WO2014038127A1 - アキュムレータ - Google Patents
アキュムレータ Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2014038127A1 WO2014038127A1 PCT/JP2013/004700 JP2013004700W WO2014038127A1 WO 2014038127 A1 WO2014038127 A1 WO 2014038127A1 JP 2013004700 W JP2013004700 W JP 2013004700W WO 2014038127 A1 WO2014038127 A1 WO 2014038127A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- tank
- desiccant
- refrigerant
- phase refrigerant
- liquid
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F25—REFRIGERATION OR COOLING; COMBINED HEATING AND REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS; HEAT PUMP SYSTEMS; MANUFACTURE OR STORAGE OF ICE; LIQUEFACTION SOLIDIFICATION OF GASES
- F25B—REFRIGERATION MACHINES, PLANTS OR SYSTEMS; COMBINED HEATING AND REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS; HEAT PUMP SYSTEMS
- F25B43/00—Arrangements for separating or purifying gases or liquids; Arrangements for vaporising the residuum of liquid refrigerant, e.g. by heat
- F25B43/006—Accumulators
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01D—SEPARATION
- B01D53/00—Separation of gases or vapours; Recovering vapours of volatile solvents from gases; Chemical or biological purification of waste gases, e.g. engine exhaust gases, smoke, fumes, flue gases, aerosols
- B01D53/02—Separation of gases or vapours; Recovering vapours of volatile solvents from gases; Chemical or biological purification of waste gases, e.g. engine exhaust gases, smoke, fumes, flue gases, aerosols by adsorption, e.g. preparative gas chromatography
- B01D53/04—Separation of gases or vapours; Recovering vapours of volatile solvents from gases; Chemical or biological purification of waste gases, e.g. engine exhaust gases, smoke, fumes, flue gases, aerosols by adsorption, e.g. preparative gas chromatography with stationary adsorbents
- B01D53/0407—Constructional details of adsorbing systems
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B01—PHYSICAL OR CHEMICAL PROCESSES OR APPARATUS IN GENERAL
- B01D—SEPARATION
- B01D2257/00—Components to be removed
- B01D2257/80—Water
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F25—REFRIGERATION OR COOLING; COMBINED HEATING AND REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS; HEAT PUMP SYSTEMS; MANUFACTURE OR STORAGE OF ICE; LIQUEFACTION SOLIDIFICATION OF GASES
- F25B—REFRIGERATION MACHINES, PLANTS OR SYSTEMS; COMBINED HEATING AND REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS; HEAT PUMP SYSTEMS
- F25B2400/00—General features or devices for refrigeration machines, plants or systems, combined heating and refrigeration systems or heat-pump systems, i.e. not limited to a particular subgroup of F25B
- F25B2400/03—Suction accumulators with deflectors
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F25—REFRIGERATION OR COOLING; COMBINED HEATING AND REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS; HEAT PUMP SYSTEMS; MANUFACTURE OR STORAGE OF ICE; LIQUEFACTION SOLIDIFICATION OF GASES
- F25B—REFRIGERATION MACHINES, PLANTS OR SYSTEMS; COMBINED HEATING AND REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS; HEAT PUMP SYSTEMS
- F25B2500/00—Problems to be solved
- F25B2500/12—Sound
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F25—REFRIGERATION OR COOLING; COMBINED HEATING AND REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS; HEAT PUMP SYSTEMS; MANUFACTURE OR STORAGE OF ICE; LIQUEFACTION SOLIDIFICATION OF GASES
- F25B—REFRIGERATION MACHINES, PLANTS OR SYSTEMS; COMBINED HEATING AND REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS; HEAT PUMP SYSTEMS
- F25B2500/00—Problems to be solved
- F25B2500/26—Problems to be solved characterised by the startup of the refrigeration cycle
Definitions
- This disclosure relates to an accumulator used in a refrigeration cycle.
- the accumulator separates the refrigerant into a gas-phase refrigerant and a liquid-phase refrigerant, and sends the gas-phase refrigerant to the compressor constituting the refrigeration cycle.
- the accumulator includes a tank that separates the refrigerant that has flowed into the vapor phase refrigerant and the liquid phase refrigerant, and stores the liquid phase refrigerant therein.
- a desiccant is built in a tank in order to remove moisture in the refrigerant.
- the desiccant is disposed below the tank, and the entire desiccant is immersed in the liquid refrigerant.
- the desiccant is disposed above the maximum liquid surface position of the liquid refrigerant, so that the entire desiccant is not immersed in the liquid refrigerant.
- the desiccant is disposed over the entire cross section of the tank, and the desiccant is located directly below the refrigerant inlet of the gas-liquid mixed refrigerant. Further, a suction port for the gas-phase refrigerant is located above the desiccant.
- the present disclosure provides an accumulator capable of preventing both abnormal noise generation at the time of starting the compressor and suction of the liquid phase refrigerant from the suction port of the gas phase refrigerant due to the collision of the liquid phase refrigerant with the desiccant.
- the purpose is to provide.
- an accumulator includes a tank and a desiccant.
- the tank separates the refrigerant flowing into the inside into a gas phase refrigerant and a liquid phase refrigerant, stores the liquid phase refrigerant therein, and causes the gas phase refrigerant to flow out to the suction side of the compressor.
- the desiccant is placed in the tank to remove moisture in the refrigerant. Of the refrigerant flowing into the tank, the liquid-phase refrigerant falls downward from a position above the desiccant and is stored below the tank.
- the gas-phase refrigerant is sucked from the suction port located above the desiccant and flows out of the tank. Furthermore, normally, at least a part of the desiccant is exposed to the gas-phase refrigerant, and the desiccant is disposed at a position avoiding the falling path of the liquid-phase refrigerant.
- the inventors of the present application have examined measures against abnormal noise generation at the time of starting the compressor, and at the time of starting the compressor, not all of the desiccant was immersed in the liquid phase refrigerant, but a part of the desiccant. It has been found from experiments that the generation of the vibration of the tank at the start of the compressor can be prevented and the generation of abnormal noise can be prevented by setting the gas refrigerant out of the liquid phase refrigerant. Note that if the desiccant is not completely immersed in the liquid refrigerant when the compressor is started, the refrigerant will not boil starting from the desiccant, thus preventing abnormal noise when the compressor is started. it can.
- the desiccant is disposed at a position avoiding the dropping path of the liquid-phase refrigerant, it is possible to prevent the falling liquid-phase refrigerant from colliding with the desiccant, and from the gas-phase refrigerant suction port. Inhalation of liquid phase refrigerant can be prevented.
- FIG. 3 is a sectional view taken along the line III-III in FIG. 2. It is a vibration measurement result in the accumulator of 1st Embodiment and a comparative example. It is a longitudinal cross-sectional view of the accumulator in a comparative example. It is a longitudinal cross-sectional view of the accumulator in 2nd Embodiment. It is VII-VII sectional drawing of FIG. It is a longitudinal cross-sectional view of the accumulator in 3rd Embodiment.
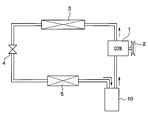
- the accumulator of this embodiment is applied to the refrigeration cycle of a vehicle air conditioner.
- the refrigeration cycle includes a compressor 1, a condenser 3, a decompression device 4, an evaporator 5, and an accumulator 10.
- Compressor 1 sucks and compresses refrigerant.
- the compressor 1 is rotationally driven by a vehicle travel engine (not shown) via a pulley 2, a belt, and the like.
- the compressor 1 can be a variable capacity compressor that can adjust the refrigerant discharge capacity by changing the discharge capacity, or a fixed capacity type compressor that adjusts the refrigerant discharge capacity by changing the operating rate of the compressor operation by switching the electromagnetic clutch. Any of the machines may be used. Further, if an electric compressor is used as the compressor 1, the refrigerant discharge capacity can be adjusted by adjusting the rotational speed of the electric motor.
- the high-pressure gas-phase refrigerant discharged from the compressor 1 flows into the condenser 3, where it is cooled and condensed by exchanging heat with the outside air.
- the liquid refrigerant condensed in the condenser 3 is then decompressed to a low pressure by the decompression device 4 to be in a mist-like gas-liquid two-phase state.
- the pressure reducing device 4 is composed of a fixed throttle such as an orifice and a nozzle, or an appropriate variable throttle.
- the low-pressure refrigerant after depressurization is evaporated in the evaporator 5 by absorbing heat from air blown from an air-conditioning blower (not shown).
- the evaporator 5 is disposed in an air conditioning case (not shown), and the cold air cooled by the evaporator 5 is adjusted in temperature by a heater core (not shown) and then blown out into the passenger compartment.
- the refrigerant that has passed through the evaporator 5 is separated into gas and liquid by the accumulator 10 and then sucked into the compressor 1.
- the accumulator 10 serves to separate the refrigerant flowing out of the evaporator 5 into a gas phase refrigerant and a liquid phase refrigerant, store the liquid phase refrigerant, and suck the gas phase refrigerant into the compressor 1.
- the accumulator 10 also serves to cause the compressor 1 to suck oil dissolved in the liquid refrigerant that accumulates on the tank bottom side.
- the accumulator 10 separates the refrigerant that has flowed into the vapor phase refrigerant and the liquid phase refrigerant, stores the liquid phase refrigerant therein, and flows the vapor phase refrigerant to the suction side of the compressor.
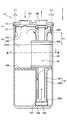
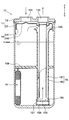
- a tank 11 is provided.
- the arrow which shows the up-down direction in FIG. 2 has shown the up-down direction of the accumulator 10 at the time of vehicle mounting.
- the tank 11 is composed of a tank body 12 and a header 13 that closes the upper end of the tank body 12.
- the tank main body 12 and the header 13 are made of metal, and the upper end portion of the tank main body 12 and the header 13 are fixed by brazing.
- the tank main body 12 has a bottomed cylindrical shape with an open upper end, and contains an umbrella-shaped member 14, a suction pipe 15, and a desiccant 16 inside. Further, the separated liquid-phase refrigerant is stored in the lower portion of the tank body 12 and the lubricating oil is stored in a state of being dissolved in the liquid-phase refrigerant.
- the header 13 is formed in a flat cylindrical shape having the same diameter as the tank body 12.
- the header 13 is formed with a circular refrigerant inlet 131 and a refrigerant outlet 132 that open in the vertical direction.
- the refrigerant inflow port 131 is connected to the evaporator 5 via a pipe so that the refrigerant heat-exchanged by the evaporator 5 can flow into the tank body 12.
- the refrigerant outlet 132 is connected to the compressor 1 via a pipe so that the gas-phase refrigerant separated in the tank body 12 can flow out to the compressor 1.
- the umbrella-shaped member 14 is a collision member with which the refrigerant introduced vertically downward from the refrigerant inlet 131 collides.
- the umbrella-shaped member 14 has a cylindrical side wall portion 141 extending in the vertical direction and an upper wall portion 142 that closes the upper end side of the side wall portion 141, and the lower end side of the side wall portion 141 is open.
- the umbrella-shaped member 14 is disposed above the inside of the tank 11 so that the upper wall 142 can be seen when the tank body 12 is viewed from the refrigerant inlet 131.
- a portion of the upper wall portion 142 that faces the refrigerant inflow port 131 protrudes upward, and a portion of the upper wall portion 142 that faces the refrigerant outlet port 132 has an opening.
- the umbrella-shaped member 14 is made of metal, and is press-fitted and fixed to the lower surface of the header 13 with the opening formed in the upper wall 142 matching the refrigerant outlet 132. Further, the outer edge of the upper wall portion 142 is located in the vicinity of the inner wall of the tank body 12.
- the accumulator 10 of the present embodiment is a collision type that separates the liquid-phase refrigerant and the gas-phase refrigerant after colliding the refrigerant introduced from the refrigerant inlet 131 with the umbrella-shaped member 14. That is, the refrigerant that has collided with the upper wall portion 142 of the umbrella-shaped member 14 diffuses in the lateral direction of the tank 11 and is guided outside the outer edge of the upper wall portion 142 of the umbrella-shaped member 14 in the lateral direction of the tank 11. Then, the liquid phase refrigerant falls from outside the outer edge of the umbrella-shaped member 14, passes through the inner wall of the tank body 12, and accumulates below the tank body 12. The gas-phase refrigerant is sucked into the suction pipe 15 from below the umbrella-like member 14 and flows out of the tank 11.
- the suction pipe 15 is a double pipe type, and has an inner pipe 151 and an outer pipe 152.
- the inner pipe 151 and the outer pipe 152 are both constituted by straight pipes and are housed in the tank body 12 in an upright posture.
- the inner pipe 151 and the outer pipe 152 are coaxial so that the inner pipe 151 is coaxial.
- the inner pipe 151 is fixed to the lower surface of the header 13.
- the inner pipe 151 is made of metal, and the upper end portion of the inner pipe 151 is press-fitted and fixed to the lower surface of the header 13 with the opening thereof and the refrigerant outlet 132 aligned.
- the outer pipe 152 is fixed to the inner pipe 151.
- the outer pipe 152 is made of plastic, and a protruding portion (thick portion) (not shown) is provided on the inner wall surface.
- the outer pipe 152 is press-fitted and fixed by inserting the inner pipe 151 inside the projecting portion.
- the outer pipe 152 is in a state in which the upper end opening 153 that forms the suction port for the gas-phase refrigerant has entered the umbrella-like member 14 while having a predetermined gap with the upper wall 142 of the umbrella-like member 14. Yes.
- the outer pipe 152 has a lower end 154 closed, and an oil return hole 155 is formed at the bottom of the lower end 154.
- the oil return hole 155 is for sucking the lubricating oil stored in the lower part of the tank body 12 by the gas phase refrigerant flowing into the inner pipe 151 and allowing the oil pipe to pass through the inner pipe 151 together with the gas phase refrigerant.
- a filter cap 156 is attached to the outside of the lower end portion 154 of the outer pipe 152.
- the filter cap 156 is formed in a bottomed cylindrical shape, and a filter 157 for removing sludge and the like contained in oil is provided on the cylindrical side wall.
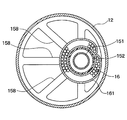
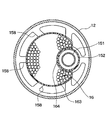
- a holding portion 158 for holding the desiccant 16 is disposed near the center of the outer pipe 152 in the vertical direction.
- the holding portion 158 is made of plastic and is integrally formed with the outer pipe 152.
- the holding portion 158 has a shape having a plurality of beams extending radially from the outer pipe 152 in the tank lateral direction.
- the holding part 158 may be separated from the outer pipe 152.
- the desiccant 16 is for removing moisture in the refrigerant, and is a particle of zeolite or the like as shown in FIG.
- the bag 161 is a desiccant container that is made of cloth such as felt and has flexibility and also functions as a filter.
- the bag 161 in which the desiccant 16 is accommodated is bound and fixed by a string-like fixing portion 162 such as a binding band in a state of being wound around the suction pipe 15.
- the desiccant 16 is located on the inner side of the outer edge of the umbrella-shaped member 14 in the lateral direction of the tank 11 and does not protrude beyond the outer edge of the umbrella-shaped member 14.
- the desiccant 16 is located in the region directly below the umbrella-like member 14 and is located at a position away from the inner wall of the tank 11 by a predetermined distance or more. This predetermined distance is an interval Y1 between the umbrella-shaped member 14 and the inner wall of the tank 11.
- the desiccant 16 is liquid when the upper end of the desiccant 16 is located below the suction port 153 and the liquid phase refrigerant is most accumulated in the tank 11 so as not to interfere with the suction port 153 of the outer pipe 152. It is installed so as to be located above the surface position (maximum liquid surface position) Lmax. That is, a part of the desiccant 16 is always exposed to the gas phase refrigerant.
- the maximum liquid level position here is the maximum liquid level position when the compressor 1 is stopped.
- the highest liquid level position is defined by the amount of refrigerant enclosed in the entire refrigeration cycle.
- the amount of refrigerant charged increases depending on the size of the refrigeration cycle, but in actual use, the amount of sealed liquid of about 1000 g is the maximum, and the liquid level at this time is the tank used by the inventor for the test.
- 11 has been confirmed by the test to be about 150 mm. Therefore, in this case, the desiccant 16 is disposed such that the upper end of the desiccant 16 is positioned between the position where the height from the bottom surface of the tank 11 is 150 mm and the suction port 153.
- the refrigerant that has flowed out of the evaporator 5 flows into the tank body 12 from the refrigerant inlet 131.
- the refrigerant flowing into the tank body 12 is gas-liquid separated by being guided to the inner wall of the tank body 12 by the umbrella-like member 14, the liquid-phase refrigerant is separated and collected at the lower part of the tank body 12, and the gas-phase refrigerant is outside.
- the pipe 152 passes through the inner pipe 151 and flows out from the refrigerant outlet 132 to the compressor 1 side.
- the desiccant 16 is disposed so that a part of the desiccant 16 is positioned above the maximum liquid level position Lmax when the compressor 1 is stopped.
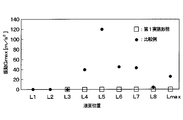
- the experimental results shown in FIG. 4 are experimental results for the accumulator 10 of this embodiment and the comparative example, and the liquid level position in the tank 11 when the compressor 1 is stopped by changing the refrigerant charging amount to the refrigeration cycle. And the vibration of the tank 11 at the time of starting the compressor 1 was measured. The operating conditions of the refrigeration cycle at this time are the same.
- shaft of FIG. 4 represents the vibration of the tank.
- the horizontal axis of FIG. 4 represents the liquid level position in the tank 11, and the liquid level position of L1 to Lmax becomes higher toward the right side of FIG. Lmax is the maximum liquid level position.
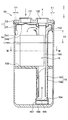
- the accumulator of the comparative example has a desiccant 16 arranged below the tank 11 as shown in FIG.
- liquid level position when the liquid level position is L3, all of the desiccant is immersed in the liquid phase refrigerant, and when the liquid level position is L4 to Lmax, a part of the desiccant is in the liquid phase. It was in a state of coming out of the refrigerant, and no vibration occurred at any liquid level position.
- the desiccant 16 is disposed at a position at least a predetermined distance from the inner wall of the tank 11. That is, the desiccant 16 is disposed at a position that avoids the dropping path of the liquid-phase refrigerant that falls from the outside of the outer edge of the umbrella-like member 14.
- the desiccant 16 is accommodated in the bag 161, and the bag 161 is fixed around the suction pipe 15 by the fixing portion 162.
- the present disclosure when the present disclosure is applied to the conventional accumulator in which the bag 161 containing the desiccant 16 is disposed below the tank 11 as in the comparative example described above, the location and fixing of the bag 161 are fixed. It is only necessary to change the method, and it is not necessary to change the design of the components of the accumulator.
- the container of the desiccant 16 is changed with respect to the first embodiment, and other configurations are the same as those in the first embodiment.
- the desiccant 16 is filled in a plastic container 163 and is fixed at a position below the suction port 153 in the outer pipe 152.
- the container 163 is disposed at a position at least a predetermined distance away from the inner wall of the tank 11 as in the first embodiment. In other words, the container 163 is disposed at a position that avoids the falling path of the liquid refrigerant that falls from the outer side of the outer edge of the umbrella-shaped member 14.
- the cross-sectional shape of the container 163 is a shape that occupies most of the cross-section of the tank 11 while avoiding the vicinity of the tank inner wall where the liquid-phase refrigerant falls.
- the desiccant container has flexibility
- the desiccant container is deformed by the weight of the desiccant, and the desiccant is biased.
- the container 163 of the present embodiment is made of plastic and is relatively hard, and thus can maintain a predetermined shape.
- the container 163 does not deform
- inclination of the desiccant 16 with which the inside of the container 163 was filled can be prevented.
- a container formed of a material other than plastic may be used as the container 163 as long as the predetermined shape can be maintained.
- the container 163 has a press-fit portion 164 having a shape along the outer peripheral surface of the suction pipe 15, and the suction pipe 15 is press-fitted and fixed to the press-fit portion 164.
- the press-fit portion 164 has a C shape corresponding to a range excluding a part of the suction pipe 15 in the circumferential direction.
- the suction pipe 15 is press-fitted into the press-fit part 164 by pressing the press-fit part 164 against the suction pipe 15 from the lateral direction.
- the plastic container 163 is press-fitted and fixed to the suction pipe 15, it is only necessary to newly prepare the container 163 having the shape described above.
- the components of the accumulator other than the container 163 The same conventional one can be used.
- the method of fixing the container 163 by press-fitting facilitates the step of assembling the desiccant 16 to the suction pipe 15 than the method of fixing the bag 161 by tying it.
- the press-fit portion 164 has a C shape, but may have an O shape.
- the container 163 is press-fitted and fixed to the suction pipe 15 by inserting the suction pipe 15 into the O-shaped press-fit portion 164.
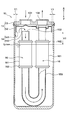
- the suction pipe is changed with respect to the first embodiment. That is, in this embodiment, as shown in FIG. 8, a U-shaped tube 159 is used as a suction pipe.
- the desiccant 16 is accommodated in a bag 161 as in the first embodiment, and this bag 161 is fixed by a fixing portion 162 in a state of being wound around a U-shaped tube 159.
- the present disclosure can be applied.
- a plastic container 163 may be used as in the second embodiment.
- the present disclosure is not limited to the above-described embodiment, and can be appropriately changed without departing from the gist of the present disclosure as illustrated below.
- the string-like fixing portion 162 is wound around the entire circumferential direction of the bag 161.
- 161 may be fixed.
- the ends of the bags 161 wound around the suction pipe 15 are sewn together with a fixing portion such as a thread, or the ring-shaped fixing portion is passed through an opening provided at the end of the bag 161, so that the bag 161 is It may be fixed to the suction pipe 15.
- the container 163 of the desiccant 16 is press-fitted and fixed to the suction pipe 15, but may be fixed by a fixing method other than press-fitting.
- the container 163 of the desiccant 16 and the outer pipe 152 of the suction pipe 15 may be integrally formed.
- the lid of the container 163 is a separate body.
- the umbrella-shaped member 14 has the shape shown in FIG. 2, but may be changed to another shape.
- the umbrella-shaped member 14 may be omitted.
- the desiccant 16 may be disposed avoiding the position directly below the refrigerant inlet 131.
- a part of the desiccant 16 is located above the maximum liquid level position Lmax when the compressor 1 is stopped. However, the desiccant 16 is entirely located. Also good.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Analytical Chemistry (AREA)
- Power Engineering (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Thermal Sciences (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- General Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Oil, Petroleum & Natural Gas (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Air-Conditioning For Vehicles (AREA)
Abstract
アキュムレータはタンクと乾燥剤を備えている。タンクは、内部に流入した冷媒を気相冷媒と液相冷媒とに分離し、液相冷媒を内部に貯留するとともに、気相冷媒を圧縮機の吸入側に流出させる。乾燥剤はタンク内に配置され、冷媒中の水分を除去する。タンク内に流入した冷媒のうち液相冷媒は、乾燥剤よりも上方の位置から下方に向けて落下して、タンク内の下方に貯留される。タンク内に流入した冷媒のうち気相冷媒は、乾燥剤よりも上方に位置する吸込口から吸い込まれて、タンクの外部に流出する。さらに、通常、乾燥剤の少なくとも一部が気相冷媒にさらされており、かつ、液相冷媒の落下経路を避けた位置に乾燥剤が配置されている。
Description
本出願は、当該開示内容が参照によって本出願に組み込まれた、2012年9月7日に出願された日本特許出願2012-197222を基にしている。
本開示は、冷凍サイクルに用いられるアキュムレータに関するものである。
アキュムレータは、冷媒を気相冷媒と液相冷媒とに分離して、冷凍サイクルを構成する圧縮機に気相冷媒を送るものである。アキュムレータは、内部に流入した冷媒を気相冷媒と液相冷媒とに分離し、液相冷媒を内部に貯留するタンクを備える。このアキュムレータとしては、特許文献1、2に開示の通り、冷媒中の水分を除去するために、タンクに乾燥剤が内蔵されたものがある。
特許文献1に開示のアキュムレータは、乾燥剤がタンクの下方に配置されており、乾燥剤の全部が液相冷媒に浸かっている。
特許文献2に開示のアキュムレータは、乾燥剤が液相冷媒の最大液面位置よりも上方に配置されており、乾燥剤の全部が液相冷媒に浸からないようになっている。このアキュムレータでは、乾燥剤がタンクの横断面全域にわたって配置されており、気液混合冷媒の冷媒流入口の真下に乾燥剤が位置している。さらに、乾燥剤の上方に気相冷媒の吸込口が位置している。
本願発明者らの検討によると、特許文献1のように、乾燥剤の全部が液相冷媒に浸かっている場合、冷凍サイクルを構成する圧縮機の起動時に、タンクから異音が発生するというおそれが生じることがわかった。これは、圧縮機の起動時にタンク内が減圧することにより、乾燥剤を起点とした急激な冷媒沸騰が起こり、これが原因でタンク内に圧力が発生してタンクが振動するためである。
一方、特許文献2のように、乾燥剤の全部が液相冷媒に浸からない場合であれば、上述の圧縮機起動時の異音発生のおそれは生じない。しかし、この場合、タンク内に流入した液相冷媒の落下経路に乾燥剤が位置するため、タンク内で落下する液相冷媒が乾燥剤に衝突して跳ね返り、気相冷媒の吸込口から液相冷媒が吸い込まれ、圧縮機が液相冷媒を吸入するおそれがある。
本開示は上記点に鑑みて、圧縮機の起動時の異音発生と、液相冷媒の乾燥剤への衝突による気相冷媒の吸込口からの液相冷媒の吸い込みとの両方を防止できるアキュムレータを提供することを目的とする。
上記目的を達成するため、本開示におけるアキュムレータはタンクと乾燥剤を備えている。タンクは、内部に流入した冷媒を気相冷媒と液相冷媒とに分離し、液相冷媒を内部に貯留するとともに、気相冷媒を圧縮機の吸入側に流出させる。乾燥剤はタンク内に配置され、冷媒中の水分を除去する。
タンク内に流入した冷媒のうち液相冷媒は、乾燥剤よりも上方の位置から下方に向けて落下して、タンク内の下方に貯留される。タンク内に流入した冷媒のうち気相冷媒は、乾燥剤よりも上方に位置する吸込口から吸い込まれて、タンクの外部に流出する。さらに、通常、乾燥剤の少なくとも一部が気相冷媒にさらされており、かつ、液相冷媒の落下経路を避けた位置に乾燥剤が配置されている。
タンク内に流入した冷媒のうち液相冷媒は、乾燥剤よりも上方の位置から下方に向けて落下して、タンク内の下方に貯留される。タンク内に流入した冷媒のうち気相冷媒は、乾燥剤よりも上方に位置する吸込口から吸い込まれて、タンクの外部に流出する。さらに、通常、乾燥剤の少なくとも一部が気相冷媒にさらされており、かつ、液相冷媒の落下経路を避けた位置に乾燥剤が配置されている。
本願発明者らが、圧縮機の起動時の異音発生についての対策を検討したところ、圧縮機の起動時に、乾燥剤の全部が液相冷媒に浸かった状態でなく、乾燥剤の一部が液相冷媒から出て気相冷媒中に位置する状態とすることで、圧縮機の起動時におけるタンクの振動の発生を防止でき、異音の発生を防止できることを、実験から見出した。なお、圧縮機の起動時に、乾燥剤の全部が液相冷媒に浸からない状態とすれば、乾燥剤を起点とする冷媒沸騰が生じないので、圧縮機の起動時の異音の発生を防止できる。
したがって、本開示によれば、圧縮機の起動時に、乾燥剤の一部または全部が液相冷媒に浸からないので、圧縮機の起動時の異音発生を防止できる。
さらに、本開示によれば、液相冷媒の落下経路を避けた位置に乾燥剤を配置しているので、落下する液相冷媒の乾燥剤への衝突を防止でき、気相冷媒の吸込口からの液相冷媒の吸い込みを防止できる。
以下、本開示の実施形態について図に基づいて説明する。なお、以下の各実施形態相互において、互いに同一もしくは均等である部分には、同一符号を付して説明を行う。
(第1実施形態)
本実施形態のアキュムレータは、車両用空調装置の冷凍サイクルに適用されるものである。図1に示すように、冷凍サイクルは、圧縮機1と、凝縮器3と、減圧装置4と、蒸発器5と、アキュムレータ10とを備えている。
(第1実施形態)
本実施形態のアキュムレータは、車両用空調装置の冷凍サイクルに適用されるものである。図1に示すように、冷凍サイクルは、圧縮機1と、凝縮器3と、減圧装置4と、蒸発器5と、アキュムレータ10とを備えている。
圧縮機1は、冷媒を吸入圧縮する。圧縮機1は、プーリー2、ベルト等を介して図示しない車両走行用エンジンにより回転駆動される。
この圧縮機1としては、吐出容量の変化により冷媒吐出能力を調整できる可変容量型圧縮機、あるいは電磁クラッチの断続により圧縮機作動の稼働率を変化させて冷媒吐出能力を調整する固定容量型圧縮機のいずれを使用してもよい。また、圧縮機1として電動圧縮機を使用すれば、電動モータの回転数調整により冷媒吐出能力を調整できる。
圧縮機1から吐出された高圧の気相冷媒は凝縮器3に流入し、ここで外気と熱交換して冷却され、凝縮される。凝縮器3で凝縮した液冷媒は次に減圧装置4にて低圧に減圧されて霧状の気液二相状態となる。この減圧装置4はオリフィス、ノズルのような固定絞り、あるいは適宜の可変絞りからなる。
減圧後の低圧冷媒は蒸発器5において、図示しない空調送風機の送風する空気から吸熱して蒸発する。蒸発器5は図示しない空調ケース内に配置され、蒸発器5で冷却された冷風は周知のごとく図示しないヒータコア部で温度調整された後に車室内へ吹き出す。蒸発器5を通過した冷媒はアキュムレータ10にて気液分離された後に圧縮機1に吸入される。
アキュムレータ10は、蒸発器5から流出の冷媒を気相冷媒と液相冷媒とに分離し、液相冷媒を貯えて気相冷媒を圧縮機1に吸入させる役割を果たす。また、アキュムレータ10は、タンク底部側に溜まる液冷媒中に溶け込んでいるオイルを圧縮機1に吸入させる役割をも果たす。
図2に示すように、アキュムレータ10は、内部に流入した冷媒を気相冷媒と液相冷媒とに分離し、液相冷媒を内部に貯留するとともに、気相冷媒を圧縮機の吸入側に流出させるタンク11を備えている。なお、図2中の上下方向を示す矢印は、車両搭載時におけるアキュムレータ10の上下方向を示している。
タンク11は、タンク本体12と、このタンク本体12の上端部を塞ぐヘッダー13とから構成されている。タンク本体12とヘッダー13は金属製であり、タンク本体12の上端部とヘッダー13とがろう付け固定されている。
タンク本体12は上端部が開放された有底円筒形状とされており、内部に傘状部材14、吸込配管15および乾燥剤16が収容されている。また、タンク本体12下部には、分離された液相冷媒が貯留されるとともに、潤滑用オイルがこの液相冷媒中に溶け込んだ状態で貯留されるようになっている。
ヘッダー13は、タンク本体12と同一径を有する扁平円柱形状に形成されている。ヘッダー13には、上下方向に開口する円形の冷媒流入口131と冷媒流出口132とが形成されている。冷媒流入口131は、配管を介して蒸発器5に連なっており、蒸発器5で熱交換された冷媒をタンク本体12内に流入し得るようになっている。冷媒流出口132は、配管を介して圧縮機1に連なっており、タンク本体12内で分離された気相冷媒を圧縮機1に流出させ得るようになっている。
傘状部材14は、冷媒流入口131から鉛直下方に導入した冷媒が衝突する衝突部材である。傘状部材14は、上下方向に延びる円筒状の側壁部141と、側壁部141の上端側を閉塞する上壁部142とを有し、側壁部141の下端側が開口している形状である。
傘状部材14は、タンク11の内部上方であって、冷媒流入口131からタンク本体12を見たときに、上壁部142が見えるように配置されている。上壁部142のうち冷媒流入口131に対向する部位は上方に向けて隆起しており、上壁部142のうち冷媒流出口132に対向する部位は開口部が形成されている。傘状部材14は、金属製であり、上壁部142に形成された開口部を冷媒流出口132に一致させた状態でヘッダー13の下面に圧入固定されている。また、上壁部142の外縁はタンク本体12の内壁近傍に位置している。
本実施形態のアキュムレータ10は、冷媒流入口131から導入した冷媒を傘状部材14に衝突させた後に、液相冷媒と気相冷媒とを分離する衝突式のものである。すなわち、傘状部材14の上壁部142に衝突した冷媒は、タンク11の横方向に拡散し、タンク11の横方向における傘状部材14の上壁部142の外縁よりも外側に導かれる。そして、液相冷媒は、傘状部材14の外縁よりも外側から落下し、タンク本体12の内壁をつたって、タンク本体12の下方に溜まる。気相冷媒は、傘状部材14の下側から吸込配管15に吸い込まれ、タンク11の外部に流出する。
吸込配管15は、本実施形態では、2重管式のものが用いられており、内側配管151と外側配管152とを有している。内側配管151と外側配管152とは、ともに直線管で構成され、直立姿勢でタンク本体12内に収められており、内側配管151と外側配管152とが同軸状となるようにして内側配管151が外側配管152内に配置されている。
内側配管151は、ヘッダー13の下面に固定されている。具体的には、内側配管151は、金属製であり、内側配管151の上端部が、その開口と冷媒流出口132とを一致させた状態でヘッダー13の下面に圧入固定されている。
外側配管152は、内側配管151に固定されている。具体的には、外側配管152は、プラスチック製であり、内壁面に図示しない突出部(厚肉部)が設けられている。この突出部の内側に内側配管151が挿入されることにより、外側配管152が圧入固定されている。
外側配管152は、気相冷媒の吸込口をなす上端開口部153が、傘状部材14の上壁部142との間に所定の隙間を持ちながら傘状部材14内に進入した状態とされている。
また、外側配管152は、下端部154が閉塞しており、下端部154の底にオイル戻し穴155が形成されている。このオイル戻し穴155は、タンク本体12下部に貯留されている潤滑用オイルを、内側配管151に流入する気相冷媒によって吸い上げて気相冷媒とともに内側配管151を通過させるためのものである。
また、外側配管152の下端部154の外側には、フィルタキャップ156が取り付けられている。フィルタキャップ156は、有底円筒形状に形成されたものであり、円筒状の側壁にオイルに含まれるスラッジ等を除去するフィルタ157が設けられている。
また、外側配管152の上下方向の中央付近に、乾燥剤16を保持するための保持部158が配置されている。この保持部158は、プラスチック製であり、外側配管152と一体成形されたものである。保持部158は、図3に示すように、外側配管152からタンク横方向に放射状に延びる複数本の梁を有する形状である。なお、保持部158を外側配管152と別体としても良い。
乾燥剤16は、冷媒中の水分を除去するものであり、図3に示すように、ゼオライト等の粒子であり、袋161に収容した状態で用いられる。この袋161は、フェルト等の布製であり、柔軟性を有するとともにフィルタとしても機能する乾燥剤容器である。
乾燥剤16が収容された袋161は、吸込配管15の周囲に巻き付けられた状態で、結束バンドのようなひも状の固定部162で結びつけられて固定されている。
このとき、乾燥剤16は、タンク11の横方向において、傘状部材14の外縁よりも内側に位置しており、傘状部材14の外縁よりも外側にはみ出していない。換言すると、乾燥剤16は、傘状部材14の真下の領域内に位置しており、タンク11の内壁から所定距離以上離れた場所に位置している。この所定距離は、傘状部材14とタンク11の内壁との間隔Y1である。
乾燥剤16は、外側配管152の吸込口153に干渉しないように、乾燥剤16の上端が吸込口153よりも下に位置し、かつ、タンク11に液相冷媒が最も多く溜まったときの液面位置(最高液面位置)Lmaxよりも上に位置するように設置されている。つまり、常に、乾燥剤16の一部が気相冷媒にさらされている。
ここでいう最高液面位置は、圧縮機1の停止時における最高液面位置である。最高液面位置は、冷凍サイクル全体に封入される封入冷媒量によって規定される。この冷媒封入量は、冷凍サイクルの大きさに因って増えるが、実使用上では1000g程度の封入量が最大であり、このときの液面高さは、本願発明者が試験に用いたタンク11においては、約150mmであることが試験より確かめられている。したがって、この場合、乾燥剤16は、タンク11の底面からの高さが150mmの位置と吸入口153との間に乾燥剤16の上端が位置するように配置される。
上記した構成のアキュムレータ10では、蒸発器5を流出した冷媒が、冷媒流入口131からタンク本体12内部に流入する。タンク本体12内部に流入した冷媒は、傘状部材14によってタンク本体12の内壁に誘導されることによって気液分離され、液相冷媒は、タンク本体12下部に分離集合し、気相冷媒は外側配管152から内側配管151を通過して冷媒流出口132から圧縮機1側に流出する。
気相冷媒が外側配管152を流出して内側配管151に流入する際には、タンク本体12下部に貯留されている潤滑用オイルが、フィルタ157およびオイル戻し穴155を介して吸い上げられ、気相冷媒とともに内側配管151を通って冷媒流出口132から圧縮機1側に流出する。
次に、本実施形態の効果について説明する。
(1)本実施形態では、圧縮機1の停止時における最高液面位置Lmaxよりも上方に乾燥剤16の一部が位置するように、乾燥剤16を配置している。これにより、本実施形態によれば、図4に示す実験結果の通り、圧縮機1の起動時におけるタンク11の振動の発生を防止でき、異音の発生を防止できる。
図4に示す実験結果は、本実施形態と比較例のアキュムレータ10についての実験結果であり、冷凍サイクルへの冷媒充填量を変えることにより、圧縮機1の停止時におけるタンク11内の液面位置を変えて、圧縮機1の起動時におけるタンク11の振動を測定した結果である。このときの冷凍サイクルの運転条件は同じである。なお、図4の縦軸はタンクの振動を表している。図4の横軸はタンク11内の液面位置を表しており、L1~Lmaxは図4の右側ほど液面位置が高くなる。Lmaxは最高液面位置である。
比較例のアキュムレータは、図5に示すように、乾燥剤16をタンク11の下方に配置したものである。
図4に示すように、比較例では、液面位置がL1~L3のとき、乾燥剤の一部が液相冷媒から出ている状態となり、振動が発生しなかった。しかし、液面位置がL4~Lmaxのとき、乾燥剤の全部が液相冷媒に浸かった状態となり、振動が発生した。
これに対して、本実施形態では、液面位置がL3のとき、乾燥剤の全部が液相冷媒に浸かった状態となり、液面位置がL4~Lmaxのとき、乾燥剤の一部が液相冷媒から出ている状態となり、どの液面位置であっても、振動が発生しなかった。
(2)本実施形態では、タンク11の内壁から少なくとも所定距離離れた位置に乾燥剤16を配置している。すなわち、傘状部材14の外縁よりも外側から落下する液相冷媒の落下経路を避けた位置に乾燥剤16を配置している。
これにより、傘状部材14の外縁よりも外側から落下する液相冷媒の乾燥剤16への衝突を防止でき、外側配管152の吸込口153からの液相冷媒の吸い込みを防止できる。
(3)本実施形態では、乾燥剤16を袋161に収容し、この袋161を吸込配管15の周囲に巻き付けた状態で、固定部162により固定している。
これによれば、上述の比較例のように、乾燥剤16が収容された袋161をタンク11の下方に配置した従来のアキュムレータに対して本開示を適用する場合、袋161の配置場所および固定方法を変更するだけで良く、アキュムレータの構成部品の設計変更が不要となる。
なお、乾燥剤16を袋161以外の容器に収容した従来のアキュムレータに対して本開示を適用する場合においても、袋161を用いる点を除き、アキュムレータの構成部品の設計変更が不要となる。
(第2実施形態)
本実施形態は、第1実施形態に対して乾燥剤16の容器を変更したものであり、その他の構成については、第1実施形態と同様である。
(第2実施形態)
本実施形態は、第1実施形態に対して乾燥剤16の容器を変更したものであり、その他の構成については、第1実施形態と同様である。
図6、7に示すように、乾燥剤16は、プラスチック製の容器163に充填されて、外側配管152のうち吸込口153よりも下方の位置に固定されている。
この容器163は、第1実施形態と同様に、タンク11の内壁から少なくとも所定距離離れた位置に配置されている。すなわち、この容器163は、傘状部材14の外縁よりも外側から落下する液相冷媒の落下経路を避けた位置に配置されている。
また、この容器163の横断面形状は、図7に示すように、液相冷媒が落下するタンク内壁の近傍を避けつつ、タンク11の横断面の大部分を占める形状である。容器163をこのような断面形状とすることで、容器の容積を拡大でき、乾燥剤16の使用量を増大できる。
ここで、乾燥剤容器が柔軟性を有する場合、乾燥剤の重さによって乾燥剤容器が変形し、乾燥剤の偏りが生じてしまう。
これに対して、本実施形態の容器163は、プラスチック製であり比較的硬いため、所定形状の維持が可能である。これにより、本実施形態によれば、容器163が、乾燥剤16の重さによって変形しないので、容器163の内部に充填された乾燥剤16の偏りを防止できる。なお、所定形状の維持が可能であれば、容器163をプラスチック以外の材料で構成された容器を用いても良い。
また、図7に示すように、容器163は、吸込配管15の外周面に沿った形状の圧入部164を有し、この圧入部164に吸込配管15が圧入されて固定されている。圧入部164は、吸込配管15の周方向の一部を除く範囲に対応したC字形状である。吸込配管15に対して横方向から圧入部164を押し当てることで、圧入部164に吸込配管15が圧入される。
このように、プラスチック製の容器163が吸込配管15に圧入固定される構成を採用することで、上記した形状の容器163を新規に用意するだけで良く、容器163以外のアキュムレータの構成部品については、従来と同じものを用いることができる。また、容器163を圧入で固定する方法の方が、袋161を縛って固定する方法よりも、乾燥剤16の吸込配管15への組み付け工程が容易となる。
なお、圧入部164は、C字形状であったが、O字形状であっても良い。この場合、O字形状の圧入部164に吸込配管15を挿入することにより、容器163が吸込配管15に圧入固定される。
(第3実施形態)
本実施形態は、第1実施形態に対して吸込配管を変更したものである。すなわち、本実施形態では、図8に示すように、吸込配管としてU字管159が用いられている。乾燥剤16は、第1実施形態と同様に、袋161に収容されており、この袋161は、U字管159に巻き付けられた状態で固定部162により固定されている。このように、吸込配管としてU字管159が用いられている場合においても、本開示の適用が可能である。
(第3実施形態)
本実施形態は、第1実施形態に対して吸込配管を変更したものである。すなわち、本実施形態では、図8に示すように、吸込配管としてU字管159が用いられている。乾燥剤16は、第1実施形態と同様に、袋161に収容されており、この袋161は、U字管159に巻き付けられた状態で固定部162により固定されている。このように、吸込配管としてU字管159が用いられている場合においても、本開示の適用が可能である。
なお、乾燥剤16の容器として、第2実施形態と同様に、プラスチック製の容器163を用いても良い。
(他の実施形態)
本開示は上記した実施形態に限定されるものではなく、以下の例示のように、本開示の趣旨を逸脱しない範囲で適宜変更が可能である。
(他の実施形態)
本開示は上記した実施形態に限定されるものではなく、以下の例示のように、本開示の趣旨を逸脱しない範囲で適宜変更が可能である。
(1)第1実施形態では、乾燥剤16入りの袋161を吸込配管15に巻き付けた状態で、袋161の周方向全域にひも状の固定部162を巻き付けたが、他の固定部により袋161を固定しても良い。例えば、吸込配管15に巻き付けた袋161の端部同士を糸等の固定部で縫いつけたり、袋161の端部に設けた開口部にリング状の固定部を通過させたりして、袋161を吸込配管15に固定しても良い。
(2)第2実施形態では、乾燥剤16の容器163を吸込配管15に圧入固定したが、圧入以外の固定方法で固定しても良い。例えば、乾燥剤16の容器163と吸込配管15の外側配管152とを一体成形しても良い。この場合、容器163の蓋を別体とする。
(3)第2実施形態では、乾燥剤16の容器163を図6、7に示す形状としたが、タンク11の横方向において、傘状部材14の外縁よりも内側に乾燥剤16を配置できれば、他の形状としても良い。
(4)上記各実施形態では、傘状部材14を図2に示す形状としたが、他の形状に変更しても良い。
(5)上記各実施形態において、傘状部材14を省略しても良い。この場合、冷媒流入口131から液相冷媒が落下するため、冷媒流入口131が液相冷媒の落下開始位置となる。そこで、この場合では、冷媒流入口131の直下の位置を避けて、乾燥剤16を配置すれば良い。
(6)上記各実施形態では、圧縮機1の停止時における最高液面位置Lmaxよりも上方に、乾燥剤16の一部が位置していたが、乾燥剤16の全部が位置するようにしても良い。
なお、上記各実施形態において、実施形態を構成する要素は、特に必須であると明示した場合および原理的に明らかに必須であると考えられる場合等を除き、必ずしも必須のものではないことは言うまでもない。また、上記各実施形態は、互いに無関係なものではなく、組み合わせが明らかに不可な場合を除き、適宜組み合わせが可能である。
Claims (5)
- 内部に流入した冷媒を気相冷媒と液相冷媒とに分離し、液相冷媒を内部に貯留するとともに、気相冷媒を圧縮機(1)の吸入側に流出させるタンク(11)と、
前記タンク内に配置され、冷媒中の水分を除去する乾燥剤(16)とを備え、
前記タンク内に流入した冷媒のうち液相冷媒は、前記乾燥剤よりも上方の位置から下方に向けて落下して、前記タンク内の下方に貯留され、
前記タンク内に流入した冷媒のうち気相冷媒は、前記乾燥剤よりも上方に位置する吸込口(153)から吸い込まれて、前記タンクの外部に流出し、
通常、前記乾燥剤の少なくとも一部が気相冷媒にさらされており、かつ、液相冷媒の落下経路を避けた位置に前記乾燥剤が配置されているアキュムレータ。 - 前記タンク内に配置され、前記吸込口を有する吸込配管(15、159)を備え、
前記乾燥剤は、柔軟性を有する乾燥剤容器(161)に収容されており、
前記乾燥剤容器は、前記吸込口よりも下方の位置に、前記吸込配管に巻き付けられた状態で、固定部(162)により固定されている請求項1に記載のアキュムレータ。 - 前記タンク内に配置され、前記吸込口を有する吸込配管(15、159)を備え、
前記乾燥剤は、所定形状の維持が可能な乾燥剤容器(163)に充填されて、前記吸込配管のうち前記吸込口よりも下方の位置に固定されている請求項1に記載のアキュムレータ。 - 前記乾燥剤容器は、前記吸込配管の外周面に沿った形状の圧入部(164)を有し、前記圧入部に前記吸込配管が圧入されて固定されている請求項3に記載のアキュムレータ。
- 前記タンクの内部上方であって、前記タンクの冷媒流入口(131)の真下に配置された傘状部材(14)を備え、
前記タンクの内部に流入した冷媒は、前記傘状部材に衝突して、前記タンクの横方向における前記傘状部材の外縁よりも外側に導かれた後、液相冷媒と気相冷媒とに分離し、
前記乾燥剤は、前記タンクの横方向における前記傘状部材の外縁よりも内側の位置に配置されている請求項1ないし4のいずれか1つに記載のアキュムレータ。
Priority Applications (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| US14/425,292 US9636622B2 (en) | 2012-09-07 | 2013-08-02 | Accumulator |
| EP13835488.1A EP2896914B1 (en) | 2012-09-07 | 2013-08-02 | Accumulator |
| CN201380046352.4A CN104603555B (zh) | 2012-09-07 | 2013-08-02 | 储液器 |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2012-197222 | 2012-09-07 | ||
| JP2012197222A JP5849909B2 (ja) | 2012-09-07 | 2012-09-07 | アキュムレータ |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2014038127A1 true WO2014038127A1 (ja) | 2014-03-13 |
Family
ID=50236765
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2013/004700 WO2014038127A1 (ja) | 2012-09-07 | 2013-08-02 | アキュムレータ |
Country Status (5)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US9636622B2 (ja) |
| EP (1) | EP2896914B1 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JP5849909B2 (ja) |
| CN (1) | CN104603555B (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2014038127A1 (ja) |
Cited By (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20170016658A1 (en) * | 2015-07-17 | 2017-01-19 | Fujikoki Corporation | Accumulator |
| US20170016657A1 (en) * | 2015-07-14 | 2017-01-19 | Fujikoki Corporation | Accumulator |
| CN107763908A (zh) * | 2016-08-17 | 2018-03-06 | 株式会社不二工机 | 储液器 |
Families Citing this family (19)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP6068909B2 (ja) * | 2012-10-02 | 2017-01-25 | 株式会社不二工機 | アキュムレータ |
| JP6155005B2 (ja) * | 2012-10-12 | 2017-06-28 | 株式会社不二工機 | アキュムレータ |
| JP6068938B2 (ja) * | 2012-11-08 | 2017-01-25 | 株式会社不二工機 | アキュムレータ |
| JP6385222B2 (ja) * | 2014-09-22 | 2018-09-05 | 株式会社不二工機 | アキュムレータ |
| DE102015110574B4 (de) * | 2015-07-01 | 2018-12-13 | Halla Visteon Climate Control Corporation | Vorrichtung zum Abscheiden und Sammeln flüssigen Kältemittels eines Kältemittelkreislaufs |
| JP6661345B2 (ja) * | 2015-07-14 | 2020-03-11 | 株式会社不二工機 | アキュームレータ |
| JP6514981B2 (ja) * | 2015-07-17 | 2019-05-15 | 株式会社不二工機 | アキュームレータ |
| ES2612306B1 (es) * | 2015-11-12 | 2018-03-07 | Carlos BAÑO ANTON | Máquina productora de fluido en estado líquido |
| JP6747857B2 (ja) * | 2016-04-28 | 2020-08-26 | サンデン・オートモーティブクライメイトシステム株式会社 | アキュムレータ及びそれを備えた車両用空気調和装置 |
| JP6500839B2 (ja) * | 2016-05-19 | 2019-04-17 | 株式会社デンソー | アキュムレータおよび冷凍サイクル |
| JP6341958B2 (ja) * | 2016-08-17 | 2018-06-13 | 株式会社不二工機 | アキュームレータ |
| JP2018077016A (ja) * | 2016-11-10 | 2018-05-17 | サンデン・オートモーティブクライメイトシステム株式会社 | アキュムレータ |
| JP2018077015A (ja) * | 2016-11-10 | 2018-05-17 | サンデン・オートモーティブクライメイトシステム株式会社 | アキュムレータ |
| KR20180118397A (ko) | 2017-04-21 | 2018-10-31 | 엘지전자 주식회사 | 어큐뮬레이터 |
| CN108759196A (zh) * | 2018-06-13 | 2018-11-06 | 苏州逸新和电子有限公司 | 一种过滤性能好的储液器 |
| CN112013581A (zh) * | 2019-05-30 | 2020-12-01 | 株式会社不二工机 | 储液器及其组装方法 |
| KR20200137837A (ko) * | 2019-05-31 | 2020-12-09 | 현대자동차주식회사 | 차량용 기액 분리장치 |
| JP7475061B2 (ja) | 2021-08-24 | 2024-04-26 | 株式会社不二工機 | アキュームレータ |
| JPWO2023026885A1 (ja) | 2021-08-24 | 2023-03-02 |
Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH11278045A (ja) * | 1997-09-24 | 1999-10-12 | Denso Corp | 冷凍サイクル装置 |
| JP2001082814A (ja) | 1999-09-09 | 2001-03-30 | Denso Corp | 冷凍サイクル装置およびそれに用いるアキュムレータ |
| JP2007232335A (ja) * | 2006-03-03 | 2007-09-13 | Denso Corp | 冷媒容器とその製造方法 |
| JP2009180469A (ja) | 2008-01-31 | 2009-08-13 | Calsonic Kansei Corp | 超臨界冷凍サイクル用アキュムレータ |
Family Cites Families (15)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US4331001A (en) * | 1981-05-11 | 1982-05-25 | General Motors Corporation | Accumulator-dehydrator assembly for an air conditioning system |
| US4509340A (en) | 1983-11-10 | 1985-04-09 | Sealed Power Corporation | Accumulator-dehydrator assembly for an air conditioning system |
| US4768355A (en) | 1987-01-27 | 1988-09-06 | Ford Motor Company | Accumulator with refrigerant processing cartridge for automotive air conditioning system |
| JPH02290480A (ja) * | 1989-04-28 | 1990-11-30 | Nissan Motor Co Ltd | 車両用リキッドタンク |
| US5282370A (en) * | 1992-05-07 | 1994-02-01 | Fayette Tubular Technology Corporation | Air-conditioning system accumulator and method of making same |
| US5289697A (en) * | 1992-10-28 | 1994-03-01 | Eaton Corporation | Refrigerant receiver/drier |
| US5814136A (en) * | 1997-04-15 | 1998-09-29 | Stanhope Products Company | Desiccant container |
| DE69834512T2 (de) * | 1997-07-31 | 2007-04-26 | Denso Corp., Kariya | Kühlkreisvorrichtung |
| US6196019B1 (en) | 1997-12-16 | 2001-03-06 | Showa Aluminum Corporation | Accumulator |
| US6330810B1 (en) * | 2000-08-11 | 2001-12-18 | Showa Denko K.K. | Condensing apparatus for use in a refrigeration cycle receiver-dryer used for said condensing apparatus |
| US6389842B1 (en) * | 2001-01-23 | 2002-05-21 | Delphi Technologies, Inc. | Accumulator-dehydrator assembly with anti-bump expansion chamber “J”-tube |
| US6481241B1 (en) * | 2001-08-29 | 2002-11-19 | Automotive Fluid Systems, Inc. | Accumulator desiccant bag and method of assembling |
| JP3870744B2 (ja) * | 2001-10-12 | 2007-01-24 | 株式会社デンソー | アキュムレータ |
| JP2008304097A (ja) | 2007-06-06 | 2008-12-18 | Calsonic Kansei Corp | アキュムレータ |
| JP5760993B2 (ja) | 2011-11-29 | 2015-08-12 | 株式会社デンソー | アキュムレータ |
-
2012
- 2012-09-07 JP JP2012197222A patent/JP5849909B2/ja active Active
-
2013
- 2013-08-02 CN CN201380046352.4A patent/CN104603555B/zh active Active
- 2013-08-02 WO PCT/JP2013/004700 patent/WO2014038127A1/ja active Application Filing
- 2013-08-02 US US14/425,292 patent/US9636622B2/en active Active
- 2013-08-02 EP EP13835488.1A patent/EP2896914B1/en active Active
Patent Citations (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPH11278045A (ja) * | 1997-09-24 | 1999-10-12 | Denso Corp | 冷凍サイクル装置 |
| JP2001082814A (ja) | 1999-09-09 | 2001-03-30 | Denso Corp | 冷凍サイクル装置およびそれに用いるアキュムレータ |
| JP2007232335A (ja) * | 2006-03-03 | 2007-09-13 | Denso Corp | 冷媒容器とその製造方法 |
| JP2009180469A (ja) | 2008-01-31 | 2009-08-13 | Calsonic Kansei Corp | 超臨界冷凍サイクル用アキュムレータ |
Cited By (6)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| US20170016657A1 (en) * | 2015-07-14 | 2017-01-19 | Fujikoki Corporation | Accumulator |
| US10190809B2 (en) * | 2015-07-14 | 2019-01-29 | Fujikoki Corporation | Accumulator |
| US20170016658A1 (en) * | 2015-07-17 | 2017-01-19 | Fujikoki Corporation | Accumulator |
| US10215461B2 (en) * | 2015-07-17 | 2019-02-26 | Fujikoki Corporation | Accumulator |
| CN107763908A (zh) * | 2016-08-17 | 2018-03-06 | 株式会社不二工机 | 储液器 |
| CN107763908B (zh) * | 2016-08-17 | 2021-04-09 | 株式会社不二工机 | 储液器 |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| EP2896914B1 (en) | 2021-04-21 |
| CN104603555B (zh) | 2016-08-24 |
| JP2014052139A (ja) | 2014-03-20 |
| EP2896914A1 (en) | 2015-07-22 |
| US20150231549A1 (en) | 2015-08-20 |
| US9636622B2 (en) | 2017-05-02 |
| CN104603555A (zh) | 2015-05-06 |
| JP5849909B2 (ja) | 2016-02-03 |
| EP2896914A4 (en) | 2016-07-06 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| JP5849909B2 (ja) | アキュムレータ | |
| EP2676085B1 (en) | Liquid vapor phase separation apparatus | |
| EP1568955B1 (en) | Oil separator and cooling-cycle apparatus using the same | |
| US9587862B2 (en) | Condenser | |
| US10215461B2 (en) | Accumulator | |
| WO2017199707A1 (ja) | アキュムレータおよび冷凍サイクル | |
| US20170016657A1 (en) | Accumulator | |
| JP2015172469A (ja) | 気液分離器 | |
| JP2003090643A (ja) | 冷凍サイクル装置 | |
| US6389842B1 (en) | Accumulator-dehydrator assembly with anti-bump expansion chamber “J”-tube | |
| JP2016061543A (ja) | アキュムレータ | |
| US7249467B2 (en) | Gas-liquid separator for refrigerant cycle system | |
| CN107763907B (zh) | 储液器 | |
| US20210180843A1 (en) | Receiver/drier for a refrigerant fluid circuit equipping a vehicle, in particular a motor vehicle | |
| CN109964090B (zh) | 储液器 | |
| JP2017198408A (ja) | アキュムレータ | |
| WO2017146054A1 (ja) | アキュムレータ | |
| JP2020094778A (ja) | アキュムレータ | |
| WO2018088127A1 (ja) | アキュムレータ | |
| KR101655469B1 (ko) | 자동차 공기조화장치용 리시버 드라이어 | |
| WO2023026885A1 (ja) | アキュームレータ | |
| EP3293472B1 (en) | Accumulator | |
| EP1831619A2 (en) | A cooling device |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 13835488 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 2013835488 Country of ref document: EP |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 14425292 Country of ref document: US |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |