestellten) Vorrichtung zur längsaxialen Förderung der Artikel, beispielsweise einer Strangbildevorrichtung, angeordnet. Die Vorrichtung 10 umfaßt im wesentlichen ein Fördermittel 11, das mindestens eine, vorzugsweise aber mehrere Aufnahmen 12 aufweist. Die Aufnahmen 12 dienen zur Abnahme mindestens eines Artikels von der Vorrichtung zur queraxialen Förderung und Abgabe des oder jeden aufgenommenen Artikels an die Vorrichtung zur längsaxialen Förderung. Hierzu ist das Fördermittel 11 um eine Achse 13 rotierend antreibbar. Mehrere, vorzugsweise zwölf Aufnahmen 12 sind gleichmäßig über den Umfang des Fördermittels 11 verteilt, wobei sämtliche Aufnahmen 12 synchron während des Betriebs der Vorrichtung 10 radial verstellbar sind. Jede Aufnahme 12 ist schwenkbar am Fördermittel 11 angeordnet, so daß Formathalter 14, die jeder Aufnahme 12 zugeordnet sind, vorzugsweise in jeder Position, insbesondere jedoch zum Zeitpunkt der Aufnahme der Artikel und Abgabe der Artikel, parallel zu den Artikeln laufen. Dies ist üblicherweise die horizontale Position. Die Formathalter 14 sind an das jeweils zu übergebene Format, insbesondere was die Länge und den Durchmesser der Artikel betrifft, angepaßt. Der Formathalter 14 kann zur Aufnahme eines einzelnen Artikels, aber auch zur Aufnahme mehrerer parallel nebeneinander angeordneter Artikel ausgebildet sein. Zur Veränderung des Durchmessers des Fördermittels 11 bzw. des durch die mit dem Fördermittel 11 rotierenden Aufnahmen 12 gebildeten bzw. beschriebenen Laufkreises L sind die Aufnahmen 12 variabel ausgebildet. Die Verstellung auf unterschiedliche Durchmesser kann manuell oder automatisiert erfolgen. In jeder Ausführungsform ist die oder jede Aufnahme 12 zur Veränderung des Laufkreises L radial verstellbar ausgebildet. Die radiale Verstellung ist durch lineare und/oder kreis- oder bogenförmige und/oder schwenkende, wippende oder anderweitig bekannte und übliche Bewegungsanordnungen erreichbar. - Das Fördermittel 11 weist zwei Scheiben 15 und 16 auf, die auf der gemeinsamen Achse 13 zentrisch positioniert sind sind. Die vorzugsweise einstückig ausgebildete Achse 13 ist parallel versetzt ausgebildet, d.h., daß sie zwei Abschnitte 13.1 und 13.2 aufweist, die versetzt zueinander angeordnet sind. Die Abschnitte 13.1 und 13.2 bzw. die Rotationsachsen 17 und 18 der Abschnitte 13.1 und 13.2 verlaufen parallel zueinander. Die äußere Scheibe 15, die am freien Ende 23 der Achse 13, genauer des Abschnitts 13.1 angeordnet ist, in der beschriebenen Ausführung also der Vorrichtung zur längsaxialen Förderung zugewandt, ist auf dem Abschnitt 13.1 angeordnet und rotiert um die Rotationsachse 17. Die innere Scheibe 16 ist auf dem Abschnitt 13.2 angeordnet und rotiert um die Rotationsachse 18. Entsprechend sind die Scheiben 15, 16 parallel und axial versetzt zueinander angeordnet. Beide Scheiben 15, 16 sind miteinander über Gelenkelemente 19 miteinander gekoppelt und dadurch in Wirkverbindung, derart, daß sie mit der gleichen Geschwindigkeit um die Rotationsachsen 17, 18 rotieren. Die Aufnahmen 12 sind der vorderen Scheibe 15 zugeordnet. Genauer sind die Aufnahmen an freien Enden 20 der Gelenkelemente 19, die aus der Scheibe 15 hervorstehen, angeordnet.
- Die Scheiben 15, 16 weisen in der gezeigten Ausführungsform denselben Durchmesser auf. Die Durchmesser können jedoch auch unterschiedlich sein. Jede Scheibe 15, 16 verfügt über Stellelemente 21. Die Stellelemente 21 sind im Bereich des Umfangs der jeweiligen Scheibe 15 bzw. 16 angeordnet. Die Anzahl der Stellelemente 21 pro Scheibe 15, 16 entspricht vorzugsweise der Anzahl der Aufnahmen 12. Die Stellelemente 21 sind segmentiert, d.h. daß jedes Stellelement 21 ist separat vom benachbarten Stellelement 21 ausgebildet ist. Jede Aufnahme 12 ist einem Stellelementepaar zugeordnet. Das Stellelementepaar ist aus einem Stellelement 21 der Scheibe 15 und einem korrespondierenden Stellelement 21 der Scheibe 16 gebildet. Die Stellelemente 21 eines Stellelementepaares sind in Vorderansicht hintereinander angeordnet. Die Verbindung zwischen den Scheiben 15, 16 bzw. zwischen den Stellelementen 21 jedes Stellelementepaares ist durch die Gelenkelemente 19 hergestellt, die ebenso wie die Achse 13 parallel versetzt oder auch abgewinkelt ausgebildet sind. Die Gelenkelemente 19 sind in den Stellelementen 21 gelagert, so daß sich die an den Gelenkelementen 19 angeordneten Aufnahmen 12 trotz Rotation der Scheiben 15, 16 stets in derselben Position in bezug auf die Ausrichtung zu den Artikeln befinden. Die Stellelemente 21 sind in Ausnehmungen 22 der Scheiben 15, 16 angeordnet.
- Das Fördermittel 11 bzw. genauer die Scheiben 15, 16 sind mittels eines Antriebs 24 rotierend antreibbar. Der Antrieb 24 ist über einen Zahnriemen 25 oder andere gängige Ubertragungselemente in Wirkverbindung mit einer der Scheiben 15, 16, vorzugsweise der inneren Scheibe 16. Durch die Gelenkelemente 19 ist die Rotation der Scheibe 16 auf die Scheibe 15 übertragbar. Beide Scheiben 15, 16 rotieren mit derselben Geschwindigkeit. Zur Veränderung des Durchmessers des Fördermittels 11 bzw. des durch die am Fördermittel 11 angeordneten Aufnahmen 12 beschriebenen Laufkreises L ist der Rotationsbewegung der Scheiben 15, 16 eine zusätzliche Bewegung überlagerbar.
- Sämtliche gezeigte Ausführungsformen gemäß der
Figuren 3 bis 7 sind grundsätzlich nach dem gleichen Prinzip aufgebaut, wie die zuvor beschriebene Ausführungsform derFiguren 1 und2 , so daß auf eine erneute Beschreibung verzichtet wird. Für gleiche Teile werden die selben Bezugsziffern verwendet. Die unterschiedlichen Ausführungsformen unterscheiden sich jedoch in der Ausbildung des Mechanismus zur Verstellung des durch die Aufnahmen 12 gebildeten Laufkreises L. Mit anderen Worten werden im folgenden verschiedene Möglichkeiten erläutert, wie der eigentlichen Rotationsbewegung des Fördermittels 11, nämlich der Scheiben 15, 16 eine zusätzliche Stellbewegung überlagert werden kann. - Gemäß der Ausführungsform der
Figuren 1 und2 ist dem Fördermittel 11 zur Überlagerung einer zusätzlichen Bewegung ein Getriebe, insbesondere ein Additionsgetriebe 26 zugeordnet. Das Additionsgetriebe 26 ist mit einem Stellantrieb 27 in Wirkverbindung und durch diesen antreibbar. Die Wirkverbindung zwischen dem Stellantrieb 27 und dem Additionsgetriebe 26 ist durch einen Zahnriemen 28 oder andere gängige Übertragungselemente hergestellt. Das Additionsgetriebe 26 umfaßt im wesentlichen zwei Planetengetriebe 29, 30, die parallel zueinander geschaltet sind. Beide Planetengetriebe 29, 30 verfügen über ein Hohlrad 31, 32, einen Satz Planetenräder 33, 34 sowie ein Sonnenrad 35, 36. Jeder Satz Planetenräder 33, 34 umfaßt mehrere Planetenräder, wobei in der gezeigten Ausführungsform zwei Planetenräder vorgesehen sind. Dabei ist jeweils ein Planetenrad des Satzes 33 mit einem Planetenrad des Satzes 34 über ein Achse 37 verbunden. Das vom Stellantrieb 27 angetriebene Sonnenrad 35 ist auf der Achse 13 zentrisch positioniert bzw. gelagert. Das Sonnenrad 36 ist drehfest auf der Achse 13 angeordnet. Das dem Satz Planetenräder 33 zugeordnete Hohlrad 31 ist integraler Bestandteil der Scheibe 16. Das Hohlrad 32 ist gleichzeitig als Stellrad 38 ausgebildet. - Dem Fördermittel 11 ist mindestens ein Stellrad zugeordnet. Vorzugsweise weist jedoch jede Scheibe 15, 16 ein Stellrad auf. Der Scheibe 15 ist das Stellrad 39 zugeordnet. Der Scheibe 16 ist das Stellrad 38 zugeordnet. Beide Stellräder 38, 39 weisen jeweils eine Plankurve 40, 41 auf. Die Plankurven 40, 41 verlaufen, ausgehend von der Achse 13 spiralförmig nach außen zum Umfang der Scheiben 15, 16. Zur Herstellung einer Wirkverbindung zwischen den Stellrädern 38, 39 und den Scheiben 15, 16 bzw. den den Scheiben 15, 16 zugeordneten Stellelementen 21 weisen letztere jeweils einen Zapfen 42 oder dergleichen auf. Die Zapfen 42 aller Stellelemente 21 sind in den Plankurven 40, 41, die auch als Steuerkurven oder Stellkurven bezeichnet werden können, geführt. Die Zapfen 42 der Stellelemente 21, die der Scheibe 16 zugeordnet sind, sind der Plankurve 40 des Stellrades 38 zugeordnet. Die Zapfen 42 der Stellelemente 21, die der Scheibe 15 zugeordnet sind, sind der Plankurve 41 des Stellrades 39 zugeordnet. Die Stellräder 38, 39 sind mittels geeigneter Kupplungselemente, vorzugsweise Schmidtkupplungen 43, zur Ausführung einer synchronen Bewegung miteinander verkuppelt. Andere bekannte Kupplungsarten, wie z.B. Oldham-Kupplungen oder auch Gelenkwellen oder andere übliche Kupplungselemente sind ebenfalls einsetzbar.
- Die Funktionsweise der Ausführungsform gemäß der
Figuren 1 und2 sowie auch der Ausführungsform derFigur 3 , die sich lediglich durch die Höhenverstellung, die weiter unten beschrieben wird, von der Ausführungsform gemäßFigur 1 und2 unterscheidet, ist wie folgt:
Das Fördermittel 11 bzw. die Scheiben 15, 16 rotieren mit derselben Geschwindigkeit und nehmen im einem Abnahmepunkt den oder die Artikel von einer ersten Vorrichtung ab und geben sie an einem Abgabepunkt an eine zweite Vorrichtung ab. Sobald ein anderes Format übergeben werden soll, wird der Rotation der Scheiben 15, 16 eine weitere Bewegung überlagert, um das Fördermittel 11 an das neue Format anzupassen. Hierzu wird der Stellantrieb 27 betätigt. Die Rotation des Sonnenrades 35 wird über die Planetenradsätze 33, 34 auf das Hohlrad 32 bzw. das Stellrad 38 und durch die Kupplung 43 auf das Stellrad 39 übertragen. Die Rotation der Stellräder 38, 39 bewirkt dann die radiale Verstellung der Stellelemente 21, denn durch die sich drehenden Stellräder 38, 39 und die sich dadurch verändernden Plankurven 40, 41 verändern sich auch die Positionen der Zapfen 42 in bezug auf die Achse 13. In Abhängigkeit der Drehrichtung des Stellantriebs 27 bewegen sich die an den Stellelementen 21 angeordneten Aufnahmen 12 radial nach außen innen, so daß der Laufkreis L somit vergrößert oder verkleinert wird. - In der Ausführungsform gemäß der
Figuren 4 und5 ist dem Fördermittel 11 ebenfalls mindestens ein Stellrad zugeordnet. Vorzugsweise ist jedoch jeder Scheibe 15, 16 ein Stellrad 44, 45 zugeordnet. Der Scheibe 16 ist das Stellrad 44 zugeordnet. Der Scheibe 15 ist das Stellrad 45 zugeordnet. Das Stellrad 44 ist integraler Bestandteil des Hohlrades 32. Dem Stellrad 44 ist weiterhin ein Kegelrad 46 zugeordnet. Das Stellrad 45 ist über geeignete Kupplungen 47, die den Kupplungen 43 entsprechen, mit dem Stellrad 44 verbunden. Dem Stellrad 45 ist ebenfalls ein Kegelrad 48 zugeordnet. - In dieser Ausführungsform verfügt jedes Stellelement 21 über eine Spindel 49. Jede der Spindeln 49 ist radial zur Achse 13 ausgerichtet und mit einem Kegelrad 50 zur Herstellung der Wirkverbindung mit einem der beiden Stellräder 44, 45 versehen. Hierzu sind die Kegelräder 50 mit den Kegelrädern 46 bzw. 48 in Eingriff. Die Spindeln 49 laufen in Gewindeführungen S1, die jedes Stellelement 21 aufweist.
- Zur Überlagerung der Stellbewegung wird der Stellantrieb 27 betätigt. Die Rotation des Sonnenrades 35 wird über die Planetenradsätze 33, 34 auf das Hohlrad 32 bzw. das Stellrad 44 und durch die Kupplung 47 auf das Stellrad 45 übertragen. Die Rotation der Stellräder 44, 45 bewirkt dann die radiale Verstellung der Stellelemente 21. Durch die Rotation der Spindeln 49, die über die Kegelradpaarungen 46, 50 bzw. 48, 50 angetrieben werden, laufen die Stellelemente 21 mit ihren Gewindeführungen 51 quasi auf den Spindeln 49 in Abhängigkeit der Drehrichtung der Stellräder 44, 45 auf und ab bzw. radial nach außen oder nach innen. Entsprechend bewegen sich die Aufnahmen 12 in radialer Richtung zu Veränderung des Durchmessers des Laufkreises L.
- Die gesamte Einheit aus Fördermittel 11, Additionsgetriebe 26 und Kupplung(en) 43 bzw. 47 ist an einem Gestell 52 angeordnet und an bzw. in Linearführungen 53 geführt. Durch einen Stellantrieb 54 ist die gesamte Einheit höhenverstellbar ausgebildet. Die Höhenverstellung dient zum Ausgleich der Durchmesserveränderung des Fördermittels 11 bzw. zum Ausgleich der radialen Verstellung der Aufnahmen 12. In der Ausführungsform gemäß
Figur 1 sind der Stellantrieb 27 und der Stellantrieb 54 als ein einziger Stellantrieb ausgebildet. Zur Höhenverstellung ist der gemeinsame Stellantrieb noch mit einer Zahnradanordnung 55 in Wirkverbindung. Gleiches gilt für die Ausführungsform gemäßFigur 4 . In der Ausführungsform gemäßFigur 3 sind die Stellantriebe 27 und 54 getrennt voneinander ausgebildet. Der Stellantrieb 54 treibt darin eine Spindel 56 an, die zur Verstellung der Höhenposition der Einheit entlang der Linearführungen 53 führt. - Die Veränderung des Laufkreises L wird in der Ausführungsform gemäß der
Figuren 6 und7 durch eine Ritzelanordnung erreicht. Dem Fördermittel 11 ist mindestens ein Stellrad zugeordnet. Vorzugsweise ist jeder Scheibe 15, 16 ein Stellrad 57, 58 zugeordnet, wobei das Stellrad 57 der Scheibe 16 und das Stellrad 58 der Scheibe 15 zugeordnet ist. Die Stellräder 57, 58 weisen eine Rillung 59 auf, die steigungslos ausgebildet ist. Die Stellräder 57, 58 sind in der Wirkungsweise einer Zahnstange entsprechend und in axialer Richtung der Achse 13 bewegbar. Mit anderen Worten ersetzen die Stellräder 57, 58 bei einer Anzahl von zwölf Aufnahmen 12 zwölf Zahnstangen. Das Stellrad 57 ist dazu mit einem Mitnehmerelement 60 in Verbindung, das auf einer Hülse 61 angeordnet ist. Die Hülse 61 ist auf einer Spindel 62 angeordnet, die drehbar, in axialer Richtung aber ortsfest im Bereich der Achse 13, vorzugsweise in einer Ausnehmung 63 der Achse 13 in deren Längserstreckung angeordnet ist. Am freien Ende 64 der Spindel 62 ist ein Kegelrad 65 angeordnet, das mit einem Kegelrad 66 einer weiteren Spindel 67 im Eingriff steht. Die Spindel 67 ist mittels des Stellantriebs 27, der gleichzeitig auch der Stellantrieb 54 zur Höhenverstellung ist, rotierend antreibbar. - Das Stellrad 58 ist über eine Kupplung 68, die der Kupplung 43 der weiter oben beschriebenen Ausführungsform entspricht, in Wirkverbindung mit dem Stellrad 57, so daß die axiale Bewegung des Stellrades 58 auf das Stellrad 57 übertragbar ist. Jedem Stellelement 21 ist ein Ritzel 69 zugeordnet, das eine Rillung 70 aufweist, die mit der Rillung 59 der Stellräder 57, 58 korrespondiert. Auch die Stellelemente 21 verfügen über eine Rillung 71. Die Ritzel 69 dienen somit zur Herstellung einer Wirkverbindung zwischen den Stellrädem 57, 58 einerseits und den Stellelementen 21 andererseits.
- Zur Überlagerung der Stellbewegung wird der Stellantrieb 27 betätigt. Durch die Rotation des Kegelrades 66 und damit des Kegelrades 65 wird die Hülse 61 in axialer Richtung in Abhängigkeit der Drehrichtung nach vorne oder hinten verschoben. Mittels des Mitnehmerelementes 60 wird diese axiale Bewegung auf das Stellrad 57 übertragen. Die Kupplung 68 überträgt die axiale Bewegung auf das Stellrad 58, so daß die axialen Bewegungen der Stellräder 57, 58 synchron verlaufen. Die axiale Bewegung der Stellräder 57, 58 wird in eine rotierende Bewegung der Ritzel 69 transformiert, wobei die rotierende Bewegung der Ritzel 69 wiederum in eine axiale Bewegung der Stellelemente 21 transformiert wird. Die axiale Bewegung der Stellelemente 21 führt zur Veränderung der Position der Aufnahmen 12, die den Laufkreis L beschreiben. Abgestimmt auf die Veränderung des Laufkreises L wird die Höhe der Einheit aus Fördermittel 11, Stellrädem 57, 58 und Kupplung(en) 68 durch die Spindel 67 angepaßt.
- Des weiteren kann der Vorrichtung 10 gemäß aller Ausführungsformen eine Steuerung zugeordnet sein, derart, daß eine Verstellung der Vorrichtung 10, also insbesondere eine radiale Verstellung der Aufnahmen 12 sowie eine Anpassung der Höhe der gesamten Einheit mittels "Knopfdruck" koordiniert automatisch durchführbar ist. Hierzu sind der Antrieb 24 sowie die Stellantriebe 27 und 54 mit der Steuerung verbunden.
Claims (24)
- Vorrichtung zur Übergabe stabförmiger Artikel, insbesondere Filterstäbe, von einer Vorrichtung zur queraxialen Förderung der Artikel auf eine Vorrichtung zur längsaxialen Förderung der Artikel oder umgekehrt, wobei die Transportrichtungen der Vorrichtungen quer zueinander verlaufen, umfassend ein rotierend antreibbares Fördermittel (11) mit mindestens einer Aufnahme (12), wobei jede Aufnahme (12) zur Abnahme mindestens eines Artikels von der Vorrichtung zur queraxialen Förderung der Artikel und Abgabe des oder jedes aufgenommenen Artikels auf die Vorrichtung zur längsaxialen Förderung oder umgekehrt ausgebildet ist, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß der durch die oder jede Aufnahme (12) gebildete Laufkreis L variabel ausgebildet ist.
- Vorrichtung nach Anspruch 1, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß die oder jede Aufnahme (12) zur Veränderung des Laufkreises L radial verstellbar ausgebildet ist.
- Vorrichtung nach Anspruch 1 oder 2, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß mehrere Aufnahmen (12) gleichmäßig über den Umfang des Fördermittels (11) verteilt angeordnet sind, wobei sämtliche Aufnahmen (12) synchron während des Betriebs der Vorrichtung (10) radial verstellbar sind.
- Vorrichtung nach einem der Ansprüche 1 bis 3, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß das Fördermittel (11) zwei Scheiben (15, 16) umfaßt, die auf einer parallel versetzten Achse (13) angeordnet sind.
- Vorrichtung nach Anspruch 4, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß die Aufnahmen (12) der vorderen, am freien Ende (23) der Achse (13) angeordneten Scheibe (15) zugeordnet sind.
- Vorrichtung nach Anspruch 4 oder 5, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß die Scheiben (15, 16) über Gelenkelemente (19) miteinander verbunden sind, derart, daß die Scheiben (15, 16) synchron rotierend antreibbar sind.
- Vorrichtung nach einem der Ansprüche 4 bis 6, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß die Scheiben (15, 16) denselben Durchmesser aufweisen.
- Vorrichtung nach einem der Ansprüche 4 bis 7, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß jede Scheibe (15, 16) über Stellelemente (21) verfügt, wobei die Stellelemente (21) im Bereich des Umfangs der jeweiligen Scheibe (15, 16) angeordnet sind.
- Vorrichtung nach Anspruch 8, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß die Anzahl der Stellelemente (21) jeder Scheibe (15, 16) der Anzahl der Aufnahmen (12) entspricht.
- Vorrichtung nach Anspruch 8 oder 9, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß jedem Stellelement (21) der ersten Scheibe (15) ein Stellelement (21) der zweiten Scheibe (16) zur Bildung eines Stellelementepaares zugeordnet ist.
- Vorrichtung nach Anspruch 10, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß jedes Stellelementepaar mittels der Gelenkelemente (19) untereinander in Wirkverbindung steht.
- Vorrichtung nach einem der Ansprüche 6 bis 11, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß die Aufnahmen (12) an freien Enden (20) der Gelenkelemente (19) angeordnet sind.
- Vorrichtung nach einem der Ansprüche 4 bis 12, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß dem Fördermittel (11) ein Antrieb (24) zugeordnet ist, wobei der Antrieb (24) in unmittelbarer Wirkverbindung mit einer der Scheiben (15, 16), vorzugsweise der hinteren Scheibe (16) steht.
- Vorrichtung nach einem der Ansprüche 1 bis 13, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß dem Fördermittel (11) ein Getriebe, insbesondere ein Additionsgetriebe (26) zugeordnet ist.
- Vorrichtung nach Anspruch 14, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß dem Additionsgetriebe (26) ein Stellantrieb (27) zur Überlagerung einer Stellbewegung der Aufnahmen (12) zusätzlich zu deren Rotation zugeordnet ist.
- Vorrichtung nach einem der Ansprüche 1 bis 15, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß dem Fördermittel (11) mindestens ein Stellrad (38, 39) mit einer Plankurve (40, 41) zugeordnet ist.
- Vorrichtung nach Anspruch 16, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß jedes Stellelement (21) einen Zapfen (42) aufweist, der zur Herstellung einer Wirkverbindung mit einem der Stellräder (38, 39) in der entsprechenden Plankurve (40, 41) positioniert ist.
- Vorrichtung nach einem der Ansprüche 1 bis 15, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß dem Fördermittel (11) mindestens ein Stellrad (44, 45) mit einem Kegelrad (46, 48) zugeordnet ist.
- Vorrichtung nach Anspruch 18, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß jedem Stellelement (21) eine Spindel (49) zugeordnet ist, die radial zur Achse (13) ausgerichtet ist und zur Herstellung einer Wirkverbindung mit einem der beiden Stellräder (44, 45) mit einem Kegelrad (50) versehen ist.
- Vorrichtung nach einem der Ansprüche 1 bis 15, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß dem Fördermittel (11) mindestens ein Stellrad (57, 58) mit einer steigungslosen Rillung (59) zugeordnet ist.
- Vorrichtung nach Anspruch 20, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß jedem Stellelement (21) ein Ritzel (69) zugeordnet ist, wobei das Ritzel (69) zur Herstellung einer Wirkverbindung mit einer der Rillung (59) der Stellräder (57, 58) korrespondierenden Rillung (70) versehen ist und mit einer korrespondierenden Rillung (71), die jedem Stellelement (21) zugeordnet ist, in Eingriff steht.
- Vorrichtung nach einem der Ansprüche 16 bis 21, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß die Stellräder (38, 39; 44, 45; 57, 58) mittels einer Kupplung (43; 47; 68), insbesondere einer Schmidtkupplung, miteinander in Wirkverbindung stehen.
- Vorrichtung nach Anspruch 22, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß die gesamte Einheit aus Fördermittel (11), Additionsgetriebe (26) bzw. Stellrädern (57, 58) und Kupplung(en) (43; 47; 68) höhenverstellbar ausgebildet ist.
- Vorrichtung nach Anspruch 23, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß der Einheit ein Stellantrieb (27, 54) zugeordnet ist.
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| PL05090268T PL1639907T3 (pl) | 2004-09-24 | 2005-09-22 | Urządzenie do przekazywania sztabkowych wyrobów |
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE102004047266A DE102004047266A1 (de) | 2004-09-24 | 2004-09-24 | Vorrichtung zur Übergabe stabförmiger Artikel |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP1639907A1 EP1639907A1 (de) | 2006-03-29 |
| EP1639907B1 true EP1639907B1 (de) | 2008-10-08 |
| EP1639907B8 EP1639907B8 (de) | 2009-01-07 |
Family
ID=35447770
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP05090268A Active EP1639907B8 (de) | 2004-09-24 | 2005-09-22 | Vorrichtung zur Übergabe stabförmiger Artikel |
Country Status (7)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US7281621B2 (de) |
| EP (1) | EP1639907B8 (de) |
| JP (1) | JP4308807B2 (de) |
| CN (1) | CN100409776C (de) |
| AT (1) | ATE410083T1 (de) |
| DE (2) | DE102004047266A1 (de) |
| PL (1) | PL1639907T3 (de) |
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP2294934A2 (de) | 2009-09-15 | 2011-03-16 | HAUNI Maschinenbau AG | Einlegen von Filtersegmenten in Filterstränge |
| DE102013220757B3 (de) * | 2013-10-15 | 2015-01-15 | Hauni Maschinenbau Ag | Koaxialzigarettenherstellung |
| DE102016111818A1 (de) * | 2016-06-28 | 2017-12-28 | Hauni Maschinenbau Gmbh | Positionierung von stabförmigen Artikeln der Tabak verarbeitenden Industrie in eine Einlegevorrichtung |
Families Citing this family (14)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE102004057091B3 (de) | 2004-11-25 | 2006-06-14 | Hauni Maschinenbau Ag | Einstoßtrommel |
| PL217886B1 (pl) * | 2009-03-13 | 2014-08-29 | Int Tobacco Machinery Poland | Układ transferujący, współpracujący z maszyną do produkcji sztabek produktów tytoniowych i filtrowych, oraz sposób transferu takich sztabek w układzie transferującym |
| DE102010002132A1 (de) * | 2010-02-18 | 2011-08-18 | Hauni Maschinenbau AG, 21033 | Tabakstrangmaschine zur Herstellung von Tabakstäben, Filteransetzmaschine zum Verbinden von Filtern mit Tabakstäben sowie Zigarettenherstellungsmaschine |
| IT1402328B1 (it) * | 2010-10-15 | 2013-08-30 | I P S S R L Internat Project Services | "dispositivo di formazione di pacchi di sacchi in plastica" |
| ITBO20110158A1 (it) * | 2011-03-28 | 2012-09-29 | Gd Spa | Tamburo di trasferimento o di accompagnamento per spezzoni di filtro o di sigaretta con teste operative portate da bracci radiali. |
| DE102011007089B4 (de) * | 2011-04-08 | 2012-11-08 | Hauni Maschinenbau Ag | Rotationsfördervorrichtung und Verfahren zum Fördern von Artikeln der tabakverarbeitenden Industrie |
| DE102011082621B4 (de) * | 2011-09-13 | 2013-07-04 | Hauni Maschinenbau Ag | Bauteil für eine zum Fördern von Artikeln der Tabak verarbeitenden Industrie ausgebildete Fördervorrichtung, Bauteilesatz mit mindestens zwei derartigen Bauteilen sowie Fördervorrichtung mit einem derartigen Bauteil |
| DE102012201927B3 (de) * | 2012-02-09 | 2013-06-06 | Hauni Maschinenbau Ag | Längsförderer für stabförmige Produkte der Tabak verarbeitenden Industrie |
| US8820513B2 (en) | 2012-04-16 | 2014-09-02 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Methods for transferring discrete articles |
| ITBO20120664A1 (it) * | 2012-12-11 | 2014-06-12 | Gd Spa | Dispositivo di trasferimento di spezzoni di filtro o di sigaretta. |
| GB201222438D0 (en) * | 2012-12-13 | 2013-01-23 | British American Tobacco Co | Apparatus for processing a moving web of material |
| US9511951B1 (en) * | 2015-06-23 | 2016-12-06 | The Procter & Gamble Company | Methods for transferring discrete articles |
| CN108244701A (zh) * | 2016-12-29 | 2018-07-06 | 贵州中烟工业有限责任公司 | 控制滤棒吸阻及硬度的方法 |
| IT202000013483A1 (it) * | 2020-06-08 | 2021-12-08 | Gd Spa | Metodo e dispositivo di trasferimento per articoli a forma di barretta |
Citations (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5188212A (en) * | 1991-05-27 | 1993-02-23 | Winkler & Dunnebier Maschinenfabrik Und Eisengiesserei Kg | Rotating transport apparatus |
Family Cites Families (22)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE244236C (de) * | 1911-03-24 | 1912-03-04 | Berlin Anhaltische Maschinenbau Ag | Riemscheibe veraenderlichen Durchmessers mit Kranzabschnitte aus biegsamen Stoff tragenden, in Fuehrungen der Nabe radial verschiebbaren Speichen |
| DE649219C (de) * | 1935-10-27 | 1937-08-18 | Oswald Langer | Verstellbare Riemenscheibe |
| DE1087317B (de) * | 1955-02-28 | 1960-08-18 | Emil Blaschke | Vorrichtung zum fortlaufenden Schneiden endloser kuenstlicher Fadenbaender oder Kabel |
| DE1632213A1 (de) * | 1967-11-09 | 1970-08-06 | Hauni Werke Koerber & Co Kg | Foerdereinrichtung mit mindestens einer Aufnahme fuer einen Zigarettenstrang oder fuer Zigaretten |
| US3567011A (en) * | 1968-10-18 | 1971-03-02 | Reynolds Tobacco Co R | Cigarette transfer apparatus for changing direction and reducing velocity of cigarettes |
| GB1471258A (en) * | 1974-02-08 | 1977-04-21 | Molins Ltd | Ledgers for the cutting device of cigarettes and like rod- making machines |
| GB1522596A (en) * | 1974-10-15 | 1978-08-23 | Hauni Werke Koerber & Co Kg | Production of filter plugs |
| DE2549512A1 (de) * | 1975-11-05 | 1977-05-18 | Hauni Werke Koerber & Co Kg | Foerdervorrichtung zum foerdern stabfoermiger artikel der tabakverarbeitenden industrie |
| DE2809160A1 (de) * | 1978-03-03 | 1979-09-06 | Hauni Werke Koerber & Co Kg | Vorrichtung zum herstellen von kombinierten filterstopfen fuer filterzigaretten oder andere stabfoermige gegenstaende der tabakverarbeitenden industrie |
| DE2846279C2 (de) * | 1978-10-24 | 1982-04-15 | Aktiebolaget Iro, Ulricehamn | Riemenscheibe |
| SU1047378A3 (ru) * | 1980-06-19 | 1983-10-07 | Хауни-Верке Кербер Унд Ко,Кг (Фирма) | Устройство дл передачи стержнеобразных изделий табачной промышленности с одного транспортера на другой |
| GB2117199A (en) * | 1982-03-19 | 1983-10-05 | Philips Electronic Associated | Frequency synthesiser |
| IT1195400B (it) * | 1983-05-27 | 1988-10-19 | D D Spa | Metodo e macchina per la produzione contemporanea di due flussi continui di sigarette |
| GB8515567D0 (en) * | 1985-06-19 | 1985-07-24 | Molins Plc | Conveyor arrangement |
| DE3641064A1 (de) * | 1986-12-01 | 1988-06-16 | Hauni Werke Koerber & Co Kg | Foerdervorrichtung zum foerdern von einem doppelstrang abgetrennter stabfoermiger artikel der tabakverarbeitenden industrie |
| DE4035326C1 (en) * | 1990-11-07 | 1992-04-16 | Khs Eti-Tec Maschinenbau Gmbh, 4006 Erkrath, De | Labelling machine with rotary plates on turntable - has cam locating with drive wheel with magnetic force generating combination |
| DE4129672C2 (de) * | 1991-09-06 | 2002-04-11 | Hauni Werke Koerber & Co Kg | Fördervorrichtung zum Fördern stabförmiger Artikel der tabakverarbeitenden Industrie |
| US5327803A (en) * | 1992-10-19 | 1994-07-12 | R. J. Reynolds Tobacco Company | Transfer apparatus for cigarettes and other rod-shaped articles |
| IT1266343B1 (it) * | 1993-05-07 | 1996-12-27 | Gd Spa | Dispositivo di cambio-passo per una successione ordinata di elementi. |
| IT1293300B1 (it) * | 1997-08-06 | 1999-02-16 | Gd Spa | Dispositivo di trasferimento di spezzoni di sigaretta. |
| DE19847152A1 (de) * | 1998-10-13 | 2000-04-20 | Decoufle Sarl | Anordnung zum Überführen von ovalen Zigaretten aus einer axialen in eine queraxiale Förderbahn |
| JP2005089190A (ja) * | 2003-09-16 | 2005-04-07 | Hauni Maschinenbau Ag | 棒状の物品を引き渡すための装置及び方法 |
-
2004
- 2004-09-24 DE DE102004047266A patent/DE102004047266A1/de not_active Ceased
-
2005
- 2005-09-14 US US11/225,071 patent/US7281621B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2005-09-22 EP EP05090268A patent/EP1639907B8/de active Active
- 2005-09-22 DE DE502005005596T patent/DE502005005596D1/de active Active
- 2005-09-22 AT AT05090268T patent/ATE410083T1/de not_active IP Right Cessation
- 2005-09-22 JP JP2005274841A patent/JP4308807B2/ja not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2005-09-22 PL PL05090268T patent/PL1639907T3/pl unknown
- 2005-09-23 CN CNB2005101089352A patent/CN100409776C/zh not_active Expired - Fee Related
Patent Citations (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5188212A (en) * | 1991-05-27 | 1993-02-23 | Winkler & Dunnebier Maschinenfabrik Und Eisengiesserei Kg | Rotating transport apparatus |
Cited By (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP2294934A2 (de) | 2009-09-15 | 2011-03-16 | HAUNI Maschinenbau AG | Einlegen von Filtersegmenten in Filterstränge |
| DE102009041318A1 (de) | 2009-09-15 | 2011-03-31 | Hauni Maschinenbau Ag | Einlegen von Filtersegmenten in Filterstränge |
| EP2628399A1 (de) | 2009-09-15 | 2013-08-21 | HAUNI Maschinenbau AG | Übergabetrommel der Tabak verarbeitenden Industrie |
| DE102013220757B3 (de) * | 2013-10-15 | 2015-01-15 | Hauni Maschinenbau Ag | Koaxialzigarettenherstellung |
| DE102016111818A1 (de) * | 2016-06-28 | 2017-12-28 | Hauni Maschinenbau Gmbh | Positionierung von stabförmigen Artikeln der Tabak verarbeitenden Industrie in eine Einlegevorrichtung |
| EP3262959A1 (de) * | 2016-06-28 | 2018-01-03 | Hauni Maschinenbau GmbH | Positionierung von stabförmigen artikeln der tabakverarbeitenden industrie in eine einlegevorrichtung |
| DE102016111818B4 (de) | 2016-06-28 | 2018-10-11 | Hauni Maschinenbau Gmbh | Positionierung von stabförmigen Artikeln der Tabak verarbeitenden Industrie in eine Einlegevorrichtung |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| DE102004047266A1 (de) | 2006-04-06 |
| EP1639907B8 (de) | 2009-01-07 |
| CN1751609A (zh) | 2006-03-29 |
| ATE410083T1 (de) | 2008-10-15 |
| US7281621B2 (en) | 2007-10-16 |
| CN100409776C (zh) | 2008-08-13 |
| EP1639907A1 (de) | 2006-03-29 |
| JP2006087433A (ja) | 2006-04-06 |
| PL1639907T3 (pl) | 2009-04-30 |
| US20060076215A1 (en) | 2006-04-13 |
| JP4308807B2 (ja) | 2009-08-05 |
| DE502005005596D1 (de) | 2008-11-20 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP1639907B1 (de) | Vorrichtung zur Übergabe stabförmiger Artikel | |
| EP2258522B1 (de) | Vorrichtung zum Schneiden eines kontinuierlich geführten Strangs in strangförmige Artikel variabler Länge sowie Strangmaschine mit einer solchen Vorrichtung | |
| DE2549512C2 (de) | ||
| EP2628399B2 (de) | Übergabetrommel der Tabak verarbeitenden Industrie | |
| EP2524608B2 (de) | Schneideinrichtung für eine Strangmaschine der Tabak verarbeitenden Industrie und Verfahren zum Einstellen der Position der oder jeder Schleifscheibe einer Schleifvorrichtung in einer Schneideinrichtung für eine Strangmaschine der Tabak verarbeitenden Industrie | |
| DE2534666A1 (de) | Vorrichtung zum herstellen von kombinierten filterstopfen fuer filterzigaretten oder andere stabfoermige gegenstaende der tabakverarbeitenden industrie | |
| DE3542473C2 (de) | Vorrichtung zur Überführung von stabförmigen Gegenständen | |
| DE60036458T2 (de) | Drückwalzvorrichtung | |
| DE102007049547A1 (de) | Maschine zur Herstellung von zusammengesetzten Filtern | |
| DE3000321C2 (de) | Rotierende Stanzvorrichtung | |
| DE3123183C2 (de) | ||
| DE2746915A1 (de) | Vorrichtung zum fuehren von werkzeugen an tabakverarbeitenden maschinen | |
| DE3445575C2 (de) | Vorrichtung zum Beabstanden und Umwenden von zwei koaxialen Zigarettenlängenabschnitten in einer Filterbestückungsmaschine | |
| EP2106707B1 (de) | Vorrichtung zum Führen und Halten in Transportrichtung T kontinuierlich geförderter, strangförmiger Artikel, Verfahren zum Anpassen einer solchen Vorrichtung an unterschiedliche Schnittlängen sowie Tubenradsatz | |
| DE69617558T2 (de) | Verarbeitungsmaschine, insbesondere Verpackungsmaschine für Zigaretten oder dergleichen | |
| EP4114210B1 (de) | Fördertrommel der tabak verarbeitenden industrie | |
| DE69320149T2 (de) | Rollvorrichtung für Maschinen zur Verbindung von Filter mit Zigaretten | |
| DE3346042C2 (de) | ||
| DE2941097A1 (de) | Verfahren und vorrichtung zum herstellen von tabakrauch-filterkomponenten, insbesondere zigarettenfilterkomponenten | |
| DE69813408T2 (de) | Vorrichtung zum überführen von zigarettenportionen | |
| DE69519757T2 (de) | Verfahren und Vorrichtung für die Herstellung von ventilierten Zigaretten | |
| DE102012103323B4 (de) | Vorrichtung zur Übergabe stabförmiger Artikel der Tabak verarbeitenden Industrie von einer Vorrichtung zur queraxialen Förderung auf eine Vorrichtung zur längsaxialen Förderung oder umgekehrt sowie Anordnung mit einer solchen Vorrichtung | |
| DE69405630T2 (de) | Verfahren zur Herstellung von Filterzigaretten | |
| DE672652C (de) | Maschine zum Herstellen eines Zigarettenstranges mit Mundstueckeinlagen | |
| EP2460421A1 (de) | Fördervorrichtung zum Fördern stabförmiger Produkte der Tabak verarbeitenden Industrie |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC NL PL PT RO SE SI SK TR |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Extension state: AL BA HR MK YU |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20060927 |
|
| AKX | Designation fees paid |
Designated state(s): AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC NL PL PT RO SE SI SK TR |
|
| TPAC | Observations filed by third parties |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNTIPA |
|
| GRAP | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR1 |
|
| GRAS | Grant fee paid |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR3 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC NL PL PT RO SE SI SK TR |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: NOT ENGLISH |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: EP |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: LANGUAGE OF EP DOCUMENT: GERMAN |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 502005005596 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 20081120 Kind code of ref document: P |
|
| RAP2 | Party data changed (patent owner data changed or rights of a patent transferred) |
Owner name: HAUNI MASCHINENBAU AG |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20081008 |
|
| NLXE | Nl: other communications concerning ep-patents (part 3 heading xe) |
Free format text: PAT. BUL. 03/2009 PAGE 396: CORR.: HAUNI MASCHINENBAU AG |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BG Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20090108 Ref country code: ES Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20090119 Ref country code: LT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20081008 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: PL Ref legal event code: T3 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LV Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20081008 Ref country code: FI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20081008 Ref country code: PT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20090218 Ref country code: IS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20090208 |
|
| PLBI | Opposition filed |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009260 |
|
| PLBP | Opposition withdrawn |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009264 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: FD4D |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20081008 Ref country code: EE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20081008 Ref country code: DK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20081008 Ref country code: RO Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20081008 |
|
| PLAX | Notice of opposition and request to file observation + time limit sent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNOBS2 |
|
| 26 | Opposition filed |
Opponent name: G.D. S.P.A Effective date: 20090707 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CZ Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20081008 Ref country code: SE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20090108 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20081008 |
|
| NLR1 | Nl: opposition has been filed with the epo |
Opponent name: G.D. S.P.A |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CH Payment date: 20090923 Year of fee payment: 5 |
|
| PLBB | Reply of patent proprietor to notice(s) of opposition received |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNOBS3 |
|
| BERE | Be: lapsed |
Owner name: HAUNI MASCHINENBAU A.G. Effective date: 20090930 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MC Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20090930 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: ST Effective date: 20100531 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20090930 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20090930 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20090109 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20090922 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20090922 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: HU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20090409 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20100930 Ref country code: CH Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20100930 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: TR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20081008 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CY Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20081008 |
|
| PLAB | Opposition data, opponent's data or that of the opponent's representative modified |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009299OPPO |
|
| R26 | Opposition filed (corrected) |
Opponent name: G.D S.P.A. Effective date: 20090707 |
|
| APBM | Appeal reference recorded |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNREFNO |
|
| APBP | Date of receipt of notice of appeal recorded |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNNOA2O |
|
| APAH | Appeal reference modified |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSCREFNO |
|
| APBM | Appeal reference recorded |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNREFNO |
|
| APBP | Date of receipt of notice of appeal recorded |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNNOA2O |
|
| APBQ | Date of receipt of statement of grounds of appeal recorded |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNNOA3O |
|
| APBQ | Date of receipt of statement of grounds of appeal recorded |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNNOA3O |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 20120925 Year of fee payment: 8 |
|
| PLAB | Opposition data, opponent's data or that of the opponent's representative modified |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009299OPPO |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 20130922 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20130922 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: PL Payment date: 20140825 Year of fee payment: 10 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Payment date: 20140921 Year of fee payment: 10 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R100 Ref document number: 502005005596 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| APBU | Appeal procedure closed |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNNOA9O |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: NL Ref legal event code: MM Effective date: 20151001 |
|
| PLCK | Communication despatched that opposition was rejected |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNREJ1 |
|
| PLBN | Opposition rejected |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009273 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: OPPOSITION REJECTED |
|
| 27O | Opposition rejected |
Effective date: 20160119 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R081 Ref document number: 502005005596 Country of ref document: DE Owner name: HAUNI MASCHINENBAU GMBH, DE Free format text: FORMER OWNER: HAUNI MASCHINENBAU AG, 21033 HAMBURG, DE |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20151001 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: PL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20150922 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R081 Ref document number: 502005005596 Country of ref document: DE Owner name: KOERBER TECHNOLOGIES GMBH, DE Free format text: FORMER OWNER: HAUNI MASCHINENBAU GMBH, 21033 HAMBURG, DE |
|
| P01 | Opt-out of the competence of the unified patent court (upc) registered |
Effective date: 20230608 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20230928 Year of fee payment: 19 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Payment date: 20230927 Year of fee payment: 19 |