WO2010109836A1 - 通知装置、通知システム、通知装置の制御方法、制御プログラム、及び該プログラムを記録したコンピュータ読み取り可能な記録媒体 - Google Patents
通知装置、通知システム、通知装置の制御方法、制御プログラム、及び該プログラムを記録したコンピュータ読み取り可能な記録媒体 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2010109836A1 WO2010109836A1 PCT/JP2010/001996 JP2010001996W WO2010109836A1 WO 2010109836 A1 WO2010109836 A1 WO 2010109836A1 JP 2010001996 W JP2010001996 W JP 2010001996W WO 2010109836 A1 WO2010109836 A1 WO 2010109836A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- position information
- notification
- mobile phone
- user
- unit
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06Q—INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES; SYSTEMS OR METHODS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- G06Q10/00—Administration; Management
- G06Q10/10—Office automation; Time management
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G06—COMPUTING; CALCULATING OR COUNTING
- G06Q—INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY [ICT] SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES; SYSTEMS OR METHODS SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR ADMINISTRATIVE, COMMERCIAL, FINANCIAL, MANAGERIAL OR SUPERVISORY PURPOSES, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- G06Q30/00—Commerce
- G06Q30/02—Marketing; Price estimation or determination; Fundraising
- G06Q30/0241—Advertisements
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04L—TRANSMISSION OF DIGITAL INFORMATION, e.g. TELEGRAPHIC COMMUNICATION
- H04L67/00—Network arrangements or protocols for supporting network services or applications
- H04L67/50—Network services
- H04L67/52—Network services specially adapted for the location of the user terminal
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H04—ELECTRIC COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUE
- H04W—WIRELESS COMMUNICATION NETWORKS
- H04W4/00—Services specially adapted for wireless communication networks; Facilities therefor
- H04W4/02—Services making use of location information
- H04W4/021—Services related to particular areas, e.g. point of interest [POI] services, venue services or geofences
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a notification device or the like for notifying the user of the fact when entering a range set with reference to a pre-registered point.
- Patent Document 1 discloses a portable information terminal that notifies a user when the current position of the device and a spot registered in advance by the user are within a predetermined distance. . Similar techniques are disclosed in Patent Documents 2 to 5 below.
- the user can recognize that the point is close by registering in advance the point that he / she wants to go to. It becomes easy to drop in at the point.
- the user can stop at a registered point near the place where he / she takes the portable terminal. Is also possible. This has the advantage that the user can easily go to the point where he / she wants to go, and the store or the like has the advantage that many people can go there.
- the present invention has been made in view of the above-described problems, and its purpose is to facilitate registration of a point to be notified to the user without requiring the user to perform an operation of selecting and registering each individual desired point.
- An object of the present invention is to provide a notification device or the like that can be performed on
- the notification device of the present invention is a notification device that notifies the user of the own device when the current location of the own device falls within a predetermined range.
- a data storage unit for storing both the data including and the data not including the position information; a specifying unit for specifying data including the position information from the data stored in the data storage unit; and Position information extracting means for extracting position information used as a reference for setting the predetermined range from the data specified to include, and range setting for setting the predetermined range based on the position information extracted by the position information extracting means
- a notification means for notifying a user of the own apparatus when the current position of the own apparatus falls within the predetermined range set by the range setting means.
- the notification device control method of the present invention controls the notification device that notifies the user of the device when the current position of the device is within a predetermined range.
- a method for specifying data including position information from data stored in a data storage unit that stores both data including position information and data not including position information, and the position in the specifying step A position information extraction step for extracting position information used as a reference for setting the predetermined range from data specified to include information, and the predetermined range is set based on the position information extracted in the position information extraction step.
- the data including the position information is specified from the data stored in the data storage unit, and the position information is extracted from the data. Then, a predetermined range is set using the extracted position information, and the user is notified based on the predetermined range.
- the user can distinguish the data including the position information from the data not including the position information, that is, without being aware of the presence or absence of the position information included in the data. It is possible to receive a notification based on the position information only by performing an extremely simple operation of storing in the storage. Therefore, according to the configuration or method described above, there is an effect that it is possible to easily register a location to be notified without requiring the user to perform an operation of selecting and registering each desired location.
- a notification system in which the notification device notifies a user of the notification device, and the position information transmission device includes a data storage unit that stores both data including position information and data not including position information; , Specifying means for specifying data including position information from data stored in the data storage unit, and position information used as a reference for setting the predetermined range from the data specified by the specifying means as including position information Position information extracting means for extracting the position information, and position information transmitting means for transmitting the position information extracted by the position information extracting means to the notification device.
- a notification apparatus receives the positional information which the positional information extraction apparatus specified and extracted the data containing positional information from the data memorize
- the user performs an extremely simple operation of storing data including position information in the data storage unit of the position information extraction device without distinguishing from data not including position information.
- the notification based on the position information can be received from the notification device. Therefore, according to said structure, there exists an effect that the registration of the point to notify can be performed easily.
- the notification device of the present invention includes a data storage unit that stores both data including location information and data not including location information, and includes location information from the data stored in the data storage unit.
- the specifying means for specifying data, the position information extracting means for extracting position information used as a reference for setting the predetermined range from the data specified as including the position information by the specifying means, and the position information extracting means A range setting means for setting the predetermined range based on the position information, and a notification to the user of the own apparatus when the current position of the own apparatus falls within the predetermined range set by the range setting means And a notification means.
- control method of the notification device of the present invention is a specifying step of specifying data including position information from data stored in a data storage unit that stores both data including position information and data not including position information.
- a position information extracting step for extracting position information used as a reference for setting the predetermined range from the data specified as including the position information in the specifying step, and the position information extracted in the position information extracting step as a reference
- a range setting step for setting the predetermined range
- a notification step for notifying a user of the own device when the current position of the own device enters the predetermined range set in the range setting step. It is.
- the notification system of the present invention is configured such that when the current position of the notification device falls within a predetermined range set based on the position information transmitted by the position information transmission device, the notification device is a user of the notification device.
- the position information transmitting device is configured to store both data including position information and data not including position information, and stored in the data storage section. Identifying means for identifying data including position information from existing data, and position information extracting means for extracting position information to be used as a reference for setting the predetermined range from the data specified by the identifying means to include position information; And a positional information transmitting unit that transmits the positional information extracted by the positional information extracting unit to the notification device.
- the user stores the data including the position information in the data storage unit without distinguishing the data including the position information from the data not including the position information, that is, whether or not the position information is included. It is possible to receive a notification based on the position information from the notification device without performing an operation for selecting a point to be notified only by performing an extremely simple operation. Therefore, it is possible to easily register the location to be notified.
- An example of a process of notifying that when a destination is set includes a notification range of a store of the same genre as a store where a coupon can be used on the set route, and a route guide to the store
- FIG. 2 is a diagram showing an outline of the operation of the mobile phone of the present invention.
- the mobile phone (notification device, location information transmission device) 1 of the present invention is a store where coupons can be used when entering the notification range A defined based on the location P of the store where coupons can be used. Is notified to the user of the terminal.
- the mobile phone 1 when the mobile phone 1 enters the notification range A, it generates a sound and vibrates. Then, the mobile phone 1 displays a message M1 indicating that there is a store where the coupon can be used nearby, an image C of the available coupon, and a key K1 for setting the store as the destination of the route guide.
- the user can recognize that there is a store where the coupon stored in the mobile phone 1 can be used in the vicinity of his current location. That is, the mobile phone 1 can increase opportunities for the user to use the coupon.
- the route guide to the store can be performed by the mobile phone 1 by selecting the key K1. Thereby, the user can access the store where the coupon can be used very easily.
- FIG. 3 is a diagram showing an example of a route guide display screen.
- a message to start navigation (route guide) is displayed and a map is displayed as shown. The route from the current location to the destination is displayed on the map, so that the user can easily access a store where the coupon as the destination can be used.
- the coupon in this embodiment refers to the image in which the positional information which shows the position of a store, a facility, etc. was incorporated. That is, by displaying the image of the coupon, the user can confirm the content of the coupon (for example, a privilege such as discount that can be received by presenting the coupon). Then, by using the position information incorporated in the coupon, the user can cause the mobile phone 1 to execute a route guide to a store or facility where the coupon can be used.
- the user of the mobile phone 1 may recognize the presence of the store or the like when stopping near a store or the like where the coupon can be used. it can. Further, when the user wants to go to the store or the like indicated by the coupon, the user can easily reach the store by causing the mobile phone 1 to execute the route guide.
- FIG. 4 is a diagram illustrating an example of a coupon acquisition method.
- the mobile phone 1 can obtain a coupon from another mobile phone in a state attached to e-mail, for example.
- the coupon can be transmitted and received in exactly the same manner as when transmitting a normal image (an image in which position information or the like is not incorporated). it can.
- coupons can be transmitted and received using communication means such as infrared rays.
- the mobile phone 1 can also obtain a coupon by distributing or downloading from the service.
- the user can download a desired coupon from a homepage such as a store and save it in the mobile phone 1.
- the coupon may be distributed to the mobile phone 1 by attaching the service to an e-mail, and the distributed coupon may be stored automatically by the mobile phone 1 or manually by the user of the mobile phone 1.
- a coupon recorded on a recording medium such as a removable medium can be copied to the mobile phone 1 and acquired.
- the mobile phone 1 notifies the user based on the location information. Therefore, the data including the position information is not limited to the coupon as described above, and the mobile phone 1 can notify the user based on arbitrary data including the position information.
- the current location of the mobile phone 1 may be registered as position information, or a point selected from the map may be registered as position information.
- a general mobile phone has a phone book function for registering a phone number. By registering the location information together with the telephone number in this telephone directory, it is possible to receive a notification to that effect when coming near a person's house registered in the telephone directory.
- the mobile phone 1 is provided with a function for specifying a coupon from data stored in its own terminal. Thereby, no matter how much data other than the coupon is stored in the mobile phone 1, the coupon is automatically specified.
- the user of the mobile phone 1 only needs to store a desired coupon in the mobile phone 1 and does not need to perform any data management.
- the received coupon may be automatically stored as image data in the mobile phone 1, and in this case, the user does not need to perform an operation of storing the coupon, and therefore is aware of the existence of the coupon. It is possible to easily use coupons according to the place wherever you go without having to.
- the identification method of a coupon is not specifically limited, since it is assumed here that a coupon is an image in which position information is incorporated, for example, the image data is identified from the data extension, and the image is identified. Whether or not the image is a coupon can be determined based on whether or not the position information (or information indicating that the data includes position information) is incorporated in the header information of the processed data. .
- the notification range A in the example of FIG. 2 is a circular range centered on the position P of the store where the coupon can be used. As described above, when the mobile phone 1 enters the inside of the circle, that is, when the distance between the mobile phone 1 and the position P becomes shorter than the radius of the circle, the coupon of the store at the position P is the mobile phone 1. Is displayed.
- the radius of this circle can be set as needed. This radius may be always constant, but the mobile phone 1 obtains the moving speed of the user, and when the moving speed of the user is slow (for example, when moving on foot), the radius of the circle is narrowed. When the moving speed of the user is fast (for example, when moving by car), the radius of the circle is set wide. This is because even if it is difficult to stop on foot, you can easily stop by car.
- the mobile phone 1 can be connected to a car navigation device (hereinafter referred to as a car navigation system) via a short-range communication means.
- the mobile phone 1 determines that it is moving by car when it is connected to the car navigation system via the short-range communication means, and otherwise determines that it is moving on foot.
- the shape of the notification range is not limited to a circle, and can be any shape. This will be described with reference to FIG. FIG. 5 is a diagram illustrating an example of a notification range.
- the notification range A1 in FIG. 5A is a square shape with the position P as the center. Of course, it is not limited to a square shape, and an arbitrary polygonal range can be set as the notification range.
- the notification range A2 in FIG. 6B is a circular notification range as in FIG. 2, but the circular range near the position P is excluded from the notification range.
- the notification range A3 in (c) in the figure is a square notification range as in (a) in the same figure, but the square range in the vicinity of the position P is excluded from the notification range.
- the notification range may not be one continuous area, and may be set at a location away from the store position P where coupons can be used. This will be described with reference to FIG. FIG. 6 is a diagram illustrating an example in which a notification range is set at a place away from the position P of a store where coupons can be used.
- a notification range A centering on the position P of a store where a coupon can be used is set, and a notification range A ′ centering on a position P ′ of a store of the same genre as the store is set.
- the genre indicates the type of store. For example, a restaurant, a clothing store, a beauty salon, or the like can be used as a genre indicating the type of store.
- the mobile phone 1 when the mobile phone 1 enters the notification range A ′, the mobile phone 1 has a message M2 indicating that there is a store that can use the coupon in the same genre as the store at the position P ′, and an image of the available coupon. C and a key K1 for setting the store as the destination of the route guide are displayed. In order to inform the user of this, voice is output and the mobile phone 1 vibrates.
- the mobile phone 1 tries to purchase clothes and tries to stop at a clothing store that cannot use the coupon, the mobile phone 1 presents a coupon of a clothing store that can use the coupon. Thereby, the user can change the place where clothes are purchased into a clothing store where coupons can be used.
- FIG. 7 is a diagram illustrating an example in which a coupon is presented when a route to a destination is included in the notification range.
- a key K2 for selecting a destination and a key K3 for displaying the current location are displayed as shown.
- a key K4 for selecting from registered locations registered in advance as destination candidates and a key K5 for selecting the destination from the map are displayed.
- the keys K6 to K8 for selecting the registration location are displayed.
- the registration location corresponding to the selected key is set as the destination.
- a map is displayed and the user designates a place to be set as the destination on the map.
- the mobile phone 1 searches for a route from the current location (or the departure location specified by the user) to the destination (in this example, “XX park”).
- the current location is not included in the notification range A, but a part of the searched route is included in the notification range A. That is, when the user moves to the destination according to this route, the user passes near the store at the position P on the way.
- the mobile phone 1 displays a store coupon corresponding to the notification range A.
- the mobile phone 1 outputs a sound and vibrates.
- the user can recognize the existence of a store where the coupon can be used, and can stop by the store.
- Some coupons are set with conditions such as expiration date, usable time zone, day of the week, and the like. Moreover, if it is outside the business hours of a store, it is natural that coupons cannot be used at that store. That is, when the user comes close to the store, simply presenting the store coupon may cause a case where the coupon cannot be used even though the user visits the store.
- the mobile phone 1 determines whether or not the coupon can be used from now on, and does not notify the user when it is determined that the coupon cannot be used. can do. Thereby, the user is relieved from the trouble of receiving notification of an unusable coupon, and avoids a situation in which the coupon cannot be used even though the user has visited the store notified by the mobile phone 1. be able to.
- the mobile phone 1 determines whether the coupon can be used from now on. It is also possible to notify the user that the coupon has been approached but the coupon can no longer be used. Thereby, since the user can grasp
- FIG. 8 shows that when a coupon that does not match the condition (a coupon that cannot be used from now on) is set to non-notification and when it is set to notification, the point indicated by the coupon that does not match the condition is approached It is a figure which shows an example of the screen which the mobile telephone 1 displays sometimes.
- the display of the mobile phone 1 is also a standby screen when approaching a point indicated by a coupon that does not meet the conditions (when entering the notification range of the coupon). It remains unchanged.
- the coupon cannot be used, the coupon cannot be used at all, as it has expired, and it cannot be used now because it is out of the available date, time zone, day of the week, etc. And when available.
- the key K9 for deleting the coupon is preferably displayed in the former case. Thereby, only the coupon which will not be used in the future can be deleted.
- the mobile phone 1 can switch between notification / non-notification of coupons that do not meet the conditions by a user input operation. At the time of this switching, for example, a screen as shown in FIG. 9 is displayed.
- FIG. 9 is a diagram illustrating an example of a setting screen for switching notification / non-notification of coupons that do not meet the conditions.
- a message M4 for setting a non-matching coupon to non-notification As shown in the figure, a message M5 for setting a non-matching coupon for notification, and a setting key K10 for confirming switching between notification / non-notification And are displayed.
- a check box is displayed on the left side of each of the messages M4 and M5. In the illustrated example, the check box next to M4 is checked. Therefore, when the setting key K10 is selected in this state, a coupon that does not meet the conditions is set to non notification.
- FIG. 10 is a diagram illustrating an example of a display screen when a list of store names is displayed.
- the names of four stores are listed. That is, these four stores are stores near the current location of the mobile phone 1 or in the vicinity of the route to the set destination, and can use coupons, or stores of the same genre as the stores.
- icon I1 indicates that a store of the same genre as the store exists near the current location of the mobile phone 1 or in the vicinity of the route to the set destination.
- icon I2 has shown that the coupon of the store is possessed, but the coupon cannot be used now.
- Each store name displayed as a list in this way can be selected by a user operation, and by selecting the store name, images such as FIGS. Image).
- FIG. 11 is a diagram illustrating an example of a hardware configuration of the mobile phone 1, the car navigation system 30, the coupon distribution server 50, and the regional information distribution server 60.
- the car navigation system 30 is a device that can be connected to the mobile phone 1 by short-distance communication means
- the coupon distribution server 50 is a server that distributes coupons to the mobile phone 1
- the regional information distribution server 60 is designated by the mobile phone 1. This is a server that transmits peripheral information (tourist information, map, store, facility, etc.) of a point to the mobile phone 1.
- the mobile phone 1 is a communication terminal having a call function, an electronic mail (E-mail) transmission function, and a GPS function, and is configured to be communicable with the car navigation system 30 and the coupon distribution server 50.
- a mobile phone 1 includes a position acquisition unit 2, a telephone network communication unit 3, a voice input unit 4, a voice output unit 5, a mobile phone control unit 6, a primary storage unit 7, a mobile phone storage unit (data storage unit). ) 8, a short-range communication unit (communication means) 9, an operation unit 10, a display unit 11, and a vibration unit 12.
- the position acquisition unit 2 acquires the current position of the mobile phone 1. That is, the GPS function of the mobile phone 1 is realized by the position acquisition unit 2.
- the position acquisition part 2 should just be able to detect the present position of the mobile telephone 1, and does not necessarily need to utilize GPS.
- the position acquisition unit 2 may detect the current position of the mobile phone 1 by determining which base station is the currently communicable base station.
- the telephone network communication unit 3 is used for making calls and sending / receiving e-mails with other mobile phones or general telephones via the mobile phone network or the like, or for communicating with the Internet.
- the mobile phone 1 communicates with the coupon distribution server 50 and the regional information distribution server 60 via the telephone network communication unit 3.
- the telephone network communication unit 3 connects to the Internet via a mobile phone network (3G), and communicates with the coupon distribution server 50 and the regional information distribution server 60 via the Internet.
- the call function, the Internet connection function, and the communication function with the coupon distribution server 50 or the regional information distribution server 60 may be realized by separate communication units.
- the voice input unit 4 is for inputting a voice signal to the mobile phone 1 during a call, for example.
- the voice output unit 5 is based on a voice signal received by the telephone network communication unit 3 during a call or the like. This is for outputting sound.
- the voice output unit 5 also outputs voice or the like indicating an incoming call or mail.
- the audio input unit 4 and the audio output unit 5 may be any units that can input and output audio, respectively, and those used in a conventional mobile phone or the like can also be applied.
- the mobile phone control unit 6 controls the operation of the mobile phone 1 in an integrated manner, and can be composed of, for example, a CPU.
- the mobile phone control unit 6 operates using, for example, a primary storage unit 7 configured by a RAM or the like as a work area. Details of the processing performed by the mobile phone control unit 6 will be described later in detail.
- the mobile phone storage unit 8 stores programs and data as shown in the figure.
- the mobile phone 1 executes a predetermined operation by the mobile phone control unit 6 reading the program stored in the mobile phone storage unit 8 into the primary storage unit 7 and executing it. Further, for example, data such as mail received by the telephone network communication unit 3 and data such as a telephone number and mail address recorded by the user of the mobile phone 1 are also stored in the mobile phone storage unit 8.
- the mobile phone storage unit 8 may be configured to be detachable from the main body of the mobile phone 1. Details of the data stored in the mobile phone storage unit 8 will be described later.
- the near field communication unit 9 is for the mobile phone 1 to communicate with other devices, and is used to communicate with a car navigation (notification device, external device) 30, for example.
- the mobile phone 1 determines that it is moving by car when it is connected to the car navigation system 30 via the short-range communication unit 9, and otherwise determines that it is moving on foot.
- the short-range communication unit 9 performs Bluetooth (registered trademark) communication. If it is Bluetooth communication, if it is a passenger car of a general size, it is sufficiently possible to communicate between the mobile phone 1 possessed by the user sitting in each seat and the car navigation system 30. . Further, since the communicable range is not too wide, the possibility of reaching the mobile phone 1 outside the vehicle is low. In Bluetooth communication, it is possible to communicate with a device having a radius of about 100 m at the maximum. Here, it is assumed that communication with a device having a radius of about 10 m is set.
- the communication method of the short-range communication unit 9 is not limited to Bluetooth communication.
- ZigBee registered trademark
- UWB Ultra Wide Band
- IEEE 802.11 radio such as Wi-Fi (registered trademark)
- the mobile phone 1 and the car navigation system 30 may be configured to be communicable and may be connected by wire.
- the operation unit 10 is for a user of the mobile phone 1 to input an operation to the mobile phone 1, and is not particularly limited as long as the user can input a desired operation.
- the operation unit 10 includes operation keys provided on the surface of the main body of the mobile phone 1.
- various menu keys for displaying a menu screen related to e-mail, a menu screen related to Internet connection, and the like on the display unit 11, keys for inputting start and end of a call, and the display unit 11, up / down / left / right direction keys for selecting an item, a determination key for determining a selected item, a character input key for inputting numbers and characters, a switching key for switching characters to be input, and the like.
- a plurality of operation keys are included.
- the operation unit 10 may be configured on the display unit 11 and may be a touch panel system that detects a touch on the screen as an input operation.
- the display unit 11 displays an image in accordance with an instruction from the mobile phone control unit 6.
- the display part 11 should just be what displays an image according to the instruction
- the display unit 11 can be configured by, for example, an LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) display panel or an EL (Electro Luminescence) display panel.
- the vibration unit 12 vibrates in accordance with an instruction from the mobile phone control unit 6, and the entire mobile phone 1 vibrates (vibration operation) when the vibration unit 12 vibrates. Due to the vibration of the vibration unit 12, notification to the effect that the user has entered the notification range and notification to the user such as an incoming call are performed.
- the car navigation system 30 is a device that displays a map and performs route guidance to a destination.
- the short-range communication unit 31 the position acquisition unit 32, the voice input unit 33, the voice output unit 34, and the car navigation control unit. 35, a primary storage unit 36, a car navigation storage unit 37, a vehicle signal input unit 38, an operation unit 39, and a display unit 40.
- the near field communication unit 31 is for communicating with the near field communication unit 9 of the mobile phone 1.
- the short-range communication unit 31 is configured to perform communication using the same communication method as the communication method of the short-range communication unit 9 of the mobile phone 1.
- the short-range communication unit 31 of the car navigation system 30 is also configured to be able to perform Bluetooth communication.
- the position acquisition unit 32 acquires the current position of the car navigation system 30 (that is, the current location of the car on which the car navigation system 30 is mounted) using the GPS.
- the car navigation system 30 based on the current location, a map near the current location is displayed on the display unit 40, and the current position of the vehicle is displayed superimposed on the map.
- the voice input unit 33 is used to input voice to the car navigation system 30 and includes, for example, a microphone.
- an input operation can be performed from the operation unit 39, and an input operation can also be performed by voice from the voice input unit 33.
- the audio output unit 34 outputs audio in accordance with instructions from the car navigation control unit 35, and is composed of, for example, a speaker. From the audio output unit 34, for example, audio for route guide is output.
- the car navigation control unit 35 controls the operation of the car navigation 30 in an integrated manner, and can be configured by a CPU or the like, for example.
- the car navigation control unit 35 operates using, for example, a primary storage unit 36 configured by a RAM or the like as a work area.
- the car navigation storage unit 37 stores programs and data
- the car navigation control unit 35 reads the program stored in the car navigation storage unit 37 into the primary storage unit 36 and executes the program. A predetermined operation is executed. Further, for example, map data, voice data for voice output, and the like are also stored in the car navigation storage unit 37.
- the car navigation storage unit 37 may be configured to be detachable from the main body of the car navigation 30.
- the vehicle signal input unit 38 receives an input of a detection result of a parking brake sensor that detects whether or not a parking brake is applied and a detection result of a vehicle speed sensor that detects a vehicle speed, and controls these detection results by car navigation control. Send to part 35.
- the operation unit 39 is for the user to perform an input operation on the car navigation system 30, and the display unit 40 is an input screen for setting a destination, a map, a route to the destination, etc. in accordance with instructions from the car navigation control unit 35. Is displayed. In the car navigation system 30, it is assumed that the operation unit 39 performs input by a so-called touch panel method in which contact with the display unit 40 is detected as an input operation.
- the operation unit 39 may be configured to accept a user input operation.
- the operation unit 39 may be configured with a plurality of input buttons.
- the coupon distribution server 50 is a server that distributes coupons to the mobile phone 1, and as shown in the figure, the communication unit 51, the server control unit 52, the primary storage unit 53, the server storage unit 54, the operation unit 55, and the display unit 56. It has.
- the regional information distribution server 60 is a server that distributes regional information to the mobile phone 1, and as illustrated, a communication unit 61, a server control unit 62, a primary storage unit 63, a server storage unit 64, an operation unit 65, And a display unit 66.
- the communication units 51 and 61 are for communicating with the telephone network communication unit 3 of the mobile phone 1. For this reason, the communication units 51 and 61 are configured to perform communication using the same communication method as that of the telephone network communication unit 3 of the mobile phone 1. Here, since it is assumed that the telephone network communication unit 3 of the mobile phone 1 performs communication via the Internet, the communication units 51 and 61 are also configured to be able to perform communication via the Internet.
- the server control unit 52 controls the operation of the coupon distribution server 50 in an integrated manner, and the server control unit 62 controls the operation of the regional information distribution server 60 in an integrated manner.
- These control units can be constituted by, for example, a CPU or the like.
- the server control unit 52 operates using, for example, a primary storage unit 53 configured by a RAM or the like as a work area, and the server control unit 62 operates using a primary storage unit 63 configured by, for example, a RAM or the like as a work area.
- the server control unit 52 of the coupon distribution server 50 when receiving a coupon distribution request from the mobile phone 1, the server control unit 52 of the coupon distribution server 50 performs a process of transmitting the requested coupon to the mobile phone 1.
- the server control unit 52 also performs processing for automatically distributing coupons to terminals registered as coupon distribution destinations. That is, when the mobile phone 1 is registered as a coupon distribution destination in the coupon distribution server 50, the server control unit 52 distributes the coupon to the mobile phone 1 when there is a coupon to be distributed. I do.
- the server control unit 62 of the regional information distribution server 60 receives the location information and the peripheral information request from the mobile phone 1, the store, facility, and sightseeing spot existing around the point specified by the received positional information. And the like, a map of the vicinity of the point, and the like, a process of delivering information that is considered useful when the user goes to the point to the mobile phone 1 is performed.
- Such information may be stored in the server storage unit 64 in advance, or may be acquired by the server control unit 62 by searching through the Internet or the like, for example.
- the server storage units 54 and 64 store programs and data.
- the coupon distribution server 50 stores the program stored in the server storage unit 54 and the server control unit 52 stores it in the primary storage unit 53.
- a predetermined operation is executed by reading and executing.
- the regional information distribution server 60 performs a predetermined operation by causing the server control unit 62 to read and execute the program stored in the server storage unit 64 to the primary storage unit 63.
- the operation unit 55 is for performing an input operation on the coupon distribution server 50, and the display unit 56 displays an image in accordance with an instruction from the server control unit 52. Thereby, input operation can be performed to the coupon delivery server 50, confirming the image displayed on the display part 56.
- FIG. The same applies to the operation unit 65 and the display unit 66 of the regional information distribution server 60.
- each block of the mobile phone 1, the car navigation system 30, the coupon distribution server 50, and the regional information distribution server 60 particularly the mobile phone control unit 6, the car navigation control unit 35, and the server control units 52 and 62.
- the mobile phone 1, the car navigation system 30, the coupon distribution server 50, and the regional information distribution server 60 are a CPU (central processing unit) that executes instructions of a control program that realizes each function, and a ROM (read only) that stores the program. memory), a RAM (random access memory) for expanding the program, and a storage device (recording medium) such as a memory for storing the program and various data.
- CPU central processing unit
- ROM read only
- memory random access memory
- storage device recording medium
- the object of the present invention is to provide program codes (execution format program, intermediate code program, intermediate code program, control program for mobile phone 1, car navigation system 30, coupon distribution server 50, and regional information distribution server 60 that are software for realizing the functions described above.
- the recording medium in which the source program is recorded so as to be readable by the computer is supplied to the mobile phone 1, the car navigation system 30, the coupon distribution server 50, and the regional information distribution server 60, and the computer (or CPU or MPU) serves as the recording medium. This can also be achieved by reading and executing the recorded program code.
- Examples of the recording medium include tapes such as magnetic tapes and cassette tapes, magnetic disks such as floppy (registered trademark) disks / hard disks, and disks including optical disks such as CD-ROM / MO / MD / DVD / CD-R.
- Card system such as IC card, IC card (including memory card) / optical card, or semiconductor memory system such as mask ROM / EPROM / EEPROM / flash ROM.
- the mobile phone 1, the car navigation system 30, the coupon distribution server 50, and the regional information distribution server 60 may be configured to be connectable to a communication network, and the program code may be supplied via the communication network.
- the communication network is not particularly limited.
- the Internet intranet, extranet, LAN, ISDN, VAN, CATV communication network, virtual private network, telephone line network, mobile communication network, satellite communication. A net or the like is available.
- the transmission medium constituting the communication network is not particularly limited.
- infrared rays such as IrDA and remote control, Bluetooth (Registered trademark), 802.11 wireless, HDR, mobile phone network, satellite line, terrestrial digital network, and the like can also be used.
- the functions of the mobile phone 1, the car navigation system 30, the coupon distribution server 50, and the regional information distribution server 60 are also realized in the form of computer data signals embedded in a carrier wave, in which the program code is embodied by electronic transmission. Can be done.
- the mobile phone control unit 6, the car navigation control unit 35, and the server control units 52 and 62 may be configured by hardware logic.
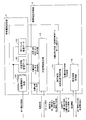
- FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing a main configuration of the mobile phone 1.
- the mobile phone storage unit 8 stores an image with position information 100, position information management data 101, genre management data 102, and a notification list 103.
- the position information-added image 100 is an image in which position information is incorporated, and corresponds to the above-described coupon.
- the mobile phone storage unit 8 stores the image with position information 100 without being particularly distinguished from other data. However, the image with position information 100 is automatically specified from the stored data and the user Used to notify
- the location information management data 101 is data for managing location information and the like used for notifying the user that the store or the like indicated by the location information-attached image 100 is approaching. Although details will be described later, in the position information management data 101, in addition to position information, conditions, and genres extracted from the image with position information 100, a notification range set based on the position information and the like are managed.
- the same genre management data 102 is data for managing position information and the like used for notifying the user that a store or the like of the same genre as the store or the like indicated by the image with position information 100 is approached. Although details will be described later, the same genre management data 102 includes the position information of the same genre store, the genre, information indicating the corresponding image 100 with position information, a notification range set based on the position information, and the like. Managed.
- the notification list 103 is data in which position information determined to be notified to the user among the position information managed by the position information management data 101 or the genre management data 102 is listed.
- the mobile phone 1 notifies the user based on the notification list 103.
- the mobile phone control unit 6 includes a location information extraction unit (identification unit, location information extraction unit, related location information acquisition unit) 110, a mobile phone determination unit (range setting unit, route determination unit, condition Determination means, association determination means, boarding determination means, moving speed acquisition means, approach determination means) 111, mobile phone notification section (notification means) 112, mobile phone short-range communication control section (position information transmission means) 113, timing section 114 , A route search unit (route setting unit) 115, a peripheral information acquisition unit 116, and a route guide execution unit (guidance unit) 117 are included.
- a location information extraction unit identification unit, location information extraction unit, related location information acquisition unit
- a mobile phone determination unit range setting unit, route determination unit, condition Determination means, association determination means, boarding determination means, moving speed acquisition means, approach determination means
- mobile phone notification section notification means
- mobile phone short-range communication control section position information transmission means
- timing section 114 timing section
- a route search unit route setting unit
- the location information extraction unit 110 identifies data including location information from the data stored in the mobile phone storage unit 8, and extracts location information and the like from the identified data. Then, the position information extraction unit 110 generates the position information management data 101 and the same genre management data 102 using the extracted position information and the like.
- the mobile phone determination unit 111 checks whether or not the current location of the mobile phone 1 is within the notification range included in the location information management data 101 or the genre management data 102, and the location information etc. within the notification range Is added to the notification list 103.
- the mobile phone notification unit 112 notifies the user based on the location information and the like included in the notification list 103.
- the mobile phone short-range communication control unit 113 controls communication via the short-range communication unit 9 (see FIG. 11).
- the mobile phone short-range communication control unit 113 connects when the connection request is received from the car navigation 30.
- a communication connection between the mobile phone 1 and the car navigation system 30 is established by returning a permission.
- the connection request may be transmitted from the mobile phone 1 side.
- the timer unit 114 has a function as a clock and a calendar, and sends the current date and time and day of the week to the mobile phone determination unit 111.
- the route search unit 115 searches for a route between points indicated by the input position information, and outputs information indicating a route as a search result. Specifically, when position information indicating the position of the destination point is input, the route search unit 115 outputs information indicating the route from the current location acquired by the position acquisition unit 2 (see FIG. 11) to the destination point. To do. Further, when position information of the departure point and the destination point is input, information indicating a route from the departure point to the destination point is output. A route guide or the like is performed according to the information indicating the route. One or more waypoints may be included between the departure point and the destination point.
- the peripheral information acquisition unit 116 acquires the peripheral information of the point indicated by the input position information.
- the peripheral information may be stored in the mobile phone storage unit 8, or may be acquired from the regional information distribution server 60 or the like by transmitting a peripheral information request via the telephone network communication unit 3, for example.
- the route guide execution unit 117 performs processing for guiding the user along the route searched by the route search unit 115. Specifically, the route guide execution unit 117 sends the position information of the departure point and the destination point to the route search unit 115, and receives the route from the departure point to the destination point. Then, a map near the current location is read from the mobile phone storage unit 8 and displayed on the display unit 11, and the route is displayed superimposed on the displayed map so that the user can follow the displayed route. Let the audio output unit 5 perform audio guidance. When the coupon notification range is entered, the route guide execution unit 117 performs a process of guiding the user to the coupon store.
- FIG. 12 is a diagram illustrating an example of the position information management data 101.
- the location information management data 101 includes “No.”, “Name”, “Location information”, “Notification range (walking)”, “Notification range (car)”, “Genre”, and “Condition” 7 items are included.
- “No.” is a management number for managing the position information, and one management number is assigned to the position information extracted from one coupon (image 100 with position information).
- This data set is called a position information set. That is, the position information management data 101 is a collection of position information sets.
- “Name” is a name for identifying the coupon.
- the name of a facility or the like represented by the coupon or the file name of the coupon image may be used as the “name”.
- “Position information” is information indicating the position of the store of the coupon, and is acquired by extracting, for example, header information included in the coupon image.
- the “location information” is not particularly limited as long as the mobile phone 1 can recognize the point indicated by the information, but may be data indicating longitude and latitude, for example, as illustrated.
- Notification range (walking)” and “notification range (car)” indicate a range for notifying the user of the presence of the coupon, and “notification range (walking)” is a notification applied when moving on foot.
- the “notification range (car)” indicates a notification range that is applied when moving by car. These notification ranges are set based on the “position information”.
- “Genre” indicates the genre of the coupon, and this data is acquired by extracting the data incorporated in the coupon image together with the position information.
- Condition indicates a condition for using the coupon, and this data is acquired by extracting what is incorporated in the coupon image together with the position information.
- the “condition” may be anything as long as it indicates a condition for using the coupon. For example, as shown in the drawing, a period, a time zone, a day of the week, weather, and the like may be set as the “condition”.
- the weather is used as a “condition” for facilities and events that are affected by the weather, such as outdoor sports facilities and outdoor sports watching.
- FIG. 13 is a diagram illustrating an example of the genre management data 102.
- the genre management data 102 includes “No.”, “Name”, “Location information”, “Notification range (walking)”, “Notification range (car)”, “Genre”, and “Correspondence”. Seven items of “save coupon No.” are included.
- “No.” is a management number for managing the same genre management data, and one management number is assigned to one same genre store.
- the same genre store is a store of the same genre as the coupon store included in the position information management data 101. Detected by performing a search from another coupon store included in the location information management data 101, a store searched from the map information stored in the mobile phone storage unit 8 (for example, map information for route guide), or the Internet. The store becomes the same genre store.
- “Name” is a name for identifying the store of the same genre.
- the name of the store may be used as the “name”.
- the “location information” is information indicating the location of the same genre store, and is acquired from data stored in the mobile phone storage unit 8 such as the location information management data 101 or acquired via the Internet.
- Notification range (walking)” and “notification range (car)” indicate a range for notifying the user of the presence of a coupon corresponding to the same genre store when approaching the same genre store. “Notification range (walking)” indicates a notification range applied when moving on foot, and “Notification range (car)” indicates a notification range applied when moving by car.
- “Genre” indicates the genre of the same genre store.
- the “corresponding stored coupon No.” is “No.” in the position information management data 101 of the coupon corresponding to the same genre store, that is, the coupon notified to the user when entering the notification range of the same genre store. Is shown.
- FIG. 14 is a diagram illustrating an example of the notification list 103.
- the notification list 103 includes seven items of “No.”, “Name”, “Location information”, “Same genre flag”, “Condition NG flag”, “Genre”, and “Condition”. include.
- No. is a management number for managing coupons determined to be notified to the user, and one management number is assigned to one coupon.
- “Name” indicates the store name of the coupon, and “Name” in the location information management data 101 is used as “Name” in the notification list 103.
- location information in the location information management data 101 is used as “location information” in the notification list 103 for “location information”.
- the “same genre flag” indicates that the same genre store managed by the same genre management data 102 exists.
- the same genre store exists, and the “same genre flag” column is “ ⁇ ” in the notification range in the same genre store.
- the coupon in which the same genre store exists is notified to the user not only when the mobile phone 1 enters the notification range of the coupon store, but also when the mobile phone 1 enters the notification range of the same genre store.
- “Condition NG flag” is a flag indicating that the user is notified even if the condition is not met. In the example shown in the figure, even if the conditions are not met, what is notified to the user is “ ⁇ ” in the “Condition NG flag” column.
- “Genre” and “Condition” indicate the genre of the store specified by the location information and the conditions for using the coupon at the store, and the “genre” and “condition” of the location information management data 101 are notified. Used as “genre” and “condition” in the list 103.
- FIG. 15 is a flowchart illustrating an example of processing for generating the location information management data 101.
- the mobile phone 1 generates the location information management data 101
- the car navigation system 30 may generate the location information management data 101.
- the car navigation system 30 When the car navigation system 30 generates the location information management data 101 and the mobile phone 1 notifies the coupon, the car navigation system 30 transmits the generated location information management data 101 to the mobile phone 1. Further, when the car navigation system 30 generates the location information management data 101 and notifies the user of the coupon, communication with the mobile phone 1 is unnecessary.
- the mobile phone 1 receives the coupon with position information in various modes as shown in FIG. 4 (YES in S1), and stores the received coupon in the mobile phone storage unit 8 (S2). Note that images other than coupons that do not include position information are also received (acquired) in the same manner as coupons, and stored in the mobile phone storage unit 8 in the same manner as coupons. That is, the mobile phone 1 acquires the coupon and the image that is not so by the same handling and stores them in the mobile phone storage unit 8.
- the location information extraction unit 110 checks whether the location information is included in the header information of the stored data, and the location information is included. If the data is present, it is determined that the data is a coupon with position information.
- the generation processing of the location information management data 101 may be performed at a timing when data is stored in the mobile phone storage unit 8 or may be performed at a timing when a specific application is activated on the mobile phone 1. Alternatively, it may be performed at predetermined time intervals.
- the position information extraction unit 110 includes position information for each predetermined time for data stored in the mobile phone storage unit 8. Identify the data.
- the location information extraction unit 110 determines that the data stored in the cellular phone storage unit 8 is a coupon
- the location information management data 101 has an empty No. (“No.” in which position information or the like is not stored) is the most No. Are searched for (S3).
- the location information extraction unit 110 detects the empty number detected in S3.
- various information extracted from the coupon is added (S4).
- the location information extraction unit 110 extracts “location information”, “genre”, and “condition” incorporated as header information of the coupon, adds them to the location information management data 101, and The file name is added to the position information management data 101 as “name”. Further, based on this “position information”, “notification range (walking)” and “notification range (car)” are generated and added to the position information management data 101.
- the position information extraction unit 110 performs the same genre management data update process and updates the same genre management data 102 (S5). In S5, when the same genre management data 102 has not yet been generated, the position information extraction unit 110 does not update the same genre management data 102 but generates it.
- FIG. 16 is a flowchart showing an example of processing for generating the genre management data 102.
- the process for generating the genre management data 102 is a process performed in S5 of the flowchart of FIG.
- the location information extraction unit 110 searches the own terminal for information on stores (including location information on the stores, etc.) of the same genre as the coupon acquired and stored in S1 and 2 of FIG. 15 (S10).
- the location information management data 101 is an example of the store information stored in the terminal.
- information such as a store described in a map used by the route guide execution unit 117 for the route guide may be used.
- information such as stores of the same genre as the coupon stored in the mobile phone storage unit 8 is referred to as the same genre candidate.
- the position information extraction unit 110 searches for the same genre candidate from the map information stored in the mobile phone storage unit 8 and also from the service via the Internet (S11).
- the position information extracting unit 110 creates a temporary same genre candidate list including the same genre candidates detected in the processes of S10 and S11 (S12).
- the list generated here includes candidates for the same genre detected by Internet search. For this reason, the list includes the same genre candidate at a position far from the current position, and the list may become meaninglessly large.
- the position information extraction unit 110 narrows down the same genre candidates included in the provisional same genre candidate list (S13).
- the narrowing down can be performed, for example, by extracting candidates of the same genre that are within a certain distance from the current position of the mobile phone 1 acquired by the position acquisition unit 2.
- the position information extraction unit 110 reads one genre candidate from the generated tentative same genre candidate list (S14). Then, it is confirmed whether or not the read genre candidate has been registered in the genre management data 102 (S15).
- the position information extraction unit 110 stores the vacancy No. of the genre management data 102. The one with the smallest number is searched (S16). The position information extraction unit 110 then detects the detected empty No. The read information is added to (S17), and the process proceeds to S19.
- the information added here is “name”, “location information”, “genre”, and “corresponding stored coupon No.”. Further, the position information extraction unit 110 generates and adds “notification range (walking)” and “notification range (car)” based on the “position information” (see FIG. 13).
- the position information extraction unit 110 confirms whether all the same genre candidates included in the same genre candidate list generated in S12 have been read. If there is a same genre candidate that has not been read (NO in S19), the position information extraction unit 110 returns to the process of S14 and reads the next same genre candidate from the same genre candidate list. On the other hand, when all the same genre candidates are read out (YES in S19), the position information extraction unit 110 ends the generation process of the same genre management data 102.
- FIG. 17 is a flowchart showing an example of update processing of the position information management data 101 and the genre management data 102 at the time of coupon deletion.
- the location information extraction unit 110 reads from the location information management data 101.
- the position information set (all of “No.”, “name”, “position information”, etc.) corresponding to the coupon is deleted (S21).
- the position information extraction unit 110 deletes “No.” of the deleted coupon from “corresponding stored coupon No.” in the same genre management data 102 (S22). Thereby, even when the mobile phone 1 approaches the notification range of the same genre store, the presence of the deleted coupon is not notified to the user.
- the position information extracting unit 110 deletes the information from the genre management data 102 (S23). Thereby, the update process of the position information management data 101 and the genre management data 102 at the time of coupon deletion is completed.
- FIG. 18 is a flowchart illustrating an example of notification of a store where a coupon can be used and route guide processing to the store.
- the mobile phone determination unit 111 acquires the current location of the mobile phone 1 from the position acquisition unit 2 (S30). Further, the mobile phone determination unit 111 acquires the moving speed and the traveling direction of the mobile phone 1 based on the temporal change of the current location of the mobile phone 1 acquired from the position acquisition unit 2 (S31).
- the mobile phone determination unit 111 performs notification list generation processing to generate (or update) the notification list 103 (see FIG. 14) (S32). If there is no information to be notified to the user in the information included in the generated notification list 103 (NO in S33), the process returns to S30. On the other hand, if there is something to be notified to the user (YES in S33), the mobile phone determination unit 111 transmits the fact to the mobile phone notification unit 112.
- the mobile phone notification unit 112 that has received the transmission from the mobile phone determination unit 111 notifies the user that there is information to be notified (S34). Specifically, the mobile phone notification unit 112 causes the audio output unit 5 to output a predetermined notification sound, vibrates the vibration unit 12, reads a coupon image from the mobile phone storage unit 8, and displays it on the display unit 11. Display (see FIG. 2 etc.).
- the mobile phone notification unit 112 checks whether or not the coupon position (store location where the coupon can be used) is set as the destination (S35).
- the coupon position stored location where the coupon can be used
- the input key K1 for setting the store of the coupon as the destination of the route guide is displayed, thereby setting the position of the coupon as the destination. Therefore, when the input operation for selecting the key K1 is detected, the mobile phone notification unit 112 determines that the location of the store in the image C is set as the destination. On the other hand, when the key K1 is not selected and the screen is switched to another screen, the mobile phone notification unit 112 determines that the destination has not been set.
- the coupon position may be set as a waypoint.
- the destination point is input.
- the route guide to the coupon position is performed, the route guide from the coupon position to the destination point is performed.
- the process returns to S30.
- the position information indicating the position set as the destination is read from the notification list 103 and sent to the route guide execution unit 117. Instruct to run route guide to position.
- the route guide execution unit 117 Upon receiving the instruction, the route guide execution unit 117 sends the position information received from the mobile phone notification unit 112 to the route search unit 115, and routes information indicating the route from the current position of the mobile phone 1 to the position indicated by the position information. Received from the search unit 115. Then, the route guide execution unit 117 causes the display unit 11 to display an image obtained by superimposing an image indicating the route and the current position of the mobile phone 1 on the map image stored in the mobile phone storage unit 8, so that the destination ( Navigation (route guide) to the coupon store) is started (S36).
- the mobile phone notification unit 112 sends location information indicating the location of the destination to the surrounding information acquisition unit 116.
- the peripheral information acquisition unit 116 that has received the location information transmits the location information to the service via the telephone network communication unit 3 (S37).
- the service receives position information and returns information related to the position information.
- the area information distribution server 60 in FIG. 11 corresponds to this service.
- the surrounding information acquisition part 116 acquires the surrounding information of the destination from a service (S38). This post-processing returns to S30.
- FIG. 19 is a flowchart illustrating an example of the notification list generation process.
- the mobile phone determination unit 111 acquires information indicating the connection status (whether communication connection has been established) with the car navigation system 30 from the mobile phone short-range communication control unit 113 (S40), and the mobile phone storage unit 8
- One position information set is read from the position information management data 101 (S41).
- the position information set may be read in ascending order of “No.”.
- the mobile phone determination unit 111 determines whether the car navigation system 30 and the mobile phone 1 are connected for communication based on the information acquired in S41 (S42). If it is determined that the communication connection is established (YES in S42), the process proceeds to S43. In S43, it is determined to apply the notification range (“notification range (vehicle)” in FIG. 12) for the vehicle movement included in the position information set read in S41. On the other hand, if it is determined that the communication connection is not established (NO in S42), the process proceeds to S44. In S44, it is determined to apply the notification range for walking movement included in the position information set read in S41 ("notification range (walking)" in FIG. 12).
- the mobile phone determination unit 111 corrects the determined notification range to a range corresponding to the moving speed of the mobile phone 1 (S45). Thereby, the notification range for determining the position information added by the mobile phone determination unit 111 to the notification list 103 is determined.
- the correction of the notification range is not an essential process, for example, by performing the following correction, the position information is notified within the appropriate notification range according to the moving speed of the mobile phone 1, that is, the moving speed of the user. be able to.
- the moving speed of the mobile phone 1 acquired in S31 of FIG. 18 is determined from a predetermined value (for example, 40 km / hr for car movement, 5 km / hr for walking movement) from a predetermined magnification (for example, 1 .5 times, 0.5 times, etc.) when the speed is faster or slower, the value obtained by multiplying the magnification by the distance distance of “notification range (car)” or “notification range (walk)” of the location information management data 101
- the notification range is determined as the range distance.
- the mobile phone determination unit 111 may receive the moving speed from the car navigation system 30 in S31 of FIG. 19 and use the received moving speed as the moving speed of the mobile phone 1.
- the mobile phone determination unit 111 determines whether or not the current position of the mobile phone 1 is within the determined notification range (S46). Whether or not the current position is in the notification range can be determined as follows, for example.
- the notification range is a square as shown in FIG. 5A and the notification distance is L (km), that is, when a square notification range having a side of 2 L (km) is set.
- the current position of the mobile phone 1 is (X1, Y1).
- both the following formulas (1) and (2) are established, it is determined that the current position of the mobile phone 1 is in the notification range.
- the mobile phone determination unit 111 proceeds to the process of S52. In this case, the position information is not added to the notification list 103.
- the mobile phone determination unit 111 determines that the moving direction of the mobile phone 1 is a point of position information (coupon store or genre store). It is determined whether or not the vehicle is facing (S47).
- the determination of the movement direction is not an essential process, for example, the movement direction of the mobile phone 1, that is, the movement direction of the mobile phone 1 is determined by determining the movement direction as follows and determining whether the movement direction is directed to the position information position. By being present in the direction in which the user is heading, it is possible to notify only the location information of the store where the user can easily visit.
- the distance between the current position of the mobile phone 1 and the location information location (coupon store or the same genre store) to be determined is calculated, and after a certain period (for example, 1 minute), the distance between the two is calculated again. calculate. If the calculated distance is shorter, it is determined that the vehicle is heading to that point. Since the above determination cannot be performed when the user is not moving, if the calculated distance is the same, the process waits until the current position of the mobile phone 1 changes.
- the mobile phone determination unit 111 proceeds to the process of S52. In this case, the position information is not added to the notification list 103.
- the mobile phone determination unit 111 passes the current date and time acquired from the time measuring unit 114 and the telephone network communication unit 3. Then, it is confirmed whether or not the current weather acquired from the Internet is applicable to the “condition” stored in the position information management data 101 (S48).
- the “No. 2” coupon of the location information management data 101 in FIG. 12 is associated with a time zone of “11:00 to 13:00” and a weather of “sunny” as “condition”. ing. Therefore, when the current date and time is included in the time zone “11:00 to 13:00” and the current weather is “sunny”, it is determined that the “condition” is met.
- the mobile phone determination unit 111 checks whether or not the condition is satisfied in this way, and if it is determined that the condition is satisfied (YES in S48), the process proceeds to S51. On the other hand, if it is determined that the condition is not satisfied (NO in S48), it is confirmed whether or not the setting is made so as to notify the one that does not meet the condition (S49). It should be noted that the setting of whether or not to notify what does not meet the conditions is performed in advance (see FIG. 9).
- the mobile phone determination unit 111 proceeds to the process of S52. In this case, the position information is not added to the notification list 103.
- the mobile phone determination unit 111 determines to turn on the condition NG flag of the location information. Then (S50), the process proceeds to S51.
- the condition NG flag is a flag indicating that the coupon of the position information is presented to the user even when the condition is not met.
- the location information coupon with the condition NG flag is displayed together with a message that the coupon cannot be used, such as message M3 in FIG.
- the mobile phone determination unit 111 adds information (name, position information, genre, condition) included in the position information set and information indicating the presence or absence of the NG flag to the notification list (see FIG. 14). Then, the process proceeds to S52, and the mobile phone determination unit 111 confirms whether or not all the location information management data 101 has been read. That is, the mobile phone determination unit 111 finishes checking whether or not the current location of the mobile phone 1 is within the notification range of the location information set for all location information sets included in the location information management data 101. Check if it is.
- FIG. 20 is a flowchart illustrating an example of notification of a store where a coupon can be used and route guide processing to the store, which is performed when the notification range of the store of the same genre as the store where the coupon can be used is entered.
- the notification of the store where the coupon can be used and the route guide processing to the store performed when entering the notification range of the store of the same genre as the store where the coupon can be used are the processing of S32 in FIG.
- the process is the same as that of FIG. 18 except that the process is changed to S60.
- the same reference number is attached
- the notification list generation process is performed in S32 of FIG. 18, but the same genre notification list generation process for generating or updating the notification list 103 based on the same genre management data 102 is performed in S60 of FIG.
- FIG. 21 is a flowchart illustrating an example of the genre notification list generation process.
- the genre notification list generation process is substantially the same as the notification list generation process of FIG.
- the data used for generating the notification list 103 is changed from the position information management data 101 to the same genre management data 102, the contents of the processing are slightly different.
- the mobile phone determination unit 111 acquires the connection status with the car navigation system 30 (S40), and reads one piece of the same genre store information from the same genre management data 102 of the mobile phone storage unit 8 (S70). Note that the same-genre store information may be read in ascending order of “No.”. Then, a notification range to be applied is determined according to whether or not it is connected to the car navigation system 30, and the notification range is corrected by the moving speed of the mobile phone 1 (S42 to 45).
- the mobile phone determination unit 111 determines whether or not the current position of the mobile phone 1 is in the notification range. If the mobile phone 1 is in the notification range, the moving direction of the mobile phone 1 is the location information position. It is determined whether the vehicle is heading (a point specified by the position information included in the read same-genre store information) (S46, 47).
- the mobile phone determination unit 111 reads “corresponding storage coupon” of the same genre store information read in S70. No. ”(see FIG. 13) is read (S71). Then, the mobile phone determination unit 111 reads the corresponding stored coupon No. It is determined to turn on the same genre flag of the position information set specified in (S72).
- the “same genre flag” in the notification list 103 is “ ⁇ ” (see FIG. 14).
- the coupon corresponding to the position information set whose genre flag is ON is a message indicating that “there are stores where the coupon can be used in the same genre” when the mobile phone 1 enters the set notification range. (For example, message M2 in FIG. 6).
- the mobile phone determination unit 111 checks whether or not the current date and time and the weather apply to the “condition” included in the position information set, and if so, the position information and the like (name) included in the position information set. , Position information, genre), and information indicating whether or not the genre flag is set is added to the notification list (see FIG. 14). In addition, when the setting is made to notify the information that does not meet the condition but does not meet the condition, the position information included in the position information set is added to the notification list with the condition NG flag turned ON ( S48-51).
- the mobile phone determination unit 111 confirms whether or not all the corresponding stored coupons have been read (S73).
- the mobile phone determination unit 111 returns to the process of S71 and reads the corresponding stored coupon.
- the mobile phone determination unit 111 confirms whether or not all the same genre store information included in the same genre management data 102 has been read ( S74). If it is confirmed that there is the same genre store information that has not been read (NO in S74), the process returns to S70, and the next same genre store information is read. On the other hand, when it is confirmed that all the same genre store information has been read (YES in S74), the mobile phone determination unit 111 ends the same genre notification list generation process.
- FIG. 22 is a flowchart illustrating an example of processing for notifying a user of a store when the set route is within the notification range of the store where the coupon can be used, and route guide processing to the store.
- the position information of the set destination is sent to the route search unit 115.
- the route search unit 115 that has received the location information of the destination guides the route from the current location (or set departure point) of the mobile phone 1 acquired by the location acquisition unit 2 to the point specified by the received location information. Is created (S81).
- the mobile phone determination unit 111 performs destination setting notification list generation processing that is notification list generation processing performed when the destination is set (S82). By this process, the notification list 103 is generated.
- the process after the generation is substantially the same as the process of FIG.
- the mobile phone determination unit 111 transmits the information to the mobile phone notification unit 112, and the received mobile phone notification unit 112 receives the notification.
- the user is notified that there is information to be notified (S33, 34).
- the mobile phone notification unit 112 checks whether or not the coupon position (store location where the coupon can be used) is set as the destination (S35).
- the mobile phone notification unit 112 ends the process. In this case, route guidance to the destination set in S80 is performed.
- the mobile phone notification unit 112 reads the position information indicating the point set as the destination from the notification list 103, and the route guide. The instruction is sent to the execution unit 117 and instructed to execute the route guide to that point. That is, in this case, the destination of the route guide is changed.
- the destination set here may be set as a stopover on the way to the destination set in S80. In this case, after stopping at the coupon store, a route guide to the destination set in S80 is performed.
- the route guide execution unit 117 starts navigation (route guide) to the set destination (S36).
- the mobile phone notification unit 112 sends location information indicating the location of the destination to the surrounding information acquisition unit 116, and the surrounding information acquisition unit 116 acquires the surrounding information of the destination from the service (S38). After this, route guidance to the destination is performed.
- FIG. 23 is a flowchart illustrating an example of destination setting notification list generation processing.
- the mobile phone determination unit 111 acquires information indicating the connection status with the car navigation 30 from the mobile phone short-range communication control unit 113 and reads one location information set from the location information management data 101 of the mobile phone storage unit 8. . Then, the mobile phone determination unit 111 determines a notification range to be applied depending on whether or not the car navigation system 30 is connected (S40 to 44).
- the notification range is corrected by the moving speed of the mobile phone 1. Absent. Of course, even when the destination is set, the notification range may be corrected at the moving speed of the mobile phone 1.
- the mobile phone determination unit 111 determines whether or not the guidance route created in S81 of FIG. 22 is within the determined notification range (S90). Whether or not the route is in the notification range can be determined by, for example, picking up points on the created route at regular intervals and determining whether or not each picked-up point is included in the notification range. Then, whether or not each point is included in the notification range can also be determined using the above formulas (1) and (2).
- the mobile phone determination unit 111 proceeds to the process of S52. In this case, the position information is not added to the notification list 103.
- the mobile phone determination unit 111 includes the “condition” in which the current date and weather are included in the position information set read in S41. It is confirmed whether or not this is true (S48).
- the mobile phone determination unit 111 determines whether or not the position information and the like (name, position information, genre, condition) included in the position information management data read in S41 and the condition NG flag are present. Is added to the notification list (see FIG. 14). In addition, when the setting is made so that information that does not meet the conditions but does not meet the conditions is set, the position information included in the position information set read in S41 is set to the notification list with the condition NG flag turned ON. It is added (S48-51).
- the mobile phone determination unit 111 confirms whether or not all position information sets have been read (S52). If it is confirmed that there is a position information set that has not been read (NO in S52), the process returns to S41. On the other hand, when it is confirmed that all the position information sets have been read (YES in S52), the mobile phone determination unit 111 ends the destination setting notification list generation process.
- FIG. 24 shows a process of notifying that when a notification range of a store of the same genre as the store where the coupon can be used is included on the set route, which is performed when setting the destination, and a route guide to the store It is a flowchart which shows an example of the process to perform.
- the illustrated process is the same as the process of FIG. 22 except that the process of S82 of FIG. 22 is changed to the process of S100. That is, the destination setting notification list generation processing is performed in S82 of FIG. 22, but in S100 of FIG. 24, the same genre notification at destination setting for generating or updating the notification list 103 based on the same genre management data 102. List generation processing is performed.
- FIG. 25 is a flowchart illustrating an example of the same genre notification list generation process at the time of destination setting.
- the destination setting same genre notification list generation processing is substantially the same processing as the destination setting notification list generation processing of FIG.
- the data used for generating the notification list 103 is changed from the position information management data 101 to the same genre management data 102, the contents of the processing are slightly different.
- the mobile phone determination unit 111 acquires the connection status with the car navigation system 30 (S40), and reads the same genre store information from the same genre management data 102 of the mobile phone storage unit 8 (S70). Then, a notification range to be applied is determined according to whether or not the car navigation system 30 is connected (S42 to 44).
- the mobile phone determination unit 111 determines whether or not the guidance route created in S81 of FIG. 24 is within the determined notification range, and if it is within the notification range, reads in S70.
- the “corresponding stored coupon No.” included in the same genre store information is read (S71). When there are a plurality of “corresponding stored coupon numbers”, the smallest number is stored. Can be read out.
- the mobile phone determination unit 111 determines to turn on the same genre flag of the position information set identified by the read “corresponding stored coupon No.”, and the current date and weather are included in the position information set. It is confirmed whether or not the “condition” included is satisfied (S72, 48).
- the position information and the like (name, position information, genre, condition) included in the position information set are added to the notification list with the genre flag turned ON. (See FIG. 14).
- the position information included in the position information set is added to the notification list with the condition NG flag turned ON ( S48-51).
- the mobile phone determination unit 111 confirms whether or not all the corresponding stored coupons have been read (S73).
- the mobile phone determination unit 111 returns to the process of S71 and reads the corresponding stored coupon.
- the mobile phone determination unit 111 stores all the same genre management data (all the same genre store information included in the same genre management data 102). It is confirmed whether or not it has been read (S74). If it is confirmed that there is the same genre store information that has not been read (NO in S74), the process returns to S70. On the other hand, when it is confirmed that all the same genre store information has been read (YES in S74), the mobile phone determination unit 111 ends the same genre notification list generation process when setting the destination.
- the notification list 103 is generated using either the position information management data 101 or the same genre management data 102 has been described. However, the notification is performed using both the position information management data 101 and the same genre management data 102.
- the list 103 may be generated.
- the notification range is registered in two ways, when moving by car and when walking, and the notification range is corrected according to the moving speed of the user.
- the notification range may be determined.
- the notification range may be changed stepwise according to the moving speed, or may be changed continuously. Further, the notification range may be manually set and changed by the user.
- FIG. 26 is a diagram illustrating an outline of operations performed by the mobile phone 1 and the car navigation system 30.
- the mobile phone 1 of this embodiment transmits the stored coupons to the car navigation system 30 in a batch.
- the car navigation system 30 approaches the point indicated by the coupon received from the mobile phone 1 (when entering the coupon notification range)
- the car navigation system 30 notifies the user of that fact.
- a message M1 indicating that there is a store where a coupon can be used, a coupon image C, and a key K1 for setting the store as a destination are displayed. Yes.
- this key K1 is selected, as shown in the figure, the store is set as the destination of the car navigation system 30 and a route guide to this store is performed.
- the car navigation system 30 executes a part of the processing performed by the mobile phone 1 in the above embodiment, thereby realizing the same function as in the above embodiment.
- FIG. 27 is a diagram illustrating an example of a display screen displayed when the mobile phone 1 and the car navigation system 30 are operated.
- the car navigation system 30 When the car engine on which the car navigation system 30 is mounted is started, the car navigation system 30 is turned on. Then, the car navigation system 30 establishes a communication connection via the mobile phone 1 and the short-range communication unit 31 with the trigger of the power supply of its own device being turned on. That is, if the user of the mobile phone 1 is in a car on which the car navigation system 30 is mounted, the communication connection between the mobile phone 1 and the car navigation system 30 is automatically established, and the user does not need to perform any operation at that time. . In addition, when performing Bluetooth communication, it is necessary to perform pairing (a process of registering each other as a communication partner) in advance, but here, it is assumed that pairing has already been performed.
- the car navigation system 30 may display a message M6 indicating that the communication connection with the mobile phone 1 is established as illustrated. Similarly, when a communication connection with the car navigation system 30 is established, the mobile phone 1 may display a message M7 indicating that effect. Thereby, the user can confirm the establishment of the communication connection.
- the mobile phone 1 transmits to the car navigation system 30 coupons stored in its own terminal. At this time, as illustrated, a message M9 indicating that a coupon is being transmitted may be displayed. Similarly, the car navigation system 30 may display a message M8 indicating that a coupon is being received.
- the mobile phone 1 and the car navigation system 30 each return to normal operation. That is, the mobile phone 1 displays a standby screen and enters an incoming call waiting state, and the car navigation system 30 displays a message M10 indicating that the current location of the device itself (that is, the current location of the car) and then displays the current location on the map. To do.
- the car navigation system 30 determines whether or not the point of the coupon has been approached, that is, whether or not the notification range set with reference to the point indicated by the coupon position information has been entered, and determined that the vehicle has entered the notification range. Sometimes, this is notified to the user.
- a message M1 indicating that there is a store where the coupon can be used nearby, a coupon image C, and a key K1 set for the destination are displayed.
- the store of the coupon of the image C is set as the destination of the route guide, and the route guide to the store is performed. Further, when the destination is set, the surrounding information around the set destination is transmitted from the car navigation system 30 to the mobile phone 1.
- the mobile phone 1 that has received this may display a message M11 indicating that the peripheral information has been received. Thereby, the user of the mobile phone 1 can confirm that the peripheral information has been received. In addition, since the peripheral information is stored in the mobile phone 1, the user can check the peripheral information at an arbitrary timing. For example, when the user is driving, it can be confirmed at the time of parking or the like after arrival at the destination.
- FIG. 28 is a block diagram showing a main configuration of the mobile phone 1.
- the block diagram of FIG. 28 includes a notification list 103, a mobile phone determination unit 111, a mobile phone notification unit 112, a time measuring unit 114, a route search unit 115, and a route guide execution unit 117, as compared with the block diagram of FIG. Not different.
- These configurations are provided in the car navigation 30 instead of the mobile phone 1.
- the mobile phone 1 may be provided with these configurations, but for the sake of simplicity, only the configuration necessary for realizing the functions of the mobile phone 1 of the present embodiment is described here. ing.
- the image with position information 100, the position information management data 101, and the genre management data 102 stored in the mobile phone storage unit 8 are the same as those described in the above embodiment.
- the position information extraction unit 110 of the mobile phone control unit 6 is the same as that described in the above embodiment.
- the mobile phone short-range communication control unit 113 returns a connection permission when a connection request from the car navigation system 30 is received, and establishes a communication connection with the car navigation system 30 via the short-range communication unit 9.
- a position information request is transmitted from the car navigation system 30.
- the cellular phone short-range communication control unit 113 reads the location information-added image 100, the location information management data 101, and the genre management data 102 from the cellular phone storage unit 8 and transmits them to the car navigation system 30.
- position information indicating the position of the set destination and peripheral information about the destination are transmitted to the mobile phone 1.
- the mobile phone short-range communication control unit 113 receives the peripheral information and the position information, the mobile phone short-range communication control unit 113 sends the received peripheral information and the position information to the peripheral information acquisition unit 116.
- the peripheral information acquisition unit 116 displays a message indicating that fact (for example, M11 in FIG. 27) on the display unit 11. Further, the peripheral information acquisition unit 116 transmits a peripheral information request for the received position information to, for example, the regional information distribution server 60 via the telephone network communication unit 3, and acquires peripheral information other than the peripheral information received from the car navigation system 30. To do.
- the peripheral information acquired by the peripheral information acquisition unit 116 is stored in the mobile phone storage unit 8. The user can confirm the peripheral information at a desired timing by operating the operation unit 10.
- FIG. 29 is a block diagram illustrating a main configuration of the car navigation system 30.
- the car navigation storage unit 37 stores an image with position information 100, position information management data 101, genre management data 102, and a notification list 103.
- the car navigation control unit 35 includes a car navigation near field communication control unit 120, a car navigation determination unit (range setting unit, route determination unit, condition determination unit, association determination unit, movement speed acquisition unit, approach determination unit) 121, car navigation notification A unit (notification unit, route notification unit, association notification unit) 122, a timing unit 123, a route search unit (route setting unit) 124, a peripheral information transmission unit 125, and a route guide execution unit (guidance unit) 126 are included. .
- the notification list 103 is generated and updated by the car navigation determination unit 121.
- the car navigation near field communication control unit 120 transmits a connection request from the near field communication unit 31 when the power of the car navigation system 30 is turned on.
- a connection request is received by the mobile phone 1 paired with the car navigation system 30, a connection permission is transmitted from the mobile phone 1, and a communication connection between the mobile phone 1 and the car navigation system 30 is established.
- the car navigation short-range communication control unit 120 transmits a position information request to the mobile phone 1 and receives the position information-added image 100, the position information management data 101, and the same genre management data 102.
- the received data is stored in the car navigation storage unit 37.
- the car navigation determination unit 121, the car navigation notification unit 122, the timing unit 123, the route search unit 124, and the route guide execution unit 126 are the mobile phone determination unit 111, the mobile phone notification unit 112, the timing unit 114, and the route search unit of the first embodiment. 115 and the route guide execution unit 117 (see FIG. 1).
- the peripheral information transmission unit 125 receives the positional information of the destination from the car navigation notification unit 122 and acquires the peripheral information of the point specified by the received positional information. . Then, the peripheral information transmission unit 125 transmits the acquired peripheral information and the received position information to the mobile phone 1 via the car navigation near field communication control unit 120.
- FIG. 30 is a flowchart illustrating an example of a connection process between the mobile phone 1 and the car navigation system 30 and a coupon transmission process.
- the cellular phone short-range communication control unit 113 of the cellular phone 1 confirms whether there is a connection request (S110), and if there is a connection request, establishes a communication connection with the car navigation system 30 that is the transmission source of the connection request (S111). ).
- a position information request is transmitted from the car navigation system 30 and the mobile phone 1 receives this request.
- the mobile phone short-range communication control unit 113 checks whether or not the position information, that is, the image with position information 100 is stored in the mobile phone storage unit 8 (S113). When it is confirmed that the data is stored (YES in S113), the mobile phone short-range communication control unit 113 detects the position information and management data (specifically, the image with position information 100, the position information management data 101). And the same genre management data 102) are transmitted to the car navigation system 30 (S114). Thereafter, the process returns to S110.
- the position information and management data specifically, the image with position information 100, the position information management data 101.
- the same genre management data 102 are transmitted to the car navigation system 30 (S114). Thereafter, the process returns to S110.
- the mobile phone short-range communication control unit 113 displays NACK indicating that the image with position information 100 is not stored. Is transmitted to the car navigation system 30 (S115), and the process returns to S110.
- the car navigation near field communication control unit 120 of the car navigation system 30 causes the near field communication unit 31 to transmit a connection request to the surroundings of the car navigation system 30 (S121).
- a connection permission transmitted in response to this connection request a communication connection with the mobile phone 1 is established (S122).
- the car navigation near field communication control unit 120 transmits a location information request to the mobile phone 1 (S123), and the location information and management data (specifically, location information attached) from the mobile phone 1 are transmitted. Reception of the image 100, the position information management data 101, and the genre management data 102) is awaited (S124).
- the car navigation short-range communication control unit 120 stores the received position information and management data in the car navigation storage unit 37 (S125). . Thereafter, the car navigation system 30 performs a process of notifying the user of the position information based on the stored position information and management data. This will be described later with reference to FIG.
- the car navigation short-range communication control unit 120 informs the route search unit 124 to that effect.
- the car navigation system 30 operates as a normal car navigation system.
- the route search unit 124 that has received the notification acquires position information indicating the current location of the car navigation system 30 from the position acquisition unit 32 (S126), instructs the route guide execution unit 126 to place the acquired current location on the map. It is displayed (S127). After this, the route search unit 124 continues to execute acquisition of the current location and an instruction to display the current location. That is, normal processing as car navigation is performed.
- FIG. 31 is a flowchart illustrating an example of notification of stores where coupons can be used and route guide processing to the stores, which is performed by the car navigation system 30.
- the car navigation determination unit 121 acquires position information indicating the current location of the car navigation 30 from the position acquisition unit 32 (S30), and acquires a speed and a traveling direction (S31).
- the speed and the traveling direction may be acquired from the vehicle signal input unit 38 (see FIG. 11) or may be calculated from a change in time of the current position.
- the car navigation determination unit 121 performs a car navigation side notification list generation process (S130). As a result, the notification list 103 is generated or updated. And the car navigation determination part 121 confirms whether this notification list 103 contains what should be notified (S33). If nothing to be notified is included (NO in S33), the process returns to S30.
- the car navigation determination unit 121 transmits that fact to the car navigation notification unit 122, and the received car navigation notification unit 122 notifies the user (S34). ). Specifically, as shown in FIG. 26, the car navigation notification unit 122 displays a message indicating that there is a store where coupons can be used nearby, an image of the coupon, a key for setting the destination, and the like on the display unit 40. And the sound output unit 34 outputs a notification sound.
- the car navigation notification unit 122 confirms whether or not the store of the displayed coupon is set as the destination (S35). Here, when it is confirmed that it has not been set (NO in S35), the process returns to S30. On the other hand, if it is confirmed that the destination is set (YES in S35), navigation to the destination is started (S36).
- the car navigation notification unit 122 transmits position information indicating the set destination position to the surrounding information transmission unit 125.
- the peripheral information transmission unit 125 that has received the position information acquires the peripheral information of the position specified by the received position information, using the map information or the like stored in the car navigation storage unit 37. Then, the peripheral information transmission unit 125 instructs the car navigation short-range communication control unit 120 to transmit the acquired peripheral information and the position information received from the car navigation notification unit 122 to the mobile phone 1 (S131). Thereafter, the process returns to S30.
- FIG. 32 is a flowchart illustrating an example of the car navigation side notification list generation process.
- the car navigation determination unit 121 reads one location information set from the location information management data 101 of the car navigation storage unit 37, and determines to apply the range of vehicle movement as the notification range. In addition, the car navigation determination unit 121 corrects the determined notification range according to the moving speed of the car navigation 30 (S41, 43, 45).
- the car navigation determination unit 121 determines whether or not the current position acquired by the position acquisition unit 32 is within the notification range (S46). Here, if it is determined that it is not in the notification range (NO in S46), the process proceeds to S52, where it is confirmed whether all the position information sets have been read. If not read, the process returns to S41.
- the car navigation determination unit 121 determines whether the current date and weather apply to the “condition” included in the read position information set. It is confirmed whether or not (S48).
- the car navigation determination unit 121 confirms whether or not all position information sets have been read. If it is confirmed that there is a position information set that has not been read (NO in S52), the process returns to S41. On the other hand, when it is confirmed that all the position information sets have been read (YES in S52), the car navigation determination unit 121 ends the car navigation side notification list generation process.
- FIG. 33 is a flowchart illustrating an example of processing for notifying a user of a store when the set route is in a notification range of the store where the coupon can be used, and route guide processing to the store, performed by the car navigation system 30. It is.
- the position information of the set destination is sent to the route search unit 124, and the route search unit 124 guides the user to the destination specified by the received position information. Is created (S81). Then, the route search unit 124 sends information indicating the created route to the car navigation determination unit 121.
- the car navigation determination unit 121 that has received the information indicating the route performs a car navigation side destination setting list generation process (S140). As a result, the notification list 103 is generated or updated. And the car navigation determination part 121 confirms whether this notification list 103 contains what should be notified (S33). If nothing to be notified is included (NO in S33), the process ends. In this case, route guidance to the destination set in S80 is performed.
- the car navigation determination unit 121 transmits that fact to the car navigation notification unit 122, and the received car navigation notification unit 122 notifies the user (S34). ). Specifically, as shown in FIG. 26, the car navigation notification unit 122 displays a message indicating that there is a store where coupons can be used nearby, an image of the coupon, a key for setting the destination, and the like on the display unit 40. And the sound output unit 34 outputs a notification sound.
- the car navigation notification unit 122 confirms whether or not the store of the displayed coupon is set as the destination (S35). Here, if it is confirmed that it has not been set (NO in S35), the process ends. On the other hand, if it is confirmed that the destination is set (YES in S35), navigation to the destination is started (S36).
- the car navigation notification unit 122 transmits position information indicating the set destination position to the surrounding information transmission unit 125.
- the peripheral information transmission unit 125 that has received the position information acquires the peripheral information of the position specified by the received position information, using the map information or the like stored in the car navigation storage unit 37. Then, the peripheral information transmission unit 125 instructs the car navigation short-range communication control unit 120 to transmit the acquired peripheral information and the position information received from the car navigation notification unit 122 to the mobile phone 1 (S131). Thereby, the process ends.
- FIG. 34 is a flowchart illustrating an example of a car navigation side destination setting notification list generation process.
- the car navigation determination unit 121 reads one location information set from the location information management data 101 of the car navigation storage unit 37 (S41), and determines to apply a notification range for vehicle movement (S43). Since it is considered that the user of the car navigation system 30 often does not start moving at the time of setting the destination, the notification range is not corrected with the moving speed of the car navigation system 30 in the illustrated example. Of course, even when the destination is set, the notification range may be corrected at the moving speed of the car navigation system 30.
- the car navigation determination unit 121 determines whether or not the guidance route created in S81 of FIG. 33 is within the determined notification range (S90). If it is determined that the route is not within the notification range (NO in S90), the process proceeds to S52. In this case, the position information is not added to the notification list 103.
- the car navigation determination unit 121 determines whether or not the current date and weather and the “condition” included in the position information set apply. Is confirmed (S48).
- the car navigation determination unit 121 When it is confirmed that the condition is met, the car navigation determination unit 121 adds position information and the like (name, position information, genre, condition) included in the position information set read in S41 to the notification list (FIG. 14). reference). In addition, when it is set to notify those that do not meet the conditions but do not meet the conditions, the position information included in the position information set and information indicating that the condition NG flag is ON are displayed. Add to notification list (S48-51).
- the car navigation determination unit 121 confirms whether or not all position information sets have been read (S52). If it is confirmed that there is a position information set that has not been read (NO in S52), the process returns to S41. On the other hand, if it is confirmed that all the position information sets have been read (YES in S52), the car navigation determination unit 121 ends the car navigation side destination setting notification list generation process.
- the example of generating the notification list 103 using the same genre management data 102 is omitted, but the notification list 103 using the same genre management data 102 is generated by the same processing as in the first embodiment. Is possible.
- the mobile phone 1 reads position information from the coupon.
- the genre management data 102 and the notification list 103 can also be generated.
- the mobile phone 1 only needs to transmit the acquired coupon to the car navigation system 30.
- FIG. 3 Another embodiment of the cellular phone 1 according to the present invention will be described below with reference to FIGS.
- members and processes having the same functions as those in the drawings described in the above embodiment are given the same reference numerals, and descriptions thereof are omitted.
- the hardware configuration of the mobile phone 1 and the car navigation system 30 of this embodiment is as shown in FIG.
- FIG. 35 is a diagram showing an outline of operations performed by the mobile phone 1 and the car navigation system 30.
- the mobile phone 1 of the present embodiment transmits the coupon to the car navigation system 30 when approaching the point indicated by the coupon (when entering the coupon notification range). Then, the car navigation system 30 displays the coupon received from the mobile phone 1.
- a message M1 indicating that there is a store where a coupon can be used, a coupon image C, and a key K1 for setting the store as a destination are displayed. Yes.
- this key K1 is selected, as shown in the figure, the store is set as the destination of the car navigation system 30 and a route guide to this store is performed.
- the car navigation system 30 executes a part of the processing that the mobile phone 1 alone performed in the first embodiment.
- FIG. 36 is a diagram showing an example of a display screen displayed when the mobile phone 1 and the car navigation system 30 are operated.
- the car navigation system 30 When the car engine on which the car navigation system 30 is mounted is turned on, the power of the car navigation system 30 is turned on, and an operation similar to a general car navigation system is started. That is, the car navigation system 30 performs an operation of displaying the current position of the own device on the map.
- the mobile phone 1 stores a plurality of coupons, and whether or not the stored coupon point is approached, that is, whether or not the notification range set based on the point indicated by the coupon position information is entered. Judgment is made.
- the mobile phone 1 when it is determined that the notification range has been entered, the mobile phone 1 notifies the user to that effect, and transmits the coupon at the approached point to the car navigation system 30.
- the notification to the user in the mobile phone 1 may be performed by displaying a message M1 indicating that there is a store where the coupon can be used nearby and an image C of the coupon, as illustrated.
- the car navigation system 30 that receives the coupon from the mobile phone 1 also notifies the user.
- a key K1 for setting the coupon point as the destination is displayed.
- the user can cause the car navigation system 30 to execute a route guide to the coupon point by selecting the key K1. Note that since the user who is driving cannot view the screen of the mobile phone 1, the notification of only the car navigation system 30 may be used.
- the mobile phone 1 that has received the message may display a message M11 indicating that the peripheral information has been received. Thereby, the user of the mobile phone 1 can confirm that the peripheral information has been received.
- FIG. 37 is a block diagram showing a main configuration of the mobile phone 1.
- route search unit 115 and the route guide execution unit 117 are not included. These configurations are provided in the car navigation system 30. Of course, the mobile phone 1 may be provided with these configurations, but for the sake of simplicity, only the configuration necessary for realizing the functions of the mobile phone 1 of the present embodiment is described here. ing.
- the mobile phone 1 according to the present embodiment is different from the first and second embodiments in that the mobile phone notification unit 112 notifies the user by transmitting the image with position information 100 (coupon) to the car navigation system 30. That is, the mobile phone 1 of the present embodiment functions as a position information transmission device that transmits position information to the car navigation system 30.
- the car navigation 30 functions as a notification device that notifies the user based on the position information received from the mobile phone 1.
- the user is notified by the communication system including the mobile phone 1 and the car navigation system 30.
- FIG. 38 is a block diagram showing a main configuration of the car navigation system 30. As shown in FIG.
- the car navigation storage unit 37 stores an image 100 with position information. This is received from the mobile phone 1.
- the car navigation control unit 35 includes a car navigation near field communication control unit 120, a car navigation notification unit 122, a route search unit 124, a peripheral information transmission unit 125, and a route guide execution unit 126.
- the car navigation near field communication control unit 120 transmits a connection request from the near field communication unit 31 when the power of the car navigation system 30 is turned on.
- a connection request is received by the mobile phone 1 paired with the car navigation system 30, a connection permission is transmitted from the mobile phone 1, and a communication connection between the mobile phone 1 and the car navigation system 30 is established.
- the car navigation near field communication control unit 120 transmits the received image with position information 100 to the car navigation storage unit 37. And notifies the car navigation notification unit 122 accordingly.
- the car navigation notification unit 122 When receiving the above notification from the car navigation short-range communication control unit 120, the car navigation notification unit 122 reads the position information-added image 100 from the car navigation storage unit 37, and performs a predetermined message or the like (for example, the message M1 and the key in FIG. 35). Displayed on the display unit 40 together with K1).
- a predetermined message or the like for example, the message M1 and the key in FIG. 35.
- the car navigation notification unit 122 extracts the position information from the read position information-added image 100 and uses the extracted position information as the peripheral information.
- the data is transmitted to the transmission unit 125 and the route guide execution unit 126.
- the peripheral information transmission unit 125 acquires the peripheral information of the spot specified by the position information and transmits it to the mobile phone 1.
- the route guide execution unit 126 cooperates with the route search unit 124 to perform a route guide to the point specified by the position information.
- FIG. 39 is a flowchart illustrating an example of notification of a store where a coupon can be used and route guide processing to the store, which is performed by the mobile phone 1 transmitting the coupon to the car navigation system 30.
- the mobile phone determination unit 111 of the mobile phone 1 acquires position information indicating the current location of the mobile phone 1 from the position acquisition unit 2 (S30), and acquires a speed and a traveling direction (S31).
- the mobile phone determination unit 111 performs notification list generation processing shown in FIG. 19 (S32). As a result, the notification list 103 is generated or updated. Instead of S32, the same genre notification list generation process (S60) of FIG. 21 may be performed.
- the mobile phone determination unit 111 checks whether or not the notification list 103 includes what should be notified (S33). If nothing to be notified is included (NO in S33), the process returns to S30.
- the mobile phone determination unit 111 transmits the notification to the mobile phone notification unit 112, and the received mobile phone notification unit 112 should notify the user
- the position information (here, the position information-added image 100 that is an image in which the position information is incorporated) is transmitted to the car navigation system 30 (S150).
- the mobile phone notification unit 112 may display a message indicating that there is a store where the coupon can be used nearby, an image of the coupon, and the like on the display unit 40.
- the mobile phone notification unit 112 waits for reception of the destination periphery information from the car navigation system 30.
- the process returns to S30.
- the mobile phone notification unit 112 extracts the position information from the notification list 103, and the extracted position information is used as the surrounding information. It transmits to the acquisition unit 116.
- the peripheral information acquisition unit 116 that has received the location information sends the received location information and a peripheral information request for requesting transmission of the peripheral information around the point specified by the location information via the telephone network communication unit 3 ( For example, the information is transmitted to the regional information distribution server 60 in FIG. 11 (S37), and the peripheral information is acquired from the service (S38). Thereafter, the mobile phone 1 returns to a normal operation as a mobile phone (for example, enters an incoming call waiting state).
- the car navigation system 30 performs a normal operation as a car navigation system until it receives position information (here, the image 100 with position information) from the mobile phone 1. Thereby, the present location of the car navigation system 30 is displayed on the map on the display unit 40 of the car navigation system 30 (S127).
- the car navigation near field communication control unit 120 confirms whether or not the position information (image 100 with position information) has been received from the mobile phone 1 (S160). If the reception is not confirmed (NO in S160), the process of S127 is performed. Return. On the other hand, when the reception is confirmed (YES in S160), the received image 100 with position information is stored in the car navigation storage unit 37, and the car navigation notification unit 122 is notified of this.
- the car navigation notification unit 122 Upon receipt of the notification, the car navigation notification unit 122 extracts the position information from the image 100 with position information in the car navigation storage unit 37 and transmits the extracted position information to the peripheral information transmission unit 125 and the route guide execution unit 126. Thereby, the route guide execution unit 126 starts navigation to the point specified by the position information in cooperation with the route search unit 124 (S36).
- the peripheral information transmission unit 125 acquires peripheral information of the spot specified by the position information and transmits it to the mobile phone 1 (S131).
- the notification list 103 is generated using the genre management data 102 and the example in which the notification list 103 is generated at the time of destination setting are omitted, but the same processing as in the first or second embodiment is performed.
- the notification list 103 using the genre management data 102 can be generated, and the notification list 103 at the time of destination setting can be generated.
- the notification device of the present invention includes a data storage unit that stores both data including location information and data not including location information, and includes location information from the data stored in the data storage unit.
- the specifying means for specifying data the position information extracting means for extracting position information used as a reference for setting a predetermined range from the data specified as including the position information by the specifying means, and the position information extracting means Range setting means for setting the predetermined range on the basis of position information, and notification for notifying the user of the own apparatus when the current position of the own apparatus enters the predetermined range set by the range setting means And means.
- the user stores the data including the position information in the data storage unit without distinguishing the data including the position information from the data not including the position information, that is, whether or not the position information is included. It is possible to receive a notification based on the position information from the notification device without performing an operation for selecting a point to be notified only by performing an extremely simple operation.
- the data storage unit stores image data in which position information is incorporated and image data in which position information is not incorporated, and the specifying means stores the image data stored in the data storage unit. It is preferable to identify image data including position information by confirming whether position information is incorporated in the data.
- the data including the position information is the image data including the position information
- the data including the position information can be handled in the same manner as normal image data not including the position information. For example, it is easy to send and receive emails attached to e-mails, receive distribution from services, and download from services.
- the user can receive notification based on the position information simply by storing the image in which the position information is incorporated and the normal image not including the position information in the data storage unit without particularly distinguishing them. it can. In this case, the user does not need an operation of selecting an image to be notified. Further, data including position information can be easily identified by confirming whether or not the position information is incorporated in the image data.
- the position information may be incorporated as header information of image data, for example. In this case, it is possible to easily confirm whether or not the position information is incorporated by referring to the header information.
- the notification device includes guidance means for guiding the user to the point indicated by the position information, and the notification means provides the guidance device with the guidance device when the current position of the device falls within the predetermined range. It is preferable to guide the user to a point indicated by position information used as a reference for setting a predetermined range.
- the notification device when entering the range set based on the position information, guides to the point indicated by the position information. As a result, the user of the notification device can smoothly reach the point indicated by the position information.
- the point indicated by the position information is set as a destination point, guidance to that point is performed, and when it is set as a waypoint, after arrival at that point, to another destination point Make a guidance.
- the notification device determines whether a route setting means for setting a route for guiding the user of the device itself and at least a part of the route set by the route setting means are included in the predetermined range.
- a route determination unit for determining, and the notification unit notifies the user of the device when the route determination unit determines that at least a part of the route is included in the predetermined range. Is preferred.
- the user is notified when at least a part of the route for guiding the user is included in the range.
- the user can recognize the presence of a point in the vicinity of the route (a point where the position information is stored in the data storage unit), and can also stop at the point when moving along the route.
- the route may be, for example, a route connecting the departure point and the destination point input to the notification device, or a route connecting the destination point input to the notification device and the current position of the notification device. Also good.
- the position information is position information of a point where the user may stop, and the position information is associated with a condition for determining whether or not the user stops at the point.
- Condition determining means for determining whether or not the condition associated with the position information used as a reference for setting the predetermined range is satisfied when the current position of the apparatus falls within the predetermined range.
- the notification means preferably notifies the user to that effect or cancels the notification to the user when the condition determination means determines that the condition is not satisfied.
- the notification device of the present invention performs notification so that the user can stop at the location of the location information, but depending on the situation at that time, there may be no point in stopping at that location. For example, when the location information indicates a location of a store, the user cannot use the store even if he / she stops at a time when the store is closed.
- the user if the condition for determining whether or not the user stops at the point is satisfied, the user is notified as usual, and if not, the user is notified accordingly. Or not to notify the user.
- the user can be notified only when the conditions are met. Further, by notifying the fact when the condition is not satisfied, the user can recognize that the existence of the point and the condition are not satisfied. Therefore, based on this recognition, the user can choose to stop at the point from now on, stop at a later date, or not. Note that it is preferable that the user can set whether to notify when the condition is not satisfied.
- condition determining means determines whether the condition is satisfied based on the current date and time.
- whether or not the user stops at a certain point may be determined based on the date and time. For example, when a store exists at the above point (when the location information indicates a point where the store exists), if the current date and time belongs to a time zone when the store is closed, the user is now at that point. Can be determined not to stop by. Conversely, when the current date and time belongs to the time zone in which the store is open, it can be determined that there is a possibility that the user will stop at that point.
- a period, a day of the week, a date, a time zone etc. are mentioned, for example. That is, it is sufficient that at least one of the period, day of the week, date, and time zone is associated with the position information as the condition.
- condition is a condition that can determine whether or not the condition is satisfied based on the weather, and the condition determination unit can determine whether or not the condition is satisfied based on the current weather. preferable.
- the point indicated by the position information is an outdoor sports facility or the like that cannot be used depending on the weather at that time, notification is not performed, or For convenience, the user can be notified that the facility cannot be used.
- condition determination means may determine that the condition is satisfied when the weather indicated by the condition matches the current weather. Further, when the weather indicated by the above condition does not match the current weather, it may be determined that the condition is satisfied.
- the position information is associated with attribute information indicating an attribute of the position information, and a position of a point having an attribute corresponding to the attribute information associated with the position information is determined.
- Related position information acquisition means for acquiring the related position information to be shown, and at least a part of the current position of the own apparatus or a route set to guide the user of the own apparatus is acquired by the related position information acquisition means.
- Relevance determining means for determining whether or not the information is included within a predetermined range set based on the information, and the notifying means determines whether the relevance determining means indicates the current position of the own device or the user of the own device Notifying the user when it is determined that at least a part of the route set for guidance is included in a predetermined range set based on the related position information Preferred.
- the point search is performed based on the attribute information associated with the position information, and the position information of the detected point is acquired as the related position information. Then, a range is set based on the related position information, and notification is given when this range includes at least a part of the current position of the own apparatus or a route set for guiding the user.
- the user can recognize the point indicated by the position information even when entering the range set based on the point related to the point indicated by the position information.
- the point indicated by the position information is a store or a facility
- the genre (category) or the like of the store or the facility can be used as the attribute information.
- the notification device includes a communication unit for communicating with an external device that notifies the user in accordance with an instruction from the own device, and the notification unit is configured when the current position of the own device falls within the predetermined range.
- the user can recognize that the user has entered the above range by a notification from the external device.
- the notification device is a portable device and the external device is an in-vehicle device such as a car navigation system.
- the notification device when riding in a car, it hinders driving, and thus the screen of the portable device cannot be seen.
- notification from the car navigation system allows notification to be confirmed even during driving.
- the notification device includes a communication unit for communicating with an external device that guides the user to a point indicated by the input position information, and the notification unit includes the current position of the device within the predetermined range. Sometimes, it is preferable to transmit the position information used as a reference for setting the predetermined range to the external device via the communication means.
- the notification device does not have a function of guiding the user to the point by an operation such as displaying a route to the input point
- the user who has received the notification receives the position information. It is also possible that you do not know the route to stop at.
- the position information is transmitted to an external device having a function of guiding the user. Therefore, since guidance to the point indicated by the position information is performed by the external device, the user can easily stop at the point of the position information.
- the data storage unit stores image data in which position information is incorporated and image data in which position information is not incorporated, and the notification means specifies that the specifying means includes position information.
- the image data is preferably transmitted to the external apparatus via the communication means.
- the notification device when the notification device enters the range set based on the position information extracted from the image data, the image data is transmitted to the guidance device. Since this image data includes position information, the guidance device can extract the position information from the image data and guide the user to the point indicated by the position information.
- the position information when the position information is transmitted in a state of being incorporated in the image data, there is an advantage that the position information can be transmitted in the same manner as normal image data not including the position information. For example, it can be transmitted as an attached file of a mail or transmitted by infrared communication.
- the predetermined range is preferably variable.
- the above range may always be a fixed range, but by making the range variable as in the above configuration, the user can be notified within an appropriate range according to the situation at that time. Note that the range may be changed manually by the user or automatically by the notification device.
- the notification device includes a boarding determination unit that determines whether or not a user of the device itself is in the vehicle, and the range setting unit is configured to perform the predetermined range according to a determination result of the boarding determination unit. Is preferably changed.
- the movement speed differs greatly between when the user is in the vehicle and when the user is moving on foot. That is, when the user is on the vehicle, the user's range of action is wide, and when the user is walking, the range of action is narrow.
- the above range is changed depending on whether or not the user of the own device is in the vehicle. Thereby, the location information point where the user can reasonably stop can be notified.
- the range may be changed so that the range is wider when the user is on the vehicle than when the user is walking.
- the notification device when the notification device automatically changes the range, the notification device includes a movement speed acquisition unit that acquires the movement speed of the own device, and the range setting unit includes the movement speed acquisition unit according to the movement speed acquired by the movement speed acquisition unit.
- the predetermined range may be changed.
- the above range may be changed stepwise according to the moving speed or may be changed continuously. As a specific method of changing the range, for example, the range may be wider when the moving speed is faster than when it is slower.
- the notification device includes an approach determination unit that determines whether or not the point of the position information is close to the current position of the own device, and the notification unit is configured such that the approach determination unit determines whether the current position of the own device is present. It is preferable to notify the user of the device when the user enters the predetermined range set based on the position information determined to be approaching.
- the notification device may be realized by a computer.
- a control program for realizing the notification device by the computer by operating the computer as each unit of the notification device, and recording the program Such computer-readable recording media also fall within the scope of the present invention.
- a terminal such as a mobile music player or a mobile game machine is carried by the user. It can be suitably applied to.
- In-vehicle devices such as car navigation devices also move with the user, and can be suitably applied to such devices.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Business, Economics & Management (AREA)
- Strategic Management (AREA)
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation (AREA)
- Economics (AREA)
- Finance (AREA)
- Development Economics (AREA)
- Accounting & Taxation (AREA)
- Computer Networks & Wireless Communication (AREA)
- Marketing (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Business, Economics & Management (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Theoretical Computer Science (AREA)
- Signal Processing (AREA)
- Human Resources & Organizations (AREA)
- Game Theory and Decision Science (AREA)
- Quality & Reliability (AREA)
- Tourism & Hospitality (AREA)
- Operations Research (AREA)
- Data Mining & Analysis (AREA)
- Management, Administration, Business Operations System, And Electronic Commerce (AREA)
- Navigation (AREA)
- Mobile Radio Communication Systems (AREA)
Abstract
Description
本発明の一実施形態について図1から図25に基づいて説明する。ここでは、まず本発明の概要について図2に基づいて説明する。図2は、本発明の携帯電話の動作概要を示す図である。図示のように、本発明の携帯電話(通知装置、位置情報送信装置)1は、クーポンが利用できる店舗の位置Pを基準に定められた通知範囲Aに入ったときに、クーポンが利用できる店舗が近くに存在することを自端末のユーザに通知する。
ここで、携帯電話1には、クーポン以外の様々なデータが格納されている。そして、ユーザに通知を行うのは、クーポンのみであるから、クーポンとそれ以外のデータとを分けて管理する必要がある。しかし、データを管理する作業は、ユーザにとってわずらわしい作業である。
図2の例の通知範囲Aは、クーポンが利用できる店舗の位置Pを中心とする円形の範囲である。上述のように、この円の内側に携帯電話1が入ったとき、つまり携帯電話1と位置Pとの距離が円の半径よりも短くなったときに、位置Pの店舗のクーポンが携帯電話1に表示される。
携帯電話1は、ルートガイド機能によって探索された目的地までの経路が、上記通知範囲に含まれている場合にも、クーポンの提示を行う。これについて、図7に基づいて説明する。図7は、目的地までの経路が通知範囲に含まれている場合に、クーポンの提示を行う例を示す図である。
クーポンの中には、使用期限や使用可能な時間帯、曜日等の条件が設定されているものがある。また、店舗の営業時間外であれば、当然のことながらその店舗でクーポンを利用することはできない。つまり、ユーザが店舗の近くに来たときにその店舗のクーポンを提示するだけでは、その店舗にユーザが足を運んだにも拘らず、クーポンが利用できないというようなケースが生じ得る。
携帯電話1では、携帯電話1の現在位置、またはルートガイド機能によって探索された経路が、複数の店舗(クーポンが利用できる店舗またはその店舗と同ジャンルの店舗)の通知範囲に入る場合には、その店舗の名称を例えば図10のように一覧表示する。図10は、店舗名称を一覧表示したときの表示画面の一例を示す図である。
続いて、携帯電話1のハードウェア構成について、図11に基づいて説明する。図11は、携帯電話1、カーナビ30、クーポン配信サーバ50、及び地域情報配信サーバ60のハードウェア構成の一例を示す図である。なお、カーナビ30は携帯電話1と近距離通信手段で接続可能な装置であり、クーポン配信サーバ50は携帯電話1にクーポンを配信するサーバであり、地域情報配信サーバ60は携帯電話1が指定する地点の周辺情報(観光情報、地図、店舗、施設等の情報)を該携帯電話1に送信するサーバである。
携帯電話1は、通話機能と電子メール(Eメール)送信機能とGPS機能とを備えた通信端末であり、カーナビ30及びクーポン配信サーバ50と通信可能に構成されている。図示のように、携帯電話1は、位置取得部2、電話網通信部3、音声入力部4、音声出力部5、携帯電話制御部6、一次記憶部7、携帯電話記憶部(データ記憶部)8、近距離通信部(通信手段)9、操作部10、表示部11、及び振動部12を備えている。
カーナビ30は、地図を表示して目的地までのルートガイドを行う装置であり、図示のように、近距離通信部31、位置取得部32、音声入力部33、音声出力部34、カーナビ制御部35、一次記憶部36、カーナビ記憶部37、車両信号入力部38、操作部39、及び表示部40を備えている。
クーポン配信サーバ50は、携帯電話1にクーポンを配信するサーバであり、図示のように、通信部51、サーバ制御部52、一次記憶部53、サーバ記憶部54、操作部55、及び表示部56を備えている。また、地域情報配信サーバ60は、携帯電話1に地域情報を配信するサーバであり、図示のように、通信部61、サーバ制御部62、一次記憶部63、サーバ記憶部64、操作部65、及び表示部66を備えている。
続いて、携帯電話1のより詳細な構成について、図1に基づいて説明する。図1は、携帯電話1の要部構成を示すブロック図である。図示のように、携帯電話記憶部8には、位置情報付画像100、位置情報管理データ101、同ジャンル管理データ102、及び通知リスト103が格納されている。
続いて、位置情報管理データ101の詳細について、図12に基づいて説明する。図12は、位置情報管理データ101の一例を示す図である。図示のように、位置情報管理データ101には、「No.」、「名前」、「位置情報」、「通知範囲(徒歩)」、「通知範囲(車)」、「ジャンル」、及び「条件」の7つの項目が含まれている。
次に、同ジャンル管理データ102の詳細について、図13に基づいて説明する。図13は、同ジャンル管理データ102の一例を示す図である。図示のように、同ジャンル管理データ102には、「No.」、「名前」、「位置情報」、「通知範囲(徒歩)」、「通知範囲(車)」、「ジャンル」、及び「対応保存クーポンNo.」の7つの項目が含まれている。
次に、通知リスト103の詳細について、図14に基づいて説明する。図14は、通知リスト103の一例を示す図である。図示のように、通知リスト103には、「No.」、「名前」、「位置情報」、「同ジャンルフラグ」、「条件NGフラグ」、「ジャンル」、及び「条件」の7つの項目が含まれている。
続いて、位置情報管理データ101の生成処理の流れについて、図15に基づいて説明する。図15は、位置情報管理データ101を生成する処理の一例を示すフローチャートである。なお、以下では、位置情報管理データ101を携帯電話1が生成する例について説明するが、カーナビ30が生成してもよい。
次に、同ジャンル管理データ102を生成(更新)する処理の流れについて図16に基づいて説明する。図16は、同ジャンル管理データ102を生成する処理の一例を示すフローチャートである。上述のように、同ジャンル管理データ102を生成する処理は、図15のフローチャートのS5で行われる処理である。
携帯電話記憶部8にクーポンが追加されたときには、図15及び16のような処理によって位置情報管理データ101及び同ジャンル管理データ102の生成または更新が行われる。そして、携帯電話記憶部8からクーポンが削除されたときには、位置情報管理データ101及び同ジャンル管理データ102の更新が行われる。ここでは、クーポンを削除したときに行われる位置情報管理データ101及び同ジャンル管理データ102の更新処理の流れについて、図17に基づいて説明する。図17は、クーポン削除時における位置情報管理データ101及び同ジャンル管理データ102の更新処理の一例を示すフローチャートである。
次に、携帯電話1が、携帯電話記憶部8に格納されているクーポンが利用できる店舗をユーザに通知し、また該店舗までのルートガイドを実行する処理の流れについて、図18に基づいて説明する。図18は、クーポンが利用できる店舗の通知及び該店舗までのルートガイド処理の一例を示すフローチャートである。
続いて、図18のS32で行われる通知リスト生成処理の流れについて図19に基づいて説明する。図19は、通知リスト生成処理の一例を示すフローチャートである。
X-L≦X1≦X+L …(1)
Y-L≦Y1≦Y+L …(2)
上記のような判定の結果、現在位置が通知範囲に入っていないと判断した場合(S46でNO)には、携帯電話判定部111はS52の処理に進む。この場合には、当該位置情報は、通知リスト103に追加されない。
次に、携帯電話1が、携帯電話記憶部8に格納されているクーポンが利用できる店舗と、同ジャンルの店舗の通知範囲に入ったときに、上記クーポンが利用できる店舗をユーザに通知し、また該店舗までのルートガイドを実行する処理の流れについて、図20に基づいて説明する。図20は、クーポンが利用できる店舗と同ジャンルの店舗の通知範囲に入ったときに行われる、クーポンが利用できる店舗の通知及び該店舗までのルートガイド処理の一例を示すフローチャートである。
次に、図20のS60で行われる同ジャンル通知リスト生成処理の流れについて、図21に基づいて説明する。図21は、同ジャンル通知リスト生成処理の一例を示すフローチャートである。図示のように、同ジャンル通知リスト生成処理は、図19の通知リスト生成処理とほぼ同様の処理である。ただし、通知リスト103を生成するために用いるデータが位置情報管理データ101から同ジャンル管理データ102に変わっていることにより、処理の内容が若干異なっている。
次に、携帯電話1にルートガイドを行わせるときに作成される出発位置から目的位置までの経路が、クーポンが利用できる店舗の通知範囲に入っているときに、上記クーポンが利用できる店舗をユーザに通知し、また該店舗までのルートガイドを実行する処理の流れについて、図22に基づいて説明する。図22は、設定された経路がクーポンを利用できる店舗の通知範囲に入っているときに、該店舗をユーザに通知する処理、及び該店舗までのルートガイド処理の一例を示すフローチャートである。
続いて、図22のS82で行われる目的地設定時通知リスト生成処理の流れについて図23に基づいて説明する。図23は、目的地設定時通知リスト生成処理の一例を示すフローチャートである。
次に、経路を設定したときに、設定した経路が、携帯電話記憶部8に格納されているクーポンが利用できる店舗と同じジャンルの店舗の通知範囲に含まれるときに、上記クーポンが利用できる店舗をユーザに通知し、また該店舗までのルートガイドを実行する処理の流れについて、図24に基づいて説明する。図24は、目的地設定時に行われる、設定した経路上にクーポンが利用できる店舗と同じジャンルの店舗の通知範囲が含まれるときに、その旨を通知する処理、及び該店舗までのルートガイドを行う処理の一例を示すフローチャートである。
次に、目的地設定時同ジャンル通知リスト生成処理の流れについて、図25に基づいて説明する。図25は、目的地設定時同ジャンル通知リスト生成処理の一例を示すフローチャートである。図示のように、目的地設定時同ジャンル通知リスト生成処理は、図23の目的地設定時通知リスト生成処理とほぼ同様の処理である。ただし、通知リスト103を生成するために用いるデータが位置情報管理データ101から同ジャンル管理データ102に変わっていることにより、処理の内容が若干異なっている。
上記では、位置情報管理データ101または同ジャンル管理データ102の何れか一方を用いて通知リスト103を生成する例について説明したが、位置情報管理データ101及び同ジャンル管理データ102の両方を用いて通知リスト103を生成してもよい。
本発明に関する他の実施形態について、図26~34に基づいて説明すれば、以下のとおりである。なお、説明の便宜上、上記実施形態にて説明した図面と同じ機能を有する部材及び処理については同じ参照符号を付し、その説明を省略する。なお、本実施形態の携帯電話1及びカーナビ30のハードウェア構成は、図11に示した通りである。
まず、本実施形態の携帯電話1及びカーナビ30の実行する動作の概要について、図26に基づいて説明する。図26は、携帯電話1及びカーナビ30が実行する動作の概要を示す図である。
続いて、携帯電話1及びカーナビ30の動作例について、図27に基づいて説明する。図27は、携帯電話1及びカーナビ30の動作時に表示される表示画面の一例を示す図である。
次に、本実施形態の携帯電話1の詳細な構成について、図28に基づいて説明する。図28は、携帯電話1の要部構成を示すブロック図である。
続いて、本実施形態のカーナビ30の詳細な構成について、図29に基づいて説明する。図29は、カーナビ30の要部構成を示すブロック図である。
次に、携帯電話1とカーナビ30との接続処理及びクーポンの送信処理の流れについて、図30に基づいて説明する。図30は、携帯電話1とカーナビ30との接続処理及びクーポンの送信処理の一例を示すフローチャートである。
次に、カーナビ30が、携帯電話1から受信したクーポンが利用できる店舗をユーザに通知し、また該店舗までのルートガイドを実行する処理の流れについて、図31に基づいて説明する。図31は、カーナビ30が行う、クーポンが利用できる店舗の通知及び該店舗までのルートガイド処理の一例を示すフローチャートである。
続いて、図31のS130で行われるカーナビ側通知リスト生成処理の流れについて図32に基づいて説明する。図32は、カーナビ側通知リスト生成処理の一例を示すフローチャートである。
次に、カーナビ30にルートガイドを行わせるときに作成される出発位置から目的位置までの経路が、クーポンが利用できる店舗の通知範囲に入っているときに、上記クーポンが利用できる店舗をユーザに通知し、また該店舗までのルートガイドを実行する処理の流れについて、図33に基づいて説明する。図33は、カーナビ30が行う、設定された経路がクーポンを利用できる店舗の通知範囲に入ったときに、該店舗をユーザに通知する処理、及び該店舗までのルートガイド処理の一例を示すフローチャートである。
続いて、図33のS140で行われるカーナビ側目的地設定時通知リスト生成処理の流れについて図34に基づいて説明する。図34は、カーナビ側目的地設定時通知リスト生成処理の一例を示すフローチャートである。
本発明の携帯電話1に関する他の実施形態について、図35~39に基づいて説明すれば、以下のとおりである。なお、説明の便宜上、上記実施形態にて説明した図面と同じ機能を有する部材及び処理については同じ参照符号を付し、その説明を省略する。なお、本実施形態の携帯電話1及びカーナビ30のハードウェア構成は、図11に示した通りである。
まず、本実施形態の携帯電話1及びカーナビ30の実行する動作の概要について、図35に基づいて説明する。図35は、携帯電話1及びカーナビ30が実行する動作の概要を示す図である。
続いて、携帯電話1及びカーナビ30の動作例について、図36に基づいて説明する。図36は、携帯電話1及びカーナビ30の動作時に表示される表示画面の一例を示す図である。
次に、本実施形態の携帯電話1の詳細な構成について、図37に基づいて説明する。図37は、携帯電話1の要部構成を示すブロック図である。
続いて、本実施形態のカーナビ30の詳細な構成について、図38に基づいて説明する。図38は、カーナビ30の要部構成を示すブロック図である。
次に、本実施形態の携帯電話1とカーナビ30とが、クーポンが利用できる店舗をユーザに通知し、また該店舗までのルートガイドを実行する処理の流れについて、図39に基づいて説明する。図39は、携帯電話1がカーナビ30にクーポンを送信することによって行う、クーポンが利用できる店舗の通知及び該店舗までのルートガイド処理の一例を示すフローチャートである。
8 携帯電話記憶部(データ記憶部)
9 近距離通信部(通信手段)
30 カーナビ(通知装置、外部装置)
110 位置情報抽出部(特定手段、位置情報抽出手段、関連位置情報取得手段)
111 携帯電話判定部(範囲設定手段、経路判定手段、条件判定手段、関連判定手段、乗車判定手段、移動速度取得手段、接近判定手段)
112 携帯電話通知部(通知手段)
113 携帯電話近距離通信制御部(位置情報送信手段)
115 経路探索部(経路設定手段)
117 ルートガイド実行部(誘導手段)
121 カーナビ判定部(範囲設定手段、経路判定手段、条件判定手段、関連判定手段、移動速度取得手段、接近判定手段)
122 カーナビ通知部(通知手段、経路通知手段、関連通知手段)
124 経路探索部(経路設定手段)
126 ルートガイド実行部(誘導手段)
Claims (19)
- 自装置の現在位置が所定の範囲内に入ったときに自装置のユーザに対して通知を行う通知装置であって、
位置情報を含むデータと位置情報を含まないデータとの両方を記憶するデータ記憶部と、
上記データ記憶部に記憶されているデータから位置情報を含むデータを特定する特定手段と、
上記特定手段が位置情報を含むと特定したデータから、上記所定の範囲を設定する基準として用いる位置情報を抽出する位置情報抽出手段と、
上記位置情報抽出手段が抽出した位置情報を基準に上記所定の範囲を設定する範囲設定手段と、
自装置の現在位置が上記範囲設定手段が設定した上記所定の範囲に入ったときに自装置のユーザに対して通知を行う通知手段とを備えていることを特徴とする通知装置。 - 上記データ記憶部には、位置情報が組み込まれた画像データと、位置情報が組み込まれていない画像データとが記憶されており、
上記特定手段は、上記データ記憶部に記憶されている画像データに位置情報が組み込まれているか否かを確認することによって、位置情報を含む画像データを特定することを特徴とする請求項1に記載の通知装置。 - 位置情報が示す地点までユーザを誘導する誘導手段を備え、
上記通知手段は、自装置の現在位置が上記所定の範囲内に入ったときに、上記誘導手段に、当該所定の範囲を設定する基準として用いた位置情報が示す地点までユーザを誘導させることを特徴とする請求項1または2に記載の通知装置。 - 自装置のユーザを誘導するための経路を設定する経路設定手段と、
上記経路設定手段が設定した経路の少なくとも一部が上記所定の範囲に含まれているか否かを判定する経路判定手段とを備え、
上記通知手段は、上記経路判定手段が、上記経路の少なくとも一部が上記所定の範囲に含まれると判定したときに自装置のユーザに対して通知を行うことを特徴とする請求項1から3の何れか1項に記載の通知装置。 - 上記位置情報は、ユーザが立ち寄る可能性がある地点の位置情報であり、該位置情報には、当該地点にユーザが立ち寄るか否かを判定するための条件が対応付けられており、
自装置の現在位置が上記所定の範囲内に入ったときに、当該所定の範囲を設定する基準として用いた位置情報に対応付けられている上記条件を満たしているか否かを判定する条件判定手段を備え、
上記通知手段は、上記条件判定手段が条件を満たしていないと判断した場合に、その旨をユーザに通知するか、またはユーザへの通知を中止することを特徴とする請求項1から4の何れか1項に記載の通知装置。 - 上記条件は、該条件を満たしているか否かを日時に基づいて判断できる条件であり、
上記条件判定手段は、現在の日時に基づいて上記条件を満たしているか否かを判定することを特徴とする請求項5に記載の通知装置。 - 上記条件は、該条件を満たしているか否かを天気に基づいて判断できる条件であり、
上記条件判定手段は、現在の天気に基づいて上記条件を満たしているか否かを判定することを特徴とする請求項5または6に記載の通知装置。 - 上記位置情報には、該位置情報の属性を示す属性情報が対応付けられており、
上記位置情報に対応付けられている属性情報に対応する属性を有する地点の位置を示す関連位置情報を取得する関連位置情報取得手段と、
自装置の現在位置または自装置のユーザを誘導するために設定された経路の少なくとも一部が、上記関連位置情報取得手段が取得した関連位置情報を基準として設定される所定の範囲内に含まれているか否かを判定する関連判定手段とを備え、
上記通知手段は、上記関連判定手段が、自装置の現在位置または自装置のユーザを誘導するために設定された経路の少なくとも一部が上記関連位置情報を基準として設定される所定の範囲内に含まれていると判定したときに、ユーザに対して通知を行うことを特徴とする請求項1から7の何れか1項に記載の通知装置。 - 自装置からの指示に従ってユーザに通知を行う外部装置と通信するための通信手段を備え、
上記通知手段は、自装置の現在位置が上記所定の範囲内に入ったときに、上記通信手段を介して上記外部装置に指示を送信してユーザへの通知を行わせることを特徴とする請求項1から8の何れか1項に記載の通知装置。 - 入力された位置情報が示す地点までユーザを誘導する外部装置と通信するための通信手段を備え、
上記通知手段は、自装置の現在位置が上記所定の範囲内に入ったときに、上記所定の範囲を設定する基準として用いた位置情報を、上記通信手段を介して上記外部装置に送信することを特徴とする請求項1から9の何れか1項に記載の通知装置。 - 上記データ記憶部には、位置情報が組み込まれた画像データと、位置情報が組み込まれていない画像データとが記憶されており、
上記通知手段は、上記特定手段が位置情報を含むと特定した画像データの位置情報を基準として設定された所定の範囲内に自装置の現在位置が入ったときに、当該画像データを上記通信手段を介して上記外部装置に送信することを特徴とする請求項9または10に記載の通知装置。 - 上記所定の範囲は可変であることを特徴とする請求項1から11の何れか1項に記載の通知装置。
- 自装置のユーザが車両に乗車しているか否かを判定する乗車判定手段を備え、
上記範囲設定手段は、上記乗車判定手段の判定結果に応じて、上記所定の範囲を変更することを特徴とする請求項12に記載の通知装置。 - 自装置の移動速度を取得する移動速度取得手段を備え、
上記範囲設定手段は、上記移動速度取得手段が取得した移動速度に応じて上記所定の範囲を変更することを特徴とする請求項12に記載の通知装置。 - 上記位置情報の地点と自装置の現在位置とが近付いているか否かを判定する接近判定手段を備え、
上記通知手段は、上記接近判定手段が、自装置の現在位置と近付いていると判定した位置情報を基準として設定された上記所定の範囲に入ったときに、自装置のユーザに対して通知を行うことを特徴とする請求項1から14の何れか1項に記載の通知装置。 - 通知装置の現在位置が、位置情報送信装置が送信する位置情報を基準として設定された所定の範囲内に入ったときに、上記通知装置が該通知装置のユーザに対して通知を行う通知システムであって、
上記位置情報送信装置は、
位置情報を含むデータと位置情報を含まないデータとの両方を記憶するデータ記憶部と、
上記データ記憶部に記憶されているデータから位置情報を含むデータを特定する特定手段と、
上記特定手段が位置情報を含むと特定したデータから、上記所定の範囲を設定する基準として用いる位置情報を抽出する位置情報抽出手段と、
上記位置情報抽出手段が抽出した位置情報を上記通知装置に送信する位置情報送信手段とを備えていることを特徴とする通知システム。 - 自装置の現在位置が所定の範囲内に入ったときに自装置のユーザに対して通知を行う通知装置の制御方法であって、
位置情報を含むデータと位置情報を含まないデータとの両方を記憶するデータ記憶部に記憶されているデータから位置情報を含むデータを特定する特定ステップと、
上記特定ステップで位置情報を含むと特定したデータから、上記所定の範囲を設定する基準として用いる位置情報を抽出する位置情報抽出ステップと、
上記位置情報抽出ステップで抽出した位置情報を基準に上記所定の範囲を設定する範囲設定ステップと、
自装置の現在位置が上記範囲設定ステップで設定した上記所定の範囲に入ったときに自装置のユーザに対して通知を行う通知ステップとを含むことを特徴とする通知装置の制御方法。 - 請求項1から15の何れか1項に記載の通知装置を動作させるための制御プログラムであって、コンピュータを上記各手段として機能させるための制御プログラム。
- 請求項18に記載の制御プログラムを記録したコンピュータ読み取り可能な記録媒体。
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US13/257,898 US8700067B2 (en) | 2009-03-24 | 2010-03-19 | Notification device, notification system, method for controlling notification device, and computer readable recording medium having a control program recorded thereupon |
| CN2010800129934A CN102362285A (zh) | 2009-03-24 | 2010-03-19 | 通知装置、通知系统、通知装置的控制方法、控制程序以及存储有该程序的计算机可读取存储介质 |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2009072281A JP5546784B2 (ja) | 2009-03-24 | 2009-03-24 | 通知装置、通知システム、通知装置の制御方法、制御プログラム、及び該プログラムを記録したコンピュータ読み取り可能な記録媒体 |
| JP2009-072281 | 2009-03-24 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2010109836A1 true WO2010109836A1 (ja) | 2010-09-30 |
Family
ID=42780535
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2010/001996 WO2010109836A1 (ja) | 2009-03-24 | 2010-03-19 | 通知装置、通知システム、通知装置の制御方法、制御プログラム、及び該プログラムを記録したコンピュータ読み取り可能な記録媒体 |
Country Status (4)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US8700067B2 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JP5546784B2 (ja) |
| CN (1) | CN102362285A (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2010109836A1 (ja) |
Cited By (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN103179258A (zh) * | 2011-12-23 | 2013-06-26 | 联想(北京)有限公司 | 一种提示方法、装置及电子设备 |
| CN103327061A (zh) * | 2011-12-12 | 2013-09-25 | 株式会社电装 | 服务提供系统 |
| JP2019120670A (ja) * | 2018-01-11 | 2019-07-22 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | 行先情報検索装置、プログラム及び行先情報検索システム |
| WO2019240070A1 (ja) * | 2018-06-11 | 2019-12-19 | 本田技研工業株式会社 | 動作確認システム |
| WO2019240062A1 (ja) * | 2018-06-11 | 2019-12-19 | 本田技研工業株式会社 | 報知システム |
| JP2021071984A (ja) * | 2019-10-31 | 2021-05-06 | 株式会社ドワンゴ | 特典配信システム、特典配信方法及び特典配信プログラム |
Families Citing this family (36)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US10095375B2 (en) | 2008-07-09 | 2018-10-09 | Apple Inc. | Adding a contact to a home screen |
| US20190188122A1 (en) * | 2017-12-20 | 2019-06-20 | Rainforest Qa, Inc. | Electronic product testing systems |
| US8719188B2 (en) * | 2011-01-13 | 2014-05-06 | Qualcomm Incorporated | Determining a dynamic user profile indicative of a user behavior context with a mobile device |
| WO2012142443A2 (en) * | 2011-04-13 | 2012-10-18 | Douglas Krone | Systems and methods for facilitating the sale of goods and/or services via incentives |
| US20130061147A1 (en) * | 2011-09-07 | 2013-03-07 | Nokia Corporation | Method and apparatus for determining directions and navigating to geo-referenced places within images and videos |
| JP5825984B2 (ja) * | 2011-11-09 | 2015-12-02 | 謙二 田中 | クーポンの配布および広告の配信のための方法、システム、サーバ装置、端末装置およびプログラム |
| JP5893373B2 (ja) * | 2011-12-08 | 2016-03-23 | 富士通テン株式会社 | 表示装置、プログラム、および、表示方法 |
| JP5942510B2 (ja) * | 2012-03-19 | 2016-06-29 | 株式会社リコー | 通信システム、管理情報の通知方法及びプログラム |
| JP5189701B1 (ja) * | 2012-03-21 | 2013-04-24 | 春佳 西守 | ポイントシステム |
| JP5965708B2 (ja) * | 2012-04-19 | 2016-08-10 | オリンパス株式会社 | 無線通信装置、メモリ装置、無線通信システム、無線通信方法、およびプログラム |
| US8611930B2 (en) * | 2012-05-09 | 2013-12-17 | Apple Inc. | Selecting informative presentations based on navigation cues and user intent |
| CN102711041B (zh) * | 2012-06-05 | 2015-08-12 | 宇龙计算机通信科技(深圳)有限公司 | 移动终端导航的方法及其系统 |
| US10354004B2 (en) | 2012-06-07 | 2019-07-16 | Apple Inc. | Intelligent presentation of documents |
| US10878439B2 (en) | 2012-06-11 | 2020-12-29 | Retailmenot, Inc. | Mobile-offer creation |
| US20140164121A1 (en) * | 2012-12-07 | 2014-06-12 | Ebay Inc. | Coupon display system |
| KR102056485B1 (ko) | 2013-05-09 | 2019-12-17 | 삼성전자 주식회사 | 수신 메시지 특성에 따른 메시지 수신 알림 방법 및 장치 |
| JP5765383B2 (ja) * | 2013-08-20 | 2015-08-19 | カシオ計算機株式会社 | 配信管理装置、店舗端末装置及びプログラム |
| JP6160399B2 (ja) * | 2013-09-20 | 2017-07-12 | 富士通株式会社 | 行先情報提供プログラム、行先情報提供装置および行先情報提供方法 |
| JP6456623B2 (ja) * | 2013-09-30 | 2019-01-23 | 株式会社 ディー・エヌ・エー | ファン管理サーバ装置、ファン管理プログラム、及びファン管理方法 |
| WO2015099693A1 (en) * | 2013-12-23 | 2015-07-02 | Intel Corporation | Methods and apparatus for pairing items for security |
| JP6414473B2 (ja) | 2015-01-21 | 2018-10-31 | 株式会社デンソー | 車両用表示システム、携帯端末装置、車両用表示プログラム |
| CA3006903C (en) * | 2015-05-01 | 2020-08-18 | Martin Labrie | Location based information service application |
| KR101675364B1 (ko) * | 2015-05-21 | 2016-11-22 | 주식회사 엠투브 | 비콘을 이용한 차량용 obd 단말기와의 페어링 방법 및 차량용 obd 단말기 |
| US10929867B1 (en) * | 2015-06-05 | 2021-02-23 | Groupon, Inc. | Apparatus and method for utilizing immediate gratification promotions |
| US10977678B1 (en) | 2015-06-05 | 2021-04-13 | Groupon, Inc. | Apparatus and method for utilizing proximity density mapping to assist relevance determinations |
| US10521815B1 (en) * | 2015-06-05 | 2019-12-31 | Groupon, Inc. | Apparatus and method for utilizing immediate gratification promotions |
| JP6217698B2 (ja) * | 2015-06-11 | 2017-10-25 | カシオ計算機株式会社 | 配信管理装置、端末装置及びプログラム |
| US10462122B2 (en) | 2015-08-27 | 2019-10-29 | Pivotal Software, Inc. | Push notification aggregation |
| DE102016200239B4 (de) * | 2016-01-12 | 2024-06-06 | Siemens Healthineers Ag | Verfahren und System zur Lokalisierung von einer Bildaufnahmeeinrichtung zugeordneten Komponenten und/oder Personen in einer räumlichen Umgebung |
| US10395234B1 (en) * | 2016-03-15 | 2019-08-27 | Cray Pay Inc. | Mobile device enablement of universal prepaid cards |
| US10687167B1 (en) | 2016-03-31 | 2020-06-16 | Groupon, Inc. | Methods and systems for detecting aggregation events |
| JP2017199121A (ja) * | 2016-04-26 | 2017-11-02 | 株式会社Nttドコモ | 情報処理装置 |
| US10584974B2 (en) * | 2016-10-04 | 2020-03-10 | Bose Corporation | Platform for experiencing geotagged media content |
| US10445779B2 (en) * | 2017-04-26 | 2019-10-15 | International Business Machines Corporation | Boundary-specific electronic offers |
| US11042893B1 (en) * | 2018-11-05 | 2021-06-22 | Inmar Clearing, Inc. | System for processing a digital promotion based upon geographic destination determined from a ride-sharing application and related methods |
| JP6929477B1 (ja) * | 2021-01-18 | 2021-09-01 | 株式会社LogicLinks | 通知システム、通知方法及びプログラム |
Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2003044768A (ja) * | 2001-07-30 | 2003-02-14 | Sanyo Electric Co Ltd | 電子クーポン管理方法、電子クーポン管理サーバ、およびその方法を利用可能な移動通信端末 |
| JP2003157401A (ja) * | 2001-11-21 | 2003-05-30 | Ntt Docomo Inc | クーポン券配布システム、コンテンツサーバ、携帯情報端末およびクーポン券管理プログラム |
| JP2004062688A (ja) * | 2002-07-30 | 2004-02-26 | Alpine Electronics Inc | 位置情報に基づく情報提供システム、情報提供装置、情報取得装置 |
| JP2004279299A (ja) * | 2003-03-18 | 2004-10-07 | Pia Corp | 電子クーポン利用システムとそれを実現するためのコンピュータプログラムとその方法 |
| JP2007060368A (ja) * | 2005-08-25 | 2007-03-08 | Ntt Docomo Inc | コンテンツ送信装置、通信装置及びコンテンツ送信方法 |
| JP2008229092A (ja) * | 2007-03-22 | 2008-10-02 | Equos Research Co Ltd | 携帯情報端末機器 |
| JP2008244590A (ja) * | 2007-03-26 | 2008-10-09 | Nec Corp | 自動マナーモード付き携帯端末装置、その方法及びそのプログラム |
Family Cites Families (11)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2000112347A (ja) | 1998-10-08 | 2000-04-21 | Sharp Corp | 周辺エリア情報を報知する情報処理装置 |
| JP4066587B2 (ja) | 2000-02-28 | 2008-03-26 | 三菱電機株式会社 | 目的位置通知方法並びに目的位置通知システム、携帯型無線端末、位置情報送信端末 |
| US6680675B1 (en) | 2000-06-21 | 2004-01-20 | Fujitsu Limited | Interactive to-do list item notification system including GPS interface |
| JP2002044271A (ja) | 2000-07-24 | 2002-02-08 | Nec Telecom Syst Ltd | 自動手順実行機能付き携帯電話機及びその手順実行方法 |
| JP4656757B2 (ja) | 2001-05-23 | 2011-03-23 | シャープ株式会社 | 携帯情報端末及びナビゲーション方法 |
| JP2004094406A (ja) * | 2002-08-29 | 2004-03-25 | Toshiba Corp | クーポン配信システム及びクーポン配信方法 |
| AU2003283697A1 (en) * | 2002-12-16 | 2004-07-09 | Koninklijke Philips Electronics N.V. | Electronic shopping information system |
| JP2007265365A (ja) * | 2006-03-30 | 2007-10-11 | Nec Corp | クーポン配信システム、管理サーバ、クーポン配信方法及びプログラム |
| US7684790B2 (en) * | 2006-06-08 | 2010-03-23 | Cartmell Brian R | Advertising technique |
| US8229458B2 (en) * | 2007-04-08 | 2012-07-24 | Enhanced Geographic Llc | Systems and methods to determine the name of a location visited by a user of a wireless device |
| CN101373141B (zh) * | 2008-10-16 | 2012-01-04 | 深圳市凯立德科技股份有限公司 | 导航系统及在连续结点路段进行语音提示的导航方法 |
-
2009
- 2009-03-24 JP JP2009072281A patent/JP5546784B2/ja not_active Expired - Fee Related
-
2010
- 2010-03-19 US US13/257,898 patent/US8700067B2/en active Active
- 2010-03-19 CN CN2010800129934A patent/CN102362285A/zh active Pending
- 2010-03-19 WO PCT/JP2010/001996 patent/WO2010109836A1/ja active Application Filing
Patent Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2003044768A (ja) * | 2001-07-30 | 2003-02-14 | Sanyo Electric Co Ltd | 電子クーポン管理方法、電子クーポン管理サーバ、およびその方法を利用可能な移動通信端末 |
| JP2003157401A (ja) * | 2001-11-21 | 2003-05-30 | Ntt Docomo Inc | クーポン券配布システム、コンテンツサーバ、携帯情報端末およびクーポン券管理プログラム |
| JP2004062688A (ja) * | 2002-07-30 | 2004-02-26 | Alpine Electronics Inc | 位置情報に基づく情報提供システム、情報提供装置、情報取得装置 |
| JP2004279299A (ja) * | 2003-03-18 | 2004-10-07 | Pia Corp | 電子クーポン利用システムとそれを実現するためのコンピュータプログラムとその方法 |
| JP2007060368A (ja) * | 2005-08-25 | 2007-03-08 | Ntt Docomo Inc | コンテンツ送信装置、通信装置及びコンテンツ送信方法 |
| JP2008229092A (ja) * | 2007-03-22 | 2008-10-02 | Equos Research Co Ltd | 携帯情報端末機器 |
| JP2008244590A (ja) * | 2007-03-26 | 2008-10-09 | Nec Corp | 自動マナーモード付き携帯端末装置、その方法及びそのプログラム |
Cited By (11)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN103327061A (zh) * | 2011-12-12 | 2013-09-25 | 株式会社电装 | 服务提供系统 |
| CN103327061B (zh) * | 2011-12-12 | 2016-10-19 | 株式会社电装 | 服务提供系统 |
| CN103179258A (zh) * | 2011-12-23 | 2013-06-26 | 联想(北京)有限公司 | 一种提示方法、装置及电子设备 |
| JP2019120670A (ja) * | 2018-01-11 | 2019-07-22 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | 行先情報検索装置、プログラム及び行先情報検索システム |
| WO2019240070A1 (ja) * | 2018-06-11 | 2019-12-19 | 本田技研工業株式会社 | 動作確認システム |
| WO2019240062A1 (ja) * | 2018-06-11 | 2019-12-19 | 本田技研工業株式会社 | 報知システム |
| JPWO2019240062A1 (ja) * | 2018-06-11 | 2021-06-24 | 本田技研工業株式会社 | 報知システム |
| JPWO2019240070A1 (ja) * | 2018-06-11 | 2021-07-29 | 本田技研工業株式会社 | 動作確認システム |
| JP7424973B2 (ja) | 2018-06-11 | 2024-01-30 | 本田技研工業株式会社 | 報知システム |
| JP2021071984A (ja) * | 2019-10-31 | 2021-05-06 | 株式会社ドワンゴ | 特典配信システム、特典配信方法及び特典配信プログラム |
| WO2021085121A1 (ja) * | 2019-10-31 | 2021-05-06 | 株式会社ドワンゴ | 特典配信システム、特典配信方法及び特典配信プログラム |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| US20120088523A1 (en) | 2012-04-12 |
| CN102362285A (zh) | 2012-02-22 |
| US8700067B2 (en) | 2014-04-15 |
| JP5546784B2 (ja) | 2014-07-09 |
| JP2010224933A (ja) | 2010-10-07 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5546784B2 (ja) | 通知装置、通知システム、通知装置の制御方法、制御プログラム、及び該プログラムを記録したコンピュータ読み取り可能な記録媒体 | |
| US20180082335A1 (en) | Method of creating and joining social group, user device for executing the method, server, and storage medium | |
| KR100985838B1 (ko) | 휴대단말장치 및 기록미디어 | |
| TW200831862A (en) | Virtual location markers for mobile mapping | |
| JP6045354B2 (ja) | 案内システム、サーバ、端末装置、案内方法およびプログラム | |
| JP2004309368A (ja) | ナビゲーション装置、ナビゲーション方法、経路データ生成プログラム、および、ナビゲーションシステムにおけるサーバ装置 | |
| JP2001023076A (ja) | 歩行者ナビゲーション機能を有する携帯端末 | |
| JP2006012144A (ja) | 移動体端末 | |
| US9918193B1 (en) | Hybrid electronic navigation and invitation system | |
| US9958286B2 (en) | Image display system, mobile terminal, server, non-transitory physical computer-readable medium | |
| WO2005060279A1 (ja) | 情報配信システムおよび情報配信サーバならびに携帯端末および情報配信方法 | |
| KR20150018950A (ko) | 여행 일정을 관리하는 방법 및 시스템 | |
| JP5122646B2 (ja) | ナビゲーション装置及びナビゲーションシステム | |
| JP2012073061A (ja) | ナビゲーション装置、ナビゲーションプログラム、およびセンタシステム | |
| US20170371613A1 (en) | Client and program | |
| JP2004102175A (ja) | 記憶補助装置及びシステム | |
| JP2010063019A (ja) | 位置取得支援装置、通信端末、位置取得支援システム、位置取得支援装置の制御方法、通信端末の制御方法、位置取得支援プログラム、通信端末制御プログラム、及び該プログラムを記録したコンピュータ読み取り可能な記録媒体 | |
| KR102081728B1 (ko) | 가상 펜스 기반의 일정 서비스 제공 사용자 장치, 서비스 장치, 시스템 그리고 제공 방법 및 컴퓨터 프로그램이 기록된 기록매체 | |
| JP2013110600A (ja) | 携帯通信端末及び情報表示方法 | |
| JP2008171068A (ja) | 接近情報通知システム | |
| JP6313059B2 (ja) | 情報処理システム | |
| JP3952498B2 (ja) | 情報提供装置及びコンピュータ・プログラム | |
| KR101612933B1 (ko) | 사용자 단말 장치, 관리 서버 및 이들의 제어 방법 | |
| JP3904149B2 (ja) | 情報提供装置及び方法、並びにコンピュータ・プログラム | |
| JPWO2003069881A1 (ja) | 情報提供装置、提供情報提示装置、および情報提供方法 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 201080012993.4 Country of ref document: CN |
|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 10755639 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| DPE1 | Request for preliminary examination filed after expiration of 19th month from priority date (pct application filed from 20040101) | ||
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 13257898 Country of ref document: US |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 10755639 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |