WO2017018191A1 - 加湿装置 - Google Patents
加湿装置 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2017018191A1 WO2017018191A1 PCT/JP2016/070485 JP2016070485W WO2017018191A1 WO 2017018191 A1 WO2017018191 A1 WO 2017018191A1 JP 2016070485 W JP2016070485 W JP 2016070485W WO 2017018191 A1 WO2017018191 A1 WO 2017018191A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- air
- adsorbent
- ceiling
- moisture
- space
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60H—ARRANGEMENTS OF HEATING, COOLING, VENTILATING OR OTHER AIR-TREATING DEVICES SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR PASSENGER OR GOODS SPACES OF VEHICLES
- B60H3/00—Other air-treating devices
- B60H3/02—Moistening ; Devices influencing humidity levels, i.e. humidity control
- B60H3/022—Moistening ; Devices influencing humidity levels, i.e. humidity control for only humidifying the air
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60H—ARRANGEMENTS OF HEATING, COOLING, VENTILATING OR OTHER AIR-TREATING DEVICES SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR PASSENGER OR GOODS SPACES OF VEHICLES
- B60H1/00—Heating, cooling or ventilating [HVAC] devices
- B60H1/00007—Combined heating, ventilating, or cooling devices
- B60H1/00207—Combined heating, ventilating, or cooling devices characterised by the position of the HVAC devices with respect to the passenger compartment
- B60H2001/00235—Devices in the roof area of the passenger compartment
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60H—ARRANGEMENTS OF HEATING, COOLING, VENTILATING OR OTHER AIR-TREATING DEVICES SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR PASSENGER OR GOODS SPACES OF VEHICLES
- B60H3/00—Other air-treating devices
- B60H3/02—Moistening ; Devices influencing humidity levels, i.e. humidity control
- B60H2003/026—Moistening ; Devices influencing humidity levels, i.e. humidity control the devices being located in the passenger compartment
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B60—VEHICLES IN GENERAL
- B60H—ARRANGEMENTS OF HEATING, COOLING, VENTILATING OR OTHER AIR-TREATING DEVICES SPECIALLY ADAPTED FOR PASSENGER OR GOODS SPACES OF VEHICLES
- B60H3/00—Other air-treating devices
- B60H3/02—Moistening ; Devices influencing humidity levels, i.e. humidity control
- B60H2003/028—Moistening ; Devices influencing humidity levels, i.e. humidity control the devices comprising regeneration means
Definitions
- the present disclosure relates to a humidifying device that provides humidified air to a room.
- Patent Document 1 discloses a form of a humidifying device that supplies humidified air to passengers in a vehicle interior.
- the humidifier operates a pair of blowers, sucks air in the vehicle compartment from the suction port, and passes the air through the pair of adsorbents.
- the air passing through each adsorbent is dehumidified air by moisture adsorbed by the adsorbent.
- the dehumidified air is guided to the first air outlet and the second air outlet by the switching damper, and is blown out from the first air outlet toward the front window and from the second air outlet toward the occupant.
- the humidifier When the humidifier blows humidified air, the humidifier operates only one heater and a pair of blowers, sucks the air in the passenger compartment from the inlet and passes it through the pair of adsorbents.
- One adsorbent is heated by the heater and released to the air passing through the adsorbed moisture. Therefore, the air passing through one adsorbent becomes humidified air containing moisture released from the adsorbent.
- the humidified air is guided to the second air outlet by the switching damper and is blown out from the second air outlet toward the occupant. Further, since the other adsorbent is not heated by the heater, the air passing through the other adsorbent is adsorbed by the adsorbent and becomes dehumidified air.
- the dehumidified air is guided to the first air outlet by the switching damper and blown out from the first air outlet toward the front window.
- Patent Document 1 For example, in the winter season when humidification is required, the passenger compartment is heated, so the air in the passenger compartment is dried due to a decrease in relative humidity.
- the apparatus of Patent Document 1 is a so-called desiccant system that takes in air in a passenger compartment, collects moisture in the air, and uses it when supplying humidified air thereafter. Therefore, the water necessary for humidification cannot be recovered, and there is a possibility that sufficient humidification ability cannot be ensured.
- This indication is made in view of the above-mentioned point, and it aims at providing the humidification device which aims at suppression of the humidification capability fall by vehicle interior heating.
- the humidifier according to the first aspect of the present disclosure is a vehicle humidifier that supplies humidified air humidified by moisture desorbed from an adsorbent that has adsorbed moisture in the air to the vehicle interior.
- the humidifier includes an adsorbent module and a blower.
- the adsorbent module has an adsorbent, and adsorbs moisture contained in the passing air to the adsorbent or desorbs the moisture adsorbed on the adsorbent from the air passing through.
- the blower blows the passing air to the adsorbent module.
- the air blowing unit takes in air in the ceiling space formed between the vehicle top plate and the ceiling interior member in the vehicle interior, and the air is supplied to the adsorbent module. The air is blown to adsorb moisture in the air with the adsorbent.
- the moisture contained in the air in the ceiling space defined between the vehicle top plate and the ceiling interior member in the passenger compartment is adsorbed by the adsorbent, so that the relative humidity is increased by heating.
- Moisture can be recovered from air that is less affected by heating than the air in the passenger compartment. Accordingly, it is possible to perform adsorption with higher moisture collection efficiency than to collect moisture from the air in the heated vehicle compartment, and it is possible to provide humidified air that secures the humidifying capacity at the next desorption. Therefore, it is possible to provide a humidifier that can suppress a decrease in humidification capacity due to vehicle interior heating.
- the humidifying device is a humidifying device for a vehicle that supplies humidified air that has been humidified by moisture desorbed from an adsorbent that has adsorbed moisture in the air to a humidification target space.
- the humidifier includes an adsorbent module and a blower.
- the adsorbent module has an adsorbent, and adsorbs moisture contained in the passing air to the adsorbent, and desorbs moisture adsorbed on the adsorbent to the passing air.
- the blower blows the passing air to the adsorbent module.
- the blower unit takes in air outside the vehicle, blows the air to the adsorbent module, and adsorbs moisture in the air with the adsorbent.
- the humidification apparatus which can aim at suppression of the humidification capability fall by vehicle interior heating can be provided also by the 2nd mode.
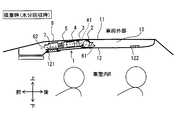
- FIG. 1 It is a schematic diagram which shows the position where the humidification apparatus which concerns on 1st Embodiment is mounted in a vehicle. It is sectional drawing which shows the general
- the humidifying device of the present disclosure is mounted on the back side of the ceiling interior member 12 in the vehicle interior R, and the vehicle interior R is used as a humidification target space.
- the humidifier disclosed in each embodiment sets the vehicle interior R as a humidification target space.
- the vehicle on which the humidifier 1 is mounted includes a vehicle air conditioner that adjusts the temperature of the passenger compartment R.
- the humidifier 1 is installed in a ceiling space 13 that is partitioned between a vehicle top plate 11 and a ceiling interior member 12.
- the ceiling interior space 13 is partitioned from the vehicle interior R by the ceiling interior member 12. Since the ceiling interior space 13 is a predetermined space defined between the vehicle top plate 11 and the ceiling interior member 12, it is not a space that is completely blocked from the vehicle interior R. Depending on the pressure difference between the ceiling space 13 and the vehicle interior R, some air may enter and leave the ceiling space 13 through a gap between members.
- the up and down arrows shown in each figure indicate directions in a state where the humidifying device 1 is mounted on the vehicle. Therefore, the upper side and the lower side are the upper side and the lower side in the vertical direction of the vehicle, respectively, and the front side and the rear side are the front side and the rear side in the front and rear direction of the vehicle, respectively.
- the humidifier 1 accommodates a blower 2, a heating device 3, an adsorbent module 4, a cooling device 5 and the like inside a casing 6 that forms an outer shell thereof.
- the blower 2, the heating device 3, the adsorbent module 4, and the cooling device 5 are arranged in this order in the direction A ⁇ b> 2 in which air flows when desorbing moisture from the adsorption element. Is installed. Accordingly, the air introduced into the ceiling space 13 from the first opening 61 at the time of desorption is heated by the heating device 3, passes through the adsorbent module 4, and is added with moisture, and the cooling device 5. After being cooled, the air is blown into the vehicle interior R from the vehicle interior outlet.
- the vehicle interior outlet is referred to as the outlet 121.
- the flow of air at the time of desorption is indicated by solid arrows in FIG.
- the humidifying device 1 is arranged in the order of the cooling device 5, the adsorbent module 4, the heating device 3, and the blower 2 in the direction A ⁇ b> 1 in which air flows when adsorbing moisture to the adsorption element. is set up. Therefore, the air introduced into the ceiling space 13 from the second opening 62 at the time of adsorption is cooled by the cooling device 5 and then passes through the adsorbent module 4 to release moisture to the adsorbent. After being heated at 3, the air is blown out from the first opening 61 into the ceiling space 13. The flow of air at the time of adsorption is indicated by broken-line arrows in FIG.
- the first opening 61 is formed in the casing 6 which is an apparatus case, and is a desorption inlet for sucking air in the ceiling space 13 into the casing 6 during desorption.
- the first opening 61 is also a suction outlet for discharging the air after moisture is adsorbed by the adsorbent (air after moisture recovery) to the ceiling space 13 during adsorption.
- the first opening 61 as the desorption inlet port enables air to be taken into the ceiling space 13 by the blower 2 and the air to be blown to the adsorbent module 4 at the time of desorption.
- the second opening 62 is formed in the casing 6 and is a suction inlet portion that sucks air in the ceiling space 13 into the casing 6 during suction.
- the first opening 61 is provided on the opposite side of the casing 6 from the second opening 62.
- the first opening 61 is provided at the rear end of the casing 6, and the second opening 62 is provided at the front end of the casing 6.
- the air blower 2 is provided in the vicinity position adjacent to the 1st opening part 61 which is a discharge port part at the time of adsorption
- the air outlet 121 opens toward the lower passenger compartment R and forms a passage that penetrates the casing 6 and the ceiling interior member 12.
- the air outlet 121 is provided, for example, so as to open above an occupant seated in the front seat of the passenger compartment R.
- a sun visor is provided at a location that is located forward of the air outlet portion 121 in the ceiling interior member 12. It is preferable that a filter that collects dust, dust, and the like carried together with air is installed at the outlet 121.
- a switching door 7 as a switching member is provided in the second opening 62 (suction port at the time of adsorption).
- the switching door 7 allows air to be taken into the space 13 in the ceiling at the time of adsorption in which moisture in the air is adsorbed by the adsorbent, and desorbs from the air passing through the moisture adsorbed by the adsorbent.
- the air that has passed through the adsorbent module 4 is supplied to the vehicle interior R.
- the second opening 62 is provided at a location adjacent to the air outlet 121, and the second opening 62 and the air outlet 121 are switched between an open state and a closed state by the switching door 7.
- the switching door 7 is controlled by the control device so as to close the second opening 62 and open the air outlet 121 when desorbing, and close the air outlet 121 and open the second opening 62 during adsorption. Accordingly, the switching door 7 is provided at the front end of the casing 6 so as to be positioned in front of the cooling device 5 in the casing 6.
- the blower 2 is installed at a position closer to the first opening 61 than other devices, but the installation position of the blower 2 is not limited to this position. Therefore, the blower 2 can be installed at an arbitrary position in the air passage formed between the first opening 61 and the second opening 62.
- the blower 2 is, for example, an electric blower that rotationally drives an axial fan with an electric motor, and constitutes a blower that blows air that passes through the adsorbent module 4.
- the blower 2 can switch the flow direction of the air blown by the blower 2 to the opposite direction by switching the rotation direction of the electric motor by the control device.
- the blower 2 is a blower unit in which the operating rate, that is, the rotation speed and the amount of air to be blown are controlled by a control voltage output from the control device.
- the volume occupied by the amount of air blown into the vehicle interior R during humidification is set to be smaller than the volume of the ceiling space 13.
- the volume occupied by the blown air volume for one time at the time of humidification is about 0.167 m 3 .
- the ceiling space 13 is set to have a volume larger than about 0.167 m 3 .
- the second opening 62 which is the suction port at the time of adsorption, is separated from the peripheral edge of the ceiling interior member 12 where the vehicle top plate 11 and the ceiling interior member 12 can come into contact.
- the second opening 62 has a distance between the second opening 62 and the peripheral edge of the ceiling interior member 12 between the second opening 62 and the first opening 61. It is preferable that the ceiling interior member 12 is separated from the peripheral edge so as to be longer than the distance between them.
- the peripheral part of the ceiling interior member 12 and the vehicle top plate 11 are also seams that define the space 13 in the ceiling. Since the first opening 61 is located not in the vicinity of the peripheral edge of the ceiling interior member 12 but in a separated position, the air in the vehicle interior R drawn into the ceiling interior space 13 during humidification can be brought into contact with the vehicle top plate 11. it can. In winter, for example, the outside air temperature is 0 ° C., the air temperature in the ceiling space 13 is 18 ° C., the relative humidity is 30%, the air temperature in the passenger compartment R is 25 ° C., and the relative humidity is 15%. is there. As shown in FIG. 2, during humidification, the air in the passenger compartment R drawn into the ceiling interior space 13 is cooled by contacting the vehicle top plate 11. Therefore, the relative humidity of the air before reaching the adsorbent module 4 can be increased, and the relative humidity of the humidified air can be further increased. This effect is particularly remarkable in winter when the outside air temperature is low.
- Air in the ceiling interior space 13 is sucked into the air passage in the casing 6 from the second opening 62, flows in the order of the cooling device 5, the adsorbent module 4, and the heating device 3, and becomes dehumidified air in the first opening. 61 is blown out into the ceiling space 13.
- the air in the ceiling space 13 is sucked into the casing 6 and is blown out into the ceiling space 13 after the water is collected, so that the ceiling space 13 does not become a negative pressure with respect to the vehicle interior R. Thereby, the air in the vehicle interior R is not drawn into the ceiling interior space 13 through the gap between the vehicle top plate 11 and the ceiling interior member 12.
- the casing 6 is formed in a box shape with resin or metal, and forms an air passage through which air blown from the blower 2 is circulated.
- the casing 6 is formed in a thin rectangular parallelepiped shape extending along the vehicle top plate 11 and the ceiling interior member 12.
- the adsorbent module 4 is configured by laminating and arranging a plurality of metal plate-like members carrying adsorbents at intervals. Therefore, a passage through which air passes is formed between adjacent plate-like members.
- the contact area between air and the adsorbent can be increased by arranging a plurality of plate-like members carrying the adsorbent in this way.
- the adsorbing material a polymeric adsorbing material or a hygroscopic material such as zero light, which is a polyhedron obtained by drying gelatinous soft mud, is employed.
- the heating device 3 is a heater capable of heating the air flowing through the air passage in the casing 6.
- the heating device 3 can employ various methods as the heating method as long as it can heat the air.
- a device having a heating element that generates heat when energized, or a device that heats indoor air by exchanging heat between a medium and air that is higher in temperature than indoor air can be used.
- the heating device 3 is, for example, a device having a nichrome wire heater, a PTC (Positive Temperature Coefficient) heater, a heat exchanger, or the like.
- a heating element such as hot water, a refrigerant, engine cooling water, or an electronic component that generates heat in the vehicle can be used as a medium having a temperature higher than that of air used in the heat exchanger.
- the cooling device 5 is a cooler capable of cooling the air flowing through the air passage in the casing 6. As long as the cooling device 5 can cool the air, various methods can be adopted as the cooling method.
- a heat sink capable of conducting heat with the vehicle top plate 11 can be used.
- the cooling device 5 may be a device having a Peltier element that absorbs heat when energized, or a device that cools indoor air by exchanging heat between a medium and air having a temperature lower than that of the indoor air.
- the cooling device 5 can be a heat exchanger through which a low-temperature medium flows. As a medium having a temperature lower than that of air used for the heat exchanger, outside air, conditioned air, a refrigerant flowing through a refrigeration cycle used for an air conditioner, or the like can be employed.
- a heat exchanger using outside air as a low-temperature medium has a heat sink.
- the heat sink is a heat transfer member having a plurality of fins formed of a metal such as aluminum or copper having excellent heat transfer properties.
- the heat sink is attached to the vehicle top plate 11, for example.
- the heat sink performs a function of transferring heat of outside air outside the vehicle to the air passage in the casing 6.
- the heat sink can exchange heat between the outside air outside the vehicle and the air flowing through the air passage in the casing 6.
- the heat sink is a cooler that cools the air by allowing the cool air that the outside air cools to air that blows into the vehicle interior R, or a cooler that cools the air by dissipating the heat that the air has to the outside air.
- the control device is composed of a microcomputer including a CPU, a ROM, a RAM and the like and its peripheral circuits, and controls the operation of the blower 2 and the switching door 7 connected to the output side. Further, the control device may control a heating action or a cooling action by the heating device 3 or the cooling device 5.
- the input side of the control device is connected to an inside air sensor as an inside air temperature detecting unit for detecting the air temperature in the vehicle interior R, an outside air sensor as an outside air temperature detecting unit for detecting the outside air temperature, and the like. Detection signals from these sensors are input to the control device. Further, an operation switch for operating the humidifying device 1 is connected to the input side of the control device, and operation signals of these switches are input to the control device.
- control device may be configured integrally with, for example, an air conditioning control device that controls the operation of each component device of the vehicle air conditioning device. Further, this control device may be separate from the air conditioning control device, and may communicate information regarding the control state of the device to be controlled.
- the humidifier 1 operates when the operation switch is turned on by the operation of the occupant in a state where the temperature of the vehicle interior R is adjusted by the vehicle air conditioner.
- the humidifier 1 is operated when the outside air temperature is relatively low and the vehicle interior R is easy to dry, such as in winter.
- the control device causes the electric motor of the blower 2 to rotate forward and the switching door 7 opens the blowout port 121, reverses the electric motor, and switches the switching door 7. Switches the state of opening the second opening 62 alternately, for example, every predetermined time.
- the ventilation path at the time of desorption in which air flows as shown by the solid line arrow in FIG. 2 and the ventilation path at the time of adsorption as shown by the broken line arrow in FIG. 3 are switched every predetermined time.
- the control device rotates the electric motor of the blower 2 in the normal direction and controls the switching door 7 so as to open the air outlet 121.
- air having a temperature of 18 ° C. and a relative humidity of 30% in the ceiling space 13 is sucked into the casing 6 through the first opening 61.
- the air sucked into the air passage in the casing 6 is heated when passing through the heating device 3.
- the control device operates the heating device 3 at a constant output so that the temperature of the air after passing through the heating device 3 is higher than the temperature of the air in the ceiling space 13 by a predetermined temperature, for example, about 5 ° C.
- the output of the heating device 3 is controlled according to the temperature change of the air. Therefore, the temperature of the air after passing through the heating device 3 rises to about 23 ° C.
- the air after passing through the heating device 3 flows into the adsorbent module 4.
- the relative humidity of the air whose temperature has increased through the heating device 3 is lower than the relative humidity of the air in the ceiling space 13. Therefore, when the air whose relative humidity has decreased after passing through the heating device 3 is brought into contact with the adsorbent of the adsorbent module 4, the water adsorbed on the adsorbent is easily desorbed into the air. That is, the air whose relative humidity has been lowered by the heating device 3 tends to contain moisture held by the adsorbent, and the air after flowing out of the adsorbent module 4 becomes humidified air that has been sufficiently humidified.
- this humidified air is further cooled by the cooling device 5, the temperature of the humidified air whose temperature has been increased by the heating device 3 decreases. Thereby, it can provide toward a passenger
- the temperature of the air can be quickly raised. Furthermore, since the relative humidity of the air can be lowered quickly due to the rapid rise in air temperature, moisture desorption in the adsorbent module 4 is actively performed, and the air after flowing out of the adsorbent module 4 The relative humidity can be increased quickly.
- the control device reverses the electric motor of the blower 2 and controls the switching door 7 so as to open the second opening 62
- the temperature in the ceiling space 13 is 18 ° C. and the relative humidity is 30%. Air is sucked into the casing 6 through the second opening 62. The air sucked into the air passage in the casing 6 is cooled when passing through the cooling device 5.
- the air after passing through the cooling device 5 flows into the adsorbent module 4.
- the relative humidity of the air whose temperature has decreased after passing through the cooling device 5 is higher than the relative humidity of the air in the ceiling space 13.
- the humidifying device 1 may be configured such that when the air is taken into the casing 6 at the time of desorption, the air in the vehicle interior R is taken in.
- the first opening 161 provided in the vicinity of the blower 2 in the casing 6 opens toward the vehicle interior R to communicate the interior of the casing 6 and the vehicle interior R. Configure the passage.
- the air after moisture collection at the time of adsorption may be discharged into the vehicle interior R.
- the check valve 107 ⁇ / b> A allows the flow of air flowing into the casing 6 from the ceiling interior space 13 through the second opening 62, and the ceiling interior space 13 from the interior of the casing 6. It has a valve function to block the flow of air flowing out to Accordingly, the check valve 107A is elastically deformed into the shape illustrated by the broken line in FIG. 5 to allow the air flow in the direction A1 during the adsorption, and has the shape illustrated by the solid line in FIG. The air leakage from the inside of the casing 6 to the ceiling space 13 during detachment is prohibited.
- the check valve 107 ⁇ / b> B allows the flow of air flowing out of the casing 6 into the vehicle interior R at the air outlet 121, and allows the air flowing into the casing 6 from the vehicle interior R into the casing 6.
- the check valve 107B is elastically deformed into a shape illustrated by a solid line in FIG. 5 to allow an air flow in the direction A2 during detachment, and has a shape illustrated by a broken line in FIG. To prevent air leakage from the casing 6 to the vehicle interior R during adsorption.
- the humidifier 1 is a vehicular humidifier that supplies humidified air humidified by moisture desorbed from an adsorbent that has adsorbed moisture in the air to the vehicle interior R.
- the humidifier 1 has an adsorbent, and adsorbent module 4 that adsorbs moisture contained in the passing air to the adsorbent and desorbs moisture adsorbed on the adsorbent to the air passing through the adsorbent.
- a blower 2 that blows air to the adsorbent module 4.
- the blower 2 takes in the air in the ceiling space 13 defined between the vehicle top plate 11 and the ceiling interior member 12 and sucks the air to the adsorbent module 4 at the time of adsorption. To adsorb moisture in the air.
- the casing 6 of the humidifier 1 is installed in the ceiling space 13.
- the blower 2 takes air in the ceiling space 13 from the suction inlet provided in the casing 6 and blows the air to the adsorbent module 4.
- the casing 6 that accommodates the functional components of the humidifying device 1 is accommodated in the ceiling interior space 13 and the suction port portion at the time of adsorption is provided in the casing 6, the device does not jump into the vehicle interior R, It is possible to provide a humidifier that is compact in terms of mounting.
- the blower 2 sucks air in the ceiling space 13 when adsorbing and adsorbs moisture with the adsorbent, and then discharges it to the ceiling space 13, and takes in the air in the ceiling space 13 when desorbing, The air is blown to the adsorbent module 4.
- the air in the ceiling space 13 is sucked and the moisture in the air is collected and then discharged to the ceiling space 13, so that the ceiling space 13 does not become negative pressure. Therefore, it can suppress that the air of the vehicle interior R enters the ceiling interior space 13, and it can prevent that the relative humidity of the air in the ceiling interior space 13 falls by taking in the air of the dry interior R of the vehicle interior.
- the air in the ceiling interior space 13 is taken in, so that the dry air in the vehicle interior R is taken in, so that the relative humidity of the humidified air can be improved.
- the first opening 61 is a suction outlet for discharging the air after moisture is adsorbed by the adsorbent during the suction to the ceiling space 13.
- the suction outlet port is provided on the opposite side of the humidifier 1 to the outlet 121 from which humidified air is blown out toward the vehicle interior R during desorption.
- the humidifier 1 is provided between the first opening 61 and the outlet 121.
- the blower 2 is provided at a position adjacent to the suction outlet portion. Specifically, a distance L3 between the blower 2 and the first opening 61 (a suction outlet portion) is shorter than a distance L4 between the blower 2 and the outlet portion 121.
- the cooling device 5 is a heat exchanger that cools the air by exchanging heat between the air flowing through the casing 6 and the outside air. According to this, since the outside air having a low temperature in winter can be used as a cooling medium, power for cooling is unnecessary, and an energy-saving and low-cost cooling device can be configured.
- the humidifier 101 of the second embodiment is different from the first embodiment in that air outside the vehicle is taken into the casing 6 instead of the air in the ceiling space 13 at the time of adsorption.
- the humidifier 101 includes a second opening 111 that communicates with the outside of the vehicle.
- the second opening 111 constitutes a passage that penetrates the casing 6 and the vehicle top plate 11.
- the second opening 111 is a suction inlet for suction that sucks air outside the vehicle into the casing 6 during suction.
- the second opening 111 is preferably provided with a filter that collects dust, dust and the like carried together with air.
- air outside the vehicle introduced from the second opening 111 is cooled by the cooling device 5, passes through the adsorbent module 4, releases moisture to the adsorbent, and is further heated by the heating device 3. After that, the air is blown out from the first opening 61 to the space 13 in the ceiling.
- the flow of air at the time of adsorption is indicated by broken-line arrows in FIG.
- the 2nd opening part 111 is provided in the place which opposes an up-down direction with respect to the blower outlet part 121. As shown in FIG. The second opening 111 and the outlet 121 are switched between an open state and a closed state by the switching door 207.
- the switching door 207 is a switching member, and is controlled by the control device so as to close the second opening 111 and open the outlet 121 when desorbing, and close the outlet 121 and open the second opening 111 during adsorption. Is done. Therefore, the switching door 207 is located in front of the cooling device 5 in the casing 6 and provided at the front end of the casing 6.
- the blower 2 takes in air outside the vehicle at the time of adsorption, blows the air to the adsorbent module 4, and adsorbs moisture in the air with the adsorbent.
- moisture contained in the air outside the vehicle is adsorbed by the adsorbent, so that moisture is removed from the air having less influence on heating than the air in the vehicle interior R whose relative humidity has been lowered by heating. Can be recovered.
- the humidification apparatus 101 which can aim at suppression of the humidification capability fall by vehicle interior heating can be provided.
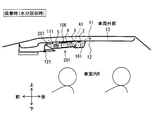
- the third embodiment is different from the first embodiment in that the ceiling interior member 12 includes a communication opening 122 that allows the space 13 in the ceiling and the vehicle interior R to communicate with each other.
- the communication opening 122 opens toward the lower vehicle interior R so as to penetrate the ceiling interior member 12, and constitutes a passage that connects the ceiling interior space 13 and the vehicle interior R.
- the communication opening 122 is provided, for example, so as to open above an occupant seated in a rear seat of the vehicle interior R.
- the communication opening 122 is preferably provided with a filter that collects dust, dust and the like carried together with air.
- the communication opening 122 is provided at a position closer to the first opening 61 that is the suction outlet (desorption inlet) than the second opening 62 that is the suction inlet.
- the distance L1 between the communication opening 122 and the first opening 61 is shorter than the distance L2 between the communication opening 122 and the second opening 62. That is, the first opening 61 is located between the second opening 62 and the communication opening 122 in the front-rear direction.
- the communication opening 122 communicates the ceiling interior space 13 and the vehicle interior R at a position closer to the rear seat than the front seat. Accordingly, the communication opening 122 is located on the side opposite to the side where the casing 6 is installed in the ceiling interior space 13.
- the air introduced into the ceiling space 13 from the first opening 61 is heated by the heating device 3 and then moisture is added by the adsorbent module 4. Further, after being cooled by the cooling device 5, the air is blown out from the air outlet portion 121 to the vehicle interior R. At this time, the air in the ceiling interior space 13 flows in the direction A2 indicated by the solid line arrow in FIG. As a result, the air in the vehicle interior R is drawn into the ceiling interior space 13 through the communication opening 122. That is, the same amount of air in the vehicle interior R as the humidified air supplied to the vehicle interior R through the air outlet portion 121 during humidification is sucked into the ceiling interior space 13 through the communication opening 122.
- the air in the ceiling space 13 is sucked into the casing 6 and is blown out to the ceiling space 13 after the moisture is collected. Therefore, the ceiling space 13 does not become negative pressure with respect to the vehicle interior R. . Thereby, the air in the vehicle interior R is not drawn into the ceiling interior space 13 through the communication opening 122.
- the communication opening 122 that allows the ceiling space 13 and the vehicle interior R to communicate with each other is provided in a position closer to the desorption suction port than the suction suction port. Air can be actively taken into the ceiling space 13 from the communication opening 122. According to this, the air approach path from the vehicle interior R to the ceiling interior space 13 can be limited, which contributes to the stable temperature and humidity of the ceiling interior space 13 around the humidifier 1.
- the communication opening 122 is located on the opposite side to the side where the casing 6 is installed in the ceiling interior space 13, so that the air entry path from the vehicle interior R to the ceiling interior space 13 is away from the humidifier 1. Can be set to According to this, the temperature and humidity state of the space 13 in the ceiling around the humidifier 1 can be further stabilized.
- the humidifier of the fourth embodiment includes a cylindrical member 123 that is provided on the side of the space 13 in the ceiling of the communication opening 122 and has a gap with the vehicle top plate 11.
- the tubular member 123 extends from the communication opening 122 toward the vehicle top plate 11, and a gap is formed between the tubular member 123 and the vehicle top plate 11.
- a wind direction guide member 123a is provided in the ceiling space 13 located on the downstream side of the communication opening 122. The wind direction guide member 123a is opposed to the vehicle top plate 11 on the vehicle top plate 11 side of the tubular member 123 and extends to the casing 6 side.
- the wind direction guide member 123 a extends from the end of the tubular member 123 on the vehicle top plate 11 side toward the casing 6.
- the wind direction guiding member 123a has a function of guiding the air in the vehicle interior R taken into the ceiling interior space 13 through the communication opening 122 when detached, along the vehicle top plate 11.
- the wind direction guide member 123 a is a plate-like member that extends along the inner surface of the vehicle top plate 11.
- the air direction guide member 123a causes the air flowing in from the communication opening 122 and rising in the ceiling space 13 to flow along the vehicle top plate 11 in the direction toward the first opening 61, as indicated by solid arrows in FIG. To guide.
- the air in the vehicle interior R can flow down toward the first opening 61 along the vehicle top plate 11. Since the vehicle top plate 11 is cooler than the heated and air-conditioned vehicle interior R, the air in the vehicle interior R can be efficiently cooled, and the moisture recovery efficiency of the humidifier can be further improved.
- the humidifying device 201 of the fifth embodiment is not installed in the ceiling interior space 13 but is installed on the lower surface of the ceiling interior member 12 that forms the ceiling interior space 13 above the passenger. Is different.
- the humidifier 201 includes a second opening 111 that communicates with the ceiling space 13.
- the second opening 111 constitutes a passage that penetrates the casing 106 and the ceiling interior member 12.
- the second opening 111 is a suction inlet for suction that sucks air in the ceiling space 13 into the casing 6 during suction.
- the second opening 111 is preferably provided with a filter that collects dust, dust, and the like.
- a first opening 161 provided in the casing 106 in the vicinity of the blower 2 constitutes a passage that penetrates the casing 106 and the ceiling interior member 12, and discharges the air after the moisture collection to the ceiling interior space 13. This is the exit.
- the air introduced into the ceiling space 13 from the second opening 111 is cooled by the cooling device 5 and then passes through the adsorbent module 4 to release moisture to the adsorbent. After being heated, the air is blown out from the first opening 161 to the ceiling space 13.
- the flow of air at the time of adsorption is indicated by broken-line arrows in FIG.
- the blower 2, the heating device 3, the adsorbent module 4, the cooling device 5 and the like are arranged at intervals.
- at least two of the blower 2, the heating device 3, the adsorbent module 4, and the cooling device 5 may be integrated and have a plurality of functions.
- the arrangement of the heating device 3, the adsorbent module 4, and the cooling device 5 inside the humidifying device 1 is not limited to the form described in the above-described embodiment. A configuration in which these devices are arranged separately in an air passage that is lined up and down in two stages may be employed. Further, the humidifying device 1 may be configured such that an air passage at the time of adsorption and an air passage at the time of desorption are arranged in two stages vertically, and each device is installed at a predetermined position of each passage.
- the adsorbent module 4 is configured by stacking and arranging a plurality of metal plate-like members carrying the adsorbent at intervals.
- an adsorbent may be supported on a corrugated plate bent in a wave shape, and the corrugated plates may be stacked and arranged at intervals.
- the adsorbent may be supported on a honeycomb member having a passage formed in a hexagonal cross section.
- the blower may have a wind direction changing function that can change the wind direction guided by the guide member to a direction opposite to the direction A1 and the direction A2 by a guide member whose rotational position changes.
- the air outlet portion 121 is located on the front seat side and the communication opening portion 122 is located on the rear seat side so that the humidified air is supplied to the front seat side of the vehicle.
- the positional relationship between the air outlet 121 and the communication opening 122 is not limited to this example.
- the air outlet portion 121 is arranged to open toward the upper body side of the occupant seated in the front seat, but the position of the air outlet portion is not limited to this example.
- the communication opening 122 of the third embodiment can also be applied to the humidifying device 101 of the second embodiment. Moreover, the communication opening part 122 of 3rd Embodiment is applicable also to the humidification apparatus 201 of 5th Embodiment.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Air-Conditioning For Vehicles (AREA)
- Central Air Conditioning (AREA)
- Air Conditioning Control Device (AREA)
- Air Humidification (AREA)
Abstract
加湿装置は、吸着材モジュール(4)と送風部(2)を有する。吸着材モジュールは、吸着材を有し、通過する空気に含まれる水分を吸着材に吸着したり、吸着材に吸着されている水分を通過する空気に対して脱離したりする。送風部は、吸着材モジュールに対して空気を送風する。送風部は、吸着材に空気中の水分を吸着させる吸着時には、車両天板(11)と車室内の天井内装部材(12)との間に区画形成された天井内空間(13)内の空気を取り込み、当該空気を吸着材モジュールに対して送風して、吸着材で当該空気中の水分を吸着させる。
Description
本出願は、当該開示内容が参照によって本出願に組み込まれた、2015年7月29日に出願された日本特許出願2015-150011号を基にしている。
本開示は、室内に対して加湿空気を提供する加湿装置に関する。
特許文献1は、車室内の乗員に対して加湿された空気を供給する加湿装置の一形態を開示している。この加湿装置は、除湿空気を送風する場合には、一対のブロアを運転し、吸入口から車室内の空気を吸入し一対の吸着材に通過させる。各吸着材を通過する空気は、吸着材によって水分を吸着されて除湿空気となる。除湿空気は、切替ダンパによって第1吹出口と第2吹出口へ案内されて、第1吹出口からフロントウィンドへ向けて吹き出されるとともに、第2吹出口から乗員に向けて吹き出される。
加湿装置は、加湿空気を送風する場合には、一方のヒータのみと一対のブロアを運転し、吸入口から車室内の空気を吸入し一対の吸着材に通過させる。一方の吸着材は、ヒータにより加熱されて吸着していた水分を通過する空気に対して放出する。したがって、一方の吸着材を通過する空気は、吸着材から放出された水分を含んだ加湿空気となる。この加湿空気は、切替ダンパによって第2吹出口へ案内されて、第2吹出口から乗員に向けて吹き出される。また、他方の吸着材はヒータにより加熱されていないので、他方の吸着材を通過する空気は、吸着材によって水分を吸着されて除湿空気となる。この除湿空気は、切替ダンパによって第1吹出口へ案内されて、第1吹出口からフロントウィンドへ向けて吹き出される。
例えば、加湿が必要となる冬期には、車室内が暖房されるため、車室内の空気は相対湿度が低下して乾燥することになる。特許文献1の装置は、車室内の空気を取り入れて、当該空気中の水分を回収してその後の加湿空気の供給時に用いる、いわゆるデシカント方式である。したがって、加湿に必要な水分を回収することができず、十分な加湿能力を確保できないおそれがある。
本開示は、上記点に鑑みてなされたものであり、車室内暖房による加湿能力低下の抑制を図る加湿装置を提供することを目的とする。
本開示の第1態様に係る加湿装置は、空気中の水分を吸着した吸着材から、脱離させた水分によって加湿した加湿空気を車室内に供給する車両用の加湿装置である。加湿装置は、吸着材モジュールと送風部を備える。吸着材モジュールは、吸着材を有し、通過する空気に含まれる水分を吸着材に吸着したり、吸着材に吸着されている水分を通過する空気に対して脱離したりする。送風部は、吸着材モジュールに対して当該通過する空気を送風する。
送風部は、吸着材に空気中の水分を吸着させる吸着時には、車両天板と車室内の天井内装部材との間に区画形成された天井内空間の空気を取り込み、当該空気を吸着材モジュールに対して送風して、吸着材で当該空気中の水分を吸着させる。
この第1態様によれば、吸着時に、車両天板と車室内の天井内装部材との間に区画形成された天井内空間の空気に含まれる水分を吸着材で吸着するため、暖房によって相対湿度が低くなった車室内の空気よりも暖房の影響が少ない空気から水分を回収できる。これにより、暖房された車室内の空気から水分を回収するよりも、水分回収効率を高めた吸着を実施することができ、次の脱離時に加湿能力を確保した加湿空気を提供できる。したがって、車室内暖房による加湿能力低下の抑制が図れる加湿装置を提供できる。
本開示の第2態様に係る加湿装置は、空気中の水分を吸着した吸着材から、脱離させた水分によって加湿した加湿空気を加湿対象空間に供給する車両用の加湿装置である。加湿装置は、吸着材モジュールと送風部を備える。吸着材モジュールは、吸着材を有し、通過する空気に含まれる水分を吸着材に吸着したり、吸着材に吸着されている水分を、通過する空気に対して脱離したりする。送風部は、吸着材モジュールに対して当該通過する空気を送風する。
送風部は、吸着材に空気中の水分を吸着させる吸着時には、車両外部の空気を取り込み、当該空気を吸着材モジュールに対して送風して、吸着材で当該空気中の水分を吸着させる。
この第2態様によれば、吸着時に、車両外部の空気に含まれる水分を吸着材で吸着するため、暖房によって相対湿度が低くなった車室内の空気よりも暖房の影響が少ない空気から水分を回収できる。これにより、暖房された車室内の空気から水分を回収するよりも、外気からの水分回収効率を高めた吸着を実施することができ、次の脱離時に加湿能力を確保した加湿空気を提供できる。したがって、第2態様によっても、車室内暖房による加湿能力低下の抑制が図れる加湿装置を提供できる。
本開示についての上記目的およびその他の目的、特徴や利点は、添付の図面を参照しながら下記の詳細な記述により、より明確になる。
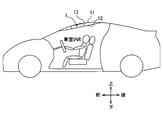
第1実施形態に係る加湿装置が車両に搭載される位置を示す概要図である。
第1実施形態の加湿装置の概要構成と脱離時の空気の流れとを示す断面図である。
第1実施形態の加湿装置の概要構成と吸着時の空気の流れとを示す断面図である。
第1実施形態の加湿装置の他の形態として、脱離時に車室内の空気を取り入れる加湿装置を示す部分断面図である。
第1実施形態の加湿装置の他の形態として、逆止弁を備える加湿装置を示す部分断面図である。
第2実施形態の加湿装置の概要構成と吸着時の空気の流れとを示す断面図である。
第3実施形態の加湿装置の概要構成と脱離時の空気の流れとを示す断面図である。
第3実施形態の加湿装置の概要構成と吸着時の空気の流れとを示す断面図である。
風向案内部材を備える第4実施形態の加湿装置を示す部分断面図である。
第5実施形態の加湿装置の概要構成と吸着時の空気の流れとを示す断面図である。
以下に、図面を参照しながら本開示を実施するための複数の形態を説明する。各形態において先行する形態で説明した事項に対応する部分には同一の参照符号を付して重複する説明を省略する場合がある。各形態において構成の一部のみを説明している場合は、構成の他の部分については先行して説明した他の形態を適用することができる。各実施形態で具体的に組み合わせが可能であることを明示している部分同士の組み合わせばかりではなく、特に組み合わせに支障が生じなければ、明示してなくとも実施形態同士を部分的に組み合わせることも可能である。
(第1実施形態)
本開示の加湿装置は、車室内Rの天井内装部材12の裏側に装着され、車室内Rを加湿対象空間とする。以下の各実施形態では、加湿装置の一例として、図1に図示するように車両に適用した場合を説明する。したがって、各実施形態に開示する加湿装置は、車室内Rを加湿対象空間とする。さらに、加湿装置1が搭載される車両は、車室内Rの温度調整を行う車両用空調装置を備える。
本開示の加湿装置は、車室内Rの天井内装部材12の裏側に装着され、車室内Rを加湿対象空間とする。以下の各実施形態では、加湿装置の一例として、図1に図示するように車両に適用した場合を説明する。したがって、各実施形態に開示する加湿装置は、車室内Rを加湿対象空間とする。さらに、加湿装置1が搭載される車両は、車室内Rの温度調整を行う車両用空調装置を備える。
図1、図2、図3に示すように、加湿装置1は、車両天板11と天井内装部材12との間に区画形成された天井内空間13に設置される。天井内空間13は、天井内装部材12によって車室内Rと仕切られている。天井内空間13は、車両天板11と天井内装部材12との間に区画形成された所定の空間であるから、車室内Rに対して完全に遮断されている空間ではない。天井内空間13には、天井内空間13と車室内Rとの圧力差に応じて、部材間の隙間等を通じた多少の空気が出入りすることがある。
また、各図に記載した上下前後の各矢印は、加湿装置1を車両に搭載した状態における各方向を示している。したがって、上側および下側はそれぞれ車両の上下方向における上方および下方であり、前側および後側はそれぞれ車両の前後方向における前方および後方である。加湿装置1は、その外殻を形成するケーシング6の内部に、送風機2、加熱装置3、吸着材モジュール4、冷却装置5等を収容している。
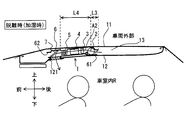
図2に示すように、加湿装置1においては、吸着素子から水分が脱離する脱離時に空気が流れる方向A2に、送風機2、加熱装置3、吸着材モジュール4、冷却装置5の順に並ぶように設置されている。したがって、脱離時に、第1開口部61から天井内空間13内に導入された空気は、加熱装置3で加熱されてから、吸着材モジュール4を通過して水分が加えられ、さらに冷却装置5で冷却された後、車室内吹出口部から車室内Rへ吹き出される。以下、車室内吹出口部を吹出口部121と称する。この脱離時の空気の流れは、図2において実線の矢印で示されている。
図3に示すように、加湿装置1には、吸着素子に水分が吸着される吸着時に空気が流れる方向A1に、冷却装置5、吸着材モジュール4、加熱装置3、送風機2の順に並ぶように設置されている。したがって、吸着時に、第2開口部62から天井内空間13に導入された空気は、冷却装置5で冷却されてから、吸着材モジュール4を通過して水分を吸着材に放出し、さらに加熱装置3で加熱された後、第1開口部61から天井内空間13へ吹き出される。この吸着時の空気の流れは、図3において破線の矢印で示されている。
第1開口部61は、装置ケースであるケーシング6に形成され、脱離時に天井内空間13内の空気をケーシング6内に吸入する脱離時吸入口部である。第1開口部61はまた、吸着時に、吸着材で水分が吸着された後の空気(水分回収後の空気)を天井内空間13へ排出する吸着時排出口部でもある。脱離時吸入口部としての第1開口部61は、脱離時において、送風機2による天井内空間13への空気の取り込みと、吸着材モジュール4に対する当該空気の送風とを可能とする。第2開口部62は、ケーシング6に形成され、吸着時に天井内空間13内の空気をケーシング6内に吸入する吸着時吸入口部である。第1開口部61は、ケーシング6において、第2開口部62とは反対側に設けられる。例えば、第1開口部61はケーシング6において後方側の端部に設けられ、第2開口部62は、ケーシング6において前方側の端部に設けられる。この場合、送風機2は、吸着時排出口部である第1開口部61に隣接する近傍位置に設けられる。
吹出口部121は、下方の車室内Rに向けて開口し、ケーシング6と天井内装部材12とを貫通する通路を構成する。吹出口部121は、例えば、車室内Rの前席に着座する乗員の上方において開口するように設けられている。また、天井内装部材12において吹出口部121よりも前方に位置する場所には、サンバイザが設けられている。吹出口部121には、空気とともに運ばれる塵、埃等を捕集するフィルタが設置されることが好ましい。
第2開口部62(吸着時吸入口部)には、切替部材としての切換用ドア7が設けられている。切換用ドア7は、吸着材に空気中の水分を吸着させる吸着時には、天井内空間13への空気の取り込みを可能とし、吸着材に吸着されている水分を通過する空気に対して脱離する脱離時には、車室内Rに吸着材モジュール4を通過した空気を供給させる。第2開口部62は吹出口部121に対して隣接する場所に設けられ、第2開口部62と吹出口部121とは、切換用ドア7によって開放状態と閉鎖状態とに切り換えられる。切換用ドア7は、脱離時に第2開口部62を閉じるとともに吹出口部121を開き、吸着時に吹出口部121を閉じるとともに第2開口部62を開くように制御装置によって制御される。したがって、切換用ドア7は、ケーシング6内において冷却装置5よりも前方に位置してケーシング6における前方側の端部に設けられる。
送風機2は、他の装置よりも第1開口部61に近い位置に設置されているが、送風機2の設置位置は、この位置に限定されない。したがって、送風機2は、第1開口部61と第2開口部62との間に形成される空気通路において、任意の位置に設置することができる。
送風機2は、例えば、軸流式のファンを電動モータにて回転駆動する電動送風機であり、吸着材モジュール4に対して通過する空気を送風する送風部を構成する。この場合、送風機2は、制御装置によって電動モータの回転方向が切り替えられることで、送風機2が送風する空気の流れ方向を相反する向きに切り替えることができる。また、送風機2は、制御装置から出力される制御電圧によって稼働率、すなわち回転数や送風する空気量が制御される送風部である。
例えば、制御装置が電動モータを正転させると、空気は、図2の実線矢印に示す方向A2のように流れる。天井内空間13内の空気は、第1開口部61からケーシング6内の空気通路へ吸い込まれ、加熱装置3、吸着材モジュール4、冷却装置5の順に流れ、加湿空気となって吹出口部121から車室内Rへ吹き出される。加湿空気を車室内Rに供給する加湿時は、天井内空間13内の空気をケーシング6内に吸い込んで、車室内Rに吹き出すため、天井内空間13が車室内Rに対して若干負圧になる。これにより、車室内Rの空気は、車両天板11と天井内装部材12との隙間から天井内空間13に多少引き込まれることになる。
また、加湿時1回分の車室内Rへの吹出し風量が占める体積は、天井内空間13の容積よりも小さくなるように設定される。例えば、加湿時における単位時間あたりの風量が10m3/時で1回の加湿が1分行われる場合、加湿時1回分の吹出し風量が占める体積は、約0.167m3となる。天井内空間13は約0.167m3よりも大きな容積となるように設定される。天井内空間13の容積をこのような大きさに設定することで、1回の加湿運転において車室内Rから天井内空間13に引き込まれる空気の量が、天井内空間13内の空気の量に対して小さくなる。その結果、車室内Rの乾燥した空気が加湿装置に多く取り込まれてしまうことを回避できる。したがって、所望の相対湿度を有する加湿空気を車室内Rへ提供することができる。
また、吸着時吸入口部である第2開口部62は、車両天板11と天井内装部材12とが接触し得る天井内装部材12の周縁部に対して離れていることが好ましい。例えば、図2に図示するように、第2開口部62は、第2開口部62と天井内装部材12の周縁部との間の距離が、第2開口部62と第1開口部61との間の距離よりも長くなるように、天井内装部材12の周縁部から離間していることが好ましい。
天井内装部材12の周縁部と車両天板11とは、天井内空間13を区画形成する継ぎ目でもある。第1開口部61が天井内装部材12の周縁部の近傍でなく離れた位置にあることにより、加湿時に天井内空間13に引き込まれた車室内Rの空気を車両天板11に接触させることができる。冬期には、例えば、外気温度が0℃、天井内空間13内の空気の温度が18℃、相対湿度が30%であり、車室内Rの空気の温度が25℃、相対湿度が15%である。図2に図示するように、加湿時には、天井内空間13に引き込まれた車室内Rの空気は車両天板11に接触することで冷却される。したがって、吸着材モジュール4に到達する前の空気の相対湿度を上げることができ、さらに加湿空気の相対湿度を高めることができる。この効果は特に外気温度が低い冬期において顕著に発揮される。
一方、制御装置が電動モータを反転させると、空気は、図3の破線矢印に示すように流れる。天井内空間13内の空気は、第2開口部62からケーシング6内の空気通路へ吸い込まれ、冷却装置5、吸着材モジュール4、加熱装置3の順に流れ、除湿空気となって第1開口部61から天井内空間13に吹き出される。この吸着時には、天井内空間13内の空気をケーシング6内に吸い込んで、水分回収後、天井内空間13に吹き出すため、天井内空間13が車室内Rに対して負圧にならない。これにより、車室内Rの空気が車両天板11と天井内装部材12との隙間から天井内空間13に引き込まれることはない。
ケーシング6は、樹脂または金属によって箱状に形成され、内部に送風機2から送風された空気を流通させる空気通路を形成している。ケーシング6は、車両天板11や天井内装部材12に沿って広がる薄形の直方体状に形成されている。
吸着材モジュール4は、吸着材を担持させた複数の金属製の板状部材を間隔をあけて積層配置することで構成されている。そのため、隣り合う板状部材の間には空気を通過させる通路が形成されている。この実施形態の吸着材モジュール4では、このように吸着材を担持させた複数の板状部材を積層配置することで、空気と吸着材との接触面積を増加させることができる。吸着材としては、高分子吸着材、ゼラチン質の軟泥が乾燥して多面体を作ったものであるゼロライト等の吸湿材料を採用している。
加熱装置3は、ケーシング6内の空気通路を流通する空気を加熱可能な加熱器である。加熱装置3は、空気を加熱可能な構成であれば、その加熱方法として各種の方法を採用できる。加熱装置3として、通電によって発熱する発熱体を有する装置や、室内の空気よりも高温の媒体と空気とを熱交換することによって室内の空気を加熱する装置を用いることができる。加熱装置3は、例えば、ニクロム線ヒータ、PTC(Positive Temperature Coefficient)ヒータを有する装置、熱交換器等である。熱交換器に用いる空気よりも高温の媒体には、温水、冷媒、エンジン冷却水、車両において発熱する電子部品等の発熱体を採用することができる。
冷却装置5は、ケーシング6内の空気通路を流通する空気を冷却可能な冷却器である。冷却装置5は、空気を冷却可能な構成であれば、その冷却方法として各種の方法を採用できる。冷却装置5として、車両天板11と熱伝導可能なヒートシンクを用いることができる。また、冷却装置5には、通電によって吸熱するペルチェ素子を有する装置や、室内の空気よりも低温の媒体と空気とを熱交換することによって室内の空気を冷却する装置を用いることができる。また、冷却装置5には、低温の媒体が流通する熱交換器を用いることができる。熱交換器に用いる空気よりも低温の媒体として、外気、空調空気、空調装置に用いられる冷凍サイクルを流れる冷媒等を採用することができる。
低温の媒体として外気を用いる熱交換器には、ヒートシンクがある。ヒートシンクは、伝熱性に優れるアルミニウムや銅などの金属で形成された複数のフィンを有する伝熱部材である。ヒートシンクは、例えば、車両天板11に取り付けられる。ヒートシンクは、車両外部の外気の熱をケーシング6内の空気通路に伝熱する機能を果たす。ヒートシンクは、車両外部の外気とケーシング6内の空気通路を流通する空気とを熱交換させることができる。このヒートシンクは、外気の有する冷熱を車室内Rに送風する空気に放冷することによって当該空気を冷却する冷却器、または、空気の有する熱を外気に放熱させることによって当該空気を冷却する冷却器を構成する。
制御装置は、CPU、ROM及びRAM等を含むマイクロコンピュータとその周辺回路から構成されており、その出力側に接続された送風機2及び切換用ドア7の作動を制御する。また、制御装置は、加熱装置3や冷却装置5による加熱作用や冷却作用を制御するものであってもよい。
制御装置の入力側には、車室内Rの空気温度を検出する内気温検出部としての内気センサ、外気温度を検出する外気温検出部としての外気センサ等が接続されている。これらのセンサの検出信号が制御装置に入力される。さらに、制御装置の入力側には、加湿装置1を作動させる作動スイッチ等が接続されており、これらのスイッチの操作信号が制御装置に入力される。
また、この制御装置は、例えば、車両用空調装置の各構成機器の作動を制御する空調用制御装置等と一体的に構成されるものでもよい。また、この制御装置は、空調用制御装置と別体で、制御対象とする装置の制御状態に関する情報を互いに通信するものであってもよい。
次に、加湿装置1の作動について説明する。加湿装置1は、例えば、車室内Rが車両用空調装置によって温度調整された状態で、乗員の操作によって作動スイッチがONされると作動する。
例えば、加湿装置1は、冬季のように比較的外気温が低く、車室内Rが乾燥しやすいときに作動させる。加湿装置1の作動スイッチが投入されると、制御装置は、送風機2の電動モータを正転させるとともに切換用ドア7が吹出口部121を開く状態と、電動モータを反転させるとともに切換用ドア7が第2開口部62を開く状態とを、例えば所定時間毎に交互に切り替える。これにより、空気が図2の実線矢印に示すように流れる脱離時の通風経路と、図3の破線矢印に示すように流れる吸着時の通風経路とが所定時間毎に切り替えられることになる。
脱離時には、制御装置が送風機2の電動モータを正転させ、吹出口部121を開くように切換用ドア7を制御する。これにより、天井内空間13内の温度18℃、相対湿度30%の空気が、第1開口部61を介して、ケーシング6内へ吸い込まれる。ケーシング6内の空気通路に吸い込まれた空気は、加熱装置3を通過するときに加熱される。この際、加熱装置3を通過後の空気の温度が天井内空間13内の空気の温度よりも所定温度、例えば、5℃程度高くなるように、制御装置が加熱装置3を一定出力で作動させる、もしくは空気の温度変化に応じて加熱装置3の出力を制御する。したがって、加熱装置3を通過後の空気の温度が23℃程度に上昇する。
加熱装置3を通過後の空気は、吸着材モジュール4に流入する。この際、加熱装置3を通過して温度上昇した空気の相対湿度は、天井内空間13内の空気の相対湿度よりも低下している。したがって、加熱装置3を通過して相対湿度が下がった空気を吸着材モジュール4の吸着材に接触させることで、吸着材に吸着している水分が空気に脱離しやすい状況となる。つまり、加熱装置3によって相対湿度が下げられた空気は、吸着材が保持している水分を含みやすく、吸着材モジュール4を流出後の空気は、十分に加湿された加湿空気となる。
この加湿空気は、さらに冷却装置5によって冷却されるため、加熱装置3によって温度上昇された加湿空気の温度が低下することになる。これにより、加湿空気を涼風にした状態で、吹出口部121から乗員に向けて提供できる。したがって、加湿装置1によれば、脱離時に、加熱装置3による加熱によって十分に加湿された空気を、冷却装置5によって涼風にすることで、乗員の快適性を向上する加湿風を提供できる。
この脱離時には、吸着材モジュール4に供給する前の空気を加熱装置3で加熱するため、当該空気を迅速に温度上昇させることができる。さらに、空気温度が迅速に上昇したことにより、空気の相対湿度を迅速に下げることができるため、吸着材モジュール4での水分脱離が活発に行われ、吸着材モジュール4を流出後の空気の相対湿度を迅速に高めることができる。
次に吸着時には、制御装置が送風機2の電動モータを反転させ、第2開口部62を開くように切換用ドア7を制御すると、天井内空間13内の、温度18℃、相対湿度30%の空気が、第2開口部62を介してケーシング6内へ吸い込まれる。ケーシング6内の空気通路に吸い込まれた空気は、冷却装置5を通過するときに冷却される。
冷却装置5を通過後の空気は、吸着材モジュール4に流入する。この際、冷却装置5を通過後の温度低下した空気の相対湿度は、天井内空間13内の空気の相対湿度よりも上昇している。これにより、天井内空間13内の空気に対して相対湿度が高まった空気を吸着材に接触させることができるので、空気中の水分が吸着材に吸着しやすい状況となる。つまり、冷却装置5によって相対湿度が上げられた空気は、吸着材に水分を吸着させやすく、吸着材モジュール4を流出後の空気は、十分に除湿された除湿空気となる。さらに、吸着材モジュール4を流出した空気は、加熱装置3を通過する際に加熱され、第1開口部61から、天井内空間13に吹き出される。
この吸着時には、吸着材モジュール4に供給する前の空気を冷却装置5で冷却するため、当該空気を迅速に温度低下させることができる。さらに、空気温度が迅速に低下したことにより、空気の相対湿度を迅速に高めることができるため、吸着材モジュール4での水分吸着が活発に行われ、吸着材モジュール4を流出後の空気の相対湿度を迅速に低下させることができる。
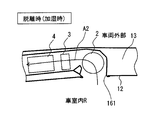
また、加湿装置1の他の形態として、脱離時にケーシング6内に空気を取り入れるときに、車室内Rの空気を取り入れるように構成してもよい。この場合、図4に図示するように、ケーシング6において送風機2の近傍に設けられた第1開口部161は、車室内Rに向けて開口して、ケーシング6内と車室内Rとを連通させる通路を構成する。
また、加湿装置1の他の形態として、吸着時に水分回収後の空気を車室内Rに排出するように構成してもよい。
また、加湿装置1の他の形態として、切換用ドア7の代わりに、切替部材として二つの逆止弁107A、逆止弁107Bを備える構成としてもよい。この場合、図5に図示するように、逆止弁107Aは、第2開口部62において、天井内空間13からケーシング6内に流入する空気の流れを許容し、ケーシング6内から天井内空間13へ流出する空気の流れを阻止する弁機能を有する。したがって、逆止弁107Aは、図5に破線で図示する形状に弾性変形して吸着時の方向A1の空気流れを許容し、図5に実線で図示する形状となることで第2開口部62を塞いで脱離時のケーシング6内から天井内空間13への空気漏れを禁止する。
さらに図5に図示するように、逆止弁107Bは、吹出口部121において、ケーシング6内から車室内Rへ流出する空気の流れを許容し、車室内Rからケーシング6内に流入する空気の流れを阻止する弁機能を有する。したがって、逆止弁107Bは、図5に実線で図示する形状に弾性変形して脱離時の方向A2の空気流れを許容し、図5に破線で図示する形状となることで吹出口部121を塞いで吸着時のケーシング6内から車室内Rへの空気漏れを禁止する。
次に、第1実施形態の加湿装置1がもたらす作用効果について説明する。加湿装置1は、空気中の水分を吸着した吸着材から、脱離させた水分によって加湿した加湿空気を車室内Rに供給する車両用の加湿装置である。加湿装置1は、吸着材を有し、通過する空気に含まれる水分を吸着材に吸着したり、吸着材に吸着されている水分を通過する空気に対して脱離したりする吸着材モジュール4と、吸着材モジュール4に対して空気を送風する送風機2と、を備える。送風機2は、吸着時には、車両天板11と天井内装部材12との間に区画形成された天井内空間13内の空気を取り込み、当該空気を吸着材モジュール4に対して送風して、吸着材で当該空気中の水分を吸着させる。
この構成によれば、吸着時に、天井内空間13内の空気に含まれる水分を吸着材で吸着するため、暖房によって相対湿度が低くなった車室内Rの空気よりも暖房の影響が少ない空気から水分を回収できる。これにより、暖房された車室内Rの空気から水分を回収するよりも、水分回収効率を高めた吸着を実施することができ、次の脱離時に加湿能力を確保した加湿空気を提供できる。したがって、加湿装置1によれば、車室内暖房による加湿能力低下の抑制が図れる装置を提供できる。
また、加湿装置1のケーシング6は天井内空間13に設置される。送風機2は、吸着時には、ケーシング6に設けられた吸着時吸入口部から天井内空間13内の空気を取り込み、当該空気を吸着材モジュール4に対して送風する。この構成によれば、加湿装置1の機能部品を収容するケーシング6が天井内空間13に収容され、ケーシング6に吸着時吸入口部が設けられるため、車室内Rへの装置の飛び出しがなく、搭載上コンパクトな加湿装置を提供できる。
また、送風機2は、吸着時には、天井内空間13内の空気を吸入して吸着材で水分を吸着した後、天井内空間13に排出し、脱離時には天井内空間13内の空気を取り込み、当該空気を吸着材モジュール4に対して送風する。
この構成によれば、吸着時に、天井内空間13内の空気を吸い込み、当該空気内の水分を回収してから天井内空間13に排出するため、天井内空間13が負圧にならない。したがって、車室内Rの空気が天井内空間13に進入することを抑制でき、乾燥した車室内Rの空気が取り込まれることによって天井内空間13内の空気の相対湿度が低下することを防止できる。また、脱離時には、天井内空間13内の空気を取り込むことにより、乾燥した車室内Rの空気が取り込まれるため、加湿空気の相対湿度を向上させることができる。
第1開口部61は、吸着時に吸着材で水分が吸着された後の空気を天井内空間13に排出する吸着時排出口部である。吸着時排出口部は、脱離時に加湿空気が車室内Rに向けて吹き出される吹出口部121とは加湿装置1において反対側に設けられる。換言すれば、加湿装置1は、第1開口部61と吹出口部121との間に設けられている。送風機2は吸着時排出口部に隣接する位置に設けられる。具体的には、送風機2と第1開口部61(吸着時排出口部)との間の距離L3が、送風機2と吹出口部121との間の距離L4よりも短くなっている。この構成によれば、送風機2に隣接する吸着時排出口部は吹出口部121とは離れた位置にあるため、送風機2の運転による騒音が車室内Rに漏れることを抑制できる。したがって、騒音の抑制が図れる加湿装置1を提供できる。
冷却装置5は、ケーシング6内を流通する空気と外気とを熱交換することにより、当該空気を冷却する熱交換器である。これによれば、冬季の低温である外気を冷却用の媒体として利用できるため、冷却のための動力が不要であり、省エネルギで低コストの冷却装置を構成できる。
(第2実施形態)
第2実施形態について図6を参照して説明する。第2実施形態において、第1実施形態に係る図面と同一符号を付した構成部品及び説明しない構成は、第1実施形態と同様であり、同様の作用効果を奏するものである。第2実施形態では、第1実施形態と異なる部分のみ説明する。
第2実施形態について図6を参照して説明する。第2実施形態において、第1実施形態に係る図面と同一符号を付した構成部品及び説明しない構成は、第1実施形態と同様であり、同様の作用効果を奏するものである。第2実施形態では、第1実施形態と異なる部分のみ説明する。
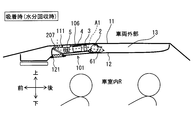
第2実施形態の加湿装置101は、吸着時に天井内空間13内の空気ではなく車両外部の空気をケーシング6内に取り込む点が第1実施形態と相違する。図6に示すように、加湿装置101は、車両外部に通じる第2開口部111を備える。第2開口部111は、ケーシング6と車両天板11とを貫通する通路を構成する。第2開口部111は、吸着時に車両外部の空気をケーシング6内に吸入する吸着時吸入口部である。第2開口部111は、空気とともに運ばれる塵、埃等を捕集するフィルタが設置されることが好ましい。吸着時に、第2開口部111から導入された車両外部の空気は、冷却装置5で冷却されてから、吸着材モジュール4を通過して水分を吸着材に放出し、さらに加熱装置3で加熱された後、第1開口部61から天井内空間13へ吹き出される。この吸着時の空気の流れは、図6において破線の矢印で示されている。
第2開口部111は吹出口部121に対して上下方向に対向する場所に設けられている。第2開口部111と吹出口部121とは、切換用ドア207によって開放状態と閉鎖状態とに切り換えられる。切換用ドア207は切替部材であり、脱離時に第2開口部111を閉じるとともに吹出口部121を開き、吸着時に吹出口部121を閉じるとともに第2開口部111を開くように制御装置によって制御される。したがって、切換用ドア207は、ケーシング6内において冷却装置5よりも前方に位置してケーシング6における前方側の端部に設けられる。
第2実施形態の加湿装置101によれば、送風機2は、吸着時には、車両外部の空気を取り込み、当該空気を吸着材モジュール4に対して送風して、吸着材で当該空気中の水分を吸着させる。この構成によれば、吸着時に、車両外部の空気に含まれる水分を吸着材で吸着するため、暖房によって相対湿度が低くなった車室内Rの空気よりも暖房への影響が少ない空気から水分を回収できる。これにより、暖房された車室内Rの空気から水分を回収するよりも、外気からの水分回収効率を高めた吸着を実施することができ、次の脱離時に加湿能力を確保した加湿空気を提供できる。したがって、第2実施形態によれば、車室内暖房による加湿能力低下の抑制が図れる加湿装置101を提供できる。
(第3実施形態)
第3実施形態について図7及び図8を参照して説明する。第3実施形態において、第1実施形態に係る図面と同一符号を付した構成部品及び説明しない構成は、第1実施形態と同様であり、同様の作用効果を奏するものである。第3実施形態では、第1実施形態と異なる部分のみ説明する。
第3実施形態について図7及び図8を参照して説明する。第3実施形態において、第1実施形態に係る図面と同一符号を付した構成部品及び説明しない構成は、第1実施形態と同様であり、同様の作用効果を奏するものである。第3実施形態では、第1実施形態と異なる部分のみ説明する。
第3実施形態は、天井内装部材12に、天井内空間13と車室内Rとを連通させる連通開口部122を備える点が第1実施形態と相違する。連通開口部122は、天井内装部材12を貫通するように下方の車室内Rに向けて開口し、天井内空間13と車室内Rとを連通する通路を構成する。連通開口部122は、例えば、車室内Rの後席に着座する乗員の上方において開口するように設けられている。連通開口部122には、空気とともに運ばれる塵、埃等を捕集するフィルタが設置されることが好ましい。
連通開口部122は、吸着時吸入口部である第2開口部62よりも、吸着時排出口部(脱離時吸入口部)である第1開口部61に近い位置に設けられる。換言すれば、連通開口部122と第1開口部61との間の距離L1は、連通開口部122と第2開口部62との間の距離L2よりも短くなっている。つまり、第1開口部61が、前後方向において第2開口部62と連通開口部122との間に位置している。連通開口部122は、前席よりも後席寄りの位置で天井内空間13と車室内Rとを連通させている。したがって、連通開口部122は、天井内空間13においてケーシング6が設置されている側とは反対側に位置している。
図7に示すように、加湿装置1では、脱離時に、第1開口部61から天井内空間13に導入された空気は加熱装置3で加熱されてから吸着材モジュール4で水分が加えられ、さらに冷却装置5で冷却された後、吹出口部121から車室内Rへ吹き出される。このとき天井内空間13内の空気は、図7の実線矢印に示す方向A2のように流れるため、天井内空間13が車室内Rに対して若干負圧になる。これにより、車室内Rの空気は、連通開口部122を通じて天井内空間13に引き込まれることになる。つまり、加湿時に吹出口部121を通じて車室内Rに供給された加湿空気と同じ量の車室内Rの空気が、連通開口部122を通じて天井内空間13に吸い込まれる。
図8に図示する吸着時には、天井内空間13内の空気をケーシング6内に吸い込んで、水分回収後、天井内空間13に吹き出すため、天井内空間13が車室内Rに対して負圧にならない。これにより、車室内Rの空気が連通開口部122を通じて天井内空間13に引き込まれることはない。
第3実施形態によれば、天井内空間13と車室内Rとを連通させる連通開口部122を、吸着時吸入口部よりも脱離時吸入口部に近い位置に備えるため、車室内Rの空気を連通開口部122から積極的に天井内空間13に取り込むことができる。これによれば、車室内Rから天井内空間13への空気進入経路を限定することができ、加湿装置1の周囲における天井内空間13の温度及び湿度を安定した状態にすることに寄与する。
さらに連通開口部122は、天井内空間13においてケーシング6が設置されている側とは反対側に位置するため、車室内Rから天井内空間13への空気進入経路を加湿装置1から離れた場所に設定することができる。これによれば、加湿装置1の周囲における天井内空間13の温度及び湿度の状態をさらに安定させることができる。
(第4実施形態)
第4実施形態について図9を参照して説明する。第3実施形態において、第3実施形態に係る図面と同一符号を付した構成部品及び説明しない構成は、第3実施形態と同様であり、同様の作用効果を奏するものである。第4実施形態では、第3実施形態と異なる部分のみ説明する。
第4実施形態について図9を参照して説明する。第3実施形態において、第3実施形態に係る図面と同一符号を付した構成部品及び説明しない構成は、第3実施形態と同様であり、同様の作用効果を奏するものである。第4実施形態では、第3実施形態と異なる部分のみ説明する。
第4実施形態の加湿装置は、図9に示すように、連通開口部122の天井内空間13側に設けられて、車両天板11との間に隙間を有する筒状部材123を備える。換言すれば、筒状部材123は、連通開口部122から車両天板11に向かって延びており、筒状部材123と車両天板11との間には隙間が形成されている。連通開口部122よりも下流側に位置する天井内空間13において風向案内部材123aを備える。風向案内部材123aは、筒状部材123の車両天板11側において、車両天板11と対向するとともに、ケーシング6側に延出している。具体的には、風向案内部材123aは、筒状部材123の車両天板11側の端部からケーシング6に向かって延びている。風向案内部材123aは、脱離時に連通開口部122を介して天井内空間13に取り込まれる車室内Rの空気を車両天板11に沿うように案内する機能を有する。
風向案内部材123aは、車両天板11の内表面に沿うように延びる板状部材である。風向案内部材123aは、図9に実線矢印で示すように、連通開口部122から流入し天井内空間13を上昇した空気を第1開口部61へ向かう方向に車両天板11に沿って流すように案内する。
第4実施形態の加湿装置によれば、前述する風向案内部材123aを備えるため、車室内Rの空気を車両天板11に沿わせるように第1開口部61へ向けて流下させることができる。車両天板11は、暖房空調された車室内Rよりも低温であるので、車室内Rの空気を効率的に冷やすことができ、加湿装置の水分回収効率をさらに向上させることができる。
(第5実施形態)
第5実施形態について図10を参照して説明する。第5実施形態において、第1実施形態及び第2実施形態に係る図面と同一符号を付した構成部品及び説明しない構成は、これらの実施形態と同様であり、同様の作用効果を奏するものである。第5実施形態では、前出の第1実施形態と異なる部分のみ説明する。
第5実施形態について図10を参照して説明する。第5実施形態において、第1実施形態及び第2実施形態に係る図面と同一符号を付した構成部品及び説明しない構成は、これらの実施形態と同様であり、同様の作用効果を奏するものである。第5実施形態では、前出の第1実施形態と異なる部分のみ説明する。
第5実施形態の加湿装置201は、天井内空間13に設置されるのではなく、乗員の上方において天井内空間13を形成する天井内装部材12の下面に設置される点が第1実施形態と相違する。
図10に示すように、加湿装置201は、天井内空間13に通じる第2開口部111を備える。第2開口部111は、ケーシング106と天井内装部材12とを貫通する通路を構成する。第2開口部111は、吸着時に天井内空間13内の空気をケーシング6内に吸入する吸着時吸入口部である。第2開口部111は、塵、埃等を捕集するフィルタが設置されることが好ましい。ケーシング106において送風機2の近傍に設けられた第1開口部161は、ケーシング106と天井内装部材12とを貫通する通路を構成し、水分回収後の空気を天井内空間13へ排出する吸着時排出口部である。
吸着時に、第2開口部111から天井内空間13に導入された空気は、冷却装置5で冷却されてから、吸着材モジュール4を通過して水分を吸着材に放出し、さらに加熱装置3で加熱された後、第1開口部161から天井内空間13へ吹き出される。この吸着時の空気の流れは、図10において破線の矢印で示されている。
(他の実施形態)
以上、開示された開示の好ましい実施形態について説明したが、開示された開示は上述した実施形態に何ら制限されることなく、種々変形して実施することが可能である。上記実施形態の構造は、あくまで例示であって、開示された開示の技術的範囲はこれらの記載の範囲に限定されるものではない。開示された開示の技術的範囲は、本開示の記載と均等の意味及び範囲内での全ての変更を含むものである。
以上、開示された開示の好ましい実施形態について説明したが、開示された開示は上述した実施形態に何ら制限されることなく、種々変形して実施することが可能である。上記実施形態の構造は、あくまで例示であって、開示された開示の技術的範囲はこれらの記載の範囲に限定されるものではない。開示された開示の技術的範囲は、本開示の記載と均等の意味及び範囲内での全ての変更を含むものである。
前述の実施形態では、送風機2、加熱装置3、吸着材モジュール4、冷却装置5等は、間隔をあけて配置されている。しかしながら、送風機2、加熱装置3、吸着材モジュール4、冷却装置5のうち少なくとも2つの装置が一体一体化されて複数機能を有してもよい。
加湿装置1の内部における加熱装置3、吸着材モジュール4、冷却装置5に係る配列は、前述の実施形態で説明した形態に限定されるものではない。上下に二段並ぶ空気通路にこれらの機器が別れて配列される形態でもよい。また、加湿装置1の内部に、吸着時の空気通路と脱離時の空気通路とが上下に二段並ぶように設けられ、各通路の所定の位置に各機器が設置される形態でもよい。
前述の実施形態では、吸着材を担持させた複数の金属製の板状部材を間隔を開けて積層配置することによって吸着材モジュール4が構成された例を説明したが、吸着材モジュール4の構成は、この例に限定されない。例えば、波状に折り曲げられたコルゲート板に吸着材を担持させて、このコルゲート板を間隔を開けて積層配置してもよい。あるいは、断面六角形に形成された通路を有するハニカム部材に吸着材を担持させてもよい。
前述の第1実施形態では、制御装置が送風機2の電動モータを正転あるいは逆転させることによって、通風の向きを切り換える例について説明したが、通風経路の切り替えはこの例に限定されない。
前述の実施形態では、送風機2のファンの回転方向を反転させることで送風方向を逆向きにする例を説明したが、送風方向を逆向きにする方法はこの例に限定されない。例えば、送風機は、回転位置が変化するガイド部材によって、このガイド部材に案内される風向を方向A1と方向A2との相反する向きに変更可能な風向変更機能を有してもよい。
また、前述の実施形態では、加湿空気が車両の前席側に供給されるように吹出口部121が前席側に位置し、連通開口部122が後席側に位置している。しかしながら、吹出口部121と連通開口部122の位置関係は、この例に限定されない。
また、前述の実施形態では、吹出口部121を前席に着座している乗員の上半身側に向かって開口させるように配置しているが、吹出口部の位置はこの例に限定さない。
第3実施形態の連通開口部122は、第2実施形態の加湿装置101にも適用することができる。また、第3実施形態の連通開口部122は、第5実施形態の加湿装置201にも適用することができる。
Claims (20)
- 空気中の水分を吸着した吸着材から、脱離させた水分によって加湿した加湿空気を車室内(R)に供給する車両用の加湿装置(1,201)であって、
前記吸着材を有し、通過する空気に含まれる水分を前記吸着材に吸着したり、前記吸着材に吸着されている水分を通過する空気に対して脱離したりする吸着材モジュール(4)と、
前記吸着材モジュールに対して前記通過する空気を送風する送風部(2)と、を備え、
前記送風部は、前記吸着材に空気中の水分を吸着させる吸着時には、車両天板(11)と車室内の天井内装部材(12)との間に区画形成された天井内空間(13)内の空気を取り込み、当該空気を前記吸着材モジュールに対して送風して、前記吸着材で当該空気中の水分を吸着させる加湿装置。 - 前記吸着材モジュール及び前記送風部を収容し、前記天井内空間に設けられる装置ケース(6)を備え、
前記送風部は、前記吸着時には、前記装置ケースに設けられた吸着時吸入口部(62)から前記天井内空間の空気を取り込み、当該空気を前記吸着材モジュールに対して送風する請求項1に記載の加湿装置。 - 前記送風部は、
前記吸着時には、前記天井内空間の空気を取り込み前記吸着材で水分を吸着した後、前記天井内空間に排出し、
前記吸着材に吸着されている水分を通過する空気に対して脱離する脱離時には、前記天井内空間の空気を取り込み前記吸着材モジュールに対して送風する請求項1または請求項2に記載の加湿装置。 - 前記送風部は、前記吸着材に吸着されている水分を通過する空気に対して脱離する脱離時には、前記天井内空間の空気を取り込み、当該空気を前記吸着材モジュールに対して送風し、
前記天井内装部材には、前記天井内空間と前記車室内とを連通させる連通開口部(122)が設けられ、
前記装置ケースには、前記脱離時に前記天井内空間の空気が前記装置ケースの内部に取り込まれる脱離時吸入口部(61)が設けられ、
前記連通開口部は、前記吸着時吸入口部よりも、前記脱離時吸入口部に近い位置に設けられる請求項2に記載の加湿装置。 - 前記連通開口部は、前記天井内空間において前記装置ケースが設置されている側とは反対側に位置する請求項4に記載の加湿装置。
- 前記脱離時に前記連通開口部を介して前記天井内空間に取り込まれる前記車室内の空気を前記車両天板に沿うように案内する風向案内部材(123a)を備える請求項4または請求項5に記載の加湿装置。
- 空気中の水分を吸着した吸着材から脱離させた水分によって加湿した加湿空気を加湿対象空間(R)に供給する車両用の加湿装置(101)であって、
前記吸着材を有し、通過する空気に含まれる水分を前記吸着材に吸着したり、前記吸着材に吸着されている水分を、通過する空気に対して脱離したりする吸着材モジュール(4)と、
前記吸着材モジュールに対して前記通過する空気を送風する送風部(2)と、を備え、
前記送風部は、前記吸着材に空気中の水分を吸着させる吸着時には、車両外部の空気を取り込み、当該空気を前記吸着材モジュールに対して送風して、前記吸着材で当該空気中の水分を吸着させる加湿装置。 - 前記吸着時に前記吸着材で水分が吸着された後の空気を、車両天板(11)と車室内の天井内装部材(12)との間に区画形成された天井内空間(13)に排出する吸着時排出口部(61)を備え、
前記吸着時排出口部は、前記吸着材に吸着されている水分を通過する空気に対して脱離する脱離時に、前記加湿空気が前記車室内に向けて吹き出される車室内吹出口部(121)とは前記加湿装置において反対側に設けられ、
前記送風部は前記吸着時排出口部に隣接する位置に設けられる請求項1または請求項7に記載の加湿装置。 - 車両天板(11)と車室内(R)の天井内装部材(12)との間に区画形成された天井内空間(13)に設けられ、空気中の水分を吸着した吸着材から脱離させた水分によって加湿した加湿空気を前記車室内に供給する車両用の加湿装置(1,201)であって、
前記吸着材を有し、通過する空気に含まれる水分を前記吸着材に吸着したり、前記吸着材に吸着されている水分を通過する空気に対して脱離したりする吸着材モジュール(4)と、
前記吸着材モジュールに対して空気を送風する送風部(2)と、を備え、
前記送風部は、前記吸着材に空気中の水分を吸着させる吸着時には、前記天井内空間の空気を取り込み、当該空気を前記吸着材モジュールに対して送風して、前記吸着材で当該空気中の水分を吸着させる加湿装置。 - 前記吸着材モジュール及び前記送風部を収容し、前記天井内空間に設けられる装置ケース(6)を備え、
前記吸着時には、前記送風部は、前記装置ケースに設けられた吸着時吸入口部(62)から前記天井内空間の空気を取り込み、当該空気を前記吸着材モジュールに対して送風する請求項9に記載の加湿装置。 - 前記送風部は、
前記吸着時には、前記天井内空間の空気を取り込み、前記吸着材によって水分を吸着された後の空気を前記天井内空間に排出し、
前記吸着材に吸着されている水分を通過する空気に対して脱離する脱離時には、前記天井内空間の空気を取り込み、当該空気を前記吸着材モジュールに対して送風する請求項9または10に記載の加湿装置。 - 前記吸着時吸入口部には、切替部材(7,107A,107B,207)が設けられており、
前記切替部材は、
前記吸着時には、前記天井内空間への空気の取り込みを可能とし、
前記吸着材に吸着されている水分を通過する空気に対して脱離する脱離時には、前記車室内に前記吸着材モジュールを通過した空気を供給する請求項10または11に記載の加湿装置。 - 前記切替部材は、切換用ドア(7,207)もしくは逆止弁(107A,107B)である請求項12に記載の加湿装置。
- 前記天井内装部材に設けられ、前記天井内空間と前記車室内とを連通させる連通開口部(122)と、
前記装置ケースに設けられ、前記吸着材に吸着されている水分を通過する空気に対して脱離する脱離時において、前記送風部による前記天井内空間への空気の取り込みと、前記吸着材モジュールに対する当該空気の送風とを可能とする脱離時吸入口部(61)とを有し、
前記連通開口部と前記脱離時吸入口部(61)との間の距離(L1)は、前記連通開口部と前記吸着時吸入口部(62)との間の距離(L2)よりも短くなっている請求項10に記載の加湿装置。 - 前記脱離時吸入口部(61)は、前記吸着時吸入口部(62)と前記連通開口部(122)との間に位置している請求項14に記載の加湿装置。
- 前記連通開口部の前記天井内空間側に設けられて、前記車両天板との間に隙間を有する筒状部材(123)を備える請求項14または15に記載の加湿装置。
- 前記筒状部材(123)の前記車両天板側には、前記車両天板と対向するとともに、前記装置ケース側に延出する風向案内部材(123a)が設けられている請求項16に記載の加湿装置。
- 車両天板(11)と車室内(R)の天井内装部材(12)との間に区画形成された天井内空間(13)に設けられ、空気中の水分を吸着した吸着材から脱離させた水分によって加湿した加湿空気を加湿対象空間(R)に供給する車両用の加湿装置(101)であって、
前記吸着材を有し、通過する空気に含まれる水分を前記吸着材に吸着したり、前記吸着材に吸着されている水分を、通過する空気に対して脱離したりする吸着材モジュール(4)と、
前記吸着材モジュールに対して空気を送風する送風部(2)と、を備え、
前記送風部は、前記吸着材に空気中の水分を吸着させる吸着時には、前記車両の外部の空気を取り込み、当該空気を前記吸着材モジュールに対して送風して、前記吸着材で当該空気中の水分を吸着させる加湿装置。 - 前記吸着時に、前記吸着材で水分が吸着された後の空気を前記天井内空間に排出する吸着時排出口部(61)と、
前記吸着材に吸着されている水分を通過する空気に対して脱離する脱離時に、前記加湿空気を前記車室内に向けて吹き出す車室内吹出口部(121)と、を備え、
前記吸着時排出口部と前記車室内吹出口部との間に、前記加湿装置が設けられている請求項9または18に記載の加湿装置。 - 前記送風部と前記吸着時排出口部との間の距離(L3)が、前記送風部と前記車室内吹出口部との間の距離(L4)よりも短くなっている請求項19に記載の加湿装置。
Priority Applications (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201680043794.7A CN107848377B (zh) | 2015-07-29 | 2016-07-12 | 加湿装置 |
| DE112016003388.5T DE112016003388T5 (de) | 2015-07-29 | 2016-07-12 | Befeuchtungseinrichtung |
| US15/740,171 US10675951B2 (en) | 2015-07-29 | 2016-07-12 | Humidifying device |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2015150011A JP6304164B2 (ja) | 2015-07-29 | 2015-07-29 | 加湿装置 |
| JP2015-150011 | 2015-07-29 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2017018191A1 true WO2017018191A1 (ja) | 2017-02-02 |
Family
ID=57885238
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2016/070485 WO2017018191A1 (ja) | 2015-07-29 | 2016-07-12 | 加湿装置 |
Country Status (5)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US10675951B2 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JP6304164B2 (ja) |
| CN (1) | CN107848377B (ja) |
| DE (1) | DE112016003388T5 (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2017018191A1 (ja) |
Families Citing this family (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2022021029A (ja) * | 2020-07-21 | 2022-02-02 | 株式会社東芝 | 湿度調整フィルター、及び磁気記録再生装置 |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH06143997A (ja) * | 1992-11-04 | 1994-05-24 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | 車両用加湿装置 |
| JP2009280148A (ja) * | 2008-05-23 | 2009-12-03 | Denso Corp | 車両用除加湿装置及びその装置の運転方法 |
| WO2014162644A1 (ja) * | 2013-04-05 | 2014-10-09 | 株式会社デンソー | 加湿装置 |
| JP2015101234A (ja) * | 2013-11-26 | 2015-06-04 | 株式会社前川製作所 | 車両用空調装置 |
Family Cites Families (14)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US5873256A (en) * | 1994-07-07 | 1999-02-23 | Denniston; James G. T. | Desiccant based humidification/dehumidification system |
| US5509275A (en) * | 1994-09-22 | 1996-04-23 | General Motors Corporation | Dehumidifying mechanism for auto air conditioner |
| US6029462A (en) * | 1997-09-09 | 2000-02-29 | Denniston; James G. T. | Desiccant air conditioning for a motorized vehicle |
| US5878590A (en) * | 1998-02-25 | 1999-03-09 | General Motors Corporation | Dehumidifying mechanism for auto air conditioner with improved space utilization and thermal efficiency |
| JP2005112297A (ja) * | 2003-10-10 | 2005-04-28 | Denso Corp | 車両用空調装置 |
| JP5055944B2 (ja) * | 2006-10-18 | 2012-10-24 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | 車両用除加湿装置 |
| JP5266657B2 (ja) * | 2007-03-30 | 2013-08-21 | 三菱樹脂株式会社 | 車両用除加湿装置 |
| JP2008254638A (ja) | 2007-04-06 | 2008-10-23 | Toyota Motor Corp | 車両用加湿装置 |
| JP4720772B2 (ja) * | 2007-04-06 | 2011-07-13 | トヨタ自動車株式会社 | 車両用除加湿装置 |
| US20090277195A1 (en) * | 2008-05-09 | 2009-11-12 | Thermo King Corporation | Refrigeration system including a desiccant |
| JP5239717B2 (ja) * | 2008-10-06 | 2013-07-17 | 株式会社デンソー | 除加湿装置 |
| DE102009028931A1 (de) * | 2009-08-27 | 2011-03-03 | BSH Bosch und Siemens Hausgeräte GmbH | Verfahren zum Betreiben eines Adsorptions-Trockners und Trockner zur Realisierung des Verfahrens |
| DE102013112825A1 (de) * | 2013-11-20 | 2015-05-21 | Valeo Klimasysteme Gmbh | Frontmodul eines Fahrzeugs |
| JP6394521B2 (ja) | 2014-08-21 | 2018-09-26 | 株式会社デンソー | 加湿装置 |
-
2015
- 2015-07-29 JP JP2015150011A patent/JP6304164B2/ja not_active Expired - Fee Related
-
2016
- 2016-07-12 WO PCT/JP2016/070485 patent/WO2017018191A1/ja active Application Filing
- 2016-07-12 DE DE112016003388.5T patent/DE112016003388T5/de not_active Withdrawn
- 2016-07-12 US US15/740,171 patent/US10675951B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2016-07-12 CN CN201680043794.7A patent/CN107848377B/zh not_active Expired - Fee Related
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH06143997A (ja) * | 1992-11-04 | 1994-05-24 | Matsushita Electric Ind Co Ltd | 車両用加湿装置 |
| JP2009280148A (ja) * | 2008-05-23 | 2009-12-03 | Denso Corp | 車両用除加湿装置及びその装置の運転方法 |
| WO2014162644A1 (ja) * | 2013-04-05 | 2014-10-09 | 株式会社デンソー | 加湿装置 |
| JP2015101234A (ja) * | 2013-11-26 | 2015-06-04 | 株式会社前川製作所 | 車両用空調装置 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN107848377B (zh) | 2020-07-07 |
| US10675951B2 (en) | 2020-06-09 |
| DE112016003388T5 (de) | 2018-04-05 |
| CN107848377A (zh) | 2018-03-27 |
| JP6304164B2 (ja) | 2018-04-04 |
| JP2017030409A (ja) | 2017-02-09 |
| US20180312043A1 (en) | 2018-11-01 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| EP2143574B1 (en) | Dehumidification/humidification device for vehicle | |
| JP6394521B2 (ja) | 加湿装置 | |
| WO2014065255A1 (ja) | バッテリ温度調整ユニット及びこれを搭載した車両 | |
| WO2014162644A1 (ja) | 加湿装置 | |
| JP4539343B2 (ja) | 空気調和装置 | |
| JP2000108655A (ja) | 除湿装置 | |
| JP2008254618A (ja) | 車両用除加湿装置 | |
| JP2000146220A (ja) | 空気調和手段及び空気調和装置 | |
| JP2009274587A (ja) | 車両用除加湿装置 | |
| JP4538846B2 (ja) | 空気調和装置 | |
| JP6413680B2 (ja) | 加湿装置 | |
| JP5089254B2 (ja) | 自動車用調湿空調システム | |
| CN111907287A (zh) | 车辆用空调系统及其二氧化碳收集模块 | |
| JP6831167B2 (ja) | 電動車両 | |
| JP2009262580A (ja) | 車両用除加湿装置 | |
| JP5083035B2 (ja) | 車両用除加湿装置及びその装置の運転方法 | |
| WO2017018191A1 (ja) | 加湿装置 | |
| JP2013035484A (ja) | 車両用空調装置 | |
| JP2009280149A (ja) | 車両用除加湿装置 | |
| JP6350483B2 (ja) | 加湿装置 | |
| JP2006143042A (ja) | 車両用空調装置 | |
| JP2018118630A (ja) | 加湿装置 | |
| WO2017130547A1 (ja) | 加湿装置 | |
| JP2005254954A (ja) | 車両空調装置 | |
| CN113276638A (zh) | 车辆用净化装置 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 16830296 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 15740171 Country of ref document: US |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 112016003388 Country of ref document: DE |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 16830296 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |