WO2015087674A1 - 吸収体の製造装置 - Google Patents
吸収体の製造装置 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2015087674A1 WO2015087674A1 PCT/JP2014/080611 JP2014080611W WO2015087674A1 WO 2015087674 A1 WO2015087674 A1 WO 2015087674A1 JP 2014080611 W JP2014080611 W JP 2014080611W WO 2015087674 A1 WO2015087674 A1 WO 2015087674A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- duct
- upstream
- plate portion
- bottom plate
- absorbent
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- A—HUMAN NECESSITIES
- A61—MEDICAL OR VETERINARY SCIENCE; HYGIENE
- A61F—FILTERS IMPLANTABLE INTO BLOOD VESSELS; PROSTHESES; DEVICES PROVIDING PATENCY TO, OR PREVENTING COLLAPSING OF, TUBULAR STRUCTURES OF THE BODY, e.g. STENTS; ORTHOPAEDIC, NURSING OR CONTRACEPTIVE DEVICES; FOMENTATION; TREATMENT OR PROTECTION OF EYES OR EARS; BANDAGES, DRESSINGS OR ABSORBENT PADS; FIRST-AID KITS
- A61F13/00—Bandages or dressings; Absorbent pads
- A61F13/15—Absorbent pads, e.g. sanitary towels, swabs or tampons for external or internal application to the body; Supporting or fastening means therefor; Tampon applicators
- A61F13/15577—Apparatus or processes for manufacturing
- A61F13/15617—Making absorbent pads from fibres or pulverulent material with or without treatment of the fibres
- A61F13/15642—Making absorbent pads from fibres or pulverulent material with or without treatment of the fibres by depositing continuous layers or pads of fibrous material on single sheets or webs
Definitions
- the present invention relates to an absorber manufacturing apparatus.
- Absorbers used for absorbent articles such as disposable diapers, sanitary napkins, incontinence pads, etc. are concave portions formed on the outer peripheral surface of the rotating drum by placing the raw material of the absorbent body containing pulp fibers and absorbent polymer on an air flow. Then, the stacked fiber body deposited in the recess is coated with a water-permeable sheet material. The air flow mixes the polymer and pulp supplied from the spray tube, and the fluffed pulp carries the absorbent polymer in the transverse air flow.
- the weight of the absorbent polymer is very heavy compared to the weight of the pulp fiber, the amount of pulp flowing around the center of the spray pipe is small and the mixing property is poor, so the dispersion of the absorbent polymer becomes non-uniform.
- Patent Document 1 describes an absorbent body manufacturing apparatus in which a plurality of polymer input members for supplying an absorbent polymer are disposed so as to cross a pulp fiber distribution path for distributing pulp fibers to a recess on an outer peripheral surface of a rotating drum. ing.
- the absorbent body manufactured by the manufacturing apparatus described in Patent Document 1 since the absorbent polymer is partially dispersed in the raw material of the absorbent body, gel blocking is unlikely to occur, and the absorbent performance of the absorbent body Will improve.
- the present invention includes a rotating drum having an accumulation concave portion for collecting the raw material of the absorbent body including the fiber material and the absorbent particles on the outer peripheral surface, and the raw material of the absorber is scattered toward the outer peripheral surface of the rotary drum.
- the manufacturing apparatus of the absorber which has a duct to supply. In the duct, the cross-sectional area of the flow path in the spraying region in which the absorbent particles are dispersed in the duct is greater than the cross-sectional area of the flow path located in the uppermost stream of the duct and the cross-sectional area of the flow path located in the most downstream. Is also formed small.
- the duct has means for correcting the flow direction of the fiber material and concentrating the fiber material in the spray area upstream of the spray area.
- FIG. 1 is a schematic perspective view showing a first embodiment of an absorbent body manufacturing apparatus according to the present invention.
- FIG. 2A is a schematic side view of the manufacturing apparatus shown in FIG. 1 viewed from the side
- FIG. 2B is a schematic view of the manufacturing apparatus shown in FIG. ) Is a graph showing the relationship between the cross-sectional area of the flow path and the position in the spray region in the duct.
- FIG. 3 is a cross-sectional view of an absorber manufactured by the manufacturing apparatus shown in FIG. 4A is a schematic side view of the manufacturing apparatus according to the first embodiment of the present invention as viewed from the side
- FIG. 4B is a schematic view of the manufacturing apparatus according to the first embodiment as viewed from the top. .
- FIG. 4A is a schematic side view of the manufacturing apparatus according to the first embodiment of the present invention as viewed from the side
- FIG. 4B is a schematic view of the manufacturing apparatus according to the first embodiment as viewed from the top. .
- FIG. 5 is a cross-sectional view of the absorber manufactured by the manufacturing apparatus shown in FIG.
- FIG. 6A is a schematic side view of the manufacturing apparatus according to the second embodiment of the present invention viewed from the side
- FIG. 6B is a schematic view of the manufacturing apparatus of the second embodiment viewed from the top.
- FIG. 7A is a schematic side view of the manufacturing apparatus of the third embodiment of the present invention viewed from the side
- FIG. 7B is a schematic view of the manufacturing apparatus of the third embodiment viewed from the top.
- FIG. 8 is the schematic side view which looked at the manufacturing apparatus of 4th Embodiment of this invention from the side
- FIG. 9 is the schematic side view which looked at the manufacturing apparatus of 5th Embodiment of this invention from the side.
- the absorbent body manufactured by the manufacturing apparatus described in Patent Document 1 is arranged such that the absorbent polymer is partially dispersed in the raw material of the absorbent body, if viewed macroscopically, the absorbent polymer The part which gathered is only the form disperse
- the present invention relates to an absorber manufacturing apparatus that can eliminate the drawbacks of the prior art described above.
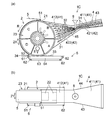
- FIG. 1 schematically shows a fiber stacking apparatus 1A according to a first preferred embodiment of the absorbent body manufacturing apparatus of the present invention.
- the fiber stacking apparatus 1 ⁇ / b> A of the first embodiment includes a rotary drum 2 having an accumulation recess 22 in the outer circumferential surface 21 for accumulating the raw material of the absorbent body including the fiber material 31 and the absorbent particles 32, and the outer circumferential surface of the rotary drum 2. And a duct 4 for supplying the raw material of the absorbent body in a scattered state toward 21.
- the fiber stacking apparatus 1 ⁇ / b> A is adjacent to the rotary drum 2 that is rotationally driven in the direction of arrow R, the duct 4 that supplies the raw material of the absorber to the outer peripheral surface 21 of the rotary drum 2, and the downstream side of the duct 4.
- the pressing belt 5 that presses down the absorbent material material pile 33 disposed along the outer peripheral surface 21 of the rotating drum 2 and accumulated in the collecting recess 22, and the vacuum conveyor 6 disposed below the rotating drum 2.
- a fiber material supply unit 7 for supplying the fiber material 31 which is a raw material of the absorber to the duct 4.
- a polymer spray pipe 8 for supplying the absorbent particles 32 into the duct 4 is disposed in the duct 4.
- the rotating drum 2 has a cylindrical shape, and receives power from a motor (not shown) such as a motor, so that members forming the outer peripheral surface 21 rotate around the horizontal axis in the direction of arrow R. To do.
- the drum body 23 located inside the member forming the outer peripheral surface 21 is fixed and does not rotate.
- the rotary drum 2 has an accumulation recess 22 on the outer peripheral surface 21 in which the raw material of the absorber is stacked.
- a plurality of the accumulation recesses 22 are arranged at predetermined intervals in the circumferential direction (2X direction) of the rotary drum 2.
- the 2X direction is the circumferential direction of the rotating drum 2
- the 2Y direction is the width direction of the rotating drum 2 (a direction parallel to the rotation axis of the rotating drum 2).
- the rotary drum 2 has a plurality of mutually independent spaces, and the fiber stacking apparatus 1A has five spaces A to E.
- the spaces A to E are partitioned by a plate provided from the rotating shaft side of the rotating drum 2 toward the outer peripheral surface 21 side.
- An intake fan (not shown) is connected to the rotary drum 2, and the pressure in the partitioned spaces A to E in the rotary drum 2 can be adjusted by driving the intake fan.
- spaces A and B are maintained at a negative pressure.
- the rotating drum 2 corresponds to the suction force of the upstream region (region corresponding to the space A) corresponding to the filter layer forming region made of the fiber material 31 and the mixed layer forming region made of the fiber material 31 and the absorbent particles 32.
- Adjustment means for adjusting the suction force of the downstream region is provided. Accordingly, the suction force in the upstream region (region corresponding to the space A) can be made stronger or weaker than the suction force in the downstream region (region corresponding to the space B).
- the spaces C and D of the rotating drum 2 are normally set to a negative pressure or zero pressure (atmospheric pressure) that is weaker than the space B, and the space E is set to atmospheric pressure (zero pressure) or positive pressure.
- the spaces C and D are made to have a weak negative pressure until the piled product in the stacking recess 22 is transferred onto the vacuum conveyor 6, and the piled product is made to be a stacking recess. It is preferable that the pressure is held in the space 22, but if there is no particular problem in the transportability, the pressure in the spaces C to E is preferably zero in consideration of transferability.
- each accumulation recess 22 is made of a porous member. While the accumulation recess 22 passes over the spaces A and B maintained at negative pressure, the pores of the porous member on the bottom surface 22a of the accumulation recess 22 function as suction holes.
- the porous member those conventionally used in this type of fiber stacking apparatus can be used without particular limitation. For example, many metal members or resin mesh plates or metal or resin plates can be etched or punched. Those having fine pores can be used.
- the raw material of the absorbent body 3 various materials conventionally used for absorbent bodies of absorbent articles such as sanitary napkins, panty liners, and disposable diapers can be used without particular limitation.
- the fiber material 31 that is a raw material of the absorbent body short fibers of cellulose fibers such as pulp fibers, rayon fibers, and cotton fibers, short fibers obtained by hydrophilizing synthetic fibers such as polyethylene, polypropylene, and polyethylene terephthalate are preferable. . These fibers may be used alone or in combination of two or more.
- the fiber material 31 preferably contains pulp fibers, and the ratio of the pulp fibers in the fiber material 31 is preferably 1 to 100% by mass, more preferably 100% by mass.
- Examples of the absorbent particles 32 that are raw materials of the absorber include starch-based, cellulose-based, synthetic polymer, and super-absorbent polymer-based ones.
- Examples of superabsorbent polymers include starch-acrylic acid (salt) graft copolymers, saponified starch-acrylonitrile copolymers, cross-linked sodium carboxymethylcellulose, and acrylic acid (salt) polymers.
- a deodorant, an antibacterial agent, or the like can be used as necessary together with the fiber material 31 and the absorbent particles 32.
- the duct 4 extends from the fiber material supply unit 7 to be described later over the rotary drum 2, and an outer peripheral surface in which the opening on the downstream side of the duct 4 is located in the spaces A and B of the rotary drum 2 maintained at negative pressure. 21 is covered.
- the duct 4 includes a top plate 41 that forms a top surface, a bottom plate 42 that forms a bottom surface, and both side walls 43 and 44 that form both side surfaces. Due to the operation of the intake fan (not shown) of the rotating drum 2, the absorber is directed toward the outer peripheral surface 21 of the rotating drum 2 in the space surrounded by the top plate 41, the bottom plate 42 and the side walls 43, 44 of the duct 4. An air flow for flowing the raw material is generated.
- the top plate 41 of the duct 4 includes an upstream top plate portion 411 located on the upstream side and a downstream top plate located on the downstream side. And plate portion 412.
- the bottom plate 42 of the duct 4 includes an upstream bottom plate portion 421 located on the upstream side and a downstream bottom plate portion 422 located on the downstream side.
- the upstream top plate portion 411 and the upstream bottom plate portion 421 are gradually narrowed from the upstream side toward the downstream side.
- the downstream top plate portion 412 and the downstream bottom plate portion 422 have a constant width from the upstream side toward the downstream side.
- the widths of the downstream top plate portion 412 and the downstream bottom plate portion 422 are the same as the widths of the upstream-side top plate portion 411 and the portion located on the most downstream side of the upstream bottom plate portion 421.
- the distance between the top plate 41 and the bottom plate 42 of the duct 4 is constant between the upstream top plate portion 411 and the upstream bottom plate portion 421.
- the distance between the downstream top plate portion 412 and the downstream bottom plate portion 422 is gradually increased from the upstream top plate portion 411 and the upstream bottom plate portion 421 toward the outer peripheral surface 21 of the rotary drum 2.
- Both side walls 43 and 44 of the duct 4 are provided on the side edges of the top plate 41 composed of the upstream top plate portion 411 and the downstream top plate portion 412, and the upstream bottom plate portion 421 and the downstream bottom plate portion. It is disposed along both side edges of the bottom plate 42 made of 422.
- the polymer spray tube 8 for supplying the absorbent particles 32 into the duct 4 is disposed on the top plate 41 of the duct 4. More specifically, the polymer spray tube 8 is arranged at the downstream end of the upstream top plate portion 411 constituting the top plate 41. The polymer spray tube 8 is arranged so that the lower end thereof is positioned at the upstream end of the partition plate 45 described later.
- the duct 4 having the top plate 41, the bottom plate 42, and both side walls 43 and 44 having the above-described shape is provided in the flow path in the spraying region in which the absorbent particles 32 are sprayed.
- the cross-sectional area is formed smaller than the cross-sectional area of the flow channel located at the uppermost stream of the duct 4 and the cross-sectional area of the flow channel located at the most downstream side of the duct 4.
- the “spreading region” means a region having a certain range on the upstream side or the downstream side from the position where the polymer spraying tube 8 that sprays the absorbent particles 32 is disposed.
- the duct 4 has a top plate 41 in the spraying region in which the absorbent particles 32 are sprayed by the polymer spraying tube 8, as shown in FIGS. 2 (a) to 2 (c).
- the cross-sectional area of the flow path surrounded by the bottom plate 42 and the side walls 43 and 44 is surrounded by the top plate 41, the bottom plate 42 and the side walls 43 and 44 located at the upstream end of the duct 4 closest to the fiber material supply unit 7.
- the cross-sectional area of the flow path is smaller than the cross-sectional area of the flow path surrounded by the top plate 41, the bottom plate 42, and the side walls 43, 44 located at the downstream end of the duct 4 closest to the rotary drum 2. ing.
- the width of the upstream top plate portion 411 of the top plate 41 and the upstream bottom plate portion 421 of the bottom plate 42 gradually decreases from the upstream side toward the downstream side. Therefore, in the upstream-side top plate portion 411 and the upstream-side bottom plate portion 421, the cross-sectional area of the flow path surrounded by the top plate 41, the bottom plate 42, and both side walls 43, 44 gradually decreases from the upstream side toward the downstream side. Yes.
- the distance between the downstream top plate portion 412 of the top plate 41 and the downstream bottom plate portion 422 of the bottom plate 42 gradually increases from the upstream side toward the downstream side
- the cross-sectional area of the flow path surrounded by the top plate 41, the bottom plate 42, and both side walls 43, 44 gradually increases from the upstream side toward the downstream side. Therefore, the cross-sectional area of the flow path in the spraying region in which the absorbent particles 32 are sprayed by the polymer spraying tube 8 disposed at the downstream end of the upstream top plate 411 is relatively small.
- the cross-sectional area of the flow path at the lower end of the polymer spraying tube 8 or the upstream end of the partition plate 45 described later is formed to be the smallest.
- the duct 4 is provided with a partition plate 45 that regulates the flow direction of the absorbent particles 32 supplied therein in the fiber stacking apparatus 1A.
- the partition plate 45 extends from the boundary portion between the upstream top plate portion 411 and the downstream top plate portion 412 toward the rotary drum 2 across both side walls 43 and 44 of the duct 4. Yes. More specifically, the partition plate 45 extends toward the tip of the plate that separates the space A and the space B of the rotary drum 2. Since the partition plate 45 is arranged inside the duct 4, the flow direction of the absorbent particles 32 is regulated, and the flow branches only into the flow of flowing the fiber material 31 and the flow of flowing the fiber material 31 and the absorbent particles 32. Will come to be.
- the presser belt 5 is disposed along the outer peripheral surface 21 of the rotating drum 2 adjacent to the downstream side of the position of the duct 4 of the rotating drum 2 and rotates. It is arranged along the outer peripheral surface 21 located in the spaces C and D set to a negative pressure or zero pressure (atmospheric pressure) that is weaker than the space B of the drum 2.
- the presser belt 5 is an endless breathable or non-breathable belt, is stretched over the roll 51 and the roll 52, and is rotated along with the rotation of the rotary drum 2.
- the pressing belt 5 is a breathable belt, it is preferable that the material in the accumulation recess 22 is not substantially allowed to pass through. Even if the pressure in the spaces C to E is set to atmospheric pressure, the presser belt 5 can hold the piled material in the stacking recess 22 in the stacking recess 22 until it is transferred onto the vacuum conveyor 6.
- the vacuum conveyor 6 is disposed below the rotary drum 2, and is a space E set at a weak positive pressure or zero pressure (atmospheric pressure) of the rotary drum 2. It is arranged on the outer peripheral surface 21 located at the position.
- the vacuum conveyor 6 is opposed to an endless breathable belt 63 spanned between the drive roll 61 and the driven rolls 62 and 62 and the outer peripheral surface 21 located in the space E of the rotary drum 2 with the breathable belt 63 interposed therebetween.
- a vacuum box 64 arranged at the position.
- a core wrap sheet 34 made of tissue paper or liquid permeable nonwoven fabric is introduced.
- the fiber material supply part 7 is a part which supplies the fiber material 31 which is the raw material of an absorber to the duct 4, as shown in FIG.
- the fiber material supply unit 7 includes a defibrator 71. By introducing the sheet-shaped raw fabric 30 of the fiber material 31 into the defibrating machine 71, the original fabric 30 is defibrated, and the defibrated fiber material 31 is supplied to the flow path in the duct 4.
- the suction fans (not shown) connected to the spaces A and B in the rotary drum 2 and the vacuum box 64 are operated to make negative pressure.
- an air flow (vacuum air) is generated in the duct 4 to convey the raw material of the absorber to the outer peripheral surface 21 of the rotary drum 2.
- the rotary drum 2 is rotated and the pressing belt 5 is operated.
- the defibrating machine 71 of the fiber material supply unit 7 is operated to defibrate the sheet-shaped raw material of the fiber material 31, and the defibrated fiber material 31 is supplied to the flow path in the duct 4. Further, the absorbent particles 32 are supplied into the duct 4 by the polymer spray tube 8 disposed on the top plate 41 of the duct 4.
- the duct 4 has a cross-sectional area of the flow path in the spraying region in which the absorbent particles 32 are sprayed in the duct 4 at the most upstream of the duct 4. It is formed smaller than the cross-sectional area of the flow path located and the cross-sectional area of the flow path located on the most downstream side of the duct 4. Therefore, the flow of the defibrated fiber material 31 supplied into the duct 4 is narrowed in the spray area where the absorbent particles 32 are sprayed by the polymer spray pipe 8. In the spraying region, the squeezed fiber material 31 is efficiently mixed with the polymer, and then the flow of the squeezed fiber material 31 rides on the flow spreading toward the most downstream side of the duct 4.
- the absorbent particles 32 dispersed in the dispersion region are efficiently mixed with the fiber material, they are scattered along the flow of the fiber material 31 and are heavier than the fiber material 31 as well as the fiber material 31.
- the absorbent particles 32 are likely to spread throughout the duct 4. That is, the fiber material 31 is confined to the spraying region of the absorbent particles 32, and the fiber material 31 and the absorbent particles 32 are efficiently mixed (entangled), whereby the absorbent particles 32 that have a high specific gravity and are difficult to follow along the airflow.
- the fiber material 31 that is light in specific gravity and easy to follow along with the air flow can be uniformly dispersed in a form that is assisted.
- the cross-sectional area of the flow path surrounded by the top plate 41, the bottom plate 42, and both side walls 43 and 44 is upstream. Since the diameter gradually decreases from the downstream side toward the downstream side, the flow of the defibrated fiber material 31 supplied into the duct 4 is easily restricted in the spraying region in which the absorbent particles 32 are sprayed by the polymer spraying tube 8. ing.
- the cross-sectional area of the flow path surrounded by the top plate 41, the bottom plate 42, and both side walls 43 and 44 is upstream. Since the flow gradually increases toward the downstream side, the flow of the narrowed fiber material 31 easily spreads throughout the thickness direction of the duct 4, and the dispersed absorbent particles 32 follow the flow of the fiber material 31. The fiber material 31 and the absorbent particles 32 are more likely to spread throughout the duct 4.
- the duct 4 is formed in a straight shape without restricting the flow path, and the flow path located at the uppermost stream of the duct 4 is cut off.
- the fiber material sheet width raw fabric width
- the fiber material 31 may be insufficiently defibrated.
- the sheet width (raw fabric width) is narrowed, the consumption speed of the raw fabric is increased and the replacement frequency is increased, resulting in an increase in production loss. Accordingly, it is preferable that the sheet width (raw fabric width) is wide, and therefore it is preferable that the cross-sectional area of the flow path located at the uppermost stream of the duct 4 is also wide.
- the absorbent particles 32 dispersed in the spray region are scattered along the flow of the fiber material 31, and the fiber material 31 and the absorbent particles 32 spread throughout the duct 4, and the accumulation recess 22 on the outer peripheral surface 21 of the rotary drum 2. , The absorbent particles 32 are easily dispersed uniformly in the fiber material 31 and the pile 33 of the absorbent particles 32 in the thickness direction of the accumulation recesses 22.
- a partition plate 45 is arranged in the duct 4. Therefore, a filter layer made of the fiber material 31 is easily formed in a region corresponding to the space A on the upstream side of the rotary drum 2. Further, in a region corresponding to the space B of the rotary drum 2 on the downstream side of the space A, a mixed layer composed of the fiber material 31 and the absorbent particles 32 is easily formed. Thus, in the duct 4 above the partition plate 45, the dispersed absorbent particles 32 are easily scattered along the flow of the fiber material 31, and the fiber material 31 and the absorbent particles 32 are easily spread. .
- the filter layer is for preventing the absorbent particles 32 from being clogged in the mesh pores at the bottom of the accumulation recess 22.
- the rotary drum 2 includes an adjusting unit that adjusts the suction force, for example, by adjusting the balance between the suction force in the region corresponding to the space B and the suction force in the region corresponding to the space A, Furthermore, the fiber material 31 and the absorbent particles 32 can be easily spread in the duct 4 above the partition plate 45. More specifically, for example, if the suction force of the space A is too strong with respect to the suction force of the space B, the filter layer made of the fiber material 31 is excessively formed, and the absorbent particles dispersed in the spraying region accordingly.
- the absorbent particles 32 that cannot be mixed with the fiber material 31 cannot be dispersed and aggregated in the piled product 33.
- the adjusting means by adjusting the balance between the suction force of the region corresponding to the space B and the suction force of the region corresponding to the space A using the adjusting means, the formation of an excessive filter layer is suppressed, and the absorbent particles A sufficient amount of the fiber material 31 to be mixed with the fiber material 32 can be distributed to the spraying region.
- the sprayed absorbent particles 32 are reliably mixed with the fiber material 31, and the duct 4 upwards from the partition plate 45.
- the fiber material 31 and the absorbent particles 32 can be easily spread inside.
- the rotating drum 2 is further rotated and stacked by the presser belt 5 as shown in FIG. It conveys to the vacuum conveyor 6 while pressing the pile 33 in the concave part 22 for use. Then, when the pile 33 in the accumulation recess 22 comes to a position opposite to the vacuum box 64, it is released from the accumulation recess 22 by suction from the vacuum box 64 and is introduced onto the vacuum conveyor 6. It is delivered onto a core wrap sheet 34 made of tissue paper or a liquid-permeable nonwoven fabric.
- both side portions along the conveying direction of the core wrap sheet 34 are folded back, and the upper and lower surfaces of the piled article 33 are covered with the core wrap sheet 34.
- the piled article 33 covered with the core wrap sheet 34 is cut together with the core wrap sheet 34 by cutting means of a cutting device (not shown). In this way, the absorbent body 3 in which the piled material 33 is coated on the core wrap sheet 34 is continuously obtained.
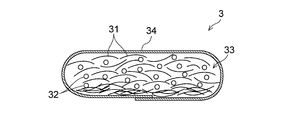
- the absorbent particles 32 are uniformly distributed not only in the width direction of the fiber pile 33 but also in the thickness direction. Is distributed. Therefore, the absorbent body 3 obtained using the fiber stacking apparatus 1A is less likely to cause gel blocking during use, and has high quality suitable as an absorbent body used for absorbent articles such as disposable diapers, sanitary napkins, and incontinence pads. It has become a thing.
- the absorbent particles 32 are uniformly dispersed not only in the width direction of the fiber pile 33 but also in the thickness direction. 3 can be stably produced.
- fiber stacking apparatuses 1B to 1E according to second to fifth embodiments of the present invention will be described.
- differences from the fiber-spreading apparatus 1A of the first embodiment will be mainly described, and the same points will be denoted by the same reference numerals and description thereof will be omitted. .
- the description relating to the fiber stacking apparatus 1A of the first embodiment is applied as appropriate.
- the effects of the fiber stacking devices 1B to 1E of the second to fifth embodiments will be described with respect to differences from the effects of the fiber stacking device 1A of the first embodiment. This is the same as the effect, and the description of the effect of the fiber stacking apparatus 1A is applied as appropriate.
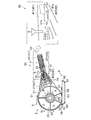
- the fiber stacking apparatus 1A As shown in FIGS. 4A and 4B, the fiber stacking apparatus 1A according to the first embodiment described above has a top plate 41 in the duct 4 according to the characteristics of the defibrator 71 of the fiber material supply unit 7.
- the amount of fiber material 31 that has been defibrated may increase on the bottom plate 42 side (downward) in the thickness direction with the bottom plate 42.
- fibers are formed in a region corresponding to the space A on the upstream side of the rotary drum 2.
- the filter layer made of the material 31 may be formed excessively. As shown in FIG.
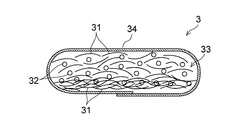
- the piled product 33 of the absorbent body 3 obtained under such circumstances has an excessively formed filter layer of the fiber material 31 made of only the fiber material 31 in the thickness direction downward, and in the spreading region. Since the fiber material 31 to be mixed with the dispersed absorbent particles 32 is reduced, the absorbent particles 32 that cannot be mixed with the fiber material 31 are not completely dispersed and are present in an aggregated state in the piled fabric 33. End up. Even if the suction force of the space B is adjusted to be stronger than the suction force of the space A, the absorbent particles 32 having a high specific gravity cannot be mixed with the flow of the fiber material 31 having a low specific gravity in the spray region above the partition plate 45. Therefore, the absorbent particles 32 may not be sufficiently dispersed.
- the stacked fiber In order to increase the amount of the fiber material 31 flowing in the spraying region and concentrate the fiber material 31 near the tip of the spraying tube so that it can be easily mixed with the absorbent particles 32, the stacked fiber according to the second embodiment described below.
- the fiber stacking apparatus 1E of the apparatus 1B to the fifth embodiment is effective.
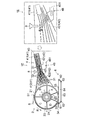
- the fiber stacking apparatus 1B of the second embodiment has the fiber material 31 on the upstream side of the spraying region in which the absorbent particles 32 are sprayed in the duct 4.
- Means for correcting the flow direction and concentrating the fiber material 31 in the spraying region are provided.
- the fiber stacking apparatus 1 ⁇ / b> B of the second embodiment has a correction guide 46 for correcting the flow direction of the fiber material 31 inside the duct 4.
- the correction guide 46 is located in the upstream top plate portion 411 of the top plate 41 of the duct 4 and the upstream bottom plate portion 421 of the bottom plate 42, and extends upstream of the bottom plate 42 across both side walls 43, 44 of the duct 4.
- the bottom plate portion 421 extends from the upper surface toward the downstream side.
- the correction guide 46 is arranged such that the lower end of the polymer spray tube 8 or the upstream end of the partition plate 45 is positioned on the extended line of the upper surface. Since the fiber stacking apparatus 1B is provided with the guide 46, there is also an advantage that arbitrary control can be performed by changing the guide position according to the conditions.
- the duct 4 has a cross-sectional area of the flow path in the spraying region in which the absorbent particles 32 are sprayed, as in the fiber stacking apparatus 1A of the first embodiment.
- the cross-sectional area of the flow channel located at the uppermost stream of the duct 4 and the cross-sectional area of the flow channel located at the most downstream side of the duct 4 are formed smaller. Therefore, the flow of the defibrated fiber material 31 supplied into the duct 4 is narrowed in the spray area where the absorbent particles 32 are sprayed by the polymer spray pipe 8.
- the straightening guide 46 for correcting the flow direction of the fiber material 31 is provided inside the duct 4, the fiber material that has been defibrated toward the spraying region in which the absorbent particles 32 are sprayed.
- the flow of 31 is concentrated. Therefore, when the flow of the squeezed fiber material 31 collides with the absorbent particles 32 dispersed in the spray region and becomes easy to be mixed, the absorbent particles 32 are released when released toward the most downstream side of the duct 4.
- the absorbent particles 32 that are further scattered along the flow of the fiber material 31 and are heavier than the fiber material 31 as well as the fiber material 31 are more likely to spread throughout the duct 4.
- the pile 33 of the absorbent body 3 obtained using the pile apparatus 1 ⁇ / b> B is similar to the pile 33 of the absorbent body 3 obtained using the pile apparatus 1 ⁇ / b> A of the first embodiment.
- the absorbent particles 32 are uniformly dispersed not only in the width direction of the piled product 33 but also in the thickness direction. Accordingly, gel blocking is unlikely to occur in the absorbent body 3 during use, and the absorbent body 3 is of a high quality suitable as an absorbent body used in absorbent articles such as disposable diapers, sanitary napkins, and incontinence pads.
- the absorbent particles 32 can stably distribute the absorbent body 3 uniformly dispersed not only in the width direction of the fiber stack 33 but also in the thickness direction. Can be manufactured.
- the fiber stacking apparatus 1C of the third embodiment has fibers on the upstream side of the spraying region in which the absorbent particles 32 are sprayed in the duct 4.
- Means for correcting the flow direction of the material 31 and concentrating the fiber material 31 in the spraying region is provided.
- the upstream-side bottom plate portion 421 of the bottom plate 42 of the duct 4 is arranged to be inclined. More specifically, the upstream bottom plate portion 421 is arranged so that the lower end of the polymer spray tube 8 or the upstream end portion of the partition plate 45 is positioned on the extended line of the upper surface thereof. 421 is a means for concentrating the fiber material 31 in the spraying region.
- the distance between the top plate 41 and the bottom plate 42 is as shown in FIG. 7 (a).
- the distance between the plate portion 411 and the upstream bottom plate portion 421 is gradually narrowed toward the spraying region, and the distance between the downstream top plate portion 412 and the downstream bottom plate portion 422 is the upstream top plate portion 411 and The width gradually increases from the upstream bottom plate portion 421 toward the outer peripheral surface 21 of the rotary drum 2.
- the downstream end of the upstream bottom plate 421 is located upstream of the end of the partition plate 45, and as shown in FIG.7 (b), the upstream top plate 411 and the upstream bottom plate 421 are:
- the width gradually decreases from the upstream side toward the downstream side. For this reason, the cross-sectional area of the flow path in the spraying region in which the absorbent particles 32 are sprayed by the polymer spraying tube 8 disposed at the downstream end of the upstream top plate 411 is further reduced. Since the space
- a dead space is generated in the lower portion, so that eddy currents may occur or pulp powder may gradually accumulate.
- the fiber stacking apparatus 1C is improved so as not to have such a dead space.
- the duct 4 has a cross-sectional area of the flow path in the spraying region in which the absorbent particles 32 are sprayed, as compared with the fiber stacking apparatus 1A of the first embodiment.
- the cross-sectional area of the flow path located at the uppermost stream of the duct 4 and the cross-sectional area of the flow path located at the most downstream side of the duct 4 are further reduced. Therefore, the flow of the defibrated fiber material 31 supplied into the duct 4 is narrowed in the spray area where the absorbent particles 32 are sprayed by the polymer spray pipe 8.
- the flow direction of the fiber material 31 is corrected by the upstream bottom plate portion 421 in the duct 4, and the fiber material 31 is defibrated toward the spraying region where the absorbent particles 32 are sprayed. Is concentrated. Therefore, the flow of the squeezed fiber material 31 easily collides with the absorbent particles 32 dispersed in the application region, and the absorbent particles 32 are released from the fiber material 31 when released toward the most downstream side of the duct 4. The absorbent particles 32 that are further scattered along the flow and are heavier than the fiber material 31 as well as the fiber material 31 are more likely to spread throughout the duct 4.
- the pile 33 of the absorbent body 3 obtained using the fiber pile device 1 ⁇ / b> C is similar to the pile 33 of the absorbent body 3 obtained using the fiber pile device 1 ⁇ / b> A of the first embodiment.
- the absorbent particles 32 are uniformly dispersed not only in the width direction of the piled product 33 but also in the thickness direction. Accordingly, gel blocking is unlikely to occur in the absorbent body 3 during use, and the absorbent body 3 is of a high quality suitable as an absorbent body used in absorbent articles such as disposable diapers, sanitary napkins, and incontinence pads.
- the absorbent particles 32 can stably disperse the uniformly dispersed absorbent body 3 not only in the width direction but also in the thickness direction of the fiber stack 33. Can be manufactured.
- the fiber stacking apparatus 1D of the fourth embodiment corrects the flow direction of the fiber material 31 upstream of the spraying region in which the absorbent particles 32 are sprayed in the duct 4, Means for concentrating the fiber material 31 in the spraying region is provided.
- the duct 4 has a correction guide 47 for correcting the flow direction of the fiber material 31 inside.
- the correction guide 47 is located in the upstream top plate portion 411 of the top plate 41 of the duct 4 and the upstream bottom plate portion 421 of the bottom plate 42, and extends upstream of the bottom plate 42 across both side walls 43, 44 of the duct 4.
- the bottom plate portion 421 extends from the upper surface toward the downstream side. As shown in FIG.
- the correction guide 47 has a shape that is narrowed to the center in the width direction at the downstream end. That is, the correction guide 47 has a shape in which both side portions in the width direction are pushed up at the downstream end portion thereof and are narrowed down to the center portion in the width direction.
- the correction guide 47 is arranged so that the lower end of the polymer spray tube 8 or the upstream end of the partition plate 45 is positioned on the extended line of the upper surface of the central portion in the width direction at the downstream end.
- the duct 4 has a cross-sectional area of the flow path in the spraying region in which the absorbent particles 32 are sprayed, as in the fiber stacking apparatus 1A of the first embodiment.
- the cross-sectional area of the flow channel located at the uppermost stream of the duct 4 and the cross-sectional area of the flow channel located at the most downstream side of the duct 4 are formed smaller. Therefore, the flow of the defibrated fiber material 31 supplied into the duct 4 is narrowed in the spray area where the absorbent particles 32 are sprayed by the polymer spray pipe 8.
- the straightening guide 47 for correcting the flow direction of the fiber material 31 is provided inside the duct 4, the solution is directed toward the central portion in the width direction of the spraying region where the absorbent particles 32 are sprayed.
- the flow of the fibrillated fiber material 31 is concentrated. Therefore, the flow of the squeezed fiber material 31 easily collides with the absorbent particles 32 dispersed in the application region, and the absorbent particles 32 are released from the fiber material 31 when released toward the most downstream side of the duct 4.
- the absorbent particles 32 that are further scattered along the flow and are heavier than the fiber material 31 and are heavier than the fiber material 31 are more likely to spread throughout the duct 4, and the fiber material 31 and the absorbent particles 32 are more efficiently mixed. Is done.
- the pile 33 of the absorbent body 3 obtained using the fiber pile device 1 ⁇ / b> C is similar to the pile 33 of the absorbent body 3 obtained using the fiber pile device 1 ⁇ / b> A of the first embodiment.
- the absorbent particles 32 are uniformly dispersed not only in the width direction of the piled product 33 but also in the thickness direction. Accordingly, gel blocking is unlikely to occur in the absorbent body 3 during use, and the absorbent body 3 is of a high quality suitable as an absorbent body used in absorbent articles such as disposable diapers, sanitary napkins, and incontinence pads.
- the absorbent particles 32 can stably disperse the uniformly dispersed absorbent body 3 not only in the width direction but also in the thickness direction of the fiber stack 33. Can be manufactured.
- the fiber stacking apparatus 1E of the fifth embodiment corrects the flow direction of the fiber material 31 upstream of the spraying region in which the absorbent particles 32 are sprayed in the duct 4, Means for concentrating the fiber material 31 in the spraying region is provided.
- the duct 4 has an air blow device 48 that is an air discharge means for correcting the flow direction of the fiber material on the upstream side of the spraying region, The fiber material 31 is concentrated in the spray area by the air discharge means (air blow device) 48.
- the air blowing port is arranged on the upstream bottom plate part 421 of the bottom plate 42 of the duct 4, and the air blown from the blowing port is the lower end of the polymer spray pipe 8 or the upstream side of the partition plate 45. It is arranged to go to the end of the.
- the air blow device 48 is connected to an air source (not shown) by a conduit 481 as shown in FIG.
- the duct 4 has a cross-sectional area of the flow path in the spraying region in which the absorbent particles 32 are sprayed, as in the fiber stacking apparatus 1A of the first embodiment.
- the cross-sectional area of the flow channel located at the uppermost stream of the duct 4 and the cross-sectional area of the flow channel located at the most downstream side of the duct 4 are formed smaller. Therefore, the flow of the defibrated fiber material 31 supplied into the duct 4 is narrowed in the spray area where the absorbent particles 32 are sprayed by the polymer spray pipe 8.
- the air discharge means (air blow apparatus) 48 for correcting the flow direction of the fiber material 31 is provided inside the duct 4, it is directed toward the spraying area where the absorbent particles 32 are sprayed.
- the flow of the fibrillated fiber material 31 is concentrated. Therefore, the flow of the squeezed fiber material 31 easily collides with the absorbent particles 32 dispersed in the application region, and the absorbent particles 32 are released from the fiber material 31 when released toward the most downstream side of the duct 4.
- the absorbent particles 32 that are further scattered along the flow and are heavier than the fiber material 31 as well as the fiber material 31 are more likely to spread throughout the duct 4.
- the pile 33 of the absorbent body 3 obtained using the pile apparatus 1E is similar to the pile 33 of the absorbent body 3 obtained using the pile apparatus 1A of the first embodiment.
- the absorbent particles 32 are uniformly dispersed not only in the width direction of the piled product 33 but also in the thickness direction. Accordingly, gel blocking is unlikely to occur in the absorbent body 3 during use, and the absorbent body 3 is of a high quality suitable as an absorbent body used in absorbent articles such as disposable diapers, sanitary napkins, and incontinence pads.
- the absorbent particles 32 can stably disperse the uniformly dispersed absorbent body 3 not only in the width direction but also in the thickness direction of the fiber stack 33. Can be manufactured.
- the manufacturing apparatus of the absorbent body of the present invention is not limited to the fiber stacking apparatuses 1A to 1E of the first to fifth embodiments described above, and can be changed as appropriate.
- the constituent elements in the fiber stacking apparatuses 1A to 1E of the first to fifth embodiments described above can be appropriately combined and implemented within a range that does not impair the gist of the present invention.
- the upstream top plate portion 411 of the top plate 41 and the upstream bottom plate portion 421 of the bottom plate 42 in the duct 4 are directed from the upstream side toward the downstream side.
- the width is gradually narrowed, it may be narrowed in stages.
- the distance between the downstream top plate portion 412 of the top plate 41 and the downstream bottom plate portion 422 of the bottom plate 42 in the duct 4 is from the upstream side to the downstream side. Although it becomes gradually wider toward, it may be gradually increased.
- the shape of the piled product 33 to be manufactured may be flexibly changed by changing the shape of the concave portion 22 for accumulation.
- the absorbent body produced in the present invention is preferably used as an absorbent body for absorbent articles.
- the absorbent article is mainly used to absorb and retain body fluids excreted from the body such as urine and menstrual blood.
- Absorbent articles include, for example, disposable diapers, sanitary napkins, incontinence pads, panty liners, etc., but are not limited to these, and widely include articles used to absorb liquid discharged from the human body. To do.
- a rotary drum having an accumulation recess for collecting the raw material of the absorbent body including the fiber material and the absorbent particles on the outer peripheral surface; and a duct for supplying the raw material of the absorber in a scattered state toward the outer peripheral surface of the rotary drum;
- An absorbent body manufacturing apparatus comprising: In the duct, the cross-sectional area of the flow path in the spraying region in which the absorbent particles are dispersed in the duct is greater than the cross-sectional area of the flow path located in the uppermost stream of the duct and the cross-sectional area of the flow path located in the most downstream.
- the manufacturing apparatus of the absorber which is also formed small.
- the said duct is an manufacturing apparatus of the absorber as described in said ⁇ 1> which has a means which corrects the flow direction of the said fiber material, and concentrates this fiber material on this spreading area upstream from the said spreading area.
- ⁇ 4> The apparatus for manufacturing an absorbent body according to any one of ⁇ 1> to ⁇ 3>, wherein the correction guide has a shape narrowed to a central portion in the width direction at an end portion on the downstream side thereof.
- the duct has air discharge means for correcting the flow direction of the fiber material upstream from the spray area, and the fiber material is concentrated in the spray area by the air discharge means.
- the absorbent body manufacturing apparatus according to any one of the above items ⁇ 1> to ⁇ 5>, comprising an adjusting means for adjusting.
- ⁇ 7> The absorbent manufacturing apparatus according to any one of ⁇ 1> to ⁇ 6>, wherein the absorbent manufacturing apparatus is a fiber stacking apparatus.
- ⁇ 8> The absorbent manufacturing apparatus according to any one of ⁇ 1> to ⁇ 7>, wherein a plurality of the accumulation recesses are arranged at a predetermined interval in a circumferential direction (2X direction) of the rotating drum.
- the rotating drum has a plurality of mutually independent spaces inside, An intake fan is connected to the rotating drum, and the pressure of the space partitioned in the rotating drum can be adjusted by driving the intake fan,
- the fiber material include short fibers of cellulose fibers such as pulp fibers, rayon fibers, and cotton fibers, short fibers obtained by hydrophilizing synthetic fibers such as polyethylene, polypropylene, and polyethylene terephthalate.
- ⁇ 11> The absorbent production apparatus according to any one of ⁇ 1> to ⁇ 10>, wherein starch, cellulose, synthetic polymer, or superabsorbent polymer is used as the absorbent particles.
- ⁇ 12> The absorbent manufacturing apparatus according to any one of ⁇ 1> to ⁇ 11>, wherein the absorbent particles are heavier than the fiber material.
- the absorber manufacturing apparatus includes a fiber material supply unit that supplies the fiber material to the duct.
- the duct extends from the fiber material supply unit to the rotating drum, and an opening on the downstream side of the duct covers an outer peripheral surface located in the space of the rotating drum maintained at a negative pressure.
- ⁇ 14> The manufacture of the absorber according to any one of ⁇ 1> to ⁇ 13>, wherein the duct includes a top plate that forms a top surface, a bottom plate that forms a bottom surface, and both side walls that form both side surfaces. apparatus.
- the top plate of the duct consists of an upstream top plate portion located on the upstream side and a downstream top plate portion located on the downstream side
- the duct bottom plate is composed of an upstream bottom plate portion located on the upstream side and a downstream bottom plate portion located on the downstream side
- the upstream top plate portion and the upstream bottom plate portion are gradually narrowed from the upstream side toward the downstream side, and the downstream top plate portion and the downstream bottom plate portion are from the upstream side to the downstream side.
- the width is constant toward the ⁇ 1> to ⁇ 14, wherein the downstream top plate portion and the downstream bottom plate portion have the same width as that of a portion located on the most downstream side of the upstream top plate portion and the upstream bottom plate portion.
- the distance between the top plate of the duct and the bottom plate of the duct is such that the distance between the upstream top plate portion and the upstream bottom plate portion is constant, and the distance between the downstream top plate portion and the downstream bottom plate portion is The apparatus for manufacturing an absorbent body according to ⁇ 14> or ⁇ 15>, wherein the interval gradually increases from the upstream top plate portion and the upstream bottom plate portion toward the outer peripheral surface of the rotary drum.
- a polymer spray pipe for supplying the absorbent particles into the duct is disposed on a top plate of the duct.
- the said polymer dispersion tube is a manufacturing apparatus of the absorber as described in said ⁇ 17> distribute
- the duct includes a partition plate that regulates the flow direction of the absorbent particles supplied therein,
- the said polymer dispersion tube is a manufacturing apparatus of the absorber as described in said ⁇ 17> or ⁇ 18> arrange
- ⁇ 20> The absorbent body manufacturing apparatus according to ⁇ 19>, wherein the cross-sectional area of the flow path at the lower end of the polymer spray pipe or the upstream end of the partition plate is the smallest in the spray region. . ⁇ 21> Inside the duct, on the upstream side of the spray area, has a correction guide for correcting the flow direction of the fiber material, The straightening guide is located in the upstream top plate portion of the top plate of the duct and the upstream bottom plate portion of the bottom plate of the duct and across the both side walls of the duct, the upstream side plate portion of the duct bottom plate.
- the absorbent manufacturing apparatus according to any one of ⁇ 1> to ⁇ 20> which extends from the upper surface toward the downstream side. ⁇ 22>
- the fibrous material is confined to the spraying region of the absorbent particles, and the fibrous material and the absorbent particles are efficiently mixed (entangled), whereby the absorbent particles having a high specific gravity and difficult to follow the air flow are obtained. It is possible to disperse uniformly in a form that is assisted by a fiber material that has a low specific gravity and is easy to follow along the air flow in terms of shape. As a result, gel blocking is unlikely to occur, and an absorbent body that can fully utilize the absorbent performance of the absorbent body can be stably produced.
Landscapes
- Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Vascular Medicine (AREA)
- Epidemiology (AREA)
- Biomedical Technology (AREA)
- Heart & Thoracic Surgery (AREA)
- Manufacturing & Machinery (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Animal Behavior & Ethology (AREA)
- General Health & Medical Sciences (AREA)
- Public Health (AREA)
- Veterinary Medicine (AREA)
- Absorbent Articles And Supports Therefor (AREA)
Abstract
本発明の吸収体(3)の製造装置(1)は、繊維材料(31)及び吸収性粒子(32)を含む吸収体(3)の原料を集積する集積用凹部(22)を外周面(21)に有する回転ドラム(2)と、回転ドラム(2)の外周面(21)に向けて吸収体(3)の原料を飛散状態にて供給するダクト(4)とを有する。ダクト(4)は、ダクト(4)内に吸収性粒子(32)を散布する散布領域における流路の断面積が、該ダクト(4)の最上流に位置する流路の断面積及び最下流に位置する流路の断面積よりも小さく形成されている。
Description
本発明は、吸収体の製造装置に関する。
使い捨ておむつ、生理用ナプキン、失禁パッド等の吸収性物品に用いられる吸収体は、空気流に乗せてパルプ繊維及び吸収性ポリマーを含む吸収体の原料を、回転ドラムの外周面に形成された凹部に吸引して堆積させ、次いで、該凹部内に堆積した積繊体を透水性のシート材で被覆して製造されている。空気流は、散布管から供給されるポリマーとパルプを混合させ、横送り空気流に綿状にしたパルプが吸収性ポリマーを持ち乗せる。しかし、吸収性ポリマーの重量がパルプ繊維の重量に比べて非常に重く、散布管中心当りに流れるパルプ量が少なく混合性が悪いため、吸収性ポリマーの分散が不均一なものとなってしまう。
特許文献1には、回転ドラムの外周面の凹部にパルプ繊維を散布するパルプ繊維散布経路を横切るように、吸収性ポリマーを投入するポリマー投入部材を複数本配置した吸収体の製造装置が記載されている。特許文献1に記載の製造装置で製造された吸収体は、吸収性ポリマーが、吸収体の原料中に部分的に分散して配置されているので、ゲルブロッキングが起こり難く、吸収体の吸収性能が向上する。
本発明は、繊維材料及び吸収性粒子を含む吸収体の原料を集積する集積用凹部を外周面に有する回転ドラムと、該回転ドラムの外周面に向けて前記吸収体の原料を飛散状態にて供給するダクトとを有する吸収体の製造装置である。前記ダクトは、該ダクト内に前記吸収性粒子を散布する散布領域における流路の断面積が、該ダクトの最上流に位置する流路の断面積及び最下流に位置する流路の断面積よりも小さく形成されている。前記ダクトは、前記散布領域よりも上流側に、前記繊維材料の流れ方向を矯正し、該繊維材料を該散布領域に集中させる手段を有する。
特許文献1に記載の製造装置で製造された吸収体は、吸収性ポリマーが、吸収体の原料中に部分的に分散して配置されているとは言え、巨視的に見れば、吸収性ポリマーが集まった部分が、吸収体の原料中に分散している形態となっているだけである。その為、各吸収性ポリマーが集まった部分においては、やはりゲルブロッキングが生じており、吸収体の吸収性能を十分に活かすことができなかった。
本発明は、前述した従来技術が有する欠点を解消し得る吸収体の製造装置に関する。
以下に、本発明について、その好ましい実施形態に基づき図面を参照しながら説明する。
図1には、本発明の吸収体の製造装置の好ましい第1実施形態の積繊装置1Aの概略が示されている。第1実施形態の積繊装置1Aは、繊維材料31及び吸収性粒子32を含む吸収体の原料を集積する集積用凹部22を外周面21に有する回転ドラム2と、該回転ドラム2の外周面21に向けて吸収体の原料を飛散状態にて供給するダクト4とを有する。詳述すると、積繊装置1Aは、矢印R方向に回転駆動される回転ドラム2と、回転ドラム2の外周面21に吸収体の原料を供給するダクト4と、ダクト4の下流側に隣接して回転ドラム2の外周面21に沿って配されて集積用凹部22に集積された吸収体の原料の積繊物33を押さえる押さえベルト5と、回転ドラム2の下方に配されたバキュームコンベア6と、ダクト4に吸収体の原料である繊維材料31を供給する繊維材料供給部7とを備えている。更に、ダクト4には、吸収性粒子32をダクト4内に供給するポリマー散布管8が配されている。
図1には、本発明の吸収体の製造装置の好ましい第1実施形態の積繊装置1Aの概略が示されている。第1実施形態の積繊装置1Aは、繊維材料31及び吸収性粒子32を含む吸収体の原料を集積する集積用凹部22を外周面21に有する回転ドラム2と、該回転ドラム2の外周面21に向けて吸収体の原料を飛散状態にて供給するダクト4とを有する。詳述すると、積繊装置1Aは、矢印R方向に回転駆動される回転ドラム2と、回転ドラム2の外周面21に吸収体の原料を供給するダクト4と、ダクト4の下流側に隣接して回転ドラム2の外周面21に沿って配されて集積用凹部22に集積された吸収体の原料の積繊物33を押さえる押さえベルト5と、回転ドラム2の下方に配されたバキュームコンベア6と、ダクト4に吸収体の原料である繊維材料31を供給する繊維材料供給部7とを備えている。更に、ダクト4には、吸収性粒子32をダクト4内に供給するポリマー散布管8が配されている。
回転ドラム2は、図1に示すように、円筒状をなし、モータ等の原動機(不図示)からの動力を受けて、その外周面21を形成する部材が水平軸回りを矢印R方向に回転する。外周面21を形成する部材よりも内側に位置するドラム本体23は固定されていて回転しない。回転ドラム2は、図2に示すように、その外周面21に、吸収体の原料が積繊される集積用凹部22を有している。集積用凹部22は、回転ドラム2の周方向(2X方向)に所定の間隔で複数配置されている。図1中、2X方向が回転ドラム2の周方向、2Y方向が回転ドラム2の幅方向(回転ドラム2の回転軸と平行な方向)である。
回転ドラム2は、図2に示すように、内部に相互に独立した複数の空間を有しており、積繊装置1Aにおいては5つの空間A~Eを有している。空間A~Eどうしの間は、回転ドラム2の回転軸側から外周面21側に向かって設けられたプレートにより仕切られている。回転ドラム2には吸気ファン(不図示)が接続されており、該吸気ファンの駆動により、回転ドラム2内の仕切られた空間A~Eの圧力が調整できるようになっており、積繊装置1Aにおいては、空間A及びBが負圧に維持されるようになっている。回転ドラム2は、繊維材料31からなるフィルター層形成領域に対応する上流側領域(空間Aに対応する領域)の吸引力と、繊維材料31及び吸収性粒子32からなる混合層形成領域に対応する下流側領域(空間Bに対応する領域)の吸引力とを調整する調整手段を備えている。従って、上流側領域(空間Aに対応する領域)の吸引力を、下流側領域(空間Bに対応する領域)の吸引力よりも強くしたり弱くしたりすることができる。
尚、回転ドラム2の空間C、Dは、通常、空間Bよりも弱い負圧又は圧力ゼロ(大気圧)に設定され、空間Eは大気圧(圧力ゼロ)又は陽圧に設定される。集積用凹部22内の積繊物をバキュームコンベア6上に転写するまでは、該積繊物の搬送性の観点から、空間C,Dを弱い負圧にして、該積繊物を集積用凹部22内に吸引保持させておくことが好ましいが、搬送性に特に問題がなければ、転写性を考慮すると、空間C~Eは圧力ゼロが好ましい。
各集積用凹部22の底面22aは、図1に示すように、多孔性部材から構成されている。集積用凹部22が負圧に維持された空間A及びB上を通過している間、集積用凹部22の底面22aの多孔性部材の細孔が吸引孔として機能する。多孔性部材としては、この種の積繊装置に従来用いられるものを特に制限なく使用することができ、例えば、金属又は樹脂製のメッシュプレートや、金属又は樹脂製の板にエッチングやパンチングで多数の細孔を形成したもの等を用いることができる。
吸収体3の原料は、従来、生理用ナプキンやパンティライナー、使い捨ておむつ等の吸収性物品の吸収体に用いられている各種のものを特に制限なく用いることができる。吸収体の原料である繊維材料31としては、パルプ繊維、レーヨン繊維、コットン繊維とのセルロース系繊維の短繊維や、ポリエチレンやポリプロピレン、ポリエチレンテレフタレートなどの合成繊維の親水化処理した短繊維等が好ましい。これらの繊維は、1種を単独で用いても良いし2種以上を組み合わせて用いることもできる。繊維材料31は、パルプ繊維を含むものが好ましく、繊維材料31中のパルプ繊維の割合は1~100質量%であることが好ましく、より好ましくは100質量%である。吸収体の原料である吸収性粒子32としては、例えば、デンプン系、セルロース系、合成ポリマー、高吸収性ポリマー系のものが挙げられる。高吸収性ポリマーとしては、例えば、デンプン-アクリル酸(塩)グラフト共重合体、デンプン-アクリロニトリル共重合体のケン化物、ナトリウムカルボキシメチルセルロースの架橋物、アクリル酸(塩)重合体からなるもの等を用いることができる。吸収体の原料として、繊維材料31及び吸収性粒子32と共に、消臭剤や抗菌剤等を必要に応じて用いることもできる。
ダクト4は、後述する繊維材料供給部7から回転ドラム2に亘って延びており、ダクト4の下流側の開口が、負圧に維持される回転ドラム2の空間A及びBに位置する外周面21を覆っている。ダクト4は、図1に示すように、天面を形成する天板41、底面を形成する底板42、及び両側面を形成する両側壁43,44を有している。回転ドラム2の吸気ファン(不図示)の作動により、ダクト4の天板41、底板42及び両側壁43,44で囲まれた空間内には、回転ドラム2の外周面21に向けて吸収体の原料を流す空気流が生じるようになっている。
積繊装置1Aにおいて、ダクト4の天板41は、図2(a),図2(b)に示すように、上流側に位置する上流側天板部411と下流側に位置する下流側天板部412とからなる。ダクト4の底板42も同様に、上流側に位置する上流側底板部421と下流側に位置する下流側底板部422とからなる。上流側天板部411及び上流側底板部421は、上流側から下流側に向かって幅が漸次狭くなっている。下流側天板部412及び下流側底板部422は、上流側から下流側に向かって幅が一定となっている。下流側天板部412及び下流側底板部422の幅は、上流側天板部411及び上流側底板部421の最も下流側に位置する部位の幅と同じ幅である。
ダクト4の天板41と底板42との間隔は、図2(a),図2(b)に示すように、上流側天板部411と上流側底板部421との間の間隔が一定に配されており、下流側天板部412と下流側底板部422との間隔が、上流側天板部411及び上流側底板部421から回転ドラム2の外周面21に向かって漸次広くなっている。ダクト4の両側壁43,44は、以上のように構成された上流側天板部411及び下流側天板部412からなる天板41の両側縁と、上流側底板部421及び下流側底板部422からなる底板42の両側縁とに沿って配置されている。
ダクト4の天板41には、図1,図2(a)に示すように、吸収性粒子32をダクト4内に供給するポリマー散布管8が配されている。詳述すると、ポリマー散布管8は、天板41を構成する上流側天板部411の下流側の端部に配されている。そしてポリマー散布管8は、その下端が、後述する仕切り板45の上流側の端部に位置するように配されている。
上述した形状の天板41、底板42及び両側壁43,44を有するダクト4は、図2(c)に示すように、該ダクト4内に吸収性粒子32を散布する散布領域における流路の断面積が、該ダクト4の最上流に位置する流路の断面積及び該ダクト4の最下流に位置する流路の断面積よりも小さく形成されている。ここで、「散布領域」とは、吸収性粒子32を散布するポリマー散布管8が配された位置から上流側又は下流側に、ある程度の範囲を有する領域を意味する。詳述すると、ダクト4は、積繊装置1Aにおいては、図2(a)~図2(c)に示すように、ポリマー散布管8により吸収性粒子32を散布する散布領域における天板41、底板42及び両側壁43,44で囲まれた流路の断面積が、最も繊維材料供給部7寄りのダクト4の上流端部に位置する天板41、底板42及び両側壁43,44で囲まれた流路の断面積、及び最も回転ドラム2寄りのダクト4の下流端部に位置する天板41、底板42及び両側壁43,44で囲まれた流路の断面積よりも小さく形成されている。更に詳述すると、積繊装置1Aのダクト4においては、天板41の上流側天板部411及び底板42の上流側底板部421が上流側から下流側に向かって幅が漸次狭くなっているので、上流側天板部411及び上流側底板部421では、天板41、底板42及び両側壁43,44で囲まれた流路の断面積が上流側から下流側に向かって漸次小さくなっている。また、積繊装置1Aのダクト4においては、天板41の下流側天板部412と底板42の下流側底板部422との間隔が上流側から下流側に向かって漸次広くなっているので、下流側天板部412及び下流側底板部422では、天板41、底板42及び両側壁43,44で囲まれた流路の断面積が上流側から下流側に向かって漸次大きくなっている。従って、上流側天板部411の下流側の端部に配されたポリマー散布管8により吸収性粒子32を散布する散布領域における流路の断面積が、相対的に小さく形成されている。該散布領域の中でも、ポリマー散布管8の下端、或いは後述する仕切り板45の上流側の端部における前記流路の断面積が、最も小さく形成されていることが好ましい。
ダクト4は、図2(a)に示すように、積繊装置1Aにおいては、その内部に供給された吸収性粒子32の流れ方向を規制する仕切り板45が配されている。具体的には、仕切り板45は、ダクト4の両側壁43,44に亘って、上流側天板部411と下流側天板部412との境界部分から回転ドラム2に向かって延在している。更に詳述すると、仕切り板45は、回転ドラム2の空間Aと空間Bとを別けるプレートの先端に向かって延在している。ダクト4の内部に仕切り板45が配されていることにより、吸収性粒子32の流れ方向が規制され、繊維材料31のみを流す流れと、繊維材料31及び吸収性粒子32を流す流れとに分岐されるようになる。
押さえベルト5は、図1及び図2(a)に示すように、回転ドラム2のダクト4の位置よりも下流側に隣接して回転ドラム2の外周面21に沿って配されており、回転ドラム2の空間Bよりも弱い負圧又は圧力ゼロ(大気圧)に設定されている空間C,Dに位置する外周面21に沿って配されている。押さえベルト5は、無端状の通気性又は非通気性のベルトであり、ロール51及びロール52に架け渡されて、回転ドラム2の回転と共に連れ回るようになっている。尚、押さえベルト5が通気性のベルトである場合には、実質的に集積用凹部22内の原料を通過させないものであることが好ましい。押さえベルト5により、空間C~Eの圧力を大気圧に設定しても、集積用凹部22内の積繊物をバキュームコンベア6上に転写するまで、集積用凹部22内に保持できる。
バキュームコンベア6は、図1及び図2(a)に示すように、回転ドラム2の下方に配されており、回転ドラム2の弱い陽圧又は圧力ゼロ(大気圧)に設定されている空間Eに位置する外周面21に配されている。バキュームコンベア6は、駆動ロール61及び従動ロール62,62に架け渡された無端状の通気性ベルト63と、通気性ベルト63を挟んで回転ドラム2の空間Eに位置する外周面21と対向する位置に配されたバキュームボックス64とを備えている。バキュームコンベア6上には、ティッシュペーパー又は透液性の不織布等からなるコアラップシート34が導入されるようになっている。
繊維材料供給部7は、図1に示すように、ダクト4に吸収体の原料である繊維材料31を供給する部分である。繊維材料供給部7は、解繊機71を備えている。繊維材料31のシート状の原反30を解繊機71に導入することにより原反30を解繊し、解繊された繊維材料31をダクト4内の流路に供給する。
次に、前述した積繊装置1Aを用いて吸収体を連続的に製造する方法について説明する。
先ず、回転ドラム2内の空間A,B及びバキュームボックス64内を、それぞれに接続された吸気ファン(不図示)を作動させて負圧にする。空間A,B内を負圧にすることで、ダクト4内に、吸収体の原料を、回転ドラム2の外周面21に搬送する空気流(バキュームエアー)が生じる。また、回転ドラム2を回転させ、押さえベルト5を作動させる。
先ず、回転ドラム2内の空間A,B及びバキュームボックス64内を、それぞれに接続された吸気ファン(不図示)を作動させて負圧にする。空間A,B内を負圧にすることで、ダクト4内に、吸収体の原料を、回転ドラム2の外周面21に搬送する空気流(バキュームエアー)が生じる。また、回転ドラム2を回転させ、押さえベルト5を作動させる。
次いで、繊維材料供給部7の解繊機71を作動させて、繊維材料31のシート状の原反を解繊し、解繊された繊維材料31をダクト4内の流路に供給する。また、ダクト4の天板41に配されたポリマー散布管8により、ダクト4内に吸収性粒子32を供給する。
ここで、上述したように、図2(c)に示す如く、ダクト4は、該ダクト4内に吸収性粒子32を散布する散布領域における流路の断面積が、該ダクト4の最上流に位置する流路の断面積及び該ダクト4の最下流に位置する流路の断面積よりも小さく形成されている。その為、ダクト4内に供給された解繊された繊維材料31の流れが、ポリマー散布管8により吸収性粒子32を散布する散布領域において絞られる。そして、散布領域において、絞られた繊維材料31はポリマーと効率的に混合され、その後ダクト4の最下流に向かって広がる流れに乗って、絞られた繊維材料31の流れがダクト4の天板41と底板42との間の厚み方向全域に広げられる。その際、散布領域において散布された吸収性粒子32は繊維材料と効率的に混合されているため、繊維材料31の流れに沿って散らばり、繊維材料31のみならず繊維材料31よりも重量の重い吸収性粒子32がダクト4内全体に広がり易い。即ち、繊維材料31が吸収性粒子32の散布領域に絞られ、繊維材料31と吸収性粒子32が効率的に混合され(絡み合い)、それによって比重が重く空気流に沿い難い吸収性粒子32が、比重が軽く且つ形状的にも空気流に沿い易い繊維材料31にアシストされる形で均一に分散可能となっている。特に、積繊装置1Aにおいては、ダクト4の上流側天板部411及び上流側底板部421では、天板41、底板42及び両側壁43,44で囲まれた流路の断面積が上流側から下流側に向かって漸次小さくなっているので、ダクト4内に供給された解繊された繊維材料31の流れが、ポリマー散布管8により吸収性粒子32を散布する散布領域において絞られ易くなっている。また、積繊装置1Aにおいては、ダクト4の下流側天板部412及び下流側底板部422では、天板41、底板42及び両側壁43,44で囲まれた流路の断面積が上流側から下流側に向かって漸次大きくなっているので、絞られた繊維材料31の流れがダクト4の厚み方向全域に広がり易くなっており、散布された吸収性粒子32が繊維材料31の流れに沿って更に散らばり易く、繊維材料31及び吸収性粒子32がダクト4内全体に更に広がり易くなっている。また、吸収性粒子32の散布領域に繊維材料31を集中させる別の方法としては、流路を絞らずに、ダクト4の形状をストレート形状とし、ダクト4の最上流に位置する流路の断面積と散布領域の流路の断面積を同じにする方法があるが、その場合、繊維材料シート幅(原反幅)を狭くし、更にシートを解繊機へ送るスピードを速くする必要があり、繊維材料31の解繊不足が起こることが懸念される。加えて、シート幅(原反幅)を狭くすると、原反の消費スピードは速くなり、交換頻度が増えるため、生産ロスが増大するという問題もある。したがって、シート幅(原反幅)は広い方が好ましく、それゆえダクト4の最上流に位置する流路の断面積も広い方が好ましい。
散布領域において散布された吸収性粒子32が繊維材料31の流れに沿って散らばり、繊維材料31及び吸収性粒子32がダクト4内全体に広がりながら、回転ドラム2の外周面21の集積用凹部22に供給されると、集積用凹部22の厚み方向に、吸収性粒子32が、繊維材料31及び吸収性粒子32の積繊物33中に均一に分散し易くなる。
また、積繊装置1Aにおいては、図2(a)に示すように、ダクト4内に仕切り板45が配されている。その為、回転ドラム2の上流側の空間Aに対応する領域においては、繊維材料31からなるフィルター層が形成され易くなっている。また、空間Aよりも下流側の回転ドラム2の空間Bに対応する領域においては、繊維材料31及び吸収性粒子32からなる混合層が形成され易くなっている。このように、仕切り板45よりも上方向のダクト4内において、散布された吸収性粒子32が繊維材料31の流れに沿って散らばり易く、繊維材料31及び吸収性粒子32が広がり易くなっている。ここで、フィルター層とは集積用凹部22底部のメッシュ細孔に吸収性粒子32が目詰まりすることを防止するためのものである。また、回転ドラム2は、吸引力を調整する調整手段を備えているので、例えば、空間Bに対応する領域の吸引力と空間Aに対応する領域の吸引力とのバランスを調整することにより、更に、仕切り板45よりも上方向のダクト4内において、繊維材料31及び吸収性粒子32が広がり易くすることができる。より詳述すると、例えば、空間Aの吸引力が空間Bの吸引力に対して強すぎると、繊維材料31からなるフィルター層が過剰に形成され、その分、散布領域において散布された吸収性粒子32と混合する繊維材料31が少なくなるため、繊維材料31と混合しきれなかった吸収性粒子32が分散しきれず、積繊物33中に凝集して存在してしまう。そのような場合、調整手段を用いて空間Bに対応する領域の吸引力と空間Aに対応する領域の吸引力とのバランスを調整することにより、過剰なフィルター層の形成を抑え、吸収性粒子32と混合させるのに十分な量の繊維材料31を散布領域に分配でき、その結果、散布された吸収性粒子32が繊維材料31と確実に混合され、仕切り板45よりも上方向のダクト4内において、繊維材料31及び吸収性粒子32を広がり易くすることができる。
以上のようにして、集積用凹部22内に吸収体の原料を積繊させて積繊物33を得た後、図1に示すように、更に回転ドラム2を回転させ、押さえベルト5で集積用凹部22内に積繊物33を押さえつけながら、バキュームコンベア6上まで搬送する。そして、集積用凹部22内の積繊物33は、バキュームボックス64の対向位置にくると、バキュームボックス64からの吸引によって、集積用凹部22から離型し、バキュームコンベア6上に導入された、ティッシュペーパー又は透液性の不織布等からなるコアラップシート34上へと受け渡される。
その後、コアラップシート34の搬送方向に沿う両側部が折り返され、積繊物33の上下両面がコアラップシート34に被覆される。そして、コアラップシート34に被覆された状態の積繊物33は、コアラップシート34と共に、切断装置(不図示)の切断手段によって切断される。こうして、コアラップシート34に積繊物33が被覆された吸収体3が連続して得られる。
積繊装置1Aを用いて得られる吸収体3の積繊物33は、図3に示すように、吸収性粒子32が、積繊物33の幅方向のみならず、厚み方向にも、均一に分散している。従って、積繊装置1Aを用いて得られる吸収体3は、使用中にゲルブロッキングが発生し難く、使い捨ておむつ、生理用ナプキン、失禁パッド等の吸収性物品に用いられる吸収体として好適な高品質なものとなっている。このように、第1実施形態の積繊装置1Aを用いた製造方法によれば、吸収性粒子32が、積繊物33の幅方向のみならず、厚み方向にも、均一に分散した吸収体3を安定的に製造することができる。
次に、本発明の第2~第5実施形態の積繊装置1B~1Eについて説明する。第2~第5実施形態の積繊装置1B~1Eについては、第1実施形態の積繊装置1Aと異なる点について主として説明し、同様の点については同一の符号を付して説明を省略する。特に言及しない点については、第1実施形態の積繊装置1Aに関する説明が適宜適用される。また、第2~第5実施形態の積繊装置1B~1Eの効果については、第1実施形態の積繊装置1Aの効果と異なる点について説明し、特に説明しない点は、積繊装置1Aの効果と同様であり、積繊装置1Aの効果の説明が適宜適用される。
上述した第1実施形態の積繊装置1Aは、図4(a),図4(b)に示すように、繊維材料供給部7の解繊機71の特性により、ダクト4内の天板41と底板42との間の厚み方向における底板42側(下方)に、解繊された繊維材料31の量が多くなってしまう場合がある。このように下方に繊維材料31の量が多くなってしまうと、積繊装置1Aにおいては、図4(a)に示すように、回転ドラム2の上流側の空間Aに対応する領域に、繊維材料31からなるフィルター層が過剰に形成されてしまう場合がある。このような状況下で得られる吸収体3の積繊物33は、図5に示すように、繊維材料31のみからなる繊維材料31のフィルター層が厚み方向下方に過剰に形成され、散布領域において散布された吸収性粒子32と混合する繊維材料31が少なくなるため、繊維材料31と混合しきれなかった吸収性粒子32が分散しきれず、積繊物33中に凝集して存在するようになってしまう。仮に、空間Bの吸引力を空間Aの吸引力よりも強く調整しても、仕切り板45上方の散布領域において比重が重い吸収性粒子32を比重が軽い繊維材料31の流れに混合させられないため、吸収性粒子32が十分に分散できなくなる場合がある。散布領域に流れる繊維材料31の量を多くして、散布管先端付近に繊維材料31を集中させ吸収性粒子32とより混合し易くするためには、以下に説明する第2実施形態の積繊装置1B~第5実施形態の積繊装置1Eが有効である。
第2実施形態の積繊装置1Bは、図6(a),図6(b)に示すように、ダクト4内に吸収性粒子32を散布する散布領域よりも上流側に、繊維材料31の流れ方向を矯正し、該繊維材料31を該散布領域に集中させる手段を有している。具体的に、第2実施形態の積繊装置1Bにおいては、ダクト4内部に繊維材料31の流れ方向を矯正する矯正ガイド46を有している。矯正ガイド46は、ダクト4の天板41の上流側天板部411及び底板42の上流側底板部421内に位置して、ダクト4の両側壁43,44に亘って、底板42の上流側底板部421の上面から下流側に向かって延在している。そして矯正ガイド46は、その上面の延長線上に、ポリマー散布管8の下端、或いは仕切り板45の上流側の端部が位置するように配されている。積繊装置1Bはガイド46を設けているため、条件に応じてガイド位置を変更して任意のコントロールができるという利点もある。
積繊装置1Bを用いて吸収体を連続的に製造すると、第1実施形態の積繊装置1Aと同様に、ダクト4は、吸収性粒子32を散布する散布領域における流路の断面積が、該ダクト4の最上流に位置する流路の断面積及び該ダクト4の最下流に位置する流路の断面積よりも小さく形成されている。その為、ダクト4内に供給された解繊された繊維材料31の流れが、ポリマー散布管8により吸収性粒子32を散布する散布領域において絞られる。特に、積繊装置1Bにおいては、ダクト4内部に繊維材料31の流れ方向を矯正する矯正ガイド46を有しているので、吸収性粒子32を散布する散布領域に向かって解繊された繊維材料31の流れが集中している。その為、絞られた繊維材料31の流れが散布領域において散布された吸収性粒子32と衝突して混合され易くなり、ダクト4の最下流に向かって解放される際に、吸収性粒子32が繊維材料31の流れに沿って更に散らばり、繊維材料31のみならず繊維材料31よりも重量の重い吸収性粒子32がダクト4内全体に更に広がり易い。
積繊装置1Bを用いて得られる吸収体3の積繊物33は、第1実施形態の積繊装置1Aを用いて得られる吸収体3の積繊物33と同様に、図3に示す如く、吸収性粒子32が、積繊物33の幅方向のみならず、厚み方向にも、均一に分散している。従って、吸収体3には使用中にゲルブロッキングが発生し難く、使い捨ておむつ、生理用ナプキン、失禁パッド等の吸収性物品に用いられる吸収体として好適な高品質なものとなっている。このように、積繊装置1Bを用いた製造方法によれば、吸収性粒子32が、積繊物33の幅方向のみならず、厚み方向にも、均一に分散した吸収体3を安定的に製造することができる。
次に、第3実施形態の積繊装置1Cは、図7(a),図7(b)に示すように、ダクト4内に吸収性粒子32を散布する散布領域よりも上流側に、繊維材料31の流れ方向を矯正し、該繊維材料31を該散布領域に集中させる手段を有している。具体的に、第3実施形態の積繊装置1Cにおいては、ダクト4の底板42の上流側底板部421が傾斜して配されている。更に詳述すると、上流側底板部421は、その上面の延長線上に、ポリマー散布管8の下端、或いは仕切り板45の上流側の端部が位置するように配されており、上流側底板部421が繊維材料31を散布領域に集中させる手段となっている。
積繊装置1Cのように、ダクト4の上流側底板部421が傾斜して配されていると、天板41と底板42との間隔は、図7(a)に示すように、上流側天板部411と上流側底板部421との間の間隔が、散布領域に向かって、漸次狭くなり、下流側天板部412と下流側底板部422との間隔が、上流側天板部411及び上流側底板部421から回転ドラム2の外周面21に向かって漸次広くなる。上流側底板部421の下流側の端部が仕切り板45の端部より上流側に位置して、図7(b)に示すように、上流側天板部411及び上流側底板部421は、上流側から下流側に向かって幅が漸次狭くなる。その為、上流側天板部411の下流側の端部に配されたポリマー散布管8により吸収性粒子32を散布する散布領域における流路の断面積が、更に絞られている。上流側天板部411と上流側底板部421の間隔が狭くなることによって繊維材料31と吸収性粒子32が突撃してより混合し易くなる。尚、上述した第2実施形体の積繊装置1Bにおいては、下部にデッドスペースが生じるため、渦流が発生したり、パルプ粉が徐々に堆積してくる可能性があるが、第3実施形態の積繊装置1Cは、そのようなデッドスペースがないように改良されている。
積繊装置1Cを用いて吸収体を連続的に製造すると、第1実施形態の積繊装置1Aに比べ、ダクト4は、吸収性粒子32を散布する散布領域における流路の断面積が、該ダクト4の最上流に位置する流路の断面積及び該ダクト4の最下流に位置する流路の断面積よりも更に絞られている。その為、ダクト4内に供給された解繊された繊維材料31の流れが、ポリマー散布管8により吸収性粒子32を散布する散布領域において絞られる。特に、積繊装置1Cにおいては、ダクト4内部に繊維材料31の流れ方向を上流側底板部421により矯正し、吸収性粒子32を散布する散布領域に向かって解繊された繊維材料31の流れが集中している。その為、絞られた繊維材料31の流れが散布領域において散布された吸収性粒子32と衝突し易く、ダクト4の最下流に向かって解放される際に、吸収性粒子32が繊維材料31の流れに沿って更に散らばり、繊維材料31のみならず繊維材料31よりも重量の重い吸収性粒子32がダクト4内全体に更に広がり易い。
積繊装置1Cを用いて得られる吸収体3の積繊物33は、第1実施形態の積繊装置1Aを用いて得られる吸収体3の積繊物33と同様に、図3に示す如く、吸収性粒子32が、積繊物33の幅方向のみならず、厚み方向にも、均一に分散している。従って、吸収体3には使用中にゲルブロッキングが発生し難く、使い捨ておむつ、生理用ナプキン、失禁パッド等の吸収性物品に用いられる吸収体として好適な高品質なものとなっている。このように、積繊装置1Cを用いた製造方法によれば、吸収性粒子32が、積繊物33の幅方向のみならず、厚み方向にも、均一に分散した吸収体3を安定的に製造することができる。
次に、第4実施形態の積繊装置1Dは、図8に示すように、ダクト4内に吸収性粒子32を散布する散布領域よりも上流側に、繊維材料31の流れ方向を矯正し、該繊維材料31を該散布領域に集中させる手段を有している。具体的に、第4実施形態の積繊装置1Dにおいては、ダクト4内部に繊維材料31の流れ方向を矯正する矯正ガイド47を有している。矯正ガイド47は、ダクト4の天板41の上流側天板部411及び底板42の上流側底板部421内に位置して、ダクト4の両側壁43,44に亘って、底板42の上流側底板部421の上面から下流側に向かって延在している。そして矯正ガイド47は、図8に示すように、その下流側の端部において、幅方向中央部分に絞られた形状を有している。即ち、矯正ガイド47は、その下流側の端部において、幅方向両側部が迫上がり、幅方向中央部分に絞られた形状となっている。矯正ガイド47は、下流側の端部における幅方向中央部分の上面の延長線上に、ポリマー散布管8の下端、或いは仕切り板45の上流側の端部が位置するように配されている。
積繊装置1Dを用いて吸収体を連続的に製造すると、第1実施形態の積繊装置1Aと同様に、ダクト4は、吸収性粒子32を散布する散布領域における流路の断面積が、該ダクト4の最上流に位置する流路の断面積及び該ダクト4の最下流に位置する流路の断面積よりも小さく形成されている。その為、ダクト4内に供給された解繊された繊維材料31の流れが、ポリマー散布管8により吸収性粒子32を散布する散布領域において絞られる。特に、積繊装置1Dにおいては、ダクト4内部に繊維材料31の流れ方向を矯正する矯正ガイド47を有しているので、吸収性粒子32を散布する散布領域の幅方向中央部に向かって解繊された繊維材料31の流れが集中している。その為、絞られた繊維材料31の流れが散布領域において散布された吸収性粒子32と衝突し易く、ダクト4の最下流に向かって解放される際に、吸収性粒子32が繊維材料31の流れに沿って更に散らばり、繊維材料31のみならず繊維材料31よりも重量の重い吸収性粒子32がダクト4内全体に更に広がり易く、繊維材料31と吸収性粒子32とが更に効率的に混合される。
積繊装置1Cを用いて得られる吸収体3の積繊物33は、第1実施形態の積繊装置1Aを用いて得られる吸収体3の積繊物33と同様に、図3に示す如く、吸収性粒子32が、積繊物33の幅方向のみならず、厚み方向にも、均一に分散している。従って、吸収体3には使用中にゲルブロッキングが発生し難く、使い捨ておむつ、生理用ナプキン、失禁パッド等の吸収性物品に用いられる吸収体として好適な高品質なものとなっている。このように、積繊装置1Cを用いた製造方法によれば、吸収性粒子32が、積繊物33の幅方向のみならず、厚み方向にも、均一に分散した吸収体3を安定的に製造することができる。
次に、第5実施形態の積繊装置1Eは、図9に示すように、ダクト4内に吸収性粒子32を散布する散布領域よりも上流側に、繊維材料31の流れ方向を矯正し、該繊維材料31を該散布領域に集中させる手段を有している。具体的に、第5実施形態の積繊装置1Eにおいては、ダクト4が、前記散布領域よりも上流側に、繊維材料の流れ方向を矯正するエアー吐出手段であるエアーブロー装置48を有し、該エアー吐出手段(エアーブロー装置)48により繊維材料31を散布領域に集中させるようになっている。エアーブロー装置48は、エアーの吹き出し口がダクト4の底板42の上流側底板部421に配されており、吹き出し口から吹き付けられるエアーが、ポリマー散布管8の下端、或いは仕切り板45の上流側の端部に向かうように配されている。尚、エアーブロー装置48は、図9に示すように、導管481によってエアー源(不図示)に接続されている。
積繊装置1Eを用いて吸収体を連続的に製造すると、第1実施形態の積繊装置1Aと同様に、ダクト4は、吸収性粒子32を散布する散布領域における流路の断面積が、該ダクト4の最上流に位置する流路の断面積及び該ダクト4の最下流に位置する流路の断面積よりも小さく形成されている。その為、ダクト4内に供給された解繊された繊維材料31の流れが、ポリマー散布管8により吸収性粒子32を散布する散布領域において絞られる。特に、積繊装置1Eにおいては、ダクト4内部に繊維材料31の流れ方向を矯正するエアー吐出手段(エアーブロー装置)48を有しているので、吸収性粒子32を散布する散布領域に向かって解繊された繊維材料31の流れが集中している。その為、絞られた繊維材料31の流れが散布領域において散布された吸収性粒子32と衝突し易く、ダクト4の最下流に向かって解放される際に、吸収性粒子32が繊維材料31の流れに沿って更に散らばり、繊維材料31のみならず繊維材料31よりも重量の重い吸収性粒子32がダクト4内全体に更に広がり易い。
積繊装置1Eを用いて得られる吸収体3の積繊物33は、第1実施形態の積繊装置1Aを用いて得られる吸収体3の積繊物33と同様に、図3に示す如く、吸収性粒子32が、積繊物33の幅方向のみならず、厚み方向にも、均一に分散している。従って、吸収体3には使用中にゲルブロッキングが発生し難く、使い捨ておむつ、生理用ナプキン、失禁パッド等の吸収性物品に用いられる吸収体として好適な高品質なものとなっている。このように、積繊装置1Cを用いた製造方法によれば、吸収性粒子32が、積繊物33の幅方向のみならず、厚み方向にも、均一に分散した吸収体3を安定的に製造することができる。
本発明の吸収体の製造装置は、上述の第1~第5実施形態の積繊装置1A~1Eに何ら制限されるものではなく、適宜変更可能である。また、上述の第1~第5実施形態の積繊装置1A~1Eにおける各構成要件は、本発明の趣旨を損なわない範囲で、適宜組み合わせて実施できる。
例えば、第1~第5実施形態の積繊装置1A~1Eにおいては、ダクト4における天板41の上流側天板部411及び底板42の上流側底板部421が上流側から下流側に向かって幅が漸次狭くなっているが、段階的に狭くなっていてもよい。また、第1~第5実施形態の積繊装置1A~1Eにおいては、ダクト4における天板41の下流側天板部412と底板42の下流側底板部422との間隔が上流側から下流側に向かって漸次広くなっているが、段階的に広くなっていてもよい。
また、製造される積繊物33の形状は、集積用凹部22の形状等を変更することにより柔軟に変更してもよい。
本発明で製造する吸収体は、吸収性物品の吸収体として好ましく用いられる。吸収性物品は、主として尿、経血等の身体から排泄される体液を吸収保持するために用いられるものである。吸収性物品には、例えば使い捨ておむつ、生理用ナプキン、失禁パッド、パンティライナー等が包含されるが、これらに限定されるものではなく、人体から排出される液の吸収に用いられる物品を広く包含する。
上述した実施形態に関し、さらに以下の吸収体の製造装置を開示する。
<1>
繊維材料及び吸収性粒子を含む吸収体の原料を集積する集積用凹部を外周面に有する回転ドラムと、該回転ドラムの外周面に向けて前記吸収体の原料を飛散状態にて供給するダクトとを有する吸収体の製造装置であって、
前記ダクトは、該ダクト内に前記吸収性粒子を散布する散布領域における流路の断面積が、該ダクトの最上流に位置する流路の断面積及び最下流に位置する流路の断面積よりも小さく形成されている吸収体の製造装置。
繊維材料及び吸収性粒子を含む吸収体の原料を集積する集積用凹部を外周面に有する回転ドラムと、該回転ドラムの外周面に向けて前記吸収体の原料を飛散状態にて供給するダクトとを有する吸収体の製造装置であって、
前記ダクトは、該ダクト内に前記吸収性粒子を散布する散布領域における流路の断面積が、該ダクトの最上流に位置する流路の断面積及び最下流に位置する流路の断面積よりも小さく形成されている吸収体の製造装置。
<2>
前記ダクトは、前記散布領域よりも上流側に、前記繊維材料の流れ方向を矯正し、該繊維材料を該散布領域に集中させる手段を有する前記<1>に記載の吸収体の製造装置。
<3>
前記ダクトは、前記散布領域よりも上流側に、前記繊維材料の流れ方向を矯正する矯正ガイドを有し、該矯正ガイドにより該繊維材料を該散布領域に集中させる前記<1>又は<2>に記載の吸収体の製造装置。
<4>
前記矯正ガイドは、その下流側の端部において、幅方向中央部分に絞られた形状を有している前記<1>~<3>の何れか1に記載の吸収体の製造装置。
<5>
前記ダクトは、前記散布領域よりも上流側に、前記繊維材料の流れ方向を矯正するエアー吐出手段を有し、該エアー吐出手段により該繊維材料を該散布領域に集中させる前記<1>~<4>の何れか1に記載の吸収体の製造装置。
<6>
前記ダクトの内部には、供給された前記吸収性粒子の流れ方向を規制する仕切り板が配されており、
前記回転ドラムは、前記繊維材料からなるフィルター層形成領域に対応する上流側領域の吸引力と、前記繊維材料及び前記吸収性粒子からなる混合層形成領域に対応する下流側領域の吸引力とを調整する調整手段を備える前記<1>~<5>の何れか1に記載の吸収体の製造装置。
<7>
前記吸収体の製造装置は、積繊装置である前記<1>~<6>の何れか1に記載の吸収体の製造装置。
<8>
前記集積用凹部は、前記回転ドラムの周方向(2X方向)に所定の間隔で複数配置されている前記<1>~<7>の何れか1に記載の吸収体の製造装置。
<9>
前記回転ドラムは、内部に相互に独立した複数の空間を有しており、
前記回転ドラムには吸気ファンが接続されており、該吸気ファンの駆動により、該回転ドラム内の仕切られた前記空間の圧力が調整できるようになっており、
前記複数空間の圧力はそれぞれ、弱い負圧、圧力ゼロ(大気圧)、及び陽圧に設定される前記<1>~<8>の何れか1に記載の吸収体の製造装置。
<10>
前記繊維材料としては、パルプ繊維、レーヨン繊維、コットン繊維などのセルロース系繊維の短繊維や、ポリエチレンやポリプロピレン、ポリエチレンテレフタレートなどの合成繊維を親水化処理した短繊維等を、1種を単独で又は2種以上を組み合わせて用いる前記<1>~<9>の何れか1に記載の吸収体の製造装置。
<11>
前記吸収性粒子としては、デンプン系、セルロース系、合成ポリマー、高吸収性ポリマー系のものを用いる前記<1>~<10>の何れか1に記載の吸収体の製造装置。
<12>
前記吸収性粒子は前記繊維材料よりも重量が重い前記<1>~<11>の何れか1に記載の吸収体の製造装置。
前記ダクトは、前記散布領域よりも上流側に、前記繊維材料の流れ方向を矯正し、該繊維材料を該散布領域に集中させる手段を有する前記<1>に記載の吸収体の製造装置。
<3>
前記ダクトは、前記散布領域よりも上流側に、前記繊維材料の流れ方向を矯正する矯正ガイドを有し、該矯正ガイドにより該繊維材料を該散布領域に集中させる前記<1>又は<2>に記載の吸収体の製造装置。
<4>
前記矯正ガイドは、その下流側の端部において、幅方向中央部分に絞られた形状を有している前記<1>~<3>の何れか1に記載の吸収体の製造装置。
<5>
前記ダクトは、前記散布領域よりも上流側に、前記繊維材料の流れ方向を矯正するエアー吐出手段を有し、該エアー吐出手段により該繊維材料を該散布領域に集中させる前記<1>~<4>の何れか1に記載の吸収体の製造装置。
<6>
前記ダクトの内部には、供給された前記吸収性粒子の流れ方向を規制する仕切り板が配されており、
前記回転ドラムは、前記繊維材料からなるフィルター層形成領域に対応する上流側領域の吸引力と、前記繊維材料及び前記吸収性粒子からなる混合層形成領域に対応する下流側領域の吸引力とを調整する調整手段を備える前記<1>~<5>の何れか1に記載の吸収体の製造装置。
<7>
前記吸収体の製造装置は、積繊装置である前記<1>~<6>の何れか1に記載の吸収体の製造装置。
<8>
前記集積用凹部は、前記回転ドラムの周方向(2X方向)に所定の間隔で複数配置されている前記<1>~<7>の何れか1に記載の吸収体の製造装置。
<9>
前記回転ドラムは、内部に相互に独立した複数の空間を有しており、
前記回転ドラムには吸気ファンが接続されており、該吸気ファンの駆動により、該回転ドラム内の仕切られた前記空間の圧力が調整できるようになっており、
前記複数空間の圧力はそれぞれ、弱い負圧、圧力ゼロ(大気圧)、及び陽圧に設定される前記<1>~<8>の何れか1に記載の吸収体の製造装置。
<10>
前記繊維材料としては、パルプ繊維、レーヨン繊維、コットン繊維などのセルロース系繊維の短繊維や、ポリエチレンやポリプロピレン、ポリエチレンテレフタレートなどの合成繊維を親水化処理した短繊維等を、1種を単独で又は2種以上を組み合わせて用いる前記<1>~<9>の何れか1に記載の吸収体の製造装置。
<11>
前記吸収性粒子としては、デンプン系、セルロース系、合成ポリマー、高吸収性ポリマー系のものを用いる前記<1>~<10>の何れか1に記載の吸収体の製造装置。
<12>
前記吸収性粒子は前記繊維材料よりも重量が重い前記<1>~<11>の何れか1に記載の吸収体の製造装置。
<13>
前記吸収体の製造装置は、前記ダクトに前記繊維材料を供給する繊維材料供給部を備えており、
前記ダクトは、前記繊維材料供給部から前記回転ドラムに亘って延びており、該ダクトの下流側の開口が、負圧に維持される前記回転ドラムの前記空間に位置する外周面を覆っている前記<1>~<12>の何れか1に記載の吸収体の製造装置。
<14>
前記ダクトは、天面を形成する天板、底面を形成する底板、及び両側面を形成する両側壁を有している前記<1>~<13>の何れか1に記載の吸収体の製造装置。
<15>
前記ダクトの天板は、上流側に位置する上流側天板部と下流側に位置する下流側天板部とからなり、
前記ダクトの底板は、上流側に位置する上流側底板部と下流側に位置する下流側底板部とからなり、
前記上流側天板部及び前記上流側底板部は、上流側から下流側に向かって幅が漸次狭くなっており、前記下流側天板部及び前記下流側底板部は、上流側から下流側に向かって幅が一定となっており、
前記下流側天板部及び前記下流側底板部の幅は、前記上流側天板部及び前記上流側底板部の最も下流側に位置する部位の幅と同じ幅である前記<1>~<14>の何れか1に記載の吸収体の製造装置。
<16>
前記ダクトの天板と前記ダクトの底板との間隔は、上流側天板部と上流側底板部との間の間隔が一定に配されており、下流側天板部と下流側底板部との間隔が、該上流側天板部及び該上流側底板部から前記回転ドラムの外周面に向かって漸次広くなっている前記<14>又は<15>に記載の吸収体の製造装置。
<17>
前記ダクトの天板には、前記吸収性粒子を該ダクト内に供給するポリマー散布管が配されている前記<14>~<16>の何れか1に記載の吸収体の製造装置。
<18>
前記ポリマー散布管は、前記ダクトの天板を構成する上流側天板部の下流側の端部に配されている前記<17>に記載の吸収体の製造装置。
<19>
前記ダクトは、その内部に供給された前記吸収性粒子の流れ方向を規制する仕切り板を備え、
前記ポリマー散布管は、その下端が、前記仕切り板の上流側の端部に位置するように配されている前記<17>又は<18>に記載の吸収体の製造装置。
<20>
前記散布領域の中でも、前記ポリマー散布管の下端、或いは前記仕切り板の上流側の端部における前記流路の断面積が、最も小さく形成されている前記<19>に記載の吸収体の製造装置。
<21>
前記ダクト内部に、前記散布領域よりも上流側に、前記繊維材料の流れ方向を矯正する矯正ガイドを有し、
前記矯正ガイドは、前記ダクトの天板の上流側天板部及び前記ダクトの底板の上流側底板部内に位置して、該ダクトの両側壁に亘って、前記ダクトの底板の上流側底板部の上面から下流側に向かって延在している前記<1>~<20>の何れか1に記載の吸収体の製造装置。
<22>
前記吸収体は、使い捨ておむつ、生理用ナプキン、失禁パッド等の吸収性物品に用いられる吸収体である前記<1>~<21>の何れか1に記載の吸収体の製造装置。
前記吸収体の製造装置は、前記ダクトに前記繊維材料を供給する繊維材料供給部を備えており、
前記ダクトは、前記繊維材料供給部から前記回転ドラムに亘って延びており、該ダクトの下流側の開口が、負圧に維持される前記回転ドラムの前記空間に位置する外周面を覆っている前記<1>~<12>の何れか1に記載の吸収体の製造装置。
<14>
前記ダクトは、天面を形成する天板、底面を形成する底板、及び両側面を形成する両側壁を有している前記<1>~<13>の何れか1に記載の吸収体の製造装置。
<15>
前記ダクトの天板は、上流側に位置する上流側天板部と下流側に位置する下流側天板部とからなり、
前記ダクトの底板は、上流側に位置する上流側底板部と下流側に位置する下流側底板部とからなり、
前記上流側天板部及び前記上流側底板部は、上流側から下流側に向かって幅が漸次狭くなっており、前記下流側天板部及び前記下流側底板部は、上流側から下流側に向かって幅が一定となっており、
前記下流側天板部及び前記下流側底板部の幅は、前記上流側天板部及び前記上流側底板部の最も下流側に位置する部位の幅と同じ幅である前記<1>~<14>の何れか1に記載の吸収体の製造装置。
<16>
前記ダクトの天板と前記ダクトの底板との間隔は、上流側天板部と上流側底板部との間の間隔が一定に配されており、下流側天板部と下流側底板部との間隔が、該上流側天板部及び該上流側底板部から前記回転ドラムの外周面に向かって漸次広くなっている前記<14>又は<15>に記載の吸収体の製造装置。
<17>
前記ダクトの天板には、前記吸収性粒子を該ダクト内に供給するポリマー散布管が配されている前記<14>~<16>の何れか1に記載の吸収体の製造装置。
<18>
前記ポリマー散布管は、前記ダクトの天板を構成する上流側天板部の下流側の端部に配されている前記<17>に記載の吸収体の製造装置。
<19>
前記ダクトは、その内部に供給された前記吸収性粒子の流れ方向を規制する仕切り板を備え、
前記ポリマー散布管は、その下端が、前記仕切り板の上流側の端部に位置するように配されている前記<17>又は<18>に記載の吸収体の製造装置。
<20>
前記散布領域の中でも、前記ポリマー散布管の下端、或いは前記仕切り板の上流側の端部における前記流路の断面積が、最も小さく形成されている前記<19>に記載の吸収体の製造装置。
<21>
前記ダクト内部に、前記散布領域よりも上流側に、前記繊維材料の流れ方向を矯正する矯正ガイドを有し、
前記矯正ガイドは、前記ダクトの天板の上流側天板部及び前記ダクトの底板の上流側底板部内に位置して、該ダクトの両側壁に亘って、前記ダクトの底板の上流側底板部の上面から下流側に向かって延在している前記<1>~<20>の何れか1に記載の吸収体の製造装置。
<22>
前記吸収体は、使い捨ておむつ、生理用ナプキン、失禁パッド等の吸収性物品に用いられる吸収体である前記<1>~<21>の何れか1に記載の吸収体の製造装置。
<23>
前記<1>~<22>の何れか1に記載の吸収体の製造装置を用いた吸収体の製造方法。
前記<1>~<22>の何れか1に記載の吸収体の製造装置を用いた吸収体の製造方法。
本発明によれば、繊維材料が吸収性粒子の散布領域に絞られ、繊維材料と吸収性粒子が効率的に混合され(絡み合い)、それによって比重が重く空気流に沿いにくい吸収性粒子が、比重が軽く且つ形状的にも空気流に沿いやすい繊維材料にアシストされる形で均一に分散可能となる。その結果、ゲルブロッキングが生じ難く、吸収体の吸収性能を十分に活かすことができる吸収体を安定的に製造することができる。
Claims (26)
- 繊維材料及び吸収性粒子を含む吸収体の原料を集積する集積用凹部を外周面に有する回転ドラムと、該回転ドラムの外周面に向けて前記吸収体の原料を飛散状態にて供給するダクトとを有する吸収体の製造装置であって、
前記ダクトは、該ダクト内に前記吸収性粒子を散布する散布領域における流路の断面積が、該ダクトの最上流に位置する流路の断面積及び最下流に位置する流路の断面積よりも小さく形成されて、
前記ダクトは、前記散布領域よりも上流側に、前記繊維材料の流れ方向を矯正し、該繊維材料を該散布領域に集中させる手段を有する吸収体の製造装置。 - 前記吸収性粒子を前記ダクト内に供給する散布管を有し、
前記繊維材料を前記散布領域に集中させる手段は、前記散布管の下端に前記繊維材料を集中させる請求項1に記載の吸収体の製造装置。 - 前記ダクト内部に、前記散布領域よりも上流側に、前記繊維材料の流れ方向を矯正する矯正ガイドを有し、該矯正ガイドにより該繊維材料を該散布領域に集中させる請求項1又は2に記載の吸収体の製造装置。
- 前記矯正ガイドは、その下流側の端部において、幅方向中央部分に絞られた形状を有している請求項3に記載の吸収体の製造装置。
- 前記ダクトは、前記散布領域よりも上流側に、前記繊維材料の流れ方向を矯正するエアー吐出手段を有し、該エアー吐出手段により該繊維材料を該散布領域に集中させる請求項1~4の何れか1項に記載の吸収体の製造装置。
- 前記ダクトの内部には、供給された前記吸収性粒子の流れ方向を規制する仕切り板が配されており、
前記回転ドラムは、前記繊維材料からなるフィルター層形成領域に対応する上流側領域の吸引力と、前記繊維材料及び前記吸収性粒子からなる混合層形成領域に対応する下流側領域の吸引力とを調整する調整手段を備える請求項1~5の何れか1項に記載の吸収体の製造装置。 - 前記吸収体の製造装置は、積繊装置である請求項1~6の何れか1項に記載の吸収体の製造装置。
- 前記集積用凹部は、前記回転ドラムの周方向に所定の間隔で複数配置されている請求項1~7の何れか1項に記載の吸収体の製造装置。
- 前記回転ドラムは、内部に相互に独立した複数の空間を有しており、
前記回転ドラムには吸気ファンが接続されており、該吸気ファンの駆動により、該回転ドラム内の仕切られた前記空間の圧力が調整できるようになっており、
前記複数空間の圧力はそれぞれ、弱い負圧、大気圧、及び陽圧に設定される請求項1~8の何れか1項に記載の吸収体の製造装置。 - 前記繊維材料としては、セルロース系繊維の短繊維及び合成繊維を親水化処理した短繊維からなる群から選択される1種を単独で又は2種以上を組み合わせて用い、該セルロース系繊維の短繊維はパルプ繊維、レーヨン繊維及びコットン繊維のうちの少なくとも何れかを含み、該合成繊維はポリエチレン繊維、ポリプロピレン繊維及びポリエチレンテレフタレート繊維のうちの少なくとも何れかを含む請求項1~9の何れか1項に記載の吸収体の製造装置。
- 前記吸収性粒子としては、デンプン系、セルロース系、合成ポリマー及び高吸収性ポリマー系のものからなる群から選択される1種を単独で又は2種以上を組み合わせて用いる請求項1~10の何れか1項に記載の吸収体の製造装置。
- 前記吸収性粒子は前記繊維材料よりも重量が重い請求項1~11の何れか1項に記載の吸収体の製造装置。
- 前記吸収体の製造装置は、前記ダクトに前記繊維材料を供給する繊維材料供給部を備えており、
前記ダクトは、前記繊維材料供給部から前記回転ドラムに亘って延びており、該ダクトの下流側の開口が、負圧に維持される前記回転ドラムの前記空間に位置する外周面を覆っている請求項1~12の何れか1項に記載の吸収体の製造装置。 - 前記ダクトは、天面を形成する天板、底面を形成する底板、及び両側面を形成する両側壁を有している請求項1~13の何れか1項に記載の吸収体の製造装置。
- 前記ダクトの天板は、上流側に位置する上流側天板部と下流側に位置する下流側天板部とからなり、
前記ダクトの底板は、上流側に位置する上流側底板部と下流側に位置する下流側底板部とからなり、
前記上流側天板部及び前記上流側底板部は、上流側から下流側に向かって幅が漸次狭くなっており、前記下流側天板部及び前記下流側底板部は、上流側から下流側に向かって幅が一定となっており、
前記下流側天板部及び前記下流側底板部の幅は、前記上流側天板部及び前記上流側底板部の最も下流側に位置する部位の幅と同じ幅である請求項1~14の何れか1項に記載の吸収体の製造装置。 - 前記ダクトの天板と前記ダクトの底板との間隔は、上流側天板部と上流側底板部との間の間隔が一定に配されており、下流側天板部と下流側底板部との間隔が、該上流側天板部及び該上流側底板部から前記回転ドラムの外周面に向かって漸次広くなっている請求項14又は15に記載の吸収体の製造装置。
- 前記ダクトの天板には、前記吸収性粒子を該ダクト内に供給するポリマー散布管が配されている請求項14~16の何れか一項に記載の吸収体の製造装置。
- 前記ポリマー散布管は、前記ダクトの天板を構成する上流側天板部の下流側の端部に配されている請求項17に記載の吸収体の製造装置。
- 前記ダクトの底板は、上流側に位置する上流側底板部と下流側に位置する下流側底板部とからなり、該上流側底板部が傾斜して配され、
前記上流側底板部は、その上面の延長線上に、前記ポリマー散布管の下端が位置するように配されており、該上流側底板部が前記繊維材料を散布領域に集中させる手段となっている請求項17又は18に記載の吸収体の製造装置。 - 前記ダクトは、その内部に供給された前記吸収性粒子の流れ方向を規制する仕切り板を備え、
前記ポリマー散布管は、その下端が、前記仕切り板の上流側の端部に位置するように配されている請求項17~19の何れか一項に記載の吸収体の製造装置。 - 前記ダクトの底板は、上流側に位置する上流側底板部と下流側に位置する下流側底板部とからなり、該上流側底板部が傾斜して配され、
前記上流側底板部は、その上面の延長線上に、前記仕切り板の上流側の端部が位置するように配されており、該上流側底板部が前記繊維材料を散布領域に集中させる手段となっている請求項20に記載の吸収体の製造装置。 - 前記散布領域の中でも、前記ポリマー散布管の下端、或いは前記仕切り板の上流側の端部における前記流路の断面積が、最も小さく形成されている請求項20又は21に記載の吸収体の製造装置。
- 前記ダクトの底板は、上流側に位置する上流側底板部と下流側に位置する下流側底板部とからなり、
前記上流側天板部と前記上流側底板部との間の間隔が、前記散布領域に向かって、漸次狭くなっている請求項19~22の何れか1項に記載の吸収体の製造装置。 - 前記ダクト内部に、前記散布領域よりも上流側に、前記繊維材料の流れ方向を矯正する矯正ガイドを有し、
前記矯正ガイドは、前記ダクトの天板の上流側天板部及び前記ダクトの底板の上流側底板部内に位置して、該ダクトの両側壁に亘って、前記ダクトの底板の上流側底板部の上面から下流側に向かって延在している請求項14~23の何れか1項に記載の吸収体の製造装置。 - 前記吸収体は、吸収性物品に用いられる吸収体であり、該吸収性物品は使い捨ておむつ、生理用ナプキン又は失禁パッドのうちの少なくとも何れかである請求項1~24の何れか1項に記載の吸収体の製造装置。
- 請求項1~25の何れか1項に記載の吸収体の製造装置を用いた吸収体の製造方法。
Priority Applications (1)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN201480067570.0A CN105813609B (zh) | 2013-12-13 | 2014-11-19 | 吸收体的制造装置 |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2013258044A JP5953296B2 (ja) | 2013-12-13 | 2013-12-13 | 吸収体の製造装置 |
| JP2013-258044 | 2013-12-13 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2015087674A1 true WO2015087674A1 (ja) | 2015-06-18 |
Family
ID=53370988
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2014/080611 WO2015087674A1 (ja) | 2013-12-13 | 2014-11-19 | 吸収体の製造装置 |
Country Status (3)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| JP (1) | JP5953296B2 (ja) |
| CN (1) | CN105813609B (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2015087674A1 (ja) |
Families Citing this family (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP6176685B2 (ja) * | 2016-01-28 | 2017-08-09 | 大王製紙株式会社 | 吸収性物品の製造方法 |
| JP6864466B2 (ja) * | 2016-12-15 | 2021-04-28 | 花王株式会社 | 吸収体の製造装置 |
| CN108236542B (zh) | 2016-12-27 | 2023-03-10 | 大王制纸株式会社 | 吸收性物品的制造方法和吸收性物品 |
| JP6174286B1 (ja) * | 2017-05-22 | 2017-08-02 | 大王製紙株式会社 | 吸収性物品 |
| US11191675B2 (en) * | 2017-10-03 | 2021-12-07 | Kao Corporation | Method for manufacturing absorbent body and device for manufacturing absorbent body |
| US11207218B2 (en) | 2017-11-28 | 2021-12-28 | Kao Corporation | Method for producing absorber and method for producing absorbent article |
| WO2022205579A1 (zh) * | 2021-03-29 | 2022-10-06 | 上海智联精工机械有限公司 | 柔性脱模装置、芯体成型设备及形成芯体的方法 |
| CN113151982B (zh) * | 2021-04-28 | 2023-06-27 | 上海智联精工机械有限公司 | 刚性脱模成型装置 |
Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2006500155A (ja) * | 2002-09-26 | 2006-01-05 | キンバリー クラーク ワールドワイド インコーポレイテッド | 複数の重ね合わされた繊維層を持つ物品を空気形成する方法及び装置 |
| JP2006016727A (ja) * | 2004-07-01 | 2006-01-19 | Kao Corp | 積繊体製造装置 |
| JP2006115999A (ja) * | 2004-10-20 | 2006-05-11 | Daio Paper Corp | 吸収体の製造装置 |
| JP2006141615A (ja) * | 2004-11-18 | 2006-06-08 | Uni Charm Corp | 吸液性芯材成型ドラム |
| JP2009114555A (ja) * | 2007-11-01 | 2009-05-28 | Kao Corp | 堆積体の製造方法及び製造装置 |
| JP2012139381A (ja) * | 2010-12-28 | 2012-07-26 | Unicharm Corp | 体液吸収性のコアを含む体液吸収性物品、およびそのコアを製造する方法 |
| JP2012147957A (ja) * | 2011-01-19 | 2012-08-09 | Unicharm Corp | 吸収体の製造装置 |
Family Cites Families (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP4325994B2 (ja) * | 2003-07-31 | 2009-09-02 | 株式会社リブドゥコーポレーション | シート状体の製造方法および装置並びにシート状体を用いた使い捨て吸収性物品の製造方法 |
| US20060276092A1 (en) * | 2005-06-01 | 2006-12-07 | Topolkaraev Vasily A | Fibers and nonwovens with improved properties |
| ES2428871T3 (es) * | 2006-04-27 | 2013-11-12 | Sca Hygiene Products Ab | Procedimiento y disposición para la detección de una marca de sincronización que se usa en el posicionamiento sincronizado de por lo menos una banda de material esencialmente continuo |
| KR20120091391A (ko) * | 2009-12-04 | 2012-08-17 | 가오 가부시키가이샤 | 흡수체의 제조방법 및 제조장치 |
-
2013
- 2013-12-13 JP JP2013258044A patent/JP5953296B2/ja active Active
-
2014
- 2014-11-19 CN CN201480067570.0A patent/CN105813609B/zh active Active
- 2014-11-19 WO PCT/JP2014/080611 patent/WO2015087674A1/ja active Application Filing
Patent Citations (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2006500155A (ja) * | 2002-09-26 | 2006-01-05 | キンバリー クラーク ワールドワイド インコーポレイテッド | 複数の重ね合わされた繊維層を持つ物品を空気形成する方法及び装置 |
| JP2006016727A (ja) * | 2004-07-01 | 2006-01-19 | Kao Corp | 積繊体製造装置 |
| JP2006115999A (ja) * | 2004-10-20 | 2006-05-11 | Daio Paper Corp | 吸収体の製造装置 |
| JP2006141615A (ja) * | 2004-11-18 | 2006-06-08 | Uni Charm Corp | 吸液性芯材成型ドラム |
| JP2009114555A (ja) * | 2007-11-01 | 2009-05-28 | Kao Corp | 堆積体の製造方法及び製造装置 |
| JP2012139381A (ja) * | 2010-12-28 | 2012-07-26 | Unicharm Corp | 体液吸収性のコアを含む体液吸収性物品、およびそのコアを製造する方法 |
| JP2012147957A (ja) * | 2011-01-19 | 2012-08-09 | Unicharm Corp | 吸収体の製造装置 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| CN105813609B (zh) | 2019-11-08 |
| JP5953296B2 (ja) | 2016-07-20 |
| CN105813609A (zh) | 2016-07-27 |
| JP2015112393A (ja) | 2015-06-22 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5953296B2 (ja) | 吸収体の製造装置 | |
| JP5969104B2 (ja) | 吸収体の製造方法 | |
| JP7027103B2 (ja) | 吸収体の製造方法及び吸収体の製造装置 | |
| JP2017046928A (ja) | 吸収体の製造方法 | |
| JP2019063371A (ja) | 吸収体の製造方法及び吸収体の製造装置 | |
| JP6663893B2 (ja) | 吸収体の製造方法 | |
| JP6982453B2 (ja) | 吸収体の製造方法及び吸収体の製造装置 | |
| JP6386350B2 (ja) | 吸収体の製造装置 | |
| JP6774308B2 (ja) | 吸収体の製造方法及び製造装置 | |
| JP2019063368A (ja) | 吸収体の製造方法 | |
| JP2019063372A (ja) | 吸収体の製造方法 | |
| JP6699980B2 (ja) | 吸収体の製造方法及び吸収体の製造装置 | |
| JP6603830B2 (ja) | 吸収体の製造方法 | |
| CN110636821B (zh) | 吸收体和吸收性物品的制造方法、以及吸收体和吸收性物品的制造装置 | |
| WO2019106731A1 (ja) | 吸収体の製造方法及び吸収性物品の製造方法 | |
| JP7425073B2 (ja) | 吸収体の製造装置および方法 | |
| JP6647009B2 (ja) | 吸収体の製造装置及び製造方法 | |
| RU2774349C2 (ru) | Способ изготовления впитывающего элемента | |
| JP6864466B2 (ja) | 吸収体の製造装置 | |
| JP6822246B2 (ja) | 吸収体、該吸収体を備える吸収性物品、前記吸収体の製造方法および製造装置 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 14869617 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: IDP00201603963 Country of ref document: ID |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 14869617 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |