WO2017199707A1 - アキュムレータおよび冷凍サイクル - Google Patents
アキュムレータおよび冷凍サイクル Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2017199707A1 WO2017199707A1 PCT/JP2017/016319 JP2017016319W WO2017199707A1 WO 2017199707 A1 WO2017199707 A1 WO 2017199707A1 JP 2017016319 W JP2017016319 W JP 2017016319W WO 2017199707 A1 WO2017199707 A1 WO 2017199707A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- desiccant
- refrigerant
- pipe
- accumulator
- phase refrigerant
- Prior art date
Links
Images
Classifications
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F25—REFRIGERATION OR COOLING; COMBINED HEATING AND REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS; HEAT PUMP SYSTEMS; MANUFACTURE OR STORAGE OF ICE; LIQUEFACTION SOLIDIFICATION OF GASES
- F25B—REFRIGERATION MACHINES, PLANTS OR SYSTEMS; COMBINED HEATING AND REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS; HEAT PUMP SYSTEMS
- F25B43/00—Arrangements for separating or purifying gases or liquids; Arrangements for vaporising the residuum of liquid refrigerant, e.g. by heat
- F25B43/006—Accumulators
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F25—REFRIGERATION OR COOLING; COMBINED HEATING AND REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS; HEAT PUMP SYSTEMS; MANUFACTURE OR STORAGE OF ICE; LIQUEFACTION SOLIDIFICATION OF GASES
- F25B—REFRIGERATION MACHINES, PLANTS OR SYSTEMS; COMBINED HEATING AND REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS; HEAT PUMP SYSTEMS
- F25B40/00—Subcoolers, desuperheaters or superheaters
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F25—REFRIGERATION OR COOLING; COMBINED HEATING AND REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS; HEAT PUMP SYSTEMS; MANUFACTURE OR STORAGE OF ICE; LIQUEFACTION SOLIDIFICATION OF GASES
- F25B—REFRIGERATION MACHINES, PLANTS OR SYSTEMS; COMBINED HEATING AND REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS; HEAT PUMP SYSTEMS
- F25B43/00—Arrangements for separating or purifying gases or liquids; Arrangements for vaporising the residuum of liquid refrigerant, e.g. by heat
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F25—REFRIGERATION OR COOLING; COMBINED HEATING AND REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS; HEAT PUMP SYSTEMS; MANUFACTURE OR STORAGE OF ICE; LIQUEFACTION SOLIDIFICATION OF GASES
- F25B—REFRIGERATION MACHINES, PLANTS OR SYSTEMS; COMBINED HEATING AND REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS; HEAT PUMP SYSTEMS
- F25B43/00—Arrangements for separating or purifying gases or liquids; Arrangements for vaporising the residuum of liquid refrigerant, e.g. by heat
- F25B43/003—Filters
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F25—REFRIGERATION OR COOLING; COMBINED HEATING AND REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS; HEAT PUMP SYSTEMS; MANUFACTURE OR STORAGE OF ICE; LIQUEFACTION SOLIDIFICATION OF GASES
- F25B—REFRIGERATION MACHINES, PLANTS OR SYSTEMS; COMBINED HEATING AND REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS; HEAT PUMP SYSTEMS
- F25B43/00—Arrangements for separating or purifying gases or liquids; Arrangements for vaporising the residuum of liquid refrigerant, e.g. by heat
- F25B43/02—Arrangements for separating or purifying gases or liquids; Arrangements for vaporising the residuum of liquid refrigerant, e.g. by heat for separating lubricants from the refrigerant
-
- F—MECHANICAL ENGINEERING; LIGHTING; HEATING; WEAPONS; BLASTING
- F25—REFRIGERATION OR COOLING; COMBINED HEATING AND REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS; HEAT PUMP SYSTEMS; MANUFACTURE OR STORAGE OF ICE; LIQUEFACTION SOLIDIFICATION OF GASES
- F25B—REFRIGERATION MACHINES, PLANTS OR SYSTEMS; COMBINED HEATING AND REFRIGERATION SYSTEMS; HEAT PUMP SYSTEMS
- F25B2400/00—General features or devices for refrigeration machines, plants or systems, combined heating and refrigeration systems or heat-pump systems, i.e. not limited to a particular subgroup of F25B
- F25B2400/05—Compression system with heat exchange between particular parts of the system
- F25B2400/051—Compression system with heat exchange between particular parts of the system between the accumulator and another part of the cycle
Definitions
- the disclosure in this specification relates to accumulators and refrigeration cycles.
- Patent Document 1 discloses one form of an accumulator that is used in a refrigeration cycle and contains a desiccant.
- a part of the desiccant is located above the highest liquid level position of the liquid refrigerant in the tank when the compressor is stopped, and the desiccant is located at a position avoiding the liquid refrigerant drop path. Is arranged. With this configuration, the accumulator of Patent Document 1 can reduce the level of noise because the desiccant is not completely immersed in the liquid refrigerant when the compressor is started.
- Patent Document 1 can reduce the level of abnormal noise, but there is room for improvement because abnormal noise can occur due to boiling of the refrigerant from some of the desiccant present in the liquid.
- the desiccant is installed in the upper part of the tank so as not to be immersed in the liquid, there is a risk that a useless volume that does not function as a space capable of storing liquid in the tank increases.
- An object of the present disclosure is to provide an accumulator and a refrigeration cycle that can suppress sudden boiling from a desiccant and an increase in tank size.
- the accumulator includes a tank, a desiccant, and a suction pipe.
- the tank separates the refrigerant flowing into the inside into a gas phase refrigerant and a liquid phase refrigerant, the liquid phase refrigerant is stored inside, and the gas phase refrigerant flows out to the suction side of the compressor.
- the desiccant is contained in a container to remove moisture in the refrigerant.
- the suction pipe is installed inside the tank and has a suction port for sucking the gas-phase refrigerant.
- the desiccant is installed inside the suction pipe.
- the desiccant installed inside the suction pipe is discharged from the liquid phase refrigerant. You will be exposed to the gas. As a result, the pressure inside the suction pipe decreases and the temperature also decreases, so that even a desiccant with a large heat capacity can be quickly cooled. In addition, even if a slight amount of liquid refrigerant remains in the desiccant, it is possible to prevent the liquid refrigerant from becoming overheated, so that it is possible to realize a state in which rapid boiling is unlikely to occur.
- the desiccant is installed inside the suction pipe that can also be used as a liquid storage space where the refrigerant stagnates when the compressor is stopped, it can be configured so that the wasteful volume that does not function as a liquid storage space in the tank does not increase. According to the above, it is possible to provide an accumulator that can suppress sudden boiling from the desiccant and enlargement of the tank.
- FIG. 3 is a cross-sectional view of the III-III cross section of FIG. 2 as viewed in the direction of the arrow. It is a figure which shows the structure of the desiccant of this indication. It is sectional drawing which shows the structure of the accumulator which concerns on 2nd Embodiment of this indication.
- the disclosed accumulator can be applied to a vehicle or stationary refrigeration cycle.
- the refrigeration cycle can be used for air conditioning for air-conditioning a predetermined target space such as a passenger compartment, a living room, or a test room.
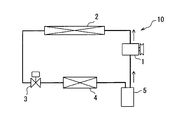
- the refrigeration cycle 10 for air conditioning will be described.
- the refrigeration cycle 10 includes at least a compressor 1, a condenser 2, a pressure reducing valve 3, an evaporator 4, and an accumulator 5, and a circuit in which these are annularly connected by piping.
- the compressor 1 is a refrigerant driving device that is driven by a driving source such as an engine or a motor to suck in refrigerant and pump it.
- the condenser 2 is an example of a heat exchanger for heat radiation because it releases the heat of the refrigerant to the outside.
- the pressure reducing valve 3 depressurizes the liquid refrigerant condensed in the condenser 2 to form a mist-like gas-liquid two-phase state.
- the pressure reducing valve 3 is a pressure reducing device that can be constituted by a fixed throttle such as an orifice and a nozzle, and a variable throttle that can change the passage opening.
- the refrigerant depressurized by the pressure reducing valve 3 evaporates by absorbing heat from the air blown by the air conditioning blower in the evaporator 4.
- the evaporator 4 is an example of a cooling heat exchanger that is installed in a case of an air conditioner and absorbs heat from outside into a refrigerant.
- the air cooled by the evaporator 4 is adjusted to the target temperature and blown out to the air-conditioning target space.
- the accumulator 5 functions to gas-liquid separate the refrigerant that has flowed out of the evaporator 4 and return the gas-phase refrigerant separated from the liquid-phase refrigerant to the compressor 1. Further, the accumulator 5 also functions to cause the compressor 1 to suck oil dissolved in the liquid refrigerant accumulated at the bottom of the tank 50.
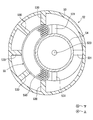
- FIG. 2 is a cross-sectional view showing the configuration of the accumulator 5.
- the accumulator 5 separates the refrigerant that has flowed into the vapor phase refrigerant and the liquid phase refrigerant, stores the liquid phase refrigerant therein, and flows the vapor phase refrigerant to the suction side of the compressor.
- a tank 50 is provided.
- the arrow direction shown in FIGS. 2 and 3 indicates the direction in a state where the accumulator 5 is mounted on the refrigeration cycle 10.
- the tank 50 includes a tank main body 502 having a space capable of storing liquid phase refrigerant therein, and a lid 501 fixed so as to cover the upper end opening of the tank main body 502. .
- the tank body 502 and the lid 501 are made of a metal material.
- the upper end of the tank body 502 and the lid 501 are integrated by welding.
- the tank main body 502 has a bottomed cylindrical shape with an open upper end, and accommodates the umbrella-shaped member 51, the suction pipe 52, and the desiccant 55 therein.
- the separated liquid phase refrigerant is stored, and the lubricating oil is stored in a state dissolved in the liquid phase refrigerant.
- the suction pipe 52 includes an outer pipe 53 having a suction port 532 for sucking a gas-phase refrigerant, and an inner pipe 54 installed inside the outer pipe 53.
- the lid portion 501 has a flat cylindrical shape having the same outer diameter as the tank main body portion 502.
- the lid portion 501 is provided with a circular refrigerant inlet port 501a and a refrigerant outlet port 501b that respectively penetrate in the vertical direction.
- the refrigerant inlet 501a is connected to the evaporator 4 through a connected pipe.
- the refrigerant heat-exchanged by the evaporator 4 flows into the tank main body 502 through the piping and the refrigerant inlet 501a.
- the refrigerant outlet 501b is connected to the compressor 1 through a connected pipe.
- the gas-phase refrigerant separated inside the tank body 502 is sucked into the compressor 1 through the refrigerant outlet 501b and piping.
- the umbrella-like member 51 is a member with which the refrigerant that has flowed vertically downward into the tank 50 from the refrigerant inlet 501a collides.
- the umbrella-shaped member 51 has a cylindrical side wall part 511 extending in the vertical direction and a top wall part 510 that closes the upper end side of the side wall part 511, and has a shape in which the lower end side of the side wall part 511 is opened.
- the umbrella-shaped member 51 is installed inside the tank 50 so that the top wall portion 510 exists vertically below the refrigerant inlet 501a.
- a side wall portion 511 extending downward from the outer peripheral edge of the top wall portion 510 is located in the vicinity of the inner wall surface of the tank main body portion 502.
- the umbrella-like member 51 is made of a metal material.
- the inner pipe 54 in the suction pipe 52 which is a double pipe is press-fitted and fixed to a lower end 501c protruding downward with the upper end 541 fitted inside the refrigerant outlet 501b.
- a portion facing the refrigerant inlet 501a is raised upward, and an opening is formed at a portion facing the refrigerant outlet 501b.
- the peripheral edge forming the opening is located at a position corresponding to the refrigerant outlet 501b, and the large-diameter portion 542 and the lid portion 501 of the inner pipe 54 press-fitted and fixed to the lower end portion 501c of the lid portion 501.
- the large-diameter portion 542 is a portion having an outer diameter dimension larger than that of the upper end portion 541 at a position below the upper end of the inner tube 54 by a predetermined length. Thus, it can be formed by being deformed so as to increase its diameter.
- the large diameter portion 542 can be formed by resin molding using a mold.
- the accumulator 5 separates the liquid-phase refrigerant and the gas-phase refrigerant after colliding the refrigerant introduced from the refrigerant inlet 501a with the umbrella-shaped member 51.
- the refrigerant that has collided with the top wall portion 510 of the umbrella-shaped member 51 diffuses in the lateral direction inside the tank 50 and is guided outside the outer edge of the top wall portion 510 of the umbrella-shaped member 51 in the lateral direction of the tank 50.
- the liquid phase refrigerant falls along the side wall portion 511 from the outer side of the outer edge of the umbrella-shaped member 51, and accumulates below the tank main body portion 502 through the inner wall of the tank main body portion 502.
- the gas-phase refrigerant is sucked into the suction pipe 52 from the lower side of the umbrella-like member 51 through the suction port 532 at the upper end of the outer pipe 53.
- Both the inner tube 54 and the outer tube 53 are formed by straight tubes whose axes are straight, and are accommodated in the tank body 502 in an upright posture.
- the inner tube 54 and the outer tube 53 are installed so that their axes are coaxial.
- the inner tube 54 is formed of a metal material including aluminum, for example.
- the outer tube 53 is made of a material having higher heat insulation than the inner tube 54.
- the outer tube 53 is formed of a resin material having excellent heat insulation.
- the outer tube 53 is fixed to the inner tube 54.
- a plurality of projecting portions 531 projecting inward from the inner wall surface are provided at the lower portion of the outer tube 53.
- the lower portion of the inner tube 54 is press-fitted inside the plurality of protrusions 531, so that the outer tube 53 is integrated with the inner tube 54 with the plurality of protrusions 531 supporting the outer peripheral surface of the lower portion of the inner tube 54. It is fixed to.
- the upper end opening that forms the gas-phase refrigerant suction port 532 enters a position above the lower end of the umbrella-shaped member 51 with a predetermined gap between the upper-end opening 510 and the top wall 510 of the umbrella-shaped member 51. It is installed to be in a state.
- the outer pipe 53 is formed with an oil return hole 533 penetrating the lower end portion. Therefore, the lower end portion of the outer tube 53 is closed except for the oil return hole 533.
- the oil return hole 533 is located at a position facing the lower end opening 540 of the inner tube 54.
- the oil return hole 533 sucks the lubricating oil stored in the lower part of the tank main body 502 by the gas-phase refrigerant flowing into the inner pipe 54 and passes it through the inner pipe 54 together with the gas-phase refrigerant so as to be outside the accumulator 5. It is an oil return passage for sending to.
- the oil return hole 533 contributes to ensuring the amount of oil circulation in the refrigeration cycle 10.
- the outer pipe 53 has a plurality of supports that protrude inward on the inner surface and have a vertical length that contacts most of the vertical length of the desiccant 55.
- a part 530 is provided.
- the support portion 530 is a portion integrally formed with the outer tube 53 and is formed of a resin material.
- the support part 530 is configured by a rib having a rectangular cross section.
- the plurality of support portions 530 are arranged at intervals in the circumferential direction inside the outer tube 53.
- the desiccant 55 is installed in a state of being interposed between the plurality of support portions 530 and the outer surface of the inner tube 54.
- the desiccant 55 is pressed against the inner tube 54 side by the circumferential length in which the plurality of support portions 530 are arranged in the circumferential direction. A sufficient area can be secured.
- the desiccant 55 is installed in contact with both the inner tube 54 and the outer tube 53 while being supported by the plurality of support portions 530.
- the plurality of support portions 530 hold the desiccant 55 so as not to move in the radial direction with the desiccant 55 sandwiched between the inner tube 54.
- the support portion 530 is formed in a shape that is inclined with respect to the side surface of the inner tube 54 so that the lower end surface is located on the inner side as it goes downward, that is, closer to the inner tube 54. With this configuration, the lower inclined end surface supports the bottom of the desiccant 55, and the downward movement of the desiccant 55 can be suppressed. Further, the support portion 530 may be configured to have a stepped portion having a protruding dimension larger from the inner surface of the outer tube 53 in the lower portion than in the upper portion so as to support the bottom portion of the desiccant 55. With this configuration, a portion having a large downward projecting dimension can support the bottom of the desiccant 55 and prevent the desiccant 55 from slipping downward.
- the support portion 530 is formed in a shape that is inclined with respect to the side surface of the inner tube 54 so that the upper end surface is located on the outer side in the radial direction, that is, away from the inner tube 54.
- the accumulator 5 In manufacturing the accumulator 5, first, with the umbrella-shaped member 51 set, the upper end portion 541 of the inner tube 54 is inserted into the lower portion of the lid portion 501, expanded and fixed, and the lid portion 501 and the suction tube 52 are integrated. To make goods. When the outer tube 53 is press-fitted and fixed to the integrated product, a desiccant 55 is installed between the plurality of support portions 530 and the inner tube 54. Next, the lid 501 and the upper end of the tank main body 502 are welded and joined with the suction pipe 52 positioned in the tank main body 502. Thereby, the accumulator 5 which incorporates the desiccant 55, the suction pipe 52, and the umbrella-shaped member 51 can be manufactured.
- the desiccant 55 is for removing moisture in the refrigerant in the refrigeration cycle 10, and is particles of zeolite or the like as shown in FIG. 4 and is accommodated in a bag-like container 550.
- the container 550 is made of a cloth such as ferrite, and has flexibility and functions as a filter. Since the shape of the container 550 is easily deformed, the container 550 is easily deformed into a shape that follows the outer peripheral surface of the inner tube 54 when installed between the plurality of support portions 530 and the inner tube 54.
- the refrigerant that has flowed out of the evaporator 4 flows into the tank body 502 from the refrigerant inlet 501a.
- the refrigerant flowing into the tank main body 502 is separated into gas and liquid by being guided to the inner wall of the tank main body 502 by the umbrella-like member 51, and the liquid phase refrigerant is separated from the gas-phase refrigerant and separated from the tank main body 502. Gather at the bottom of The gas-phase refrigerant passes through the desiccant 55 inside the outer pipe 53, then passes through the inside of the inner pipe 54, and flows out from the refrigerant outlet 501b to the compressor 1 side.
- the accumulator 5 includes a tank 50 in which the refrigerant flowing into the interior is separated into a gas phase refrigerant and a liquid phase refrigerant, the liquid phase refrigerant is stored inside, and the gas phase refrigerant flows out to the suction side of the compressor 1; And a suction pipe 52 that is installed in the tank 50 and sucks the gas-phase refrigerant.
- the desiccant 55 is installed inside the suction pipe 52.
- the liquid phase refrigerant in the suction pipe 52 is quickly discharged from the accumulator 5, so that the liquid phase refrigerant in the suction pipe 52 that has been sleeping when the compressor 1 is stopped is It is discharged outside the accumulator 5. Therefore, the desiccant 55 in the suction pipe 52 is exposed to the gas. That is, when the compressor is started, the desiccant 55 is not immediately applied to the liquid refrigerant. As described above, since the pressure in the suction pipe 52 is lowered and the temperature is lowered by the discharge of the liquid-phase refrigerant by the operation of the compressor 1, the drying agent 55 having a large heat capacity can be quickly cooled. Thereby, it is possible to suppress sudden boiling without causing the desiccant 55 to be submerged when the compressor 1 is started.
- the desiccant 55 is present in the suction pipe 52 that can be used as a liquid storage space in which the refrigerant stagnates when the compressor 1 is stopped, the interior of the tank 50 is prevented so that a useless volume that does not function as a liquid storage available space does not increase.
- a space can be configured.
- the accumulator 5 reduces the volume in which the desiccant is immersed in the liquid refrigerant in order to reduce the size of the noise caused by boiling, and the tank volume opposite to this. Realize a configuration that does not suffer from the dilemma of suppressing the increase. According to the above, the accumulator 5 can suppress sudden boiling from the desiccant 55 and an increase in the size of the tank 50.
- the suction pipe 52 includes an outer pipe 53 having a suction port 532 and an inner pipe 54 installed inside the outer pipe 53.
- the desiccant 55 can be installed in the inner space of the inner tube 54 or in the space formed between the inner surface of the outer tube 53 and the outer surface of the inner tube 54. Regardless of where the desiccant 55 is installed, the desiccant 55 that can be exposed to the liquid refrigerant by the stagnation of the refrigerant when the compressor 1 is stopped is immediately exposed to the gas-phase refrigerant by the suction input when the compressor 1 is started. Can be put into a state. In this way, the configuration of the accumulator 5 that suppresses sudden boiling can be realized regardless of the installation location of the desiccant 55 in the suction pipe 52.
- the desiccant 55 is installed inside the outer tube 53 and outside the inner tube 54. According to this configuration, the desiccant 55 can be installed so as to be sandwiched between the inner surface of the outer tube 53 and the outer surface of the inner tube 54, and a structure in which the holding force and assemblability of the desiccant 55 can be easily secured can be provided.
- the inner tube 54 is made of a metal material having thermal conductivity.
- the desiccant 55 is installed inside the suction pipe 52 in contact with the inner pipe 54. According to this configuration, when the compressor 1 is started, the liquid phase refrigerant in the suction pipe 52 is discharged and the pressure is lowered, so that the ambient temperature of the desiccant is lowered and the inner pipe 54 is cooled. By cooling the inner tube 54, the temperature of the desiccant 55 can be quickly reduced. Thereby, since the temperature drop of the desiccant 55 is not greatly delayed with respect to the pressure drop, the refrigerant adhering to the desiccant 55 is not overheated. Therefore, even when the liquid refrigerant is slightly left inside the desiccant 55, the occurrence of a sudden boiling can be suppressed.
- the inner tube 54 is made of a metal material having thermal conductivity.
- the outer tube 53 is made of a material having higher heat insulation than the inner tube 54.
- the desiccant 55 is placed in contact with both the inner tube 54 and the outer tube 53. According to this configuration, since the desiccant 55 is also in contact with the outer tube 53 in addition to the operation and effect when the desiccant 55 is installed in contact with the inner tube 54 as described above, It can be reduced that the heat of the liquid refrigerant in contact with the outer surface of the outer tube 53 is transferred to the desiccant 55. Thereby, since the heat transfer from the liquid refrigerant to the desiccant 55 is suppressed and the heat transfer from the desiccant 55 to the inner pipe 54 is promoted, a rapid temperature drop of the desiccant 55 can be realized.
- the outer tube 53 has a plurality of support portions 530 that protrude inward on the inner surface.
- the desiccant 55 is in contact with the inner tube 54 while being supported by the plurality of support portions 530. According to this configuration, since the desiccant 55 can be pressed against the inner tube 54 by the plurality of support portions 530, the contact area between the desiccant 55 and the outer surface of the inner tube 54 can be increased, and a reliable contact state can be provided. Furthermore, since the desiccant 55 comes into contact with the plurality of support portions 530, the contact area between the desiccant 55 and the outer tube 53 can be reduced. Thereby, since the heat transfer from the liquid phase refrigerant to the desiccant 55 is suppressed and the heat transfer from the desiccant 55 to the inner tube 54 is promoted, a rapid temperature drop of the desiccant 55 can be reliably realized.
- the refrigeration cycle 10 also decompresses the accumulator 5, the compressor 1 that circulates the refrigerant, the condenser 2 that releases the heat of the refrigerant discharged from the compressor 1, and the refrigerant that flows out of the condenser 2.
- the pressure reducing valve 3 and the evaporator 4 that absorbs heat by the refrigerant decompressed by the pressure reducing valve 3 are provided.
- the accumulator 5 described above since the accumulator 5 described above is provided, the liquid-phase refrigerant in the suction pipe 52 can be quickly discharged out of the accumulator 5 when the compressor 1 is started, and is installed in the suction pipe 52.
- the desiccant 55 that has been applied can be exposed to the gas.
- the pressure inside the suction pipe 52 is lowered and the temperature is also lowered. Therefore, even the desiccant 55 having a large heat capacity can be quickly cooled, and a sudden boiling can hardly occur inside the desiccant 55. . Furthermore, since the desiccant 55 is installed in the suction pipe 52, it can be used as a liquid storage space in which the refrigerant stagnates when the compressor 1 is stopped, and the useless volume that cannot be stored in the accumulator 5 can be prevented from increasing. By providing the accumulator 5 having the above effects, it is possible to provide the refrigeration cycle 10 that can suppress sudden boiling from the desiccant 55 and an increase in the size of the tank 50 of the accumulator 5.
- the accumulator 105 of the second embodiment is different from the accumulator 5 of the first embodiment in the configuration of the suction pipe.
- the suction pipe of the accumulator 105 includes an end portion 152 a provided with the suction port 1532 and another end portion 152 b communicating with the refrigerant outlet 501 b through which the gas-phase refrigerant flows out to the suction side of the compressor 1.
- tube 152 which has.
- the single tube 152 has a shape that bends in a U shape from one end 152a to the other end 152b.
- the one end 152a may be a first end, and the other end 152b may be a second end.
- the desiccant 55 is held by a holding member 1530 installed on the one end 152 a side inside the single tube 152.
- the desiccant 55 is installed in the single tube 152 in a state of being curved in a C shape or a donut shape. Further, the cross-sectional area of the part where the desiccant 55 is installed in the single pipe 152 is formed larger than the other parts in the single pipe 152.
- the holding member 1530 is provided with an opening that communicates with the suction port 1532 or that corresponds to the suction port 1532.
- the gas-phase refrigerant sucked into the single pipe 152 from the suction port 1532 passes through the desiccant 55, flows down in the single pipe 152 toward the refrigerant outlet 501b, and is discharged toward the compressor 1 side. .
- the flow of the refrigerant generated when the compressor 1 is started in the accumulator 105 is the same as that described in the first embodiment. Accordingly, also in the accumulator 105, the pressure in the single pipe 152 is lowered and the temperature is also lowered by the discharge of the liquid phase refrigerant, so that the desiccant 55 can be cooled quickly. Thereby, in the accumulator 105, it is possible to suppress sudden boiling without causing the desiccant 55 to be submerged when the compressor 1 is started.
- the desiccant 55 is installed inside the single tube 152.
- the desiccant 55 can be installed by being inserted into the single tube 152 from the one end portion 152a side, and a structure in which assembling property of the desiccant 55 can be easily secured can be provided.
- the single pipe 152 includes an oil return hole 533 that allows the inside and the outside of the single pipe 152 to communicate with each other.
- the desiccant 55 is installed inside the single pipe 152 between the oil return hole 533 and the suction port 1532. According to this configuration, since the desiccant 55 is not provided in a place where the oil returns from the liquid refrigerant accumulated at the bottom of the tank main body 502 into the single pipe 152, the refrigerant is easily discharged from the desiccant 55. There is an effect.
- this accumulator 105 contributes to quickly cooling the desiccant 55.
- the disclosure of this specification is not limited to the illustrated embodiments.
- the disclosure encompasses the illustrated embodiments and variations by those skilled in the art based thereon.
- the disclosure is not limited to the combination of components and elements shown in the embodiments, and various modifications can be made.
- the disclosure can be implemented in various combinations.
- the disclosure may have additional parts that can be added to the embodiments.
- the disclosure includes those in which the components and elements of the embodiment are omitted.
- the disclosure encompasses parts, element replacements, or combinations between one embodiment and another.
- the technical scope disclosed is not limited to the description of the embodiments.
- the refrigerant inlet and the refrigerant outlet in the above-described embodiment are not limited to the form provided in the ceiling portion of the tank 50.
- the refrigerant inlet may be provided in the upper part of the tank 50, and the refrigerant outlet may be provided in the lower part of the tank 50.
- coolant outflow port may connect with the channel
- path which penetrates a side wall in the tank 50 may be sufficient.
- the accumulators 5 and 105 described above are not limited to being applied only to the refrigeration cycle 10 described in the above embodiment.
- the accumulators 5 and 105 can be applied to a refrigerant cycle having components and circuit configurations different from those of the refrigeration cycle 10.
- a filter for removing sludge and the like contained in oil may be installed in the oil return passage in the above-described embodiment.
- the desiccant 55 in the first embodiment described above may be installed inside the inner tube 54.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Thermal Sciences (AREA)
- General Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Analytical Chemistry (AREA)
- Power Engineering (AREA)
- Compressor (AREA)
- Air-Conditioning For Vehicles (AREA)
Abstract
アキュムレータは、タンク(50)と、乾燥剤(55)と、吸込み管(52;152)と、を備える。タンクは、内部に流入した冷媒を気相冷媒と液相冷媒とに分離し、液相冷媒が内部に貯留し気相冷媒が圧縮機(1)の吸入側へ流出する。乾燥剤は、容器(550)に収容されて冷媒中の水分を除去する。吸込み管は、タンクの内部に設置され、気相冷媒を吸い込む吸込口(532;1532)を有する。乾燥剤は吸込み管の内部に設置されている。このアキュムレータによれば、乾燥剤からの急激な沸騰発生とタンクの大型化とを抑制できる。
Description
本出願は、2016年5月19日に出願された日本出願番号2016-100779号に基づくもので、ここにその記載内容を援用する。
この明細書における開示は、アキュムレータおよび冷凍サイクルに関する。
特許文献1は、冷凍サイクルに用いられて乾燥剤を内蔵するアキュムレータの一形態を開示している。特許文献1のアキュムレータは、圧縮機の停止時におけるタンク内の液相冷媒の最高液面位置よりも上方に乾燥剤の一部が位置し、液相冷媒の落下経路を避けた位置に乾燥剤が配置されている。この構成により、特許文献1のアキュムレータは、圧縮機の起動時に乾燥剤の全部が液相冷媒に浸からないため、異音のレベルを低減することができる。
特許文献1のアキュムレータは、異音のレベルを低減できるが、液中に存在する乾燥剤の一部から冷媒沸騰が生じることで異音が発生しうるため、改善の余地がある。一方、液に浸からないように乾燥剤をタンク内の上部に設置すると、タンク内に貯液可能な空間として機能しない無駄な容積が増加してしまうというおそれがある。
発明者は、冷凍サイクルの起動時等にタンク内の乾燥剤から急激な沸騰が発生する原因を調査した。その結果、発明者は、タンク内の圧力低下に対して乾燥剤の温度低下が遅れることで過熱度を持つ液冷媒状態になってしまい、沸騰を引き起こすことをつきとめた。したがって、乾燥剤からの急激な沸騰を抑制するためには、冷凍サイクルの起動時に速やかに乾燥剤から液相冷媒を排出して、速やかに乾燥剤の雰囲気温度を低下させることが有用であることに着目した。
本開示の目的は、乾燥剤からの急激な沸騰発生とタンクの大型化とを抑制できるアキュムレータ及び冷凍サイクルを提供することである。
本開示の第1態様によると、アキュムレータは、タンクと、乾燥剤と、吸込み管と、を備える。タンクは、内部に流入した冷媒を気相冷媒と液相冷媒とに分離し、液相冷媒が内部に貯留し気相冷媒が圧縮機の吸入側へ流出する。乾燥剤は、容器に収容されて冷媒中の水分を除去する。吸込み管は、タンクの内部に設置され、気相冷媒を吸い込む吸込口を有する。乾燥剤は吸込み管の内部に設置されている。
第1態様のアキュムレータによれば、圧縮機が起動すると吸込み管内の液相冷媒が速やかにアキュムレータ外に排出されるので、吸込み管の内部に設置されている乾燥剤は液相冷媒が排出されて気体中にさらされることになる。これにより、吸込み管の内部は圧力が低下するとともに温度も低下するので、熱容量が大きい乾燥剤でも速やかに冷却することができる。また、乾燥剤の内部にわずかに液相冷媒が残っていたとしても、この液相冷媒が過熱状態になることを防止できるので、急激な沸騰が起こりにくい状態を実現できる。さらに乾燥剤は圧縮機の停止時に冷媒が寝込む貯液空間としても活用できる吸込み管の内部に設置されているので、タンク内を貯液可能空間として機能しない無駄な容積が増加しないように構成できる。以上によれば、乾燥剤からの急激な沸騰発生とタンクの大型化とを抑制できるアキュムレータを提供できる。
以下に、図面を参照しながら本開示を実施するための複数の形態を説明する。各形態において先行する形態で説明した事項に対応する部分には同一の参照符号を付して重複する説明を省略する場合がある。各形態において構成の一部のみを説明している場合は、構成の他の部分については先行して説明した他の形態を適用することができる。各実施形態で具体的に組み合わせが可能であることを明示している部分同士の組み合わせばかりではなく、特に組み合わせに支障が生じなければ、明示してなくとも実施形態同士を部分的に組み合わせることも可能である。
(第1実施形態)
開示するアキュムレータは、車両用または定置用の冷凍サイクルに適用することができる。例えば、冷凍サイクルは、車室内、居室内、試験室等の所定の対象空間を空調するための空調用に用いることができる。以下、空調用の冷凍サイクル10について説明する。
開示するアキュムレータは、車両用または定置用の冷凍サイクルに適用することができる。例えば、冷凍サイクルは、車室内、居室内、試験室等の所定の対象空間を空調するための空調用に用いることができる。以下、空調用の冷凍サイクル10について説明する。
図1に示すように、冷凍サイクル10は、圧縮機1と、凝縮器2と、減圧弁3と、蒸発器4と、アキュムレータ5と、を少なくとも備え、これらを配管によって環状に接続した回路を構成する。圧縮機1は、エンジンやモータなどの駆動源により駆動されて冷媒を吸入して圧送する冷媒駆動装置である。
圧縮機1から吐出された気相冷媒は、凝縮器2に流入し、外気と熱交換して冷却されて凝縮する。凝縮器2は、冷媒の熱を外部に放出するので放熱用熱交換器の一例である。減圧弁3は、凝縮器2で凝縮した液冷媒を減圧して霧状の気液二相状態にする。減圧弁3はオリフィス、ノズル等の固定絞り、通路開度を変更可能な可変絞りによって構成することができる減圧装置である。
減圧弁3によって減圧された冷媒は、蒸発器4において空調用送風機による送風空気から吸熱して蒸発する。蒸発器4は、空調装置のケース内に設置されて、外部から熱を冷媒に吸熱する冷却用熱交換器の一例である。蒸発器4で冷却された空気は、目標温度に温度調整されて空調対象空間へ吹き出される。アキュムレータ5は、蒸発器4を流出した冷媒を気液分離し、内部で液相冷媒と分離された気相冷媒を圧縮機1へ戻す働きをする。さらにアキュムレータ5は、タンク50の底部に溜まっている液冷媒中に溶け込んでいるオイルを圧縮機1に吸入させる機能も果たしている。
図2はアキュムレータ5の構成を示した断面図である。図2に示すように、アキュムレータ5は、内部に流入した冷媒を気相冷媒と液相冷媒とに分離し、液相冷媒を内部に貯留するとともに、気相冷媒を圧縮機の吸入側に流出させるタンク50を備えている。図2および図3に示す矢印方向は、アキュムレータ5を冷凍サイクル10に搭載した状態における向きを示している。
タンク50は、内部に液相冷媒を貯液可能な空間を有するタンク本体部502と、タンク本体部502の上端開口部に蓋をするように固定されている蓋部501と、を備えている。タンク本体部502と蓋部501は金属の材質で形成されている。タンク本体部502の上端と蓋部501とは溶接接合により一体になっている。
タンク本体部502は、上端が開口した有底筒状であって、内部に傘状部材51、吸込み管52および乾燥剤55を収容している。タンク本体部502の内部には、分離された液相冷媒が貯留されるとともに、潤滑用オイルが液相冷媒中に溶け込んだ状態で貯えられる。吸込み管52は、気相冷媒を吸い込む吸込口532を有する外側管53と、外側管53の内側に設置される内側管54と、を備えている。
蓋部501は、タンク本体部502と同一の外径を有する扁平円柱状である。蓋部501には、それぞれ上下方向に貫通する、円形の冷媒流入口501aと冷媒流出口501bとが設けられている。冷媒流入口501aは、接続されている配管を介して蒸発器4につながっている。蒸発器4で熱交換された冷媒は、配管、冷媒流入口501aを通じてタンク本体部502の内部に流入する。冷媒流出口501bは、接続されている配管を介して圧縮機1につながっている。タンク本体部502の内部で分離された気相冷媒は、冷媒流出口501b、配管を通じて圧縮機1に吸入される。
傘状部材51は、冷媒流入口501aからタンク50内へ鉛直下方に向けて流入した冷媒が衝突する部材である。傘状部材51は、上下方向に延びる円筒状の側壁部511と、側壁部511の上端側を閉塞する天壁部510とを有し、側壁部511の下端側が開口した形状である。傘状部材51は、冷媒流入口501aの鉛直下方に天壁部510が存在するようにタンク50の内部に設置されている。天壁部510の外周縁から下方に延びる側壁部511は、タンク本体部502の内壁面の近傍に位置している。傘状部材51は、金属の材質で形成されている。
二重管である吸込み管52における内側管54は、上端部541が冷媒流出口501bに内嵌めされた状態で、下方に突出する下端部501cに圧入固定されている。傘状部材51は、冷媒流入口501aに対向する部位が上方に向けて隆起しており、冷媒流出口501bに対向する部位に開口部が形成されている。傘状部材51においてこの開口部を形成する周縁部は、冷媒流出口501bに一致した位置で、蓋部501の下端部501cに圧入固定される内側管54における大径部542と蓋部501の下端部501cとにより挟持される構成によって固定されている。すなわち、内側管54は蓋部501の下部に固定されている。大径部542は、内側管54の上端から所定長さ下方に位置する箇所に上端部541よりも外径寸法が大きく形成されている部分であり、内側管54を製造する過程においてプレス加工等により直径を拡大するように変形させて形成することができる。また内側管54を樹脂材料で製作する場合には、大径部542は、金型を用いた樹脂成型によって形成することができる。
アキュムレータ5は、冷媒流入口501aから導入した冷媒を傘状部材51に衝突させた後に、液相冷媒と気相冷媒とを分離する。傘状部材51の天壁部510に衝突した冷媒は、タンク50の内部で横方向に拡散し、タンク50の横方向における傘状部材51の天壁部510の外縁よりも外側に導かれる。液相冷媒は、傘状部材51の外縁よりも外側から側壁部511に沿って落下し、タンク本体部502の内壁をつたってタンク本体部502の下方に溜まる。気相冷媒は、傘状部材51の下側から、外側管53の上端の吸込口532から吸込み管52の内部に吸い込まれる。
内側管54と外側管53とは、ともに軸線が直線となる直線管で構成されており、直立姿勢でタンク本体部502の内部に収容されている。内側管54と外側管53とは、軸線が同軸になるように設置されている。内側管54は、例えば、アルミニウムを含む金属の材質で形成されている。外側管53は内側管54よりも断熱性が高い材質で構成されている。例えば、外側管53は断熱性に優れた樹脂材料で形成されている。
図2および図3に図示するように、外側管53は内側管54に固定されている。外側管53の下部には、内壁面から部分的に内側に突出する複数の突出部531が設けられている。複数の突出部531の内側に内側管54の下部が圧入されることで、外側管53は、複数の突出部531が内側管54の下部における外周面を支持する状態で、内側管54に一体に固定されている。
外側管53は、気相冷媒の吸込口532をなす上端開口部が、傘状部材51の天壁部510との間に所定の隙間をあけて傘状部材51の下端よりも上方に進入した状態となるように設置されている。外側管53は、下端部に貫通するオイル戻し穴533が形成されている。したがって、外側管53の下端部は、オイル戻し穴533を除いた部分が閉塞している。オイル戻し穴533は、内側管54の下端開口部540に対向する位置にある。オイル戻し穴533は、タンク本体部502の下部に貯留されている潤滑用オイルを、内側管54に流入する気相冷媒によって吸い上げて気相冷媒とともに内側管54内を通過させてアキュムレータ5の外部に送るためのオイル戻し通路である。このオイル戻し穴533によれば、冷凍サイクル10のオイル循環量を確保することに寄与する。
図2および図3に図示するように、外側管53には、内面においてそれぞれ内側に向かって突出し、かつ乾燥剤55の上下方向長さの大部分に接触する上下方向長さを有する複数の支持部530が設けられている。支持部530は、外側管53と一体成形された部分であり、樹脂材料によって形成されている。支持部530は横断面が矩形状であるリブによって構成されている。複数の支持部530は、外側管53の内側において周方向に間隔を設けて並んでいる。乾燥剤55は、複数の支持部530と内側管54の外面との間に介在した状態で設置されている。乾燥剤55は、複数の支持部530が周方向に並ぶ周方向長さ分、内側管54側に押し付けられるので、周方向の広範囲にわたって内側管54の外周面に接触し、熱移動可能な接触面積を十分に確保することができる。乾燥剤55は、複数の支持部530に支持された状態で内側管54と外側管53の両方に接触して設置されている。複数の支持部530は、内側管54とで乾燥剤55を挟んで径方向に移動しないように乾燥剤55を保持している。
支持部530は、下部の端面が下方に向かうほど径内側に位置するように、すなわち内側管54に接近するように内側管54の側面に対して傾斜する形状に形成されている。この構成により、下部の傾斜する端面が乾燥剤55の底部を支持して、乾燥剤55の下方への移動を抑えることができる。また、支持部530は、乾燥剤55の底部を支持するように、下部に上方よりも下方の方が外側管53の内面から突出寸法が大きくなる段差部を有するように構成してもよい。この構成により、下方の突出寸法が大きい部分が乾燥剤55の底部を支持して、乾燥剤55が下方にずれ落ちることを防止することができる。
支持部530は、上部の端面が上方に向かうほど径外側に位置するように、すなわち内側管54から離れるように内側管54の側面に対して傾斜する形状に形成されている。この構成により、乾燥剤55を外側管53と内側管54との間に設置する際に、支持部530における上部の傾斜する端面によって乾燥剤55の底部が引っ掛からないように円滑に差し込むことができる。乾燥剤55は、上端が外側管53の上端開口よりも下方に位置し、下端が内側管54の下端開口部540よりも上方に位置するように設置されている。
アキュムレータ5の製造において、まず、傘状部材51をセットした状態で内側管54の上端部541を蓋部501の下部に挿入して拡管して固定し、蓋部501と吸込み管52とを一体品にする。この一体品に対して、外側管53を圧入固定する際、複数の支持部530と内側管54との間に乾燥剤55を設置する。次に、吸込み管52をタンク本体部502内に位置させた状態で、蓋部501とタンク本体部502の上端とを溶接接合する。これにより、乾燥剤55、吸込み管52および傘状部材51を内蔵するアキュムレータ5を製造できる。
乾燥剤55は、冷凍サイクル10内の冷媒中の水分を除去するものであり、図4に示すようにゼオライト等の粒子であり、袋状の容器550に収容されている。容器550は、例えばフェライト等の布製であり、柔軟性を有するとともにフィルタとしても機能する。容器550は、その形状が容易に変形するため、複数の支持部530と内側管54との間に設置される際に内側管54の外周面にならう形状に変形しやすい。
アキュムレータ5では、蒸発器4を流出した冷媒が、冷媒流入口501aからタンク本体部502の内部に流入する。タンク本体部502の内部に流入した冷媒は、傘状部材51によってタンク本体部502の内壁に誘導されることにより気液分離され、液相冷媒は、気相冷媒と分離してタンク本体部502の下部に集合する。気相冷媒は、外側管53の内部で乾燥剤55を通過した後、内側管54の内部を通過して冷媒流出口501bから圧縮機1側へ流出する。気相冷媒が外側管53を流出して内側管54に流入する際には、タンク本体部502内の下部に貯留されている潤滑用オイルがオイル戻し穴533を介して吸い上げられ、気相冷媒とともに内側管54内を通って冷媒流出口501bから圧縮機1側へ流出する。
次に、第1実施形態のアキュムレータ5がもたらす作用効果について説明する。アキュムレータ5は、内部に流入した冷媒を気相冷媒と液相冷媒とに分離し液相冷媒が内部に貯留し気相冷媒が圧縮機1の吸入側へ流出するタンク50と、乾燥剤55と、タンク50内に設置され、気相冷媒を吸い込む吸込み管52と、を備える。乾燥剤55は吸込み管52の内部に設置されている。
このアキュムレータ5によれば、圧縮機1が起動すると吸込み管52内の液相冷媒が速やかにアキュムレータ5から排出されるので、圧縮機1の停止時に寝込んでいた吸込み管52内の液相冷媒がアキュムレータ5の外部に排出される。したがって、吸込み管52内の乾燥剤55は気体中にさらされることになる。つまり、圧縮機の起動時に乾燥剤55は速やかに液冷媒につからない状態になる。このように圧縮機1の機動により、吸込み管52内は、圧力が低下するとともに液相冷媒の排出により温度も低下するので、熱容量が大きい乾燥剤55でも速やかに冷却することができる。これにより、圧縮機1の起動時に乾燥剤55を液没させることなく、急激な沸騰が起こることを抑制できる。
また、乾燥剤55の内部にわずかに液相冷媒が残っていた場合でも、この液相冷媒が過熱状態になることを防止できるため、急激な沸騰が起こりにくい状態を実現できる。さらに乾燥剤55は、圧縮機1の停止時に冷媒が寝込む貯液空間としても活用できる吸込み管52内に存在するため、貯液可能空間として機能しない無駄な容積が増加しないようにタンク50の内部空間を構成できる。したがって、アキュムレータ5は、特許文献1に開示のアキュムレータのように、沸騰による異音の大きさを低減するために乾燥剤が液冷媒に浸かる容積を減少することと、これに背反するタンク容積の増加を抑制することとのジレンマに悩まされない構成を実現する。以上によれば、アキュムレータ5は、乾燥剤55からの急激な沸騰発生とタンク50の大型化とを抑制することができる。
また、吸込み管52は、吸込口532を有する外側管53と外側管53の内側に設置される内側管54とを備えて構成されている。この構成によれば、乾燥剤55を内側管54の内部空間あるいは外側管53の内面と内側管54の外面との間に形成される空間に設置することができる。乾燥剤55がどちらに設置されていても、圧縮機1の停止時に冷媒の寝込みにより液冷媒にさらされうる乾燥剤55を、圧縮機1の起動時にその吸入力によって速やかに気相冷媒にさらされる状態にすることができる。このように吸込み管52内における乾燥剤55の設置場所によらず、急激な沸騰を抑制するアキュムレータ5の構成を実現できる。
また、乾燥剤55は、外側管53の内側であって内側管54の外側に設置されている。この構成によれば、乾燥剤55を外側管53の内面と内側管54の外面とで挟むようにして設置することができ、乾燥剤55の保持力や組立性を確保しやすい構造を提供できる。
また、内側管54は熱伝導性を有する金属の材質で構成されている。乾燥剤55は内側管54に接触した状態で吸込み管52の内部に設置されている。この構成によれば、圧縮機1の起動時に吸込み管52内の液相冷媒が排出されて圧力が低下することに伴い、乾燥剤の周囲温度が低下して内側管54が冷却される。内側管54が冷却されることによって乾燥剤55の温度を迅速に低下させることができる。これにより、乾燥剤55の温度低下が圧力低下に対して大きく遅れることがないため、乾燥剤55に付着している冷媒が過熱状態にならない。したがって、乾燥剤55の内部にわずかに液相冷媒が残っていた場合でも、急激な沸騰の発生を抑制できる。
また、内側管54は熱伝導性を有する金属の材質で構成されている。外側管53は内側管54よりも断熱性が高い材質で構成されている。乾燥剤55は内側管54と外側管53との両方に接触した状態で設置されている。この構成によれば、前述のように乾燥剤55が内側管54に接触した状態で設置されている場合の作用、効果に加えて、乾燥剤55が外側管53にも接触しているため、外側管53の外面に接触している液相冷媒の熱が乾燥剤55に熱伝達することを低減できる。これにより、液相冷媒から乾燥剤55への熱移動を抑え、乾燥剤55から内側管54への熱移動を促進するので、乾燥剤55の迅速な温度低下を実現することができる。
外側管53は、内面において内側に向けて突出する複数の支持部530を有する。乾燥剤55は複数の支持部530に支持された状態で内側管54に接触している。この構成によれば、複数の支持部530によって乾燥剤55を内側管54に押しつけることができるので、乾燥剤55を内側管54の外面と接触面積を大きくし、確実な接触状態を提供できる。さらに乾燥剤55は複数の支持部530と接触するため、乾燥剤55と外側管53との接触面積を小さくすることができる。これにより、液相冷媒から乾燥剤55への熱移動を抑え、乾燥剤55から内側管54への熱移動を促進するので、乾燥剤55の迅速な温度低下を確実に実現することができる。
また、冷凍サイクル10は、前述のアキュムレータ5と、冷媒を循環させる圧縮機1と、圧縮機1から吐出された冷媒の熱を放出する凝縮器2と、凝縮器2から流出した冷媒を減圧する減圧弁3と、減圧弁3で減圧された冷媒によって吸熱する蒸発器4と、を備える。この冷凍サイクル10によれば、前述のアキュムレータ5を備えるため、圧縮機1が起動すると吸込み管52内の液相冷媒を速やかにアキュムレータ5の外に排出することができ、吸込み管52内に設置されている乾燥剤55を気体中にさらすことができる。これにより、吸込み管52の内部は圧力が低下するとともに温度も低下するので、熱容量が大きい乾燥剤55であっても迅速に冷却でき、乾燥剤55の内部で急激な沸騰が起こりにくい状態にできる。さらに乾燥剤55は吸込み管52内に設置されているので、圧縮機1の停止時に冷媒が寝込む貯液空間としても活用でき、アキュムレータ5内に貯液できない無駄な容積が増加しないようにできる。以上の効果を奏するアキュムレータ5を備えることにより、乾燥剤55からの急激な沸騰発生とアキュムレータ5のタンク50の大型化とを抑制できる冷凍サイクル10を提供できる。
(第2実施形態)
第2実施形態について図5を参照して説明する。第2実施形態において、第1実施形態に係る図面と同一符号を付した構成部品及び説明しない構成は、第1実施形態と同様であり、同様の作用効果を奏するものである。第2実施形態では、第1実施形態と異なる部分のみ説明する。
第2実施形態について図5を参照して説明する。第2実施形態において、第1実施形態に係る図面と同一符号を付した構成部品及び説明しない構成は、第1実施形態と同様であり、同様の作用効果を奏するものである。第2実施形態では、第1実施形態と異なる部分のみ説明する。
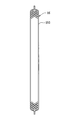
第2実施形態のアキュムレータ105は、第1実施形態のアキュムレータ5に対して、吸込み管の構成が相違する。図5に図示するように、アキュムレータ105の吸込み管は、吸込口1532が設けられる一端部152aと圧縮機1の吸入側へ気相冷媒が流出する冷媒流出口501bに連通する他端部152bとを有する単管152である。他端部152bは、第1実施形態の上端部541に相当する。単管152は、一端部152aから他端部152bにかけてU字状に屈曲する形状を呈している。一端部152aは第1端部でも良く、他端部152bは第2端部でも良い。
乾燥剤55は、単管152の内部の一端部152a側に設置された保持部材1530によって保持されている。乾燥剤55は、単管152内において、C字状、ドーナツ状に湾曲した状態で設置されている。また、単管152内において乾燥剤55が設置されている部位の断面積は、単管152内の他の部位よりも大きく形成されている。
保持部材1530には、吸込口1532と連通し、または吸込口1532に相当する開口部が設けられている。吸込口1532から単管152内に吸入される気相冷媒は、乾燥剤55を通過して単管152の内部を冷媒流出口501bに向けて流下し、圧縮機1側に向けて排出される。アキュムレータ105において圧縮機1の起動時に発生する冷媒の流れは、前述の第1実施形態での説明と同様である。したがって、アキュムレータ105においても、単管152内は、圧力が低下するとともに液相冷媒の排出により温度も低下するので、乾燥剤55を速やかに冷却することができる。これにより、アキュムレータ105では、圧縮機1の起動時に乾燥剤55を液没させることなく、急激な沸騰が起こることを抑制できる。
第2実施形態によれば、乾燥剤55は、単管152の内部に設置されている。このアキュムレータ105によれば、乾燥剤55を一端部152a側から単管152に挿入して設置することができ、乾燥剤55の組立性を確保しやすい構造を提供できる。
また、単管152は、単管152の内部と外部とを連通するオイル戻し穴533を備える。乾燥剤55は、オイル戻し穴533と吸込口1532との間において単管152の内部に設置されている。この構成によれば、タンク本体部502の底部に溜まっている液相冷媒からオイルが単管152内に戻る場所に乾燥剤55が設けられていないため、乾燥剤55から冷媒を排出しやすいという効果を奏する。また、オイルが単管152内に戻る場所に乾燥剤55が設けられていないため、乾燥剤55にオイルが付着しにくいので、乾燥剤55の内部から冷媒を流出すること妨げないという効果を奏する。したがって、このアキュムレータ105は、乾燥剤55を速やかに冷却することに寄与する。
この明細書の開示は、例示された実施形態に制限されない。開示は、例示された実施形態と、それらに基づく当業者による変形態様を包含する。例えば、開示は、実施形態において示された部品、要素の組み合わせに限定されず、種々変形して実施することが可能である。開示は、多様な組み合わせによって実施可能である。開示は、実施形態に追加可能な追加的な部分をもつことができる。開示は、実施形態の部品、要素が省略されたものを包含する。開示は、ひとつの実施形態と他の実施形態との間における部品、要素の置き換え、または組み合わせを包含する。開示される技術的範囲は、実施形態の記載に限定されない。
前述の実施形態における冷媒流入口、冷媒流出口は、タンク50において天井部に設けられる形態に限定されない。冷媒流入口はタンク50において上部に設けられ、冷媒流出口はタンク50において下部に設けられる形態でもよい。また、冷媒流入口、冷媒流出口はタンク50において側壁を貫通する通路と連通するように設けられている形態でもよい。
前述のアキュムレータ5,105は、前述の実施形態に記載した冷凍サイクル10に適用することのみに限定されない。アキュムレータ5,105は、冷凍サイクル10とは異なる構成部品や回路構成を有する冷媒サイクルに適用可能である。
前述の実施形態におけるオイル戻し通路には、オイルに含まれるスラッジ等を除去するフィルタを設置するようにしてもよい。
前述の第1実施形態における乾燥剤55は、内側管54の内側に設置されている構成としてもよい。
本開示は、実施例に準拠して記述されたが、本開示は当該実施例や構造に限定されるものではないと理解される。本開示は、様々な変形例や均等範囲内の変形をも包含する。加えて、様々な組み合わせや形態が本開示に示されているが、それらに一要素のみ、それ以上、あるいはそれ以下、を含む他の組み合わせや形態をも、本開示の範疇や思想範囲に入るものである。
Claims (9)
- 内部に流入した冷媒を気相冷媒と液相冷媒とに分離し、液相冷媒が内部に貯留し気相冷媒が圧縮機(1)の吸入側へ流出するタンク(50)と、
容器(550)に収容されて冷媒中の水分を除去する乾燥剤(55)と、
前記タンクの内部に設置され、気相冷媒を吸い込む吸込口(532;1532)を有する吸込み管(52;152)と、
を備え、
前記乾燥剤は前記吸込み管の内部に設置されているアキュムレータ。 - 前記吸込み管は、前記吸込口を有する外側管(53)と前記外側管の内側に設置される内側管(54)とを備えている請求項1に記載のアキュムレータ。
- 前記乾燥剤は、前記外側管の内側であって前記内側管の外側に設置されている請求項2に記載のアキュムレータ。
- 前記内側管は金属で構成されており、
前記乾燥剤は前記内側管に接触している請求項2または請求項3に記載のアキュムレータ。 - 前記内側管は金属で構成されており、
前記外側管は前記内側管よりも断熱性が高い材質で構成されており、
前記乾燥剤は前記内側管と前記外側管との両方に接触している請求項2に記載のアキュムレータ。 - 前記外側管は、内面において内側に向けて突出する複数の支持部(530)を有し、
前記乾燥剤は前記複数の支持部に支持された状態で前記内側管に接触している請求項5に記載のアキュムレータ。 - 前記吸込み管は、前記吸込口(1532)が設けられる第1端部(152a)と前記圧縮機の吸入側へ気相冷媒が流出する流出口(501b)に連通する第2端部(152b)とを有する単管(152)であり、
前記乾燥剤は、前記単管の内部に設置されている請求項1に記載のアキュムレータ。 - 前記単管は、前記単管の内部と外部とを連通するオイル戻し通路(533)を備え、
前記乾燥剤は、前記オイル戻し通路と前記吸込口との間において前記単管の内部に設置されている請求項7に記載のアキュムレータ。 - 回路に冷媒を循環させる圧縮機(1)と、
前記圧縮機から吐出された冷媒の熱を放出する放熱用熱交換器(2)と、
前記放熱用熱交換器から流出した冷媒を減圧する減圧装置(3)と、
前記減圧装置により減圧された冷媒によって吸熱する冷却用熱交換器(4)と、
前記冷却用熱交換器と前記圧縮機との間の通路に設けられた請求項1から請求項8のいずれか一項に記載のアキュムレータ(5;105)と、
を備える冷凍サイクル。
Priority Applications (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| DE112017002550.8T DE112017002550T5 (de) | 2016-05-19 | 2017-04-25 | Speicher und kältemittelkreislauf |
| CN201780030265.8A CN109154462B (zh) | 2016-05-19 | 2017-04-25 | 储液器和制冷循环 |
| US16/192,055 US11009274B2 (en) | 2016-05-19 | 2018-11-15 | Accumulator, and refrigeration cycle |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2016100779A JP6500839B2 (ja) | 2016-05-19 | 2016-05-19 | アキュムレータおよび冷凍サイクル |
| JP2016-100779 | 2016-05-19 |
Related Child Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| US16/192,055 Continuation US11009274B2 (en) | 2016-05-19 | 2018-11-15 | Accumulator, and refrigeration cycle |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2017199707A1 true WO2017199707A1 (ja) | 2017-11-23 |
Family
ID=60326565
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2017/016319 WO2017199707A1 (ja) | 2016-05-19 | 2017-04-25 | アキュムレータおよび冷凍サイクル |
Country Status (5)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US11009274B2 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JP6500839B2 (ja) |
| CN (1) | CN109154462B (ja) |
| DE (1) | DE112017002550T5 (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2017199707A1 (ja) |
Families Citing this family (8)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN108426392A (zh) * | 2018-05-05 | 2018-08-21 | 珠海格力电器股份有限公司 | 冷媒提纯装置 |
| CN108759196A (zh) * | 2018-06-13 | 2018-11-06 | 苏州逸新和电子有限公司 | 一种过滤性能好的储液器 |
| CN108826769B (zh) * | 2018-08-15 | 2024-02-20 | 珠海凌达压缩机有限公司 | 一种容积可变的储液器及空调系统 |
| JP7192347B2 (ja) * | 2018-09-21 | 2022-12-20 | 株式会社富士通ゼネラル | 冷凍サイクル装置 |
| CN112013581A (zh) * | 2019-05-30 | 2020-12-01 | 株式会社不二工机 | 储液器及其组装方法 |
| CN112013580A (zh) * | 2019-05-30 | 2020-12-01 | 株式会社不二工机 | 储液器及其组装方法 |
| JP7475061B2 (ja) * | 2021-08-24 | 2024-04-26 | 株式会社不二工機 | アキュームレータ |
| WO2024116757A1 (ja) * | 2022-11-30 | 2024-06-06 | 株式会社アイシン | マニホールド |
Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2000088402A (ja) * | 1998-07-13 | 2000-03-31 | Showa Alum Corp | アキュムレ―タ |
| JP2008164272A (ja) * | 2006-12-05 | 2008-07-17 | Calsonic Kansei Corp | 貯液器 |
| JP5849909B2 (ja) * | 2012-09-07 | 2016-02-03 | 株式会社デンソー | アキュムレータ |
Family Cites Families (7)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JPS5849909B2 (ja) | 1978-09-29 | 1983-11-07 | 日本アビオニクス株式会社 | 連続用紙のマ−ク自動読取りさん孔機 |
| US4768355A (en) * | 1987-01-27 | 1988-09-06 | Ford Motor Company | Accumulator with refrigerant processing cartridge for automotive air conditioning system |
| US6389842B1 (en) * | 2001-01-23 | 2002-05-21 | Delphi Technologies, Inc. | Accumulator-dehydrator assembly with anti-bump expansion chamber “J”-tube |
| JP5760993B2 (ja) | 2011-11-29 | 2015-08-12 | 株式会社デンソー | アキュムレータ |
| CN103712385B (zh) * | 2012-10-02 | 2017-09-19 | 株式会社不二工机 | 储存器 |
| JP5991496B2 (ja) | 2014-11-21 | 2016-09-14 | 株式会社NttデータSms | 監視システム、監視方法、及びプログラム |
| JP6537911B2 (ja) * | 2015-07-17 | 2019-07-03 | 株式会社不二工機 | アキュームレータ |
-
2016
- 2016-05-19 JP JP2016100779A patent/JP6500839B2/ja not_active Expired - Fee Related
-
2017
- 2017-04-25 WO PCT/JP2017/016319 patent/WO2017199707A1/ja active Application Filing
- 2017-04-25 CN CN201780030265.8A patent/CN109154462B/zh not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2017-04-25 DE DE112017002550.8T patent/DE112017002550T5/de not_active Withdrawn
-
2018
- 2018-11-15 US US16/192,055 patent/US11009274B2/en active Active
Patent Citations (3)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2000088402A (ja) * | 1998-07-13 | 2000-03-31 | Showa Alum Corp | アキュムレ―タ |
| JP2008164272A (ja) * | 2006-12-05 | 2008-07-17 | Calsonic Kansei Corp | 貯液器 |
| JP5849909B2 (ja) * | 2012-09-07 | 2016-02-03 | 株式会社デンソー | アキュムレータ |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| JP6500839B2 (ja) | 2019-04-17 |
| CN109154462B (zh) | 2020-11-10 |
| JP2017207251A (ja) | 2017-11-24 |
| US11009274B2 (en) | 2021-05-18 |
| US20190086131A1 (en) | 2019-03-21 |
| CN109154462A (zh) | 2019-01-04 |
| DE112017002550T5 (de) | 2019-02-14 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| WO2017199707A1 (ja) | アキュムレータおよび冷凍サイクル | |
| JP5849909B2 (ja) | アキュムレータ | |
| JP4548350B2 (ja) | エジェクタ式冷凍サイクル用ユニット | |
| JP3925158B2 (ja) | 冷媒凝縮器 | |
| JP2004526934A (ja) | 内部熱交換器アキュムレータ | |
| US20070130988A1 (en) | Vapor compression refrigerating systems | |
| CN106352618B (zh) | 储存器 | |
| JP2003090643A (ja) | 冷凍サイクル装置 | |
| JP2017207251A5 (ja) | ||
| JP2009281593A (ja) | 蒸発器ユニット | |
| US6341647B1 (en) | Separator-integrated condenser for vehicle air conditioner | |
| JP2008249242A (ja) | 冷凍サイクル用アキュムレータ | |
| JP2007071511A (ja) | アキュームレータ構造 | |
| JP6514981B2 (ja) | アキュームレータ | |
| JP4897464B2 (ja) | 蒸気圧縮式冷凍サイクル | |
| EP3293471B1 (en) | Accumulator | |
| JP2017198408A (ja) | アキュムレータ | |
| JP6815036B2 (ja) | アキュームレータ | |
| JP2000074527A (ja) | 受液器一体型冷媒凝縮器 | |
| WO2018088127A1 (ja) | アキュムレータ | |
| JP2003042601A (ja) | 受液器 | |
| WO2024158023A1 (ja) | アキュームレータ | |
| EP3293472B1 (en) | Accumulator | |
| CN210772906U (zh) | 一体式制冷机组及冷藏车 | |
| JP6924438B2 (ja) | 貯液器 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 17799137 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| 122 | Ep: pct application non-entry in european phase |
Ref document number: 17799137 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |