EP1200656B1 - Verfahren und vorrichtung zur herstellung schmelzersponnener endlosfäden - Google Patents
Verfahren und vorrichtung zur herstellung schmelzersponnener endlosfäden Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP1200656B1 EP1200656B1 EP00943920A EP00943920A EP1200656B1 EP 1200656 B1 EP1200656 B1 EP 1200656B1 EP 00943920 A EP00943920 A EP 00943920A EP 00943920 A EP00943920 A EP 00943920A EP 1200656 B1 EP1200656 B1 EP 1200656B1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- preparation
- threads
- filaments
- thread
- draw
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Expired - Lifetime
Links
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 19
- 238000002360 preparation method Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 42
- 238000011144 upstream manufacturing Methods 0.000 claims abstract 3
- 238000004804 winding Methods 0.000 claims description 7
- 238000001816 cooling Methods 0.000 claims description 6
- 239000003795 chemical substances by application Substances 0.000 abstract description 8
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 abstract description 8
- 239000012209 synthetic fiber Substances 0.000 abstract 1
- 229920002994 synthetic fiber Polymers 0.000 abstract 1
- 238000009987 spinning Methods 0.000 description 5
- 239000003086 colorant Substances 0.000 description 4
- 238000010438 heat treatment Methods 0.000 description 3
- 239000000835 fiber Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000010186 staining Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000005056 compaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000007613 environmental effect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000003595 mist Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000005507 spraying Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D01—NATURAL OR MAN-MADE THREADS OR FIBRES; SPINNING
- D01D—MECHANICAL METHODS OR APPARATUS IN THE MANUFACTURE OF ARTIFICIAL FILAMENTS, THREADS, FIBRES, BRISTLES OR RIBBONS
- D01D5/00—Formation of filaments, threads, or the like
- D01D5/08—Melt spinning methods
- D01D5/096—Humidity control, or oiling, of filaments, threads or the like, leaving the spinnerettes
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D06—TREATMENT OF TEXTILES OR THE LIKE; LAUNDERING; FLEXIBLE MATERIALS NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- D06B—TREATING TEXTILE MATERIALS USING LIQUIDS, GASES OR VAPOURS
- D06B11/00—Treatment of selected parts of textile materials, e.g. partial dyeing
- D06B11/0003—Treatment of selected parts of textile materials, e.g. partial dyeing of fibres, slivers or rovings
- D06B11/0006—Treatment of selected parts of textile materials, e.g. partial dyeing of fibres, slivers or rovings in connection with a spinning step
Definitions
- the invention relates to a method for producing melt-spun endless Multi-color yarn according to the preamble of claim 1 and a device for performing the method according to the preamble of claim 5.
- DE 196 49 809 A1 describes a method for spinning, drawing and winding a synthetic thread in which the thread is subjected to heat treatment is subjected. Before the heat treatment, the thread receives a preparation and a post-treatment after the heat treatment. The procedure is not for crimped multi-colored yarns can be used.
- EP 0 784 109 A2 describes a method and a device for generating a described multi-colored yarns, in which differently colored or differently colored Partial threads are treated so that before a final joint Compacting the individual threads again, individually another so-called Subcompacted, merged, compacted and wound up. Again, the goal is a compactness of the threads and distinguishable To achieve colors in the yarn.
- a the first compacting is arranged directly behind the preparation; this causes, that part of the preparation is driven out of the thread by the compacting is and is therefore lost to the manufacturing process. This part continues nebulizing the preparation due to the action of compressed air; because of this one There is a risk to the health of the operating personnel and the environment that mist is caught and disposed of. Finally, they form through the compacting created nodes an inhomogeneity and disrupt the stretching.
- the invention is for the production of various multicolored yarn qualities such as e.g. BCF (Bulced Continuous Filament; carpet fiber) suitable.
- BCF Bending Continuous Filament; carpet fiber
- the process includes the Steps spinning and cooling the filaments, preparing and stripping the filaments summarized filaments, drawing, texturing, compacting and winding.
- Filament describes in the designs a single fiber, while thread or yarn is an aggregated variety of filaments.
- a thread or a Yarn is composed of several threads, which are before a merger processed separately.
- the object of the invention is a method for producing melt-spun continuous filaments with the minimal use of aids, such as compressed air and preparation agent, an optimal thread run on the godets at the same time high occupancy, better behavior in further treatment steps, such as Stretching and texturing, and a great color contrast for multi-colored threads is achieved.
- Another object is to provide a device for performing the to create method according to the invention.
- the first object is according to the invention by the characterizing features of the claim 1 solved.
- the preparation agent that is applied in a first place in this way has enough time to penetrate far into the thread and to close here to distribute; this process is particularly intensified when the deflection element is deflected, where the thread is subjected to flexing.
- the second preparation causes the preparation as a whole largely evenly over the entire surface of all filaments and can be applied without a significant excess. This favors the heat transfer between thread and godet and further processing, such as. a stretch.
- a thread keeps a compact shape without splitting. This makes it possible to pull many threads over a godet, and / or to drive a large number of loops without a compacting for this is required. At the same time, very high thread speeds are possible. The The risk of filament breakage is reduced.
- the limitation of the amount of preparation agent according to claim 3 prevents losses and environmental damage from spraying the agent off the thread.
- Claim 5 solves the second problem.
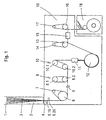
- the figure shows an apparatus for producing a multi-colored melt-spun Continuous yarn using the example of three colors.
- a spinning shaft 2.1, 2.2, 2.3 arranged in which the different dyed or staining filaments 3.1, 3.2, 3.3, which the nozzle plates 1.1, 1.2, 1.3 leave, be cooled.
- a large number of filaments 3.1, 3.2, 3.3 is in front of the further treatment in each case combined into a single thread 4.1, 4.2, 4.3.
- Galette 6 and deflection roller 7 form the first trigger element.
- a second preparation device 9.1, 9.2, 9.3 arranged between the godet 6 and a first pair of godets 8 .
- the pair of godets 8 consists of two vertically spaced, each drivable and heatable godets 8.1, 8.2 and is multiple, e.g. 5 to 13 times wrapped in threads 4.1, 4.2, 4.3. Behind it is a second one Pair of godets 10, which is also wrapped several times by the threads 4.1, 4.2, 4.3.
- the associated godets 10.1, 10.2 can each be driven and both horizontally and also vertically spaced.
- the threads 4.1, 4.2, 4.3 are combined behind the godet 10.1.
- a texturing device 11 is also arranged, followed by one drivable cooling roller 12. After the cooling roller 12, the thread 4 passes over a drivable Galette 13 and a deflection roller 14 to the compacting device 15. The thread 4 is then via a drivable godet 16 and a deflection roller 17 to a winding device 18 led.
- the entire device from the first preparation device 5, but without the winding device 18, is expediently mounted on a frame 19.
- the threads 4.1, 4.2, 4.3 are in the first preparation device 5.1, 5.2, 5.3 wetted with preparation agent; the amount is e.g. approx. 75% of the total amount required.
- the preparation agent causes that the threads 4.1, 4.2, 4.3 largely during the further processing are compact and that good heat transfer between threads and e.g. Galette is achieved.
- the threads 4.1, 4.2, 4.3 are on the godet 6 and the deflection 7 withdrawn and fed to the second preparation device 9. Because the preparation, that was applied to the first preparation device 5.1, 5.2, 5.3, could largely penetrate the threads 4.1, 4.2, 4.3, it is now possible to remove the missing Apply the amount of preparation for optimal processing. without a significant excess being required.
- the threads 4.1, 4.2, 4.3 are then known Stretched by means of the pairs of godets 8, 10 and then combined in the Texturing device 11 crimped, cooled on the cooling roll 12, in the compacting device 15 tangled and finally by means of the winding machine 18 on spools wound.
- the godets 13, 16 with the deflection rollers 14, 17 each serve the trigger of thread 4.
- the device shown as an example in the figure can also be designed such that several, e.g. 2, 4, 6 or 8 threads 4 can be processed simultaneously and in parallel.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Textile Engineering (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Materials Engineering (AREA)
- Spinning Methods And Devices For Manufacturing Artificial Fibers (AREA)
- Yarns And Mechanical Finishing Of Yarns Or Ropes (AREA)
Description
Claims (7)
- Verfahren zur Herstellung von schmelzersponnenem endlosem Mehrfarbengarn aus einer Vielzahl von Filamenten, wobei die unterschiedlich gefärbten oder anfärbbaren Filamente gruppenweise zu mindestens zwei Fäden zusammengefaßt und abgezogen werden,
mit mindestens den weiteren Schrittendadurch gekennzeichnet, daß mindestens eine zweite Präparierung hinter dem ersten Abzugsorgan und vor dem Verstrecken durchgeführt wird.Präparieren, wobei eine Präparierung der Fäden mit einem Präparationsmittel mindestens vor einem ersten Abzugsorgan durchgeführt wird,Verstrecken,Texturieren, wobei die Fäden gekräuselt werden,Kühlen,Kompaktieren undAufwickeln der Fäden, - Verfahren nach Anspruch 1, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß die Fäden bis einschließlich zum Verstrecken getrennt gehalten werden, dann als Garn zusammengefaßt und gemeinsam texturiert, gekühlt, kompaktiert sowie aufgewickelt werden.
- Verfahren nach Anspruch 1 oder 2, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß bei der ersten Präparierung gerade so viel Präparationsmittel aufgetragen wird, daß ein guter Lauf auf dem ersten Abzugsorgan gewährleistet ist.
- Verfahren nach Anspruch 1 bis 3, dadurch gekennzeichet, daß bei der ersten Präparierung und der zweiten Präparierung unterschiedliche Präparationsmittel eingesetzt werden.
- Vorrichtung zur Herstellung von schmelzersponnenem endlosem Mehrfarbengam aus einer Vielzahl von Filamenten (3), wobei die unterschiedlich gefärbten oder anfärbbaren Filamente (3.1, 3.2, 3.3) gruppenweise zu mindestens zwei Fäden (4.1, 4.2, 4.3) zusammengefaßt werden, mit mindestensdadurch gekennzeichnet, daß eine zweite Präparationsvorrichtung (9.1, 9.2, 9.3) zwischen dem Abzugsorgan (6, 7) und dem ersten Galettenpaar (8.1, 8.2) angeordnet ist.einem Abzugsorgan, bestehend aus einer Galette (6) und einer Umlenkrolle (7),mindestens einer Präpariervorrichtung (5.1, 5.2, 5.3), wobei eine vor dem Abzugsorgan angeordnet ist,zwei Galettenpaaren (8, 10), zwischen denen die Fäden (4) verstreckt werden,einer Texturiereinrichtung (11),einer Kühlwalze (12),einer Kompaktiervorrichtung (15) undeiner Aufspulvorrichtung (18),
- Vorrichtung nach Anspruch 5, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß die zweite Präparationsvorrichtung (9.1, 9.2, 9.3) für jeden Faden (4.1, 4.2, 4.3) getrennt angeordnet ist.
- Vorrichtung nach Anspruch 5 oder 6, dadurch gekennzeichnet, daß die Präparationsvorrichtung (5, 9.1, 9.2, 9.3) aus zwei unmittelbar benachbarten Präpariereinheiten besteht.
Applications Claiming Priority (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE19929817 | 1999-06-30 | ||
| DE19929817A DE19929817B4 (de) | 1999-06-30 | 1999-06-30 | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur Herstellung schmelzersponnener Endlosfäden |
| PCT/EP2000/006008 WO2001002633A1 (de) | 1999-06-30 | 2000-06-28 | Verfahren und vorrichtung zur herstellung schmelzersponnener endlosfäden |
Publications (2)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP1200656A1 EP1200656A1 (de) | 2002-05-02 |
| EP1200656B1 true EP1200656B1 (de) | 2004-05-12 |
Family
ID=7912958
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP00943920A Expired - Lifetime EP1200656B1 (de) | 1999-06-30 | 2000-06-28 | Verfahren und vorrichtung zur herstellung schmelzersponnener endlosfäden |
Country Status (6)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US6814828B1 (de) |
| EP (1) | EP1200656B1 (de) |
| JP (1) | JP2003504522A (de) |
| AT (1) | ATE266752T1 (de) |
| DE (2) | DE19929817B4 (de) |
| WO (1) | WO2001002633A1 (de) |
Families Citing this family (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE10116959A1 (de) * | 2001-04-05 | 2002-10-10 | Neumag Gmbh & Co Kg | Vorrichtung zum Schmelzspinnen und Ablegen mehrerer Spinnkabel |
| CN100400728C (zh) | 2001-09-11 | 2008-07-09 | 诺马格有限及两合公司 | 纺丝-拉伸-卷曲变形机 |
| DE10326850A1 (de) * | 2003-06-14 | 2004-12-30 | Saurer Gmbh & Co. Kg | Vorrichtung zum Spinnen und Behandeln synthetischer Fäden |
| ITMI20041137A1 (it) * | 2004-06-04 | 2004-09-04 | Fare Spa | Apparecchiatura per il trattamento di filati sintetici |
| JP6021640B2 (ja) * | 2009-06-05 | 2016-11-09 | インヴィスタ テクノロジーズ エスアエルエル | 断続的に着色された糸を製造するシステムおよびその方法 |
| CN103154334B (zh) * | 2010-10-21 | 2015-09-02 | 欧瑞康纺织有限及两合公司 | 多丝复合纱线的制造方法和熔体纺丝设备 |
| CN103911676B (zh) * | 2014-04-03 | 2016-03-16 | 湖州厉华妤婕联合纺织有限公司 | 一种熔纺生成装置 |
| CN109338550A (zh) * | 2018-04-04 | 2019-02-15 | 苏州帝达化纤机械制造有限公司 | 一种膨体连续长丝的纺丝设备 |
| CN109930276A (zh) * | 2019-04-09 | 2019-06-25 | 龙福环能科技股份有限公司 | 聚乳酸生产膨化纤维的牵伸装置及应用 |
Family Cites Families (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GB1066697A (en) | 1964-04-07 | 1967-04-26 | Du Pont | Bulked filament bundles and process for producing them |
| US3427192A (en) * | 1964-05-20 | 1969-02-11 | Deering Milliken Res Corp | Textile sizing composition |
| JPS60246808A (ja) * | 1984-05-21 | 1985-12-06 | Toray Ind Inc | 合成繊維の製造方法 |
| DE3735752C2 (de) * | 1986-10-29 | 1994-03-31 | Barmag Barmer Maschf | Verfahren zur Herstellung von Glattgarn aus Polyamid oder Polyester |
| US4995884A (en) * | 1989-12-08 | 1991-02-26 | Henkel Corporation | Polyalphaolefin emulsions for fiber and textile applications |
| US5251363A (en) * | 1990-11-10 | 1993-10-12 | Barmag Ag | Method and apparatus for combining differently colored threads into a multi-colored yarn |
| US5350529A (en) | 1992-08-28 | 1994-09-27 | E. I. Du Pont De Nemours And Company | Low fume finish for wet air-jet texturing |
| DE19649809A1 (de) * | 1995-12-05 | 1997-06-12 | Barmag Barmer Maschf | Verfahren zum Spinnen, Verstrecken und Aufspulen eines synthetischen Fadens |
| CN1078636C (zh) * | 1996-01-12 | 2002-01-30 | 里特机械公司 | 由长丝构成的不同颜色的单纱生产彩色纱线的方法和设备 |
-
1999
- 1999-06-30 DE DE19929817A patent/DE19929817B4/de not_active Expired - Fee Related
-
2000
- 2000-06-28 DE DE50006424T patent/DE50006424D1/de not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2000-06-28 JP JP2001508402A patent/JP2003504522A/ja active Pending
- 2000-06-28 US US09/979,957 patent/US6814828B1/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2000-06-28 EP EP00943920A patent/EP1200656B1/de not_active Expired - Lifetime
- 2000-06-28 AT AT00943920T patent/ATE266752T1/de not_active IP Right Cessation
- 2000-06-28 WO PCT/EP2000/006008 patent/WO2001002633A1/de not_active Ceased
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| DE19929817A1 (de) | 2001-01-11 |
| DE19929817B4 (de) | 2004-07-15 |
| US6814828B1 (en) | 2004-11-09 |
| ATE266752T1 (de) | 2004-05-15 |
| DE50006424D1 (de) | 2004-06-17 |
| EP1200656A1 (de) | 2002-05-02 |
| JP2003504522A (ja) | 2003-02-04 |
| WO2001002633A1 (de) | 2001-01-11 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP0784109B1 (de) | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur Erzeugung eines mehrfarbigen Garnes aus unterschiedlich farbigen Teilfäden aus Endlosfilament | |
| DE69107411T2 (de) | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zum Kombinieren von Fäden mit verschiedenen Farben um ein mehrfarbiges Garn zu machen. | |
| EP2630279B1 (de) | Verfahren zur herstellung eines multifilen verbundfadens und schmelzspinnvorrichtung | |
| DE10235936A1 (de) | Vorrichtung zum Spinnen und Aufwickeln | |
| DE3720237A1 (de) | Verfahren zum herstellen von luftblastexturiertem naehgarn | |
| EP0133198B1 (de) | Verfahren und Anordnung zur Herstellung eines ungezwirnten Kräuselgarns aus mindestens zwei Fadenbündeln unterschiedlicher Farbe oder Färbbarkeit | |
| EP2567008B1 (de) | Verfahren und vorrichtung zum schmelzspinnen, verstrecken und aufwickeln mehrerer synthetischer fäden | |
| DE69013893T2 (de) | Verfahren zur Herstellung einer teilweise lösbaren und spaltbaren Micro-Verbundfaser. | |
| EP1200656B1 (de) | Verfahren und vorrichtung zur herstellung schmelzersponnener endlosfäden | |
| EP3568510A1 (de) | Vorrichtung und verfahren zur erzeugung eines mehrfarbigen garnes | |
| DE2953527C2 (de) | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur Herstellung von Effektgarn | |
| EP0718424B1 (de) | Anordnung von Streck-Texturiermaschinen für Synthetikfäden | |
| DE2328499A1 (de) | Spinnstrecken und spinnstrecktexturierung von multifilgarnen | |
| DE19746878B4 (de) | Verfahren zur Herstellung eines Mehrkomponentenfadens | |
| DE2855763C2 (de) | ||
| WO2017063913A1 (de) | Verfahren und vorrichtung zur herstellung feiner multifiler fäden | |
| EP1838908B1 (de) | Verfahren und vorrichtung zum schmelzspinnen und texturieren einer vielzahl von multifilen faeden | |
| WO2019034488A1 (de) | Verfahren und vorrichtung zur herstellung eines multifilen vollverstreckten fadens aus einer polyamidschmelze | |
| EP1258547A1 (de) | Lufttexturierter Faden sowie Verfahren zu dessen Herstellung | |
| EP2673406A1 (de) | Verfahren und vorrichtung zum texturieren eines synthetischen fadens | |
| DE1660400C3 (de) | Verfahren zur Herstellung von kompakten Mehrfadengarnen | |
| DE3243998C2 (de) | ||
| WO2003002796A1 (de) | Verfahren und einrichtung zur herstellung von fäden, sowie nach dem verfahren hergestellter faden | |
| EP1527219A1 (de) | Verfahren und vorrichtung zum spinnen und texturieren von synthetischen fäden | |
| DE3813898A1 (de) | Verfahren zum herstellen von luftblastexturiertem naehgarn |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 20020130 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): AT BE CH CY DE DK ES FI FR GB GR IE IT LI LU MC NL PT SE |
|
| GRAP | Despatch of communication of intention to grant a patent |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR1 |
|
| GRAS | Grant fee paid |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: EPIDOSNIGR3 |
|
| GRAA | (expected) grant |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009210 |
|
| RAP1 | Party data changed (applicant data changed or rights of an application transferred) |
Owner name: SAURER GMBH & CO. KG |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: B1 Designated state(s): AT BE CH CY DE DK ES FI FR GB GR IE IT LI LU MC NL PT SE |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: NL Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20040512 Ref country code: CY Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20040512 Ref country code: GB Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20040512 Ref country code: IE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20040512 Ref country code: FI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20040512 Ref country code: FR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20040512 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: GB Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: NOT ENGLISH |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: EP |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: FG4D Free format text: GERMAN |
|
| REF | Corresponds to: |
Ref document number: 50006424 Country of ref document: DE Date of ref document: 20040617 Kind code of ref document: P |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: LU Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20040628 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: MC Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20040630 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: NV Representative=s name: KEMENY AG PATENTANWALTBUERO |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: SE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20040812 Ref country code: DK Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20040812 Ref country code: GR Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20040812 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: ES Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF FAILURE TO SUBMIT A TRANSLATION OF THE DESCRIPTION OR TO PAY THE FEE WITHIN THE PRESCRIBED TIME-LIMIT Effective date: 20040823 |
|
| NLV1 | Nl: lapsed or annulled due to failure to fulfill the requirements of art. 29p and 29m of the patents act | ||
| GBV | Gb: ep patent (uk) treated as always having been void in accordance with gb section 77(7)/1977 [no translation filed] |
Effective date: 20040512 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: IE Ref legal event code: FD4D |
|
| PLBE | No opposition filed within time limit |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009261 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: NO OPPOSITION FILED WITHIN TIME LIMIT |
|
| 26N | No opposition filed |
Effective date: 20050215 |
|
| EN | Fr: translation not filed | ||
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AT Payment date: 20060608 Year of fee payment: 7 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BE Payment date: 20060613 Year of fee payment: 7 Ref country code: CH Payment date: 20060613 Year of fee payment: 7 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Payment date: 20060630 Year of fee payment: 7 |
|
| PGFP | Annual fee paid to national office [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: DE Payment date: 20060821 Year of fee payment: 7 |
|
| BERE | Be: lapsed |
Owner name: *SAURER G.M.B.H. & CO. K.G. Effective date: 20070630 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: PT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20041012 |
|
| REG | Reference to a national code |
Ref country code: CH Ref legal event code: PL |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: AT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20070628 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: BE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20070630 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: CH Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20070630 Ref country code: DE Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20080101 Ref country code: LI Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20070630 |
|
| PG25 | Lapsed in a contracting state [announced via postgrant information from national office to epo] |
Ref country code: IT Free format text: LAPSE BECAUSE OF NON-PAYMENT OF DUE FEES Effective date: 20070628 |