WO2010058640A1 - 光電変換装置 - Google Patents
光電変換装置 Download PDFInfo
- Publication number
- WO2010058640A1 WO2010058640A1 PCT/JP2009/064570 JP2009064570W WO2010058640A1 WO 2010058640 A1 WO2010058640 A1 WO 2010058640A1 JP 2009064570 W JP2009064570 W JP 2009064570W WO 2010058640 A1 WO2010058640 A1 WO 2010058640A1
- Authority
- WO
- WIPO (PCT)
- Prior art keywords
- layer
- photoelectric conversion
- film
- intermediate contact
- contact layer
- Prior art date
Links
- 238000006243 chemical reaction Methods 0.000 title claims abstract description 67
- 239000000758 substrate Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 55
- UFHFLCQGNIYNRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N Hydrogen Chemical compound [H][H] UFHFLCQGNIYNRP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 claims abstract description 14
- 150000001875 compounds Chemical class 0.000 claims abstract description 14
- 239000001257 hydrogen Substances 0.000 claims abstract description 14
- 229910052739 hydrogen Inorganic materials 0.000 claims abstract description 14
- 238000010248 power generation Methods 0.000 claims description 40
- 229910005191 Ga 2 O 3 Inorganic materials 0.000 claims description 20
- 239000010408 film Substances 0.000 description 87
- 229910021417 amorphous silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 17
- 229910021419 crystalline silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 14
- XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicon Chemical compound [Si] XUIMIQQOPSSXEZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 13
- 229910052710 silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 13
- 239000010703 silicon Substances 0.000 description 13
- 239000002019 doping agent Substances 0.000 description 11
- 230000015572 biosynthetic process Effects 0.000 description 10
- 238000010329 laser etching Methods 0.000 description 9
- 238000000034 method Methods 0.000 description 9
- 238000012545 processing Methods 0.000 description 9
- 239000010409 thin film Substances 0.000 description 7
- 229910003363 ZnMgO Inorganic materials 0.000 description 6
- 229910021424 microcrystalline silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 6
- RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N Copper Chemical compound [Cu] RYGMFSIKBFXOCR-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 5
- 239000011889 copper foil Substances 0.000 description 5
- 230000000694 effects Effects 0.000 description 5
- 239000005038 ethylene vinyl acetate Substances 0.000 description 5
- 239000007789 gas Substances 0.000 description 5
- 238000007689 inspection Methods 0.000 description 5
- 229920001200 poly(ethylene-vinyl acetate) Polymers 0.000 description 5
- 239000012298 atmosphere Substances 0.000 description 4
- 230000002093 peripheral effect Effects 0.000 description 4
- 238000005268 plasma chemical vapour deposition Methods 0.000 description 4
- 238000005498 polishing Methods 0.000 description 4
- 230000007423 decrease Effects 0.000 description 3
- 238000001755 magnetron sputter deposition Methods 0.000 description 3
- 238000004519 manufacturing process Methods 0.000 description 3
- 239000000463 material Substances 0.000 description 3
- 230000010355 oscillation Effects 0.000 description 3
- 239000004065 semiconductor Substances 0.000 description 3
- 229910000577 Silicon-germanium Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 239000000853 adhesive Substances 0.000 description 2
- 230000001070 adhesive effect Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000003513 alkali Substances 0.000 description 2
- QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N atomic oxygen Chemical compound [O] QVGXLLKOCUKJST-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 2
- 230000004888 barrier function Effects 0.000 description 2
- 239000003795 chemical substances by application Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000005530 etching Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000011521 glass Substances 0.000 description 2
- 238000005259 measurement Methods 0.000 description 2
- 239000001301 oxygen Substances 0.000 description 2
- 229910052760 oxygen Inorganic materials 0.000 description 2
- 238000009832 plasma treatment Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000004544 sputter deposition Methods 0.000 description 2
- 238000002230 thermal chemical vapour deposition Methods 0.000 description 2
- 229910004298 SiO 2 Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N Silicium dioxide Chemical compound O=[Si]=O VYPSYNLAJGMNEJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910006404 SnO 2 Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- CDBYLPFSWZWCQE-UHFFFAOYSA-L Sodium Carbonate Chemical compound [Na+].[Na+].[O-]C([O-])=O CDBYLPFSWZWCQE-UHFFFAOYSA-L 0.000 description 1
- 229910009372 YVO4 Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- LEVVHYCKPQWKOP-UHFFFAOYSA-N [Si].[Ge] Chemical compound [Si].[Ge] LEVVHYCKPQWKOP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 239000006061 abrasive grain Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000004140 cleaning Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000013078 crystal Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000007547 defect Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000000151 deposition Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000008021 deposition Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000010586 diagram Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000009826 distribution Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000000835 fiber Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000945 filler Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000005329 float glass Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000011888 foil Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000011810 insulating material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000010849 ion bombardment Methods 0.000 description 1
- 239000012528 membrane Substances 0.000 description 1
- 239000000203 mixture Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000003647 oxidation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 238000007254 oxidation reaction Methods 0.000 description 1
- 238000011056 performance test Methods 0.000 description 1
- 229910021420 polycrystalline silicon Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 238000004382 potting Methods 0.000 description 1
- 230000005855 radiation Effects 0.000 description 1
- 239000002994 raw material Substances 0.000 description 1
- 238000007789 sealing Methods 0.000 description 1
- HBMJWWWQQXIZIP-UHFFFAOYSA-N silicon carbide Chemical compound [Si+]#[C-] HBMJWWWQQXIZIP-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910052814 silicon oxide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 229910000679 solder Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 239000004575 stone Substances 0.000 description 1
- 230000008646 thermal stress Effects 0.000 description 1
- XOLBLPGZBRYERU-UHFFFAOYSA-N tin dioxide Chemical compound O=[Sn]=O XOLBLPGZBRYERU-UHFFFAOYSA-N 0.000 description 1
- 229910001887 tin oxide Inorganic materials 0.000 description 1
- 238000011144 upstream manufacturing Methods 0.000 description 1
Images
Classifications
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L31/00—Semiconductor devices sensitive to infrared radiation, light, electromagnetic radiation of shorter wavelength or corpuscular radiation and specially adapted either for the conversion of the energy of such radiation into electrical energy or for the control of electrical energy by such radiation; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof
- H01L31/04—Semiconductor devices sensitive to infrared radiation, light, electromagnetic radiation of shorter wavelength or corpuscular radiation and specially adapted either for the conversion of the energy of such radiation into electrical energy or for the control of electrical energy by such radiation; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof adapted as photovoltaic [PV] conversion devices
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C23—COATING METALLIC MATERIAL; COATING MATERIAL WITH METALLIC MATERIAL; CHEMICAL SURFACE TREATMENT; DIFFUSION TREATMENT OF METALLIC MATERIAL; COATING BY VACUUM EVAPORATION, BY SPUTTERING, BY ION IMPLANTATION OR BY CHEMICAL VAPOUR DEPOSITION, IN GENERAL; INHIBITING CORROSION OF METALLIC MATERIAL OR INCRUSTATION IN GENERAL
- C23C—COATING METALLIC MATERIAL; COATING MATERIAL WITH METALLIC MATERIAL; SURFACE TREATMENT OF METALLIC MATERIAL BY DIFFUSION INTO THE SURFACE, BY CHEMICAL CONVERSION OR SUBSTITUTION; COATING BY VACUUM EVAPORATION, BY SPUTTERING, BY ION IMPLANTATION OR BY CHEMICAL VAPOUR DEPOSITION, IN GENERAL
- C23C14/00—Coating by vacuum evaporation, by sputtering or by ion implantation of the coating forming material
- C23C14/06—Coating by vacuum evaporation, by sputtering or by ion implantation of the coating forming material characterised by the coating material
- C23C14/08—Oxides
- C23C14/086—Oxides of zinc, germanium, cadmium, indium, tin, thallium or bismuth
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B23—MACHINE TOOLS; METAL-WORKING NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- B23K—SOLDERING OR UNSOLDERING; WELDING; CLADDING OR PLATING BY SOLDERING OR WELDING; CUTTING BY APPLYING HEAT LOCALLY, e.g. FLAME CUTTING; WORKING BY LASER BEAM
- B23K26/00—Working by laser beam, e.g. welding, cutting or boring
- B23K26/02—Positioning or observing the workpiece, e.g. with respect to the point of impact; Aligning, aiming or focusing the laser beam
- B23K26/06—Shaping the laser beam, e.g. by masks or multi-focusing
- B23K26/062—Shaping the laser beam, e.g. by masks or multi-focusing by direct control of the laser beam
- B23K26/0622—Shaping the laser beam, e.g. by masks or multi-focusing by direct control of the laser beam by shaping pulses
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B23—MACHINE TOOLS; METAL-WORKING NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- B23K—SOLDERING OR UNSOLDERING; WELDING; CLADDING OR PLATING BY SOLDERING OR WELDING; CUTTING BY APPLYING HEAT LOCALLY, e.g. FLAME CUTTING; WORKING BY LASER BEAM
- B23K26/00—Working by laser beam, e.g. welding, cutting or boring
- B23K26/08—Devices involving relative movement between laser beam and workpiece
- B23K26/083—Devices involving movement of the workpiece in at least one axial direction
- B23K26/0853—Devices involving movement of the workpiece in at least in two axial directions, e.g. in a plane
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B23—MACHINE TOOLS; METAL-WORKING NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- B23K—SOLDERING OR UNSOLDERING; WELDING; CLADDING OR PLATING BY SOLDERING OR WELDING; CUTTING BY APPLYING HEAT LOCALLY, e.g. FLAME CUTTING; WORKING BY LASER BEAM
- B23K26/00—Working by laser beam, e.g. welding, cutting or boring
- B23K26/36—Removing material
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B23—MACHINE TOOLS; METAL-WORKING NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- B23K—SOLDERING OR UNSOLDERING; WELDING; CLADDING OR PLATING BY SOLDERING OR WELDING; CUTTING BY APPLYING HEAT LOCALLY, e.g. FLAME CUTTING; WORKING BY LASER BEAM
- B23K26/00—Working by laser beam, e.g. welding, cutting or boring
- B23K26/36—Removing material
- B23K26/362—Laser etching
- B23K26/364—Laser etching for making a groove or trench, e.g. for scribing a break initiation groove
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B23—MACHINE TOOLS; METAL-WORKING NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- B23K—SOLDERING OR UNSOLDERING; WELDING; CLADDING OR PLATING BY SOLDERING OR WELDING; CUTTING BY APPLYING HEAT LOCALLY, e.g. FLAME CUTTING; WORKING BY LASER BEAM
- B23K26/00—Working by laser beam, e.g. welding, cutting or boring
- B23K26/36—Removing material
- B23K26/40—Removing material taking account of the properties of the material involved
-
- C—CHEMISTRY; METALLURGY
- C23—COATING METALLIC MATERIAL; COATING MATERIAL WITH METALLIC MATERIAL; CHEMICAL SURFACE TREATMENT; DIFFUSION TREATMENT OF METALLIC MATERIAL; COATING BY VACUUM EVAPORATION, BY SPUTTERING, BY ION IMPLANTATION OR BY CHEMICAL VAPOUR DEPOSITION, IN GENERAL; INHIBITING CORROSION OF METALLIC MATERIAL OR INCRUSTATION IN GENERAL
- C23C—COATING METALLIC MATERIAL; COATING MATERIAL WITH METALLIC MATERIAL; SURFACE TREATMENT OF METALLIC MATERIAL BY DIFFUSION INTO THE SURFACE, BY CHEMICAL CONVERSION OR SUBSTITUTION; COATING BY VACUUM EVAPORATION, BY SPUTTERING, BY ION IMPLANTATION OR BY CHEMICAL VAPOUR DEPOSITION, IN GENERAL
- C23C14/00—Coating by vacuum evaporation, by sputtering or by ion implantation of the coating forming material
- C23C14/22—Coating by vacuum evaporation, by sputtering or by ion implantation of the coating forming material characterised by the process of coating
- C23C14/34—Sputtering
- C23C14/3407—Cathode assembly for sputtering apparatus, e.g. Target
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L31/00—Semiconductor devices sensitive to infrared radiation, light, electromagnetic radiation of shorter wavelength or corpuscular radiation and specially adapted either for the conversion of the energy of such radiation into electrical energy or for the control of electrical energy by such radiation; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof
- H01L31/02—Details
- H01L31/0224—Electrodes
- H01L31/022466—Electrodes made of transparent conductive layers, e.g. TCO, ITO layers
- H01L31/022483—Electrodes made of transparent conductive layers, e.g. TCO, ITO layers composed of zinc oxide [ZnO]
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L31/00—Semiconductor devices sensitive to infrared radiation, light, electromagnetic radiation of shorter wavelength or corpuscular radiation and specially adapted either for the conversion of the energy of such radiation into electrical energy or for the control of electrical energy by such radiation; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof
- H01L31/04—Semiconductor devices sensitive to infrared radiation, light, electromagnetic radiation of shorter wavelength or corpuscular radiation and specially adapted either for the conversion of the energy of such radiation into electrical energy or for the control of electrical energy by such radiation; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof adapted as photovoltaic [PV] conversion devices
- H01L31/054—Optical elements directly associated or integrated with the PV cell, e.g. light-reflecting means or light-concentrating means
- H01L31/0547—Optical elements directly associated or integrated with the PV cell, e.g. light-reflecting means or light-concentrating means comprising light concentrating means of the reflecting type, e.g. parabolic mirrors, concentrators using total internal reflection
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L31/00—Semiconductor devices sensitive to infrared radiation, light, electromagnetic radiation of shorter wavelength or corpuscular radiation and specially adapted either for the conversion of the energy of such radiation into electrical energy or for the control of electrical energy by such radiation; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof
- H01L31/04—Semiconductor devices sensitive to infrared radiation, light, electromagnetic radiation of shorter wavelength or corpuscular radiation and specially adapted either for the conversion of the energy of such radiation into electrical energy or for the control of electrical energy by such radiation; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof adapted as photovoltaic [PV] conversion devices
- H01L31/06—Semiconductor devices sensitive to infrared radiation, light, electromagnetic radiation of shorter wavelength or corpuscular radiation and specially adapted either for the conversion of the energy of such radiation into electrical energy or for the control of electrical energy by such radiation; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof adapted as photovoltaic [PV] conversion devices characterised by potential barriers
- H01L31/068—Semiconductor devices sensitive to infrared radiation, light, electromagnetic radiation of shorter wavelength or corpuscular radiation and specially adapted either for the conversion of the energy of such radiation into electrical energy or for the control of electrical energy by such radiation; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof adapted as photovoltaic [PV] conversion devices characterised by potential barriers the potential barriers being only of the PN homojunction type, e.g. bulk silicon PN homojunction solar cells or thin film polycrystalline silicon PN homojunction solar cells
- H01L31/0687—Multiple junction or tandem solar cells
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L31/00—Semiconductor devices sensitive to infrared radiation, light, electromagnetic radiation of shorter wavelength or corpuscular radiation and specially adapted either for the conversion of the energy of such radiation into electrical energy or for the control of electrical energy by such radiation; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof
- H01L31/04—Semiconductor devices sensitive to infrared radiation, light, electromagnetic radiation of shorter wavelength or corpuscular radiation and specially adapted either for the conversion of the energy of such radiation into electrical energy or for the control of electrical energy by such radiation; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof adapted as photovoltaic [PV] conversion devices
- H01L31/06—Semiconductor devices sensitive to infrared radiation, light, electromagnetic radiation of shorter wavelength or corpuscular radiation and specially adapted either for the conversion of the energy of such radiation into electrical energy or for the control of electrical energy by such radiation; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof adapted as photovoltaic [PV] conversion devices characterised by potential barriers
- H01L31/075—Semiconductor devices sensitive to infrared radiation, light, electromagnetic radiation of shorter wavelength or corpuscular radiation and specially adapted either for the conversion of the energy of such radiation into electrical energy or for the control of electrical energy by such radiation; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof adapted as photovoltaic [PV] conversion devices characterised by potential barriers the potential barriers being only of the PIN type, e.g. amorphous silicon PIN solar cells
- H01L31/076—Multiple junction or tandem solar cells
-
- H—ELECTRICITY
- H01—ELECTRIC ELEMENTS
- H01L—SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES NOT COVERED BY CLASS H10
- H01L31/00—Semiconductor devices sensitive to infrared radiation, light, electromagnetic radiation of shorter wavelength or corpuscular radiation and specially adapted either for the conversion of the energy of such radiation into electrical energy or for the control of electrical energy by such radiation; Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment thereof or of parts thereof; Details thereof
- H01L31/18—Processes or apparatus specially adapted for the manufacture or treatment of these devices or of parts thereof
- H01L31/1884—Manufacture of transparent electrodes, e.g. TCO, ITO
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B23—MACHINE TOOLS; METAL-WORKING NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- B23K—SOLDERING OR UNSOLDERING; WELDING; CLADDING OR PLATING BY SOLDERING OR WELDING; CUTTING BY APPLYING HEAT LOCALLY, e.g. FLAME CUTTING; WORKING BY LASER BEAM
- B23K2101/00—Articles made by soldering, welding or cutting
- B23K2101/36—Electric or electronic devices
- B23K2101/40—Semiconductor devices
-
- B—PERFORMING OPERATIONS; TRANSPORTING
- B23—MACHINE TOOLS; METAL-WORKING NOT OTHERWISE PROVIDED FOR
- B23K—SOLDERING OR UNSOLDERING; WELDING; CLADDING OR PLATING BY SOLDERING OR WELDING; CUTTING BY APPLYING HEAT LOCALLY, e.g. FLAME CUTTING; WORKING BY LASER BEAM
- B23K2103/00—Materials to be soldered, welded or cut
- B23K2103/50—Inorganic material, e.g. metals, not provided for in B23K2103/02 – B23K2103/26
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02E—REDUCTION OF GREENHOUSE GAS [GHG] EMISSIONS, RELATED TO ENERGY GENERATION, TRANSMISSION OR DISTRIBUTION
- Y02E10/00—Energy generation through renewable energy sources
- Y02E10/50—Photovoltaic [PV] energy
- Y02E10/52—PV systems with concentrators
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02E—REDUCTION OF GREENHOUSE GAS [GHG] EMISSIONS, RELATED TO ENERGY GENERATION, TRANSMISSION OR DISTRIBUTION
- Y02E10/00—Energy generation through renewable energy sources
- Y02E10/50—Photovoltaic [PV] energy
- Y02E10/544—Solar cells from Group III-V materials
-
- Y—GENERAL TAGGING OF NEW TECHNOLOGICAL DEVELOPMENTS; GENERAL TAGGING OF CROSS-SECTIONAL TECHNOLOGIES SPANNING OVER SEVERAL SECTIONS OF THE IPC; TECHNICAL SUBJECTS COVERED BY FORMER USPC CROSS-REFERENCE ART COLLECTIONS [XRACs] AND DIGESTS
- Y02—TECHNOLOGIES OR APPLICATIONS FOR MITIGATION OR ADAPTATION AGAINST CLIMATE CHANGE
- Y02E—REDUCTION OF GREENHOUSE GAS [GHG] EMISSIONS, RELATED TO ENERGY GENERATION, TRANSMISSION OR DISTRIBUTION
- Y02E10/00—Energy generation through renewable energy sources
- Y02E10/50—Photovoltaic [PV] energy
- Y02E10/548—Amorphous silicon PV cells
Definitions
- the present invention relates to a solar cell, and more particularly to a thin-film solar cell in which a power generation layer is formed by film formation.
- Photoelectric conversion devices used in solar cells that convert solar energy into electrical energy include p-type silicon-based semiconductors (p-layers), i-type silicon-based semiconductors (i-layers), and n-type silicon-based semiconductors (n-layers).
- p-layers p-type silicon-based semiconductors
- i-layers i-type silicon-based semiconductors
- n-layers n-type silicon-based semiconductors
- the thin-film silicon solar cell includes that the area can be easily increased and that the film thickness is as thin as about 1/100 that of a crystalline solar cell, and that the material can be reduced. For this reason, the thin film silicon solar cell can be manufactured at a lower cost than the crystalline solar cell.
- a disadvantage of the thin-film silicon solar cell is that the conversion efficiency is lower than that of the crystal system. In this technical field, improvement of conversion efficiency is an important issue, and a tandem solar cell having a photoelectric conversion layer in which two power generation cell layers are stacked has been proposed.
- an intermediate contact layer made of a transparent conductive film is inserted for the purpose of suppressing dopant interdiffusion between the first power generation cell layer and the second power generation cell layer and adjusting the light quantity distribution. Is done.
- the intermediate contact layer it is common to use Ga-doped ZnO (GZO).
- GZO is a material having a refractive index of 2.0 and lower than Si, excellent plasma resistance, and excellent transparency.
- GZO has a low resistivity
- leakage current is caused in the cell connection portion, and the open circuit voltage and FF are reduced.
- solutions such as adding a laser processing part to the structure of the connection part have been proposed.
- the effective area is reduced and the cost is increased due to an increase in processes.
- the conductivity of GZO can be controlled by reducing dopants or adjusting the amount of oxygen supplied during film formation to promote oxidation of GZO.
- This invention is made
- the electrical conductivity after hydrogen plasma exposure is set to the appropriate range, and the photoelectric conversion apparatus which the leakage current was suppressed and conversion efficiency improved is provided. .
- the present invention provides a photoelectric conversion device including a photoelectric conversion layer including at least two power generation cell layers on a substrate, and an intermediate contact layer interposed between the adjacent power generation cell layers.
- the intermediate contact layer mainly contains a compound represented by Zn 1-x Mg x O 2 (0.096 ⁇ x ⁇ 0.183).
- an intermediate contact layer mainly composed of a compound obtained by adding MgO to ZnO By using an intermediate contact layer mainly composed of a compound obtained by adding MgO to ZnO, it is possible to prevent a decrease in resistance (that is, an increase in conductivity) after exposure to hydrogen plasma.
- the conductivity of the intermediate contact layer after exposure to hydrogen plasma is determined as the contact resistance while suppressing the leakage current at the cell connection portion. It becomes controllable to the value by which a raise is suppressed. For this reason, it can be set as the photoelectric conversion apparatus which a form factor is improved and has high conversion efficiency.
- the intermediate contact layer is made of a compound represented by Zn 1-x Mg x O 2 (0.096 ⁇ x ⁇ 0.183) to which Ga 2 O 3 is added. It may be included mainly.
- the sheet resistance of the intermediate contact layer after exposure to hydrogen plasma is preferably 10 k ⁇ / ⁇ or more and 100 k ⁇ / ⁇ or less.
- the sheet resistance of the intermediate contact layer after exposure to hydrogen plasma is desirably 10 k ⁇ / ⁇ or more.
- the contact resistance (series resistance) in the stacking direction (direction perpendicular to the substrate film-forming surface) increases. Therefore, the sheet resistance of the intermediate contact layer after exposure to hydrogen plasma is preferably 100 k ⁇ / ⁇ or less.
- An interface layer mainly including a compound represented by ZnO or Zn 1-x Mg x O 2 (0 ⁇ x ⁇ 0.096) is provided between the power generation cell layer on the substrate side and the intermediate contact layer. Also good.
- ZnO or Zn 1-x Mg x O 2 having the above composition range whose Mg concentration is lower than that of the intermediate contact layer of the present invention is mainly formed on the power generation cell layer formed on the substrate side.
- the interface layer is formed, the contact resistance in the film stacking direction can be further reduced. As a result, the form factor can be further improved, and a photoelectric conversion device having higher photoelectric conversion efficiency can be obtained.
- the interface layer is represented by ZnO to which Ga 2 O 3 is added or Zn 1-x Mg x O 2 (0 ⁇ x ⁇ 0.096).
- a compound may be mainly contained.
- the thickness of the interface layer is preferably 5 nm or more and 10 nm or less.
- the contact resistance can be improved.
- the leakage resistance increases and the form factor decreases.
- the thickness of the interface layer is not less than 5 nm and not more than 10 nm, it is possible to improve the contact resistance and suppress the leakage resistance and improve the photoelectric conversion efficiency.
- an intermediate contact layer mainly containing a compound represented by Zn 1-x Mg x O 2 (0.096 ⁇ x ⁇ 0.183) between adjacent power generation cell layers leakage current in the cell connection portion And the contact resistance in the direction perpendicular to the film can be reduced. Therefore, the form factor is improved and a photoelectric conversion device having high photoelectric conversion efficiency can be obtained. Further, by forming an interface layer mainly composed of Zn 1 or Zn 1-x Mg x O 2 having a lower Mg concentration than the intermediate contact layer between the power generation cell layer on the substrate side and the intermediate contact layer, the contact layer Can be further reduced. As a result, the photoelectric conversion efficiency can be further improved.
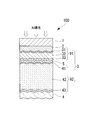
- FIG. 1 is a schematic diagram showing the configuration of the photoelectric conversion device of the present invention.
- the photoelectric conversion device 100 is a tandem silicon solar cell, and includes a substrate 1, a transparent electrode layer 2, a first power generation cell layer 91 (amorphous silicon system) and a second power generation cell layer as the solar cell photoelectric conversion layer 3. 92 (crystalline silicon type), an intermediate contact layer 5, and a back electrode layer 4.
- the silicon-based is a generic name including silicon (Si), silicon carbide (SiC), and silicon germanium (SiGe).
- the crystalline silicon system means a silicon system other than the amorphous silicon system, and includes microcrystalline silicon and polycrystalline silicon.
- a method for manufacturing a photoelectric conversion device according to the first embodiment will be described by taking a process for manufacturing a solar cell panel as an example.
- 2 to 5 are schematic views showing a method for manufacturing the solar cell panel of the present embodiment.
- FIG. 2 (a) A soda float glass substrate (substrate area is 1 m 2 or more, for example, 1.4 m ⁇ 1.1 m ⁇ plate thickness: 3.5 mm to 4.5 mm) is used as the substrate 1.
- the end face of the substrate is preferably subjected to corner chamfering or R chamfering to prevent damage due to thermal stress or impact.
- FIG. 2 (b) As the transparent conductive layer 2, a transparent conductive film having a thickness of about 500 nm to 800 nm and having tin oxide (SnO 2 ) as a main component is formed at about 500 ° C. with a thermal CVD apparatus. At this time, a texture with appropriate irregularities is formed on the surface of the transparent electrode film.
- an alkali barrier film (not shown) may be formed between the substrate 1 and the transparent electrode film.
- a silicon oxide film (SiO 2 ) is formed at a temperature of about 500 ° C. with a thermal CVD apparatus at 50 nm to 150 nm.
- FIG. 2 (c) Thereafter, the substrate 1 is set on an XY table, and the first harmonic (1064 nm) of the YAG laser is irradiated from the film surface side of the transparent electrode film as indicated by an arrow in the figure.
- the laser power is adjusted to be appropriate for the processing speed, and the transparent electrode film is moved relative to the direction perpendicular to the series connection direction of the power generation cells so that the substrate 1 and the laser light are moved relative to each other to form the groove 10.
- FIG. 2 (d) As the first power generation cell layer 91, a p layer, an i layer, and an n layer made of an amorphous silicon thin film are formed by a plasma CVD apparatus. Using SiH 4 gas and H 2 gas as main raw materials, the amorphous silicon p layer 31 from the side on which sunlight is incident on the transparent electrode layer 2 at a reduced pressure atmosphere: 30 Pa to 1000 Pa and a substrate temperature: about 200 ° C. Then, an amorphous silicon i layer 32 and an amorphous silicon n layer 33 are formed in this order.
- the amorphous silicon p layer 31 is mainly made of amorphous B-doped silicon and has a thickness of 10 nm to 30 nm.
- the amorphous silicon i layer 32 has a thickness of 200 nm to 350 nm.
- the amorphous silicon n layer 33 is mainly P-doped silicon containing microcrystalline silicon in amorphous silicon, and has a thickness of 30 nm to 50 nm.
- a buffer layer may be provided between the amorphous silicon p layer 31 and the amorphous silicon i layer 32 in order to improve interface characteristics.
- An intermediate contact layer 5 serving as a semi-reflective film is provided between the first power generation cell layer 91 and the second power generation cell layer 92 in order to improve contact and to obtain current matching.
- target Ga 2 O 3 doped ZnO—MgO mixed target (MgO ratio: 5 to 10% by mass), RF power: 1.1 to 4.4 W / cm 2 , film forming pressure: 0.
- the film is formed under conditions of 13 to 0.67 Pa and substrate temperature: 25 ° C. (near room temperature).
- an intermediate contact layer mainly composed of Zn 1-x Mg x O 2 (0.096 ⁇ x ⁇ 0.183) having a film thickness of 20 nm to 100 nm is formed.
- the sheet resistance of the intermediate contact layer 5 immediately after film formation is about 10 M ⁇ / ⁇ . Note that the intermediate contact layer may not contain Ga 2 O 3 .
- the second power generation cell layer 92 is formed on the first power generation cell layer 91 using a plasma CVD apparatus at a reduced pressure atmosphere: 3000 Pa or less, a substrate temperature: about 200 ° C., and a plasma generation frequency: 40 MHz or more and 100 MHz or less.
- a crystalline silicon p layer 41, a crystalline silicon i layer 42, and a crystalline silicon n layer 43 are sequentially formed.
- the crystalline silicon p layer 41 is mainly made of B-doped microcrystalline silicon and has a thickness of 10 nm to 50 nm.
- the crystalline silicon i layer 42 is mainly made of microcrystalline silicon and has a film thickness of 1.2 ⁇ m or more and 3.0 ⁇ m or less.
- the crystalline silicon n layer 43 is mainly made of P-doped microcrystalline silicon and has a thickness of 20 nm to 50 nm.
- an amorphous silicon n layer may be formed at the interface between the crystalline silicon i layer 42 and the crystalline silicon n layer 43.
- the distance d between the plasma discharge electrode and the surface of the substrate 1 is preferably 3 mm or more and 10 mm or less. If it is smaller than 3 mm, it is difficult to keep the distance d constant from the accuracy of each component device in the film forming chamber corresponding to the large substrate, and there is a possibility that the discharge becomes unstable because it is too close. When it is larger than 10 mm, it is difficult to obtain a sufficient film forming speed (1 nm / s or more), and the uniformity of the plasma is lowered and the film quality is lowered by ion bombardment.
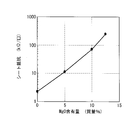
- FIG. 6 shows the relationship between the MgO content in the ZnMgO-based compound and the sheet resistance of the ZnMgO-based film after the hydrogen plasma treatment.
- the horizontal axis represents the MgO content
- the vertical axis represents the sheet resistance.
- a ZnMgO-based film is formed by using a target: ZnO sintered body (Ga 2 O 3 dopant) target or ZnO—MgO mixed target (Ga 2 O 3 dopant, MgO mass ratio: 5 to 12.5%), substrate temperature: The measurement was carried out under the conditions of 25 ° C., RF power: 4.4 W / cm 2 , target-substrate distance: 90 mm, film forming speed 0.17 nm / s, and film thickness: 70 nm. The hydrogen plasma treatment after film formation was performed under the conditions of H 2 gas flow rate: 0.1 slm, pressure: 133 Pa, applied power density: 0.5 W / cm 2 , treatment time: 5 minutes.
- the leakage current can be reduced when the sheet resistance of the intermediate contact layer is 10 k ⁇ / ⁇ or more.
- the sheet resistance of the intermediate contact layer is preferably 100 k ⁇ / ⁇ . From FIG. 6, it can be said that a ZnMgO-based film having a sheet resistance of 10 k ⁇ / ⁇ or more and 100 k ⁇ / ⁇ or less with an MgO mass of 5% (9.6 mol%) to 10% (18.3 mol%) is obtained.
- FIG. 2 (e) The substrate 1 is placed on an XY table, and the second harmonic (532 nm) of the laser diode-pumped YAG laser is irradiated from the film surface side of the photoelectric conversion layer 3 as shown by the arrow in the figure.
- Pulse oscillation 10 kHz to 20 kHz
- laser power is adjusted so as to be suitable for the processing speed
- laser etching is performed so that grooves 11 are formed on the lateral side of the laser etching line of the transparent electrode layer 2 from about 100 ⁇ m to 150 ⁇ m.
- this laser may be irradiated from the substrate 1 side.
- photoelectric conversion is performed by using a high vapor pressure generated by energy absorbed by the amorphous silicon-based first power generation cell layer of the photoelectric conversion layer 3. Since the layer 3 can be etched, a more stable laser etching process can be performed. The position of the laser etching line is selected in consideration of positioning tolerances so as not to intersect with the etching line in the previous process.
- FIG. 3 An Ag film / Ti film is formed as the back electrode layer 4 by a sputtering apparatus at a reduced pressure atmosphere and at a film forming temperature of 150 ° C. to 200 ° C.
- an Ag film 150 nm or more and 500 nm or less
- a Ti film having a high anticorrosion effect 10 nm or more and 20 nm or less are stacked in this order to protect them.
- the back electrode layer 4 may have a laminated structure of an Ag film having a thickness of 25 nm to 100 nm and an Al film having a thickness of 15 nm to 500 nm.
- a film thickness of 50 nm or more and 100 nm or less is formed between the photoelectric conversion layer 3 and the back electrode layer 4 by a sputtering apparatus.
- a GZO (Ga-doped ZnO) film may be formed and provided.
- FIG. 3 (b) The substrate 1 is placed on an XY table, and the second harmonic (532 nm) of the laser diode-pumped YAG laser is irradiated from the substrate 1 side as indicated by the arrow in the figure.
- the laser light is absorbed by the photoelectric conversion layer 3, and the back electrode layer 4 is exploded and removed using the high gas vapor pressure generated at this time.
- Pulse oscillation laser power is adjusted so as to be suitable for the processing speed from 1 kHz to 10 kHz, and laser etching is performed so that grooves 12 are formed on the lateral side of the laser etching line of the transparent electrode layer 2 from 250 ⁇ m to 400 ⁇ m. .
- FIG. 3 (c) and FIG. 4 (a) The power generation region is divided to eliminate the influence that the serial connection portion due to laser etching is likely to be short-circuited at the film edge around the substrate edge.
- the substrate 1 is set on an XY table, and the second harmonic (532 nm) of the laser diode pumped YAG laser is irradiated from the substrate 1 side.
- the laser light is absorbed by the transparent electrode layer 2 and the photoelectric conversion layer 3, and the back electrode layer 4 explodes using the high gas vapor pressure generated at this time, and the back electrode layer 4 / photoelectric conversion layer 3 / transparent electrode layer 2 is removed.
- Pulse oscillation 1 kHz or more and 10 kHz or less
- the laser power is adjusted so as to be suitable for the processing speed, and the position of 5 mm to 20 mm from the end of the substrate 1 is placed in the X-direction insulating groove as shown in FIG.
- Laser etching is performed to form 15.
- FIG.3 (c) since it becomes X direction sectional drawing cut
- the insulating groove formed to represent the Y-direction cross section at the position will be described as the X-direction insulating groove 15.
- the Y-direction insulating groove does not need to be provided because the film surface polishing removal processing of the peripheral film removal region of the substrate 1 is performed in a later process.
- the insulating groove 15 exhibits an effective effect in suppressing external moisture intrusion into the solar cell module 6 from the end portion of the solar cell panel by terminating the etching at a position of 5 mm to 15 mm from the end of the substrate 1. Therefore, it is preferable.
- the laser beam in the above steps is a YAG laser
- a YVO4 laser or a fiber laser there are some that can use a YVO4 laser or a fiber laser in the same manner.
- FIG. 4 (a: view from the solar cell film side, b: view from the substrate side of the light receiving surface) Since the laminated film around the substrate 1 (peripheral film removal region 14) has a step and is easy to peel off in order to ensure a sound adhesion / seal surface with the back sheet 24 via EVA or the like in a later process, The film is removed to form a peripheral film removal region 14. When removing the film over the entire periphery of the substrate 1 at 5 to 20 mm from the end of the substrate 1, the X direction is closer to the substrate end than the insulating groove 15 provided in the step of FIG.
- the back electrode layer 4 / photoelectric conversion layer 3 / transparent electrode layer 2 are removed by using grinding stone polishing, blast polishing, or the like on the substrate end side with respect to the groove 10 near the side portion. Polishing debris and abrasive grains were removed by cleaning the substrate 1.
- FIGS. 5 (a) and 5 (b) An attachment portion of the terminal box 23 is provided with an opening through window in the back sheet 24 to take out the current collector plate. Insulating materials are installed in a plurality of layers in the opening through window portion to suppress intrusion of moisture and the like from the outside. Processing so that power can be taken out from the terminal box 23 on the back side of the solar battery panel by collecting copper foil from one end of the photovoltaic power generation cells arranged in series and the other end of the solar power generation cell. To do. In order to prevent a short circuit with each part, the copper foil arranges an insulating sheet wider than the copper foil width.
- an adhesive filler sheet made of EVA (ethylene vinyl acetate copolymer) or the like is disposed so as to cover the entire solar cell module 6 and not protrude from the substrate 1. .
- a back sheet 24 having a high waterproof effect is installed on the EVA.
- the back sheet 24 has a three-layer structure of PET sheet / Al foil / PET sheet so that the waterproof and moisture-proof effect is high.
- the one with the back sheet 24 arranged in a predetermined position is deaerated inside in a reduced pressure atmosphere by a laminator and pressed at about 150 to 160 ° C., and EVA is crosslinked and brought into close contact.
- FIG. 5 (a) The terminal box 23 is attached to the back side of the solar cell module 6 with an adhesive.
- FIG. 5 (b) The copper foil and the output cable of the terminal box 23 are connected by solder or the like, and the inside of the terminal box 23 is filled with a sealing agent (potting agent) and sealed. Thus, the solar cell panel 50 is completed.
- FIG. 5 (c) A power generation inspection and a predetermined performance test are performed on the solar cell panel 50 formed in the steps up to FIG. The power generation inspection is performed using a solar simulator of AM1.5 and solar radiation standard sunlight (1000 W / m 2 ).
- FIG. 5 (d) Before and after the power generation inspection (FIG. 5C), a predetermined performance inspection is performed including an appearance inspection.
- the resistivity of the intermediate contact layer 5 is controlled to be 10 k ⁇ / ⁇ or more and 100 k ⁇ / ⁇ or less, the leakage current at the cell connection portion is reduced and the contact resistance in the film stacking direction is reduced. Reduce. Therefore, the form factor increases and the photoelectric conversion efficiency is improved.
- the photoelectric conversion device includes an interface layer between the first power generation cell layer 91 and the intermediate contact layer 5 in FIG.
- the interface layer mainly contains a compound represented by ZnO or Zn 1-x Mg x O 2 (provided that 0 ⁇ x ⁇ 0.096 is satisfied). That is, the interface layer does not contain Mg or has a lower Mg content than the intermediate contact layer.
- ZnO or Zn 1-x Mg x O 2 as the interface layer may contain Ga 2 O 3 as a dopant.
- the film formation of the interface layer may be performed in a film formation chamber different from the intermediate contact layer or in the same film formation chamber.
- the interfacial layer is formed by using an RF magnetron sputtering apparatus, target: Ga 2 O 3 doped ZnO sintered body or Ga 2 O 3 doped ZnO—MgO mixed target (MgO ratio: 0 to 5 mass%, 0 mass%)
- RF power is 1.1 to 4.4 W / cm 2
- film forming pressure is 0.13 to 0.67 Pa
- substrate temperature is 25 ° C. (near room temperature).
- an interface layer mainly composed of ZnO or Zn 1-x Mg x O 2 (0 ⁇ x ⁇ 0.096) is formed.
- the film thickness of the interface layer is preferably 5 nm or more and 10 nm or less.
- an intermediate contact layer having a higher MgO content than the interface layer is formed under the same conditions as in the first embodiment.
- the total film thickness of the interface layer and the intermediate contact layer is 20 nm or more and 100 nm or less.
- a Ga 2 O 3 doped ZnO sintered body or a Ga 2 O 3 doped ZnO—MgO mixed target (MgO ratio: 0 to 5 mass%, provided that 0
- a substrate transport type RF magnetron sputtering apparatus in which a Ga 2 O 3 -doped ZnO—MgO mixed target (MgO ratio: 5 to 10 mass%) is arranged in parallel is used.
- the substrate transport speed and the width of each target in the substrate transport direction are set so that the film thickness of the interface layer is 5 nm to 10 nm and the total film thickness of the interface layer and the intermediate contact layer is 20 nm to 100 nm.
- film formation is performed while conveying the substrate from the ZnO sintered body or the low Mg content mixed target side to the high Mg content mixed target side, with the film formation conditions being substantially the same as those described above.
- the boundary between the interface layer and the intermediate contact layer is not clear, unlike when each layer is formed in a different film forming chamber. It is considered that the Mg content continuously increases from the center toward the intermediate contact layer.
- the contact resistance between the first power generation cell layer and the interface layer is lower than the contact resistance between the first power generation cell layer and the intermediate contact layer in the first embodiment.
- the leakage current in the cell connection direction is further suppressed by setting the interface layer to a film thickness of 5 nm or more and 10 nm or less. For this reason, in the solar cell of 2nd Embodiment, a photoelectric conversion efficiency improves further.
- Example 1 A tandem solar cell module having the structure shown in FIG. 1 was formed on a glass substrate (5 cm square). The film thickness of the i layer of the first power generation cell layer was 250 nm, and the film thickness of the i layer of the second power generation cell layer was 1.9 ⁇ m.
- the intermediate contact layer is formed by using a target: ZnO sintered body target (Ga 2 O 3 dopant) or ZnO—MgO mixed target (Ga 2 O 3 dopant, MgO mass ratio: 5 to 12.5%), substrate temperature: The measurement was carried out under the conditions of 25 ° C., RF power: 4.4 W / cm 2 , target-substrate distance: 90 mm, film forming speed 0.17 nm / s, and film thickness: 70 nm.
- a target ZnO sintered body target (Ga 2 O 3 dopant) or ZnO—MgO mixed target (Ga 2 O 3 dopant, MgO mass ratio: 5 to 12.5%
- substrate temperature The measurement was carried out under the conditions of 25 ° C., RF power: 4.4 W / cm 2 , target-substrate distance: 90 mm, film forming speed 0.17 nm / s, and film thickness: 70 nm.
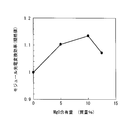
- FIG. 7 shows the relationship between the MgO content of the intermediate contact layer and the module form factor.
- the horizontal axis represents the MgO content
- the vertical axis represents the module shape factor normalized by the value when the MgO content is 0%.
- FIG. 8 shows the relationship between the MgO content of the intermediate contact layer and the photoelectric conversion efficiency of the module.
- the horizontal axis represents the MgO content
- the vertical axis represents the photoelectric conversion efficiency of the module normalized by the value when the MgO content is 0%.
- the form factor and photoelectric conversion efficiency were improved by applying a ZnMgO-based material to the intermediate contact layer.
- Example 2 A tandem solar cell module was formed on a glass substrate (5 cm square). The film thickness of the i layer of the first power generation cell layer was 250 nm, and the film thickness of the i layer of the second power generation cell layer was 1.9 ⁇ m. In the tandem solar cell module of Example 2, an interface layer was provided between the first power generation cell layer and the intermediate contact layer. The interface layer was formed using a ZnO sintered body target (Ga 2 O 3 dopant) under the same conditions as those for forming the intermediate contact layer of Example 1. The film thickness of the interface layer was 5 nm to 15 nm.
- a ZnO sintered body target Ga 2 O 3 dopant
- the intermediate contact layer was formed under the same conditions as in Example 1 using a ZnO—MgO mixed target (Ga 2 O 3 dopant, MgO mass ratio: 10%).
- the film thickness of the intermediate contact layer was 70 nm.
- the interface layer and the intermediate contact layer were formed in different film forming chambers.
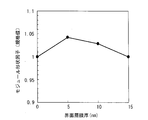
- FIG. 9 shows the relationship between the interface layer thickness and the module form factor.
- the horizontal axis represents the interface layer thickness
- the vertical axis represents the module shape factor normalized by the value when the interface layer thickness is 0 nm (only the intermediate contact layer).
- FIG. 10 shows the relationship between the interface layer thickness and the module photoelectric conversion efficiency.
- the horizontal axis represents the interface layer thickness
- the vertical axis represents the module photoelectric conversion efficiency normalized by the value when no interface layer is provided.
- the interface layer thickness is 5 nm or more and 10 nm or less
- the module shape factor and photoelectric conversion efficiency are improved as compared with the case where the interface layer is not provided.
- the interface layer was 15 nm
- the module shape factor and photoelectric conversion efficiency were reduced. This is considered to be because when the interface layer is thick, leakage current is generated in the interface layer and the contact property is deteriorated. Even when the MgO content of the intermediate contact layer was 5% by mass, the same effect was observed.
- Example 3 A tandem solar cell module having the same configuration as that of Example 2 was formed.
- the interface layer and the intermediate contact layer were formed in the same film forming chamber.
- a substrate transport type film forming apparatus in which eight targets are arranged in parallel in the substrate transport direction was used.
- One target on the substrate introduction side (upstream side) is a ZnO sintered body target (Ga 2 O 3 dopant), and the remaining target is a ZnO—MgO mixed target (Ga 2 O 3 dopant, MgO mass ratio: 10%). It was.
- the film forming conditions were the same as in Example 1 and Example 2.
- the intermediate contact layer was formed at a conveyance speed at which the total film thickness was 70 nm.
- the form factor and photoelectric conversion efficiency of the tandem solar cell module of Example 3 were 1.03 and 1.05 times that of the tandem solar cell module that does not form the intermediate contact layer, respectively.
- tandem solar cell has been described as a solar cell, but the present invention is not limited to this example.
- the present invention can be similarly applied to a triple solar cell.
Landscapes
- Engineering & Computer Science (AREA)
- Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Optics & Photonics (AREA)
- Chemical & Material Sciences (AREA)
- Mechanical Engineering (AREA)
- Condensed Matter Physics & Semiconductors (AREA)
- General Physics & Mathematics (AREA)
- Computer Hardware Design (AREA)
- Microelectronics & Electronic Packaging (AREA)
- Power Engineering (AREA)
- Electromagnetism (AREA)
- Plasma & Fusion (AREA)
- Life Sciences & Earth Sciences (AREA)
- Sustainable Energy (AREA)
- Sustainable Development (AREA)
- Chemical Kinetics & Catalysis (AREA)
- Materials Engineering (AREA)
- Metallurgy (AREA)
- Organic Chemistry (AREA)
- Manufacturing & Machinery (AREA)
- Crystallography & Structural Chemistry (AREA)
- Photovoltaic Devices (AREA)
Abstract
Description
界面層を形成することにより、コンタクト抵抗を改善することができるが、界面層が厚くなると、漏れ抵抗が増加して形状因子が低減する。界面層の膜厚が、5nm以上10nm以下であるときに、コンタクト抵抗の改善と漏れ抵抗の抑制とを両立させて、光電変換効率を向上させることができる。
また、基板側の発電セル層と中間コンタクト層との間に、ZnOまたは中間コンタクト層よりもMg濃度が低いZn1-xMgxO2を主とする界面層を形成することにより、コンタクト層をより低減させることも可能である。この結果、光電変換効率を更に向上させることができる。
第1実施形態に係る光電変換装置の製造方法を、太陽電池パネルを製造する工程を例に挙げて説明する。図2から図5は、本実施形態の太陽電池パネルの製造方法を示す概略図である。
基板1としてソーダフロートガラス基板(基板面積が1m2以上、例えば1.4m×1.1m×板厚:3.5mm~4.5mm)を使用する。基板端面は熱応力や衝撃などによる破損防止にコーナー面取りやR面取り加工されていることが望ましい。
透明導電層2として、酸化錫(SnO2)を主成分とする膜厚約500nm以上800nm以下の透明導電膜を、熱CVD装置にて約500℃で製膜する。この際、透明電極膜の表面には、適当な凹凸のあるテクスチャーが形成される。透明導電層2として、透明電極膜に加えて、基板1と透明電極膜との間にアルカリバリア膜(図示されず)を形成しても良い。アルカリバリア膜は、酸化シリコン膜(SiO2)を50nm~150nm、熱CVD装置にて約500℃で製膜処理する。
その後、基板1をX-Yテーブルに設置して、YAGレーザーの第1高調波(1064nm)を、図の矢印に示すように、透明電極膜の膜面側から照射する。加工速度に適切となるようにレーザーパワーを調整して、透明電極膜を発電セルの直列接続方向に対して垂直な方向へ、基板1とレーザー光を相対移動して、溝10を形成するように幅約6mmから15mmの所定幅の短冊状にレーザーエッチングする。
第1発電セル層91として、非晶質シリコン薄膜からなるp層、i層及びn層を、プラズマCVD装置により製膜する。SiH4ガス及びH2ガスを主原料にして、減圧雰囲気:30Pa以上1000Pa以下、基板温度:約200℃にて、透明電極層2上に太陽光の入射する側から非晶質シリコンp層31、非晶質シリコンi層32、非晶質シリコンn層33の順で製膜する。非晶質シリコンp層31は非晶質のBドープシリコンを主とし、膜厚10nm以上30nm以下である。非晶質シリコンi層32は、膜厚200nm以上350nm以下である。非晶質シリコンn層33は、非晶質シリコンに微結晶シリコンを含有するPドープシリコンを主とし、膜厚30nm以上50nm以下である。非晶質シリコンp層31と非晶質シリコンi層32の間には、界面特性の向上のためにバッファー層を設けても良い。
図6に、ZnMgO系化合物におけるMgO含有量と、水素プラズマ処理後のZnMgO系膜のシート抵抗との関係を示す。同図において、横軸はMgO含有量、縦軸はシート抵抗である。ZnMgO系膜の製膜は、ターゲット:ZnO焼結体(Ga2O3ドーパント)ターゲットまたはZnO-MgO混合ターゲット(Ga2O3ドーパント、MgO質量比率:5~12.5%)、基板温度:25℃、RFパワー:4.4W/cm2、ターゲット-基板距離:90mm、製膜速度0.17nm/s、膜厚:70nmの条件で実施した。製膜後の水素プラズマ処理は、H2ガス流量:0.1slm、圧力:133Pa、印加電力密度:0.5W/cm2、処理時間:5分の条件で実施した。
本実施形態のモジュール構造に対応する等価回路を用いて形状因子への影響を解析したところ、中間コンタクト層のシート抵抗を10kΩ/□以上であると漏れ電流を低減することができる。また、膜垂直方向(積層方向)においては、直列抵抗増加の要因となるコンタクト抵抗を低くすることが不可欠である。解析の結果、中間コンタクト層のシート抵抗は、100kΩ/□であることが望ましい。
図6より、MgO質量5%(9.6mol%)から10%(18.3mol%)で、シート抵抗10kΩ/□以上100kΩ/□以下のZnMgO系膜が得られると言える。
基板1をX-Yテーブルに設置して、レーザーダイオード励起YAGレーザーの第2高調波(532nm)を、図の矢印に示すように、光電変換層3の膜面側から照射する。パルス発振:10kHzから20kHzとして、加工速度に適切となるようにレーザーパワーを調整して、透明電極層2のレーザーエッチングラインの約100μmから150μmの横側を、溝11を形成するようにレーザーエッチングする。またこのレーザーは基板1側から照射しても良く、この場合は光電変換層3の非晶質シリコン系の第1発電セル層で吸収されたエネルギーで発生する高い蒸気圧を利用して光電変換層3をエッチングできるので、更に安定したレーザーエッチング加工を行うことが可能となる。レーザーエッチングラインの位置は前工程でのエッチングラインと交差しないように位置決め公差を考慮して選定する。
裏面電極層4としてAg膜/Ti膜を、スパッタリング装置により、減圧雰囲気、製膜温度:150℃から200℃にて製膜する。本実施形態では、Ag膜:150nm以上500nm以下、これを保護するものとして防食効果の高いTi膜:10nm以上20nm以下を、この順に積層する。あるいは、裏面電極層4を、25nmから100nmの膜厚を有するAg膜と、15nmから500nmの膜厚を有するAl膜との積層構造としても良い。結晶質シリコンn層43と裏面電極層4との接触抵抗低減と光反射向上を目的に、光電変換層3と裏面電極層4との間に、スパッタリング装置により、膜厚:50nm以上100nm以下のGZO(GaドープZnO)膜を製膜して設けても良い。
基板1をX-Yテーブルに設置して、レーザーダイオード励起YAGレーザーの第2高調波(532nm)を、図の矢印に示すように、基板1側から照射する。レーザー光が光電変換層3で吸収され、このとき発生する高いガス蒸気圧を利用して裏面電極層4が爆裂して除去される。パルス発振:1kHz以上10kHz以下として加工速度に適切となるようにレーザーパワーを調整して、透明電極層2のレーザーエッチングラインの250μmから400μmの横側を、溝12を形成するようにレーザーエッチングする。
発電領域を区分して、基板端周辺の膜端部においてレーザーエッチングによる直列接続部分が短絡し易い影響を除去する。基板1をX-Yテーブルに設置して、レーザーダイオード励起YAGレーザーの第2高調波(532nm)を、基板1側から照射する。レーザー光が透明電極層2と光電変換層3で吸収され、このとき発生する高いガス蒸気圧を利用して裏面電極層4が爆裂して、裏面電極層4/光電変換層3/透明電極層2が除去される。パルス発振:1kHz以上10kHz以下として加工速度に適切となるようにレーザーパワーを調整して、基板1の端部から5mmから20mmの位置を、図3(c)に示すように、X方向絶縁溝15を形成するようにレーザーエッチングする。なお、図3(c)では、光電変換層3が直列に接続された方向に切断したX方向断面図となっているため、本来であれば絶縁溝15位置には裏面電極層4/光電変換層3/透明電極層2の膜研磨除去をした周囲膜除去領域14がある状態(図4(a)参照)が表れるべきであるが、基板1の端部への加工の説明の便宜上、この位置にY方向断面を表して形成された絶縁溝をX方向絶縁溝15として説明する。このとき、Y方向絶縁溝は後工程で基板1周囲膜除去領域の膜面研磨除去処理を行うので、設ける必要がない。
後工程のEVA等を介したバックシート24との健全な接着・シール面を確保するために、基板1周辺(周囲膜除去領域14)の積層膜は、段差があるとともに剥離し易いため、この膜を除去して周囲膜除去領域14を形成する。基板1の端から5~20mmで基板1の全周囲にわたり膜を除去するにあたり、X方向は前述の図3(c)工程で設けた絶縁溝15よりも基板端側において、Y方向は基板端側部付近の溝10よりも基板端側において、裏面電極層4/光電変換層3/透明電極層2を、砥石研磨やブラスト研磨などを用いて除去を行う。
研磨屑や砥粒は基板1を洗浄処理して除去した。
端子箱23の取付け部分はバックシート24に開口貫通窓を設けて集電板を取出す。この開口貫通窓部分には絶縁材を複数層で設置して外部からの湿分などの浸入を抑制する。
直列に並んだ一方端の太陽電池発電セルと、他方端部の太陽電池発電セルとから銅箔を用いて集電して太陽電池パネル裏側の端子箱23の部分から電力が取出せるように処理する。銅箔は各部との短絡を防止するために銅箔幅より広い絶縁シートを配置する。
集電用銅箔などが所定位置に配置された後に、太陽電池モジュール6の全体を覆い、基板1からはみ出さないようにEVA(エチレン酢酸ビニル共重合体)等による接着充填材シートを配置する。
EVAの上に、防水効果の高いバックシート24を設置する。バックシート24は本実施形態では防水防湿効果が高いようにPETシート/Al箔/PETシートの3層構造よりなる。
バックシート24までを所定位置に配置したものを、ラミネータにより減圧雰囲気で内部の脱気を行い約150~160℃でプレスしながら、EVAを架橋させて密着させる。
太陽電池モジュール6の裏側に端子箱23を接着剤で取付ける。
(12)図5(b)
銅箔と端子箱23の出力ケーブルとをハンダ等で接続し、端子箱23の内部を封止剤(ポッティング剤)で充填して密閉する。これで太陽電池パネル50が完成する。
(13)図5(c)
図5(b)までの工程で形成された太陽電池パネル50について発電検査ならびに、所定の性能試験を行う。発電検査は、AM1.5、全天日射基準太陽光(1000W/m2)のソーラシミュレータを用いて行う。
(14)図5(d)
発電検査(図5(c))に前後して、外観検査をはじめ所定の性能検査を行う。
第2実施形態に係る光電変換装置は、図1における第1発電セル層91と中間コンタクト層5との間に、界面層を備える。
界面層は、ZnO、または、Zn1-xMgxO2(ただし、0<x≦0.096を満たす)で表される化合物を主として含む。すなわち、界面層は、Mgを含まないか、中間コンタクト層よりもMg含有量が少ない。界面層としてのZnOまたはZn1-xMgxO2は、ドーパントとしてGa2O3を含んでも良い。
界面層の製膜は、RFマグネトロンスパッタリング装置を用い、ターゲット:Ga2O3ドープZnO焼結体またはGa2O3ドープZnO-MgO混合ターゲット(MgO比率:0~5質量%、但し0質量%を含まず)、RFパワー:1.1~4.4W/cm2、製膜圧力:0.13~0.67Pa、基板温度:25℃(室温付近)の条件で実施する。上記条件での製膜により、ZnOまたはZn1-xMgxO2(0<x≦0.096)を主とする界面層を形成する。第1セル層と界面層とのコンタクト抵抗、及び、セル接続部における漏れ電流を考慮すると、界面層の膜厚は、5nm以上10nm以下であることが好ましい。
界面層形成後、第1実施形態と同様の条件により、界面層よりもMgO含有量が多い中間コンタクト層を形成する。本実施形態において、界面層及び中間コンタクト層の合計膜厚は、20nm以上100nm以下とされる。
(実施例1)
ガラス基板(5cm角)上に、図1に示す構造のタンデム型太陽電池モジュールを形成した。なお、第1発電セル層のi層の膜厚を250nm、第2発電セル層のi層の膜厚を1.9μmとした。
中間コンタクト層の製膜は、ターゲット:ZnO焼結体ターゲット(Ga2O3ドーパント)またはZnO-MgO混合ターゲット(Ga2O3ドーパント、MgO質量比率:5~12.5%)、基板温度:25℃、RFパワー:4.4W/cm2、ターゲット-基板距離:90mm、製膜速度0.17nm/s、膜厚:70nmの条件で実施した。
図7及び図8に示すように、中間コンタクト層にZnMgO系材料を適用することにより、形状因子及び光電変換効率が向上した。MgO含有量5質量%(9.6mol%)から10質量%(18.3mol%)の範囲で、高い形状因子及び光電変換効率が得られた。MgO含有量が10質量%を超えると、コンタクト抵抗上昇のために、形状因子及び光電変換効率が減少する傾向が見られた。
ガラス基板(5cm角)上に、タンデム型太陽電池モジュールを形成した。なお、第1発電セル層のi層の膜厚を250nm、第2発電セル層のi層の膜厚を1.9μmとした。
実施例2のタンデム型太陽電池モジュールでは、第1発電セル層と中間コンタクト層との間に界面層を設けた。界面層の製膜は、ZnO焼結体ターゲット(Ga2O3ドーパント)を用い、実施例1の中間コンタクト層製膜と同じ条件で実施した。界面層の膜厚は、5nmから15nmとした。中間コンタクト層の製膜は、ZnO-MgO混合ターゲット(Ga2O3ドーパント、MgO質量比率:10%)を用い、実施例1と同じ条件で実施した。中間コンタクト層の膜厚は、70nmとした。なお、実施例2において、界面層及び中間コンタクト層の製膜は、異なる製膜室中で実施した。
界面層膜厚5nm以上10nm以下で、界面層を設けない場合と比較してモジュールの形状因子及び光電変換効率が向上した。界面層が15nmの場合は、モジュールの形状因子及び光電変換効率が低下した。これは、界面層が厚い場合には、界面層において漏れ電流が発生してコンタクト性が悪化するためと考えられた。
中間コンタクト層のMgO含有量を5質量%とした場合でも、同様の効果が見られた。
実施例2と同様の構成のタンデム型太陽電池モジュールを形成した。実施例3では、界面層及び中間コンタクト層の製膜を、同一製膜室内で実施した。
基板搬送方向に8つのターゲットが並列配置された基板搬送型の製膜装置を用いた。基板導入側(上流側)の一のターゲットを、ZnO焼結体ターゲット(Ga2O3ドーパント)とし、残りのターゲットをZnO-MgO混合ターゲット(Ga2O3ドーパント、MgO質量比率:10%)とした。製膜条件は、実施例1及び実施例2と同様とした。中間コンタクト層の総膜厚が70nmとなる搬送速度で製膜した。
実施例3のタンデム型太陽電池モジュールの形状因子及び光電変換効率は、中間コンタクト層を形成しないタンデム型太陽電池モジュールに対して、それぞれ1.03倍、1.05倍となった。
2 透明電極層
3 光電変換層
4 裏面電極層
5 中間コンタクト層
6 太陽電池モジュール
31 非晶質シリコンp層
32 非晶質シリコンi層
33 非晶質シリコンn層
41 結晶質シリコンp層
42 結晶質シリコンi層
43 結晶質シリコンn層
91 第1発電セル層
92 第2発電セル層
100 光電変換装置
Claims (6)
- 基板上に、少なくとも2層の発電セル層を備える光電変換層と、前記発電セル層の間に介在する中間コンタクト層とを含む光電変換装置であって、
前記中間コンタクト層が、Zn1-xMgxO2(0.096≦x≦0.183)で表される化合物を主として含むことを特徴とする光電変換装置。 - 前記中間コンタクト層が、Ga2O3が添加されたZn1-xMgxO2(0.096≦x≦0.183)で表される化合物を主として含むことを特徴とする請求項1に記載の光電変換装置。
- 水素プラズマ曝露後の前記中間コンタクト層のシート抵抗が、10kΩ/□以上100kΩ/□以下であることを特徴とする請求項1または請求項2に記載の光電変換装置。
- 前記基板側の前記発電セル層と前記中間コンタクト層との間に、ZnOまたはZn1-xMgxO2(0<x≦0.096)で表される化合物を主として含む界面層を備えることを特徴とする請求項1乃至請求項3のいずれかに記載の光電変換装置。
- 前記界面層が、Ga2O3が添加されたZnOまたはZn1-xMgxO2(0<x≦0.096)で表される化合物を主として含むことを特徴とする請求項4に記載の光電変換装置。
- 前記界面層の膜厚が、5nm以上10nm以下であることを特徴とする請求項4または請求項5に記載の光電変換装置。
Priority Applications (3)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| CN2009801298886A CN102113127B (zh) | 2008-11-19 | 2009-08-20 | 光电转换装置 |
| EP09827421A EP2348541A1 (en) | 2008-11-19 | 2009-08-20 | Photoelectric conversion device |
| US13/003,615 US8598447B2 (en) | 2008-11-19 | 2009-08-20 | Photoelectric conversion device |
Applications Claiming Priority (2)
| Application Number | Priority Date | Filing Date | Title |
|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008295750A JP5022341B2 (ja) | 2008-11-19 | 2008-11-19 | 光電変換装置 |
| JP2008-295750 | 2008-11-19 |
Publications (1)
| Publication Number | Publication Date |
|---|---|
| WO2010058640A1 true WO2010058640A1 (ja) | 2010-05-27 |
Family
ID=42198079
Family Applications (1)
| Application Number | Title | Priority Date | Filing Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT/JP2009/064570 WO2010058640A1 (ja) | 2008-11-19 | 2009-08-20 | 光電変換装置 |
Country Status (6)
| Country | Link |
|---|---|
| US (1) | US8598447B2 (ja) |
| EP (1) | EP2348541A1 (ja) |
| JP (1) | JP5022341B2 (ja) |
| KR (1) | KR20110018951A (ja) |
| CN (1) | CN102113127B (ja) |
| WO (1) | WO2010058640A1 (ja) |
Cited By (2)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP2472595A1 (en) * | 2009-08-26 | 2012-07-04 | Sharp Kabushiki Kaisha | Stacked photovoltaic element and method for manufacturing stacked photovoltaic element |
| WO2012102449A1 (en) * | 2011-01-25 | 2012-08-02 | Lg Innotek Co., Ltd. | Solar cell and method for manufacturing the same |
Families Citing this family (4)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CN103229306B (zh) | 2010-09-22 | 2016-08-03 | 第一太阳能有限公司 | 具有氧化锌镁窗口层的薄膜光伏装置 |
| US20140246083A1 (en) | 2013-03-01 | 2014-09-04 | First Solar, Inc. | Photovoltaic devices and method of making |
| WO2016056546A1 (ja) | 2014-10-06 | 2016-04-14 | 株式会社カネカ | 太陽電池および太陽電池モジュール、ならびに太陽電池および太陽電池モジュールの製造方法 |
| DE102019006095A1 (de) * | 2019-08-29 | 2021-03-04 | Azur Space Solar Power Gmbh | Vereinzelungsverfahren zur Vereinzelung einer mehrere Solarzellenstapel umfasssenden Halbleiterscheibe |
Citations (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008270562A (ja) * | 2007-04-20 | 2008-11-06 | Sanyo Electric Co Ltd | 多接合型太陽電池 |
Family Cites Families (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP3434259B2 (ja) | 1999-03-05 | 2003-08-04 | 松下電器産業株式会社 | 太陽電池 |
| JP4240889B2 (ja) | 2001-02-01 | 2009-03-18 | キヤノン株式会社 | 透明導電膜の形成方法、及び光起電力素子の製造方法 |
| CN1307707C (zh) | 2003-09-19 | 2007-03-28 | 中国科学院上海微系统与信息技术研究所 | 一种含镁锌氧的金属-绝缘层-半导体结构及制备工艺 |
| EP2061041A4 (en) * | 2007-02-26 | 2011-06-29 | Murata Manufacturing Co | LADDERING FILM AND METHOD FOR PRODUCING A CONDUCTIVE FILM |
| JP4425296B2 (ja) * | 2007-07-09 | 2010-03-03 | 三洋電機株式会社 | 光起電力装置 |
-
2008
- 2008-11-19 JP JP2008295750A patent/JP5022341B2/ja not_active Expired - Fee Related
-
2009
- 2009-08-20 US US13/003,615 patent/US8598447B2/en not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2009-08-20 WO PCT/JP2009/064570 patent/WO2010058640A1/ja active Application Filing
- 2009-08-20 CN CN2009801298886A patent/CN102113127B/zh not_active Expired - Fee Related
- 2009-08-20 EP EP09827421A patent/EP2348541A1/en not_active Withdrawn
- 2009-08-20 KR KR1020117001308A patent/KR20110018951A/ko not_active Application Discontinuation
Patent Citations (1)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JP2008270562A (ja) * | 2007-04-20 | 2008-11-06 | Sanyo Electric Co Ltd | 多接合型太陽電池 |
Cited By (5)
| Publication number | Priority date | Publication date | Assignee | Title |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EP2472595A1 (en) * | 2009-08-26 | 2012-07-04 | Sharp Kabushiki Kaisha | Stacked photovoltaic element and method for manufacturing stacked photovoltaic element |
| EP2472595A4 (en) * | 2009-08-26 | 2013-10-30 | Sharp Kk | STACKED PHOTOVOLTAIC ELEMENT AND METHOD FOR PRODUCING THE STACKED PHOTOVOLTAIC ELEMENT |
| WO2012102449A1 (en) * | 2011-01-25 | 2012-08-02 | Lg Innotek Co., Ltd. | Solar cell and method for manufacturing the same |
| CN103222068A (zh) * | 2011-01-25 | 2013-07-24 | Lg伊诺特有限公司 | 太阳能电池及其制造方法 |
| US9818902B2 (en) | 2011-01-25 | 2017-11-14 | Lg Innotek Co., Ltd. | Solar cell and method for manufacturing the same |
Also Published As
| Publication number | Publication date |
|---|---|
| KR20110018951A (ko) | 2011-02-24 |
| US8598447B2 (en) | 2013-12-03 |
| EP2348541A1 (en) | 2011-07-27 |
| CN102113127B (zh) | 2013-06-05 |
| JP5022341B2 (ja) | 2012-09-12 |
| US20110120521A1 (en) | 2011-05-26 |
| JP2010123737A (ja) | 2010-06-03 |
| CN102113127A (zh) | 2011-06-29 |
Similar Documents
| Publication | Publication Date | Title |
|---|---|---|
| AU2008233856B2 (en) | Photovoltaic device and process for producing same. | |
| JP5022341B2 (ja) | 光電変換装置 | |
| JP5330723B2 (ja) | 光電変換装置 | |
| WO2010052953A1 (ja) | 光電変換装置の製造方法及び光電変換装置 | |
| WO2010050035A1 (ja) | 光電変換装置の製造方法 | |
| JP4764469B2 (ja) | 光電変換装置及び光電変換装置の製造方法 | |
| WO2011030598A1 (ja) | 光電変換装置の製造方法 | |
| WO2011061956A1 (ja) | 光電変換装置 | |
| JP5030745B2 (ja) | 光電変換装置の製造方法 | |
| WO2011070805A1 (ja) | 光電変換装置の製造方法 | |
| WO2010064455A1 (ja) | 光電変換装置 | |
| JP2011061124A (ja) | 光電変換装置の製造方法及び光電変換装置 | |
| WO2012014550A1 (ja) | 光電変換装置の製造方法 | |
| WO2012036074A1 (ja) | 光電変換装置の製造方法 | |
| JP4875566B2 (ja) | 光電変換装置の製造方法 | |
| WO2010061667A1 (ja) | 光電変換装置の製造方法 | |
| WO2011033885A1 (ja) | 光電変換装置 | |
| JP2009158667A (ja) | 光電変換装置及びその製造方法 | |
| US20110318871A1 (en) | Process for producing photovoltaic device | |
| JP2010251424A (ja) | 光電変換装置 | |
| JP2010135637A (ja) | 光電変換装置 | |
| JP2008251914A (ja) | 多接合型光電変換装置 | |
| JP2011077380A (ja) | 光電変換装置 | |
| JP2011096848A (ja) | 光電変換装置の製造方法 | |
| JP2010199305A (ja) | 光電変換装置の製造方法 |
Legal Events
| Date | Code | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 200980129888.6 Country of ref document: CN |
|
| 121 | Ep: the epo has been informed by wipo that ep was designated in this application |
Ref document number: 09827421 Country of ref document: EP Kind code of ref document: A1 |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 13003615 Country of ref document: US |
|
| ENP | Entry into the national phase |
Ref document number: 20117001308 Country of ref document: KR Kind code of ref document: A |
|
| WWE | Wipo information: entry into national phase |
Ref document number: 2009827421 Country of ref document: EP |
|
| NENP | Non-entry into the national phase |
Ref country code: DE |