EP1580435B1 - Turbomolekularpumpe - Google Patents
Turbomolekularpumpe Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP1580435B1 EP1580435B1 EP05003720A EP05003720A EP1580435B1 EP 1580435 B1 EP1580435 B1 EP 1580435B1 EP 05003720 A EP05003720 A EP 05003720A EP 05003720 A EP05003720 A EP 05003720A EP 1580435 B1 EP1580435 B1 EP 1580435B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- blades
- turbomolecular pump
- vacuum side
- angle
- attack
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F04—POSITIVE - DISPLACEMENT MACHINES FOR LIQUIDS; PUMPS FOR LIQUIDS OR ELASTIC FLUIDS
- F04D—NON-POSITIVE-DISPLACEMENT PUMPS
- F04D19/00—Axial-flow pumps
- F04D19/02—Multi-stage pumps
- F04D19/04—Multi-stage pumps specially adapted to the production of a high vacuum, e.g. molecular pumps
- F04D19/042—Turbomolecular vacuum pumps
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F04—POSITIVE - DISPLACEMENT MACHINES FOR LIQUIDS; PUMPS FOR LIQUIDS OR ELASTIC FLUIDS
- F04D—NON-POSITIVE-DISPLACEMENT PUMPS
- F04D29/00—Details, component parts, or accessories
- F04D29/26—Rotors specially for elastic fluids
- F04D29/32—Rotors specially for elastic fluids for axial flow pumps
- F04D29/321—Rotors specially for elastic fluids for axial flow pumps for axial flow compressors
- F04D29/324—Blades
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F04—POSITIVE - DISPLACEMENT MACHINES FOR LIQUIDS; PUMPS FOR LIQUIDS OR ELASTIC FLUIDS
- F04D—NON-POSITIVE-DISPLACEMENT PUMPS
- F04D29/00—Details, component parts, or accessories
- F04D29/40—Casings; Connections of working fluid
- F04D29/52—Casings; Connections of working fluid for axial pumps
- F04D29/54—Fluid-guiding means, e.g. diffusers
- F04D29/541—Specially adapted for elastic fluid pumps
- F04D29/542—Bladed diffusers
- F04D29/544—Blade shapes
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F05—INDEXING SCHEMES RELATING TO ENGINES OR PUMPS IN VARIOUS SUBCLASSES OF CLASSES F01-F04
- F05D—INDEXING SCHEME FOR ASPECTS RELATING TO NON-POSITIVE-DISPLACEMENT MACHINES OR ENGINES, GAS-TURBINES OR JET-PROPULSION PLANTS
- F05D2250/00—Geometry
- F05D2250/70—Shape
Definitions
- the invention relates to a turbomolecular pump having a plurality of alternately arranged axially one behind the other and provided with blades rotor and stator, wherein the blades in the direction of the high vacuum side have a steeper angle of attack than the blades in the vacuum side.
- the invention relates to a method for producing a blade-provided rotor or stator of such a turbomolecular pump.
- turbomolecular pumps are known, for example by the DE 2 035 063 B3 or the DE 27 17 366 B2 ,
- the blades shown there have the shape of a parallelogram in cross section. The angle of attack is depending on the axial position of the blades 25 ° to 40 °.
- a turbomolecular pump in which the blade deviates greatly in cross-section from a parallelogram and has approximately an airfoil shape.
- the average angle of attack is about 45 °.
- a turbomolecular pump which discloses all the features of the preamble of claim 1 and wherein the blades of a first, suction side arranged group of blades, called suction group A, an angle of attack of 30 ° to 40 ° and the blades of a second group, called compression group B. consisting of the remaining blade stages have an angle of 17 ° to 30 °.
- the second group, compression group can be divided into two subgroups whose blades have an angle of attack of 25 ° to 30 ° or of 17 ° to 25 °.
- the pump-active components of a turbomolecular pump consist of the rotor blades and stator disks provided with blades, which are arranged alternately axially one behind the other. Through the interaction of these discs, the pumping effect is generated in a known manner.
- the characteristic features of a turbomolecular pump are its compression and pumping capacity. Both properties are mainly determined by the following parameters: the peripheral speed of the blade ring of the rotor disks, the number of blades, the angle of attack of the blades and the gradation of the different disks of the entire disk package. Within the gradation, the angle of attack of the blade from the intake opening towards the gas outlet opening decrease.
- the invention is the technical problem of a turbomolecular pump in such a way that heat generation and power consumption are reduced and good Vorvakuumver joskeit and compression are created.
- This technical problem is solved by a significant reduction of the angle of attack of the blades in the compression or exhaust stage, and that is the angle of attack of the blades to the vacuum side to be less than 8 °.
- the flatter formation of the angle of attack has a number of positive effects: First, the number of blades per disc is reduced at the same coverage ratio despite small disc height. In addition, vortex formations are avoided in the high pressure range, resulting in a reduction in the recording power and heat generation. The low disc and blade height leads to a lower collision rate of the molecules and thus to fewer losses and finally to a short overall length of the pump. The reduction in the number of teeth leads to a further reduction of the compression power. In addition, a robust construction of the pumping stages, in particular against dust and corrosive gases, is possible. This in turn has advantages in terms of compression forces.
- the inventive design leads to a compact design and a significant performance improvement in the exhaust stages and thus the entire turbomolecular pump.
- a further increase of the aforementioned advantages can be achieved if the angle of attack of the blades to the vacuum side is less than 6 °.
- the angle of attack of the blades toward the vacuum side may be 5.9 ° to 4.6 °.
- the reduction of the disc height means that the axial thickness of the blades is less than 5.0 millimeters, in particular equal to or less than 4.5 millimeters and in extreme cases even reduced to 3.0 to 4.5 millimeters.
- the blades can have at least approximately the shape of a parallelogram in cross-section.
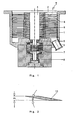
- the turbomolecular pump (T) comprises a housing (1) on which on the one hand an intake flange (2) is integrally formed and on the other hand a Exhaust flange (3) is mounted.
- the housing (1) has a rotor shaft (4) on rolling bearings (5, 6) rotatably mounted.
- the rotor shaft (4) is put into high-speed rotation via an electromotive drive (7).
- the rotor disks (8) fastened to the rotor shaft (4) interact with the stator disks (9) inserted in the housing (1).
- the angle of attack ⁇ is in Fig. 2 the clearer representation because of greatly enlarged drawn.
- the pane thickness (D) is between 3.0 millimeters and 4.5 millimeters.
- the blade (10) has a cross section which has at least approximately a trapezoidal shape.
- the so-called high-speed cutting was used, in which the material of the thin discs (8, 9) for the production of the blades (10) is removed without pressure.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Geometry (AREA)
- Non-Positive Displacement Air Blowers (AREA)
Description
- Die Erfindung bezieht sich auf eine Turbomolekularpumpe mit einer Mehrzahl von abwechselnd axial hintereinander angeordneten und mit Schaufeln versehenen Rotor- und Statorscheiben, wobei die Schaufeln in Richtung zur Hochvakuumseite einen steileren Anstellwinkel aufweisen als die Schaufeln in Richtung Vakuumseite.
- Außerdem bezieht sich die Erfindung auf ein Verfahren zur Herstellung einer mit Schaufeln versehenen Rotor- oder Statorscheibe einer solchen Turbomolekularpumpe.
- Derartige Turbomolekularpumpen sind bekannt, zum Beispiel durch die
DE 2 035 063 B3 oder dieDE 27 17 366 B2 . Die dort dargestellten Schaufeln weisen im Querschnitt die Form eines Parallelogramms auf. Der Anstellwinkel beträgt je nach axialer Lage der Schaufeln 25° bis 40°. - Durch die
DE 101 03 230 A1 ist eine Turbomolekularpumpe bekannt, bei der die Schaufel im Querschnitt von einem Parallelogramm stark abweicht und in etwa eine Tragflächenform aufweist. Der mittlere Anstellwinkel beträgt etwa 45°. - Durch die
DE 72 37 362 U1 ist eine Turbomolekularpumpe bekannt, die alle Merkmale des Oberbegriffs des Anspruchs 1 offenbart und bei der die Schaufeln einer ersten, ansaugseitig angeordneten Gruppe von Schaufeln, genannt Sauggruppe A, einen Anstellwinkel von 30° bis 40° und die Schaufeln einer zweiten Gruppe, genannt Kompressionsgruppe B, bestehend aus den restlichen Schaufelstufen einen Anstellwinkel von 17° bis 30° aufweisen. Die zweite Gruppe, Kompressionsgruppe, kann in zwei Untergruppen aufgeteilt sein, deren Schaufeln einen Anstellwinkel von 25° bis 30° beziehungsweise von 17° bis 25° aufweisen. - Aus der Praxis sind durch das Modell Alcatel ATH 1600M flache Schaufeln mit einem Anstellwinkel größer als 19° und durch das Modell Leybold MAG 2000 Schaufeln mit einem Anstellwinkel größer als 9° bekannt geworden.
- Die pumpaktiven Bauteile einer Turbomolekularpumpe bestehen aus den mit Schaufeln versehenen Rotor- und Statorscheiben, die abwechselnd axial hintereinander angeordnet sind. Durch das Zusammenwirken dieser Scheiben wird in bekannter Weise der Pumpeffekt erzeugt.
- Die charakteristischen Eigenschaften einer Turbomolekularpumpe sind Kompressions- und Saugvermögen. Beide Eigenschaften werden hauptsächlich durch folgende Parameter bestimmt: Die Umfangsgeschwindigkeit des Schaufelkranzes der Rotorscheiben, die Anzahl der Schaufeln, der Anstellwinkel der Schaufeln und die Abstufung der unterschiedlichen Scheiben des gesamten Scheibenpakets. Innerhalb der Abstufung verkleinern sich die Anstellwinkel der Schaufel von der Ansaugöffnung hin zur Gasaustrittsöffnung.
- In den Kompressionsstufen oder Auspuffstufen wird maßgeblich die Wärme erzeugt, die zum unerwünschten Aufheizen des Rotors führt. Außerdem sind diese Stufen für die Vorvakuumverträglichkeit und der Leistungsaufnahme bei hohen Vorvakuumdrücken der Pumpe von großer Bedeutung. So zeigen die bekannten Ausbildungen eine unbefriedigende Vorvakuumverträglichkeit, eine hohe Leistungsaufnahme und eine starke Erwärmung des Rotors.
- Aufgrund dieser Gegebenheiten liegt der Erfindung das technische Problem zugrunde, eine Turbomolekularpumpe so auszubilden, dass Wärmeentwicklung und Leistungsaufnahme vermindert sind und eine gute Vorvakuumverträglichkeit sowie Kompression geschaffen sind.
- Dieses technische Problem wird durch eine wesentliche Verkleinerung des Anstellwinkels der Schaufeln in der Kompressions- oder Auspuffstufe gelöst, und zwar soll der Anstellwinkel der Schaufeln zur Vakuumseite hin weniger als 8° betragen.
- Die flachere Ausbildung des Anstellwinkels hat eine Reihe von positiven Auswirkungen: Zunächst verringert sich bei gleichem Überdeckungsverhältnis trotz kleiner Scheibenhöhe die Anzahl der Schaufeln pro Scheibe. Außerdem werden Wirbelbildungen im hohen Druckbereich vermieden, wodurch es zu einer Verringerung der Aufnahmeleistung und der Wärmeentwicklung kommt. Die geringe Scheiben- und Schaufelhöhe führt zu einer geringeren Stoßrate der Moleküle und damit zu weniger Verlusten und schließlich zu einer geringen Baulänge der Pumpe. Die Verringerung der Anzahl von Zähnen führt zu einer weiteren Reduzierung der Kompressionsleistung. Zudem ist ein insbesondere gegen Staub und korrosive Gase robuster Aufbau der Pumpstufen möglich. Dies hat wiederum Vorteile in Bezug auf die Kompressionskräfte. Je weniger Schaufeln vorhanden sind, desto geringer sind die axial auf die Schaufeln wirkenden Kompressionskräfte und umso weniger Energie wird für den Antrieb der Turbomolekularpumpe benötigt. Insgesamt führt die erfindungsgemäße Ausbildung zu einer kompakten Bauform und zu einer wesentlichen Leistungsverbesserung in den Auspuffstufen und damit der gesamten Turbomolekularpumpe.
- Eine weitere Steigerung der vorgenannten Vorteile kann erzielt werden, wenn der Anstellwinkel der Schaufeln zur Vakuumseite hin weniger als 6° beträgt.
- Schließlich sind die Vorteile besonders ausgeprägt, wenn im Extremfall der Anstellwinkel der Schaufeln zur Vakuumseite hin sogar weniger als 5° beträgt.
- Beispielsweise kann bei einer erfindungsgemäßen Turbomolekularpumpe der Anstellwinkel der Schaufeln zur Vakuumseite hin 5,9° bis 4,6° betragen.
- Die Verringerung der Scheibenhöhe bedeutet, dass die axiale Dicke der Schaufeln kleiner als 5,0 Millimeter ist, insbesondere auch gleich oder kleiner 4,5 Millimeter und im Extremfall sogar bis auf 3,0 bis 4,5 Millimeter vermindert ist.
- Bisher wurden bei Turbomolekularpumpen beispielsweise 24 Schaufeln bei einem Pumpendurchmesser von 250 Millimetern vorgesehen. Die Schaufeln waren Bestandteil von Scheiben, die wenigstens 5 Millimeter dick waren. Mit der neuen Ausbildung ist es möglich, bei gleichem Pumpendurchmesser mit 16 oder sogar 12 Schaufeln auszukommen, wobei die Scheibenhöhe nur 3,0 bis 4,5 Millimeter beträgt.
- Bei der erfindungsgemäßen Turbomolekularpumpe können die Schaufeln im Querschnitt mindestens in etwa die Form eines Parallelogramms haben.
- Zur Herstellung solcher flachen Winkel beziehungsweise dünner Scheiben und entsprechend noch dünnerer Wanddicken der Schaufeln wird insbesondere vorgeschlagen, als Fertigungsverfahren das so genannte High-Speed-Cutting anzuwenden, bei dem das Material ohne Druck abgetragen wird.
- Weitere Merkmale und Vorteile der Erfindung ergeben sich anhand der zugehörigen Zeichnung, in der ein Ausführungsbeispiel einer erfindungsgemäßen Vorrichtung nur beispielhaft dargestellt ist. In der Zeichnung zeigen:
-
Fig. 1 eine Turbomolekularpumpe in schematisierter Darstellung im mittigen Längsschnitt; -
Fig. 2 einen Schnitt durch eine Schaufel der Turbomolekularpumpe nachFig. 1 . - In
Fig. 1 umfasst die Turbomolekularpumpe (T) ein Gehäuse (1), an dem endseitig einerseits ein Ansaugflansch (2) angeformt und andererseits ein Ausstoßflansch (3) angebracht ist. Im Gehäuse (1) ist eine Rotorwelle (4) auf Wälzlagern (5, 6) drehbeweglich gelagert. Die Rotorwelle (4) wird über einen elektromotorischen Antrieb (7) in hochtourige Drehung versetzt. Hierbei wirken die an der Rotorwelle (4) befestigten Rotorscheiben (8) mit den in dem Gehäuse (1) eingelegten Statorscheiben (9) zusammen. - Die Gruppe von Rotorscheiben (8) und Statorscheiben (9), die nahe der Ausstoßseite, dem Ausstoßflansch (3), angeordnet sind, weisen Schaufeln (10) auf, deren Anstellwinkel zwischen 4,6° und 5,9° liegen. Der Anstellwinkel α ist in
Fig. 2 der deutlicheren Darstellung wegen stark vergrößert gezeichnet. Die Scheibendicke (D) beträgt dabei zwischen 3,0 Millimeter und 4,5 Millimeter. - Die Schaufel (10) hat einen Querschnitt, der mindestens in etwa eine Trapezform aufweist. Zu ihrer Herstellung wurde das so genannte High-Speed-Cutting angewendet, bei dem das Material der dünnen Scheiben (8, 9) zur Herstellung der Schaufeln (10) ohne Druck abgetragen wird.
-
- 1
- Gehäuse
- 2
- Ansaugflansch
- 3
- Ausstoßflansch
- 4
- Rotorwelle
- 5
- Wälzlager
- 6
- Wälzlager
- 7
- Antrieb
- 8
- Rotorscheibe
- 9
- Statorscheibe
- 10
- Schaufel
- T
- Turbomolekularpumpe
- D
- Scheibendicke
- α
- Anstellwinkel der Schaufel
Claims (9)
- Turbomolekularpumpe mit einer Mehrzahl von abwechselnd axial hintereinander angeordneten, mit Schaufeln (10) versehenen Rotor- und Statorscheiben (8, 9), wobei die Schaufeln (10) zur Hochvakuumseite (2) hin einen steileren Anstellwinkel α aufweisen als die Schaufeln (10) zur Vakuumseite (3) hin, dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass der Anstellwinkel α der Schaufeln (10) zur Vakuumseite (3) hin weniger als 8° beträgt.
- Turbomolekularpumpe nach Anspruch 1, dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass der Anstellwinkel α der Schaufeln (10) zur Vakuumseite (3) hin weniger als 6° beträgt.
- Turbomolekularpumpe nach Anspruch 2, dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass der Anstellwinkel α der Schaufeln (10) zur Vakuumseite (3) hin weniger als 5° beiträgt.
- Turbomolekularpumpe nach Anspruch 2, dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass der Anstellwinkel α der Schaufeln (10) zur Vakuumseite (3) hin 5,9° bis 4,6° beträgt.
- Turbomolekularpumpe nach einem der Ansprüche 1 bis 4, dadurch gekenn' zeichnet, dass die axiale Dicke (D) der Schaufeln (10) kleiner als 5 Millimeter ist.
- Turbomolekularpumpe nach Anspruch 5, dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass die axiale Dicke (D) der Schaufeln (10) gleich oder kleiner 4,5 Millimeter ist.
- Turbomolekularpumpe nach Anspruch 6, dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass die axiale Dicke (D) der Schaufeln (10) 3,0 bis 4,5 Millimeter ist.
- Turbomolekularpumpe nach einem der Ansprüche 1 bis 7, dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass die Schaufeln (10) im Querschnitt mindestens in etwa die Form eines Parallelogramms aufweisen.
- Verfahren zur Herstellung einer mit Schaufeln (10) versehenen Rotor- oder Statorscheibe (8, 9) einer Turbomolekularpumpe (T) nach einem der Ansprüche 1 bis 8, dadurch gekennzeichnet, dass als Fertigungsverfahren das so genannte High-Speed-Cutting angewendet wird, bei dem das Material ohne Druck abgetragen wird.
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE102004012713A DE102004012713A1 (de) | 2004-03-16 | 2004-03-16 | Turbomolekularpumpe |
| DE102004012713 | 2004-03-16 |
Publications (4)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP1580435A2 EP1580435A2 (de) | 2005-09-28 |
| EP1580435A3 EP1580435A3 (de) | 2009-12-30 |
| EP1580435B1 true EP1580435B1 (de) | 2011-08-31 |
| EP1580435B2 EP1580435B2 (de) | 2020-11-18 |
Family
ID=34853986
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP05003720.9A Expired - Lifetime EP1580435B2 (de) | 2004-03-16 | 2005-02-22 | Turbomolekularpumpe |
Country Status (5)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US8398362B2 (de) |
| EP (1) | EP1580435B2 (de) |
| JP (1) | JP2005264932A (de) |
| AT (1) | ATE522725T1 (de) |
| DE (1) | DE102004012713A1 (de) |
Families Citing this family (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP2088327B1 (de) * | 2008-02-11 | 2011-08-31 | Agilent Technologies Italia S.p.A. | Stütze für Wälzlager |
| GB2498816A (en) | 2012-01-27 | 2013-07-31 | Edwards Ltd | Vacuum pump |
| DE102014114326A1 (de) * | 2014-10-02 | 2016-04-07 | Pfeiffer Vacuum Gmbh | Verfahren zur Herstellung einer Rotor- oder Statorscheibe für eine Vakuumpumpe sowie Rotor- oder Statorscheibe für eine Vakuumpumpe |
| GB2612781B (en) * | 2021-11-10 | 2024-04-10 | Edwards Ltd | Turbomolecular pump bladed disc |
Family Cites Families (22)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BE757354A (fr) † | 1969-10-27 | 1971-03-16 | Sargent Welch Scientific Co | Pompe turbomoleculaire a stators et rotors perfectionnes |
| DE2035063C3 (de) * | 1970-07-15 | 1974-05-30 | Arthur Pfeiffer-Vakuumtechnik Gmbh, 6330 Wetzlar | Laufrad für eine Turbomolekularpumpe |
| DE7237362U (de) * | 1972-10-12 | 1973-01-11 | Leybold Heraeus Gmbh & Co Kg | Turbomolekularvakuumpumpe |
| CH557468A (de) * | 1973-04-30 | 1974-12-31 | Bbc Brown Boveri & Cie | Turbine axialer bauart. |
| US3969039A (en) † | 1974-08-01 | 1976-07-13 | American Optical Corporation | Vacuum pump |
| DE2654055B2 (de) * | 1976-11-29 | 1979-11-08 | Kernforschungsanlage Juelich Gmbh, 5170 Juelich | Rotor- und Statorscheibe für Turbomolekularpumpe |
| JPS5898696A (ja) * | 1981-12-09 | 1983-06-11 | Hitachi Ltd | 分子ポンプのステ−タ |
| DE3402549A1 (de) * | 1984-01-26 | 1985-08-01 | Leybold-Heraeus GmbH, 5000 Köln | Molekularvakuumpumpe |
| JPS6125993A (ja) * | 1984-07-13 | 1986-02-05 | Ulvac Corp | タ−ボ分子ポンプ |
| JPS61123797A (ja) * | 1984-11-19 | 1986-06-11 | Mitsubishi Heavy Ind Ltd | 高真空排気装置 |
| JPH0261387A (ja) * | 1988-08-24 | 1990-03-01 | Seiko Seiki Co Ltd | ターボ分子ポンプ |
| JPH02201100A (ja) * | 1989-01-20 | 1990-08-09 | Ntn Corp | ターボ分子ポンプ |
| JP2865888B2 (ja) * | 1991-03-05 | 1999-03-08 | 日本原子力研究所 | マルチターボ型真空ポンプ |
| US5358373A (en) * | 1992-04-29 | 1994-10-25 | Varian Associates, Inc. | High performance turbomolecular vacuum pumps |
| JP3898785B2 (ja) * | 1996-09-24 | 2007-03-28 | 株式会社日立製作所 | 高低圧一体型蒸気タービン用動翼と高低圧一体型蒸気タービン及びコンバインド発電システム並びに複合発電プラント |
| JP3047292B1 (ja) * | 1998-11-24 | 2000-05-29 | セイコー精機株式会社 | ターボ分子ポンプ及び真空装置 |
| JP2001132683A (ja) * | 1999-10-29 | 2001-05-18 | Applied Materials Inc | ターボ分子ポンプ |
| DE10046506A1 (de) * | 2000-09-20 | 2002-03-28 | Leybold Vakuum Gmbh | Turbomolekularvakuumpumpe mit Rotorschaufelreihen und Statorschaufelreihen |
| DE10103230A1 (de) * | 2001-01-25 | 2002-08-01 | Leybold Vakuum Gmbh | Turbomolekularvakuumpumpe mit Rotor-und Statorschaufeln |
| EP1249613B1 (de) * | 2001-03-15 | 2004-01-28 | VARIAN S.p.A. | Turbinenpumpe mit einer Statorstufe integriert mit einem Distanzring |
| JP3978001B2 (ja) * | 2001-06-29 | 2007-09-19 | 三菱重工業株式会社 | ターボ分子ポンプ |
| US6760971B2 (en) * | 2002-07-15 | 2004-07-13 | Pratt & Whitney Canada Corp. | Method of making a gas turbine engine diffuser |
-
2004
- 2004-03-16 DE DE102004012713A patent/DE102004012713A1/de not_active Withdrawn
-
2005
- 2005-02-22 EP EP05003720.9A patent/EP1580435B2/de not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2005-02-22 AT AT05003720T patent/ATE522725T1/de active
- 2005-03-03 JP JP2005058364A patent/JP2005264932A/ja active Pending
- 2005-03-14 US US11/079,649 patent/US8398362B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP1580435B2 (de) | 2020-11-18 |
| EP1580435A2 (de) | 2005-09-28 |
| DE102004012713A1 (de) | 2005-10-06 |
| US8398362B2 (en) | 2013-03-19 |
| US20050207884A1 (en) | 2005-09-22 |
| JP2005264932A (ja) | 2005-09-29 |
| EP1580435A3 (de) | 2009-12-30 |
| ATE522725T1 (de) | 2011-09-15 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| DE602004006323T2 (de) | Verfahren zur Herstellung einer Turbine mit Turbinenschaufeln unterschiedlicher Resonanzfrequenzen samt einer solchen Turbine | |
| EP2304186B1 (de) | Axialturbomaschine mit geringen spaltverlusten | |
| DE2654055B2 (de) | Rotor- und Statorscheibe für Turbomolekularpumpe | |
| CH532199A (de) | Axiale Turbomolekularpumpe | |
| EP1948939A1 (de) | Radialverdichter-laufrad | |
| DE10202810A1 (de) | Turbinenlaufschaufel für den Läufer eines Gasturbinentriebwerks | |
| EP2251547B1 (de) | Vakuumpumpe | |
| EP1580435B1 (de) | Turbomolekularpumpe | |
| CH646229A5 (de) | Verfahren zur herstellung eines rotors mit mindestens einem schaufelkranz fuer eine turbomolekularpumpe und nach diesem verfahren hergestellter rotor. | |
| EP0363503A1 (de) | Pumpenstufe für eine Hochvakuumpumpe | |
| WO2000058629A1 (de) | Seitenkanalverdichter | |
| EP1201928B1 (de) | Scheiben für eine Turbomolekularpumpe | |
| EP3088743B1 (de) | Seitenkanal-vakuumpumpstufe mit einem unterbrecher, der auf der saugseite abgeschrägt ist | |
| EP4108931A1 (de) | Molekularvakuumpumpe mit verbessertem saugvermögen sowie verfahren zum betreiben einer molekularvakuumpumpe zur erzielung eines verbesserten saugvermögens | |
| WO2017045738A1 (de) | Turbinenrad für eine turbine eines abgasturboladers | |
| DE29715035U1 (de) | Reibungsvakuumpumpe | |
| EP1850011A2 (de) | Rotor- oder Statorscheibe für eine Molekularpumpe | |
| DE3402549C2 (de) | ||
| DE60311165T2 (de) | Kreiselpumpe für niedrige Flussraten mit verbesserter Ansaughöhe | |
| EP2385257B1 (de) | Vakuumpumpstufe | |
| EP2295813B1 (de) | Turbomolekularpumpenrotor | |
| EP3835592A1 (de) | Lüfterrad mit reduzierter massenträgheit für ein atemtherapiegerät | |
| DE102013112185B4 (de) | Vakuumpumpe sowie Vakuumpumpe mit wenigstens einer Turbomolekularpumpstufe | |
| EP1541871B1 (de) | Seitenkanalpumpstufe | |
| DE10354204A1 (de) | Molekularpumpe |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A2 Designated state(s): AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU MC NL PL PT RO SE SI SK TR |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Extension state: AL BA HR LV MK YU |
|
| PUAL | Search report despatched |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009013 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A3 Designated state(s): AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU MC NL PL PT RO SE SI SK TR |
|
| AX | Request for extension of the european patent |
Extension state: AL BA HR LV MK YU |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20100611 |
|
| AKX | Designation fees paid |
Designated state(s): AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU MC NL PL PT RO SE SI SK TR |
|
| GRAP | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR1 |
|
| RIC1 | Information provided on ipc code assigned before grant |
Ipc: F04D 19/04 20060101AFI20110315BHEP |
|
| GRAS | Grant fee paid |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR3 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU MC NL PL PT RO SE SI SK TR |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: NOT ENGLISH Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: EP |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: LANGUAGE OF EP DOCUMENT: GERMAN |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R096 Ref document number: 502005011825 Country of ref document: DE Effective date: 20111124 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: NL Ref legal event code: VDEP Effective date: 20110831 |
|
| LTIE | Lt: invalidation of european patent or patent extension |
Effective date: 20110831 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20110831 Ref country code: LT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20110831 Ref country code: SE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20110831 Ref country code: FI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20110831 Ref country code: IS Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20111231 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20111201 Ref country code: CY Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20110831 Ref country code: SI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20110831 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: FD4D |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CZ Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20110831 Ref country code: SK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20110831 Ref country code: IE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20110831 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: PL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20110831 Ref country code: EE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20110831 Ref country code: PT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20120102 Ref country code: RO Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20110831 |
|
| PLBI | Opposition filed |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009260 |
|
| PLBI | Opposition filed |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009260 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20110831 |
|
| PLAB | Opposition data, opponent's data or that of the opponent's representative modified |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009299OPPO |
|
| 26 | Opposition filed |
Opponent name: OERLIKON LEYBOLD VACUUM GMBH Effective date: 20120530 |
|
| 26 | Opposition filed |
Opponent name: EDWARDS LIMITED Effective date: 20120531 Opponent name: OERLIKON LEYBOLD VACUUM GMBH Effective date: 20120530 |
|
| PLAX | Notice of opposition and request to file observation + time limit sent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNOBS2 |
|
| R26 | Opposition filed (corrected) |
Opponent name: OERLIKON LEYBOLD VACUUM GMBH Effective date: 20120530 Opponent name: EDWARDS LIMITED Effective date: 20120531 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R026 Ref document number: 502005011825 Country of ref document: DE Effective date: 20120530 |
|
| BERE | Be: lapsed |
Owner name: PFEIFFER VACUUM G.M.B.H. Effective date: 20120228 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MC Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20120229 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CH Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20120229 Ref country code: LI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20120229 |
|
| PLBB | Reply of patent proprietor to notice(s) of opposition received |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNOBS3 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20120228 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: AT Ref legal event code: MM01 Ref document number: 522725 Country of ref document: AT Kind code of ref document: T Effective date: 20120222 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: ES Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20111211 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20120222 Ref country code: BG Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20111130 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: TR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20110831 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20120222 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: HU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20050222 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: PLFP Year of fee payment: 12 |
|
| PLAB | Opposition data, opponent's data or that of the opponent's representative modified |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009299OPPO |
|
| R26 | Opposition filed (corrected) |
Opponent name: LEYBOLD GMBH Effective date: 20120530 |
|
| RIC2 | Information provided on ipc code assigned after grant |
Ipc: F04D 29/54 20060101ALI20161031BHEP Ipc: F04D 19/04 20060101ALI20161031BHEP Ipc: F04D 29/32 20060101AFI20161031BHEP |
|
| PLAB | Opposition data, opponent's data or that of the opponent's representative modified |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009299OPPO |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: PLFP Year of fee payment: 13 |
|
| R26 | Opposition filed (corrected) |
Opponent name: EDWARDS LIMITED Effective date: 20120531 |
|
| APBM | Appeal reference recorded |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNREFNO |
|
| APBP | Date of receipt of notice of appeal recorded |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNNOA2O |
|
| APAH | Appeal reference modified |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSCREFNO |
|
| APBQ | Date of receipt of statement of grounds of appeal recorded |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNNOA3O |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: FR Ref legal event code: PLFP Year of fee payment: 14 |
|
| APBU | Appeal procedure closed |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNNOA9O |
|
| PUAH | Patent maintained in amended form |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009272 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: PATENT MAINTAINED AS AMENDED |
|
| 27A | Patent maintained in amended form |
Effective date: 20201118 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B2 Designated state(s): AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB GR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU MC NL PL PT RO SE SI SK TR |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R102 Ref document number: 502005011825 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20240109 Year of fee payment: 20 Ref country code: GB Payment date: 20240125 Year of fee payment: 20 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Payment date: 20240125 Year of fee payment: 20 Ref country code: FR Payment date: 20240226 Year of fee payment: 20 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: DE Ref legal event code: R071 Ref document number: 502005011825 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: PE20 Expiry date: 20250221 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: GB Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF EXPIRATION OF PROTECTION Effective date: 20250221 |