CN102473759A - 光电转换装置和其制造方法 - Google Patents
光电转换装置和其制造方法 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- CN102473759A CN102473759A CN2010800358789A CN201080035878A CN102473759A CN 102473759 A CN102473759 A CN 102473759A CN 2010800358789 A CN2010800358789 A CN 2010800358789A CN 201080035878 A CN201080035878 A CN 201080035878A CN 102473759 A CN102473759 A CN 102473759A
- Authority
- CN
- China
- Prior art keywords
- type layer
- layer
- photoelectric conversion
- microcrystal silicon
- silicon layer
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Pending
Links
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 13
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 90
- 238000002425 crystallisation Methods 0.000 claims abstract description 60
- 230000008025 crystallization Effects 0.000 claims abstract description 60
- XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicon Chemical compound [Si] XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims description 51
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 claims description 51
- 229910052710 silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 50
- 239000010703 silicon Substances 0.000 claims description 50
- 238000000576 coating method Methods 0.000 claims description 43
- 239000011248 coating agent Substances 0.000 claims description 42
- 239000013081 microcrystal Substances 0.000 claims description 42
- 239000011521 glass Substances 0.000 claims description 21
- 238000001069 Raman spectroscopy Methods 0.000 claims description 13
- 239000002019 doping agent Substances 0.000 claims description 13
- 238000013459 approach Methods 0.000 claims description 11
- 238000010276 construction Methods 0.000 claims description 10
- 238000009826 distribution Methods 0.000 abstract description 6
- 229910021424 microcrystalline silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 abstract description 4
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 abstract description 3
- 239000010408 film Substances 0.000 description 52
- 229910021417 amorphous silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 33
- 239000007789 gas Substances 0.000 description 33
- 229910021419 crystalline silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 25
- ORQBXQOJMQIAOY-UHFFFAOYSA-N nobelium Chemical compound [No] ORQBXQOJMQIAOY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 21
- 230000000052 comparative effect Effects 0.000 description 18
- 238000005266 casting Methods 0.000 description 14
- 238000005268 plasma chemical vapour deposition Methods 0.000 description 12
- 238000009413 insulation Methods 0.000 description 10
- 238000000151 deposition Methods 0.000 description 9
- 230000005693 optoelectronics Effects 0.000 description 9
- 239000003085 diluting agent Substances 0.000 description 8
- UFHFLCQGNIYNRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N Hydrogen Chemical compound [H][H] UFHFLCQGNIYNRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 7
- XLOMVQKBTHCTTD-UHFFFAOYSA-N Zinc monoxide Chemical compound [Zn]=O XLOMVQKBTHCTTD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 7
- 230000007423 decrease Effects 0.000 description 7
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 7
- 229910052739 hydrogen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 7
- 239000001257 hydrogen Substances 0.000 description 7
- BLRPTPMANUNPDV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silane Chemical compound [SiH4] BLRPTPMANUNPDV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 6
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 6
- 238000000059 patterning Methods 0.000 description 6
- 229910000077 silane Inorganic materials 0.000 description 6
- OKTJSMMVPCPJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N Carbon Chemical compound [C] OKTJSMMVPCPJKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- 229910052799 carbon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 5
- 239000006185 dispersion Substances 0.000 description 5
- XYFCBTPGUUZFHI-UHFFFAOYSA-N Phosphine Chemical compound P XYFCBTPGUUZFHI-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicium dioxide Chemical compound O=[Si]=O VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 4
- VNWKTOKETHGBQD-UHFFFAOYSA-N methane Chemical compound C VNWKTOKETHGBQD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 4
- 239000003595 mist Substances 0.000 description 4
- 238000002156 mixing Methods 0.000 description 4
- 238000012856 packing Methods 0.000 description 4
- 230000008676 import Effects 0.000 description 3
- ZOXJGFHDIHLPTG-UHFFFAOYSA-N Boron Chemical compound [B] ZOXJGFHDIHLPTG-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- OAICVXFJPJFONN-UHFFFAOYSA-N Phosphorus Chemical compound [P] OAICVXFJPJFONN-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229910006404 SnO 2 Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000004411 aluminium Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910052782 aluminium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 229910052796 boron Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- ZOCHARZZJNPSEU-UHFFFAOYSA-N diboron Chemical compound B#B ZOCHARZZJNPSEU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 125000003963 dichloro group Chemical group Cl* 0.000 description 2
- 230000003292 diminished effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- PZPGRFITIJYNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N disilane Chemical compound [SiH3][SiH3] PZPGRFITIJYNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 238000005516 engineering process Methods 0.000 description 2
- AMGQUBHHOARCQH-UHFFFAOYSA-N indium;oxotin Chemical compound [In].[Sn]=O AMGQUBHHOARCQH-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 239000011777 magnesium Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910052751 metal Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000002184 metal Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910052698 phosphorus Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000011574 phosphorus Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000000377 silicon dioxide Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000007921 spray Substances 0.000 description 2
- 239000010409 thin film Substances 0.000 description 2
- XOLBLPGZBRYERU-UHFFFAOYSA-N tin dioxide Chemical compound O=[Sn]=O XOLBLPGZBRYERU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 229910001887 tin oxide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- PXGOKWXKJXAPGV-UHFFFAOYSA-N Fluorine Chemical compound FF PXGOKWXKJXAPGV-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- FYYHWMGAXLPEAU-UHFFFAOYSA-N Magnesium Chemical compound [Mg] FYYHWMGAXLPEAU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000004642 Polyimide Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000001237 Raman spectrum Methods 0.000 description 1
- BQCADISMDOOEFD-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silver Chemical compound [Ag] BQCADISMDOOEFD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- ATJFFYVFTNAWJD-UHFFFAOYSA-N Tin Chemical compound [Sn] ATJFFYVFTNAWJD-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N aluminium Chemical compound [Al] XAGFODPZIPBFFR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- -1 aluminium metals Chemical class 0.000 description 1
- 230000003321 amplification Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000004458 analytical method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910052787 antimony Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- WATWJIUSRGPENY-UHFFFAOYSA-N antimony atom Chemical compound [Sb] WATWJIUSRGPENY-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 238000003556 assay Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000005540 biological transmission Effects 0.000 description 1
- 230000002950 deficient Effects 0.000 description 1
- 229910052731 fluorine Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000011737 fluorine Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000000227 grinding Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000012535 impurity Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000003475 lamination Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910052749 magnesium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 238000005259 measurement Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000003199 nucleic acid amplification method Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000035699 permeability Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000004033 plastic Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229910021420 polycrystalline silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229920001721 polyimide Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229920005591 polysilicon Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000011347 resin Substances 0.000 description 1
- 229920005989 resin Polymers 0.000 description 1
- 229910052709 silver Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000004332 silver Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000011787 zinc oxide Substances 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L31/00—Semiconductor devices sensitive to infrared radiation, light, electromagnetic radiation of shorter wavelength or corpuscular radiation and specially adapted either for the conversion of the energy of such radiation into electrical energy or for the control of electrical energy by such radiation; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof
- H01L31/04—Semiconductor devices sensitive to infrared radiation, light, electromagnetic radiation of shorter wavelength or corpuscular radiation and specially adapted either for the conversion of the energy of such radiation into electrical energy or for the control of electrical energy by such radiation; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof adapted as photovoltaic [PV] conversion devices
- H01L31/06—Semiconductor devices sensitive to infrared radiation, light, electromagnetic radiation of shorter wavelength or corpuscular radiation and specially adapted either for the conversion of the energy of such radiation into electrical energy or for the control of electrical energy by such radiation; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof adapted as photovoltaic [PV] conversion devices characterised by potential barriers
- H01L31/075—Semiconductor devices sensitive to infrared radiation, light, electromagnetic radiation of shorter wavelength or corpuscular radiation and specially adapted either for the conversion of the energy of such radiation into electrical energy or for the control of electrical energy by such radiation; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof adapted as photovoltaic [PV] conversion devices characterised by potential barriers the potential barriers being only of the PIN type, e.g. amorphous silicon PIN solar cells
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L31/00—Semiconductor devices sensitive to infrared radiation, light, electromagnetic radiation of shorter wavelength or corpuscular radiation and specially adapted either for the conversion of the energy of such radiation into electrical energy or for the control of electrical energy by such radiation; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof
- H01L31/0248—Semiconductor devices sensitive to infrared radiation, light, electromagnetic radiation of shorter wavelength or corpuscular radiation and specially adapted either for the conversion of the energy of such radiation into electrical energy or for the control of electrical energy by such radiation; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof characterised by their semiconductor bodies
- H01L31/036—Semiconductor devices sensitive to infrared radiation, light, electromagnetic radiation of shorter wavelength or corpuscular radiation and specially adapted either for the conversion of the energy of such radiation into electrical energy or for the control of electrical energy by such radiation; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof characterised by their semiconductor bodies characterised by their crystalline structure or particular orientation of the crystalline planes
- H01L31/0368—Semiconductor devices sensitive to infrared radiation, light, electromagnetic radiation of shorter wavelength or corpuscular radiation and specially adapted either for the conversion of the energy of such radiation into electrical energy or for the control of electrical energy by such radiation; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof characterised by their semiconductor bodies characterised by their crystalline structure or particular orientation of the crystalline planes including polycrystalline semiconductors
- H01L31/03682—Semiconductor devices sensitive to infrared radiation, light, electromagnetic radiation of shorter wavelength or corpuscular radiation and specially adapted either for the conversion of the energy of such radiation into electrical energy or for the control of electrical energy by such radiation; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof characterised by their semiconductor bodies characterised by their crystalline structure or particular orientation of the crystalline planes including polycrystalline semiconductors including only elements of Group IV of the Periodic Table
- H01L31/03685—Semiconductor devices sensitive to infrared radiation, light, electromagnetic radiation of shorter wavelength or corpuscular radiation and specially adapted either for the conversion of the energy of such radiation into electrical energy or for the control of electrical energy by such radiation; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof characterised by their semiconductor bodies characterised by their crystalline structure or particular orientation of the crystalline planes including polycrystalline semiconductors including only elements of Group IV of the Periodic Table including microcrystalline silicon, uc-Si
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C23—COATING METALLIC MATERIAL; COATING MATERIAL WITH METALLIC MATERIAL; CHEMICAL SURFACE TREATMENT; DIFFUSION TREATMENT OF METALLIC MATERIAL; COATING BY VACUUM EVAPORATION, BY SPUTTERING, BY ION IMPLANTATION OR BY CHEMICAL VAPOUR DEPOSITION, IN GENERAL; INHIBITING CORROSION OF METALLIC MATERIAL OR INCRUSTATION IN GENERAL
- C23C—COATING METALLIC MATERIAL; COATING MATERIAL WITH METALLIC MATERIAL; SURFACE TREATMENT OF METALLIC MATERIAL BY DIFFUSION INTO THE SURFACE, BY CHEMICAL CONVERSION OR SUBSTITUTION; COATING BY VACUUM EVAPORATION, BY SPUTTERING, BY ION IMPLANTATION OR BY CHEMICAL VAPOUR DEPOSITION, IN GENERAL
- C23C16/00—Chemical coating by decomposition of gaseous compounds, without leaving reaction products of surface material in the coating, i.e. chemical vapour deposition [CVD] processes
- C23C16/22—Chemical coating by decomposition of gaseous compounds, without leaving reaction products of surface material in the coating, i.e. chemical vapour deposition [CVD] processes characterised by the deposition of inorganic material, other than metallic material
- C23C16/24—Deposition of silicon only
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C23—COATING METALLIC MATERIAL; COATING MATERIAL WITH METALLIC MATERIAL; CHEMICAL SURFACE TREATMENT; DIFFUSION TREATMENT OF METALLIC MATERIAL; COATING BY VACUUM EVAPORATION, BY SPUTTERING, BY ION IMPLANTATION OR BY CHEMICAL VAPOUR DEPOSITION, IN GENERAL; INHIBITING CORROSION OF METALLIC MATERIAL OR INCRUSTATION IN GENERAL
- C23C—COATING METALLIC MATERIAL; COATING MATERIAL WITH METALLIC MATERIAL; SURFACE TREATMENT OF METALLIC MATERIAL BY DIFFUSION INTO THE SURFACE, BY CHEMICAL CONVERSION OR SUBSTITUTION; COATING BY VACUUM EVAPORATION, BY SPUTTERING, BY ION IMPLANTATION OR BY CHEMICAL VAPOUR DEPOSITION, IN GENERAL
- C23C16/00—Chemical coating by decomposition of gaseous compounds, without leaving reaction products of surface material in the coating, i.e. chemical vapour deposition [CVD] processes
- C23C16/44—Chemical coating by decomposition of gaseous compounds, without leaving reaction products of surface material in the coating, i.e. chemical vapour deposition [CVD] processes characterised by the method of coating
- C23C16/52—Controlling or regulating the coating process
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02104—Forming layers
- H01L21/02365—Forming inorganic semiconducting materials on a substrate
- H01L21/02518—Deposited layers
- H01L21/02521—Materials
- H01L21/02524—Group 14 semiconducting materials
- H01L21/02532—Silicon, silicon germanium, germanium
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02104—Forming layers
- H01L21/02365—Forming inorganic semiconducting materials on a substrate
- H01L21/02518—Deposited layers
- H01L21/0257—Doping during depositing
- H01L21/02573—Conductivity type
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02104—Forming layers
- H01L21/02365—Forming inorganic semiconducting materials on a substrate
- H01L21/02518—Deposited layers
- H01L21/02587—Structure
- H01L21/0259—Microstructure
- H01L21/02595—Microstructure polycrystalline
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02104—Forming layers
- H01L21/02365—Forming inorganic semiconducting materials on a substrate
- H01L21/02612—Formation types
- H01L21/02617—Deposition types
- H01L21/0262—Reduction or decomposition of gaseous compounds, e.g. CVD
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L31/00—Semiconductor devices sensitive to infrared radiation, light, electromagnetic radiation of shorter wavelength or corpuscular radiation and specially adapted either for the conversion of the energy of such radiation into electrical energy or for the control of electrical energy by such radiation; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof
- H01L31/0248—Semiconductor devices sensitive to infrared radiation, light, electromagnetic radiation of shorter wavelength or corpuscular radiation and specially adapted either for the conversion of the energy of such radiation into electrical energy or for the control of electrical energy by such radiation; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof characterised by their semiconductor bodies
- H01L31/036—Semiconductor devices sensitive to infrared radiation, light, electromagnetic radiation of shorter wavelength or corpuscular radiation and specially adapted either for the conversion of the energy of such radiation into electrical energy or for the control of electrical energy by such radiation; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof characterised by their semiconductor bodies characterised by their crystalline structure or particular orientation of the crystalline planes
- H01L31/0376—Semiconductor devices sensitive to infrared radiation, light, electromagnetic radiation of shorter wavelength or corpuscular radiation and specially adapted either for the conversion of the energy of such radiation into electrical energy or for the control of electrical energy by such radiation; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof characterised by their semiconductor bodies characterised by their crystalline structure or particular orientation of the crystalline planes including amorphous semiconductors
- H01L31/03762—Semiconductor devices sensitive to infrared radiation, light, electromagnetic radiation of shorter wavelength or corpuscular radiation and specially adapted either for the conversion of the energy of such radiation into electrical energy or for the control of electrical energy by such radiation; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof characterised by their semiconductor bodies characterised by their crystalline structure or particular orientation of the crystalline planes including amorphous semiconductors including only elements of Group IV of the Periodic Table
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L31/00—Semiconductor devices sensitive to infrared radiation, light, electromagnetic radiation of shorter wavelength or corpuscular radiation and specially adapted either for the conversion of the energy of such radiation into electrical energy or for the control of electrical energy by such radiation; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof
- H01L31/04—Semiconductor devices sensitive to infrared radiation, light, electromagnetic radiation of shorter wavelength or corpuscular radiation and specially adapted either for the conversion of the energy of such radiation into electrical energy or for the control of electrical energy by such radiation; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof adapted as photovoltaic [PV] conversion devices
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L31/00—Semiconductor devices sensitive to infrared radiation, light, electromagnetic radiation of shorter wavelength or corpuscular radiation and specially adapted either for the conversion of the energy of such radiation into electrical energy or for the control of electrical energy by such radiation; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof
- H01L31/18—Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment of these devices or of parts thereof
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L31/00—Semiconductor devices sensitive to infrared radiation, light, electromagnetic radiation of shorter wavelength or corpuscular radiation and specially adapted either for the conversion of the energy of such radiation into electrical energy or for the control of electrical energy by such radiation; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof
- H01L31/18—Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment of these devices or of parts thereof
- H01L31/1804—Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment of these devices or of parts thereof comprising only elements of Group IV of the Periodic Table
- H01L31/182—Special manufacturing methods for polycrystalline Si, e.g. Si ribbon, poly Si ingots, thin films of polycrystalline Si
- H01L31/1824—Special manufacturing methods for microcrystalline Si, uc-Si
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02104—Forming layers
- H01L21/02365—Forming inorganic semiconducting materials on a substrate
- H01L21/02367—Substrates
- H01L21/0237—Materials
- H01L21/02422—Non-crystalline insulating materials, e.g. glass, polymers
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02104—Forming layers
- H01L21/02365—Forming inorganic semiconducting materials on a substrate
- H01L21/02367—Substrates
- H01L21/02428—Structure
- H01L21/0243—Surface structure
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L21/00—Processes or apparatus adapted for the manufacture or treatment of semiconductor or solid state devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02—Manufacture or treatment of semiconductor devices or of parts thereof
- H01L21/02104—Forming layers
- H01L21/02365—Forming inorganic semiconducting materials on a substrate
- H01L21/02436—Intermediate layers between substrates and deposited layers
- H01L21/02439—Materials
- H01L21/02491—Conductive materials
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02E—REDUCTION OF GREENHOUSE GAS [GHG] EMISSIONS, RELATED TO ENERGY GENERATION, TRANSMISSION OR DISTRIBUTION
- Y02E10/00—Energy generation through renewable energy sources
- Y02E10/50—Photovoltaic [PV] energy
- Y02E10/545—Microcrystalline silicon PV cells
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02E—REDUCTION OF GREENHOUSE GAS [GHG] EMISSIONS, RELATED TO ENERGY GENERATION, TRANSMISSION OR DISTRIBUTION
- Y02E10/00—Energy generation through renewable energy sources
- Y02E10/50—Photovoltaic [PV] energy
- Y02E10/548—Amorphous silicon PV cells
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02P—CLIMATE CHANGE MITIGATION TECHNOLOGIES IN THE PRODUCTION OR PROCESSING OF GOODS
- Y02P70/00—Climate change mitigation technologies in the production process for final industrial or consumer products
- Y02P70/50—Manufacturing or production processes characterised by the final manufactured product
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Condensed Matter Physics & Semiconductors (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Computer Hardware Design (AREA)
- Microelectronics & Electronic Packaging (AREA)
- Power Engineering (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Manufacturing & Machinery (AREA)
- Electromagnetism (AREA)
- Crystallography & Structural Chemistry (AREA)
- General Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Materials Engineering (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Metallurgy (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Inorganic Chemistry (AREA)
- Photovoltaic Devices (AREA)
- Chemical Vapour Deposition (AREA)
- Solid State Image Pick-Up Elements (AREA)
Abstract
使光电转换装置的面板面内的光电转换效率的分散变小。在包括微晶硅光电转换元件(104)的光电转换装置的制造方法中,包括形成i型层(42)的工序,该工序形成第一i型层(42a),而且在第一i型层(42a)上按照与第一i型层(42a)相比结晶率高且结晶率的面内分布变低的条件形成第二i型层(42b),其中所述微晶硅光电转换元件(104)具备p型层(40)、i型层(42)和n型层(44)的层叠结构,所述i型层包括成为发电层的微晶硅层。
Description
技术领域
本发明涉及光电转换装置和其制造方法。
背景技术
已知有将多晶硅、微晶硅或非晶硅作为光电转换层使用的太阳能电池。特别是具有将微晶硅或非晶硅的薄膜进行层叠的结构的光电转换装置,从资源消耗的观点、降低成本的观点和效率化的观点出发被关注。
一般而言,光电转换装置在表面为绝缘性的基板上依次层叠第一电极、由半导体薄膜构成的光电转换单元和第二电极而形成。光电转换单元从光入射一侧层叠p型层、i型层和n型层而构成。作为提高光电转换装置的转换效率的方法,已知有将两种以上的光电转换单元在光入射方向层叠的方法。在这种情况下,例如在光电转换装置的光入射一侧配置包括帯隙宽的光电转换层的第一光电转换元件,然后配置包括帯隙比第一光电转换元件窄的光电转换层的第二光电转换元件元件。由此,能够遍及入射光的大的波长范围地进行光电转换,作为装置整体能够实现转换效率的提高。例如已知有以非晶硅(a-Si)光电转换元件为顶部单元、以微晶硅(μc-Si)光电转换元件为底部单元的结构。
将包括微晶相的微晶硅作为发电层即i型层使用的μc-Si光电转换元件,与非晶硅相比具有在光稳定性方面优异等优点,但是存在在膜中由悬挂键(dangling bond)等引起的缺陷多的问题。因此,考虑有通过使i型层内的硅的结晶率和氢含有量在层厚方向变化来提高光电动势的转换效率的技术(例如,参照专利文献1)。
现有技术文献
专利文献
专利文献1:日本专利3679595号公报
发明内容
发明所要解决的问题
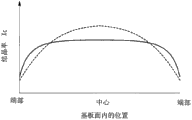
因此,在形成微晶硅薄膜的情况下,根据其成膜条件能够使膜中的晶相与非晶相之比率(结晶率)变化。当在p型层上形成微晶硅的i型层时,在以在光电转换装置的面板的中央附近形成结晶率高的微晶硅薄膜的条件进行成膜的情况下,如图3中以虚线所示,光电转换装置的面板面内的结晶率的分散变大,在面板中央附近结晶率高,能够得到光电转换效率高的光电转换单元,但是在面板端部附近结晶率低,只能得到光电转换效率低的光电转换单元。其结果是,存在以光电转换装置的面板整体看转换效率低的问题。
用于解决问题的方式
本发明的一个方式为一种光电转换装置的制造方法,所述光电转换装置包括p型层、i型层和n型层的层叠结构,所述i型层包括成为发电层的微晶硅层,在该光电转换装置的制造方法中,包括形成i型层的工序,该工序形成第一微晶硅层,并且在第一微晶硅层上以与第一微晶硅层相比结晶率高且结晶率的面内分布低的条件形成第二微晶硅层。
本发明的另一个方式是光电转换装置,该光电转换装置具备p型层、i型层和n型层的层叠结构,所述i型层包括成为发电层的微晶硅层,在该光电转换装置中,i型层具有第一微晶硅层与第二微晶硅层的层叠结构,所述第二微晶硅层以与第一微晶硅层相比结晶率高且结晶率的面内分布低的条件而形成。
发明的效果
根据本发明,能够使光电转换装置的面板面内的光电转换效率的分散变小。
附图说明
图1是表示本发明的实施方式的光电转换装置的结构的图。
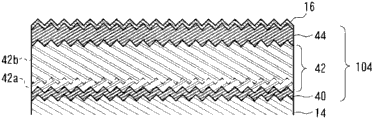
图2是表示本发明的实施方式的光电转换装置的μc-Si元件的结构的图。
图3是表示本发明的实施方式的μc-Si元件的i型层的结晶率的分布的图。
图4是表示本发明的实施例和比较例的光电转换装置的特性测定点的图。
图5是表示本发明的实施方式的μc-Si元件的i型层的结晶率的测定结果的图。
图6是表示本发明的实施方式的光电转换装置的μc-Si元件的结构的另一个例子的图。
图7是表示测定本发明的实施方式的光电转换装置的效率的基板面内分布而得的结果的图。
图8是表示测定本发明的实施方式的光电转换装置的效率的基板面内分布而得的结果的图。
具体实施方式
图1是表示本发明的实施方式的光电转换装置100的结构的截面图。本实施方式的光电转换装置100具有如下结构:以透明绝缘基板10为光入射侧,从光入射侧层叠有透明导电膜12、作为顶部单元的具有宽的帯隙的非晶硅(a-Si)(光电转换)元件102、中间层14、作为底部单元的与a-Si元件102相比帯隙窄的微晶硅(μc-Si)(光电转换)元件104、第一背面电极层16、第二背面电极层18、填充材料20和保护膜22。此处,a-Si元件102和μc-Si元件104分别作为本发明的实施方式的光电转换装置100的发电层发挥作用。
以下对本发明的实施方式的光电转换装置100的结构和制造方法进行说明。本发明的实施方式的光电转换装置100在包含于μc-Si元件104的i型层具有特征,因此特别对包含于μc-Si元件104的i型层进行详细说明。
透明绝缘基板10例如能够使用玻璃基板、塑料基板等至少在可见光波长区域具有透过性的材料。在透明绝缘基板10上形成有透明导电膜12。透明导电膜12优选使用在氧化锡(SnO2)、氧化锌(ZnO)、铟锡氧化物(ITO)等中掺杂锡(Sn)、锑(Sb)、氟(F)、铝(Al)等而得到的透明导电性氧化物(TCO)之中的至少一种或将多种组合使用。特别是氧化锌(ZnO)因为透光性高、电阻率低、耐等离子体特性方面也优异,所以优选。透明导电膜12例如能够利用溅射等形成。透明导电膜12的膜厚优选为0.5μm以上5μm以下的范围。此外,优选在透明导电膜12的表面设置有具有光封入效果的凹凸。
在透明导电膜12上依次层叠p型层、i型层、n型层的硅类薄膜而形成a-Si元件102。a-Si元件102能够通过将混合有稀释气体的混合气体等离子体化而进行成膜的等离子体CVD来形成,所述稀释气体包括:硅烷(SiH4)、乙硅烷(Si2H6)、二氯(甲)硅烷(SiH2Cl2)等含有硅的气体、甲烷(CH4)等含有碳的气体、乙硼烷(B2H6)等含有p型掺杂剂的气体、磷化氢(PH3)等含有n型掺杂剂的气体和氢(H2)等。
等离子体CVD例如优选使用13.56MHz的RF等离子体CVD。RF等离子体CVD能够为平行平板型。也可以采用在平行平板型的电极中的未配置透明绝缘基板10的一侧设置有用于供给原料的混合气体的气体喷淋孔的结构。等离子体的投入电力密度优选为5mW/cm2以上100mW/cm2以下。
一般而言,p型层、i型层、n型层分别在不同的成膜室被成膜。成膜室能够通过真空泵真空排气,内置有用于RF等离子体CVD的电极。此外,附设有透明绝缘基板10的输送装置、用于RF等离子体CVD的电源和匹配装置和气体供给用配管等。
p型层在透明导电膜12上形成。p型层为掺杂有p型掺杂剂(硼等)的膜厚10nm以上100nm以下的p型非晶硅层(p型a-Si:H)。就p型层的膜质而言,能够通过调整含有硅的气体、含有碳的气体、含有p型掺杂剂的气体和稀释气体的混合比、压力和用于产生等离子体的高频功率而使其变化。i型层为在p型层上形成的、未被掺杂的、膜厚50nm以上500nm以下的非晶硅膜。就i型层的膜质而言,能够通过调整含有硅的气体和稀释气体的混合比、压力和用于产生等离子体的高频功率而使其变化。此外,i型层成为a-Si元件102的发电层。n型层为在i型层上形成的、掺杂有n型掺杂剂(磷等)的、膜厚10nm以上100nm以下的n型非晶硅层(n型a-Si:H)或n型微晶硅层(n型μc-Si:H)。就n型层的膜质而言,能够通过调整含有硅的气体、含有碳的气体、含有n型掺杂剂的气体和稀释气体的混合比、压力和用于产生等离子体的高频功率而使其变化。
在a-Si元件102上形成中间层14。中间层14优选使用氧化锌(ZnO)、氧化硅(SiOx)等透明导电性氧化物(TCO)。特别优选使用掺杂有镁(Mg)的氧化锌(ZnO)和/或氧化硅(SiOx)。中间层14能够利用溅射等形成。中间层14的膜厚优选为10nm以上200nm以下的范围。另外,中间层14也可以不设置。
在中间层14上,如图2的放大截面图所示,形成将p型层40、i型层42和n型层44依次层叠而得到的μc-Si元件104。μc-Si元件104能够通过使混合有稀释气体的混合气体等离子体化而进行成膜的等离子体CVD来形成,所述稀释气体包括:硅烷(SiH4)、乙硅烷(Si2H6)、二氯(甲)硅烷(SiH2Cl2)等含有硅的气体、甲烷(CH4)等含有碳的气体、乙硼烷(B2H6)等含有p型掺杂剂的气体、磷化氢(PH3)等含有n型掺杂剂的气体和氢(H2)等。
等离子体CVD例如优选使用RF等离子体CVD或VHF等离子体CVD。RF等离子体CVD和VHF等离子体CVD能够为平行平板型。也可以在平行平板型的电极中的未配置透明绝缘基板10的一侧设置有用于供给原料的混合气体的气体喷淋孔。等离子体的投入电力密度优选为5mW/cm2以上1000mW/cm2以下。
p型层40在中间层14或a-Si元件102的n型层上形成。p型层40为掺杂有p型掺杂剂(硼等)的、膜厚5nm以上50nm以下的p型微晶硅层(p型μc-Si:H)。就p型层40的膜质而言,能够通过调整含有硅的气体、含有碳的气体、含有p型掺杂剂的气体和稀释气体的混合比、压力和用于产生等离子体的高频功率来使其变化。i型层42为在p型层40上形成的、未被掺杂的、膜厚0.5μm以上5μm以下的微晶硅膜。对于i型层42的详细情况后述。n型层44在i型层42上形成。n型层44为掺杂有n型掺杂剂(磷等)的、膜厚5nm以上50nm以下的n型微晶硅层(n型μc-Si:H)。但是,μc-Si元件104并不限定于此,而只要使用以下说明的i型微晶硅层(i型μc-Si:H)作为发电层即可。
在本实施方式中,i型层42在至少两个不同的成膜条件下形成。在接近p型层的一侧,当在玻璃基板等作为单膜进行成膜时以如下的成膜条件形成第一i型层42a,所述成膜条件为:在基板的面内中心附近结晶率Xc低,如图3中以实线所示,在基板的面内结晶率Xc的均匀性变高。第一i型层42a的结晶率Xc在作为单膜而进行成膜为约500nm的膜的情况下优选为2~4左右。此外,在与第一i型层42a相比离p型层更远的一侧,当在玻璃基板作为单膜进行成膜时以如下的成膜条件形成第二i型层42b,所述成膜条件为:在基板的面内的中心附近结晶率Xc比第一i型层42a高,如图3中以虚线所示,在基板的面内结晶率Xc的均匀性变得比第一i型层42a低。第二i型层42b的结晶率Xc在作为单膜而进行成膜为约500nm的膜的情况下优选为4~6左右。
第一i型层42a优选将硅烷(SiH4)/氢(H2)比为0.005以上0.1以下的混合气体以1330Pa以上4000Pa以下的压力导入并且利用等离子体成膜法进行成膜。作为等离子体成膜法,优选使用频率13.56MHz以上70MHz以下的VHF等离子体成膜法。此外,优选成膜时的基板温度为160℃以上230℃以下,对于等离子体的导入电力为0.05W/cm2以上5W/cm2以下。第二i型层42b优选将硅烷(SiH4)/氢(H2)比为0.005以上0.1以下的混合气体以1330Pa以上4000Pa以下的压力导入并且利用等离子体成膜法进行成膜。作为等离子体成膜法,优选使用频率13.56MHz以上70MHz以下的VHF等离子体成膜法。此外,优选成膜时的基板温度为160℃以上230℃以下,对于等离子体的导入电力为0.05W/cm2以上5W/cm2以下。
第一i型层42a的膜厚优选为100nm以上2000nm以下,更优选为500nm以上1500nm以下。第二i型层42b的膜厚优选为500nm以上3000nm以下,更优选为1000nm以上2500nm以下。当第一i型层42a的膜厚未达到100nm时难以达到使面板面内的光电转换效率的分散变小的效果。第一i型层42a的膜厚比2500nm大或第二i型层42b的膜厚比3500nm大时,第一i型层42a与第二i型层42b的合计膜厚过厚,光电转换效率可能下降。
在μc-Si元件104上,作为第一背面电极层16和第二背面电极层18形成反射性金属与透明导电性氧化物(TCO)的层叠结构。作为第一背面电极层16,使用氧化锡(SnO2)、氧化锌(ZnO)、铟锡氧化物(ITO)等透明导电性氧化物(TCO)。TCO例如能够利用溅射等形成。此外,作为第二背面电极层18,能够使用银(Ag)、铝(Al)等金属。优选第一背面电极层16和第二背面电极层18的合计膜厚为1μm左右。优选在第一背面电极层16和第二背面电极层18中的至少一方设置用于提高光封入效果的凹凸。
而且,通过填充材料20第二背面电极层18的表面被保护膜22覆盖。填充材料20和保护膜22能够为EVA、聚酰亚胺等树脂材料。由此,能够防止水分向光电转换装置100的发电层的侵入等。
另外,也可以采用以下结构:通过使用YAG激光(基波1064nm,2倍高次谐波532nm)进行透明导电膜12、a-Si元件102、中间层14、μc-Si元件104、第一背面电极层16和第二背面电极层18的分离加工,从而将多个单元串列连接。
<实施例>
以下说明本发明的实施例和比较例。
(实施例1)
作为透明绝缘基板10,使用550mm×650mm四方形、4mm厚的玻璃基板。在透明绝缘基板10上,利用热CVD形成有在表面具有凹凸形状的600nm厚的SnO2作为透明导电膜12。然后,利用YAG激光对透明导电膜12进行图案化形成为长方形。YAG激光使用波长1064nm、能量密度13J/cm2、脉冲频率3kHz的激光。
接着,将a-Si元件102的p型层、i型层和n型层依次层叠。a-Si元件102的p型层、i型层和n型层在表1所示的成膜条件中形成。接着,在a-Si元件102的n型层上形成有μc-Si元件104。μc-Si元件104的p型层40、i型层42和n型层44在表2所示的成膜条件中形成。另外,乙硼烷(B2H6)和磷化氢(PH3)是以氢为基础1%的浓度的气体流量。此处,i型层42为第一i型层42a和第二i型层42b的层叠结构,该第一i型层42a当在玻璃基板等作为单膜进行成膜时以如下的成膜条件形成:在基板的面内中心附近结晶率Xc低,并且在基板的面内结晶率Xc的均匀性变高,该第二i型层42b当在玻璃基板作为单膜进行成膜时以如下的成膜条件形成:在基板的面内的中心附近结晶率Xc比第一i型层42a高,在基板的面内结晶率Xc的均匀性比第一i型层42a低。第一i型层42a的膜厚为1.5μm,第二i型层42b的膜厚为1.0μm。
【表1】
【表2】
然后,向横向距离透明导电膜12的图案化位置50μm的位置照射YAG激光,将a-Si元件102和μc-Si元件104进行图案化形成为长方形。YAG激光使用能量密度0.7J/cm2、脉冲频率3kHz的激光。
接着,利用溅射形成ZnO膜作为第一背面电极层16,利用溅射形成Ag电极作为第二背面电极层18。然后,向横向距离a-Si元件102和μc-Si元件104的图案化位置50μm的位置照射YAG激光,将第一背面电极层16和第二背面电极层18进行图案化形成为长方形。YAG激光使用能量密度0.7J/cm2、脉冲频率4kHz的激光。
(实施例2)
以与上述实施例1相同的成膜条件,使第一i型层42a的膜厚为1.0μm,使第二i型层42b的膜厚为1.5μm。
(比较例1)
以与上述实施例1相同的成膜条件,使第一i型层42a的膜厚为2.5μm,不形成第二i型层42b。
(比较例2)
以与上述实施例1相同的成膜条件,不形成第一i型层42a,使第二i型层42b的膜厚为2.5μm直接形成于a-Si元件102的n型层上。
(比较例3)
与上述实施例1相对,使第一i型层42a和第二i型层42b的成膜顺序颠倒。即,在a-Si元件102的n型层上先形成膜厚1.0μm的第二i型层42b,接着形成膜厚为1.5μm的第一i型层42a。
(比较例4)
与比较例3相同,使第一i型层42a和第二i型层42b的成膜顺序颠倒。使第二i型层42b的膜厚为1.5μm,使第一i型层42a的膜厚为1.0μm。
表3表示实施例1和2以及比较例1~4的光电转换装置的开放电压Voc,短路电流密度Jsc,填充因数(fill factor)FF和效率η。光电转换测定如图4所示,对光电转换装置的面板面内的中央100mm×100mm内的8点和分别距面板的角两边仅55mm的内侧的一点进行测定。对面板面内的中央8点计算平均值,将开放电压Voc、短路电流密度Jsc、填充因数FF和效率的平均值η分别设为1进行标准化地表示。
【表3】
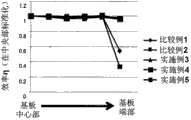
在实施例1中,在面板面的端部附近,短路电流密度Jsc和填充因数FF的下降也变小,作为单元(cell)的光电转换的效率η与中央附近的值相比也下降。此外,在实施例2中,与实施例1相比短路电流密度Jsc的下降明显,但是填充因数FF升高,作为单元的光电转换的效率η与中央附近的值相比下降(幅度)小。
另一方面,在如比较例1那样不形成第二i型层42b而仅由第一i型层42a构成的情况下,开放电压Voc和填充因数FF与中央附近的值相比大幅下降,但是短路电流密度Jsc大幅升高,作为单元的光电转换的效率η与中央附近的值相比下降(幅度)变小。但是,各单元的效率η的绝对值与实施例1和实施例2相比大幅下降,未能满足绝对的效率η的提高和面板面内的效率η的均匀化者两者。
此外,在如比较例2那样不形成第一i型层42a而仅由第二i型层42b构成的情况下,开放电压Voc与中央附近的值相比升高若干,但是短路电流密度Jsc和填充因数FF显著下降,作为单元的光电转换的效率η与中央附近的值相比大幅下降。这样,在不形成第一i型层42a的情况下,不能使面板面内的效率η均匀化。
此外,在如比较例3和4那样使第一i型层42a与第二i型层42b的层叠顺序颠倒的情况下,短路电流密度Jsc和填充因数FF下降,作为单元的光电转换的效率η与中央附近的值相比大幅下降。
能够推测得到上述那样的结果的理由是:通过将面内的结晶率Xc的分布比较均匀的第一i型层42a作为基底形成,在其上形成的第二i型层42b继续第一i型层42a的结晶率Xc的均匀性,并且作为绝对值的结晶率Xc也更加高。
图5表示将第一i型层42a的结晶率Xc和在第一i型层42a上形成了第二i型层42b的状态的结晶率Xc在光电转换装置100的面板的对角线上改变与端部之间的距离进行测定而得的结果。测定方法为,在形成光电转换装置100后切出测定位置,利用拉曼光谱法对向厚度方向倾斜实施研磨而仅留下第一i型层42a的区域和在第一i型层42a上留下第二i型层42b的区域的结晶率Xc进行测定。对利用拉曼分光分析使用波长514nm的激光而测定的拉曼光谱,分离为以结晶硅为起因的520cm-1附近的拉曼散射强度Ic和以非晶硅为起因的480cm-1附近的拉曼散射强度Ia的峰,结晶率Xc定义为这些峰的高度之比Ic/Ia。
如图5所示,在距离面板端部5cm~11cm的区域,仅第一i型层42a的结晶率Xc(图5的粗线)与在第一i型层42a上形成有第二i型层42b时的结晶率Xc(图5的细线)相比较高。即,在距面板端部5cm~11cm的区域,测定上述结晶率的膜厚方向的变化,确认整个i型层40(在第一i型层42a上形成有第二i型层42b的状态)的结晶率Xc比在膜厚方向进行研磨而仅留下成为基底层的第一i型层42a的状态的结晶率Xc小,由此能够判定本申请发明是否适用。
另外,在本实施方式中,以非晶硅光电转换元件102和微晶硅光电转换元件104的串列结构为例进行了说明,但是并不限于此,也可以为微晶硅光电转换元件104的单个结构,还可以为与非晶硅光电转换元件102以外的光电转换元件的层叠结构或三个以上的光电转换元件的层叠结构。
在本实施方式中,将第一i型层42a和第二i型层42b在p型层40上直接形成。此处,如图6所示,是在p型层40与第一i型层42a之间设置有缓冲层42c的结构。
缓冲层42c优选利用等离子体成膜法进行成膜。作为等离子体成膜法,优选使用频率13.56MHz以上70MHz以下的VHF等离子体成膜法。此外,优选成膜时的基板温度为160℃以上230℃以下,对等离子体的导入电力优选为0.15W/cm2以上0.4W/cm2以下。
缓冲层42c的膜厚优选为20nm以上50nm以下。缓冲层42c优选为,在玻璃基板等作为单膜进行成膜时的结晶率Xc比在玻璃基板等作为单膜进行成膜的第一i型层42a和第二i型层42b的结晶率Xc高。此外,优选在玻璃基板等将缓冲层42c作为单膜进行成膜时的基板的面内的结晶率Xc的分布,比在玻璃基板等将第一i型层42a和第二i型层42b作为单膜进行成膜时的结晶率Xc的分布均匀。
具体而言,缓冲层42c的结晶率Xc优选为10以上,更优选为13以上。此时,当缓冲层42c的结晶率Xc为10以上未达到13时,缓冲层42c的膜厚优选为40nm以上。当缓冲层42c的结晶率Xc为13以上时,缓冲层42c的膜厚虽然没有特别限定,但是优选为30nm以上。
另外,在本实施方式中,缓冲层42c作为未被掺杂的i型层的一个而形成,但是也可以添加p型杂质作为p型层的一个而形成。
(实施例3~5)
与实施例1同样地准备透明绝缘基板10和透明导电膜12。将透明导电膜12进行图案化形成为长方形后,与实施例1一样以表1所示的条件依次层叠a-Si元件102的p型层、i型层和n型层。
μc-Si元件104以表4所示的条件形成。在a-Si元件102上形成p型层40后,形成缓冲层42c。缓冲层42c与实施例1一样,形成有第一i型层42a和第二i型层42b以及n型层44。另外,在表4中,乙硼烷(B2H6)和磷化氢(PH3)是以氢为基础1%的浓度的气体流量。
【表4】
表4所示的成膜条件是:在玻璃基板等将缓冲层42c作为单膜而进行成膜时的结晶率Xc,比在玻璃基板等作为单膜进行成膜的第一i型层42a和第二i型层42b的结晶率Xc高;和在玻璃基板等将缓冲层42c作为单膜进行成膜时的基板的面内的结晶率Xc的分布,比在玻璃基板等将第一i型层42a和第二i型层42b作为单膜进行成膜时的结晶率Xc的分布均匀。
然后,与实施例1一样,将a-Si元件102和μc-Si元件104进行图案化形成为长方形,利用溅射形成第一背面电极层16和第二背面电极层18。进而,将第一背面电极层16、第二背面电极层18进行图案化形成为长方形。
此处,将以在玻璃基板等将缓冲层42c作为单膜进行成膜时的结晶率Xc(Ic/Ia)为10的条件成膜为膜厚40nm的样品作为实施例3。此外,将以结晶率Xc(Ic/Ia)成为13的条件成膜为膜厚30nm的样品作为实施例4,和将以结晶率Xc(Ic/Ia)成为13的条件成膜为膜厚40nm的样品作为实施例5。另外,缓冲层42c的结晶率Xc能够通过变更向成膜时的等离子体导入的功率来进行调整。此外,使第一i型层42a的膜厚为1.5μm,使第二i型层42b的膜厚为1.0μm。
(比较例5和比较例6)
将以在玻璃基板等将缓冲层42c作为单膜进行成膜时的结晶率Xc(Ic/Ia)成为7的条件成膜为膜厚30nm的样品作为比较例5。此外,将以结晶率Xc(Ic/Ia)成为10的条件成膜为膜厚30nm的样品作为比较例6。
表4和图7表示与实施例5的基板面上的位置相对的效率η的分布。在图7中,对于除了不形成缓冲层42c以外以与实施例5相同的条件形成的比较例的结果也一并表示。此外,效率η表示以基板中央的值进行了标准化的值。
【表5】
| 效率η(端部/中央部) | |
| 没有缓冲层42c | 0.85 |
| 实施例5 | 0.99 |
如表4和图7所示,在所形成的没有缓冲层42c的样品中,在基板端部相对于基板中央部效率η下降至0.85倍,与此相对,在形成有缓冲层42c的实施例5中,在基板端部相对于基板中央部效率η为0.99倍几乎没下降。
表6和图8表示针对比较例5和6以及实施例3-5测定基板端部的效率η的结果。在表6和图8,与图7一样,效率η表示以基板中央的值进行了标准化的值。
【表6】
在实施例3-5的样品中,在基板端部相对于基板中央部,效率η维持为0.962倍~0.985倍,能够看到使光电转换装置的面板面内的光电转换效率的分散变小的效果。另一方面,在比较例5和6的样品中,在基板端部相对于基板中央部,效率η下降为0.542倍和0.330倍。
如上所述,通过在形成第一i型层42a之前在玻璃基板作为单膜进行成膜的情况下形成结晶率Xc(Ic/Ia)和其面内分布比第一i型层42a和第二i型层42b高的缓冲层42c,能够使光电转换装置的面板面内的光电转换效率的分散变小。特别是在缓冲层42c的结晶率Xc(Ic/Ia)为10以上和其膜厚为40nm以上,或者结晶率Xc(Ic/Ia)为13以上中,效果显著。
附图标记的说明
10 透明绝缘基板
12 透明导电膜
14 中间层
16 第一背面电极层
18 第二背面电极层
20 填充材料
22 保护膜
40 p型层
42 i型层
42a 第一i型层
42b 第二i型层
44 n型层
100 光电转换装置
102 非晶硅光电转换元件
104 微晶硅光电转换元件
Claims (8)
1.一种光电转换装置的制造方法,所述光电转换装置具备p型层、i型层和n型层的层叠结构,所述i型层包括成为发电层的微晶硅层,所述光电转换装置的制造方法的特征在于:
包括形成所述i型层的工序,所述工序形成第一微晶硅层,并且在所述第一微晶硅层上,以与所述第一微晶硅层相比结晶率高且结晶率的面内分布低的条件形成第二微晶硅层。
2.如权利要求1所述的光电转换装置的制造方法,其特征在于:
所述第一微晶硅层在玻璃基板上作为单膜进行成膜的情况下,以如下条件形成:拉曼光谱法的520cm-1附近的拉曼散射强度Ic和480cm-1附近的拉曼散射强度Ia的峰高度之比Ic/Ia为2~4的范围,
所述第二微晶硅层,在玻璃基板上作为单膜进行成膜的情况下,以所述峰高度之比Ic/Ia为4~6的范围的条件形成。
3.如权利要求1或2所述的光电转换装置的制造方法,其特征在于:
在形成所述第一微晶硅层之前,还包括按照与所述第一微晶硅层和所述第二微晶硅层相比结晶率高且结晶率的面内分布高的条件形成缓冲层的工序。
4.如权利要求3所述的光电转换装置的制造方法,其特征在于:
所述缓冲层,在玻璃基板上作为单膜进行成膜的情况下,拉曼光谱法的520cm-1附近的拉曼散射强度Ic和480cm-1附近的拉曼散射强度Ia的峰高度之比Ic/Ia为10以上并且其膜厚为40nm以上,或者所述峰高度之比Ic/Ia为13以上。
5.一种光电转换装置,具备p型层、i型层和n型层的层叠结构,所述p型层包括p型掺杂剂,所述i型层包括成为发电层的微晶硅层,所述n型层包括n型掺杂剂,所述光电转换装置的特征在于:
所述i型层具有第一微晶硅层和第二微晶硅层的层叠结构,所述第二微晶硅层以与所述第一微晶硅层相比结晶率高且结晶率的面内分布低的条件形成。
6.如权利要求5所述的光电转换装置,其特征在于:
所述第一微晶硅层的膜厚在100nm以上250nm以下的范围。
7.如权利要求5或6所述的光电转换装置的制造方法,其特征在于:
还包括按照与所述第一微晶硅层和所述第二微晶硅层相比结晶率高且结晶率的面内分布高的条件形成的缓冲层,
在所述缓冲层上形成有所述第一微晶硅层。
8.如权利要求7所述的光电转换装置,其特征在于:
所述缓冲层,在玻璃基板上作为单膜进行成膜的情况下,拉曼光谱法的520cm-1附近的拉曼散射强度Ic与480cm-1附近的拉曼散射强度Ia的峰高度之比Ic/Ia为10以上并且其膜厚为40nm以上,或者所述峰高度之比Ic/Ia为13以上。
Applications Claiming Priority (5)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2009272011 | 2009-11-30 | ||
| JP2009-272011 | 2009-11-30 | ||
| JP2010-253550 | 2010-11-12 | ||
| JP2010253550A JP4902779B2 (ja) | 2009-11-30 | 2010-11-12 | 光電変換装置及びその製造方法 |
| PCT/JP2010/070853 WO2011065343A1 (ja) | 2009-11-30 | 2010-11-24 | 光電変換装置及びその製造方法 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| CN102473759A true CN102473759A (zh) | 2012-05-23 |
Family
ID=44066448
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN2010800358789A Pending CN102473759A (zh) | 2009-11-30 | 2010-11-24 | 光电转换装置和其制造方法 |
Country Status (6)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US20120145239A1 (zh) |
| EP (1) | EP2458644A4 (zh) |
| JP (1) | JP4902779B2 (zh) |
| KR (1) | KR20120042894A (zh) |
| CN (1) | CN102473759A (zh) |
| WO (1) | WO2011065343A1 (zh) |
Families Citing this family (9)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| WO2013022086A1 (ja) * | 2011-08-11 | 2013-02-14 | 株式会社カネカ | 積層型光電変換装置の製造方法 |
| KR101770266B1 (ko) * | 2011-09-15 | 2017-08-22 | 엘지전자 주식회사 | 박막 태양전지 모듈 |
| KR101770267B1 (ko) * | 2011-10-04 | 2017-08-22 | 엘지전자 주식회사 | 박막 태양전지 모듈 |
| WO2013065538A1 (ja) * | 2011-11-03 | 2013-05-10 | 三洋電機株式会社 | 光電変換装置 |
| WO2013080803A1 (ja) * | 2011-11-30 | 2013-06-06 | 三洋電機株式会社 | 光起電力装置 |
| KR101302373B1 (ko) | 2011-12-21 | 2013-09-06 | 주식회사 테스 | 태양전지 제조방법 |
| KR101453967B1 (ko) * | 2012-02-20 | 2014-10-29 | 고려대학교 산학협력단 | 다중 밴드갭 적층형 태양전지 및 다중 밴드갭 적층형 태양전지 형성 방법 |
| TWI469380B (zh) * | 2013-11-08 | 2015-01-11 | Ind Tech Res Inst | 異質接面太陽電池結構 |
| WO2017195722A1 (ja) * | 2016-05-09 | 2017-11-16 | 株式会社カネカ | 積層型光電変換装置およびその製造方法 |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20030079771A1 (en) * | 1998-02-26 | 2003-05-01 | Canon Kabushiki Kaisha | Stacked photovoltaic device |
| CN1501513A (zh) * | 2002-11-13 | 2004-06-02 | ������������ʽ���� | 叠层型光电元件 |
| CN101415861A (zh) * | 2006-03-29 | 2009-04-22 | 株式会社Ihi | 微晶硅膜形成方法以及太阳电池 |
| CN101569017A (zh) * | 2006-12-25 | 2009-10-28 | 夏普株式会社 | 光电转换装置及其制造方法 |
Family Cites Families (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2984537B2 (ja) * | 1994-03-25 | 1999-11-29 | キヤノン株式会社 | 光起電力素子 |
| JPH11251612A (ja) * | 1998-03-03 | 1999-09-17 | Canon Inc | 光起電力素子の製造方法 |
| JP4488550B2 (ja) * | 1999-06-09 | 2010-06-23 | 富士電機システムズ株式会社 | 薄膜太陽電池とその製造方法 |
| JP4780929B2 (ja) * | 2003-05-13 | 2011-09-28 | 京セラ株式会社 | 光電変換装置およびこれを用いた光発電装置 |
| DE102004061360A1 (de) * | 2004-12-21 | 2006-07-13 | Forschungszentrum Jülich GmbH | Verfahren zur Herstellung einer Dünnschichtsolarzelle mit mikrokristallinem Silizium sowie Schichtfolge |
| JP5473187B2 (ja) * | 2006-09-04 | 2014-04-16 | 三菱重工業株式会社 | 製膜条件設定方法、光電変換装置の製造方法及び検査方法 |
| JP5330723B2 (ja) * | 2008-03-28 | 2013-10-30 | 三菱重工業株式会社 | 光電変換装置 |
-
2010
- 2010-11-12 JP JP2010253550A patent/JP4902779B2/ja not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2010-11-24 KR KR1020127002699A patent/KR20120042894A/ko active IP Right Grant
- 2010-11-24 WO PCT/JP2010/070853 patent/WO2011065343A1/ja active Application Filing
- 2010-11-24 EP EP10833189.3A patent/EP2458644A4/en not_active Withdrawn
- 2010-11-24 CN CN2010800358789A patent/CN102473759A/zh active Pending
- 2010-11-24 US US13/391,570 patent/US20120145239A1/en not_active Abandoned
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20030079771A1 (en) * | 1998-02-26 | 2003-05-01 | Canon Kabushiki Kaisha | Stacked photovoltaic device |
| CN1501513A (zh) * | 2002-11-13 | 2004-06-02 | ������������ʽ���� | 叠层型光电元件 |
| CN101415861A (zh) * | 2006-03-29 | 2009-04-22 | 株式会社Ihi | 微晶硅膜形成方法以及太阳电池 |
| CN101569017A (zh) * | 2006-12-25 | 2009-10-28 | 夏普株式会社 | 光电转换装置及其制造方法 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2011135053A (ja) | 2011-07-07 |
| EP2458644A4 (en) | 2013-04-10 |
| JP4902779B2 (ja) | 2012-03-21 |
| US20120145239A1 (en) | 2012-06-14 |
| EP2458644A1 (en) | 2012-05-30 |
| WO2011065343A1 (ja) | 2011-06-03 |
| KR20120042894A (ko) | 2012-05-03 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| CN102473759A (zh) | 光电转换装置和其制造方法 | |
| US20080245414A1 (en) | Methods for forming a photovoltaic device with low contact resistance | |
| US20150136210A1 (en) | Silicon-based solar cells with improved resistance to light-induced degradation | |
| JP4767365B2 (ja) | 薄膜太陽電池及びその製造方法 | |
| CN102668111A (zh) | 光电转换装置和其制造方法 | |
| Myong et al. | Superstrate type flexible thin-film Si solar cells using flexible glass substrates | |
| US20100307574A1 (en) | Solar cell and manufacturing method thereof | |
| Heo et al. | ZnO: B back reflector with high haze and low absorption enhanced triple-junction thin film Si solar modules | |
| EP2599127B1 (en) | Multiple-junction photoelectric device and its production process | |
| US8759667B2 (en) | Photoelectric conversion device | |
| US20130298987A1 (en) | Method for manufacturing a multilayer of a transparent conductive oxide | |
| CN102725856A (zh) | 光电转换装置 | |
| CN102473749A (zh) | 太阳能电池的制造方法和制造装置 | |
| US20100326507A1 (en) | Solar cell and manufacturing method thereof | |
| US20130291933A1 (en) | SiOx n-LAYER FOR MICROCRYSTALLINE PIN JUNCTION | |
| US20130000711A1 (en) | Photoelectric conversion device | |
| US20110056560A1 (en) | Solar cell module and manufacturing method thereof | |
| KR20110012992A (ko) | 태양전지 및 그 제조방법 | |
| WO2011105166A1 (ja) | 光電変換モジュール及びその製造方法 | |
| JP2010283162A (ja) | 太陽電池及びその製造方法 | |
| US20100330734A1 (en) | Solar cell and manufacturing method thereof | |
| WO2014072399A1 (en) | Solar module, set of solar modules and corresponding method | |
| WO2012098051A1 (en) | Method for manufacturing a multilayer of a transparent conductive oxide | |
| JP2013065805A (ja) | 薄膜太陽電池モジュール | |
| JP2013026602A (ja) | 光電変換装置 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| C06 | Publication | ||
| PB01 | Publication | ||
| C10 | Entry into substantive examination | ||
| SE01 | Entry into force of request for substantive examination | ||
| C02 | Deemed withdrawal of patent application after publication (patent law 2001) | ||
| WD01 | Invention patent application deemed withdrawn after publication |
Application publication date: 20120523 |