EP0446447B1 - Liefervorrichtung für laufende Fäden - Google Patents
Liefervorrichtung für laufende Fäden Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0446447B1 EP0446447B1 EP90123730A EP90123730A EP0446447B1 EP 0446447 B1 EP0446447 B1 EP 0446447B1 EP 90123730 A EP90123730 A EP 90123730A EP 90123730 A EP90123730 A EP 90123730A EP 0446447 B1 EP0446447 B1 EP 0446447B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- thread
- delivery device
- particular according
- guide tube
- suction
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
- 239000004753 textile Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 3
- 238000003780 insertion Methods 0.000 claims description 4
- 230000037431 insertion Effects 0.000 claims description 4
- 238000006073 displacement reaction Methods 0.000 claims description 3
- 230000008093 supporting effect Effects 0.000 claims description 2
- 230000002093 peripheral effect Effects 0.000 claims 7
- 238000007664 blowing Methods 0.000 description 21
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 5
- 230000008569 process Effects 0.000 description 5
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000002349 favourable effect Effects 0.000 description 3
- 230000005484 gravity Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000010276 construction Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000007789 sealing Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000011144 upstream manufacturing Methods 0.000 description 2
- 230000004913 activation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000001154 acute effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000005465 channeling Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000009849 deactivation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000011161 development Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000018109 developmental process Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000000605 extraction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 125000006850 spacer group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 230000007704 transition Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000009941 weaving Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D03—WEAVING
- D03D—WOVEN FABRICS; METHODS OF WEAVING; LOOMS
- D03D47/00—Looms in which bulk supply of weft does not pass through shed, e.g. shuttleless looms, gripper shuttle looms, dummy shuttle looms
- D03D47/34—Handling the weft between bulk storage and weft-inserting means
- D03D47/36—Measuring and cutting the weft
- D03D47/361—Drum-type weft feeding devices
- D03D47/364—Yarn braking means acting on the drum
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B65—CONVEYING; PACKING; STORING; HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL
- B65H—HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL, e.g. SHEETS, WEBS, CABLES
- B65H51/00—Forwarding filamentary material
- B65H51/16—Devices for entraining material by flow of liquids or gases, e.g. air-blast devices
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B65—CONVEYING; PACKING; STORING; HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL
- B65H—HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL, e.g. SHEETS, WEBS, CABLES
- B65H57/00—Guides for filamentary materials; Supports therefor
- B65H57/003—Arrangements for threading or unthreading the guide
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D03—WEAVING
- D03D—WOVEN FABRICS; METHODS OF WEAVING; LOOMS
- D03D47/00—Looms in which bulk supply of weft does not pass through shed, e.g. shuttleless looms, gripper shuttle looms, dummy shuttle looms
- D03D47/34—Handling the weft between bulk storage and weft-inserting means
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D03—WEAVING
- D03D—WOVEN FABRICS; METHODS OF WEAVING; LOOMS
- D03D47/00—Looms in which bulk supply of weft does not pass through shed, e.g. shuttleless looms, gripper shuttle looms, dummy shuttle looms
- D03D47/34—Handling the weft between bulk storage and weft-inserting means
- D03D47/36—Measuring and cutting the weft
- D03D47/361—Drum-type weft feeding devices
- D03D47/364—Yarn braking means acting on the drum
- D03D47/366—Conical
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B65—CONVEYING; PACKING; STORING; HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL
- B65H—HANDLING THIN OR FILAMENTARY MATERIAL, e.g. SHEETS, WEBS, CABLES
- B65H2701/00—Handled material; Storage means
- B65H2701/30—Handled filamentary material
- B65H2701/31—Textiles threads or artificial strands of filaments
Definitions
- the invention relates to a delivery device for running threads, in particular for use on textile machines, according to the preamble of claim 1.
- a delivery device of the type in question is known from DE-OS 37 34 284, wherein the thread end conveyed by compressed air through the thread guide tube, after leaving the thread guide tube in the area in front of the storage drum, is directed from a blow nozzle oriented approximately parallel to the drum axis into a radially slotted guide channel becomes. This passes through the brake ring in the area of the root of the bristles and forms a channel section curved beyond the brake ring in the direction of the drum axis. A further blowing air nozzle opens into this in such a way that its jet runs radially to the drum axis and directs the thread into a channel-like, approximately triangular section of the head cone. The thread end is guided through this into the area of a suction blowing nozzle.
- a disadvantage of this configuration is the complex construction of the thread delivery device, due to the blowing air nozzles and additional channels required at the deflection points.
- the object on which the invention is based is now to design a delivery device of the aforementioned type in a technically simple manner in such a way that automatic, reliable threading of the thread is made possible with a minimum of components and nozzles.
- a generic delivery device for running threads with a simple structure is specified, which is characterized by reliable threading of the thread using compressed air.
- the number of nozzles working with compressed air is reduced to a minimum.
- the thread blown through the thread guide tube now emerges in a plane vertically above the thread take-off eyelet in such a way that the thread end runs approximately parallel to the drum jacket surface, then is grasped along the jacket surface of the head cone by means of the suction air flow and is further conveyed while passing through the thread take-off eye. This is done using the force of gravity acting on the thread end, which has a supporting effect on the threading process.
- the thread end is therefore always detected with certainty and sucked into the thread take-off eyelet.
- Additional deflection nozzles in order to obtain a corresponding course of the thread direction can accordingly be dispensed with, combined with reduced manufacturing costs for the delivery device.
- a channeling of the head cone is also not necessary, so that it can maintain its smooth surface, which favors the thread take-off.
- the configuration according to the invention allows working with customary, available compressed air values.
- the threading process is further supported by the fact that the suction blow nozzle assigned to the thread take-off eyelet is arranged in a baffle for the blowing stream emerging from the thread guide tube.
- this baffle fulfills a double function: on the one hand, it serves to hold the suction blowing nozzle and, on the other hand, there is also a deflection wall for the thread end, so that it does not shoot past the suction blowing nozzle, but favors the threading process.
- Manufacturing advantages of the delivery device also result from a suction blow nozzle in front of the end of the thread guide tube on the insertion side.
- This suction blow nozzle can have the same structure as the thread take-off eyelet designed as an axial suction blow nozzle, while reducing the number of different components.
- the brake ring In order to enable threading of the thread, the brake ring must first have been displaced in the axial direction of the storage drum in such a way that its bristles leave a gap to the drum jacket surface, so that the thread end can take its intended path under the bristles.
- the brake ring In order to achieve a favorable position of the brake ring in its working and disengaging position, the brake ring is adjustable on a sliding carriage. Independent of the displacement stroke of the brake ring, the individual setting can therefore always be made.
- the thread guide tube bent in the axial direction of the drum always directs the thread end in such a way that it is directed into the previously left gap. The thread end therefore always comes to the thread take-off eye as intended.
- the thread in which a correspondingly bent guide end is missing on the thread guide tube, the thread can be taken over and deflected by a deflection channel running in the axial direction, into which the mouth end of the thread guide tube is directed.
- a deflection channel running in the axial direction, into which the mouth end of the thread guide tube is directed.
- the suction blow nozzle arranged at the insertion end of the thread guide tube, the thread end is always brought into the suction area of the thread take-off eyelet designed as an axial suction blow nozzle.
- These two suction blow nozzles work on the Venturi principle.
- the suction blowing nozzles are constructed so that an annular chamber is arranged upstream of their annular gap. The wall forming the same annular gap is provided with a ring of air passage holes.
- the bristles can be adjusted in a simple manner by means of an adjusting screw accessible from the head end.
- an adjusting screw accessible from the head end.
- the sliding carriage carrying the brake ring changes its position in relation to the storage drum.
- This set screw passes through an opening in the baffle and can be operated from there.
- the lateral surface area of the head cone lying behind the baffle runs in a straight line from the base edge to the tip of the cone, achieving a favorable thread steering. This in turn ends in front of the suction blowing nozzle there.
- the air supply to both suction blowing nozzles is approximately the same, so that work can be carried out with the same pressure and the same line cross sections, which likewise contributes to a simplification in the construction of the delivery device.
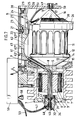
- the delivery device has a housing 1 to be fastened, for example, to a carrier of a weaving machine.
- This houses a stator 3 in a housing cavity 2, in which a rotor 4 rotates.
- the latter is penetrated by a rotor shaft 5.
- Its thread-threading end sits in a roller bearing 6, which is inserted in a cover 7 closing the housing cavity 2.
- a cross-sectionally larger collar 8 of the rotor shaft 5 facing away from the threading end starts from an inclined thread guide tube 9, the mouth end 10 of which is bent in the axial direction of a storage drum 11 arranged coaxially to the rotor shaft 5.
- the storage drum 11 forms a thread run-up truncated cone surface 12, so that when the thread guide tube 9 rotates, the rear thread turns advance the front thread turns already on the storage drum toward the head end of the storage drum 11.
- the storage drum itself is rotatably arranged. So that it does not rotate together with the thread guide tube 9, it is firmly connected to a truncated cone 13 equipped with magnets, not shown. Its magnets are located opposite to fixed magnets 14 of a ring 15 on the housing side.
- the storage drum 11 At its free-flying front end, the storage drum 11 carries a head cone 16. Its base lies against the front side of the storage drum and is somewhat smaller than the diameter of the storage drum 11.
- the lateral surface area M of the head cone 16 starts from the base edge B and extends in a straight line up to to the cone tip 17. The same extends to the inlet opening 18 of a thread take-off eye 19.
- the extension arm 21 which extends beyond the storage drum 11 is located at such a parallel distance from the storage drum 11 that it does not impair the orbital movement of the thread guide tube 9.
- the boom 21 receives a compressed air cylinder 22. Its piston rod 23 engages a sliding carriage 24 which is longitudinally displaceable in the interior of the boom 21. Relative to this, a carrier 25 is guided for a brake ring 26 that runs concentrically to the storage drum axis.
- the sliding carriage 24 supports an adjusting screw 27, for the actuating end 28 of which the baffle 20 forms an opening 29. Rotating the actuating handle 28 is accompanied by a longitudinal displacement of the carrier 25, depending on the direction in which the brake ring 26 is to be adjusted.
- the brake ring 26 is provided with bristles 30 directed toward the drum in such a way that they are aligned with the lateral surface of the head cone 16. In the working position, the bristle ends rest against the head cone 16 of the storage drum 11.
- the thread guide tube 9 continues into a thread channel 31 which extends centrally through the rotor shaft and which widens at the end on the threading side.
- a suction blow nozzle 32 is provided in the housing cover 7.
- a spacer sleeve 33 In a central opening of the housing cover 7 there is a spacer sleeve 33 in which the nozzle housing 34 is firmly inserted.
- the nozzle housing 34 receives at its end facing the rotor shaft 5 a sealing collar 35 which extends to the free end of the rotor shaft 5. Accordingly, the thread channel 31 directly adjoins the outlet opening 36 of the sealing collar 35.
- the outlet opening 36 in turn is connected to a short through-flow channel 37 of the nozzle body 34, which channel 37 subsequently widens into a frustoconical channel 38 in order to then merge into a circular-cylindrical channel section 39.
- a nozzle body 40 is pressed into this. In the middle, it forms a thread passage channel 41, which is smaller in diameter than that of the flow channel 37 in the nozzle body 34.
- the nozzle body 40 is equipped with a truncated cone section 42, the cone angle of which is smaller than that of the truncated cone Channel 38.
- the smallest diameter of the truncated cone section 42 is smaller than that of the flow channel 37, so that an annular gap 43 remains accordingly.
- the nozzle body 40 On its circular-cylindrical remaining length, the nozzle body 40 forms an annular chamber 44, in whose wall 45 on the annular gap side a ring of air passage holes 46 is provided. A compressed air supply line 47 opens into the annular chamber 44. A threading eyelet 48 is then arranged upstream of the nozzle body 40 and is in turn firmly embedded in the nozzle housing 44.
- the thread take-off eye 19 is also designed as a suction blowing nozzle. It has a nozzle housing 49 inserted into the baffle wall 20 with a nozzle body 50 which corresponds in structure to that of the suction blowing nozzle 32.
- a common valve 52 is assigned to the feed lines 47, 51 of the two suction blowing nozzles 19, 32. The latter is connected to a compressed air source 54 via a compressed air line 53.
- a feed line 55 extends from the valve 52 to a distributor 56, which is connected both to the supply lines 47, 51 and to the supply line 57, which leads to the compressed air cylinder 22 .
- the valve 52 can be controlled by means of a handle 58.
- both the suction blowing nozzles 19, 32 and the compressed air cylinder 22 are fed via the compressed air line 53 and feed line 55 via the distributor 56, which displaces the brake ring 26 in the axial direction in such a way that its bristles enter a gap position with respect to the drum surface, see gap 60 in Fig. 3.
- the aforementioned handle 58 is advantageously located on a box 59 connected to the housing 1, in which the valve 52 as well as the distributor 56 and the corresponding connections are accommodated.
- the width of the baffle 20 receiving the suction blowing nozzle 19 corresponds approximately to one third of the diameter of the storage drum 11.
- the rotor shaft 5 Before threading a thread F, the rotor shaft 5 is stopped in such a position that the thread guide tube 9 originating from the collar 8 or its mouth end 10 lies in a plane vertically above the thread take-off eye 19.
- the handle 58 is then to be actuated, the suction blowing nozzles 19, 32 receiving compressed air at the same time.
- This also applies to the compressed air cylinder 22, which displaces the brake ring 26 via its piston rod 23 and sliding carriage 24, so that its bristles reach a gap-forming release position, cf. Fig. 3.
- the thread end is now to be brought into the area of the threading eyelet 48.
- the radially inward on the thread take-off Eyelet 19 directed deflection then takes place by means of the suction air flow lying on the lateral surface of the head cone 16, which deflection is supported by the gravity of the thread end.
- the baffle 20 represents a limitation of the trajectory, so that the thread end does not go beyond the baffle, but surely reaches the extraction eyelet 19 designed as a suction blow nozzle and from there also emerges from the venturi principle.
- the handle 58 can return to its starting position with the interruption of the compressed air supply.
- a spring, not shown, housed in the compressed air cylinder 22 then returns the brake ring 26 to its starting position.
- the bent mouth end 10 is missing in the thread guide tube 9.
- the mouth end 61 which in this second exemplary embodiment extends in the same direction as the thread guide tube, is directed into a deflection channel 62 running parallel to the storage drum axis direction. This is located in a block 63 inserted into the boom 21 and extending below the compressed air cylinder 22.
- the deflection channel 62 has three adjoining bottom sections 62 ', 62 ", 62"'.
- the third bottom section 62'" runs at an opposite angle to the drum axis and directs the thread end into the gap 60 between bristles 30 and storage drum in the direction of the head cone 16, baffle 20 and suction blow nozzle 19.
- the threading process is also carried out while the handle 58 is pressed.
- the deflection of the thread now takes place in the transition region between the mouth end 61 and the suction blowing nozzle 19 through the deflection channel 62, so that additional deflection nozzles can also be omitted in this version.
- the funnel-shaped enlargement 64 of the deflection channel 62 on the input side has a facilitating effect during the threading process.
- the threading of the thread always takes place in the position in which the mouth end 51 of the thread guide tube 9 is located in a plane vertically above the thread take-off eye. Then both the force of gravity and the corresponding lateral surface of the head cone located in the same plane can be used for thread guidance.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Textile Engineering (AREA)
- Forwarding And Storing Of Filamentary Material (AREA)
- Looms (AREA)
- Yarns And Mechanical Finishing Of Yarns Or Ropes (AREA)
- Spinning Methods And Devices For Manufacturing Artificial Fibers (AREA)
- Coiling Of Filamentary Materials In General (AREA)
- Extrusion Moulding Of Plastics Or The Like (AREA)
- Application Of Or Painting With Fluid Materials (AREA)
- Braiding, Manufacturing Of Bobbin-Net Or Lace, And Manufacturing Of Nets By Knotting (AREA)
- Treatment Of Fiber Materials (AREA)
- Spinning Or Twisting Of Yarns (AREA)
Description
- Die Erfindung betrifft eine Liefervorrichtung für laufende Faden, insbesondere zum Einsatz an Textilmaschinen, gemäß Gattungsbegriff des Patentanspruches 1.
- Eine Liefervorrichtung der in Rede stehenden Art ist bekannt aus der DE-OS 37 34 284, wobei das durch Druckluft durch das Fadenführungsrohr geförderte Fadenende nach Verlassen des Fadenführungsrohres im Bereich vor der Speichertrommel von einer etwa parallel zur Trommelachse ausgerichteten Blasdüse in einen radial geschlitzen Führungskanal gelenkt wird. Dieser durchgreift den Bremsring im Bereich der Wurzel der Borsten und bildet jenseits des Bremsringes einen in Richtung der Trommelachse gekrümmten Kanalabschnitt aus. In diesen mündet eine weitere Blasluftdüse derart, daß deren Strahl radial zur Trommelachse verläuft und den Faden in einen kanalartigen, etwa dreieckförmigen Ausschnitt des Kopfkegels lenkt. Durch diesen wird das Fadenende in den Bereich einer Saugblasdüse geleitet. Nachteilig an dieser Ausgestaltung ist der aufwendige Aufbau der Fadenliefervorrichtung, bedingt durch die an den Umlenkstellen erforderlichen Blasluftdüsen und zusätzlichen Kanäle.
- Die der Erfindung zugrundeliegende Aufgabe besteht nun darin, eine Liefervorrichtung der vorgenannten Art in herstellungstechnisch einfacher Weise so auszugestalten, daß mit einem Mindestaufwand an Bauteilen und Düsen ein automatisches, zuverlässiges Einfädeln des Fadens ermöglicht ist.
- Gelöst wird diese Aufgabe durch die im Kennzeichen des Patentanspruches 1 angegebenen Merkmale.
- Die Unteransprüche betreffen vorteilhafte Weiterbildungen der erfinderischen Lösung.
- Zufolge derartiger Ausgestaltung ist eine gattungsgemäße Liefervorrichtung für laufende Fäden bei einfachem Aufbau angegeben, die sich durch ein zuverlässiges Einfädeln des Fadens mittels Druckluft auszeichnet. Die Anzahl von mit Druckluft arbeitenden Düsen ist auf ein Minimum reduziert. Der durch das Fadenführungsrohr geblasene Faden tritt nun in einer Ebene vertikal oberhalb der Fadenabzugsöse aus derart, daß das Fadenende etwa parallel zur Trommelmantelfläche verläuft, danach entlang der Mantelfläche des Kopfkegels mittels des Saugluftstromes erfaßt und unter Durchsetzen der Fadenabzugsöse weiter gefördert wird. Dies geschieht unter Ausnutzung der auf das Fadenende wirkenden Schwerkraft, was sich unterstützend auf den Einfädelvorgang auswirkt. Das Fadenende wird daher stets mit Sicherheit erfaßt und in die Fadenabzugsöse eingesaugt. Zusätzliche Umlenkdüsen, um einen entsprechenden Fadenrichtungsverlauf zu erhalten, können demgemäß entfallen verbunden mit verringerten Herstellungskosten für die Liefervorrichtung. Auch eine Kanalisierung des Kopfkegels ist nicht erforderlich, so daß dieser seine glatte, den Fadenabzug begünstigende Oberfläche beibehalten kann. Im übrigen läßt es die erfindungsgemäße Ausgestaltung zu, mit üblichen, zur Verfügung stehenden Druckluftwerten zu arbeiten. Unterstützt wird der Einfädelvorgang noch durch die Tatsache, daß die der Fadenabzugsöse zugeordnete Saugblasdüse in einer Prallwand für den aus dem Fadenführungsrohr austretenden Blasstrom angeordnet ist. Demgemäß erfüllt diese Prallwand eine Doppelfunktion: Einerseits dient sie zur Halterung der Saugblasdüse und andererseits stellt sich noch eine Umlenkwand für das Fadenende dar, so daß dieses nicht über die Saugblasdüse hinaus an dieser vorbeischießt, sondern den Einfädelvorgang begünstigt. Herstellungstechnische Vorteile der Liefervorrichtung ergeben sich ferner durch eine Saugblasdüse vor dem einführseitigen Ende des Fadenführungsrohres. Diese Saugblasdüse kann den gleichen Aufbau wie die als axiale Saugblasdüse gestaltete Fadenabzugsöse besitzen unter Verringerung der unterschiedlichen Bauteile. Um das Einfädeln des Fadens zu ermöglichen, muß zuvor der Bremsring in axialer Richtung der Speichertrommel verlagert worden sein derart, daß seine Borsten einen Spalt zur Trommelmantelfläche belassen, so daß das Fadenende unter den Borsten her seinen bestimmungsgemäßen Weg nehmen kann. Zwecks Erzielung einer günstigen Position des Bremsringes in seiner Arbeits- und Ausrückstellung ist der Bremsring einstellbar auf einem Verschiebeschlitten. Unabhängig von dem Verlagerungshub des Bremsringes kann daher stets die individuelle Einstellung erfolgen. Das in Achsrichtung der Trommel abgebogene Fadenführungsrohr lenkt das Fadenende stets so, daß es in den zuvor belassenen Spalt gerichtet ist. Das Fadenende gelangt daher bestimmungsgemäß stets zur Fadenabzugsöse. Bei einer erfindungsgemäßen Varianten, bei welcher ein entsprechend abgebogenes Führungsende am Fadenführungsrohr fehlt, kann die Übernahme und Umlenkung des Fadens durch einen in Achsrichtung verlaufenden Umlenkkanal erfolgen, in welchen das Mündungsende des Fadenführungsrohres hineingerichtet ist. Durch die am einführseitigen Ende des Fadenführungsrohres angeordnete Saugblasdüse wird daher stets das Fadenende bis in den Ansaugbereich der als axiale Saugblasdüse gestalteten Fadenabzugsöse gebracht. Diese beiden Saugblasdüsen arbeiten nach dem Venturi-Prinzip. Im Detail sind die Saugblasdüsen so aufgebaut, daß ihrem Ringspalt eine Ringkammer vorgeordnet ist. Die zur Bildung derselben ringspaltseitige Wand ist mit einen Kranz von Luftdurchtrittslöchern versehen. Es erfolgt daher eine gleichmäßige Speisung des Ringspaltes mit Druckluft unter Erzielung optimaler Saugblaswirkung. Es bietet sich dabei die Möglichkeit an, beide Saugblasdüsen über ein gemeinsames Ventil zu speisen. Auf aufwendige Folgesteuerungen kann daher verzichtet werden. Hierzu trägt auch das parallel zur Saugblasdüsen-Versorgung gesteuerte Zu- und Abstellen des Bremsringes bei. Im Detail sieht dies so aus, daß der Bremsring mittels eines Druckluftzylinders abgestellt und durch Federkraft wieder zurückgestellt ist. Herstellungstechnisch vereinfachend wirkt sich das Merkmal aus, daß die Prallwand an einem den Verschiebeschlitten des Bremsringes lagernden oberen Ausleger sitzt. Demgemäß wird ein Bauteil für verschiedene Aufgabe herangezogen. Einen günstigen Fadenumlenkeffekt erzeugen die Borsten dadurch, daß sie entsprechend der Mantelfläche des Kopfkegels ausgerichtet sind. Das Einstellen der Borsten läßt sich in einfacher Weise mittels einer vom Kopfende her zugänglichen Stellschraube vornehmen. Mit einem Verdrehen derselben verändert der den Bremsring tragende Verschiebeschlitten seine Position zur Speichertrommel. Diese Stellschraube durchsetzt eine Öffnung der Prallwand und kann von dort aus betätigt werden. Der hinter der Prallwand liegende Mantelflächenbereich des Kopfkegels verläuft dabei unter Erzielung einer günstigen Fadenlenkung in geradliniger Erstreckung von der Basiskante bis zur Kegelspitze. Diese wiederum endet vor der dortigen Saugblasdüse. Hervorzuheben ist noch, daß die Luftversorgung beider Saugblasdüsen etwa gleich ist, so daß mit gleichem Druck und gleichen Leitungsquerschnitten gearbeitet werden kann, was ebenfalls zu einer Vereinfachung im Aufbau der Liefervorrichtung beiträgt.
- Nachstehend werden zwei Ausführungsbeispiele der Erfindung anhand von Zeichnungen erläutert. Es zeigt
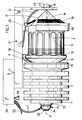
- Fig. 1 eine Liefervorrichtung für laufende Fäden gemäß dem ersten Ausführungsbeispiel in Ansicht,
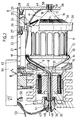
- Fig. 2 teilweise im Längsschnitt und teilweise in Ansicht die Fadenliefervorrichtung vor dem Einfädeln des Fadens,
- Fig. 3 eine der Fig. 2 entsprechende Darstellung, jedoch bei in Achsrichtung zur Speichertrommel verlagertem Bremsring bei eingefädeltem Faden,
- Fig. 4 in starker Vergrößerung einen Längsschnitt durch die am einführseitigen Ende des Fadenführungsrohres befindliche Saugblasdüse, die in ihrem Aufbau der am abzugsseitigen Ende befindlichen Saugblasdüse entspricht,
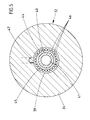
- Fig. 5 einen Querschnitt durch die Saugblasdüse auf Höhe der Ringkammer, in Richtung der mit Luftdurchtrittslöchern ausgestatteten ringspaltseitigen Wand gesehen,
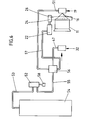
- Fig. 6 ein Blockschaltbild hinsichtlich der Druckluftbeaufschlagung der Saugblasdüsen und des dem Bremsring zugeordneten Druckluftzylinders,
- Fig. 7 teilweise im Längsschnitt, teilweise in Ansicht die Liefervorrichtung gemäß der zweiten Ausführungsform und
- Fig. 8 eine Unteransicht des den Umlenkkanal aufweisenden Blockes.
- Die Liefervorrichtung gemäß dem ersten Ausführungsbeispiel, dargestellt in den Fig. 1 - 6, besitzt ein beispielsweise an einem Träger einer Webmaschine zu befestigendes Gehäuse 1. Dieses nimmt in einer Gehäusehöhlung 2 einen Stator 3 auf, in welchem ein Rotor 4 umläuft. Letzterer wird durchsetzt von einer Rotorwelle 5. Deren fadeneinfädelungsseitiges Ende sitzt in einem Wälzlager 6, das in einem die Gehäusehöhlung 2 verschließenden Deckel 7 eingesetzt ist.
- Von einem querschnittsgrößeren, dem Einfädelungsende abgekehrten Bund 8 der Rotorwelle 5 geht ein geneigt gerichtetes Fadenführungsrohr 9 aus, dessen Mündungsende 10 in Achsrichtung einer koaxial zur Rotorwelle 5 angeordneten Speichertrommel 11 abgebogen ist. Auf Höhe des Mündungsendes 10 formt die Speichertrommel 11 eine Fadenauflauf-Kegelstumpffläche12, so daß beim Umlauf des Fadenführungsrohres 9 die rückwärtigen Fadenwindungen die vorderen, bereits auf der Speichertrommel befindlichen Fadenwindungen zum Kopfende der Speichertrommel 11 hin vorschieben. Die Speichertrommel selbst ist drehbar angeordnet. Damit sie jedoch nicht zusammen mit dem Fadenführungsrohr 9 umläuft, ist sie mit einem mit nicht veranschaulichten Magneten bestückten Kegelstumpf 13 fest verbunden. Dessen Magnete befinden sich in Gegenüberlage zu ortsfesten Magneten 14 eines gehäuseseitigen Ringes 15.
- An seinem freifliegenden Stirnende trägt die Speichertrommel 11 einen Kopfkegel 16. Dessen Basis liegt an der Stirnseite der Speichertrommel an und ist etwas kleiner als der Durchmesser der Speichertrommel 11. Der Mantelflächenbereich M des Kopfkegels 16 geht von der Basiskante B aus und verläuft in geradliniger Erstreckung bis zur Kegelspitze 17. Dieselbe erstreckt sich bis zur Einlaßöffnung 18 einer Fadenabzugsöse 19.
- Als Träger der vorgenannten Fadenabzugsöse 19 dient eine Prallwand 20, die vertikal verläuft und an ihrem oberen Ende von einem im Querschnitt U-förmigen, am Gehäuse 1 befestigten Ausleger 21 gehalten ist. Der sich über die Speichertrommel 11 hinaus erstreckende Ausleger 21 befindet sich in einem solchen parallelen Abstand zur Speichertrommel 11, daß er die Umlaufbewegung des Fadenführungsrohres 9 nicht beeinträchtigt.
- In seinem Innenraum nimmt der Ausleger 21 einen Druckluftzylinder 22 auf. Dessen Kolbenstange 23 greift an einem im Innenraum des Auslegers 21 längsverschieblich geführten Verschiebeschlitten 24 an. Relativ zu diesem ist ein Träger 25 für einen konzentrisch zur Speichertrommelachse verlaufenden Bremsring 26 geführt. Der Verschiebeschlitten 24 lagert eine Stellschraube 27, für deren Betätigungsende 28 die Prallwand 20 eine Öffnung 29 ausbildet. Mit einem Verdrehen der Betätigungshandhabe 28 geht eine Längsverschiebung des Trägers 25 einher, und zwar in Abhängigkeit davon, in welche Richtung der Bremsring 26 verstellt werden soll.
- Der Bremsring 26 ist mit trommeleinwärts gerichteten Borsten 30 versehen derart, daß diese entsprechend der Mantelfläche des Kopfkegels 16 ausgerichtet sind. In der Arbeitsstellung liegen die Borstenenden an dem Kopfkegel 16 der Speichertrommel 11 an.
- Das Fadenführungsrohr 9 setzt sich in einen die Rotorwelle zentral durchgreifenden Fadenkanal 31 fort, welcher sich am einfädelungsseitigen Ende erweitert. Dort ist in dem Gehäusedeckel 7 eine Saugblasdüse 32 vorgesehen. In einer zentralen Öffnung des Gehäusesdeckels 7 befindet sich eine Distanzbüchse 33, in welcher das Düsengehäuse 34 fest eingesetzt ist. Das Düsengehäuse 34 nimmt an seinem der Rotorwelle 5 zugekehrten Ende einen Dichtkragen 35 auf, der bis zum freien Stirnende der Rotorwelle 5 reicht. Demgemäß schließt sich der Fadenkanal 31 unmittelbar an die Austrittsöffnung 36 des Dichtkragens 35 an. Die Austrittsöffnung 36 steht ihrerseits in Verbindung mit einem kurzen Durchströmkanal 37 des Düsenkörpers 34, welcher Kanal 37 sich im Anschluß daran zu einem kegelstumpfförmigen Kanal 38 erweitert, um danach in einen kreiszylindrischen Kanalabschnitt 39 überzugehen. In diesen ist ein Düsenkörper 40 eingepreßt. Mittig bildet er einen Fadendurchgangskanal 41 aus, der im Durchmesser kleiner ist als derjenige des Durchströmkanals 37 im Düsenkörper 34. Etwa auf seiner halben, dem Durchströmkanal 37 zugekehrten Länge ist der Düsenkörper 40 mit einem Kegelstumpfabschnitt 42 ausgestattet, dessen Kegelwinkel geringer ist als derjenige des kegelstumpfförmigen Kanales 38. Der kleinste Durchmesser des Kegelstumpfabschnittes 42 ist kleiner als derjenige des Durchströmkanales 37, so daß demgemäß ein Ringspalt 43 verbleibt. Auf seiner kreiszylindrisch gestalteten Restlänge bildet der Düsenkörper 40 eine Ringkammer 44, in deren ringspaltseitiger Wand 45 ein Kranz von Luftdurchtrittslöchern 46 vorgesehen ist. In die Ringkammer 44 mündet eine Druckluftzuführleitung 47. Dem Düsenkörper 40 ist dann noch eine Einfädelungsöse 48 vorgeordnet, die ihrerseits im Düsengehäuse 44 fest eingebettet ist.
- Die Fadenabzugsöse 19 ist ebenfalls als Saugblasdüse gestaltet. Sie besitzt ein in die Prallwand 20 eingesetztes Düsengehäuse 49 mit einem Düsenkörper 50, der in seinem Aufbau demjenigen der Saugblasdüse 32 entspricht. Den Zuleitungen 47, 51 beider Saugblasdüsen 19, 32 ist ein gemeinsames Ventil 52 zugeordnet. Letzteres steht über eine Druckluftleitung 53 in Verbindung mit einer Druckluftquelle 54. Von dem Ventil 52 geht eine Speiseleitung 55 zu einem Verteiler 56 aus, der sowohl mit den Zuleitungen 47, 51 als auch mit der Zuleitung 57 in Verbindung steht, welche zum Druckluftzylinder 22 führt. Das Ventil 52 ist mittels einer Handhabe 58 steuerbar. Durch Einwärtsverlagerung derselben werden über die Druckluftleitung 53 und Speiseleitung 55 über den Verteiler 56 sowohl die Saugblasdüsen 19, 32 als auch der Druckluftzylinder 22 gespeist, welcher den Bremsring 26 in axialer Richtung verlagert derart, daß seine Borsten in eine Spaltstellung zur Trommelmantelfläche treten, siehe Spalt 60 in Fig. 3.
- Die vorgenannte Handhabe 58 befindet sich vorteilhafterweise an einem mit dem Gehäuse 1 verbundenen Kasten 59, in dem das Ventil 52 als auch der Verteiler 56 und die entsprechenden Anschlüsse untergebracht sind.
- Die die Saugblasdüse 19 aufnehmende Prallwand 20 entspricht in ihrer Breite etwa einem Drittel des Durchmessers der Speichertrommel 11.
- Vor dem Einfädeln eines Fadens F wird die Rotorwelle 5 in einer solchen Stellung stillgesetzt, daß das vom Bund 8 ausgehende Fadenführungsrohr 9 bzw. dessen Mündungsende 10 in einer Ebene vertikal oberhalb der Fadenabzugsöse 19 liegt. Danach ist die Handhabe 58 zu betätigen, wobei gleichzeitig die Saugblasdüsen 19, 32 Druckluftzufuhr erhalten. Dies trifft auch zu auf den Druckluftzylinder 22, welcher über seine Kolbenstange 23 und Verschiebeschlitten 24 den Bremsring 26 verlagert, so daß dessen Borsten in eine spaltbildende Freigabestellung gelangen, vgl. Fig. 3. Es ist nun das Fadenende in den Bereich der Einfädelungsöse 48 zu bringen. Zufolge der in die Ringkammer 44 eintretenden Druckluft, welche die Luftdurchtrittslöcher 46 durchwandert und von dort aus den Ringspalt 43 verläßt, um in den Fadenkanal 31 einzuströmen, entsteht im Fadendurchgangskanal 41 ein Unterdruck, durch welchen der Faden F angesogen wird. Sobald der Faden F in den Durchströmkanal 37 gelangt, wird er durch die dort mit Druck austretende Luft mitgenommmen und durch das Fadenführungsrohr 9 weitergefördert. Druckluftbeaufschlagt verläßt das Fadenende das Mündungsende 10 des Fadenführungsrohres 9, verläuft etwa parallel oberhalb der Speichertrommel 11 und durchsetzt den Spalt 60 zwischen Speichertrommel 11 und Borsten 30 des Bremsringes 26. Die radial einwärts auf die Fadenabzugsöse 19 gerichtete Umlenkung erfolgt dann mittels des auf der Mantelfläche des Kopfkegels 16 liegenden Saugluftstromes, welche Umlenkung unterstützt wird durch die Schwerkraft des Fadenendes. Die Prallwand 20 stellt dabei eine Begrenzung der Flugbahn dar, so daß das Fadenende nicht über die Prallwand hinausgeht, sondern mit Sicherheit zur als Saugblasdüse gestalteten Abzugsöse 19 gelangt und von dort ebenfalls nach dem Venturi-Prinzip aus dieser austritt. Nach erfolgter Einfädelung des Fadens F kann die Handhabe 58 in ihre Ausgangsstellung zurückkehren unter Unterbrechung der Druckluftzufuhr. Eine im Druckluftzylinder 22 untergebrachte, nicht veranschaulichte Feder stellt dann den Bremsring 26 wieder in seine Ausgangsstellung zurück.
- Bei der in den Fig. 7 und 8 veranschaulichten zweiten Ausführungsform tragen gleiche Bauteile gleiche Bezugsziffern. Abweichend von der ersten Ausführungsform fehlt beim Fadenführungsrohr 9 das abgebogene Mündungsende 10. Das sich bei diesem zweiten Ausführungsbeispiel in gleicher Richtung zum Fadenführungsrohr erstreckende Mündungsende 61 ist in einen parallel zur Speichertrommel-Achsrichtung verlaufenden Umlenkkanal 62 gerichtet. Dieser befindet sich in einem in den Ausleger 21 eingesetzten, sich unterhalb des Druckluftzylinders 22 erstreckenden Block 63. Der Umlenkkanal 62 besitzt drei sich anschließende Bodenabschnitte 62', 62", 62"'. Diese sind so angeordnet, daß der erste Bodenabschnitt 62' spitzwinklig ansteigend in Fadendurchlaufrichtung verläuft und das Fadenende zum parallel zur Trommelachse gerichteten Bodenabschnitt 62" lenkt. Der dritte Bodenabschnitt 62'" verläuft entgegengesetzt spitzwinklig zur Trommelachse und lenkt das Fadenende in den Spalt 60 zwischen Borsten 30 und Speichertrommel in Richtung des Kopfkegels 16, Prallwand 20 und Saugblasdüse 19. Der Einfädelvorgang wird ebenfalls bei gedrückter Handhabe 58 vorgenommen. Die Umlenkung des Fadens geschieht nun im Übergangsbereich zwischen Mündungsende 61 und Saugblasdüse 19 durch den Umlenkkanal 62, so daß auch bei dieser Version zusätzliche Umlenkdüsen entfallen können. Erleichternd wirkt sich beim Einfädelungsvorgang die eingangsseitige trichterförmige Erweiterung 64 des Umlenkkanales 62 aus.
- Ferner erfolgt bei dieser Version die Einfädelung des Fadens stets in der Stellung, in welcher sich das Mündungsende 51 des Fadenführungsrohres 9 in einer Ebene vertikal oberhalb der Fadenabzugsöse befindet. Dann kann sowohl die Schwerkraft als auch die entsprechende in der gleichen Ebene befindliche Mantelfläche des Kopfkegels zur Fadenführung herangezogen werden.
- Die in der vorstehenden Beschreibung, der Zeichnung und den Ansprüchen offenbarten Merkmale der Erfindung können sowohl einzeln als auch in beliebiger Kombination für die Verwirklichung der Erfindung von Bedeutung sein.
- Alle offenbarten Merkmale sind erfindungswesentlich. In die Offenbarung der Anmeldung wird hiermit auch der Offenbarungsinhalt der zugehörigen/beigefügten Prioritätsunterlagen (Abschrift der Voranmeldung) vollinhaltlich mit einbezogen.
Claims (15)
Priority Applications (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP94119612A EP0657379A2 (de) | 1990-03-07 | 1990-12-10 | Liefervorrichtung für laufende Fäden |
| EP94116058A EP0659918B1 (de) | 1990-03-07 | 1990-12-10 | Liefervorrichtung für laufende Fäden |
| DE9018101U DE9018101U1 (de) | 1990-03-07 | 1990-12-10 | Liefervorrichtung für laufende Fäden |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE4007131A DE4007131C2 (de) | 1990-03-07 | 1990-03-07 | Liefervorrichtung für laufende Fäden |
| DE4007131 | 1990-03-07 |
Related Child Applications (3)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP94116058.2 Division-Into | 1990-12-10 | ||
| EP94116058A Division EP0659918B1 (de) | 1990-03-07 | 1990-12-10 | Liefervorrichtung für laufende Fäden |
| EP94119612.3 Division-Into | 1990-12-10 |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0446447A1 EP0446447A1 (de) | 1991-09-18 |
| EP0446447B1 true EP0446447B1 (de) | 1995-07-05 |
| EP0446447B2 EP0446447B2 (de) | 2000-11-22 |
Family
ID=6401592
Family Applications (3)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP90123730A Expired - Lifetime EP0446447B2 (de) | 1990-03-07 | 1990-12-10 | Liefervorrichtung für laufende Fäden |
| EP94119612A Withdrawn EP0657379A2 (de) | 1990-03-07 | 1990-12-10 | Liefervorrichtung für laufende Fäden |
| EP94116058A Expired - Lifetime EP0659918B1 (de) | 1990-03-07 | 1990-12-10 | Liefervorrichtung für laufende Fäden |
Family Applications After (2)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP94119612A Withdrawn EP0657379A2 (de) | 1990-03-07 | 1990-12-10 | Liefervorrichtung für laufende Fäden |
| EP94116058A Expired - Lifetime EP0659918B1 (de) | 1990-03-07 | 1990-12-10 | Liefervorrichtung für laufende Fäden |
Country Status (9)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US5181544A (de) |
| EP (3) | EP0446447B2 (de) |
| JP (1) | JP3021712B2 (de) |
| CN (1) | CN1026424C (de) |
| AT (2) | ATE253134T1 (de) |
| BR (1) | BR9100911A (de) |
| CZ (1) | CZ281399B6 (de) |
| DE (3) | DE4007131C2 (de) |
| ES (1) | ES2074112T3 (de) |
Families Citing this family (28)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE9117045U1 (de) * | 1991-06-18 | 1995-05-11 | Iro Ab, Ulricehamn | Fadenspeicher- und -liefervorrichtung |
| IT226136Y1 (it) * | 1991-09-19 | 1997-04-18 | Roy Electrotex Spa | Miglioramenti costruttivi per porgitrama per telai di tessitura. |
| IT1259551B (it) * | 1992-04-22 | 1996-03-20 | Lgl Electronics Spa | Dispositivo elettropneumatico per l'infilaggio automatico di apparecchi alimentatori di trama a macchine tessili ed apparecchio alimentatore di trama incorporante detto dispositivo |
| IT1258241B (it) * | 1992-11-05 | 1996-02-22 | Alimentatore di trama | |
| IT1263623B (it) * | 1993-02-23 | 1996-08-27 | Roj Electrotex Nuova Srl | Alimentatore di filo |
| SE508469C2 (sv) * | 1993-04-21 | 1998-10-12 | Sipra Patent Beteiligung | Garnmataranordning i en textilmaskin samt förfarande för användning av garnmataranordning |
| DE9307967U1 (de) * | 1993-05-26 | 1994-10-06 | Palitex Project-Company GmbH, 47804 Krefeld | Doppeldraht-Zwirnspindel |
| TW286331B (de) * | 1994-03-03 | 1996-09-21 | Micron Instr | |
| DE9406102U1 (de) * | 1994-04-13 | 1995-08-10 | Sobrevin Société de brevets industriels-Etablissement, Vaduz | Fadenspeicher mit Fadenabzugsbremse |
| US5546994A (en) * | 1994-10-14 | 1996-08-20 | Sobrevin Societe De Brevets Industriels-Etablissement | Thread storage drum with frustoconical brake strip |
| IT1280434B1 (it) * | 1995-07-18 | 1998-01-20 | Lgl Electronics Spa | Dispositivo elettropneumatico perfezionato per l'infilaggio automatico di apparecchi alimentatori di trama ed alimentatore di |
| US5947403A (en) * | 1995-07-24 | 1999-09-07 | Iro Ab | Yarn feeding device |
| DE19533310A1 (de) * | 1995-07-24 | 1997-01-30 | Iro Ab | Fadenliefergerät |
| DE19533547A1 (de) * | 1995-09-11 | 1997-03-13 | Iro Ab | Pneumatische Ventileinrichtung für ein Fadenliefergerät und Fadenliefergerät |
| DE19609871A1 (de) * | 1996-03-13 | 1997-09-18 | Iro Ab | Fadenliefergerät |
| IT239803Y1 (it) * | 1996-09-03 | 2001-03-13 | Lgl Electronics Spa | Dispositivo di ritegno a sgancio rapido del supporto portafreno diapparecchi alimentatori di trama per macchine tessili |
| IT1302068B1 (it) * | 1998-02-26 | 2000-07-20 | Lgl Electronics Spa | Metodo e dispositivo di infilaggio pneumatico di apparecchialimentatori di trama a macchine tessili. |
| DE10107688A1 (de) * | 2001-02-19 | 2002-08-29 | Iro Patent Ag Baar | Fadenliefergerät |
| ITTO20020023U1 (it) * | 2002-02-01 | 2003-08-01 | Lgl Electronics Spa | ,,dispositivo di ritegno del supporto portafreno in dispositivi alimentatori di trama,, |
| DE10358283A1 (de) * | 2003-12-12 | 2005-07-21 | Iro Ab | Fadenmessliefergerät |
| SE0400861D0 (sv) * | 2004-04-01 | 2004-04-01 | Iropa Ag | Garnmatningsanordning |
| CN102634913A (zh) * | 2012-04-06 | 2012-08-15 | 经纬纺织机械股份有限公司 | 无捻度变化储纬装置 |
| IT201800007866A1 (it) * | 2018-08-06 | 2020-02-06 | Lgl Electronics Spa | Dispositivo frena-trama per alimentatori di filato ad accumulo |
| CZ2019389A3 (cs) * | 2019-06-19 | 2020-12-30 | Rieter Cz S.R.O. | Zařízení pro nasávání a dopravu příze pro uspořádání na obslužném robotu textilního stroje pro výrobu příze, obslužný robot pro obsluhu pracovního místa textilního stroje a textilní stroj |
| CN112553764A (zh) * | 2020-12-01 | 2021-03-26 | 张家港市凯利雅特种纺织纱线有限公司 | 氨纶纱输纱装置 |
| CN112609299B (zh) * | 2020-12-10 | 2022-08-19 | 青岛村田机械制造有限公司 | 一种在操作时避免储纬器处断纬或漏纬的纺织储纬装置 |
| CN114000246B (zh) * | 2021-11-30 | 2022-11-29 | 嵊州市三凌动力科技有限公司 | 储纬器用三角压片及其制造方法 |
| CN119160714B (zh) * | 2024-11-22 | 2025-03-18 | 山东明福染业有限公司 | 一种用于植物染色的纱线收集装置 |
Family Cites Families (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BE759801A (fr) * | 1969-12-04 | 1971-05-17 | Snia Viscosa | Perfectionnements apportes aux dispositifs pour ramasser, aspirer et eliminer des filaments et fils textiles, ainsi que les dispositifs perfectionnes obtenus |
| IT1133900B (it) * | 1980-10-15 | 1986-07-24 | Roy Electrotex Spa | Mezzi per effettuare la frenatura del filato in uscita in dispositivi alimentatori di filato a tensione costante e regolabile,particolarmente per macchine tessili |
| DE8712946U1 (de) * | 1987-09-25 | 1987-12-10 | Aktiebolaget Iro, Ulricehamn | Fadenspeicher- und -liefervorrichtung |
| US4969489A (en) * | 1988-07-14 | 1990-11-13 | Nissan Motor Co., Ltd. | Weft threading system for fluid jet loom using the storage drum winding arm |
| US5016680A (en) * | 1989-03-03 | 1991-05-21 | Kabushiki Kaisha Toyoda Jidoshokki Seisakusho | Weft processing and releasing apparatus in a jet loom |
| IT1236993B (it) * | 1989-12-29 | 1993-05-12 | Roy Electrotex Spa | Alimentatore di trama per telai di tessitura a pinze e a proiettili |
| FR2978758B1 (fr) | 2011-08-02 | 2013-08-02 | Saint Gobain | Enceinte de flottage du verre |
-
1990
- 1990-03-07 DE DE4007131A patent/DE4007131C2/de not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 1990-12-10 EP EP90123730A patent/EP0446447B2/de not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1990-12-10 AT AT94116058T patent/ATE253134T1/de not_active IP Right Cessation
- 1990-12-10 DE DE59010936T patent/DE59010936D1/de not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 1990-12-10 DE DE59009377T patent/DE59009377D1/de not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1990-12-10 EP EP94119612A patent/EP0657379A2/de not_active Withdrawn
- 1990-12-10 AT AT90123730T patent/ATE124732T1/de not_active IP Right Cessation
- 1990-12-10 EP EP94116058A patent/EP0659918B1/de not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1990-12-10 ES ES90123730T patent/ES2074112T3/es not_active Expired - Lifetime
-
1991
- 1991-01-29 US US07/647,052 patent/US5181544A/en not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 1991-02-20 CN CN91101057A patent/CN1026424C/zh not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 1991-03-06 CZ CS91584A patent/CZ281399B6/cs unknown
- 1991-03-06 BR BR919100911A patent/BR9100911A/pt unknown
- 1991-03-07 JP JP3041947A patent/JP3021712B2/ja not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP3021712B2 (ja) | 2000-03-15 |
| CS9100584A2 (en) | 1991-09-15 |
| CN1026424C (zh) | 1994-11-02 |
| DE59010936D1 (de) | 2003-12-04 |
| CZ281399B6 (cs) | 1996-09-11 |
| EP0659918A2 (de) | 1995-06-28 |
| EP0446447B2 (de) | 2000-11-22 |
| EP0659918B1 (de) | 2003-10-29 |
| JPH04213561A (ja) | 1992-08-04 |
| CN1054624A (zh) | 1991-09-18 |
| DE59009377D1 (de) | 1995-08-10 |
| ATE253134T1 (de) | 2003-11-15 |
| DE4007131C2 (de) | 1999-12-30 |
| EP0659918A3 (de) | 1997-11-19 |
| EP0657379A2 (de) | 1995-06-14 |
| ATE124732T1 (de) | 1995-07-15 |
| ES2074112T3 (es) | 1995-09-01 |
| BR9100911A (pt) | 1991-11-05 |
| EP0446447A1 (de) | 1991-09-18 |
| US5181544A (en) | 1993-01-26 |
| DE4007131A1 (de) | 1991-09-12 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP0446447B1 (de) | Liefervorrichtung für laufende Fäden | |
| WO2008095631A1 (de) | Luftspinnvorrichtung | |
| CH681894A5 (de) | ||
| CH682913A5 (de) | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zum Vorbereiten zu spleissender Fadenenden. | |
| DE3444821A1 (de) | Vorrichtung zum einlegen des fadenendes einer textilspule in die spulenhuelse | |
| EP0365472B1 (de) | Vorrichtung zum Einfädeln eines Fadens in einer Webmaschine | |
| DE102016119983A1 (de) | Pneumatisches Fadenspeicherorgan, Arbeitsstelle einer Textilmaschine mit einem Fadenspeicherorgan und Textilmaschine mit einer Vielzahl von Arbeitsstellen mit einem Fadenspeicherorgan | |
| DE2758064B2 (de) | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zum Beseitigen einer Unregelmäßigkeit im Faden an einer Spinnstelle einer Offen-End-Spinnvorrichtung | |
| DE3025068A1 (de) | Vorrichtung fuer die zufuehrung von textilem bandmaterial an einen verbraucher | |
| DE3819426C2 (de) | ||
| DE3607206C2 (de) | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zum Herstellen einer Spleißverbindung | |
| EP0527355A1 (de) | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zum pneumatischen Einführen von Faserband in eine Spinnereimaschine | |
| DE3734284A1 (de) | Fadenspeicher- und -liefervorrichtung | |
| EP0822276B1 (de) | Vorrichtung zur Steuerung eines Luftstromes in einer Offenend-Spinnvorrichtung | |
| DE4000856A1 (de) | Schussseitig angeordnete fadenschneidevorrichtung einer luftwebmaschine | |
| CH652994A5 (de) | Verfahren und spulmaschine zum aufwickeln eines mit hoher geschwindigkeit kontinuierlich angelieferten fadens auf eine spule. | |
| DE9018101U1 (de) | Liefervorrichtung für laufende Fäden | |
| DE10150565B4 (de) | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur Vorbereitung eines abgelängten Fadenendes für das Wiederanspinnen einer Offenend-Spinnvorrichtung | |
| EP1129973B1 (de) | Verfahren zum Bilden von Reservewindungen auf einer Leerhülse und Vorrichtung hierfür | |
| DE1535570B1 (de) | Saugkanal zur Bildung einer Schleife eines Schussfadens an Webmaschinen mit Entnahme des Schussfadens von ortsfesten Spulen | |
| DE3247288C2 (de) | Verfahren zur Aufbereitung eines Garnendes für das Anspinnen in einem Spinnrotor einer Offenendspinneinheit und Vorrichtung zur Durchführung des Verfahrens | |
| DE3915608A1 (de) | Aufspulmaschine | |
| DE1069044B (de) | Anzwirnvorrichtung für eine Streckzwirnmaschine | |
| EP0294795B1 (de) | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zum Anspinnen eine Garnes an einer Friktionsspinnvorrichtung | |
| DE102006018242A1 (de) | Luftdüsenspinnvorrichtung |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AT BE CH DE DK ES FR GB GR IT LI LU NL SE |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 19910912 |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 19930824 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AT BE CH DE DK ES FR GB GR IT LI LU NL SE |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DK Effective date: 19950705 Ref country code: GR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 19950705 |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 124732 Country of ref document: AT Date of ref document: 19950715 Kind code of ref document: T |
|
| XX | Miscellaneous (additional remarks) |
Free format text: TEILANMELDUNG 94116058.2 EINGEREICHT AM 10/12/90. |
|
| ET | Fr: translation filed | ||
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 59009377 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 19950810 |
|
| GBT | Gb: translation of ep patent filed (gb section 77(6)(a)/1977) |
Effective date: 19950720 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: ES Ref legal event code: FG2A Ref document number: 2074112 Country of ref document: ES Kind code of ref document: T3 |
|
| ITF | It: translation for a ep patent filed | ||
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LU Payment date: 19951101 Year of fee payment: 6 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AT Payment date: 19951213 Year of fee payment: 6 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Payment date: 19951230 Year of fee payment: 6 |
|
| PLBI | Opposition filed |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009260 |
|
| PLBQ | Unpublished change to opponent data |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS OPPO |
|
| 26 | Opposition filed |
Opponent name: IRO AB Effective date: 19951208 |
|
| NLR1 | Nl: opposition has been filed with the epo |
Opponent name: IRO AB |
|
| PLBF | Reply of patent proprietor to notice(s) of opposition |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS OBSO |
|
| PLBF | Reply of patent proprietor to notice(s) of opposition |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS OBSO |
|
| RDAH | Patent revoked |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS REVO |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 19961210 Ref country code: AT Effective date: 19961210 |
|
| APAC | Appeal dossier modified |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS NOAPO |
|
| APAE | Appeal reference modified |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS REFNO |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Effective date: 19970701 |
|
| NLV4 | Nl: lapsed or anulled due to non-payment of the annual fee |
Effective date: 19970701 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Payment date: 19971015 Year of fee payment: 8 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Payment date: 19971218 Year of fee payment: 8 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: ES Payment date: 19971230 Year of fee payment: 8 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 19981210 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 19981211 |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 19981210 |
|
| APAE | Appeal reference modified |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS REFNO |
|
| APAC | Appeal dossier modified |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS NOAPO |
|
| PLAW | Interlocutory decision in opposition |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS IDOP |
|
| PLAW | Interlocutory decision in opposition |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOS IDOP |
|
| PUAH | Patent maintained in amended form |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009272 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: PATENT MAINTAINED AS AMENDED |
|
| 27A | Patent maintained in amended form |
Effective date: 20001122 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B2 Designated state(s): AT BE CH DE DK ES FR GB GR IT LI LU NL SE |
|
| XX | Miscellaneous (additional remarks) |
Free format text: TEILANMELDUNG 94116058.2 EINGEREICHT AM 10/12/90. |
|
| ET3 | Fr: translation filed ** decision concerning opposition | ||
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: AEN Free format text: AUFRECHTERHALTUNG DES PATENTES IN GEAENDERTER FORM |
|
| ITF | It: translation for a ep patent filed | ||
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: ES Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20010304 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Payment date: 20011220 Year of fee payment: 12 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CH Payment date: 20020110 Year of fee payment: 12 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20021231 Ref country code: CH Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20021231 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20030901 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: ST |
|
| APAH | Appeal reference modified |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSCREFNO |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BE Payment date: 20061205 Year of fee payment: 17 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Payment date: 20071220 Year of fee payment: 18 |
|
| BERE | Be: lapsed |
Owner name: SOC. DE BREVETS INDUSTRIELS-ETABLISSEMENT *SOBREVI Effective date: 20071231 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20071231 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: ES Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 19981231 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20100222 Year of fee payment: 20 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF EXPIRATION OF PROTECTION Effective date: 20101210 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20081210 |