WO2017183609A1 - 運転支援装置 - Google Patents
運転支援装置 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2017183609A1 WO2017183609A1 PCT/JP2017/015468 JP2017015468W WO2017183609A1 WO 2017183609 A1 WO2017183609 A1 WO 2017183609A1 JP 2017015468 W JP2017015468 W JP 2017015468W WO 2017183609 A1 WO2017183609 A1 WO 2017183609A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- distance
- notification
- driving support
- illuminance
- support device
- Prior art date
- Legal status (The legal status is an assumption and is not a legal conclusion. Google has not performed a legal analysis and makes no representation as to the accuracy of the status listed.)
- Ceased
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60K—ARRANGEMENT OR MOUNTING OF PROPULSION UNITS OR OF TRANSMISSIONS IN VEHICLES; ARRANGEMENT OR MOUNTING OF PLURAL DIVERSE PRIME-MOVERS IN VEHICLES; AUXILIARY DRIVES FOR VEHICLES; INSTRUMENTATION OR DASHBOARDS FOR VEHICLES; ARRANGEMENTS IN CONNECTION WITH COOLING, AIR INTAKE, GAS EXHAUST OR FUEL SUPPLY OF PROPULSION UNITS IN VEHICLES
- B60K35/00—Instruments specially adapted for vehicles; Arrangement of instruments in or on vehicles
- B60K35/20—Output arrangements, i.e. from vehicle to user, associated with vehicle functions or specially adapted therefor
- B60K35/28—Output arrangements, i.e. from vehicle to user, associated with vehicle functions or specially adapted therefor characterised by the type of the output information, e.g. video entertainment or vehicle dynamics information; characterised by the purpose of the output information, e.g. for attracting the attention of the driver
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60Q—ARRANGEMENT OF SIGNALLING OR LIGHTING DEVICES, THE MOUNTING OR SUPPORTING THEREOF OR CIRCUITS THEREFOR, FOR VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60Q9/00—Arrangement or adaptation of signal devices not provided for in one of main groups B60Q1/00 - B60Q7/00, e.g. haptic signalling
- B60Q9/008—Arrangement or adaptation of signal devices not provided for in one of main groups B60Q1/00 - B60Q7/00, e.g. haptic signalling for anti-collision purposes
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60R—VEHICLES, VEHICLE FITTINGS, OR VEHICLE PARTS, NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- B60R21/00—Arrangements or fittings on vehicles for protecting or preventing injuries to occupants or pedestrians in case of accidents or other traffic risks
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G08—SIGNALLING
- G08G—TRAFFIC CONTROL SYSTEMS
- G08G1/00—Traffic control systems for road vehicles
- G08G1/16—Anti-collision systems
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G08—SIGNALLING
- G08G—TRAFFIC CONTROL SYSTEMS
- G08G1/00—Traffic control systems for road vehicles
- G08G1/16—Anti-collision systems
- G08G1/161—Decentralised systems, e.g. inter-vehicle communication
- G08G1/163—Decentralised systems, e.g. inter-vehicle communication involving continuous checking
-
- G—PHYSICS
- G08—SIGNALLING
- G08G—TRAFFIC CONTROL SYSTEMS
- G08G1/00—Traffic control systems for road vehicles
- G08G1/16—Anti-collision systems
- G08G1/166—Anti-collision systems for active traffic, e.g. moving vehicles, pedestrians, bikes
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60K—ARRANGEMENT OR MOUNTING OF PROPULSION UNITS OR OF TRANSMISSIONS IN VEHICLES; ARRANGEMENT OR MOUNTING OF PLURAL DIVERSE PRIME-MOVERS IN VEHICLES; AUXILIARY DRIVES FOR VEHICLES; INSTRUMENTATION OR DASHBOARDS FOR VEHICLES; ARRANGEMENTS IN CONNECTION WITH COOLING, AIR INTAKE, GAS EXHAUST OR FUEL SUPPLY OF PROPULSION UNITS IN VEHICLES
- B60K2360/00—Indexing scheme associated with groups B60K35/00 or B60K37/00 relating to details of instruments or dashboards
- B60K2360/16—Type of output information
- B60K2360/179—Distances to obstacles or vehicles
Definitions
- the present disclosure relates to a driving support device that supports driving by a driver of a moving object.
- the present disclosure has been made to solve the above-described problems, and a main purpose thereof is to provide a driving support device capable of appropriately operating a notification device.
- the present disclosure is a driving support device that is provided in a moving body and notifies a driver of the moving body of the approach between the moving body and a surrounding object, and is provided in at least one environment around and inside the moving body.
- the information is obtained based on the environment information acquisition unit that acquires the environment information that is the information indicating the width of the driver's visual recognition range, and the distance at which the notification is performed as the visual recognition range indicated by the environmental information is narrower.
- a distance setting unit that increases the notification distance; and a notification control unit that notifies the driver when the distance between the moving body and the object is smaller than the notification distance.
- the driver's visible range is narrow during driving of the moving body, the driver is less likely to notice the approach to objects around the moving body. Therefore, it is possible to suppress the malfunction of the notification function by performing the notification of the approach to the object earlier.
- approaching the driver to an object around the moving body at an early stage may be a cause of unnecessary operation of the notification function.
- the visual recognition range of the driver changes depending on at least one environment around and inside the moving body, and information indicating the width of the visual recognition range is acquired as environmental information. Since the notification distance is increased as the visual recognition range indicated by the environmental information is narrow, the approach to the object can be notified earlier in an environment where the visual recognition range of the driver is narrow. As a result, it is possible to achieve both suppression of the malfunction of the notification function and suppression of unnecessary operation.
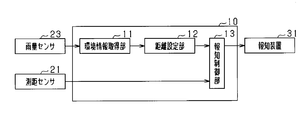
- FIG. 1 is a configuration diagram of a driving support apparatus according to the first embodiment.
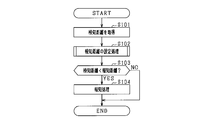
- FIG. 2 is a flowchart showing a process executed by the driving support apparatus according to the first embodiment.
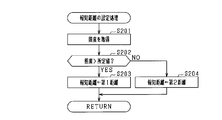
- FIG. 3 is a subroutine showing notification distance setting processing in the first embodiment.
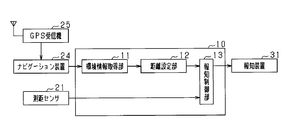
- FIG. 4 is a configuration diagram of the driving support apparatus according to the second embodiment.
- FIG. 5 is a configuration diagram of the driving support apparatus according to the third embodiment.
- FIG. 6 is a configuration diagram of the driving support apparatus according to the fourth embodiment.
- FIG. 7 is a time chart showing processing executed by the driving support apparatus according to the fifth embodiment.
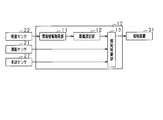
- the driving support apparatus 10 is mounted on a vehicle that is a moving body, detects an object existing around the vehicle, and notifies the driver of the vehicle of the approach between the vehicle and the object. .
- the driving support device 10 is a computer including a CPU, a ROM, a RAM, an I / O, and the like.
- the CPU implements each function by executing a program installed in the ROM.
- the driving support device 10 is connected with a distance measuring sensor 21 and an illuminance sensor 22 as sensor devices for inputting various types of detection information.
- the distance measuring sensor 21 is an ultrasonic sensor, for example, and has a function of transmitting an ultrasonic wave of 20 to 100 kHz as an exploration wave and a function of receiving an exploration wave reflected from an object as a reflected wave.
- the distance sensor 21 has a threshold value of the amplitude of the reflected wave. When the distance sensor 21 receives a reflected wave having an amplitude equal to or larger than the threshold value, the transmission time of the exploration wave and the reception time of the reflected wave are used. Then, the distance to the object is obtained, and the distance is input to the driving support device 10 as the detection distance.
- the illuminance sensor 22 is a sensor that detects the illuminance outside the vehicle. Specifically, the illuminance sensor 22 includes a photodiode. The photodiode generates a current by receiving light, and the generated current increases as the illuminance increases. The current value is detected, and the current value is converted into an illuminance value and input to the driving support device 10.
- the environment information acquisition unit 11 included in the driving support device 10 acquires illuminance from the illuminance sensor 22 as information indicating the environment around the vehicle, and inputs the illuminance value to the distance setting unit 12.
- the notification distance setting unit sets a notification distance used for comparison with the detection distance. Specifically, if the illuminance value acquired from the environment information acquisition unit 11 is greater than a predetermined value, the first distance is set as the notification distance, and if the illuminance value is equal to or less than the predetermined value, the first notification distance is set. A second distance that is larger than the distance is set. The first distance and the second distance are predetermined values.
- the notification control unit 13 compares the notification distance acquired from the distance setting unit 12 with the detection distance acquired from the distance measuring sensor 21. If the detection distance is smaller than the notification distance, it means that the distance between the vehicle and the object is shortened, and therefore the notification device 31 is instructed to perform notification.
- the notification device 31 is a device that notifies the driver that the distance between the vehicle and the object has approached. Specifically, as the notification device 31, a speaker and a display device provided on the instrument panel are used. When a notification instruction is received from the notification control unit 13 of the driving support device 10, The driver is notified of the approach to the object by performing at least one of the light emission displays by the display device.
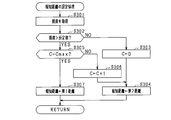
- step S101 a detection distance that is a distance to an object is acquired from the distance measuring sensor 21. At this time, if an object is not detected, information indicating that may be acquired. Then, it progresses to step S102 and the process which sets alerting
- step S102 If the notification distance is set in step S102, the process proceeds to step S103, and it is determined whether or not the detection distance is smaller than the notification distance. If an affirmative determination is made in step S103, that is, if the detection distance is smaller than the notification distance, the process proceeds to step S104, and a notification process for operating the notification device 31 is performed. Then, a series of processing ends. On the other hand, if a negative determination is made in step S103, that is, if the detected distance is equal to or greater than the notification distance, the distance between the vehicle and the object is sufficiently far away and there is no need for notification, so the series of processing ends.
- step S201 the illuminance is acquired from the illuminance sensor 22. Subsequently, in step S202, it is determined whether or not the illuminance is greater than a predetermined value. At this time, the predetermined value to be compared with the illuminance is a predetermined value. If a positive determination is made in step S202, that is, if the illuminance is greater than a predetermined value, the process proceeds to step S203, and the first distance is set as the notification distance. If a negative determination is made in step S202, that is, if the illuminance is less than or equal to a predetermined value, the process proceeds to step S204, and a second distance that is larger than the first distance is set as the notification distance. If the notification distance is set in step S203 or step S204, the subroutine processing is terminated.
- the driving support device 10 has the following effects.
- ⁇ The smaller the illuminance value acquired from the illuminance sensor 22, the darker the vehicle is, so the driver's visual range is narrowed. And when a driver
- the environment information acquired by the environment information acquisition unit 11 is different from that of the first embodiment.
- the configuration of the driving support apparatus 10 according to the present embodiment will be described with reference to FIG.
- the driving support device 10 acquires rainfall as environmental information.
- the rain sensor 23 is attached to the windshield of the vehicle, and the environment information acquisition unit 11 of the driving support device 10 acquires the rain detected by the rain sensor 23 as environment information.
- the rain sensor 23 includes a light emitting diode and a photodiode.
- the mounting angle of the light emitting diode and the photodiode is set so that the light emitted from the light emitting diode is totally reflected on the outer surface of the windshield and enters the photodiode. If raindrops adhere to the outer surface of the windshield, the light is refracted outward on the outer surface of the glass. As a result, as the amount of raindrops adhering to the outer surface of the windshield increases, the light incident on the photodiode decreases. Based on this principle, rainfall is estimated.
- the distance setting unit 12 sets the detection distance to the second distance when the rainfall acquired from the environment information acquisition unit 11 is greater than a predetermined value. On the other hand, when the rainfall is below a predetermined value, the detection distance is set to the first distance.
- the rain sensor 23 reacts in the same manner as in the case of raindrops even when dirt is attached to the windshield. Since the driver's field of view is blocked if the windshield is dirty, the notification distance is set in the same manner as when there is a lot of rain.
- the degree of cloudiness on the inner surface of the windshield can be determined. If the windshield is fogged, the driver's field of view is blocked, so the notification distance may be changed by determining the fog on the inner surface of the windshield.
- the driving support apparatus 10 according to the present embodiment has the following effects in addition to the effects similar to the effects achieved by the driving support apparatus 10 according to the first embodiment.
- Raindrops attached to the windshield increase as the amount of rain increases, and the visibility of the driver is reduced. Moreover, if there is much rainfall, the frequency
- the rainfall is detected by the rainfall sensor 23, and if the acquired rainfall is greater than a predetermined value, the notification distance is set to the second distance, and the notification device 31 is activated earlier. Thereby, in a situation where the driver's visual recognition range is likely to be narrowed, the notification function can be prevented from being deactivated by operating the notification earlier.
- the environment information acquired by the environment information acquisition unit 11 is different from that of the first embodiment.
- the configuration of the driving support device 10 according to the present embodiment will be described with reference to FIG.
- the vehicle includes a navigation device 24 that is a map display device and a GPS receiver 25 that is a position acquisition device that acquires the current position of the vehicle.
- the navigation device 24 stores map information in a hard disk drive provided therein, and displays a map based on the map information, the current position of the vehicle acquired from the GPS receiver 25, and the like on the display unit. Note that the specific configuration of the navigation device 24 is a known one, and a specific description thereof will be omitted.
- the map information possessed by the navigation device 24 includes a road type including information indicating the road width and road type, an intersection type including information indicating the presence or absence of traffic lights at the intersection, and the like.
- the driving support apparatus 10 acquires map information in the vicinity of the current position as environment information.
- the environment information acquisition unit 11 of the driving support device 10 acquires an intersection type located near the current position, for example, within a predetermined distance.
- the distance setting unit 12 sets the notification distance to the second distance when the intersection type acquired by the environment information acquisition unit 11 indicates that the intersection has poor visibility.
- criteria for judging that the intersection is poor in visibility it is an intersection where no traffic lights are provided, an intersection where roads whose width is smaller than a predetermined value intersect, and there is a building at a corner What is necessary is just to use that it is an intersection.
- the driving support device 10 according to the present embodiment has an effect similar to the effect of the driving support device 10 according to the first embodiment.
- the environment information acquired by the environment information acquisition unit 11 is different from that of the first embodiment.
- the configuration of the driving support device 10 according to the present embodiment will be described with reference to FIG.
- the vehicle is provided with a communication device 26 that acquires information from outside the vehicle via a wireless communication line.
- the communication device 26 may be provided in advance in the vehicle, or a mobile terminal or the like owned by the driver may be connected to the vehicle by wire or wirelessly.
- the communication device 26 acquires information on air pollution around the vehicle. Specifically, the concentration of particulate matter floating in the atmosphere or the concentration of photochemical smog floating in the atmosphere is acquired.
- Information regarding air pollution acquired by the communication device 26 is input to the vehicle control device, and the environment information acquisition unit 11 acquires the information regarding air pollution as environment information.
- the environment information acquisition unit 11 transmits the acquired environment information to the distance setting unit 12.
- the distance setting unit 12 sets the notification distance to the second distance when the information on air pollution acquired by the environment information acquisition unit 11 indicates that the driver's viewing range is narrow, for example, when the concentration is equal to or greater than a predetermined value. Set to.
- the information acquired by the communication device 26 is not limited to information related to air pollution, and other information may be acquired, for example.
- the weather near the current position of the vehicle is acquired, and the weather may be used as environment information.
- the notification distance can be set as in the second embodiment.
- the driving support apparatus 10 according to the present embodiment has an effect similar to that of the first embodiment.
- part of the processing executed by the distance setting unit 12 is different from that of the first embodiment. Note that the configuration of the driving support device 10 is the same as that of the first embodiment, and a specific description thereof will be omitted.
- FIG. 7 it is assumed that the vehicle is traveling during the daytime in fine weather.
- the illuminance is larger than a predetermined value, and the notification distance is set to the first distance. If the vehicle enters the tunnel, the illuminance measured by the illuminance sensor 22 decreases. If the illuminance falls below a predetermined value at time t1, the notification distance is set to a second distance that is greater than the first distance.
- the illuminance increases, and at time t2, the illuminance becomes larger than a predetermined value.
- the visual recognition range becomes narrow until the driver's eyes get used to the brightness. That is, even if the illuminance increases, the driver's visible range remains narrow.
- the state in which the notification distance is the second distance is maintained from time t2 to time t3 after a predetermined time has elapsed. That is, when the illuminance changes brighter and the notification distance is made smaller based on the change in illuminance, it can be said that the notification distance before the change in illuminance is maintained for a predetermined period. Then, the notification distance is set as the first distance at time t3.
- FIG. 8 shows a subroutine of step S102 in FIG.
- the illuminance is acquired in step S301, and in the subsequent step S302, it is determined whether or not the illuminance is greater than a predetermined value. If a negative determination is made in step S302, that is, if the illuminance is less than or equal to a predetermined value, the process proceeds to step S303.
- the counter value C is set to zero. This counter value C is used to measure the time when the notification distance is the second distance when the illuminance changes from a state below the predetermined value to a state larger than the predetermined value.
- the second distance is set as the notification distance, and the subroutine processing is terminated.
- step S302 If an affirmative determination is made in step S302, that is, if the illuminance is greater than a predetermined value, the process proceeds to step S305, where it is determined whether or not the counter value C is the maximum value Cmax. This maximum value Cmax indicates the length of time during which the notification distance is kept at the second distance, and is a predetermined value. If a negative determination is made in step S305, that is, if the counter value C is smaller than the maximum value Cmax, the process proceeds to step S306, where the counter value C is added. In the subsequent step S304, the second distance is set as the notification distance, and the subroutine processing is terminated.
- step S305 determines whether the counter value C is the maximum value Cmax, a sufficient time has passed since the illuminance is greater than the predetermined value. If an affirmative determination is made in step S305, that is, if the counter value C is the maximum value Cmax, a sufficient time has passed since the illuminance is greater than the predetermined value, so the process proceeds to step S307, and the notification distance is reached.
- the first distance is set as follows. Then, the subroutine processing ends.
- the driving support apparatus 10 according to the present embodiment has the following effects in addition to the effects exhibited by the driving support apparatus 10 according to the first embodiment.
- the notification distance is changed from the second distance to the first distance after a lapse of a predetermined time after the illuminance changes from a state below the predetermined value to a state larger than the predetermined value.
- the notification control unit 13 selects one of a first notification mode and a second notification mode for performing a notification different from the first notification mode as a notification mode, and gives an instruction to the notification device 31. More specifically, in the first notification mode and the second notification mode, the light emission display by the display device is common to the first notification mode, and the notification using the speaker is the first notification mode. Is done at a louder volume. That is, it can be said that the second notification mode is a notification that is easier for the driver to recognize than the first notification mode.
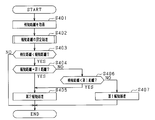
- step S401 a detection distance that is a distance to an object is acquired from the distance measuring sensor 21. Then, it progresses to step S402 and the process which sets alerting
- step S402 one of the processes shown in FIG. 3 of the first embodiment and the process shown in FIG. 8 of the fifth embodiment is performed.
- step S404 determines whether or not the notification distance is set to the second distance. If an affirmative determination is made in step S406, that is, if the detected distance is smaller than the first distance, the process proceeds to step S405, and the notification process is performed in the second notification mode. Then, a series of processing ends.
- the notification is performed in the second notification mode. It becomes.
- the reference distance since the notification is performed in the second notification mode if the detection distance is less than the first distance regardless of the setting state of the notification distance, the reference distance may be referred to for the first distance.
- the driving support apparatus 10 according to the present embodiment has the following effects in addition to the effects exhibited by the driving support apparatus 10 according to the first embodiment.
- the notification control unit 13 acquires the vehicle speed, which is the moving speed, from the vehicle speed sensor 27. If the acquired vehicle speed is zero, the notification control unit 13 notifies the notification device 31 even when the detection distance is smaller than the notification distance. No instructions are given. By carrying out like this, it can suppress that the alerting
- the notification device 31 is operated for a distant object, which can be said to be an unnecessary operation. Therefore, when the vehicle speed is zero, the notification device 31 is activated on the condition that the detection distance is less than the first distance regardless of whether the notification distance is set to the first distance or the second distance. It is good also as what makes it.
- the driving support device 40 acquires a relative speed between the vehicle and the object in addition to the distance between the vehicle and the object from the distance measuring sensor 21. And when the relative speed of a vehicle and an object is maintained, it is determined whether the alerting
- the environment information acquisition unit 41 acquires the illuminance value from the illuminance sensor 22 and inputs the illuminance value to the timing setting unit 42 as in the first embodiment.
- the timing setting unit 42 sets a notification timing that is a timing for starting notification by the notification device 31 and an operation timing that is a timing for starting the operation of the brake device 32 as timings used for comparison with the collision time. Note that the larger the notification timing is, the faster the notification device is operated. That is, the greater the notification timing, the greater the detection distance for operating the notification device. Therefore, the greater the notification timing, the larger the notification distance used in the processing in the first to seventh embodiments. It can be said.
- the collision time calculation unit 43 calculates the collision time by dividing the detection distance acquired from the distance measuring sensor 21 by the relative speed with the object acquired by the distance measuring sensor 21.
- the notification control unit 44 acquires the notification timing from the timing setting unit 42. That is, one of the first timing and the second timing set as the notification timing is acquired. Further, the collision time is acquired from the collision time calculation unit 43. And if the collision time is less than the set notification timing, a command is sent to the notification device 31.
- the braking control unit 45 acquires the operation timing from the timing setting unit 42 and acquires the collision time from the collision time calculation unit 43. If the collision time is less than the operation timing of the brake device 32, the brake device 32 is instructed.
- the driving support device 40 according to the present embodiment has an effect similar to that of the driving support device 10 according to the first embodiment.
- an ultrasonic sensor is used as the distance measuring device.
- the distance measuring device is not limited to the ultrasonic sensor, and another device such as a radar device or a stereo camera may be used.
- the illuminance sensor 22 that measures the illuminance using a photodiode is exemplified, but means for acquiring the illuminance is not limited to this.
- a phototransistor or a photoresistor may be employed. It is also common to mount a camera on a vehicle and use the camera as means for detecting the positions of surrounding objects. Therefore, it is good also as what acquires illumination intensity based on the image acquired from the camera with which the vehicle is mounted.
- the notification distance when the illuminance is less than or equal to a predetermined value, the notification distance is set to a second value that is a larger value.
- a predetermined value to be compared with the illuminance a first predetermined value and a second predetermined value larger than the first predetermined value may be provided.
- the illuminance during the daytime in fine weather is set to be between the first predetermined value and the second predetermined value.
- the notification distance is set as the second distance. In this way, when the illuminance is excessively large and the driver's viewing range is likely to be narrowed, such as during backlighting, the notification distance can be set large.
- the illuminance is measured by the illuminance sensor 22.
- the driver recognizes that the illuminance is low when the driver performs an operation of turning on the headlight of the vehicle. Therefore, the operation state of the headlight by the driver may be set as environment information indicating the illuminance, and the illuminance may be determined to be smaller than a predetermined value if an operation of turning on the headlight is performed.
- the rain sensor 23 is also provided on the inner side of the windshield, and the process of determining the fog on the inner side of the windshield by the rain sensor 23 is exemplified.
- fogging of the windshield is caused by the humidity inside the vehicle and the temperature difference between the inside and outside of the vehicle. Therefore, these pieces of information may be acquired as environmental information to determine whether the windshield is fogged.
- the process of determining the rainfall, the fog on the inside of the windshield, and the dirt on the windshield by the rain sensor 23 is exemplified.
- a camera may be mounted inside the vehicle, and the amount of rain, fogging inside the windshield, and dirt on the windshield may be determined based on an image acquired from the camera.
- the rainfall is detected by the rainfall sensor 23.
- the driver increases the operating speed of the wiper. Therefore, the operation state of the wiper by the driver may be acquired as environmental information indicating the amount of rain.
- an intersection type is acquired as map information, and a notification distance is set based on the intersection type.
- the notification distance may be set based on other map information.
- the illumination intensity is low and the viewing range is narrowed.
- the viewing range is narrowed. Therefore, when the position of the vehicle is in a tunnel, an indoor parking lot, or the like, the notification distance may be set to the second distance.
- -It is good also as what acquires the map by communication while adding the function of position acquisition apparatuses, such as a GPS receiver, to the communication apparatus 26 in 4th Embodiment. By doing so, it is possible to perform processing equivalent to that of the third embodiment using the communication device 26.
- the notification distance is changed after a predetermined time has elapsed from the time of the change.
- the volume or the like in the notification may be gradually increased as the detection distance becomes smaller.
- the volume when switching between the first notification mode and the second notification mode as in the sixth embodiment, when switching from the first notification mode to the second notification mode, The volume may be set so as to increase gradually.
- the notification by the notification device 31 when the vehicle speed is zero, the notification by the notification device 31 is performed. In this regard, if the driver intends to start the vehicle even if the vehicle speed is zero, notification should be performed. Therefore, when the vehicle is a vehicle equipped with an automatic transmission, if the drive range or the reverse range is selected, the notification is made, and if the neutral range or the reverse range is selected, the notification is not made.
- the collision time is calculated by dividing the detection distance by the vehicle speed.
- the driving assistance device 40 may also acquire the acceleration of the vehicle, and calculate the collision time using the detection distance, the vehicle speed, and the acceleration.
- the relative speed between the vehicle and the object may be acquired instead of the vehicle speed, and the collision time may be calculated by dividing the detection distance by the relative speed.
- relative acceleration may also be used.
- the notification distance may be set to be larger when the first embodiment and the second embodiment are combined and the illuminance is small and the rainfall is large.
- the notification distance is set to one of the first distance and the second distance.
- the notification distance may be set to three or more values according to the environmental information. Further, as in the first embodiment, if the environment information is indicated by a numerical value, it may be changed in proportion to the numerical value.
- the driving support devices 10 and 40 are mounted on the vehicle, but may be mounted on a moving body other than the vehicle and notify the driver of the moving body.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Human Computer Interaction (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Combustion & Propulsion (AREA)
- Transportation (AREA)
- Traffic Control Systems (AREA)
- Control Of Driving Devices And Active Controlling Of Vehicle (AREA)
Priority Applications (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE112017002121.9T DE112017002121T5 (de) | 2016-04-21 | 2017-04-17 | Fahrunterstützungsvorrichtung |
| CN201780024716.7A CN109074745B (zh) | 2016-04-21 | 2017-04-17 | 驾驶辅助装置 |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2016085382A JP6583121B2 (ja) | 2016-04-21 | 2016-04-21 | 運転支援装置 |
| JP2016-085382 | 2016-04-21 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2017183609A1 true WO2017183609A1 (ja) | 2017-10-26 |
Family
ID=60116492
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2017/015468 Ceased WO2017183609A1 (ja) | 2016-04-21 | 2017-04-17 | 運転支援装置 |
Country Status (4)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP6583121B2 (enExample) |
| CN (1) | CN109074745B (enExample) |
| DE (1) | DE112017002121T5 (enExample) |
| WO (1) | WO2017183609A1 (enExample) |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US11180164B2 (en) | 2017-11-30 | 2021-11-23 | Honda Motor Co., Ltd. | Vehicle control apparatus, vehicle, and control method |
Families Citing this family (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2020166485A (ja) * | 2019-03-29 | 2020-10-08 | 本田技研工業株式会社 | 運転支援装置 |
| JP7375678B2 (ja) * | 2020-06-02 | 2023-11-08 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | 車両制御方法、車両制御プログラム、及び車両制御システム |
| JP7372382B2 (ja) * | 2022-03-31 | 2023-10-31 | 本田技研工業株式会社 | 交通安全支援システム |
| JP2025135996A (ja) * | 2024-03-06 | 2025-09-19 | 本田技研工業株式会社 | 車両制御装置 |
Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH06231397A (ja) * | 1993-02-05 | 1994-08-19 | Suzuki Motor Corp | 車両用警報装置 |
| JPH09150647A (ja) * | 1995-09-27 | 1997-06-10 | Mazda Motor Corp | 車両の走行状態検出方法および検出装置 |
| JPH10119676A (ja) * | 1996-10-11 | 1998-05-12 | Honda Access Corp | 車両の衝突警報システム |
| JP2000082198A (ja) * | 1998-09-07 | 2000-03-21 | Toyota Motor Corp | 車両制御装置および車両制御方法 |
| JP2004164187A (ja) * | 2002-11-12 | 2004-06-10 | Nissan Motor Co Ltd | 車両用報知装置 |
| JP2015011538A (ja) * | 2013-06-28 | 2015-01-19 | 矢崎エナジーシステム株式会社 | 車載器 |
Family Cites Families (19)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH10297355A (ja) * | 1997-04-22 | 1998-11-10 | Harness Sogo Gijutsu Kenkyusho:Kk | ヘッドランプ制御装置および制御方法 |
| DE19847013A1 (de) | 1998-10-13 | 2000-04-20 | Bosch Gmbh Robert | Einparkhilfesystem |
| JP4027008B2 (ja) * | 2000-03-23 | 2007-12-26 | 横河電機株式会社 | 通信制御装置 |
| JP2002274257A (ja) * | 2001-03-19 | 2002-09-25 | Nissan Motor Co Ltd | 車両用監視装置 |
| JP2003112568A (ja) * | 2001-10-04 | 2003-04-15 | Koito Mfg Co Ltd | 車両用照明装置 |
| JP4743658B2 (ja) * | 2005-12-26 | 2011-08-10 | アイシン・エィ・ダブリュ株式会社 | 道路認識装置、道路認識方法及び道路認識プログラム |
| KR101075615B1 (ko) * | 2006-07-06 | 2011-10-21 | 포항공과대학교 산학협력단 | 주행 차량의 운전자 보조 정보 생성 장치 및 방법 |
| US8039799B2 (en) * | 2007-12-31 | 2011-10-18 | Honeywell International Inc. | Motion detection system and method |
| JP5045796B2 (ja) * | 2009-12-03 | 2012-10-10 | 株式会社デンソー | 車両接近警告システム、携帯警告端末、および車載通信機 |
| JP5637302B2 (ja) * | 2011-04-13 | 2014-12-10 | 日産自動車株式会社 | 走行支援装置及びその隣接車両検出方法 |
| KR20120139432A (ko) * | 2011-06-17 | 2012-12-27 | 현대자동차주식회사 | 차간거리 제어 시스템의 활성화 장치 및 그 방법 |
| JP5966440B2 (ja) * | 2012-02-29 | 2016-08-10 | 株式会社デンソー | 運転支援装置 |
| CN103679127B (zh) * | 2012-09-24 | 2017-08-04 | 株式会社理光 | 检测道路路面的可行驶区域的方法和装置 |
| DE102013009339A1 (de) * | 2013-06-04 | 2014-12-04 | Volkswagen Aktiengesellschaft | Verfahren und Vorrichtung zur Notfallassistenz |
| CN103523055B (zh) * | 2013-09-23 | 2014-12-10 | 华中科技大学 | 一种大坡度盾构隧道内运输车防碰撞预警系统及其工作方法 |
| CN104065930B (zh) * | 2014-06-30 | 2017-07-07 | 青岛歌尔声学科技有限公司 | 集成摄像头模组和光传感器的视觉辅助方法及装置 |
| WO2016027312A1 (ja) * | 2014-08-19 | 2016-02-25 | 三菱電機株式会社 | 後方路面照射装置 |
| JP2016085382A (ja) | 2014-10-27 | 2016-05-19 | Jsr株式会社 | レジストパターン形成方法及び感放射線性樹脂組成物 |
| CN104392581A (zh) * | 2014-11-27 | 2015-03-04 | 国家电网公司 | 高压线路防外力破坏激光监测预警系统 |
-
2016
- 2016-04-21 JP JP2016085382A patent/JP6583121B2/ja active Active
-
2017
- 2017-04-17 DE DE112017002121.9T patent/DE112017002121T5/de not_active Ceased
- 2017-04-17 WO PCT/JP2017/015468 patent/WO2017183609A1/ja not_active Ceased
- 2017-04-17 CN CN201780024716.7A patent/CN109074745B/zh active Active
Patent Citations (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH06231397A (ja) * | 1993-02-05 | 1994-08-19 | Suzuki Motor Corp | 車両用警報装置 |
| JPH09150647A (ja) * | 1995-09-27 | 1997-06-10 | Mazda Motor Corp | 車両の走行状態検出方法および検出装置 |
| JPH10119676A (ja) * | 1996-10-11 | 1998-05-12 | Honda Access Corp | 車両の衝突警報システム |
| JP2000082198A (ja) * | 1998-09-07 | 2000-03-21 | Toyota Motor Corp | 車両制御装置および車両制御方法 |
| JP2004164187A (ja) * | 2002-11-12 | 2004-06-10 | Nissan Motor Co Ltd | 車両用報知装置 |
| JP2015011538A (ja) * | 2013-06-28 | 2015-01-19 | 矢崎エナジーシステム株式会社 | 車載器 |
Cited By (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US11180164B2 (en) | 2017-11-30 | 2021-11-23 | Honda Motor Co., Ltd. | Vehicle control apparatus, vehicle, and control method |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP2017194861A (ja) | 2017-10-26 |
| DE112017002121T5 (de) | 2019-01-03 |
| JP6583121B2 (ja) | 2019-10-02 |
| CN109074745B (zh) | 2024-03-08 |
| CN109074745A (zh) | 2018-12-21 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP6956121B2 (ja) | 気象検出用レーダおよび車両システムの動的制御ならびに作動 | |
| JP6583121B2 (ja) | 運転支援装置 | |
| US9694736B2 (en) | Vehicle state indication system | |
| EP3659876B1 (en) | Vehicle cleaner system | |
| KR101993104B1 (ko) | 차량 상태 표시 시스템 | |
| RU2700635C1 (ru) | Способ и устройство обнаружения мест для парковки | |
| JP5353999B2 (ja) | 運転者支援装置 | |
| US20200086790A1 (en) | Virtual lane lines for connected vehicles | |
| US9868389B2 (en) | Vehicle state indication system | |
| JP2017111576A (ja) | 運転支援装置 | |
| US20170088039A1 (en) | Vehicle state indication system | |
| CN112277962B (zh) | 车载设备控制装置 | |
| JP6500724B2 (ja) | 危険情報報知システム、サーバ及びコンピュータプログラム | |
| JP6394440B2 (ja) | 汚れ判定装置 | |
| US9056581B2 (en) | On-vehicle light distribution control system | |
| JP2010000893A (ja) | 車両の前照灯制御装置 | |
| JP2016173652A5 (enExample) | ||
| KR20220010900A (ko) | 차량용 레이더 장치 및 제어방법 | |
| JP7164309B2 (ja) | 周辺監視装置および周辺監視システム | |
| JP4992643B2 (ja) | 接触事故防止装置 | |
| JP2018127063A (ja) | ワイパ駆動制御装置、ワイパ駆動制御方法及びコンピュータプログラム | |
| JP2018122645A (ja) | 制御装置、制御方法及びコンピュータプログラム | |
| JP2009255710A (ja) | 車両用ワイパ制御装置 | |
| JP4702171B2 (ja) | 車両用制御装置 | |
| JP2009086711A (ja) | 車両用事故防止システム |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 201780024716.7 Country of ref document: CN |
|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 17785947 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 17785947 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |