EP2242146A2 - Klemmaufbau sowie Lastschaltleiste oder Trenner mit Klemmaufbau - Google Patents
Klemmaufbau sowie Lastschaltleiste oder Trenner mit Klemmaufbau Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP2242146A2 EP2242146A2 EP10160092A EP10160092A EP2242146A2 EP 2242146 A2 EP2242146 A2 EP 2242146A2 EP 10160092 A EP10160092 A EP 10160092A EP 10160092 A EP10160092 A EP 10160092A EP 2242146 A2 EP2242146 A2 EP 2242146A2
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- cage
- clamping
- yoke
- clamping structure
- recess
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Granted
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01R—ELECTRICALLY-CONDUCTIVE CONNECTIONS; STRUCTURAL ASSOCIATIONS OF A PLURALITY OF MUTUALLY-INSULATED ELECTRICAL CONNECTING ELEMENTS; COUPLING DEVICES; CURRENT COLLECTORS
- H01R4/00—Electrically-conductive connections between two or more conductive members in direct contact, i.e. touching one another; Means for effecting or maintaining such contact; Electrically-conductive connections having two or more spaced connecting locations for conductors and using contact members penetrating insulation
- H01R4/28—Clamped connections, spring connections
- H01R4/30—Clamped connections, spring connections utilising a screw or nut clamping member
- H01R4/36—Conductive members located under tip of screw
- H01R4/363—Conductive members located under tip of screw with intermediate part between tip and conductive member
- H01R4/366—Conductive members located under tip of screw with intermediate part between tip and conductive member intermediate part attached to the tip of the screw
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01R—ELECTRICALLY-CONDUCTIVE CONNECTIONS; STRUCTURAL ASSOCIATIONS OF A PLURALITY OF MUTUALLY-INSULATED ELECTRICAL CONNECTING ELEMENTS; COUPLING DEVICES; CURRENT COLLECTORS
- H01R9/00—Structural associations of a plurality of mutually-insulated electrical connecting elements, e.g. terminal strips or terminal blocks; Terminals or binding posts mounted upon a base or in a case; Bases therefor
- H01R9/22—Bases, e.g. strip, block, panel
- H01R9/24—Terminal blocks
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a clamping structure for connecting cables to connecting rails and load-switching strips or disconnectors with such a clamping structure.
- Such a clamp construction is known, for example from the DE 44 35 057 ,
- the clamping structure described there has a closed clamping cage, through the bridge of a pressure pin accesses a pressure piece, so that with the help of the pressure piece after both terminal rail and cable have been arranged in the terminal cage, the cable can be pressed against the terminal rail.
- This clamping structure is intended for use on V-shaped connecting rails. It can not be used on flat connecting rails.
- the insertion of the cable in the terminal cage is very difficult to accomplish, especially for large cable cross-sections.
- the clamping cage To connect a cable to the connecting rail, the clamping cage must first be pushed onto the connecting rail or onto the cable. Then the corresponding cable must be brought in the direction of the axis of the connecting rail in the clamping cage. Only then you can clamp the pressure piece with the help of the pressure bolt on the one hand, and connecting rail on the other hand in the clamping cage.
- cables with large cross sections often have a very large bending radius. If these cables have already been assembled and routed, they usually can not be different in the longitudinal direction.
- the cable Although they can be moved transversely to the cable direction, e.g. However, a longitudinal displacement is usually not possible. Therefore, in order to connect with the aid of the described clamping structure, the cable must first be raised in the transverse direction and then bent accordingly in order to thread the cable end into the clamping cage. This bending, however, is difficult or impossible to accomplish with cables having large cable cross-sections.
- Another disadvantage of the known clamping structure is that the axial position of the clamping structure is not fixed. In other words, the clamping structure can be moved in the direction of the busbar axis or the cable axis during assembly. This can cause the terminal structure with other adjacent components comes into undesirable contact or that connecting rail or cable are no longer optimally clamped in the clamping cage. This is the case, for example, with some connection bars for disconnectors or safety edges customary to provide the connecting rail with a V-shaped connecting portion, which adjoins a substantially flat band-shaped portion.
- the clamping structure for this purpose has a substantially U-shaped cage bracket, which has two leg portions and a bottom portion connecting the leg portions, a cage yoke which substantially at the side facing away from the bottom portion of the leg portions connects to each other, so that between the cage yoke on the one hand and cage bracket on the other a cage cell is formed, a clamping piece disposed between the two leg portions in the cage cell, and a clamping plate disposed within the cage cell between the cage yoke and clamping piece, the clamping plate being reciprocable between an open position and a clamping position, and wherein the cage yoke from the cage bracket is removable.
- the clamping plate is connected to a threaded pin and the cage yoke has a threaded bore for receiving the threaded pin, so that when recorded in the threaded bore of the cage yoke threaded pin, the clamping plate can be brought by turning the threaded pin from the open position to a clamping position.
- This measure has the advantage that the clamping plate can be moved perpendicular to the cable axis by simply turning the threaded pin, which may be formed for example as a screw.
- by connecting the clamping plate with the threaded pin ensures that during disassembly by turning the grub screw in the opposite direction, the clamping plate can be easily detached from the cable.
- the pressure piece is not connected to the corresponding pressure pin, so that the pressure piece from the cable can not be solved by means of the pressure bolt, but must be removed manually during disassembly of this from the clamping cage.
- a terminal space for receiving a connecting rail is provided between the clamping piece and the bottom portion of the cage bracket.
- the clamping piece divides the cage cell into a terminal space and a cable space so that the clamping piece is arranged between the cable and the terminal rail.
- the clamping piece may be concave on its side facing the cable, so that the clamping piece better adapts to the outer contour of the cable, while the side facing away from the cable of the clamping piece can be adapted to the shape of the connecting rail.
- the clamping structure it is possible with the aid of the clamping structure to fix a cable to a connecting rail, which is originally provided for connection to the cable via corresponding pole shoes, which are screwed to the connecting rail.
- the two leg portions are formed cranked, so that the two leg sections at the end facing away from the bottom portion each have a projecting in the direction of the other leg portion portion, wherein the distance between the two projecting portions of the leg portions is smaller than the length of Käfigjochs, so that the cage yoke can not be removed or only by a bending apart of the leg portions of the bottom portion away from the cage bracket.
- This embodiment facilitates for some applications, the assembly and disassembly of the cable to the connecting rails.
- At least one leg section has a projection on its side facing the other leg section. This projection serves to hold the cage yoke in its substantially opposite to the bottom portion position of the leg portions. The cage yoke can be easily removed if the leg sections are bent slightly outwards.
- a leg portion may have a substantially U-shaped through hole surrounding a tongue portion, with the tongue portion toward the other Leg portion is bent and forms the projection.
- This can be formed in a cost effective manner, the projection. It is possible, for example, to form the cage bracket as a stamped and bent part.
- the object is achieved in that a corresponding terminal structure is provided in the load switch bar or the disconnector.
- the load switch bar or the separator may have a connection rail associated recess into which a push insert is inserted, wherein the push insert has a recess for receiving the clamping structure.
- the clamping structure is first inserted into the recess of the push insert.
- the push insert is inserted together with the terminal structure in the corresponding recess of the load switch bar or the disconnector.
- the recess in the connecting rail is designed such that when inserting the push insert, the connecting rail extends into the terminal space of the clamping structure. Now, only the cable must be applied to the clamping piece and the clamping plate are brought into the clamping position.
- the push insert on a stop element, which prevents a displacement of the clamping structure relative to the push insert in the direction of the recess or in the opposite direction.
- a stop element which prevents a displacement of the clamping structure relative to the push insert in the direction of the recess or in the opposite direction.
- two stop elements are provided which receive the clamping structure such that a relative movement in the direction of the recess and in the opposite direction is prevented.
- the push insert and / or the recess in the load switch bar or the separator has a movable or deformable locking element and the recess in the load switch bar or the separator and / or the push insert has a recess for receiving the latching element.
- the push insert is pushed into the corresponding recess until the locking element engages in the recess. Now the push insert is in the exact position and the assembly can be done.
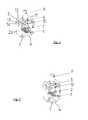
- FIG. 1 a first embodiment of a clamping structure according to the invention is shown.
- the clamping structure has a substantially U-shaped cage bracket 1, which has two leg sections 2, 3 and a bottom section 4 connecting the leg sections 2, 3. Furthermore, a cage yoke 5 is provided, which substantially at the side facing away from the bottom portion 4 of the leg sections 2, 3 connects to each other, so that between the cage yoke 5 on the one hand and cage bracket 1 on the other hand, a space is formed, which is also called cage cell below.
- a clamping piece 6 is arranged between the two leg sections 2, 3. This clamping piece 6 divides the cage cell into a terminal space 7 for a connecting rail and a cable space 8 for receiving the cable.
- connection space 7 is essentially limited by the clamping piece 6 and the bottom portion 4, while the cable space 8 is bounded by the clamping piece 6, the two leg portions 2, 3 and the cage yoke 5.
- the cage yoke 5 has a threaded through bore through which a threaded pin 9 is connected to a clamping plate 10 which is arranged in the cable space 8. By turning the threaded pin 9, the clamping plate 10 can be moved in the direction of the clamping piece 6 or away from it.
- the two leg sections 2, 3 have two cranked sections 11, 12 at their end facing away from the bottom section 4. These cranked portions 11, 12 are formed such that the distance between them is slightly smaller than the corresponding extent of the cage yoke 5, so that in the in FIG.
- both legs have an approximately U-shaped recess 13 which surrounds a corresponding tongue portion 14.
- This tongue portion 14 has been bent in the production something in the direction of the cage cell, so that in the in FIG. 1 shown position the cage yoke 5 on both sides of the corresponding tongue portion 14 is supported.
- the leg sections must be bent slightly outwards, or the cage yoke must be pushed forward (or rearward).
- the in FIG. 1 shown embodiment is provided for connection to substantially flat connecting rails, therefore, the terminal compartment 7 is formed according to the rail shape.
- FIG. 2 therefore, another embodiment is shown which differs from the embodiment of FIG. 1 essentially differs in that clamping piece 6 on the one hand and bottom section 4 on the other hand are deviating shaped to receive a substantially V-shaped connecting rail.
- the clamping piece 6 is provided between the connecting rail and cable, so that the clamping piece 6 may be formed concave on its side facing the cable space to adapt to the shape of the cable, and at the terminal space side facing the expected shape of the Connecting rail can be formed.
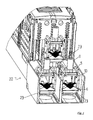
- FIG. 3 an embodiment of a push insert is shown.
- the push insert 15 has a recess 16, in which the bottom portion 4 of the clamping structure can be used.
- the recess 16 is bounded by lateral cheeks 18, 19 and a front stop surface 17.
- the push insert on two locking elements 20 which are elastically deformable.
- the push insert 15 has a recess 21 for receiving a fastening nut. If the push insert together with the in FIG. 1 used clamp construction, so it is not necessary to arrange a nut in the recess 21.
- FIG. 4 is a perspective view of a corresponding switching strip 22 is shown.
- This switching strip 22 has three connecting rails, which must be connected with appropriate cables. Therefore, refer to the corresponding connection bars in the in FIG. 4 already shown the corresponding U-shaped cage bracket 1, 1 'and 1 "placed
- FIG. 5 is another perspective view of the switching strip 22 can be seen. In this view, the substantially band-shaped connecting rails 23 are clearly visible. These are already arranged in the corresponding connection space 7 of the clamping structure.
- the cage yoke 5 is mounted on the cage bracket 1.
- the cables can either be in the in FIG. 5 shown position or in the FIG. 4 Position are introduced into the cage cell.
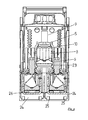
- FIG. 6 shows a sectional view through the embodiment of FIG.
- the insertion direction is in FIG. 3 marked with an arrow.
- the corresponding locking elements 20 then engage in corresponding recesses 25 in the recess 24 of the switching strip 22, so that the push insert 15 is positioned relative to the switching strip 22.
- the clamping structure has exactly the correct position in the FIGS. 4 to 6 is shown.
- the cable if necessary, after previous removal of the cage yoke 5, are easily introduced into the cable space 8.
- the clamping plate 10 can then be moved in the direction of the clamping piece 6, so that the cable is securely clamped securely in the cable compartment 8 and the connecting rail 23 in the terminal compartment 7.
- the connecting rails are designed to be used with pole pieces.
- the clamping structure 1 together with the push insert 15 is pulled out of the recess 24.
- the clamp assembly is removed and a nut inserted into the corresponding recess 21 of the drawer insert 15.
- the push insert 15 can be inserted again into the corresponding recess 24.
- the connecting rails 23 already have through holes 26, so that it is easily possible to put the pole pieces on the nut received in the recess 21 and by means of a screw which passes through both pole piece and through hole 26 in the connecting rail 23, with the mother in connect the recess 21 and thus to connect the cable lugs firmly to the connecting rail.
Landscapes
- Connections Arranged To Contact A Plurality Of Conductors (AREA)
- Installation Of Indoor Wiring (AREA)
- Details Of Indoor Wiring (AREA)
Abstract
Description
- Die vorliegende Erfindung betrifft einen Klemmaufbau zum Anschließen von Kabeln an Anschlußschienen sowie Lastschaltleisten oder Trenner mit einem solchen Klemmaufbau.
- Ein solcher Klemmaufbau ist beispielsweise bekannt aus der
DE 44 35 057 . Der dort beschriebene Klemmaufbau weist einen geschlossenen Klemmkäfig auf, durch dessen Brücke ein Druckbolzen auf ein Druckstück zugreift, so daß mit Hilfe des Druckstücks, nachdem sowohl Anschlußschiene als auch Kabel in dem Klemmkäfig angeordnet worden sind, das Kabel an die Anschlußschiene gepreßt werden kann. - Dieser Klemmaufbau ist für die Verwendung an V-förmigen Anschlußschienen vorgesehen. Er kann nicht an flach ausgebildeten Anschlußschienen verwendet werden. Zudem ist das Einlegen des Kabels in den Klemmkäfig insbesondere bei großen Kabelquerschnitten nur sehr schwer zu bewerkstelligen. Für den Anschluß eines Kabels an die Anschlußschiene muß zunächst der Klemmkäfig auf die Anschlußschiene oder auf das Kabel geschoben werden. Dann muß das entsprechende Kabel in Richtung der Achse der Anschlußschiene in den Klemmkäfig gebracht werden. Erst dann kann man das Druckstück mit Hilfe des Druckbolzens an Kabel einerseits und Anschlußschiene andererseits im Klemmkäfig festklemmen. Kabel mit großen Querschnitten haben jedoch häufig einen sehr großen Biegeradius. Sind diese Kabel bereits entsprechend konfektioniert und verlegt, lassen sie sich in Längsrichtung in der Regel nicht mehr verschieden. Sie können zwar quer zur Kabelrichtung bewegt, z.B. angehoben werden, eine Längsverschiebung ist jedoch in der Regel nicht möglich. Daher muß das Kabel, um es mit Hilfe des beschriebenen Klemmaufbaus anzuschließen, zunächst in Querrichtung angehoben werden und dann entsprechend gebogen werden, um das Kabelende in den Klemmkäfig einzufädeln. Dieses Verbiegen ist jedoch bei Kabeln mit großen Kabelquerschnitten schwer bis gar nicht zu bewerkstelligen.
- Ein weiterer Nachteil des bekannten Klemmaufbaus besteht darin, daß die axiale Position des Klemmaufbaus nicht festgelegt ist. Mit anderen Worten kann der Klemmaufbau in Richtung der Anschlußschienenachse bzw. der Kabelachse bei der Montage verschoben werden. Dies kann dazu führen, daß der Klemmaufbau mit anderen benachbarten Bauteilen in unerwünschten Kontakt kommt oder daß Anschlußschiene oder Kabel nicht mehr optimal im Klemmkäfig geklemmt werden. So ist es beispielsweise bei manchen Anschlußschienen für Trenner oder Schaltleisten üblich, die Anschlußschiene mit einem V-förmigen Anschlußabschnitt zu versehen, der sich an eine im wesentlichen ebene bandförmigen Abschnitt anschließt. Wird nun der Klemmaufbau in axialer Richtung zu weit in Richtung des Trenners bzw. der Schaltleiste verschoben, so kann es vorkommen, daß bereits der bandförmige Abschnitt der Anschlußschiene in den Klemmkäfig gerät, so daß das Kabel mit Hilfe des Druckstücks nicht mehr sicher im Klemmkäfig gehalten wird. Wird diese axiale Fehlanpassung während der Montage übersehen, so kann dies bei der späteren Verwendung der Schaltleiste oder des Trenners zu einem hochohmigen Kontakt und damit zu einer unerwünschten Wärmeentwicklung bis hin zu Entladungsfunken führen.
- Es ist daher Aufgabe der vorliegenden Erfindung, einen Klemmaufbau zum Anschließen von Kabeln an Anschlußschienen bereitzustellen, der auch bei Kabeln mit großem Kabelquerschnitt einen einfachen Anschluß des Kabels an die Anschlußschiene ermöglicht.
- Erfindungsgemäß hat der Klemmaufbau dazu einen im wesentlichen U-förmigen Käfigbügel, der zwei Schenkelabschnitte und einen die Schenkelabschnitte verbindenden Bodenabschnitt aufweist, ein Käfigjoch, welches im wesentlichen an der dem Bodenabschnitt abgewandten Seite der Schenkelabschnitte diese miteinander verbindet, so daß zwischen Käfigjoch einerseits und Käfigbügel andererseits eine Käfigzelle gebildet wird, ein zwischen den beiden Schenkelabschnitten in der Käfigzelle angeordnetes Klemmstück und eine Klemmplatte, die innerhalb der Käfigzelle zwischen Käfigjoch und Klemmstück angeordnet ist, wobei die Klemmplatte zwischen einer offenen Position und einer Klemmposition hin- und herbewegt werden kann und wobei das Käfigjoch vom Käfigbügel abnehmbar ist.
- Dadurch, daß das Käfigjoch vom Käfigbügel abgenommen werden kann, ist es insbesondere beim Anschluß von Kabeln mit großem Kabelquerschnitt nun einfach möglich, nach Abnahme des Käfigjochs vom Käfigbügel das Kabel von oben, d.h. durch die normalerweise vom Käfigjoch verschlossene Öffnung, in die Käfigzelle zu bringen. Diese Art der Montage hat zudem den Vorteil, daß beim Einfädeln des Kabels in die Käfigzelle der Klemmaufbau im allgemeinen nicht versehentlich in axialer Richtung verschoben wird, so daß die Gefahr einer axialen Fehlausrichtung des Klemmaufbaus verringert wird.
- In einer bevorzugten Ausführungsform ist die Klemmplatte mit einem Gewindestift verbunden und das Käfigjoch weist eine Gewindebohrung zur Aufnahme des Gewindestifts auf, so daß bei in der Gewindebohrung des Käfigjochs aufgenommenem Gewindestift die Klemmplatte durch Drehen des Gewindestifts von der offenen Position in eine Klemmposition gebracht werden kann. Diese Maßnahme hat zum einen den Vorteil, daß die Klemmplatte durch einfaches Drehen des Gewindestifts, der beispielsweise auch als Schraube ausgebildet sein kann, senkrecht zur Kabelachse bewegt werden kann. Zum anderen wird durch die Verbindung der Klemmplatte mit dem Gewindestift gewährleistet, daß bei der Demontage durch Drehen des Gewindestifts in die entgegengesetzte Richtung die Klemmplatte einfach von dem Kabel gelöst werden kann. Im Gegensatz dazu ist beispielsweise bei der in der eingangs erwähnten
DE 44 35 057 beschriebenen Ausführungsform das Druckstück nicht mit dem entsprechenden Druckbolzen verbunden, so daß das Druckstück vom Kabel nicht mit Hilfe des Druckbolzens gelöst werden kann, sondern bei der Demontage dieses manuell aus dem Klemmkäfig entfernt werden muß. - In einer weiteren bevorzugten Ausführungsform ist zwischen Klemmstück und Bodenabschnitt des Käfigbügels ein Anschlußraum zur Aufnahme einer Anschlußschiene vorgesehen. Mit anderen Worten teilt das Klemmstück die Käfigzelle in einen Anschlußraum und einen Kabelraum, so dass das Klemmstück zwischen Kabel und Anschlußschiene angeordnet ist.
- So kann beispielsweise das Klemmstück an seiner dem Kabel zugewandten Seite konkav ausgebildet sein, so daß sich das Klemmstück besser an die Außenkontur des Kabels anpaßt, während die dem Kabel abgewandte Seite des Klemmstücks an die Form der Anschlußschiene angepaßt sein kann.
- Beispielsweise ist es möglich, mit Hilfe des Klemmaufbaus ein Kabel an einer Anschlußschiene zu befestigen, die ursprünglich für eine Verbindung mit dem Kabel über entsprechende Polschuhe, die mit der Anschlußschiene verschraubt werden, vorgesehen ist.
- In einer weiteren bevorzugten Ausführungsform sind die beiden Schenkelabschnitte gekröpft ausgebildet, so daß die beiden Schenkelabschnitte an dem dem Bodenabschnitt abgewandten Ende jeweils einen in Richtung des anderen Schenkelabschnitts vorspringenden Abschnitt aufweisen, wobei der Abstand zwischen den beiden vorspringenden Abschnitten der Schenkelabschnitte kleiner ist als die Länge des Käfigjochs, so daß das Käfigjoch nicht oder nur durch ein Auseinanderbiegen der Schenkelabschnitte von dem Bodenabschnitt weg aus dem Käfigbügel entfernt werden kann. Diese Ausführungsform erleichtert für manche Anwendungsfälle die Montage und Demontage der Kabel an den Anschlußschienen.
- In einer weiteren bevorzugten Ausführungsform weist zumindest ein Schenkelabschnitt an seiner dem anderen Schenkelabschnitt zugewandten Seite einen Vorsprung auf. Dieser Vorsprung dient dazu, das Käfigjoch in seiner im wesentlichen an der dem Bodenabschnitt abgewandten Position der Schenkelabschnitte zu halten. Das Käfigjoch kann leicht entfernt werden, wenn die Schenkelabschnitte leicht nach außen gebogen werden.
- Beispielsweise kann ein Schenkelabschnitt eine im wesentlichen U-förmige Durchgangsöffnung aufweisen, die einen Zungenabschnitt umgibt, wobei der Zungenabschnitt in Richtung des anderen Schenkelabschnitts gebogen ist und den Vorsprung bildet. Dadurch kann auf kostengünstige Weise der Vorsprung ausgebildet werden. Es ist beispielsweise möglich, den Käfigbügel als Stanzbiegeteil auszubilden.
- Hinsichtlich der eingangs genannten Lastschaltleiste oder des Trenners wird die Aufgabe dadurch gelöst, daß in der Lastschaltleiste oder dem Trenner ein entsprechender Klemmaufbau vorgesehen ist.
- Dabei kann die Lastschaltleiste oder der Trenner eine der Anschlußschiene zugeordnete Ausnehmung aufweisen, in die ein Schubeinsatz einschiebbar ist, wobei der Schubeinsatz eine Ausnehmung zur Aufnahme der Klemmaufbaus aufweist. Mit anderen Worten wird bei der Montage der Klemmaufbau zunächst in die Ausnehmung des Schubeinsatzes eingesetzt. Dann wird der Schubeinsatz zusammen mit dem Klemmaufbau in die entsprechende Ausnehmung der Lastschaltleiste oder des Trenners eingeschoben. Dabei ist die Ausnehmung in der Anschlußschiene derart ausgebildet, daß beim Einschieben des Schubeinsatzes die Anschlußschiene sich in den Anschlußraum des Klemmaufbaus erstreckt. Nun muß lediglich das Kabel auf das Klemmstück aufgebracht werden und die Klemmplatte in die Klemmposition gebracht werden. In einer bevorzugten Ausführungsform weist der Schubeinsatz ein Anschlagelement auf, das eine Verschiebung des Klemmaufbaus relativ zum Schubeinsatz in Richtung der Ausnehmung oder in der Gegenrichtung verhindert. Vorzugsweise sind zwei Anschlagelemente vorgesehen, die den Klemmaufbau derart aufnehmen, daß eine Relativbewegung in Richtung der Ausnehmung und in der Gegenrichtung verhindert wird. Beim Einschieben des Schubeinsatzes wird daher sichergestellt, daß der Klemmaufbau in der exakten Position in Bezug auf die Anschlußschiene angeordnet ist.
- Um ein versehentliches Verschieben des Schubeinsatzes innerhalb der Ausnehmung zu verhindern, ist in einer weiteren bevorzugten Ausführungsform vorgesehen, daß das Schubeinsatz und/oder die Ausnehmung in der Lastschaltleiste oder dem Trenner ein bewegliches oder verformbares Rastelement aufweist und die Ausnehmung in der Lastschaltleiste oder dem Trenner und/oder das Schubeinsatz eine Vertiefung zur Aufnahme des Rastelements aufweist. Mit anderen Worten wird der Schubeinsatz in die entsprechende Ausnehmung geschoben, bis das Rastelement in die Vertiefung einrastet. Nun ist der Schubeinsatz in der exakten Position und die Montage kann erfolgen.
- Weitere Vorteile, Merkmale und Anwendungsmöglichkeiten werden deutlich anhand der folgenden Beschreibung einiger bevorzugter Ausführungsformen. Es zeigen:
- Figur 1
- eine perspektivische Ansicht einer ersten Ausführungsform eines Klemmaufbaus,
- Figur 2
- eine perspektivische Ansicht einer zweiten Ausführungsform eines Klemmeinsat- zes,
- Figur 3
- eine perspektivische Ansicht einer Ausführungsform eines Schubeinsatzes,
- Figur 4
- eine perspektivische Ansicht einer Lastschaltleiste mit entsprechendem Klemm- aufbau ohne Käfigjoch,
- Figur 5
- eine perspektivische Ansicht einer Lastschaltleiste mit einer Ausführungsform des Klemmaufbaus mit Käfigjoch und
- Figur 6
- eine Schnittansicht durch die Ausführungsform von
Figur 5 . - In
Figur 1 ist eine erste Ausführungsform eines erfindungsgemäßen Klemmaufbaus gezeigt. Der Klemmaufbau weist einen im wesentlichen U-förmigen Käfigbügel 1 auf, der zwei Schenkelabschnitte 2, 3 und einen die Schenkelabschnitte 2, 3 verbindenden Bodenabschnitt 4 aufweist. Weiterhin ist ein Käfigjoch 5 vorgesehen, welches im wesentlichen an der dem Bodenabschnitt 4 abgewandten Seite der Schenkelabschnitte 2, 3 diese miteinander verbindet, so daß zwischen Käfigjoch 5 einerseits und Käfigbügel 1 andererseits ein Raum gebildet wird, der im folgenden auch Käfigzelle genannt wird. In der Käfigzelle ist zwischen den beiden Schenkelabschnitten 2, 3 ein Klemmstück 6 angeordnet. Dieses Klemmstück 6 unterteilt die Käfigzelle in einen Anschlußraum 7 für eine Anschlußschiene und einen Kabelraum 8 für die Aufnahme des Kabels. Der Anschlußraum 7 wird im wesentlichen begrenzt durch das Klemmstück 6 und den Bodenabschnitt 4, während der Kabelraum 8 von dem Klemmstück 6, den beiden Schenkelabschnitten 2, 3 und dem Käfigjoch 5 begrenzt wird. Das Käfigjoch 5 weist eine Gewindedurchgangsbohrung auf, durch die ein Gewindestift 9 mit einer Klemmplatte 10, die im Kabelraum 8 angeordnet ist, verbunden ist. Durch Drehen des Gewindestifts 9 kann die Klemmplatte 10 in Richtung des Klemmstücks 6 oder von diesem weg bewegt werden. Die beiden Schenkelabschnitte 2, 3 weisen an ihrem dem Bodenabschnitt 4 abgewandten Ende zwei gekröpfte Abschnitte 11, 12 auf. Diese gekröpften Abschnitte 11, 12 sind derart ausgebildet, daß der Abstand zwischen diesen etwas kleiner ist als die entsprechende Ausdehnung des Käfigjochs 5, so daß in der inFigur 1 gezeigten Position das Käfigjoch 5 nicht nach oben aus dem Käfigbügel entnommen werden kann, ohne daß die beiden Schenkel nach außen gebogen werden. Weiterhin weisen beide Schenkel eine in etwa U-förmige Ausnehmung 13 auf, die einen entsprechenden Zungenabschnitt 14 umgibt. Dieser Zungenabschnitt 14 ist bei der Herstellung etwas in Richtung der Käfigzelle gebogen worden, so daß sich in der inFigur 1 gezeigten Position das Käfigjoch 5 beidseitig auf den entsprechenden Zungenabschnitt 14 abstützt. Zur Entnahme des Käfigjochs müssen entweder die Schenkelabschnitte etwas nach außen gebogen werden oder das Käfigjoch muß nach vorne (oder hinten) herausgeschoben werden. Man erkennt, daß die inFigur 1 gezeigte Ausführungsform für den Anschluß an im wesentlichen ebene Anschlußschienen vorgesehen ist, daher ist der Anschlußraum 7 entsprechend der Schienenform ausgebildet. - In
Figur 2 ist daher eine andere Ausführungsform gezeigt, die sich von der Ausführungsform vonFigur 1 im wesentlichen dadurch unterscheidet, daß Klemmstück 6 einerseits und Bodenabschnitt 4 andererseits abweichend geformt sind, um eine im wesentlichen V-förmige Anschlußschiene aufzunehmen. In beiden Fällen ist das Klemmstück 6 zwischen Anschlußschiene und Kabel vorgesehen, so daß das Klemmstück 6 an seiner dem Kabelraum zugewandten Seite konkav ausgebildet sein kann, um sich an die Form des Kabels anzupassen, und an der dem Anschlußraum zugewandten Seite entsprechend der erwarteten Form der Anschlußschiene ausgebildet sein kann. - Zur Verbindung eines Kabels an eine entsprechende Anschlußschiene wird daher zunächst der Klemmaufbau, wie er beispielsweise in
Figur 1 gezeigt ist, auf die Anschlußschiene aufgeschoben, so daß die Anschlußschiene im Anschlußraum 7 aufgenommen ist. Dann kann das Käfigjoch 5 entfernt werden, so daß das entsprechende Kabel ohne weiteres von oben in den Spalt zwischen den beiden Schenkelabschnitten 2, 3 eingeführt werden kann. Danach wird das Joch 5 wieder in der inFigur 1 gezeigten Position montiert, und mittels des Gewindestifts 9 wird die Klemmplatte 10 in Richtung des Klemmstücks 6 bewegt, bis das Kabel sicher zwischen Klemmstück 6 und Klemmplatte 10 gehalten wird. Man erkennt, daß das Klemmstück 6 relativ zum Käfigbügel bewegbar ist, so daß durch Drehen des Gewindestifts 9 nicht nur der Kabelraum 8 verkleinert werden kann, sondern dies in gleicher Weise auch mit dem Anschlußraum 7 geschieht, wodurch die Anschlußschiene fest gehalten wird. - In
Figur 3 ist eine Ausführungsform eines Schubeinsatzes gezeigt. Der Schubeinsatz 15 weist eine Ausnehmung 16 auf, in die der Bodenabschnitt 4 des Klemmaufbaus eingesetzt werden kann. Die Ausnehmung 16 ist von seitlichen Wangen 18, 19 sowie einer vorderen Anschlagfläche 17 begrenzt. Weiterhin weist der Schubeinsatz zwei Rastelemente 20 auf, die elastisch verformbar sind. Weiterhin weist der Schubeinsatz 15 eine Ausnehmung 21 zur Aufnahme einer Befestigungsmutter auf. Wird der Schubeinsatz zusammen mit dem inFigur 1 gezeigten Klemmaufbau verwendet, so ist es nicht notwendig, in der Ausnehmung 21 eine Mutter anzuordnen. - In
Figur 4 ist eine perspektivische Ansicht einer entsprechenden Schaltleiste 22 gezeigt. Diese Schaltleiste 22 weist drei Anschlußschienen auf, die mit entsprechenden Kabeln verbunden werden müssen. Daher sind auf die entsprechenden Anschlußschienen in der inFigur 4 gezeigten Ansicht bereits die entsprechenden U-förmigen Käfigbügel 1, 1' und 1" aufgesetzt. InFigur 5 ist eine weitere perspektivische Ansicht der Schaltleiste 22 zu sehen. In dieser Ansicht sind die im wesentlichen bandförmigen Anschlußschienen 23 deutlich zu erkennen. Diese sind bereits in dem entsprechenden Anschlußraum 7 des Klemmaufbaus angeordnet. In der inFigur 5 gezeigten Position ist das Käfigjoch 5 auf dem Käfigbügel 1 befestigt. Die Kabel können entweder in der inFigur 5 gezeigten Position oder in der inFigur 4 Position in die Käfigzelle eingebracht werden.Figur 6 zeigt eine Schnittansicht durch die Ausführungsform vonFigur 5 . Auch hier ist deutlich zu erkennen, daß das Klemmstück 6 die Käfigzelle in einen Anschlußraum 7 und einen Kabelraum 8 trennt. Im Anschlußraum 7 ist bereits eine Anschlußschiene 23 angeordnet. Um den Klemmaufbau 1 in axialer Richtung, d.h. senkrecht zur Papierebene derFigur 6 , zu positionieren, werden Schubeinsätze verwendet, wie sie inFigur 3 gezeigt sind. Zur vereinfachten Darstellung sind diese Schubeinsätze inFigur 6 nicht dargestellt. Zunächst wird daher der Klemmaufbau 1 in die entsprechende Ausnehmung 16 des Schubeinsatzes 15 gestellt. Die seitlichen Wangen 18, 19 und die vordere Anschlagfläche 17 stellen sicher, daß der Klemmaufbau relativ zum Schubeinsatz 15 richtig positioniert ist. Der Schubeinsatz 15 wird dann in die entsprechenden Ausnehmungen 24 der Schaltleiste 22 eingesetzt. Die Einschubrichtung ist inFigur 3 mit einem Pfeil gekennzeichnet. Die entsprechenden Rastelemente 20 rasten dann in entsprechende Vertiefungen 25 in der Ausnehmung 24 der Schaltleiste 22 ein, so daß der Schubeinsatz 15 relativ zur Schaltleiste 22 positioniert ist. Durch diese Maßnahme ist sichergestellt, daß der Klemmaufbau exakt die korrekte Position hat, die in denFiguren 4 bis 6 gezeigt ist. Nun kann das Kabel, gegebenenfalls nach vorheriger Entfernung des Käfigjochs 5, leicht in den Kabelraum 8 eingebracht werden. Durch Drehen des Gewindestifts 9 kann dann die Klemmplatte 10 in Richtung zum Klemmstück 6 bewegt werden, so daß das Kabel sicher im Kabelraum 8 und die Anschlußschiene 23 sicher im Anschlußraum 7 festgeklemmt wird. - In einigen Fällen weisen die Kabel, die an die Schaltleiste angeschlossen werden sollen, an ihren Enden Polschuhe auf, die dafür vorgesehen sind, mit der Anschlußschiene verschraubt zu werden.
- Bei den bislang bekannten Ausführungsformen einer Schaltleiste muß dann eine andere Schaltleiste verwendet werden, deren Anschlußschienen entsprechend ausgebildet sind, um mit Polschuhen verwendet zu werden.
- Bei der in den Figuren gezeigten Ausführungsform ist dies nicht notwendig. Sollen Polschuhe verwendet werden, wird der Klemmaufbau 1 samt Schubeinsatz 15 aus der Ausnehmung 24 herausgezogen. Der Klemmaufbau wird entfernt und eine Mutter in die entsprechende Ausnehmung 21 des Schubeinsatzes 15 eingesetzt. Nun kann der Schubeinsatz 15 wieder in die entsprechende Ausnehmung 24 eingeschoben werden. Die Anschlußschienen 23 haben bereits Durchgangslöcher 26, so daß es leicht möglich ist, die Polschuhe auf die in der Ausnehmung 21 aufgenommene Mutter zu legen und mit Hilfe einer Schraube, die sowohl Polschuh als auch Durchgangsbohrung 26 in der Anschlußschiene 23 durchgreift, mit der Mutter in der Ausnehmung 21 zu verbinden und somit die Kabelschuhe fest mit der Anschlußschiene zu verbinden.
-
- 1, 1', 1"
- Käfigbügel
- 2, 3
- Schenkelabschnitte
- 4
- Bodenabschnitt
- 5
- Käfigjoch
- 6
- Klemmstück
- 7
- Anschlußraum
- 8
- Kabelraum
- 9
- Gewindestift
- 10
- Klemmplatte
- 11, 12
- gekröpfte Abschnitte
- 13
- Ausnehmung
- 14
- Zungenabschnitt
- 15
- Schubeinsatz
- 16
- Ausnehmung
- 17
- vordere Anschlagfläche
- 18, 19
- seitliche Wangen
- 20
- Rastelemente
- 21
- Ausnehmung
- 22
- Schaltleiste
- 23
- Anschlußschienen
- 24
- Ausnehmungen
- 25
- Vertiefungen
- 26
- Durchgangslöcher
Claims (13)
- Klemmaufbau zum Anschließen von Kabeln an Anschlussschienen mit einem im wesentlichen U-förmigen Käfigbügel, der zwei Schenkelabschnitte und einen die Schenkelabschnitte verbindenden Bodenabschnitt aufweist,
einem Käfigjoch, welches im wesentlichen an der dem Bodenabschnitt abgewandten Seite der Schenkelabschnitte diese miteinander verbindet, so dass zwischen Käfigjoch einerseits und Käfigbügel andererseits eine Käfigzelle gebildet wird,
einem zwischen den beiden Schenkelabschnitten in der Käfigzelle angeordneten Klemmstück und
einer Klemmplatte, die innerhalb der Käfigzelle zwischen Käfigjoch und Klemmstück angeordnet ist,
wobei die Klemmplatte zwischen einer offenen Position und einer Klemmposition hin und her bewegt werden kann und
wobei das Käfigjoch vom Käfigbügel abnehmbar ist. - Klemmaufbau nach Anspruch 1, dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass die Klemmplatte mit einem Gewindestift verbunden ist und das Käfigjoch eine Gewindebohrung zur Aufnahme des Gewindestiftes aufweist, so dass bei in der Gewindebohrung des Käfigjochs aufgenommenen Gewindestift, die Klemmplatte durch Drehen des Gewindestiftes von der offenen Position in eine Klemmposition gebracht werden kann.
- Klemmaufbau nach Anspruch 1 oder 2, dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass zwischen Klemmstück und Bodenabschnitt des Käfigbügels ein Anschlussraum zur Aufnahme einer Anschlussschiene vorgesehen ist.
- Klemmaufbau nach einem der Ansprüche 1 bis 3, dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass die beiden Schenkelabschnitte gekröpft ausgebildet sind, so dass die beiden Schenkelabschnitten am dem Bodenabschnitt abgewandten Ende jeweils einen in Richtung des anderen Schenkelabschnitts vorspringenden Abschnitt aufweisen, wobei der Abstand zwischen den beiden vorspringenden Abschnitten der Schenkelabschnitte kleiner ist als die Länge des Käfigjochs, so dass das Käfigjoch nicht oder nur durch ein Auseinanderbiegen der Schenkelabschnitte von dem Bodenabschnitt weg aus dem Käfigbügel entfernt werden kann.
- Klemmaufbau nach einem der Ansprüche 1 bis 4, dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass zumindest ein Schenkelabschnitt an seiner dem anderen Schenkelabschnitt zugewandten Seite einen Vorsprung aufweist
- Klemmaufbau nach Anspruch 5, dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass zumindest ein Schenkelabschnitt eine im wesentlichen U-förmige Durchgangsöffnung aufweist, die einen Zungenabschnitt umgibt, wobei der Zungenabschnitt in Richtung des anderen Schenkelabschnitt gebogen ist und den Vorsprung bildet.
- Klemmaufbau nach einem der Ansprüche 1 bis 6, dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass der Käfigbügel als Stanzbiegeteil ausgebildet ist.
- Klemmaufbau nach einem der Ansprüche 1 bis 7, dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass das Klemmstück relativ zum Bodenabschnitt des Käfigbügels bewegbar ist.
- Klemmaufbau nach einem der Ansprüche 1 bis 8, dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass eine Verliersicherung für das Käfigjoch vorgesehen ist, wobei die Verliersicherung vorzugsweise ein Faden oder Draht ist, der das Käfigjoch am Käfigbügel befestigt, so dass das Käfigjoch zwar vom Käfigbügel abgenommen werden kann, jedoch mit diesem über die Verliersicherung verbunden bleibt.
- Lastschaltleiste oder Trenner mit einem Klemmaufbau nach einem der Ansprüche 1 bis 9.
- Lastschaltleiste oder Trenner nach Anspruch 10, dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass die Lastschaltleiste oder Trenner eine der Anschlussschiene zugeordnete Ausnehmung aufweist, in die ein Schubeinsatz einschiebbar ist, wobei das Schubeinsatz eine Ausnehmung zur Aufnahme des Klemmaufbau aufweist.
- Lastschaltleiste oder Trenner nach Anspruch 11, dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass das Schubeinsatz ein Anschlagselement aufweist, die eine Verschiebung des Klemmaufbaus relativ zum Schubeinsatz in Richtung der Ausnehmung oder in der Gegenrichtung verhindert.
- Lastschaltleiste oder Trenner nach Anspruch 11 oder 12, dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass das Schubeinsatz und/oder die Ausnehmung in der Lastschaltleiste oder Trenner ein bewegliches oder verformbares Rastelement aufweist, und die Ausnehmung in der Lastschaltleiste oder Trenner und/oder das Schubeinsatz eine Vertiefung zur Aufnahme des Rastelementes aufweist.
Applications Claiming Priority (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE102009002470A DE102009002470A1 (de) | 2009-04-17 | 2009-04-17 | Klemmaufbau sowie Lastschaltleiste oder Trenner mit Klemmaufbau |
Publications (3)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP2242146A2 true EP2242146A2 (de) | 2010-10-20 |
| EP2242146A3 EP2242146A3 (de) | 2014-04-16 |
| EP2242146B1 EP2242146B1 (de) | 2016-06-29 |
Family
ID=42320065
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP10160092.2A Active EP2242146B1 (de) | 2009-04-17 | 2010-04-15 | Lastschaltleiste oder Trenner mit Klemmaufbau |
Country Status (4)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| EP (1) | EP2242146B1 (de) |
| DE (1) | DE102009002470A1 (de) |
| ES (1) | ES2589379T3 (de) |
| PL (1) | PL2242146T3 (de) |
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN105375136A (zh) * | 2015-10-28 | 2016-03-02 | 国家电网公司 | 电力电缆用快速连接器 |
| EP3018759A1 (de) | 2014-11-10 | 2016-05-11 | Elektro-Bauelemente GmbH | Klemmrahmen, elektrische kontaktklemme und herstellverfahren hierfür |
| CN106911054A (zh) * | 2017-04-01 | 2017-06-30 | 菲尼克斯亚太电气(南京)有限公司 | 一种外置式开关螺钉转接组件 |
Citations (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE4435057A1 (de) | 1994-09-30 | 1996-04-04 | Efen Elektrotech Fab | Klemmaufbau zum Anschließen von Kabeln an Schienen |
Family Cites Families (12)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE1200407B (de) * | 1958-09-26 | 1965-09-09 | Siemens Ag | Klemme fuer elektrische Leiter |
| FR1229919A (fr) * | 1959-03-25 | 1960-09-12 | Cie De Construction Electr | Borne de connexion |
| FR77617E (fr) * | 1960-04-26 | 1962-03-30 | Materiel Electr Soc Ind De | Raccord pour câbles électriques |
| SE346427B (de) * | 1968-02-20 | 1972-07-03 | Asea Ab | |
| FR2058441A5 (de) * | 1969-09-04 | 1971-05-28 | Sicame Sa | |
| DE7317383U (de) * | 1973-05-09 | 1973-09-13 | Geyer Ch | Kabelklemme |
| FR2427698A1 (fr) * | 1978-05-30 | 1979-12-28 | Arnould App Electr | Raccord de conducteurs electriques |
| DE19833150C1 (de) * | 1998-07-23 | 1999-10-14 | Moeller Gmbh | Anschlußklemme |
| AU1161700A (en) * | 1998-12-18 | 2000-07-12 | Moeller Gmbh | Connecting terminal |
| DE10013157B4 (de) * | 2000-03-17 | 2008-02-14 | Aeg Niederspannungstechnik Gmbh & Co Kg | Anschlusskontaktsystem |
| DE20318855U1 (de) * | 2003-12-05 | 2004-02-26 | Moeller Gmbh | Anschlußmodul für Leistungsschalter |
| EP2063491B1 (de) * | 2007-11-23 | 2012-01-11 | Jean Müller GmbH Elektrotechnische Fabrik | Anschlussklemme für einen Transformator |
-
2009
- 2009-04-17 DE DE102009002470A patent/DE102009002470A1/de active Pending
-
2010
- 2010-04-15 PL PL10160092.2T patent/PL2242146T3/pl unknown
- 2010-04-15 EP EP10160092.2A patent/EP2242146B1/de active Active
- 2010-04-15 ES ES10160092.2T patent/ES2589379T3/es active Active
Patent Citations (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE4435057A1 (de) | 1994-09-30 | 1996-04-04 | Efen Elektrotech Fab | Klemmaufbau zum Anschließen von Kabeln an Schienen |
Cited By (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP3018759A1 (de) | 2014-11-10 | 2016-05-11 | Elektro-Bauelemente GmbH | Klemmrahmen, elektrische kontaktklemme und herstellverfahren hierfür |
| DE102014116353A1 (de) | 2014-11-10 | 2016-05-12 | Elektro-Bauelemente Gmbh | Klemmrahmen, elektrische Kontaktklemme und Herstellverfahren hierfür |
| CN105375136A (zh) * | 2015-10-28 | 2016-03-02 | 国家电网公司 | 电力电缆用快速连接器 |
| CN106911054A (zh) * | 2017-04-01 | 2017-06-30 | 菲尼克斯亚太电气(南京)有限公司 | 一种外置式开关螺钉转接组件 |
| CN106911054B (zh) * | 2017-04-01 | 2024-03-19 | 菲尼克斯亚太电气(南京)有限公司 | 一种外置式开关螺钉转接组件 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| DE102009002470A1 (de) | 2010-10-21 |
| PL2242146T3 (pl) | 2016-12-30 |
| ES2589379T3 (es) | 2016-11-14 |
| EP2242146B1 (de) | 2016-06-29 |
| EP2242146A3 (de) | 2014-04-16 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP1956684B1 (de) | Universalkontakt | |
| EP2729991B1 (de) | Elektrische anschlussklemme | |
| EP2019449B1 (de) | Schraubanschlussklemme und Verfahren zu deren Herstellung | |
| DE10161248B4 (de) | Kastenartige Anschlussklemme einer elektrischen Vorrichtung | |
| EP0334975B1 (de) | Leiteranschluss | |
| DE4408985B4 (de) | Elektrische Einrichtung, insbesondere Reihenklemme, mit einer Klemme für eine Schnellverbindung | |
| EP0823752A2 (de) | Zugfederanschluss für elektrische Leiter | |
| DE1083888B (de) | Elektrische Klemmleiste | |
| DE102006037720A1 (de) | Vorrichtung zum elektrischen Verbinden von midestens zwei Hauptleitern eines Energieversorgungskabels, insbesondere Kabelabzweigklemme | |
| DE102020128775B4 (de) | Leiteranschlussklemme in Form eines Verteilerklemmenblocks | |
| DE2619035C2 (de) | Schraubenlose Anschluß- und/oder Verbindungsklemme | |
| EP2242146B1 (de) | Lastschaltleiste oder Trenner mit Klemmaufbau | |
| DE102018206849B4 (de) | Vorrichtung zur klemmenden Befestigung | |
| DE4138547C1 (en) | Pole terminal clamp esp. for car battery - has inclined surface formed on small end face of at least one bowed flange extending in parallel to axis of recess in flat material part | |
| WO2011128205A1 (de) | Anschlussvorrichtung | |
| EP0809325A1 (de) | Elektrisches Installationsgerät und Anschlussklemme für das Installationsgerät | |
| EP0704931B1 (de) | Klemmaufbau zum Anschliessen von Kabeln an Schienen | |
| DE102007030061A1 (de) | Elektrische Hilfsverbindung zur Verbindung von wenigstens zwei Anschlussblöcken | |
| EP3995705A1 (de) | Vorrichtung zum befestigen an einem länglichen element | |
| EP3855572A1 (de) | Verbindungsklemme | |
| DE102020008160A1 (de) | Leiteranschlussklemme in Form eines Verteilerklemmenblocks | |
| DE102021105362A1 (de) | Frontschraubklemme | |
| EP3826113B1 (de) | Leiteranschlussklemme | |
| DE202014101428U1 (de) | Kontaktbuchse für eine Steckdose oder Kupplung | |
| DE102020101857B3 (de) | Elektrische Anschlussklemme |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A2 Designated state(s): AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Extension state: AL BA ME RS |
|
| PUAL | Search report despatched |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009013 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A3 Designated state(s): AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Extension state: AL BA ME RS |
|
| RIC1 | Information provided on ipc code assigned before grant |
Ipc: H01R 4/36 20060101AFI20140310BHEP Ipc: H01R 9/24 20060101ALN20140310BHEP |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20141009 |
|
| RBV | Designated contracting states (corrected) |
Designated state(s): AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| GRAP | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR1 |
|
| INTG | Intention to grant announced |
Effective date: 20160122 |
|
| GRAS | Grant fee paid |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR3 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO PL PT RO SE SI SK SM TR |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: NOT ENGLISH |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: EP |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: AT Ref legal event code: REF Ref document number: 809754 Country of ref document: AT Kind code of ref document: T Effective date: 20160715 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: LANGUAGE OF EP DOCUMENT: GERMAN |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: NV Representative=s name: ISLER AND PEDRAZZINI AG, CH |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R096 Ref document number: 502010011899 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: NL Ref legal event code: FP |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: SE Ref legal event code: TRGR |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: LT Ref legal event code: MG4D |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20160629 Ref country code: LT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20160629 Ref country code: NO Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20160929 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: ES Ref legal event code: FG2A Ref document number: 2589379 Country of ref document: ES Kind code of ref document: T3 Effective date: 20161114 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: HR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20160629 Ref country code: LV Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20160629 Ref country code: GR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20160930 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20160629 Ref country code: IS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20161029 Ref country code: CZ Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20160629 Ref country code: EE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20160629 Ref country code: RO Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20160629 Ref country code: SK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20160629 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SM Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20160629 Ref country code: PT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20161031 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R097 Ref document number: 502010011899 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20160629 |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed |
Effective date: 20170330 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20160629 Ref country code: BG Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20160929 |
|
| GBPC | Gb: european patent ceased through non-payment of renewal fee |
Effective date: 20170415 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: MM4A |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: ST Effective date: 20171229 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: FR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20170502 Ref country code: MC Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20160629 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20170415 Ref country code: GB Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20170415 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: BE Ref legal event code: MM Effective date: 20170430 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20170415 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20170430 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20160629 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: HU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT; INVALID AB INITIO Effective date: 20100415 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CY Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20160629 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20160629 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: TR Payment date: 20240321 Year of fee payment: 15 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: ES Payment date: 20240503 Year of fee payment: 15 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AT Payment date: 20240320 Year of fee payment: 15 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Payment date: 20240427 Year of fee payment: 15 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: PL Payment date: 20250324 Year of fee payment: 16 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Payment date: 20250427 Year of fee payment: 16 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20250429 Year of fee payment: 16 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CH Payment date: 20250501 Year of fee payment: 16 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: SE Ref legal event code: EUG |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: AT Ref legal event code: MM01 Ref document number: 809754 Country of ref document: AT Kind code of ref document: T Effective date: 20250415 |