WO2014024583A1 - エアベアリング装置及び塗布装置 - Google Patents
エアベアリング装置及び塗布装置 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2014024583A1 WO2014024583A1 PCT/JP2013/067076 JP2013067076W WO2014024583A1 WO 2014024583 A1 WO2014024583 A1 WO 2014024583A1 JP 2013067076 W JP2013067076 W JP 2013067076W WO 2014024583 A1 WO2014024583 A1 WO 2014024583A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- air bearing
- coating
- bearing device
- exhaust
- gas
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Ceased
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F16—ENGINEERING ELEMENTS AND UNITS; GENERAL MEASURES FOR PRODUCING AND MAINTAINING EFFECTIVE FUNCTIONING OF MACHINES OR INSTALLATIONS; THERMAL INSULATION IN GENERAL
- F16C—SHAFTS; FLEXIBLE SHAFTS; ELEMENTS OR CRANKSHAFT MECHANISMS; ROTARY BODIES OTHER THAN GEARING ELEMENTS; BEARINGS
- F16C32/00—Bearings not otherwise provided for
- F16C32/06—Bearings not otherwise provided for with moving member supported by a fluid cushion formed, at least to a large extent, otherwise than by movement of the shaft, e.g. hydrostatic air-cushion bearings
- F16C32/0603—Bearings not otherwise provided for with moving member supported by a fluid cushion formed, at least to a large extent, otherwise than by movement of the shaft, e.g. hydrostatic air-cushion bearings supported by a gas cushion, e.g. an air cushion
- F16C32/0614—Bearings not otherwise provided for with moving member supported by a fluid cushion formed, at least to a large extent, otherwise than by movement of the shaft, e.g. hydrostatic air-cushion bearings supported by a gas cushion, e.g. an air cushion the gas being supplied under pressure, e.g. aerostatic bearings
- F16C32/0622—Bearings not otherwise provided for with moving member supported by a fluid cushion formed, at least to a large extent, otherwise than by movement of the shaft, e.g. hydrostatic air-cushion bearings supported by a gas cushion, e.g. an air cushion the gas being supplied under pressure, e.g. aerostatic bearings via nozzles, restrictors
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/67—Apparatus specially adapted for handling semiconductor or electric solid state devices during manufacture or treatment thereof; Apparatus specially adapted for handling wafers during manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or electric solid state devices or components ; Apparatus not specifically provided for elsewhere
- H01L21/67005—Apparatus not specifically provided for elsewhere
- H01L21/67011—Apparatus for manufacture or treatment
- H01L21/6715—Apparatus for applying a liquid, a resin, an ink or the like
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/67—Apparatus specially adapted for handling semiconductor or electric solid state devices during manufacture or treatment thereof; Apparatus specially adapted for handling wafers during manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or electric solid state devices or components ; Apparatus not specifically provided for elsewhere
- H01L21/677—Apparatus specially adapted for handling semiconductor or electric solid state devices during manufacture or treatment thereof; Apparatus specially adapted for handling wafers during manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or electric solid state devices or components ; Apparatus not specifically provided for elsewhere for conveying, e.g. between different workstations
- H01L21/67784—Apparatus specially adapted for handling semiconductor or electric solid state devices during manufacture or treatment thereof; Apparatus specially adapted for handling wafers during manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or electric solid state devices or components ; Apparatus not specifically provided for elsewhere for conveying, e.g. between different workstations using air tracks
Definitions
- the present invention relates to an air bearing device and a coating device including the air bearing device, and more specifically to an air bearing device capable of controlling a flow of discharged gas and a coating device including the air bearing device.
- a coating apparatus disclosed in Patent Document 1 is provided with a nozzle that applies a coating liquid, a rectangular parallelepiped surface plate on which an object to be coated is placed, and a nozzle that is transverse to the short side of the surface plate. And a holding member constituting the gantry is supported in a non-contact manner by an air bearing with respect to the surface plate. Further, the object to be coated with the coating liquid is fixed to the surface plate by vacuum suction.
- the nozzle is scanned by moving the gantry relative to the coating object fixed on the surface plate, and the coating liquid is discharged from the nozzle and coated on the surface of the coating object.
- the present invention has been made in view of such circumstances. That is, it aims at providing the coating device provided with the air bearing apparatus which can raise the thickness precision and flatness precision of a coating film, and the said air bearing apparatus.
- a first aspect of an air bearing device of the present invention includes a pad portion that floats by a levitation force generated by discharging a gas, and the pad portion contains gas. It has a bearing surface provided with a jet outlet for discharging, and airflow control means for controlling the flow direction of the gas discharged from the jet outlet.
- the air bearing device according to the first aspect, wherein the air flow control means is not so surrounded as to partially or completely surround the ejection port. It has an exhaust groove disposed on the bearing surface that extends continuously or continuously.
- the air bearing device according to the second aspect, wherein the air flow control means communicates with the exhaust groove and passes through the pad portion. Has a road.
- the exhaust groove is annular in a plan view of the bearing surface.
- the first aspect of the coating apparatus of the present invention includes a coating unit for coating a coating liquid on a member to be coated, and a coating liquid by the coating unit.
- a placement object having a coating region where the member to be coated is located when coating, an air bearing device that discharges a gas for allowing the coating means to float a predetermined distance from the placement object, and a discharge from the air bearing device
- Air flow control means for controlling the flow direction of the gas to be prevented and preventing the gas from entering the application region.
- the coating device of this invention is a coating device of the said 1st aspect, Comprising:
- the said airflow control means is provided in at least one of the said air bearing apparatus and the said figurine, It is an exhaust path for exhausting the gas discharged from the air bearing device.
- the coating device of this invention is a coating device of the said 2nd aspect, Comprising:
- the said air-bearing apparatus used for the said coating device is equipped with the jet nozzle which discharges the said gas,
- the exhaust path has an exhaust groove that extends discontinuously or continuously so as to partially or completely surround the ejection port.
- the coating device of this invention is a coating device of the said 2nd or 3rd aspect, Comprising:
- the said exhaust path penetrates at least one of the said air bearing apparatus and said figurine. It has an exhaust passage.
- the exhaust groove communicates with the exhaust through path.
- the exhaust path is a suction unit that can supply negative pressure to the exhaust path. It is connected.
- the air flow control means is provided in at least one of the air bearing device and the above-described figurine, A partition member extending so as to contact at least the other of the air bearing device and the above-described figurine, and the partition member allows a floating space between the air bearing device and the figurine to be the application region in a front view. The side is closed.
- the air bearing device according to the present invention can control the flow of gas discharged from the air bearing device by the air flow control means, it is possible to prevent the influence of the discharged gas on the peripheral objects of the air bearing device. Furthermore, the influence of the discharge gas on the coating film formed on the coating object can be eliminated by the airflow control means of the coating apparatus according to the present invention. Therefore, the thickness accuracy and flatness accuracy of the coating film can be increased, and the coating film can be thinned and flattened, and thus the product can be downsized.
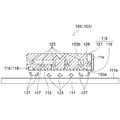
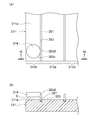
- FIG. 4 is a cross-sectional view of the pad portion taken along line IV-IV in FIG. 3.
- A) is a top view which shows the relationship between the surface plate and pad part of the coating device which concerns on 2nd Embodiment,
- (b) is sectional drawing along line VV of Fig.5 (a). is there.
- (A) is a top view which shows the relationship between the surface plate and pad part of the coating device which concerns on 3rd Embodiment,
- (b) is sectional drawing along line VI-VI of Fig.6 (a). is there.
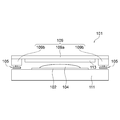
- FIG. 1 is a perspective view schematically showing a part of a coating apparatus 101 according to the embodiment
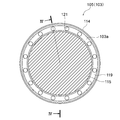
- FIG. 2 is a front view schematically showing main components of the coating apparatus 101 shown in FIG. 3 is a bottom view of the pad portion 114 of the coating apparatus 101 shown in FIG. 1
- FIG. 4 is a cross-sectional view of the pad portion 114 taken along line IV-IV in FIG.
- the support portion 109b and the side support air bearing device 107 attached to the support portion 109b shown in FIG. 1 are omitted for clarity of the drawing.
- the coating apparatus 101 of the embodiment mainly applies a resist solution 104 by a slot nozzle 113 that constitutes a coating means for applying a resist solution 104 that is a coating solution to a glass substrate 102 that is a member to be coated, and the slot nozzle 113.
- a platen 111 having a coating region 112a on which the glass substrate 102 is placed, and an air bearing device 103 for discharging a gas to float the slot nozzle 113 at a predetermined distance from the platen 111;
- An airflow control unit that controls the flow direction of the gas ejected from the air bearing device 103 and prevents the gas from entering the application region 112a.
- the surface plate 111 has a rectangular parallelepiped shape, and the flat upper surface 111a includes a rectangular application region 112a in a plan view, and a support region 112b that is disposed across the application region 112a in the short direction of the upper surface 111a.
- the application area 112a is an area where the glass substrate 102 placed on the upper surface 111a of the surface plate 111 is applied by the slit nozzle 113, and the support area 112b is the pad portion 114 of the upper surface support air bearing device 105. It is a moving area.
- the upper surface 111a of the surface plate 111 of the present embodiment is separated into the coating region 112a and the support region 112b by the boundary groove 153 extending in the longitudinal direction of the surface plate 111, but the surface plate without the boundary groove 153 is used. Needless to say, it can also be used.
- the gantry 109 includes a horizontal holding portion 109 a on which the slot nozzle 113 is mounted and two support portions 109 b that are continuous to both ends in the longitudinal direction of the horizontal holding portion 109 a, and is fixed by the upper surface support air bearing device 105. It is supported without contacting the upper surface 111a of the board 111.
- Each support portion 109b extends in a direction perpendicular to the horizontal holding portion 109a.
- One end portion of each support portion 109b is connected to one end portion of the horizontal holding portion 109a, and the other end portion of each support portion 109b. Is coupled to the side support air bearing device 107.
- a pedestal portion 109c is attached to a corner defined by the horizontal holding portion 109a and the support portion 109b, and the pedestal portion 109c is padded to the upper surface support bearing 105 via a conventionally known ball joint (not shown). Supported by the portion 114.
- the gantry 109 is levitated at a predetermined distance from the upper surface 111a and the side surface 111b of the surface plate 111 by the upper surface support air bearing device 105 and the side surface support air bearing device 107, and the gantry 109 The movement in the longitudinal direction of the 109 horizontal holding portions 109 a is regulated by the side support air bearing device 107.
- the upper surface support air bearing device 105 and the side surface support air bearing device 107 of the air bearing device 103 used in the coating apparatus 101 are a gas supply source such as a compressor that supplies compressed gas to the air bearing device 103 ( (Not shown) and pad portions 114 and 116, and a predetermined amount and a predetermined pressure of compressed gas are supplied from the gas supply source to the porous body 115 by the drive signal from the control section 131. A levitation force is applied to the pad portions 114 and 116 by discharging compressed gas from the pores provided.
- the upper surface support air bearing device 105 and the side surface support air bearing device 107 have the same configuration except for the pad portions 114 and 116. Therefore, the air bearing device 103 will be described using the upper surface support air bearing device 105.
- the pad portion 114 has a circular shape in a bottom view, and the hatched portion is a region where a jet port is provided, and is composed of a porous body 115.
- the porous body 115 is a disk-shaped member having pores communicating with each other for ejecting gas.
- a gas supply source (not shown) communicates with the pores of the porous body 115 via an air supply path 117 formed inside the pad portion 114, and the gas 123 supplied from the gas supply source is porous. By discharging from the pores of the material body 115, the pad portion 114 floats from the upper surface 111 a of the surface plate 111.
- the pad unit 114 includes an exhaust path 118 which is an air flow control means for controlling the flow direction of the jetted gas and preventing the gas from entering the coating region 112a.
- the exhaust path 118 includes an exhaust groove 119 and an exhaust through path 121.
- the exhaust groove 119 is on the bearing surface 103a of the pad portion 114 facing the upper surface 111a of the surface plate 111, and is concentric with the bearing surface 103a so as to completely surround the porous body 115 on the outer peripheral side of the porous body 115. Are continuously engraved in a ring shape.
- the exhaust groove 119 communicates with one end of an exhaust through passage 121 having a predetermined diameter and penetrating the pad portion 114, and the other end of the exhaust through passage 121 communicates with the outside of the pad portion 114 (atmospheric communication). ing.
- a plurality of exhaust through passages 121 are arranged spaced apart from each other at equal intervals along the circumferential direction of the bearing surface 103a, and in the thickness direction of the pad portion 114 (the direction intersecting the paper surface of FIG. 3, the vertical direction of FIG. 4). It is extended.
- the cross-sectional shape of the exhaust groove 119 (the cross-sectional shape along the vertical plane passing through the center of the bearing surface 103a) is a quadrangle, but various shapes such as a circle, an ellipse, and a polygon can be used. It goes without saying that you can do it.
- the exhaust groove 119 does not need to be annular as long as it is continuous, and may have a form that completely surrounds the porous body 115 (or the pores constituting the discharge port), such as a rectangle or a zigzag shape. If applicable. Furthermore, the number and shape of the exhaust through passage 121 can be changed as appropriate.
- the upper surface support air bearing device 105 configured as described above receives a drive signal from the control unit 131, compressed gas is supplied to the pad unit 114 from a gas supply source.
- the gas (reference numeral 123 in FIG. 4) supplied to the pad portion 114 passes through the air supply path 117 and is discharged from the pores of the porous body 115 (reference numeral 125 in FIG. 4), and is applied to the upper surface 111a of the surface plate 111. Colliding and applying levitation force to the pad portion 114.
- the gas discharged from the porous body 115 passes through a relatively narrow space between the bearing surface 103a and the upper surface 111a of the surface plate 111 and reaches the exhaust groove 119.
- the gas (reference numeral 127 in FIG. 4) that has reached the exhaust groove 119 enters the exhaust through passage 121 via the exhaust groove 119 and is finally the anti-bearing that is the upper surface facing the bearing surface 103a of the pad portion 114. It is discharged from the surface 103b to the outside.
- the pad portion 116 of the side support air bearing device 107 is not provided with an exhaust path (that is, an exhaust groove and an exhaust through path).
- an exhaust path that is, an exhaust groove and an exhaust through path.
- the gas supplied to the side support air bearing device 107 may affect the coating film on the glass substrate 102 on the upper surface 111 a of the surface plate 111, the exhaust gas is exhausted in the same manner as the upper surface support air bearing device 105.
- a configuration in which a groove and an exhaust through-passage are provided is also possible.
- the coating apparatus 101 is supplied with a gas having a predetermined pressure (that is, compressed gas) from the compressed gas source to the upper surface support air bearing device 105 and the side surface support air bearing device 107 in accordance with a drive signal from the control unit 131. Then, the compressed gas is discharged from the pores of the porous body 115, and the gantry 109 is supported in a state of being separated from the upper surface 111a and the side surface 111b of the surface plate 111 by a predetermined distance.
- a gas having a predetermined pressure that is, compressed gas
- the gantry 109 is scanned and moved relative to the glass substrate 102 by a driving means (not shown), A resist solution 104 is applied from the nozzle 113.
- the gas discharged from the pores of the porous body 115 collides with the support region 112b of the upper surface 111a of the surface plate 111 (reference numeral 125 in FIG. 4) to generate a levitation force. After that, it flows in the outer peripheral direction of the bearing surface 103a and further reaches the exhaust groove 119 (reference numeral 127 in FIG. 4).
- the gas 128 that has entered the exhaust groove 119 is discharged from the opposite bearing surface 103 b of the pad portion 114 to the outside through the exhaust through hole 121. Therefore, it is possible to eliminate the influence of the gas discharged from the bearing surface 103a such that the resist solution 104 on the glass substrate 102 is partially dried or blown off.
- the exhaust groove 119 has a closed shape surrounding the porous body 115 (or the pores constituting the discharge port). However, it is not always necessary to completely surround the porous body 115 (or the discharge port). It is also possible to extend so as to partially enclose the pores constituting the. That is, for example, an exhaust groove 119 may be provided at a position where the discharged gas can be prevented from entering the application region 112a on which the object is placed, such as an arc shape or a zigzag shape. Further, the bearing surface 103a of the pad portion 114 is not limited to a circle, and various shapes such as an ellipse and a polygon can be employed.
- the exhaust groove 119 of the present embodiment is configured by a continuous arc-shaped (that is, circular) groove having a single radius of curvature. It is also possible to comprise a groove extending in the direction. Moreover, it is also possible to comprise an exhaust groove from a plurality of grooves extending linearly.
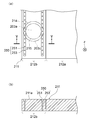
- FIG. 5A is a plan view showing a part of the surface plate 211 of the coating apparatus according to the second embodiment, showing the relationship between the surface plate 211 and the pad portion 214
- FIG. 4 is a cross-sectional view taken along line IV-IV in FIG.
- the configuration of elements that are not particularly mentioned in the coating apparatus and the modifications thereof are the same as those of the coating apparatus according to the first embodiment, and are therefore omitted.
- the pad portion 214 is indicated by a two-dot chain line.
- the coating apparatus of 2nd Embodiment is the structure provided with the exhaust path 250 which is an airflow control means in the surface plate 211 which is a mounting object.
- An exhaust path 250 is provided in the support region 212 b of the surface plate 211 that faces the bearing surface 203 a of the pad portion 214. That is, the horizontal projection position of the porous body 215 of the pad portion 214, which is horizontally projected onto the upper surface 211a of the surface plate 211, is not overlapped with the porous body 215 and is disposed within the outer periphery 203b of the bearing surface 203a. It is formed.
- the horizontal projection position means the position of the member when the coating device is viewed in the Z direction (direction intersecting the paper surface of FIG. 5A).
- the exhaust groove 251 constituting the exhaust path 250 has two linear regions that are arranged at a predetermined distance from each other in plan view. Further, the plurality of exhaust through passages 253 constituting the exhaust passage 250 communicate with the exhaust groove 251, are spaced apart from each other, and pass through the surface plate 211. As in the first embodiment, the exhaust passage 253 communicates with the outside of the surface plate 211, that is, the outside of the coating apparatus 201 at a position that does not affect the coating liquid (see the reference numeral 104 in FIG. 1). is doing.
- the airflow control means of the second embodiment is configured to be provided on the surface plate 211, but has an exhaust groove (see reference numeral 119 in FIG. 3) as in the first embodiment. It is also possible to adopt a configuration in which only the exhaust passage 253 is provided without providing the exhaust groove 251.
- FIG. 6A is a plan view showing a part of the surface plate 311 of the coating apparatus according to the second embodiment, showing the relationship between the surface plate 311 and the pad portion 314, and FIG. FIG. 6A is a cross-sectional view taken along line VI-VI in FIG.
- FIGS. 6A and 6B show only the pad portion 314 disposed on one side (left side) of the upper surface support air bearing device.
- the coating apparatus according to the third embodiment includes a partition member 351 as airflow control means. Unlike the first and second embodiments, the bearing surface of the pad portion has a discharge port composed of a porous body, but does not have an exhaust path.
- the airflow control means includes a partition member 351 for preventing the gas discharged from the pad portion 314 from flowing from the support region 312b to the application region 312a.
- the partition member 351 is disposed along a boundary groove 353 that forms a boundary between the application region 312a on the upper surface 311a of the surface plate 311 that is a placement object and the support region 312b through which the pad portion 314 passes.
- One end of the partition member 351 is fixed in a boundary groove 353 provided on the upper surface 311 a of the surface plate 311, and the pad portion 314 floats from the upper surface 311 a of the surface plate 311 at the other end of the partition member 351.
- the pad portion 314 is dimensioned so as to be in contact with the outer peripheral surface 303c. That is, in the front view of FIG. 6B, the application region 312 a side of the floating space S between the pad portion 314 of the air bearing device and the upper surface 311 a of the surface plate 311 is closed.
- the partition member 351 can be comprised from resin or the flexible member made from rubber
- an exhaust through-passage is provided on the surface plate, and the exhaust is performed in the direction of the floor surface on which the coating apparatus is disposed. Therefore, when the coating apparatus is used in a clean room, even when a downflow airflow is formed in the cleanroom, the airflow can be prevented from being disturbed.
- the gas is discharged from the exhaust path communicating with the atmosphere, but the suction means such as a pump for supplying negative pressure is connected to the exhaust path. It is also possible. By controlling the gas supply means and the suction means by the control means, it is possible to efficiently prevent the gas ejected from the air bearing device from interfering with the coating liquid landed on the coating object.
- the object to be coated is supported in a non-contact manner, but the present invention is not limited to this structure.
- the effects and operations of the present invention can be achieved even with a coating apparatus that is placed in a state in which a glass substrate is adsorbed or brought into contact with a surface plate.
- the airflow control means according to the first to third embodiments can be appropriately combined.
- the porous body is used for the ejection port for discharging the gas.
- the ejection port is configured by engraving fine holes in the plate member. It is also possible to do.
- the surface plates 111, 211, and 311 having an application region are used as the mounting object, but the mounting object of the present invention is not limited to the surface plate.
- Various platforms having a flat surface having a predetermined flatness for use in application work, measurement work, etc., and having a predetermined rigidity, hardness, and wear resistance can be used as a mounting object.
- As the surface plate a cast iron box-type surface plate, a JIS surface plate, a stone surface plate, or the like can be used.
- the air bearing device of the present invention can be applied not only to a coating device but also to a device for supporting a supported object in a non-contact manner, and it goes without saying that the applied device exhibits the effects and functions of the present invention.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Microelectronics & Electronic Packaging (AREA)
- Condensed Matter Physics & Semiconductors (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Manufacturing & Machinery (AREA)
- Computer Hardware Design (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Power Engineering (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Magnetic Bearings And Hydrostatic Bearings (AREA)
- Coating Apparatus (AREA)
- Exposure Of Semiconductors, Excluding Electron Or Ion Beam Exposure (AREA)
- Spray Control Apparatus (AREA)
- Details Or Accessories Of Spraying Plant Or Apparatus (AREA)
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| KR20157003630A KR20150040924A (ko) | 2012-08-06 | 2013-06-21 | 에어 베어링 장치 및 도포 장치 |
| CN201380041409.1A CN104583618A (zh) | 2012-08-06 | 2013-06-21 | 空气轴承装置及涂布装置 |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012174198A JP2014031865A (ja) | 2012-08-06 | 2012-08-06 | エアベアリング装置及び塗布装置 |
| JP2012-174198 | 2012-08-06 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2014024583A1 true WO2014024583A1 (ja) | 2014-02-13 |
Family
ID=50067824
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2013/067076 Ceased WO2014024583A1 (ja) | 2012-08-06 | 2013-06-21 | エアベアリング装置及び塗布装置 |
Country Status (5)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP2014031865A (enExample) |
| KR (1) | KR20150040924A (enExample) |
| CN (1) | CN104583618A (enExample) |
| TW (1) | TW201412409A (enExample) |
| WO (1) | WO2014024583A1 (enExample) |
Cited By (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPWO2015125756A1 (ja) * | 2014-02-18 | 2017-03-30 | オイレス工業株式会社 | エアベアリング装置及び測定装置 |
| US11643355B2 (en) | 2016-01-12 | 2023-05-09 | Corning Incorporated | Thin thermally and chemically strengthened glass-based articles |
| US11697617B2 (en) | 2019-08-06 | 2023-07-11 | Corning Incorporated | Glass laminate with buried stress spikes to arrest cracks and methods of making the same |
| US11795102B2 (en) | 2016-01-26 | 2023-10-24 | Corning Incorporated | Non-contact coated glass and related coating system and method |
| US11891324B2 (en) | 2014-07-31 | 2024-02-06 | Corning Incorporated | Thermally strengthened consumer electronic glass and related systems and methods |
| US12064938B2 (en) | 2019-04-23 | 2024-08-20 | Corning Incorporated | Glass laminates having determined stress profiles and methods of making the same |
| US12338159B2 (en) | 2015-07-30 | 2025-06-24 | Corning Incorporated | Thermally strengthened consumer electronic glass and related systems and methods |
| US12410090B2 (en) | 2017-11-30 | 2025-09-09 | Corning Incorporated | Non-iox glasses with high coefficient of thermal expansion and preferential fracture behavior for thermal tempering |
Families Citing this family (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP3719443B1 (en) | 2019-04-03 | 2021-06-09 | Hexagon Technology Center GmbH | Coordinate-measuring machine with self-cleaning air bearing |
| CN111894983A (zh) * | 2020-07-30 | 2020-11-06 | 西安工业大学 | 微孔节流的静压气体止推轴承 |
| CN114251362A (zh) * | 2020-09-24 | 2022-03-29 | 武汉科技大学 | 一种微纳多孔节流气浮球面轴承 |
| FR3139869A1 (fr) * | 2022-09-16 | 2024-03-22 | Micro-Contrôle - Spectra-Physics | Appareil pour la réduction des vibrations dans un système de régulation de mouvement à coussin d’air |
Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS60113816A (ja) * | 1983-11-22 | 1985-06-20 | Miyoutoku:Kk | エア−スライド装置 |
| JPS62180114A (ja) * | 1986-01-31 | 1987-08-07 | Kyocera Corp | 静圧気体直線案内装置 |
| JPH09222124A (ja) * | 1996-02-19 | 1997-08-26 | Nippon Seiko Kk | 静圧気体軸受 |
| JP2001200843A (ja) * | 1999-11-22 | 2001-07-27 | Nikon Corp | 真空中で動作する流体ベアリング |
| JP2008149238A (ja) * | 2006-12-15 | 2008-07-03 | Chugai Ro Co Ltd | 塗布装置 |
Family Cites Families (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TWI222423B (en) * | 2001-12-27 | 2004-10-21 | Orbotech Ltd | System and methods for conveying and transporting levitated articles |
| JP2004019760A (ja) * | 2002-06-14 | 2004-01-22 | Nsk Ltd | 静圧軸受 |
| JP4468059B2 (ja) * | 2004-04-23 | 2010-05-26 | 太平洋セメント株式会社 | 静圧軸受け装置 |
| US7607647B2 (en) * | 2007-03-20 | 2009-10-27 | Kla-Tencor Technologies Corporation | Stabilizing a substrate using a vacuum preload air bearing chuck |
| JP2011133724A (ja) * | 2009-12-25 | 2011-07-07 | Nikon Corp | 流体静圧軸受、移動体装置、露光装置、デバイス製造方法、及び清掃装置 |
-
2012
- 2012-08-06 JP JP2012174198A patent/JP2014031865A/ja active Pending
-
2013
- 2013-06-21 CN CN201380041409.1A patent/CN104583618A/zh active Pending
- 2013-06-21 WO PCT/JP2013/067076 patent/WO2014024583A1/ja not_active Ceased
- 2013-06-21 KR KR20157003630A patent/KR20150040924A/ko not_active Withdrawn
- 2013-08-01 TW TW102127675A patent/TW201412409A/zh unknown
Patent Citations (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS60113816A (ja) * | 1983-11-22 | 1985-06-20 | Miyoutoku:Kk | エア−スライド装置 |
| JPS62180114A (ja) * | 1986-01-31 | 1987-08-07 | Kyocera Corp | 静圧気体直線案内装置 |
| JPH09222124A (ja) * | 1996-02-19 | 1997-08-26 | Nippon Seiko Kk | 静圧気体軸受 |
| JP2001200843A (ja) * | 1999-11-22 | 2001-07-27 | Nikon Corp | 真空中で動作する流体ベアリング |
| JP2008149238A (ja) * | 2006-12-15 | 2008-07-03 | Chugai Ro Co Ltd | 塗布装置 |
Cited By (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPWO2015125756A1 (ja) * | 2014-02-18 | 2017-03-30 | オイレス工業株式会社 | エアベアリング装置及び測定装置 |
| US11891324B2 (en) | 2014-07-31 | 2024-02-06 | Corning Incorporated | Thermally strengthened consumer electronic glass and related systems and methods |
| US12338159B2 (en) | 2015-07-30 | 2025-06-24 | Corning Incorporated | Thermally strengthened consumer electronic glass and related systems and methods |
| US11643355B2 (en) | 2016-01-12 | 2023-05-09 | Corning Incorporated | Thin thermally and chemically strengthened glass-based articles |
| US11795102B2 (en) | 2016-01-26 | 2023-10-24 | Corning Incorporated | Non-contact coated glass and related coating system and method |
| US12410090B2 (en) | 2017-11-30 | 2025-09-09 | Corning Incorporated | Non-iox glasses with high coefficient of thermal expansion and preferential fracture behavior for thermal tempering |
| US12064938B2 (en) | 2019-04-23 | 2024-08-20 | Corning Incorporated | Glass laminates having determined stress profiles and methods of making the same |
| US11697617B2 (en) | 2019-08-06 | 2023-07-11 | Corning Incorporated | Glass laminate with buried stress spikes to arrest cracks and methods of making the same |
| US12043575B2 (en) | 2019-08-06 | 2024-07-23 | Corning Incorporated | Glass laminate with buried stress spikes to arrest cracks and methods of making the same |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN104583618A (zh) | 2015-04-29 |
| TW201412409A (zh) | 2014-04-01 |
| KR20150040924A (ko) | 2015-04-15 |
| JP2014031865A (ja) | 2014-02-20 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| WO2014024583A1 (ja) | エアベアリング装置及び塗布装置 | |
| JP4884871B2 (ja) | 塗布方法及び塗布装置 | |
| KR101546395B1 (ko) | 이동 스테이지 | |
| JP4183525B2 (ja) | 薄板の搬送用支持装置 | |
| JP2011213435A (ja) | 搬送装置及び塗布システム | |
| JP6765751B2 (ja) | 被加工物の保持機構及び加工装置 | |
| JP2018064048A (ja) | レーザ照射装置、レーザ照射方法、及び半導体装置の製造方法 | |
| JP2023054081A (ja) | 基板を保持するための研磨ヘッドおよび基板処理装置 | |
| JP6605871B2 (ja) | 基板浮上搬送装置 | |
| JP2010245336A (ja) | 搬送方向転換装置及び浮上搬送システム | |
| KR20140144236A (ko) | 반송 장치 | |
| KR20070051732A (ko) | 부상 장치 및 반송 장치 | |
| KR102782195B1 (ko) | 기판 처리 장치 및 방법 | |
| CN109760418B (zh) | 搬运台和使用该搬运台的喷墨装置 | |
| JP2004172321A (ja) | ワーク搬送テーブル、ワーク搬送装置、液滴吐出装置、電気光学装置、電気光学装置の製造方法および電子機器 | |
| KR102390540B1 (ko) | 디스플레이 패널용 비접촉 이송장치 | |
| JP2014107318A (ja) | 基板保持装置、液滴吐出装置 | |
| WO2011129152A1 (ja) | 旋回流形成体及び非接触搬送装置 | |
| JP6685894B2 (ja) | エアベアリング装置及び測定装置 | |
| JP5848812B1 (ja) | 吸着装置、及び、吸着装置の制御方法 | |
| JP2007144848A (ja) | 画像形成装置 | |
| KR20140144237A (ko) | 반송 장치 | |
| JP2010189106A (ja) | 浮上搬送装置 | |
| JP2011230463A (ja) | 吸着装置および液滴吐出装置 | |
| JP4768577B2 (ja) | 非接触支持装置 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 13828469 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 20157003630 Country of ref document: KR Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 13828469 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |