WO2015106720A1 - 以生物质电厂灰为原料制备超级活性炭的方法 - Google Patents
以生物质电厂灰为原料制备超级活性炭的方法 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2015106720A1 WO2015106720A1 PCT/CN2015/071016 CN2015071016W WO2015106720A1 WO 2015106720 A1 WO2015106720 A1 WO 2015106720A1 CN 2015071016 W CN2015071016 W CN 2015071016W WO 2015106720 A1 WO2015106720 A1 WO 2015106720A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- activated carbon
- power plant
- plant ash
- biomass power
- raw material
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C01—INORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- C01B—NON-METALLIC ELEMENTS; COMPOUNDS THEREOF; METALLOIDS OR COMPOUNDS THEREOF NOT COVERED BY SUBCLASS C01C
- C01B32/00—Carbon; Compounds thereof
- C01B32/30—Active carbon
- C01B32/312—Preparation
- C01B32/342—Preparation characterised by non-gaseous activating agents
Definitions
- the invention relates to an activated carbon preparation technology, in particular to a method for preparing super activated carbon from biomass power plant ash.
- Activated carbon is widely used in water treatment, air purification, flue gas desulfurization and off-sale, and catalyst carriers due to its large specific surface area, abundant pores and stable chemical properties.
- high-performance activated carbon has been increasingly developed and applied to blood purification, automotive cans, supercapacitor electrode materials, lithium ion battery anode materials, and high-demand fields such as military and aerospace.
- the output of activated carbon in China is very large, most of them are low-end products.
- High-performance activated carbon still needs a large number of imports, so the preparation of high-performance activated carbon is still a research hotspot in the field of carbon materials.
- the preparation methods of activated carbon mainly include physical activation method, chemical activation method, and physical chemical combined activation method.
- the physical activation method mainly uses any one of CO 2 and H 2 O as an activator, and the raw material is activated by raising the temperature to 600 to 1200 ° C, and the obtained activated carbon product has a specific surface area of less than 1500 m 2 /g, and the yield is lower than 30%, this is because CO 2 is difficult to diffuse in the pores of carbon particles, the diffusion rate is slow, and the proximity of CO 2 and micropores is greatly restricted, so industrially, CO 2 activation is rare; and H 2 O molecules It is smaller than CO 2 molecule, and it has fast diffusion. The activation speed is faster at higher activation temperature, and the reaction is difficult to control. It is difficult to prepare activated carbon with high specific surface area.
- the chemical activation method adopts carbonization and activation processes simultaneously, and the activation time is short, and the pore structure of the activated carbon is mainly the pore formed by the activator to remove hydrogen and oxygen atoms in the raw material by dehydration, so the yield of carbon is high, but The pollution is large.
- activated carbon with high specific surface is mainly activated by coal-based and petroleum coke-based raw materials by KOH strong base in N 2 atmosphere to 700-900 ° C, and the activated carbon has a specific surface area of up to 3000 m 2 /g, but The preparation of high-performance activated carbon from solid waste has not been reported, and due to the high price of KOH and high corrosivity, the cost of super activated carbon obtained by industrialization is relatively high.
- the physical and chemical combined activation method combines chemical activation and physical activation, adding chemicals to the raw materials, first carbonizing in an inert atmosphere for a certain period of time, and then introducing a physical activator for joint activation.
- the activated carbon is mainly prepared by the combination of KOH-CO 2 , KOH-H 2 O, ZnCl 2 -CO 2 and ZnCl 2 -H 2 O as activators, and the activated carbon prepared by KOH series chemical agent is mostly microporous.
- the specific surface area is as high as 3500 m 2 /g, but the use of KOH causes strong corrosion to the equipment, and the high price of KOH makes the prepared activated carbon costly.
- the activated carbon prepared by ZnCl 2 series is mainly mesoporous, the specific surface area is at a medium level, and the activation temperature of ZnCl 2 is low, 500-700 ° C, thus reducing the series of problems caused by energy consumption and high temperature operation, but ZnCl 2 will cause greater pollution to the environment, and waste water and waste gas must be recycled, so that the cost is greatly increased, and the use of ZnCl 2 will introduce zinc ions into the product, which limits the application of activated carbon.
- the traditional activated carbon preparation raw materials mainly use coal-based, petroleum coke base and coconut shell.
- the biomass power plant ash is an industrial waste. If it is directly discarded, the active ingredients inside can not be fully utilized and pollute the environment.
- the object of the present invention is to provide a method for preparing super activated carbon by using biomass power plant ash as raw material, which can not only waste biomass ash into treasure, purify the environment, but also obtain high specific surface area and narrow pore size distribution. Super activated carbon with low ash.
- the method for preparing super activated carbon by using biomass power plant ash as raw material comprises the following steps:
- the first insoluble matter obtained in the step 1) is washed in water for 2 to 3 times, and then placed in a hydrochloric acid solution, and the pH is controlled to be 1 to 3, and the mixture is stirred and separated to obtain a second insoluble matter by filtration. ;
- the carbon residue obtained in the step 3) is activated in a mixed gas atmosphere of water vapor and CO 2 at a temperature of 600 to 800 ° C to obtain an activated carbon intermediate product;
- the activated carbon intermediate obtained in the step 4) is mixed with the NaOH solid, and is heated from room temperature to 600 to 900 ° C in a nitrogen atmosphere to be activated to obtain an activated product;
- the activated product obtained in the step 5) is washed at least once with water, and then washed with water having a mass percentage of 20 to 25% for 1 to 4 times, and then washed with water until the pH of the filtrate is 6 to 7, and finally at 90 to 110. Dry at °C to obtain super activated carbon.
- the stirring time is 4 to 7 hours.
- the volume ratio of water vapor to CO 2 in the mixed gas is 0.5 to 3:1.
- the flow rate of the mixed gas is 100 to 400 ml/min, and the activation time is 1 to 3 hours.
- the flow rate of the mixed gas is 100 to 400 ml/min, and the activation time is 1 to 3 hours.
- the weight ratio of the activated carbon intermediate product to the NaOH solid is 1:2 to 5.
- the heating rate is 3 to 7 ° C / min, and the activation time is 1 to 4 h.
- the biomass power plant ash has a pore diameter of 20 to 50 ⁇ m.
- the super activated carbon has a pore diameter of 1 to 5 nm.
- the sodium silicate solution is sent to a process for producing white carbon black, and the white carbon black is processed.
- the mass percentage of each component in the biomass power plant ash is: SiO 2 : 55 to 75%; CaO: 8 to 15%; K 2 O: 3 to 9%; 4 to 8%; the balance is Fe 2 O 3 , MgO, P 2 O 5 and unavoidable impurities.
- the mass percentage of each component in the biomass power plant ash is: SiO 2 : 60 to 70%; CaO: 10 to 12%; K 2 O: 5 to 7%; 4 to 6%; the balance is Fe 2 O 3 , MgO, P 2 O 5 , and unavoidable impurities.
- the present invention first pre-activates the carbon residue extracted from the biomass power plant ash with a mixture of carbon dioxide and water vapor, and then chemically activates it with NaOH to prepare a higher-grade activated carbon. Since the physical activation alone relies on the oxidation-reduction reaction between the activator and the carbon source to form a pore structure, the yield of the activated carbon is not high, 10% to 25%, and pre-carbonization is carried out before activation, and the total activation time can reach 17h. Pre-activation using a mixture of carbon dioxide and water vapor overcomes the shortcomings of slow activation of carbon dioxide and long reaction time, as well as the short-term activation speed and poor stability of water vapor. After pre-activation of the mixture for 1 to 3 hours, the pores are obtained.
- the activated carbon intermediate is mixed with NaOH to further expand the pores to obtain super activated carbon having a pore diameter of about 1 to 5 nm.
- high surface area activated carbon can still be prepared with NaOH as the activator, and the price of NaOH is much lower than that of KOH.
- the purpose of combining water vapor and CO 2 mixed activation with NaOH activation is that the activation time of mixing with water vapor and CO 2 alone takes 6 to 10 hours, and the yield is low, 15%; combined with NaOH activation, utilizing chemical activation reaction
- the rapidity on the basis of the previous step of water vapor and CO 2 mixed activation and reaming, can obtain products with excellent performance parameters within 2 to 6 hours, and the yield of the product can be controlled above 40%.
- the raw materials are biomass power plant ash, turning waste into treasure, and optimizing resource utilization.
- the prepared activated carbon has high specific surface area, narrow pore size distribution and low ash, and is suitable as a supercapacitor electrode material.
- the super activated carbon obtained by the invention is compared with the activated carbon prepared by the traditional method: in the prior patent, only the residual carbon is extracted from the waste of the power plant, and the residual carbon is cleaned and removed, and dried without activation and reaming of the residual carbon. After testing, the residual carbon content of the non-reaming treatment is 141m 2 /g, the pore structure is not developed, and it is difficult to apply it to the actual; the specific surface area of the product can reach 2600m 2 /g, the pore structure is developed, and the ash content is low. It can be applied to high-end fields such as electrode materials for supercapacitors.
- the particle size of the power plant ash is 30-50 ⁇ m, and the composition is 60-70% SiO 2 , 10% CaO, 5% K 2 O, 4-6% residual carbon and a small amount of Fe 2 .
- O 3 , MgO and P 2 O 5 because the carbon residue is instantaneous combustion at high temperature, its density is lower than that of petroleum coke, pitch coke and lignite, and it is suitable as a raw material for preparing super activated carbon after impurity removal.
- Figure 1 is a process flow diagram of the present invention.
- a method for preparing super activated carbon from biomass power plant ash comprising the following steps:
- the biomass power plant ash with a particle size of 20-50 ⁇ m is added to the NaOH solution with a mass percentage of 25 to 35%, and is immersed for 1.5 to 2.5 hours at a temperature of 85-90 ° C to fully filter and separate.
- the first insoluble matter obtained in the step 1) is washed in water for 2 to 3 times, and then placed in a hydrochloric acid solution to control the pH to 1-3, and then subjected to closed stirring for 4 to 7 hours, followed by filtration and separation. Obtaining a second insoluble matter;
- the carbon residue obtained in the step 3) is activated in a mixed gas atmosphere of water vapor and CO 2 at a temperature of 700 ° C to obtain an activated carbon intermediate product, wherein the volume ratio of water vapor to CO 2 in the mixed gas is 1: 1, the mixed gas flow rate is 200ml / min, the activation time is 1h;
- the activated carbon intermediate obtained in the step 4) is mixed with the NaOH solid, and heated at room temperature to 3 ° C / min at room temperature to 800 ° C and then activated for 3 h to obtain an activated product; wherein the activated carbon intermediate product
- the weight ratio to NaOH solids is 1:2
- the activated product obtained in the step 5) is washed twice with water, and then washed with hydrochloric acid having a mass fraction of 25% for 1 to 4 times, and then washed with water until the pH of the filtrate is 6 to 7, and finally dried at 100 ° C.
- a super activated carbon having a pore diameter of 1 to 5 nm was obtained.
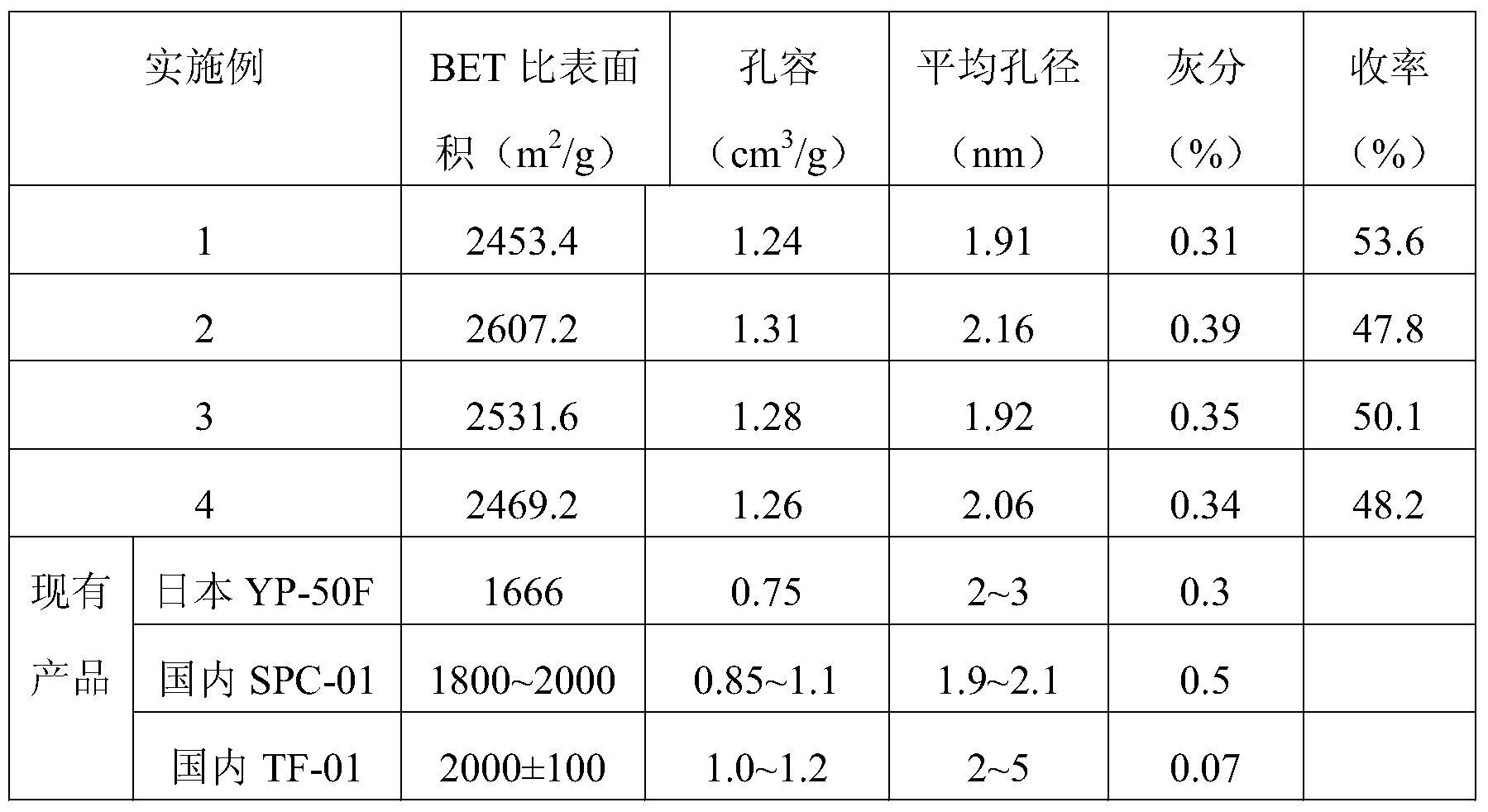
- the performance indicators of the products are shown in Table 1.
- a method for preparing super activated carbon from biomass power plant ash comprising the following steps:
- the carbon residue was prepared by the method of Example 1, except that:
- the obtained carbon residue is activated in a mixed gas atmosphere of water vapor and CO 2 at a temperature of 800 ° C to obtain an activated carbon intermediate product in which a volume ratio of water vapor to CO 2 in the mixed gas is 2:1, mixed.
- the gas flow rate is 100ml/min, and the activation time is 2h;
- step 2) mixing the activated carbon intermediate obtained in the step 2) with NaOH, and heating at room temperature to 4 ° C / min at room temperature to 800 ° C for 2 h; obtaining an activated product; wherein the activated carbon intermediate product and The weight ratio of NaOH is 1:4.
- the activated product obtained in the step 5) is washed twice with water, and then washed with a mass percentage of 20% hydrochloric acid for 1 to 4 times, and then washed with water until the pH of the filtrate is 6 to 7, and finally dried at 100 ° C.
- a super activated carbon having a pore diameter of 1 to 5 nm was obtained.
- the performance indicators of the products are shown in Table 1.
- the mass percentage of each component in the biomass power plant ash is: SiO 2 : 60 ⁇ 70%; CaO: 10 ⁇ 12%; K 2 O: 5 ⁇ 7%; carbon residue: 4 ⁇ 6%; 2 O 3 , MgO, P 2 O 5 , and unavoidable impurities.
- a method for preparing super activated carbon from biomass power plant ash comprising the following steps:
- the residual carbon was prepared by the method of Example 1,
- the obtained carbon residue is activated in a mixed gas atmosphere of water vapor and CO 2 at a temperature of 600 ° C to obtain an activated carbon intermediate product in which a volume ratio of water vapor to CO 2 in the mixed gas is 3:1, and the mixture is mixed.
- the gas flow rate is 400ml/min, and the activation time is 2h;
- step 2) mixing the activated carbon intermediate obtained in the step 2) with NaOH, and heating at room temperature to 5 ° C / min at room temperature to 900 ° C for 1 h; obtaining an activated product; wherein the activated carbon intermediate product and The weight ratio of NaOH is 1:5,
- the activated product obtained in the step 5) is washed twice with water, and then washed with a mass percentage of 22% hydrochloric acid for 1 to 4 times, and then washed with water until the pH of the filtrate is 6 to 7, and finally dried at 110 ° C.
- a super activated carbon having a pore diameter of 1 to 5 nm was obtained.
- the performance indicators of the products are shown in Table 1.
- the mass percentage of each component in the biomass power plant ash is: SiO 2 : 55 to 75%; CaO: 8 to 15%; K 2 O: 3 to 9%; carbon residue: 4 to 8%; 2 O 3 , MgO, P 2 O 5 and unavoidable impurities.
- a method for preparing super activated carbon from biomass power plant ash comprising the following steps:
- the residual carbon was prepared by the method of Example 1,
- the obtained carbon residue is activated in a mixed gas atmosphere of water vapor and CO 2 at a temperature of 800 ° C to obtain an activated carbon intermediate product in which a volume ratio of water vapor to CO 2 in the mixed gas is 1:2, mixed.
- the gas flow rate is 300ml/min, and the activation time is 4h;
- step 2) mixing the activated carbon intermediate obtained in the step 2) with NaOH, and heating at room temperature to 6 ° C / min at room temperature to 600 ° C for 4 h; obtaining an activated product; wherein the activated carbon intermediate product and The weight ratio of NaOH is 1:3.
- the activated product obtained in the step 5) is washed twice with water, and then washed with 25% by mass of 25% hydrochloric acid, and then washed with water until the pH of the filtrate is 6-7, and finally dried at 90 °C.
- a super activated carbon having a pore diameter of 1 to 5 nm was obtained.
- the performance indicators of the products are shown in Table 1.
- the mass percentage of each component in the biomass power plant ash is: SiO 2 : 60 ⁇ 70%; CaO: 10 ⁇ 12%; K 2 O: 5 ⁇ 7%; carbon residue: 4 ⁇ 6%; 2 O 3 , MgO, P 2 O 5 , and unavoidable impurities.
- the existing products are activated carbon products for supercapacitor electrode materials which have been industrialized on the market.
- the super activated carbon prepared by the invention has higher specific surface area than the existing products, the pore volume is equivalent, and the ash is slightly higher than the existing products. This is because the present invention uses power plant waste as a raw material, which itself contains more impurities than other coal-based or coconut shell raw materials.
- the TF-01 product is obtained by activation of KOH as an activator. Although the ash content is low, the product obtained by using KOH as an activator has a high cost, causing serious corrosion to the equipment and high cost of the product.
- the super activated carbon prepared by the invention has more price advantage in the market under the condition that the product performance parameters are equivalent.
Landscapes
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Inorganic Chemistry (AREA)
- Carbon And Carbon Compounds (AREA)
Abstract
提供一种以生物质电厂灰为原料制备超级活性炭的方法,包括:将生物质电厂灰经碱煮后过滤,滤出不溶物,不溶物中加入盐酸溶液,经除杂、水洗后得残炭,将残炭在水蒸汽和CO 2混合气的气氛下升温活化,得到中间产物,而后将中间产物与NaOH混合,在N 2气氛下升温活化,活化产物经洗涤、干燥后得到超级活性炭。该方法以生物质电厂废弃物为原料,得到了高附加值的超级电容器用活性炭。
Description
本发明涉及活性碳制备技术,具体地指一种以生物质电厂灰为原料制备超级活性炭的方法。
活性炭由于具有较大的比表面积、丰富的孔隙以及稳定的化学性质而被广泛应用于水处理、空气净化、烟气脱硫脱销以及催化剂载体等领域。近年来,由于高新科技领域的需要,高性能的活性炭也被越来越多地开发应用到血液净化、汽车炭罐、超级电容器电极材料,锂离子电池负极材料以及军事、航天等高要求领域。虽然我国活性炭的产量很大,但是大部分都是中低端产品,高性能的活性炭仍然需要靠大量的进口,所以制备高性能的活性炭仍然是碳材料领域的研究热点。
目前,活性炭的制备方法主要有物理活化法、化学活化法、以及物理化学联合活化法。
物理活化法主要是以CO2和H2O中的任意一种作为活化剂,升温至600~1200℃对原料进行活化,得到的活性炭产物比表面积低于1500m2/g,且收率低于30%,这是由于CO2在炭颗粒的孔道内扩散比较困难,扩散速度慢,使CO2与微孔的接近受到较大限制,所以工业上用CO2活化很少;而H2O分子比CO2分子小,扩散快,在较高的活化温度下活化速度较快,反应难以控制,难制备高比表面积的活性炭。
化学活化法采用炭化、活化过程同时进行,活化时间较短,且活性炭的孔隙结构主要是活化剂把原料中的氢、氧原子通过脱水除去而形成的孔隙,所以碳的得率较高,但是污染较大。目前高比表面的活性炭主要是以煤基、石油焦基为原料通过KOH强碱在N2气氛下升温至700~900℃进行活化,得到的活性炭比表面积最高可达3000m2/g,但是以固体废弃物为原料制备高性能活性炭未见报导,并且由于KOH的高价格,腐蚀性强而使得工业化得到的超级活性炭成本较高。
物理化学联合活化法就是将化学活化和物理活化相结合,在原料中加入化学药品,先在惰性气氛下炭化一段时间,再通入物理活化剂进行联合活化。目前主要是以KOH-CO2、KOH-H2O、ZnCl2-CO2和ZnCl2-H2O为活化剂进行物理化学联合活化制备活性炭,KOH系列化学剂制备出的活性炭多以微孔为主,比表面积高达3500m2/g,但是KOH的使用会对设备造成强烈的腐蚀,并且KOH价格高,使得制备出的活性炭成本高。ZnCl2系列制备出的活性炭多以中孔为主,比表面积处于中等水平,并且ZnCl2活化温度较低,为500~700℃,因此减少了能耗及高温操作带来的一系列难题,但是ZnCl2会对环境产生较大的污染,必须对废水、废气进行回收处理,使成本大大增加,并且ZnCl2的使用会使产物中引入锌离子,限制了活性炭的应用。
传统的活性炭制备原料主要采用煤基、石油焦基和椰壳等,生物质电厂灰是一种工业废弃物,如果直接丢弃,里面的有效成分不能充分利用,而且污染环境。
鉴于目前大环境下能源的缺乏,寻求以廉价的废弃物为原料制备超级活性炭一直是本领域技术人员努力探索的方向。
发明内容
本发明的目的就是要提供一种以生物质电厂灰为原料制备超级活性炭的方法,其不仅可以将生物质电厂灰变废为宝、净化环境,而且可以获得具有比表面积高、孔径分布窄、灰分低的超级活性炭。
为实现上述目的,本发明所提供的以生物质电厂灰为原料制备超级活性炭的方法,包括以下步骤:
1)将生物质电厂灰加入质量百分数为25~35%的NaOH溶液中,在温度为85~90℃的条件下浸煮1.5~2.5h,使其充分反应,过滤分离得到硅酸钠溶液和一级不溶物;
2)将步骤1)中得到的一级不溶物置于水中清洗2~3次,再将其置于盐酸溶液中,控制pH为1~3的条件下进行密闭搅拌,过滤分离得到二级不溶物;
3)将步骤2)得到的二级不溶物在50~80℃的条件下用水洗涤,直至pH为中性,得到残炭;
4)将步骤3)得到的残炭置于温度为600~800℃的水蒸汽和CO2的混合气体环境下
活化,得到活性炭中间产物;
5)将步骤4)得到的活性炭中间产物与NaOH固体混合,并在氮气环境下由室温升温至600~900℃后进行活化,得到活化产物;
6)将步骤5)得到的活化产物用水至少洗涤1次,再用质量百分数为20~25%的盐酸洗涤1~4次,然后用水洗涤至滤液的pH为6~7,最后在90~110℃条件下干燥,得到超级活性炭。
进一步地,所述步骤2)中,搅拌时间为4~7h。
再进一步地,所述步骤4)中,混合气体中水蒸汽和CO2的体积比为0.5~3∶1。
再进一步地,所述步骤4)中,混合气体的流量为100~400ml/min,活化时间为1~3h。
再进一步地,所述步骤4)中,混合气体的流量为100~400ml/min,活化时间为1~3h。
再进一步地,所述步骤5)中,活性炭中间产物与NaOH固体的重量比为1∶2~5。
再进一步地,所述步骤5)中,升温速率为3~7℃/min,活化时间为1~4h。
再进一步地,所述步骤1)中,生物质电厂灰的孔径为20~50μm。
再进一步地,所述步骤6)中,超级活性炭的孔径为1~5nm。
再进一步地,所述步骤1)中,硅酸钠溶液输送至生产白炭黑的工序,加工得到白炭黑。
再进一步地,所述步骤1)中,生物质电厂灰中各组份质量百分数为:SiO2:55~75%;CaO:8~15%;K2O:3~9%;残炭:4~8%;余量为Fe2O3、MgO、P2O5以及不可避免的杂质。
再进一步地,所述步骤1)中,生物质电厂灰中各组份质量百分数为:SiO2:60~70%;CaO:10~12%;K2O:5~7%;残炭:4~6%;余量为Fe2O3、MgO、P2O5,以及不可避免的杂质。
本发明的有益效果在于:
1、本发明先用二氧化碳-水蒸气的混合物对生物质电厂灰中提取的残炭进行预活化,之后与NaOH混合进行化学活化以制备高级活性炭。由于单独的物理活化主要依靠活化剂与碳源发生氧化还原反应而生成孔隙结构,所以活性炭的收率不高,为10%~25%,而且活化之前要进行预炭化,总活化时间可达17h;采用二氧化碳与水蒸气的混合物进行
预活化,克服了二氧化碳单独活化反应慢、反应时间长的缺点以及水蒸气单独活化速度快、稳定性差的缺点,经过混合物1~3h的预活化,得到孔隙较为发达的活性炭中间体,并且短时间的活化使收率下降不大。将活性炭中间体与NaOH混合,进行进一步扩孔,得到孔径为1~5nm左右的超级活性炭。有了物理活化的微孔作为基础,用NaOH做活化剂仍能制备出高表面积的活性炭,并且NaOH价格较KOH低很多。将水蒸气和CO2混合活化与NaOH活化相结合的目的在于:单独用水蒸气和CO2混合活化耗时长,需要6~10h,并且收率低,为15%;结合NaOH活化,利用化学活化反应的快速性,在前一步水蒸气和CO2混合活化扩孔的基础上,可在2~6h内得到性能参数优良的产品,并且产品的收率可以控制在40%以上。
2、原料为生物质电厂灰,变废为宝,资源利用最优化。
3、制备的活性炭比表面积高,孔径分布窄,灰分低,适合作为超级电容器电极材料。
4、产品成本低。原料为零成本,并且电厂灰粒径小,不需要再进行粉碎工作;二氧化碳和水蒸气为低成本活化剂;NaOH价格远低于KOH。
5、本发明得到超级活性炭与传统方法制备的活性炭相比:之前专利中仅仅从电厂废弃物中提取出了残炭以及将残炭清洗除杂、干燥而并未对残炭有活化扩孔处理,经测试,未扩孔处理的残炭比表面积为141m2/g,孔结构不发达,很难应用到实际中;而本产品的比表面积可达2600m2/g,孔结构发达,灰分低,可应用到超级电容器的电极材料等高端领域中。
6、经分析后可知电厂灰的粒径为30~50μm,组成为60~70%的SiO2、10%的CaO、5%的K2O、4~6%的残炭以及少量的Fe2O3、MgO和P2O5,由于残炭是在高温下的瞬时燃烧,其致密程度比石油焦、沥青焦以及褐煤等低,经除杂后适合作为制备超级活性炭的原料。
图1为本发明的工艺流程图。
为了更好地解释本发明,以下结合具体实施例进一步阐明本发明的主要内容,但本发明的内容不仅仅局限于以下实施例。
实施例1
一种以生物质电厂灰为原料制备超级活性炭的方法,包括以下步骤:
1)将粒径为20~50μm的生物质电厂灰加入质量百分数为25~35%的NaOH溶液中,在温度为85~90℃的条件下浸煮1.5~2.5h,使其充分反应过滤分离得到硅酸钠溶液和一级不溶物;得到的硅酸钠溶液进入生产白炭黑的工序得到白炭黑,其中,生物质电厂灰中各组份质量百分数为:SiO2:55~75%;CaO:8~15%;K2O:3~9%;残炭:4~8%;余量为Fe2O3、MgO、P2O5以及不可避免的杂质;
2)将步骤1)中得到的一级不溶物置于水中清洗2~3次,再将其置于盐酸溶液中,控制pH为1~3的条件下,进行密闭搅拌4~7h后,过滤分离得到二级不溶物;
3)将步骤2)得到的二级不溶物在50~80℃的条件下用水洗涤直至pH为中性,得到残炭;
4)将步骤3)得到的残炭置于温度为700℃的水蒸汽和CO2的混合气体环境下活化,得到活性炭中间产物,其中,混合气体中水蒸汽和CO2的体积比为1∶1,混合气体的流量为200ml/min,活化时间为1h;
5)将步骤4)得到的活性炭中间产物与NaOH固体混合,并在氮气环境下、以升温速率为3℃/min由室温升温至800℃后进行活化3h,得到活化产物;其中,活性炭中间产物与NaOH固体的重量比为1∶2,
6)将步骤5)得到的活化产物用水进行洗涤2次后,再用质量分数为25%的盐酸洗涤1~4次,然后用水洗涤至滤液的pH为6~7,最后在100℃下干燥,得到孔径为1~5nm的超级活性炭。产品的性能指标见表1。
实施例2
一种以生物质电厂灰为原料制备超级活性炭的方法,包括以下步骤:
以实施例1方法制备得到残炭,不同之处在于:
1)将得到的残炭置于温度为800℃的水蒸汽和CO2的混合气体环境下活化,得到活性炭中间产物,其中,混合气体中水蒸汽和CO2的体积比为2∶1,混合气体的流量为100ml/min,活化时间为2h;
2)将步骤2)得到的活性炭中间产物与NaOH混合,并在氮气环境下、以升温速率为4℃/min由室温升温至800℃后进行活化2h;得到活化产物;其中,活性炭中间产物与NaOH的重量比为1∶4,
3)将步骤5)得到的活化产物用水进行洗涤2次后,再用质量百分数为20%盐酸洗涤1~4次,然后用水洗涤至滤液的pH为6~7,最后在100℃下干燥,得到孔径为1~5nm的超级活性炭。产品的性能指标见表1。
其中,生物质电厂灰中各组份质量百分数为:SiO2:60~70%;CaO:10~12%;K2O:5~7%;残炭:4~6%;余量为Fe2O3、MgO、P2O5,以及不可避免的杂质。
实施例3
一种以生物质电厂灰为原料制备超级活性炭的方法,包括以下步骤:
以实施例1方法制备得到残炭,
1)将得到的残炭置于温度为600℃的水蒸汽和CO2的混合气体环境下活化,得到活性炭中间产物,其中,混合气体中水蒸汽和CO2的体积比为3∶1,混合气体的流量为400ml/min,活化时间为2h;
2)将步骤2)得到的活性炭中间产物与NaOH混合,并在氮气环境下、以升温速率为5℃/min由室温升温至900℃后进行活化1h;得到活化产物;其中,活性炭中间产物与NaOH的重量比为1∶5,
3)将步骤5)得到的活化产物用水进行洗涤2次后,再用质量百分数为22%盐酸洗涤1~4次,然后用水洗涤至滤液的pH为6~7,最后在110℃下干燥,得到孔径为1~5nm的超级活性炭。产品的性能指标见表1。
其中,生物质电厂灰中各组份质量百分数为:SiO2:55~75%;CaO:8~15%;K2O:3~9%;残炭:4~8%;余量为Fe2O3、MgO、P2O5以及不可避免的杂质。
实施例4
一种以生物质电厂灰为原料制备超级活性炭的方法,包括以下步骤:
以实施例1方法制备得到残炭,
1)将得到的残炭置于温度为800℃的水蒸汽和CO2的混合气体环境下活化,得到活性炭中间产物,其中,混合气体中水蒸汽和CO2的体积比为1∶2,混合气体的流量为300ml/min,活化时间为4h;
2)将步骤2)得到的活性炭中间产物与NaOH混合,并在氮气环境下、以升温速率为6℃/min由室温升温至600℃后进行活化4h;得到活化产物;其中,活性炭中间产物与NaOH的重量比为1∶3,
3)将步骤5)得到的活化产物用水进行洗涤2次后,再用质量百分数为25%盐酸洗涤1~4次,然后用水洗涤至滤液的pH为6~7,最后在90℃下干燥,得到孔径为1~5nm的超级活性炭。产品的性能指标见表1。
其中,生物质电厂灰中各组份质量百分数为:SiO2:60~70%;CaO:10~12%;K2O:5~7%;残炭:4~6%;余量为Fe2O3、MgO、P2O5,以及不可避免的杂质。
表1 超级活性炭的性能参数
其中收率=超级活性炭质量/残炭质量
现有产品为市场上已经工业化的超级电容电极材料用活性炭产品,对比产品参数可知,本发明制备的超级活性炭比表面积比现有产品高,孔容孔径相当,灰分比现有产品略高,这是因为本发明是以电厂废弃物为原料,其本身含有较其它煤基或椰壳原料更多的杂质。TF-01产品是以KOH为活化剂进行活化而得到的,此产品虽然灰分低,但是以KOH为活化剂得到的产品代价较高,对设备腐蚀严重,产品的成本高,相比之下,在产品性能参数相当的条件下,本发明制备的超级活性炭在市场上更具价格优势。
其它未详细说明的部分均为现有技术。尽管上述实施例对本发明做出了详尽的描述,但它仅仅是本发明一部分实施例,而不是全部实施例,人们还可以根据本实施例在不经创造性前提下获得其他实施例,这些实施例都属于本发明保护范围。
Claims (12)
- 一种以物质电厂灰为原料制备超级活性炭的方法,其特征在于:包括以下步骤:1)将生物质电厂灰加入质量百分数为25~35%的NaOH溶液中,在温度为85~90℃的条件下浸煮1.5~2.5h,使其充分反应,过滤分离得到硅酸钠溶液和一级不溶物;2)将步骤1)中得到的一级不溶物置于水中清洗2~3次,再将其置于盐酸溶液中,控制pH为1~3的条件下进行密闭搅拌,过滤分离得到二级不溶物;3)将步骤2)得到的二级不溶物在50~80℃的条件下用水洗涤,直至pH为中性,得到残炭;4)将步骤3)得到的残炭置于温度为600~800℃的水蒸汽和CO2的混合气体环境下活化,得到活性炭中间产物;5)将步骤4)得到的活性炭中间产物与NaOH固体混合,并在氮气环境下由室温升温至600~900℃后进行活化,得到活化产物;6)将步骤5)得到的活化产物用水至少洗涤1次,再用质量百分数为20~25%的盐酸洗涤1~4次,然后用水洗涤至滤液的pH为6~7,最后在90~110℃条件下干燥,得到超级活性炭。
- 根据权利要求1所述以生物质电厂灰为原料制备超级活性炭的方法,其特征在于:所述步骤2)中,搅拌时间为4~7h。
- 根据权利要求1或2所述以生物质电厂灰为原料制备超级活性炭的方法,其特征在于:所述步骤4)中,混合气体中水蒸汽和CO2的体积比为0.5~3∶1。
- 根据权利要求1或2所述以生物质电厂灰为原料制备超级活性炭的方法,其特征在于:所述步骤4)中,混合气体的流量为100~400ml/min,活化时间为1~3h。
- 根据权利要求3所述以生物质电厂灰为原料制备超级活性炭的方法,其特征在于:所述步骤4)中,混合气体的流量为100~400ml/min,活化时间为1~3h。
- 根据权利要求1或2所述以生物质电厂灰为原料制备超级活性炭的方法,其特征在于:所述步骤5)中,活性炭中间产物与NaOH固体的重量比为1∶2~5。
- 根据权利要求1或2所述以生物质电厂灰为原料制备超级活性炭的方法,其特征在于:所述步骤5)中,升温速率为3~7℃/min,活化时间为1~4h。
- 根据权利要求6所述以生物质电厂灰为原料制备超级活性炭的方法,其特征在于:所述步骤1)中,生物质电厂灰的孔径为20~50μm。
- 根据权利要求1或2所述以生物质电厂灰为原料制备超级活性炭的方法,其特征在于:所述步骤6)中,超级活性炭的孔径为1~5nm。
- 根据权利要求1或2所述以生物质电厂灰为原料制备超级活性炭的方法,其特征在于:所述步骤1)中,硅酸钠溶液输送至生产白炭黑的工序,加工得到白炭黑。
- 根据权利要求1或2所述以生物质电厂灰为原料制备超级活性炭的方法,其特征在于:所述步骤1)中,生物质电厂灰中各组份质量百分数为:SiO2:55~75%;CaO:8~15%;K2O:3~9%;残炭:4~8%;余量为Fe2O3、MgO、P2O5以及不可避免的杂质。
- 根据权利要求11所述以生物质电厂灰为原料制备超级活性炭的方法,其特征在于:所述步骤1)中,生物质电厂灰中各组份质量百分数为:SiO2:60~70%;CaO:10~12%;K2O:5~7%;残炭:4~6%;余量为Fe2O3、MgO、P2O5,以及不可避免的杂质。
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201410024084.2A CN103771407B (zh) | 2014-01-20 | 2014-01-20 | 以生物质电厂灰为原料制备超级活性炭的方法 |
| CN201410024084.2 | 2014-01-20 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2015106720A1 true WO2015106720A1 (zh) | 2015-07-23 |
Family
ID=50564249
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/CN2015/071016 WO2015106720A1 (zh) | 2014-01-20 | 2015-01-19 | 以生物质电厂灰为原料制备超级活性炭的方法 |
Country Status (2)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| CN (1) | CN103771407B (zh) |
| WO (1) | WO2015106720A1 (zh) |
Cited By (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN105236408A (zh) * | 2015-10-30 | 2016-01-13 | 上海市政工程设计研究总院(集团)有限公司 | 一种连续多级孔道活性炭的制备方法 |
| CN106927461A (zh) * | 2017-03-28 | 2017-07-07 | 南平元力活性炭有限公司 | 一种高容量长寿命超级电容器用活性炭生产工艺 |
| CN112938974A (zh) * | 2021-03-23 | 2021-06-11 | 中国科学院化学研究所 | 一种超高比表面积多孔炭材料及其制备方法 |
| CN114906847A (zh) * | 2022-05-16 | 2022-08-16 | 内蒙古科技大学 | 一种气化渣残碳的湿法活化方法及其应用 |
| CN115092941A (zh) * | 2022-07-11 | 2022-09-23 | 哈尔滨工业大学 | 利用低温碱熔法从煤气化细灰中回收残碳及硅酸钠的方法及应用 |
| CN115739203A (zh) * | 2022-10-26 | 2023-03-07 | 东北大学 | 一种基于气化渣再利用的负载氧化铁活性炭及其制备方法 |
Families Citing this family (11)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN103771407B (zh) * | 2014-01-20 | 2015-12-30 | 中盈长江国际新能源投资有限公司 | 以生物质电厂灰为原料制备超级活性炭的方法 |
| CN104003387A (zh) * | 2014-06-10 | 2014-08-27 | 厦门大学 | 一种以生物质热解炭为原料制备活性炭的方法 |
| CN104163426B (zh) * | 2014-08-18 | 2016-06-08 | 深圳市环境科学研究院 | 一种活性炭制备方法及芦竹活性炭 |
| CN104129777B (zh) * | 2014-08-26 | 2016-03-30 | 武汉科技大学 | 一种多功能化生物炭及其制备方法 |
| CN104528714B (zh) * | 2014-11-28 | 2016-06-15 | 巫溪县绿野实业有限公司 | 一种松籽壳活性炭的制备方法 |
| CN107892298B (zh) * | 2017-11-28 | 2020-07-03 | 福建省鑫森炭业股份有限公司 | 一种超级电容器活性炭及其制备方法 |
| CN110342511A (zh) * | 2019-07-17 | 2019-10-18 | 光大环保技术研究院(南京)有限公司 | 一种利用改性飞灰提高活性炭品质的方法 |
| CN111591986B (zh) * | 2020-04-10 | 2022-03-11 | 山东大学 | 一种基于石化企业副产物石油焦提质利用的厂区VOCs治理方法及系统 |
| CN113044839B (zh) * | 2021-04-02 | 2022-09-16 | 清创人和生态工程技术有限公司 | 一种分级多孔炭材料的制备方法及应用 |
| CN114804102A (zh) * | 2022-05-06 | 2022-07-29 | 国家能源集团宁夏煤业有限责任公司 | 氮掺杂活性炭及其制备方法 |
| CN115249589B (zh) * | 2022-07-11 | 2023-04-28 | 哈尔滨工业大学 | 一种利用煤气化细灰制备超级电容器用活性炭的方法 |
Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN1478722A (zh) * | 2002-08-28 | 2004-03-03 | 中国林科院林产化工研究所江苏省溧阳 | 铂族金属催化剂载体专用活性炭制取方法 |
| CN101012059A (zh) * | 2006-12-08 | 2007-08-08 | 清华大学 | 利用废轮胎制备废水处理用活性炭的方法 |
| CN101112984A (zh) * | 2007-07-03 | 2008-01-30 | 四川大学 | 利用废弃麻疯树果壳制备活性炭的方法 |
| CN101264885A (zh) * | 2008-04-10 | 2008-09-17 | 江南大学 | 一种稻壳灰制取优质活性炭的生产方法 |
| CN101397136A (zh) * | 2008-11-04 | 2009-04-01 | 昆明理工大学 | 一种物理活化法制备高比表面积颗粒活性炭的方法 |
| CN101475167A (zh) * | 2009-02-11 | 2009-07-08 | 溧阳竹溪活性炭有限公司 | 铂催化剂载体专用活性炭制取方法 |
| CN103771407A (zh) * | 2014-01-20 | 2014-05-07 | 中盈长江国际新能源投资有限公司 | 以生物质电厂灰为原料制备超级活性炭的方法 |
Family Cites Families (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BR9304771A (pt) * | 1993-04-09 | 1994-11-08 | Social Welfare Foundation Hokk | Carvão ativado, e processo e aparelho para preparação de carvão ativado |
| CN1110957A (zh) * | 1994-04-28 | 1995-11-01 | 中国林业科学研究院林产化学工业研究所 | 食用米制备高性能活性炭的方法 |
| CN102020272A (zh) * | 2009-09-17 | 2011-04-20 | 黑龙江万禾园油脂有限公司 | 一种利用稻壳灰生产水玻璃和活性炭的方法 |
| FI20105717A (fi) * | 2010-06-21 | 2011-12-22 | Gasek Oy | Menetelmä aktiivihiilen valmistamiseksi |
| CN102557047B (zh) * | 2011-10-18 | 2014-08-20 | 武汉凯迪工程技术研究总院有限公司 | 以生物质电厂灰为原料制备介孔二氧化硅的方法 |
| JP5159970B1 (ja) * | 2012-05-16 | 2013-03-13 | 株式会社アルメディオ | 活性炭及びその製造方法 |
-
2014
- 2014-01-20 CN CN201410024084.2A patent/CN103771407B/zh active Active
-
2015
- 2015-01-19 WO PCT/CN2015/071016 patent/WO2015106720A1/zh active Application Filing
Patent Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN1478722A (zh) * | 2002-08-28 | 2004-03-03 | 中国林科院林产化工研究所江苏省溧阳 | 铂族金属催化剂载体专用活性炭制取方法 |
| CN101012059A (zh) * | 2006-12-08 | 2007-08-08 | 清华大学 | 利用废轮胎制备废水处理用活性炭的方法 |
| CN101112984A (zh) * | 2007-07-03 | 2008-01-30 | 四川大学 | 利用废弃麻疯树果壳制备活性炭的方法 |
| CN101264885A (zh) * | 2008-04-10 | 2008-09-17 | 江南大学 | 一种稻壳灰制取优质活性炭的生产方法 |
| CN101397136A (zh) * | 2008-11-04 | 2009-04-01 | 昆明理工大学 | 一种物理活化法制备高比表面积颗粒活性炭的方法 |
| CN101475167A (zh) * | 2009-02-11 | 2009-07-08 | 溧阳竹溪活性炭有限公司 | 铂催化剂载体专用活性炭制取方法 |
| CN103771407A (zh) * | 2014-01-20 | 2014-05-07 | 中盈长江国际新能源投资有限公司 | 以生物质电厂灰为原料制备超级活性炭的方法 |
Cited By (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN105236408A (zh) * | 2015-10-30 | 2016-01-13 | 上海市政工程设计研究总院(集团)有限公司 | 一种连续多级孔道活性炭的制备方法 |
| CN106927461A (zh) * | 2017-03-28 | 2017-07-07 | 南平元力活性炭有限公司 | 一种高容量长寿命超级电容器用活性炭生产工艺 |
| CN112938974A (zh) * | 2021-03-23 | 2021-06-11 | 中国科学院化学研究所 | 一种超高比表面积多孔炭材料及其制备方法 |
| CN112938974B (zh) * | 2021-03-23 | 2022-06-14 | 中国科学院化学研究所 | 一种超高比表面积多孔炭材料及其制备方法 |
| CN114906847A (zh) * | 2022-05-16 | 2022-08-16 | 内蒙古科技大学 | 一种气化渣残碳的湿法活化方法及其应用 |
| CN115092941A (zh) * | 2022-07-11 | 2022-09-23 | 哈尔滨工业大学 | 利用低温碱熔法从煤气化细灰中回收残碳及硅酸钠的方法及应用 |
| CN115739203A (zh) * | 2022-10-26 | 2023-03-07 | 东北大学 | 一种基于气化渣再利用的负载氧化铁活性炭及其制备方法 |
| CN115739203B (zh) * | 2022-10-26 | 2024-03-15 | 东北大学 | 一种基于气化渣再利用的负载氧化铁活性炭及其制备方法 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN103771407A (zh) | 2014-05-07 |
| CN103771407B (zh) | 2015-12-30 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| WO2015106720A1 (zh) | 以生物质电厂灰为原料制备超级活性炭的方法 | |
| CN104528720B (zh) | 一种多级孔炭材料的制备方法及产品 | |
| CN108439400A (zh) | 一种氮掺杂甘蔗渣活性炭及其制备方法 | |
| CN106167263B (zh) | 一种使用造纸黑液木质素制备活性炭的方法 | |
| CN103936006A (zh) | 一种用米糠制备多孔活性炭材料的方法 | |
| CN107628597B (zh) | 一种利用SiO2包覆法制备具有微孔及介孔结构生物质碳材料的方法 | |
| CN104709905A (zh) | 一种利用混合熔盐为活化剂制备超级电容器用活性炭的方法 | |
| CN110429264B (zh) | 一种制备稻壳基负极材料的方法 | |
| CN111547722B (zh) | 一种生物质衍生碳材料的制备方法 | |
| CN106629723A (zh) | 一种生物质基含n,s,p共掺杂多孔碳及其应用 | |
| CN113135568A (zh) | 一种氮掺杂多孔碳材料及其制备方法和应用 | |
| CN111017925A (zh) | 一种新型高储能性能多孔碳材料的制备及其应用 | |
| CN114956037A (zh) | 一种钠离子电池负极用碳材料及其制备方法以及钠离子电池负极极片和钠离子电池 | |
| CN107151014B (zh) | 一种生物多孔碳基锂硫电池正极材料及其制备方法 | |
| CN110330014B (zh) | 用于超级电容器电极材料的淀粉多孔碳微球的制备方法 | |
| CN111799098A (zh) | 一种多孔碳/金属氧化物复合材料及其制备方法和应用 | |
| CN112194131A (zh) | 一种化学活化法制备造纸污泥碳质吸附剂方法和应用 | |
| CN117133908A (zh) | 一种红磷碳电池负极材料及其制备方法及其应用 | |
| CN102190298A (zh) | 一种林木剩余物快速热解副产炭制备活性炭的方法 | |
| CN110697708A (zh) | 锂离子电容器用的氮掺杂多孔炭材料及其低温共融溶剂活化生物质废弃物高效的制备方法 | |
| CN112691666A (zh) | 一种非晶态羟基氧化铁-生物炭复合材料及其制备方法 | |
| CN117416956A (zh) | 一种竹基活性炭及高吸附性竹基活性炭复合吸附剂制备工艺 | |
| CN112441584A (zh) | 一种蔗渣活性炭及其制备方法 | |
| CN112028188A (zh) | 一种不对称电容脱盐器件用生物质碳基电极的制备方法 | |
| CN112875700A (zh) | 一种沥青基炭微球的制备及其在超级电容器电极的应用 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 15736999 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 15736999 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |