JP6419184B2 - 改善されたSiGeファセットによる改善されたシリサイド形成 - Google Patents
改善されたSiGeファセットによる改善されたシリサイド形成 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- JP6419184B2 JP6419184B2 JP2016536476A JP2016536476A JP6419184B2 JP 6419184 B2 JP6419184 B2 JP 6419184B2 JP 2016536476 A JP2016536476 A JP 2016536476A JP 2016536476 A JP2016536476 A JP 2016536476A JP 6419184 B2 JP6419184 B2 JP 6419184B2
- Authority
- JP
- Japan
- Prior art keywords
- gate structure
- semiconductor material
- field oxide
- forming
- gate
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
- 229910000577 Silicon-germanium Inorganic materials 0.000 title claims description 89
- 229910021332 silicide Inorganic materials 0.000 title claims description 27
- FVBUAEGBCNSCDD-UHFFFAOYSA-N silicide(4-) Chemical compound [Si-4] FVBUAEGBCNSCDD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 title claims description 27
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 title description 3
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 claims description 79
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 claims description 69
- 238000000407 epitaxy Methods 0.000 claims description 47
- 125000006850 spacer group Chemical group 0.000 claims description 42
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 claims description 36
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 29
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 claims description 29
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 claims description 29
- LEVVHYCKPQWKOP-UHFFFAOYSA-N [Si].[Ge] Chemical compound [Si].[Ge] LEVVHYCKPQWKOP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 26
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 claims description 12
- 229910021334 nickel silicide Inorganic materials 0.000 claims 2
- RUFLMLWJRZAWLJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N nickel silicide Chemical compound [Ni]=[Si]=[Ni] RUFLMLWJRZAWLJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims 2
- 229910052732 germanium Inorganic materials 0.000 claims 1
- GNPVGFCGXDBREM-UHFFFAOYSA-N germanium atom Chemical compound [Ge] GNPVGFCGXDBREM-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims 1
- VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicium dioxide Chemical compound O=[Si]=O VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 16
- 229910052581 Si3N4 Inorganic materials 0.000 description 8
- 239000000377 silicon dioxide Substances 0.000 description 8
- 235000012239 silicon dioxide Nutrition 0.000 description 8
- HQVNEWCFYHHQES-UHFFFAOYSA-N silicon nitride Chemical compound N12[Si]34N5[Si]62N3[Si]51N64 HQVNEWCFYHHQES-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 8
- 239000003989 dielectric material Substances 0.000 description 7
- 229910021420 polycrystalline silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 6
- 238000005530 etching Methods 0.000 description 5
- 229920002120 photoresistant polymer Polymers 0.000 description 4
- 229920005591 polysilicon Polymers 0.000 description 4
- 238000004518 low pressure chemical vapour deposition Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000000059 patterning Methods 0.000 description 3
- MHAJPDPJQMAIIY-UHFFFAOYSA-N Hydrogen peroxide Chemical compound OO MHAJPDPJQMAIIY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- PXHVJJICTQNCMI-UHFFFAOYSA-N Nickel Chemical compound [Ni] PXHVJJICTQNCMI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- NBIIXXVUZAFLBC-UHFFFAOYSA-N Phosphoric acid Chemical compound OP(O)(O)=O NBIIXXVUZAFLBC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicon Chemical compound [Si] XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- QAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-N Sulfuric acid Chemical compound OS(O)(=O)=O QAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229910000449 hafnium oxide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- WIHZLLGSGQNAGK-UHFFFAOYSA-N hafnium(4+);oxygen(2-) Chemical compound [O-2].[O-2].[Hf+4] WIHZLLGSGQNAGK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 238000002955 isolation Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229910021421 monocrystalline silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- RVTZCBVAJQQJTK-UHFFFAOYSA-N oxygen(2-);zirconium(4+) Chemical compound [O-2].[O-2].[Zr+4] RVTZCBVAJQQJTK-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 238000000623 plasma-assisted chemical vapour deposition Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229910052710 silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000010703 silicon Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910010271 silicon carbide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 229910001928 zirconium oxide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- ZOXJGFHDIHLPTG-UHFFFAOYSA-N Boron Chemical compound [B] ZOXJGFHDIHLPTG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- RTAQQCXQSZGOHL-UHFFFAOYSA-N Titanium Chemical compound [Ti] RTAQQCXQSZGOHL-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- NRTOMJZYCJJWKI-UHFFFAOYSA-N Titanium nitride Chemical compound [Ti]#N NRTOMJZYCJJWKI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910000147 aluminium phosphate Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910003481 amorphous carbon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 238000004380 ashing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910052796 boron Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000013078 crystal Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000000151 deposition Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000008021 deposition Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005286 illumination Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000012212 insulator Substances 0.000 description 1
- 150000002500 ions Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 229910044991 metal oxide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 150000004706 metal oxides Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052759 nickel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 230000003647 oxidation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000007254 oxidation reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000001590 oxidative effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- BPUBBGLMJRNUCC-UHFFFAOYSA-N oxygen(2-);tantalum(5+) Chemical compound [O-2].[O-2].[O-2].[O-2].[O-2].[Ta+5].[Ta+5] BPUBBGLMJRNUCC-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000005360 phosphosilicate glass Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000000206 photolithography Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000001020 plasma etching Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000005498 polishing Methods 0.000 description 1
- HBMJWWWQQXIZIP-UHFFFAOYSA-N silicon carbide Chemical compound [Si+]#[C-] HBMJWWWQQXIZIP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- -1 silicon carbide nitride Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 239000000126 substance Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910001936 tantalum oxide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000010936 titanium Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910052719 titanium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- WFKWXMTUELFFGS-UHFFFAOYSA-N tungsten Chemical compound [W] WFKWXMTUELFFGS-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052721 tungsten Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000010937 tungsten Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000001039 wet etching Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L27/00—Devices consisting of a plurality of semiconductor or other solid-state components formed in or on a common substrate
- H01L27/02—Devices consisting of a plurality of semiconductor or other solid-state components formed in or on a common substrate including semiconductor components specially adapted for rectifying, oscillating, amplifying or switching and having potential barriers; including integrated passive circuit elements having potential barriers
- H01L27/04—Devices consisting of a plurality of semiconductor or other solid-state components formed in or on a common substrate including semiconductor components specially adapted for rectifying, oscillating, amplifying or switching and having potential barriers; including integrated passive circuit elements having potential barriers the substrate being a semiconductor body
- H01L27/08—Devices consisting of a plurality of semiconductor or other solid-state components formed in or on a common substrate including semiconductor components specially adapted for rectifying, oscillating, amplifying or switching and having potential barriers; including integrated passive circuit elements having potential barriers the substrate being a semiconductor body including only semiconductor components of a single kind
- H01L27/085—Devices consisting of a plurality of semiconductor or other solid-state components formed in or on a common substrate including semiconductor components specially adapted for rectifying, oscillating, amplifying or switching and having potential barriers; including integrated passive circuit elements having potential barriers the substrate being a semiconductor body including only semiconductor components of a single kind including field-effect components only
- H01L27/088—Devices consisting of a plurality of semiconductor or other solid-state components formed in or on a common substrate including semiconductor components specially adapted for rectifying, oscillating, amplifying or switching and having potential barriers; including integrated passive circuit elements having potential barriers the substrate being a semiconductor body including only semiconductor components of a single kind including field-effect components only the components being field-effect transistors with insulated gate
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/40—Electrodes ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/43—Electrodes ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by the materials of which they are formed
- H01L29/45—Ohmic electrodes
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/04—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof the devices having potential barriers, e.g. a PN junction, depletion layer or carrier concentration layer
- H01L21/18—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof the devices having potential barriers, e.g. a PN junction, depletion layer or carrier concentration layer the devices having semiconductor bodies comprising elements of Group IV of the Periodic Table or AIIIBV compounds with or without impurities, e.g. doping materials
- H01L21/28—Manufacture of electrodes on semiconductor bodies using processes or apparatus not provided for in groups H01L21/20 - H01L21/268
- H01L21/28008—Making conductor-insulator-semiconductor electrodes
- H01L21/28017—Making conductor-insulator-semiconductor electrodes the insulator being formed after the semiconductor body, the semiconductor being silicon
- H01L21/28026—Making conductor-insulator-semiconductor electrodes the insulator being formed after the semiconductor body, the semiconductor being silicon characterised by the conductor
- H01L21/28123—Lithography-related aspects, e.g. sub-lithography lengths; Isolation-related aspects, e.g. to solve problems arising at the crossing with the side of the device isolation; Planarisation aspects
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/70—Manufacture or treatment of devices consisting of a plurality of solid state components formed in or on a common substrate or of parts thereof; Manufacture of integrated circuit devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/77—Manufacture or treatment of devices consisting of a plurality of solid state components or integrated circuits formed in, or on, a common substrate
- H01L21/78—Manufacture or treatment of devices consisting of a plurality of solid state components or integrated circuits formed in, or on, a common substrate with subsequent division of the substrate into plural individual devices
- H01L21/82—Manufacture or treatment of devices consisting of a plurality of solid state components or integrated circuits formed in, or on, a common substrate with subsequent division of the substrate into plural individual devices to produce devices, e.g. integrated circuits, each consisting of a plurality of components
- H01L21/822—Manufacture or treatment of devices consisting of a plurality of solid state components or integrated circuits formed in, or on, a common substrate with subsequent division of the substrate into plural individual devices to produce devices, e.g. integrated circuits, each consisting of a plurality of components the substrate being a semiconductor, using silicon technology
- H01L21/8232—Field-effect technology
- H01L21/8234—MIS technology, i.e. integration processes of field effect transistors of the conductor-insulator-semiconductor type
- H01L21/823412—MIS technology, i.e. integration processes of field effect transistors of the conductor-insulator-semiconductor type with a particular manufacturing method of the channel structures, e.g. channel implants, halo or pocket implants, or channel materials
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/70—Manufacture or treatment of devices consisting of a plurality of solid state components formed in or on a common substrate or of parts thereof; Manufacture of integrated circuit devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/77—Manufacture or treatment of devices consisting of a plurality of solid state components or integrated circuits formed in, or on, a common substrate
- H01L21/78—Manufacture or treatment of devices consisting of a plurality of solid state components or integrated circuits formed in, or on, a common substrate with subsequent division of the substrate into plural individual devices
- H01L21/82—Manufacture or treatment of devices consisting of a plurality of solid state components or integrated circuits formed in, or on, a common substrate with subsequent division of the substrate into plural individual devices to produce devices, e.g. integrated circuits, each consisting of a plurality of components
- H01L21/822—Manufacture or treatment of devices consisting of a plurality of solid state components or integrated circuits formed in, or on, a common substrate with subsequent division of the substrate into plural individual devices to produce devices, e.g. integrated circuits, each consisting of a plurality of components the substrate being a semiconductor, using silicon technology
- H01L21/8232—Field-effect technology
- H01L21/8234—MIS technology, i.e. integration processes of field effect transistors of the conductor-insulator-semiconductor type
- H01L21/823418—MIS technology, i.e. integration processes of field effect transistors of the conductor-insulator-semiconductor type with a particular manufacturing method of the source or drain structures, e.g. specific source or drain implants or silicided source or drain structures or raised source or drain structures
- H01L21/823425—MIS technology, i.e. integration processes of field effect transistors of the conductor-insulator-semiconductor type with a particular manufacturing method of the source or drain structures, e.g. specific source or drain implants or silicided source or drain structures or raised source or drain structures manufacturing common source or drain regions between a plurality of conductor-insulator-semiconductor structures
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/70—Manufacture or treatment of devices consisting of a plurality of solid state components formed in or on a common substrate or of parts thereof; Manufacture of integrated circuit devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/77—Manufacture or treatment of devices consisting of a plurality of solid state components or integrated circuits formed in, or on, a common substrate
- H01L21/78—Manufacture or treatment of devices consisting of a plurality of solid state components or integrated circuits formed in, or on, a common substrate with subsequent division of the substrate into plural individual devices
- H01L21/82—Manufacture or treatment of devices consisting of a plurality of solid state components or integrated circuits formed in, or on, a common substrate with subsequent division of the substrate into plural individual devices to produce devices, e.g. integrated circuits, each consisting of a plurality of components
- H01L21/822—Manufacture or treatment of devices consisting of a plurality of solid state components or integrated circuits formed in, or on, a common substrate with subsequent division of the substrate into plural individual devices to produce devices, e.g. integrated circuits, each consisting of a plurality of components the substrate being a semiconductor, using silicon technology
- H01L21/8232—Field-effect technology
- H01L21/8234—MIS technology, i.e. integration processes of field effect transistors of the conductor-insulator-semiconductor type
- H01L21/823437—MIS technology, i.e. integration processes of field effect transistors of the conductor-insulator-semiconductor type with a particular manufacturing method of the gate conductors, e.g. particular materials, shapes
- H01L21/823443—MIS technology, i.e. integration processes of field effect transistors of the conductor-insulator-semiconductor type with a particular manufacturing method of the gate conductors, e.g. particular materials, shapes silicided or salicided gate conductors
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L27/00—Devices consisting of a plurality of semiconductor or other solid-state components formed in or on a common substrate
- H01L27/02—Devices consisting of a plurality of semiconductor or other solid-state components formed in or on a common substrate including semiconductor components specially adapted for rectifying, oscillating, amplifying or switching and having potential barriers; including integrated passive circuit elements having potential barriers
- H01L27/0203—Particular design considerations for integrated circuits
- H01L27/0207—Geometrical layout of the components, e.g. computer aided design; custom LSI, semi-custom LSI, standard cell technique
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/02—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/06—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions
- H01L29/08—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape; characterised by the shapes, relative sizes, or dispositions of the semiconductor regions ; characterised by the concentration or distribution of impurities within semiconductor regions with semiconductor regions connected to an electrode carrying current to be rectified, amplified or switched and such electrode being part of a semiconductor device which comprises three or more electrodes
- H01L29/0843—Source or drain regions of field-effect devices
- H01L29/0847—Source or drain regions of field-effect devices of field-effect transistors with insulated gate
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/02—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/12—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by the materials of which they are formed
- H01L29/16—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by the materials of which they are formed including, apart from doping materials or other impurities, only elements of Group IV of the Periodic Table
- H01L29/161—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by the materials of which they are formed including, apart from doping materials or other impurities, only elements of Group IV of the Periodic Table including two or more of the elements provided for in group H01L29/16, e.g. alloys
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/02—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/12—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by the materials of which they are formed
- H01L29/16—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by the materials of which they are formed including, apart from doping materials or other impurities, only elements of Group IV of the Periodic Table
- H01L29/161—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by the materials of which they are formed including, apart from doping materials or other impurities, only elements of Group IV of the Periodic Table including two or more of the elements provided for in group H01L29/16, e.g. alloys
- H01L29/165—Semiconductor bodies ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by the materials of which they are formed including, apart from doping materials or other impurities, only elements of Group IV of the Periodic Table including two or more of the elements provided for in group H01L29/16, e.g. alloys in different semiconductor regions, e.g. heterojunctions
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/40—Electrodes ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/41—Electrodes ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape, relative sizes or dispositions
- H01L29/417—Electrodes ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by their shape, relative sizes or dispositions carrying the current to be rectified, amplified or switched
- H01L29/41725—Source or drain electrodes for field effect devices
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/40—Electrodes ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/43—Electrodes ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor characterised by the materials of which they are formed
- H01L29/45—Ohmic electrodes
- H01L29/456—Ohmic electrodes on silicon
- H01L29/458—Ohmic electrodes on silicon for thin film silicon, e.g. source or drain electrode
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/66—Types of semiconductor device ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/66007—Multistep manufacturing processes
- H01L29/66075—Multistep manufacturing processes of devices having semiconductor bodies comprising group 14 or group 13/15 materials
- H01L29/66227—Multistep manufacturing processes of devices having semiconductor bodies comprising group 14 or group 13/15 materials the devices being controllable only by the electric current supplied or the electric potential applied, to an electrode which does not carry the current to be rectified, amplified or switched, e.g. three-terminal devices
- H01L29/66409—Unipolar field-effect transistors
- H01L29/66477—Unipolar field-effect transistors with an insulated gate, i.e. MISFET
- H01L29/665—Unipolar field-effect transistors with an insulated gate, i.e. MISFET using self aligned silicidation, i.e. salicide
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/66—Types of semiconductor device ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/66007—Multistep manufacturing processes
- H01L29/66075—Multistep manufacturing processes of devices having semiconductor bodies comprising group 14 or group 13/15 materials
- H01L29/66227—Multistep manufacturing processes of devices having semiconductor bodies comprising group 14 or group 13/15 materials the devices being controllable only by the electric current supplied or the electric potential applied, to an electrode which does not carry the current to be rectified, amplified or switched, e.g. three-terminal devices
- H01L29/66409—Unipolar field-effect transistors
- H01L29/66477—Unipolar field-effect transistors with an insulated gate, i.e. MISFET
- H01L29/66568—Lateral single gate silicon transistors
- H01L29/66636—Lateral single gate silicon transistors with source or drain recessed by etching or first recessed by etching and then refilled
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L29/00—Semiconductor devices specially adapted for rectifying, amplifying, oscillating or switching and having potential barriers; Capacitors or resistors having potential barriers, e.g. a PN-junction depletion layer or carrier concentration layer; Details of semiconductor bodies or of electrodes thereof ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/66—Types of semiconductor device ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor
- H01L29/68—Types of semiconductor device ; Multistep manufacturing processes therefor controllable by only the electric current supplied, or only the electric potential applied, to an electrode which does not carry the current to be rectified, amplified or switched
- H01L29/76—Unipolar devices, e.g. field effect transistors
- H01L29/772—Field effect transistors
- H01L29/78—Field effect transistors with field effect produced by an insulated gate
- H01L29/7842—Field effect transistors with field effect produced by an insulated gate means for exerting mechanical stress on the crystal lattice of the channel region, e.g. using a flexible substrate
- H01L29/7848—Field effect transistors with field effect produced by an insulated gate means for exerting mechanical stress on the crystal lattice of the channel region, e.g. using a flexible substrate the means being located in the source/drain region, e.g. SiGe source and drain
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Power Engineering (AREA)
- Microelectronics & Electronic Packaging (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Condensed Matter Physics & Semiconductors (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Computer Hardware Design (AREA)
- Ceramic Engineering (AREA)
- Manufacturing & Machinery (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Crystallography & Structural Chemistry (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Insulated Gate Type Field-Effect Transistor (AREA)
- Metal-Oxide And Bipolar Metal-Oxide Semiconductor Integrated Circuits (AREA)
- Electrodes Of Semiconductors (AREA)
- Thin Film Transistor (AREA)
Description
Claims (20)
- 集積回路であって、
基板であって、前記基板の頂部表面まで延在する半導体材料を含む、前記基板と、
前記基板内に配置されるフィールド酸化物と、
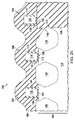
前記フィールド酸化物に近接する前記半導体材料の上の第1のゲート構造であって、前記半導体材料の上のゲート誘電体層と、前記第1のゲート構造の前記ゲート誘電体層上のゲートとを含む、前記第1のゲート構造と、
前記フィールド酸化物の上の第2のゲート構造であって、前記第2のゲート構造のゲートが前記第1のゲート構造に面する前記フィールド酸化物の側壁に重ならないように、前記第2のゲート構造のゲート誘電体層上の前記ゲートを含む、前記第2のゲート構造と、
前記第1のゲート構造と前記第2のゲート構造との間の前記基板におけるシリコンゲルマニウムソース/ドレイン領域であって、前記シリコンゲルマニウムソース/ドレイン領域が、前記半導体材料の頂部表面よりも下であって前記半導体材料の頂部表面から前記シリコンゲルマニウムソース/ドレイン領域の深さの3分の1よりも延在しない点で前記フィールド酸化物に接する頂部端を備えるファセットを有する、前記シリコンゲルマニウムソース/ドレイン領域と、
前記シリコンゲルマニウムソース/ドレイン領域上まで延在する、前記第2のゲート構造の前記ゲートの横方向表面の近隣の誘電体スペーサと、
前記シリコンゲルマニウムソース/ドレイン領域のファセット上の金属シリサイドと、
前記第1のゲート構造と前記第2のゲート構造との間のコンタクトであって、前記コンタクトの底部の少なくとも半分が、前記シリコンゲルマニウムソース/ドレイン領域のファセット上の前記金属シリサイドに直接的に接するようになっている、前記コンタクトと、
を含む、集積回路。 - 請求項1に記載の集積回路であって、
前記第1のゲート構造の中心から前記第2のゲート構造の中心までの横方向距離が、前記集積回路を製造するために用いられる設計ルールに従ったコンタクトされるゲート構造のための最小距離である、集積回路。 - 請求項1に記載の集積回路であって、
前記第1のゲート構造の中心から前記第2のゲート構造の中心までの横方向距離が150ナノメートル未満である、集積回路。 - 請求項1に記載の集積回路であって、
前記コンタクトの前記底部が幅40ナノメートル未満である、集積回路。 - 請求項1に記載の集積回路であって、
前記金属シリサイドがニッケルシリサイドを含む、集積回路。 - 請求項1に記載の集積回路であって、
前記シリコンゲルマニウムソース/ドレイン領域の深さが、50ナノメートル〜80ナノメートルである、集積回路。 - 請求項1に記載の集積回路であって、
前記金属シリサイドが実質的に平坦である、集積回路。 - 請求項1に記載の集積回路であって、
前記フィールド酸化物の頂部表面が、前記第1のゲート構造の下の前記半導体材料の頂部表面の15ナノメートル内の共面である、集積回路。 - 集積回路を形成する方法であって、
基板を提供することであって、前記基板が、前記基板の頂部表面まで延在する半導体材料を含む、前記提供することと、
前記基板にフィールド酸化物を形成することと、
前記フィールド酸化物に近接して前記半導体材料の上に第1のゲート構造のゲートを形成することと、
前記フィールド酸化物の近隣の前記半導体材料に重ならないように前記フィールド酸化物の上に第2のゲート構造のゲートを形成することと、
前記第1のゲート構造と前記第2のゲート構造との間の前記半導体材料の一部を露出させるように前記第2のゲート構造の上にエピタキシーハードマスクを形成することであって、前記エピタキシーハードマスクが前記第1のゲート構造と前記第2のゲート構造との間の前記フィールド酸化物の近隣の前記半導体材料の頂部表面に重なる、前記エピタキシーハードマスクを形成することと、
ソース/ドレインキャビティを形成するように前記エピタキシーハードマスクによって露出された前記第1のゲート構造と前記第2のゲート構造との間のソース/ドレイン領域における前記半導体材料を取り除くことと、
前記ソース/ドレインキャビティにおいてシリコンゲルマニウムソース/ドレイン領域を形成することであって、前記シリコンゲルマニウムソース/ドレイン領域が、前記半導体材料の頂部表面よりも下であって前記半導体材料の頂部表面から前記シリコンゲルマニウムソース/ドレイン領域の深さの3分の1よりも延在しない点で前記フィールド酸化物の側壁に接する頂部端を備えるファセットを有するように、前記シリコンゲルマニウムソース/ドレイン領域を形成することと、
誘電体スペーサが前記シリコンゲルマニウムソース/ドレイン領域上まで延在するように、前記第2のゲート構造の前記ゲートの横方向表面の近隣に前記誘電体スペーサを形成することと、
前記シリコンゲルマニウムソース/ドレイン領域のファセット上に金属シリサイドを形成することと、
前記第1のゲート構造と前記第2のゲート構造との間にコンタクトを形成することであって、前記コンタクトの底部の少なくとも半分が前記シリコンゲルマニウムソース/ドレイン領域のファセット上の前記金属シリサイドに直接的に接する、前記コンタクトを形成することと、
を含む、方法。 - 集積回路を形成する方法であって、
基板を提供することであって、前記基板が、前記基板の頂部表面まで延在する半導体材料を含む、前記提供することと、
前記基板にフィールド酸化物を形成することと、
前記フィールド酸化物に近接して前記半導体材料の上に第1のゲート構造のゲートを形成することと、
前記フィールド酸化物の近隣の前記半導体材料に重ならないように前記フィールド酸化物の上に第2のゲート構造のゲートを形成することと、
前記第1のゲート構造と前記第2のゲート構造との間の前記半導体材料の一部を露出させるように前記第2のゲート構造の上にエピタキシーハードマスクを形成することであって、前記エピタキシーハードマスクが前記第1のゲート構造と前記第2のゲート構造との間の前記フィールド酸化物の近隣の前記半導体材料の頂部表面に重なる、前記エピタキシーハードマスクを形成することと、
ソース/ドレインキャビティを形成するように前記エピタキシーハードマスクによって露出された前記第1のゲート構造と前記第2のゲート構造との間のソース/ドレイン領域における前記半導体材料を取り除くことと、
前記ソース/ドレインキャビティにおいてシリコンゲルマニウムソース/ドレイン領域を形成することであって、前記フィールド酸化物の側壁における前記シリコンゲルマニウムソース/ドレイン領域の頂部端が前記半導体材料の頂部表面から前記シリコンゲルマニウムソース/ドレイン領域の深さの3分の1より多く延在しない、前記シリコンゲルマニウムソース/ドレイン領域を形成することと、
誘電体スペーサが前記シリコンゲルマニウムソース/ドレイン領域上まで延在するように、前記第2のゲート構造の前記ゲートの横方向表面の近隣に前記誘電体スペーサを形成することと、
前記シリコンゲルマニウムソース/ドレイン領域上に金属シリサイドを形成することと、
前記第1のゲート構造と前記第2のゲート構造との間にコンタクトを形成することであって、前記コンタクトの底部の少なくとも半分が前記シリコンゲルマニウムソース/ドレイン領域上の前記金属シリサイドに直接的に接する、前記コンタクトを形成することと、
を含み、
前記エピタキシーハードマスクを形成することが、
前記第1のゲート構造と前記第2のゲート構造と前記半導体材料と前記フィールド酸化物との上にエピタキシーハードマスク層を形成することと、
前記第2のゲート構造を覆い、前記第1のゲート構造と前記第2のゲート構造との間の前記エピタキシーハードマスク層の一部を露出させるように、前記エピタキシーハードマスク層の上にエピタキシーマスクを形成することであって、前記エピタキシーマスクが前記第1のゲート構造と前記第2のゲート構造との間の前記フィールド酸化物の近隣の前記半導体材料の頂部表面に重なる、前記エピタキシーマスクを形成することと、
前記エピタキシーハードマスクを形成するように前記エピタキシーマスクによって露出された前記エピタキシーハードマスク層を取り除くことと、
を含む、方法。 - 請求項9又は10に記載の方法であって、
前記ソース/ドレイン領域における前記半導体材料を取り除くことが、前記ソース/ドレインキャビティにおける前記フィールド酸化物の前記側壁の一部が露出されるように実施される、方法。 - 請求項9又は10に記載の方法であって、
前記ソース/ドレイン領域における前記半導体材料を取り除くことが、前記半導体材料が前記エピタキシーハードマスクの直下の前記フィールド酸化物の前記側壁上に残るように実施される、方法。 - 請求項9又は10に記載の方法であって、
前記シリコンゲルマニウムソース/ドレイン領域を形成することが、エピタキシャルプロセスによって実施される、方法。 - 請求項9又は10に記載の方法であって、
前記第1のゲート構造の中心から前記第2のゲート構造の中心までの横方向距離が、前記集積回路を製造するために用いられる設計ルールに従ったコンタクトされるゲート構造のための最小距離である、方法。 - 請求項9又は10に記載の方法であって、
前記第1のゲート構造の中心から前記第2のゲート構造の中心までの横方向距離が150ナノメートル未満である、方法。 - 請求項9又は10に記載の方法であって、
前記コンタクトの前記底部が幅40ナノメートル未満である、方法。 - 請求項9又は10に記載の方法であって、
前記金属シリサイドがニッケルシリサイドを含む、方法。 - 請求項9又は10に記載の方法であって、
前記シリコンゲルマニウムソース/ドレイン領域の深さが50ナノメートル〜80ナノメートルである、方法。 - 請求項9又は10に記載の方法であって、
前記金属シリサイドが実質的に平坦である、方法。 - 請求項9又は10に記載の方法であって、
前記フィールド酸化物の頂部表面が、前記第1のゲート構造の下の前記半導体材料の前記頂部表面の15ナノメートル内の共面である、方法。
Applications Claiming Priority (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US13/972,973 US9093298B2 (en) | 2013-08-22 | 2013-08-22 | Silicide formation due to improved SiGe faceting |
| US13/972,973 | 2013-08-22 | ||
| PCT/US2014/052253 WO2015027141A1 (en) | 2013-08-22 | 2014-08-22 | Improved silicide formation by improved sige faceting |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| JP2016532296A JP2016532296A (ja) | 2016-10-13 |
| JP2016532296A5 JP2016532296A5 (ja) | 2017-09-21 |
| JP6419184B2 true JP6419184B2 (ja) | 2018-11-07 |
Family
ID=52479609
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2016536476A Active JP6419184B2 (ja) | 2013-08-22 | 2014-08-22 | 改善されたSiGeファセットによる改善されたシリサイド形成 |
Country Status (5)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (3) | US9093298B2 (ja) |
| EP (1) | EP3036769B1 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JP6419184B2 (ja) |
| CN (1) | CN105453264B (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2015027141A1 (ja) |
Families Citing this family (19)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US9847225B2 (en) * | 2011-11-15 | 2017-12-19 | Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company, Ltd. | Semiconductor device and method of manufacturing the same |
| US9093298B2 (en) * | 2013-08-22 | 2015-07-28 | Texas Instruments Incorporated | Silicide formation due to improved SiGe faceting |
| US9721947B2 (en) * | 2014-02-12 | 2017-08-01 | Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company, Ltd. | Semiconductor device and method of manufacturing |
| KR102200922B1 (ko) * | 2014-07-17 | 2021-01-11 | 삼성전자주식회사 | 절연 패턴을 갖는 반도체 소자 및 그 형성 방법 |
| US9385197B2 (en) | 2014-08-29 | 2016-07-05 | Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Co., Ltd | Semiconductor structure with contact over source/drain structure and method for forming the same |
| US9324820B1 (en) * | 2014-10-28 | 2016-04-26 | Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Co., Ltd | Method for forming semiconductor structure with metallic layer over source/drain structure |
| US10026837B2 (en) * | 2015-09-03 | 2018-07-17 | Texas Instruments Incorporated | Embedded SiGe process for multi-threshold PMOS transistors |
| US20170141228A1 (en) * | 2015-11-16 | 2017-05-18 | Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Co., Ltd. | Field effect transistor and manufacturing method thereof |
| US10141443B2 (en) * | 2016-03-24 | 2018-11-27 | Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Co., Ltd. | Semiconductor devices FinFET devices with optimized strained-sourece-drain recess profiles and methods of forming the same |
| US10177241B2 (en) | 2016-10-28 | 2019-01-08 | Globalfoundries Inc. | Methods of forming a gate contact for a transistor above the active region and an air gap adjacent the gate of the transistor |
| US9899321B1 (en) * | 2016-12-09 | 2018-02-20 | Globalfoundries Inc. | Methods of forming a gate contact for a semiconductor device above the active region |
| US10297675B1 (en) * | 2017-10-27 | 2019-05-21 | Globalfoundries Inc. | Dual-curvature cavity for epitaxial semiconductor growth |
| US10714334B2 (en) | 2017-11-28 | 2020-07-14 | Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Co., Ltd. | Conductive feature formation and structure |
| US10796968B2 (en) * | 2017-11-30 | 2020-10-06 | Intel Corporation | Dual metal silicide structures for advanced integrated circuit structure fabrication |
| US11881520B2 (en) * | 2017-11-30 | 2024-01-23 | Intel Corporation | Fin patterning for advanced integrated circuit structure fabrication |
| US10580875B2 (en) * | 2018-01-17 | 2020-03-03 | Globalfoundries Inc. | Middle of line structures |
| US10121517B1 (en) | 2018-03-16 | 2018-11-06 | Videolicious, Inc. | Systems and methods for generating audio or video presentation heat maps |
| US10388770B1 (en) | 2018-03-19 | 2019-08-20 | Globalfoundries Inc. | Gate and source/drain contact structures positioned above an active region of a transistor device |
| CN110634743B (zh) * | 2018-06-25 | 2023-06-09 | 中芯国际集成电路制造(上海)有限公司 | 半导体结构及其形成方法 |
Family Cites Families (26)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5571733A (en) * | 1995-05-12 | 1996-11-05 | Micron Technology, Inc. | Method of forming CMOS integrated circuitry |
| US6107157A (en) * | 1998-02-27 | 2000-08-22 | Micron Technology, Inc. | Method and apparatus for trench isolation process with pad gate and trench edge spacer elimination |
| US6448129B1 (en) * | 2000-01-24 | 2002-09-10 | Micron Technology, Inc. | Applying epitaxial silicon in disposable spacer flow |
| CN100499045C (zh) * | 2005-09-15 | 2009-06-10 | 中芯国际集成电路制造(上海)有限公司 | 形成硅锗源漏结构的集成工艺方法 |
| JP5380827B2 (ja) * | 2006-12-11 | 2014-01-08 | ソニー株式会社 | 半導体装置の製造方法 |
| CN101330006A (zh) * | 2007-06-18 | 2008-12-24 | 中芯国际集成电路制造(上海)有限公司 | 栅极结构及其制造方法 |
| KR101409374B1 (ko) * | 2008-04-10 | 2014-06-19 | 삼성전자 주식회사 | 반도체 집적 회로 장치의 제조 방법 및 그에 의해 제조된반도체 집적 회로 장치 |
| US7838366B2 (en) * | 2008-04-11 | 2010-11-23 | United Microelectronics Corp. | Method for fabricating a metal gate structure |
| KR101050405B1 (ko) * | 2009-07-03 | 2011-07-19 | 주식회사 하이닉스반도체 | 스트레인드채널을 갖는 반도체장치 제조 방법 |
| DE102009039522B4 (de) * | 2009-08-31 | 2015-08-13 | GLOBALFOUNDRIES Dresden Module One Ltd. Liability Company & Co. KG | Verfahren zur Herstellung eines Halbleiterbauelements mit vergrabener Ätzstoppschicht in Grabenisolationsstrukturen für eine bessere Oberflächenebenheit in dicht gepackten Halbleiterbauelementen |
| US8455859B2 (en) * | 2009-10-01 | 2013-06-04 | Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company, Ltd. | Strained structure of semiconductor device |
| US8377784B2 (en) * | 2010-04-22 | 2013-02-19 | Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company, Ltd. | Method for fabricating a semiconductor device |
| US9064688B2 (en) * | 2010-05-20 | 2015-06-23 | Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company, Ltd. | Performing enhanced cleaning in the formation of MOS devices |
| US8236659B2 (en) * | 2010-06-16 | 2012-08-07 | Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company, Ltd. | Source and drain feature profile for improving device performance and method of manufacturing same |
| US8680625B2 (en) * | 2010-10-15 | 2014-03-25 | Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company, Ltd. | Facet-free semiconductor device |
| CN102456739A (zh) * | 2010-10-28 | 2012-05-16 | 中国科学院微电子研究所 | 半导体结构及其形成方法 |
| US8435848B2 (en) * | 2010-10-28 | 2013-05-07 | Texas Instruments Incorporated | PMOS SiGe-last integration process |
| US8455930B2 (en) * | 2011-01-05 | 2013-06-04 | Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company, Ltd. | Strained semiconductor device with facets |
| US8643069B2 (en) * | 2011-07-12 | 2014-02-04 | United Microelectronics Corp. | Semiconductor device having metal gate and manufacturing method thereof |
| US8835267B2 (en) * | 2011-09-29 | 2014-09-16 | Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company, Ltd. | Semiconductor device and fabrication method thereof |
| US8927374B2 (en) * | 2011-10-04 | 2015-01-06 | Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company, Ltd. | Semiconductor device and fabrication method thereof |
| KR20130045716A (ko) * | 2011-10-26 | 2013-05-06 | 삼성전자주식회사 | 반도체 소자 및 그 제조 방법 |
| US8735255B2 (en) * | 2012-05-01 | 2014-05-27 | Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company, Ltd. | Method of manufacturing semiconductor device |
| US9219129B2 (en) * | 2012-05-10 | 2015-12-22 | International Business Machines Corporation | Inverted thin channel mosfet with self-aligned expanded source/drain |
| US9006071B2 (en) * | 2013-03-27 | 2015-04-14 | International Business Machines Corporation | Thin channel MOSFET with silicide local interconnect |
| US9093298B2 (en) * | 2013-08-22 | 2015-07-28 | Texas Instruments Incorporated | Silicide formation due to improved SiGe faceting |
-
2013
- 2013-08-22 US US13/972,973 patent/US9093298B2/en active Active
-
2014
- 2014-08-22 JP JP2016536476A patent/JP6419184B2/ja active Active
- 2014-08-22 WO PCT/US2014/052253 patent/WO2015027141A1/en active Application Filing
- 2014-08-22 CN CN201480043691.1A patent/CN105453264B/zh active Active
- 2014-08-22 EP EP14838365.6A patent/EP3036769B1/en active Active
-
2015
- 2015-06-19 US US14/744,384 patent/US9202883B2/en active Active
- 2015-10-05 US US14/875,343 patent/US9406769B2/en active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP3036769B1 (en) | 2021-06-30 |
| EP3036769A1 (en) | 2016-06-29 |
| US9202883B2 (en) | 2015-12-01 |
| US9093298B2 (en) | 2015-07-28 |
| EP3036769A4 (en) | 2017-04-12 |
| WO2015027141A1 (en) | 2015-02-26 |
| CN105453264B (zh) | 2019-05-03 |
| US20150287801A1 (en) | 2015-10-08 |
| US20150054084A1 (en) | 2015-02-26 |
| US9406769B2 (en) | 2016-08-02 |
| CN105453264A (zh) | 2016-03-30 |
| US20160027888A1 (en) | 2016-01-28 |
| JP2016532296A (ja) | 2016-10-13 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP6419184B2 (ja) | 改善されたSiGeファセットによる改善されたシリサイド形成 | |
| TWI701830B (zh) | 半導體裝置及其形成方法 | |
| KR101802715B1 (ko) | 반도체 디바이스의 제조 방법 | |
| JP4718908B2 (ja) | 半導体装置および半導体装置の製造方法 | |
| TWI509736B (zh) | 半導體結構及其形成方法 | |
| KR100498476B1 (ko) | 리세스 채널 mosfet 및 그 제조방법 | |
| KR100642754B1 (ko) | 식각 저항성 l형 스페이서를 구비하는 반도체 소자 및이의 제조 방법 | |
| US20130020640A1 (en) | Semiconductor device structure insulated from a bulk silicon substrate and method of forming the same | |
| US20080283960A1 (en) | Production of a Carrier Wafer Contact in Trench Insulated Integrated Soi Circuits Having High-Voltage Components | |
| US8962430B2 (en) | Method for the formation of a protective dual liner for a shallow trench isolation structure | |
| CN106683999A (zh) | 形成金属栅极以缓解天线缺陷的方法 | |
| WO2014063381A1 (zh) | Mosfet的制造方法 | |
| US9337259B2 (en) | Structure and method to improve ETSOI MOSFETS with back gate | |
| US9099570B2 (en) | Method for the formation of dielectric isolated fin structures for use, for example, in FinFET devices | |
| CN112951765B (zh) | 半导体结构及其形成方法 | |
| JP2004039985A (ja) | 半導体装置及びその製造方法 | |
| TWI852377B (zh) | 積體晶片及其形成方法 | |
| US20120126337A1 (en) | Source/drain-to-source/drain recessed strap and methods of manufacture of same | |
| CN114121663B (zh) | 半导体器件的形成方法 | |
| TWI713973B (zh) | 記憶體結構 | |
| JP2011014750A (ja) | 半導体装置及びその製造方法 | |
| JP2007324430A (ja) | 半導体装置の製造方法 | |
| TW202416538A (zh) | 積體晶片及其形成方法 | |
| TW202405948A (zh) | 半導體裝置結構及其形成方法 | |
| JP2005019432A (ja) | 半導体装置の製造方法 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20170808 |
|
| A621 | Written request for application examination |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A621 Effective date: 20170808 |
|
| A131 | Notification of reasons for refusal |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A131 Effective date: 20180530 |
|
| A521 | Request for written amendment filed |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A523 Effective date: 20180830 |
|
| TRDD | Decision of grant or rejection written | ||
| A01 | Written decision to grant a patent or to grant a registration (utility model) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A01 Effective date: 20180919 |
|
| A61 | First payment of annual fees (during grant procedure) |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: A61 Effective date: 20181009 |
|
| R150 | Certificate of patent or registration of utility model |
Ref document number: 6419184 Country of ref document: JP Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R150 |
|
| S111 | Request for change of ownership or part of ownership |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R313117 |
|
| S533 | Written request for registration of change of name |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R313533 |
|
| R350 | Written notification of registration of transfer |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R350 |
|
| R360 | Written notification for declining of transfer of rights |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R360 |
|
| R350 | Written notification of registration of transfer |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R350 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |
|
| R250 | Receipt of annual fees |
Free format text: JAPANESE INTERMEDIATE CODE: R250 |