EP4063602B1 - Drehkippfenster oder drehkipptür mit tief liegendem loslager - Google Patents
Drehkippfenster oder drehkipptür mit tief liegendem loslager Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP4063602B1 EP4063602B1 EP22162207.9A EP22162207A EP4063602B1 EP 4063602 B1 EP4063602 B1 EP 4063602B1 EP 22162207 A EP22162207 A EP 22162207A EP 4063602 B1 EP4063602 B1 EP 4063602B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- window
- pin
- frame
- door according
- door
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Active
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- E—FIXED CONSTRUCTIONS
- E05—LOCKS; KEYS; WINDOW OR DOOR FITTINGS; SAFES
- E05D—HINGES OR SUSPENSION DEVICES FOR DOORS, WINDOWS OR WINGS
- E05D15/00—Suspension arrangements for wings
- E05D15/48—Suspension arrangements for wings allowing alternative movements
- E05D15/52—Suspension arrangements for wings allowing alternative movements for opening about a vertical as well as a horizontal axis
- E05D15/5217—Tilt-lock devices
-
- E—FIXED CONSTRUCTIONS
- E05—LOCKS; KEYS; WINDOW OR DOOR FITTINGS; SAFES
- E05C—BOLTS OR FASTENING DEVICES FOR WINGS, SPECIALLY FOR DOORS OR WINDOWS
- E05C9/00—Arrangements of simultaneously actuated bolts or other securing devices at well-separated positions on the same wing
- E05C9/06—Arrangements of simultaneously actuated bolts or other securing devices at well-separated positions on the same wing with three or more sliding bars
- E05C9/063—Arrangements of simultaneously actuated bolts or other securing devices at well-separated positions on the same wing with three or more sliding bars extending along three or more sides of the wing or frame
- E05C9/066—Locks for windows or doors specially adapted for tilt and turn
-
- E—FIXED CONSTRUCTIONS
- E05—LOCKS; KEYS; WINDOW OR DOOR FITTINGS; SAFES
- E05C—BOLTS OR FASTENING DEVICES FOR WINGS, SPECIALLY FOR DOORS OR WINDOWS
- E05C9/00—Arrangements of simultaneously actuated bolts or other securing devices at well-separated positions on the same wing
- E05C9/18—Details of fastening means or of fixed retaining means for the ends of bars
- E05C9/1808—Keepers
-
- E—FIXED CONSTRUCTIONS
- E05—LOCKS; KEYS; WINDOW OR DOOR FITTINGS; SAFES
- E05D—HINGES OR SUSPENSION DEVICES FOR DOORS, WINDOWS OR WINGS
- E05D15/00—Suspension arrangements for wings
- E05D15/48—Suspension arrangements for wings allowing alternative movements
- E05D15/52—Suspension arrangements for wings allowing alternative movements for opening about a vertical as well as a horizontal axis
-
- E—FIXED CONSTRUCTIONS
- E05—LOCKS; KEYS; WINDOW OR DOOR FITTINGS; SAFES
- E05Y—INDEXING SCHEME ASSOCIATED WITH SUBCLASSES E05D AND E05F, RELATING TO CONSTRUCTION ELEMENTS, ELECTRIC CONTROL, POWER SUPPLY, POWER SIGNAL OR TRANSMISSION, USER INTERFACES, MOUNTING OR COUPLING, DETAILS, ACCESSORIES, AUXILIARY OPERATIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR, APPLICATION THEREOF
- E05Y2900/00—Application of doors, windows, wings or fittings thereof
- E05Y2900/10—Application of doors, windows, wings or fittings thereof for buildings or parts thereof
- E05Y2900/13—Type of wing
- E05Y2900/132—Doors
-
- E—FIXED CONSTRUCTIONS
- E05—LOCKS; KEYS; WINDOW OR DOOR FITTINGS; SAFES
- E05Y—INDEXING SCHEME ASSOCIATED WITH SUBCLASSES E05D AND E05F, RELATING TO CONSTRUCTION ELEMENTS, ELECTRIC CONTROL, POWER SUPPLY, POWER SIGNAL OR TRANSMISSION, USER INTERFACES, MOUNTING OR COUPLING, DETAILS, ACCESSORIES, AUXILIARY OPERATIONS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR, APPLICATION THEREOF
- E05Y2900/00—Application of doors, windows, wings or fittings thereof
- E05Y2900/10—Application of doors, windows, wings or fittings thereof for buildings or parts thereof
- E05Y2900/13—Type of wing
- E05Y2900/148—Windows
Definitions
- the invention relates to a window or a door with a frame and a tiltable and pivotable sash.
- Every tilt-and-turn sash requires at least 2 bearing points on the lower side of the sash to enable tilting around a tilt axis.
- a bearing point is usually a fixed bearing, i.e. a corner bearing, which enables the tilt bearing (horizontal axis) of the sash in addition to the lower pivot bearing (vertical axis).
- This corner bearing is located below the scissor bearing, which forms the upper pivot bearing.
- the second tilt bearing point on a tilt-and-turn sash is solved by a loose bearing. This loose bearing is available in various designs. A simple form of the loose bearing is described here.
- the DE 1 003 084 B discloses a tiltable and pivotable window with a support plate that can be moved by a drive rod latch to grip around a support roller.
- the DE 2 243 916 A1 discloses a tilt bolt lock with a latch pocket on the frame, into which a latch attachment on the sash side can be inserted when tilting.
- Other tilt bolt lock fittings with a corresponding pocket are available from the DE 2 255 042 A1 and the DE 7 149 173 U became known.
- the DE 6 926 148 U discloses a fitting for tilt-and-turn windows in which a sash-side pin engages behind a locking piece mounted on the horizontal beam of a window frame in the tilt position.
- the DE 10 2008 007 095 A1 discloses a tilt-and-turn fitting with a holding element and a locking element, wherein both the holding element and the locking element are designed like stud bolts.
- the DE 10 2012 218 887 A1 and DE 201 14 422 U1 each reveal a locking piece with a guide rail.
- the DE 75 28 905 U discloses a tilt-and-turn fitting with a joint-forming pin which, in the tilt position, snaps into a recess of a fitting that can be connected to the frame.
- a tilt-and-turn fitting has become known in which a tilt pin bearing and a tilt pin interact in such a way that when the fitting is adjusted from the turn to the tilt position, the corner of a sash containing the tilt pin is displaced in the opening direction with respect to a frame.
- the object of the invention is thus achieved by a window or a door with a frame, a tiltable and pivotable sash, a locking piece arranged on a vertical beam of the frame and a drive rod with a pin that can engage behind the locking piece to form a joint for tilting, wherein the center of the pin in the tilt position has a distance of between 4 mm and 29 mm to the top of the rebate of the frame.
- the pin is located approximately at the height of a horizontal corner bearing axis, so that when the sash is tilted, high contact pressure from a sash overhang on the frame can be avoided.
- the pin engages behind the locking piece in a horizontal direction.
- the locking piece serves as a tilting anchor for the pin.
- the center of the tenon in the lowest position preferably has a minimum distance of 4mm, especially 8mm, when the sash is resting on the frame.
- the center of the tenon in the lowest position has a maximum distance of 15mm to the top of the rebate of the frame when the sash is resting on the frame.
- the tenon (bolt) is therefore in a particularly low position in its lowest position.
- the pin can preferably be moved by the drive rod (push rod) with a linear movement in one direction from the closed position to the turn-open position and from the turn-open position to the tilt position.
- the sash has a turn-tilt standard closing sequence.
- the lowest position of the pin corresponds to the tilt position.
- the center of the pin preferably has a horizontal distance of 9 mm or 13 mm to the front of the frame. In the case of a horizontal distance of 9 mm to the front of the frame, the maximum distance of the center of the pin is preferably 12 mm to the top of the rebate of the frame.
- the sash has a tilt-first closing sequence.
- this tilt-first closing sequence the lowest position of the pin corresponds to the rotary opening position.
- the pin can be moved by the drive rod with a linear movement in one direction from the closed position to the tilt position and from the tilt position to the rotary opening position.
- the center of the pin preferably has a horizontal distance of 13 mm from the front of the frame.
- the rebate area refers in particular to the inner circumferential area between the frame and the sash frame.
- the top of the rebate of the frame is understood to mean in particular the highest point of the frame in the rebate area - apart from any seal that may be present.
- top, bottom, inside, outside refers to the installed state of the window or door.
- closed position refers to the positions of the pin on the locking piece as well as to the positions of the sash and the window or door.
- the drive rod and/or the pin protrude downwards over the underside of the rebate of the sash in the tilt position when the sash is resting against the frame.
- the underside of the sash's rebate is understood to mean in particular the lowest point of the sash frame in the rebate area - apart from any seal that may be present.
- the underside of the sash's rebate is preferably located adjacent to the fitting part groove.
- the sash can have a handle and a gear to convert a pivoting movement of the handle into a linear movement of the drive rod.
- the drive rod is preferably provided on the gear side of the sash.
- the window or door may have an electric drive to move the drive rod.
- the locking piece can have a first contact web, which the pin engages behind in the tilted position. This enables a particularly simple design of the locking piece.
- the first contact bar can be tapered towards the top, with the pin engaging behind the first contact bar in the gap ventilation position at the tapered point.
- the wall of the contact bar is partially This allows a gap ventilation position to be provided for the window or door in a particularly simple construction. The higher the pin is moved in the vertical direction, the more play the sash has outwards away from the frame side. In addition, the provision of the gap ventilation position prevents the sash from being lifted out in the tilt position.
- the pin in the case of the standard turn-tilt closing sequence, can be moved by the drive rod into the following positions one after the other: closed position, turn-open position, gap ventilation position, tilt position.
- the locking piece can have a second contact bar, which the pin engages behind in the closed position.
- the locking piece can have a through hole between the first contact bar and the second contact bar, through which the pin can pass the locking piece in the rotary opening position.
- the locking piece can therefore be designed in a butterfly shape. This further simplifies the structural design and manufacture of the locking piece.
- the locking piece can be used for left-hand and right-hand stop if the locking piece is mirror-symmetrical, in particular mirror-symmetrical to a central plane running perpendicular to its longitudinal axis.
- the locking piece is also preferably designed without a slot and/or as a single piece (one-piece). Due to the slot-free design, the locking piece is open on one long side and is only gripped by the pin on the opposite long side. This makes the locking piece particularly easy to manufacture.
- the window or door may have an angled corner connector for attaching a central post.
- the corner connector may protrude beyond the fiberglass edge.
- the locking piece is preferably designed to be particularly narrow.
- the width of the locking piece is particularly preferably less than 18mm, in particular less than 17mm, preferably less than 16mm. This measure also makes the locking piece particularly material-saving.
- the pin can be designed in the form of a mushroom-head pin and the locking piece can have a rear handle that can be gripped behind the mushroom head. This makes the window or door particularly burglar-proof.
- the pin can be arranged eccentrically on the drive rod. This allows the contact pressure of the sash on the frame to be adjusted in the closed position.
- the pin can be riveted to the drive rod in order to enable a particularly simple structural attachment of the pin to the drive rod.
- the pin is cylindrical.
- the pin can be arranged in a T-shape on the drive rod.
- the pin is thus arranged straight on the drive rod, does not form a Z shape with the drive rod and can therefore absorb particularly large forces.
- the window or door can have a mounting bracket arranged at the corner of the sash to guide the drive rod.
- the mounting bracket (connecting bracket / corner connector) enables the drive rod and the pin to be guided securely in the corner of the sash.
- the mounting bracket can be attached to a horizontal lower wing spar using a vertically aligned screw.
- the screw is therefore not covered by the drive rod and is easily accessible for a fitter.
- the mounting bracket can have a support surface on the underside to support the sash on the top of a horizontal lower frame beam. If the sash sags or sinks, the sash can support itself on the frame when closing and can be reliably guided into the closed position.
- the window or door can have a corner drive coupled to the drive rod and a central lock coupled to the corner drive.
- the window or door can include a corner bearing with a horizontal corner bearing axis at a lower wing corner.
- the corner bearing axis is preferably designed to be immovable in the vertical direction.
- a faceplate bar on the sash has a horizontal support for the run-up on the locking piece, in particular for the run-up on the upper side of the second contact web.
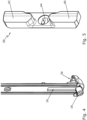
- Fig. 1 shows a window 10 with a frame (fixed frame) 12 and a sash 14, the sash 14 in Fig. 1 for reasons of clarity is largely hidden and only indicated by dashed lines (see also Fig. 11 ).
- the wing 14 is at least lockable, rotatable and tiltable (in Fig. 1 the rotary opening position is shown).
- the sash 14 has a drive rod 16 on which a pin 18 is arranged.
- the pin 18 is intended to engage behind a locking piece 20.
- the locking piece 20 is arranged on a vertical frame beam 22.
- the pin 18 is arranged vertically movable on a vertical sash beam 24 .
- the locking piece 20 and the pin 18 form a loose bearing 25.
- the sash 14 is held on the horizontally opposite sash corner by a corner bearing 26, here in the form of a fixed bearing, on the frame 12.
- the drive rod 16 is held on the sash 14 by a mounting bracket 28.
- the mounting bracket 28 is fastened to a horizontal sash beam 32 by a vertical screw 30.
- the mounting bracket 28 can have a lower run-on surface 33 for support on an upper side of a horizontal lower frame beam 34 .
- Fig. 2 shows the window 10 in the tilt position.
- Fig. 2 it is evident that the corner bearing 26 has a horizontal corner bearing axis 35.
- the horizontal corner bearing axis 35 is vertically offset from the tilt axis of the pin 18 in the tilt position. This causes stresses in the sash 14 (see Fig. 11 ), which are, however, significantly reduced according to the invention.
- Fig. 3 shows the window 10 according to Fig. 2 supplemented by a corner deflection 36 and a central lock 38. This also makes it possible to realize large sash widths with the window 10 according to the invention or the door according to the invention.
- the corner deflection 36 and central lock 38 are coupled in terms of movement to the drive rod 16.
- Fig. 4 shows the drive rod 16 together with the mounting bracket 28 and the pin 18.
- the pin 18 protrudes straight from the drive rod 16.
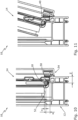
- Fig. 5 shows the locking piece 20.
- Fig. 5 it can be seen that the locking piece 20 is designed symmetrically. It has a first contact web 40 and a second contact web 42. Between the contact webs 40, 42 there is a through-hole 44 for fastening the locking piece 20 by means of a screw (not shown).
- Fig. 6 shows the window 10 in the closed position. In this position, the pin 18 engages behind the second contact web 42.
- Fig. 7 shows the window 10 according to Fig. 6 in the rotary opening position.
- the pin 18 can pass through a central through opening 46 of the locking piece 20.
- the through opening 46 extends in the width of the locking piece 20.
- Fig. 8 shows the window 10 according to Fig. 7 in the gap ventilation position.
- the sash 14 can be opened slightly (by a few degrees).
- the first contact web 40 has a taper 48.
- the sash 14 can be tilted until the pin 18 rests against the taper 48.
- Fig. 9 finally, the window 10 is shown with fittings in the tilt position. In this position, the pin 18 engages behind the first contact web 40 at a non-tapered point.
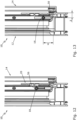
- Fig. 10 shows the window 10 according to Fig. 9 with a dimension. From Fig. 10 it is evident that the centre of the tenon 18 in the tilted position is located by the dimension X above the rebate top 50 of the frame 12. Furthermore, the centre of the tenon 18 is located by the dimension Y below the rebate bottom 52 of the sash 14.
- the values for X are preferably between 4mm and 15mm, in particular between 8mm and 15mm.
- the values for Y are preferably between -4mm and 3mm.
- the centre of the tenon 18 is therefore significantly below the rebate underside 52. This enables the sash 14 to be tilted with as little stress as possible and largely prevents a sash overlap 54 from being pressed against the frame 12 when the sash 14 is tilted.
- the center of the pin 18 is offset horizontally by the dimension Z to the front of the frame 12.
- the dimension Z is preferably 9 mm or 13 mm.
- Fig. 11 shows the window 10 in the tilt position, whereby Fig. 11 It is clear that because the first support web 40 projects far upwards, the pin 18 is not lifted over the first support web 40. Therefore, even in the case of a "swinging tilt", the wing is not lifted.
- Fig. 12 shows a window 10 with a tilt-first closing sequence, with a pin 18 on a sash 14 in the closed position.
- the pin 18 rests against a thickened section 56 of a locking piece 20.
- Fig. 13 shows the window 10 with the pin 18 in the tilt position. Fig. 13 it is evident that the center of the tenon 18 is offset by the dimension X above the top of the rebate 50 of the frame 12 when the sash 14 is in contact with the frame 12.
- the dimension X is preferably 26.5 mm.
- the dimension Z is preferably 13 mm.
- Fig. 14 shows the window 10 with the pin 18 in the tilt position. Fig. 14 It can be seen that the pin 18 rests against a first contact web 40 of the locking piece 20 when the sash 14 is tilted.
- Fig. 15 shows the window 10 with the pin 18 in the rotary opening position. In this lowest position of the pin 18, the pin 18 can pass the locking piece 20, in particular the first contact web 40, preferably on the underside.
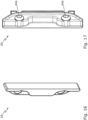
- Fig. 16 shows the locking piece 20.
- the locking piece 20 is mirror-symmetrical to a central plane running perpendicular to its longitudinal axis
- the locking piece 20 is therefore suitable for both a left-hand stop and a right-hand stop.
- the locking piece 20 is designed without a slot and in one piece.
- Fig. 17 also shows the locking piece 20.
- Fig. 17 It can be seen that the locking piece 20 has through-holes 44a, 44b for fastening the locking piece by means of screws (not shown).
- the invention relates in summary to a window 10 or a door with a tiltable and pivotable sash 14.
- a tilt axis of the sash 14 is realized at a sash corner by a horizontally extending pin 18 which, in the tilt position, engages behind a locking piece 20 on a vertical frame part.
- the pin 18 is arranged only between 4 mm and 29 mm above the rebate top 50 of the frame 12 in order to achieve a tension-free tilting of the sash 14 and to avoid a strong pressure of a sash overlap 54 on the frame 12.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Wing Frames And Configurations (AREA)
Description
- Die Erfindung betrifft ein Fenster oder eine Tür mit einem Blendrahmen und einem kippbaren und drehöffenbaren Flügel.
- Jeder Drehkippflügel benötigt mindestens 2 Lagerstellen an der unteren Seite des Flügels, um ein Kippen um eine Kippachse zu ermöglichen. Eine Lagerstelle ist üblicherweise ein Festlager, d.h. ein Ecklager, welches neben der unteren Drehlagerung (senkrechte Achse) auch die Kipplagerung (horizontale bzw. waagrechte Achse) des Flügels ermöglicht. Dieses Ecklager sitzt unterhalb des Scherenlagers, welches das obenliegende Drehlager bildet. Die zweite Kipp-Lagerstelle wird bei einem Drehkippflügel durch ein Loslager gelöst. Dieses Loslager gibt es in verschiedenen Ausbildungen. Eine einfache Form des Loslagers wird vorliegend beschrieben.
- Die
DE 1 003 084 B offenbart ein kippbares und drehöffenbares Fenster mit einem durch einen Treibstangenriegel verschiebbaren Auflageblech zum Umgreifen einer Stützrolle. - Aus der
DE 1 708 312 A1 ist eine Kippachsenlagerung in einem Langloch bekannt geworden. - Die
DE 2 243 916 A1 offenbart einen Kippriegelverschluss mit einer Riegeltasche am Blendrahmen, in die ein flügelseitiger Riegelansatz beim Kippen eintauchen kann. Weitere, mit einer entsprechenden Tasche versehene Kippriegel-Verschlussbeschläge sind aus derDE 2 255 042 A1 und derDE 7 149 173 U bekannt geworden. - Die
DE 6 926 148 U offenbart einen Beschlag für Dreh-Kipp-Fenster, bei dem ein flügelseitiger Zapfen in der Kippstellung ein am horizontalen Holm eines Blendrahmens montiertes Schließstück hintergreift. - Aus der
DE 10 2006 035 398 A1 ist ein Kipplager mit einem Tasterkopf bekannt geworden, das sich an der Oberseite des horizontalen Holms eines Blendrahmens abstützt. - Die
DE 10 2008 007 095 A1 offenbart einen Dreh-Kipp-Beschlag mit einem Halteelement und einem Riegelelement, wobei sowohl das Halteelement als auch das Riegelelement stehbolzenartig ausgebildet sind. - Aus der
DE 10 2008 021 047 A1 ist ein weiterer Dreh-Kipp-Beschlag bekannt geworden, der am horizontalen Holm eines Blendrahmens ein erstes Schließstück und am senkrechten Holm des Blendrahmens ein zweites Schließstück aufweist. Die Schließstücke können gleich ausgebildet sein. - Die
DE 10 2012 218 887 A1 undDE 201 14 422 U1 offenbaren jeweils ein Schließstück mit einer Kulissenführung. - Aus der
DE 27 22 692 A1 ist ein asymmetrisch ausgebildetes Schließstück bekannt geworden, das ein Ausheben eines Flügels beim Kippen effektiv verhindern soll. DieDE 75 28 905 U offenbart einen Dreh-Kipp-Beschlag mit einem gelenkbildenden Zapfen, der in der Kippstellung in eine Aussparung eines mit dem Blendrahmen verbindbaren Beschlages einrastet. - Aus der
DE 200 04 941 U1 ist ein Dreh-Kipp-Beschlag bekannt geworden, bei dem ein Kippzapfenlager und ein Kippzapfen derart zusammenwirken, dass beim Verstellen des Beschlags von der Dreh- in die Kippstellung die den Kippzapfen aufweisende Ecke eines Flügels bezüglich eines Blendrahmens in Öffnungsrichtung verschoben wird. - Die
DE 26 48 735 A1 offenbart einen Dreh-Kipp-Beschlag, wobei dieser Dreh-Kipp-Beschlag aufweist: - ein an einem vertikalen Blendrahmenholm angeordnetes Schließstück,
- eine in ihre Längsrichtung bewegbare Treibstange am Flügel, wobei die Treibstange einen Zapfen aufweist, der das Schließstück in der Schließstellung hintergreift und in der Kippstellung gelenkbildend hintergreift.
- Es ist demgegenüber Aufgabe der Erfindung, ein Fenster oder eine Tür mit einem konstruktiv einfachen Drehkipp-Beschlag bereitzustellen, der ein spannungsfreies Kippen eines Flügels ermöglicht.
- Diese Aufgabe wird erfindungsgemäß gelöst durch ein Fenster oder eine Tür gemäß Patentanspruch 1. Die abhängigen Patentansprüche geben bevorzugte Weiterbildungen wieder.
- Die erfindungsgemäße Aufgabe wird somit gelöst durch ein Fenster oder eine Tür mit einem Blendrahmen, einem kippbaren und drehöffenbaren Flügel, einem an einem vertikalen Holm des Blendrahmens angeordneten Schließstück und einer Treibstange mit einem Zapfen, der das Schließstück gelenkbildend zum Kippen hintergreifen kann, wobei die Zapfenmitte in der Kippstellung einen Abstand zwischen 4mm und 29mm zur Falzoberseite des Blendrahmens aufweist. Hierdurch befindet sich der Zapfen etwa in Höhe einer horizontalen Ecklagerachse, sodass beim Kippen des Flügels ein hoher Anpressdruck eines Flügelüberstands auf den Blendrahmen vermieden werden kann.
- Der Zapfen hintergreift das Schließstück in horizontaler Richtung. Das Schließstück dient dabei als Kippanker für den Zapfen.
- Die Mitte des Zapfens in der untersten Stellung weist bei am Blendrahmen anliegendem Flügel vorzugsweise einen Mindestabstand von 4mm, insbesondere 8mm, auf. Alternativ oder zusätzlich dazu weist die Mitte des Zapfens in der untersten Stellung bei am Blendrahmen anliegendem Flügel einen Maximalabstand von 15mm zur Falzoberseite des Blendrahmens auf. Der Zapfen (Bolzen) befindet sich in seiner untersten Stellung dadurch an einer besonders tiefen Position.
- Der Zapfen kann vorzugsweise durch die Treibstange (Schubstange) mit einer linearen Bewegung in eine Richtung nach der Schließstellung in die Drehöffnungsstellung und nach der Drehöffnungsstellung in die Kippstellung bewegt werden. In dieser Ausführungsform der Erfindung weist der Flügel eine Dreh-Kipp-Standardschließreihenfolge auf. In dieser Dreh-Kipp-Standardschließreihenfolge entspricht die unterste Stellung des Zapfens der Kippstellung. Dabei weist die Mitte des Zapfens vorzugsweise einen horizontalen Abstand von 9mm oder 13mm zur Vorderseite des Blendrahmens auf. Im Falle eines horizontalen Abstands von 9mm zur Vorderseite des Blendrahmens beträgt der Maximalabstand der Mitte des Zapfens vorzugsweise 12mm zur Falzoberseite des Blendrahmens.
- In einer alternativen Ausführungsform der Erfindung weist der Flügel eine Tilt-First-Schließreihenfolge auf. In dieser Tilt-First-Schließreihenfolge entspricht die unterste Stellung des Zapfens der Drehöffnungsstellung. Dabei kann der Zapfen durch die Treibstange mit einer linearen Bewegung in eine Richtung nach der Schließstellung in die Kippstellung und nach der Kippstellung in die Drehöffnungsstellung bewegt werden. Vorzugsweise weist die Mitte des Zapfens in diesem Fall einen horizontalen Abstand von 13mm zur Vorderseite des Blendrahmens auf.
- Unter dem Falzbereich wird insbesondere der innere umlaufende Bereich zwischen Blendrahmen und Flügelrahmen verstanden.
- Unter der Falzoberseite des Blendrahmens wird insbesondere der höchste Punkt des Blendrahmens im Falzbereich - abgesehen von einer eventuell vorhandenen Dichtung - verstanden.
- Die Angaben "oben", "unten", "innen", "außen" etc. beziehen sich auf den montierten Zustand des Fensters oder der Tür. Die Begriffe "Schließstellung", "Drehöffnungsstellung", "Spaltlüftstellung" und "Kippstellung" beziehen sich sowohl auf die Positionen des Zapfens am Schließstück als auch auf die Stellungen des Flügels und des Fensters bzw. der Tür.
- Erfindungsgemäß steht/stehen die Treibstange und/oder der Zapfen in der Kippstellung bei am Blendrahmen anliegendem Flügel nach unten über die Falzunterseite des Flügels über.
- Unter der Falzunterseite des Flügels wird insbesondere der niedrigste Punkt des Flügelrahmens im Falzbereich -abgesehen von einer eventuell vorhandenen Dichtung - verstanden. Vorzugsweise befindet sich die Falzunterseite des Flügels benachbart zur Beschlagteilnut.
- Der Flügel kann einen Griff und ein Getriebe aufweisen, um eine Schwenkbewegung des Griffs in eine lineare Bewegung der Treibstange umzusetzen. Die Treibstange ist dabei vorzugsweise getriebeseitig am Flügel vorgesehen.
- Alternativ oder zusätzlich dazu kann das Fenster oder die Tür einen elektrischen Antrieb zur Bewegung der Treibstange aufweisen.
- In weiter bevorzugter Ausgestaltung der Erfindung kann das Schließstück einen ersten Anlagesteg aufweisen, den der Zapfen in der Kippstellung hintergreift. Dies ermöglicht eine konstruktiv besonders einfache Gestaltung des Schließstücks.
- Der erste Anlagesteg kann nach oben hin verjüngt ausgebildet sein, wobei der Zapfen den ersten Anlagesteg in der Spaltlüftstellung an der verjüngten Stelle hintergreift. In der Spaltlüftstellung ist die Wandung des Anlagestegs partiell nach au-ßen zurückgesetzt. Hierdurch kann auf konstruktiv besonders einfache Art und Weise eine Spaltlüftstellung für das Fenster oder die Tür vorgesehen werden. Je höher der Zapfen in vertikaler Richtung bewegt wird, umso mehr Spiel erhält der Flügel nach außen von der Blendrahmenseite weg. Darüber hinaus wird durch das Vorsehen der Spaltlüftstellung ein Ausheben des Flügels in der Kippstellung verhindert.
- Vorzugsweise kann der Zapfen im Fall der Dreh-Kipp-Standardschließreihenfolge durch die Treibstange nacheinander in die folgenden Stellungen bewegt werden: Schließstellung, Drehöffnungsstellung, Spaltlüftstellung, Kippstellung.
- Zusätzlich zum ersten Anlagesteg kann das Schließstück einen zweiten Anlagesteg aufweisen, den der Zapfen in der Schließstellung hintergreift. Das Schließstück kann zwischen dem ersten Anlagesteg und dem zweiten Anlagesteg eine Durchgangsöffnung aufweisen, durch die der Zapfen in der Drehöffnungsstellung das Schließstück passieren kann. Das Schließstück kann mithin schmetterlingsförmig ausgebildet werden. Die konstruktive Ausbildung und Herstellung des Schließstücks werden hierdurch weiter vereinfacht.
- Das Schließstück kann zum linksseitigen und rechtsseitigen Anschlag eingesetzt werden, wenn das Schließstück spiegelsymmetrisch, insbesondere spiegelsymmetrisch zu einer senkrecht zu seiner Längsachse verlaufenden Mittenebene, ausgebildet ist.
- Weiter bevorzugt ist das Schließstück kulissenfrei und/oder einstückig (einteilig) ausgebildet. Durch die kulissenfreie Ausbildung ist das Schließstück an einer Längsseite offen ausgebildet und wird nur an der gegenüberliegenden Längsseite vom Zapfen hintergriffen. Das Schließstück ist hierdurch besonders leicht fertigbar.
- Das Fenster oder die Tür kann einen winkligen Eckverbinder zur Befestigung eines Mittelpfostens aufweisen. Der Eckverbinder kann dabei über die Glasfaserkante hinausragen. Um für diesen Fall eine Kollision des Eckverbinders mit dem Schließstück zu vermeiden, ist das Schließstück vorzugsweise besonders schmal ausgebildet. Besonders bevorzugt beträgt die Breite des Schließstücks weniger als 18mm, insbesondere weniger als 17mm, vorzugsweise weniger als 16mm. Das Schließstück wird durch diese Maßnahme darüber hinaus besonders materialsparend ausgebildet.
- Der Zapfen kann in Form eines Pilzkopfzapfens ausgebildet sein und das Schließstück kann einen vom Pilzkopf hintergreifbaren Hintergriff aufweisen. Hierdurch kann das Fenster oder die Tür besonders einbruchsicher gestaltet werden.
- In weiterer Ausgestaltung der Erfindung kann der Zapfen exzentrisch drehbar an der Treibstange angeordnet sein. Hierdurch ist der Anpressdruck des Flügels an den Blendrahmen in der Schließstellung einstellbar.
- Alternativ oder zusätzlich dazu kann der Zapfen an die Treibstange genietet sein, um eine konstruktiv besonders einfache Befestigung des Zapfens an der Treibstange zu ermöglichen.
- Vorzugsweise ist der Zapfen zylinderförmig ausgebildet.
- Der Zapfen kann T-förmig an der Treibstange angeordnet sein. Der Zapfen ist somit gerade an der Treibstange angeordnet, bildet mit der Treibstange keine Z-Form aus und kann mithin besonders große Kräfte aufnehmen.
- Das Fenster oder die Tür kann einen an der Flügelecke angeordneten Montagewinkel zur Führung der Treibstange aufweisen. Der Montagewinkel (Verbindungswinkel / Eckverbinder) ermöglicht die sichere Führung der Treibstange und des Zapfens in der Flügelecke.
- Der Montagewinkel kann durch eine vertikal ausgerichtete Schraube an einem horizontalen unteren Flügelholm befestigt sein. Die Schraube wird dadurch nicht von der Treibstange verdeckt und ist für einen Monteur gut zugänglich.
- Weiterhin kann der Montagewinkel eine unterseitige Auflauffläche zur Abstützung des Flügels an der Oberseite eines horizontalen unteren Blendrahmenholms aufweisen. Im Falle eines Durchhängens bzw. Absenken des Flügels kann sich der Flügel beim Schließen hierdurch am Blendrahmen abstützen und zuverlässig in die Schließstellung geführt werden.
- Um auch breite Flügel sicher am Blendrahmen verriegeln zu können, kann das Fenster oder die Tür eine mit der Treibstange gekoppelte Eckumlenkung und einen mit der Eckumlenkung gekoppelten Mittelverschluss aufweisen.
- Das Fenster oder die Tür kann an einer unteren Flügelecke ein Ecklager mit einer horizontalen Ecklagerachse umfassen. Die Ecklagerachse ist vorzugsweise in vertikaler Richtung unbeweglich ausgebildet.
- In weiterer Ausgestaltung der Erfindung weist eine Stulpstange am Flügel eine horizontale Abstützung zum Auflauf am Schließstück, insbesondere zum Auflauf an der Oberseite des zweiten Anlagestegs, auf.
- Weitere Vorteile der Erfindung ergeben sich aus der Beschreibung und der Zeichnung. Die gezeigten und beschriebenen Ausführungsformen sind nicht als abschließende Aufzählung zu verstehen, sondern haben vielmehr beispielhaften Charakter für die Schilderung der Erfindung.
-
- Fig. 1
- zeigt eine isometrische Ansicht eines Fensters mit Dreh-Kipp-Standardschließreihenfolge in der Drehöffnungsstellung.
- Fig. 2
- zeigt eine isometrische Ansicht des Fensters aus
Fig. 1 in der Kippstellung. - Fig. 3
- zeigt eine isometrische Ansicht des Fensters aus
Fig. 2 mit ergänzter Eckumlenkung und ergänztem Mittelverschluss. - Fig. 4
- zeigt eine isometrische Ansicht einer Treibstange mit einem Zapfen und einem Montagewinkel zur Führung der Treibstange in einer Flügelecke des Fensters gemäß den
Fign. 1 und2 , wobei sich der Zapfen in der Kippstellung befindet. - Fig. 5
- zeigt eine isometrische Ansicht eines mit dem Zapfen gemäß
Fig. 4 zusammenwirkenden Schließstücks. - Fig. 6
- zeigt eine seitliche Schnittansicht des Fensters aus den
Fign. 1 und2 in der Schließstellung, wobei sich der Zapfen in der Schließstellung befindet. - Fig. 7
- zeigt eine seitliche Schnittansicht des Fensters aus
Fig. 6 in der Drehöffnungsstellung, wobei sich der Zapfen in der Drehöffnungsstellung befindet. - Fig. 8
- zeigt eine seitliche Schnittansicht des Fensters aus
Fig. 7 in der Spaltlüftstellung, wobei sich der Zapfen in der Spaltlüftstellung befindet. - Fig. 9
- zeigt eine seitliche Schnittansicht des Fensters aus
Fig. 8 in der Kippstellung, wobei sich der Zapfen in der Kippstellung befindet. - Fig. 10
- zeigt die seitliche Schnittansicht des Fensters aus
Fig. 9 mit Bemaßung. - Fig. 11
- zeigt eine seitliche Schnittansicht des Fensters aus
Fig. 9 bei gekipptem Flügel, wobei Beschlagbauteile infolge der Kippbewegung vertikal angehoben und horizontal nach innen bewegt sind. - Fig. 12
- zeigt eine seitliche Schnittansicht einer weiteren Ausführungsform eines Fensters mit Tilt-First-Schließreihenfolge, wobei sich ein Zapfen in der Schließstellung befindet.
- Fig. 13
- zeigt eine seitliche Schnittansicht des Fensters aus
Fig. 12 mit am Blendrahmen anliegendem Flügel, wobei sich der Zapfen in der Kippstellung befindet. - Fig. 14
- zeigt eine seitliche Schnittansicht des Fensters aus
Fig. 13 , wobei sich der Zapfen bei gekipptem Flügel in der Kippstellung befindet. - Fig. 15
- zeigt eine seitliche Schnittansicht des Fensters aus
Fig. 14 , wobei sich der Zapfen in der Drehöffnungsstellung befindet. - Fig. 16
- zeigt eine isometrische Vorderansicht eines Schließstück des Fensters gemäß der
Fign. 12 bis 15 . - Fig. 17
- zeigt eine isometrische Rückansicht des Schließstücks aus
Fig. 16 . -
Fig. 1 zeigt ein Fenster 10 mit einem Blendrahmen (festen Rahmen) 12 und einem Flügel 14, wobei der Flügel 14 inFig. 1 aus Gründen der Übersichtlichkeit weitestgehend ausgeblendet und lediglich gestrichelt angedeutet ist (siehe hierzu auchFig. 11 ). Der Flügel 14 ist zumindest schließbar, drehöffenbar und kippbar (inFig. 1 ist die Drehöffnungsstellung dargestellt). - Zur Wahl dieser Stellungen weist der Flügel 14 eine Treibstange 16 auf, an der ein Zapfen 18 angeordnet ist. Der Zapfen 18 ist zum Hintergriff eines Schließstücks 20 vorgesehen. Das Schließstück 20 ist an einem vertikalen Blendrahmenholm 22 angeordnet. Der Zapfen 18 ist an einem vertikalen Flügelholm 24 vertikal bewegbar angeordnet.
- Das Schließstück 20 und der Zapfen 18 bilden ein Loslager 25. Der Flügel 14 ist auf der horizontal gegenüberliegenden Flügelecke durch ein Ecklager 26, hier in Form eines Festlagers, am Blendrahmen 12 gehalten.
- Die Treibstange 16 wird am Flügel 14 durch einen Montagewinkel 28 gehalten. Der Montagewinkel 28 wird durch eine vertikale Schraube 30 an einem horizontalen Flügelholm 32 befestigt. Der Montagewinkel 28 kann eine unterseitige Auflauffläche 33 zur Abstützung an einer Oberseite eines horizontalen unteren Blendrahmenholms 34 aufweisen.
-
Fig. 2 zeigt das Fenster 10 in der Kippstellung. AusFig. 2 ist ersichtlich, dass das Ecklager 26 eine horizontale Ecklagerachse 35 aufweist. Die horizontale Ecklagerachse 35 ist vertikal versetzt zur Kippachse des Zapfens 18 in der Kippstellung. Hierdurch entstehen Spannungen im Flügel 14 (sieheFig. 11 ), die erfindungsgemäß jedoch signifikant verringert sind. -
Fig. 3 zeigt das Fenster 10 gemäßFig. 2 ergänzt um eine Eckumlenkung 36 und einen Mittelverschluss 38. Hierdurch können auch große Flügelbreiten mit dem erfindungsgemäßen Fenster 10 bzw. der erfindungsgemäßen Tür realisiert werden. Eckumlenkung 36 und Mittelverschluss 38 sind dabei mit der Treibstange 16 bewegungsgekoppelt. -
Fig. 4 zeigt die Treibstange 16 zusammen mit dem Montagewinkel 28 und dem Zapfen 18. Der Zapfen 18 steht geradlinig von der Treibstange 16 ab. -
Fig. 5 zeigt das Schließstück 20. AusFig. 5 ist ersichtlich, dass das Schließstück 20 symmetrisch ausgebildet ist. Es weist einen ersten Anlagesteg 40 und einen zweiten Anlagesteg 42 auf. Zwischen den Anlagestegen 40, 42 ist eine Durchgangsausnehmung 44 zur Befestigung des Schließstücks 20 mittels einer Schraube (nicht gezeigt) vorgesehen. -
Fig. 6 zeigt das Fenster 10 in der Schließstellung. In dieser Stellung hintergreift der Zapfen 18 den zweiten Anlagesteg 42. -
Fig. 7 zeigt das Fenster 10 gemäßFig. 6 in der Drehöffnungsstellung. In dieser Stellung kann der Zapfen 18 eine mittige Durchgangsöffnung 46 des Schließstücks 20 passieren. Die Durchgangsöffnung 46 erstreckt sich in der Breite des Schließstücks 20. -
Fig. 8 zeigt das Fenster 10 gemäßFig. 7 in der Spaltlüftstellung. In dieser Stellung kann der Flügel 14 leicht (um wenige Grad) geöffnet werden. Hierzu weist der erste Anlagesteg 40 eine Verjüngung 48 auf. Der Flügel 14 kann gekippt werden, bis der Zapfen 18 an der Verjüngung 48 anliegt. -
Fig. 9 schließlich zeigt das Fenster 10 mit Beschlagteilen in der Kippstellung. In dieser Stellung hintergreift der Zapfen 18 den ersten Anlagesteg 40 an einer unverjüngten Stelle. -
Fig. 10 zeigt das Fenster 10 gemäßFig. 9 mit einer Bemaßung. AusFig. 10 ist ersichtlich, dass sich die Mitte des Zapfens 18 in der Kippstellung um das Maß X oberhalb der Falzoberseite 50 des Blendrahmens 12 befindet. Weiterhin befindet sich die Mitte des Zapfens 18 um das Maß Y unterhalb der Falzunterseite 52 des Flügels 14. Die Werte für X betragen vorzugsweise zwischen 4mm und 15mm, insbesondere zwischen 8mm und 15mm. Die Werte für Y betragen vorzugsweise zwischen-4mm und 3mm. Die Mitte des Zapfens 18 ist mithin signifikant unterhalb der Falzunterseite 52 angeordnet. Hierdurch wird ein weitestgehend spannungsfreies Kippen des Flügels 14 ermöglicht und ein Anpressen eines Flügelüberschlags 54 am Blendrahmen 12 beim Kippen des Flügels 14 weitestgehend verhindert. - Die Mitte des Zapfens 18 ist um das Maß Z horizontal zur Vorderseite des Blendrahmens 12 versetzt. Beim vorliegenden Ausführungsbeispiel mit Dreh-Kipp-Standardschließreihenfolge beträgt das Maß Z vorzugsweise 9mm oder 13mm.
-
Fig. 11 zeigt das Fenster 10 in der Kippstellung, wobei ausFig. 11 ersichtlich ist, dass aufgrund des weit nach oben ragenden ersten Anlagestegs 40 kein Ausheben des Zapfens 18 über den ersten Anlagesteg 40 erfolgt. Mithin erfolgt auch bei einem "schwungvollen Kippen" kein Ausheben des Flügels. -
Fig. 12 zeigt ein Fenster 10 mit einer Tilt-First-Schließreihenfolge, wobei sich ein Zapfen 18 an einem Flügel 14 in der Schließstellung befindet. Der Zapfen 18 liegt dabei an einem verdickten Abschnitt 56 eines Schließstücks 20 an. -
Fig. 13 zeigt das Fenster 10 mit dem Zapfen 18 in der Kippstellung. AusFig. 13 ist ersichtlich, dass sich die Mitte des Zapfens 18 bei am Blendrahmen 12 anliegendem Flügel 14 um das Maß X nach oben versetzt über der Falzoberseite 50 des Blendrahmens 12 befindet. Das Maß X beträgt vorzugsweise 26,5mm. Das Maß Z beträgt vorzugsweise 13mm. -
Fig. 14 zeigt das Fenster 10 mit dem Zapfen 18 in der Kippstellung. AusFig. 14 ist ersichtlich, dass der Zapfen 18 bei gekipptem Flügel 14 an einem ersten Anlagesteg 40 des Schließstücks 20 anliegt. -
Fig. 15 zeigt das Fenster 10 mit dem Zapfen 18 in der Drehöffnungsstellung. In dieser untersten Stellung des Zapfens 18 kann der Zapfen 18 das Schließstück 20, insbesondere den ersten Anlagesteg 40, vorzugsweise unterseitig, passieren. -
Fig. 16 zeigt das Schließstück 20. AusFig. 16 ist ersichtlich, dass das Schließstück 20 spiegelsymmetrisch zu einer senkrecht zu seiner Längsachse verlaufenden Mittenebene ausgebildet ist. Das Schließstück 20 ist hierdurch sowohl für einen linksseitigen Anschlag als auch für einen rechtsseitigen Anschlag geeignet. Weiterhin ist das Schließstück 20 kulissenfrei und einstückig ausgebildet. -
Fig. 17 zeigt ebenfalls das Schließstück 20. AusFig. 17 ist ersichtlich, dass das Schließstück 20 Durchgangsausnehmungen 44a, 44b zur Befestigung des Schließstücks mittels Schrauben (nicht gezeigt) aufweist. - Unter Vornahme einer Zusammenschau aller Figuren der Zeichnung betrifft die Erfindung zusammenfassend ein Fenster 10 oder eine Tür mit einem kippbaren und drehöffenbaren Flügel 14. Eine Kippachse des Flügels 14 wird an einer Flügelecke durch einen sich horizontal erstreckenden Zapfen 18 realisiert, der in der Kippstellung ein Schließstück 20 an einem vertikalen Blendrahmenteil hintergreift. Bei am Blendrahmen 12 anliegendem Flügel 14 ist der Zapfen 18 lediglich zwischen 4mm und 29mm oberhalb der Falzoberseite 50 des Blendrahmens 12 angeordnet, um ein spannungsfreies Kippen des Flügels 14 zu erreichen und ein starkes Anpressen eines Flügelüberschlags 54 am Blendrahmen 12 zu vermeiden.
-
- 10
- Fenster
- 12
- Blendrahmen
- 14
- Flügel
- 16
- Treibstange
- 18
- Zapfen
- 20
- Schließstück
- 22
- vertikaler Blendrahmenholm
- 24
- vertikaler Flügelholm
- 25
- Loslager
- 26
- Ecklager
- 28
- Montagewinkel
- 30
- vertikale Schraube
- 32
- horizontaler Flügelholm
- 33
- unterseitige Auflauffläche
- 34
- horizontaler unterer Blendrahmenholm
- 35
- horizontale Ecklagerachse
- 36
- Eckumlenkung
- 38
- Mittelverschluss
- 40
- erster Anlagesteg
- 42
- zweiter Anlagesteg
- 44, 44a, b
- Durchgangsausnehmung
- 46
- Durchgangsöffnung
- 48
- Verjüngung
- 50
- Falzoberseite des Blendrahmens 12
- 52
- Falzunterseite des Flügels 14
- 54
- Flügelüberschlag
- 56
- verdickter Abschnitt des Schließstücks 20
- X
- Vertikaler Versatz der Mitte des Zapfens 18 zur Falzoberseite 50 des Blendrahmens 12
- Y
- Vertikaler Versatz der Mitte des Zapfens 18 zur Falzunterseite 52 des Flügels 14
- Z
- Horizontaler Versatz der Mitte des Zapfens 18 zur Vorderseite des Blendrahmens 12
Claims (16)
- Fenster (10) oder Tür mit einem Blendrahmen (12) und einem kippbaren und drehöffenbaren Flügel (14), wobei das Fenster (10) oder die Tür Folgendes aufweist:a) Ein an einem vertikalen Blendrahmenholm (22) angeordnetes Schließstück (20);b) eine in ihre Längsrichtung bewegbare Treibstange (16) am Flügel (14), wobei die Treibstange (16) einen Zapfen (18) aufweist, der das Schließstück (20) in der Schließstellung hintergreift und in der Kippstellung gelenkbildend hintergreift;wobei die Mitte des Zapfens (18) in der Kippstellung bei am Blendrahmen (12) anliegendem Flügel (14) einen Abstand (X) zwischen 4mm und 29mm zur Falzoberseite (50) des Blendrahmens (12) aufweist, wobei die Treibstange (16) und/oder der Zapfen (18) in der Kippstellung nach unten über die Falzunterseite (52) des Flügels (14) übersteht/überstehen.
- Fenster oder Tür nach Anspruch 1, bei dem die Mitte des Zapfens (18) in seiner untersten Stellung bei am Blendrahmen (12) anliegendem Flügel (14) einen Abstand (X) zwischen 4mm und 15mm zur Falzoberseite (50) des Blendrahmens (12) aufweist.
- Fenster oder Tür nach Anspruch 1 oder 2, bei dem das Fenster (10) oder die Tür eine Dreh-Kipp-Standardschließreihenfolge oder eine Tilt-First-Schließreihenfolge aufweist.
- Fenster oder Tür nach einem der vorhergehenden Ansprüche, bei dem/der der Flügel (14) einen Griff und ein Getriebe aufweist, um eine Schwenkbewegung des Griffs in die lineare Bewegung der Treibstange (16) umzusetzen.
- Fenster oder Tür nach einem der vorhergehenden Ansprüche, bei dem/der das Schließstück (20) einen ersten Anlagesteg (40) aufweist, den der Zapfen (18) in der Kippstellung hintergreift.
- Fenster oder Tür nach Anspruch 5, bei dem/der der erste Anlagesteg (40) nach oben zur Blendrahmenaußenseite hin verjüngt ausgebildet ist, wobei der Zapfen (18) den ersten Anlagesteg (40) an der verjüngten Position in der Spaltlüftstellung hintergreift.
- Fenster oder Tür nach Anspruch 5 oder 6, bei dem das Schließstück (20) einen zweiten Anlagesteg (42) aufweist, den der Zapfen (18) in der Schließstellung hintergreift, wobei das Schließstück (20) zwischen dem ersten Anlagesteg (40) und dem zweiten Anlagesteg (42) eine horizontale Durchgangsöffnung (46) aufweist, durch die der Zapfen (18) in der Drehöffnungsstellung das Schließstück (20) passieren kann.
- Fenster oder Tür nach einem der vorhergehenden Ansprüche, bei dem/der das Schließstück (20) spiegelsymmetrisch zu einer senkrecht zu seiner Längsachse verlaufenden Mittenebene ausgebildet ist.
- Fenster oder Tür nach einem der vorhergehenden Ansprüche, bei dem das Schließstück (20) zur Führung des Zapfens (18) kulissenfrei ausgebildet ist und/oder einstückig ausgebildet ist.
- Fenster oder Tür nach einem der vorhergehenden Ansprüche, bei dem/der der Zapfen (18) exzentrisch drehbar an der Treibstange (16) angeordnet ist.
- Fenster oder Tür nach einem der vorhergehenden Ansprüche, bei dem/der der Zapfen (18) T-förmig an der Treibstange (16) angeordnet ist.
- Fenster oder Tür nach einem der vorhergehenden Ansprüche, bei dem/der das Fenster (10) oder die Tür einen an einer Flügelecke angeordneten Montagewinkel (28) zur Führung der Treibstange (16) aufweist.
- Fenster oder Tür nach Anspruch 12, bei dem/der der Montagewinkel (28) durch eine vertikal ausgerichtete Schraube (30) an einem horizontalen unteren Flügelholm (32) befestigt ist.
- Fenster oder Tür nach Anspruch 12 oder 13, bei dem/der der Montagewinkel (28) eine unterseitige Auflauffläche (33) zur Abstützung an der Oberseite eines horizontalen unteren Blendrahmenholms (34) aufweist.
- Fenster oder Tür nach einem der vorhergehenden Ansprüche, bei dem/der das Fenster (10) oder die Tür eine mit der Treibstange (16) bewegungsgekoppelte Eckumlenkung (36) und einen mit der Eckumlenkung (36) bewegungsgekoppelten Mittelverschluss (38) aufweist.
- Fenster oder Tür nach einem der vorhergehenden Ansprüche, bei dem/der der Flügel (14) an einer unteren Flügelecke in der Kippstellung durch den Zapfen (18) gelagert ist und an der gegenüberliegenden unteren Flügelecke in der Kippstellung durch ein Ecklager (26) des Fensters (10) oder der Tür mit einer horizontalen Ecklagerachse (35) gelagert ist.
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE102021202969.8A DE102021202969A1 (de) | 2021-03-25 | 2021-03-25 | Drehkippfenster oder Drehkipptür mit tief liegendem Loslager |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP4063602A1 EP4063602A1 (de) | 2022-09-28 |
| EP4063602B1 true EP4063602B1 (de) | 2025-01-08 |
Family
ID=80780711
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP22162207.9A Active EP4063602B1 (de) | 2021-03-25 | 2022-03-15 | Drehkippfenster oder drehkipptür mit tief liegendem loslager |
Country Status (4)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP4063602B1 (de) |
| DE (1) | DE102021202969A1 (de) |
| ES (1) | ES3014585T3 (de) |
| PL (1) | PL4063602T3 (de) |
Family Cites Families (19)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE1003084B (de) | 1954-05-20 | 1957-02-21 | Hans Bilstein | Kippgelenk fuer Schwenk-Kipp-Fluegel von Fenstern, Tueren od. dgl. |
| DE1149636B (de) * | 1956-06-05 | 1963-05-30 | Wilhelm Schaefer & Co | Kippgelenk fuer Kipp-Schwenk-Fluegel von Fenstern, Tueren od. dgl. |
| DE1935885U (de) | 1966-01-25 | 1966-03-31 | Jaeger Frank K G | Schliessgehaeuse fuer zum verriegeln der fluegel von fenstern, tueren od. dgl. dienende kantengetriebe. |
| DE1708312A1 (de) | 1967-09-21 | 1971-05-19 | Bilstein August Fa | Vorderes Kipplager fuer Dreh-Kipp-Fenster,-Tueren od. dgl. |
| DE6926148U (de) | 1969-07-01 | 1969-10-30 | Wilhelm Weidtmann | Verstellbare kippvorrichtung fuer drehkipp-fenster od. dgl. |
| DE7149173U (de) | 1971-12-29 | 1973-02-08 | Fuhr C | Beschlag fuer dreh-kipp-fenster |
| DE2243916C2 (de) | 1972-09-07 | 1985-02-21 | Siegenia-Frank Kg, 5900 Siegen | Kippriegel Verschluß für Drehkippfenster, -türen od.dgl. |
| DE2255042C3 (de) | 1972-11-10 | 1980-04-24 | Siegenia-Frank Kg, 5900 Siegen-Kaan- Marienborn | Kippriegel- und Verschlußvorrichtung für Drehkippflügel-Fenster und -Türen o.dgl |
| DE2445855C2 (de) * | 1974-09-26 | 1983-12-08 | Siegenia-Frank Kg, 5900 Siegen | Sperrvorrichtung an Fenstern, Türen od. dgl. mit zwei in einem Rahmen mit festem Mittelpfosten nebeneinander angeordneten, voneinander unabhängig betätigbare Treibstangenverschlüsse aufweisenden Flügeln |
| DE7528905U (de) | 1975-09-12 | 1976-04-15 | Keller, Eberhard, 7121 Freudental | Verriegelungsgestaenge bei einem fenster u.dgl. |
| FR2330836A1 (fr) * | 1975-11-07 | 1977-06-03 | Ferco Int Usine Ferrures | Dispositif de verrouillage pour fenetres, portes et autres a ouverture oscillo-battante |
| DE2557320A1 (de) * | 1975-12-19 | 1977-06-30 | Ver Baubeschlag Gretsch Co | Riegelvorrichtung fuer kippbare fluegel von fenstern, tueren o.dgl. |
| AT369851B (de) | 1976-06-30 | 1983-02-10 | Hrachowina Bauelemente Prod | Kipplager fuer drehkippfluegel von fenstern od. tueren |
| DE20004941U1 (de) | 2000-03-17 | 2000-06-21 | Schüring GmbH & Co. Fenster-Technologie KG, 53842 Troisdorf | Kippzapfenaufnahme für Kippschließvorrichtung |
| DE20114422U1 (de) | 2001-08-31 | 2001-11-08 | Roto Frank Ag, 70771 Leinfelden-Echterdingen | Beschlag an einem Fenster, einer Tür o.dgl. mit einem Riegelzapfen sowie einem Kippverriegelungsteil |
| DE102006035398A1 (de) | 2006-11-06 | 2008-05-29 | Aug. Winkhaus Gmbh & Co. Kg | Kipplager für ein Fenster, Fenster mit einem solchen Kipplager und Verwendung eines solchen Kipplagers |
| DE102008007095B4 (de) | 2008-02-01 | 2011-07-14 | Roto Frank Ag, 70771 | Dreh-Kipp-Beschlag |
| DE102008021047B4 (de) | 2008-04-26 | 2011-02-10 | Roto Frank Aktiengesellschaft | Beschlag für ein Fenster, eine Tür oder dergleichen sowie Fenster, Tür oder dergleichen mit einem Beschlag und Verfahren zum Verriegeln und Kipplagern einer Flügelecke eines Flügels |
| DE102012218887B4 (de) | 2012-10-17 | 2014-12-04 | Roto Frank Ag | Schließstück für ein Fenster, eine Tür oder dergleichen |
-
2021
- 2021-03-25 DE DE102021202969.8A patent/DE102021202969A1/de active Pending
-
2022
- 2022-03-15 PL PL22162207.9T patent/PL4063602T3/pl unknown
- 2022-03-15 ES ES22162207T patent/ES3014585T3/es active Active
- 2022-03-15 EP EP22162207.9A patent/EP4063602B1/de active Active
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP4063602A1 (de) | 2022-09-28 |
| DE102021202969A1 (de) | 2022-09-29 |
| ES3014585T3 (en) | 2025-04-23 |
| PL4063602T3 (pl) | 2025-04-28 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP4473182B1 (de) | Profilanordnung eines fensters oder einer tür mit einem flügelprofil, insbesondere einem schiebeflügelprofil | |
| EP3102759B1 (de) | Beschlag eines zumindest hebbaren und verschiebbaren flügels von fenstern oder türen | |
| DE8702660U1 (de) | Fenster- oder Tür-Konstruktion mit einem bewegbar gehaltenen, verriegelbaren Flügel | |
| EP1045092B1 (de) | Sicherheitsvorrichtung für ein Fenster und Fenster mit einer solchen Sicherheitsvorrichtung | |
| EP4573255A1 (de) | Profilanordnung eines fensters oder einer tür mit einem flügelprofil, insbesondere einem schiebeflügelprofil | |
| EP0844348B1 (de) | Band für Türen oder Fenster | |
| EP4063602B1 (de) | Drehkippfenster oder drehkipptür mit tief liegendem loslager | |
| EP1678402B1 (de) | Vorrichtung zur aufnahme des gewichtes einer ein- oder zweiflügeligen tür für einen schaltschrank | |
| EP4155497B1 (de) | Fenster | |
| DE9202933U1 (de) | Beschlag für einen um eine etwa mittlere Achse drehbaren Flügel | |
| DE2243916C2 (de) | Kippriegel Verschluß für Drehkippfenster, -türen od.dgl. | |
| EP1425489B1 (de) | Drehkippbeschlag | |
| DE19603415C1 (de) | Vorrichtung zur Verriegelung eines zwischen zwei Endstellungen um eine Achse schwenkbaren, in Verschlußstellung befindlichen Bauteils zum Verschließen einer Zugangsöffnung zu einem von Wänden umschlossenen Raum | |
| AT393712B (de) | Schliessplatte fuer fenster- und tuerverschluesse od.dgl. | |
| EP2740865B1 (de) | Verschlussleistenbeschlag sowie Verschlussleistenbeschlagsanordnung und entsprechend ausgerüstetes Fenster oder dergleichen | |
| EP1659241B1 (de) | Beschlag zur Einbruchsicherung für ein mehrflügeliges Fenster oder Tür | |
| EP3444417B1 (de) | Ladensystem für gebäudeöffnungen | |
| DE29800306U1 (de) | Beschlag für einen Flügelrahmen von Fenstern oder Türen | |
| EP2261453B1 (de) | Fenster oder Tür | |
| DE29509178U1 (de) | Vertikalführungselement | |
| DE10110631A1 (de) | Kippzapfenaufnahme für Kippschließvorrichtung | |
| DE29602615U1 (de) | Vorrichtung zur Sicherung eines zwischen zwei Endstellungen bewegbaren Bauteils zum Verschließen einer Wandöffnung eines Gebäudes | |
| DE29920160U1 (de) | Dreh-Kipp-Beschlagsystem | |
| DE29513202U1 (de) | Funktionselement | |
| CH657180A5 (en) | Espagnolette fastening for the bottom-closing wing of two-wing windows or doors without a mullion |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: THE APPLICATION HAS BEEN PUBLISHED |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: REQUEST FOR EXAMINATION WAS MADE |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20220905 |
|
| RBV | Designated contracting states (corrected) |
Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| GRAP | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR1 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: GRANT OF PATENT IS INTENDED |
|
| INTG | Intention to grant announced |
Effective date: 20241017 |
|
| GRAS | Grant fee paid |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR3 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: THE PATENT HAS BEEN GRANTED |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: NOT ENGLISH |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: EP |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R096 Ref document number: 502022002608 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: LANGUAGE OF EP DOCUMENT: GERMAN |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20250319 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: ES Ref legal event code: FG2A Ref document number: 3014585 Country of ref document: ES Kind code of ref document: T3 Effective date: 20250423 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AT Payment date: 20250417 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Payment date: 20250324 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: TR Payment date: 20250327 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: LT Ref legal event code: MG9D |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: NL Ref legal event code: MP Effective date: 20250108 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20250108 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: RS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20250408 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: PL Payment date: 20250228 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: ES Payment date: 20250416 Year of fee payment: 4 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NO Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20250408 Ref country code: IS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20250508 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: HR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20250108 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: PT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20250508 Ref country code: LV Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20250108 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20250409 Ref country code: BG Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20250108 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20250108 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SM Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20250108 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R097 Ref document number: 502022002608 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20250108 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MC Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20250108 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: EE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20250108 Ref country code: CZ Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20250108 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: RO Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20250108 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: H13 Free format text: ST27 STATUS EVENT CODE: U-0-0-H10-H13 (AS PROVIDED BY THE NATIONAL OFFICE) Effective date: 20251024 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20250108 |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20250315 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: BE Ref legal event code: MM Effective date: 20250331 |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed |
Effective date: 20251009 |