EP0636718A1 - Broche textile - Google Patents
Broche textile Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- EP0636718A1 EP0636718A1 EP94109596A EP94109596A EP0636718A1 EP 0636718 A1 EP0636718 A1 EP 0636718A1 EP 94109596 A EP94109596 A EP 94109596A EP 94109596 A EP94109596 A EP 94109596A EP 0636718 A1 EP0636718 A1 EP 0636718A1
- Authority
- EP
- European Patent Office
- Prior art keywords
- spindle
- bearing
- textile
- joint
- shaft
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Withdrawn
Links
- 239000004753 textile Substances 0.000 title claims abstract description 24
- 238000005452 bending Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 10
- 238000013016 damping Methods 0.000 claims description 13
- 230000007935 neutral effect Effects 0.000 claims description 5
- 238000009434 installation Methods 0.000 claims 1
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 4
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 description 3
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000010354 integration Effects 0.000 description 2
- 230000002028 premature Effects 0.000 description 2
- 229910000831 Steel Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 238000006073 displacement reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000005489 elastic deformation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000005461 lubrication Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000007789 sealing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 125000006850 spacer group Chemical group 0.000 description 1
- 239000010959 steel Substances 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- D—TEXTILES; PAPER
- D01—NATURAL OR MAN-MADE THREADS OR FIBRES; SPINNING
- D01H—SPINNING OR TWISTING
- D01H7/00—Spinning or twisting arrangements
- D01H7/02—Spinning or twisting arrangements for imparting permanent twist
- D01H7/04—Spindles
- D01H7/045—Spindles provided with flexible mounting elements for damping vibration or noise, or for avoiding or reducing out-of-balance forces due to rotation
Definitions
- the invention relates to a textile spindle according to the preamble of claim 1.
- Such a textile spindle is already known from EP-A1-0 209 799, which allows an unbalance compensation by approximation of the actual main mass inertia axis to the axis of rotation of the spindle bearing over two degrees of freedom of the spindle shaft.
- the spindle shaft the shaft of which is rotatably supported in a spindle bearing housing via a neck bearing and a foot bearing, is able to execute a wobbling movement around the neck bearing against the action of a damping device arranged inside the spindle bearing housing.
- the spindle bearing housing is in turn connected at a distance from the spindle bench via a mounting sleeve to the one end of axially parallel bending spring bars distributed over its circumference, the opposite ends of which are anchored to the spindle bench via a further mounting sleeve.
- the whorl is arranged on the spindle shaft in the area of the neck bearing.
- the spindle shaft with the upper part carrying the yarn spool can tip over the neck bearing to the extent of its ability to tumble against the action of the damping device.
- the mutually parallel bending spring rods of the same length form, together with the mounting sleeves, a spatially formed, parallelogram-like connection, the imaginary pairs of joints of which each lie in one of two axially spaced radial planes, that run parallel to the spindle bench.
- the spindle bearing housing can thus only be moved practically in the sense of a parallel displacement in the radial direction, counter to the spring tension of the spiral spring bars.
- the belt tensile force acts as a result of the whorl arrangement in the area of the neck bearing, an inclined position of the spindle shaft or its upper part carrying the spool is thus avoided; the spindle bearing housing executes the radial movements at right angles to the spindle bank.
- the spindle bearing housing In order to compensate for unbalance when rotating the spindle, the spindle bearing housing, in the position displaced parallel from the neutral position, carries out a translatory torsional vibration movement together with the associated mounting sleeve.
- the spindle bearing housing alone represents a relatively large mass. In the supercritical speed range, the inertia hinders the dynamic mobility in the radial direction of the spindle shaft. This is accompanied by an increase in the undesirable bearing reaction forces between the spindle shaft and the neck bearing and the foot bearing. This leads to premature wear of the bearings mentioned.
- the object of the invention is to provide a textile spindle in which, while reducing the reaction forces in the bearings and by reducing the stress on the bending-elastic elements involved, the design and material and production costs can be reduced and the range of application can thus be expanded.
- the solution is based on the knowledge that the bearing reaction forces can be most effectively achieved by reducing the mass involved in the vibrations.
- the flexurally elastic configuration of the shaft of the spindle shaft between the neck bearing and the foot bearing has an effect, which allows a spring-elastic shaft bearing element and therefore its resonating mass to be avoided.
- the arrangement according to the invention of the tilting joint at a distance from the neck bearing which enables the radial deflection of the spindle shaft in the neck bearing area, only a reduced part of the total mass resonates and is therefore effective for the inertia of interest here.
- the whorl is arranged on the spindle shaft below the neck bearing.
- the deformation of the two resilient elements, i.e. of the shaft part of the spindle shaft and of the tilt joint lead to opposite, practically compensating deflections in relation to the upper part of the spindle shaft.
- the deflection resulting from the tilting of the bearing sleeve causes the spindle shaft to be inclined approximately in a direction corresponding to the belt force, during which the deflection of the shaft part of the spindle shaft results in the deflection of the upper part thereof in the opposite direction.
- the upper part of the spindle shaft assumes an almost vertical position with respect to the spindle bank.
- the tilting joint is distanced from the neck bearing approximately by the length of the shaft part of the spindle shaft, so that the extent of the elastic deformation in the tilting joint can be kept small for a given radial movement of the neck bearing from the neutral position.
- the neutral position of a bearing axis is denoted by 1, which also corresponds to the neutral position of the spindle shaft 2 represented by its axis.
- the axis 1 is cut by the imaginary articulation axis 3 of a flexurally flexible tilting joint that leads in a horizontal plane.
- the tilting joint which is actually rigidly connected to the spindle bank, is shown at 9 at one end as being held stationary, while at its other end the lower end of a bearing sleeve 4 is connected.
- a (elastically shown) flexurally elastic shaft part 2a 'of the spindle shaft 2 is rotatably mounted in a neck bearing 5 and a foot bearing 6 shown coincident with the articulation axis 3.
- the tensile force F (corresponding to the direction of the arrow) of a drive belt indicated as attacking at 8 acts on a whorl 4 seated on the spindle shaft 2.
- the bearing sleeve 4 under the action of the tensile force F , has assumed a position pivoted by an angle 1 with respect to the bearing axis 1.
- the location of the attack 8 of the tensile force F on the whorl at a distance h below the neck bearing 5 has caused a bending moment F * h on the shaft part 2a.
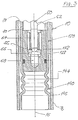
- the textile spindle shown physically in FIG. 2 comprises a tubular spindle housing 10 which is provided with an external thread 12 for rigid attachment in a bore in the spindle bench (not shown).
- a thin-walled intermediate tube 20 forming the bearing sleeve.
- a cup-shaped head piece 42 rigidly attached in the lower end 22 of the intermediate tube 20 in the lower end 22 of the intermediate tube 20 in the lower end 22 of the intermediate tube 20 in the lower end 22 of the intermediate tube 20 is a press fit 24 a cup-shaped head piece 42 rigidly attached.
- the head piece 42 forms part of a single-axis tilt joint, generally designated 40, which comprises a web 44 and a foot piece 46.
- the rocker joint 40 takes with its web 44 a position coaxial to the longitudinal axis 16 of the housing a.
- the foot 46 is pressed into the lower end 18 of the spindle housing 10.
- the tilting joint 40 is made in one piece and consists of steel, which is made flexible in the area of the web 44 by reducing the cross-section.
- a bearing bush 62 receiving a neck bearing 60 is pressed into the upper end 26 of the intermediate tube 20.
- the neck bearing 60 rotatably receives a spindle shaft 50, which will be described in more detail below and which carries a belt-driven whorl 30 and a yarn spool (not shown) on an upper part (not shown).
- the whorl 30, which is connected to the spindle shaft 50 in a rotationally rigid manner, is arranged below the neck bearing 60, i.e. with respect to the latter axially offset in the direction of the tilt joint 40.
- the shaft part 52 of the spindle shaft 50 which extends in the interior of the intermediate tube 20 below the neck bearing 60 is designed to be flexurally elastic by appropriate tapering.
- a foot bearing 64 designed as a sliding bearing which is arranged in the cup-shaped head piece 42, receives an end piece 54 of the shaft part 52, the spherically shaped end face 56 of which rests on a sliding plate 66 acting as an axial bearing.
- a pin 68 inserted into the head piece 42 supports the sliding plate 66 and therefore the entire spindle shaft 50 in the intermediate tube 20.
- the neck bearing 60 is a known radial roller bearing equipped with a circular clearance between the shaft and bearing rollers.
- the foot bearing 64 has sufficient bearing play to allow misalignments between the shaft part axis - resulting from the deflection - and the bearing axis. The latter coincides with the housing axis 16 if the intermediate tube does not fail the vertical position shown is deflected.
- the flexurally elastic shaft part 52 is surrounded by a damping device 70 provided in the intermediate tube 20 approximately in the region of the greatest deflection.
- the damping device 70 has a guide bush 72 designed as a slide bearing, a thin-walled spring sleeve 74 and a damping element 76 designed as a spiral spring.
- the guide bush 72 which receives the part 52 of the spindle shaft 50, is pressed into the spring sleeve 74 and transmits to it the forces exerted on the former.
- the spring sleeve 74 is arranged in the damping element 76 and secured by end widenings 78.
- the former distributes the forces absorbed over the length of the damping element 76, which is supported on the inside 28 of the intermediate tube 20. In the axial direction, the damping element 76 is held between a thin-walled spacer sleeve 80 standing on the head piece 42 and the bearing sleeve 62.
- At least the cup-shaped head piece 42 contains an oil bath for bearing lubrication, but this can also completely or partially fill the intermediate pipe 20, so that the damping device 70 is also located therein. Accordingly, a sealing ring 49 cooperating with the intermediate tube 20 is provided in a circumferential groove 48 provided in the head piece 42 in order to prevent oil from flowing out.
- the intermediate tube 20 in the spindle housing 10 can deflect by the radial play indicated at 19, or tip out of the housing axis 16, specifically by the lower end thereof adjoining tilt joint 40.
- the stresses occurring in the web 44 are small due to the axial distance from the neck bearing 60.
- the tilt joint Since the radial deflection of the intermediate tube or bearing sleeve 20 can take place with its parts by tipping over the tilt joint, only a fraction of the mass involved is also oscillating; the lower end of the bearing sleeve, which itself is low in mass, remains practically stationary in this regard. Due to the distance to the neck bearing and the corresponding leverage, the tilt joint is subject to low stresses. Thus, there are no high requirements to be met with regard to material and processing, in particular surface quality, and the tilting joint can be produced inexpensively. Due to the flexible design of the shaft part of the shaft itself, the deflection of the upper part of the spindle shaft around the neck bearing is realized in a simple and low-mass manner.
- FIG. 3 corresponds completely to that according to FIG. 1 with regard to the design and mounting of the spindle shaft 50, the same parts bearing the same reference numerals. However, this differs mainly in that a tilt joint 140 is provided as part of an intermediate tube 120. An independent, cup-shaped bearing element 132 is pressed into a lower end part 122 of the intermediate tube 120, which is distanced from the neck bearing and thus from the spindle bank and which replaces the head piece 42 according to FIG. 1 with regard to its function as a bearing holder.
- the tilting joint 140 comprises, in addition to the part 122, a tubular section 144 which is designed as a bellows and is thus designed to be flexible, and a tubular foot part 146 this foot part 146 in turn is rigidly fixed, in that it has a larger diameter than the part 122 and is pressed into the lower end 18.
- the exemplary embodiment according to FIG. 3 has no differences from that according to FIG. 2.
- the tilt joint 140 is designed as a spring-elastic element.
- the spring-elastic element is again integrated into the intermediate tube 220.
- a cup-shaped bearing element 232 which corresponds functionally to that according to FIG. 3, protrudes from below into the spindle housing 210 and is rigidly fastened in the lower end 216 thereof.
- a foot part 246 of the tilting joint 240 is pressed onto a collar 234 of the bearing element 232 which is tapered in diameter and which comprises a tubular section 244 designed as a bellows.
- the part of the intermediate pipe 220 surrounding the damping device 70 directly adjoins the pipe section 244.
- the resilient, resilient part of the tilting joints 140 and 240 is formed by a section of a tube designed as a bellows, specifically the intermediate tube 120 and 220, respectively, this flexibility can be used as an alternative by means of other measures which sufficiently reduce the rigidity of the corresponding pipe section, while maintaining the structure of the textile spindle described in each case.
- the tilt joint as part of another component, i.e. Integrated into the intermediate tube or into the bearing housing, this can also be designed as an independent component, corresponding to the tilt joint 40 of FIG. 1.
- the tilt joint provided according to the invention in the spindle housing instead of an arrangement between the spindle housing and the intermediate tube, as shown in FIG. 2 or an integration into the intermediate tube according to FIGS. 3 and 4, and that directly above the bearing element, the same as in Fig. 4 is pressed into the lower end of the spindle housing.
- the rigid holding element is formed by the main part of the spindle housing adjoining above the tilt joint.
- the tilt joint can be provided in the part of the intermediate tube 120 or 220 adjoining the bearing part 132 or 232, without impairing the principle of action of two mutually independent, spring-elastic degrees of freedom of the spindle shaft.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Textile Engineering (AREA)
- Spinning Or Twisting Of Yarns (AREA)
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CH2293/93 | 1993-07-28 | ||
| CH229393 | 1993-07-28 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| EP0636718A1 true EP0636718A1 (fr) | 1995-02-01 |
Family
ID=4230390
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| EP94109596A Withdrawn EP0636718A1 (fr) | 1993-07-28 | 1994-06-22 | Broche textile |
Country Status (3)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US5528892A (fr) |
| EP (1) | EP0636718A1 (fr) |
| JP (1) | JP2759870B2 (fr) |
Families Citing this family (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DE19536874A1 (de) * | 1995-10-03 | 1997-04-10 | Novibra Gmbh | Spindel für Spinn- oder Zwirnmaschinen |
| DE19612121A1 (de) * | 1996-03-27 | 1997-10-02 | Stahlecker Fritz | Spindel für Spinn- oder Zwirnmaschinen |
| DE19726216B4 (de) * | 1997-06-20 | 2007-11-22 | Novibra Gmbh | Spindel für Spinn- oder Zwirnmaschinen |
| US6273611B1 (en) * | 1998-12-03 | 2001-08-14 | Fritz Stahlecker | Bearing for spindles in spinning or twisting machines |
| DE102009031886A1 (de) * | 2009-07-06 | 2011-01-20 | Rotorcraft Ag | Spindellagerung für eine Ringspinnmaschine |
Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CA515112A (fr) * | 1950-05-01 | 1955-07-26 | Universal Winding Company | Broche de filature |
| FR1204630A (fr) * | 1957-04-27 | 1960-01-27 | Support de broches à rotation rapide, notamment de broches à filer ou à retordre | |
| FR1293897A (fr) * | 1960-08-08 | 1962-05-18 | Rieter Ag Maschf | Broche pour métiers à filer et à retordre |
| DE3843651A1 (de) * | 1988-01-29 | 1989-08-03 | Rieter Ag Maschf | Spinn- oder zwirnspindel |
| DE3942403A1 (de) * | 1989-12-21 | 1991-06-27 | Stahlecker Fritz | Spinn- oder zwirnspindel |
| DE4121979A1 (de) * | 1990-08-08 | 1992-02-13 | Stahlecker Fritz | Spinn- oder zwirnspindel |
Family Cites Families (17)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FR1150447A (fr) * | 1956-05-04 | 1958-01-13 | Alsacienne Constr Meca | Broche de métier à filer ou à retordre |
| BE558023A (fr) * | 1956-06-15 | |||
| CH379985A (de) * | 1960-04-29 | 1964-07-15 | Rieter Ag Maschf | Spinn- und Zwirnspindel |
| US3708888A (en) * | 1971-01-14 | 1973-01-09 | Royal Oak Charcoal Co | Apparatus for activating comminuted material |
| US3797219A (en) * | 1972-03-01 | 1974-03-19 | Whitin Machine Works | Spindle bolster |
| DE2228246C3 (de) * | 1972-06-09 | 1981-02-12 | Zinser Textilmaschinen Gmbh, 7333 Ebersbach | Spinn- oder Zwirnmaschine |
| CH539697A (de) * | 1972-07-10 | 1973-07-31 | Uster Spindel Motoren Maschf | Textilspindel |
| DE2348908C2 (de) * | 1973-09-28 | 1982-07-22 | Spindel, Motoren & Maschinenfabrik AG, Uster, Zürich | Spinn- oder Zwirnspindel mit einem durch einen Wirtel antreibbaren Spindelschaft |
| DE2749389C3 (de) * | 1977-11-04 | 1980-11-06 | Skf Kugellagerfabriken Gmbh, 8720 Schweinfurt | Lagerung für den Schaft einer Spinn- und Zwirnspindel |
| DD236762A1 (de) * | 1985-04-29 | 1986-06-18 | Spindel Und Spinnfluegelfabrik | Justierbare spindel fuer spinn- oder zwirnmaschinen |
| CH667112A5 (de) * | 1985-07-24 | 1988-09-15 | Uster Spindel Motoren Maschf | Einrichtung zum radial beweglichen befestigen eines spindellagergehaeuses einer spinn- oder zwirnspindel an einer spindelbank. |
| US5201170A (en) * | 1989-12-23 | 1993-04-13 | Fritz Stahlecker | Spinning or twisting spindle having a spindle shaft |
| US5359842A (en) * | 1989-11-17 | 1994-11-01 | Fritz Stahlecker | Spinning or twisting shaft bearing assembly with vibration isolation connection arrangement |
| DE4036353C2 (de) * | 1989-12-23 | 2000-11-02 | Stahlecker Fritz | Spinn- oder Zwirnspindel |
| DE4004046A1 (de) * | 1990-02-10 | 1991-08-14 | Stahlecker Fritz | Lagerung fuer eine spinn- oder zwirnspindel |
| US5119620A (en) * | 1990-05-17 | 1992-06-09 | Wilhelm Stahlecker Gmbh | Holding arrangement for a spindle of ring spinning or ring twisting machines |
| CH683430A5 (de) * | 1991-07-10 | 1994-03-15 | Rieter Ag Maschf | Spinn- oder Zwirnspindel. |
-
1994
- 1994-06-22 EP EP94109596A patent/EP0636718A1/fr not_active Withdrawn
- 1994-07-27 US US08/280,999 patent/US5528892A/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 1994-07-28 JP JP6195906A patent/JP2759870B2/ja not_active Expired - Lifetime
Patent Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CA515112A (fr) * | 1950-05-01 | 1955-07-26 | Universal Winding Company | Broche de filature |
| FR1204630A (fr) * | 1957-04-27 | 1960-01-27 | Support de broches à rotation rapide, notamment de broches à filer ou à retordre | |
| FR1293897A (fr) * | 1960-08-08 | 1962-05-18 | Rieter Ag Maschf | Broche pour métiers à filer et à retordre |
| DE3843651A1 (de) * | 1988-01-29 | 1989-08-03 | Rieter Ag Maschf | Spinn- oder zwirnspindel |
| DE3942403A1 (de) * | 1989-12-21 | 1991-06-27 | Stahlecker Fritz | Spinn- oder zwirnspindel |
| DE4121979A1 (de) * | 1990-08-08 | 1992-02-13 | Stahlecker Fritz | Spinn- oder zwirnspindel |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| US5528892A (en) | 1996-06-25 |
| JPH0754223A (ja) | 1995-02-28 |
| JP2759870B2 (ja) | 1998-05-28 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| DE4121279A1 (de) | Bohr- und/oder schlaghammer | |
| EP0395964B1 (fr) | Dispositif pour l'équilibrage des forces dues aux masses dans une machine à manivelle, notamment une machine à poinçonner | |
| WO2005092575A1 (fr) | Transmission a came oscillante | |
| EP0636718A1 (fr) | Broche textile | |
| DE4129797C2 (de) | Schwingungstilger | |
| EP1837425B1 (fr) | Balancement d'un appareil de serrage dans une peigneuse | |
| DE3924373C2 (de) | Textilspindel mit einzelmotorischem Antrieb, wobei der Rotor gedämpft aufgehängt ist | |
| EP0209799B1 (fr) | Dispositif de fixation radialement mobile d'une boîte de palier d'une broche à filer ou à retordre sur un banc à broches | |
| DE1290856B (de) | Gewichtsausgleich von Fadenfuehrungselementen bei Spinn- oder Zwirnmaschinen | |
| DE2348908C2 (de) | Spinn- oder Zwirnspindel mit einem durch einen Wirtel antreibbaren Spindelschaft | |
| DE4019671C2 (fr) | ||
| DE4006117C2 (fr) | ||
| EP1206652A1 (fr) | Amortisseur a friction | |
| DE2310323A1 (de) | Hochtourige spindelanordnung fuer spinnmaschinen und lagerung fuer derartige spindeln | |
| DE19726216B4 (de) | Spindel für Spinn- oder Zwirnmaschinen | |
| DE19534339A1 (de) | Spindel für Spinn- oder Zwirnmaschinen | |
| DE19622238C1 (de) | Leitwalze für Bahnmaterial, insb. für Papiermaschinen | |
| DE3835811C2 (fr) | ||
| CH690441A5 (de) | Vorrichtung zum selbsttätigen Spulenwechsel an einer Spinnereimaschine. | |
| DE2928723C2 (de) | Spinn- und Zwirnspindel | |
| DE4234434A1 (de) | Ringspinn- bzw. Zwirnspindel, die von Tangentialriemen oder einem Vierspindelbandantrieb angetrieben wird | |
| DE2306925A1 (de) | Kraftwerkzeug | |
| EP0656999B1 (fr) | Accouplement homocinetique | |
| DE19612121A1 (de) | Spindel für Spinn- oder Zwirnmaschinen | |
| DE4429833A1 (de) | Spindel für Spinn- oder Zwirnmaschinen |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| PUAI | Public reference made under article 153(3) epc to a published international application that has entered the european phase |
Free format text: ORIGINAL CODE: 0009012 |
|
| AK | Designated contracting states |
Kind code of ref document: A1 Designated state(s): CH DE ES FR IT LI |
|
| 17P | Request for examination filed |
Effective date: 19950708 |
|
| 17Q | First examination report despatched |
Effective date: 19961209 |
|
| STAA | Information on the status of an ep patent application or granted ep patent |
Free format text: STATUS: THE APPLICATION IS DEEMED TO BE WITHDRAWN |
|
| 18D | Application deemed to be withdrawn |
Effective date: 19970422 |